泮托拉唑说明书
- 格式:docx
- 大小:17.13 KB
- 文档页数:3

泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊说明书泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊(泮立苏)适用于活动性消化性溃疡(胃、十二指肠溃疡),反流性食管炎和卓-艾氏综合症。
下面是学习啦小编整理的泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊说明书,欢迎阅读。
泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊商品介绍通用名:泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊生产厂家: 杭州中美华东制药有限公司批准文号:国药准字H20010032药品规格:40mg*7粒药品价格:¥50元泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊说明书【通用名称】泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊【商品名称】泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊(泮立苏)【英文名称】PantoprazoleSodiumEnteric-CoatedCapsules【拼音全码】panTuoLacuoNaChangRongJiaoNang(panLiSu)【主要成份】泮托拉唑。
【性状】泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊(泮立苏)为白色或类白色疏松块或粉末,专用溶媒为无色的澄明液体。
【适应症/功能主治】适用于活动性消化性溃疡(胃、十二指肠溃疡),反流性食管炎和卓-艾氏综合症。
【规格型号】40mg*7s【用法用量】口服,每日早晨餐前一粒(40mg)。
十二指肠溃疡疗程通常为2-4周,胃溃疡和反流性食管炎疗程通常为4【不良反应】偶见头晕、失眠、嗜睡、恶心、腹泻、便秘、皮疹和肌肉疼痛等症状。
大剂量使用时可出现心律失常、氨基转移酶升高、肾功能改变、粒细胞降低等。
【禁忌】对泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊(泮立苏)过敏者禁用;妊娠期与哺乳期妇女禁用。
【注意事项】①泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊(泮立苏)抑制胃酸分泌的作用强,时间长,故应用泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊(泮立苏)时不宜同时再服用其他抗酸剂或抑酸剂。
为防止抑酸过度,在一般消化性溃疡等病时,不建议大剂量长期应用(卓-艾综合征例外)。
②肾功能受损者不须调整剂量;肝功能受损者需要酌情减量。
③治疗胃溃疡时应排除胃癌后才能使用泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊(泮立苏),以免延误诊断和治疗。
④动物实验中,长期大量使用泮托拉唑钠肠溶胶囊(泮立苏)后,观察到高胃泌素血症及继发胃ECL-细胞增大和良性肿瘤的发生,这种变化在应用其他抑酸剂及施行胃大部切除术后亦可出现。

药品名称:通用名称:注射用泮托拉唑钠英文名称:Pantoprazole Sodium for Injection商品名称:注射用泮托拉唑钠成份:本品主要成份为泮托拉唑钠。
辅料为甘露醇、依地酸二钠。
主要用于1.消化性溃疡出血。
2.非甾体类抗炎药引起的急性胃粘膜损伤和应激状态下溃疡大出血的发生。
3.全身麻醉或大手术后以及衰弱昏迷患者防止胃酸反流合并吸入性肺炎。
规格:60mg(以泮托拉唑计)静脉滴注。
一次40—80mg,每日1—2次,临用前将10ml 0.9%氯化钠注射液注入冻干粉小瓶内,将溶解后的药液加入0.9%氯化钠注射液100—250ml中稀释后供静脉滴注。
静脉滴注,要求15—60分钟内滴完。
本品溶解和稀释后必须在4小时内用完,禁止用其他溶剂或其他药物溶解和稀释。
不良反应:偶见头晕、失眠、嗜睡、恶心、腹泻、便秘、皮疹、肌肉疼痛等症状。
大剂量使用时可出现心律不齐,转氨酶升高,肾功能改变,粒细胞降低等。
1.对本品过敏者禁用。
2.妊娠期与哺乳期妇女禁用。
1.本品抑制胃酸分泌的作用强,时间长,故应用本品时不宜同时再服用其它抗酸剂或抑酸剂。
为防止抑酸过度,在一般消化性溃疡等病时,不建议大剂量长期应用(卓一艾综合征例外)。
2.肾功能受损者不须调整剂量;肝功能受损者需要酌情减量。
3.治疗溃疡时应排除胃癌后才能使用本品,以免延误诊断和治疗。
孕妇及哺乳期妇女用药:孕妇及哺乳期妇女禁用。
儿童用药:尚无儿童静脉应用本品的经验。
老年用药:老年人用药剂量无须调整。
药物相互作用:本品与肝脏细胞色素P450酶的亲和力较低,并有Ⅱ期代谢的途径,因而与通过细胞色素P450酶系代谢的其他药物相互作用较奥美拉唑和兰索拉唑少。
泮托拉唑为质子泵抑制剂,通过与胃壁细胞的H<SUP>+- K<SUP>+ATP酶系统的两个位点共价结合而抑制酸产生的最后步骤。
该作用呈剂量依赖性并使基础和刺激状态下的胃酸分泌均受抑制。
本品H<SUP>+-K<SUP>+ATP酶的结合可导致其抗胃酸分泌作用持续24小时以上。
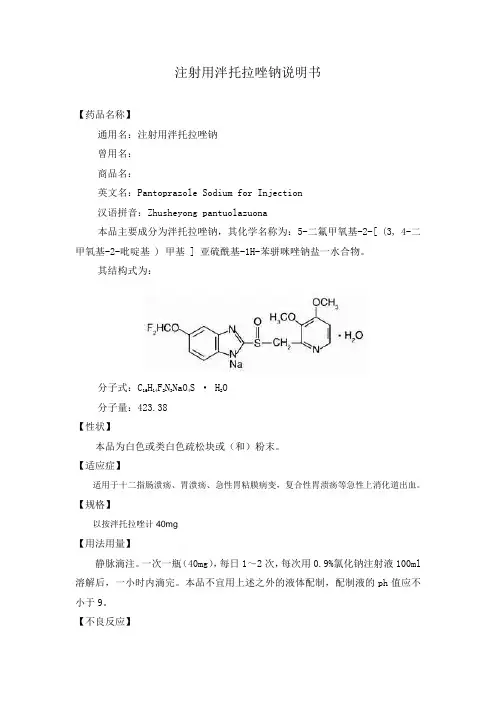
注射用泮托拉唑钠说明书【药品名称】通用名:注射用泮托拉唑钠曾用名:商品名:英文名:Pantoprazole Sodium for Injection汉语拼音:Zhusheyong pantuolazuona本品主要成分为泮托拉唑钠,其化学名称为:5-二氟甲氧基-2-[ (3, 4-二甲氧基-2-吡啶基 ) 甲基 ] 亚硫酰基-1H-苯骈咪唑钠盐一水合物。
其结构式为:分子式:C16H14F2N3NaO4S · H2O分子量:423.38【性状】本品为白色或类白色疏松块或(和)粉末。
【适应症】适用于十二指肠溃疡、胃溃疡、急性胃粘膜病变,复合性胃溃疡等急性上消化道出血。
【规格】以按泮托拉唑计40mg【用法用量】静脉滴注。
一次一瓶(40mg),每日1~2次,每次用0.9%氯化钠注射液100ml 溶解后,一小时内滴完。
本品不宜用上述之外的液体配制,配制液的ph值应不小于9。
【不良反应】偶见头晕、失眠、嗜睡、恶心、腹泻、便秘、皮疹和肌肉疼痛等症状,但程度较轻。
【禁忌】对本品过敏者或严重肝功能不全者禁用。
【注意事项】①应用本品时应首先排除癌症的可能,因为本品治疗可减轻胃癌症状,从而延误诊断。
②肝、肾功能不全者慎用,根据需要酌情较轻。
【孕妇及哺乳期妇女用药】本品禁用。
【儿童用药】未进行该项实验且我可靠参考文献。
【老年患者用药】老年患者应用泮托拉唑后药代动力学(清除率、半衰期、生物利用度)无明显变化,因此老年人不需要改变剂量。
【药物相互作用】1.在体内较高剂量的泮托拉唑不改变安定的清除率,其血清浓度不受安定的影响,表明安定不影响泮托拉唑的代谢。
2.泮托拉唑与氨茶碱、华法令、避孕药、苯妥英钠、氨基比林、地高辛、双氯芬酸、美托洛尔及抗酸剂等之间无相互作用。
【药物过量】大药剂使用时可出现心律不齐,转氨酶升高,肾功能改变,粒细胞降低等。
【药理毒理】本品通过特异性的作用于胃粘膜壁细胞,降低壁细胞中的H+、K+-ATP酶的活性,从而抑制胃酸的分泌。

泮托拉唑的功能主治1. 什么是泮托拉唑?泮托拉唑是一种常用的胃肠道药物,属于质子泵抑制剂(PPI)的一种。
它通过阻断胃中质子泵的功能,抑制胃酸的分泌,从而达到治疗胃酸相关疾病的效果。
2. 泮托拉唑的功能泮托拉唑具有以下功能:•抑制胃酸分泌:泮托拉唑可以特异地抑制胃黏膜细胞中质子泵的功能,从而减少胃酸的分泌。
它通过与质子泵酶结合,形成稳定的共价键,使质子泵失去活性。
这种抑制作用可以持续24小时。
•促进胃溃疡的愈合:由于泮托拉唑能够抑制胃酸的分泌,使得胃黏膜能更好地进行修复和愈合。
它可以加速胃溃疡的病情缓解,并预防复发。
•减少食管反流:泮托拉唑可以缓解胃食管反流的症状,减少胃酸对食管黏膜的损害。
它被广泛应用于治疗胃食管反流性疾病、食管炎等食管疾病。
•治疗幽门螺杆菌感染:幽门螺杆菌是导致胃溃疡和胃癌的重要致病因子。
泮托拉唑可以与抗生素联合应用,共同治疗幽门螺杆菌感染,提高治疗有效率。
•防止非甾体抗炎药引起的胃肠道损伤:非甾体抗炎药(NSAIDs)长期使用会引起胃肠道损伤,包括胃溃疡和出血等。
泮托拉唑可以减少NSAIDs 对胃黏膜的刺激和损伤,并降低胃肠道并发症的发生率。
•辅助治疗胃食管静脉曲张出血:泮托拉唑可以减少胃食管静脉曲张出血的复发率,降低术后并发症的风险。
•外科手术前后的胃酸抑制:术前给予泮托拉唑可以减少手术过程中的胃酸分泌,降低术后并发症的风险。
术后给予泮托拉唑可以促进胃黏膜的修复和愈合。
3. 使用注意事项使用泮托拉唑时需要注意以下事项:•建议在医生指导下使用:泮托拉唑是处方药物,使用前应请医生评估病情并根据需要进行开具处方。
•注意使用剂量和用法:泮托拉唑通常以胶囊或片剂的形式口服,剂量和用法应严格按照医生的指示来进行。
不得随意更改剂量或用法。
•注意药物的副作用:泮托拉唑在使用过程中可能出现一些副作用,包括头痛、腹痛、恶心、腹泻等。
如果出现不适症状,应及时告知医生。
•参考药物相互作用:泮托拉唑可能与其他药物产生相互作用,例如与拜阿司匹林等非甾体消炎药同时使用时可能增加胃肠道出血的风险。

注射用泮托拉唑钠说明书【药品名称】通用名:注射用泮托拉唑钠曾用名:商品名:英文名:Pantoprazole Sodium for Injection汉语拼音:Zhusheyong pantuolazuona本品主要成分为泮托拉唑钠,其化学名称为:5-二氟甲氧基-2-[ (3, 4-二甲氧基-2-吡啶基 ) 甲基 ] 亚硫酰基-1H-苯骈咪唑钠盐一水合物。
其结构式为:分子式:C16H14F2N3NaO4S · H2O分子量:423.38【性状】本品为白色或类白色疏松块或粉末,专用溶媒为无色的澄明液体。
【药理毒理】本品为胃壁细胞质子泵抑制剂,在中性和弱酸性条件下相对稳定,在强酸性条件下迅速活化,其pH依赖的活化特性,使其对H+、K+-ATP酶的作用具有更好的选择性。
本品能特异性地抑制壁细胞顶端膜构成的分泌性微管和胞浆内的管状泡上的H+、K+-ATP酶,引起该酶不可逆性的抑制,从而有效地抑制胃酸的分泌。
由于H+、K+-ATP酶是壁细胞泌酸的最后一个过程,故本品抑酸能力强大。
它不仅能非竞争性抑制促胃液素、组胺、胆碱引起的胃酸分泌,而且能抑制不受胆碱或H2受体阻断剂影响的部分基础胃酸分泌。
本品与其它药物伍用时,具有药物间相互作用小的优点。
本品通过肝细胞内的细胞色素P450酶系的第I系统进行代谢,同时也可以通过第II系统进行代谢。
当与其它通过P450酶系代谢的药物伍用时,本品的代谢途径可以通过第II 酶系统进行,从而不易发生药物代谢酶系的竞争性作用,减少体内药物间的相互作用。
无致突变、致癌和致畸作用。
【药代动力学】本品具有较高的生物利用度,首次口服时即可以达到70%~80%,达峰时间1小时,有效抑酸达24小时。
静脉注射与口服给药的生物利用度比值为1.2。
口服40mg时的t max为2~4小时,C max约为2~3μg/ml,清除半衰期约为1.1小时。
约80%的口服或静注本品的代谢物经尿中排泄,肾功能不全不影响药代动力学,肝功能不全时可延缓清除。


pantroprazole的中文说明书【药品名称】通用名称:泮托拉唑肠溶片商品名称:潘妥洛克英文名称:PantoprazoleEnteric-CoatedTablets汉语拼音:PanTuoLaZuoChangRongPian【成份】泮托拉唑(Pantoprazole)倍半水合钠盐。
化学名:5-二氟甲氧基-2-[(3,4-二甲氧基-2-吡啶甲基)亚硫酰]-1氢苯并咪唑钠倍半水合物分子式:C16H14F2NaO4S·1.5H2O分子量:432 【性状】本品为黄色肠溶衣片,除去包衣后显白色或类白色。
【适应症】适用1.十二指肠溃疡;2.胃溃疡;3.中重度反流性食管炎等。
【用法用量】潘妥洛克若无医师特殊处方应按下述方法服用请遵守这些方法否则可能疗效不佳。
对伴有幽门螺杆菌感染的十二指肠溃疡或胃溃疡须用联合疗法根除感染泮托拉唑与抗菌药物的联合使用可采取下述任何一种方案:1.片泮托拉唑肠溶片×2次/日+1000mg阿莫西林×2次/日+500mg克拉霉素×2次/日2.片泮托拉唑肠溶片×2次/日+500mg甲硝唑×2次/日+500mg克拉霉素×2次/日3.片泮托拉唑肠溶片×2次/日+1000mg阿莫西林×2次/日+500mg甲硝唑×2次/日在联合疗法中有甲硝唑的方案仅在其他方案不能根除幽门螺杆菌感染的情况下方予使用。
若患者无联合疗法的指征如检查幽门螺杆菌阴性泮托拉唑可按下述剂量单独使用除非另有医师处方。
十二指肠溃疡胃溃疡和反流性食管炎患者一般每日服用片泮托拉唑肠溶片个别病例特别是在其它治疗方法无效的情况下可将剂量加倍(即每日片泮托拉唑肠溶片)。
本品不能咀嚼或咬碎,应在早餐前1小时配水完整服用。
【不良反应】1.消化系统常见(≥1%~<10%)上腹痛腹泻便秘或腹胀不常见(≥0.1%~<1%)恶心。
2.全身系统和注射部位罕见(<0.01%)周围性水肿在治疗结束时消失。

核准日期:修订日期:泮托拉唑钠肠溶片40mg说明书请仔细阅读说明书并在医师指导下使用。
【药品名称】通用名称:泮托拉唑钠肠溶片商品名称:潘妥洛克®英文名称:Pantoprazole Sodium Enteric-Coated Tablets汉语拼音:Pan Tuo La Zuo Na Chang Rong Pian【成份】本品主要成份为:泮托拉唑(Pantoprazole)倍半水合钠盐。
化学名称:5-二氟甲氧基-2-[(3,4-二甲氧基-2-吡啶甲基)亚磺酰]-1氢-苯并咪唑倍半水合钠盐化学结构式:分子式:C16H14F2N3NaO4S 1.5H2O分子量:432.4【性状】本品为黄色肠溶衣片,除去包衣后显白色或类白色。
【适应症】-十二指肠溃疡-胃溃疡-中、重度反流性食管炎-与下述药物配伍用能够根除幽门螺杆菌感染:-克拉霉素和阿莫西林,或-克拉霉素和甲硝唑,或-阿莫西林和甲硝唑(详见用药方法)以减少该微生物感染所致的十二指肠溃疡与胃溃疡的复发。
提示泮托拉唑不用于治疗病变轻微的胃肠道疾患,如神经性消化不良。
在应用泮托拉唑治疗胃溃疡前,须除外胃与食道的恶性病变,以免因症状缓解而延误诊断。
反流性食管炎的诊断应经内镜检查核实。
【规格】40mg/片,每片潘妥洛克肠溶片含:45.1 mg 泮托拉唑倍半水合钠盐(相当于40mg泮托拉唑)。
【用法用量】本品若无医师特殊处方,应按下述方法服用,请遵守这些方法,否则可能疗效不佳。
对伴有幽门螺杆菌感染的十二指肠溃疡或胃溃疡须用联合疗法根除感染。
泮托拉唑与抗菌药物的联合使用可采取下述任何一种方案:a.1片泮托拉唑钠肠溶片× 2次/日+ 1000 mg 阿莫西林× 2次/日+ 500 mg 克拉霉素× 2次/日b. 1片泮托拉唑钠肠溶片× 2次/日+ 500 mg甲硝唑× 2次/日+ 500 mg克拉霉素× 2次/日c.1片泮托拉唑钠肠溶片× 2次/日+ 1000 mg阿莫西林× 2次/日+ 500 mg甲硝唑× 2次/日在联合疗法中,有甲硝唑的方案仅在其他方案不能根除幽门螺杆菌感染的情况下方予使用。

泮托拉唑钠肠溶片(U比乐)的说明书日常生活当中人们总离不开吃饭问题,由于一部分人群生活不规律,造成了胃肠疾病的发生。
因此,及时治疗胃肠疾病就成了如今的当务之急。
泮托拉唑钠肠溶片(U比乐)是如今治疗胃肠疾病非常好的药物,它对于各种胃肠消化功能障碍具有非常好的效果,能起到立竿见影的功效,下面我们来看看具体介绍吧。
【药品名称】通用名称:泮托拉唑钠肠溶片商品名称:泮托拉唑钠肠溶片(U比乐)英文名称:Pantoprazole Sodium Enteric-Coated Tablets拼音全码:ZuoTuoLaZuoNaChangRongPian(UBiLe)【主要成份】泮托拉唑钠。
【性状】本品为肠溶衣片,除去包衣后显白色或类白色。
【适应症/功能主治】适用于活动性消化性溃疡(胃、十二指肠溃疡)反流性食管炎和卓艾氏综合症。
【规格型号】40mg*7s【用法用量】口服,每日早晨餐前40mg(1片)十二指肠溃疡疗程通常为2~4周,胃溃疡和反流性食管炎疗程通常为4~6周。
【不良反应】临床应用偶有头晕、失眠、嗜睡、恶心、腹泻和便秘、皮疹、肌肉疼痛等症状。
【禁忌】对本品过敏者、哺乳期妇女及妊娠头三个月妇女禁用。
【注意事项】1.大剂量使用时,可出现心律不齐、转氨酶增高、肾功能改变、粒细胞降低等。
2.本品为肠溶制剂,服用时请勿咀嚼。
3.当怀疑胃溃疡时,应首先排除癌症的可能性,因为本品治疗可减轻其症状,从而延误诊断。
4.肝肾功能不全者慎用,严重肝病时本品清除延缓,应减少用量。
【儿童用药】本品儿童用药疗效及安全性资料尚未建立。
婴幼儿禁用。
【老年患者用药】无剂量调整要求。
【孕妇及哺乳期妇女用药】哺乳期妇女及妊娠三个月内妇女禁用。
【药物相互作用】泮托拉唑与其他药物的相互作用小,与奥美拉唑相比,对细胞色素P450系统作用较小,不影响安定的作用时间,与口服避孕药、地高辛、华法林、苯妥英或茶碱无明显相互作用。
【药物过量】尚不明确。
【药理毒理】本品通过特异性地作用于胃粘膜壁细胞,降低壁细胞中的H+-K+-ATP酶的活性,从而抑制胃酸的分泌。

泮托拉唑钠肠溶片说明书请仔细阅读说明书并在医师指导下服用【药品名称】通用名:泮托拉唑钠肠溶片英文名:Pantoprazole Sodium Enteric-Coated Tablets汉语拼音:Pantuolazuona Changrong Pian【成份】本品主要成份为:泮托拉唑钠,其化学名称为:5-二氟甲氧基-2-[ (3, 4-二甲氧基-2-吡啶基) 甲基] 亚硫酰基-1H-苯骈咪唑钠盐一水合物。
分子式:C16H14F2N3O4SNa.H2O分子量:423.38【性状】本品为肠溶衣片,除去包衣后显白色。
【药理毒理】药理作用泮托拉唑为质子泵抑制剂,通过与胃壁细胞的H+ -K+ ATP酶系统的两个位点共价结合而抑制胃酸产生的最后步骤。
该作用呈剂量依赖性并使基础和刺激状态下的胃酸分泌均受抑制。
本品与H+ -K+ ATP酶的结合可导致其抗胃酸分泌作用持续24小时以上。
毒理研究遗传毒性:泮托拉唑的人淋巴细胞染色体畸变试验、中国仓鼠卵巢细胞/HGPRT 正向突变试验及二次小鼠微核试验中的一次结果均为阳性,而大鼠肝脏DNA共价结合试验结果难以判断。
Ames试验、大鼠肝细胞程序外DNA合成试验(UDS)、AS52/GPT哺乳动物细胞正向基因突变试验、小鼠淋巴瘤L5178Y 细胞胸腺嘧啶激酶突变试验及体内大鼠骨髓细胞染色体畸变试验结果均为阴性。
生殖毒性:雄性大鼠经口给予泮托拉唑500mg/kg/d(按体表面积折算,约为临床推荐口服剂量的98倍),雌性大鼠经口给予泮托拉唑450mg/kg/d(约为临床推荐口服剂量的88倍)时,生育力和生殖行为未见明显异常。
雌性大鼠经口给予泮托拉唑450mg/kg/d(约为临床推荐口服剂量的88倍),家兔经口给予泮托拉唑40 mg/kg/d(约为临床推荐口服剂量的16倍),对生育力和胎仔均未见明显损害。
泮托拉唑及其代谢产物可以从家兔乳汁中分泌。
致癌性:SD大鼠连续24个月经口给予泮托拉唑0.5-200mg/kg/d(以50kg人每日口服40mg计,按体表面积折算,其暴露剂量为人用剂量的0.1-40倍),胃底出现剂量依赖性的肠嗜铬样细胞增生及良性和恶性的神经内分泌细胞瘤。

HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use PROTONIX safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PROTONIX.PROTONIX (pantoprazole sodium) delayed-release tablets PROTONIX (pantoprazole sodium) for delayed-release oral suspension Initial U.S. approval: 2000———————— RECENT MAJOR CHANGES ———————— Indications and Usage, Pediatric (1) 11/2009 Dosage and Administration, Pediatric (2) 11/2009 Contraindications (4) 11/2009 Warnings and Precautions, Bone Fracture (5.4) 0x/2010 ———————— INDICATIONS AND USAGE ———————— PROTONIX is a proton pump inhibitor indicated for the following: ∙Short-Term Treatment of Erosive Esophagitis Associated with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) (1.1)∙Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis (1.2)∙Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions Including Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (1.3)——————— DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ——————Indication Dose FrequencyShort-Term Treatment of Erosive Esophagitis Associated With GERD (2.1)Adults 40 mg Once Daily for up to 8 wks Children (5 years and older)≥ 15 kg to < 40 kg 20 mg Once Daily for up to 8 wks≥ 40 kg 40 mgMaintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis (2.1)Adults 40 mg Once DailyPathological Hypersecretory Conditions Including Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (2.1)Adults 40 mg Twice DailySee full prescribing information for administration instructions—————— DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS —————— ∙Delayed-Release Tablets, 20 mg and 40 mg (3)∙For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension, 40 mg (3) ————————— CONTRAINDICATIONS ———————— Known hypersensitivity to any component of the formulation or to substituted benzimidazoles (4)——————— WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS —————— ∙Symptomatic response does not preclude presence of gastric malignancy (5.1)∙Atrophic gastritis has been noted with long-term therapy (5.2)∙ Bone FractureLong-term and multiple daily dose PPI therapy may be associatedwith an increased risk for osteoporosis-related fractures of thehip, wrist or spine. (5)————————— ADVERSE REACTIONS ————————— The most frequently occurring adverse reactions are as follows: ∙For adult use (>2%) are headache, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, flatulence, dizziness, and arthralgia. (6) ∙For pediatric use (>4%) are URI, headache, fever, diarrhea, vomiting, rash, and abdominal pain. (6)To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-800-934-5556 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or /medwatch————————— DRUG INTERACTIONS ————————— ∙Do not co-administer with atazanavir or nelfinavir (7.1)∙Concomitant warfarin use may require monitoring (7.2)∙May interfere with the absorption of drugs where gastric pH is important for bioavailability (7.3)∙May produce false-positive urine screen for THC (7.4)See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION andFDA-approved patient labeling.Revised: 12/2009FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS *1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE1.1 Short-Term Treatment of Erosive Esophagitis Associated WithGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)1.2 Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis1.3 Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions Including Zollinger-EllisonSyndrome2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION2.1 Recommended Dosing Schedule2.2 Administration Instructions3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS4 CONTRAINDICATIONS5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS5.1 Concurrent Gastric Malignancy5.2 Atrophic Gastritis5.3 Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B-12) Deficiency5.4 Bone Fracture5.5 Tumorigenicity5.6 Interference with Urine Screen for THC6 ADVERSE REACTIONS6.1 Clinical Trial Experience6.2 Postmarketing Experience7 DRUG INTERACTIONS7.1 Interference with Antiretroviral Therapy7.2 Coumarin Anticoagulants7.3 Drugs for Which Gastric pH Can Affect Bioavailability7.4 False Positive Urine Tests for THC* Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS8.1 Pregnancy8.3 Nursing Mothers8.4 Pediatric Use8.5 Geriatric Use8.6 Gender8.7 Patients with Hepatic Impairment10 OVERDOSAGE11 DESCRIPTION12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY12.1 Mechanism of Action12.2 Pharmacodynamics12.3 Pharmacokinetics12.4 Pharmacogenomics13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology14 CLINICAL STUDIES14.1 Erosive Esophagitis (EE) Associated with Gastroesophageal RefluxDisease (GERD)14.2 Long-Term Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis14.3 Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions Including Zollinger-EllisonSyndrome16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATIONFULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION1 INDICATIONS AND USAGEPROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension and PROTONIX Delayed-Release Tablets are indicated for:1.1 Short-Term Treatment of Erosive Esophagitis Associated With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)PROTONIX is indicated in adults and pediatric patients five years of age and older for the short-term treatment (up to 8 weeks) in the healing and symptomatic relief of erosive esophagitis. For those adult patients who have not healed after 8 weeks of treatment, an additional 8-week course of PROTONIX may be considered. Safety of treatment beyond 8 weeks in pediatric patients has not been established.1.2 Maintenance of Healing of Erosive EsophagitisPROTONIX is indicated for maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis and reduction in relapse rates of daytime and nighttime heartburn symptoms in adult patients with GERD. Controlled studies did not extend beyond 12 months.1.3 Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions Including Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome PROTONIX is indicated for the long-term treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions, including Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION2.1 Recommended Dosing SchedulePROTONIX is supplied as delayed-release granules in packets for preparation of oral suspensions or as delayed-release tablets. The recommended dosages are outlined in Table 1.Table 1: Recommended Dosing Schedule for PROTONIXIndication Dose FrequencyShort-Term Treatment of Erosive Esophagitis Associated With GERDAdults 40 mg Once daily for up to 8 weeks*Children (5 years and older)≥ 15 kg to < 40 kg 20 mg Once daily for up to 8 weeks≥ 40 kg 40 mgMaintenance of Healing of Erosive EsophagitisAdults 40 mg Once dailyPathological Hypersecretory Conditions Including Zollinger-Ellison SyndromeAdults 40 mg Twice daily*** For adult patients who have not healed after 8 weeks of treatment, an additional 8-week course of PROTONIX may be considered.** Dosage regimens should be adjusted to individual patient needs and should continue for as long as clinically indicated. Doses up to 240 mg daily have been administered.2.2 Administration InstructionsDirections for method of administration for each dosage form are presented in Table 2.Table 2: Administration InstructionsFormulation Route Instructions*Delayed-Release TabletsFor Delayed-Release Oral Administered in 1 teaspoonful of applesauce or apple Oral Suspension juice approximately 30 minutes prior to a mealFor Delayed-Release Nasogastric See instructions belowOral Suspension tube* Patients should be cautioned that PROTONIX Delayed-Release Tablets and PROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension should not be split, chewed, or crushed.PROTONIX Delayed-Release TabletsPROTONIX Delayed-Release Tablets should be swallowed whole, with or without food in the stomach. If patients are unable to swallow a 40 mg tablet, two 20 mg tablets may be taken. Concomitant administration of antacids does not affect the absorption of PROTONIXDelayed-Release Tablets.PROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral SuspensionPROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension should only be administered approximately 30 minutes prior to a meal via oral administration in apple juice or applesauce or nasogastric tube in apple juice only. Because proper pH is necessary for stability, do not administer PROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension in liquids other than apple juice, or foods other than applesauce.Do not divide the 40 mg PROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension packet to create a 20 mg dosage for pediatric patients who are unable to take the tablet formulation. PROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension - Oral Administration in Applesauce∙Open packet.∙Sprinkle granules on one teaspoonful of applesauce. DO NOT USE OTHER FOODS OR CRUSH OR CHEW THE GRANULES.∙Take within 10 minutes of preparation.∙Take sips of water to make sure granules are washed down into the stomach. Repeat water sips as necessary.PROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension - Oral Administration in Apple Juice∙Open packet.∙Empty granules into a small cup or teaspoon containing one teaspoon of apple juice.∙Stir for 5 seconds (granules will not dissolve) and swallow immediately.∙To make sure that the entire dose is taken, rinse the container once or twice with apple juice to remove any remaining granules. Swallow immediately.PROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension - Nasogastric (NG) Tube or Gastrostomy Tube AdministrationFor patients who have a nasogastric tube or gastrostomy tube in place, PROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension can be given as follows:∙Remove the plunger from the barrel of a 2 ounce (60 mL) catheter-tip syringe. Discard the plunger.∙Connect the catheter tip of the syringe to a 16 French (or larger) tube.∙Hold the syringe attached to the tubing as high as possible while giving PROTONIX For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension to prevent any bending of the tubing.∙Empty the contents of the packet into the barrel of the syringe.∙ Add 10 mL (2 teaspoonfuls) of apple juice and gently tap and/or shake the barrel of the syringe to help rinse the syringe and tube. Repeat at least twice more using the sameamount of apple juice (10 mL or 2 teaspoonfuls) each time. No granules should remain in the syringe.3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSDelayed-Release Tablets:∙40 mg, yellow oval biconvex tablets imprinted with PROTONIX (brown ink) on one side∙20 mg, yellow oval biconvex tablets imprinted with P20 (brown ink) on one sideFor Delayed-Release Oral Suspension:40 mg, pale yellowish to dark brownish, enteric-coated granules in a unit dose packet4 CONTRAINDICATIONSPROTONIX is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any component of the formulation [see Description (11)] or any substituted benzimidazole.5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS5.1 Concurrent Gastric MalignancySymptomatic response to therapy with PROTONIX does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy.5.2 Atrophic GastritisAtrophic gastritis has been noted occasionally in gastric corpus biopsies from patients treated long-term with PROTONIX, particularly in patients who were H. pylori positive.5.3 Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B-12) DeficiencyGenerally, daily treatment with any acid-suppressing medications over a long period of time (e.g., longer than 3 years) may lead to malabsorption of cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B-12) caused by hypo- or achlorhydria. Rare reports of cyanocobalamin deficiency occurring with acid-suppressing therapy have been reported in the literature. This diagnosis should be considered if clinical symptoms consistent with cyanocobalamin deficiency are observed.5.4 Bone FractureSeveral published observational studies suggest that proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy may be associated with an increased risk for osteoporosis-related fractures of the hip, wrist, or spine. The risk of fracture was increased in patients who received high-dose, defined as multiple daily doses, and long-term PPI therapy (a year or longer). Patients should use the lowest dose and shortest duration of PPI therapy appropriate to the condition being treated. Patients at risk for osteoporosis-related fractures should be managed according to established treatment guidelines [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].5.5 TumorigenicityDue to the chronic nature of GERD, there may be a potential for prolonged administration of PROTONIX. In long-term rodent studies, pantoprazole was carcinogenic and caused rare types of gastrointestinal tumors. The relevance of these findings to tumor development in humans is unknown [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].5.6 Interference with Urine Screen for THCSee Drug Interactions (7.4).6 ADVERSE REACTIONSThe adverse reaction profiles for PROTONIX (pantoprazole sodium) For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension and PROTONIX (pantoprazole sodium) Delayed-Release Tablets are similar.6.1 Clinical Trial ExperienceBecause clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.AdultsSafety in nine randomized comparative US clinical trials in patients with GERD included 1,473 patients on oral PROTONIX (20 mg or 40 mg), 299 patients on an H2-receptor antagonist, 46 patients on another proton pump inhibitor, and 82 patients on placebo. The most frequently occurring adverse reactions are listed in Table 3.Table 3: Adverse Reactions Reported in Clinical Trials of Adult Patients with GERD at aFrequency of > 2%PROTONIX Comparators Placebo(n=1473) (n=345) (n=82)% %% Headache 12.2 12.8 8.5 Diarrhea 8.8 9.6 4.9 Nausea 7.0 5.2 9.8 Abdominal pain 6.2 4.1 6.1 Vomiting 4.3 3.5 2.4 Flatulence 3.9 2.9 3.7 Dizziness 3.0 2.9 1.2 Arthralgia 2.8 1.4 1.2 Additional adverse reactions that were reported for PROTONIX in clinical trials with a frequency of ≤ 2% are listed below by body system:Body as a Whole: allergic reaction, pyrexia, photosensitivity reaction, facial edema Gastrointestinal: constipation, dry mouth, hepatitisHematologic: leukopenia, thrombocytopeniaMetabolic/Nutritional: elevated CK (creatine kinase), generalized edema, elevated triglycerides, liver enzymes elevatedMusculoskeletal: myalgiaNervous: depression, vertigoSkin and Appendages: urticaria, rash, pruritusSpecial Senses: blurred visionPediatric PatientsSafety of PROTONIX in the treatment of Erosive Esophagitis (EE) associated with GERD was evaluated in pediatric patients ages 1 year through 16 years in three clinical trials. Safety trials involved pediatric patients with EE; however, as EE is uncommon in the pediatric population, 249 pediatric patients with endoscopically-proven or symptomatic GERD were also evaluated. All adult adverse reactions to PROTONIX are considered relevant to pediatric patients. In patients ages 1 year through 16 years, the most commonly reported (> 4%) adverse reactions include: URI, headache, fever, diarrhea, vomiting, rash, and abdominal pain.For safety information in patients less than 1 year of age see Use in Specific Populations (8.4). Additional adverse reactions that were reported for PROTONIX in pediatric patients in clinical trials with a frequency of ≤ 4% are listed below by body system:Body as a Whole: allergic reaction, facial edemaGastrointestinal: constipation, flatulence, nauseaMetabolic/Nutritional: elevated triglycerides, elevated liver enzymes, elevated CK (creatine kinase)Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, myalgiaNervous: dizziness, vertigoSkin and Appendages: urticariaThe following adverse reactions seen in adults in clinical trials were not reported in pediatric patients in clinical trials, but are considered relevant to pediatric patients: photosensitivity reaction, dry mouth, hepatitis, thrombocytopenia, generalized edema, depression, pruritus, leukopenia, and blurred vision.Zollinger-Ellison SyndromeIn clinical studies of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, adverse reactions reported in 35 patients taking PROTONIX 80 mg/day to 240 mg/day for up to 2 years were similar to those reported in adult patients with GERD.6.2 Postmarketing ExperienceThe following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of PROTONIX. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.These adverse reactions are listed below by body system:Immune System Disorders: anaphylaxis (including anaphylactic shock)Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: severe dermatologic reactions (some fatal), including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN, some fatal), and angioedema (Quincke’s edema)Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: rhabdomyolysis, bone fractureRenal and Urinary Disorders: interstitial nephritisHepatobiliary Disorders: hepatocellular damage leading to jaundice and hepatic failure Psychiatric Disorders: hallucination, confusion7 DRUG INTERACTIONS7.1 Interference with Antiretroviral TherapyConcomitant use of atazanavir or nelfinavir with proton pump inhibitors is not recommended. Coadministration of atazanavir or nelfinavir with proton pump inhibitors is expected to substantially decrease atazanavir or nelfinavir plasma concentrations and may result in a loss of therapeutic effect and development of drug resistance.7.2 Coumarin AnticoagulantsThere have been postmarketing reports of increased INR and prothrombin time in patients receiving proton pump inhibitors, including PROTONIX, and warfarin concomitantly. Increases in INR and prothrombin time may lead to abnormal bleeding and even death. Patients treated with proton pump inhibitors and warfarin concomitantly should be monitored for increases in INR and prothrombin time.7.3 Drugs for Which Gastric pH Can Affect BioavailabilityPantoprazole causes long-lasting inhibition of gastric acid secretion. Therefore, pantoprazole may interfere with absorption of drugs where gastric pH is an important determinant of their bioavailability (e.g., ketoconazole, ampicillin esters, and iron salts).7.4 False Positive Urine Tests for THCThere have been reports of false positive urine screening tests for tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in patients receiving proton pump inhibitors. An alternative confirmatory method should be considered to verify positive results.8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS8.1 PregnancyTeratogenic EffectsPregnancy Category BReproduction studies have been performed in rats at oral doses up to 88 times the recommended human dose and in rabbits at oral doses up to 16 times the recommended human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to pantoprazole. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)]. 8.3 Nursing MothersPantoprazole and its metabolites are excreted in the milk of rats. Pantoprazole excretion in human milk has been detected in a study of a single nursing mother after a single 40 mg oral dose. The clinical relevance of this finding is not known. Many drugs which are excreted in human milk have a potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants. Based on the potential for tumorigenicity shown for pantoprazole in rodent carcinogenicity studies, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the benefit of the drug to the mother.8.4 Pediatric UseThe safety and effectiveness of PROTONIX for short-term treatment (up to eight weeks) of erosive esophagitis (EE) associated with GERD have been established in pediatric patients 1 year through 16 years of age. Effectiveness for EE has not been demonstrated in patients less than 1 year of age. In addition, for patients less than 5 years of age, there is no appropriate dosage strength in an age-appropriate formulation available. Therefore, PROTONIX is indicated for the short-term treatment of EE associated with GERD for patients 5 years and older. The safety and effectiveness of PROTONIX for pediatric uses other than EE have not been established.1 year through 16 years of ageUse of PROTONIX in pediatric patients 1 year through 16 years of age for short-term treatment (up to eight weeks) of EE associated with GERD is supported by: a) extrapolation of results from adequate and well-controlled studies that supported the approval of PROTONIX for treatment of EE associated with GERD in adults, and b) safety, effectiveness, and pharmacokinetic studies performed in pediatric patients [see Clinical Studies (14.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Safety of PROTONIX in the treatment of EE associated with GERD in pediatric patients 1 through 16 years of age was evaluated in three multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-treatment studies, involving 249 pediatric patients, including 8 with EE (4 patients ages 1 yearto 5 years and 4 patients 5 years to 11 years). The children ages 1 year to 5 years with endoscopically diagnosed EE (defined as an endoscopic Hetzel-Dent score ≥ 2) were treated once daily for 8 weeks with one of two dose levels of PROTONIX (approximating 0.6 mg/kg or 1.2 mg/kg). All 4 of these patients with EE were healed (Hetzel-Dent score of 0 or 1) at 8 weeks. Because EE is uncommon in the pediatric population, predominantly pediatric patients with endoscopically-proven or symptomatic GERD were also included in these studies. Patients were treated with a range of doses of PROTONIX once daily for 8 weeks. For safety findings see Adverse Reactions (6.1). Because these pediatric trials had no placebo, active comparator, or evidence of a dose response, the trials were inconclusive regarding the clinical benefit of PROTONIX for symptomatic GERD in the pediatric population. The effectiveness of PROTONIX for treating symptomatic GERD in pediatric patients has not been established. Although the data from the clinical trials support use of PROTONIX for the short-term treatment of EE associated with GERD in pediatric patients 1 year through 5 years, there is no commercially available dosage formulation appropriate for patients less than 5 years of age [see Dosage and Administration (2)].In a population pharmacokinetic analysis, clearance values in the children 1 to 5 years old with endoscopically proven GERD had a median value of 2.4 L/h. Following a 1.2 mg/kg equivalent dose (15 mg for ≤ 12.5 kg and 20 mg for > 12.5 to < 25 kg), the plasma concentrations of pantoprazole were highly variable and the median time to peak plasma concentration was 3 to 6 hours. The estimated AUC for patients 1 to 5 years old was 37% higher than for adults receiving a single 40 mg tablet, with a geometric mean AUC value of 6.8 µg•hr/mL. Neonates to less than one year of agePROTONIX was not found to be effective in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, treatment-withdrawal study of 129 pediatric patients 1 through 11 months of age. Patients were enrolled if they had symptomatic GERD based on medical history and had not responded to non-pharmacologic interventions for GERD for two weeks. Patients received PROTONIX daily for four weeks in an open-label phase, then patients were randomized in equal proportion to receive PROTONIX treatment or placebo for the subsequent four weeks in a double-blind manner. Efficacy was assessed by observing the time from randomization to study discontinuation due to symptom worsening during the four-week treatment-withdrawal phase. There was no statistically significant difference between PROTONIX and placebo in the rate of discontinuation.In this trial, the adverse reactions that were reported more commonly (difference of ≥ 4%) in the treated population compared to the placebo population were elevated CK, otitis media, rhinitis, and laryngitis.In a population pharmacokinetic analysis, the systemic exposure was higher in patients less than 1 year of age with GERD compared to adults who received a single 40 mg dose (geometric mean AUC was 103% higher in preterm infants and neonates receiving single dose of 2.5 mg of PROTONIX, and 23% higher in infants 1 through 11 months of age receiving a single dose of approximately 1.2 mg/kg). In these patients, the apparent clearance (CL/F) increased with age (median clearance: 0.6 L/hr, range: 0.03 to 3.2 L/hr).These doses resulted in pharmacodynamic effects on gastric but not esophageal pH. Following once daily dosing of 2.5 mg of PROTONIX in preterm infants and neonates, there was an increase in the mean gastric pH (from 4.3 at baseline to 5.2 at steady-state) and in the mean % time that gastric pH was > 4 (from 60% at baseline to 80% at steady-state). Following once daily dosing of approximately 1.2 mg/kg of PROTONIX in infants 1 through 11 months of age, there was an increase in the mean gastric pH (from 3.1 at baseline to 4.2 at steady-state) and in the mean % time that gastric pH was > 4 (from 32% at baseline to 60% at steady-state). However, no significant changes were observed in mean intraesophageal pH or % time that esophageal pH was < 4 in either age group.Because PROTONIX was not shown to be effective in the randomized, placebo-controlled study in this age group, the use of PROTONIX for treatment of symptomatic GERD in infants less than 1 year of age is not indicated.8.5 Geriatric UseIn short-term US clinical trials, erosive esophagitis healing rates in the 107 elderly patients (≥ 65 years old) treated with PROTONIX were similar to those found in patients under the age of 65. The incidence rates of adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in patients aged 65 years and older were similar to those associated with patients younger than 65 years of age.8.6 GenderErosive esophagitis healing rates in the 221 women treated with PROTONIX Delayed-Release Tablets in US clinical trials were similar to those found in men. In the 122 women treatedlong-term with PROTONIX 40 mg or 20 mg, healing was maintained at a rate similar to that in men. The incidence rates of adverse reactions were also similar for men and women.8.7 Patients with Hepatic ImpairmentDoses higher than 40 mg/day have not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].10 OVERDOSAGEExperience in patients taking very high doses of PROTONIX (> 240 mg) is limited. Spontaneous post-marketing reports of overdose are generally within the known safety profile of PROTONIX.Pantoprazole is not removed by hemodialysis. In case of overdosage, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive.Single oral doses of pantoprazole at 709 mg/kg, 798 mg/kg, and 887 mg/kg were lethal to mice, rats, and dogs, respectively. The symptoms of acute toxicity were hypoactivity, ataxia, hunched sitting, limb-splay, lateral position, segregation, absence of ear reflex, and tremor.11 DESCRIPTIONThe active ingredient in PROTONIX (pantoprazole sodium) For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension and PROTONIX (pantoprazole sodium) Delayed-Release Tablets is a substituted benzimidazole, sodium 5-(difluoromethoxy)-2-[[(3,4-dimethoxy-2-pyridinyl)methyl] sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole sesquihydrate, a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion. Its empirical formula is C16H14F2N3NaO4S x 1.5 H2O, with a molecular weight of 432.4. The structural formula is:Pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate is a white to off-white crystalline powder and is racemic. Pantoprazole has weakly basic and acidic properties. Pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate is freely soluble in water, very slightly soluble in phosphate buffer at pH 7.4, and practically insoluble in n-hexane.The stability of the compound in aqueous solution is pH-dependent. The rate of degradation increases with decreasing pH. At ambient temperature, the degradation half-life is approximately 2.8 hours at pH 5 and approximately 220 hours at pH 7.8.PROTONIX (pantoprazole sodium) is supplied as a for delayed-release oral suspension, available in one strength (40 mg), and as a delayed-release tablet, available in two strengths (20 mg and 40 mg).Each PROTONIX (pantoprazole sodium) Delayed-Release Tablet contains 45.1 mg or22.56 mg of pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate (equivalent to 40 mg or 20 mg pantoprazole, respectively) with the following inactive ingredients: calcium stearate, crospovidone, hypromellose, iron oxide, mannitol, methacrylic acid copolymer, polysorbate 80, povidone, propylene glycol, sodium carbonate, sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, and triethyl citrate. PROTONIX Delayed-Release Tablets (40 mg and 20 mg) complies with USP dissolution test 2.PROTONIX (pantoprazole sodium) For Delayed-Release Oral Suspension, 40 mg, contains the active ingredient pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate in the form of enteric-coated granules in unit dose packets. Each unit dose packet contains enteric-coated granules containing 45.1 mg pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate (equivalent to 40 mg of pantoprazole) with the following inactive ingredients: crospovidone, hypromellose, methacrylic acid copolymer, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 80, povidone, sodium carbonate, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, titanium dioxide, triethyl citrate, and yellow ferric oxide.。
打针用泮托拉唑钠解释书【通用名】打针用泮托拉唑钠【英文名】PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM FOR INJECTION【拼音名】ZHUSHEYONG PANTUOLAZUONA【药品类别】抗酸药及抗溃疡病药【化学名】5-二氟甲氧基-2-[(3,4-二甲氧基-2-吡啶基)甲基]亚硫酰基-1H-苯骈咪唑钠盐一水合物【构造式】【分子式】C16H14F2N3NaO4S·H2O【分子量】【性状】本品为白色或类白色松散块或粉末,专用溶媒为无色的澄明液体.【药理毒理】本品为胃壁细胞质子泵克制剂,在中性和弱酸性前提下相对稳固,在强酸性前提下敏捷活化,其pH依附的活化特征,使其对H+.K+-ATP酶的作器具有更好的选择性.本品能特异性地克制壁细胞顶端膜组成的渗出性微管和胞浆内的管状泡上的H+.K+-ATP酶,引起该酶不成逆性的克制,从而有用地克制胃酸的渗出.因为H+.K+-ATP酶是壁细胞泌酸的最后一个进程,故本品抑酸才能壮大.它不但能非竞争性克制促胃液素.组胺.胆碱引起的胃酸渗出,并且能克制不受胆碱或H2受体阻断剂影响的部分基本胃酸渗出.本品与其它药物伍用时,具有药物间互相感化小的长处.本品经由过程肝细胞内的细胞色素P450酶系的第I体系进行代谢,同时也可以经由过程第II体系进行代谢.当与其它经由过程P450酶系代谢的药物伍用时,本品的代谢门路可以经由过程第II 酶体系进行,从而不轻易产生药物代谢酶系的竞争性感化,削减体内药物间的互相感化.无致突变.致癌和致畸感化.【药代动力学】本品具有较高的生物运费用,初次口服时即可以达到70%~80%,达峰时光1小时,有用抑酸达24小时.静脉打针与口服给药的生物运费用比值为1.2.口服40mg时的tmax为2~4小时,Cmax约为2~3μg/ml,消除半衰期约为1.1小时.约80%的口服或静注本品的代谢物经尿中渗出,肾功效不全不影响药代动力学,肝功效不全时可延缓消除.t1/2.消除率和表不雅散布容积与给药剂量无关.顺应症重要用于:①消化性溃疡出血.②非甾体类抗炎药引起的急性胃黏膜毁伤和应激状况下溃疡大出血的产生;③全身麻醉或大手术后以及虚弱晕厥患者防止胃酸反流归并吸入性肺炎.【用法用量】静脉滴注.一次40mg,每日1~2次,临用前将10ml专用溶剂注入冻干粉小瓶内,将上述消融后的药液参加0.9%氯化钠打针液100ml中稀释后供静脉滴注,静脉滴注时光请求15~30分钟内滴完.本品消融和稀释后必须在3小时内用完,制止用其它溶剂或其它药物消融和稀释.【不良反响】偶见头晕.掉眠.嗜睡.恶心.腹泻.便秘.皮疹和肌肉痛苦悲伤等症状.大剂量运用时可消失心律不齐.转氨酶升高.肾功效转变.粒细胞下降等.禁忌症对本品过敏者禁用;怀胎期与哺乳期妇女禁用.【留意事项】①本品克制胃酸渗出的感化强,时光长,故运用本品时不宜同时再服用其它抗酸剂或抑酸剂.为防止抑酸过度,在一般消化性溃疡等病时,不建议大剂量长期运用(卓-艾分解征破例).②肾功效受损者不须调剂剂量;肝功效受损者须要酌情减量.③治疗胃溃疡时应消除胃癌后才干运用本品,以免耽搁诊断和治疗.④动物试验中,长期大量运用本品后,不雅察到高胃泌素血症及继发胃ECL-细胞增大和良性肿瘤的产生,这种变更在运用其它抑酸剂及施行胃大部切除术后亦可消失.【妊妇及哺乳期妇女用药】怀胎期与哺乳期妇女禁用.【儿童用药】尚无儿童静脉运用本品的经验.【老年患者用药】老年人用药剂量无需调剂.【药物互相感化】【药物过量】【贮藏】密闭,遮光保管.【包装】【有用期】。
泮托拉唑服用方法正确的是泮托拉唑是一种常用的抗酸药物,通常用于治疗胃溃疡、十二指肠溃疡、胃食管反流病等消化系统疾病。
正确的使用方法对于药效的发挥至关重要,下面我们来详细介绍泮托拉唑的正确服用方法。
首先,泮托拉唑通常是口服药物,可以在饭前或者饭后服用。
一般来说,如果是治疗胃溃疡或十二指肠溃疡,建议在早餐前服用;如果是治疗胃食管反流病,可以在早餐前或晚餐前服用。
建议在医生的指导下确定具体的服用时间。
其次,泮托拉唑的剂量一般为20毫克,每天一次。
但具体的剂量和使用频率应根据患者的病情和医生的建议来确定。
在使用泮托拉唑之前,一定要咨询医生,不要随意增减剂量或改变使用频率。
另外,泮托拉唑通常需要空腹服用,即在饭前30分钟到1小时服用。
这样可以提高药物的吸收效果,使药效更好地发挥。
如果因为特殊原因无法空腹服用,也可以在饭后1小时服用,但不建议在饭后立即服用。
此外,泮托拉唑通常需要连续服用一段时间才能见效。
一般来说,治疗胃溃疡或十二指肠溃疡需要4-8周的治疗;治疗胃食管反流病需要4-8周的治疗,如果症状持续,还可以延长治疗时间。
在使用过程中,一定要按照医生的建议坚持使用,不要随意中断或停止服用。
最后,泮托拉唑在使用过程中可能会出现一些副作用,如头痛、腹泻、恶心、乏力等。
如果出现严重不良反应,如皮疹、呼吸困难、肿胀等,应立即就医。
在使用过程中,一定要密切关注自身的身体状况,如有异常应及时就医。
总之,正确的泮托拉唑服用方法对于治疗消化系统疾病非常重要。
在使用前一定要咨询医生,确定正确的剂量和使用频率;在使用过程中要按照医生的建议坚持使用,不要随意中断或停止服用;同时要密切关注自身的身体状况,如有异常应及时就医。
希望患者能够根据以上建议正确使用泮托拉唑,早日康复。
商品名
称:
泮托拉唑肠溶片(潘妥洛克) 通用名
称:
泮托拉唑肠溶片
规格: 40mg×7片/盒,双铝泡罩
成份: 潘妥洛克40mg×7片主要成份为泮托拉唑(Pantoprazole)倍半水合钠盐化学名:5-二氟甲氧基-2-[(3,4-二甲氧基-2-吡啶甲基)亚硫酰]-1氢苯并咪唑钠倍半水合物分子式:C16H14F2NaO4S×1.5H2O分子量:432
性状: 本品为黄色肠溶衣片,除去包衣后显白色或类白色。
用法用量: 本品若无医师处方,应按下述方法服用,请遵守这些方法,否则可能疗效不佳。
对伴有幽门螺杆菌感染的十二指肠溃疡或胃溃疡须用联合疗法根除感染。
潘妥洛克与抗菌药物的联合使用可采取下述任何一种方案:a、1片潘妥洛克肠溶片×2/日+1000mg阿莫西林×2/日+500mg 克拉霉素×2/日b、1片潘妥洛克肠溶片×2/日+500mg甲硝唑×2/日+500mg克拉霉素×2/日c、1片潘妥洛克肠溶片×2/日+1000mg阿莫西林×2/日+500mg甲硝唑×2/日在联合疗法中,有甲硝唑的方案仅在其他方案不能根除幽门螺杆菌感染的情况下方予使用。
若患者无联合疗法的指征,如检查幽门螺杆菌阴性,潘妥洛克可按下述剂量单独使用,除非另有医师处方:a、十二指肠溃疡、胃溃疡和反流性食管炎患者一般每日服用1片潘妥洛克肠溶片。
b、个别病例,特别是在其它治疗方法无效的情况下,可将剂量加倍(即每日2片潘妥洛克肠溶片)。
注意:a、肾功能受损和老年患者每日潘妥洛克的剂量一般不应超过40mg,但有些情况例外。
b、为根除幽门螺杆菌感染而使用联合疗法时,老年患者在1周治疗中也使用常规剂量(40mg×2/日)的潘妥洛克。
c、严重肝功能受损衰竭的患者剂量应减少至隔日1片
(40mg)潘妥洛克。
功能主治(适应症): 1.十二指肠溃疡2.胃溃疡3.中重度反流性食管炎4.与下述药物配伍用能够根除幽门螺杆菌感染(1)克拉霉素和阿莫西林(2)克拉霉素和甲硝唑(详见用药方法)以减少该微生物感染所致的十二指肠溃疡与胃溃疡的复发。
提示泮托拉唑不用于治疗病变轻微的胃肠道疾患如神经性消化不良。
在应用泮托拉唑治疗胃溃疡前须除外胃与食道的恶性病变以免因症状缓解而延误诊断。
反流性食管炎的诊断应经内镜检查核实。
不良反应: 1.消化系统常见(≥1%~<10%)上腹痛腹泻便秘或腹胀不常见
(≥0.1%~<1%)恶心。
2.全身系统和注射部位罕见(<0.01%)周围性水肿在治疗结束时消失。
3.肝胆系统罕见(<0.01%)出现黄疸的严重肝细胞损害伴或不伴肝衰竭。
4.免疫系统罕见(<0.01%)过敏性反应如过敏性休克。
5.测定值罕见(<0.01%)肝酶测定值增加(转氨酶?-GT)甘油三酯水平增高发热治疗结束时恢复正常。
6.骨骼肌肉系统结缔组织罕见(<0.01%)肌痛在治疗结束时消失。
7.神经系统常见
(≥1%~<10%)头痛不常见(≥0.1%~<1%)头晕或视力障碍(视力模糊)。
8.精神系统罕见(<0.01%)抑郁在治疗结束时消失。
9.肾和泌
尿系统罕见(<0.01%)间质性肾炎。
10.皮肤及皮下组织不常见
(≥0.1%~<1%)过敏反应如瘙痒皮疹罕见(<0.01%)荨麻疹血管神经性水肿严重的皮肤反应如StevensJ
禁忌: 1.潘妥洛克不能用于已知对该药的某种成分过敏的患者。
2.在根除幽门螺杆菌感染的联合疗法中有中重度肝肾功能障碍的患者禁用潘妥洛克片因为目前尚缺乏联合疗法对这类患者疗效及安全性的临床经验。
注意事项: 1.当与其他药物联合使用时每种药物的用药原则均应予以遵守遇有严重肝功能障碍(肝衰竭)的患者应定期监测肝脏酶谱的变化若其测定值增加必须停止用药。
2.不要使用过期的泮托拉唑。
3.药品应存放在儿童接触不到的地方。
相互作用: 1.潘妥洛克可能减少生物利用度取决于胃内PH值的药物(如酮康唑)的吸收请注意这也适用于口服潘妥洛克40mg×7片之前的短暂时间内所应用的药物。
2.泮托拉唑的活性成分在肝脏内通过细胞色素P450酶系代谢因此凡通过该酶系代谢的其它药物均不能除外与之有相互作用的可能性然而对许多这类药物进行专门检测如卡马西平咖啡因安定双氯芬酸地高辛乙醇格列本脲美托洛尔萘普生硝苯地平苯丙香豆素苯妥英吡罗昔康茶碱华法林和口服避孕药等却未观察到泮托拉唑与之有明显临床意义的相互作用。
3.泮托拉唑与同时使用的抗酸药也没有相互作用。
4.对泮托拉唑与同时服用的抗生素(克拉霉素甲硝唑阿莫西林)进行人体动力学研究未发现有临床意义的相互作用。
孕妇及哺乳期用药: 对孕妇的临床经验有限动物试验中在剂量超过5mg/kg时有轻度胚胎毒性作用无泮托拉唑进入人体乳汁的报道只有当泮托拉唑对母体的益处大于其对胎儿或婴儿的潜在危害时才可使用潘妥洛克。
儿童用
药:
目前还没有将之用于儿童的经验。
药代动力学: 即使单次口服本品40mg,泮托拉唑会被迅速吸收并达最大血药浓度。
平均2.5小时达到峰值浓度2-3μg/ml,多次给药仍可维持此浓度。
其表现分布容积为0.15L/kg,清除率为0.1L/h/kg,清除半衰期
(tl/2)约为1小时。
少数病人有清除延迟现象。
由于泮托拉唑特异性激活壁细胞,清除半衰期与作用时间(抑制酸分泌)无关。
单次或多次给药,药代动力学一致。
在剂量范围为10-80mg,口服或静脉注射泮托拉唑的血浆动力学均呈线性。
泮托啦唑血浆蛋白结合率为98%。
该药几乎均在肝内代谢。
其大部分(约80%)由肾脏排出,其余从粪便中排出。
血浆和尿中的主要代谢物为去甲基泮托拉唑,并与硫酸酯相连。
主要代谢物的半衰期(约1.5小时)不超过泮托拉唑的半衰期。
生物利用度,口服后泮托拉唑被完全吸收。
片剂的绝对生物利用度为77%。
同服的食物对AUC,最大血药浓度和生物利用度没有影响。
同服的食物只能使延迟期延长。
患者的药代动力学特征,肾功能不全(包括肾透析)的患者使用泮托拉唑不需减量。
同健康人群一样,患者的泮托拉唑半衰期很短。
只有极少量的泮托拉唑被透析。
尽管主要代谢物有中度延迟的半衰期(2-3小时),排泄仍然很快,不会发生蓄积。
肝昏迷的患者(Child分级A和B),半衰期延长至7-9小时,
AUC系数增加5-7,最大血药浓度与健康者相比只增加了1.5倍。
老年
志愿者与青年组对照,AUC和Cmax轻微升高,但无临床意义。
批准文
H20130162
号:
厂家
(生产
TakedaGmbHproductionsiteOranienburg
厂
家):。