各种润滑油换油标准-修正版.pdf
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.45 MB
- 文档页数:14


设备换油标准
设备换油:
1. 在用润滑油品经目测检查,凡符合下列条件之一者,应部分置换或更换新油:外观颜色明显变黑、乳化严重、变干变硬、有明显可见的固体颗粒。
2. 在用润滑油品做常规分析,凡符合下列条件之一者,应部分置换或更换新油:粘度超过润滑油粘度等级的±15%、酸值超过标准的15%、闪点低于标准的10%、机械杂质高于0.1%、水含量高于0.1%。
对油品质量有更高要求的,各事业部可根据设备实际要求规定换油标准。
3. 润滑油常规分析项目为:粘度、酸值、闪点、水份、杂质五项。
有特殊要求的设备可适当增加分析项目。
如冷冻机油应增加凝固点分析等。
各机组具体分析项目由设备动力部润滑油专业人员确定,报主管领导批准后执行。
4. 换油必须对设备油箱进行清洗。
运行中的大型机组润滑油应每月至少检验一次,条件恶劣或运行后期可根据实际情况适当增加检验次数,不合格应及时处理。
其他设备每3-6月采样分析一次,具体采样分析间隔时间可根据设备润滑手册的要求进行;生产上有需要时,可临时增加采样分析次数,当设备大修或装置停工检修后,开车前均应采样分析一次。
润滑油的检验报告由生产车间或设备动力部妥善保管,以备查询。

润滑油检测和更换标准润滑油检测和更换标准一.设备中使用的润滑油应定期检测是对设备的润滑故障采取早期预防和对已发生的润滑故障采取科学的处置对策,分析润滑故障的表现形式和原因、对润滑故障进行监测和诊断。
及时换油且应推行定期查,按状态维修或换油的办法,与维修体制一样,变定时为按状态(按质)换油,加强定期的检查和测试是十分必要的。
二.油品检测指标的相关说明1.理化指标检测:比如粘度、水分、酸值、抗乳化、闪点、机杂、腐蚀、抗氧化稳定性等等,与标准对比即可。
[粘度]:粘度增加可能是基于油品的氧化,不溶物含量增高,高粘度油品或水分的渗入。
粘度降低可能是基于低粘度油品,水,冷剂或燃料的渗入;或是油品内高分子聚合物受剪切力而产生变化。
[闪点]:闪点降低显示油品被燃物所稀释,或是油品过高温度而裂化。
[不溶物]:戊烷不溶物显示油品里固体物质的总含量,包含有机物和无机物。
甲苯能溶解大部分的有机物质,故此甲苯不溶物只包含污垢沙粒,磨损金属微粒及未燃烧碳屑。
戊烷与甲苯不溶物的差额代表胶质及氧化物的含量。
通常戊烷不溶物超越某一限额时才量度甲苯不溶物。
[颜色]:在极短时期内油品颜色变深显示油品被污染或开始被氧化。
[水分]:油品中有水显示系统穿漏或空气中的水分凝结。
水分会引起腐蚀和氧化,亦会使油品乳化。
故此应以离心法,隔滤法或真空处理清除。
[酸性及碱性]:酸碱度(pH)—pH增高代表渗入了碱性油品。
pH 降低代表油品开始变酸。
[总酸值(TAN)]:油品的总酸值是量度因氧化而产生酸性物质的指标。
[总碱值(TBN)]:总碱值增高,可能是被另一种含碱量高的油品污染所造成。
总碱值降低,可能是因为高碱度添加剂的损耗,用于中和酸性的燃烧及氧化产物,或被渗入的水分冲走。
金属元素分析用于验明污染情况,证实添加剂的含量及显示机件的磨损状2磨屑检测:光谱仪,分析油中金属磨粒的化学元素含量,对比使用时间和油中金属含量的增加速度,分析设备摩擦副中的磨损情况。


Oil Change Criteria1. GEARING SYSTEMSFluid Function : Lubricate moving partsProvide coolingPrevent corrosion Performance Factors : ViscosityRust inhibitionEP propertiesAnti-wearThermal & oxidation stabilityAnti foamTest Frequency : Every 6 monthsBP Product Range include: Energol GR-XPEnergol GR-XFEnersyn SGEnersyn SG-XPEnersyn HTX Enersyn EPX Hypogear EP Gear Oil EP Gear OilApplication : Generally gearboxes consist of white metals or rolling element bearings, and steelon steel gears, or steel on bronze gears of various configurations, fitted with anenclosure. Speeds & loads vary considerably, dependent upon application and geartype. Lubrication may be integral or fed from the oil system of the driving machine.Often gearbox lubricant is rationalised with the driving system lubricant, (such asengine oil).Gear Lubricants Analysis2. STEAM & GAS TURBINES AND GENERAL CIRCULATION SYSTEMSFluid Function : Lubricate moving partsLubricate reductiongearingProvide coolingRust & oxidation corrosionPerformance Factors : ViscosityOxidation resistanceWater shedding (demulse) Test Frequency : Every 6 monthsBP Product Range include : Energol THBEnergol TH-HTTurbinolTurbinol EP Energol CS Energol CSM Energol HPApplication : Steam turbines are used for main propulsion, electrical power generation and for other directdrive power requirements, (e.g. centrifugal compressors & pumps). The system oil often alsoprovides lubrication for any fitted gear train.The oils are high quality mineral oils inhibited with additive to provide R&O protection.NB. Turbine oils must under no circumstances be contaminated with oils containingdetergents and basic additives (e.g. engine oils). Contamination will result in foaming andstable emulsion formations with any water present, Turbine oils contain acidic additiveswhich when mixed with basic additives found in engine oils form soaps. A contributory factorto this problem is that engine oils have some anti-form additive added to reduce the foamingpropensity of the detergents.Turbine & Circulatory Lubricants Analysis3. Air & Gas Compressor SystemsFluid Function : Lubricate moving partsProvide coolingPrevent corrosionSeal against blow-by gasesPerformance Factors : ViscosityRust inhibitionAnti-wearThermal & oxidationstability Detergency & dispersancy Chemical stability (gas compressors)Test Frequency : Every 4 monthsBP Product Range include : Energol RCEnergol RC-REnersyn RC-SEnersyn RXEnersyn GCS 180Application : Positive displacement compressor systems could be broadly divided into rotary andreciprocating compressors. Reciprocating compressor oils are required to seal against blow-by inthe piston-ring area, dissipate heat to the crankcase walls and protect against corrosion. In thereciprocating compressor, a very thin film of oil is subjected to high temperatures generated inthe cylinder head and valve area by the compression process, which promotes oxidation and theformation of deposits.Rotary compressors are mostly oil flooded types whereby the lubricant is in direct contact withthe compressed air at temperatures between 80 °C and 100 °C. The oil is fed into the bearingsand gears and injected in large volumes into the compressed space in fine droplet form, afterwhich the oil/air mixture is discharged and passed into a separator before being re-circulated. Assuch, compressor oils must have very high oxidation stability, good air release and low foamingtendency. The contamination with engine oils, widely used in reciprocating compressors, willalso cause problems of emulsification, poor filterability and air release in the presence ofmoisture.Air & Gas Compressor Oil Analysis4. HYDRAULIC SYSTEMSFluid Function : Energy transferLubrication of moving partsCorrosion preventionCoolingPerformance Factors : Viscosity & viscosity indexRust inhibitionEP propertiesGood demulsibilityGood filterabilityAnti-wearThermal & oxidation stabilityAnti foamAir releaseTestFrequency :Every 3 monthsBP Product Range include : Energol HLPEnergol HLP-HMEnergol HLP-HM HvEnergol HLP-DEnergol HL-XPEnergol SHFEnergol SHF-LTBartran HvApplication : Hydraulic systems cover a wide variety of systems. Usage of both hydraulic and hydro-static energy transfer systems are becoming increasingly widespread.System cleanliness is the most critical aspect of any fluid energy system. To maximise efficiency and to increase the powerto equipment size ratio, hydraulic pressures have been progressively increased requiring finer clearances of moving parts toprevent leakage. In fact, modern hydraulic systems operate with some of the finest clearances of any type of machinery.Generally hydraulic systems are self contained and are fitted with adequate filtration equipment.NB. Hydraulic oils must under no circumstances be contaminated with oils containing detergents and basic additives, (e.g.engine oils). Hydraulic oils contain acidic additives which when mixed with the basic additive components of engine oils,form soaps resulting in the propensity to foam and form stable emulsions if water is present.Hydraulic Oil Analysis5. THERMAL HEATING SYSTEMS FluidFunction :Transport of thermal energyPerformance Factors : ViscosityFlash point Oxidation stabilityTest Frequency : Most industrial systems are monitored once per year. More frequent monitoring, up to 12 times per year may be needed where the system layout or operating conditions are particularly severe on the fluid, or where there is a need to monitor for contamination from the heated process. The purpose of monitoring is to identify changes in the condition of the fluid. Boiling off light fractions, partial renewal or flushing and complete system fluid renewal are the methods for returning the system to normal condition.BP Product Range include : Transcal N Transcal LT Transcal SAApplication : Thermal fluid systems are generally sealed pumped systems, operating at bulk oil temperatures up to 320 °C (normal working temperatures around 280 °C). Systems should be designed to ensure oil temperatures at heated surfaces does not exceed 340 °C. If this temperature isexceeded, thermal cracking of the oil will occur. Cracking results in lighter fractions of oil being produced with associated depression ofthe flash point value, and reduction in viscosity. This process proceeds further by a process of polymerisation of the heavier (carbon rich)fractions resulting in tar formations. This latter process causes a rise in viscosity.Thermal fluid service life is largely a function of the system design and system management. Poor design or unsatisfactory operation of thefired section may result in localised overheating causing thermal cracking and tar formations. Inadequate blanketing of the header tank andcirculation of hot oil to the header tank can lead to rapid oxidation of the oil. Correct operating procedures are very important, particularlythe adequate cooling down of the fired section prior to stopping thermal fluid circulation, and also the correct adjustment of a fired sectionto prevent local over heating.Heat Transfer Oil Analysis6. DIESEL & GASOLINE ENGINE SYSTEMSFluid Function : Lubricate relative moving partsProvide cooling, (particularly pistons & under crowns)Neutralisation of acidic combustion productsPrevent deposits and lacquer formationsPerformance Factors : ViscosityDetergencyDispersancyAnti-wear Thermal & oxidation stability AlkalinityEP PropertiesTest Frequency : Every 4 months (Medium speed diesels)BP Product Rangeinclude :BP engine oils can be split into 2 main categories :High speed diesels & gasoline mainly for automotive & transport sector applications running on clean low sulphur fuel &gasoline.- Visco 5000/Visco Sports 5000 (API SJ/CF)- Visco 3000 (API SJ/CF)- Visco 2000 (API SJ/SH/CF/CD)- Visco 2000 (API SG/CD)- Visco Sports 3000- Visco Sports 2000- Super V (API SF/CC)- Energol HDX/Super HD (API SE/CC)- Visco Pick-Up 5000- Visco Pick-Up 3000- Vanellus C3 Extra- Vanellus C3 Multigrade (CG-4)- Vanellus C3 Multigrade/Visco Diesel/ Visco Pick-Up 2000 (API CF-4/SG)- Vanellus C3 Multigrade- Vanellus C3 Monograde (API CF/CD)- Energol SHPD 40Medium/Low speed diesels mainly for marine, railroad and power generation applications.- Energol IC-HFX- Energol DS3- Energol DL-MP- Energol IC-RG- Energol IC-DGApplication : Engine lubrication systems are the most complex to interpret. Engine oils are required to manage large amounts of contaminants, including fuel combustion products and water. The lubricantperforms several other functions as well as lubrication and must continue to perform these functionsthroughout its lifetime.Modern engines with low oil consumption and operating on poor quality fuels increase performancedemands. Oil consumption enables a system to receive oil replenishment which returns some of theperformance properties which may be consumed in operation, and an equilibrium condition isusually achieved.TBN levels are normally expected to stabilise at some level below the new oil value. This stablelevel is a function of consumption of BN by neutralisation and replenishment of TBN by lubricanttop-up.High Speed Diesel & Gasoline Engine Lubricants AnalysisMedium Speed Diesel Engine Lubricants Analysis7. REFRIGERATION SYSTEMSFluid Function : Lubricate moving partsProvide coolingPrevent corrosionPerformance Factors : Low temperature viscosityChemical stabilityAnti-wearThermal & oxidation stabilityPour pointTest Frequency : Every 4 monthsBP Product Range include : Energol LPTEnergol LPT-FEnersyn LPSEnersyn LPS-POApplication : Refrigeration systems are used for the removal of heat from air, water or any substance which it isdesired to cool by means of transferring heat to a suitable cooling medium by means of a refrigerant.The lubrication of the compressor in a refrigerant system is an important factor in the satisfactoryoperation and efficiency of the whole system. Compressor oils are mainly straight naphthenicbasestocks or synthesised hydrocarbons for more severe operations.Although the refrigeration compressor is similar in operation to a conventional air compressor,additional demands are placed on the lubricants as quite low temperatures exist near the reciprocatingcompressor cylinder hear and high temperatures near the cylinder head. The lubricant is also exposedto the refrigerant at different temperatures and pressures and can absorb appreciable amounts ofrefrigerant vapour, falling in viscosity in the process.Refrigeration Compressor Lubricants Analysis。
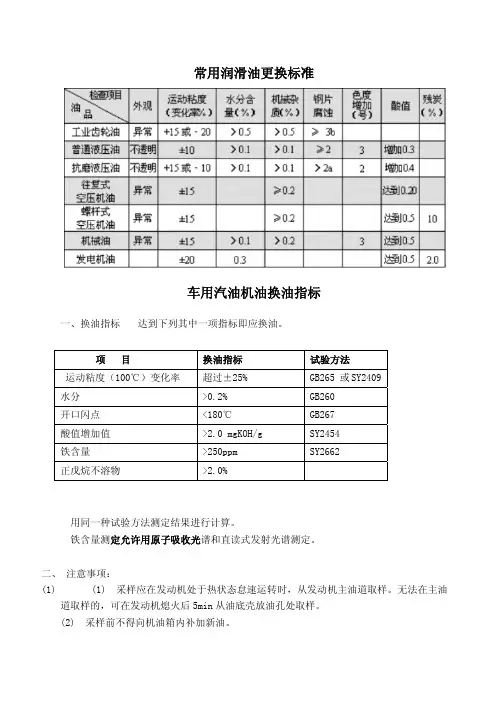
常用润滑油更换标准车用汽油机油换油指标一、换油指标 达到下列其中一项指标即应换油。
项 目 换油指标 试验方法运动粘度(100℃)变化率 超过±25% GB265 或SY2409水分 >0.2% GB260开口闪点 <180℃ GB267酸值增加值 >2.0 mgKOH/g SY2454铁含量 >250ppm SY2662正戊烷不溶物 >2.0%用同一种试验方法测定结果进行计算。
铁含量测定允许用原子吸收光谱和直读式发射光谱测定。
二、 注意事项:(1) (1) 采样应在发动机处于热状态怠速运转时,从发动机主油道取样。
无法在主油道取样的,可在发动机熄火后5min从油底壳放油孔处取样。
(2) 采样前不得向机油箱内补加新油。
(3) 每次采样量不得过多,以足够分析项目使用数量为准。
(4) 采样容器要清洁,无水杂。
汽车柴油机油换油指标一、换油指标 达到下列其中一项指标即应换油。
项 目 换油指标 试验方法运动粘度(100℃)变化率 超过±25%~-15% GB265酸值 < 2.0 mgKOH/g GB264不溶物石油醚不溶物 苯不溶物 > 2.5%> 1.5% SY2667铁含量 > 400 ppm SY2662二 、注意事项:(1) 必须在补加新油前,热车状态怠速运转下,在机油主油道通往空气压缩机处取样400ml左右。
推荐换油周期的里程,仅作为无油品分析手段下时按质换油的过渡过程。
拖拉机柴油机油换油指标一、换油指标 达到下列其中一项指标即应换油。
项 目 换油指标 试验方法运动粘度(100℃)变化率 超过±35%~-25% SY 2409及SY 2454酸值 > 2.0 mgKOH/g碱值 < 1 mgKOH/g SY 2455水分 < 0.5% GB 260不溶物石油醚不溶物 苯不溶物 > 3% > 1.5%二、 注意事项:(1) 采样应在柴油机热车怠速工况下和补加新油前。

各类润滑油/脂的质量标准(1)车用润滑油:①按质量等级分:按API(美国石油协会)标准进行分级汽机油:SA、SB、SC、SD、SE、SF、SG、SH、SJ、SL、SMSA、SB、SC、SD已被淘汰国标目前没有SG及以上级别标准柴机油:CA、CB、CC、CD、CE、CF、CF-2、CF-4、CG-4、CI-4CA、CB已被淘汰国标目前没有CF及以上级别标准柴汽通用②按粘度级别分:按SAE(美国汽车工程师协会)标准进行分级,单级油和多级油单级油:SAE20、SAE30、SAE 40、SAE 50、SAE 60多级油:以SAE xWy表示x为低温粘度级,分别为0W、5W、10W、15W、20W、25W,数字越小,表明适应最低温度越低;Y分别为20、30、40、50、60,数字越大,粘度越大。
(2)车辆齿轮油:API:GL-3、GL-4、GL-5SAE:单级粘度:90、140多级粘度:75W90、80W90、85W90、85W140质量等级的选用。
中等速度和负荷比较苛刻的齿轮或螺旋齿轮选用普通车辆齿轮油,例如CA1091等车型的变速器和转向机选用普通车辆齿轮油;低速大扭矩或高速低扭矩下工作的齿轮及使用条件不太苛刻的准双曲线齿轮选用GL-4级,如BJ2022、EQ-1090E、EQ2090等车的变速器;高速冲击负荷、高速低扭矩和低速、高扭矩下工作的齿轮及使用条件缓和或苛刻的准双曲线齿轮选用GL-5级,如捷达、红旗、奥迪、夏利、上海桑塔纳、北京切诺基等车的变速器和主减速器。
某些重型工程车辆主传动器的齿轮为双曲线齿轮,齿面压力可达(200~400)104kPa,齿面滑动速度达8~10m/s以上,油温最高达120~130℃,同时接触压力也很高,这种车辆主传动器选用GL-5级齿轮油。
(3)自动传动液ATFi. GM标准:TextronⅡ、TextronⅢ、TextronⅥ化ii. FORD标准:Mercon-1、Mercon-2、Mercon-3iii. Allison标准:Allison-3、Allison-4、Allison-5iv. Caterpillar标准:To-2、To-3、To-4、我国未建立相应的规格标准(4)刹车油:更换期为1-2年汽车制动液又称刹车油,是用于汽车液压制动系统中传递压力的液体1、制动液应具备的性质(1)较高的沸点,较低的蒸发损失(2)适宜的高低温粘度,较好的润滑性(3)良好的低温流动性(4)对刹车系统中的各种金属部件有较好的保护作用(5)具有良好的橡胶适应性(6)具有良好的热安定些,化学稳定性和水解安定性(7)良好的混容性(8)吸潮性要低,沸点不易下降2、分类(1)按美国联邦机动车安全委员会FMV-SS NO.116分为DOT3 DOT4 DOT5(2)SAE标准分为:SAE J1703 SAE J1703。
车辆润滑油换油指标普通车用齿轮油换油指标一、换油指标达到下列其中一项指标即应换油。
二、注意事项:(1) 被润滑的部件技术状况良好,各齿轮工况正常,不漏油。
(2) 认真执行“一保”,“二保”维修,保证润滑部件正常。
(3) 采样要在车辆运行至少3km后,立即用注射器从油孔抽出150ml油样。
(4) 取样工具和容器必须洁净。
(5)取样前不得向润滑部件内补加新油。
汽车柴油机油换油指标一、换油指标达到下列其中一项指标即应换油。
二、注意事项:(1) 必须在补加新油前,热车状态怠速运转下,在机油主油道通往空气压缩机处取样400ml左右。
推荐换油周期的里程,仅作为无油品分析手段下时按质换油的过渡过程。
车用汽油机油换油指标一、换油指标达到下列其中一项指标即应换油。
(使用中油的粘度实测值–新油粘度实测值)粘度变化率(%)= * 100新油粘度实测值用同一种试验方法测定结果进行计算。
铁含量测定允许用原子吸收光谱和直读式发射光谱测定。
二、注意事项:(1)(1) 采样应在发动机处于热状态怠速运转时,从发动机主油道取样。
无法在主油道取样的,可在发动机熄火后5min从油底壳放油孔处取样。
(2) 采样前不得向机油箱内补加新油。
(3) 每次采样量不得过多,以足够分析项目使用数量为准。
(4) 采样容器要清洁,无水杂。
发动机油的换油周期多长为合适?影响换油期的主要因素?通常来讲,同一台车在车况没有明显变化的情况下,同一品牌的机油,级别越高的,其更换周期可以延长,如API SJ级就可比SG级的机油换油里程适当的延长。
质量级别较高的机油采用更优化的配方和高品质的基础油和添加剂,加上先进的调和工艺,使机油具有更加优异的抗磨性、抗腐蚀性、氧化安定等使用性能,机油在使用时不易老化变质,同时,发动机也得到更好的保护。
当然,在使用机油的时候,具体的换油周期还要根据车辆厂家规定的换油周期换油,一般轿车类为7500公里以内,卡车或客车等柴油发动机类的为8000-10000公里,另外还要按照实际的车况及使用情况来定。
矿山机械设备润滑油换油标准1齿轮油:
1.1铁谱:
1.1.1低速重载部位(工作面设备各部位):
①大于35-40μm钢铁磨粒240个以上/ml;
②2-5μm球形颗粒200个以上/ml;
③大于20μm铜铝磨粒200个/ml。
1.1.2轻中负荷,高速部位(辅助设备):
①大于25μm钢铁磨粒300个/ml;
②2-5μm球形颗粒200个/ml;
③大于15μm铜铝磨粒200个/ml。
1.2理化:
1.2.1粘度:
1.2.2水分:大于0.5%
1.2.3酸值:
2液压油:
2.1铁谱(滤膜):
①大于15-20μm钢铁磨粒180个/ml;
②2-5μm球形颗粒120个/ml;
③污染物达到一定量。
5u以上污染颗粒要控制在1000-1500个/ml 以内(系统压力升高,要从严控制)
2.2理化:
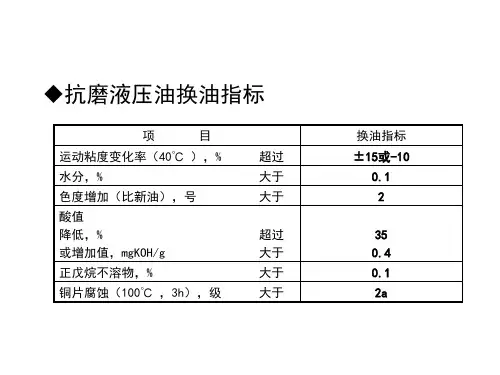
2.2.1粘度:40℃运动粘度 +15%或-10% (应该严格控制)
2.2.2水分:大于0.1%
2.2.3酸值:—35%或+0.4mgkOH/g
3.泵系统
①大于20μm钢铁磨粒200个/ml;
②2-5μm球形颗粒100个/ml;
③大于15μm铜铝磨粒100个/ml。
4.空压机
①大于15—20μm钢铁磨粒160个/ml;
②2-5μm球形颗粒80个/ml;
③大于15μm铜铝磨粒100个/ml。
5.柴油机
铁谱,滤膜》15-20u以上磨粒160个/ml
以上判断标准根据工矿条件可有一定伸缩性。
如何决定运行中的汽轮机油是否需要更换1.电厂运行中汽轮机油质量标准国内关于电厂运行中汽轮机油质量标准目前是GB/T 7596-2000标准,见表1:1) 参考国外标准控制极限值NAS 1638规定8~9级或MOOC规定6级见附录A(提示的附录),有的300MW汽轮机润滑系统和调速系统共用壹个油箱,也用矿物油,此时油中颗粒度指标应按制造厂提供的指标;2) 参考国外标准,极限值为600/痕迹mL;3) 参考国外标准,控制极限值为10min;4) 在冷油器处取样,对200MW及以上的水轮机油中质量指标为≤200mg/L;5) 对200MW机组油中颗粒度测定,应创造条件,开展检验;由上表可知,不同装机容量的汽轮机组,对油质要求是不相同的。
如250MW以上的机组提出了油品清洁度、水分、起泡性和空气释放性要求。
2.L-TSA汽轮机油换油指标1996年由中国石化总公司制定了SH/T 0636-1996 L-TSA换油标准见表2。
本标适用于设备完好运行正常的汽轮机组中润滑油的换油指标。
所提出的6项指标有一项不合要求就应换油。
V1---表示新油40℃运动粘度V2---表示运行油40℃运动粘度然而石化总公司提出的换油指标并未为全国电厂所接受。
其原因是,电厂用油质量变差是需要综合考虑的。
如:油品外观、颜色、浊度、泡沫、乳化情况、沉淀物等。
以破乳化为例,油质乳化一般要有三个条件:即水分、乳化剂及高速搅拌,而水分是主要条件。
但有的电厂使用国产汽轮机油,运行十七年,酸值0.19mgKOH/g,从外观看,油的颜色很深,但油质仍透明,不乳化,原因是不漏水。
有的电厂使用美国汽轮机油,运行几十年,酸值已超过运行指标,油色也很深,但油质仍透明,虽然破乳化指标也超标,而运行中油不乳化,其原因也是该机组不漏水。
这充分说明油质乳化主要是由机组漏水引起的。
所以若机械照搬SH/T 0636-1996换油指标的规定(有一项不合格就换油),既不利于电厂长周期运转,其换油费用也不是一笔小数目。