“一般过去时”
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:597.50 KB
- 文档页数:1

三.一般过去时(simple past tense)1.概念一般过去时表示过去某一时刻,某一段时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
一般过去时用动词的过去式表示。
2.构成一般过去时用动词的过去式表示。
be的过去式有was,were两种; have 的过去式是had;规则动词的过去式在动词词尾加-ed,具体构成规则如下:1)一般情况,动词后加ed,例词work-worked,clean-cleaned,play-played,wash-washed2)以不发音的e结尾,-d,例词live-lived,move-moved,hope-hoped,arrive-arrived 3)以辅音字母+y结尾,变y为 i再加-ed,例词study-studied,carry-carried,cry-cried,identify-identified 4)以辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节,双写最后一个辅音字母加-ed,例词plan-plannedstop-stopped,beg-begged,grab-grabbed 3.用法 (1) 表示发生在过去的动作或存在的状态。
如:He went shopping with his friends last week.They arrived ten minutes ago.He became a hotel manager ten years ago.Did you go to the concert last night?(2) 表示在过去经常发生的动作或习惯动作。
如:He visited his grandparents once a month last year.She usually went to work by car last year.When I was at school, I always went to school by bus.4.如何识别一般过去时常见的标志词有:1). yesterday, the day before yesterday.2). last week / year / month / term …(简称last系列)3). two hours ago, three years ago, a moment ago…(简称ago系列)4). in / on + 过去的年/月/日,如 in 1999, on April, 20055). just now, once upon a time, one day…5.易错点例析:(1)——Your phone number again? I _________ quite catch it.——It’s 4331577A. didn’tB. couldn’tC. don’tD. can’t(2)——Mr. Smith isn’t coming tonight.——But he _________.A. promisesB. promisedC. will promiseD. had promised(3) ——Hey, look where you are going!——Oh, I’m terribly sorry. _________.A. I’m not noticingB. I wasn’t noticingC. I haven’t noticedD. I don’t notice(4) ——Oh it’s you ! I _________ you.——I’ve had my hai r cut.A. didn’t realizeB. haven’t realizedC. didn’t recognizeD. don’t recognized(5) ——Since you’ve agreed to go, why aren’t you getting ready?——But I _________ that you would have me start at once.A. don’t realizeB. didn’t realizeC. hadn’t realizedD. haven’t realized(6) ——It’s twelve o’clock, I think I must be off now.——Oh, really? I _________ it at all.A. don’t realizeB. haven’t realizedC. didn’t realizeD. hadn’t realizedKey:ABBCBC6.中考真题及模拟(2009朝阳区一模)He went into his room, _______ the light and began to work.A. has turned onB. will turn onC. turns onD. turned on(2009海淀一模)——What’s the best food have you had in Beijing, Alex?——Roast duck! I _________to a famous restaurant to have it last week.A. have goneB. goC. will goD. went(2009宣武区一模)——Do you know how many gold medals the 23-year-old Michael Phelps _____________at the 2008 Summer Olympic Games?——Eight.A. winB. winsC. wonD. has won(2008北京)We were in Qingdao last week and __________ great fun there.A. will haveB. have hadC. hadD. have(2007北京)——What did you do after school yesterday?——I _________basketball with my friends.A. playB. playedC. will playD. am playing(2005北京)---Hi, Kate. You look tired. What’s the matter?---I ______well last night.A. didn’t sleepB. don’t sleepC. haven’t sleptD. won’t sleep (2008四川泸州)Yesterday,Tony’s family _________ a good time.A. hasB. haveC. had(2007湖南湘潭)I’m sorry you’ve missed the train. It _______10 minutes ago.A. leftB. has leftC. had left(2007福州)——Mr Green, __________you________ Three Lanes and Alleys(三坊七巷)last Sunday?——No, but I’ll visit them next week.A. will; go toB. have; been toC. did; go toD. have; gone to (2007浙江)——What did the teacher say just now?——He __________us not to play computer games all day.A. tellsB. toldC. has toldD. is told(2007江西)——Inventors have changed the way we live.——So they are famous for the great things they _________.A. doB. didC. are doingD. had done(06江西)——Where’s the cake I made this morning?——We _______ it, mum. Can you make another one for us?A. ateB. eatC. will itD. were eating。

一般过去时的用法及结构1.一般过去时的基本用法一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,也可表示过去经常或反复发生的动作。
常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如yesterday, last week, last night, in 2003, two days ago 等。
【举例】 I got up at 6:30 yesterday. 我昨天6:30起床。
My father was very busy last week. 我父亲上周很忙。
2.一般过去时的基本结构⑴肯定句“主语+动词过去式+其他”或者“主语+was/were+其他”。
【举例】 I played tennis last weekend. 我上周末打网球了。
My school trip was great. 我的学校郊游棒极了。
⑵否定句“主语+didn’t+动词原形+其他”或“主语+wasn’t/weren’t+其他”。
【举例】 The girl didn’t play computer games yesterday afternoon.这个女孩昨天下午没玩电子游戏。
Old Henry wasn’t happy last Friday. 上星期五老亨利不高兴。
⑶一般疑问句“Did+主语+动词原形+其他?”肯定回答为“Yes,主语+did”,否定回答为“No,主语+didn’t”或者“Was/Were+主语+其他?”肯定回答为“Yes,主语+was/were”,否定回答为“No,主语+wasn’t/weren’t”。
【举例】— Did you go to the beach? 你们去海滩了吗?— Yes, we did./No, we didn’t. 是的,我们去了。
/不,我们没有。
— Was your weekend OK? 你的周末过得还行吧?— Yes, it was./No, it wasn’t. 是的,还行。
/不,不行。

一般过去时的定义以及用法概念我们在英语语法中遇到的一般过去时,它的定义与运用方法是怎么样的呢?以下是小编给大家带来一般过去时的概念及用法,以供大家参阅!一般过去时的定义一般过去时表示过去某一时候或某一段时间所发生了的事情或存在的状态。
常与过去时间yesterday, this morning, just now, a moment ago, in May, last night / year / week, once upon a time, the other day, before , when clause, in the past连用。
如:I was there a moment ago. 刚才我在那儿。
What did you do yesterday? 昨天你干了什么?I met Lin Tao this morning. 今天上午我会到了林涛。
一般过去时的概念1、表示过去某个特定时间或某一段时间发生的动作或情况。
这种用法的过去时间可以是指明的,也可以是不指明的。
例句:He never smoked.他以前从不吸烟。
The skies cleared after lunch.午饭后天放晴了。
2、在表示时间或条件等的状语从句中代替过去将来时。
例句:We would not leave until he came back.他回来我们才会离开。
I didnt go to the party that evening as I started the next day.那天晚上我没有去参加聚会,因为我第二天就要出发。
3、表示现在时间。
这种用法使句子在语气上较为婉转客气,能这样用的动词为数不多,如:hope,wish,want,wonder,think,intend 等。
例句:I hoped you would come and have dinner with us.我希望你能来和我们一起吃饭。

一般过去时一.一般过去时口诀:1.一般过去时并不难,表示过去动作、状态记心间。
2.动词要用过去式,时间状语句末站。
3.否定句很简单,didn't 站在动词原形前,其它部分不要变。
4.一般疑问句也好变,did放在句子前,主语、动原、其它部分依次站。
5. 特殊疑问句也简单,疑问词加一般疑问句记心间。
6. 最后一条请注意,动词过去二.一般过去时的结构(可分三类不同的结构)概念:一般过去时用来表示过去某一时间内发生的动作或存在的状态以及过去习惯性、反复性的动作。
谓语动词要用动词的过去式,常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如yesterday昨天、last night昨晚、last week上周、last year去年等。
Be动词的一般过去时在没有实义动词的句子中使用be动词,am is 的过去式为was; are的过去式为were肯定句式:主语+ be(was , were) + 其它.否定句式:主语+ be(was , were) + not + 其它.一般疑问句:Be(was , were) + 主语+ 其它?注:在这种构成中,be动词有人称和数的变化,即要根据主语选用was / were。
Be动词分为单数和复数,was是表示单数,were是表示复数。
2实义动词的一般过去时态肯定句要使用动词的过去式,否定句和疑问句要使用助动词do和does 的过去式did.肯定句式:主语+ 动词(过去式)+ 其它否定句式:主语+ didn’t + 动词(原形)+ 其它【did not = didn’t】一般疑问句:Did + 主语+ 动词(原形)+ 其它【do , does的过去时均为did】?注 1. did和didn’t 是构成一般过去时的助动词,其特点是要在其后跟动词的原形。
2. 实意动词do的一般过去时I do my homework every day.(用yesterday改写句子)I did my homework yesterday.I didn’t do my homework yesterday.(否定句)Did you do your homework yesterday?Yes ,I did. /No, I didn’t.(一般疑问句)3情态动词的一般过去时态情态动词的过去式:can→could , may→might , must→must ,will-would,should-should。
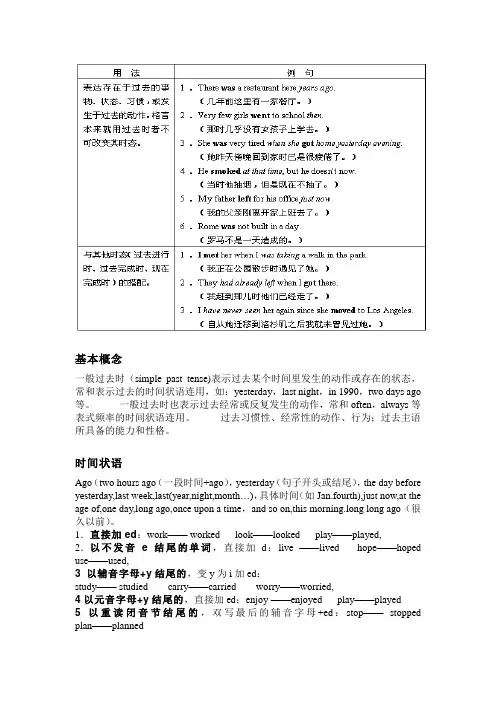
基本概念一般过去时(simple past tense)表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如:yesterday,last night,in 1990,two days ago 等。
一般过去时也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常和often,always等表式频率的时间状语连用。
过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为;过去主语所具备的能力和性格。
时间状语Ago(two hours ago(一段时间+ago),yesterday(句子开头或结尾),the day before yesterday,last week,last(year,night,month…),具体时间(如Jan.fourth),just now,at the age of,one day,long ago,once upon a time,and so on,this morning.long long ago(很久以前)。
1.直接加ed:work—— worked look——looked play——played,2.以不发音e结尾的单词,直接加d:live ——lived hope——hoped use——used,3 以辅音字母+y结尾的,变y为i加ed:study—— studied carry——carried worry——worried,4以元音字母+y结尾的,直接加ed:enjoy ——enjoyed play——played5 以重读闭音节结尾的,双写最后的辅音字母+ed:stop——stopped plan——planned不规则变化的动词过去式:have---had are---were get---got say---said feel---felt do/does---didis---was基本结构主语+动词过去式+其他否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词一般疑问句①Did+主语+do+其他?②Was\Were+主语+ do sth例句:She often came to help us in those days.I didn't know you are so busy.特殊疑问句疑问词+did+主语+动词原形+其他一般过去式的构成形式肯定式疑问式否定式疑问否定式I worked Did I work?I did not work Did I not work?He(she,it) worked Did he(she,it) work? He (she,it)did not work Did he(she,it)not work? We worked Did we work? We did not work Did we not work?You worked Did you work? You did not work Did you not work? They worked Did they work? They did not work Did they not work?用法(1)一般过去时表示在过去某个特定时间发生,也可以表示过去习惯性、经常性的动作。

一般过去时的变化规则1. 对一般动词加-ed:。
一般地,动词的过去式是在动词后加-ed形成的,如:walked、loved、played等。
2.对以字母e结尾的动词,加-d:例如:taste-->tasted,live-->lived,smile-->smiled等等。
3. 对于以 a、i、o、u 结尾的动词,通常是双写这个字母,再加-ed:。
例如:stop→stopped,run→runned,plan→planned,skin→skinned等等。
4. 对于以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,先变y为i,再加-ed:例如:study→studied,try → tried,carry → carried等等。
5.对于某些不规则动词,它们的过去式变化是不规则的:动词原形过去式。
be was / were。
build built。
catch caught。
choose chosen。
do did。
fall fell。
fight fought。
find found。
fly flew。
forget forgot。
get got 。
give gave。
go went。
have had。
hear heard。
know knew。
leave left。
make made。
meet met。
pay paid。
ride rode。
see saw。
say said。
send sent。
show showed。
speak spoke。
spend spent。
stand stood。
take took。
tell told。
think thought。
understand understood。
wear wore。
win won。
6.有些动词的过去式和原形相同:例如:put,cut,hit,cost,let等等。
以上是一般过去时的变化规则。
1、用于过去时的动作或状态:She walked to the store. 她走到商店了。

一般过去时的时间状语简介一、一般过去时的概念一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,通常表示过去的事实或经历,不涉及现在的情况。
例如:He lived in Beijing for ten years. 他在北京住了十年。
She bought a new dress yesterday. 她昨天买了一件新裙子。
一般过去时也可以表示过去经常反复发生的动作,常和often, always, sometimes等频率副词连用。
例如:He often played football with his friends when he was young. 他年轻时经常和朋友们踢足球。
二、一般过去时的构成一般过去时的肯定句和否定句的构成方法是在动词原形后加-ed或不规则变化,否定句在动词前加did not。
例如:动词原形过去式肯定句否定句work worked I worked hard.I did not work hard.study studied He studied English.He did not study English.go went She went to the park.She did not go to the park.see saw They saw a movie.They did not see a movie.一般过去时的一般疑问句和特殊疑问句的构成方法是在句首加did或疑问词+did,动词用原形。
例如:动词原形过去式一般疑问句特殊疑问句work worked Did you work hard?What did you work on?study studied Did he study English?How did he study English?go went Did she go to the park?Where did she go?see saw Did they see a movie?What movie did they see?三、一般过去时的用法一般过去时常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如yesterday, last week, ago等。

一般过去时总结一般过去时的定义一般过去时是英语中用来表示过去发生的动作、状态或习惯性事件的一种时态。
它主要用于描述在过去的某个时间点发生的事情。
一般过去时的构成动词的变化在一般过去时中,动词的原形通常会变化,变化规则如下:- 对于大部分动词,其过去式形式是在动词词尾加上了-ed。
- 例如:play → played, watch → watched -对于以辅音字母+y结尾的动词,将y变为i,再加-ed。
- 例如:study → studied -对于以“辅音字母+元音字母+辅音字母”结尾的重读闭音节动词,双写最后一个辅音字母,再加-ed。
- 例如:stop → stopped - 具体的动词过去式变化形式需根据不规则变化的动词列表参考。
句子结构在一般过去时中,陈述句的基本结构如下:主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他成分•例如:I played football yesterday.–我昨天踢了足球。
一般过去时的使用场景过去发生的动作一般过去时主要用于描述在过去的某个时间点发生的动作。
- 例如:She walked to school this morning. - 她今天早上走路去学校了。
过去的状态一般过去时也可以用来描述在过去的某个时间段内持续存在或者不再存在的状态。
- 例如:He lived in London for five years. - 他在伦敦住了五年。
过去的习惯一般过去时还可以用来描述过去经常或习惯性发生的动作或事件。
- 例如:They always played board games on Sundays. - 他们过去总是在周日玩桌游。
一般过去时和现在完成时的区别在描述过去发生的事情时,一般过去时和现在完成时有着一些区别。
一般过去时强调动作或事件在过去的某个时间发生,并且与现在没有直接的联系;而现在完成时则强调与现在的相关性。
一般过去时•用于过去某个时间发生的动作或事件上,强调过去的内容。

一般过去时1一般过去时是英语语法中的一种时态,表示过去某个时间发生的动作或状态。
这种时态通常用于叙述过去发生的事情,或者描述过去某个时间点的状态。
在英语语法中,一般过去时的形式通常是通过动词的过去式来表示。
一、一般过去时的形式一般过去时的形式可以通过动词的过去式来表示,常用的过去式包括:be动词的过去式(was/were),do/does的过去式(did),have/has的过去式(had),go/come/fly的过去式(went/came/flew)等。
这些动词的过去式的基本形式是在动词后面加上-ed结尾。
二、一般过去时的用法1.表示过去某个时间发生的动作或状态。
例如:I went to the parkyesterday.(我昨天去了公园。
)2.表示过去某个时间点的状态。
例如:The book was on the table at 9o'clock yesterday morning.(昨天早上九点钟这本书在桌子上。
)3.叙述已经发生的事情,用于回忆或讲述历史。
例如:In the 1980s,computers were not widely used.(20世纪80年代,计算机还没有被广泛使用。
)4.表达过去的习惯或常规。
例如:My father used to go jogging everymorning.(我父亲过去每天早上都去慢跑。
)三、一般过去时的句式结构在英语中,一般过去时的句式结构通常包括主语+动词的过去式+宾语。
例如:1.They walked to the store yesterday.(昨天他们走路去商店。
)2.She played the piano for an hour yesterday afternoon.(昨天下午她弹了一个小时钢琴。
)3.We visited our grandparents last weekend.(上周末我们拜访了祖父母。

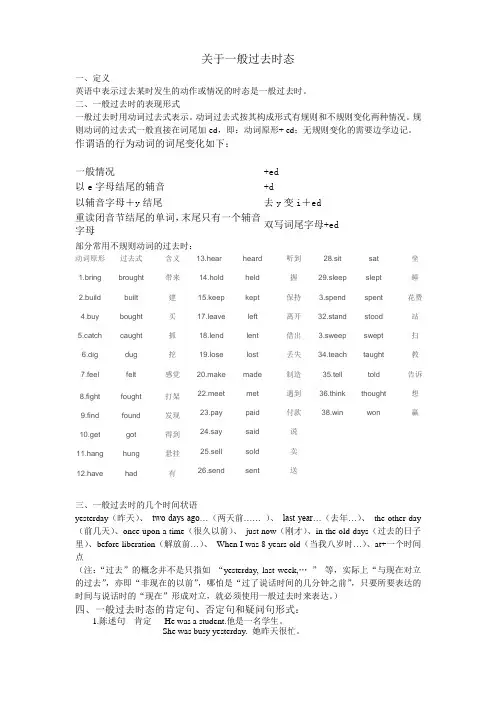
关于一般过去时态一、定义英语中表示过去某时发生的动作或情况的时态是一般过去时。
二、一般过去时的表现形式一般过去时用动词过去式表示。
动词过去式按其构成形式有规则和不规则变化两种情况。
规则动词的过去式一般直接在词尾加-ed,即:动词原形+ ed;无规则变化的需要边学边记。
作谓语的行为动词的词尾变化如下:一般情况+ed以e字母结尾的辅音+d以辅音字母+y结尾去y变i+ed重读闭音节结尾的单词,末尾只有一个辅音字母双写词尾字母+ed部分常用不规则动词的过去时:动词原形过去式含义1.bring brought 带来2.build built 建4.buy bought 买5.catch caught 抓6.dig dug 挖7.feel felt 感觉8.fight fought 打架9.find found 发现10.get got 得到11.hang hung 悬挂12.have had 有13.hear heard 听到14.hold held 握15.keep kept 保持17.leave left 离开18.lend lent 借出19.lose lost 丢失20.make made 制造22.meet met 遇到23.pay paid 付款24.say said 说25.sell sold 卖26.send sent 送28.sit sat 坐29.sleep slept 睡3.spend spent 花费32.stand stood 站3.sweep swept 扫34.teach taught 教35.tell told 告诉36.think thought 想38.win won 赢三、一般过去时的几个时间状语yesterday(昨天)、two days ago…(两天前…… )、last year…(去年…)、the other day (前几天)、once upon a time(很久以前)、just now(刚才)、in the old days(过去的日子里)、before liberation(解放前…)、When I was 8 years old(当我八岁时…)、at+一个时间点(注:“过去”的概念并不是只指如“yesterday, last week,…”等,实际上“与现在对立的过去”,亦即“非现在的以前”,哪怕是“过了说话时间的几分钟之前”,只要所要表达的时间与说话时的“现在”形成对立,就必须使用一般过去时来表达。
一般过去时讲解一般过去时是英语中最基本的过去时态,它用于描述已经发生或已经完成的动作、事件或状态。
在句子中,一般过去时通常使用动词的过去式形式。
一般过去时的形式一般过去时的谓语动词通常是动词的过去式形式,常见的规则动词过去式是在动词原形的基础上加上-ed或-d。
例如:•walk → walked•watch → watched•play → played对于以不发音的e结尾的动词,只需要在其后面添加-d。
例如:•live → lived•dance → danced对于以辅音字母+y结尾的动词,将y变为i,再加-ed。
例如:•study → studied•try → tried对于以短元音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词,需要先双写最后一个辅音字母,再加-ed。
例如:•stop → stopped•plan → planned不规则动词的过去式需要特殊记忆。
例如:•go → went•have → had•say → said一般过去时的用法1.描述过去的动作或事件一般过去时常用于描述过去发生的动作或事件。
例如:–I walked to the park yesterday.(我昨天走到了公园。
)–They played soccer last weekend.(他们上个周末踢了足球。
)2.描述过去的习惯或常态一般过去时还可用于描写过去的习惯或常态,表示过去经常发生的动作或状态。
通常会和表示频率的副词或状语连用,如often(经常)、usually(通常)、always (总是)等。
例如:–He often visited his grandmother when he lived in the city.(他住在城市时经常去看他的奶奶。
)–I always went to bed early when I was a child.(我小时候总是很早就睡觉。
)3.用于虚拟语气一般过去时也可用于虚拟语气,表示对现在或将来的假设或建议。
一般过去时用法一般过去时是英语中最常用的过去时态之一,用于描述过去发生的动作、事件或状态。
本文将介绍一般过去时的用法、时态转换、标志词及常见注意事项。
一、一般过去时的用法一般过去时用于以下情况:1. 过去发生的具体动作或事件:- We went to the beach last summer.(我们去年夏天去了海滩。
)- He cooked dinner yesterday.(他昨天做了晚餐。
)2. 过去的习惯或经常性动作:- She always walked to school when she was young.(她小时候总是步行去学校。
)- We used to play basketball every Saturday.(我们过去每个星期六都会打篮球。
)3. 对现在具有影响的过去经历或经验:- I learned how to swim when I was a child, and now I love swimming.(我小时候学会游泳了,现在我非常喜欢游泳。
)- They lived abroad for five years and now they can speak fluent English.(他们在国外生活了五年,现在能够说一口流利的英语。
)二、时态转换1. 肯定句:一般过去时的肯定句结构为:主语 + 动词过去式(或助动词did + 动词原形)+ 其他。
- I studied Chinese for three years.(我学了三年中文。
)- She played tennis with her friends yesterday.(她昨天和朋友们打网球。
)2. 否定句:一般过去时的否定句结构为:主语 + did not (didn't) + 动词原形 +其他。
- We didn't go to the party last night.(我们昨晚没有去参加派对。
一般过去时知识点归纳与总结一般过去时的概念:一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
常和表示过去的时间状语连用,如:last year, yesterday等。
例如:I saw him in the street yesterday. 昨天我在街上看见他了。
一般过去时的结构1、肯定形式:主语动词过去式其他例句:She often came to help us in those days.2、否定形式:①was/were not;②在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词例句:I didn't know you like coffee.3、一般疑问句:①Did 主语谓语动词原型其他?②WasWere 主语表语?例如:-Did you go to Beijing last week?-Yes, we did. (No, we didn't.)4、一般过去时的特殊疑问句的构成:疑问词+did 主语+动词原形+其它?例如:-What did you do last night?-I did my homework.动词过去式的构成:(1)规则动词过去式的构成有四条规则:①一般在动词原形末尾直接加上-ed。
如:look-looked。
②以不发音的字母e结尾的动词,去e再加-ed。
如:live-lived。
③末尾只有一个辅音字母的重读闭音节(辅元辅结构),先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed。
如:stop-stopped。
④末尾是辅音字母y结尾的动词,先变y为i,然后再加-ed。
如:study-studied。
(2)不规则动词的过去式需特殊记忆。
如:am(is)-was, are-were, go-went, come-came, take-took, have (has)-had等。
一般过去时口诀一般过去时并不难,表示过去动作、状态记心间。
动词要用过去式,时间状语句末站。
一般过去时的知识点归纳一般过去时知识点归纳一、一般过去时的定义一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)用于描述在过去某个具体时间发生的动作或存在的状态,以及过去经常或反复发生的动作。
二、一般过去时的构成1. 规则动词:一般在动词原形后加-ed。
- 例:worked, played, visited2. 不规则动词:需记忆其过去式形式。
- 例:went, saw, ate三、一般过去时的用法1. 描述过去具体时间发生的动作或状态。
- 例:He walked to school yesterday.2. 表示过去经常或反复发生的动作。
- 例:When I was a child, I often played football after school.3. 用于时间、条件状语从句中,表示过去将来的动作。
- 例:I said I would call her when I got home.四、一般过去时的标志词1. 具体的时间状语:yesterday, last week, in 1990等。
2. 过去的时间状语:a moment ago, just now, the other day等。
3. 频率副词:never, seldom, sometimes, often, usually等。
五、不规则动词的过去式变化1. 改变元音字母:sing-sang, swim-swam2. 改变辅音字母:begin-began, run-ran3. 完全不规则变化:go-went, come-came, eat-ate六、一般过去时与现在完成时的区别1. 一般过去时强调过去某个时间点发生的具体动作,而现在完成时强调过去发生的动作对现在的影响或结果。
- 例:I visited the museum last week. (强调上周的动作)- 例:I have visited the museum before. (强调现在对博物馆的了解)七、一般过去时的否定句和疑问句1. 否定句:在动词前加did not (didn't)。
一般过去时的概念1.一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用。
一般过去时也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作感谢。
2.Be动词在一般过去时中的变化:⑴am和is在一般过去时中变为was。
(was not=wasn’t)⑵are在一般过去时中变为were。
(were not=weren’t)⑶带有was或were的句子,其否定、疑问的变化和is, am, are一样,即否定句在was或were后加not,一般疑问句把was或were调到句首。
3.句中没有be动词的一般过去时的句子否定句:didn’t +动词原形,如:Jim didn’t go home yesterday.一般疑问句:在句首加did,句子中的动词过去式变回原形。
如:DidJim go home yesterday?特殊疑问句:⑴疑问词+did+主语+动词原形?如:What did Jim do yesterday?⑵疑问词当主语时:疑问词+动词过去式?如:Who went to homeyesterday?动词过去式变化规则:1.一般在动词末尾加-ed,如:pull-pulled, cook-cooked2.结尾是e加d,如:taste-tasted3.末尾只有一个元音字母和一个辅音字母的重读闭音节,应双写末尾的辅音字母,再加-ed,如:stop-stopped4.以“辅音字母+y”结尾的,变y为i,再加-ed,如:study-studied5.不规则动词过去式:am,is-was, are-were, do-did, see-saw, say-said,give-gave,get-got,go-went,come-came,have-had,eat-ate,take-took,run-ran,sing-sang,put-put,make-made,read-read,write-wrote,draw-drew,drink-drank,fly-flew,ride-rode,speak-spoke,sweep-swept,swim-swam, sit-sat1/ 1。