传动系统离合器论文中英文对照资料外文翻译文献
- 格式:doc
- 大小:60.00 KB
- 文档页数:11

CLUTCHThe engine produces the power to drive the vehicle. The drive line or drive train transfers the power of the engine to the wheels. The drive train consists of the parts from the back of the flywh eel to the wheels. These parts include the clutch, th e transmission, the drive shaft, and the final drive assembly (Figure 8-1).The clutch which includes the flywheel, clutch disc, pressure plate, springs, pressure plate cover and the linkage necessary to operate the clutch is a rotating mechanism between t he engine and the transmission (Figure 8-2). It operates through friction which comes from contact between the parts. That is the reason why the clutch is called a friction mechanism. After engagement, the clutch must continue to transmit all the engine torque to the transmission depending on the friction without slippage. The clutch is also used to disengage the engine from the drive train whenever the gears in the transmission are being shifted from one gear ratio to another.To start the engine or shift the gears, the driver has to depress the clutch pedal with the purpose of disengagement the transmission from the engine. At that time, the driven members connected to the transmission input shaft are either stationary or rotating at a speed that is slower or faster than the driving members connected to the engine crankshaft. There is no spring pressure on the clutch assembly parts. So there is no friction between the driving members and driven members. As the driver lets loose the clutch pedal, spring pre ssure increases on the clutch parts. Friction between the parts also increases. The pressure exerted by the springs on the driven members is controlled by the driver through the clutch pedal and linkage. The positive engagement of the driving and driven members is made possible by the friction between the surfaces of the members. When full spring pressure is applied, the speed of the driving and driven members should be the same. At themoment, the clutch must act as a solid coupling device and transmit al l engine power to the transmission, without slipping.However, the transmission should be engaged to the engine gradually in order to operate the car smoothly and minimize torsional shock on the drive train because an engine at idle just develops little power. Otherwise, the driving members are connected with the driven members too quickly and the engine would be stalled.The flywheel is a major part of the clutch. The flywheel mounts to the engine’s crankshaft and transmits engine torque to the clutch assembly. The flywheel, when coupled with the clutch disc and pressure plate makes and breaks the flow of power from the engine to the transmission.The flywheel provides a mounting location for the clutch assembly as well. When the clutch is applied, the flyw heel transfers engine torque to the clutch disc. Because of its weight, the flywheel helps to smooth engine operation. The flywheel also has a large ring gear at its outer edge, which engages with a pinion gear on the starter motor during engine cranking.The clutch disc fits between the flywheel and the pressure plate. The clutch disc has a splined hub that fits over splines on the transmission input shaft. A splined hub has grooves that match splines on the shaft. These splines fit in the grooves. Thus, t he two parts are held together. However, back-and-forth movement of the disc on the shaft is possible. Attached to the input shaft, At disc turns at the speed of the shaft.The clutch pressure plate is generally made of cast iron. It is round and about the same diameter as the clutch disc. One side of the pressure plate is machined smooth. This side will press th e clutch disc facing are against the flywheel. The outer side has various shapes to facilitate attachment of spring and release mechanisms. The two primary types of pressure plate assemblies are coil spri ng assembly and diaphragmspring (Figure 8-3).In a coil spring clutch the pressure plate is backed by a number of coil springs and housed with them in a pressed-steel cover bolted to the flywheel. The springs push against the cover. Neither the driven plate nor the pressure plate is connected rigidly to the flywheel and both can move either towards it or away. When the clutch pedal is depressed a thrust pad riding on a carbon or ball thrust bearing i s forced towards the flywheel. Levers pivoted so that they engage with the thrust pad at one end and the pressure plate at the other end pull the pressure plate back against its springs. This releases pressure on the driven plate disconnecting the gearbox from the engine (Figure 8-4).Diaphragm spring pressure plate assemblies are widely used in most modern cars. The diaphragm spring is a single thin sheet of metal which yields when pressure is applied to it. When pressure is removed the metal springs back to its original shape. The centre portion of the diaphragm spring is slit into numerous fingers that act as release levers. When the clutch assembly rotates with the engine these weights are flung outwards by centrifugal forces and cause the levers to pre ss against the pressure plate. During disengagement of the clutch the fingers are moved forward by the release bearing. The spring pivots over the fulcrum ring and its outer rim moves away from the flywheel. The retracting spring pulls the pressure plate a way from the clutch plate thus disengaging the clutch (Figure 8-5).When engaged the release bearing and the fingers of the diaphragm spring move towards the transmission. As the diaphragm pivots over the pivot ring its outer rim forces the pressure plate against the clutch disc so that the clutch plate is engaged to the flywheel.The advantages of a diaphragm type pres sure plate assembly are its compactness, lower weight, fewer moving parts, less effort to en gage, reduces rotational imbalance by providin g a balanced force around the pressure plate and less chances of clutch slippage.The clutch pedal is connected to the disengagement mechanism either by a cable or, more com monly, by a hydraulic system. Either way, pushing the pedal down operates the dise ngagement mechanism which puts pressure on the fingers of the clutch diaphragm via a release bearing and causes the diaphragm to release the clutch plate. With a hydraulic mechanism, the clutch pedal arm operates a piston in the clutch master cylinder. Thi s forces hydraulic fluid through a pipe to the clutch release cylinder where another piston operates the clutch disengagement mechanism. The alternative is to link the clutch pedal to the disengagement mechanism by a cable.The other parts including the cl utch fork, release bearing, bell-housing, bell housing cover, and pilot bushing are needed to couple and uncouple the transmission. The clutch fork, which connects to the linkage, actually operates the clutch. The release bearing fits between the clutch fork and the pressure plate assembly. The bell housing covers the clutch assembly. The bell housing c over fastens to the bottom of the bell housing. This removable cover allows a mechanic to inspect the clutch without removing the transmission and bell housing. A pilot bushing fits into the back of th e crankshaft and holds the transmission input shaft.Torque ConverterThe BasicsJust like manual transmission cars, cars with automatic transmissions need a way to let the en gine turn while the wheels and gears in the transmission come to a stop. Manual transmission cars use a clutch, which completely disconnects the engine from the transmission. Automatic transmis sion cars use a torque converter.A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling, which allows the engine to spin somewhat independently of the transmission. If the engine is turning slowly, such as when the car is idling at a stoplight,the amount of torque passed through the torque converter is very small, so keeping the car still requires only a li ght pressure on the brake pedal.If you were to step on the gas pedal while the car is stopped, you would have to press harder on the brake to keep the car from moving. This is because when you step on the gas, the engine speeds up and pumps more fluid into the torque converter, causing more torque to be transmitted to the wheels.Inside a Torque ConverterThere are four components inside the very strong housing of the torque converter:1. Pump;2. Turbine;3. Stator;4. Transmission fluid.The housing of the torque converter is bolted to the flywheel of the engine, so it turns at what ever speed the engine is running at. The fins that make up the pump of the torque converter are at tached to the housing, so they also turn at the same speed as the engine. The cutaway below shows how everything is connected inside the torque converter (Figure 8-6).The pump inside a torque converter is a type of centrifugal pump. As it spins, fluid is flung to the outside, much as the spin cycle of a washing machine flings water and clothes to the outside of the wash tub. As fluid is flung to the outside, a vacuum is created that draws more fluid in at the center.The fluid then enters the blades of the turbine, which is connected to the transmission. The turbine causes the transmission to spin, which basically moves the car. The blades of the turbine are curved. This means that the fluid, which enters the turbine from the outside, has to change direction before it exits the center of the turbine. It is this directional change that causes the turbine to spin.The fluid exits the turbine at the center, moving in a different direction than when it entered. The fluid exits the turbine moving opposite the direction that the pump (and engine) is turning. If the fluid were allowed to hit the pump, it would slow the engine down, wasting power. This is why a torque converter has a stator.The stator resides in the very center of the torque converter. Its job is to redirect the fluid returning from the turbine before it hits the pump again. This dramatically increases the efficiency of the torque converter.The stator has a very aggressive blade design that almost completely reverses the direction of the fluid. A one-way clutch (inside the stator) connects the stator to a fixed shaft i n the transmission. Because of this arrangement, the stator cannot spin with the fluid - i tc a n s p i n o n l y i n t h e o p p o s i t ed i re c t i o n,f o r c i ng th e f l ui d t oc h a n g ed i re c t i o n a s i t h i t s t h e s t a t o r b l a d e s.Something a little bit tricky happens when the car gets moving. There is a point, around 40 mph (64 kph), at which both the pump and the turbine are spinning at almost the same speed (the pump always spins slightly faster). At this point, the fluid returns from the turbine, entering the pump already moving in the same direction as the pump, so the stator is not needed.Even though the turbine changes the direction of the fluid and flings it out the back, the fluid still ends up moving in the direction that the turbine is spinning because the turbine is spinning faster in one direction than the fluid is being pumped in the other direction. If you were standing in the back of a pickup moving at 60 mph, and you threw a ball out the back of that pickup at 40 mph, the ball would still be going forward at 20 mph. This is similar to what happens in the tur bine: The fluid is being flung out the back in one direction, but not as fast as it was going to start with in the other direction.At these speeds, the fluid actually strikes the back sides of the stator blades, causing the stator to freewheel on its one-way clutch so it doesn’t hinder the fluid moving through it.Benefits and Weak PointsIn addition to the very important job of allowing a car come to a complete stop without stalling the engine; the torque converter a ctually gives the car more torque when you accelerate out of a Stop. Modern torque converters can multiply the torque of the engine by two to three times. This effect only happens when the engine is turning much faster than the transmission.At higher speeds, the transmission catches up to the engine, eventually moving at almost the same speed. Ideally, though, the transmission would move at exactly the same speed as the engine, because this difference in speed wastes power. This is part of the reason why cars with automatic transmissions get worse gas mileage than cars with manual transmissions.To counter this effect, some cars have a torque converter with a lockup clutch. When the two halves of the torque converter get up to speed, this clutch locks them together, eliminating the slip page and improving efficiency.离合器发动机产生动力用以驱动车辆。

Clutch technology development historyIn the 100 years of the history of the development of automobile, almost all of the components in terms of technology development have experienced great changes: reliability, production cost, convenient maintenance, energy saving and emission reduction and so on, have been and will always be the automotive industry in the pursuit of goals, these goals for Automotive engineers continue to develop solutions newer and better.Technically, it was not until 1910 that the reciprocating piston internal combustion engine was significantly more efficient than cars and electric vehicles. In 1902, a gasoline engine car first broke the record of the highest speed, and before that, the highest speed record has been created by steam cars and electric cars. Supporters of the three different drivers of the car have been racing and racing for the first ten years of twentieth Century to break the record.Liquid fuel to drive the car to "steam and electric vehicles" (steam and electric vehicle supporters habit called) has a very prominent advantage is its nearly ideal torque characteristics, they do not need a clutch, does not need the transmission, so it is easy to operate, less failure, easier to maintain. Since the reciprocating piston internal combustion engine can only output torque when it reaches a certain speed, it is necessary to have a separate joint between the engine and the transmission. Gasoline engines need to use the clutch engagement function to start the car, because only when the engine reaches a certain speed, the output torque. In addition to the engagement of the clutch, the clutch's separation function is also important because it is free to move in the vehicle. In view of the complexity of the related problems, there is no clutch engagement function in many small car design structures in the early stage.Origin of clutchThe working principle of first generation clutch from the early use of mechanical equipment factory industrial society. Through the analogy of belt transmission, a kind of flat belt is introduced into the car. By means of the tension of the belt pulley, the belt transfers the output torque of the engine to the driving gear, and when the belt is relaxed by adjusting the roller, the belt slipping is equivalent to the separation of the clutch. Because this process causes the abrasion of the belt is too fast, people will adopt a new method: install a drive pulley with the same size of the idler wheel, by pulling the lever, the drive belt from the idler wheel to drive wheel.This belt drive is a disadvantage, low efficiency, easy to wear, especially the transfer of power shortage in rainy days; on the other hand is the requirement of transmission gear to increase engine torque to constantly improve, this has prompted engineers to explore better to replace the clutch.The result is clutch invented a variety of people, including modern clutch pioneer -- Based on the principle of friction clutch. This is a disc located at the end of the crankshaft and connected to another stationary disk. When the two disks are in contact, the friction is produced, and the stationary disk begins to rotate. With the increase of the clamping force, the driving disc drives the driven disc to make thespeed of the driven disk continuously improve until the transmission is working normally, and the two disks rotate at the same speed. Before the two disks are fully engaged, they are in contact with one side and slip, and most of the kinetic energy from the engine is converted into heat. This structure can meet the following two requirements: on the one hand gently gently engage in when starting a car engine will stall, it will not cause the transmission jitter; on the other hand, the clutch can be nondestructively torque to the transmission.Clutch pedal to work through. Press the clutch pedal, pull the conical seat ring through the separation fork, release the spring, so as to separate the clutch.Early clutchIn 1889, Daimler's steel wheel car had used the basic form of this design principle: equipped with a tapered / bevel friction clutch. The freely movable conical disc is located on the transmission shaft, and the flywheel with a tapered groove on the crankshaft can be firmly engaged. The coil spring presses the conical disc into the tapered groove of the flywheel and the clutch is engaged; the foot pedal can be stepped down, and the conical disc can be pulled back by separating the sleeve and the spring, thereby separating the clutch and interrupting the power transmission. Originally used as a conical disc friction surface material, but was quickly replaced the leather. The latter is soaked in castor oil, can prevent moisture, oil / fat. The utility model has the advantages that the utility model can be automatically adjusted, and the input shaft of the transmission is not stressed. On the one hand, the wear of friction plate is too fast, the replacement is too complex, after the friction in the design of the friction plate spring pin or drive to improve. On the other hand, the flywheel and clutch cone is too large, so that the inertia torque is larger and the clutch is much slower than the required separation process.To solve the above problems, around 1910s, with another clutch brake or brake transmission, it through a second foot pedal to play a role, usually the second pedal and the clutch pedal are connected together, and are located in the rear of the pedal shaft.When changing the speed, many drivers are used to make the clutch slipping and not shift, then the flywheel heating degree is more serious than only by the tapered disc friction cone disc by friction layer of leather to heat. After a long period of long-distance driving, due to the thermal expansion of the flywheel, the cone may be more engaging with the flywheel, but when the flywheel temperature drops, it is difficult to separate the cone from the flywheel.Until the first World War period, metal friction began to spread up. Previously, people also experimented with other different materials, such as NAG company designed a camelhair cone disc thin steel sheet pressing, and fitted with a fanlike blade used for cooling, it engages in the two part, bolted to the flywheel on the leather ring line. The two part of the structure allows the free movement of the leather wire ring, thereby simplifying the clutch maintenance and reducing the number of times the clutch is stuck.Daimler motor company has developed an open friction clutch with an aluminum cone. In order to separate the soft, the oil on the friction layer.Because of the simple structure, the cone disc clutch has been the dominant position in the whole 1920s. Cylindrical friction surfaces are not accepted because of their poor operating performance. Only cylindrical clutch spring clutch with the evolution version, due to its creative design, only by Daimler in late nineteenth Century early twentieth Century with the Mercedes Benz car, and continued until the first world war.The traditional single disc dry clutchIn spring clutch, a wearable spiral spring, and the input shaft of the transmission drum end, mounted in the recess of the flywheel. One end of the spiral spring plate is connected with the flywheel, and the other end is fastened on the spring cover. The clutch pedal presses the spring plate, the leaf spring is more and more tight around the drum shape (automatic enhancement), and drives the transmission input shaft. Only a small force can compress the spring and make the clutch soft.About the development of spring clutch in the Daimler company at the same time, Professor Hele-Shaw from the UK also completed the test of multi disc clutch, which is also considered a precursor to the current traditional single disc dry clutch. One of the key advantages of the "Weston" clutch, which can be produced on a large scale, is that it has a large area of friction and can be continuously engaged in a smaller mounting space.In multi disc clutch, flywheel connected to the drum cover, and according to the outer shape of the coil inside the slot, and allow the disc to rotate with the crankshaft and flywheel, and longitudinal movement. The same number of concave disks are positioned in the center of the hub, and the hub is connected to the clutch shaft. These disks can be moved longitudinally along the clutch shaft on the hub. During the installation, the internal and external driven plates of the clutch are alternately connected to form a set of disks, such as the active and driven disks are always connected with each other.The driven disc work like this: start the bronze plate is always facing the steel wheel, and the spiral spring under the pressure plate is pressed together. In this way, all disks are continuously engaged. The gradual increase in the friction force allows the clutch to engage very softly. With the decrease of the spring pressure, the driven plate is separated, and the supporting part of the driving plate starts to bend from the plane of the driven plate. By changing the number of driven disc pairs, the clutch can be adjusted to fit the output power of each engine.Multi disc clutch for oil / gasoline, can also be dry. The dry type is special, and the friction layer is riveted by rivets. Multi disc clutch, especially the oil bath type multi disc clutch, its biggest drawback is a certain degree of hysteresis, which can only be part of the separation, resulting in difficult shift.After several years, single disc clutch has eliminated the cone disc and multi disc clutch. De Dion and Bouton are the first to realize that a single disc clutch is the future direction of the clutch. With the appearance of Ferodo asbestos friction sheet, clutch technology has made great progress. Asbestos friction sheet has been used since 1920s, until it is replaced by non asbestos friction sheet. The advantage of a single disc dry clutch is obvious: the lower drive disc mass allows it to stop fasterafter separation, thus making it easier to shift gears - a complete farewell to the transmission brake structure.The original structure single disc dry relatively complex. The clutch housing is bolted to the flywheel and the clutch cover is bolted to the clutch housing. The clutch cover with the spring to the inner side of the compression lever is transferred from the intermediate plate through the friction disc, and the torque from the flywheel is transmitted to the transmission. The friction disc is connected to the connection or transmission input shaft by the driver. The clutch is separated and joined by means of a sliding ring plate that allows the tapered disc to move forward and backward. Each side of the cone disc acts on the separating lever correspondingly, and the separating lever is operated by a spiral spring, and is pressed or separated. Due to the fact that the cone is rotating and the sliding ring is stationary, it needs to be lubricated periodically.The spiral spring clutch pressing force provided by the spring, won the people's recognition. At first, the coil spring is placed in the middle of the test, but only a few smaller spiral or spiral spring along the outer ring of the clutch housing arrangement of the structure to be mass production. The release lever compresses the coil spring by a separate bearing which can move freely on the transmission input shaft to separate the clutch. The pressing force can be due to the use of different spring and change, but there is a fatal disadvantage, namely with the increase of engine speed, a spiral spring located in the outer ring of the pressure plate, due to the centrifugal force to the spring cover direction to the outward pressure, the friction between the spring and the cover, the pressing force performance curve change.As the engine speed increases, the clutch becomes heavier and heavier. In addition, the separation bearing used to separate the lever has been in a state of pressure, so that it and the clutch cover is easy to wear, especially in the high speed of the engine gear shift, will soon wear.The birth of diaphragm clutchIn order to solve the problems of these systems, we developed a diaphragm spring clutch diaphragm spring clutch, the research laboratory was born in 1936 of general motors, and mass production in late 1930s in the United states. In Europe, after the Second World War, people began to be familiar with the diaphragm spring clutch through the American General Company military truck, and in the middle of 1950s in a number of single European models. Porsche 356, BMW Goggomobil 700 and DKW Munga is the first batch of the diaphragm spring clutch is equipped with German cars. Diaphragm spring clutch mass production began in 1965 with the Opel Rekord models.Because of the diaphragm spring clutch can be balanced and symmetrical rotation, so it is not affected by the engine speed. The diaphragm spring clutch was a success in 1960s, when the camshaft top mounted high speed engine (Glas, BMW, Alpha Romeo) was widely used to replace the camshaft engine. By the end of the 1960s, almost all car manufacturers have adopted diaphragm spring clutch.Here need to emphasize is: let LuK in diaphragm spring clutch mass production, played a crucial role. Replace all the separate lever helical spring system withdiaphragm spring, brings a lot of advantages: simple structure, constant pressing force, installation space is relatively high pressing force only needs a relatively small (very important for transverse engine) and is not affected by the impact of engine speed. Because of these characteristics, almost all of the modern use of diaphragm spring clutch, and its application in the multi-function car is also more and more - has been the use of spiral spring clutch.With the development of correspondingly, clutch disc has been optimized. Reciprocating piston internal combustion engine changes in the speed and torque generated by the vibration of the crankshaft, clutch, transmission input shaft to the transmission, resulting in noise and severe gear wear. In the modern automobile, the weight of the flywheel and the vehicle is increasing, so the clutch driven disc with the torque damper and the wave spring is developed.Long time operated clutch needs a strong thigh, because the pedal force must be transferred through the connecting rod or shaft / cable. With the application of the clutch and the hydraulic separation mechanism in 1950s in 1930s, the driving comfort has been improved.To try different clutch automatic clutch to make operation more simple: in 1918, Wolseley first proposed the concept of electromagnetic clutch. In the early 1930s, the French Cotal company produced a luxury car with a magnetic clutch, a pre selector transmission. The most famous is the centrifugal clutch to adjust the clamping force by centrifugal force and automatic clutch, such as Saxomat (Fichtel & Sax company), LuKomat (LuK), Manumatik (Borg & Beck) and Ferlec (Ferodo).离合器技术发展史在100多年的汽车发展史中,几乎所有的零部件在技术方面都经历过巨大的发展变化:可靠性、生产成本、维护便利性、节能减排性等,都已经且将一直成为汽车行业的追求目标,这些发展目标要求汽车工程师们不断地开发出更新更好的解决方案。

附录附录A外文文献原文7-Speed Dual Clutch Transmission System for Sporty Application ABSTRACT:With its 7-speed dual clutch transmission, ZF has introduced an innovative transmission for sporty applications. The close ratios combined with extremely spontaneous drive behavior makes it an ideal transmission for sporty applications. This article describes the compact gear set with lubrication by injection for improving the level of efficiency and increasing the engine-speed-strength, the dual clutch unit as well as the hydraulic control unit, which is based on the pre-control principle, are also described in detail. The hy-draulic control principle provides the option of a hydraulic cruise mode in the event of an electronics failure. In addition to the transmission design, functional features that also highlight the sporty character of the transmission are described in detail.Key words: Automatic transmission; Dual clutch; Vehicle connection; Efficiency1 IntroductionWhen it comes to the field of automatic transmissions, dual clutch systems currently represent the benchmark in terms of spontaneity and sportiness. In this type of transmission, which is based on a countershaft transmission, these advantages are combined with a very direct "vehicle connection", high rpm performance, and excellent transmission efficiency.The 7-speed dual clutch transmission for the standard driveline presented here is designed for a torque capacity of up to 520 Nm and rotational speeds of up to 9250 rpms. In order to be able to achieve these performance data in the existing installation space, a concept was developed in which an oil chamber as well as lubrication by injection are used. Before introducing the transmission′s several unique features in more detail below, an overview of the basic transmission design will be presented, Fig. 1.The engine torque is introduced to the dual clutch via a torsion damper (not shown in Fig. 1). The multidisk clutches in the dual clutch are radially nested in one another and transfer the torque to both input shafts in the countershaft transmission gear set. In this case, due to the installation space, the countershaft is not located under the main shaft, but is tilted laterally. This becomes possible because the concept is based on lubrication by injection with a dry sump. On the one hand, lubrication by injection improves heat removal, on the other, there are nonoticeable losses due to the gears splashing in the oil pan. The oil is supplied to the transmission via an internal gear pump which is driven by a spur gear train behind the dual clutch. With the help of a spur gear train, the drive unit has the advantage that, via different gear ratio phases and depending on the intended use, the flow rate and the max. speed of the pump can be adapted. An additional advantage is that based on theresulting I proved installation space, an optimal ratio between the pump width and the pump diameter can be achieved for the pump′s level of efficiency. The hydraulic control unit is arranged under the gear set. The hydraulic unit supplies the clutch, based on need, with pressure and cooling oil as well as shift actuators. The latter are arranged laterally to the gear set and work with double-acting cylinders. The sensor for detecting the position of the gearshifts is attached directly onto the four gearshifts. The transmission has an external control unit.Fig.1Overview dual clutch transmission (DCT)2 Seven speeds with sophisticated stepping-a concept for extrme sporti- nessThe gear set concept of the dual clutch transmission introduced here was developed in house taking into consideration the following requirements:High power densityHigh speed endurance strength up to 9250 rpm Variability and modular designRepresentation of transmission-ratio spreads of about 4.7 and 6.8 with 7 speedsUse of existing synergies for manual transmissionsAfter extensive systematic development of the gear set in which many thousands of variants were produced and compared, the gear set concept that is illustrated in Fig. 2 is the final variant and the ideal concept for achieving the goals specified.The gear set selected is based on the constant drive concept and consists of two concentric drive shafts each of which are driven by one of the two multidisk clutches in theFig.2Gear set scheme of 7D variantdual clutch, two countershafts also concentric to one another, a main shaft and an output shaft. The gear ratios are engaged by the four synchronizer units A/B, C/D, E/F, and G/H, which are arranged on the main shaft and on the hollow countershaft and these are connected to the loose wheels or the adjacent shafts. An important feature in the gear set is the connectability of both countershafts through the C/D synchronizer unit. In the D shift position, the gear ratios selected in this way can be doubly used which reduces construction costs compared to conventional dual clutch gear sets. Similarly, this feature is used in first gear because then the vehicle is started up using the more powerful K1 clutch. Because of this dual use of the last gear level in the transmission for the first and second gear, the desired ratio step 1-2 is achieved through the transmission ratios of both constant drive phases.The use of the K1 clutch for starting up in first gear results inevitably in the direct gear also being assigned to the odd subsection. In this case, the fifth and seventh gears can be selected as a direct drive. With this feature, it was possible to develop a modular gear set which, on just a few changes,contains two different transmission gear ratio variants with fundamentally different characters.For the first version, with an overall spread of about 4 . 7 , the seventh gear is selected as a direct gear (called the 7D variant). Fig. 2 shows the relevant gear set diagram with the performance flows in all speeds. Due to its sophisticated gear steps, this transmission is highly suitable for very sporty vehicles that need only a "little" transmission stepping due to the high rotating engine. Optimal tractive power can be provided at any time duringvehicle operation.The second version is based on the 7D variant, however, fifth gear was selected as the direct drive. When maintaining the torque multiplication ratio and in adapting the transmission ratio of several lower gear levels, you get the 5D variant with a considerably higher transmission-ratio spread for vehicles with increased comfort demands and simultaneously reduced consumption.Fig. 3 illustrates the design of the 7D variant. The main similarity with existing manual transmissions for standard transmissions is noticeable. Due to the compact gear set design, the sufficient shaft dimensioning and the favorable arrangement in proximity of the bearing of the high transmitting ratios, central bearing glasses were not necessary despite the proportionally large bearing clearance.Overall, only two housing bearing levels are necessary where the front level is located behind both constant gears. In addition, a very compact and inexpensive transmission design could be implemented based on the bearing concept selected, especially in the area of the hollow shaft.Fig.3Sectional Drawing of 7D variant3 The dual clutchThe central module of this highly topical transmission concept is the wet dual clutch. With a broad spectrum of technical features, it implements the functional provisions of the transmission control unit and thus distinguishes the special character of this transmission concept.Very fast delay times, low inertia and good, comfortable friction value progressions facilitate, very sporty handling with highly dynamic gear shifting and comfortable cruising at a high level of efficiency. The dual clutch placed directly on the transmission input accepts the engine torque from thtorsion damper and feeds it to one of the two subsections, depending on the situation.Safety considerations have led to a "normall open" design.The radial arrangement of the multidisk pack age represents the best combination of performanc and installation space need, Fig. 4.Fig.4Dual clutchCareful lining and oil selection as well as intensive enhancement of this tribological system are the requirements for comfort and performance of this clutch throughout its service life.Through intense testing and detailed calculations, it was possible to achieve a very high therma loading capacity. As part of the process, the lining type, dimensioning, and grooving as well as equal distribution of thermal load and oil flow in the multidisk package are decisive design features.Low torque drag even with low temperatures as well as high speed endurance strength support comfort and a high level of sportiness, but are also important safety requirements.Rotating, centrifugal force-compensating clutch cylinders with hysteresis optimized gaskets make the clutches easy to control. Integrated plate springs reliably accept rapid piston resetting even at high speeds.In the case of an open clutch, only transmission input shafts with very low additional mass inertia are used. This supports rapid synchronizing sequences and a long service life of the synchronizer units.4 The hydraulic control unitIn the present dual clutch transmission, the hydraulic control unit fulfills the following tasks:Actuating the dual clutchShifting the gearshifts, i. e. engaging/synchronizing the gearCooling the dual clutchGear lubricationEmergency stop function in case of complete failure of transmission electronicsSeveral features in the hydraulic control unit as well as criteria for the selection of the control concept are going to be described in more detail below.4.1 PerformanceThe use of the dual clutch transmission in sporty vehicles demands high performance from the hydraulic control unit, especially with regard to the first two tasks because the timely "handling" of these tasks come into play in gear shifting and gear shifting times.That is why particular value is placed on the selection of the right control unit concept as part of the system design. During the decision process, the choice was made, in principle, between two concepts, Fig. 5.Fig.5Control concept direct control / precontrolPrecontrol of the valvesDirect control of the valves (so-called cartridge valves)In case of direct control, the valve that is used for pressure control, e.g. a clutch, is directly connected to the power-generating proportional solenoids and provides the main pressure to the corresponding clutch pressure.The precontrol uses the pressure that is supplied by a pressure controller, for example, to actuate an additional valve that supplies the clutch pressure from the main pressure.To assess the performance of both concepts, a larger number of compared measurements were performed with different systems, of which two systems shall be considered here:ZF hydraulic control unit with precontrol for DCT standard driveComparative hydraulic control unit with direct controlA reference clutch was used as the clutch to engage. Criteria for assessing the performance were (see also Fig. 6):Fig.6Delay, increase/rise, and fall times. Red curve: Power /Electric current. Green curve: ClutchpressureDelay time, 1 to 4Time of step response until clutch inflation pressure, 1 to 2Time of the step response up to 90% of the main pressure 1 to 3Time of pressure drop (emptying times), 5 to 6Fig. 6 shows, as an example, the times for a transmission oil temperature of + 20°C to be reached. One notices that the direct control first in dicates a lower delay time (14.3 ms) compared to the precontrol (30.1 ms), see also time of brand 1to 4.For increase to clutch inflation pressure or to 90% of the main pressure shows, however, the advantage of the precontrolled system (see also summarizing tab 1).Emptying times, also present a disadvantage for direct control. Trans-mission oil temperature of -20°C also show comparable results for step responses and fall times.All of the tests support the statement that direct control has an advantageous effect with small oil volumes. However, if large oil volumes have to be transported, precontrol valves are to be preferred due to larger opening cross-sections.4.2 Operational safetyOperational safety is determined essentially due to the soiling tendency because the so-called silting can lead to the valves getting jammed. Provocation tests with transmission-specific environmental conditions (dirty oil) demonstrated the influences of soiling on the characteristic curves. Technical, trouble-free characteristic curve progressions could be illustrated only with a high dither amplitude in valve actuation, which leads, in turn, to increased valve wear-and-tear due to the micro movements that it causes. The increased tendency toward soiling can result needing a fine filter.4.3 CostsIn addition to the delay time comparison as well as assessing the operational safety, the costs were relevant for a final evaluation. The compari son with regard to the hydraulic and electro-mag netic components shows that a precontrol system has cost benefits compared to a direct control system. Added to this are the higher flows with the actuation of direct control valves, which, in turn, result in a more expensive TCU. Furthermore, in opting for precontrol, ZF is able to "pool" together pressure controllers in large quantities because these, too, are used in the automatic ZF planetary gear set.4.4 Emergency stop functionIn case there is a complete outage in the transmission electronics, a hydraulic emergency stop function is actuated in the transmission. The clutch that is pressurized with a larger amount of pressure in the event of a system outage will continue to be pressurized. This condition is maintained until an adjustable engine speed threshold is achieved, then the clutch opens in order to prevent the engine from being choked. It is not possible to re-start this system.5 Sporty functionsFor function developers, the dual clutch transmission offers the opportunity to combine the comfort of a stepped automatic transmission with the dynamics and sportiness of a countershaft transmission. Connected, therefore, are typical " catalog values," such as time from zero to 100 kilometers per hour or the time from 80 to 120 kilometers per hour with correspondingly fast kick-down shifting, but also subjective acceleration sensitivity during a shifting sequence where the purist among the manual transmission drivers still wants to feel that jolt of acceleration.One function especially designed for the dual clutch transmission in sports cars is the "race start"function. The race start is a function used to achieve optimal acceleration from astandstill, i.e. in the shortest time from 0 to 100 km/h. The sequence progresses as follows: The engine is brought to a suitably high rpm with the clutch engaged in first gear. The driver simultaneously actuates the brakes with the lef foot so that the clutch can already be lightly engaged and the gas pedal (full throttle) in order to bring the vehicle up to the target speed. By simultaneously pressing and holding an operating element, such as the selector lever or a push button on the steering wheel, the race start intention is conveyed to the system, the engine speed adjusted and the start up prevented until the driver releases the brake. During the race start, the clutch is closed under the control of the wheel slip with which the optimal acceleration is achieved and by exploiting the dynamic engine torque (inertia torque). The entire procedure progresses automatically once the driver releases so that even an inexperienced drivercan achieve the best possible drive performance figures. Obviously, the driver can cancel the procedure by removing his/her foot from the gas pedal or touching the brakes. Also, the system recognizes when the street conditions do not permit a race start, such as wet roads, for example. Due to the optimal start-up and a shifting sequence into second gear free of traction interruption (see also sports shifting), the race start function enables the acceleration time of 0 to 100 km/h to be improved by an average of 0.2 sec compared to a car with a manual transmission. At the same time, this functionality helps avoid improper use and resulting clutch overload.The top chart in Fig. 7 illustrates the engine and transmission input shaft speed, the lower chart shows the vehicle′s longitudinal acceleration. Starting with a cranking speed of 6,800 rpm, the clutch begins to close, which leads to an engine pressure up to about 4,000 rpm. The dynamic engine torque used to achieve this results in an acceleration of 0.7-0.9 g. In the process, noticeable vibrations in the transmission input shaft speed signal develop due to the wheel slip regulation. After about 1.2 sec, the vehicle is accelerated only by the engine torque with approx. 0.5 g. It must be mentioned here that this test was performed using a vehicle with very high traction. In most cases, a starting speed of only up to about 4,000 rpm is reasonable.A further function developed for the dual clutch transmission is so-called sports shifting. This is described in more detail below.In general, a gear-shift change by the driver is only perceived acoustically by the change in the engine speed. The transition from the acceleration level of the original gear toFig.7Measurement of a race starthe new gear should be made smoothly and continuously. This also corresponds to the standard shifting sequences in auto-matic and dual clutch transmissions. However, many drivers of sporty cars wish that they had the option of both distinctive comfort shifting sequences as well as sporty shifting sequences, which, besides the haptic response (acceleration jolt), also have an acceleration advantage as a result. To this end, the dynamic engine torque can also be used again. The requirement for this is the torque capacity of the dual clutch which has to be able to transmit this torque increase. As the possible torque increase depends on the gradients of the engine speed, this can be used particularly effectively in shifting gears with a large speed difference with the target gear (large ratio spread/ratio step), which is why the gear changes 1-2, 2-3, and 3-4 are offered. In the process, sports shifting from the frst to second gear can serve as a supplement to the ace start for improving the acceleration time from to 100 km/h. As the use of the dynamic torque is pure application topic, we distinguish, as a rule,between three shifting systems. Fig. 8 illustrates he stylized differences and features between the hifting systems, Fig. 9 shows an original measurement from a prototype vehicle.The top chart shows the respective engine and ransmission speed, the bottom chart shows the orques from both clutches. The bottom line in the hart represents the clutch from the target gear that is used to achieve the torque increase during engine sp eed adjustment and thereby acceleration gains.Fig.8Simplified depiction of acceleration procedures with Fig.9Measurement of sports shift 2-3 in the vehicle附录B外文文献翻译运动型7速双离合器变速器系统摘要:ZF公司的7速双离合器变速器是一款创新型的、适用于运动型车辆的变速器。

附录How Does the Clutch WorkThe clutch is a device to engage and disengage power from the engine, allowing the vehicle to stop and start.A pressure plate or “driving member” is bolted to the engine flywheel, and a clutch plate or “driven member” is loc ated between the flywheel and the pressure plate. The clutch plate is spline to the shaft extending from the transmission to the flywheel, commonly called a clutch shaft or input shaft. When the clutch and pressure plates are locked together by friction, the clutch shaft rotates with the engine crankshaft. Power is transferred from the engine to the transmission, where it is routed through different gear rations to obtain the best speed and power to start and keep the vehicle moving.The flywheel is located at the rear of the engine and is bolted to the crankshaft. It helps absorb power impulses, resulting in a smoothly-idling engine and provides momentum to carry the engine through its operating cycle. The rear surface of the flywheel is machined flat and the clutch components are attached to it. The driving member is commonly called the pressure plate. It is bolted to the engine flywheel and its main purpose is to exert pressure against the clutch plate, holding the plate tight against the flywheel and allowing the power to flow from the engine to the transmission. It must also be capable of interrupting the power flow by releasing the pressure on the clutch plate. This allows the clutch plate to stop rotating while the flywheel and pressure plate continues to rotate.The pressure plate consist of a heavy metal plate, coil springs or diaphragm spring, release levers (fingers), and a cover. When coil springs are used, they are evenly spaced around the metal plate and located between the plate and the metal cover. This places an even pressure against the plate, which in turn presses the clutch plate tight against the flywheel. The cover is bolted tightly to the flywheel and the metal pate is movable, due to internal linkages. The coil springs are arranged to exert direct or indirect tension on the metal plate, depending upon the manufacturer’s design. Three release levers (fingers), evenly spaced around the cover, are used on most pressure plates to release the holding pressure of the springs on the clutch plate, allowing it to disengage the power flow.When a diaphragm spring is used instead of coil springs, the internal linkage is necessarily different to provide an “over-center” action to release the clutch plate from the flywheel. Its operation can be compared to the operation of an oilcan. When depressing the slightly curved metal on the bottom of the oilcan, it goes over-center and gives out a loud “clicking” noise; when released, the noise is again heard as the metal returns to its originalposition. A click is not heard in the clutch operation, but the action of the diaphragm spring is the same as the oilcan.The clutch plate or driven member consists of a round metal plate attached to a splined hub. The outer portion of the round plate is covered with a friction material of molded or woven asbestos and is riveted or bonded to the plate. The thickness of the clutch plate and /or facings may be warped to give a softer clutch engagement. Coil springs are often installed in the hub to help provide a cushion against the twisting force of engagement. The splined hub is mated to (and turns) a splined transmission shaft when the clutch is engaged.The release (throw out) bearing is usually a ball bearing unit, mounted on a sleeve, and attached to the release or throw out lever. Its purpose is to apply pressure to the diaphragm spring or release levers in the pressure plate. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the pressure of the release bearing or lever actuates the internal linkages of the pressure plate, releasing the clutch plate and interrupting the power flow. The release bearing is not in constant contract with the pressure plate. A linkage adjustment clearance should be maintained.The clutch pedal provides mechanical means for the driver to control the engagement and disengagement of the clutch. The pedal is connected mechanically to either a cable or rods, which are directly connected to the release bearing lever.When the clutch pedal is depressed, the linkage moves the release bearing lever. The release lever is attached at the opposite end to a release bearing which straddles the transmission clutch shaft, and presses inward on the pressure plate gingers or the diaphragm spring. This inward pressure acts upon the fingers and internal linkage of the pressure plate and allows the clutch plate to move away from the flywheel, interrupting the flow of power.While the clutch pedal is depressed and the power flow interrupted, the transmission can be shifted in to any gear. The clutch pedal is slowly released to gradually move the clutch pate toward the flywheels under pressure of the pressure plate springs. The friction between the clutch plate and flywheel becomes greater as the pedal is released and the engine speed increased. Once the vehicle is moving, the need for clutch slippage is lessened, and the clutch pedal can be fully released.Coordination between the clutch pedal and accelerator is important to avoid engine stalling, shock to the driveline components and excessive clutch slippage and overheating.离合器如何工作离合器是传递和分离发动机动力的装置,实现车辆的停车和启动。

附录 AClutch between engine and transmission installed in the car to travel from the start the whole process, often need to use the clutch. Its role is to make the engine and transmission can be gradually between the joint, thus ensuring a smooth start car; temporarily cut off the link between the engine and transmission to shift at the time of shift and reduce the impact; When the car when emergency braking from Separate role in preventing the transmission and other drive system overload, play a protective role.Clutch similar to the switch, splice or break away from the power transmission and, accordingly, have any form of auto clutch, but the form is different.By the friction plate clutch, springs, pressure plate and the power output shaft composed, arranged between the engine and gearbox, the engine flywheel to the torque is passed to the stored transmission, to ensure that vehicles in different driving conditions passed to the driver Wheel driving force and the right amount of torque, is the scope of the powertrain. In the half-time of linkage, clutch and power input power output allowed speed difference, that is, the speed error to achieve through its transfer an appropriate amount of power. Clutch is divided into three work status, ie the clutch all connections, some of the half clutch linkage and the clutch is not linked.When a vehicle in normal driving, the pressure plate is jammed against the friction plate on the flywheel, pressure plate and friction plate at this time the friction between the largest between the input shaft and output shaft remained relatively static friction, both the same speed . When the vehicle is started, the driver depresses the clutch, clutch pedal movement by pulling back pressure plate, which is the separation of the pressure plate and friction disc, pressure plate and flywheel at this time no contact, but also the relative friction does not exist. Last one, that is, half of the clutch linkage status. At this point, the pressure plate and friction disc friction less than the full-linked state. Clutch pressure plate and flywheel friction plate on the sliding friction between the state. Flywheel speed is greater than the output shaft speed, transmission out of the power from the flywheel to the transmission part of the pass. Between the engine and driving wheels at this time is equivalent to a soft connection status.In general, the clutch and the shift in the vehicle when starting to play a role, this time a transmission shaft and the speed difference between the two shafts, engine power must be cut with a shaft after the synchronizer can be very good a shaft speed will be kept synchronized with the second axis, gear hanging up after, and then through the clutch shaft and the engine power will be a combination of the power continue to be transmitted. In the clutch, there is an essential buffer device, which consists of two similar to the flywheel with the disc, the disc hit a rectangular groove, the groove arrangement of the spring, in the face of fierce shock between the two disc springs between the elastic effect, buffer external stimuli. Effective protection of the engine and clutch. Various parts of the clutch, pressure plate spring strength, friction coefficient of friction plate, clutch diameter, location, and the clutch friction disc clutch performance is to determine the number of key factors, the greater the stiffness of the spring, the higher the friction coefficient of friction plates, the larger the diameter of the clutch, clutch performance, the better.附录 B离合器安装在发动机与变速器之间,汽车从启动到行驶的整个过程中,经常需要使用离合器。
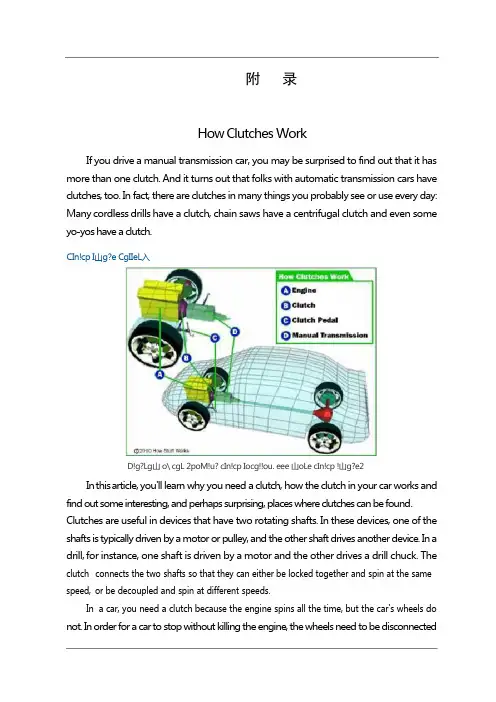
附录How Clutches WorkIf you drive a manual transmission car, you may be surprised to find out that it has more than one clutch. And it turns out that folks with automatic transmission cars have clutches, too. In fact, there are clutches in many things you probably see or use every day: Many cordless drills have a clutch, chain saws have a centrifugal clutch and even some yo-yos have a clutch.CIn!cp I山g?e CgIIeL入D!g?Lg山 o\ cgL 2poM!u? cIn!cp Iocg!!ou. eee 山oLe cIn!cp !山g?e2In this article, you'll learn why you need a clutch, how the clutch in your car works and find out some interesting, and perhaps surprising, places where clutches can be found. Clutches are useful in devices that have two rotating shafts. In these devices, one of the shafts is typically driven by a motor or pulley, and the other shaft drives another device. In a drill, for instance, one shaft is driven by a motor and the other drives a drill chuck. The clutch connects the two shafts so that they can either be locked together and spin at the same speed,or be decoupled and spin at different speeds.In a car,you need a clutch because the engine spins all the time,but the car's wheels do not. In order for a car to stop without killing the engine, the wheels need to be disconnectedf rom the engine somehow. The clutch allows us to smoothly engage a spinning engine to a non-spinning transmission by controlling the slippage between them.To understand how a clutch works, it helps to know a little bit about friction, which is a measure of how hard it is to slide one object over another. Friction is caused by the peaks and valleys that are part of every surface -- even very smooth surfaces still have microscopic peaks and valleys. The larger these peaks and valleys are, the harder it is to slide the object. You can learn more about friction in How Brakes Work.A clutch works because of friction between a clutch plate and a flywheel. We'll look at how these parts work together in the next section.Fly Wheels,Clutch Plates and FrictionIn a car’s clutch, a flywheel connects to the engine, and a clutch plate connects to the transmission. You can see what this looks like in the figure below.When your foot is off the pedal, the springs push the pressure plate against the clutch disc, which in turn presses against the flywheel. This locks the engine to the transmission input shaft, causing them to spin at the same speed.Pressure plateThe amount of force the clutch can hold depends on the friction between the clutch plate and the flywheel, and how much force the spring puts on the pressure plate. The friction force in the clutch works just like the blocks described in the friction section of How Brakes Work, except that the spring presses on the clutch plate instead of weight pressing the block into the ground.W h en the clutch pedal is pressed, a cable or hydraulic piston pushes on the release fork, which presses the throw-out bearing against the middle of the diaphragm spring. As the middle of the diaphragm spring is pushed in, a series of pins near the outside of the spring causes the spring to pull the pressure plate away from the clutch disc (see below). This r eleases the clutch from the spinning engine.Common ProblemsFrom the 1950s to the 1970s, you could count on getting between 50,000 and 70,000 miles from your car's clutch. Clutches can now last for more than 80,000 miles if you use them gently and maintain them well. If not cared for, clutches can start to break down at 35,000 miles. Trucks that are consistently overloaded or that frequently tow heavy loads can also have problems with relatively new clutches.Photo courtesy Carolina MustangClutch plateThe clutch only wears while the clutch disc and the flywheel are spinning at different speeds. When they are locked together, the friction material is held tightly against the flywheel, and they spin in sync. It's only when the clutch disc is slipping against the flywheel that wearing occurs. So, if you are the type of driver who slips the clutch a lot, you'll wear out your clutch a lot faster.Sometimes the problem is not with slipping, but with sticking. If your clutch won't release properly, it will continue to turn the input shaft. This can cause grinding, or completely p revent your car from going into gear. Some common reasons a clutch may stick are: Broken or stretched clutch cable - The cable needs the right amount of tension to push and pull effectively.Leaky or defective slave and/or master clutch cylinders - Leaks keep the cylinders from building the necessary amount of pressure.Air in the hydraulic line - Air affects the hydraulics by taking up space the fluid needs to build pressure.Misadjusted linkage - When your foot hits the pedal, the linkage transmits the wrong amount of force.Mismatched clutch components - Not all aftermarket parts work with your clutch.depress fully. If you have to press hard on the pedal, there may be something wrong. Sticking or binding in the pedal linkage, cable, cross shaft, or pivot ball are common causes. S o metimes a blockage or worn seals in the hydraulic system can also cause a hard clutch. Another problem associated with clutches is a worn throw-out bearing, sometimes called a clutch release bearing. This bearing applies force to the fingers of the spinning pressure plate to release the clutch.If you hear a rumbling sound when the clutch engages,you might have a problem with the throw-out.Types of ClutchesThere are many other types of clutches in your car and in your garage.An automatic transmission contains several clutches. These clutches engage and disengage various sets of planetary gears. Each clutch is put into motion using pressurized hydraulic fluid. When the pressure drops, springs cause the clutch to release. Evenly spacedridges, called splines, line the inside and outside of the clutch to lock into the gears and the clutch housing. You can read more about these clutches in How Automatic Transmissions Work.An air conditioning, compressor in a car has an electromagnetic clutch. This allows the compressor to shut off even while the engine is running. When current flows through a magnetic coil in the clutch, the clutch engages. As soon as the current stops, such as when you turn off your air conditioning, the clutch disengages.Most cars that have an engine-driven cooling fan have a thermostatically controlled viscous clutch -- the temperature of the fluid actually drives the clutch. This clutch is positioned at the hub of the fan, in the airflow coming through the radiator. This type of clutch is a lot like the viscous coupling sometimes found in all-wheel drive cars. The fluid in the clutch gets thicker as it heats up, causing the fan to spin faster to catch up with the engine rotation. When the car is cold, the fluid in the clutch remains cold and the fan spins s lowly, allowing the engine to quickly warm up to its proper operating temperature.Many cars have limited slip differentials or viscous couplings, both of which use clutches to help increase traction. When your car turns, one wheel spins faster than the other, which makes the car hard to handle. The slip differential makes up for that with the help of its clutch. When one wheel spins faster than the others, the clutch engages to slow it down and match the other three. Driving over puddles of water or patches of ice can also spin your wheels. You can learn more about differentials and viscous couplings in How Differentials Work.Gas-powered chain saws and weed eaters have centrifugal clutches, so that the chains or strings can stop spinning without you having to turn off the engine. These clutches work automatically through the use of centrifugal force. The input is connected to the engine crankshaft. The output can drive a chain, belt or shaft. As the rotations per minute increase, w eighted arms swing out and force the clutch to engage. Centrifugal clutches are also often found in lawn mowers, go-karts, mopeds and mini-bikes. Even some yo-yos are m anufactured with centrifugal clutches.C lu tches are valuable and necessary to a number of applications. For more information on clutches and related topics, check out the links on the following page.离合器工作原理如果您驾驶手动变速箱的汽车,您可能会惊讶地发现,它有一个以上的离合器。

附 录录1Clutch of new developments in technologyAbstract: in recent years car design and manufacturing technology progress for all to see. In order to further improve product performance, prolong service life, common mechanical clutch technology is also produced a remarkable change. No matter from structural characteristics, product process performance, or control technology, mechanical clutch of technological progress in some extent reflects the development of design concepts, and possible technology trends in the future.Keywords: clutch; Technology development1, introductionIn car technology rapid development today, especially with the electronic technology in cars, the extensive application of vehicle drivetrain is had great progress, as an important part of the transmission of the clutch assembly force transmission, the burden of reducing vibration and prevent system overload very important role. To make sure that the power transmission and reliable, separate thoroughly, combined with soft, damping good, small volume, light weight, easy, long service life, making the clutch product either cash from the performance, structure, or manufacturing mode and control, in the occurrence of a lot of change. They greatly optimized clutch all aspects of performance, to some extent look, these changes are also reflected the development direction of the clutch.2, engine flywheel new structureAs one of the flywheel storage components engine, is also part of the clutch initiative. As the car transmission belong to multi-freedom torsional vibration system, whether the incentive and transmission system, or the associated force vibration type and the coupling vibration with other statements are very complex. In order to adapt to car driving conditions of vibration and noise reduction of reducing the need, making cars, ride comfort the role of torsional shock absorber is extremely important. It should be able to adjust the system inherent frequency, the system mainly low-order resonance critical speed remove common, also need to use speed range, still need to decrease amplitude damping of transmission system can reduce idle noise, ease the impact of the special case load. Previous clutch platen set on by a twist of shock absorber, decorate a space place is restricted, shock absorber work reverse Angle small, torsion stiffness big, capacity small, springs, and therefore not guarantee the intensity of vibration reduction is limited.In recent years, the emergence of a reverse damping characteristics and performance to price are ideal double quality flywheel structure. The flywheel by primary flywheel, reverse shock absorber and subprime flywheel composition, among them, the primary flywheel on one hand we should provide for the shock absorber and clutch installation space, on theother hand also with appropriate rotational inertia insure a car, and reduce passed back starting the amplitude. Generally, double quality flywheel adopts with circular arc shape along the spiral spring primary flywheel outer periphery decorate way, in limited circumstances decorate a space, the arrangement to obtain larger primary flywheel rotational inertia. The inertia and the clutch after brief increase engine speed fluctuation of related parts, shorten their service life. To avoid the above phenomenon, often need additional Settings special damping, such, can increase the difficulty and cost of product development. Because the engine of the car front front drive type of transmission installation space is limited, so this kind of structure in FF type cars to the promotion. Meanwhile, this kind of decorate spring along the circumference, due to high speed double quality flywheel centrifugal role, spring wear when, or even produces broken.Using radial layout springs can improve the double quality flywheel of the above mentioned products defect. It consists of primary flywheel, 3 ~ 4 springs box, damping dish and subprime flywheel composition. Because the suspension spring box of radial layout, the primary flywheel rely on four posts the muscles of rib takes form enough flywheel stiffness and produced similar with traditional flywheel inertia.This kind is decorated in a small space to with smaller quality to gain the maximum rotation inertia, help reduce the assembly structure, the axial dimensions for subprime flywheel and clutch decorate a space make more. Its damping device by a wear-resisting plastic gasket, a belt of steel plate and a slot disc spring washers constitute, they set in damping plate, rely on damping disc hole flanging positioning and compaction, the damping disk with primary flywheel riveted by the subprime, plastic gasket flywheel slot drive. Practice proves that the double quality than ever, this structure can be the flywheel in a limited space get quite good vibration reduction.Engine for the job, usually by the flywheel, inertia and the clutch clutch disc provides together. The ideal flywheel structure should be to offer the same, and ensure enough inertia structure stiffness premise to minimize the flywheel quality, stamping steel way to replace traditional casting can obtain the flywheel ways to produce the effect. Change the pressure by casting lron yuntechtc ring, start toothed ring and steel blunt system drivers disk of three parts. In the ring gear driving plate welding, pressure rings and drivers disk riveting, pressure ring of moment of inertia of the subject constitutes a flywheel, and provide for the clutch friction surface and heat conduction. Drivers disk improve enough flywheel stiffness, and using laser welding and clutch cover, this is connected to this structure forms of changescan be compared to traditional iron flywheel reduce quality 5% ~ 10%. USES the steel plate stamping type flywheel, and clutch cover and flywheel connections between after replacing bolt connection with welding, reducing the number and machinery manufactured parts, which reduces the production cost. The foregoing radial layout springs double quality can use this stamping yuntechtc for structure form, reducing axial dimensions []17. 3, clutch discClutch platen design of the main contradiction is facing, on one hand, hope to have as played platen diameter, in order to obtain the good preach torsional characteristic, reducing friction slices wear quantity and improve the service life, on the other hand, hope the decrease of the platen as possible, so as to shorten the rotational inertia of the variable transmission shift, ensure the synchronization time of smooth, transmission clutch platen ontology conscious drops, and therefore made wavy often difficult to coordinate the contradiction. When using triangle groove platen ontology structure, while keeping the original way wavy platen ontology has the axial elastic properties at the same time, because of its large on the plane can be formed, enough to make its and friction slices adhesive is used to connect the replacement of traditional riveting, so that in friction chip will not need the thickness of the steel back to reserve rivet, so clutch friction slices thickness, which can reduce the platen axial dimensions, and can be reduced by 10% of inertia can reduce nearly 25%. In other words, keep the premise of inertia unchanged, possible will platen diameter increases, so can the arrangement for torsional shock absorber, let a space when damper spring job increase, the rigidity of the shock absorber in diameter can be reduced greatly, increasing the space for setting also provides an ideal damping components fundamental conditions. On the other hand, because platen diameter increases, the optimization of diaphragm spring separation means it can obviously reduce leverage than the load bearing separation.Using triangle groove platen ontology and friction piece of adhesive technology, still can make clutch friction slices surface pressure distribution, and more uniform can improve the service life of friction slices.4, clutch diaphragm springUsing the diaphragm spring of a nonlinear elastic properties, can increase the ability of clutch abrasion resistance. Usually, can pass the clutch when installation, adjustment diaphragm spring axial position, to keep the spring of compaction force, but due to the manufacturing process of previous position error is quite large, so often wasted spring this portion of elastic energy, enables the abrasion resistance ability get full play. When the clutch cover and flywheel connection with the above welding way to finish, the clutch assembly may allow such position when the adjustment, thus, the corresponding clutchscratch-resistant ability can improve the 4% ~ 30%.To improve the ability to change its antiwear properties, but also can the diaphragm spring is reinforced by controlling method of separation means and the rib disc supporting ring approach to getting.[]175, clutch control systemAutomatic transmission in cars growing popularity of today, due to its lack of transmission efficiency of cars, and motorists feel lost control, makes mechanical clutch still has wide market. Along with the computer technology and the rapid development of modern control technology has to clutch may reality automatic control, automatic clutch management system (CMC) is the product of this idea. The driver speaking, clutch automatic control system is that it is the most obvious advantage of cancelled the clutch pedal, thus improve the driving comfort, whether in the city the frequent change of traffic environment, or in the ramp, its advantages are started is quite clear. Meanwhile, in order to reduce the transmission low noise and vibration, CMC is likely to clutch real-time control of sliding, all these can improve automobile driving safety. Although the automatic transmission can also play the same role in price, but the CMC, fuel efficiency, engine braking and rapid response, etc but again the obvious advantage. In addition, it has no peristalsis phenomenon, and can make control shift timing. Drivers On the other hand, for car itself, because the CMC reduced because the actual driving quite frequent false operation produces drivetrain stress, therefore, can reduce the transmission and its transmission parts design dimensions, in general driving conditions, electronic control ensures the accuracy and speed than artificially operation circumstance clutch of wear small, long service life.CMC consists of three parts: namely is used to identify the driver intention and the clutch, the transmission working state of sensors,Clutch actuators and electronic control unit, drivers shift HuanDangGan movements and intention through the release of the accelerator pedal to identify, this requires signal judge strategy and control must be very quick, to avoid the feeling of driver produce shift block, when pilots inadvertently tinkering with the transmission system when rod may not false action. In addition, the CMC through the engine speed, the transmission input shaft speed and throttle position signal to clutch slip for mind control, which can eliminate the car driving common vibration and noise. Such as a limit control to prevent slip in 1 and 2, block small throttle low-speed driving, the car slightly tilted forward, generating about 1Hz very uncomfortable zitterbewegung, through in the clutch of transient torsional direction change quickly, to eliminate the separation clutch in clutch under the condition of incomplete combinations, when pilots alternate relaxation and trample accelerator pedal, because thetransmission torque change to the sharp produced recoiling sickening crash; or depressing Through the precise relative slip between 50 ~ 100rpm control, can eliminate in high-grade, high and low speed conditions when the engine driving torque values in the passenger cabin can smell the low-frequency resonance produced, and when the transmission in 2 ~ 3 block,engine speed 12 ~ 2500rpm and high load, the transmission possible beats noise; Through the separation clutch, convenient when the elimination of the idle will clutch and neutral transmission combine, engine torque peak in the transmission of idle speed noise produced. The key is to prevent vibration noise sensitivity and accuracy, this system requirements system has high control ability, rely on modern computer and hydraulic control technology has been possible this some.[]186, closingBy adopting a new design concept, can make clutch axial dimensions is much shorter, platen diameter increases, power transmission more reliable, clutch capacity increases, separation bearing load is reduced, torsion vibration reduction improve, processing manufacturing easier, lower cost, service life can be extended 50% and than before can be expected, along with the automatic control technology mature gradually perfect, clutch control mode will also continue to rapid development.附 录录 2汽车离合器技术的新发展摘要:近年来汽车设计和制造技术的进步有目共睹。

汽车离合器中英文对照外文翻译文献(文档含英文原文和中文翻译)Fethermal analysis of a ceramic clutch1. IntroductionAbrasive dry running vehicle clutches are force closure couplings. Torque and speed transmission are ensured by the frictional force generated between two pressed surfaces. Reasons for the application of ceramic as a friction medium include good heat and wear resistance properties, which provide the opportunity to drive higher pressures, and a low density. Thus, an increasing power density is enabled with a parallel minimization of construction space.Measurements with a first prototype of a clutch disk using ceramic facings were performed at Karlsruhe University in a laboratory specialized in passenger car drive system testing. In the course of analysis the finite element (FE) model was to be constructed with the knowledge of measurement data and measurement conditions. Calculations were intended to determine the temperature distribution of the clutch disk and its environment at each moment in time corresponding to measurements. It is essential to be familiar with the temperature range in order to examine the wear characteristics of the system. Thus,important information is derived from measurement data. In critical load cases, the highest expected temperatures must be forecast in space and time in order to protect measuring instruments close to the location of heat generation.The goal of this study is to analyze and modify the clutch system to provide better operating conditions by improving the heat conduction and convection of the system or to increase the amount of the energy converted into frictional heat. Furthermore, it is desired to find better design solutions for more efficient clutch systems.Calculations were performed by the Cosmos Design Star software. During model development, great care had to be taken for proper simplification of geometry, the selection of element sizes, and the correct adjustment of time steps due to the substantial hardware requirements for transient calculations. Changes in thermal parameters such as the surface heat convection coefficient and thermal load had to be taken into consideration on an on-going basis in terms of time and location. The two sides of the analyzed test clutch system can only be managed by two independent models linked by heat partition, according to the hypothesis that the contact temperature must be identical on both sides while there is proper contact between them and its value must be adjusted by iteration. Calculations revealed that the heat partition changed by cycle and it differed along the inner and outer contact rings. As a result of the different cooling characteristics between the ceramic and steel side, a heat flow is launched from the ceramic side to the steel side. This heat flow was also determined by iteration, its value also changes by cycle and differs along the inner and outer contact rings.2. First prototype of a clutch using engineering ceramics as friction materialThe examined clutch disk was developed according to the “specific ceramic” product development process established at the Institute for Product Development (IPEK) at the University of Karlsruhe. This development process already has the possibility for connection to a real transmission shaft; further, it has a cushion spring device for the facings allowing good start behaviour. Abrasive clutches must comply with the following basic requirements:●high torque transmission according to high friction coefficients,●high comfort (no vibrations through self-induced chattering),●homogeneous temperature distribution,●low wear characteristic.A critical element of the switch is the abrasive disk.With regard to the design utmost care must be taken to select the right material. A high and constant friction coefficient,,wear resistance and thermal resistance are desired characteristics. The clutch disk has instead of the generally applied ring-shaped abrasive inlet two rows of SSIC (as sintered) ceramic pellets. These pellets are placed on 6 separate segments. The segments are fixed to the central hub by rivets. Each segment consists of 4 plates, 2 working as facing springs and 2 as carriers.3. MeasurementsMeasurements were performed at the department of power train development of the Institute for Product Development (IPEK) at the Karlsruhe University (TH) Research University, where a category IV component test rig is used for tests of new frictional materials and examinations of new materials in real clutch disks. Real conditions are applied by the simulation of driving resistance (e.g. starting in the plane, starting at the hill). It is a component test rig leveled on the fourth position of the tribological testing environment.In order to give an idea of dimensions: the equipment length is about 4-5m. The two electric motors and the axial force are controlled independently by computer; thereby many operational states can be realized. This enables the equipment to complete a myriad of tribological measurements all while properly modeling the operation of a clutch disk in a passenger car. It is also equipped with an automatic IT measurement system. Measurable quantities include the following:●two heavy-duty electric motors (150 KW, Baumuller DS 160L-305),●device suitable for exerting axial force,●torque meter (Manner Sensortelemetrie MF100),●axial force meter,●steel disk in friction,●replaceable head to affix the device to be tested,●temperature along two different radii at 0.4mm below the abrasive surface of the steeldisk (Omega HJMTSS-IM100U-150-2000,J-typeiro-constantan thermocouples),●revolutions per minute for both sides (Polytene LSV 065).The greatest challenge out of these is temperature measurement as we would like to know the temperature of the revolving steel disk. The two thermoelements placed in the steel disk forward data to the computer through a wireless blue tooth system and are placed 0.4mm below the abrasive surface of the steel disk on the two opposite arcs of the clutch disk.3.2. Measurement processDue to component analyses and cost reduction only one side of the clutch disk is mounted with ceramic facings. Thus, the clutch disk and its fitting will be referred to as the ceramic side, and the abrasive steel disk with its environment revolving together will be referred to as the steel side. In the course of measurements, data were collected at a sampling frequency of 100 and 1000HZ. Measurements were conducted according to the time curves.The measurement starts by increasing the revolutions per minute of the steel side (the driving side) to a specific value (1500 rpm here). Then the ceramic side (the driven side), held at zero rpm, is pushed towards the steel disk and the axial force is applied until a designated value is reached (nominally 4200N here). Upon reaching the designated axial force the ceramic side is released and the two sides start to synchronize. A few seconds after synchronization, the axial load is discontinued and after some time both the steel and the ceramic sides—revolving at the same speed—are slowed down. This is deemed to be one measurement cycle. Ten cycles are completed in the course of a single measurement. During application of the axial force the ceramic side is held at zero rpm until the desired force is reached to ensure synchronization occurs at nearly the same time of each cycle. This is unfavorable from the viewpoint of both measurements and calculations. Measurements are usually conducted by changing only 3 parameters: the speed, the axial load and the inertia. The following figures are applied in various combinations:●speed n: 700, 1100 and 1500 (rpm),●axial force F: 4200, 6400 and 8400 (N) andinertia I: 1, 1.25 and 1.5 (kgm2).Experimental measurements are launched with approx.10-15 min intervals, during which the system cools down to about 30-40 1C. This makes calculations difficult, as the exact temperature distribution of the system is not known at the commencement of the measurement. However, it can be assumed that a period of 10-15min is sufficient for a nearly homogeneous temperature distribution to be produced. The parameters for the following simulation have been chosen for an intermediate case with a speed n =1500 rpm, an axial force F = 4200 N and an inertia I = 1 kg m2.4. Calculations of heat generationThe mechanical energy consumed during the friction of two bodies is transformed into heat. The generated heat can be calculated by the following simple formula: Q =μ·ν·F [W] .where m is the the frictional coefficient; v is the sliding velocity; F is the force perpendicularly compressing the surfaces. And the heat flux density per surface unit is q=μ·ν·p [Wm2].where p is the the pressure calculated as a ratio of the force and the contacting surface. As the ceramic tablets are placed at two different radii along the clutch disk, the heat generated must be calculated separately for each radii. Sliding can be divided into two sections. In the first section, the ceramic side is kept in a stationary position by braking, meanwhile the axial load is increased; therefore compression changes in the course of time while the speed difference between the two sides is constant. In the second section (at synchronization) the speed difference is equalized while the force value is constant, so velocity changes in time. On the basis thereof, the heat generated is.The nominal contact area is the aggregate of the contacting surfaces of the 24 and 18 ceramic tablets on the given ring. The diameter of ceramic tablets is:.Calculations were performed for the load case to be characterized by the following parameters:.Based on experimental measurements a constant friction coefficient of 0.4 was established..The velocity can be calculated with the knowledge of the radius and the speed..Surface pressure can be calculated as a ratio of the axial force and the contacting surface. This produces the same figure for each ceramic pellet, assuming an even load distribution..Thus, the maximum values of the generated heat are.In the first section of sliding, the generated heat is rising due to the increase of the load force; in the second section, it is decreasing due to the equalization of the speed difference. It is necessary to know the time of each sliding section in order to be able to specify the generated heat time curve. These can be determined from measurement dataseries. Synchronization time can be easily determined from the speed of the ceramic side. Speed increase is linear. Force increase is non-linear. For the sake of simplicity, force increase was substituted by a straight line in calculations so that the area below the straight line is nearly identical with the area measured below the curve. Thus, the time difference between the two terminal points of the straight line is the time of the first sliding section.The above-mentioned method was applied for each cycle and their average was specified. Based on these results, the following values were determined for sliding times:.Now the time curve of heat generation can be produced. The same curve was used in each cycle as there were no significant differences between parameters in each cycle. The generated heat-calculated this way-will appear as thermal load in the thermal model. It must be distributed appropriately between the contacting surfaces by taking into consideration heat partition. Heat partition requires the contact temperatures to be identical at both surfaces. Correct adjustment requires repeated iterations.有限元热分析的陶瓷离合器1 引言磨料空转车辆离合器是力封闭联轴器。

汽车变速器的设计外文文献翻译、中英文翻译、外文翻译A manual n。
also known as a standard n。
XXX。
It consistsof gears。
synchros。
roller bearings。
shafts。
and gear selectors。
The main clutch assembly is used to engage and disengage the engine from XXX gears are used to select the desired。
and the sector fork moves gears from one to another using the gearshift knob。
Synchros are used to slow the gear to a。
before it is XXX。
The counter shaft holds the gears in place and against the main input and output shaft。
Unlike automatic ns。
XXX。
as there isno XXX。
Note: XXX "n Shifter" was deleted as it had no XXX.)XXX have four to six forward gears and one reverse gear。
However。
some cars may have up to eight forward gears。
while semi trucks XXX by the number of forward gears。
such as a 5-speed standard n.The n of a standard n includes three shafts: the input shaft。

中英文对照资料外文翻译文献外文原文:PASSAGE A Power TrainThe power train serves two functions:it transmits power from the engine to the drive wheels, and it varies the amount of torque. The power train includes:1.engine:that produces power;2.transmission:either manual or automatic;3.clutch:used only on manual transmission, or torque converter.:used only on automatic transmission;4.drive shaft:that transmits the power from transmission to differential;5.that carries the power to the two wheel axles.See Fig.5-1.Manual transmissionThe function of a manual transmission,shown in Fig.5-2, is to transfer engine power to the drive shaft and rear wheels. Gears inside the transmission change the car’s drive-wheel speed and torque in relation to engine speed and torque.This keeps the engine’s output matched as close as possible to varying road speeds and loads.A manual transaxle,shown in the Fig.5-3.,is a single unit composed of a manual transmission, differential, and drive axles. Most front-wheel-drive(FWD)cars are equipped with a transaxle. Such transaxle are also found on some front-engined or rear-wheel-drive (RWD),four-wheel-drive(4WD)cars and on rear-enginedand rear-wheel-drive cars.A manual transmission requires use of a clutch to apply and remove engine torque to the transmission input shaft.The clutch allows this to happpen gradually so that the car can be started from a complete stop.Manual transmission usually have four or five speeds, and often have “overdrive”, which means that the output shaft can turn faster than the input Shaft for fuel economy on the highway. When you use it, it will reduce the engine speed by one-third,while maintaining the same road speed.ClutchDriving a car with a manual transmission, you depress the clutch, select a gear, and release the clutch while applying power to get the car to move. The clutch allows engine power to be applied gradually when a vehicle is starting out, and interrupts power to avoid gear crunching when shifting. Engaging the clutch allows power to transfer from the engine to transmissionand drive wheel. Disengaging the clutch stops the power transfer and allows the engine to continue turning without force to the drive wheels.The clutch basic components are:the flywheel, clutch disk, pressure plate,release bearing and linkage. See Fig.5-4.The flywheel is bolted to the crankshaft of the engine. Its main function is to transfer engine torque from the engine to the transmission.The clutch disk is basically a steel plate, covered with a frictional material that goes between the flywheel and the pressure plate.A pressure plate is bolted to the flywheel. It includes a sheet metal cover, heavy release springs, a metal pressure ring that provides a friction surface for the clutch disk.The release bearing is the heart of clutch operation. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the throw-out bearing moves toward the flywheel, pushing in the pressure plate’s release fingers and moving the pressure plate fingers or levers against pressure plate spring force.The linkage transmits and multiplies the driver’s leg force to the fork of the clutch pressure plate. A mechanical clutch linkage usually consists of the clutch pedal, a series of linkage rods and arms, or a cable. A hydraulic clutch linkage typically includes a clutch master cylinder and reservoir, a hydraulic line and a slave cylinder.Automatic transmissionBoth an automatic transmission and a manual transmission accomplish exactly the same thing, but they do it in totally different ways. The key difference between a manual and an automatic transmissions is that the manual transmission locks and unlocks and different sets of gears to the output shaft to achieve the various gear ratios, while in an automatic transmission, the same set of gears produces all of different gear ratios. The planetary gear-set is the device that makes this possible in an automatic.Automatic transmissions are used in many rear-wheel-drive and four-wheel-drive vehicles. Automatic transaxles are used in most front-wheel-drive vehicles. The major components of a transaxle are the same as those in a transmission, except the transaxle assembly includes the final drive and differential gears, in addition to the transmission.An automatic transmission receives engine power through a torque converter, which is driven by the engine’s crankshaft. Hydraulic pressure in the converter allows power to flow from the torque converter to the transmission’s input shaft. The input shaft drives a planetary gear set that provides the different forward gears, a neutral position, and one reverse gear. Power flow through the gears is controlled by multiple-disk clutches, one-way clutches, and friction bands.Passage B Power TrainTorque ConverterThe key to the modern automatic transmission is the torque converter. It takes the place of a clutch in a manual transmission to send the power from the engine to the transmission input shaft. The torque converter offers theadvantage of multiplying the turning power provided by the engine.It has three parts that help multiply the power:an impeller(or pump)connected to the engine’s crankshaft, a turbine to turn the turbine shaft which is connected to the gears, and a stator(or guide wheel)between the two. See Fig. 5-6.The torque converter is filled with transmission fluid that is moved by impeller blades. When the impeller spins above a certain speed, the turbine spins, driven by the impeller.Planetary GearingPlanetary gears provide for the different gear ratios needed to move a vehicle in the desired direction at the correct speed. A planetary gear set consists of a sun gear, planet gears, and a internal ring. See Fig. 5-7.In the center of the planetary gear set is the sun gear.Planet gears surround the sun gear, just like the earth and other planets in our solar system. These gears are mounted and supported by the planet carrier and each gear spins on its own separate shaft. The planet gears are in constant mesh with the sun and ring gears. The ring gear is the outer gear of the gear set. Its has internal teeth and surrounds the rest of the gear set. Its gear teeth are in constant mesh with the planet gears. The number of planet gearsused in a planetary gear set varies according to the loads the transmission is designed to face. For heavy loads, the number of planet gears is increasedto spread the work load over more gear teeth.The planetary gear set can provide a gear reduction or overdrive, direct drive or reverse, or a neutral position. Because the gears in constant mesh, gear changes are made without engaging or disengaging gears, as is required in a manual transmission. Rather, clutches and bands are used to either hold or release different members of the gear set to get the proper direction ofrotation and/or gear ratio.DifferentOn FWD cars, the differential unit is normally part of the transaxle assembly. On RWD cars, it is part of the rear axle assembly. Located inside the differential case are the differential pinion shafts and gears and the differential side gears. See Fig.5-8The differential assembly revolves with the ring gear. Axle side gears are splined to the rear axle or front axle drive shafts.When an automobile is moving straight ahead, both wheels are free to rotate. Engine power is applied to the pinion gear, which rotates the ring gear. Beveled pinion gears are carried around by the ring gear and rotate as one unit. Each axle receives the same power, so each wheel turns at the same speed. See Fig. 5-9.When the car turns a sharp corner, only one wheel rotates freely. Torque still comes in on the pinion gear and rotates the ring gear, carrying the beveledpinions around with it. However, one axle is held stationary and the beveled pinions are forced to rotate on their own axis and “walk around”their gear. The other side is forced to rotate because it is subjected to the turning force of the ring gear, which is transmitted through the pinions. See Fig. 5-10.Drive shaftA drive shaft and universal joints(U-joints)connect the transmission to the rear drive axle on most rear-wheel-drive vehicles. Many four-wheel-drive vehicles also use drive shafts and universal joints, with one drive shaft between the transfer case and rear drive axle and a second drive shaft between the transfer case and the front drive axle. The drive shaft is sometimes called a propeller shaft.The drive shaft and U-joints provide a means of transferring engine torqueto drive axles. The universal joints allow the drive shaft to move up and down, to allow for suspension travel. Some drive shaft also have a slip joints that allows the drive shaft to make minor length changes as the vehicle suspension height changes.Gears and gear driveGears are the most durable and rugged of all mechanical drives. They can transmit high power at efficiencies up to 98% and with long service lives. For this reason, gears rather than belts or chains are found in automotive transmissions and most heavy-duty machine drives. On the other hand, gears are more expensive than other drives, especially if they are machined and not made from power metal or plastic.Gear cost increases sharply with demands for high precision and accuracy. So it is important to establish tolerance requirements appropriate for the application.Gears that transmit heavy loads or than operate at high speeds are not particularly expensive, but gears that must do both are costly.Silent gears also are expensive. Instrument and computer gears tend to be costly because speed or displacement ratios must be exact. At the other extreme, gears operating at low speed in exposed locations are normally termed no critical and are made to minimum quality standards.For tooth forms, size, and quality, industrial practice is to follow standards set up by the American Gear Manufactures Association (AGMA).Tooth formStandards published by AGMA establish gear proportions and tooth profiles.Tooth geometry is determined primarily by pitch, depth, and pressure angle. Pitch:Standards pitches are usually whole numbers when measured as diametral pitch P.Coarse-pitch gearing has teeth larger than 20 diametral pitch –usually 0.5 to 19.99. Fine-pitch gearing usually has teeth of diametral pitch 20 to 200.Depth: Standardized in terms of pitch. Standard full-depth have working depth of 2/p. If the teeth have equal addenda(as in standard interchangeable gears) the addendum is 1/p. Stub teeth have a working depth usually 20% less than full-depth teeth. Full-depth teeth have a larger contract ratio than stub teeth. Gears with small numbers of teeth may have undercut so than they do not interfere with one another during engagement. Undercutting reduce active profile and weakens the tooth. Mating gears with long and short addendum have larger load-carrying capacity than standard gears. The addendum of the smaller gear (pinion) is increased while that of larger gear is decreased, leaving the whole depth the same. This form is know as recess-action gearing.Pressure Angle: Standard angles are 025. Earlier standards include a20and 014-02/1pressure angle that is still used. Pressure angle affects the force that tends to separate mating gears. High pressure angle decreases the contact ratio (ratio of the number of teeth in contact) but provides a tooth of higher capacity and allows gears to have fewer teeth without undercutting.Backlash: Shortest distances between the non-contacting surfaces of adjacent teeth .Gears are commonly specified according to AGMA Class Number, which is a code denoting important quality characteristics. Quality number denote tooth-element tolerances. The higher the number, the closer the tolerance. Number 8 to 16 apply to fine-pitch gearing.Gears are heat-treated by case-hardening, through-hardening, nitriding, or precipitation hardening. In general, harder gears are stronger and last longer than soft ones. Thus, hardening is a device that cuts the weight and size of gears. Some processes, such as flame-hardening, improve service life but do not necessarily improve strength.Design checklistThe larger in a pair is called the gear, the smaller is called the pinion.Gear Ratio: The number of teeth in the gear divide by the number of teeth in the pinion. Also, ratio of the speed of the pinion to the speed of the gear. In reduction gears, the ratio of input to output speeds.Gear Efficiency: Ratio of output power to input power. (includes consideration of power losses in the gears, in bearings, and from windage and churning of lubricant.)Speed: In a given gear normally limited to some specific pitchline velocity. Speed capabilities can be increased by improving accuracy of the gear teeth and byimproving balance of the rotating parts.Power: Load and speed capacity is determined by gear dimensions and by type of gear. Helical and helical-type gears have the greatest capacity (to approximately 30,000 hp). Spiral bevel gear are normally limited to 5,000 hp, and worm gears are usually limited to about 750 hp.Special requirementsMatched-Set Gearing:In applications requiring extremely high accuracy, it may be necessary to match pinion and gear profiles and leads so that mismatch does not exceed the tolerance on profile or lead for the intended application. Tooth Spacing: Some gears require high accuracy in the circular of teeth. Thus, specification of pitch may be required in addition to an accuracy class specification.Backlash: The AMGA standards recommend backlash ranges to provide proper running clearances for mating gears. An overly tight mesh may produce overload. However, zero backlash is required in some applications.Quiet Gears:To make gears as quit as possible, specify the finest pitch allowable for load conditions. (In some instances, however, pitch is coarsened to change mesh frequency to produce a more pleasant, lower-pitch sound.) Use a low pressure angle. Use a modified profile to include root and tip relief. Allow enough backlash. Use high quality numbers. Specify a surface finish of 20 in. or better. Balance the gear set. Use a nonintegral ratio so that the same teeth do not repeatedly engage if both gear and pinion are hardened steel. (If the gear is made of a soft material, an integral ratio allows the gear to cold-work and conform to the pinion, thereby promoting quiet operation.) Make sure critical are at least 20% apart from operating speeding or speed multiples and from frequency of tooth mesh.Multiple mesh gearMultiple mesh refers to move than one pair of gear operating in a train. Can be on parallel or nonparallel axes and on intersection or nonintersecting shafts. They permit higer speed ratios than are feasible with a single pair of gears .Series trains:Overall ratio is input shaft speed divided by output speed ,also the product of individual ratios at each mesh ,except in planetary gears .Ratio is most easily found by dividing the product of numbers of teeth of driven gears by the product of numbers of teeth of driving gears.Speed increasers (with step-up rather than step-down ratios) may require special care in manufacturing and design. They often involve high speeds and may creste problems in gear dynamics. Also, frictional and drag forces are magnified which, in extreme cases , may lead to operational problems.Epicyclic Gearing:Normally, a gear axis remains fixed and only the gears rotates. But in an epicyclic gear train, various gears axes rotate about one anther to provide specialized output motions. With suitable clutchse and brakes, an epicyclic train serves as the planetary gear commonly found in automatic transmissions.Epicyclic trains may use spur or helical gears, external or internal, or bevel gears.In transmissions, the epicyclic (or planetary) gears usually have multiple planets to increase load capacity.In most cases, improved kinematic accuracy in a gearset decreases gear mesh excitation and results in lower drive noise. Gearset accuracy can be increased by modifying the tooth involute profile, by substituting higher quality gearing with tighter manufacturing tolerances, and by improving tooth surface finish. However, if gear mesh excitation generaters resonance somewhere in the drive system, nothing short of a “perfect” gearset will substantially reduce vibration and noise.Tooth profiles are modified to avoid interferences which can result from deflections in the gears, shafts, and housing as teeth engage and disendgage. If these tooth interferences are not compensated for by profile modifications, gears load capacity can be seriously reduced. In addition, the drive will be noisier because tooth interferences generate high dynamic loads. Interferences typically are eliminated by reliving the tooth tip, the tooth flank, or both. Such profile modifications are especially important for high-load , high-speed drives. The graph of sound pressure levelvs tip relief illustrates how tooth profile modifications can affect overall drive noise. If the tip relief is less than this optimum value, drive noise increases because of greater tooth interference; a greater amount of tip relief also increase noise because the contact ratio is decreased.Tighter manufacturing tolerances also produce quietier gears. Tolerances for such parameters as profile error, pitch AGMA quality level. For instance, the graph depicting SPL vs both speed and gear quality shows how noise decreases example, noise is reduced significantly by an increase in accuracy from an AGMA Qn 11 quality to an AGNA Qn 15 quality. However, for most commercial drive applications, it is doubtful that the resulting substantial cost increase for such an accuracy improvement can be justified simply on the basis of reduced drive noise. Previously, it was mentioned that gears must have adequate clearance when loaded to prevent tooth interference during the course of meshing. Tip and flank relief are common profile modifications that control such interference. Gears also require adequate backlash and root clearance. Noise considerations make backlash an important parameter to evaluate during drive design. Sufficient backlash must be provided under all load and temperature conditions to avoid a tight mesh, which creates excessively high noise level. A tight mesh due to insufficient backlashoccurs when the drive and coast side of a tooth are in contact simultaneously. On the other hand, gears with excessive backlash also are noisy because of impacting teeth during periods of no load or reversing load. Adequate backlash should be provided by tooth thinning rather than by increase in center distance. Tooth thinning dose not decrease the contact ratio, whereas an increase in center distance does. However, tooth thinning does reduce the bending fatigue, a reduction which is small for most gearing systems.译文:动力传动系A动力传动系有两个作用:它把动力从发动机传送到驱动轮上,并且改变扭矩的大小。

TRANSMISSIONManual transmission is one of the most common transmission, referredto as MT. Its basic structure in a single sentence is a central axis, twoinput shaft, namely, the axial and axial oart, they constituted the transmission of the subject, and, of course, a reverse axis. Manual transmission gear transmission and manual, contain can in axial sliding gears, through different meshing gears to change gear of torsional purpose.The typical structure and principle of the manual transmission.Input shaft also says, it's in front of the spline shaft directly withclutch platen, thus the spline set by the engine relay of torque. The firstshaft gear meshing gears, often with oart as input shaft, and the gear on oart will turn. Also called shaft, because even more solid shaft of gear. The output shaft, and the second shaft position have the drive shaftgear, may at any time and under the influence of the control devices and the corresponding oart gear, thus changing the speed and torque itself. The output shaft is associated with tail spline shaft torque transmissionshaft, through to drive to gear reducer.Predictably, transmission gear drive forward path is: input shaftgear - oart gnaws gnaws gear - because the second shaft gear - corresponding corresponding gear. Pour on the axle gear can also controldevice, by moving axis in the strike, and the output shaft gear and oart gear, in the opposite direction.Most cars have five forward and reverse gear, each one has certain ratio,the majority of gear transmission more than 1, 4 gears transmission is 1, called directly, and ratio is less than 1 of article 5 gear shift accelerated called. The output axis gear in the mesh position, can acceptpower transmission.Due to the gearbox output shaft to input shaft and the speed of theirgear rotating, transform an "synchronization problem". Two rotating speeddifferent meshing gears forcibly inevitable impact and collision damage gear. Therefore, the old transmission shift to use "two feet clutch" method, ShengDang in neutral position shift to stay for a while, in the space location on the door, in order to reduce gear speed. But this operation is more complex, difficult to grasp accurately. Thereforedesigners to create "synchronizer", through the synchronizer will makethe meshing gears reach speed and smooth.Currently the synchronous transmission adopts is inertial synchronizer, it mainly consists of joints, synchronizer lock ring etc,it is characteristic of the friction effect on achieving synchronization.Mating, synchronizer and mating locking ring gear tooth circle have chamfering (locking horns), the synchronizer lock ring inside surface ofgear engagement ring and the friction surface contact. The lock horns with cone when designing the proper choice, has been made to the surface friction of meshing gears with gear synchronous, also can rapid producesa locking function, prevent the synchronous before meshing gears. When synchronous lock ring of gear engagement with surface contact surface, the outer circle in friction torque under the action of gear speed rapiddecrease (increase) or to synchronous speed equal, both locking ring spunconcurrent, relative to lock ring gear synchronous speed is zero, thus inertia moment also disappear, then in force, driven by the junction of unimpeded with synchronous lock ring gear engagement, and further to engagement with the engagement ring gear tooth and complete shift process.functional (1) change ratio, meet different driving conditions for tractionengine, the need to work in the favorable conditions and meet the speed may request. In a wide range of vehicle speed changing the size and automobile driving wheel on the size of the torque. Due to the differentdemands, automobile driving conditions of vehicle speed and torque can drive in a broad range of change. For example, in high speed can be reachedon 100km/h, while in the urban district, speed in 50km/h. In the empty flat roads, road, very little resistanceWhen When carrying carrying carrying uphill, uphill, uphill, driving driving driving resistance resistance resistance was was was great. great. great. And And And the thecharacteristics of automobile engine speed range is lesser, and torque changes more cannot meet the actual conditions range. (2) drive backward, to satisfy the need to drive car backwards. Realizing the backing, engine crankshaft are generally only to a direction,and sometimes need to back, so, often used in the transmission of reverseto realize the car drive backward.(3) in power, interruption, idle running engine starting, auto shift or need to stop the dynamic output, interrupted to transfer the power ofthe drive wheels.(4), when the clutch engagement realize gap, gearbox can not power output. For example, can ensure drivers in engine flameout loosen the clutch when leaving drivers seat.constituteBy continuously variable transmission gearbox and speed control twoparts. The main function of the variable transmission torque and speed is the change of numerical and direction, The main function of theoperation is controlled transmission mechanism, realize thetransformation of transmission ratio, shift to speed torque. Principle,Mechanical transmission main application of the principle of geartransmission velocity. Say simply, there are a number of differenttransmission gearbox group of gear pair of vehicle, and behavior, is alsoshifting gears trunk by manipulating institutions make different gearpair work. As in low-speed, ratio of gear pair work, and in high-speed, let ratio of small gear pair work.Classification,1, according to the change of transmission, transmission way, there can be divided into grade level and synthetical three.(a) : several levels of transmission ratio, can choose the fixed by gear. And can be divided into: gear axis of ordinary gear transmission and fixed gear planetary gear (part) of planetary gear transmission axisof rotation.b) stepless type transmission: ratio can be continuous variation within a certain range, commonly, mechanical and electric hydraulic typeetc.(c) comprehensive type transmission by a class type, transmission andstepless type transmission, the ratio of the maximum and minimum values can be in between the scope for several section stepless change.2, press control can be divided into compulsory manipulation, transmission, automatic control and semi-automatic control 3 kinds.(a) mandatory manipulation of transmission by direct manipulation, change gear shift lever drivers.(b) automatic control type transmission ratio of choice and change: the shift is automatic. Drivers simply manipulate accelerated pedal, transmission can according to the engine speed and load control signal signal actuator, realize the transformation of gear.(c) semi-automatic control type transmission can be divided into twokinds: one kind is part of gear, automatic shift gears, manual (mandatory)shift, Another kind is selected by button in mining under gear clutch pedalor accelerated release pedal, the executing agency to shift. Transmission of maintenance1 transmission gears maintenanceTransmission gears are always changing speed, load, gear toothsurface by bluntThe impact of load, which struck gear tooth surface (especially) damage. Common injuries are:(1) gear transmission is worn gear under normal working conditions, shows the wear uniform angled tooth gear, long wear along the directionTooth thickness shouldof the tooth should not exceed 30 percent longer,not exceed usd, Gear tooth surface area of not less than two-thirds, Running gear mesh clearance shall be commonly used, 0.15-0.26 mm to 0.8 mm limit, Gear engagement between 0.10-0.15 mm, should use limit for 0.60mm. Available batches or soft metal rivalries. If more than clearance method for measuring the pairs, should be replaced.due to fail togear clearance is mainly(2) gear teeth,broken toothmeet the requirements, gear meshing parts or work under great impact load.If you are not greater than 2mm edge of gear oil can smile ShiXiuafter-grinding continue to use, If the scope or have more than three pairs,should smile.(3) often mesh surface of the helical gear often wear face due. 10-0.30mm, in order to ensure that the axial clearance, if tooth gear good operation within the wear, can repair tank, but the amount of grinding grinding should not exceed. 50.(4) often meshing gears shaft neck, needle roller bearing and wear into seat hole hole meshing gears seat with needle bearings and shaft neckwith clearance should be 0.01 - three 0.08 mm, otherwise must be changed.2 the overhaul. Transmission shellGearbox shell is transmissions, to ensure the basis of each part of the transmission is correct position, work under load. Common injuries are:(1) the abrasion of shell bearing hole hole wear will destroy its bearing assembly relation with the bearing, the direct impact of input, output shaft transmission position relative to the hole. Bearing seat with0-0.03 mm clearance shall be used for the maximum limit, should be replacedor 0.10 mm) shell or pile hole repair.(2) shell threaded holes repair note oil ROM plug hole, dumping screwhole threads connecting bolts damage and between shellThreaded hole, can take damage with screw repair.3 transmission shaft of maintenanceTransmission in the process of operation, each bearing the torsionalmoment of change, and bending moment, JianChi part is under pressure, impact and sliding friction etc. Various axial load of common injuries are:(1) the shaft neck and neck too worn wear axis gear axis will not onlyoffset, and can bring the change gear clearance, when making noisetransmission shaft neck. Also make coordination relationship with bearingdamage, may cause ablation. So roller bearings in a place with no more than 0.02 axis wear mm needle bearing shaft neck wear with place, otherwisethan 0.07 mm landscape change or chrome.side of thein stress and more seriouswear JianChi wear(2) JianChispline. JianChi with check, when more than 0.25 or and wear with more thanusd keyway apprentice, gear engagement mm, combining with the gear with JianChi weeks, according to the mm apprentice woodruff key and shaft neckkeyways apprentice to JianChi 0.08 mm over there when the keyway weeks, or should be repaired or replaced shaft.(3) transmission shaft bending thimble resist transmission shaft withmaintenance on both ends of the roof, using pinhole batches of shaft radial micrometers, check the deviation should be less than 0.10 mm) pressure correction repair.4 synchronizer overhaulA. lock ring type inertial synchronizer ring maintenance: lock hornscone a about six degrees - 7 degrees, in use, cone Angle deformation ofrapid synchronous, and not be change in time. B. B. locking locking locking pin pin pin type type type inertial inertial inertial synchronizer: synchronizer: synchronizer: locking locking locking pin pin pin type type synchronizer major damage for cone rim wear, when, cone-disk cone rim on the thread of groove depth 0.40 mm wear to 010mm deep, should be replaced.If the cone rim are scratching, face to face, but two turning machining, must not be more than 1mm should be replaced.变速器手动变速器是最常见的变速器,简称MT MT。
附录附录A Clutch Performance AnalysisA clutch is a subcomponent of an engine’s transmission designed to allow engagement or disengagement of the engine to whatever apparatus is being driven. A clutch may also be a device on a shaft that will “slip” wh en higher than normal resistance is encountered.There are many different clutch designs, but most are based on one or more friction discs, pressed tightly together or against a flywheel using springs. The spring pressure is released when the clutch pedal is depressed and the discs are held less tightly and allowed to rotate freely.Clutches are useful in devices with two rotating shafts. In these devices, one of the shafts is typically driven by a motor or pulley, and the other shaft is driving another device. The clutch connects the two shafts so that they can either be locked together and spin at the same speednc.qoos.www, or be decoupled and spin at different speeds.In a car, the engine spins all the time and the car wheels don’t. In order for a car to stop without killing the engine, the wheels need to be disconnected from the engine somehow. The clutch smoothly engage a spinning engine to a non-spinning transmission by controlling the slippage between them.The flywheel is connected to the engine, and the clutch plate is connected to the transmission.When your foot is off the pedal, the springs will push the pressure plate against the clutch disc, which in turn presses against the flywheel. This locks the engine to the transmission input shaft, causing them to spin at the same speed.The amount of force the clutch can hold depends on the friction between the clutch plate and the flywheel, and how much force the spring puts on the pressure plate. The friction force in the clutch works just like the blocks in the friction sectionof brake, except that the spring presses on the clutch plate instead of weight pressing the block into the ground.When the clutch pedal is pressed, a cable or bydraulic piston pushes on the release fork, which presses the throw-out bearing against the middle of the diaphragm spring. As the middle of the diaphragm spring is pushed in, a series of pins near the outside of the spring causes the spring to pull the pressure plate away from the clutch disc. This releases the clutch from the spinning engine.Note the springs in the clutch plate. These springs help to isolate the transmission from the shock of the clutch engaging.The most common problem with clutches is that the friction material on the disc wears out. The friction material on a clutch disc is very similar to the friction material on the pads of a disc brake, or the shoes of a drum brake-after a while, it wears away. When most or all of the friction material is gone, the clutch will start to slip, and eventually it won’t transmit any power from the engine to the wheels.The clutch only wears while the clutch disc and the flywheel are spinning at different speeds. When they are locked together, the friction material is held tightly against the flywheel, and they spin in sync. It is only when to clutch disc is slipping against the flywheel that wearing occurs. So if you are the type of driver who slips the clutch a lot, you will wear out your clutch a lot faster.In a car it is operated by the left-most pedal. No pressure on the pedal means that the clutch plates are engaged (driving) , while depressing the pedal will disengage the clutch plates, allowing the driver to shift gears. When the right-most pedal (the accelerator) is pressed while the clutch pedal is being let out.Cars equipped with automatic transmissions normally do not have a clutch. On these, the transmission operates automaticaly so that the driver is not required to use a clutch to shift gears.附录 B 离合器的性能分析离合器是发动机传动系中的一个基础部件,无论什么样的发动机,传动系都可以接上或脱开。
中英文对照资料外文翻译文献Transmission SystemA Basic Parts of the transmission systemThe transmission system applies to the components needed to transfer the drive from the engine to the road wheels. The main components and their purposes are (1) Clutch --- to disengage the drive--- to provide a smooth take-up of the drive(2) Gearbox --- to increase the torque applied to the driving road wheels--- to enable the engine to operate within a given range of speed irrespective of the vehicle speed--- to give reverse motion of the vehicle--- to provide a neutral position so that the engine can run without moving the vehicle(3) Final drive --- to turn the drive through 90°--- to reduce the speed of the drive by a set amount to match the engine to the vehicle(4) Differential --- to allow the inner driving road wheel to rotate slower than the outerwheel when the vehicle is cornering, whilst it ensures that adrive is applied equally to both wheels.B Clutch and Clutch ServiceIn order to transmit the power of the engine to the road wheels of a car, a friction clutch and a change-speed gearbox are normally employed. The former is necessary in order to enable the drive to be taken up gradually and smoothly, while the latter provides different ratios of speed reduction from the engine to the wheels, to suit the particular conditions of running,A clutch performs two tasks:(1) it disengages the engine from the gearbox to allow for gear changing.(2) it is a means for gradually engaging the engine to the driving wheels, when a vehicle is to be moved from rest the clutch must engage a stationary gearbox shaft with the engine; this must be rotating at a high speed to provide sufficient power or else the load will be too great and the engine will start (come to test).C Clutch ActionTo start the engine, the driver must depress the clutch pedal. This disengages the gearbox from the engine. To move the car, the driver must reengage the gearbox to the engine. However, the engagement of the parts must be gradual. An engine at idle develops little power. If the two parts were connected too quickly, the engine would stall. The load must be applied gradually to operate the car smoothly.A driver depresses the clutch pedal to shift the gears inside the gearbox. After the driver releases the clutch pedal, the clutch must act as solid coupling device. It must transmit all engine power to the gearbox, without slipping.The clutch mechanism include three basic parts: driving member, driven member, operating members.●The driving memberThe driving member consists of two parts: the flywheel and the pressure plate. The flywheel is bolted directly to the engine crankshaft and rotates when the crankshaft turns. The pressure plate is bolted to the flywheel. The result is that both flywheel and pressure plate rotate together.●The driven memberThe driven member, or clutch disc, is located between the flywheel and pressure plate. The disc has a splined hub that locks to the splined input shaft on the gearbox .Any rotation of the clutch disc turns the input shaft .Likewise, any motion of the input shaft moves the clutch disc. The splines allow the clutch disc to move forward and backward on the shaft as it engages and disengages.The inner part of the clutch disc, called the hub flange, has a number of small coil springs. These springs are called torsional springs. They let the middle part of theclutch disc turn slightly on the hub. Thus, the springs absorb the torsional vibrations of the crankshaft. When the springs have compressed completely, the clutch moves back until the springs relax. In other words, the clutch absorbs these engine vibrations, preventing the vibrations from going through the drive train.●Operating MembersThese are the parts that release pressure from the clutch disc. The operating members consist of the clutch pedal, clutch return spring, clutch linkage, clutch fork, and throwout bearing. The clutch linkage includes the clutch pedal and a mechanical or hydraulic system to move the other operating members.When the clutch pedal is depressed, the clutch linkage operates the clutch fork .The clutch fork, or release fork, moves the throwout bearing against the pressure plate release levers. These levers then compress springs that normally hold the clutch disc tightly against the flywheel.At this point, the torque of the engine cannot turn the gearbox input shaft. The gears in the gearbox may be shifted or the vehicle can be brought to a full stop.When the clutch pedal is released, the pressure plate forces the clutch disc against the flywheel. The clutch return spring helps raise the pedal.D Clutch ServiceThe major parts of the clutch assembly need no maintenance or lubrication during normal service. However, all linkage parts need lubrication at points of contact. The linkage itself must be adjusted to prevent wear of the clutch disc.●Free-play AdjustmentYou can make only one adjustment on the clutch linkage —the free-play adjustment. Free play is the allowable space between the throwout bearing and the pressure plate release levers. This space is important because it prevents pressure on the levers that could keep the clutch from engaging fully. In other words, the throwout bearing must be slightly away from the pressure plate levers so that the bearing applies no pressure on the levers. On the other hand, there must not be too much freeplay between the bearing and the levers. With too much clearance, the clutch cannot fully disengaged when the driver press the clutch pedal to the floor. In most cases, you measure the free play at the clutch pedal, rather than at the bell housing.The free play allows some motion at the beginning of the clutch pedal travel, before the pedal meets resistance. Since the distance varies with the type of pressure plate, check the service manual. Usually, free play should be about 20 to 25mm.Free play can be adjusted at some point where the clutch linkage consists of threaded rods with locknuts. The rod closest to the clutch fork is the most common adjustment point. Begin by locating the rod and locknut beneath the vehicle. Then determine which way to turn the adjustment nuts to get the correct free play at the pedal. You can get a rough estimate of free play by moving the clutch fork to see if it still has some movement. The best way to make the adjustment is to loosen the locknut and move the adjustment nut a few turns. Then check the free play at the pedal. Continue making adjustments until you have the correct free play. When the free-play adjustment meets the manufacturer’s specification, tighten the locknut.Check the free-play adjustment every six months and make any adjustment. Clutches need adjustment that often, since free play decreases slightly as the clutch disc wears. However, the need for frequent adjustments means a problem in the clutch mechanism itself.There must be free play between the throwout bearing and pressure plate release levers. Problems can result from “riding the clutch”. A driver who rests one foot on the clutch pedal causes the throwout bearing to rub against the clutch release levers. As a result, the throwout bearing becomes worn quickly. Also, the clutch disc may wear out due to slippage because the parts are not fully engaged.●Clutch FaultsThe following are the main faults:Slip —failure of the surface to grip resulting in the driven plate revolving slower than the engine flywheel : Clutch gets hot and emits an odor.Spin or drag —failure of the plates to separate resulting in noise from thegearbox when selecting a gear: most noticeable when thevehicle is stationary.Judder —a vibration which occurs when the clutch is being engaged , i.e. when the vehicle is stationary.Fierceness —sudden departure of the vehicle even though the pedal is being released gradually.E The Clutches(supplementary contract)A clutch is a friction device used to connect and disconnect a driving force from a driven member. In automotive applications, it is used in conjunction with an engine flywheel to provide smooth engagement and disengagement of the engine and manual transmission.Since an internal combustion engine develops little power or torque at low rpm, it must gain speed before it will move the vehicle. However, if a rapidly rotating engine is suddenly connected to the drive line of a stationary vehicle, a violent shock will result.So gradual application of load, along with some slowing of engine speed , is needed to provide reasonable and comfortable starts. In vehicles equipped with a manual transmission, this is accomplished by means of a mechanical clutch.The clutch utilizes friction for its operation. The main parts of the clutch are a pressure plate, and a driven disk. The pressure plate is coupled with the flywheel, while the driven disk is fitted to the disk by the springs so that the torque is transmitted owing to friction forces from the engine to the input shaft of the transmission. Smooth engagement is ensured by slipping of the disk before a full pressure is applied.The automobiles are equipped with a dry spring-loaded clutch. The clutch is termed “dry”because the surfaces of the pressure plate and driven disks are dry in contrast to oil-bath clutches in which the plate and disks operate in a bath of oil. It is called “springloaded”because the pressure plate and the driven disk are always pressed to each other by springs and are released only for a time to shift gears or to brake the automobile.In addition to the plate and disk, the clutch includes a cover, release levers, a release yoke, pressure springs and a control linkage. The clutch cover is a steel stamping bolted to the flywheel. The release levers are secured inside the cover on the supporting bolts. The outer ends of the release levers are articulated to the pressure plate. Such a construction allows the pressure plate to approach the cover or move away from it, all the time rotating with the cover or move away from it, all the time rotating with the flywheel. The springs spaced around the circumference between the pressure plate and the clutch cover clamp the driven disk between the pressure plate and the flywheel.The springs are installed with the aid of projections and sockets provided on the cover and pressure plate. The pressure plate sockets have thermal-insulation gaskets for protecting the springs against overheating.The clutch release mechanism can be operated either mechanically or hydraulically. The mechanically-operated release mechanism consists of a pedal, a return spring, a shaft with lever, a rod m release yoke lever, a release yoke, a release ball bearing with support and a clutch release spring. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the rod and shaft with yoke shift the release bearing and support assembly. The release bearing presses the inner ends of the release levers, the pressure plate is moved away from the driven disk and the clutch is disengaged. To engage the clutch , the pedal is released, the release bearing and support assembly is shifted back by the return spring thus releasing the release levers so that the pressure plate is forced by its springs towards the flywheel to clamp the driven disk and engage the clutch.The clutch hydraulically-operated release mechanism consists of a clutch pedal , clutch release spring , a main cylinder , a pneumatic booster, pipelines and hoses and a lever of the clutch release yoke shaft. Time main cylinder accommodates a piston with a cup. The pneumatic booster serves to decrease the pedal force required disengage the clutch. The booster includes two housings with the servo diaphragm clamped in between. The housing accommodates pneumatic, hydraulic and servo plungers. When the clutch pedal is pushed, the fluid pressure from the main cylinder is transmitted through the pipelines and hoses to the hydraulic and servo plungers of the pneumaticbooster.The servo arrangement is intended for automatic change of the air pressure in the pneumatic cylinder proportionally to the force applied to the pedal. The plunger moves with the diaphragm, the outlet valve closes and the inlet valve opens thus admitting the compressed air to the pneumatic plunger piston. The forces created by the pneumatic and hydraulic plungers are added together and are applied through the push rod to the release yoke shaft lever; the lever turns the shaft and the release yoke, thus disengaging the clutch. After the clutch pedal is released, the outlet valve opens and the air from the cylinder is let out to the atmosphere.Automatic clutches were used in certain U.S. and European cars. American Motors’“E-Stick”clutch eliminated the need for physical operation of the clutch system called “Hydrak”, which consisted of a fluid flywheel connected to a single, dry disk clutch.In the “E-Stick” set up, the pressure plate levers “engage” the clutch disk rather than “release” them. Also, the clutch remains disengaged until a servo unit is applied by oil pressure when the shift lever is placed “in gear” with the engine running.The “Hydrak”unit also begins operation when the lever is “in gear”. This activates a booster unit, which disengages the clutch disk. The hydraulic clutch parts are bridged over by a free-wheel unit, which goes into action when the speed of the rear wheel is higher than the speed of the engine. A special device controls engagement of the mechanical clutch, depending on whether the rear axle is in traction or is pushed by car momentum.A more-or-les unusual clutch pressure plate set-up is used on late model Chrysler and American Motors cars. Called a semi-centrifugal clutch, the pressure plate has six cylindrical rollers which move outward under centrifugal force until they contact the cover. As engine speed increases, the rollers wedge themselves between the pressure plate and cover so that the faster the clutch rotates, the greater the pressure exerted on the pressure plate and disk.传动系统A基本传动系统的组成部份传动系统是将发动机动力转移到驱动轮的结构。
Clutch Common ProblemsFrom the 1950s to the 1970s, you could count on getting between 50,000 and 70,000 miles from your car's clutch. Clutches can now last for more than 80,000 miles if you use them gently and maintain them well. If not cared for, clutches can start to break down at 35,000 miles. Trucks that are consistently overloaded or that frequently tow heavy loads can also have problems with relatively new clutches.The most common problem with clutches is that the friction material on the disc wears out. The friction material on a clutch disc is very similar to the friction material on the pads of a disc brake or the shoes of a drum brake -- after a while, it wears away. When most or all of the friction material is gone, the clutch will start to slip, and eventually it won't transmit any power from the engine to the wheels.The clutch only wears while the clutch disc and the flywheel are spinning at different speeds. When they are locked together, the friction material is held tightly against the flywheel, and they spin in sync. It's only when the clutch disc is slipping against the flywheel that wearing occurs. So, if you are the type of driver who slips the clutch a lot, you'll wear out your clutch a lot faster.Sometimes the problem is not with slipping, but with sticking. If your clutch won't release properly, it will continue to turn the input shaft. This can cause grinding, or completely prevent your car from going into gear. Some common reasons a clutch may stick are:Broken or stretched clutch cable- The cable needs the right amount of tension to push and pull effectively.Leaky or defective slave and/or master clutch cylinders - Leaks keep the cylinders from building the necessary amount of pressure.Air in the hydraulic line - Air affects the hydraulics by taking up space the fluid needs to build pressure.Misadjusted linkage - When your foot hits the pedal, the linkage transmits the wrong amount of force.Mismatched clutch components- Not all aftermarket parts work with your clutch.A "hard" clutch is also a common problem. All clutches require some amount of force to depress fully. If you have to press hard on the pedal, there may be something wrong. Sticking or binding in the pedal linkage, cable, cross shaft, or pivot ball are common causes. Sometimes a blockage or worn seals in the hydraulic system can also cause a hard clutch.Another problem associated with clutches is a worn throw-out bearing, sometimes called a clutch release bearing. This bearing applies force to the fingers of the spinning pressure plate to release the clutch. If you hear a rumbling sound when the clutch engages, you might have a problem with the throw-out.Clutch Diagnostic TestIf you find that your clutch has failed, here is an at-homediagnostic test that anyone can perform:1. Start your car, set the parking break, and put the carin neutral.2. With your car idling, listen for a growling noisewithout pushing the clutch in. If you hear something,it's most likely a problem with the transmission. If youdon't hear a noise, proceed to step three.3. With the car still in neutral, begin to push the clutchand listen for noise. If you hear a chirping noise asyou press, it's most likely the clutch release, orthrow-out bearing. If you don't hear a noise, proceedto step four.4. Push the clutch all the way to the floor. If you hear asquealing noise, it's probably the pilot bearing orbushing.If you don't hear any noise during these four steps, then yourproblem is probably not the clutch. If you hear the noise atidle and it goes away when the clutch is pressed, it may bean issue in the contact point between the fork and pivot ball.BiomaterialsManufacturers are starting biomaterials to reduce CO2 emissions throughout the vehicles lifecycleManufacturers are starting to concentrate more closely on cutting carbon dioxide emissions from vehicles’ lifecycles. That means looking at the carbon dioxide production and disposal of the vehicle, not just the pollutants that come out of the tailpipe.European vehicle recycling laws are making carmakers that sell cars in Europe take more responsibility for the effect their vehicles Honda and Mitsubishi are the latest to develop new materials.Recycling the metal that makes up majority of the vehicle is not the hardest pert; the plastics plastics present a far greater challenge. Interiors pose a particular recycling problem as they use a lot of plastics.Honda has developed a plant-based fabric with excellent durability and resistance to sunlight for use a surface material in automobile interiors.Bio-fabrics are the most likely solution as they are derived from plants that absorb carbon dioxide ad they grow. When vehicle is scrapped and the fabrics incinerated, only some of the released carbon dioxide has come from a fossil source.Despite this benefit, plant-based fabrics have not yet been used commercially for automobile interiors. Interior quality is too important to take risks with and there have been concerns about the limited durability and aesthetics of biomaterials.Honda says it has a fabric that can overcome these issues, achieving a soft and smooth material appropriate for the surface of automobile interiors. It has high durability and its color does not fade after prolonged exposure to sunlight.Honda will use the material for seats, the interior surface of doors, roof linings and for floor mats. Series production is still some way off , however. The firm will install the bio-fabric interiors in 2009 in a fuel cell vehicle and then expand the application.The bio-fabric’s basic material is a polyester called polypropylene terephthalate (PPT). PPT is produced through the polymerization of propaneiol, which is produced from corn and terephthalic acid, a petroleum-based component.In order to improve the fabric’s stability, Honda has applied a multi-thread structure for the fiber. “The fiber is very flexible, achieving unprecedented aesthetic properties,” says Honda.The bio-fabric does not require changes to existing fabric production processes and is suitable for mass production .Using it instead of the traditional petroleum-based polyester materials reduces the amount of energy consumed in the process by between 10 and 15 percent.“The use of a plant-based ingredient can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 5Kg per vehicle,” says Honda.Mitsubishi`s environmentally friendly plastic is a little closer to production. It will be used in a concept car next year. But despite its early development stage, the firm is confident it will be used in car interiors.Mitsubishi has developed a material that uses a plant-based resin, polybutylene succinate (PBS), reinforced with bamboo fibers. They began developing the materials with the Aichi industrial technology institute, Japan in 2004.“To help stop global warming and slow the depletion of oil reserves, we plant to substitute plant-based resins and quick-growing plant fibers for materials such as petroleum-based resins and wood hardboards used in car interiors,” says Mitsubishi.PBS. The main component of the material. Is a plant-based resin composedmainly of succinct acid and 1.4-butanediol.The succinct acid for the material comes from the fermentation of sugar extracted from sugarcane or corn?The new material combines bamboo fiber with PBS in order to increase its rigidity.According to tests. The PBS/bamboo-fiber prototype achieves an estimated 50 percent cut in lifecycle CO2 emissions over petroleum-based polypropylene plastic. Volatile organic compound levels are also reduced drastically over processed wood hardboards; roughly 85 per cent in testing.Bamboo grows to its full height in just a few years, compared with the tens of years required for traditional timber. And as such may be called a potentially sustainable resource.”We expect the research to lead to further breakthroughs in the use of bamboo.” says Mitsubishi.离合器常见问题从20世纪50年代至70年代,你可以依靠离合器行驶50000公里到70000公里。
附 录附录A适用性离合器在机械自动传动中的加工控制刘海鸥,陈慧岩,丁华荣,何忠波(机械和车辆工程学校,北京技术学院,北京 100081,中国) 摘要:依靠对离合器运行过程的详细分析控制目标和适应的要求,一个主要依靠速度信号而不是依靠离合器的移动信号的控制策略迅速发展。
这既要考虑到紧缩的工作又要考虑到松弛的工作,而这些工作大多使用车辆在初始状态下的质量评估索引。
适应性控制系统和它所涉及到得模式都已经被深入的分析。
我们所讨论的是对不同其实齿轮和不同公路条件的适应性。
例如:大多数已经被证实的结果被用于证明初始阶段大多数适应性控制策略,验证试验测试数据得到一个令人比较满意的结果。
关键词:自动机械传输(AMT );传输技术;适应性控制;主要齿轮啮合无论潮湿或干燥,主要离合器的啮合加工控制策略的摩擦力是车辆技术领域的焦点,一些控制策略是依靠主离合器的移动信号,在我们的调查研究中,那些依靠主要离合器外在轴速度信号的适应性控制策略已经得到法杖,这已经被证明有广泛的适应性。
1. 控制对象和适应的有求那些普遍用于车辆其实阶段的质量评估指标是紧密和松弛的工作。
紧密—就如车辆起始阶段的平滑指标评估,紧缩是车辆纵向加速度的比率。
根据定义,紧缩的公式为:/2/2t t j da d d v d == (1)式中j 为紧缩,v 和a 分别是车辆行驶速度和加速度根据车辆动力学,车辆行驶速度是由平衡时发动机索引力和运动阻力决定,它可以表达为:()02sin 21.15gv D e t i i Gd C A T G f v r gd ηθδ=+++ (2)式中 e T 是发动机空载时的转矩,G 是车辆的总质量,r 是车轮半径,f 和θ 分别是道路阻力系数和坡度阻力, D C 为空气阻力系数.机构的功能是作为机械作用的一个部分从一个刚体传送即传递运动,一般能用作机构基本零件的机械装置有三类:1. 齿轮装置。
那是在回转轴之间进行接触传动的啮合勾结。
附录The Spin Tester for the Automobile Clutch Test with High Speed Photography SystemAbstract:The development of a new type spin tester for the automobile clutch test is introduced.A vertical flexible shaft system with rubber damper is applied to the tester.The crushing test of the clutch assembly can be done frequently on the spin tester,and the high speed photography system adopting ordinary camera can record the crushing wink.The crushing test of a clutch on this tester is also introduced.and the weak link of the clutch assembly can be found from the photograph of crushing wink.Key words:spin tester automobile clutch high speed photographyClutch by gland assembly and platen assembly which, in their rotation strength is the key parts of the quality evaluation car is an important index, rules and regulations should be acceleration in their state of the rotating speed is higher than speeding strength test to determine the safety and reliability of the clutch disc. For example, santana clutch disc assembly and driven plate total chengdu in ordinary temperature requirements in a = rad/s2 acceleration of 50 acc to 12 000 r/min, and platen assembly also requires in high temperature (250 ℃) at a = rad/s2 acceleration of 50 acc to 10 000 r/min without fracture. These tests require in the specialized testing machine.At present, the domestic is no clutch assembly strength test on the special equipment. This paper introduces the author developed a vertical multi-function of clutch rotating strength tester (see chart 1). It has a strong drive ability (1), can generate enough acceleration, the maximum weight 50 kg, with the highest speed 18 000 r/min, maximum acceleration 20 rad PI/s2 the clutch assembly strength test; (2) the strong vibration absorber system, to absorb the clutch assembly high speed rotating vibration energy; (3) the reliable and steady automation control system and absolute safety of lead brick protection recessed; (4) to observe the clutch assembly rotation experiment process and the rupture instantaneous state surveillance and high-speed photography system. To all sorts of clutch assembly, the machine can strength test, especially for high speed can be frequently do destructive testing, use convenient, safe and reliable.Figure 1 clutch rotating strength tester photos1.The main structure characteristics1.1 With rubber damping bearing on the "flexible shaft typeThis kind of test enginery due to frequent, high-speed destructive testing, the host axis should be able to complete the clutch assembly rose quickly to the whole process of destruction, so we used on the vertical "with rubber damper flexible shaft of [1], the structure see FIG. 2). Due to the vertical axis, one soft critical speed is low, order only 1800 to 2000 r/min or so, make whole high-speed area are on supercritical of smooth state. At the same time in soft shaft with a middle with "O" type of rubber ring damping bearing shaft system, when the critical speed or because the clutch assembly brought serious imbalance fierce, the vibration damping bearing can absorb vibration energy, attenuation shaft vibration [2], ensure the clutch assembly continue to rise until the complete destruction, ensure speed high-speed damage test. This structure is simple, easy to adjust, damping range. In order to prevent the clutch assembly damage time, great instantaneous vibration energy cause shaft and the lower the destruction of the transmission system, in the gentle shaft with a limit bearing, head to prevent soft shaft bending big and the bottom of the drive shaft damage components. Soft axis adopt plug-in installation, when the clutch assembly, the most serious destruction is replaced the soft shaft, head bent to the whole machine didn't have any effect, operation loading and unloading is very convenient, and ensure the tester can frequently in the clutch assembly destructive test. The vertical axis, facilitate "on the cover from the Windows of the testing process and observe specimens of installation and removal.Figure 2 rubber damper with flexible shaft1.2 The clutch assembly damage moments of high-speed photography systemThe clutch assembly by many parts assembly and become, the parts quality is directly related to the quality of the assembly. If can through the high-speed strength test find assembly parts the weak links, had better be to be in test chamber to take the parts assembly by deformation and destruction and yield spread to the whole process of, that will be very significant. Although currently not at a close range in advance, do not know when the clutch assembly of the damage happened produced high speed the whole process of destruction, but they can take to destroy the moment alone photos.Foreign is widely accepted in the specimen outside trigger coil rotor set, as the rotor fly crack, debris flying out of line, met trigger trigger circuit triggered by high speed camera shutter open, took a damage the image of the rotor moment. Obviously this design requirements must have taken the camera very high speed. For example the clutch assembly destruction speed than 10 000 r/min, the linear velocity in the 200 m/s above, if want to take clear debris flying out of the instantaneous movement condition when, captured fragments of the distance from the 2 mm moving images. So, the camera at least should have t = 2 mm / (200 m/s) = 1 x 10-5 s shooting speed, for ordinary camera it is clearly the deficits.In order to solve this problem, we developed a common cameras with the high-speed photography in the technology, with the clutch high-speed strength test machine, took the clutch assembly destruction of photographs. The moment The high-speed photography work principle of the system is shown in figure 3. The specific practices for ordinary camera, will cover the Windows in testing machine in the darkness of the test chamber outside, open shutter, in advance for shooting state. At the same time, add the rear cover outside the window between the two steel ballmust high pressure of the capacitor voltage. When the clutch assembly, high speed rotating parts fly crack damage, cut off the assembly line, the periphery of the trigger that set up light source line work trigger pin, triggering a trigger pulse, so that the air between two steel ball, a steel ball capacitor in ionization produced strong, between discharge pulse light source, then the camera narrow photographic plate, get the clutch assembly destruction of photographs. The moment The technology of the method is simple, save expensive high-speed cameras, the shooting accuracy is high.Figure 3 high-speed photography system work principle diagram2.Experimental studyWe in the testing machine to clutch cover plate assembly and made a large destructive testing. Now to the santana gland assembly damage test as an example. First, take the santana clutch cover assembly state of rest; Then, the gland assembly, and to destroy the damage process using high-speed photography system to shoot, have the following results:(1) santana clutch cover assembly in speed for 11 560 r/min, gland spring of fly out, cut off the trigger coil, took a high-speed photography photos (see chart 4), photos are the right off about 20 ° position on a spring of the flying out of the shadows. After parking the tray found not damage, but find spring of crack, the obvious skeleton spring of centrifugal force along the role in the first bending fly out broken.(2) this gland assembly continue to rise in speed for speed test, 14 010 r/min happened when the tray destruction, like on high-speed photography photos (see chart 5). Photos of the moment by damage, the whole clutch cover visible assembly gland produces serious warping deformation, radial on turn over the close (see photo) and cut off the trigger coil. As gland warping, clutch the tray imbalances fly crack damage. But did not see the gland cast iron rings (cover parts can't photographed) fly out of the shadow of the fracture.(3) from gland assembly destroyed the crack of photos skeleton (see figure 6) cansee, gland serious warping deformation in spring of installation, the gaps, but pulled gland and without breaking into several pieces, although gland lower part of the cast iron ring has fractured into seven pieces, but found no gland inside surface, cast iron rings pieces the trace of the impact.The result shows the santana car clutch cover the failure process of the instantaneous assembly for local parts, (spring of) fly out-gland serious warping deformation, in local weak section and pulled in the bottom of the gland cast iron rings and the whole gland assembly fracture failure.This tester has been put into use of factory three years, because the function is all ready, performance stability, price cheap, and solve the clutch a lot of detection, the development, and the research question, is expected to replace the imported, application.Figure 4 gland assembly spring of fly out of the moment photosFigure 5 gland assembly moments of photos. DamageFigure 6 gland assembly after damage remains of the photoReference[1] WuDaWen. "O" type rubber ring experimental study of the dynamic characteristics of the master's degree thesis: [Master's degree thesis]. Hangzhou, zhejiang university, 1998[2] QianLiXin. Ultra-high speed rotor test development speeding some issues of the study: [Ph.D. Thesis]. Hangzhou, zhejiang university, 1998带高速摄影系统的汽车离合器旋转破坏强度试验机摘要:提供了一种带高速摄影系统的汽车离合器旋转破坏强度试验机,该机可以频繁地做离合器总成的破坏性试验,并可拍摄到离合器总成破坏瞬间的独幅照片,以利找出总成零件的薄弱环节。
附录Auto transmission system will provide is to transfer the power of the engine, and so as to meet the needs of car form. In general the mechanical transmission in the car. A transmission can not completely solve the vehicle driving characteristics with the contradictions and structure required valve decorate on problems. First, because the vast majority of engine in the car is the longitudinal resettlement, in order to make its torque can drive wheels, must pass by around the main reducer drive to change the direction of transmission torque, through may still drive to solve the differential by starting to right and left the wheels of torque allocation problem. The second is the main task of the transmission by selecting the appropriate only in each file number and gear ratio, in order to make internal combustion engine torque - speed characteristics can adapt in all kinds of resistance to car under the dynamic requirements, but fish economy drive axle of the function of the main reducer lies in that when the transmission, the highest gear in cars had enough traction, appropriate maximum speed and good fuel economy. Therefore, it is required to transmission gearbox, will pass from the power, through the drive axle of the main reducer to further increase torque, reduce the speed of change. Accordingly, want to make auto transmission design is reasonable, first must choose good transmission ratio, and the total it properly allocated to the transmission and axles. The latter deceleration than than into primarily slowdown. When the transmission directly file in position, performance and fuel economy car than mainly dependent on the Lord slowdown. In a car's total layout design, should according to the working conditions and car engine, transmission, tires and other related parameters of the Lord, choosing the appropriate slowing the car with good board guarantee dynamic performance and fuel economy. Foreign some big car factory will often a certain type of automobile design has a variety of Lord deceleration than for selection and use of rising to meet the different needs of variant car and. Due to the improving, automobile engine power reduce weight and road conditions improved, than to have to reduce main slow development trend. The choice advocate deceleration than should consider when making car can meet high-speed request, and can in common speed range reduce engine speed, reducing fuel consumption, improve engine life and improve vibration and noise characteristics, etc.译文汽车传动系的总任务是传递发动机的动力,并使之适应于汽车形式的需要。
中英文对照资料外文翻译文献Transmission SystemA Basic Parts of the transmission systemThe transmission system applies to the components needed to transfer the drive from the engine to the road wheels. The main components and their purposes are (1) Clutch --- to disengage the drive--- to provide a smooth take-up of the drive(2) Gearbox --- to increase the torque applied to the driving road wheels--- to enable the engine to operate within a given range of speed irrespective of the vehicle speed--- to give reverse motion of the vehicle--- to provide a neutral position so that the engine can run without moving the vehicle(3) Final drive --- to turn the drive through 90°--- to reduce the speed of the drive by a set amount to match the engine to the vehicle(4) Differential --- to allow the inner driving road wheel to rotate slower than the outerwheel when the vehicle is cornering, whilst it ensures that adrive is applied equally to both wheels.B Clutch and Clutch ServiceIn order to transmit the power of the engine to the road wheels of a car, a friction clutch and a change-speed gearbox are normally employed. The former is necessary in order to enable the drive to be taken up gradually and smoothly, while the latter provides different ratios of speed reduction from the engine to the wheels, to suit the particular conditions of running,A clutch performs two tasks:(1) it disengages the engine from the gearbox to allow for gear changing.(2) it is a means for gradually engaging the engine to the driving wheels, when a vehicle is to be moved from rest the clutch must engage a stationary gearbox shaft with the engine; this must be rotating at a high speed to provide sufficient power or else the load will be too great and the engine will start (come to test).C Clutch ActionTo start the engine, the driver must depress the clutch pedal. This disengages the gearbox from the engine. To move the car, the driver must reengage the gearbox to the engine. However, the engagement of the parts must be gradual. An engine at idle develops little power. If the two parts were connected too quickly, the engine would stall. The load must be applied gradually to operate the car smoothly.A driver depresses the clutch pedal to shift the gears inside the gearbox. After the driver releases the clutch pedal, the clutch must act as solid coupling device. It must transmit all engine power to the gearbox, without slipping.The clutch mechanism include three basic parts: driving member, driven member, operating members.●The driving memberThe driving member consists of two parts: the flywheel and the pressure plate. The flywheel is bolted directly to the engine crankshaft and rotates when the crankshaft turns. The pressure plate is bolted to the flywheel. The result is that both flywheel and pressure plate rotate together.●The driven memberThe driven member, or clutch disc, is located between the flywheel and pressure plate. The disc has a splined hub that locks to the splined input shaft on the gearbox .Any rotation of the clutch disc turns the input shaft .Likewise, any motion of the input shaft moves the clutch disc. The splines allow the clutch disc to move forward and backward on the shaft as it engages and disengages.The inner part of the clutch disc, called the hub flange, has a number of small coil springs. These springs are called torsional springs. They let the middle part of theclutch disc turn slightly on the hub. Thus, the springs absorb the torsional vibrations of the crankshaft. When the springs have compressed completely, the clutch moves back until the springs relax. In other words, the clutch absorbs these engine vibrations, preventing the vibrations from going through the drive train.●Operating MembersThese are the parts that release pressure from the clutch disc. The operating members consist of the clutch pedal, clutch return spring, clutch linkage, clutch fork, and throwout bearing. The clutch linkage includes the clutch pedal and a mechanical or hydraulic system to move the other operating members.When the clutch pedal is depressed, the clutch linkage operates the clutch fork .The clutch fork, or release fork, moves the throwout bearing against the pressure plate release levers. These levers then compress springs that normally hold the clutch disc tightly against the flywheel.At this point, the torque of the engine cannot turn the gearbox input shaft. The gears in the gearbox may be shifted or the vehicle can be brought to a full stop.When the clutch pedal is released, the pressure plate forces the clutch disc against the flywheel. The clutch return spring helps raise the pedal.D Clutch ServiceThe major parts of the clutch assembly need no maintenance or lubrication during normal service. However, all linkage parts need lubrication at points of contact. The linkage itself must be adjusted to prevent wear of the clutch disc.●Free-play AdjustmentYou can make only one adjustment on the clutch linkage —the free-play adjustment. Free play is the allowable space between the throwout bearing and the pressure plate release levers. This space is important because it prevents pressure on the levers that could keep the clutch from engaging fully. In other words, the throwout bearing must be slightly away from the pressure plate levers so that the bearing applies no pressure on the levers. On the other hand, there must not be too much freeplay between the bearing and the levers. With too much clearance, the clutch cannot fully disengaged when the driver press the clutch pedal to the floor. In most cases, you measure the free play at the clutch pedal, rather than at the bell housing.The free play allows some motion at the beginning of the clutch pedal travel, before the pedal meets resistance. Since the distance varies with the type of pressure plate, check the service manual. Usually, free play should be about 20 to 25mm.Free play can be adjusted at some point where the clutch linkage consists of threaded rods with locknuts. The rod closest to the clutch fork is the most common adjustment point. Begin by locating the rod and locknut beneath the vehicle. Then determine which way to turn the adjustment nuts to get the correct free play at the pedal. You can get a rough estimate of free play by moving the clutch fork to see if it still has some movement. The best way to make the adjustment is to loosen the locknut and move the adjustment nut a few turns. Then check the free play at the pedal. Continue making adjustments until you have the correct free play. When the free-play adjustment meets the manufacturer’s specification, tighten the locknut.Check the free-play adjustment every six months and make any adjustment. Clutches need adjustment that often, since free play decreases slightly as the clutch disc wears. However, the need for frequent adjustments means a problem in the clutch mechanism itself.There must be free play between the throwout bearing and pressure plate release levers. Problems can result from “riding the clutch”. A driver who rests one foot on the clutch pedal causes the throwout bearing to rub against the clutch release levers. As a result, the throwout bearing becomes worn quickly. Also, the clutch disc may wear out due to slippage because the parts are not fully engaged.●Clutch FaultsThe following are the main faults:Slip —failure of the surface to grip resulting in the driven plate revolving slower than the engine flywheel : Clutch gets hot and emits an odor.Spin or drag —failure of the plates to separate resulting in noise from thegearbox when selecting a gear: most noticeable when thevehicle is stationary.Judder —a vibration which occurs when the clutch is being engaged , i.e. when the vehicle is stationary.Fierceness —sudden departure of the vehicle even though the pedal is being released gradually.E The Clutches(supplementary contract)A clutch is a friction device used to connect and disconnect a driving force from a driven member. In automotive applications, it is used in conjunction with an engine flywheel to provide smooth engagement and disengagement of the engine and manual transmission.Since an internal combustion engine develops little power or torque at low rpm, it must gain speed before it will move the vehicle. However, if a rapidly rotating engine is suddenly connected to the drive line of a stationary vehicle, a violent shock will result.So gradual application of load, along with some slowing of engine speed , is needed to provide reasonable and comfortable starts. In vehicles equipped with a manual transmission, this is accomplished by means of a mechanical clutch.The clutch utilizes friction for its operation. The main parts of the clutch are a pressure plate, and a driven disk. The pressure plate is coupled with the flywheel, while the driven disk is fitted to the disk by the springs so that the torque is transmitted owing to friction forces from the engine to the input shaft of the transmission. Smooth engagement is ensured by slipping of the disk before a full pressure is applied.The automobiles are equipped with a dry spring-loaded clutch. The clutch is termed “dry”because the surfaces of the pressure plate and driven disks are dry in contrast to oil-bath clutches in which the plate and disks operate in a bath of oil. It is called “springloaded”because the pressure plate and the driven disk are always pressed to each other by springs and are released only for a time to shift gears or to brake the automobile.In addition to the plate and disk, the clutch includes a cover, release levers, a release yoke, pressure springs and a control linkage. The clutch cover is a steel stamping bolted to the flywheel. The release levers are secured inside the cover on the supporting bolts. The outer ends of the release levers are articulated to the pressure plate. Such a construction allows the pressure plate to approach the cover or move away from it, all the time rotating with the cover or move away from it, all the time rotating with the flywheel. The springs spaced around the circumference between the pressure plate and the clutch cover clamp the driven disk between the pressure plate and the flywheel.The springs are installed with the aid of projections and sockets provided on the cover and pressure plate. The pressure plate sockets have thermal-insulation gaskets for protecting the springs against overheating.The clutch release mechanism can be operated either mechanically or hydraulically. The mechanically-operated release mechanism consists of a pedal, a return spring, a shaft with lever, a rod m release yoke lever, a release yoke, a release ball bearing with support and a clutch release spring. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the rod and shaft with yoke shift the release bearing and support assembly. The release bearing presses the inner ends of the release levers, the pressure plate is moved away from the driven disk and the clutch is disengaged. To engage the clutch , the pedal is released, the release bearing and support assembly is shifted back by the return spring thus releasing the release levers so that the pressure plate is forced by its springs towards the flywheel to clamp the driven disk and engage the clutch.The clutch hydraulically-operated release mechanism consists of a clutch pedal , clutch release spring , a main cylinder , a pneumatic booster, pipelines and hoses and a lever of the clutch release yoke shaft. Time main cylinder accommodates a piston with a cup. The pneumatic booster serves to decrease the pedal force required disengage the clutch. The booster includes two housings with the servo diaphragm clamped in between. The housing accommodates pneumatic, hydraulic and servo plungers. When the clutch pedal is pushed, the fluid pressure from the main cylinder is transmitted through the pipelines and hoses to the hydraulic and servo plungers of the pneumaticbooster.The servo arrangement is intended for automatic change of the air pressure in the pneumatic cylinder proportionally to the force applied to the pedal. The plunger moves with the diaphragm, the outlet valve closes and the inlet valve opens thus admitting the compressed air to the pneumatic plunger piston. The forces created by the pneumatic and hydraulic plungers are added together and are applied through the push rod to the release yoke shaft lever; the lever turns the shaft and the release yoke, thus disengaging the clutch. After the clutch pedal is released, the outlet valve opens and the air from the cylinder is let out to the atmosphere.Automatic clutches were used in certain U.S. and European cars. American Motors’“E-Stick”clutch eliminated the need for physical operation of the clutch system called “Hydrak”, which consisted of a fluid flywheel connected to a single, dry disk clutch.In the “E-Stick” set up, the pressure plate levers “engage” the clutch disk rather than “release” them. Also, the clutch remains disengaged until a servo unit is applied by oil pressure when the shift lever is placed “in gear” with the engine running.The “Hydrak”unit also begins operation when the lever is “in gear”. This activates a booster unit, which disengages the clutch disk. The hydraulic clutch parts are bridged over by a free-wheel unit, which goes into action when the speed of the rear wheel is higher than the speed of the engine. A special device controls engagement of the mechanical clutch, depending on whether the rear axle is in traction or is pushed by car momentum.A more-or-les unusual clutch pressure plate set-up is used on late model Chrysler and American Motors cars. Called a semi-centrifugal clutch, the pressure plate has six cylindrical rollers which move outward under centrifugal force until they contact the cover. As engine speed increases, the rollers wedge themselves between the pressure plate and cover so that the faster the clutch rotates, the greater the pressure exerted on the pressure plate and disk.传动系统A基本传动系统的组成部份传动系统是将发动机动力转移到驱动轮的结构。