九年级英语第8单元第3课时教案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:359.00 KB
- 文档页数:4



第三课时Section B(1a-1d) 祸兮福之所倚,福兮祸之所伏。
《老子·五十八章》涵亚学校陈冠宇重点单词land v.着陆;降落alien n.外星人suit n.西服;套装v.合适重点短语run after追逐;追赶catch a bus赶公共汽车重点句子He could be running for exercise.他可能在跑步锻炼身体。
教学难点让学生学会利用情态动词对身边的事情进行合理推测根据句意及音标提示写出单词及其汉语意思。
1.China has been the third country in the world to __land__ /lænd/ on the moon.__着陆;降落__2.While the girl is walking down the street,the __alien__/ˌeɪli ən/ went into a store.__外星人__3.This __suit__ /sjuːt/ makes him look very young.__西服,套装__ 4.The students were in a great hurry to __catch__ /kætʃ/ the bus after school.__赶上__环节1 新课导入1.让学生回想自己遇到过的奇怪的事情。
2.向学生展示一些不明飞行物和外星人的图片。
设计意图:利用学生丰富的想象力,激发学生的好奇心,引导学生进入本课时的学习,从而提高学生学习目标语言的积极性。
环节2 学习1a-1d1.让学生熟悉1a中的单词,并观看图片猜测发生的事情。
2.完成1a中的任务,让学生相互核对答案。
3.播放录音,完成1b的任务。
4.小组讨论,让学生写句子,续编1b中的故事。
5.抽查几个小组,当堂讲述自己编写的故事。
6.再次播放录音,完成1c的任务。
7.两人一组,根据1d中的对话,用1c中的信息编写对话。


Unit 8 I’ll help clean up the city parks.Ⅰ. Analysis of the Teaching Material1. Status and FunctionIn this unit, students learn to express what kind of volunteer work they would like to do. And they will know much about the volunteers and volunteer work. And they will learn to choose a volunteer job based on their own skills. Students will understand to do some volunteer work is good for both themselves and the others. All the students will be interested in the volunteers and volunteer work and they will make great progress in English after learning this unit.(1) The first period mainly provides some new vocabulary to the students, especially some phrasal verbs. Most new vocabulary and phrasal verbs are very useful on helping the children express what they would like to do and what they could do. And the first period gives the children lots of practice in writing, listening and speaking with the target language.(2)The activities in the second period provide the students much more listening practice and oral practice using the target language. And the students will get chances to practice the phrasal verbs by listening and speaking. All these will helpmuch in improving the students’ English.(3) In the third period, students will read an article on volunteers. They will practice getting detailed information from an article. And they will do some writing and oral practice as well. Students can improve their reading skill and know more about the volunteers.(4) The fourth period provides much practice on understanding and using the new phrasal verbs. It also gives much more listening and speaking practice. Students will enjoy the story of Jimmy and make much progress in listening. (5) The fifth period will train the students how to make notes based on an article. It also provides some practice on phrasal verbs. Students can do much speaking practice through groupwork as well.(6)The sixth period is designed to train the students’ writing skill. It also provides some more practice on using the new phrasal verbs.2. Teaching Aims and Demands(1) Knowledge ObjectsIn this unit, students learn to express the volunteer work they would like to do and give suggestions to the others. They will also learn some new phrasal verbs.(2) Ability ObjectsTo train the students to use the phrasal verbs, and to train the students’ listening, speaking and writing skills using the target language.(3) Moral ObjectBeing a volunteer is great!3. Teaching Key PointsTo help students learn and grasp the phrasal verbs and the target language. To let students know something about the volunteer work.4. Teaching Difficult PointsTo train students’ listening, speaking, reading and writing skills with the target language.To train the students to use the phrasal verbs.5. Studying WayGet students to be interested in volunteer work and do something really on it. Ⅱ. Language FunctionOffer helpⅢ. Target Language1. I’d like to work outside.2. I’ll help clean up the city parks.3. You could give out food at a food bank.Ⅳ. StructurePhrasal verbsⅤ. Vocabularyput off, hand out, call up, give away, run out of, clean up, set up, take after, fix up, cheer up, give out hunger, sign, repair.Ⅵ. Recyclingcome up with, put up, think up hospital, park, bank, food, lunch, bike, money, outside, volunteer, advertisementⅦ. Learning StrategiesSequencingDeducingⅧ. Teaching TimeSeven periodsThe First PeriodⅠ. Teaching Aims and Demands1. Knowledge Objects(1) Key Vocabularyclean up, hunger, homeless, cheer up, give out, volunteer, food, bank(2) Target LanguageI’d like to work outside.You could give out food at a food bank.2. Ability Objects(1) Train the students to express offering to help with the target language.(2) Train the students’ listening skill.3. Moral ObjectOffer help to the others as much as possible.Ⅱ. Teaching Key Points1. Key Vocabularyclean up, hunger, homeless, cheer up, give up2. Target LanguageHow to express offering to help with target language.Ⅲ. Teaching Difficult Points1. Teach the students how to use the new phrasal verbs.2. Teach the students to express offering to help with target language.Ⅳ. Teaching Methods1. Teaching by giving sample sentences and making up sentences.2. Teaching by showing pictures.Ⅴ. Teaching Aids1. A tape recorder2. Some pictures on volunteer’s offering helpⅥ. Teaching ProceduresStep Ⅰ Revision1. Revise the language points in Unit 7.Ask some questions like this: Where would you like to go on vacation? (I’d like to/I’d love to/l hope to… )Why?(Because…)2. Revise the contents in Unit 7. Say to the class like this:What things Who can say something about Singapore?do you like there and what things don’t you like about it?Ask them to give the answers without looking at the books.3. Check homework by asking some students to read their sentences they’ve made with the verbs. Let them hand in their homework.4. Dictate ten words in Unit 7.Step Ⅱ laThis activity introduces the key vocabulary and provides some writing practice. In this unit we learn to offer to help.We’ll use some phrasal verbs. Each phrasal verbs has two or three words, such as clean up, cheer up, give out.Here is an example o n how to use clean up. Look at the title of Unit 8. I’ll help clean up the city parks. Repeat it twice, please.Ask the children to read the title twice.Then go on saying, "clean up means make a place clean and tidy, put things there in order". Let’s see another example, We should always clean up after a picnic.Who can explain this sentence in your own, words?Ask one student to explain the sentence.He or she may say like this. This sentences means we should burn wastepaper, collect litter and empty bottles, etc.Then say to the class. Who can make more sentences with clean up?Ask several students to share their sentences to the class.Do the same with the other phrasal verbs.Some sample sentences1. clean up—make a place clean and tidy, put things in orderWe should always clean up the dirty parts of the sea.2. cheer up—make someone feel happyThe good news cheers everyone up.3. give out—hand out, distributeLin Tao helped the teacher give out the new textbooks to the class.Read the instructions to the students.Please look at the picture now. We can see a bulletin board and two children in it. What is the bulletin board about?Help students to answer: Volunteer Today!Then continue saying, "Who can tell me the meaning of volunteer?"Ask one student to try to explain it. Then tell them the meaning of it. Volunteer means a person who offers to do something unpleasant or dangerous. It means a person who offers to help the others sometimes. Volunteer is used as a verb in this lesson.Draw the students’ a ttention to the three posters on the board.We can see one sentence in each poster.And we can see some people in each poster, too. What are the volunteers doing in each poster? Please work in pairs and talk about the posters.Give the students a few minutes to talk about what they will say. Let them talk about all the three items. Move around and help the pairs as needed.Then read the sentences in the posters to the class. Ask the pairs of students to explain what the sentence means in their own words. Or tell what the volunteers are doing in the posters.For example, for the first poster, a pair might say:It means there is trash in the park. There are papers on the ground. We can help clean up the park by picking up papers and trash. We can make the park clean.After the students have finished all the items, ask the students to add some other ways they can help people. Get them to write the ways down in the box below the picture.At last, ask some students to share their ideas with the class. Write any new words or phrases on the board and explain these words to the class, if necessary.Some sample answers:Visit some single elderly people and help them with housework.Help clean up the neighbourhood.Cheer up the people who look sad.Help the teacher give out the papers to the students.Save money to help the poorer children.Step Ⅲ 1bThis activity gives students practice in understanding the target language in spoken conversation.Call the students’ attention to the two lists in the box in Activity lb. Ask somestudents to read the eight sentences on the lists to the class. Explain any new words and phrases in it.Make sure that all the students can understand the meanings of the eight items.Then get the children to read the instructions together.Say, we will hear four conversations.Your task is to match the items in the two lists. We can see the blanks in front of the first line of each conversation. Listen to the conversations and write the letter in front of the first line of each conversation. Put the letters of the second line of conversations in right places.Point out the sample answer to the class.Play the recording the first time. Tell the students to only listen.Then play the recording a second time.Tell them to write a letter in front of each numbered sentence this time.Check the answers.Answers1. c2. a3. d4. bTapescriptConversation 1Boy 1: I’d like to work outside.Girl 1:You could help clean up the city parks.Conversation 2Boy 2:I’d like to help homeless people.Girl 1:You could give out food at the food bank.Conversation 3Girl 2:I’d like to cheer up si ck kids.Girl 1: You could visit them in the hospital.Conversation 4Girl 1:I’d like to help kids with their schoolwork.Girl 2:You could volunteer in an after-school study program.Optional activityAsk the students to choose a volunteer job they might like to do and draw a picture of it. They can draw a picture like the posters in the textbook. They can also add a sentence describing the job. They may do this in several groups. After they’ve finished, display the pictures on a bulletin board and discuss these pictures with the class.Step Ⅳ 1cThis activity provides guided oral practice using the target language.Read the instructions with the class.Call their attention to the example in the speech bubbles in Activity la. Ask a pair of students to read this conversation to a class. Then let them practice in pairs.Note their pronunciation of "like to" in phrases such as, I’d like to help hungry people. Tell them English speakers usually pronounce the words "like to" as ifthey were spelled like-tuh.Play the I’d like to statements on the recording to demonstrate this pronunciation.After they’ve finished practicing the sample conversation, ask them to make up similar conversations based on the other two posters. Get two pairs to demonstrate two conversations first. They may say like this:S A: I’d like to cheer up sick kids.S B: You could visit sick children in the hospital.S A: I’d like to help homeless people.S B: You could give out food at a food bank.Then let the whole class practice in pairs.After that, play the recording of activity 1b and let the children read after it twice.Then ask them to practice similar conversations using the information in Activity 1b.Step Ⅴ SummarySay, In this class, we’ve learned how to express offering help. And we’ve learned several phrasal verbs. At last, we did some oral practice using target language.Step Ⅵ Homework1. Make up one sentence with each of the following phrasal verbs:clean up, cheer up, give out2. Write out three conversations of activity 1c.Step Ⅶ Blackboard DesignThe Second PeriodⅠ. Teaching Aims and DemandsKnowledge Objects(1) Key Vocabularyclean-up, sign, put off, set up, establish, come up with(2) Target LanguageI’ll help clean up the city parks.2. Ability Objects(1) Train the students’ listening skill.(2) Train the students’ communicativ e competence using the target language.(3) Train the students to use the new phrasal verbs: cheer up, set up, come up with, put off/3. Moral ObjectPlan a City Parks Clean-up Day with your good friends and come up with some ideas to tell people about it.Ⅱ. Teaching Key Points1. Listening practice with target language.2. Make communications with target language.3. How to use the phrasal verbs.Ⅲ. Teaching Difficult Points1. Make communications with target language.2. Use the phrasal verbs.Ⅳ. Teaching Methods1. Listening2. Pairwork3. Role play the conversationⅤ. Teaching AidsA tape recorderⅥ. Teaching ProceduresStep Ⅰ Revision1. Revise the knowledge points on Page 60. Ask several students to tell some ways they could help people with books closed.2. Check homework by asking several pairs to read their conversations which they wrote down.3. Check homework by asking some students to read their sentences with the phrasal verbs. Let them hand in their homework.Step Ⅱ 2aThis activity provides listening practice using the target language.We can see five pictures in Activity 2a.What can you see in each picture?Ask five different students to describe the pictures. They may say like this: Picture 1: We can see a TV screen in Picture 1.Picture 2: There is a girt putting a sign on the board.Picture 3: A boy is making a call.Picture 4: We can see a copy of newspaper with the advertisement.Picture 5: A boy is giving out advertisements to people.After that, ask a student to read the words on the TV screen, on the sign and in the newspaper.We’ll hear some students at a club meeting. They are talking about how theirclub can help clean up the city parks.Ask the class to read the instructions together. Tell them to note the box of each picture, they will have to tick in the boxes of the items they hear on the recording.Now listen to the club members talking about what they can do to clean up the city parks and tick in the right small boxes.Play the recording the first time.Students only listen.Play the recording again. Ask students to check the things they hear.Check the answers.AnswersThe following pictures should be checked: b c cTapescriptBoy 1: OK. Now we need to come up with a plan to tell people about the city park clean-up.Girl 1: Yeah, but I’m hungry, Bob. let’s have lunch first.Girl 2: No, we can’t put off making a plan. Clean-up Day is only two weeks from now.Boy 2: You’re right. Sally, while we talk, I’ll write down all our ideas. Then we can decide which ideas are best.Girl 1: U m… Well … we could put up signs.Boy 2: That’s a good idea!Girl 2: I’11 hand out advertisements after school.Boy 1: OK. Great! And we could each call up ten people and ask them to come.Boy 2: Hey, we’ve coming up with a lot of good ideas, aren’t we?Step Ⅲ 2bThis activity provides listening and writing practice using the target language. Read the instructions with the class. And let them have a look at the sentences.Read the first sentence to the students.Tell them it is a sample answer.Say, We will hear the same recording again. This time listen carefully to what the students say and fill in the blanks in the sentences.Play the tape again and the students write out the answers.Check the answers.Answers1. come up with2. put off3. write down4. put up5. hand out6. call upStep Ⅳ 2cThis activity provides guided oral practice using the target language.Ask students to look at the sample conversation first. Ask a pair to read it to the class.Ask the class to read the instructions together.Say. You’ll work in pairs to role play t he conversation in Activity 2b.Each pair will make a conversation like the sample one. You can use the sentences in Activity 2b as a guide.Ask the students to work in pairs. More around the classroom, checking the progress of the pairs and offering help as needed.Ask one or two pairs to say their conversations to the class.Step Ⅴ Grammar FocusThis activity introduces several phrasal verbs.Say, Do you remember the meaning of cheer up? Who can tell us?Ask a student to explain the phrasal verb cheer up like this:Cheer up means make someone happy.Then get students to make up some sentences with it.Say, Let’s learn some more phrasal verbs today. Please open your books at page 61. Look at the content in Grammar Focus and try to tell me the meanings of set up and come up with.Ask two children to tell their meanings like this:Set up means establish or start.Come up with means think up.Then get students to read the sample sentences in the grammar box.Write the phrasal verbs and the sentences on the blackboard.Get students to make more sentences with these phrasal verbs to get a further understanding.Step Ⅵ SummarySay, In this class, we’ve done some listening and writing practice with target language. We also did some oral practice in pairs. And we’ve discussed some phrasal verbs as well.Step Ⅶ Homework1. Write two conversations like the sample in Activity 2c.2. Make up one sentence with each of the following phrasal verbs: set up, come up with, put off, hand out, call upStep Ⅷ Blackboard DesignThe Third PeriodⅠ. Teaching Aims and Demands1. Knowledge Objects(1) Key Vocabularymajor, commitment, veterinarian, coach(2) Target LanguageI’d like to join the school volunteer project.You could help coach a football team for little kids.2. Ability ObjectsTrain students’ reading skill.Train students’ speaking skill with target languag e.Train students’ writing skill with target language.3. Moral ObjectIf there is a student volunteer project in your school, try to join it; if not, try to set up one; being a volunteer is great!Ⅱ. Teaching Key Points1. Guide students to read the article in Activity 3a.2. Help students to use the target language to express what kinds of volunteer work they could do and what they like to do.1. Teaching Difficult Points1. Read the article for comprehension.2. Use the target language to express what kinds of volunteer work they could do and what they like to do.Ⅳ. Teaching Methods1. Pairwork2. Role playⅤ. Teaching AidsSome pictures that the volunteers are working, or some signs of the volunt eers’ clubs.Ⅵ. Teaching ProceduresStep Ⅰ Revision1. Check the homework by asking some children to read their conversation.2. Check the homework by asking some children to share their sentences with the phrasal verbs with the class.3. Revise the target language they learned last class. Ask several pairs to talk about the ways they could help people, using the conversation in the speech bubbles in activity la as a sample.Step Ⅱ 3aThis activity provides reading practice using the target language.Have the students look at the picture of the three children. Ask them who they think the children are.Then call the students’ attention to the title of the article and ask the children to read it out. Ask them the question again.This time they may answer. They are three volunteers.Read the instructions to the students.This is an article about volunteers. You have two tasks to do: first underline the kinds of work the volunteers do; second circle the reasons why they like their work.Continue saying. The names of the three volunteers are Li Huiping, Lan Pei and Zhu Ming. The article tells you about the different things they do to help people.Please read the article the first time and underline the things they do. There are three questions on the blackboard to help you.Write the three questions on the blackboard and tell them to scan the passage to get the answers and underline the words.Questions1. What does Li Huiping do to help people as a volunteer?2. What does Lan Pei do?3. What does Zhu Ming do?Check the answers by asking three students to answer the questions.Read the article to the class and do some explanation on any new words. Tell the students to raise their hands when I come to any word or sentence they don’t understand. Pause and do some explanation.Try to explain the new words in English like this: major means more important, for example, a major operation, the major roads; A veterinarian means an animal doctor, a doctor who treats animals.After that, get the students to read the article a second time to circle the reasons.Check the answers with the class.Then have the students read the article loudly twice. Encourage them to ask questions if they still can’t understand any words or sentences.Move around the classroom and answer the students’ questions.AnswersUnderlined words: She helps young children learn to read after school. …volunteers every Saturday morning at an animal hospital… sings for groups of people at the City Hospital.Circled words: You can do the things you love to do…he has learned a lot about animals …he has met some wonderful people at the hospital.Step Ⅲ 3bThis activity provides reading and writing practice using the target language. Read the instructions to the students.And tell them I love English. I could teach English in an after-school program.Hui loves playing football. What could Hui do if he wants to join the school volunteer project?Help the students answer. He could coach a fcf6tball team for little kids.Tell them coach means teach or train.Then ask the students to look at the table in Activity 3b.We can see three columns in this form.There are four names in the first column.And we can know what each of them loves doing from the second column, the column of loves. Now our task is to fill in the blanks in the third column, the column of Could. Get the students to discuss in pairs and fill the results of their discussions in the blanks.Move around the classroom to make sure that they are discussing in English and offer them help as necessary.Ask several pairs to report their answers to the class. Answers will vary but should show a sense of volunteering as well as a relationship to the skill. They may give answers in completely sentences orally but write in phrases. Sample answersStep Ⅳ 3cThis activity provides listening and speaking practise using the target language.Ask a pair of the students to model the sample conversation first.S A: I’d like to join the school volunteer project, but I’m not sure what I should do.S B: What do you like doing?S A: I love playing football.S B: Well, you could help coach a football team for little kids.Write the conversation on the blackboard.Model for the rest of the class.Then let the whole class practice in pairs. Remind them to use the sample conversation, but replace the words loves and skills.Move around the classroom while they are working, checking the progress and offering help as necessary.Ask two or three pairs to share their conversations to the class.Step Ⅴ Part 4This activity provides written and oral practice using the target language.Read the instructions to the class.Call the students’ attention to the clart on the left. Point out the titles Things I like to do and volunteer work I could do to the students.At first, each of you writes down three things you like to do on the lines in the column of Things I like to do. You can write in either complete sentences or phrases. For example, you can fill in the blank with I love drawing pictures, or Drawing pictures.Get the students to write down their own answers individually.As students write, move around the room helping with vocabulary if necessary. Show some pictures of volunteers’ work to remind them as well. Ask several to read their things they like to do to the class.Then work in pairs and give each other suggestions about what volunteer work you could do with those interests. Ask a pair to model the sample conversation before they begin to practice.S A :I like to read about Chinese history.What kind of volunteer work do you think I could do?S B : You could start a Chinese History Club.Write the conversation on the blackboard.Get students to practice in pairs.As the students practice, move around the classroom, correcting some mistakes they may make and helping them answer the questions.Tell them to fill in the blanks in the column of Volunteer work I could do with the suggestions that their partners have given them.After all of them have finished writing, ask one or two pairs to share their conversations to the class.Sample answersStep Ⅵ SummaryIn this class , we’ve learned more about the volunteers and their work. And we’ve done much oraland written practice on volunteer work with target language.Step Ⅶ Homework1. Write a conversation like the sample on in Activity 3c.2. Write a conversation like the sample one in Activity 4.Step Ⅷ Blackboard DesignThe Fourth PeriodⅠ. Teaching Aims and Demands1. Knowledge Objects(1) Key Vocabularyrun out of, take after, fix up, give away, repair, not…any more, similar advertisements(2)Target LanguageWhat do you do, Jimmy?I fix up bikes and give them away.2. Ability Objects(1) Train the students’ reading,writing, speaking and listening skills with the target language.(2) Train the students to use the new phrasal verbs.3. Moral ObjectCome up with a good idea to help others. It will bring you much enjoyment. Ⅱ. Teaching Key Points1. Train the students’ reading, writing, speaking and listening skills with the target language.2. Teach the students to use the new phrasal verbs properly.Ⅲ. Teaching Difficult PointTeach the new phrasal verbs.Ⅳ. Teaching Methods1. Making up sentences2. Listening3. PairworkⅤ. Teaching AidA. tape recorder.Ⅵ. Teaching ProceduresStep I Revision1. Revise the contents of the article in Activity 3a. Section A by asking some questions like these.Questions1. What does Li Huiping love to do?And what does she do as a volunteer?2. What does Lan Pei love and what does he plan to be when he leaves school? Where does he spend every Saturday working?3. What about Zhu Ming? Say something about Zhu Ming.4. What do they say about their volunteer work?5. What do they plan to do?2. Check the homework by asking some students to read the conversations they wrote. Correct any mistakes they might have made. Let them hand in their homework.Step Ⅱ 1aThis activity introduces new target language.Read the instructions to the students.Make sure that each one knows what to do.Let the students look at the sentences in the left column first. Try to explain the four sentences in English for the children, especially the new phrasal verbs in the sentences. Say to them like this:Please look at the sentences on the left column. Let’s get the meanings of them.Let’s see the first one. I’ve run out of itHere, run out of is a phrasal verb. It means reach an end of, use up or become short of. I’ve run out of it, means I’ve used it up, nothing left.Explain the other sentences in the same way like this.2. I take after my mother.take after——be like sb. or be similar to sb.I take after my mother. ——I am like my mother.3. I fixed it up.fix up——install, fit together and place in position, repair, renewI fixed it up. ——I installed it, or I repair it.4. I gave it away.give away——make a present of, donateI gave it away.——I donated it. I gave it to someone without money.After explaining the sentences, read each sentence in the box and ask the students to repeat.Then ask several students to explain the sentences with letters in front of them.Tell them to explain them in their own sentences. For example, Sentence a, the student might respond. My bicycle was broken. I couldn’t ride it. I got new tires and a new seat. Now it works fine.Read the instructions again and ask the students to match the sentences with similar meanings.Say, Now match the numbered sentences with the lettered sentences in the box.Write the letter of one sentence in front of the number of the matching。
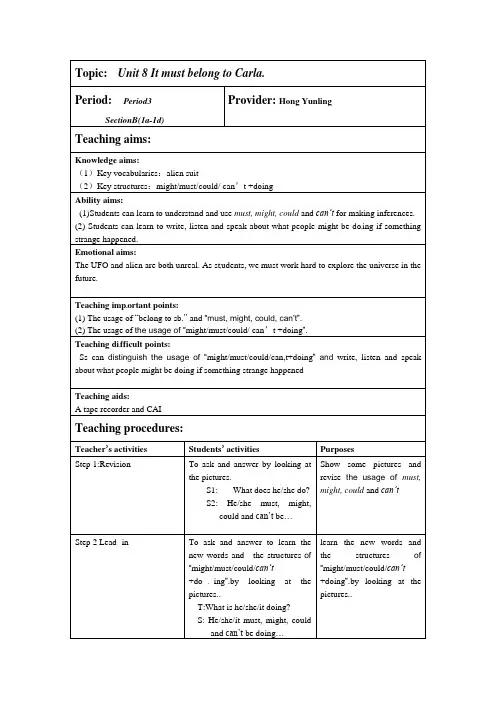
Topic:Unit 8 It must belong to Carla.Period: Period3SectionB(1a-1d)Provider: Hong YunlingTeaching aims:Knowledge aims:(1)Key vocabularies:alien suit(2)Key structures:might/must/could/can’t +doingAbility aims:(1)Students can learn to understand and use must, might, could and can’t for making inferences.(2) Students can learn to write, listen and speak about what people might be do ing if something strange happened.Emotional aims:The UFO and alien are both unreal. As st udents, we must work hard to explore the universe in the future.Teaching imp ortant points:(1) The usage of “belong to sb.” and “must, might, could, can’t”.(2) The usage of the usage of “might/must/could/can’t +doing”.Teaching difficult points:Ss can distinguish the usage of “might/must/could/can,t+doing”and write, listen and speak about what people might be doing if something strange happenedTeaching aids:A tape recorder and CAITeaching procedures:Teacher’s activities Students’ activities PurposesStep 1:Revision To ask and answer by looking atthe pictures.S1:What does he/she do?S2: He/she must, might,could and can’t be…Show some pictures and revise the usage of must, might, could and can’tStep 2 Lead -in To ask and answer to learn thenew words and the structures of“might/must/could/can’t+do ing”.by looking at thepictures..T:What is he/she/it doing?S: He/she/it must, might, couldand can’t be doing…learn the new words and the structures of “might/must/could/can’t+doing”.by looking at the pictures..Ste p3 work on 1a Look at the pictures. Then usethe words from the box to speakand write a sentence about eachpicture. To improve the speaking and writing skills.Step 4 1b List en and number the pictures. Then write two or three sentences to finish the story. 1.Listen to the tape and numberthe pictures. and check theanswers.2write two or three sentences tofinish the story.To improve the listeningskills.To improve Ss’writingability.Step 5 1c Listen again. Complete the sentences. Listen again. write the words Sshear. And then check the answersTo impr ove listening skillsand writing and speakingskills.Step 6 Listen again and fill inthe blanks according to listening material. Listen again and fill in the blanksAnd then check the answers.To consolidate Ss’listeningand writing ability.Step 7 Pairwork1.Ask the students to dopair work. Ask somepairs to act out.2.Make the similarconversations and asksome pairs to act out.. Students work in pairs:A:? B: …Students Make the similarconversations and ask some pairsto act out..in pairs:A:? B: …To improve Ss’speakingability.Consolidate key sentences.Step 8 Homework Oral workRead and try to remember the newwords and phrases.Prepare for the newwords of reading.Written workWrite a report to according to 1C. It helps Ss to consolidate the knowledge we learned today.Bb designUnit 8 It must belong to Carla.Period 1 Section B (1a—1d) chase=run after an alienIt might be readingHe could be playing basketball.He could be playing basketball.He must be painting.He can’t be doing homework.小结:must /could/might/can’t be +doing表示“一定/可能/不可能正在做…”。

九年级英语unit83a教案九年级的同学们,英语学科不能落下哦。
为大家整理的九年级英语unit83a教案,希望大家喜欢。
九年级英语unit83a教案1 Students in Grade Nine have mastered some vocabulary and grammar knowledge, some students can use simple English to express their own thoughts,but it is difficult for a small part of students to communicate in English. So I put the students of different levels in a group, let them help each other, try to make every student get different levels of harvest.一、情感态度与价值观Emotion & Attitude Goals:1.Form good study habits.2.Know history of inventions and be proud of our country. Encourage students to be a little inventor3. Help students to study actively.二、过程与方法1. Through the inventions that we can see everywhere to introduce the topic, stimulate students interest.2. Design various activities, organize students todiscuss, so that every student can get different levels of harvest .3. Work in pairs and groups.三、知识与技能Knowledge Goals:1. Key words : invent invention inventor calculator2.Target language : --When was it invented ?-- It was invented in ….3. Grammar : The passive voice : was /were + done am /is /are + doneAbility Goals:1.Read the key words correctly and understand their meanings.2.Improve listening skills.3.Make up conversations with the target language and try to improve speaking skills.4.Learn to communicate with others in English.1. key words and target language.2. The passive voice.3. Help the students to improve cooperation ability.A recorder、Multimedia教学活动1[U1] 、Lead-inT: I get to school by e-bike every day. How do you get to school ?S1: I get to school by bike.S2: I get to school by bus.T: Bus, car, taxi, bike, they are all useful inventions. What do you think of inventions?T: Now we live in a world of inventions. These inventions make our life easier and more comfortable. In this unit, we will learn some inventions and their history.教学活动2二[U2] 、PresentationShow the picture to teach new words:invent /light bulb/inventor inventionThis is Edison. He invented the light bulb. He was a great inventor.He invented about 2000 inventions all his life.Make sure the students read the new words correctlyand understand their meanings.Show pictures in 1aT: Do you know these inventions? Can you say them in English? What’s this in English?Ss: It’s a telephone/computer/television/ calculator/ car.Teach the new word: calculator教学活动3三[U3] 、Groupwork 1aT:There are five inventions in this part . Which one was invented the earliest and which one was invented the last ? Guess the dates and discuss in what order they were invented.Help them to discuss by using the following sentences:I think the television was invented after/before the telephone.I agree/ disagree.Let each group choose one student to write their result on the blackboard.教学活动4四[U4] 、listening Practice 1bT: Which group has the correct result ? We’ll listen to a girl and a woman talking about the five inventions.First, review the expression of the year.Then, play the recording the first time, Ss only listen and try to catch the main idea..Next, play the recording a second time. Say, listen to the recording and match the inventions with the dates.Finally, check the answers:d 1876 a 1885e 1927 c 1971 b 1976Clap for the groups that have correct results.教学活动5五[U5] 、PairworkPractice conversations in pairs using the information in 1b like this:A: When was ithe car invented ?B: It was invented in ….Then ask some pairs to display their conversations in front of the class.教学活动6六[U6] SummaryT: In this class we’ve learned to talk about the history of inventions with passive voice. Now let’s have a discussion about the passive voice in groups. Make sure students can master the structures of the passive voice and then each group writes five sentenses about the passive voice.教学活动7七[U7] 、PracticeShow the excercises:1、Edison was an _______(invent), he_______ (invent) many useful and important _______(invent) all his life.2、He is calculating a math problem with a _______ (calculate).3、Stamps _____ for sending letters.A. usedB. are usingC. are used4、Chinese ____ by more and more people in the world now.A. is spokenB. is speakingC. spoke5 The factory ____ in 1985.A. is builtB. was builtC. built[U1]以学生熟悉的上学方式这一话题引入主题,激发兴趣。




九年级英语上册Module8SportslifeUnit3Languageinuse教案新版外研版unit3languageinuse【数学目标】词汇准备,做某事的能力,建议做某事,做得不好!2.找到适合你的车很重要。
3.去吧。
1.复习本模块的词汇和句型。
2.一般过去时的被动语态。
句型的重点和难点[教学思路]1.复习unit1和unit2的重点词汇和句型,引入教学,使学生明确学习的话题。
2.给学生一定时间去准备本单元的内容,先独立再合作交流。
引导学生积极表现与展示。
3.要求学生使用本模块的词汇和目标语言编写调查报告。
[教学准备]黑板,录音机,卡片,多媒体等。
【教学过程】热身。
老师和学生的问候。
2.复习前两单元的知识点。
活动总结:让学生在学习新知识时回顾原有知识。
2.语言练习1。
过去时态的被动语态(2)教师和学生一起总结归纳一般过去时的被动语态的用法。
一般说来,当强调动作承受者,不必说出执行者或含糊不清的执行者时,多用被动语态。
而一般过去时的被动语态强调动作发生在过去。
主动语态变被动语态时,主动语态句中的宾语变成被动语态句中的主语,主动语态句中的主语成为被动语态句中的动作的发出者。
一般过去时的被动语态为:主语+过去/过去+及物动词的过去分词(+bysb)。
2.完成活动(1-5)④教师提出问题让学生讨论和思考:doyouknowanythingaboutthegamesin2021?① 教师要求学生两人一组讨论图片内容,用过去时态的被动语态描述图片,并注意图片下方的提示。
②用所给出的提示,写出描述图片的句子。
最后两人一组检查句子是否正确。
(4)要求学生完成整合语法的活动。
核对答案。
②教师让学生用框中的单词完成句子,并逐条翻译句子。
③最后一起核对答案。
活动总结:让学生通过练习巩固过去式被动语态。
第三步倾听1.教师让学生读活动6中的句子,让学生明确听力大意。
2.教师提出几个问题让学生试着回答。
doyouknowchenzhong?你能告诉我什么吗?3.教师播放录音,让学生听第一遍录音,判断活动6中的句子的对错。
第3课时Section B(1a~1d)【教学目标】1.通过听力训练获取有效信息,学会运用目标语言进行推测。
2.能够结合所给证据或所呈现的迹象对事物进行合理推测。
【教学重难点】重点:掌握单词land,alien,suit,camera,actor。
难点:会对我们身边的现象进行合理推测。
【课堂导学案】Step 1复习(3分钟)让学生介绍自己经历过的奇怪的事。
Step 2情景导入(5分钟)上课前,教师可以要求学生准备一些他们亲戚或者同班同学的一些照片,然后上课时,要求学生去猜他们是谁。
教师可以邀请两名学生在讲台上利用下面的对话进行猜测。
A:Who is he/she?B:He/She can't be________,because________.He/She could/might be________,because________.He/She must be________,because________.环节说明:这一环节的设置主要是继续巩固前面所学的情态动词表推测的用法,同时为下面继续学习这一用法奠定基础。
Step 3完成教材1a~1d教学任务1.要求学生翻开课本P61,迅速浏览1a中的图片,并按要求完成课本上相应的任务。
然后要求5~8名学生给出自己的答案,教师可把这些问题在黑板上列举出来,看哪个学生对图片把握得更好。
(3分钟)【参考案例】2.听第一遍录音,完成课本上1a部分的任务。
(2分钟)3.听第二遍录音,完成课本上1c部分的任务。
(2分钟)4.听力内容巩固训练。
要求学生根据所听到的内容完成下列对话。
完成后要求若干学生给出自己的答案,以巩固对听力内容的理解。
(3分钟)—He's wearing a__suit.—He might__be__late for work.—There's something in__the__sky.—It could be a helicopter.—Who's that woman with a camera?—She could be from the__TV__news.—Look at all those other people.They're actors.—They must be making__a__movie.5.听第三遍录音,并打开听力材料,全班逐句进行跟读。
Module8 Unit3 精品教案Unit 3 Language in use【教学目标】●Knowledge objectiveGet the students to be able to use the new words and expressions they learnt in this module.●Ability objectiveTo summarize and consolidate the object clauses and attributive clauses.●Moral objectiveTo be glad to take part in the party activities; To share the happiness with classmates; To realize the importance of effort and friendship.【教学重点】To be able to use the object clauses and attributive clauses correctly.【教学难点】Through listening, speaking and writing, let students practise the object clauses and attributive clauses.【教学方法】PWP method, task-based method【教学手段】Multimedia and some pictures【教学过程】Teaching Procedures:Step 1 Revision and lead-inLet Ss look at the pictures and answer the questions to review what they have learnt.How many days are left before you leave school?Do you feel nervous every day?What time do you go to bed every night?Do you have time to do exercise except studying?Step 2 Language practiceTo master the key words.1. I know ______ you will be better at maths.2. These roses are to thank three groups of people for the three most important things _______ I have learnt.3. I give the white rose to my teachers, _____ have taught me _______ there is no success without effort.4. I’m sur e that you all have your own memories about the happiness of the last three years, and the people _____ you want to thank for it.Keys: 1. that 2. that 3. who that 4. thatStep 3 Complete the sentencesComplete the sentences using which, that, who or whom. Try to explain the meaning of the words in purple.1. Finger food is the food that/which we eat with our fingers.2. A handbag is a small bag ____________________________________________.3. School-leavers are young people_______________________________________.4. A classmate is someone ______________________________________________.5. A friend is someone _________________________________________________.6. A stranger is someone _______________________________________________. Step 4 Look and discussLook at the picture and the menu to discuss the questions in pairs.1. How do you know that the party is international?2. Why are the people cheering?3. What do you think the person making a speech is saying?Keys: Because the food is international.Because they are happy about what the speaker is saying.The speaker is saying that now the speech is over and it is time to eat!Step 5 Complete the passage1.Read the passage carefully.e the correct clauses in the box to fill in the blanks.a) the success at school is important for our futures。
Module 8 Sports life Unit 3 Language in use
一、教学内容:Unit3 Language in use
二、课型:Revision and application
三、教学目标:
1、正确运用本模块的词汇及短语:stand for, point, decision, excuse,seat, no way,
fair, kick, be mad at,ability,race,pride.等。
2、能够掌握一般过去时被动语态的概念和用法。
3、能根据本模块所学的知识,调查同学参与体育活动的情况并以书面形式进行总结汇报。
4、能听懂关于体育运动的对话并获取相关的细节信息。
5、通过学习,加深对残奥会的了解。
四、教学重难点:
1、能够掌握一般过去时被动语态的概念和用法。
2、能根据本模块所学的知识,调查同学参与体育活动的情况并以书面形式进行总结汇报。
五、教学准备:
本节课型为Revision and application,根据新课标的要求,结合教材和学生特点,主要采用任务型互动式进行教学,结合情景法、交际法、听说法、归纳法等教学方法实施课堂活动,开启学生思维,通过一系列有条理的教学活动,引导学生自主探究学习和与他人互动合作学习,让学生体验愉快学习。
本节课所需教具及资料:幻灯、图片、调查表等。
六、教学过程:。
Unit 8 Detective storiesReadingⅡ1. Be able to get further understanding of the whole text;2. Be able to learn to use some important phrases properly;3. Be able to talk with the classmates about the murder.1. To learn to use some important phrases properly.2. To use the key words and the phrases to talk about the murder.Step 1 Revising time1.Watch the video of the story.T: At the beginning of the class, we will watch the video of the reading text. Watch it and try to have a revision.Students Watch the video.2.Do some true of false questions.T: Now please answer these True of False questions. If you know the answer, put up your hands. If it is right, tell me “true”. If it is false, tell me “false” and try to tell me why.The victim’s body was found in West Town.The victim sold computers.The victim worked in East Town.It is possible that the victim was killed somewhere else.The police know that the victim had some enemies.The police have one suspect so far.The suspect is a short fat man.The police have arrested the murderer.The victim’s parents are offering a reward for useful information.Step 2 Studying timeRead paragraph by paragraph. Know more about the context and pay attention to some new words and phrases.1.Read paragraphs 1-2. Try to finish the table about the victim and the murder.(language points: a 25-year-old man, sb be seen doing, whether or not)2.Read paragraph3. Finish the mind-map.(language points: clue; wound)3.Read paragraphs 4-5. Know more about the victim.(language point: be guilty of/be charged with)4.Read paragraph 6. Learn more about the suspect.(language point: breathe/breath)5.Read paragraph 7. Let’s do something for the victim’s parents.(language point: lead to)Step 3 Showing timeTry to retell the text with the help of the questions and the video.When and where was the victim last seen? (be seen doing)Are you sure the victim was killed at the place where he was found? (whether ... or)How did the victim die? (bleed)Did the victim have any criminal record? (be guilty of/ be charged with)Did we have a suspect so far? (so far)Did we have a suspect so far? (prove)1.Retell the text.2.Finish the exercises in Period 3 of Unit 8 in the workbook.。