药典注射剂通则
- 格式:doc
- 大小:35.00 KB
- 文档页数:3

《中国药典》2020年版四部通则0841《中国药典》2020年版四部通则0841是关于药物制剂中微粒大小的测定方法。
本文将详细解读这一通则,以帮助读者更好地了解药物制剂的质量控制。
一、概述《中国药典》2020年版四部通则0841规定了药物制剂中微粒大小的测定方法。
微粒大小对药物制剂的疗效、生物利用度、稳定性和安全性等方面具有重要影响。
因此,对微粒大小进行准确测定是药物制剂质量控制的重要环节。
二、测定方法1.激光散射法:该方法利用激光光源和散射光检测器,测定药物制剂中微粒的散射光强度,从而推算出微粒的大小。
适用于测定纳米级至微米级的微粒。
2.颗粒计数法:该方法通过显微镜观察药物制剂中的微粒,并对其进行计数,从而得到微粒的大小分布。
适用于测定微米级以上的微粒。
3.粒度分布测定法:该方法利用粒度分析仪,通过测定药物制剂中微粒的沉降速度或扩散速度,计算微粒的大小分布。
适用于测定纳米级至微米级的微粒。
4.比表面积法:该方法通过测定药物制剂中微粒的比表面积,推算出微粒的大小。
适用于纳米级微粒的测定。
三、注意事项1.在进行微粒大小测定时,需根据药物制剂的特性和微粒大小范围选择合适的测定方法。
2.测定过程中,应严格控制实验条件,如温度、湿度等,以确保测定结果的准确性。
3.对于不同药物制剂,应按照相关要求进行样品前处理,以消除药物溶解度、表面活性剂等因素对测定结果的影响。
4.测定结果应采用合适的统计学方法进行处理,以得到可靠的微粒大小分布数据。
四、应用实例以某药物注射剂为例,采用激光散射法测定其微粒大小。
首先,将药物注射剂进行适当稀释,使其微粒浓度适中。
然后,使用激光散射粒度分析仪进行测定。
通过数据处理,得到药物注射剂中微粒的大小分布。
根据《中国药典》2020年版四部通则0841的要求,对测定结果进行分析,确保药物注射剂的质量符合规定。
总结:《中国药典》2020年版四部通则0841为药物制剂中微粒大小的测定提供了科学、可靠的方法。



1101 无菌检查法无菌检查法系用于检查药典要求无菌的药品、生物制品、医疗器具、原料、辅料及其他品种是否无菌的一种方法。
若供试品符合无菌检查法的规定,仅表明了供试品在该检验条件下未发现微生物污染。
无菌检查应在无菌条件下进行,试验环境必须达到无菌检查的要求,检验全过程应严格遵守无菌操作,防止微生物污染,防止污染的措施不得影响供试品中微生物的检出。
单向流空气区、工作台面及环境应定期按医药工业洁净室(区)悬浮粒子、浮游菌和沉降菌的测试方法的现行国家标准进行洁净度确认。
隔离系统应定期按相关的要求进行验证,其内部环境的洁净度须符合无菌检查的要求.日常检验还需对试验环境进行监控。
培养基硫乙醇酸盐流体培养基主要用于厌氧菌的培养,也可用于需氧菌培养;胰酪大豆胨液体培养基用于真菌和需氧菌的培养。
培养基的制备及培养条件培养基可按以下处方制备,亦可使用按该处方生产的符合规定的脱水培养基或成品培养基。
配制后应采用验证合格的灭菌程序灭菌。
制备好的培养基应保存在2~25℃、避光的环境,若保存于非封闭容器中,一般在3周内使用;若保存于密闭容器中,一般可在一年内使用。
1. 硫乙醇酸盐流体培养基胰酪胨15.0g 氯化钠2.5g酵母浸出粉5。
0g 新配制的0。
1% 刃天青溶液1。
0ml无水葡萄糖5。
0g 琼脂0.75gL-胱氨酸0.5g 水1000ml硫乙醇酸钠0.5g(或硫乙醇酸) (0。
3ml)除葡萄糖和刃天青溶液外,取上述成分混合,微温溶解,调节pH为弱碱性,煮沸,滤清,加入葡萄糖和刃天青溶液,摇匀,调节pH,使灭菌后在25℃的pH值为7。
1±0.2。
分装至适宜的容器中,其装量与容器高度的比例应符合培养结束后培养基氧化层(粉红色)不超过培养基深度的1/2。
灭菌。
在供试品接种前,培养基氧化层的高度不得超过培养基深度的1/5,否则,须经100℃水浴加热至粉红色消失(不超过20分钟),迅速冷却,只限加热一次,并防止污染。
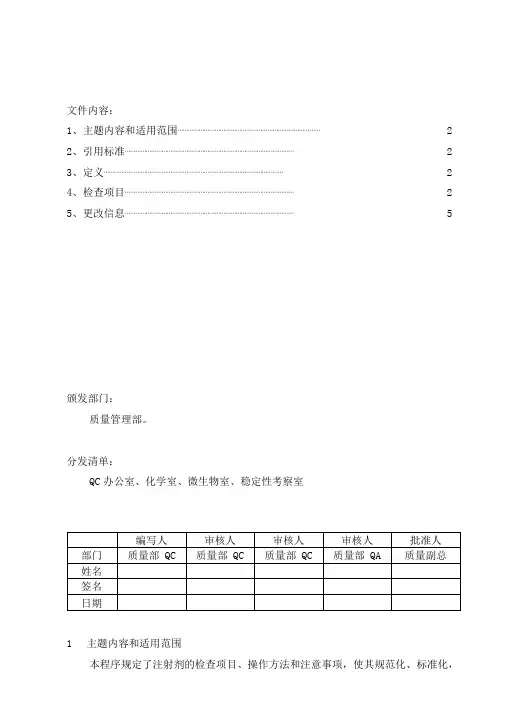
文件内容:1、主题内容和适用范围⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯ 22、引用标准⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯ 23、定义⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯ 24、检查项目⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯ 25、更改信息⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯ 5颁发部门:质量管理部。
分发清单:QC办公室、化学室、微生物室、稳定性考察室1主题内容和适用范围本程序规定了注射剂的检查项目、操作方法和注意事项,使其规范化、标准化,并描述了更改信息。
本程序适用于注射剂的检验。
2引用标准中国药典2010 年版二部附录Ⅰ B“注射剂”、中国药品检验标准操作规范2010 年版P4“注射剂”。
3定义注射剂(中国药典2010 年版二部附录Ⅰ B)系指药物与适宜的溶剂或分散介质制成的供注入体内的溶液、乳状液或混悬液,以及供临用前配制或稀释成溶液或混悬液的粉末或浓溶液的无菌制剂。
注射剂可分注射液(其中供静脉滴注用的大体积注射液也称静脉输液)、注射用无菌粉末与注射用浓溶液。
4检查项目注射剂除应按药典品种项下规定的检验项目外,还应检查“装量”或“装量差异” “可见异物”和“无菌” 。
静脉用注射剂应加查“热原”或“细菌内毒素” ;溶液型静脉用注射液、溶液型静脉注射用粉末及注射用浓溶液应加查“不溶性微粒” 。
静脉输液及插管注射用注射液应加查“渗透压摩尔浓度” 。
4.1装量本法适用于50ml及50ml以下的单剂量注射液的装量检查,其目的在于保证单剂量注射液的注射用量不少于标示量,以达到临床用药剂量要求。
标示装量为50ml 以上的注射液和注射用浓溶液,按最低装量检查法标准操作规范检查,应符合规定。
凡规定检查含量均匀度的注射液(如塞替派注射液),可不进行“装量”检查。
4.1.1仪器与用具注射器及注射针头。

药典中注射剂对抗氧剂的要求
中国药典2015年版四部 0102 注射剂通则中:配制注射剂时,可根据需要加入适宜的附加剂,如渗透压调节剂、pH 值调节剂、增溶剂、助溶剂、抗氧剂、抑菌剂、乳化剂、助悬剂等。
所用附加剂应不影响药物疗效,避免对检验产生干扰,使用浓度不得引起毒性或明显的刺激性。
常用的抗氧剂有亚硫酸钠、亚硫酸氢钠和焦亚硫酸钠等,一般浓度为0.1% 〜0.2%。
但一些产品由于其结构的特殊性,其主要成份在空气中极易氧化,有可能其抗氧剂用量需要超过0.2%时,主药才能比较稳定。
但有人说,如果抗氧剂用量比如亚硫酸氢钠用量大后,其过多的氢离子可能增加药液对血管的刺激性。
我们有一注射剂产品因主药成份极易氧化,虽然进行充氮处理并控制其残氧量,但稳定性并不是很好,通过对抗氧剂亚硫酸氢钠等用量的筛选,确定浓度为0.3%比较合适,同时进行了过敏性、溶血性、血管刺激性等试验,结果表明:家兔每日耳缘缓慢静脉滴注浓度为2.0mg/ml的该产品8ml/kg,另侧给予等体积的生理盐水,连续3次,于末次给药后24h取家兔耳缘静脉观察未见明显刺激反应。
表明该药血管刺激性试验符合要求。

注射剂注射剂系指原料药物或与适宜的辅料制成的供注入体内的无菌制剂。
注射剂可分注射液(其中供静脉滴注用的大容量注射液也可称为输液)、注射用无菌粉末与注射用浓溶液。
注射剂除应按药典品种项下规定的检验项目外,还应检查“装量”或“装量差异”、“可见异物”和“无菌”。
静脉用注射剂应加查“热原”或“细菌内毒素”;静脉注射、静脉滴注、鞘内注射、椎管内注射的溶液型的注射液、注射用无菌粉末及注射用浓溶液应检查“不溶性微粒”;静脉输液及椎管注射用注射液应加查“渗透液摩尔浓度”;另外中药注射液还应检查中药注射剂有关物质和重金属及有害元素残留量。
混悬型注射液,除另有规定外,原料药物粒度应控制在15µm以下,含15~20µm (间有个别20~50µm)者,不应超过10%,若有可见沉淀,振摇时应容易分散均匀。
混悬型注射液不得用于静脉注射或椎管内注射;乳状液型注射液不得有相分离现象,不得用于椎管注射;静脉用乳状液型注射液中90%的乳滴粒径应在lµm以下,并不得有大于5µm的乳滴。
除另有规定外,输液应尽可能与血液等渗。
“装量”检查法1 简述1.1 本法适用于50ml及50ml以下的单剂量注射液及生物制品多剂量供试品的装量检查,其目的在于保证单剂量注射液的注射用量不少于标示量,以达到临床用药剂量要求。
1.2 标示装量为50ml以上的注射液和注射用浓溶液,按最低装量检查法标准操作规范检查,应符合规定。
1.3 凡规定检查含量均匀度的注射液(如塞替派注射液),可不进行“装量”检查。
作业指导书指导书编号TYFDC-SOP-FF-015注射剂第2页共6页第二版批准李忠华初审郝娟起草吴雅凝2 仪器与用具2.1 注射器及注射针头。
2.2 量具(量入型)规格1、2、5、10、20及50ml的量具,均应经标化。
3 操作方法3.1 按下表规定取用量抽取供试品。
标示装量供试品取用量(支)2m1或2ml以下 52ml以上至50m1 33.2 取供试品,擦净瓶外壁,轻弹瓶颈部使液体全部下落,小心开启,将每支内容物分别用相应体积的干燥注射器(包括注射器针头)抽尽,然后缓慢连续地注入预经标化的量入式量筒内(量筒的大小应使待测体积至少占其额定体积的40%,不排尽针头中的液体),在室温下检视,读出每支装量。

EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.0ParenteralpreparationsMucoadhesive preparations DEFINITION Mucoadhesive preparations contain one or more active substances intended for systemic absorption through the buccal mucosa over a prolongedperiodof time.They may be supplied as mucoadhesive buccal tablets or as other mucoadhesive solid or semi-solid preparations.Mucoadhesive buccal tablets are prepared by compressionof mono-or multi-layeredtablets.They usually containhydrophilic polymers,which on wetting with the salivaproduce a flexible hydrogel that adheres to the buccal mucosa.PRODUCTION In the manufacture of mucoadhesive buccal tablets,measures are taken to ensure that they possess suitablemechanical strength to resist handling without crumbling or breaking.This may bedemonstratedby examining the Friability of uncoated tablets (2.9.7)and the Resistance to crushing of tablets (2.9.8).TESTS Dissolution .Unlessotherwisejustified and authorised,a suitable test is carried out to demonstrate the appropriate release of the active substance(s).01/2008:0520PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS Parenteralia The requirementsof this monograph do not necessarily apply to products derived fromhuman blood,toimmunological preparations,or radiopharmaceutical preparations.Special requirements may apply to preparations for veterinary use depending on the species of animal for which the preparation is intended.DEFINITION Parenteral preparations are sterilepreparations intended for administration by injection,infusion or implantation into the human or animal body.Parenteral preparations may require the use of excipients,for example to make the preparation isotonic with respect to blood,to adjustthe pH,to increase solubility,to prevent deterioration of the activesubstancesor to provideadequateantimicrobial properties,but not to adversely affect the intended medicinal action of the preparation or,at the concentrations used,to cause toxicity or undue local irritation.Containers for parenteral preparations are made as far as possible frommaterialsthat are sufficiently transparentto permit the visual inspection of the contents,except for implants and in other justified and authorised cases.Where applicable,the containers for parenteral preparations comply with the requirements for Materials used for the manufacture of containers (3.1and subsections)and Containers (3.2and subsections).Parenteral preparations are supplied in glass containers (3.2.1)or in other containers such as plastic containers (3.2.2,3.2.2.1and 3.2.9)and prefilled syringes.The tightness of the containeris ensured bysuitablemeans.Closuresensure a good seal,prevent the access of micro-organisms and other contaminants and usually permit the withdrawal ofa part or the whole of the contents without removal of the closure.The plasticmaterials or elastomers (3.2.9)used to manufacture the closures are sufficiently firm and elastic to allow the passage of a needle with the least possible shedding ofparticles.Closures for multidose containers aresufficiently elastic to ensure that the puncture is resealedwhen the needle is withdrawn.Severalcategories of parenteral preparations may be distinguished:—injections,—infusions,—concentrates for injections or infusions,—powders for injections or infusions,—gels for injections,—implants.PRODUCTIONDuringthe developmentof a parenteral preparation,theformulation for which contains an antimicrobial preservative,the effectiveness of the chosen preservative shall be demonstratedto the satisfaction of the competent authority.A suitable test method togetherwithcriteria forjudgingthe preservative properties of the formulation are provided under Efficacy of antimicrobial preservation (5.1.3).Parenteral preparations are prepared using materials and methods designed to ensure sterility and to avoidthe introduction of contaminants and thegrowth ofmicro-organisms.Recommendations on this aspect areprovided in the text on Methods of preparation of sterile products (5.1.1).Water used in the manufacture of parenteral preparationscomplies with the requirements of water for injections in bulk stated in the monograph on Water for injections (0169).TESTSParticulate contamination:sub-visible particles (2.9.19).For preparations for human use,solutions for infusion orsolutions for injection comply with the test.Inthe case of preparations for subcutaneous or intramuscular injection,higher limits may be appropriate.Radiopharmaceutical preparations are exempt from these requirements.Preparations for which the label states thatthe product is to be used with a final filter are exempt from these requirements,providing it has been demonstrated that the filter delivers a solution that complies with the test.For preparations for veterinary use,whensupplied in containers with a nominal content of more than 100ml and when the content is equivalent to a dose of more than1.4ml per kilogram of body mass,solutions for infusion orsolutions for injection comply with the test for particulate contamination:sub-visible particles.Sterility (2.6.1).Parenteral preparations comply with the test for sterility.STORAGEIn a sterile,airtight,tamper-proof container.LABELLINGThe label states:—the name andconcentration of any added antimicrobial preservative,—where applicable,that the solution is to be used in conjunction with a final filter,—where applicable,that the preparation is free frombacterial endotoxins or that it is apyrogenic.General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts 735Parenteral preparations EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA6.0InjectionsDEFINITIONInjections are sterile solutions,emulsions or suspensions. They are prepared by dissolving,emulsifying or suspending the active substance(s)and any added excipients in water,in a suitable non-aqueous liquid,that may be non-sterile where justified,or in a mixture of these vehicles.Solutions for injection,examined under suitable conditions of visibility,are clear and practically free from particles. Emulsions for injection do not show any evidence of phase separation.Suspensions for injection may show a sediment which is readily dispersed on shaking to give a suspension which remains sufficiently stable to enable the correct dose to be withdrawn.Multidose preparations.Multidose aqueous injections contain a suitable antimicrobial preservative at an appropriate concentration except when the preparation itself has adequate antimicrobial properties.When a preparation for parenteral use is presented in a multidose container, the precautions to be taken for its administration and more particularly for its storage between successive withdrawals are given.Antimicrobial preservatives.Aqueous preparations which are prepared using aseptic precautions and which cannot be terminally sterilised may contain a suitable antimicrobial preservative in an appropriate concentration.No antimicrobial preservative is added when:—the volume to be injected in a single dose exceeds15ml, unless otherwise justified,—the preparation is intended for administration by routes where,for medical reasons,an antimicrobial preservative is not acceptable,such as intracisternally,epidurally,intrathecally or by any route giving access to thecerebrospinal fluid,or intra-or retro-ocularly.Such preparations are presented in single-dose containers.PRODUCTIONIn the manufacture of injections containing dispersed particles,measures are taken to ensure a suitable and controlled particle size with regard to the intended use. Single-dose preparations.The volume of the injection in a single-dose container is sufficient to permit the withdrawal and administration of the nominal dose using a normal technique(2.9.17).TESTSUniformity of dosage units.Single-dose suspensions for injection comply with the test for uniformity of dosage units (2.9.40)or,where justified and authorised,with the test for uniformity of content shown below.Herbal drugs and herbal drug preparations present in the dosage form are not subject to the provisions of this paragraph.Uniformity of content(2.9.6).Unless otherwise prescribed or justified and authorised,single-dose suspensions for injection with a content of active substance less than2mg or less than2per cent of the total mass comply with test A for uniformity of content of single-dose preparations.Ifthe preparation contains more than one active substance, the requirement applies only to those substances that correspond to the above conditions.Bacterial endotoxins-pyrogens.A test for bacterial endotoxins(2.6.14)is carried out or,where justified and authorised,the test for pyrogens(2.6.8).Recommendations on the limits for bacterial endotoxins are given in chapter2.6.14.Preparations for human use.The preparation complies with a test for bacterial endotoxins(2.6.14)or with the test for pyrogens(2.6.8).Preparations for veterinary use.When the volume to be injected in a single dose is15ml or more and is equivalent to a dose of0.2ml or more per kilogram of body mass,the preparation complies with a test for bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)or with the test for pyrogens(2.6.8).Any preparation.Where the label states that the preparation is free from bacterial endotoxins or apyrogenic,respectively, the preparation complies with a test for bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)or with the test for pyrogens(2.6.8),respectively.InfusionsDEFINITIONInfusions are sterile,aqueous solutions or emulsions with water as the continuous phase.They are usually made isotonic with respect to blood.They are principally intended for administration in large volume.Infusions do not contain any added antimicrobial preservative.Solutions for infusion,examined under suitable conditions of visibility are clear and practically free from particles. Emulsions for infusion do not show any evidence of phase separation.PRODUCTIONIn the manufacture of infusions containing dispersed particles,measures are taken to ensure a suitable and controlled particle size with regard to the intended use. The volume of the infusion in the container is sufficientto permit the withdrawal and administration of the nominal dose using a normal technique(2.9.17).TESTSBacterial endotoxins-pyrogens.They comply with a test for bacterial endotoxins(2.6.14)or,where justified and authorised,with the test for pyrogens(2.6.8).For the latter test inject10ml per kilogram of body mass into each rabbit, unless otherwise justified and authorised. Concentrates for injections or infusions DEFINITIONConcentrates for injections or infusions are sterile solutions intended for injection or infusion after dilution.They are diluted to a prescribed volume with a prescribed liquid before administration.After dilution,they comply with the requirements for injections or for infusions.TESTSBacterial endotoxins-pyrogens.They comply with the requirements prescribed for injections or for infusions,after dilution to a suitable volume.Powders for injections or infusions DEFINITIONPowders for injections or infusions are solid,sterile substances distributed in their final containers and which,when shaken with the prescribed volume of a prescribed sterile liquid rapidly form either clear and736See the information section on general monographs(cover pages)EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.0Patches,transdermal practically particle-free solutions or uniform suspensions.After dissolution or suspension,they comply with therequirements for injections or for infusions.Freeze-dried products for parenteral use are considered aspowders for injections or infusions.PRODUCTION The uniformity of contentand uniformityof mass offreeze-dried products for parenteral use are ensured by the in-process control of the amount of the solution prior to freeze-drying.TESTS Uniformity of dosage units .Powders for injections or infusions comply with the test for uniformity of dosage units (2.9.40)or,where justified and authorised,with the tests for uniformity of content and/or uniformity of mass shown below.Herbal drugs and herbal drug preparations present in the dosage form are not subject to the provisions of this paragraph.Uniformity of content (2.9.6).Unless otherwise prescribed or justifiedand authorised,powders for injections or infusions with a content of active substance less than 2mgor less than 2per cent of the total mass,or with a unit mass equal to or less than 40mg comply with test A for uniformity of content of single-dose preparations.If the preparation contains more than one active substance,the requirement applies only to those substances that correspond to the above conditions.Uniformity of mass (2.9.5).Powders for injections or infusions complywith the test for uniformity of mass ofsingle-dose preparations.If the test for uniformity of content is prescribed for all the active substances,the test for uniformity of mass is not required.Bacterial endotoxins-pyrogens.Theycomplywith the requirements prescribed for injections or for infusions,after dissolution or suspension in a suitable volume of BELLING The label states the instructions for the preparation of injections and infusions.Gels for injections DEFINITION Gels for injections are sterile gels with a viscosity suitable to guarantee a modified release of the active substance(s)at the site of injection.Implants DEFINITION Implants are sterile,solid preparations of a size and shape suitable for parenteral implantation and release of the active substance(s)over an extended period of time.Each dose is provided in a sterile container.01/2008:1011PATCHES,TRANSDERMALEmplastra transcutaneaDEFINITIONTransdermal patches are flexible pharmaceutical preparations of varying sizes,containing one or more activesubstances.Theyare intendedto be applied to the unbrokenskin in order to deliver the active substance(s)to the systemiccirculation after passing through the skin barrier.Transdermalpatches normally consist of an outer covering which supports a preparation which contains the activesubstance(s).The transdermal patches are covered on thesite of the release surface of the preparation by a protective liner,which is removed before applying the patch to the skin.The outer covering is a backing sheet impermeable to the active substance(s)and normally impermeable to water,designed to support and protect the preparation.The outer covering may have the same dimensions as the preparation or it may be larger.In the latter case the overlapping border of the outer covering is covered by pressure-sensitive adhesive substances which assure the adhesion of the patchto the skin.The preparation contains the active substance(s)togetherwith excipients such as stabilisers,solubilisers or substances intended to modify the release rate or to enhance transdermal absorption.It may be a single layer or multi-layer solid orsemi-solid matrix,and in this case it is the compositionand structure of the matrix which determines the diffusion pattern of the active substance(s)to the skin.The matrix may contain pressure-sensitive adhesives which assure theadhesion of the preparation to the skin.The preparation may exist as a semi-solid reservoir one side of which is amembranewhich may control the release and the diffusion of the active substance(s)from the preparation.The pressure-sensitive adhesive substances may,in this case,beapplied to some or all parts of the membrane,or only aroundthe border of the membrane of the outer covering.When applied to the dried,clean and unbrokenskin,thetransdermalpatch adheres firmly to the skin by gentle pressure of the hand or the fingers and can be peeled offwithout causing appreciable injury to the skin or detachment of thepreparation from the outer covering.The patch mustnot be irritant or sensitising to the skin,even after repeated applications.The protective liner generally consists of a sheet of plastic ormetal material.When removed,the protective liner does notdetach the preparation (matrix or reservoir)or the adhesive from the patch.Transdermal patches are normally individually enclosed in sealed sachets.PRODUCTIONInthe manufacture,packaging,storage and distributionof transdermalpatches suitable means are taken to ensuretheir microbial quality;recommendations onthis aspect are provided in the text on Microbiological quality ofpharmaceutical preparations (5.1.4).TESTSUniformity ofdosageunits .Transdermal patchescomplywith the test for uniformity of dosage units (2.9.40)or,where justified and authorised,with the test for uniformity General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts 737。



EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.0ParenteralpreparationsMucoadhesive preparations DEFINITION Mucoadhesive preparations contain one or more active substances intended for systemic absorption through the buccal mucosa over a prolongedperiodof time.They may be supplied as mucoadhesive buccal tablets or as other mucoadhesive solid or semi-solid preparations.Mucoadhesive buccal tablets are prepared by compressionof mono-or multi-layeredtablets.They usually containhydrophilic polymers,which on wetting with the salivaproduce a flexible hydrogel that adheres to the buccal mucosa.PRODUCTION In the manufacture of mucoadhesive buccal tablets,measures are taken to ensure that they possess suitablemechanical strength to resist handling without crumbling or breaking.This may bedemonstratedby examining the Friability of uncoated tablets (2.9.7)and the Resistance to crushing of tablets (2.9.8).TESTS Dissolution .Unlessotherwisejustified and authorised,a suitable test is carried out to demonstrate the appropriate release of the active substance(s).01/2008:0520PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS Parenteralia The requirementsof this monograph do not necessarily apply to products derived fromhuman blood,toimmunological preparations,or radiopharmaceutical preparations.Special requirements may apply to preparations for veterinary use depending on the species of animal for which the preparation is intended.DEFINITION Parenteral preparations are sterilepreparations intended for administration by injection,infusion or implantation into the human or animal body.Parenteral preparations may require the use of excipients,for example to make the preparation isotonic with respect to blood,to adjustthe pH,to increase solubility,to prevent deterioration of the activesubstancesor to provideadequateantimicrobial properties,but not to adversely affect the intended medicinal action of the preparation or,at the concentrations used,to cause toxicity or undue local irritation.Containers for parenteral preparations are made as far as possible frommaterialsthat are sufficiently transparentto permit the visual inspection of the contents,except for implants and in other justified and authorised cases.Where applicable,the containers for parenteral preparations comply with the requirements for Materials used for the manufacture of containers (3.1and subsections)and Containers (3.2and subsections).Parenteral preparations are supplied in glass containers (3.2.1)or in other containers such as plastic containers (3.2.2,3.2.2.1and 3.2.9)and prefilled syringes.The tightness of the containeris ensured bysuitablemeans.Closuresensure a good seal,prevent the access of micro-organisms and other contaminants and usually permit the withdrawal ofa part or the whole of the contents without removal of the closure.The plasticmaterials or elastomers (3.2.9)used to manufacture the closures are sufficiently firm and elastic to allow the passage of a needle with the least possible shedding ofparticles.Closures for multidose containers aresufficiently elastic to ensure that the puncture is resealedwhen the needle is withdrawn.Severalcategories of parenteral preparations may be distinguished:—injections,—infusions,—concentrates for injections or infusions,—powders for injections or infusions,—gels for injections,—implants.PRODUCTIONDuringthe developmentof a parenteral preparation,theformulation for which contains an antimicrobial preservative,the effectiveness of the chosen preservative shall be demonstratedto the satisfaction of the competent authority.A suitable test method togetherwithcriteria forjudgingthe preservative properties of the formulation are provided under Efficacy of antimicrobial preservation (5.1.3).Parenteral preparations are prepared using materials and methods designed to ensure sterility and to avoidthe introduction of contaminants and thegrowth ofmicro-organisms.Recommendations on this aspect areprovided in the text on Methods of preparation of sterile products (5.1.1).Water used in the manufacture of parenteral preparationscomplies with the requirements of water for injections in bulk stated in the monograph on Water for injections (0169).TESTSParticulate contamination:sub-visible particles (2.9.19).For preparations for human use,solutions for infusion orsolutions for injection comply with the test.Inthe case of preparations for subcutaneous or intramuscular injection,higher limits may be appropriate.Radiopharmaceutical preparations are exempt from these requirements.Preparations for which the label states thatthe product is to be used with a final filter are exempt from these requirements,providing it has been demonstrated that the filter delivers a solution that complies with the test.For preparations for veterinary use,whensupplied in containers with a nominal content of more than 100ml and when the content is equivalent to a dose of more than1.4ml per kilogram of body mass,solutions for infusion orsolutions for injection comply with the test for particulate contamination:sub-visible particles.Sterility (2.6.1).Parenteral preparations comply with the test for sterility.STORAGEIn a sterile,airtight,tamper-proof container.LABELLINGThe label states:—the name andconcentration of any added antimicrobial preservative,—where applicable,that the solution is to be used in conjunction with a final filter,—where applicable,that the preparation is free frombacterial endotoxins or that it is apyrogenic.General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts 735Parenteral preparations EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA6.0InjectionsDEFINITIONInjections are sterile solutions,emulsions or suspensions. They are prepared by dissolving,emulsifying or suspending the active substance(s)and any added excipients in water,in a suitable non-aqueous liquid,that may be non-sterile where justified,or in a mixture of these vehicles.Solutions for injection,examined under suitable conditions of visibility,are clear and practically free from particles. Emulsions for injection do not show any evidence of phase separation.Suspensions for injection may show a sediment which is readily dispersed on shaking to give a suspension which remains sufficiently stable to enable the correct dose to be withdrawn.Multidose preparations.Multidose aqueous injections contain a suitable antimicrobial preservative at an appropriate concentration except when the preparation itself has adequate antimicrobial properties.When a preparation for parenteral use is presented in a multidose container, the precautions to be taken for its administration and more particularly for its storage between successive withdrawals are given.Antimicrobial preservatives.Aqueous preparations which are prepared using aseptic precautions and which cannot be terminally sterilised may contain a suitable antimicrobial preservative in an appropriate concentration.No antimicrobial preservative is added when:—the volume to be injected in a single dose exceeds15ml, unless otherwise justified,—the preparation is intended for administration by routes where,for medical reasons,an antimicrobial preservative is not acceptable,such as intracisternally,epidurally,intrathecally or by any route giving access to thecerebrospinal fluid,or intra-or retro-ocularly.Such preparations are presented in single-dose containers.PRODUCTIONIn the manufacture of injections containing dispersed particles,measures are taken to ensure a suitable and controlled particle size with regard to the intended use. Single-dose preparations.The volume of the injection in a single-dose container is sufficient to permit the withdrawal and administration of the nominal dose using a normal technique(2.9.17).TESTSUniformity of dosage units.Single-dose suspensions for injection comply with the test for uniformity of dosage units (2.9.40)or,where justified and authorised,with the test for uniformity of content shown below.Herbal drugs and herbal drug preparations present in the dosage form are not subject to the provisions of this paragraph.Uniformity of content(2.9.6).Unless otherwise prescribed or justified and authorised,single-dose suspensions for injection with a content of active substance less than2mg or less than2per cent of the total mass comply with test A for uniformity of content of single-dose preparations.Ifthe preparation contains more than one active substance, the requirement applies only to those substances that correspond to the above conditions.Bacterial endotoxins-pyrogens.A test for bacterial endotoxins(2.6.14)is carried out or,where justified and authorised,the test for pyrogens(2.6.8).Recommendations on the limits for bacterial endotoxins are given in chapter2.6.14.Preparations for human use.The preparation complies with a test for bacterial endotoxins(2.6.14)or with the test for pyrogens(2.6.8).Preparations for veterinary use.When the volume to be injected in a single dose is15ml or more and is equivalent to a dose of0.2ml or more per kilogram of body mass,the preparation complies with a test for bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)or with the test for pyrogens(2.6.8).Any preparation.Where the label states that the preparation is free from bacterial endotoxins or apyrogenic,respectively, the preparation complies with a test for bacterial endotoxins (2.6.14)or with the test for pyrogens(2.6.8),respectively.InfusionsDEFINITIONInfusions are sterile,aqueous solutions or emulsions with water as the continuous phase.They are usually made isotonic with respect to blood.They are principally intended for administration in large volume.Infusions do not contain any added antimicrobial preservative.Solutions for infusion,examined under suitable conditions of visibility are clear and practically free from particles. Emulsions for infusion do not show any evidence of phase separation.PRODUCTIONIn the manufacture of infusions containing dispersed particles,measures are taken to ensure a suitable and controlled particle size with regard to the intended use. The volume of the infusion in the container is sufficientto permit the withdrawal and administration of the nominal dose using a normal technique(2.9.17).TESTSBacterial endotoxins-pyrogens.They comply with a test for bacterial endotoxins(2.6.14)or,where justified and authorised,with the test for pyrogens(2.6.8).For the latter test inject10ml per kilogram of body mass into each rabbit, unless otherwise justified and authorised. Concentrates for injections or infusions DEFINITIONConcentrates for injections or infusions are sterile solutions intended for injection or infusion after dilution.They are diluted to a prescribed volume with a prescribed liquid before administration.After dilution,they comply with the requirements for injections or for infusions.TESTSBacterial endotoxins-pyrogens.They comply with the requirements prescribed for injections or for infusions,after dilution to a suitable volume.Powders for injections or infusions DEFINITIONPowders for injections or infusions are solid,sterile substances distributed in their final containers and which,when shaken with the prescribed volume of a prescribed sterile liquid rapidly form either clear and736See the information section on general monographs(cover pages)EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.0Patches,transdermal practically particle-free solutions or uniform suspensions.After dissolution or suspension,they comply with therequirements for injections or for infusions.Freeze-dried products for parenteral use are considered aspowders for injections or infusions.PRODUCTION The uniformity of contentand uniformityof mass offreeze-dried products for parenteral use are ensured by the in-process control of the amount of the solution prior to freeze-drying.TESTS Uniformity of dosage units .Powders for injections or infusions comply with the test for uniformity of dosage units (2.9.40)or,where justified and authorised,with the tests for uniformity of content and/or uniformity of mass shown below.Herbal drugs and herbal drug preparations present in the dosage form are not subject to the provisions of this paragraph.Uniformity of content (2.9.6).Unless otherwise prescribed or justifiedand authorised,powders for injections or infusions with a content of active substance less than 2mgor less than 2per cent of the total mass,or with a unit mass equal to or less than 40mg comply with test A for uniformity of content of single-dose preparations.If the preparation contains more than one active substance,the requirement applies only to those substances that correspond to the above conditions.Uniformity of mass (2.9.5).Powders for injections or infusions complywith the test for uniformity of mass ofsingle-dose preparations.If the test for uniformity of content is prescribed for all the active substances,the test for uniformity of mass is not required.Bacterial endotoxins-pyrogens.Theycomplywith the requirements prescribed for injections or for infusions,after dissolution or suspension in a suitable volume of BELLING The label states the instructions for the preparation of injections and infusions.Gels for injections DEFINITION Gels for injections are sterile gels with a viscosity suitable to guarantee a modified release of the active substance(s)at the site of injection.Implants DEFINITION Implants are sterile,solid preparations of a size and shape suitable for parenteral implantation and release of the active substance(s)over an extended period of time.Each dose is provided in a sterile container.01/2008:1011PATCHES,TRANSDERMALEmplastra transcutaneaDEFINITIONTransdermal patches are flexible pharmaceutical preparations of varying sizes,containing one or more activesubstances.Theyare intendedto be applied to the unbrokenskin in order to deliver the active substance(s)to the systemiccirculation after passing through the skin barrier.Transdermalpatches normally consist of an outer covering which supports a preparation which contains the activesubstance(s).The transdermal patches are covered on thesite of the release surface of the preparation by a protective liner,which is removed before applying the patch to the skin.The outer covering is a backing sheet impermeable to the active substance(s)and normally impermeable to water,designed to support and protect the preparation.The outer covering may have the same dimensions as the preparation or it may be larger.In the latter case the overlapping border of the outer covering is covered by pressure-sensitive adhesive substances which assure the adhesion of the patchto the skin.The preparation contains the active substance(s)togetherwith excipients such as stabilisers,solubilisers or substances intended to modify the release rate or to enhance transdermal absorption.It may be a single layer or multi-layer solid orsemi-solid matrix,and in this case it is the compositionand structure of the matrix which determines the diffusion pattern of the active substance(s)to the skin.The matrix may contain pressure-sensitive adhesives which assure theadhesion of the preparation to the skin.The preparation may exist as a semi-solid reservoir one side of which is amembranewhich may control the release and the diffusion of the active substance(s)from the preparation.The pressure-sensitive adhesive substances may,in this case,beapplied to some or all parts of the membrane,or only aroundthe border of the membrane of the outer covering.When applied to the dried,clean and unbrokenskin,thetransdermalpatch adheres firmly to the skin by gentle pressure of the hand or the fingers and can be peeled offwithout causing appreciable injury to the skin or detachment of thepreparation from the outer covering.The patch mustnot be irritant or sensitising to the skin,even after repeated applications.The protective liner generally consists of a sheet of plastic ormetal material.When removed,the protective liner does notdetach the preparation (matrix or reservoir)or the adhesive from the patch.Transdermal patches are normally individually enclosed in sealed sachets.PRODUCTIONInthe manufacture,packaging,storage and distributionof transdermalpatches suitable means are taken to ensuretheir microbial quality;recommendations onthis aspect are provided in the text on Microbiological quality ofpharmaceutical preparations (5.1.4).TESTSUniformity ofdosageunits .Transdermal patchescomplywith the test for uniformity of dosage units (2.9.40)or,where justified and authorised,with the test for uniformity General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts 737。
2020版药典制剂通则之注射剂注射剂系指原料药物或与适宜的辅料制成的供注入体内的无菌制剂。
注射剂可分为注射液、注射用无菌粉末与注射用浓溶液等。
注射液系指原料药物或与适宜的辅料制成的供注入体内的无菌液体制剂,包括溶液型、乳状液型和混悬型等注射液。
可用于皮下注射、皮内注射、肌内注射、静脉注射、静脉滴注、鞘内注射、椎管内注射等。
其中,供静脉滴注用的大容量注射液(除另有规定外,一般不小于100ml,生物制品一般不小于50ml)也可称为输液。
中药注射剂一般不宜制成混悬型注射液。
乳状液型注射液,不得用于椎管内注射。
混悬型注射液不得用于静脉注射或椎管内注射。
注射用无菌粉末系指原料药物或与适宜辅料制成的供临用前用无菌溶液配制成注射液的无菌粉末或无菌块状物,可用适宜的注射用溶剂配制后注射,也可用静脉输液配制后静脉滴注。
以冷冻干燥法制备的注射用无菌粉末,也可称为注射用冻干制剂。
注射用无菌粉末配制成注射液后应符合注射剂的要求。
注射用浓溶液系指原料药物与适宜辅料制成的供临用前稀释后注射的无菌浓溶液。
注射用浓溶液稀释后应符合注射剂的要求。
注射剂在生产与贮藏期间应符合下列规定。
一、注射剂所用的原辅料应从来源及生产工艺等环节进行严格控制并应符合注射用的质量要求。
除另有规定外,制备中药注射剂的饮片等原料药物应严格按各品种项下规定的方法提取、纯化,制成半成品、成品,并应进行相应的质量控制。
生物制品原液、半成品和成品的生产及质量控制应符合相关品种要求。
二、注射剂所用溶剂应安全无害,并与其他药用成分兼容性良好,不得影响活性成分的疗效和质量。
一般分为水性溶剂和非水性溶剂。
(1)水性溶剂最常用的为注射用水,也可用0.9%氯化钠溶液或其他适宜的水溶液。
(2)非水性溶剂常用植物油,主要为供注射用的大豆油,其他还有乙醇、丙二醇和聚乙二醇等。
供注射用的非水性溶剂,应严格限制其用量,并应在各品种项下进行相应的检查。
三、配制注射剂时,可根据需要加入适宜的附加剂,如渗透压调节剂、pH调节剂、增溶剂、助溶剂、抗氧剂、抑菌剂、乳化剂、助悬剂等。
0100本制剂通则中原料药物系指用于制剂制备的活性物质,包括中药、化学药、生物制品原料药物。
中药原料药物系指 饮片、植物油脂、提取物、有效成分或有效部位》化学药原料药物系指化学合成、或来源于天然物质或采用生物技术获 得的有效成分(即原料药);生物制品原料药物系指生物制品原液或将生物制品原液干燥后制成的原粉。
本制剂通则中各剂型、亚剂型并不适用于所有原料药物,而应取决于原料药物特性、临床给药需求以及药品的安 全性、有效性和稳定性等。
本制剂通则适用于中药、化学药和治疗用生物制品(包 括血液制品、免疫血清、细胞因子、单克隆抗体、免疫调节 剂、微生态制剂等)。
预防类生物制品,应符合本版药典三部相应品种项下的有关要求。
除另有规定外,生物制品应于2〜8X:避光贮存和运输。
片剂系指原料药物或与适宜的辅料制成的圆形或异形的 片状固体制剂。
中药还有浸膏片、半浸膏片和全粉片等。
片剂以口服普通片为主,另有含片、舌下片、口腔貼 片、咀嚼片、分散片、可溶片、泡腾片、阴道片、阴道泡腾 片、缓释片、控释片、肠溶片与口崩片等。
含片系指含于口腔中缓慢溶化产生局部或全身作用的片剂。
含片中的原料药物一般是易溶性的,主要起局部消炎、杀菌、收敛、止痛或局部麻醉等作用。
舌下片系指置于舌下能迅速溶化,药物经舌下黏膜吸 收发挥全身作用的片剂。
舌下片中的原料药物应易于直接吸收,主要适用于急症 的治疗。
口腔貼片系指粘贴于口腔,经黏膜吸收后起局部或全身作用的片剂。
口腔貼片应进行溶出度或释放度(通则0931)检查。
咀嚼片系指于口腔中咀嚼后吞服的片剂。
咀嚼片一般应选择甘露醇、山梨醉、蔗糖等水溶性辅料作填充剂和黏合剂。
咀嚼片的硬度应适宜。
分散片系指在水中能迅速崩解并均勻分散的片剂。
分散片中的原料药物应是难溶性的。
分散片可加水分散 后口服,也可将分散片含于口中吮服或吞服。
分散片应进行溶出度(通则0931)和分散均匀性检查。
可溶片系指临用前能溶解于水的非包衣片或薄膜包衣片剂。
Designation as a Pharmacy bulk package is limited to prepara-〈1〉 INJECTIONStions from Nomenclature categories 1, 2, or 3 as defined above.Pharmacy bulk packages, although containing more than one single dose, are exempt from the multiple-dose container volume limit of 30 mL and the requirement that they contain a substance or suitable mixture of substances to prevent the growth of microorganisms.Where a container is offered as a Pharmacy bulk package, the INTRODUCTIONlabel shall (a) state prominently “Pharmacy Bulk Package—Not for direct infusion,” (b) contain or refer to information on proper tech-Parenteral articles are preparations intended for injection through niques to help assure safe use of the product, and (c) bear a state-the skin or other external boundary tissue, rather than through the ment limiting the time frame in which the container may be used alimentary canal, so that the active substances they contain are ad-once it has been entered, provided it is held under the labeled stor-ministered, using gravity or force, directly into a blood vessel, or-age conditions.gan, tissue, or lesion. Parenteral articles are prepared scrupulously by methods designed to ensure that they meet Pharmacopeial re-quirements for sterility, pyrogens, particulate matter, and other con-LARGE - AND SMALL -VOLUME INJECTIONStaminants, and, where appropriate, contain inhibitors of the growth of microorganisms. An Injection is a preparation intended for par-Where used in this Pharmacopeia, the designation Large-volume enteral administration and/or for constituting or diluting a parenteral intravenous solution applies to a single-dose injection that is in-article prior to administration.tended for intravenous use and is packaged in containers labeled as containing more than 100 mL. The designation Small-volume Injec-tion applies to an Injection that is packaged in containers labeled as NOMENCLATURE AND DEFINITIONScontaining 100 mL or less.BIOLOGICSNomenclature *The following nomenclature pertains to five general types of The Pharmacopeial definitions for sterile preparations for paren-preparations, all of which are suitable for, and intended for, paren-teral use generally do not apply in the case of the biologics because teral administration. They may contain buffers, preservatives, or of their special nature and licensing requirements (see Biologics other added substances.〈1041〉).1.[DRUG] Injection—Liquid preparations that are drug sub-stances or solutions thereof.2.[DRUG] for Injection—Dry solids that, upon the addition ofINGREDIENTSsuitable vehicles, yield solutions conforming in all respects to the requirements for Injections.3.[DRUG] Injectable Emulsion—Liquid preparations of drugVehicles and Added Substancessubstances dissolved or dispersed in a suitable emulsion medium.Aqueous Vehicles—The vehicles for aqueous Injections meet 4.[DRUG] Injectable Suspension—Liquid preparations of sol-the requirements of the Pyrogen Test 〈151〉 or the Bacterial Endo-ids suspended in a suitable liquid medium.toxins Test 〈85〉, whichever is specified. Water for Injection gener-5.[DRUG] for Injectable Suspension—Dry solids that, upon theally is used as the vehicle, unless otherwise specified in the individ-addition of suitable vehicles, yield preparations conforming ual monograph. Sodium chloride may be added in amounts in all respects to the requirements for Injectable Suspensions.sufficient to render the resulting solution isotonic; and Sodium Chloride Injection, or Ringer’s Injection, may be used in whole or in part instead of Water for Injection, unless otherwise specified in Definitionsthe individual monograph. For conditions applying to other ad-juvants, see Added Substances in this chapter.Other Vehicles—Fixed oils used as vehicles for nonaqueous In-jections are of vegetable origin, are odorless or nearly so, and have PHARMACY BULK PACKAGEno odor suggesting rancidity. They meet the requirements of the test for Solid paraffin under Mineral Oil, the cooling bath being main-A Pharmacy bulk package is a container of a sterile preparation tained at 10°, have a Saponification Value between 185 and 200for parenteral use that contains many single doses. The contents are (see Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉), have an Iodine Value between 79intended for use in a pharmacy admixture program and are re-and 141 (see Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉), and meet the requirements stricted to the preparation of admixtures for infusion or, through a of the following tests.sterile transfer device, for the filling of empty sterile syringes.Unsaponifiable Matter—Reflux on a steam bath 10 mL of the oil The closure shall be penetrated only one time after constitution with 15 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 6) and 30 mL of with a suitable sterile transfer device or dispensing set which allows alcohol, with occasional shaking until the mixture becomes clear.measured dispensing of the contents. The Pharmacy bulk package Transfer the solution to a shallow dish, evaporate the alcohol on a is to be used only in a suitable work area such as a laminar flow steam bath, and mix the residue with 100 mL of water: a clear solu-hood (or an equivalent clean air compounding area).tion results.*This nomenclature has been adopted by the USP Drug Nomenclature Committee for Free Fatty Acids—The free fatty acids in 10g of oil require for implementation by supplemental revisions of USP 23-NF 18. For currently official neutralization not more than 2.0 mL of 0.020N sodium hydroxide monograph titles in the form Sterile [DRUG] that have not yet been revised, the following nomenclature continues in use in this Pharmacopeia:(1) medicaments or (see Fats and Fixed Oils 〈401〉).solutions or emulsions thereof suitable for injection, bearing titles of the form [DRUG]Synthetic mono- or diglycerides of fatty acids may be used as Injection; (2) dry solids or liquid concentrates containing no buffers, diluents, or other vehicles, provided they are liquid and remain clear when cooled to added substances, and which, upon the addition of suitable solvents, yield solutions conforming in all respects to the requirements for Injections, and which are 10° and have an Iodine Value of not more than 140 (see Fats and distinguished by titles of the form Sterile [DRUG]; (3) preparations the same as those Fixed Oils 〈401〉).described under (2) except that they contain one or more buffers, diluents, or other These and other nonaqueous vehicles may be used, provided they added substances, and which are distinguished by titles of the form [DRUG] for are safe, in the volume of Injection administered, and also provided Injection; (4) solids which are suspended in a suitable fluid medium and which are not to be injected intravenously or into the spinal canal, distinguished by titles of the form they do not interfere with the therapeutic efficacy of the preparation Sterile [DRUG] Suspension; and (5) dry solids which, upon the addition of suitable or with its response to prescribed assays and tests.vehicles, yield preparations conforming in all respects to the requirements for Sterile Added Substances—Suitable substances may be added to prepa-Suspensions, and which are distinguished by titles of the form Sterile [DRUG] for Suspension.rations intended for injection to increase stability or usefulness, un-less proscribed in the individual monograph, provided they are Containers for Injections that are intended for use as dialysis, harmless in the amounts administered and do not interfere with the hemofiltration, or irrigation solutions and that contain a volume of therapeutic efficacy or with the responses to the specified assays more than 1 L are labeled to indicate that the contents are not in-and tests. No coloring agent may be added, solely for the purpose of tended for use by intravenous infusion.coloring the finished preparation, to a solution intended for paren-Injections intended for veterinary use are labeled to that effect. teral administration (see also Added Substances under General No-The container is so labeled that a sufficient area of the container tices and Antimicrobial Effectiveness Testing 〈51〉).remains uncovered for its full length or circumference to permit in-spection of the contents.Observe special care in the choice and use of added substances inpreparations for injection that are administered in a volume exceed-ing 5 mL. The following maximum limits prevail unless otherwiseSTRENGTH AND TOTAL VOLUME FOR SINGLE- AND directed: for agents containing mercury and the cationic, surface-active compounds, 0.01%; for chlorobutanol, cresol, phenol, and MULTIPLE-DOSE INJECTABLE DRUG PRODUCTS similar types of substances, 0.5%; and for sulfur dioxide, or anequivalent amount of the sulfite, bisulfite, or metabisulfite of potas-For single-dose and multiple-dose injectable drug products, the sium or sodium, 0.2%.strength per total volume should be the primary and prominent ex-pression on the principal display panel of the label, followed in A suitable substance or mixture of substances to prevent theclose proximity by strength per mL enclosed by parentheses. For growth of microorganisms must be added to preparations intendedcontainers holding a volume of less than 1 mL, the strength per for injection that are packaged in multiple-dose containers, regard-fraction of a mL should be the only expression of strength. Strength less of the method of sterilization employed, unless one of the fol-per single mL should be expressed as mg/mL, not mg/1 mL. lowing conditions prevails: (1) there are different directions in theThe following formats are acceptable for contents of greater individual monograph; (2) the substance contains a radionuclidethan 1 mL:with a physical half-life of less than 24 hours; and (3) the activeTotal strength/total volume: 500 mg/10 mLingredients are themselves antimicrobial. Such substances are usedStrength/mL: 50 mg/mLin concentrations that will prevent the growth of or kill microorgan-orisms in the preparations for injection. Such substances also meet theTotal strength/total volume: 25,000 Units/5 mL requirements of Antimicrobial Effectiveness Testing 〈51〉 and Anti-Strength/mL: 5,000 Units/mLmicrobial Agents—Content 〈341〉. Sterilization processes are em-The following format is acceptable for contents of less than 1 ployed even though such substances are used (see also SterilizationmL: 12.5 mg/0.625 mLand Sterility Assurance of Compendial Articles 〈1211〉). The air inThere are, however, some exceptions to expressing strength per the container may be evacuated or be displaced by a chemically in-total volume. In certain cases, the primary and prominent expres-ert gas. Where specified in a monograph, information regardingsion of the total drug content per container would not be effective in sensitivity of the article to oxygen is to be provided in the labeling.preventing medication errors (e.g., insulin). An example is the useof lidocaine or other similar drugs used as a local anesthetic wherethe product is ordered and administered by percentage (e.g., 1%, LABELS AND LABELING2%) or a local anesthetic in combination with epinephrine that isexpressed as a ratio (e.g., 1:100,000). In such cases, the totalstrength should be expressed: for example, 1% (100 mg/10 mL).Dry solids, which need to be reconstituted, should follow the same Labeling format, with the exception that only the total strength of the drugshould be listed, not the strength/total volume or strength/mL. NOTE—See definitions of “label” and “labeling” in Labeling in(Official February 1, 2009) the section Preservation, Packaging, Storage, and Labeling of theGeneral Notices and Requirements.The label states the name of the preparation; in the case of a liq-Aluminum in Large-Volume Parenterals (LVPs), uid preparation, the percentage content of drug or amount of drug in Small-Volume Parenterals (SVPs), and Pharmacy a specified volume; in the case of a dry preparation, the amount ofBulk Packages (PBPs) Used in Total Parenteral active ingredient; the route of administration; a statement of storageconditions and an expiration date; the name and place of business of Nutrition (TPN) Therapythe manufacturer, packer, or distributor; and an identifying lot num-ber. The lot number is capable of yielding the complete manufactur-(a)The aluminum content of LVPs used in TPN therapy must ing history of the specific package, including all manufacturing,not exceed 25 µg per L (µg/L).filling, sterilizing, and labeling operations.(b)The package insert of LVPs used in TPN therapy must state Where the individual monograph permits varying concentrations that the drug product contains no more than 25 µg of alumi-of active ingredients in the large-volume parenteral, the concentra-num per L. This information must be contained in the “Pre-tion of each ingredient named in the official title is stated as if part cautions” section of the labeling of all LVPs used in TPN of the official title, e.g., Dextrose Injection 5%, or Dextrose (5%)therapy.and Sodium Chloride (0.2%) Injection.(c)If the maximum amount of aluminum in SVPs and PBPs is The labeling includes the following information if the complete25 µg per L (µg/L) or less, instead of stating the exact formula is not specified in the individual monograph: (1) In the case amount of aluminum that each contains, as in paragraph (d), of a liquid preparation, the percentage content of each ingredient or the immediate container label for SVPs and PBPs used in the the amount of each ingredient in a specified volume, except that preparation of TPN parenterals (with exceptions as noted be-ingredients added to adjust to a given pH or to make the solution low) may state: “Contains no more than 25 µg/L of alumi-isotonic may be declared by name and a statement of their effect;num”. If the SVP or PBP is a lyophilized powder, the im-and (2) in the case of a dry preparation or other preparation to mediate container label may state the following: “When which a diluent is intended to be added before use, the amount of reconstituted in accordance with the package insert instruc-each ingredient, the composition of recommended diluent(s) [the tions, the concentration of aluminum will be no more than 25 name(s) alone, if the formula is specified in the individual mono-µg/L”.graph], the amount to be used to attain a specific concentration of(d)The maximum level of aluminum at expiry must be stated on active ingredient and the final volume of solution so obtained, a the immediate container label of all SVPs and PBPs used in brief description of the physical appearance of the constituted solu-the preparation of TPN parenterals and injectable emulsions. tion, directions for proper storage of the constituted solution, and an The aluminum content must be stated as follows: “Contains expiration date limiting the period during which the constituted no more than __ µg/L of aluminum”. The immediate con-solution may be expected to have the required or labeled potency if tainer label of all SVPs and PBPs that are lyophilized powder it has been stored as ed in the preparation of TPN solutions must contain the fol-lowing statement: “When reconstituted in accordance with pul is prohibited, except for Potassium Chloride for Injection the package insert instructions, the concentration of alumi-Concentrate.num will be no more than __ µg/L.” This maximum amount of aluminum must be stated as the highest one of the follow-Neuromuscular Blocking and Paralyzing Agentsing three levels:(1)The highest level for the batches produced during the lastAll injectable preparations of neuromuscular blocking agents and three yearsparalyzing agents must be packaged in vials with a cautionary state-(2)The highest level for the latest five batchesment printed on the ferrules or cap overseals. Both the container cap (3)The maximum level in terms of historical levels, but only un-ferrule and the cap overseal must bear in black or white print til completion of production of the first five batches after July (whichever provides the greatest color contrast with the ferrule or 26, 2004.cap color) the words: “Warning: Paralyzing Agent” or “Paralyzing The package insert for all LVPs, SVPs, and PBPs used in the Agent” (depending on the size of the closure system). Alternatively,preparation of TPN products must contain a warning statement.the overseal may be transparent and without words, allowing for This warning must be contained in the “Warning” section of the visualization of the warning labeling on the closure ferrule.labeling and must state the following: “WARNING: This product contains aluminum that may be toxic. Aluminum may reach toxic levels with prolonged parenteral administration if kidney function is Containers for Sterile Solidsimpaired. Premature neonates are particularly at risk because their kidneys are immature, and they require large amounts of calcium Containers, including the closures, for dry solids intended for and phosphate solutions that contain aluminum. Research indicates parenteral use do not interact physically or chemically with the that patients with impaired kidney function, including premature preparation in any manner to alter the strength, quality, or purity neonates, who receive parenteral levels of aluminum at greater than beyond the official requirements under the ordinary or customary 4 to 5 µg per kg per day accumulate aluminum at levels associated conditions of handling, shipment, storage, sale, and use.with central nervous system and bone toxicity. Tissue loading may A container for a sterile solid permits the addition of a suitable occur at even lower rates of administration of TPN products.”solvent and withdrawal of portions of the resulting solution or sus-pension in such manner that the sterility of the product is maintained.PACKAGING Where the Assay in a monograph provides a procedure for the Assay preparation, in which the total withdrawable contents are to be withdrawn from a single-dose container with a hypodermic nee-dle and syringe, the contents are to be withdrawn as completely as Containers for Injectionspossible into a dry hypodermic syringe of a rated capacity not ex-ceeding three times the volume to be withdrawn and fitted with a Containers, including the closures, for preparations for injections 21-gauge needle not less than 2.5 cm (1 inch) in length, with care do not interact physically or chemically with the preparations in any being taken to expel any air bubbles, and discharged into a con-manner to alter the strength, quality, or purity beyond the official tainer for dilution and assay.requirements under the ordinary or customary conditions of han-dling, shipment, storage, sale, and use. The container is made of material that permits inspection of the contents. The type of glass Volume in Containerpreferable for each parenteral preparation is usually stated in the individual monograph. Unless otherwise specified in the individual Each container of an injection is filled with sufficient excess of monograph, plastic containers may be used for packaging injections the labeled “size” or that volume which is to be withdrawn. See (see Containers—Plastics 〈661〉).Injections under Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms 〈1151〉.For definitions of single-dose and multiple-dose containers, see Containers in the General Notices and Requirements. Containers meet the requirements under Containers—Glass 〈660〉 and Con-DETERMINATION OF VOLUME OF INJECTION INtainers—Plastics 〈661〉.Containers are closed or sealed in such a manner as to prevent CONTAINERS contamination or loss of contents. Validation of container integrity must demonstrate no penetration of microbial contamination or Suspensions and emulsions must be shaken before withdrawal of chemical or physical impurities. In addition, the solutes and the ve-the contents and before the determination of the density. Oily and hicle must maintain their specified total and relative quantities or viscous preparations may be warmed according to the instructions concentrations when exposed to anticipated extreme conditions of on the label, if necessary, and thoroughly shaken immediately be-manufacturing and processing, and storage, shipment, and distribu-fore removing the contents. The contents are then cooled to tion. Closures for multiple-dose containers permit the withdrawal of 20°–25°C before measuring the volume.the contents without removal or destruction of the closure. The clo-Single-Dose Containers—Select 1 container if the volume of the sure permits penetration by a needle and, upon withdrawal of the container is 10 mL or more, 3 containers if the nominal volume is needle, closes at once, protecting the container against contamina-more than 3 mL and less than 10 mL, or 5 containers if the nominal tion. Validation of the multiple-dose container integrity must in-volume is 3 mL or less. Take up individually the total contents of clude verification that such a package prevents microbial contami-each container selected into a dry syringe of a capacity not exceed-nation or loss of product contents under anticipated conditions of ing three times the volume to be measured and fitted with a 21-multiple entry and use.gauge needle not less than 2.5 cm (1 inch) in length. Expel any air Piggyback containers are usually intravenous infusion containers bubbles from the syringe and needle, and then discharge the con-used to administer a second infusion through a connector of some tents of the syringe, without emptying the needle, into a standard-type or an injection port on the administration set of the first fluid,ized, dry cylinder (graduated to contain rather than to deliver the thereby avoiding the need for another injection site on the patient’s designated volumes) of such size that the volume to be measured body. Piggyback containers are also known as secondary infusion occupies at least 40% of its graduated volume. Alternatively, the containers.volume of the contents in mL may be calculated as the mass, in g,divided by the density. For containers with a nominal volume of 2mL or less, the contents of a sufficient number of containers may be Potassium Chloride for Injection Concentratepooled to obtain the volume required for the measurement, provided that a separate, dry syringe assembly is used for each container. The The use of a black closure system on a vial (e.g., a black flip-off contents of containers holding 10 mL or more may be determined button and a black ferrule to hold the elastomeric closure) or the use by means of opening them and emptying the contents directly into of a black band or series of bands above the constriction on an am-the graduated cylinder or tared beaker.The volume is not less than the nominal volume in the case of Injections packaged for intravascular use that may be used for containers examined individually or, in the case of containers with a intermittent, continuous, or bolus replacement fluid administration nominal volume of 2 mL or less, is not less than the sum of the during hemodialysis or other procedures, unless excepted above,nominal volumes of the containers taken collectively.must conform to the 1-L restriction.Multi-Dose Containers—For Injections in multiple-dose con-Injections labeled for veterinary use are exempt from packaging tainers labeled to yield a specific number of doses of a stated vol-and storage requirements concerning the limitation to single-dose ume, select 1 container, and proceed as directed for single-dose containers and the limitation on the volume of multiple-dose containers, using the same number of separate syringe assemblies as containers.the number of doses specified. The volume is such that each syringe delivers not less than the stated dose.Injections in Cartridges or Prefilled Syringes—Select 1 con-FOREIGN AND PARTICULATE MATTERtainer if the volume is 10 mL or more, 3 containers if the nominal volume is more than 3 mL and less than 10 mL, or 5 containers if All articles intended for parenteral administration shall be pre-the nominal volume is 3 mL or less. If necessary, fit the containers pared in a manner designed to exclude particulate matter as defined with the accessories required for their use (needle, piston, syringe)in Particulate Matter in Injections 〈788〉 and other foreign matter.and transfer the entire contents of each container without emptying Each final container of all parenteral preparations shall be inspected the needle into a dry tared beaker by slowly and constantly depress-to the extent possible for the presence of observable foreign and ing the piston. Determine the volume in mL, calculated as the mass,particulate matter (hereafter termed “visible particulates”) in its in g, divided by the density.contents. The inspection process shall be designed and qualified to The volume measured for each of the containers is not less than ensure that every lot of all parenteral preparations is essentially free the nominal volume.from visible particulates. Qualification of the inspection process Large-Volume Intravenous Solutions—For intravenous solu-shall be performed with reference to particulates in the visible range tions, select 1 container. Transfer the contents into a dry measuring of a type that might emanate from the manufacturing or filling pro-cylinder of such a capacity that the volume to be determined occu-cess. Every container whose contents shows evidence of visible par-pies at least 40% of the nominal volume of the cylinder. Measure ticulates shall be rejected. The inspection for visible particulates the volume transferred.may take place when inspecting for other critical defects, such as The volume is not less than the nominal volume.cracked or defective containers or seals, or when characterizing the appearance of a lyophilized product.Where the nature of the contents or the container-closure system permits only limited capability for the inspection of the total con-Labeling on Ferrules and Cap Oversealstents, the 100% inspection of a lot shall be supplemented with the inspection of constituted (e.g., dried) or withdrawn (e.g., dark am-Only cautionary statements are to appear on the top (circle) sur-ber container) contents of a sample of containers from the lot.face of the ferrule or cap overseal of a vial containing an injectable All large-volume Injections for single-dose infusion and small-product. A cautionary statement is one intended to prevent an immi-volume Injections are subject to the light obscuration or micro-nent life-threatening situation if the injectable drug is used inappro-scopic procedures and limits for subvisible particulate matter set priately. Examples of such statements include but are not limited to forth in Particulate Matter In Injections 〈788〉, unless otherwise the following: “Warning”, “Dilute Before Using”, “Paralyzing specified in the individual monograph. An article packaged as both Agent”, “I.M. Use Only”, and “Chemotherapy”.a large-volume and a small-volume Injection meets the require-The text must be in contrasting color and conspicuous under ordi-ments set forth for small-volume Injections where the container is nary conditions of use. The cautionary statement may appear solely labeled as containing 100 mL or less, if the individual monograph on the ferrule, provided the cap overseal is constructed so as to al-states a test for Particulate Matter 〈788〉; it meets the requirements low the cautionary statement beneath the cap to be readily legible.set forth for large-volume Injections for single-dose infusion where Identifying numbers or letters, such as code numbers, lot num-the container is labeled as containing more than 100 mL. Injections bers, etc., may appear on the side (skirt) surface of the ferrule on administered exclusively by the intramuscular or subcutaneous vials containing injectable products. The appearance of such identi-route or packaged and labeled for use as irrigating solutions are ex-fying data on the skirt surface of the ferrule, placed where it does empt from requirements for Particulate Matter 〈788〉.not detract from, or interfere with, the cautionary statement on the top surface, should be considered to be a beneficial attribute of the in-process quality control of a product throughout the manufactur-ing process. Any anticounterfeiting scheme must not detract from or STERILITYinterfere with the cautionary statements.Under no circumstances would advertising such as company Sterility Tests—Preparations for injection meet the requirements names, logos, or product names be permitted to appear on the top under Sterility Tests 〈71〉.(circle) surface of any ferrule or cap overseal.(Official February 1, 2009)CONSTITUTED SOLUTIONSPackaging and StorageDry solids from which constituted solutions are prepared for in-jection bear titles of the form [DRUG] for Injection. Because these The volume of injection in single-dose containers provides the dosage forms are constituted at the time of use by the health care amount specified for parenteral administration at one time and in no practitioner, tests and standards pertaining to the solution as consti-case is more than sufficient to permit the withdrawal and adminis-tuted for administration are not included in the individual mono-tration of 1 L.graphs on sterile dry solids or liquid concentrates. However, in the Preparations intended for intraspinal, intracisternal, or peridural interest of assuring the quality of injection preparations as they are administration are packaged only in single-dose containers.actually administered, the following nondestructive tests are pro-Unless otherwise specified in the individual monograph, a multi-vided for demonstrating the suitability of constituted solutions when ple-dose container contains a volume of Injection sufficient to per-they are prepared just prior to use.mit the withdrawal of not more than 30 mL.Completeness and Clarity of Solution—Constitute the solution The following injections are exempt from the 1-L restriction of as directed in the labeling supplied by the manufacturer for the ster-the foregoing requirements relating to packaging:ile dry dosage form.1.Injections packaged for extravascular use as irrigation solu-A:The solid dissolves completely, leaving no visible residue tions or peritoneal dialysis solutions as undissolved matter.2.Injections packaged for intravascular use as parenteral nutri-B:The constituted solution is not significantly less clear than tion or as replacement or substitution fluid to be administeredan equal volume of the diluent or of Purified Water contained in a continuously during hemofiltrationsimilar vessel and examined similarly.。
附录ⅠB 注射剂
注射剂系指药物与适宜的溶剂或分散介质制成的供注入体内的溶液,乳状液或混悬液及供注入体内的溶液、乳状液或混悬液及供临用前配制或稀释成溶液或混悬液的粉末或浓溶液的无菌制剂。
注射剂可分为注射液、注射用无菌粉末与注射用浓溶液。
注射液包括溶液型、乳状液型或混悬型注射液,可用于肌内注射、静脉注射、静脉滴注等。
其中,供静脉注射用的大体积(除另有规定外,一般不小于100ml)注射液也称静脉输液。
注射用无菌粉末系指药物制成的供临用前用适宜的无菌溶液配制成澄清溶液或均匀混悬液的无菌粉末或无菌块状物。
可用适宜的注射用溶剂配制后注射,也可用静脉输液配制后静脉滴注。
无菌粉末用溶剂结晶法、喷雾干燥法或冷冻干燥法等制得。
注射用浓溶液系指药物制成的供临用前稀释后静脉滴注用的无菌浓溶液。
注射液在生产与贮藏期间应符合下列有关规定。
一、溶液型注射液应澄明;除另有规定外,混悬型注射液中药物粒度应控制在15µm以下,含15~20µm (间有个别20~50µm)者,不得超过10%,若有可见沉淀,振摇时应容易分散均匀,混悬型注射液不得用于静脉注射或椎管注射;乳状液型注射液应稳定,不得有相分离现象,不得用于椎管注射。
静脉用乳状液型注射液中乳滴的粒度90%应在1µm以下,不得有大于5µm的乳滴。
除另有规定外,静脉输液应尽可能与血液等渗。
二、注射剂所用的原辅料应从来源及工艺等生产环节进行严格控制并应符合注射用的质量要求。
注射剂所用溶剂必须安全无害,并不得影响疗效额质量。
一般分为水性溶剂和非水性溶剂。
(1)水性溶剂最常用的为注射用水,也可用0.9%氯化钠溶液或其他适宜的水溶液。
(2)非水性溶剂常用的为植物油,主要为供注射用大豆油,其他还有乙醇、丙二醇和聚乙二醇等溶剂。
供注射用的非水性溶剂,应严格限制其用量,并应在品种项下进行相应的检查。
三、配制注射剂时,可根据药物的性质加入适宜的附加剂。
如渗透压调节剂、pH值调节剂、增溶剂、助溶剂、抗氧剂、抑菌剂、乳化剂、助悬剂等。
所用附加剂应不影响药物疗效,避免对检验产生干扰,使用浓度不得引起毒性或明显的刺激。
常用的抗氧剂有亚硫酸钠、亚硫酸氢钠和焦亚硫酸钠等,一般浓度为01.%~0.2%;常用的抑菌剂为0.5%苯酚、0.3%甲酚和0.5%三氯叔丁醇等。
多剂量包装的注射液可加适宜的抑菌剂,,抑菌剂的用量应能抑制注射液中微生物的生长,加有抑菌剂的注射液,仍应采用适宜的方法灭菌。
静脉输液与脑池内、硬膜外、椎管内用的注射液均不得加抑菌剂。
除另有规定外,一次注射量超过15ml
的注射液,不得加抑菌剂。
四、注射剂常用容器有玻璃安瓿、玻璃瓶、塑料安瓿、塑料瓶(袋)等。
容器的密封性,须用适宜的方法确证。
除另有规定外,容器应符合有关注射用玻璃容器和塑料容器的国家标准规定。
容器用胶塞特别是多剂量包装注射液用的胶塞要有足够的弹性和稳定性,其质量应符合有关国家标准规定。
除另有规定外,容器应足够透明,以便内容物的检视。
五、生产过程中应尽可能缩短注射剂的配制时间,防止微生物与热原的污染及药物变质。
静脉输液的配制过程更应严格控制。
制备混悬型注射液、乳状液型注射液过程中,要采取必要的措施,保证粒子大小符合国家标准的要求。
注射用无菌粉末应按无菌操作制备。
注射剂必要时进行相应的安全性检查,如异常毒性、过敏反应、溶血与凝聚、降压物质、热原或细菌内毒素等,均应符合要求。
六、灌装标示装量为不大于50ml的注射剂,应按下表适当增加装量。
除另有规定外,多剂量包装的注射剂,每一容器的装量不得超过10次注射量,增加装量应能保证每次注射用量。
接触空气易变质的药物,在灌装过程中,应排除容器内空气,可填充二氧化碳或氮等气体,立即熔封或严封。
七、熔封或严封后,一般应根据药物性质选用适宜的方法灭菌,必须保证成品无菌。
注射剂在灭菌时或灭菌后,应采用减压法或其他适宜的方法进行容器检漏。
八、除另有规定外,注射剂应避光保存。
九、注射剂所用辅料,在标签或说明书中应标明其名称,抑菌剂还应标明浓度;注射用无菌粉末,应注明注射用溶剂。
除另有规定外,注射剂还应进行以下相应检查。
【装量】注射剂及注射用浓溶液照下述方法检查,应符合规定。
检查法标示装量为不大于2ml者取供试品5支,2m以上至50ml者取供试品3支;开启时注意避免损失,将内容物分别用相应体积的干燥注射器及注射针头抽尽,然后注入经标化的量入式量筒内(量筒的大小应使待测体积至少占其额定体积的40%),在室温下检视。
测定油溶液或混悬液的装量时,应先加温摇匀,再用干燥注射器及注射针头抽尽后,同前法操作,放冷,检视,每支的装量均不得少于其标示量。
标示装量为50ml以上的注射液及注射用浓溶液照最低装量检查法(附录X F)检查,应符合规定。
【装量差异】除另有规定外,注射用无菌粉末照下述方法检查,应符合规定。
检查法取供试品5瓶(支),除去标签,铝盖,容器外壁用乙醇擦净,干燥,开启时注意避免玻璃屑等异物落入容器中,分别迅速精密称定,倾出内容物,容器用水或乙醇洗净,在适宜条件下干燥后,再分别精密称定每一容器的重量,求出每瓶(支)的装量与平均装量。
每瓶(支)装量与平均装量相比较,应符合下列规定,如有1瓶(支)不符合规定,应另取10瓶(支)复试,应符合规定。
凡规定检查含量均匀度的注射用无菌粉末,一般不再进行装量差异检查。
【渗透压摩尔浓度】除另有规定外,静脉输液及椎管注射用注射液按各品种项下的规定,照渗透压摩尔浓度测定法(附录Ⅸ G)检查,应符合规定。
【可见异物】除另有规定外,照可见异物检查法(附录Ⅸ H)检查,应符合规定。
【不溶性微粒】除另有规定外,溶液型静脉用注射液、注射用无菌粉末及注射用浓溶液照不溶性微粒检查法(附录Ⅸ C)检查,应符合规定。
【无菌】照无菌检查法(附录Ⅺ H)检查,应符合规定。
【细菌内毒素】或【热原】除另有规定外,静脉用注射剂按各品种项下的规定,照细菌内毒素检查法(附录Ⅺ E)或热原检查法(附录Ⅺ D)检查,应符合规定。