红黑树的代码实现
- 格式:doc
- 大小:124.50 KB
- 文档页数:13

C语⾔实现红⿊树详细步骤+代码⽬录红⿊树的概念红⿊树的性质红⿊树的定义与树结构插⼊新增结点插⼊后维护红⿊树性质的主逻辑拆解讨论:旋转验证红⿊树与AVl树的⽐较红⿊树的应⽤总结红⿊树的概念红⿊树,是⼀种⼆叉搜索树,但在每个结点上增加⼀个存储位表⽰结点的颜⾊,可以是Red或Black。
通过对任何⼀条从根到叶⼦的路径上各个结点着⾊⽅式的限制,红⿊树确保没有⼀条路径会⽐其他路径长出俩倍,因⽽是接近平衡的概念总结:红⿊树是⼆叉搜索树的升级,结点⾥⾯存放的成员col标记当前结点的颜⾊,它的最长路径最多是最短路径的⼆倍,红⿊树通过各个结点着⾊⽅式的限制接近平衡⼆叉树,但是不同于AVL的是AVL是⼀颗⾼度平衡的⼆叉树,红⿊树只是接近平衡红⿊树的性质每个结点不是红⾊就是⿊⾊根节点是⿊⾊的如果⼀个节点是红⾊的,则它的两个孩⼦结点是⿊⾊的对于每个结点,从该结点到其所有后代叶结点的简单路径上,均包含相同数⽬的⿊⾊结点每个叶⼦结点都是⿊⾊的(此处的叶⼦结点指的是空结点)红⿊树性质总结:1、红⿊树结点的颜⾊只能是红⾊或者⿊⾊2、红⿊树根节点必须是⿊⾊3、红⿊树并没有连续的红⾊结点4、红⿊树中从根到叶⼦的每⼀条路径都包含相同的⿊⾊结点5、叶⼦是⿊⾊,表⽰空的位置最长路径和最短路径概念:最短路径:从根结点到叶⼦结点每⼀条路径的结点颜⾊都是⿊⾊的不包含红⾊最长路径:红⿊交替,⿊⾊结点和红⾊结点的个数相等思考:为什么满⾜上⾯的性质,红⿊树就能保证:其最长路径中节点个数不会超过最短路径节点个数的两倍?假设结点个数为N,那么最短路径就是logN,最长路径就是2 * logN,所有并不存在最长路径超过最短路径2倍的情况红⿊树的定义与树结构//枚举红⿊颜⾊enum colour{RED,BLACK,};//定义红⿊树结点结构template<class K,class V>struct RBTreeNode{//构造RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv = {0,0}):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _kv(kv),_col(BLACK){ }//定义三叉链RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left; //左孩⼦RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;//右孩⼦RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent; //⽗亲pair<K, V> _kv; //pair对象//节点的颜⾊colour _col; //定义枚举变量};//定义红⿊树template<class K, class V>class RBTree{typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;public://构造RBTree():_root(nullptr){}private:Node* _root; //定义树的根节点};插⼊插⼊过程类似搜索树的插⼊,重要的是维护红⿊树的性质pair<Node*, bool> Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (!_root) //空树处理{_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK;return { _root, true };}//⼆叉搜索树的插⼊逻辑Node* cur = _root, * parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)//插⼊结点⽐当前结点⼤{parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first) //插⼊结点⽐当前结点⼩{parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return { cur, false }; //插⼊失败}}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_col = RED; //新增结点颜⾊默认设置为RED//判断插⼊结点是否在parent的左边或者右边if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first) //左边{parent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}else //右边{parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}/* 红⿊树性质处理:如果这棵树⼀开始是符合红⿊树的性质,但在新增结点之后,导致失去了红⿊树的性质,这⾥需要控制结点的颜⾊和限制每条路径上⿊⾊结点的个数,以上情况都要处理*/while (parent && parent->_col == RED) //⽗亲存在且⽗亲为红⾊{Node* grandfather = parent->_parent; //祖⽗//⽗亲出现在祖⽗的左边需要考虑的情况if(parent == grandfather ->left){//1、uncle存在,uncle为红⾊/*如果parent和uncle都存在并且都为红⾊这是情况⼀,需要将parent和uncle的颜⾊变成红⾊,祖⽗颜⾊变成⿊⾊更新cur、parent、grandfather、uncle 继续向上调整*///2、uncle不存在/* 这⾥考虑两种旋转情况,直线单旋转,折线双旋/*cur出现在parent的左边 ,右单旋转经过右单旋后,parent去做树的根,祖⽗做为右⼦树//调节结点颜⾊parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;*//*cur出现在parent的右边,左右双旋经过双旋后,cur作为树的根,grandfather为右⼦树调节结点颜⾊cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;*/*/}else //⽗亲出现在祖⽗的右边{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left; //叔叔在左⼦树/*情况⼀:叔叔存在,且叔叔和⽗亲都是红⾊,那么就需要将⽗亲和叔叔结点的颜⾊变成⿊⾊,再将祖⽗的颜⾊变成红⾊,继续向上调整,更新孩⼦、⽗亲、祖⽗、叔叔的位置*//*情况⼆:叔叔不存在/*1、新增结点出现在⽗亲的右边,直线情况,左单旋处理旋转完后parent去做⽗亲的根,grandfather做⽗亲的左⼦树//调节颜⾊,根为⿊,左右孩⼦为红2、新增结点出现在⽗亲的左边,会出现折现的情况,引发双旋,旋转完后,cur变成根,parent和grandfaher去做cur的左右孩⼦//调节颜⾊,根结点为⿊,左右孩⼦为红*/*/}}//如果⽗亲不存在为了保证根结点是⿊⾊的,这⾥⼀定得将根结点处理为⿊⾊_root->_col = BLACK;}新增结点插⼊后维护红⿊树性质的主逻辑//1、⽗亲⼀定存在的情况,叔叔存在/不存在⽗亲叔叔结点颜⾊为红⾊while (parent && parent->_col == RED) //⽗亲存在且⽗亲为红⾊{Node* grandfather = parent->_parent; //祖⽗//如果⽗亲和叔叔结点颜⾊都是红⾊if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) //对应情况:uncle存在且为红{//处理:⽗亲和叔叔变成⿊⾊,祖⽗变成红⾊,继续向上调整uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//向上调整cur = grandfather; //调整孩⼦parent = cur->_parent;//调整⽗亲}else //uncle不存在,uncle存在且为⿊{//直线情况(cur在parent的左边):只考虑单旋,以grandfather为旋转点进⾏右单旋转,//旋转完后将祖⽗的颜⾊变成红⾊,将⽗亲的颜⾊变成⿊⾊if (parent->_left == cur){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else //parent->_right == cur{//折线情况(cur在parent的右边):这⾥会引发双旋RotateL(parent); //以parent为旋转点进⾏左单旋RotateR(grandfather); //以grandfather为旋转点进⾏右单旋转//旋转完后cur会去做树的根,那么设置为⿊⾊,//为了保证每条路径的⿊⾊结点个数相同,grandfather结点颜⾊设置为红cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED; //⿊⾊结点个数相同}}}else //⽗亲在右⼦树{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left; //叔叔在左⼦树if (uncle&& uncle->_col == RED) //情况⼀处理:叔叔存在,且叔叔的颜⾊是红⾊的(包含了⽗亲的颜⾊是红⾊的情况){//根据情况⼀处理即可:叔叔和⽗亲变⿊,//祖⽗变红(⽬的是为了每条路径的⿊⾊结点个数相同),继续向上cur = grandfather; //孩⼦parent = cur->_parent;//⽗亲}else //叔叔不存在{if (cur == parent->_right) //新增结点在⽗亲的右边,直线情况左单旋处理{//左单旋转,以grandfather为旋转点,旋转完后parent去做新的根,grandfather去做左⼦树RotateL(grandfather);//调节颜⾊grandfather->_col = RED;parent->_col = BLACK;}else //新增结点在⽗亲的左边,折线情况,引发双旋{//处理:以parenrt为旋转点做右单旋,再以grandfather为旋转点做左单旋RotateR(parent); //右旋RotateL(grandfather); //左旋parent->_col = grandfather->_col = RED;cur->_col = BLACK;}break;}}_root->_col = BLACK;}拆解讨论:以下只列举parent在grandfather左边的情况,⽽parent在grandfather右边的情况处理⽅式只是反过来的,读者可以⾃⾏画图,这⾥仅留参考代码Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) //对应情况:uncle存在且为红{//处理:⽗亲和叔叔变成⿊⾊,祖⽗变成红⾊,继续向上调整uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//向上调整cur = grandfather; //调整孩⼦parent = cur->_parent;//调整⽗亲}else //uncle不存在,uncle存在且为⿊{//直线情况(cur在parent的左边):只考虑单旋,以grandfather为旋转点进⾏右单旋转, //旋转完后将祖⽗的颜⾊变成红⾊,将⽗亲的颜⾊变成⿊⾊if (parent->_left == cur){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else //parent->_right == cur{//双旋转}}//折线情况(cur在parent的右边):这⾥会引发双旋RotateL(parent); //以parent为旋转点进⾏左单旋RotateR(grandfather); //以grandfather为旋转点进⾏右单旋转//旋转完后cur会去做树的根,那么设置为⿊⾊,//为了保证每条路径的⿊⾊结点个数相同,grandfather结点颜⾊设置为红cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;旋转void RotateR(Node* parent) //右单旋{Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR) subLR->_parent = parent; //防⽌subLR为nullptrsubL->_right = parent;Node* parent_parent = parent->_parent; //指针备份parent->_parent = subL;if (_root == parent) //如果parent就是树的根{_root = subL; //subL取代parent_root->_parent = nullptr;}else //如果parent并不是树的根{if (parent_parent->_left == parent) parent->_left = subL;else parent_parent->_right = subL;subL->_parent = parent_parent; //subL去做parent_parent的孩⼦ }}//左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL) subRL->_parent = parent;subR->_left = parent;Node* parent_parent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (_root == parent){_root = subR;_root->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent_parent->_left == parent) parent_parent->_left = subR; else parent_parent->_right = subR;subR->_parent = parent_parent;}}验证/*红⿊树的⼏点性质在于:1、根结点必须是红⾊的2、不会出现连续的红⾊结点3、所有路径的⿊⾊结点个数是相同的*/bool _CheckBlance(Node* root, int isBlackNum, int count){if (!root){if (isBlackNum != count){printf("⿊⾊结点个数不均等\n");return false;}return true; //遍历完整棵树,如果以上列举的⾮法情况都不存在就返回true}//检查是否出现连续的红⾊结点if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED){printf("出现了连续的红⾊结点\n");return false;}//⾛前序遍历的过程中记录每⼀条路径⿊⾊结点的个数if (root->_col == BLACK) count++;//递归左右⼦树return _CheckBlance(root->_left, isBlackNum, count) &&_CheckBlance(root->_right, isBlackNum, count);}//验证红⿊树bool CheckBlance(){if (!_root) return true; //树为null//根结点是⿊⾊的if (_root->_col != BLACK){printf("根结点不是⿊⾊的\n");return false;}//每⼀条路径⿊⾊结点的个数必须是相同的,int isBlcakNum = 0;Node* left = _root;while (left){if (left->_col == BLACK) isBlcakNum++; // 统计某⼀条路径的所以⿊⾊结点个数left = left->_left;}//检查连续的红⾊结点,检查每⼀条路径的⿊⾊结点个数是否相等return _CheckBlance(_root, isBlcakNum ,0);}红⿊树与AVl树的⽐较红⿊树与AVL树的⽐较红⿊树和AVL树都是⾼效的平衡⼆叉树,增删改查的时间复杂度都是O( log n),红⿊树不追求绝对平衡,其只需保证最长路径不超过最短路径的2倍,相对⽽⾔,降低了插⼊和旋转的次数,所以在经常进⾏增删的结构中性能⽐AVL树更优,⽽且红⿊树实现⽐较简单,所以实际运⽤中红⿊树更多。

java treemap实现原理Java TreeMap是Java中非常常用的一种数据结构,使用红黑树作为其底层实现。
它提供了一种将键映射到值的方式,键是唯一的,并且按照升序进行排序。
Java TreeMap的实现原理是非常有趣的,它主要涉及到红黑树、迭代器、比较器等知识点。
在本文中,我们将深入了解Java TreeMap的实现原理,并理解如何在代码中使用它。
1. 红黑树红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉搜索树。
它通过保持一些简单规则来保证树的平衡,以确保左右子树的高度之差不超过1,并且保证每个节点的颜色都为红色或黑色。
这些规则允许红黑树保持在O(log n)的时间复杂度下进行插入、搜索和删除操作。
在Java TreeMap中,红黑树被用作底层存储结构。
当添加一个新的键值对时,它会首先检查根节点是否为空。
如果是,则创建一个新的节点并将其设置为根节点。
否则,它会沿着树的路径查找适当的叶子节点,并将其插入为其左侧或右侧的子节点。
为了保持树的平衡,通过旋转和重新着色来调整节点的颜色和位置。
每个节点都有一个颜色标记,标记为红色或黑色,红色表示该节点是一个违反规则的节点,黑色表示该节点是一个符合规则的节点。
2. TreeMap的比较器Java TreeMap还有另一个重要的组件,即比较器。
所有元素的排序都是通过比较器来定义的。
比较器定义了如何将元素按照升序排列,应该提供一个实现了 Comparator 接口的类。
在Java TreeMap的实现中,比较器用来将元素按照顺序排列。
它允许 TreeMap 将元素按照自定义顺序排序而不是按照它们的自然顺序排序。
也就是说,比较器的作用是自定义元素排序的规则并将其存储在TreeMap中。
3. TreeMap的迭代器Java TreeMap还提供了迭代器,用于遍历TreeMap中的元素。
什么是迭代器?迭代器是用于遍历集合或列表中元素的指针。
在Java中,每个集合或列表都可以通过iterator() 方法返回它的迭代器。
#ifndef REDBLACK_INCLUDE#define REDBLACK_INCLUDEtemplate<typename T>class RedBlackTree{struct Node{T key;bool color;Node* parent;Node* left;Node* right;Node(T data_, bool color_, Node* p, Node* l, Node* r):key(data_),color(color_),parent(p),left(l),right(r){}};Node* NIL;Node* root;bool RED ;bool BLACK ;public:RedBlackTree(T data=0, bool str=false, Node* p=NULL, Node* q=NULL, Node* e=NULL):RED(true),BLACK(false){NIL = new Node(0, BLACK, NIL, NIL, NIL);//哨兵结点root = NIL;}~RedBlackTree(){DeleteTree(root);delete NIL;}void LeftRotate(Node* x);void RightRotate(Node* y);void RBInsert(T data);void RBInsertFixup(Node* z);void RBDelete(T data);void RBDeleteFixUp(Node* x);Node* TreeSearchNumber(Node* x, T k);Node* TreeSuccessor(Node* x);void DeleteTree(Node* x);void PrintTree(Node* x);Node* GetNode(void);Node* TreeMinIMUM(Node* x );};#endif//RedBlackTree_.h#ifndef REDBLACKTREE_H_INCLUDE#define REDBLACKTREE_H_INCLUDE#include "RedBlack.h"#include <assert.h>#include <string>#include <iostream>template<typename T>RedBlackTree<T>::Node* RedBlackTree<T>::TreeMinIMUM(Node* x ) {while(x->left != NIL)x = x->left;return x;}template<typename T>RedBlackTree<T>::Node* RedBlackTree<T>::GetNode(void){return root;}template<typename T>void RedBlackTree<T>::PrintTree(Node* x){if(NIL != x){if(NIL != x->left){PrintTree(x->left);}if(NIL != x->right){PrintTree(x->right);}std::cout<<x->key<<std::endl;}}template<typename T>void RedBlackTree<T>::DeleteTree(Node* x){if(x != NIL){if(NIL != x->left ){DeleteTree(x->left);}if(NIL != x->right ){DeleteTree(x->right);}delete x;x = NULL;}}template<typename T>RedBlackTree<T>::Node* RedBlackTree<T>::TreeSearchNumber(Node* x, T k) {if( x == NIL || k == x->key )return x;if( k < x->key )return TreeSearchNumber(x->left, k);elsereturn TreeSearchNumber(x->right, k);}template<typename T>RedBlackTree<T>::Node* RedBlackTree<T>::TreeSuccessor(Node* x)//存在两种情况: {if (x->right != NIL)//如果结点x的右子树非空,则x的后继即右子树中的最左的结点。

c++ 红黑树 map原理
C++中的红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉查找树,它常用于实现关联
容器中的map数据结构。
红黑树通过对节点进行着色和旋转操作来
保持树的平衡,从而确保在最坏情况下的查找、插入和删除操作的
时间复杂度为O(log n)。
红黑树的基本原理包括以下几点:
1. 节点着色,每个节点都被标记为红色或黑色,这些颜色标记
用于确保树的平衡。
2. 根节点和叶子节点,根节点是黑色的,叶子节点(NIL节点)是黑色的。
3. 红色节点规则,红色节点的子节点必须是黑色的,即不能出
现两个相连的红色节点。
4. 从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色
节点。
这保证了树的黑色平衡。
在C++中,STL中的map数据结构通常使用红黑树来实现。
map 是一种关联容器,它提供了一种将键和值关联起来的方式。
当我们向map中插入新的键值对时,红黑树会自动进行调整以保持平衡。
查找、插入和删除操作都能在O(log n)的时间复杂度内完成,这使得map非常高效。
总之,红黑树是一种高效的自平衡二叉查找树,它通过节点着色和旋转操作来维持平衡。
在C++中,map数据结构通常使用红黑树来实现,从而提供了高效的插入、删除和查找操作。
这些原理和实现细节都是为了确保数据结构的高效性和稳定性。

c语言红黑树遍历序算法红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉查找树,它具有良好的平衡性能,能够保持在较低的高度范围内。
在C语言中,我们可以使用递归或者非递归的方式来实现红黑树的遍历。
下面我将分别介绍中序遍历、前序遍历和后序遍历的算法。
1. 中序遍历算法:中序遍历的顺序是先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树。
在C语言中,我们可以使用递归实现中序遍历:c.void inOrderTraversal(struct Node root) {。
if (root != NULL) {。
inOrderTraversal(root->left);printf("%d ", root->data);inOrderTraversal(root->right);}。
}。
2. 前序遍历算法:前序遍历的顺序是先访问根节点,然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树。
同样可以使用递归实现前序遍历:c.void preOrderTraversal(struct Node root) {。
if (root != NULL) {。
printf("%d ", root->data);preOrderTraversal(root->left);preOrderTraversal(root->right);}。
}。
3. 后序遍历算法:后序遍历的顺序是先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根节点。
同样可以使用递归实现后序遍历:c.void postOrderTraversal(struct Node root) {。
if (root != NULL) {。
postOrderTraversal(root->left);postOrderTraversal(root->right);printf("%d ", root->data);}。
}。
另外,以上是使用递归实现的遍历算法,也可以使用非递归的方式来实现,利用栈来辅助实现遍历。

红黑树系列,六篇文章于今日已经完成:1、教你透彻了解红黑树2、红黑树算法的实现与剖析3、红黑树的c源码实现与剖析4、一步一图一代码,R-B Tree5、红黑树插入和删除结点的全程演示6、红黑树的c++完整实现源码------------------------------一、红黑树的介绍先来看下算法导论对R-B Tree的介绍:红黑树,一种二叉查找树,但在每个结点上增加一个存储位表示结点的颜色,可以是Red 或Black。
通过对任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各个结点着色方式的限制,红黑树确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出俩倍,因而是接近平衡的。
前面说了,红黑树,是一种二叉查找树,既然是二叉查找树,那么它必满足二叉查找树的一般性质。
下面,在具体介绍红黑树之前,咱们先来了解下二叉查找树的一般性质:1.在一棵二叉查找树上,执行查找、插入、删除等操作,的时间复杂度为O(lgn)。
因为,一棵由n个结点,随机构造的二叉查找树的高度为lgn,所以顺理成章,一般操作的执行时间为O(lgn)。
//至于n个结点的二叉树高度为lgn的证明,可参考算法导论第12章二叉查找树第12.4节。
2.但若是一棵具有n个结点的线性链,则此些操作最坏情况运行时间为O(n)。
而红黑树,能保证在最坏情况下,基本的动态几何操作的时间均为O(lgn)。
ok,我们知道,红黑树上每个结点内含五个域,color,key,left,right,p。
如果相应的指针域没有,则设为NIL。
一般的,红黑树,满足以下性质,即只有满足以下全部性质的树,我们才称之为红黑树:1)每个结点要么是红的,要么是黑的。
2)根结点是黑的。
3)每个叶结点(叶结点即指树尾端NIL指针或NULL结点)是黑的。
4)如果一个结点是红的,那么它的俩个儿子都是黑的。
5)对于任一结点而言,其到叶结点树尾端NIL指针的每一条路径都包含相同数目的黑结点。
(注:上述第3、5点性质中所说的NULL结点,包括wikipedia.算法导论上所认为的叶子结点即为树尾端的NIL指针,或者说NULL结点。

红⿊树(⼆)之C语⾔的实现概要红⿊树在⽇常的使⽤中⽐较常⽤,例如Java的和,C++的STL,以及Linux内核中都有⽤到。
之前写过⼀篇⽂章专门介绍红⿊树的,本⽂将给出红⿊数的C语⾔的实现代码,后序章节再分别给出C++和Java版本的实现。
还是那句话,三种实现原理相同,择其⼀了解即可;若⽂章有错误或不⾜的地⽅,望不吝指出!⽬录转载请注明出处:更多内容:(01)(02)(03) (04) (05) (06)红⿊树的介绍红⿊树(Red-Black Tree,简称R-B Tree),它⼀种特殊的⼆叉查找树。
红⿊树是特殊的⼆叉查找树,意味着它满⾜⼆叉查找树的特征:任意⼀个节点所包含的键值,⼤于等于左孩⼦的键值,⼩于等于右孩⼦的键值。
除了具备该特性之外,红⿊树还包括许多额外的信息。
红⿊树的每个节点上都有存储位表⽰节点的颜⾊,颜⾊是红(Red)或⿊(Black)。
红⿊树的特性:(1) 每个节点或者是⿊⾊,或者是红⾊。
(2) 根节点是⿊⾊。
(3) 每个叶⼦节点是⿊⾊。
[注意:这⾥叶⼦节点,是指为空的叶⼦节点!](4) 如果⼀个节点是红⾊的,则它的⼦节点必须是⿊⾊的。
(5) 从⼀个节点到该节点的⼦孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数⽬的⿊节点。
关于它的特性,需要注意的是:第⼀,特性(3)中的叶⼦节点,是只为空(NIL或null)的节点。
第⼆,特性(5),确保没有⼀条路径会⽐其他路径长出俩倍。
因⽽,红⿊树是相对是接近平衡的⼆叉树。
红⿊树⽰意图如下:红⿊树的C实现(代码说明)红⿊树的基本操作是添加、删除和旋转。
在对红⿊树进⾏添加或删除后,会⽤到旋转⽅法。
为什么呢?道理很简单,添加或删除红⿊树中的节点之后,红⿊树就发⽣了变化,可能不满⾜红⿊树的5条性质,也就不再是⼀颗红⿊树了,⽽是⼀颗普通的树。
⽽通过旋转,可以使这颗树重新成为红⿊树。
简单点说,旋转的⽬的是让树保持红⿊树的特性。
旋转包括两种:左旋和右旋。
下⾯分别对旋转(左旋和右旋)、添加、删除进⾏介绍。

红黑树算法原理与实现红黑树是一种自平衡二叉查找树,它能够保证查找、插入和删除操作最坏情况下的时间复杂度都为O(log n),是一种十分高效的数据结构。
本文将对红黑树算法的原理和实现进行介绍,帮助读者深入了解红黑树的运作流程和应用场景。
一、红黑树的定义和性质红黑树和其他的自平衡二叉查找树(如AVL树)一样,能够自动调整树的结构以保证平衡,并且能够保持树中每个节点的黑高相等。
下面是红黑树的具体定义:(1)每个节点要么是红色,要么是黑色。
(2)根节点是黑色。
(3)每个叶子节点(NIL节点,空节点)都是黑色的。
(4)如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
(5)任意一个节点到每个叶子节点所经过的黑色节点数都相同。
这些性质确保了红黑树的平衡,在插入和删除节点时能够自动平衡而不需要人工干预,从而保证了树的性能。
二、红黑树的基本操作红黑树的插入和删除操作是它最为关键和难点的部分,下面我们将针对这两个操作进行介绍。
(1)插入操作插入节点时,首先按照二叉查找树的方式将新节点插入到树中。
接下来需要进行的操作是将节点的颜色进行调整,保证该节点符合红黑树的五大性质。
如果插入的节点不满足性质(4),需要执行进行一系列颜色调整和旋转操作,使得节点重新满足红黑树性质。
一般情况下,情况分为两种:(a)情况1:插入的节点为根节点此时只需要将节点的颜色设置为黑色即可。
(b)情况2:插入的节点的父节点为红色此时需要进行一系列的旋转和颜色调整操作。
可以分为以下三种情况:①插入节点的叔叔节点是红色的,此时需要进行颜色调整和旋转。
②插入节点的叔叔节点是黑色的,并且插入节点为父节点的右子节点,此时需要进行左旋操作。
③插入节点的叔叔节点是黑色的,并且插入节点为父节点的左子节点,此时需要进行颜色调整、右旋操作。
(2)删除操作删除节点时,首先按照二叉查找树的方式删除节点。
接着需要对树进行自平衡操作,使之重新满足红黑树性质。
与插入操作相比,删除操作需要考虑更多的情况。
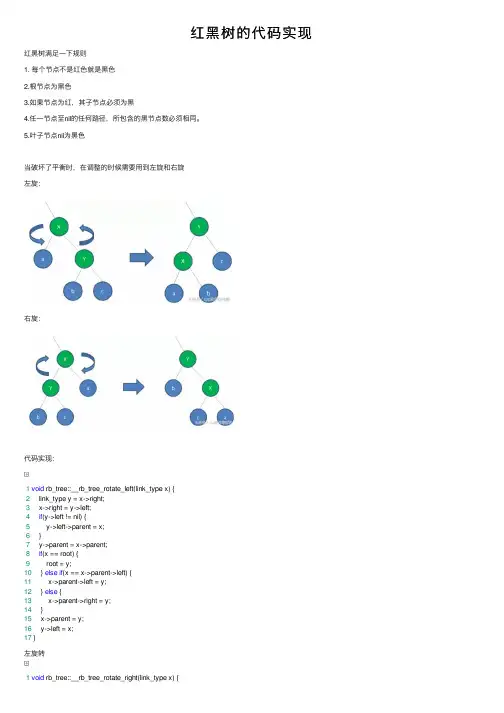
红⿊树的代码实现红⿊树满⾜⼀下规则1. 每个节点不是红⾊就是⿊⾊2.根节点为⿊⾊3.如果节点为红,其⼦节点必须为⿊4.任⼀节点⾄nil的任何路径,所包含的⿊节点数必须相同。
5.叶⼦节点nil为⿊⾊当破坏了平衡时,在调整的时候需要⽤到左旋和右旋左旋:右旋:代码实现:1void rb_tree::__rb_tree_rotate_left(link_type x) {2 link_type y = x->right;3 x->right = y->left;4if(y->left != nil) {5 y->left->parent = x;6 }7 y->parent = x->parent;8if(x == root) {9 root = y;10 } else if(x == x->parent->left) {11 x->parent->left = y;12 } else {13 x->parent->right = y;14 }15 x->parent = y;16 y->left = x;17 }左旋转1void rb_tree::__rb_tree_rotate_right(link_type x) {2 link_type y = x->left;3 x->left = y->right;4if(x->left != nil) {5 x->left->parent = x;6 }7 y->parent = x->parent;8if(x == root) {9 root = y;10 } else if(x->parent->left == x) {11 x->parent->left = y;12 } else {13 x->parent->right = y;14 }1516 x->parent = y;17 y->right = x;18 }右旋转插⼊节点时,可能会破坏红⿊树的结构,如下图,在插⼊3,8,35,75的时候,就破坏了树的结构:设定如下⽤语:新节点为X,其⽗节点为P,组⽗节点为G,伯⽗节点为S,曾祖⽗节点GG。

红黑树的介绍和实现(一)[原创]DataStructure 2010-10-0821:42:00一、红黑树(Red-Black Tree)是二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree)的一种。
二叉搜索树在最坏的情况下可能会变成一个链表(当所有节点按从小到大的顺序依次插入后)。
这种低效产生的原因是树没有维持一定的平衡性,要提高搜索效率,就要想办法来维持树左边的平衡,也就是要尽时降低树的高度,可行的做法就是用一些策略在每次修改树的内容之后都调整树的结构,使之满足一定的平衡条件。
其中一种满足一定平衡条件而且目前应用广泛的是红黑树。
它可以在每一次插入或删除节点之后都会花O(log N)的时间来对树的结构作修改,以保持树的平衡。
而红黑树的查找方法与二叉搜索树完全一样,也能够在O(log N)时间上完成。
而红黑树的插入和删除节点的的方法只是在原二叉搜索树搜索和删除算法之后经过一定的过程来维持红黑树的性质不变。
红黑树的每个节点上的属性除了有一个key、3个指针:parent、left、right以外,还多了一个属性:color。
它只能是两种颜色:红或黑,当然也可以再加一些以key 来索引的数据。
而红黑树除了具有二叉搜索树的所有性质之外,还具有以下5点性质:1. 每个节点是黑色的或是红色的。
2. 根节点是黑色的。
3. 空节点是黑色的(红黑树中,根节点的parent以及所有叶节点left、right都不指向NULL,而是指向一个定义好的空节点,这样可以保持算法的一致性,简化算法)。
4. 红色节点的父、左子、右子节点都是黑色。
5. 在任何一棵子树中,每一条从根节点向下走到空节点的路径上包含的黑色节点数量都相同。
如下图就是一棵红黑树:小记:1.在一棵红黑树中null节点是很多的,如果每个null节点都用一个真的节点的话那就太浪费空间了,我们可以对所有的null节点都使用同一个节点,这样可以简化算法又能节约空间。

红黑树 predecessor 代码红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉搜索树,每个节点都用一个颜色属性表示,是红色或黑色。
红黑树的自平衡性能使得它在插入、删除等操作时具有较高的效率。
在红黑树中,与每个节点相连的叶节点是 NIL 节点,也就是空节点。
本文将介绍红黑树的 predecessor 算法,并给出其代码实现。
Predecessor 算法Predecessor 算法旨在找到某个节点的前驱节点,即前一个较小的节点。
具体来说,对于一个节点 x,其前驱节点是在整个红黑树中所有值小于 x 值的节点中,值最大的那个节点。
我们可以使用某种方式遍历整棵红黑树,查找前驱节点。
在这里,我们使用了中序遍历算法。
中序遍历算法按照从小到大的顺序遍历整棵树,当遍历到某个节点时,比较其值与目标节点值的大小,如果当前节点值小于目标节点值,就将其标记为前驱节点。
当遍历完整棵树时,返回前驱节点即可。
需要注意的是,在进行中序遍历时,我们需要不断回溯到当前子树的根节点,这样才能找到包含左子树中所有节点的整个子树。
因此,在算法中,我们要判断从哪个方向来到当前节点,以便正确地回溯到根节点。
代码实现下面是红黑树 predecessor 算法的代码实现。
代码中,函数 find_predecessor 返回目标节点的前驱节点。
```python def find_predecessor(node): # 判断是否存在左子树 if node.left: # 进入左子树 node = node.left # 找到左子树中的最右节点 while node.right:node = node.right # 返回前驱节点return node else: parent = node.parent while parent and node == parent.left:node = parent parent = parent.parent # 返回前驱节点 return parent ```在这个代码中,我们首先判断当前节点是否存在左子树。
红黑树原理及c++建立过程红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉查找树。
它在维护二叉查找树的基本性质的还遵循一些附加规则来保持平衡。
一、红黑树的基本原理1. 定义红黑树是一种二叉查找树,在每个节点上增加一个额外的标记,即节点的颜色,可以是红色或黑色。
红黑树必须满足以下五个性质:(1)根节点是黑色。
(2)每个叶子节点(NIL节点,空节点)是黑色的。
(3)如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个子节点都是黑色的。
(4)从根节点到叶子节点的每条路径上,黑色节点的数量是相同的。
(5)任意节点到其每个叶子节点的所有路径上,不能有两个连续的红色节点。
2. 自平衡特性为了保持树的平衡,红黑树在节点插入或删除操作时需要进行相应的调整。
通过保持上述性质,红黑树能够保持整体的平衡状态,避免出现较长的路径导致性能下降。
二、红黑树的建立过程1. 插入操作红黑树的插入操作分为以下几个步骤:(1)将节点插入到二叉查找树中的合适位置,插入节点默认为红色。
(2)根据红黑树的性质进行调整,包括变色和旋转操作。
(3)根节点重新设置为黑色。
插入操作的详细过程如下:(1)如果插入节点是根节点,则将其颜色设置为黑色。
(2)如果插入节点的父节点是黑色,符合红黑树性质,不需要进行调整。
(3)如果插入节点的父节点是红色,需要进行调整。
- 如果插入节点的叔父节点也是红色,将父节点和叔父节点的颜色都设置为黑色,将祖父节点的颜色设置为红色,然后将当前节点设置为祖父节点,继续向上调整。
- 如果插入节点的叔父节点是黑色或为空节点:a. 如果插入节点是其父节点的右子节点,进行左旋操作,转化为左子节点的情况。
b. 如果插入节点是其父节点的左子节点,进行右旋操作,然后转化为右子节点的情况。
c. 进行一次右旋操作,然后将父节点设置为黑色,祖父节点设置为红色,转化为红色节点为根节点的情况进行处理。
(4)将根节点的颜色设置为黑色。
2. 删除操作红黑树的删除操作也分为以下几个步骤:(1)根据二叉查找树的规则找到需要删除的节点。
java算法实现红⿊树完整代码⽰例红⿊树定义红⿊树(英语:Red–black tree)是⼀种⾃平衡⼆叉查找树,是在计算机科学中⽤到的⼀种数据结构,典型的⽤途是实现关联数组。
红⿊树的另⼀种定义是含有红⿊链接并满⾜下列条件的⼆叉查找树:红链接均为左链接;没有任何⼀个结点同时和两条红链接相连;该树是完美⿊⾊平衡的,即任意空链接到根结点的路径上的⿊链接数量相同。
满⾜这样定义的红⿊树和相应的2-3树是⼀⼀对应的。
旋转旋转⼜分为左旋和右旋。
通常左旋操作⽤于将⼀个向右倾斜的红⾊链接旋转为向左链接。
对⽐操作前后,可以看出,该操作实际上是将红线链接的两个节点中的⼀个较⼤的节点移动到根节点上。
左旋操作如下图:右旋旋操作如下图:即:复杂度红⿊树的平均⾼度⼤约为lgN。
下图是红⿊树在各种情况下的时间复杂度,可以看出红⿊树是2-3查找树的⼀种实现,他能保证最坏情况下仍然具有对数的时间复杂度。
Java代码import java.util.NoSuchElementException;import java.util.Scanner;public class RedBlackBST<key extends="" key="">, Value> {private static final boolean RED = true;private static final boolean BLACK = false;private Node root; //root of the BSTprivate class Node {private Key key; //keyprivate Value val; //associated dataprivate Node left, right; //links to left and right subtreesprivate boolean color; //color of parent linkprivate int size; //subtree countpublic Node(Key key, Value val, boolean color, int size) {this.key = key;this.val = val;this.color = color;this.size = size;}}//is node x red?private boolean isRed(Node x) {if(x == null) {return false;}return x.color == RED;}//number of node in subtree rooted at x; 0 if x is nullprivate int size(Node x) {if(x == null) {return 0;}return x.size;}/*** return the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table* @return the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table*/public int size() {return size(root);}/*** is this symbol table empty?* @return true if this symbol table is empty and false otherwise*/public boolean isEmpty() {return root == null;}/*** return the value associated with the given key* @param key the key* @return the value associated with the given key if the key is in the symbol table, and null if it is not. */public Value get(Key key) {if(key == null) {throw new NullPointerException("argument to get() is null");}return get(root, key);}//value associated with the given key in subtree rooted at x; null if no such keyprivate Value get(Node x, Key key) {while(x != null) {int cmp = pareTo(x.key);if(cmp < 0) {x = x.left;}else if(cmp > 0) {x = x.right;}else {return x.val;}}return null;}/*** does this symbol table contain the given key?* @param key the key* @return true if this symbol table contains key and false otherwise*/public boolean contains(Key key) {return get(key) != null;}/**************************************************************************** Red-black tree insertion.***************************************************************************//*** Inserts the specified key-value pair into the symbol table, overwriting the old* value with the new value if the symbol table already contains the specified key.* Deletes the specified key (and its associated value) from this symbol table* if the specified value is null.** @param key the key* @param val the value* @throws NullPointerException if key is null*/public void put(Key key, Value val) {if (key == null) {throw new NullPointerException("first argument to put() is null");}if (val == null) {delete(key);return;}root = put(root, key, val);root.color = BLACK;}// insert the key-value pair in the subtree rooted at hprivate Node put(Node h, Key key, Value val) {if(h == null) {return new Node(key, val, RED, 1);}int cmp = pareTo(h.key);if(cmp < 0) {h.left = put(h.left, key, val);}else if(cmp > 0) {h.right = put(h.right, key, val);}else {h.val = val;}if(isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) {h = rotateLeft(h);}if(isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) {h = rotateRight(h);}if(isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) {flipColors(h);}h.size = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;return h;}/**************************************************************************** Red-black tree deletion.***************************************************************************//*** Removes the smallest key and associated value from the symbol table. * @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty*/public void deleteMin() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("BST underflow");}// if both children of root are black, set root to redif (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right))root.color = RED;root = deleteMin(root);if (!isEmpty()) root.color = BLACK;// assert check();}// delete the key-value pair with the minimum key rooted at h// delete the key-value pair with the minimum key rooted at hprivate Node deleteMin(Node h) {if (h.left == null){return null;}if (!isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left)) {h = moveRedLeft(h);}h.left = deleteMin(h.left);return balance(h);}/*** Removes the largest key and associated value from the symbol table. * @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty*/public void deleteMax() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("BST underflow");}// if both children of root are black, set root to redif (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right))root.color = RED;root = deleteMax(root);if (!isEmpty()) root.color = BLACK;// assert check();}// delete the key-value pair with the maximum key rooted at h// delete the key-value pair with the maximum key rooted at hprivate Node deleteMax(Node h) {if (isRed(h.left))h = rotateRight(h);if (h.right == null)return null;if (!isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left))h = moveRedRight(h);h.right = deleteMax(h.right);return balance(h);}/*** remove the specified key and its associated value from this symbol table * (if the key is in this symbol table).** @param key the key* @throws NullPointerException if key is null*/public void delete(Key key) {if (key == null) {throw new NullPointerException("argument to delete() is null");}if (!contains(key)) {return;}//if both children of root are black, set root to redif(!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right)) {root.color = RED;}root = delete(root, key);if(!isEmpty()) {root.color = BLACK;}}// delete the key-value pair with the given key rooted at h// delete the key-value pair with the given key rooted at hprivate Node delete(Node h, Key key) {if(pareTo(h.key) < 0) {if(!isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left)) {h = moveRedLeft(h);}h.left = delete(h.left, key);}else {if(isRed(h.left)) {h = rotateRight(h);}if (pareTo(h.key) == 0 && (h.right == null)) {return null;}if (!isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left)) {h = moveRedRight(h);}if (pareTo(h.key) == 0) {Node x = min(h.right);h.key = x.key;h.val = x.val;h.right = deleteMin(h.right);}else {h.right = delete(h.right, key);}}return balance(h);}/**************************************************************************** Red-black tree helper functions.***************************************************************************/// make a left-leaning link lean to the right// make a left-leaning link lean to the rightprivate Node rotateRight(Node h) {// assert (h != null) && isRed(h.left);Node x = h.left;h.left = x.right;x.right = h;x.color = x.right.color;x.right.color = RED;x.size = h.size;h.size = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;return x;}// make a right-leaning link lean to the left// make a right-leaning link lean to the leftprivate Node rotateLeft(Node h) {// assert (h != null) && isRed(h.right);Node x = h.right;h.right = x.left;x.left = h;x.color = x.left.color;x.left.color = RED;x.size = h.size;h.size = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;return x;}// flip the colors of a node and its two children// flip the colors of a node and its two childrenprivate void flipColors(Node h) {// h must have opposite color of its two children// assert (h != null) && (h.left != null) && (h.right != null);// assert (!isRed(h) && isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right))// || (isRed(h) && !isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.right));h.color = !h.color;h.left.color = !h.left.color;h.right.color = !h.right.color;}// Assuming that h is red and both h.left and h.left.left// are black, make h.left or one of its children red.// Assuming that h is red and both h.left and h.left.left// are black, make h.left or one of its children red.private Node moveRedLeft(Node h) {// assert (h != null);// assert isRed(h) && !isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left);flipColors(h);if (isRed(h.right.left)) {h.right = rotateRight(h.right);h = rotateLeft(h);flipColors(h);}return h;}// Assuming that h is red and both h.right and h.right.left// are black, make h.right or one of its children red.// Assuming that h is red and both h.right and h.right.left// are black, make h.right or one of its children red.private Node moveRedRight(Node h) {// assert (h != null);// assert isRed(h) && !isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left);flipColors(h);if (isRed(h.left.left)) {h = rotateRight(h);flipColors(h);}return h;}// restore red-black tree invariant// restore red-black tree invariantprivate Node balance(Node h) {// assert (h != null);if (isRed(h.right)) {h = rotateLeft(h);}if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) {h = rotateRight(h);}if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) {flipColors(h);}h.size = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;return h;}/*************************************************************************** * Utility functions.***************************************************************************//*** Returns the height of the BST (for debugging).* @return the height of the BST (a 1-node tree has height 0)*/public int height() {return height(root);}private int height(Node x) {if (x == null) {return -1;}return 1 + Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right));}/**************************************************************************** Ordered symbol table methods.***************************************************************************//*** Returns the smallest key in the symbol table.* @return the smallest key in the symbol table* @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty*/public Key min() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("called min() with empty symbol table"); }return min(root).key;}// the smallest key in subtree rooted at x; null if no such keyprivate Node min(Node x) {// assert x != null;if (x.left == null) {return x;}else {return min(x.left);}}/*** Returns the largest key in the symbol table.* @return the largest key in the symbol table* @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty*/public Key max() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("called max() with empty symbol table"); }return max(root).key;}// the largest key in the subtree rooted at x; null if no such keyprivate Node max(Node x) {// assert x != null;if (x.right == null) {return x;}else {return max(x.right);}}/*** Returns the largest key in the symbol table less than or equal to key.* @param key the key* @return the largest key in the symbol table less than or equal to key* @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no such key* @throws NullPointerException if key is null*/public Key floor(Key key) {if (key == null) {throw new NullPointerException("argument to floor() is null");}if (isEmpty()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("called floor() with empty symbol table"); }Node x = floor(root, key);if (x == null) {return null;}else {return x.key;}}// the largest key in the subtree rooted at x less than or equal to the given keyprivate Node floor(Node x, Key key) {if (x == null) {return null;}int cmp = pareTo(x.key);if (cmp == 0) {return x;}if (cmp < 0) {return floor(x.left, key);}Node t = floor(x.right, key);if (t != null) {return t;}else {return x;}}/*** Returns the smallest key in the symbol table greater than or equal to key.* @param key the key* @return the smallest key in the symbol table greater than or equal to key* @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no such key* @throws NullPointerException if key is null*/public Key ceiling(Key key) {if (key == null) {throw new NullPointerException("argument to ceiling() is null");}if (isEmpty()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("called ceiling() with empty symbol table"); }Node x = ceiling(root, key);if (x == null) {return null;}else {return x.key;}}// the smallest key in the subtree rooted at x greater than or equal to the given key private Node ceiling(Node x, Key key) {if (x == null) {return null;}int cmp = pareTo(x.key);if (cmp == 0) {return x;}if (cmp > 0) {return ceiling(x.right, key);}Node t = ceiling(x.left, key);if (t != null) {return t;}else {return x;}}/*** Return the kth smallest key in the symbol table.* @param k the order statistic* @return the kth smallest key in the symbol table* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless k is between 0 and* <em>N</em> − 1*/public Key select(int k) {if (k < 0 || k >= size()) {throw new IllegalArgumentException();Node x = select(root, k);return x.key;}// the key of rank k in the subtree rooted at xprivate Node select(Node x, int k) {// assert x != null;// assert k >= 0 && k < size(x);int t = size(x.left);if (t > k) {return select(x.left, k);}else if (t < k) {return select(x.right, k-t-1);}else {return x;}}/*** Return the number of keys in the symbol table strictly less than key. * @param key the key* @return the number of keys in the symbol table strictly less than key * @throws NullPointerException if key is null*/public int rank(Key key) {if (key == null) {throw new NullPointerException("argument to rank() is null");}return rank(key, root);}// number of keys less than key in the subtree rooted at xprivate int rank(Key key, Node x) {if (x == null) {return 0;}int cmp = pareTo(x.key);if (cmp < 0) {return rank(key, x.left);}else if (cmp > 0) {return 1 + size(x.left) + rank(key, x.right);}else {return size(x.left);}}/**************************************************************************** Range count and range search.***************************************************************************//*** Returns all keys in the symbol table as an Iterable.* To iterate over all of the keys in the symbol table named st,* use the foreach notation: for (Key key : st.keys()).* @return all keys in the symbol table as an Iterable*/public Iterable<key> keys() {if (isEmpty()) {return new Queue<key>();}return keys(min(), max());}/*** Returns all keys in the symbol table in the given range,* as an Iterable.* @return all keys in the symbol table between lo* (inclusive) and hi (exclusive) as an Iterable* @throws NullPointerException if either lo or hi* is null*/public Iterable<key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {if (lo == null) {throw new NullPointerException("first argument to keys() is null");}if (hi == null) {throw new NullPointerException("second argument to keys() is null");Queue<key> queue = new Queue<key>();// if (isEmpty() || pareTo(hi) > 0) return queue;keys(root, queue, lo, hi);return queue;}// add the keys between lo and hi in the subtree rooted at x// to the queueprivate void keys(Node x, Queue<key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) {if (x == null) {return;}int cmplo = pareTo(x.key);int cmphi = pareTo(x.key);if (cmplo < 0) {keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi);}if (cmplo <= 0 && cmphi >= 0) {queue.enqueue(x.key);}if (cmphi > 0) {keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi);}}/*** Returns the number of keys in the symbol table in the given range.* @return the number of keys in the symbol table between lo* (inclusive) and hi (exclusive)* @throws NullPointerException if either lo or hi* is null*/public int size(Key lo, Key hi) {if (lo == null) {throw new NullPointerException("first argument to size() is null");}if (hi == null) {throw new NullPointerException("second argument to size() is null");}if (pareTo(hi) > 0) {return 0;}if (contains(hi)) {return rank(hi) - rank(lo) + 1;}else {return rank(hi) - rank(lo);}}/**************************************************************************** Check integrity of red-black tree data structure.***************************************************************************/private boolean check() {if (!isBST()) System.out.println("Not in symmetric order");if (!isSizeConsistent()) System.out.println("Subtree counts not consistent");if (!isRankConsistent()) System.out.println("Ranks not consistent");if (!is23()) System.out.println("Not a 2-3 tree");if (!isBalanced()) System.out.println("Not balanced");return isBST() && isSizeConsistent() && isRankConsistent() && is23() && isBalanced(); }// does this binary tree satisfy symmetric order?// Note: this test also ensures that data structure is a binary tree since order is strictprivate boolean isBST() {return isBST(root, null, null);}// is the tree rooted at x a BST with all keys strictly between min and max// (if min or max is null, treat as empty constraint)// Credit: Bob Dondero's elegant solutionprivate boolean isBST(Node x, Key min, Key max) {if (x == null) {return true;}if (min != null && pareTo(min) <= 0) {return false;}if (max != null && pareTo(max) >= 0) {return false;return isBST(x.left, min, x.key) && isBST(x.right, x.key, max);}// are the size fields correct?private boolean isSizeConsistent() {return isSizeConsistent(root);}private boolean isSizeConsistent(Node x) {if (x == null) {return true;}if (x.size != size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1) {return false;}return isSizeConsistent(x.left) && isSizeConsistent(x.right);}// check that ranks are consistentprivate boolean isRankConsistent() {for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) {if (i != rank(select(i))) {return false;}}for (Key key : keys()) {if (pareTo(select(rank(key))) != 0) {return false;}}return true;}// Does the tree have no red right links, and at most one (left)// red links in a row on any path?private boolean is23() {return is23(root);}private boolean is23(Node x) {if (x == null) {return true;}if (isRed(x.right)) {return false;}if (x != root && isRed(x) && isRed(x.left)){return false;}return is23(x.left) && is23(x.right);}// do all paths from root to leaf have same number of black edges?private boolean isBalanced() {int black = 0; // number of black links on path from root to minNode x = root;while (x != null) {if (!isRed(x)) black++;x = x.left;}return isBalanced(root, black);}// does every path from the root to a leaf have the given number of black links? private boolean isBalanced(Node x, int black) {if (x == null) {return black == 0;}if (!isRed(x)) {black--;}return isBalanced(x.left, black) && isBalanced(x.right, black);}/*** Unit tests the RedBlackBST data type.*/public static void main(String[] args) {RedBlackBST<string, integer=""> st = new RedBlackBST<string, integer="">(); String data = "a b c d e f g h m n o p";Scanner sc = new Scanner(data);int i = 0;while (sc.hasNext()) {String key = sc.next();st.put(key, i);i++;}sc.close();for (String s : st.keys())System.out.println(s + " " + st.get(s));System.out.println();boolean result = st.check();System.out.println("check: " + result);}}输出:<code>a 0b 1c 2d 3e 4f 5g 6h 7m 8n 9o 10p 11check: true</code>总结以上就是本⽂关于java算法实现红⿊树完整代码⽰例的全部内容,希望对⼤家有所帮助。
红黑树的实现原理和应用场景分析1. 红黑树简介红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉搜索树,它在插入和删除节点时能维持整棵树的平衡性,从而保证了查找、插入和删除操作的平均时间复杂度为O(log n)。
2. 红黑树的特点红黑树具有以下几个特点:- 每个节点不是红色就是黑色。
- 根节点是黑色的。
- 每个叶子节点(NIL节点,空节点)都是黑色的。
- 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
- 从任意一个节点到其每个叶子节点的路径中包含相同数目的黑色节点。
3. 红黑树的实现原理红黑树的实现主要涉及以下几个操作:3.1 插入操作将新节点插入到红黑树中,首先按照二叉搜索树的方式找到插入位置,并将其颜色设为红色。
然后进行插入修正操作,保证树仍然符合红黑树的特性。
3.2 删除操作从红黑树中删除特定节点,删除操作需要进行修正以保持红黑树的特性。
若删除的节点存在子节点,则将子节点替代删除节点,并进行删除修正操作。
3.3 左旋和右旋红黑树的平衡操作主要通过左旋和右旋来实现。
左旋是围绕某个节点进行逆时针旋转,右旋是围绕某个节点进行顺时针旋转。
4. 红黑树的应用场景红黑树在计算机科学领域有着广泛的应用场景,以下是一些常见的应用场景:4.1 数据库索引红黑树常被用作数据库索引结构,如MySQL数据库中的InnoDB引擎使用B+树作为索引结构,而B+树实际上是红黑树的变种。
4.2 C++的STL库C++的STL库中的集合(set)和映射(map)容器底层使用了红黑树实现,这是因为红黑树具有平衡性,可以保证查找、插入和删除操作的时间复杂度较低。
4.3 Linux内核Linux内核中的进程调度器中使用红黑树来维护就绪队列,这是因为红黑树能够高效地支持插入、删除和查找操作,使得进程的调度更加高效。
4.4 路由表网络路由表通常使用字典树(Trie)的变种实现,而字典树的节点可以使用红黑树来组织,以实现高效的路由查找。
4.5 C语言解析器C语言解析器常使用红黑树来实现符号表,以高效地存储和查找变量、函数等符号的信息。
⽤Java实现红⿊树红⿊树是众多“平衡的”搜索树模式中的⼀种,在最坏情况下,它相关操作的时间复杂度为O(log n)。
1红⿊树是⼀种⼆分查找树,与普通的⼆分查找树不同的⼀点是,红⿊树的每个节点都有⼀个颜⾊(color)属性。
该属性的值要么是红⾊,要么是⿊⾊。
通过限制从根到叶⼦的任何简单路径上的节点颜⾊,红⿊树确保没有⽐任何其他路径长两倍的路径,从⽽使树近似平衡。
假设红⿊树节点的属性有键(key)、颜⾊(color)、左⼦节点(left)、右⼦节点(right),⽗节点(parent)。
⼀棵红⿊树必须满⾜下⾯有下⾯这些特性(红⿊树特性):1. 树中的每个节点要么是红⾊,要么是⿊⾊;2. 根节点是⿊⾊;3. 每个叶⼦节点(null)是⿊⾊;4. 如果某节点是红⾊的,它的两个⼦节点都是⿊⾊;5. 对于每个节点到后⾯任⼀叶⼦节点(null)的所有路径,都有相同数量的⿊⾊节点。
为了在红⿊树代码中处理边界条件⽅便,我们⽤⼀个哨兵变量代替null。
对于⼀个红⿊树tree,哨兵变量RedBlackTree.NULL(下⽂代码中)是⼀个和其它节点有同样属性的节点,它的颜⾊(color)属性是⿊⾊,其它属性可以任意取值。
我们使⽤哨兵变量是因为我们可以把⼀个节点node的⼦节点null当成⼀个普通节点。
在这⾥,我们使⽤哨兵变量RedBlackTree.NULL代替树中所有的null(所有的叶⼦节点及根节点的⽗节点)。
我们把从⼀个节点n(不包括)到任⼀叶⼦节点路径上的⿊⾊节点的个数称为⿊⾊⾼度,⽤bh(n)表⽰。
⼀棵红⿊树的⿊⾊⾼度是其根节点的⿊⾊⾼度。
关于红⿊树的搜索,求最⼩值,求最⼤值,求前驱,求后继这些操作的代码与⼆分查找树的这些操作的代码基本⼀致。
可以在查看。
结合上⽂给出下⾯的代码。
⽤⼀个枚举类Color表⽰颜⾊:public enum Color {Black("⿊⾊"), Red("红⾊");private String color;private Color(String color) {this.color = color;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return color;}}类Node表⽰节点:public class Node {public int key;public Color color;public Node left;public Node right;public Node parent;public Node() {}public Node(Color color) {this.color = color;}public Node(int key) {this.key = key;this.color = Color.Red;}public int height() {return Math.max(left != RedBlackTree.NULL ? left.height() : 0, right != RedBlackTree.NULL ? right.height() : 0) + 1;}public Node minimum() {Node pointer = this;while (pointer.left != RedBlackTree.NULL)pointer = pointer.left;return pointer;}@Overridepublic String toString() {String position = "null";if (this.parent != RedBlackTree.NULL)position = this.parent.left == this ? "left" : "right";return "[key: " + key + ", color: " + color + ", parent: " + parent.key + ", position: " + position + "]";}}类RedTreeNode表⽰红⿊树:public class RedBlackTree {// 表⽰哨兵变量public final static Node NULL = new Node(Color.Black);public Node root;public RedBlackTree() {this.root = NULL;}}2红⿊树的插⼊和删除操作,能改变红⿊树的结构,可能会使它不再有前⾯所说的某些特性性。
c++ hashset用法摘要:1.C++ hash_set概述2.构建hash_set3.插入、删除和查找元素4.迭代器和容量调整5.实用示例正文:C++中的hash_set是基于红黑树实现的,它提供了一种高效的数据结构来存储唯一的元素。
以下将介绍hash_set的用法,包括构建、插入、删除、查找、迭代器和容量调整等操作。
1.C++ hash_set概述hash_set是C++标准库中的一部分,它允许用户存储唯一的值。
通过使用哈希表技术,hash_set能够在平均情况下提供O(1)的查找、插入和删除操作。
需要注意的是,hash_set不保证元素的顺序,如果需要保持插入顺序,请使用std::vector。
2.构建hash_set要构建一个hash_set,可以使用以下语法:```cpp#include <hash_set>std::hash_set<T> name;```其中,T是你要存储的元素类型,name是hash_set的名称。
3.插入、删除和查找元素插入元素:```cpphash_set<int> numbers;umbers.insert(10);umbers.insert(20);```查找元素:```cppauto it = numbers.find(10);if (it != numbers.end()) {std::cout << "找到了元素10" << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "未找到元素10" << std::endl;}```删除元素:```cppumbers.erase(10);```4.迭代器和容量调整可以使用以下方法遍历hash_set:```cppfor (int num : numbers) {std::cout << num << " ";}```容量调整:```cpphash_set<int> numbers2(numbers);```5.实用示例下面这个示例展示了如何使用hash_set来存储学生信息(名字和年龄):```cpp#include <iostream>#include <hash_set>#include <string>void print_students(const std::string &name, int age) {std::cout << "名字:" << name << " 年龄:" << age << std::endl;}int main() {std::hash_set<std::pair<std::string, int>> students;students.insert(std::make_pair("张三", 18));students.insert(std::make_pair("李四", 19));for (const auto &student : students) {print_students(student.first, student.second);}students.erase("张三");print_students("张三", 18);return 0;}```运行上述代码,将输出:```名字:张三年龄:18名字:李四年龄:19名字:李四年龄:19```以上就是C++ hash_set的用法介绍。
treeset的ceiling方法TreeSet是Java集合框架中的一个实现类,它基于红黑树的数据结构来存储元素,且元素是有序的。
在TreeSet中,ceiling方法是一个用于获取大于等于给定元素的最小元素的方法。
本文将介绍TreeSet的ceiling方法的使用以及其在实际开发中的应用。
一、TreeSet的概述TreeSet是Java集合框架中的一个实现类,它实现了Set接口,可以存储不重复的元素,并且元素是有序的。
TreeSet内部使用红黑树作为数据结构,保证了元素的有序性。
由于红黑树的特性,TreeSet的插入、删除和查找操作的时间复杂度都为O(logN)。
二、TreeSet的ceiling方法在TreeSet中,ceiling方法是一个用于获取大于等于给定元素的最小元素的方法。
它的声明如下:```E ceiling(E e)```其中,E表示集合中的元素类型,e表示给定的元素。
ceiling方法返回大于等于给定元素e的最小元素,如果不存在这样的元素,则返回null。
三、ceiling方法的使用示例下面通过一个示例来演示ceiling方法的使用。
假设我们有一个存储整数的TreeSet集合,我们要找到大于等于某个给定整数的最小整数。
```javaimport java.util.TreeSet;public class TreeSetDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>();set.add(1);set.add(3);set.add(5);set.add(7);set.add(9);int target = 6;Integer result = set.ceiling(target);if (result != null) {System.out.println("大于等于" + target + "的最小整数是:" + result);} else {System.out.println("不存在大于等于" + target + "的整数");}}}```上述代码中,我们创建了一个存储整数的TreeSet集合,并向其中添加了一些元素。
//by svking//2012.5#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h>#define MAXSIZE 1000typedef int ElemType;#define RED 0#define BLACK 1typedef struct RBTNode{char color;ElemType data;struct RBTNode * p;struct RBTNode * left;struct RBTNode * right;}RBTNode, * PRBTNode;typedef struct RBTree{PRBTNode root;PRBTNode nil; //统一的空节点,该节点是黑的}RBTree, * PRBTree;int leftRotate (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t);int rightRotate (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t);PRBTNode insertRB (PRBTree tree, ElemType d);int insertRB_fixup (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t);int createRBTree (PRBTree tree, ElemType d[], int n); int initRB (PRBTree tree);PRBTNode maximum (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t); PRBTNode minimum (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t); PRBTNode next (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t);PRBTNode precursor (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t);int walkNext (PRBTree tree);int inOrderWalk (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t);int deleteRB_fixup (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode c); PRBTNode deleteRB (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t);int main (){PRBTNode p;int d[MAXSIZE];int n = 0;int i;RBTree tree;initRB(&tree);/*insertRB(&tree, 11);insertRB(&tree, 2);insertRB(&tree, 14);insertRB(&tree, 1);insertRB(&tree, 7);insertRB(&tree, 15);insertRB(&tree, 5);insertRB(&tree, 8);insertRB(&tree, 4);*/p= insertRB(&tree, 26);insertRB(&tree, 17);insertRB(&tree, 41);insertRB(&tree, 14);insertRB(&tree, 21);insertRB(&tree, 30);insertRB(&tree, 47);insertRB(&tree, 10);insertRB(&tree, 16);insertRB(&tree, 19);insertRB(&tree, 23);insertRB(&tree, 28);insertRB(&tree, 38);insertRB(&tree, 7);insertRB(&tree, 12);insertRB(&tree, 15);insertRB(&tree, 20);insertRB(&tree, 3);insertRB(&tree, 35);insertRB(&tree, 39);srand(time(NULL));/*puts("请输入数据的个数:");scanf("%d",&n);printf("随机生成的%d个数据是:\n",n); for (i = 0; i < n; i++){d[i] = rand()%1000;printf("%d ",d[i]);}puts("");puts("建树开始");createRBTree(&tree, d, n);*/inOrderWalk(&tree,tree.root);puts("");printf("根是%d \n",tree.root->data);printf("删除%d后:",p->data);deleteRB(&tree, p);inOrderWalk(&tree,tree.root);puts("");printf("根是%d \n",tree.root->data);return0;}PRBTNode insertRB (PRBTree tree, ElemType d){//插入元素//!!!记得插入的元素的初始化,p指向为父母节点,left和right赋值为NULL。
PRBTNode t = NULL;PRBTNode p = NULL;int flag = 0; //用来表示插入在左边的树还是右边的树t = tree->root;//插入的节点是root,并做相应的初始化if (tree->root == tree->nil){tree->root = (PRBTNode)malloc(sizeof(RBTNode));tree->root->data = d;tree->root->color = BLACK;tree->root->p = tree->root->left =tree->root->right = tree->nil;return tree->root;}while (t != tree->nil){p = t;if (d < t->data){flag = 0;t = t->left;}else{if (d > t->data){flag = 1;t = t->right;}else{if ( (flag=rand()%2) == 0)t = t->left;elset = t->right;}}}//while//将t指向带插入节点的地址,并初始化t = (PRBTNode)malloc(sizeof(RBTNode));t->data = d;t->color = RED;t->p = p;t->left = t->right = tree->nil;if (!flag)p->left = t;elsep->right = t;insertRB_fixup(tree, t);return t;}int insertRB_fixup (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t){//插入的节点可能破坏红黑树的性质。
该函数检测插入的节点是否破坏了红黑树的性质。
如果破坏了,就对树进行调整,使其满足红黑树的性质while (t->p->color == RED) //只有插入节点的父亲是红色的才会破坏红黑树的性质(4.如果一个结点是红的,那么它的俩个儿子都是黑的){if (t->p->p->left == t->p) //插入节点的父节点本身是left{if (t->p->p->right->color == RED) //case 1{t = t->p->p;t->left->color = t->right->color = BLACK;t->color = RED;}else{if (t->p->right == t) //case 2{//将case 2转换为了case 3t = t->p; //这步赋值是为了在转换为case 3时,t指向的是下面的红节点,和case 3的情况相一致leftRotate(tree, t);}//case 3t->p->color = BLACK;t->p->p->color = RED;rightRotate(tree, t->p->p);}}//ifelse//插入节点的父节点本身是right{if (t->p->p->left->color == RED) //case 1{t = t->p->p;t->left->color = t->right->color = BLACK;t->color = RED;}else{if (t->p->left == t) //case 2{//将case 2转换为了case 3t = t->p; //这步赋值是为了在转换为case 3时,t指向的是下面的红节点,和case 3的情况相一致rightRotate(tree, t);}//case 3t->p->color = BLACK;t->p->p->color = RED;leftRotate(tree, t->p->p);}}//else}//whiletree->root->color = BLACK;return0;}int leftRotate (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t){PRBTNode c; //左旋,c指向t的rightc = t->right;if (t->right == tree->nil) //左旋,t的right不能为空return1;//这个if-else用于将t的父亲节点的left或right点指向c,如果t的父节点为不存在,则树的root指向cif (t->p != tree->nil) //判断t是否为root{if (t->p->left == t) //判断t是t的父节点的left还是rightt->p->left = c;elset->p->right = c;}elsetree->root = c;c->p = t->p; //更新c的父节点t->right = c->left;if (c->left != tree->nil)c->left->p = t;c->left = t;t->p = c;return0;}int rightRotate (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t){PRBTNode c; //右旋,c指向t的leftc = t->left;if (t->left == tree->nil) //右旋,t的left不能为空return1;//这个if-else用于将t的父亲节点的left或right点指向c,如果t的父节点为不存在,则树的root指向cif (t->p != tree->nil) //判断t是否为root{if (t->p->left == t) //判断t是t的父节点的left还是rightt->p->left = c;elset->p->right = c;}elsetree->root = c;c->p = t->p; //更新c的父节点t->left = c->right;if (c->right != tree->nil)c->right->p = t;c->right = t;t->p = c;return0;}int createRBTree (PRBTree tree, ElemType d[], int n) {//用元素的插入建树int index = -1;int tmp = -1;srand(time(NULL));while (n--){index =(int) rand()%(n+1);//此时共有n+1个数据tmp = d[index];d[index] = d[n];d[n] = tmp;insertRB(tree, d[n]);printf("插入%d\t",d[n]);}puts("");return0;}//createRBTreeint initRB (PRBTree tree){//红黑树的初始化if (tree == NULL)return0;tree->nil = (PRBTNode)malloc(sizeof(RBTNode));tree->nil->color = BLACK;tree->root = tree->nil;return0;}//initRBPRBTNode minimum (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t){//返回最小值,如果t是NULL返回NULLif (t == tree->nil)return NULL;while (t->left != tree->nil)t = t->left;return t;}//minimumPRBTNode maximum (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t){//返回最大值,如果t是NULL返回NULLif (t == tree->nil)return NULL;while (t->right != tree->nil)t = t->right;return t;}//maximumPRBTNode next (PRBTree tree, PRBTNode t){//给出t的后继的节点。