国际会计学第六版_cha
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.81 MB
- 文档页数:27

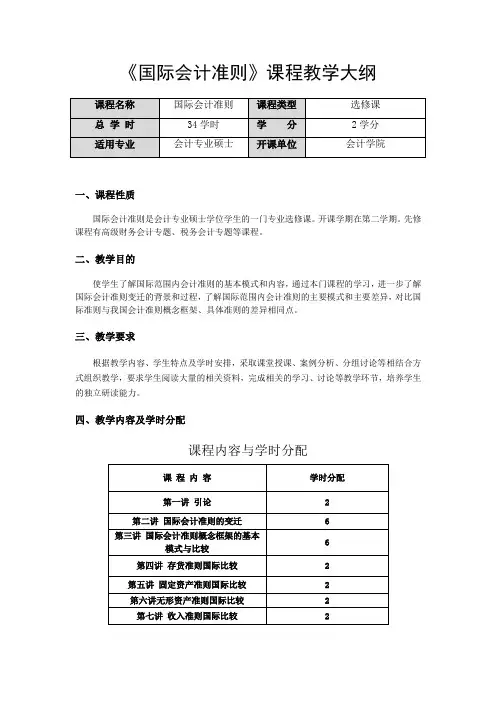
《国际会计准则》课程教学大纲一、课程性质国际会计准则是会计专业硕士学位学生的一门专业选修课。
开课学期在第二学期。
先修课程有高级财务会计专题、税务会计专题等课程。
二、教学目的使学生了解国际范围内会计准则的基本模式和内容,通过本门课程的学习,进一步了解国际会计准则变迁的背景和过程,了解国际范围内会计准则的主要模式和主要差异,对比国际准则与我国会计准则概念框架、具体准则的差异相同点。
三、教学要求根据教学内容、学生特点及学时安排,采取课堂授课、案例分析、分组讨论等相结合方式组织教学,要求学生阅读大量的相关资料,完成相关的学习、讨论等教学环节,培养学生的独立研读能力。
四、教学内容及学时分配课程内容与学时分配五、授课方式、课程考核及成绩评定授课方式采用学生参与方式教学方式。
要求对具体准则部分分小组讨论、小组课堂讲解,其他学生和老师提问方式构成。
考核方式为课程论文平时成绩占总成绩比例为30%,期末考试占70%。
平时成绩的构成:课堂小组讨论占平时成绩50%,平时作业占50%。
六、推荐教材和教学参考书七、教学具体内容和要求第一章引言一、基本要求了解国际会计准则的发展基本内容和发展情况。
二、授课方法教师讲授和学生自学相结合。
三、教学内容(一)国际会计准则的界定1.广义国际会计准则2.狭义的国际会计准则(二)课程安排和教学过程设计(三)国际会计准则的内容和变迁过程1.国际会计准则的产生2.国际会计准则的变迁(四)正在进行的全面修订四、重点难点1.国际会计准则改组的原因;2.国际会计准则的变迁过程。
五、思考与讨论1.国际会计准则与美国会计准则是如何握手言和的?2.你如何理解我国的国际协调化?3.你如何看待协调化和差异化问题?第二章国际会计准则的发展与变迁一、基本要求了解国际会计准则中国际准则、美国会计准则、中国会计准则的发展基本内容和发展情况。
二、授课方法三、教学内容(一)国际会计准则的变迁过程1.国际会计准则的产生2.国际会计准则的变迁3.国际会计准则变迁的特点(二)美国会计准则的变迁过程1.美国会计准则的产生2.美国会计准则的变迁3.美国会计准则变迁的特点(三)中国会计准则的变迁过程1.中国会计准则的产生2.中国会计准则的变迁3.中国会计准则变迁的特点四、重点难点1.国际会计准则变迁的特点和动因;2.美国会计准则的变迁特点和动因;3. 国际会计准则变迁的特点和动因;4.目标导向、原则导向、规则导向差异和特点;五、思考与讨论1.国际会计准则如何演变为国际会计发展中霸主地位的?2.国际会计准则的模式是什么?3.美国会计准则的主导模式是什么?4.美国产生财务丑闻与会计准则导向选择之间关系如何?5.你认为我国应当采用何种准则导向?为什么?第三章国际会计概念框架及比较一、基本要求了解国际会计准则中国际准则、美国会计准则、中国会计准则的概念框架的基本内容和差异。


写在前面:1. po主是中大管院学生,这学期修的【国际财务管理】(英文原书第6版);科目叫【国际金融】。
期末考试有考【名词解释】但是书上虽然每章最后给出了key words却没有释义,整理它们浪费了很多复习时间。
考完试了,就把整理的内容传上来【遗泽余芳】。
2. 条目按照【赵慧敏】老师划出的重点整理,所以并不全面,不过也涵盖大半。
如果是同样修习赵老师课程的学弟学妹,可以直接参考这篇整理稿子,不过打字不易,望能【购买】后下载使用。
其他不考名词解释的同学,考前复习此文也必然有所帮助。
3. 【名词解释】并非是解释名词,本文内容全部来自整理过的原书内容,如European Monetary System我不会解释定义是什么,但是会涵盖它建立的内容(这也是书中重点介绍的东西)4. 由于是【国际金融】而非【国际财务管理】课程,有些原书章节(1、4、8、9、10)选择性跳过5. 纯手打,可能有错误,请自行纠正。
【手打、整理辛苦,请购买下载使用】Chapter 2Bimentallism: a double standard in that free coinage was maintained for both gold & silver.Bretton Woods system: each country establish a par value in relation to the US dollar, which was pegged to gold at 35 dollar per ounce.European Montary System(EMS):a. To establish a "zone of monetary stability" in Europe.b. To coordinate exchange rate policies vis-a-vis the non-EMS currencies.c. To pave the way for the eventual European montary union.Exchange Rate Mechanism(ERM): refers to the procedure by which EMS member countries collectively manage their exchange rates.Gold standard:a. gold alone is assured of unrestricted coinage.b. there is two-way convertibility between gold and national currencies at a stable ratio.c. gold may be freely exported or imported.International monetary system: Bimentallism; Gold standard; Inter war period; Bretton Woods system; Flexible exchange rate regime.Gresham's Law: "bad" money drives out "good" money.Chapter 3Balance of payments(BOP): the statistical record of a countries' international transactions over a certain period of time presented in the form of double-entry bookkeeping.BOPI(indentity): BCA(current account)+BKA (capital account)+BRA(reserves account)=0capital account: includes all purchases and sales of assets such as stocks, bonds, bank accounts, real estate and businesses.current account: includes the exports and imports of goods and services.factor income: the third category of the current account, consists largely of payments and recepts of interest, dividends and other income on foreign investments that were previously made.J-curve effect: The curve shows the initial deterioration and the eventual improvement of the trade balance following a depreciation.official reserve account: covers all purchanses and sales of international reserve assets such as dollars, FX, gold, and special drawing rights.official settlement: we compute the cumlative BOP including the curved account, capital account, and the statistical discrepancies, we obtain the so-called overall balance or official settlement.trade balance: represents the net merchandise export.Chapter 5ask/bid price: Inter bank FX trades buy currency for inventory at the bid price and sell from inventory at the higher ask price.cross-exchange rate: is an exchange rate between a currency pair where neither currency is the US dollar.direct quotation: the price of one unit of the foreign currency in US dollar.indirect quotation: the price of one US dollar in the foreign currency.exchange-trade fund(ETF): is a portfolio of financial assets in which shares representing fractional ownership of the fund trade on an organized exchange.foreign exchange(FX) market: includes the conversion of purchasing power from one currency into another, bank deposits of foreign currency, the extension of credit denominated in a foreign currency, foreign trade financing, trading in foreign currency options and future contracts, and currency swaps.forward market: contracting today for the future purchase or sale of foreign exchange.forward premium/dicount: lt is common to express the premium or discount of a forward rate as an annualized percentage deriation from the spot rate.spot market: involves almost the immediate purchase or sale of foreign exchange.swap transaction: provide a means foe the bank to mitigate the currency exposure in a forward trade.(avoid risks)trangular arbitrage: is the process of trading out of the US dollar into a second currency, then trading it for a third one which is in turn traded for US dollars, the purpose to earn arbitrage profit.Chapter 6efficient market hypothesis(EMH): If the current assets prices fully reflect all the available and relevant information, financial market are said to be efficient.forward expectations parity(FEP): Any forward premium or discount is equal to the expected change in the exchange rate.Interest rate parity(IRP): is a no-arbitrage condition representing an equilibrium state under which investors will be indifferent to interest rates available on bank deposits in two countries.international fisher effect: is a hypothesis in international finance thatr suggests different in nominal interest rates reflect expected changes in the spot exchange reats between countries.Law of one piece: a good must sell for thr same price in all lacations.purchasing power parity: the exchange rate between two currencies should be equal to the ratio of the countries price levels.random walk hypothesis: today's exchange rate is the best predictor ofr tomorrow's exchange rate.uncovered interest rate parity: the interest rate differential between a pair of countries is equal to the expected rate of change in the exchange rate.Chapter 7American option: can be exercised at any time during the contract.call/put: An option to buy the underlying asset is a call; to sell the underlying asset is a put. European option: can be exercised only at the maturity or expiration date of the contact. exercised price(striking price): the stated price paid is known as the exercise price.futures: a future contract has standardized features and is exchangetraded, that is, traded on organized exchanges rather than over the counter.in-the- money: S T>E (C AT=C ET=Max[S T - E, 0). which will be exercised.initial performance bond: must be deposited into a collateral account to establish a future position.maintenance performance: If the investor's performance bond account falls below a maintenance performance bond level, additional funds must be deposited into the account to bring it back to the initial performance bond level in order to keep the position open.market-to-market: daily at the settlement price.open interest: This is the total number of short or long contracts outstanding for the particular delivery month.option: a right to buy or sell a given quantity if asset in the future.time value: The difference between the option premium and options' instrinsic value( which is nonnagetive.)Chapter 11Bank capital adequacy: refers to the amount of equity capotal and other securities a bank holds as reserves against risky assets to reduce the probability of a bank failure.Eurobank: Banks accepting Eurocurrency deposits.Eurocurrency: is a time deposit of money in an international bank located in a country different from the country that issued the currency.International Banking Facility(IBF): is a scpatate set of asset and liability account that are segregated on the parent bank's books; it's not a unique physical or legal entity.London Interbank Offered Rate(LIBOR): the reference rate in London for Eurocurrency deposits.negatiable certificate of deposit(NCD): kind of deposit has lower rate of LIBOR, but can be tarded freely.offshore banking center: is a country or region whose banking system is organized to pemit extenal accounts beyond the normal economic activity of the country.Chapter 12Bearer Bonds: are bonds with no registered owner. As such they offer anonymity but they also offer the same risk of loss as currency.Dual-Currency Bonds: A straight fixed-rate bond, with interest paid in one currency, and principal in another currency.Euro Bonds: is one denominated in a particular currency but sold to investors in national capital markets other than the country that issued the denominating currency.Floating-rate notes (FRNs): are typically medium-term bonds with coupon payments indexed to some reference rate.Foreign bond: is one offered by a foreign borrower to the investors in a national capital market and denominated in that nation's currency.Global bond: A global bond is a very large international bond offering by a single borrower that is simultaneously sold in North America, Europe and Asia.Market makers: stand ready to buy or sell for their own account by quoting two-way bid and ask price.Registered bonds : the owners name is registered with the issuer.Straight fixed-rate bond: have a designated maturity date at which the principal of the bond issue is promised to be repaid.Chapter 13American Depository Receipts (ADRs):It is a receipt that represents the number of foreign shares that are deposited at a U.S. bank.Cross-listing:refers to a firm having its equity shares listed on one or more foreign exchanges. Limit order: An order to your broker to buy or sell at the at a price you want, when and if he can. Market order:An order to your broker to buy or sell share immediately at the market price. Yankee stock: The direct sale of new equity capital to U.S. public investors by foreign firms.Chapter 14Currency swap: one counterparty exchanges the debt service obligations of a bond denominatedin one currency for the debt service obligations of the other counterparty denominated in another currency.Quality spread differential (QSD): represents the potential gains from the swap that can be shared between the counterparties and the swap bank.Single-currency interest rate swap: one counterparty exchanges the interest payments of a floating-rate debt obligation for the fixed-rate interest payments of the other counterparty.Swap bank: is a generic term to describe a financial institution that facilitates swaps between counterparties.ps.words in red are the questions of 2013's final exam.。

国际财务管理学第六版许艳芳引言国际财务管理是现代经济领域的重要研究方向之一。
随着全球化的深入发展,国际贸易和投资规模不断扩大,财务管理在国际化背景下的挑战也越来越多。
许艳芳教授的《国际财务管理学第六版》是该领域的经典教材之一。
本文将对该教材进行综合介绍。
第一章国际财务管理的基础概念第一章主要介绍国际财务管理的基本概念和重要性。
作者通过对国际财务管理的定义、发展历程以及研究方法的讨论,帮助读者建立起对国际财务管理的整体认识。
- 国际财务管理的定义 - 国际财务管理的发展历程 - 国际财务管理的研究方法第二章国际金融市场与汇率第二章介绍国际金融市场的组成和功能,以及汇率的基本概念和影响因素。
作者详细分析了不同国家间货币的汇率形成机制和变动原因,为后续章节的学习打下基础。
- 国际金融市场的组成和功能 - 汇率的基本概念和分类 - 汇率的影响因素和变动原因第三章跨国公司的财务目标第三章重点讨论跨国公司的财务目标和风险管理。
作者通过对不同财务目标的比较和分析,介绍了传统财务目标与现代财务目标之间的区别和联系,并讨论了跨国公司如何管理汇率和利率风险。
- 传统财务目标与现代财务目标的比较 - 跨国公司的财务目标和风险管理 - 汇率和利率风险管理策略第四章国际金融市场与金融工具第四章重点介绍国际金融市场的各种金融工具和交易方式。
作者通过具体案例分析,帮助读者理解金融市场的运作机制和交易方式,并介绍了国际证券市场、外汇市场和衍生品市场的特点和参与者。
- 国际证券市场和股票交易 - 外汇市场和汇率交易 - 衍生品市场和风险管理工具第五章国际财务报告与分析第五章主要介绍国际财务报告的基本概念和要求,以及财务分析的方法和技巧。
作者通过对国际财务报告准则和标准的解读,帮助读者理解和使用财务报表进行分析和决策。
- 国际财务报告的基本概念和要求 - 财务分析的方法和技巧 - 国际财务报告的解读与分析结论《国际财务管理学第六版》通过系统而全面地介绍了国际财务管理的理论和实践知识。

会计基础第六版知识点总结第一章会计的概念和作用1.1 会计的概念会计是通过核算、报告和分析企业经济活动,为内外部利益相关方提供决策依据的一门信息系统。
1.2 会计的作用财务会计和管理会计是企业内部用于决策和管理的两个重要分支,提供对内外部利益相关方的决策依据。
第二章会计要素和会计要素关系2.1 会计要素的内容会计要素包括资产、负债、所有者权益、收入和费用。
2.2 会计要素关系资产=负债+所有者权益,收入-费用=利润。
第三章会计核算基础3.1 会计等式资产=负债+所有者权益,是会计核算的基础。
3.2 会计分录会计分录是根据交易和事项的原始凭证,经过科目、借贷相等的规则,将交易和事项分录到会计账户中的一种记录方式。
第四章会计科目和会计账户4.1 会计科目的分类会计科目包括资产类科目、负债类科目、所有者权益类科目、成本类、收入类和费用类科目。
4.2 会计账户的设立和作用会计账户是会计科目的集中表现形式,是会计核算的基本载体,对每个会计科目进行记录。
第五章会计账簿和账务处理5.1 会计账簿的种类会计账簿包括日记账、总账、明细账、分类账等。
5.2 会计分录和填制账簿会计分录是根据凭证填写账簿的过程。
第六章会计常用凭证和凭证填制6.1 会计凭证的种类会计凭证包括收款凭证、付款凭证、转账凭证、转销凭证、记账凭证等。
6.2 凭证填制凭证填制是根据交易和事项的原始凭证,按照一定的会计规则,填写和审核凭证,进行会计核算的过程。
第七章会计账务处理流程和核算方法7.1 会计账务处理的流程会计账务处理包括出纳业务、领料业务、还款业务、开发票业务、验收业务、盘点业务、报账业务等。
7.2 核算方法核算方法包括历史成本核算法、可变成本核算法、标准成本核算法、直接成本核算法、间接成本核算法等。
第八章会计报表的编制8.1 资产负债表的编制资产负债表是以资产、负债和所有者权益为主体,反映企业财务状况的一种财务报表。
8.2 损益表的编制损益表是通过对企业收入和费用进行核算,用来反映企业经营成果的一种财务报表。



会计学基础第六版课程设计一、课程概述《会计学基础》是一门介绍会计学基本理论和实践的基础课程,旨在为学生提供必备的财务会计知识和技能,帮助学生了解企业的基本会计信息,掌握财务报表的编制和分析方法,为学生未来的职业发展打好坚实的基础。
本课程以第六版《会计学基础》为标准教材,主要包括会计学的基本概念、会计科目及账户、会计凭证的记载,会计账簿的记账方法,财务报表的编制与分析等内容。
二、教学目标1.了解会计学的基本概念和基本原则;2.熟悉会计科目分类及会计账户的设立方法;3.掌握会计凭证记载的方法,了解会计核算基础和科目的借贷规则;4.掌握会计账簿记账方法和会计核算的流程;5.了解财务报表的组成和编制方法;6.熟悉财务报表的分析方法,掌握企业的财务分析基本技能。
三、教学内容和教学安排1. 会计学的基本概念和基本原则本节课程介绍会计学的基本概念、目的和基本原则等内容,为后续内容打下基础。
教学安排:1课时2. 会计科目及账户本节课程介绍会计科目的分类、分录、会计账户设立和管理等内容。
教学安排:2课时3. 会计凭证的记载本节课程主要介绍会计凭证的记载方法和借贷规则等内容。
教学安排:2课时4. 会计账簿的记账方法本节课程主要介绍会计账簿的记账方法和标准化会计流程等内容。
教学安排:3课时5. 财务报表的编制和分析本节课程主要介绍财务报表的编制和财务指标分析方法等内容。
教学安排:4课时四、教学方法和考核方式1. 教学方法本课程将采用课堂讲解、案例分析、小组讨论等多种教学方法,旨在帮助学生更好地掌握知识和技能。
2. 考核方式本课程将采用考试和小组报告的方式进行考核。
其中考试占总成绩的70%,小组报告占总成绩的30%。
五、参考教材•《会计学基础》(第六版),杨宝华等编,中国财政经济出版社;•《会计学》,戴锦华著,高等教育出版社;•《会计学原理》,朱怀光等编,中国人民大学出版社。
以上是本课程的基本设计,为确保教学质量和效果,教师还需要根据实际情况调整和优化教学内容和教学安排,确保学生掌握所需的知识和技能,为将来的职业生涯打好坚实的基础。


国际收支平衡表编制原则与指标说明一、国际收支平衡表编制原则根据国际货币基金组织(IMF)《国际收支和国际投资头寸手册》(第六版)(以下简称《手册》第六版)制定的标准,国际收支平衡表是反映某个时期内一个国家或地区与世界其他国家或地区间的经济交易的统计报表。
国际收支统计以权责发生制为统计原则,并采用复式记账法。
中国国际收支表是反映特定时期内我国(不含中国香港、澳门和台湾,下同)与世界其他国家或地区的经济交易的统计报表。
二、国际收支平衡表指标说明根据《手册》第六版,国际收支平衡表包括经常账户、资本账户和金融账户。
经常账户可细分为货物和服务账户、初次收入账户、二次收入账户。
金融账户可细分为直接投资、证券投资、金融衍生工具、其他投资和储备资产。
具体项目的含义如下:1.经常账户:包括货物和服务、初次收入和二次收入。
1.A货物和服务:包括货物和服务两部分。
1.A.a货物:指经济所有权在我国居民与非居民之间发生转移的货物交易。
贷方记录货物出口,借方记录货物进口。
货物账户数据主要来源于海关进出口统计,但与海关统计存在以下主要区别:一是国际收支中的货物只记录所有权发生了转移的货物(如一般贸易、进料加工贸易等贸易方式的货物),所有权未发生转移的货物(如来料加工或出料加工贸易)不纳入货物统计,而纳入服务贸易统计;二是计价方面,国际收支统计要求进出口货值均按离岸价格记录,海关出口货值为离岸价格,但进口货值为到岸价格,因此国际收支统计从海关进口货值中调出国际运保费支出,并纳入服务贸易统计;三是补充部分进出口退运等数据;四是补充了海关未统计的转手买卖下的货物净出口数据。
1.A.b服务:包括加工服务,维护和维修服务,运输,旅行,建设,保险和养老金服务,金融服务,知识产权使用费,电信、计算机和信息服务,其他商业服务,个人、文化和娱乐服务以及别处未提及的政府服务。
贷方记录提供的服务,借方记录接受的服务。
1.A.b.1加工服务:又称“对他人拥有的实物投入的制造服务”,指货物的所有权没有在所有者和加工方之间发生转移,加工方仅提供加工、装配、包装等服务,并从货物所有者处收取加工服务费用。
《国际会计》课程教学大纲课程名称:国际会计International Accounting课程编码:6361F006 学分: 2 总学时:36说明【课程简介】本课程为应用型本科会计学专业财务会计方向课程。
随着中国加入世贸组织以及经济全球化进程的加快,学生不应仅把眼光局限在国内的会计实务的处理上,更应该立足于全球角度,应对会计国际化的发展趋势,因此,本课程在会计学人才培养中有着重要位置。
作为会计学的一个独立的分支,国际会计有着自己相对独立的理论和方法体系,是一门专业性很强的课程。
通过本课程学习,培养学生利用此课程中的理论和方法分析和解决问题的能力。
【课程性质】专业方向课程【适用专业】会计学专业【教学目标】通过该课程的教学,能使学生了解国际会计产生、基本知识、发展动态和会计准则的国际协调,掌握国际比较会计、国际税务筹划的不同特点、具体要求和核算方法。
通过本课程的学习,能比较完整地掌握国际会计学的基本理论框架,并能把它们运用于实践当中。
【先修课程要求】《经济学》、《管理学》、《基础会计》、《中级财务会计》、《财务管理》、《税法》等课程。
这些课程的基本原理、理论及其分析方法,是学习本课程的基础。
【能力培养要求】可以对典型国家的会计模式进行比较,对常见的国际税务问题可以分析判断。
【学习总量】总学时36学时,其中理论36学时。
学生自主学习12学时,另行安排。
【教学方法与环境要求】教学方法:依托多媒体教学环境,在讲授基础上,结合教材思考题组织课堂讨论和主题发言。
用国际会计准则与实际业务相结合的方法帮助学生借鉴和吸收国际上一切优秀的成果;联系实际发展我国的会计准则;熟悉和掌握国际通用的商用语言。
环境要求:多媒体教室。
【学时分配】【教材与主要参考书】教材:《国际会计》,常勋;常亮,东北财经大学出版社,2015年1月,第7版参考书:【1】《国际会计前沿》,王松年,上海财经大学出版社,2013年【2】《国际会计学》,徐经长、杜胜利、陈轲,中国人民大学出版社,2015年【3】《国际会计研究》,常勋,中国金融出版社,2015年【4】《国际财务报告准则—阐释与应用》(中国版),本哈德. 裴仁斯等,上海财经大学出版社,2014年【5】《国际会计学》,[美]弗雷德里克·D. S. 乔伊、卡罗尔·安·福罗斯特、加利·K. 米克著,周晓苏、方红星译,东北财经大学出版社,2010年7月【6】《国际会计》,王建新,上海财经大学出版社,2013年5月大纲内容第一章国际会计的形成与发展【教学目的和要求】了解:(1)国际会计师大会的由来与发展(2)早期国际会计定义的区别理解:(1)市场国际化对会计国际化的影响(2)跨国公司兴起对会计国际化的影响(3)会计遗产对会计国际化的影响掌握:(1)国际会计的三大问题(2)会计职业国际化的三个层次(3)各国会计师职业资格考试的差异(4)“世界会计”观的定义(5)“国别会计”观的定义(6)“实务主义”观的定义(7)崔和缪勒的定义(8)伊克彼、麦尔科和伊利马拉夫的定义(9)国际会计的主要内容运用:(1)理论联系实际能够区分会计职业界提供国际性服务的三个层次(2)通过学习各学者的观点,能够评价和比较国际会计的不同定义【内容提要】第一节会计的国际化一、市场的国际化,特别是货币、资本市场的国际化二、跨国公司的兴起和壮大三、会计世袭遗产的国际性四、特定会计方法的国际性质五、会计的国际化与国家化第二节会计职业界的国际化一、会计职业界提供国际性服务的三个层次二、会计职业界的国际组织三、会计职业国际化的阻力第三节国际会计的定义一、国际会计学家在早期对国际会计所下的定义二、20世纪70年代国际会计研究中的三种不同观点三、20世纪80年代至90年代国际会计学家对国际会计所下的定义四、国际会计的主要内容【教学重点与难点问题】教学重点:市场国际化、特别是货币市场和资本市场的国际化,是会计国际化的最主要的推动力量;跨国公司的兴起和壮大对会计国际化的双面影响;国际会计的定义。