英语语法-句子种类史上最详细
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:131.50 KB
- 文档页数:15

高中英语语法组成句子的各个部分叫句子成分。
英语句子成分有主语,谓语,表语,宾语,宾语补足语,定语,状语等。
顺序一般是主语,谓语,宾语,宾语补足语,而表语,定语,状语的位置要根据情况而定。
1、主语主语表示句子主要说明的人或事物,一般由名词,代词,数词,不定式等充当。
Helikeswatch'ingTV.他喜欢看电视。
2、谓语谓语说明主语的动作,状态或特征。
1),简单谓语由动词(或短语动词)构成。
可以有不同的时态,语态和语气。
Westud'yforthepeo'ple.我们为人民学习。
2),复合谓语:情态动词+不定式Icanspeakalit'tleEng'lish.我可以说一点英语。
3、表语表语是谓语的一部分,它位于系动词如be之后,说明主语身份,特征,属性或状态。
一般由名词,代词,形容词,副词,不定式,介词短语等充当。
Mysis'terisanurse.我姐姐是护士。
4、宾语宾语表示动作行为的对象,跟在及物动词之后,能作宾语的有名词,代词,数词,动词不定式等。
WelikeEng'lish.我们喜欢英语。
有些及物动词可以带两个宾语,往往一个指人,一个指物,指人的叫间接宾语,指物的叫直接宾语。
Hegavemesom'eink.他给了我一点墨水。
有些及物动词的宾语后面还需要有一个补足语,意思才完整,宾语和它的补足语构成复合宾语。
如:Wemakehimourmon'itor.我们选他当班长。
5、定语在句中修饰名词或代词的成分叫定语。
用作定语的主要是形容词,代词,数词,名词,副词,动词不定式,介词短语等。
形容词,代词,数词,名词等作定语时,通常放在被修饰的词前面。
Heisanewstu'dent.他是个新生。
但副词,动词不定式,介词短语等作定语时,则放在被修饰的词之后。
Thebikeintheroomismine.房间里的自行车是我的。

英语四大句子种类英语四大句子种类指的是英语语法中常见的四种句子类型,它们分别是:简单句、并列句、复合句和复杂句。
这四种句子类型在英语语法中占据着重要的地位,它们在结构和表达意思上都有各自的特点。
下面将对这四种句子类型进行详细的介绍和举例说明。
●简单句 (Simple Sentences)●简单句是指只有一个主语和一个谓语的句子。
这种句子结构简单,表达的意思也较为简单。
例如:●She sings beautifully. (她唱得很美。
)●He loves football. (他喜欢足球。
)●这些句子只有一个主语和一个谓语,因此它们是简单句。
并列句 (Compound Sentences)并列句是指由两个或两个以上的简单句组合而成的句子。
这种句子通过使用并列连词(如and、but、or等)将简单句连接在一起。
例如:●I like coffee and she likes tea. (我喜欢咖啡,她喜欢茶。
)●He is smart but he is lazy. (他很聪明但是很懒。
)●这些句子都是由两个简单句组合而成的,因此它们是并列句。
复合句 (Complex Sentences)复合句是指由一个主句和一个或多个从句组成的句子。
这种句子通常包含一个主语和一个谓语,以及一个或多个从句作为补充信息。
例如:●She believes that he is honest. (她相信他是诚实的。
)●They were surprised when the door opened. (门打开时他们感到惊讶。
)●这些句子都包含一个主句和一个或多个从句,因此它们是复合句。
复杂句 (Compound-Complex Sentences)复杂句是指由一个主句和两个或多个从句组成的句子。
这种句子通常包含一个主语和一个谓语,以及两个或多个从句作为补充信息。
例如:●We know that she is a good student, although she is often late forschool. (我们知道她是一个好学生,尽管她经常上学迟到。


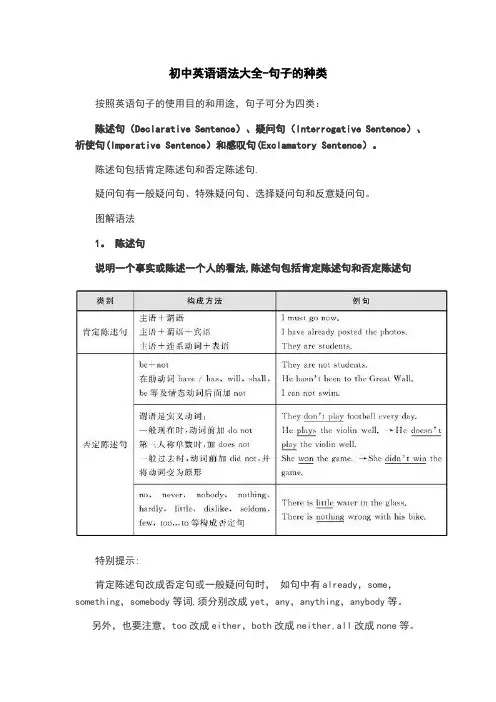
初中英语语法-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。
疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1. 陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you?”意为“请求”,“won’t you?”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you?Don’t be late again, will you?②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t it?How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she?③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?”而不用“am not I?”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I?④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t it?Nothing is difficult, is it?⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, no one,none, neither 时,疑问句的主语用theyEveryone is here, aren’t they?No one knows about it, do they?⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t it?These are grapes, aren’t they?There was a hospital here, wasn’t there?⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn’t one?⑧陈述句中有few, seldom, never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is he?You got nothing from him, did you?It is useless, isn’t it?⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important, isn’t it?⑩陈述部分由think, believe, suppose, imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t he?I don’t think he can pass the exam, can he?He believed you had seen her before, didn’t he?? have是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然They had a meeting just now, didn’t they?She’s been to many places of interest, hasn’t she?? 陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you?? 陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we?? 陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定”解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t he?You must go to Guangzhou, needn’t you?You mustn’t smoke here, must you?Tom must be at home, isn’t he?She must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t she?He must have been a policeman, wasn’t he?? 陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用 shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she?? 陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn’t he?特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。


高考英语语法基础---句子种类分类一.句子种类(按照用途分类)1.陈述句2.祈使句3.感叹句4.疑问句(一般疑问句,特殊疑问句,选择疑问句,反意疑问句。
)具体知识:1.陈述句陈述句(Declarative Sentence)是陈述一个事实或者说话人的看法。
它包括肯定句(The Affirmative Sentence)和否定句(The Negative Sentence)两种。
陈述句在书写时句末用句号,在朗读时用降调。
陈述句的五种基本句型:(1) 主语+连系动词+表语(2) 主语+谓语(不及物动词)(3) 主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语(4) 主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语(5) 主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语My uncle tells me that the key to his success is honesty.2. 祈使句祈使句常常是表达说话人对对方的劝告、叮嘱、请求或命令等。
因此,祈使句中一般没有主语,但根据其句意,实际上是省略了主语you。
祈使句句末用感叹号或句号,朗读时,常用降调。
在表达请求或劝告时,在祈使句前或句末可加上please,以使句子的语气更加缓和或客气。
祈使句一般没有时态的变化,也不能与情态动词连用。
Keep off the grass! 勿踩踏草地!Always keep in mind that your main task is to get this company running smoothly.3. 感叹句感叹句的基本构成形式1).What(+a/an)+形容词+名词+主语+谓语!2).How+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数+主语+谓语!3).How+形容词/副词+主语+谓语!You can't imagine how crucial a role the pigeons played in the battlefields.你无法想象在过去的战场山鸽子发挥了多么重要的作用。

高考英语语法基础---句子种类分类一.句子种类(按照用途分类)1.陈述句2.祈使句3.感叹句4.疑问句(一般疑问句,特殊疑问句,选择疑问句,反意疑问句。
)具体知识:1.陈述句陈述句(Declarative Sentence)是陈述一个事实或者说话人的看法。
它包括肯定句(The Affirmative Sentence)和否定句(The Negative Sentence)两种。
陈述句在书写时句末用句号,在朗读时用降调。
陈述句的五种基本句型:(1) 主语+连系动词+表语(2) 主语+谓语(不及物动词)(3) 主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语(4) 主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语(5) 主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语+宾语补足语My uncle tells me that the key to his success is honesty.2. 祈使句祈使句常常是表达说话人对对方的劝告、叮嘱、请求或命令等。
因此,祈使句中一般没有主语,但根据其句意,实际上是省略了主语you。
祈使句句末用感叹号或句号,朗读时,常用降调。
在表达请求或劝告时,在祈使句前或句末可加上please,以使句子的语气更加缓和或客气。
祈使句一般没有时态的变化,也不能与情态动词连用。
Keep off the grass! 勿踩踏草地!Always keep in mind that your main task is to get this company running smoothly.3. 感叹句感叹句的基本构成形式1).What(+a/an)+形容词+名词+主语+谓语!2).How+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数+主语+谓语!3).How+形容词/副词+主语+谓语!You can't imagine how crucial a role the pigeons played in the battlefields.你无法想象在过去的战场山鸽子发挥了多么重要的作用。
初中英语语法大全-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句.疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1。
陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you?"意为“请求",“won't you?”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you?Don’t be late again, will you?②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t it?How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she?③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?"而不用“am not I?”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I?④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t it?Nothing is difficult, is it?⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, no one, none, neither 时,疑问句的主语用they例句:Everyone is here, aren't they?No one knows about it, do they?⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t it?These are grapes, aren’t they?There was a hospital here, wasn’t there?⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn't one?⑧陈述句中有few, seldom, never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is he?You got nothing from him, did you?It is useless, isn’t it?⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important, isn’t it?⑩陈述部分由think, believe, suppose, imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t he?I don’t think he can pass the exam, can he?He believed you had seen her before, didn’t he?? have是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然例如:They had a meeting just now, didn’t they?She’s been to many places of interest, hasn't she??陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you?? 陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we?? 陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定"解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t he?You must go to Guangzhou, needn’t you?You mustn’t smoke here, must you?Tom must be at home, isn’t he?She must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t she?He must have been a policeman, wasn’t he??陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用 shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she??陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn't he?特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。

英语语法句子种类
英语语法中常见的句子种类包括:
1. 陈述句(declarative sentence):陈述句是表达一个声明、陈述或描述的句子,通常以句号结尾。
例:I like to read books.(我喜欢阅读书籍。
)
2. 疑问句(interrogative sentence):疑问句用于提出问题,通常以问号结尾。
例:Do you like ice cream?(你喜欢冰淇淋吗?)
3. 感叹句(exclamatory sentence):感叹句用于表达强烈的感情或情绪,通常以感叹号结尾。
例:What a beautiful sunset!(多么美丽的日落啊!)
4. 祈使句(imperative sentence):祈使句用于表达请求、命令、建议或要求,通常省略了主语,动词在前。
例:Please close the window.(请关上窗户。
)
5. 条件句(conditional sentence):条件句用于表达假设、条件或推断,并包含主从句。
例:If it rains, we will stay indoors.(如果下雨,我们就会呆在室内。
)
例:I like to read books, and he prefers to watch movies.(我喜欢阅读书籍,他更喜欢看电影。
)
例:She is studying English because she wants to improve her job prospects.(她正在学习英语,因为她想提高工作前景。
)以上是英语语法中常见的句子种类,每种句子种类都有其特定的用途和结构。

英语语法句子的种类一、陈述句陈述句是最常见的句子类型,用于陈述事实、描述情况或表达观点。
例句:- I go to school every day.- She is a doctor.- They live in New York.二、疑问句疑问句用于询问信息、寻求答案或确认事实。
例句:- Do you like pizza?- Where is the nearest post office?- Did you see the movie?三、祈使句祈使句用于表达请求、命令、建议或劝告。
例句:- Please close the door.- Don't forget to bring your umbrella.- Let's go for a walk.四、感叹句感叹句用于表达惊讶、赞美、失望或其他强烈的情感。
例句:- What a beautiful sunset!- How delicious the food is!- I can't believe we won the game!五、条件句条件句用于表达条件和结果之间的关系。
例句:- If it rains, we will stay indoors.- Unless you study hard, you will fail the exam.六、比较句比较句用于表示两个或多个事物之间的比较。
例句:- John is taller than Peter.- She sings better than him.- I prefer coffee to tea.七、否定句否定句用于否定陈述句中的内容。
例句:- I didn't see him at the party.- She doesn't like spicy food.- They haven't visited that museum before.。

补充内容:英语中句子种类的划分一般情况下,我们可以从两个不同的角度对句子进行分类:一是按句子的结构,可以分为简单句、并列句和主从复合句(从句);二是按句子的用途,一个简单句可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
句子分类一览表句式定义例子简单句陈述句用来说明事实或说话人的看法,包括肯定句和否定句。
She is a doctor.She doesn’t like cats.疑问句一般疑问句一般指用Yes或No回答的疑问句。
Do you like maths?特殊疑问句是以疑问词开头的疑问句。
What day is it today?选择疑问句提出两种或两种以上的情况,要求对方选择一种。
Do you like drinking tea orcoffee?反意疑问句对陈述句所叙述的事实提出的疑问。
They went out, didn’t they?祈使句用来表示请求、命令。
Be quiet!Don’t play with fire.感叹句用来表达强烈的感情。
What a fine day it is!How interesting the book is!并列句含有两个或两个以上相互并列主谓结构的句子,各分句之间靠连词和分号等来连接。
表递进and, neither...nor, notonly...but also, as well as...表转折but, still, however, yet, while...表选择or, either...or, whether...or,otherwise...表因果so, for...主从复合句(以后详细讲解)由一个或一个以上的从句构成,主句为句子的主体,从句不能独立,只用作句子的一个成分.形容词性从句(定语从句)名词性从句(主宾表同)副词性从句(状语从句)初级篇:简单句和⼗⼤词性1、陈述句:出题一般考查的是将肯定句变为否定句。
有以下几种常见情况:谓语动词部分有be 动词、助动词(have/has/had )、情态动词(can/must/should 等)直接在其后面加notShe is a singer. → She is not a singer.I have found my schoolbag.→I have not found myschoolbag. 谓语动词为实义动词时(如hit, eat 等),变否定句需要添加助动词do/does/did ,在其后加notThey like jogging.→ They don’t like jogging. 句中含有all ,both 的句子,变完全否定时,要将all 变为none, both 变为neither, both…and…变为neither…nor…要注意谓语动词的变化。
英语语法之句子的种类一、分类:按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
1. 陈述句:说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
He gets up at six. 他六点钟起床。
(说明事实)I don't think so .我不这么认为。
(说明看法)2.疑问句:提出问题。
①一般疑问句:Can you finish the work in time?你能按时完成工作吗?②特殊疑问句:Where do you live?你住那儿?How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事?③选择疑问句:Do you want tea or coffee?你是要茶还是要咖啡?④反意疑问句:He doesn't know her, does he?他不认识她,对不对?3. 祈使句:提出请求,建议或发出命令Sit down, please.请坐。
Don't be nervous!别紧张!4. 感叹句:表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪.1.陈述句:①肯定式:This is my sister .I like reading books at weekends .②否定式:A: "be+not" I am not a student.B:"do\does\did +not" He does not like playing basketball.C:"助动词\情态动词+not" I can not swim.D:用no、nothing、nobody表否定.I know nothing about it.2. 一般疑问句:①定义:用be动词、助动词或情态动词置于句首,可用“yes”或“no”来回答的问句。
②应答:用yes\no(或相当于“yes”或“no”的词)回答,并根据句首的be动词、情态动词或助动词作相应的回答。
--Is Mary a Japanese girl ? --Yes,she is.\No,she isn't.--Can you speak English? --Yes,I can .\No, I can't .--Do you like your teacher ? --Yes,I do.\No, I don't .③变形:如何将一个肯定的陈述句变为一般疑问句:A:看句中有无be动词,如果有be动词提到句首即可。
句子的种类英语句子按照其交际功能可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句四类。
1. 陈述句用于叙述一项事实的句子叫陈述句(declarative sentence)。
陈述句可以是肯定句也可以是否定句。
例如:My advice to you is to speak the truth. 我建议你说真话。
Your answer is not quite correct. 你的回答不太正确。
2. 疑问句用来提出疑问的句子叫疑问句(interrogative sentence)。
疑问句有四类:一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
1)一般疑问句用yes 或no 来回答的疑问句,叫一般疑问句(general question)。
句中的助动词或情态动词要放在主语之前,形成倒装词序。
在个别情况下,如表示猜测、惊讶、怀疑时,也可使用陈述语序。
例如:Do you find it difficult to learn a new language你认为学习一种新的语言难吗Will she accept the invitation 她会接受邀请吗2) 特殊疑问句用疑问词开头,就某一具体部分提问的疑问句,称为特殊疑问句(special question)。
引出特殊疑问句的疑问词有who(谁),whom(谁),whose (谁的),which(哪个),what(什么),where(哪里),when(何时),why(为什么),how(如何)等。
例如:Who will come tomorrow明天谁会来What are you doing there 你在那儿干什么When did they get married 他们是什么时候结婚的Where did you find the book 你在哪里找到的这本书3)选择疑问句说话人提供两种或者两种以上的情况供对方做出选择的疑问句,叫选择疑问句(alternative question)。
初中英语语法大全-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。
疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1. 陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody 等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you?”意为“请求”,“won’t you?”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you?Don’t be late again, will you?②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t it?How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she?③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?”而不用“am not I?”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I?④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t it?Nothing is difficult, is it?⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody,nobody,everybody,anybody,no one,none,neither 时,疑问句的主语用they例句:Everyone is here,aren’t they?No one knows about it,do they?⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t it?These are grapes, aren’t they?There was a hospital here, wasn’t there?⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn’t one?⑧陈述句中有few,seldom,never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is he?You got nothing from him, did you?It is useless, isn’t it?⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important,isn’t it?⑩陈述部分由think,believe,suppose,imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t he?I don’t think he can pass the exam, can he?He believed you had seen her before, didn’t he?? have是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然例如:They had a meeting just now, didn’t they?She’s been to many places of interest, hasn’t she?? 陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you?? 陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we?? 陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定”解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t he?You must go to Guangzhou, needn’t you?You mustn’t smoke here, must you?Tom must be at home, isn’t he?She must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t she?He must have been a policeman, wasn’t he?? 陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she?? 陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn’t he?特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。
英语语法之句子的种类1) 陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
Light travels faster than sound. 光比声速度快。
(说明事实)The film is rather boring. 这部电影很乏味。
(说明看法)2) 疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。
有以下四种:a. 一般疑问句(General Questions):Can you finish the work in time?你能按时完成工作吗?b. 特殊疑问句(W Questions; H Questions):Where do you live? 你住那儿?How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事?c. 选择疑问句(Alternative Questions):Do you want tea or coffee?你是要茶还是要咖啡?d. 反意疑问句(Tag-Questions):He doesn't know her, does he?他不认识她,对不对?3) 祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如:Sit down, please. 请坐。
Don't be nervous! 别紧张!4) 感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如:What good news it is! 多好的消息啊!1) 简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如:She is fond of collecting stamps. 她喜欢集邮。
(主) (谓)2) 并列句(Compound Sentences):包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接,例如:The food was good, but he had little appetite.(主) (谓) (主)(谓)食物很精美,但他却没什么胃口。