英语中句子的种类
- 格式:docx
- 大小:23.49 KB
- 文档页数:5

三句子的种类句子是一个独立的语言单位,表示一个完整的思想.按使用目的可分为陈述句、感叹句、疑问句和祈使句;从结构上又可分为简单句、并列句和复合句.按使用目的分:一、陈述句That boy always helps others.Tom was not at home yesterday.He is too late to catch the bus.二、疑问句一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句Are you a doctorHow often do you have an English partyWhich would you like better, tea or coffeeShe is too young to go to school, is she三、感叹句(一)What +a /an+形容词+可数名词的单数形式+主语+谓语 ==二How+形容词+a/an +可数名词的单数形式+主语+谓语What a beautiful girl she is == How beautiful a girl she is三 What+形容词+可数名词的复数+主语+谓语What beautiful girls they are(四)What+形容词+不可数名词+主语+谓语What fine weather it is(五)How+形容词或副词+主语+谓语How interesting the dog is(六)How+主语+谓语How time flies四、祈使句祈使句主语通常被省略,谓语动词用原型.Be quietDon’t be late从结构上分:一、简单句句子只包含一个主谓结构.如,五种基本句型列式如下:基本句型一:主+系+表基本句型二:主+谓基本句型三:主+谓+宾基本句型四:主+谓+间宾+直宾基本句型五主+谓+宾+宾补.二、并列句句子包含两个或多个主谓结构,通常有并列连词连结.由并列连词把两个或两个以上的简单句连在一起的句子叫并列句.不同的并列连词表示并列分句之间的不同关系.根据并列分句之间的关系不同,并列句可以分为以下几种: 1.表示联合关系的并列句这类并列句常用并列连词and 和,not only ... but also... 不但……而且……等来连接,这时分句之间是顺承关系或并列关系.and一般不译出来.1. We bought her a birthday present,_____ she liked it very much.A. soB. orC. andD. but2. — Didn’t you give roses to your father on Father’s Day— Oh, not only my father,_____ my grandpa got red roses.A. orB. andC. butD. until2.表示转折关系的并列句这类并列句常用but 但是;可是,yet可是;然而,while 而等来连接,后面分句与前面分句之间有意义上的转折关系.1. — Would you like to go to the concert with me— I’d love to,_____ I can’t. I have a lot of homework to do.A. orB. butC. soD. and2. The doctors tried their best to save the patient’s life,_____ failedA. orB. soC. butD. because3.表示选择关系的并列句这类并列句常用并列连词or或者,either …or …要么……,要么……等连接.1. _____ Lily _____ Lucy may go with you because one of them must stay at home.A. Not only; but alsoB. Neither; norC. Both; andD. Either; or2. None of the shoes in the shops are the right size. They are _____ too big _____ too small.A. both; andB. neither; norC. either; orD. not only; but also3. “Are you going to eat here ____ take it away” asked the waiter..A. andB. soC. orD. but.4.表示因果关系的并列句这类并列句常用并列连词so因此;所以,for 因为等连接,后面分句与前面分句之间有因果关系.1. Mother was ill,_____ Father cooked for us instead.A. butB. orC. soD. and2. There is a lot of traffic in this city,_____ look both waysbefore crossing the streetA. soB. andC. butD. for特殊的并列句1.祈使句+and+一般将来时的句子这个句型表示“如果做到了祈使句表示的事情,就会有后面句子表示的结果”.2.例如: Study hard,_____ you are sure to have a good resultin the exam.A. orB. andC. forD. but3. 2. 祈使句 + or + 一般将来时的句子这个句型表示“如果做不到祈使句表示的事情,就会有后面句子表示的结果”4.例如: 1. Be quick,_____ we’ll be late for class.A. orB. soC. andD. but2. Come a little earlier next time,_____ you’ll miss thebest part of the TV play.A. andB. butC. orD. till三、复合句复合句Complex Sentence由一个主句Principal Clause和一个或一个以上的从句Subordinate Clause构成. 主句是全句的主体,通常可以独立存在;从句则是一个句子成分,不能独立存在.从句不能单独成句,但它也有主语部分和谓语部分,就像一个句子一样.所不同在于,从句须由一个关联词引导. 我们至今学过的从句有:定语从句, 名词性从句主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句,和状语从句.1. 定语从句 He is the man who wants to see you.2. 同位语从句 She told us her hope that she would become a pianist.注意:定语和同位语从句的区别.3. 表语从句 This is what we should do4. 宾语从句注意it做形式宾语Everybody knows that money doesn't grow on treesWe think it wrong that he told a lie to everyone. it做形式宾语5.主语从句注意it做形式主语What caused the accident remains unknownIt is certain that he will win the matchit做形式主语6.状语从句MyfriendsdislikemebecauseI’mhandsomeandsuccessfu l.。


英语中的句子种类陈述句,疑问句,祈使句,感叹句(划分标准:语气)一. 陈述句1. 定义:陈述句是用于陈述一个事实或表达说话人的看法的句子。
陈述句主要分为肯定句和否定句。
2. 陈述句的肯定句式主要有五种基本句型(1)“主语+系动词+表语”I am honored. 我很荣幸。
(2)“主语+不及物动词(谓语)”The students work very hard.学生们学习很努力。
(3)“主语+及物动词(谓语)+宾语”I teach English. 我教英语。
(4)“主语+及物动词(谓语)+间接宾语+直接宾语”,间接宾语是人,直接宾语是物。
能接双宾语的动词多数要在间接宾语前加to或for。
①加to的动词有give, send, pass, take, bring, show, lend, sell等。
She sent me a present.=She sent a present to me.她寄给了我一份礼物。
②加for的动词有buy, make, build, mend, cook等。
My father bought me a bike.=My father bought a bike for me. 我爸爸给我买了一辆自行车。
(5)“主语+及物动词(谓语)+宾语+宾语补足语”The teacher asked the students to listen carefully in class. 老师要求学生上课认真听讲。
3.陈述句的否定句式(1)be动词+not(2)情态动词/助动词+not+动词原形I don't get up at six o'clock this morning.今天早上六点我没有起床。
(3)no, never, har dly, seldom, few, little, nobody, neither…nor, none 等词构成否定句。
I can hardly believe his story.我几乎不相信他的故事。


句子的种类英语基础语法汇总句子的类型句子可以从不同的角度进行分类。
按照句子的语气,句子可分为陈述句、祈使句、感叹句、疑问句四种,一般称为句类。
以下是小编整理的句子的种类英语基础语法汇总,希望大家喜欢。
(一)按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
1) 陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
Light travels faster than sound. 光比声速度快。
(说明事实)The film is rather boring. 这部电影很乏味。
(说明看法)2) 疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。
有以下四种:a. 一般疑问句(General Questions):Can you finish the work in time?你能按时完成工作吗?b. 特殊疑问句(W Questions; H Questions):Where do you live? 你住那儿?How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事?c. 选择疑问句(Alternative Questions):Do you want tea or coffee?你是要茶还是要咖啡?d. 反意疑问句(Tag-Questions):He doesn't know her, does he?他不认识她,对不对?3) 祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如:Sit down, please. 请坐。
Don't be nervous! 别紧张!4) 感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如:What good news it is! 多好的消息啊!(二)句子按其结构可以分为以下三类:1) 简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如:She is fond of collecting stamps. 她喜欢集邮。

【高中英语】高中英语语法句子的种类
【编者按】
高中英语
句子种类按采用目的,句子可以分成陈述句、疑问句、yaku和感叹句,句子按其结构可以分成简单句
并列句和复合句,本为将为你讲解这些知识,希望大家支持本站,你有什么好的文章请发布到本站
(一)按采用目的,句子可以分成陈述句、疑问句、yaku和感叹句。
1)陈述句(declarativesentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
例如:
lighttravelsfasterthansound. 光比声传播速度慢。
(表明事实)
thefilmisratherboring. 这部电影很乏味。
(说明看法)
2)疑问句(interrogativesentences):明确提出问题。
存有以下四种:
a.一般疑问句(generalquestions):
canyoufinishtheworkintime?你能够按时顺利完成工作吗?
b.特殊疑问句(wh-questions):
wheredoyoulive? 你居住那儿?
c.选择疑问句(alternativequestions):
doyouwantteaorcoffee?你就是必须茶还是必须咖啡?
d.反意疑问句(tag-questions):
hedoesn\'tknowher,doeshe?他不重新认识她,对不对?
3)祈使句(imperativesentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令。
例如:。
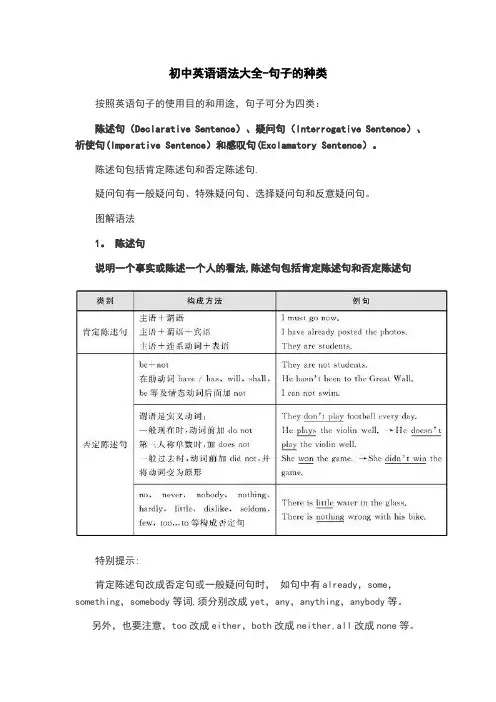
初中英语语法大全-句子的种类按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类:陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。
陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句.疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
图解语法1。
陈述句说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句特别提示:肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody等。
另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。
2. 疑问句3. 常用的特殊疑问句4. 特殊的反意疑问句①主句是祈使句时,“will you?"意为“请求",“won't you?”表示提醒对方注意。
例句:Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you?Don’t be late again, will you?②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式例句:What fine weather, isn’t it?How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she?③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?"而不用“am not I?”例句:I'm working now, aren’t I?④陈述部分主语是everything,nothing,anything或something 时,疑问句主语用it例句:Something is wrong with my radio, isn’t it?Nothing is difficult, is it?⑤陈述部分的主语是somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, no one, none, neither 时,疑问句的主语用they例句:Everyone is here, aren't they?No one knows about it, do they?⑥陈述部分的主语是:1) this或that时,问句的主语用it2) these或those时,问句主语用they3) there be句时,反意疑问句中用there例句:This is a plane, isn’t it?These are grapes, aren’t they?There was a hospital here, wasn’t there?⑦陈述部分的主语是one时,问句的主语可用one,也可用you (美语用he)例句:One should be ready to help others, shouldn't one?⑧陈述句中有few, seldom, never hardly,not,rarely,no,nobody,too…to等时,疑问句部分用肯定结构;如由前后缀构成否定词,疑问句部分仍用否定结构例句:He is never late for school, is he?You got nothing from him, did you?It is useless, isn’t it?⑨陈述部分主语是从句、不定式(短语)、动词-ing形式时,疑问句的主语用it例句:What you need is more important, isn’t it?⑩陈述部分由think, believe, suppose, imagine等引导的宾语从句:1) 主语是第一人称时,问句与从句的主谓语一致2) 主语是其他人称,问句与主句的主谓语一致例句:I think he will come, won’t he?I don’t think he can pass the exam, can he?He believed you had seen her before, didn’t he?? have是实义动词时,疑问句用助动词do,does,did;have 是助动词,则不然例如:They had a meeting just now, didn’t they?She’s been to many places of interest, hasn't she??陈述部分有have /has /had to 时,疑问句要用助动词的否定形式例句:You have to water the vegetables now, don’t you?? 陈述部分有had better时,疑问句中用hadn’t刘局:We had better go to school at once, hadn’t we?? 陈述部分有must:1) 作“一定;必须”解释时,疑问句用mustn’t或needn’t;2) 表示推测,作“一定是;必定"解释时,疑问句需根据其后的动词原形选用相应的形式;3) 对过去动作推测时,问句的助动词用did或have;4) 对过去的状态推测时,问句的be用was例句:He must work hard at physics, mustn’t he?You must go to Guangzhou, needn’t you?You mustn’t smoke here, must you?Tom must be at home, isn’t he?She must have finished her work, hasn’t/didn’t she?He must have been a policeman, wasn’t he??陈述部分有ought to,used to,疑问句要用 shouldn’t,usedn’t / didn’t例句:Jill used to be a teacher, usedn’t / didn’t she??陈述句部分是复合句时,疑问句的主语和助动词要与主句一致例句:He was reading when the teacher came in, wasn't he?特别提示:反意疑问句是“否定陈述句+肯定问句”时,如回答内容是肯定的,用“Yes+肯定结构”,反之,用“No+否定结构”。


英语句型讲解一、句子的种类句子按其结构可分为简单句、并列句和复合句。
1. 简单句:只包含一个主谓结构的句子。
例如:She is smiling.2. 并列句:包含两个或更多主谓结构的句子,由并列连词连结。
例如:I like music, but she loves dance.3. 复合句:包含一个主谓结构,和一个或多个从句,从句由从属连词引导。
例如:I know the person who lives next door.二、句子的成分一个完整的句子通常包含主语、谓语、宾语、状语等成分。
1. 主语:句子中的主要人物或事物,是动作的执行者。
例如:The cat is playing with a ball. (主语是“cat”)2. 谓语:描述主语的动作或状态。
例如:The cat is playing. (谓语是“is playing”)3. 宾语:动作的承受者。
例如:I love reading books. (宾语是“reading books”)4. 状语:用于修饰动词、形容词或副词,表示时间、地点、方式等。
例如:She sings beautifully. (状语是“beautifully”)三、句型转换1. 肯定句与否定句的转换:在否定句中,通常使用否定词“not”或“no”,有时也使用“never”、“hardly”等否定意义的副词或形容词。
例如:She is not a student. (否定句)2. 陈述句与疑问句的转换:疑问句分为一般疑问句和特殊疑问句。
一般疑问句通常以“do”、“does”、“did”等助动词开头,特殊疑问句则以疑问词开头。
例如:Do you like music? (一般疑问句)3. 主动语态与被动语态的转换:被动语态的结构通常是“be + 过去分词”,其中“be”可以是“am”、“is”、“are”、“was”、“were”。
例如:The book was written by him. (被动语态)4. 倒装句型:将句子中的谓语提前到主语之前,称为倒装句型。


(三)句子得种类句子就是一个独立得语言单位,表示一个完整得思想。
按使用目得可分为陈述句、感叹句、疑问句与祈使句;从结构上又可分为简单句、并列句与复合句。
按使用目得分:一、陈述句That boy always helps others、Tom was not at home yesterday、He is too late to catch the bus、二、疑问句(一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句与反意疑问句)Are you a doctor?How often do you have an English party?Which would you like better, tea or coffee?She is too young to go to school, is she?三、感叹句(一)What +a /an+形容词+可数名词得单数形式+主语+谓语!==(二)How+形容词+a/an +可数名词得单数形式+主语+谓语!What a beautiful girl she is! == How beautiful a girl she is!(三) What+形容词+可数名词得复数+主语+谓语!What beautiful girls they are!(四)What+形容词+不可数名词+主语+谓语!What fine weather it is!(五)How+形容词或副词+主语+谓语!How interesting the dog is!(六)How+主语+谓语!How time flies!四、祈使句(祈使句主语通常被省略,谓语动词用原型。
)Be quiet!Don’t be late!从结构上分:一、简单句(句子只包含一个主谓结构。
)如,五种基本句型列式如下:基本句型一:主+系+表基本句型二:主+谓基本句型三:主+谓+宾基本句型四:主+谓+间宾+直宾基本句型五主+谓+宾+宾补、二、并列句(句子包含两个或多个主谓结构,通常有并列连词连结。
英语语法之句子的种类一、分类:按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
1. 陈述句:说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
He gets up at six. 他六点钟起床。
(说明事实)I don't think so .我不这么认为。
(说明看法)2.疑问句:提出问题。
①一般疑问句:Can you finish the work in time?你能按时完成工作吗?②特殊疑问句:Where do you live?你住那儿?How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事?③选择疑问句:Do you want tea or coffee?你是要茶还是要咖啡?④反意疑问句:He doesn't know her, does he?他不认识她,对不对?3. 祈使句:提出请求,建议或发出命令Sit down, please.请坐。
Don't be nervous!别紧张!4. 感叹句:表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪.1.陈述句:①肯定式:This is my sister .I like reading books at weekends .②否定式:A: "be+not" I am not a student.B:"do\does\did +not" He does not like playing basketball.C:"助动词\情态动词+not" I can not swim.D:用no、nothing、nobody表否定.I know nothing about it.2. 一般疑问句:①定义:用be动词、助动词或情态动词置于句首,可用“yes”或“no”来回答的问句。
②应答:用yes\no(或相当于“yes”或“no”的词)回答,并根据句首的be动词、情态动词或助动词作相应的回答。
--Is Mary a Japanese girl ? --Yes,she is.\No,she isn't.--Can you speak English? --Yes,I can .\No, I can't .--Do you like your teacher ? --Yes,I do.\No, I don't .③变形:如何将一个肯定的陈述句变为一般疑问句:A:看句中有无be动词,如果有be动词提到句首即可。
英语语法:句子的种类句子是具有一定的语法结构,表达一个独立完整意义的语言单位。
口头表达中,句与句之间略有停顿。
书面上,这种停顿用标点符号表示,如句号、逗号、分号或感叹号。
按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
1)陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
Light travels faster than sound.光比声速度快。
(说明事实)The film is rather boring.这部电影很乏味。
(说明看法)2)疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。
有以下四种:a.一般疑问句(General Questions):Can you finish the work in time? 你能按时完成工作吗?b. 特殊疑问句(W Questions; H Questions):Where do you live?你住那儿?How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事?c.选择疑问句(Alternative Questions):Do you want tea or coffee? 你是要茶还是要咖啡?d.反意疑问句(Tag-Questions):He doesn't know her, does he? 他不认识她,对不对?3)祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,Sit down, please.请坐。
Don't be nervous!别紧张!4)感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,What good news it is!多好的消息啊!(二)句子按其结构可以分为以下三类:简单句,并列句,主从复合句1)简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,She is fond of collecting stamps.她喜欢集邮。
高中英语语法总结大全之句子的种类●要点清单句子的种类(一)按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
1)陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
Light travels faster than sound.光比声速度快。
(说明事实)The film is rather boring.这部电影很乏味。
(说明看法)2)疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。
有以下四种:a.一般疑问句(General Questions):Can you finish the work in time?你能按时完成工作吗?b.特殊疑问句(W Questions;H Questions):Where do you live?你住那儿?How do you know that?你怎么知道那件事?c.选择疑问句(Alternative Questions):Do you want tea or coffee?你是要茶还是要咖啡?d.反意疑问句(Tag-Questions):He doesn't know her,does he?他不认识她,对不对?3)祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如:Sit down,please.请坐。
Don't be nervous!别紧张!4)感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如:What good news it is!多好的消息啊!(二)句子按其结构可以分为以下三类:1)简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如:She is fond of collecting stamps.她喜欢集邮。
(主)(谓)2)并列句(Compound Sentences):包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接,例如:The food was good,but he had little appetite. (主)(谓)(主)(谓)食物很精美,但他却没什么胃口。
英语句子种类-CAL-FENGHAI.-(YICAI)-Company One1二.句子的种类1. 陈述句用来陈述一件事情或表示一种看法,可分为肯定句和否定句两种形式。
如:He went to the cinema the day before yesterday.She isn’t a doctor.2. 疑问句1)一般疑问句:指用yes或no来回答的句子。
如:Is your father a worker2)特殊疑问句:其结构:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序。
但是,如果疑问词在句子中作主语或作主语的定语,就用特殊疑问词+陈述句语序。
常用的疑问词有:what,who(whom), whose ,which ,when ,where ,how ,why等,回答时针对问句中的代词和副词来回答,不用yes或no来回答。
如:Who is speaking outsideWhere did you go yesterday3)选择疑问句:指提问者提供两种或两种以上情况,让对方从中作出选择的句子。
它的基本结构是:一般疑问句+or+一般疑问句(后一部分与前一部分相同的成分常常省略)。
回答时,不用yes或no回答,而是选择其中一种回答。
如:Which one do you like,this one or that one4)反意疑问句:提出情况和看法来问对方是否同意的句子。
它由两部分构成:前一部分是对事物的陈述,后一部分是简短的附加问句。
遵循“前肯后否,后肯前否”的原则。
如:It’s a nice day,isn’t itHe works hard,doesn’t he3. 祈使句表示请求、命令、建议或劝告等的句子叫祈使句,主语you通常省略。
1)肯定形式:一般以动词原形开头。
Open the door, please.2)否定形式:在句首谓语动词前加Don't。
Don't be late for class.4. 感叹句1)一般用感叹词how或what引导,how修饰形容词或副词,what修饰名词。
英语中句子的种类 Prepared on 22 November 2020
(三)句子的种类
句子是一个独立的语言单位,表示一个完整的思想。
按使用目的可分为陈述句、感叹句、疑问句和祈使句;
从结构上又可分为简单句、并列句和复合句。
按使用目的分:
一、陈述句
That boy always helps others.
Tom was not at home yesterday.
He is too late to catch the bus.
二、疑问句(一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句)
Are you a doctor
How often do you have an English party
Which would you like better, tea or coffee
She is too young to go to school, is she
三、感叹句
(一)What +a /an+形容词+可数名词的单数形式+主语+谓语!==(二)How+形容词+a/an +可数名词的单数形式+主语+谓语!
What a beautiful girl she is! == How beautiful a girl she is!
(三) What+形容词+可数名词的复数+主语+谓语!
What beautiful girls they are!
(四)What+形容词+不可数名词+主语+谓语!
What fine weather it is!
(五)How+形容词或副词+主语+谓语!
How interesting the dog is!
(六)How+主语+谓语!
How time flies!
四、祈使句(祈使句主语通常被省略,谓语动词用原型。
)
Be quiet!
Don’t be late!
从结构上分:
一、简单句(句子只包含一个主谓结构。
)如,五种基本句型列式如下:
基本句型一:主+系+表
基本句型二:主+谓
基本句型三:主+谓+宾
基本句型四:主+谓+间宾+直宾
基本句型五主+谓+宾+宾补.
二、并列句(句子包含两个或多个主谓结构,通常有并列连词连结。
)
由并列连词把两个或两个以上的简单句连在一起的句子叫并列句。
不同的并列连词表示并列分句之间的不同关系。
根据并列分句之间的关系不同,并列句可以分为以下几种: 1.表示联合关系的并列句这类并列句常用并列连词and (和),not only ... but also... (不但……而且……)等来连接,这时分句之间是顺承关系或并列关系。
and一般不译出来。
1. We bought her a birthday present,_____ she liked it very much.
A. so
B. or
C. and
D. but
2. — Didn’t you give roses to your father on Father’s Day
— Oh, not only my father,_____ my grandpa got red roses.
A. or
B. and
C. but
D. until
2.表示转折关系的并列句这类并列句常用but (但是;可是),yet(可是;然而),while (而)等来连接,后面分句与前面分句之间有意义上的转折关系。
1. — Would you like to go to the concert with me
— I’d love to,_____ I can’t. I have a lot of homework to do.
A. or
B. but
C. so
D. and
2. The doctors tried their best to save the patient’s life,_____ failed
A. or
B. so
C. but
D. because
3.表示选择关系的并列句这类并列句常用并列连词or(或者),either … or …(要么……,要么……)等连接。
1. _____ Lily _____ Lucy may go with you because one of them must stay at home.
A. Not only; but also
B. Neither; nor
C. Both; and
D. Either; or
2. None of the shoes in the shops are the right size. They are _____ too big _____ too small.
A. both; and
B. neither; nor
C. either; or
D. not only; but also
3. “Are you going to eat here ____ take it away” asked the waiter..
A. and
B. so
C. or
D. but。
4.表示因果关系的并列句这类并列句常用并列连词so(因此;所以),for (因为)等连接,后面分句与前面分句之间有因果关系。
1. Mother was ill,_____ Father cooked for us instead.
A. but
B. or
C. so
D. and
2. There is a lot of traffic in this city,_____ look both ways before crossing the
street
A. so
B. and
C. but
D. for
特殊的并列句
1.祈使句+and+一般将来时的句子这个句型表示“如果做到了祈使句表示的
事情,就会有后面句子表示的结果”。
2.例如: Study hard,_____ you are sure to have a good result in the exam.
A. or
B. and
C. for
D. but
3. 2. 祈使句 + or + 一般将来时的句子这个句型表示“如果做不到祈使句表
示的事情,就会有后面句子表示的结果”
4.例如: 1. Be quick,_____ we’ll be late for class.
A. or
B. so
C. and
D. but
2. Come a little earlier next time,_____ you’ll miss the best part of the TV
play.
A. and
B. but
C. or
D. till
三、复合句
复合句(Complex Sentence)由一个主句(Principal Clause)和一个或一个以上的从句(Subordinate Clause)构成。
主句是全句的主体,通常可以独立存在;从句则是一个句子成分,不能独立存在。
从句不能单独成句,但它也有主语部分和谓语部分,就像一个句子一样。
所不同在于,从句须由一个关联词引导。
我们至今学过的从句有:定语从句,名词性从句(主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句),和状语从句。
1. 定语从句 He is the man who wants to see you.
2. 同位语从句 She told us her hope that she would become a pianist.
注意:定语和同位语从句的区别。
3. 表语从句 This is what we should do
4. 宾语从句(注意it做形式宾语)
Everybody knows that money doesn't grow on trees
We think it wrong that he told a lie to everyone. (it做形式宾语)
5.主语从句(注意it做形式主语)
What caused the accident remains unknown
It is certain that he will win the match(it做形式主语)
6.状语从句
MyfriendsdislikemebecauseI’mhandsomeandsuccessfu l.。