英语语法几大从句(六级)
- 格式:docx
- 大小:23.28 KB
- 文档页数:11


初中英语语法总结(从句)英语从句三大类型按一般说法,可分为三大类14种从句。
一,名词性从句1主语从句Whether it’s right or not remains to be seen。
2宾语从句I wonder whether it's right or not.3同位语从句This is a question whether it's right or not. 4表语从句The question is whether it's right or not。
二,定语从句1限定性定语从句She is the student who can speak English well。
2非限定性定语从句She is the student, who can speak English well。
三,状语从句1时间状语从句The fact will come out when he comes here。
2地点状语从句You can go wherever you like。
3原因状语从句Pay more attention to your lessons because you are astudent。
4方式状语从句He walks as if he were a king.5目的状语从句She went to Japan so that she could learn Japanese well. 6结果状语从句She went to Japan so that she learned Japanese well.7条件状语从句I will understand it if he tells me.8让步状语从句He knows a lot though he is little.1.定语从句There are some old books in the box.The boy dressed in blue is from America。

中考英语核心语法6大词性、8大时态、3大从句,你值得拥有,希望能够帮助到你!总之,语法部分是英语学习的重点和难点。
语法知识掌握得好,将大大加快英语学习的进程。
本文归纳了六大词性、八种基本时态以及初中生需要掌握三种基本从句。
希望对广大中学生们有所帮助。
一. 词法1. 名词(1)名词的可数与不可数可数名词指表示的人或事物可以用数来计量,它有单数与复数两种形式。
不可数名词指所表示的事物不能用数来计量。
物质名词与抽象名词一般无法用数目,来统计,都成为不可数名词。
不可数名词前一般不能用冠词a、an来表示数量,没有复数形式。
要表示“一个……”这一概念,就须加a piece of这一类短语。
要注意许多名词在汉语里看来是可数名词,在英语里却不可数。
如:chalk,paper,bread,rice,grass,news等。
(2)名词复数的规则变化A.一般情况下加-s。
B.以s,x, ch,sh, 结尾的加-esC.以辅音字母加y结尾的改y为i再加-esD.以f,fe结尾的,去掉f或fe,变成v再加-es(3)名词的所有格A. 单数名词词尾加’s,复数名词词尾若没有s,也要加’s。
如:the worker's bike,the Children’s ballB. 表示几个人共有一样东西,只需在最后一个人的名字后加’ s若表示各自所有,则需在各个名字后’s。
如:This is Lucy and Licy’s room.These are Kate's and jack’s rooms.C. 如果是通过在词尾加—s构成的复数形式的名词,只加’。
如:the students’books,the girls’blouses(另外:名词+of+名词名词是有生命的,我们就用’s结构来表示所有关系。
如果名词所表示的事物是无生命的,我们就要用名词+of+名词的结构来表示所有关系。
)2. 代词人称代词,物主代词,反身代词,指示代词,不定代词(1)人称代词第一人称单数I me my mine myself复数we us our ours ourselves第二人称单数you you your yours yourself复数you you your yours yourselves第三人称单数he him his his himselfshe her her hers herselfit it its its itself复数they them their theirs themselves(2)物主代词物主代词的用法:形容词性物主代词后面一定要跟上一个名词;名词性物主代词可作主语、表语、宾语。

高考英语语法复习:八种状语从句的用法状语从句状语从句有时间、地点、原因、目的、方式、结果、条件、让步等八种。
一、时间状语从句:引导词有after,before,as,once,since,till,until,when,whenever,while,as soon as,the moment/minute…(一…就),the time,the day,every time,next time,each time,by the time of,no sooner…than(一…就),hardly…when(一…就).例如:Each/Every time he comes here,he will drop in on me.每次他来这儿他都顺便看我.He was ill last time I saw him.上次我见到他时他病了.No sooner had she heard the news than she cried.她一听到这个消息就哭了.[辨析]when与whilewhen引导的从句动词可以是延续性的或短暂性的,while引导的从句中动词必须是延续性的;在“be…when…”句式中when表“at that time(就在这时)”意,这样用的when不能换为while;while有时并不表示时间,而表示对比,意“而”、“却”,when无这样的用法。
例如:When I got home I found the door locked./While(或When)we were working in the fields,it suddenly began to rain./He was wandering through the streets when a bike hit him./His pencil is red,while mine is yellow.[辨析]till与until一般情况下可以互换,但until可以位于句首,till则不能。

考研英语基础语法扎实的语法功底对于考研解题是很重要的。
据总结,最令大多数考研学生头疼的基础语法现象主要有以下几项:英语的基本句式、形容词性(定语)从句、名词性从句(主语从句,表语从句,宾语从句和同位语从句)、副词性(状语)从句、As 的用法。
下面将对以上语法点详解,并通过练习进一步强化对它们的掌握。
一、英语的基本句式(一)英语句子的主要成分英语句子主要由主语,谓语,宾语(直接宾语和间接宾语),定语,状语,补语(主语补语和宾语补语),表语(主语补语的一种),同位语,感叹语,插入语等构成。
(二)英语的五大句式一)主+ 系+ 表语例如:You are a baby.系动词:联系动词(Link Verb)是一种表示谓语关系的动词,作为系动词,它本身有词义,但不能单独用作谓语,后边必须跟表语,构成系表结构说明主语的状况、性质、特征等情况。
系动词可以是be动词,也可以是某些实义动词。
例如:The dog looks dangerous.五大类常见系动词:1)be动词--用来表示主语状态。
例如:He is a teacher.2)“持续类”--用来表示主语继续或保持一种状况或态度。
这类系动词主要有:例如:I am sorry to have kept you waiting.This matter rests a mystery.3)“表象类”--用来表示"看起来像"这一概念这类系动词主要有:例如:He seems (to be)very sad.4)“感官类”--用来表示“感觉”“触觉”等这类系动词主要有:例1:It sounds reasonable.例2:-Do you like this sweater?-Yes, it __________ very soft.A. is feelingB. feltC. feelsD. is felt5)“变化类”--这些系动词表示主语变成什么样这类系动词主要有:例如:It worried her a bit that her hair was turning gray.The rumor proved false.His plan turned out a success.二) 主语+不及物动词+(状语)例如:He changed a lot.You cried loudly.注意:该句型可接状语。
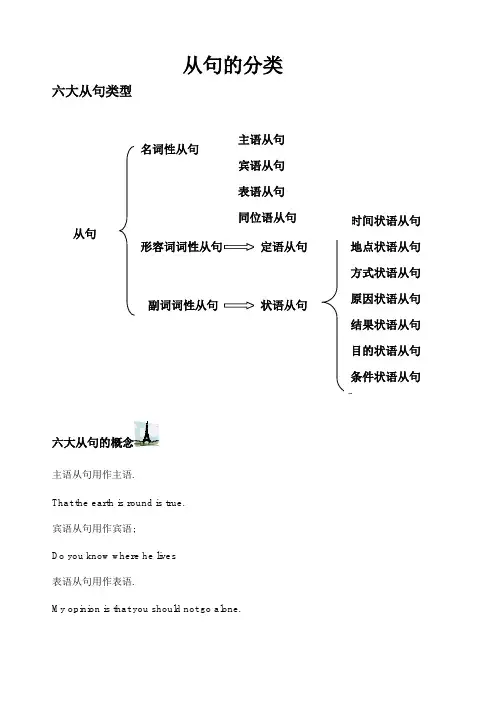
从句的分类六大从句类型主语从句用作主语.That the earth is round is true.宾语从句用作宾语;Do you know where he lives表语从句用作表语.My opinion is that you should not go alone.同位语从句用于解释说明前面的名词,与先行词同位或等同的从句叫作同位语从句;其关联词多为that;The fact that the earth is round is true.that从句用于解释说明the fact定语从句相当于一个形容词,用于修饰前面的名词;定语从句一般皆放在被它所修饰的名代词之后,这种名代词就叫作先行词Antecedent;引导定语从句的关联词为关系代词和关系副词;关系代词在定语从句中可用作主语、宾语、定语等;关系副词在定语从句中用作状语;The student who answered the question was John.状语从句相当于一个副词,修饰主句中的动词, 形容词和副词, 通常有从属连词引导, 按其意义和作用可分为时间, 地点, 条件, 原因, 让步, 目的, 结果, 方式, 比较.等When it rains, I usually go to school by bus.If he comes tomorrow, you will see him.He returned home to learn his daughter had just been engaged.You must speak louder so that /in order that you can be heard by all.Since /As the weather is so bad, we have to delay our journey.从句划分技巧主句和从句的划分方法是相同的;句子的成分从谓语动词处来划分比较容易;谓语动词前面的部分是主语,后面常接宾语,修饰谓语动词的是状语,修饰主语、宾语的是定语,若谓语是系动词,则系动词后的部分是表语;定语从句VS同位语从句定语从句是先行词的修饰语,它不涉及先行词的实质内容,在定规从句中“that”往往充当某一成分且作宾语时可以省略;同位语从句是对中心词的内容作进一步的解释和说明,表明中心词语的具体、实际内容;“that”在同位语从句中不充当任何成分且不可以省略;从句划分练习1. It is quite clear that the crime was down deliberately.2. She suggested that he do it at once.3. That the earth is round is true.4. The problem is not who will go but who will stay.5. The student who answered the question was John.6. Have you any idea how soon they’re coming.7. My original question, why he did it at all ,has not been answered.8. When it rains, I usually go to school by bus.9. What you need is more practice.10. It is still a question when we shall have our sports meet.11. I think it best that you should stay here.12. The question is whether it is worth doing.14. We must find out who did all these.15. Jack is no more frightened than Mike is.16. We expressed the hope that he would come to China again.17. The fact that the earth is round is true.18. There are many organizations whose purpose is to help the homeless.19. Do you know where he lives20. This is the reason why he refused to help us.21. Such people as you describe are rare nowadays.22. He is so humorous that we’ll never forget him.23. My opinion is that you should not go alone.24. I will stand where I can see the parade clearly.25. I’ll take whoever wants to g o with me to the theatre.26. The news that he told me was that Tom would go abroad.27. If he comes tomorrow, you will see him.28. The news that Tom would go abroad was told by him.。

英语六级常见语法知识英语六级考试是中国大学英语六级考试,主要测试学生在听、说、读、写等各个英语语言技能方面的能力。
在写作部分,良好的语法知识是取得高分的重要保证。
下面将介绍英语六级常见的语法知识点。
1. 主谓一致主谓一致是指主语和谓语在人称和数方面保持一致。
例如:- The boy is playing basketball.(这个男孩正在打篮球。
)- The girls are singing in the classroom.(女孩们正在教室里唱歌。
)2. 冠词的用法冠词用于限定名词,分为不定冠词(a/an)和定冠词(the)。
不定冠词用于表示泛指或初次提及,定冠词用于表示特指。
例如:- I bought a book yesterday.(我昨天买了一本书。
)- Can you pass me the pen?(你可以递给我那支笔吗?)3. 时态的正确运用时态是表示动作发生时间的形式,常见的时态有一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时等。
要根据句子的语境和时间状语来选择适当的时态。
例如:- They are studying for the exam.(他们正在为考试而学习。
)- He has lived in New York for five years.(他在纽约住了五年了。
)4. 从句的使用从句是由引导词引导的一个句子,在句子中作为一个整体充当名词、形容词或副词的成分。
常见的从句有定语从句、名词性从句和状语从句等。
例如:- I know the girl who is playing the piano.(我认识那个正在弹钢琴的女孩。
)- Can you tell me where the library is?(你能告诉我图书馆在哪里吗?)5. 动词的时态和语态变化动词的时态是指动词的时态形式,包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时等。
语态是指动词的主动和被动形式。
例如:- He is reading a book.(他正在读书。

三大从句定语从句1.The meeting that you have missed yesterday was very important.2. The girl who is making a speech right now is our monitor.3. The vase that I broke yesterday was very expensive.4. The boy who helped you yesterday is my neighbour.5. That's just the topic that I'm very interested in.6. He is just the boss who gave me that valuable opportunity.7. I like the cake which you bought yesterday.8. He is the teacher who helped me.9. We all like that speaker who is very humorous.10. The old lady whose two daughters are both teachers is our neighbour.11. She is the girl whom I met at the party.12. There are occasions when one must yield.13.Beijing is the place where I was born.14.Is this the reason why he refused our offer?15. His father died the year when he was born.16.He is unlikely to find the place in which he lived forty years ago.17. Do you remember the day on which you joined our club?18.This is the house in which I lived two years ago.19. He has finished the difficult exercise, which is easy for you.20.None of us know the reason for which Tom was absent from the meeting. (why = for which ). 只用that不用which的情况①先行词指物且含有不定代词(all, little, few, much, everything, anything等)Do you have anything that you want to say for yourself?All that Lily told me seems untrue.②先行词被the only, the very, the right, any, every, some, no, just等修饰This is the very bus that I am waiting for.The only thing that we can do is to lend you some money.③先行词含有最高级或含有序数词时,如:This train is the last that will go to Suzhou.This is the first two-story bus that runs in our city.What is the most interesting film that you have ever seen?④先行词既有人又有物Do you know the things and persons that they are talking about?⑤避免重复a. 主句的主语是疑问词who或whichWhich is the bike that you have lost?Who is the boy that won the gold medal?b. 两个定语从句,其中一个用which另一个用thatThey secretly built up a small factory, which produced things that could cause much pollution.c. 先行词在主句中作表语,关系词在从句中也作表语Shanghai is no longer the city that it used to be.⑥ 主句是there be 句型且关系词在从句中作主语There is a seat that is still available.2. 只用which不用that的情况① 非限制性定语从句② 关系代词前有介词(介词锁定)③ 先行词本身是that(避免重复)只用who不用that的情况:① 先行词是指人的不定代词,如:one , ones, anyone, no one, those等Those who have not got your textbooks please raise you hands.② there be结构中先行词指人There is a man who calls himself Mr. S joining our team.③ 分隔式定语从句中I was one of the persons in my office who were invited.四、关系副词when 时间时间状语I will never forget the day when we met there. (可用on which)where 地点地点状语This is the house where I was born. (可用in which)why 原因原因状语I can’t imagine the reason why he turned down my offer. (可用for which)主语从句(subject clause)一.定义:主语从句(subject clause),顾名思义就是利用一个从句来代替主语。

英语中总共有六大从句,区分方法,用法,及例子如下:1.主语从句1)主语从句可直接位于主语的位置,如果从句较长,谓语又较短,可用it作形式主语,而将从句放在句末.常见的句型有:*It is a fact\a pity\a question\good news that...*It seems\appears\happened\has turned out that...*It is clear\important\likely\possible that...*It is said\reported\estimated\has been proved that...It is said that comic books create a connection between people of the same generation.It seems that the performance is very useful.2)what引导的主语从句表示“...的东西时”,一般不用it作形式主语.What we lack is experience.3)what,who,when,why,whether等词含有各自的疑问意义,但它们引导的主语从句,都用陈述语序.How the plan is to be carried out should be discussed again.I did know why I felt like crying.2.宾语从句1)宾语从句可位于及物动词、介词和某些形容词后.连词that常可省略.介词后一般接疑问词引导的宾语从句.in that(因为),except that(除了),but that(只是)已构成固定搭配,其他介词后一般不接that引导的宾语从句.*I promised that I would change the situation.*All this is different from what American young people would say about friendship.*He is certain that watching so much television is not good for children.*This article is well-written except that it is a bit too long.2)宾语从句后如有宾补,要用形式宾语it来代替,而把宾语从句移至宾补之后.He has made it clear that he would not change his mind.3)在think,believe,suppose,expect等动词后的宾语从句中,如果谓语是否定的,一般将否定词移至主句谓语上,宾语从句则变成肯定形式.He didn't think that the money was well spent.3.表语从句表语从句出现在结构为“主语+系动词+表语从句”的句子中.表语从句除可用that,what,when,why,whether,how等引导外,还可由because,as if(though)等引导.that常可省略.如主句主语为reason,只能用that引导表语从句,不可用because.Perhaps the most important thing to remember is that there is no one common type of life in America.The reason why so many people died there is that there were not enough food supplies.It looks as if successful international cultural communication will make the world smaller.4.同位语从句同位语从句用于对前面出现的名词作进一步说明,一般用连词that引导,由于先行名词的意义不同,也可用whether,who,when,where,what,why,how等引导.常见的先行名词有fact,idea,belief,news,hope,conclusion,evidence,suggestion,order,problem,report,decision.有时由于谓语较短,将同位语从句位于谓语之后.She finally made the decision that she would join the fashion show.I had no idea how many books I could borrow at a time.The news came that their team had won the championship.5.定语从句定语从句所修饰的先行词可以是名词或代词,也可以是一个句子.定语从句通常位于先行词之后,由关系代词或关系副词引导.*限制性定语从句限制性定语从句修饰先行词,对先行词起修饰作用,紧接先行词之后,无逗号,若省去,原句意思不完整.引导定语从句的关系代词有who,whom,whose,which,that等.who,whom,whose用于指人,whose有时也可指物,相当于of which;which用于指物;that既可指人也可指物,但只用于限制性定语从句中.关系代词除了引导定语从句,替代先行词外,还在从句中担任主语、宾语、定语等.The computers and cables which make up the Internet are owned by people and organizations. Those who live alone or who are sick may have trouble in getting close to other people.The girl whose parents died in an accident is living with her grandmother.1)当先行词是all,anything,everything,something,nothing等不定代词或先行词前有first,last,any,few,much,some,no,only以及形容词最高级修饰时,只能用关系代词that引导从句. That is all that I've heard from him.He's the first person that I'm going to interview this afternoon.2)关系代词的省略在从句中作宾语的关系代词常可省略.关系代词紧跟介词,作介词宾语时不可用that,只可用which或whom引导从句,并且不可省略,但当介词位于宾语从句句末时,作为介词宾语的关系代词仍可用that,也可省略.This is one of those things with which we have to put up.This is one of those things (which\that) we have to put up with.3)引导定语从句的关系副词有when,where,why等.关系副词在从句中作状语,意义上相当于一个“介词+which”的结构.Even in comic books where(=in which) there are no words,the stories are fully expressed through the drawings.No one knows the reason why(=for which) he was so angry that day.5.定语从句*非限制性定语从句非限制性定语从句既可修饰先行词,也可修饰整个主句,起补充说明作用,与主句之间有逗号隔开,若省去,原句意思不受影响.不可用that引导非限制性定语从句.关系词不可省略. Every object has a gravitational pull,which is rather like magnetism.*“介词+which\whom\whose”引导的定语从句“介词+which\whom\whose”可引导限制性定语从句,也可引导非限制性定语从句,该结构中介词的选择取决于从句谓语动词的固定搭配,或先行词的习惯搭配.This is the computer on which he spent all his savingsIt is written by a person with whom we are all familiar.*as引导的定语从句as引导的定语从句主要用于“such...as”及“the same...as”的结构中,代替先行词是人或物的名词.as引导非限制性定语从句时,代替整个主句,从句可位于主句之前、之后或中间.These are not such problems as can be easily solved.(as代替先行词problems)As is mentioned above,no single company or group can control what happens on the Internet.(as 代替主语)6.状语从句*时间状语从句引导时间状语从句的从属连词和词组有:1)when,whenever,while,as,after,before,since,till,until,once等.We have learnt quite a lot about it since we came here.2)as soon as,hardly(scarcely)...when,no sooner...than,each(every) time,the moment,immediately(that)等.As soon as I sent an e-mail message,I received positive responses.The moment he heard the good news,he jumped with joy.*地点状语从句引导地点状语从句的连词是where,wherever.Wherever she went,she took her little daughter with her.*原因、结果和目的状语从句1)引导原因状语从句的从属连词有:because,as,since,now(that),seeing that,considering that,in that等.Considering that he is a freshman,we must say he is doing well.2)引导结果状语从句的连词有:so...that,such...that,so that,that,so等.Mickey Mouse is so attractive that the children are reluctant to leave.3)引导目的状语从句的连词有:so that,in order that,for fear that,lest等,从句常使用may,might,can,could,would等情态动词.We got up early this morning so that we could catch the first bus to the railway station.*条件和让步状语从句1)引导条件状语从句的连词和词组有if,unless,as(so) long as,on condition that,in case,provided(providing) that,supposing等.As long as you have the right equipment,you can use a telephone line to transmit computer data.2)引导让步状语从句的连词和词组有though,although,whether,even though,even if,no matter what(when,how...),whatever(whenever,wherever,however.)等.though,even if等引导状语从句可转换成含有as的部分倒装结构,具有强调意义.其结构为“形容词(副词、动词、名词)+as+主语+谓语”.No matter what you may say,I would not change my mind.Young as he is,he is quite experienced in this work.(=though he is young)Child as he is,he can speak English fluently.(=though he is a child)*方式状语从句引导方式状语从句的连词有as,just as,as if,as though等.as if,as though引导的状语从句中,谓语动词常用虚拟语气,表示与事实相反.The young man made the experiment just as the teacher had taught him.Everything went on as usual as if nothing had happened.。

从句有主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句、定语从句和状语从句6类.前四类由于主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句及同位语从句在句子的功用相当于名词,所以通称名词性从句;后两类定语从句和状语从句功用相当于形容词,称为形容词性从句.状语从句还可以分为条件状语从句、原因状语从句、方位状语从句和时间状语从句.1.主语从句(Subject Clause):用作主语的从句叫主语从句.引导主语从句的关联词有从属连词、疑问代词、疑问副词、缩合连接代词、缩合连接副词等.2.表语从句 Predicative Clause):用作表语的从句叫表语从句.引导表语从句的关联词与引导主语从句的关联词大都一样.3.宾语从句(Object Clause):在句子中起宾语作用的从句叫做宾语从句.宾语从句分为三类:动词的宾语从句,介词的宾语从句和形容词的宾语从句.第一部分一.、定义:宾语从句就是一个句子作动词或介词的宾语.二、学习宾语从句要抓住三要素:连接词、语序和时态.连接词一般都是that(指事务或人),which 指事),who 指人)1.从句为陈述句,常选择连接词that或将that省略,直接与主句相连.2.从句为一般疑问句,常选择连接词if或whether.在whether…or not结构中不能用if替换. 3.从句为特殊疑问句,常选择what,when,where,which,who,how等的疑问代、副词作连接词.★当who为主语时,句式为:who+谓语+其他判断时态情况:1.主句是一般现在时,从句为各种时态情况2.主句是一般过去时,从句为各种相应过去时态注意:从句描绘客观事实,用一般现在时3.主句是一般将来时,一般从句为一般现在时 “主将从现”)例题:〈1. The teacher told the children that the sun__B__round.A. wasB. isC. wereD. are 答案为B,属于第二种情况.宾语从句,在复合句中作宾语,位于及物动词后;Tell him which class you are in .(1)主、从句时态一致:主句谓语过去时,从句相应过去时;He answered that he was listening to me.主句谓语现在时,从句时态任所需;He says (that) he will leave a message on my desk.具体过去永不变,真理格言现在时;He told me that he was born in 1980.2)否定前移,及完成反意问句;在think / believe / suppose / guess / imagine / expect等动词后跟宾语从句否定式时,应转移到主句上去,完成反意疑问句时,应与从句主、谓保持一致.(注: 否定前移的条件是,主句主语是第一人称)I don't think you are right ,are you ?3)在表示建议suggest , advise要求demand 、desire、require、request、propose;决定decide; 命令order、command; 坚决主张insist;等动词后跟宾语从句,用 should)+v. 虚拟语气)eg.I suggested that you should)study hard.4)如果宾语从句后有宾语补足语,用it作形式宾语,把宾语从句后置eg.You may think it strange that he would live there.5)宾语从句that常可省略,但在以下情况下不能省略A.当主句谓语动词带有两个或两个以上宾语从句时,可以省略第一个that,其他不能省略. eg.I believe that)you have done your best and that things will get bet?鄄ter.B.当it作形式宾语时eg.She made it clear that she had nothing to do with him.C.当宾语从句前置时eg.That our team will win,I believe.三、分类A 、作动词的宾语:eg.I heard the newsI 主语heard 谓语动词the news.名词作宾语I主语heard 谓语动词that he would come here later on.一个句子作宾语---宾语从句B 、作介词的宾语:eg.He said nothing about this plan .He主语said 谓语动词nothing 代词作动词的宾语about 介词the plan. 名词作介词的宾语四、带有宾语从句的复合句的构成:带有宾语从句的复合句就是用连接词把一个主句和一个宾语从句连接在一起.连接词有:that(可省略),what, who, when, where, why, which, if, whether, how.五、注意:A 宾语从句必须用陈述语序.False: He is wondering when can he finish this difficult job.Right: He is wondering when he can finish this difficult job.B 有时候可以用it 作形式宾语,而把真正的宾语从句放在后面.Bad: I thought that he could finish this job in just two hours impossible.Good: I thought it impossible that he could finish this job in just two hours.Bad: He left whether we should continue this project to my judgment.Good: He left it to my judgment whether we should continue this project.C 带有宾语从句的复合句的否定形式一般是否定主句.Bad: I think he doesn’t like the English teacher.Good: I don’t think he likes the English teacher.D False: He wanted to know why he is crying in the corner.Right: He wanted to know why he was crying in the corner.4.同位语从句(Appositive Clause):与先行词同位或等同的从句叫作同位语从句.其关联词多为that.5.定语从句 Attributive Clause):用作定语的从句叫定语从句.定语从句一般皆放在被它所修饰的名 代)词之后,这种名 代)词就叫作先行词 Antecedent).引导定语从句的关联词为关系代词(或称引导词、关系词等).关系代词在定语从句中可用作主语、宾语、定语等;关系副词在定语从句中用作状语.①引导定语从句的关联词有who, whom, whose, that, when, where, why 和which. 在非限制定语从句中, 只可用which, who, whose, where , when., 如果指代前面整个句子, 多用which.例句:The dog that/which was lost has been found. 失踪的狗已经找到了.)③as 可做引导词引导定语从句, 多和such, the same 连用. As 引导的定语从句也可修饰整个句子, 既可放在先行词后,也可放在句子开头.例句:Such people as you describe are rare nowadays. 你描述的那一类人现在很少了.)④介词+which/whom/whose从句The driver is the man from whose room she had stolen the gold watch. 她就是从那个司机的房间偷了金表的.)⑤代/名+介词+which 从句He is needing a book, the name of which I don't know.( 他需要一本书,但是我不知道书名.)⑥同位语从句和定语从句The news that you told me was really exciting. 你告诉我的好个消息真的是很激动人心.)⑦难句:NO.1He is one of the men who were chosen to represent the group. 他是被选为代表该团队的人中一员.)第二部分一、时态1·主句用一般现在时,从句可用任意时态.2·主句用过去时,从句用过去某个时态.3·主句用过去时,从句是真理时,只用一般现在时.二、宾语从句的几类连接词:①从属连词连接宾语从句的从属连词主要有that,if,whether. that引导表示陈述句的宾语从句,而if和whether引导表示“是否”的宾语从句.例句:I don’t know if there will be a bus any more.我不知道是否还会有公交车.②连接代词连接代词主要有who, whom ,whose ,what ,whoever ,whomever ,whosever, whatever, whichever等.连接代词一般指疑问,但what, whatever除了指疑问外,也可以指陈述.例句:Do you know who has won Red Alert game?你知道谁赢了这一局红警游戏吗?③连接副词连接副词主要有when,where,why,how,whenever,wherever,however等.例句:He didn’t tell me when we should meet again.他没有告诉我什么时候我们能再见面.三、动词的宾语从句大多数动词都可以带宾语从句We all expect that they will win , for members of their team are stronger.我们都预料他们会赢,因为他们的队员更强壮.★部分“动词+副词”结构也可以带宾语从句例句:I have found out that all the tickets for the concert have been sold out.我发现这场音乐会的所有票都卖光了.★动词短语也可以带宾语从句常见的这些词有:make sure确保make up one’s mind下决心keep in mind牢记例句:Make sure that there are no mistakes in your papers before you turn them in.在上交试卷前确保没有任何错误.四、可运用形式宾语it代替的宾语从句①动词find,feel,consider,make,believe等后面有宾语补足语的时候,则需要用it做形式宾语而将that宾语从句后置.例句:I think it necessary that we take plenty of hot water every day .我认为每天多喝开水是有必要的.②有些动词带宾语从句时寻要在宾语与从句前加it这类动词主要有:hate, take , owe, have, see to.例句:I hate it when they with their mouths full of food.我讨厌他们满嘴食物时说话.③若宾语从句是wh-类,则不可用it代替例句:We all consider what you said to be unbelievable.我们都认为你所说的是不可信的.五、介词的宾语从句用wh-类的介词宾语从句例句:We are talking about whether we admit students into our club.我们正在讨论是否让学生加入我们的俱乐部.★用that,if引导的介词宾语从句有时候except,but,besides三个介词后可见到that引导的宾语从句例句:I know nothing about my new neighbor except that he used to work with a company.对于我的新邻居我只知道他曾在一家公司上班,其他一无所知.六、形容词的宾语从句常用来引导宾语从句的形容词有:sure,certain,glad,please,happy,sorry,afraid,satisfied,surprised例句:I am sure I will pass the exam.我确信我会通过考试.七、if,whether在宾语从句中的区别①if和whether在作“是否”解时,引导宾语从句常放在动词know,ask,care,wonder,find out等之后,介词后一般不用if②少数动词,如:leave,put,discuss,doubt后的宾语从句常用whether.③whether后可以加or not,但是if不可以.④在不定式前只能用whether.如:I can’t decide whether to stay. 我不能决定是否留下.⑤避免歧异时,我们常用whether而不用if.八、哪些宾语从句不可以省略引导词that1.当that作learn,suggest,explain,agree,wonder,prove,mean,state,feel,hold等动词的宾语时;2.当宾语从句较长时;3.当主语状语置于主句尾,宾语从句之前时;4.当主语谓语动词(包括非谓语动词)与宾语从句之间有插入语时;5.当一个动词带有两个或两个以上宾语从句时,此时第一个that可以省略,第二个that不可以省略;6.当宾语从句中的主语是this,that或this,that做主语的定语时;7.当宾语从句是双宾语中的直接宾语时;8.当宾语从句的主语是非谓语动词或主语从句时;9.当主语中的谓语动词是固定词组时;10.当宾语从句有it做其先行词时;11.在直接引语中,转述分句把宾语从句隔开时.九、宾语从句的否定转移主句的谓语动词是think,believe,imagine,suppose,consider,espect,fancy,guess等,并且主句的主语是第一人称而且为一般现在时,从句的否定词一般要转移到主句上来,其反义疑问句一般与宾语从句一致.例句:I don’t think he will come to my party.而不能说成I think he won’t come to my party.我认为他不会来我的舞会.★如果宾语从句中有某个含有否定意义的形容词或副词,其反义疑问句要用肯定形式.例句:We find that he never listens to the teacher carefully,does he?我们发现他从来不仔细听老师讲课,是不是?十、宾语从句的时态和语序当主句为现在时或将来时的时候,宾语从句的时态一般不受主句的时态所影响.当主句为过去时的时,细分为一下几种情况:①从句用一般过去时或过去进行时表示与主句谓语动词动作同时发生例句:I only knew he was studying in a western country,but I didn’t know what country he was in.我只知道他当时在西方的一个国家读书,可不知道是哪个国家.②从句过去完成时表示该动作发生在主句谓语动作之前例句:He told me that he had told Mary about the meeting already.他告诉我他已经把有关会议的事情告诉的了Mary.③从句谓语用过去将来时表示该动作发生在主句谓语动作之后例句:The reporter asked if the government would take necessary measures to put down the to-do.记者问政府是否会采取必要的措施镇压骚乱.★如果从句是一个客观真理,那么从句的时候不根据主句的时态而变化例句:The teacher said that the moon goes around the earth yesterday.老师昨天说月亮绕着地球转.★当宾语从句的引导词是who,which,what,when,where,how,why等表疑问时,不能按正常语序安排,经常将这类引导词置于句首例句:Who do you think the public might choose as their favorite singer this year?你认为今年公众会选谁为他们最喜欢的歌手.同位语从句用法比较"固定",把关键的几个词背下来 下面这个材料供参考):一、在复合句中用作同位语的从句叫同位语从句.它一般跟在某些名词后面,用以说明该名词表示的具体内容.如:I had no idea that you were here.我不知道你在这里.二、可以跟同位语从句的名词通常有news,idea,fact,promise,question,doubt,thought,hope,message,suggestion,words消息),possibility等.如:I’ve come from Mr wang with a message that he won’t be able to see you this afternoon.我从王先生那里来,他让我告诉你他今天下午不能来看你了.三、英语中引导同位语从句的词通有连词that,whether,连接副词how,when,where等.( 注:if,which 不能引导同位语从句.)如:l have no idea When he will be back.我不知道他什么时候回来.四、有时同位语从句可以不紧跟在说明的名词后面,而被别的词隔开. 如:The thought came to him that maybe the enemy had fled the city.他突然想起可能敌人已经逃出城了.五、同位语从句与定语从句的区别.1、同位语从句与前面的名词是同位关系,即说明它前面名词的内容;而定语从句与前面的名词是修饰与被修饰关系,即限定它前面的名词范围,或补充一些情况.如:The news that l have passed the exam is true.我通过了考试这一消息是真的.同位语从句,即从句所表达的意思就是前面名词的内容.)The news that he told me just now is true.他刚才告诉我的消息是真的.定语从句,从句对前面名词起修饰限制作用,即“他告诉我的”那个消息,而不是别的消息.)2、引导同位语从句的that是连词,在从句中不充当任何成份,而引导定语从句的that是关系代词,除起连接作用外,还在从句中充当主语、宾语或表语等.如:The idea that computers can recognize human voices surprises many people.计算机能够识别人的声音的想法使许多人感到惊奇.that在从句中不充当任何成份.)一个名词(或其它形式)对另一个名词或代词进行修饰,限定或说明,这个名词(或其它形式)就是同位语.同位语与被它限定的词的格要一致,并常常紧挨在一起.1) 非独立的同位语:常出现在被限定词前Bruce Lee (姓名) 李小龙Graf Schmidt (称号,浑名) 施密特伯爵Doktor Wang (职称,头衔) 王博士Uncel Liu (亲戚的称呼) 刘叔叔die Stadt Shanghai (类属名称) 上海市the Province Hebei (类属名称) 河北省das Jahr 2000 (类属名称) 2000 年three Kilo tomato (度量名称) 三公斤西红柿the University Bremen (专有名词) 不来梅大学。

大学英语六级常考语法精讲从句高校英语六级常考语法精讲:从句I 定语从句1.先行词为all, anything, something, nothing, everything, much, little, none等不定代词时,关系代词一般只用that,不用which。
在大多数状况下that可以省略.Please tell me everything you know about the matter.Thats all we can do at the moment.2.as引出的限制性定语从句在such as的结构中as可作关系代词,引出限制性定语从句。
有时和same连用,在从句中可作主语、宾语或表语等。
Such people as were recommended by him were reliable.Ive never seen such a talented young man as he is.I have the same trouble as you .3.as引出的非限制性定语从句as可作关系代词引出非限制性定语从句,代替整个主句,通常译为(正)如一样,(正)象一样等。
as引导的从句一般用逗号与主句隔开,可以位于主句的前面、中间或后面.I live a long way from work, as you know.She did not, as her friend had feared, break down.As is generally accepted, economic growth is determined by the smooth development of production.4.分隔式定语从句定语从句一般紧跟在先行词之后,但有时会被其他句子成分与先行词隔开,从而构成分隔式定语从句。
The days are gone when power politics worked.A new teacher will come tomorrow who will teach you French.5.介词+关系代词(which/whom等)引出的定语从句假如关系代词(which/whom等)在定语从句中作介词的宾语,那么这个介词可以提到从句前,构成介词+关系代词(which/whom等)+定语从句。
英语六级语法讲解英语六级语法时态部分英语中最常见以及常考的时态是一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在完成时、现在进行时等八种。
这些时态我们几乎在每次使用英语的时候,无论是说话或者是写作,都会遇到,一般用法早已熟记于心了,复习的时候只要留心他们的一些特殊用法,这里以现在完成时和现在(完成)进行时为例。
现在完成时的一些特殊用法:1、在this is(it is)the first time that…句型中,从句常用完成时态。
如:It is the seco nd time he has been out with her。
2、have been to与have gone to的区别。
前者侧重表示经历过,说话人可能已经不在那个地方,或者已经回来了。
而后者表示已经去了那里,说话的时候可能还在那里,或者在去那里的路上。
3、用在时间或条件状语从句中,表示将来某个动作发生之前业已完成的动作,如:I’ll go to see the film as soon as I have finished my homework。
我一做完作业就去看电影。
其中做完作业的动作在看电影动作之前完成。
4、when引起的疑问句中一般不用现在完成时,因为询问者关心的是事情发生的具体时间现在(完成)进行时除了表示正在进行的动作之外,主要还有以下的用法:与频度副词如always,continually,constantlyforever等状语连用,表示经常发生的,具有持续性动作的事情,或者表示不满,或者心中抱怨。
如he is always thinking英语六级语法主谓一致在英语中,最重要的一致关系就是主谓一致了,一般来说单数主语用单数动词,复数主语用复数动词。
但是主语有时候并不仅仅是简单的单数或者复数。
比如说集合名词就既能当数主语又可以作复数主语。
另外如不定代词、不定式,以及从句等都能作主语,它们的单复数就不那么容易划分了,这样使用单复数动词的相应具体规则也比较多,但是这些规则基本上都离不开三个大的原则。
英语六级基础语法常见句式引导语:下面店铺来带大家看看英语六级基础语法中的常见句式,希望能够帮助到大家。
一、强调句型这里讲的强调句主要是以it为引导词的分裂句。
其构成形式为:It is (was) +被强调部分+ that(who, which) + 句子的其他部分。
被强调的部分通常为主语、宾语和状语。
It is only when one is ill that one realizes the value of health.It is what you will do that is essential.Note:在被强调部分的后面,一般用that引出句子的其他部分。
但是如果强调的部分是表示人的名词,那么也可用who;如果是指物的名词也可用which。
It was Jane that/who lent me the money.It was this novel that/which they talked about last night.如果强调的是原因状语从句,只能用because引导,不能由since, as或why引导。
It was because(不用since或as) he had never had the opportunity that John hadn’t learned to drive.有三类句子成分不可以进行强调,即表语、谓语动词和由though, although, whereas等引导的从句。
It is although he is young that he can speak four languages. (误)Although he is young, he can speak four languages. (正)It is whereas he prefers pop song that I like classical music. (误)I like classical music whereas he prefers pop songs. (正)二、常考的几种倒装结构1.当表示否定或基本否定的词或词组位于句首作状语时用倒装。
英语八大从句类型总结主句和从句的划分方法是相同的。
句子的成分从谓语动词处来划分比较容易。
今天我们就一起来看看英语八大从句类型总结吧!英语八大从句类型总结从句是相对于主句而言的,即它是从属于某一个主句,而不能单独作一个句子。
在英语中,主要有三大从句,即名词性从句(包括主语从句,宾语从句,表语从句,同位语从句)、形容词性从句(即定语从句)、副词性从句(即状语从句,包括时间、条件、结果、目从句是相对于主句而言的,即它是从属于某一个主句,而不能单独作一个句子。
在英语中,主要有三大从句,即名词性从句(包括主语从句,宾语从句,表语从句,同位语从句)、形容词性从句(即定语从句)、副词性从句(即状语从句,包括时间、条件、结果、目的、原因、让步、地点、方式等)。
主语从句用作主语,如::That the earth is round is true.地球为圆的是真实的。
宾语从句用作宾语。
如:Do you know where he lives?表语从句用作表语,如:XXX is that you should not go alone.我的意见是你不应单独前往。
同位语从句用于解释说明前面的名词。
如:The fact that the earth is round is true.地球是圆的的究竟是实在的。
(that从句用于解释申明the fact)定语从句相当于一个形容词,用于修饰前面的名词。
如:XXX XXX XXX.回覆下列问题的学生是XXX.状语从句相当于一个副词,如:When it rains,I usually go to school by bus.天下雨时,我通常坐大众汽车上学。
(工夫状语)If XXX,you will see him.假如他明天来,你就可以瞥见他。
(if引导的前提状语从句,其结构为:if +状语从句,+主句)。
要留意在状语从句中有一个规则是“主将从现”,即主句是未来时,则从句要用普通目前时表示未来。
英语八大从句类型与用法总结从句是句子中的一种结构,可以用来增强句子的表达能力。
英语中常见的八大从句类型包括:1. 名词性从句 (Noun Clauses)名词性从句用来作为名词的替代,可以作为主语、宾语、表语或同位语等。
常见的名词性从句有:主语从句(作主语),宾语从句(作宾语),表语从句(作表语),同位语从句(作同位语)。
2. 定语从句 (Adjective Clauses)定语从句用来对一些名词或代词进行修饰和限定,一般紧跟在被修饰的名词或代词之后。
常见的引导词有:that, which, who, whom, whose 等。
3. 状语从句 (Adverbial Clauses)状语从句用来修饰动词、形容词、副词等,表示时间、地点、原因、条件、结果等。
常见的引导词有:when, while, before, after, since, because, if, unless, so that等。
4. 并列从句 (Coordination Clauses)并列从句是由连词and, but, or等连接在一起的两个或多个独立的主句。
并列从句可以使用逗号或分号分隔。
5. 让步从句 (Concessive Clauses)让步从句用来表示与主句相对抗的情况,常用的引导词有:although, though, even though, while等。
6. 条件从句 (Conditional Clauses)条件从句用来表示其中一种条件,通过条件从句的实现与结果从句的实现之间的关系。
常见的引导词有:if, unless, as long as, provided that等。
7. 结果从句 (Result Clauses)结果从句用来表示主句发生的结果,常见的引导词有:so that, such that, so...that等。
8. 目的从句 (Purpose Clauses)目的从句用来表示主句的目的或意图,常见的引导词有:so that, in order that等。
一文搞定英语6大从句(内含全部思维导图)hello,大家好,我是易图记的loridic,今天我们来讲讲英语的语法知识点之从句。
什么是从句?首先来看看句子的分类,句子可以分为三种,如下图:句子的分类而从句也是一个句子,它是符合5大基本句型结构的简单句,但这个简单句(从句)又同时在另外一个句子(复合句)中担任某种句子成分。
学习从句,至少要理解上面三个概念比如:从句是:Who is the most beautiful movie star?谁是最漂亮的电影明星?从句句型分析:who=S=主语,is=V=谓语,the most beautiful movie star=C=主语补足语(表语)复合句是:She asked who is the most beautiful movie star?他问谁是最漂亮的电影明星?复合句句型分析:she=S=主语,asked=V=谓语,who is the most beautiful movie star=O=宾语,所以Who is the most beautiful movie star?在复合句中是宾语从句。
所以,从句就是在复合句中担任某种句子成分的简单句。
我们知道,句子成分有7种:主语S,谓语V,宾语O,定语D,状语A,补语C,同位语T。
从句除了不能作谓语,其它都可以,所以常见的从句有6种,它们分别是:6种常见从句我们逐一来学习一下。
第一、主语从句主语从句就是作主语的从句。
它的连接词有连词、连接副词、连词代词,如下图:主语从句连接词比如:That she came to my birthday party made me happy.她来参加我的生日晚会了,这让我很高兴。
Where the English evening will be held has not been announced.英语晚会将在哪里举行,还没有宣布。
主语从句放在句首时,句子显得很笨重,因此常用it作形式主语,而将真正的主语后置,比如:It is a pity that you have missed such a wonderful concert.真遗憾你错过了这么精彩的一场音乐会。
英语语法:句型时态一、一般现在时:1.概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
2.时间状语:always,usually,often,sometimes,every week (day,year, month…),once a week,on Sundays,3。
基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要加(e)S)4.否定形式:am/is/are+not;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn’t,同时还原行为动词。
5。
一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
6。
例句:。
It seldom snows here。
He is always ready to help others.Action speaks louder than words。
二、一般过去时:1。
概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
2。
时间状语:ago,yesterday, the day before yesterday,last week(year, night,month…),in 1989, just now,at the age of 5,one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc。
3.基本结构:be动词;行为动词4.否定形式:was/were+not;在行为动词前加didn’t,同时还原行为动词。
5。
一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词.6.例句:She often came to help us in those days。
三、现在进行时:1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2。
时间状语:now, at this time,these days, etc。
名词性从句常见考点突破一、名词性从句的概念及分类1.顾名思义不,名词性从句就是指在句子中起名词作用的句子,功能相当于名词词组。
2.根据其在句中不同的语法功能,名词性从句可以分为主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。
同位语从句起对前面的名词进一步解释说明的作用,陈述该名词的内容。
二、名词性从句的三类引导词1.连接词,包括that,whether和if。
that用来引导陈述句,whether和if引导一般疑问句(从句中的一般疑问句要用陈述句语序,而if引导的从句不能作主语)。
2.wh-关系代词,如who,whom,whose,whatever,which等,这类词由于在句中作相应的句子成分,因此一般不能省略。
3.wh-关系副词,如when,why,how,where等,该类词一般也作相应的句子成分。
三、名词性从句的四种类型1.宾语从句①在许多情况下,作为真正宾语的that从句后置,而用it作形式宾语,此时,that不可省略。
例如:You may rely on it that I shall help you.(it作为形式宾语接在rely on后,真正的宾语是that引导的宾语从句。
另外,大多数介词不能直接跟that从句作宾语,所以此处需要it作形式宾语。
)②宾语从句分为三类:动词宾语从句、介词宾语从句和形容词宾语从句。
动词宾语从句指的是跟在动词之后且充当其宾语的从句;介词宾语从句指的是跟在一个介词之后充当其宾语的从句;同样,形容词宾语从句指的是跟在某些形容词后面,可理解为该形容词宾语的从句。
例如:I doubt whether he will come.(动词宾语从句)I'm curious as to what he will do.(介词宾语从句)I'm convinced that she is an honest girl.(形容词宾语从句)2.同位语从句①同位语从句就是跟在名词后面,表达具体内容、起解释说明作用的从句。
that是其最常见的引导词,不能省略。
②注意下列名词后面可接同位语从句:hope(希望),fact(事实),news(消息),problem(问题),conclusion(结论),rumor(流言),agreement(同意,协议),belief(信仰),concept(观念,概念),idea(想法),question (问题),suggestion(提议),thought(想法),conviction(确信,定罪),doubt(怀疑),decision(决定,决心),assumption(假定,设想),evidence(迹象,证据),等。
例如:The news that I havepassed the exam is true.③在少数情况下,可用连接代词或连接副词引导同位语从句。
例如:I have noidea why she cries.注:同位语可以分为同位语结构和同位语从句。
上文提到的是后者;而同位语结构跟在名词后,对其解释说明,与同位语从句不同的是,它只是词或词组。
例如:The only way that they canpreserve their history is to recount it as sagas--legends handed down from one generation ofstory-tellers to another.(legends作sagas的同位语,后接过去分词短语作定语。
)3.主语从句许多情况下,为了平衡句子结构,常用it代替主语从句,将主语从句后置,it只是形式主语。
例如:It is not known yet whether they will come today.(It作为形式主语置于句首,而真正的主语-----由whether引导的主语从句------由置于句末。
)4.表语从句表语从句一般接在系动词之后,在句中充当表语,常见的结构是“主语+系动词+表语从句”。
例如:The problem is that smokers can't go without smoking.(在该句中,系动词is后接一个that引导的表语从句。
)定语从句真题难句荟萃1.Since December,when the report came out,themayor,neighborhood activists and various parent-teacher associations have engaged in a fierce battle overits validity:over the guilt of the steel-casting factory onthe western edge of town,over union jobs versuschildren's health and over what,if anying,ought to bedone.分析:主干:...the mayor,...associations have engaged in a... battle(over...)①谓语用了现在完成时,与句首since引导的时间状语搭配。
when引导非限制性定语从句,修饰December(注意,不是时间状语从句)。
②句子的主语是一个名词词组,含三个中心名词(mayor,activists,associations)。
validity是“有效性,正确性”,冒号后的内容(三个并列的over...短语)进一步做了详细的说明,可以把冒号后的内容看做是over its validity的同位成分。
译文:自从12月份报告发布以来,市长,社区活跃分子和各家长教师协会就这份报告的正确性进行了激烈的争论;争论城市西郊铸钢工厂是否有责任,争论工会保护职工工作与儿童的健康之间的矛盾,争论应该采取什么样的措施(如果要采取措施的话)。
2.But Nature is indifferent to human notions of fairness,and a report by the Fish andWildlife Service showed a worrisome drop in the populations of several species of NorthAtlantic sea turtles,notably loggerheads,which can grow to as much as 400 pounds.分析:主干:...Nature is indifferent to human notions...and areport...showeda(worrisome)drop(in...)①and并列连接两个分句。
后一个分句中,介词短语by...作a report的后置定语,表示该报告的来源;介词短语in...作宾语a drop的后置定语。
②这里有好几个介词短语,分别修饰其前面的名词。
两个逗号间的notably loggerheads作turtles的同位语,后面有一个非限制性定语从句对这种海龟做进一步解释和说明。
译文:不过大自然一点都不会在乎人类所谓公平的想法。
渔业和野生动物署的一个报道表明,几种北大西洋海龟的数量急剧下降,令人担忧,尤其是能够生长到400磅重的灵龟。
定语从句常见考点突破一、如何辨别定语从句1.定语从句的概念定语从句就是修饰主句里的名词或代词的从句,本质上相当于“形容词”。
2.构成成分①先行词:定语从句通常置于所修饰的名词或代词等成分之后,这种名词或代词就叫先行词。
②关系词:引导定语从句吸关系代词,如that,which,who,whom,whose,as等,代替具体的指代对象,即先行词,其中,that既能指人,又能指物;还有关系副词,如when,where,why,how等,代替的则不单单是先行词,而是先行词和适当的介词。
3.定语从句的类型定语从句分为限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句。
大多数定语从句都对所修饰的名词或代词加以限制,去掉该从句后先行词将意义不全或失去意义。
而非限制性定语从句的作用在于补充,翻译时常常另起一个句子,与主句构成并列句。
例如:Immigrants are quickly fitting into this commonculture,which may not be altogether elevating but is hardly poisonous.(which引导的非限制性定语从句,修饰前面的culture,补充说明这种共同文化的特点。
)二、捕捉先行词先行词的位置可以紧靠着关系词,也可能与关系词之间隔着其他的成分,这时就需要慎重甄别先行词了。
例如:As a linguist,he acknowledges that all varieties of human language,including non-standard ones like Black English,can be powerfully expressive-there exists no language or dialect inthe world that cannot convey complex ideas.(句中的定语从句that cannot convey complex ideas修饰的是language or dialect,而并非紧靠着它的the world。
)三、关系词在定语从句中所充当的成分关系代词在定语从句中可用作主语、宾语、定语等,关系副词在定语从句中只用作状语。
例如:A child whose parents are dead is called an orphan.He came last night when I was out.在上述第一个句子中,关系代词whose在从句中用作定语;而在第二个句子中,关系副词when在定语从句中用作状语。
四、定语从句与同位语从句的区别1.同位语从句的形式与定语从句相似,它们之前都有先行词,但与先行词的关系有所不同:同位语从句与先行词同位或等同,定语从句与先行词则是修饰关系。
2.在定语从句中,关系词要代替先行词在从句中作适当的句子成分;而同位语从句的引导词则只起引导作用,没有代替前面名词在从句中作句子成分的作用。
试比较以下两个句子:The fact that he had not said anything surprised everbody.The fact that you are talking about is important.上述第一个句子包含一个由that引导的同位语从句,对fact的具体内容做出说明,这个that只是起引导作用,并不能代替fact在从句中作句子成分;而在第二个句子中,that you are talking about则作为定语从句对The fact做出限制和修饰,这个that在从句中作talking about的宾语。