项目管理PMP精要(中英文对照)V2
- 格式:doc
- 大小:590.50 KB
- 文档页数:32


ESSENCE OF PMBOK & PMP EXAM 考试串讲教材))PMBOK及PMP考试精要考试精要((考试串讲教材PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系 (2)项目生命周期及过程组 (10)PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPSSCOPE范围管理 (10)HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源管理 (11)COMMUNICATIONS沟通管理 (14)TIME时间管理 (16)COST成本管理 (17)RISK风险管理 (20)QUALITY质量管理 (22)PROCUREMENT采购管理 (22)INTEGRATION整体管理 (19)PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES职业道德 (19)POSSIBLE EXAM QUESTIONS考点 (20)1 PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系Knowledge Areas知识体系Primary Inputs输入Tools & Techniques工具及技术Primary Outputs输出INTEGRATION整体整体制定项目章程 Develop Project Charter 1.合同(如果适用) Contract(When applicable) 2.项目工作说明书 Project statement of work 3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 4.组织过程资产组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 1.项目选择方法 Project selection methods 2.项目管理方法论项目管理方法论 Project management methodology 3.项目管理信息系统项目管理信息系统 Project management information system 4.专家判断专家判断 Expert judgment 1.项目章程 Project charter 制定项目初步范围说明书制定项目初步范围说明书 1.项目章程 Project charter 2.项目工作说明书 Project statement of work 3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 4.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 1.项目管理方法系 Project management methodology 2.项目管理信息系统 Project management information system 3.专家判断 Expert judgment 1.项目初步范围说明书项目初步范围说明书Preliminary project scope statement 制定项目管理计划制定项目管理计划 Develop Project management Plan 1.项目初步范围说明书 Preliminary project scope statement 2.项目管理各过程 Project management processes 3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 4.组织过程生产 Organizational process assets 1.项目管理方法系 Project management methodology 2.项目管理信息系统 Project management information system 3.专家判断 Expert judgment 1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan 指导与管理项目执行 Direct and Manage Project Execution 1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan 2.批准的纠正措施 Approved corrective actions 3.批准的预防措施 Approved preventive actions 4.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 5.批准的缺陷补救 Approved defect repair 6.确认的缺陷补救 Validated defect repair 7.行政收尾程序 Administrative closure procedure 1.项目管理方法系 Project management methodology 2.项目管理信息系统 Project management information system 1.可交付成果 Deliverables 2.请求的变更 Requested changes 3.实施的变更请求 Implementde change requests 4.实施的纠正措施 Implementde corrective actions 5.实施的预防措施 Implementde preventive actions 6.实施的缺陷补救 Implementde defect repair 7.工作绩效信息 Work performance information 监控项目工作 Monitor and Control Project Work 1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan 2. 工作绩效信息 Work performance information 3.否决的变更请求否决的变更请求 Rejected change requests 1.项目管理方法系 Project management methodology 2.项目管理信息系统 Project management information system 3.实现价值技术实现价值技术 Eamed value technique(EVT) 4.专家判断 Expert judgment 1.推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 2.推荐的预防措施推荐的预防措施推荐的预防措施Recommended preventive action 3.预测预测 Forecasts 4.推荐的缺陷补救推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defect repair 5.请求的变更 Requested changes 整体变更控制 Integrated Change Control 1.项目管理计划项目管理计划 Progece management plan 2.请求的变更请求的变更 Requested changes 3.工作绩效信息工作绩效信息 Work performance information 4.推荐的纠正措施 Recommended corrective action 5.推荐的预防措施推荐的预防措施 Recommended preventive action 6.推荐的缺陷补救推荐的缺陷补救 Recommended defect repair 7.可交付成果可交付成果 Deliverables 1.项目管理方法系 Project management methodology 2.项目管理信息系统 Project management information system 3.专家判断专家判断 Expert judgment 1.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 2.否决的变更请求 Rejected change requests 3.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) 4.项目范围说明书(更新) Project scope statement(updates) 5.批准的纠正措施 Approved corrective actions 6.批准的预防措施 Approved preventive actions 7.批准的缺陷补救 Approved defect repair 8.确认的缺陷补救 Validated defect repair 9.可交付成果 Deliverables 项目收尾 Close Project 1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan 2.合同文件 Contract documentation 3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 4.组织过程资产组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 5.工作绩效信息工作绩效信息 Work performance 1.项目管理方法系 Project management methodology 2.项目管理信息系统 Project management information system 3.专家判断专家判断 Expert judgment 1.行政收尾程序 Administrative closure procedure 2.合同收尾程序合同收尾程序 Contract closure procedure 3.最终产品最终产品,服务或成果 Final product,service or result 4.组织过程资产组织过程资产(更新) 2 information 6.可交付成果 Deliverables Organizational process assets(updates) SCOPE范围范围规划范围规划 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程资产组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 3.项目章程 Project charter 4.项目初步范围说明书 Preliminary project scope statement 5.项目管理计划 Project management plan 1.专家判断 Expert judgment 2.样板样板,表格与标准表格与标准Templates,forms,standards 1.项目范围管理计划 Project scope management plan 范围定义范围定义范围定义 1.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 2.项目章程 Project charter 3.项目初步范围说明书 Preliminary project scope statement 4.项目范围管理计划 Project scope management plan 5.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 1.产品分析 Product analysis 2.其他方案识别 Alternatives identification 3.专家判断 Expert judgment 4.利害关系者分析 Stakeholder analysis 1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement 2.请求的变更 Requested changes 3.项目范围管理计划 Project scope management plan 制作工作分解结构 Create WBS 1.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 2.项目范围说明书项目范围说明书 Project scope statement 3.项目范围管理计划 Project scope management plan 4.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 1.工作分解结构模板 Work breakdown structure templates 2.分解分解 Decomposition 1.项目范围说明书(更新) Project scope statement(updates)_ 2.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure 3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary 4.范围基准 Scope baseline 5.项目范围管理计划(更新) Project scope management plan(updates) 6.请求的变更 Requested changes Scope Verification范围核实1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement 2.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary 3.项目范围管理计划 Project scope management plan 4.可交付成果 Deliverables 1.检查 Inspection 1.验收的可交付成果 Accepted deliverables 2.请求的变更请求的变更 Requested changes 3. 推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective actions 范围控制 Scope Control 1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement 2.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure 3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary 4.项目范围管理计划 Project scope management plan 5.绩效报告 Performance reports 6.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 7.工作绩效信息 Work performance information 1.变更控制系统 Change control system 2.偏差分析偏差分析 Variance analysis 3.补充规划补充规划 Replanning 4.配置管理系统配置管理系统 Configuration management system 1.项目范围说明书(更新) Project scope statement(updates) 2.工作分解结构(更新) Work breakdown structure(updates) 3.工作分解结构词汇表(更新) WBS dictionary(updates) 4.范围基准(更新) Scope baseline(updates) 5.请求的变更 Requested changes 6.推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 7.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 8.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) TIME进度活动定义 Activity Definition 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 3.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement 4.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure 5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS clictionary 6.项目管理计划 Progece management plan 1.分解 Decomposition 2.样板 Templates 3.滚动式规划 Rolling wave planning 4.专家判断 Expert judgment 5.规划组成部分 Planning componet 1.活动清单Activity list 2.活动属性 Activity attributes 3.里程碑清单 Milestone list 4.请求的变更 Requested changes 活动排序 Activity Sequencing 1.项目范围说明书项目范围说明书 Project scope statament 2.活动清单活动清单 Activity list 3.活动属性活动属性 Activity attributes 4.里程碑清单里程碑清单 Milestons list 1.紧前关系绘图法(PDM) Precedence Diagramming Method(PDM) 2.箭线绘图法箭线绘图法(ADM) Arrow Diagramming Method(ADM) 1.项目进度网络图 Project schedule network diagrams 2.活动清单活动清单(更新) Activity list (updates) 3 5.批准的变更请求批准的变更请求 Approved change requesta 3.进度网络样板进度网络样板 Schedule network tempiates 4.确定依赖关系确定依赖关系 Dependency determination 5.利用时间提前量与滞后量利用时间提前量与滞后量 Applying leads and lags 3.活动属性活动属性(更新) Activity attributes(updates) 4.请求的变更请求的变更 Requesaed changes 活动资源估算Activity Resource Estimating 1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 3.活动清单Activity list 4.活动属性Activity attributes 5.资源可利用情况 Resouce availability 6.项目管理计划Project management l 1.专家判断 Expert judgment 2.多方案分析 Alternatives analysis 3.出版的估算数据 Published estimating data 4.项目管理软件 Project management sortware 5.自上而下的估算 Bottom estimating 1.活动资源要求 Activity resource requirements 2.活动属性(更新) Activity attributes(updates) 3.资源分解结构 Resource breakdown structure 4.资源日历(更新)Resource calendars 5.请求的变更 Requested changes 活动持续时间估算Activity Duration Estimating 1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程资产组织过程资产Organizational process assets 3.项目范围说明书项目范围说明书 Project scops statement 4.活动清单活动清单 Activity list 5.活动属性活动属性 Activity attributes 6.活动资源要求活动资源要求 Activity resource requirements 7.资源日历资源日历 Resource calendars 8.项目管理计划项目管理计划 Project management plan ●风险登记册●风险登记册 Risk register ●活动费用估算●活动费用估算 Activity cost estimates 1.专家判断 Expert judgment 2.类比估算 Analogous estimating 3.参数估算 Parametric estimating 4.三点估算 Three-point estimates 5.后备分析 Reserve analysis 1.活动持续时间估算 Activity duration estimates 2.活动属性 Activity attributes(updates) 制定进度表Schedule Development 1.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 2.项目范围说明书项目范围说明书Project scope statement 3.活动清单活动清单 Activity list 4.活动属性活动属性 Activity attributes 5.项目进度网络图项目进度网络图 Project schedule network diagrams 6.活动资源要求活动资源要求 Activity resource requirements 7.资源日历资源日历 Resource calendars 8.活动持续时间估算活动持续时间估算 Activity duration estimates 9.项目管理计划项目管理计划 Project management plan ●风险登记册 Risk register 1.进度网络分析 Schedule network analysisi 2.关键路线法 Critical path method 3.进度压缩 Schsdule compression 4.假设情景分析What-if scenario analysis 5.资源平衡 Resource leveling 6.关键链法 Critical chain method 7.项目管理软件 Project management software 8.应用日历 Applying calendars 9.调整时间提前滞后量 Adjusting leads and lags 10.进度模型 Schedule model 1.项目进度表项目进度表 Project schedule 2.进度模型数据进度模型数据 Schedule model data 3.进度基准进度基准 Schedule baseline 4.资源要求资源要求 Resource requirements(updates) 5.活动属性活动属性(更新) Activity attributes(updates) 6.项目日历项目日历(更新)Project calendar 7.请求的变更请求的变更 Requesaed changes 8.项目管理计划项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) ●进度管理计划(更新) Schedule management plan(updates) 进度控制 Schedule Control 1.进度管理计划 schedule management plan 2.进度基准进度基准 Schedule baseline 3.绩效报告绩效报告 Performance reports 4.批准的变更要求批准的变更要求 Approved change requests 1.进度报告进度报告 Progress reporting 2.进度变更控制系统进度变更控制系统 Schedule change control system 3.绩效衡量绩效衡量 Performance measurement 4.项目管理软件项目管理软件 Project management software 5.偏差分析偏差分析 Variance analysisi 6.进度比较横道图进度比较横道图 Schedule comparison bar chars 1. 进度模型数据(更新) Schedule model data(updates) 2. 进度基准(更新) Schedule baseline(updates) 3. 绩效衡量 Performance measurements 4. 请求的变更 Requesaed changes 5.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 6.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 7.活动清单(更新) Activity list(updates) 8.活动属性(更新) Activity attributes(updates) 9.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) COST费用费用估算Cost Estimating 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程资产组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement 4. 工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure 1.类比估算 Analogous estimating 2.确定资源费率 Determine resource cost rates 3.自上而下估算 Bottom-up estimating 4.参数估算 Parametric estimating 5.项目管理软件 Project management 1.活动费用估算 Activity cost estimates 2.活动费用估算支持细节活动费用估算支持细节 Activity cost estimate supporting detall 3.请求的变更请求的变更 Requested 4 5 5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary 6.项目管理计划 Progece management plan ●进度管理计划●进度管理计划 Schedule management plan ●人员配备管理计划Staffing management plan ●风险登记册 Risk registor software 6.供货商投标分析 Vendor bid analysis 7.准备金分析 Reserve analysis 8.质量成本 Cost of quality changes 4.费用管理计划(更新) Cost management plan(updates) 费用预算 Cost Budgeting 1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement 2.工作分解结构工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure 3.工作分解结构词汇表工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary 4.活动费用估算活动费用估算 Activity cost estimates 5.活动费用估算支持细节活动费用估算支持细节 Activity cost estimate supporting detall 6.项目进度项目进度 Project schedule 7.资源日历资源日历 Resource calendars 8.合同合同 Contract 9.费用管理计划费用管理计划 Cost management plan 1.费用汇总费用汇总 Cost aggregation 2.储备基金分析储备基金分析 Reserve analysis 3.参数估算参数估算 Parametric esrimating 4.资金限制平衡资金限制平衡 Funding limit reconciliation 1.费用基准 Cost baseline 2.项目资金要求 Project funding requirements 3.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) 4.请求的变更 Requested changes 费用控制Cost Control 1.费用基准 Cost baseline 2.项目资金要求项目资金要求 Project funding requirements 3.绩效报告绩效报告 Performance reports 4.工作绩效信息 Work performance information 5.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 6.项目管理计划 Project management plan 1.费用变更控制系统 Cost change control system 2.绩效衡量分析绩效衡量分析 Performance measurements analysis 3.预测预测 Forecasting 4.项目绩效审核项目绩效审核 Project performance reviews 5.项目管理软件 Project management software 6.偏差管理 Variance management 1.费用估算(更新) Cost estimates(update) 2.费用基准(更新) Cost baseline(update) 3.绩效衡量绩效衡量 Performance measurements 4.预测完工预测完工 5.请求的变更请求的变更 Requested changes 6.推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 7.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 8.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) RISK 风险风险管理规划 Risk Management Planning 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程资产组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 3.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement 4.项目管理计划 Progece management plan 1.规则会议和分析 Planning meeting and analysis 1.风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan 风险识别Risk Identification 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程生产组织过程生产 Organizational process assets 3.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement 4. 风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan 5. 项目管理计划 Project management plan 1.文件审查文件审查 Documentation reviews 2.信息搜索技术信息搜索技术 Information gathering techniques 3.核对表分析核对表分析 Checklist analysis 4.假设分析假设分析 Assumptions analysis 5.图解技术图解技术 Diagiamming techniques 1.风险登记册 Risk register Qualitative Risk Analysisi 风险定性分析风险定性分析1.组织过程生产 Organizational process assets 2.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement 3. 风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan 4. 风险登记册 Risk register 1.风险概率与影响评估 Risk probability and impact assessment 2.概率和影响矩阵概率和影响矩阵 Probablity and impact matrix 3.风险数据质量评估风险数据质量评估 Risk data quality assessment 4.风险分类风险分类 Risk categorization 5.风险紧迫性评估风险紧迫性评估 Risk urgency assessment 1.风险登记册(更新) Risk register(updates) 定量风险分析 Quantitative Risk Analysis 1.组织过程生产 Organizational process assets 2.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement 3. 风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan 4. 风险登记册 Risk register 5. 项目管理计划 Project management plan ●项目进度管理计划 Project schedule management plan ●项目费用管理计划 Project cost management plan 1.数据收集和表示技术 Data gathering and representation techniques 2.定量风险分析和模型技术 Quantitative risk analysis and modeling techniques 1.风险登记册(更新) Risk register(updates) 风险应对规划 Risk Response Planning 1.风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan 2.风险登记册 Risk register 1.消极风险或威胁的应对策略 Strategies for negative risk or threats 2.积极风险或机会的应对策略积极风险或机会的应对策略 Strategies for 1.风险登记册(更新) Risk register(updates) 2.项目管理计划(更新) Project positive risk or opportunities 3.威胁或机会的应对策略威胁或机会的应对策略 Strategies for both threats and opprtunities 4.应急应对策略应急应对策略 Contingent response strategy management plan(updates) 3.与风险有关的合同协议与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-related contractual agreements 风险监控 Risk Monitoring and Control 1.风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan 2.风险登记册 Risk register 3.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 4.工作绩效信息 Work performance information 5.绩效报告 Performance reports 1.风险再评估 Risk reassessment 2.风险审计风险审计 Risk audits 3.变差和趋势分析变差和趋势分析 Variance and trend analysis 4.技术绩效分析技术绩效分析 Technical performance measurement 5.储备金分析储备金分析Reserve analysis 6.状态审查会状态审查会 Status meetings 1.风险登记册(更新) Risk register(updates) 2.请求的变更 Requested changes 3.推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 4.推荐的预防措施推荐的预防措施Recommended preventive action 5.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 6.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) QUALITY质量质量规划 Quality Planning 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement 4.项目管理计划 Progece management plan 1.成本效益分析成本效益分析 Cost-benefit analysis 2.基准对照基准对照 Benchmarking 3.试验设计试验设计 Design of experiments 5.质量成本质量成本(COQ) Cost of quality (COQ) 6.其他质量规划工具其他质量规划工具 Additional quality planning tools 1.质量管理计划质量管理计划 Quality management plan 2.质量测量指标质量测量指标 Quality metrics 3.质量核对表质量核对表 Quality checklists 4.过程改进计划过程改进计划 Process improvement plan 5.质量基准质量基准 Quality baseline 6.项目管理计划项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) 实施质量保证Perform Quality Assurance 1.质量管理计划质量管理计划 Quality management plan 2.质量测量指标质量测量指标 Quality metrics 3.过程改进计划过程改进计划 Process improvement plan 4.工作绩效信息 Work performance information 5.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 6.质量控制衡量 Quality control measurnments 7.实施的变更请求 Implementde change requests 8.实施的纠正措施 Implementde corrective actions 9.实施的缺陷补救 Implementde defect repair 10.实施的预防措施 Implementde preventive actions 1.质量规划工具与技术质量规划工具与技术 Quality planning tools and techniques 2.质量审计质量审计 Quality audits 3.过程分析过程分析 Process analysis 4.质量控制工具与技术质量控制工具与技术 Quality control tools and techniques 1.请求的变更请求的变更 Requested changes 2.推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 3.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 4.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) 实施质量监控 Perform Quality Control 1.质量管理计划质量管理计划 Quality management plan 2.质量测量指标质量测量指标 Quality metrics 3.质量核对表质量核对表 Quality checklists 4.组织过程资产组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 5.工作绩效信息工作绩效信息 Work performance information 6.批准的变更请求批准的变更请求 Approved change requests 7.可交付成果可交付成果 Deliverables 1.因果图因果图 Cause and effect diagram 2.控制图控制图 Control charts 3.流程图流程图 Flowcharting 4.直方图直方图 Histogram 5.帕雷托图帕雷托图 Pareto chart 6.趋势图趋势图 Run chart 7.散点图散点图 Scatter diagram 8,统计抽样统计抽样 Statistical sampling 9.检查检查 Inspection 10.缺陷补救审查缺陷补救审查 Defect repair review 1.质量控制衡量质量控制衡量 Quality control measurnments 2.确认的缺陷补救确认的缺陷补救 Validated defect repair 3.质量基准质量基准(更新) Quality baseline(updates) 4.推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 5.推荐的预防措施推荐的预防措施推荐的预防措施Recommended preventive action 6.请求的变更 Requested changes 7.推荐的缺陷补救推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defect repair 8.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 9.确认的可交付成果 Validated deliverables 10.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源人力资源规划人力资源规划 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 1.组织机构图和岗位描述组织机构图和岗位描述 Organization charts and position descriptions 2.交际交际 Networking 3.组织理论组织理论 Organization theory 1.角色与职责角色与职责 roles and responsibilities 2.项目组织图项目组织图 Projece organization chares 6 7 3.项目管理计划 Progece management plan ●活动资源需求 Activity resource requirements 3.人员配备管理计划人员配备管理计划 Staffinf management plan 项目团队组建 Acquire Project Team 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 3.角色与职责 roles and responsibilities 4.项目组织图 Projece organization chares 5.人员配备管理计划 Staffinf management plan 招聘惯例招聘惯例 1.预分派预分派 Pre-assignment 2.谈判谈判 Negotiation 3.招募招募 Acquisition 4.虚拟团队虚拟团队Virtual teams 1.项目人员分派到位项目人员分派到位 Project staff assignments 2.资源可利用情况资源可利用情况 Resource availability 3.人员配备管理计划人员配备管理计划(更新) Staffinf management plan(updates) 项目团队建设 Develop Project Team 1.项目人员分派 Project staff assignments 2.人员配备管理计划人员配备管理计划 Staffinf management plan 3.资源可利用情况 Resource availability 1.通用管理技能通用管理技能 General management skills 2.培训培训 Training 3.团队建设活动团队建设活动 Team-building activities 4.规则规则 Ground rules 5.集中办公集中办公 Co-location 6.奖励与表彰奖励与表彰 Recognition and rewards 1.团队绩效评估 Team performance assessment 项目团队管理 Manage Project Team 1.组织过程资产组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 2.项目人员分派项目人员分派 Project staff assignments 3.角色与职责角色与职责 roles and responsibilities 4.项目组织图项目组织图 Projece organization chares 5.人员配备管理计划 Staffinf management plan 6.团队绩效考核 Team performance assessment 7.工作绩效信息 Work performance information 8.绩效报告 Performance reports 1.观察与交谈观察与交谈 Observation and conversation 2.项目绩效评估项目绩效评估 Project performance appraisals 3.冲突管理冲突管理 Conflict management 4.问题登记薄问题登记薄 Lssue log 1.请求的变更 Requested changes 2.推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 3.推荐的预防措施推荐的预防措施Recommended preventive action 4.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 5.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) COMMUNICATIONS 沟通Communications Planning 沟通规划沟通规划1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程生产组织过程生产 Organizational process assets 3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement 4.项目管理计划 Progece management plan ● 制约因素 Constraints ● 假设 Assumptions 1.沟通需求分析沟通需求分析 Communications requirements analysls 2.沟通技术沟通技术 Communications technology 1.沟通管理计划 Communications management plan Information Distribution 信息发布发布1. 沟通管理计划 Communications management plan 1.沟通技能 Communications skills 2.信息收集和检索系统 Information gathering and retrieval system 3.信息发布系统 Information distribution methods 4.经验教训总结过程 Lessons learned process 1. 组织过程生产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 2. 请求的变更请求的变更 Requested changes Performance Reporting 绩效报告报告1.工作绩效信息 Work performance information 2.绩效衡量 Performance measurements 3.完工预测 Forecasted completion 4.质量控制衡量 Quality control measurnments 5.项目管理计划 Project management plan ●绩效衡量分析 Performance measurements baseline 6.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 7.可交付成果 Deliverables 1.信息演示工具 Information presentation tools 2.绩效信息收集和汇总 Performance information gathering and compilation 3.状态审查会 Status review meetings 4.工时汇报系统Time reporting systems 5.费用汇报系统Cost reporting systems 1.绩效报告 Performance reports 2.预测 Forecasts 3.请求的变更 Requested changes 4.推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 5.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 利害关系者管理 Manage Stakeholders 1.沟通管理计划 Communications management plan 2. 组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 1.沟通方法 Communications methods 2.问题登记薄 lssue logs 1.问题得以解决Resolved issues 2.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 3.批准的纠正措施 Approved corrective action 4.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 5.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) PROCUREMENT采购采购规划 Plan Purchases and Acquisitions 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmental factors 2.组织过程生产组织过程生产 Organizational process assets 3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement 4.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure 5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS clictionary 6.项目管理计划 Progece management plan ●风险登记册 Risk register ●与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-related contractual agreements ●资源要求 Resource requirements ●项目进度计划 Project schedule ●活动费用估算 Activity cost estimate ●费用基准 Cost baseline 1.自制或外购分析自制或外购分析 Make-or-buy analysls 2.专家判断专家判断 Expert judgment 3.合同类型合同类型 Contract types 1.采购管理计划 Procurement management plan 2.合同工作说明书 Contract statement of work 3.自制或外购决策 Maker-or-buy changes 4.请求的变更 Requested changes 发包规划 Plan Contracting 1.采购管理计划 Procurement management plan 2.合同工作说明书 Contract statement of work 3.自制或外购决策自制或外购决策 Maker-or-buy changes 4.项目管理计划 Project management plan ●风险登记册 Risk register ●与风险有关的合同协议●与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-related contractual agreements ●资源要求●资源要求 Resource requirements ●项目进度计划 Project schedule ●活动费用估算 Activity cost estimate ●费用基准 Cost baseline 1.标准表格标准表格 Standard forms 2.专家判断专家判断 Expert Judgment 1.采购文件 Procurement documents 2.评估标准 Evaluation criteria 3.合同工作说明书(更新) Contract statement of work(updates) 询价Request Seller Responses 1.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 2.采购管理计划 Procurement management plan 3.采购文件 Procurement documents 1.招标人会议招标人会议 Bldder conferences 2.刊登广告刊登广告 Advertising 3.制定合格卖方清单制定合格卖方清单 Develop qualifid sellers list 1.合格卖方清单 Qualified sellers list 2.采购文件包采购文件包 Procurement document package 3.建议书建议书 Proposals 卖方选择Select Sellers 1.组织过程资产 Organizational process assets 2.采购管理计划 Procurement management plan 3.评估标准 Evaluation criteria 4.采购文件包 Procurement document package 5.建议书 Proposals 6.合格卖方清单 Qualified sellers list 7.项目管理计划 Project management plan ●风险登记册 Risk register ●与风险有关的合同协议●与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-related contractual agreements 1.加权系统加权系统 Weighting system 2.独立估算独立估算 Independent estimates 3.筛选系统筛选系统 Screening system 4.合同谈判合同谈判 negotiation 5.卖方评级系统卖方评级系统 Seller rating systens 6.专家判断专家判断 Expert judgment 7.建议书评估技术建议书评估技术 Proposal evaluation techniques 1.选中的卖方 Selected sellers 2.合同合同 Contract 3.合同管理计划合同管理计划 Contract management plan 4.资源可利用情况资源可利用情况 Resource availability 5.采购管理计划采购管理计划(更新) Procurement management plan(updates) 6.请求的变更请求的变更 Requested changes 合同管理 Contract Administration 1.合同合同 Contract 2.合同管理计划合同管理计划 Contract management plan 3.选中的卖方选中的卖方 Selected sellers 4.绩效报告 Performance reports 5.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests 6.工作绩效信息 Work performance information 1.合同变更控制系统 Contract change control system 2.买方进行的绩效审核买方进行的绩效审核 Buyer-conducted per-formance review 3.检验和审计检验和审计 Inspections and audits 4.绩效报告绩效报告 Performance reporting 5.支付系统支付系统 Payment system 6.索赔管理索赔管理 Claims administration 7.合同档案管理系统合同档案管理系统 Records management system 8.信息技术 Information technology 1.合同文件合同文件 Contract documentation 2.请求的变更请求的变更 Requested changes 3.推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action 4.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 5.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates) ●采购管理计划 Procurement management plan ●合同管理计划 Contract management plan 合同收尾 Contract Closure 1.采购管理计划 Procurement management plan 2.合同管理计划 Contract management plan 3.合同文件 Contract documentation 4.合同收尾程序 Contract closure procedure 1.采购审计采购审计 Procurement audits 2.合同档案管理系统合同档案管理系统 Records management system 1.合同收尾Contract closures 2.组织过程资产组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates) 8 。

项目管理术语英汉对照表A•Abstract Resource 抽象资源•Abstraction 抽象•Acceleration 加速•Acceptability Criteria 验收标准•Acceptable Quality Level ("AQL") 可接受质量水平•Acceptance 验收•Acceptance Criteria 验收标准•Acceptance Letters 验收函•Acceptance Number 接受数目•Acceptance Review 验收评审•Acceptance Test 验收测试•Acquisition Methods 采购方式•Acquisition Negotiations 采购谈判•Acquisition Plan 采购计划•Acquisition Plan Review ("APR") 采购计划评审•Acquisition Planning 采购计划编制•Acquisition Process 采购过程•Acquisition Strategy 采购策略•Action 行动•Action Item 行动项•Action Item Flags 行动项标记•Action Plan 行动计划•Activation 激活•Active Listening 积极倾听•Activity Arrow Net 活动箭线网络•Activity Based Costing ("ABC") 基于活动的成本核算•Activity Based Management ("ABM") 基于活动的管理•Activity Calendar 活动日历•Activity Code 活动代码•Activity Definition 活动定义•Activity Description 活动描述•Activity Duration 活动工期活动持续时间•Activity Duration Estimating 活动工期估算•Activity Elaboration 活动详述•Activity File 活动档案•Activity ID 活动识别码•Activity List 活动清单•Activity Node Net 活动节点网络双代号网络•Activity on Arc ("AOA") 弧线表示活动双代号网络•Activity on Arrow ("AOA") 箭线表示活动双代号网络•Activity on Node节点表示活动单代号网络•Activity Oriented 面向活动•Activity Oriented Schedule 面向活动的进度计划•Activity Properties 活动属性•Activity Quantities 活动量值•Activity Status 活动状态•Activity Timing 活动定时•Actor 执行者角色•Actual 实际的•Actual and Scheduled Progress 实际进展的与计划进度•Actual Cost 实际成本•Actual Cost Data Collection 实际成本汇总•Actual Costs 实际费用•Actual Dates 实际日期•Actual Direct Costs 实际直接成本•Actual Expenditures 实际的支出•Actual Finish 实际完成•Actual Finish Date 实际完成日期•Actual Start 实际开始•Actual Start Date 实际开始日期•ACWP 已完成工作实际成本•See Actual Cost of Work Performed •Adaptation 适应•Added value 附加价值•Addendum 附录•Adequacy 适当•Adjourning 解散•Adjustment 调节•ADM•Arrow Diagram Method•ADM Project ADM 项目•Administration 管理部门•Administrative 行政的•Administrative Change 行政变更•Administrative Management 行政管理•ADP•Automated Data Processing•ADR•Alternative Dispute Resolution•Advanced Material Release ("AMR") 材料提前发布•AF•Actual Finish Date•AFE•Application for Expenditure•Authority for Expenditure•Affect 影响•Affected Parties 受影响方•Agency 代理•Agenda 议程•Aggregation 汇总•Agreement 协议•Agreement, legal 协议合同•ALAP•As-Late-As-Possible•Algorithm 算法•Alignment 排列成行•Alliance 联合•Allocated Baseline 分配的基线•Allocated Requirements 分配需求•Allocation 分配•Allowable Cost 允许成本•Allowance 预留•Alternate Resource 替代资源•Alternative Analysis 替代分析•Alternative Dispute Resolution ("ADR") 替代争议解决方案•Alternatives 可选方案•Ambiguity 含糊不清•Amendment 修订•Amount at Stake 损失量•AMR 材料提前公布•Analysis 分析•Analysis and Design 分析与设计•Analysis Time 分析期•Analyst 分析员•AND Relationship 与关系•Anecdotal 轶事•Anticipated Award Cost 预期中标价•AOA•Activity on Arrow•Activity on Arc•AON•Activity on Node•AOQ•Average Outgoing Quality•AOQL•Average Outgoing Quality Limit•APMA•Apparent Low Bidder 最低投标人•Application 应用•Application Area 应用领域•Application for Expenditure ("AFE") 支出申请•Application for Expenditure Justification 支出申请的论证•Application Programs 应用程序•Applied Direct Costs 实际直接成本•Apportioned Effort 分摊努力•Apportioned Task 分摊任务•Appraisal 评估•Approach 方法•Appropriation 拨款•Approval 批准•Approval to Proceed 批准继续•Approve 同意•Approved Bidders List 批准的投标人清单•Approved Changes 批准的变更•Approved Project Requirements 批准的项目需求•APR•Acquisition Plan Review•AQL•Acceptable Quality Level•Arbitrary 随意的•Arbitration 仲裁•Arc 弧线•Architectural Baseline 构架基线•Architectural View 构架视图•Architecture 构架•Architecture, executable 构架可执行•Archive 档案文件•Archive Plan 存档计划•Area of Project Application•Area of Project Management Application ("APMA") 项目管理的应用领域•Arrow 箭线•Arrow Diagram Method ("ADM") 箭线图方法•Arrow Diagramming 箭线图方法•Arrow Diagramming Method 箭线图方法双代号网络图•Artifact 制品•Artificial 人工的•AS•Actual Start Date•ASAP•As-Soon-As-Possible•As-built Design 实际建造设计•As-built document.tion 实际建造文档•As-Built Records•As-Built Schedule 实际建造进度计划•As-Late-As-Possible ("ALAP") 尽可能晚•As-Needed 恰如所需•As-of Dateo见Data Date.•As-Performed Schedule 实际进度计划•Assembly 组装件•Assembly Sequence 组装顺序•Assessment 评估•Assets 资产•Assignment 分配委派任务•Associated Revenue 关联收益•Association 关联关系•As-Soon-As-Possible ("ASAP") 尽快•Assumption 假设•Assumptions 假设•Assumptions List 假设清单•Assurance 保证•Assurance Programo见Quality Assurance Program.•ATPo见Acceptance Test Procedure•Attitude 态度•Attribute 属性•Attrition 损耗•Audit 审核审计•Authoritarian 独裁的•Authoritative 权威的•Authority 权威权力•Authority for Expenditure ("AFE") 开支权•Authorization 授权o见Approval•Authorize 批准•Authorized Unpriced Work 批准的未定价工作•Authorized Work 批准的工作•Authorized Works 批准的工作•Automated Data Processing ("ADP") 自动化数据处理•Automatic Decision Event 自动决策事件•Automatic Generation 自动生成•Automatic Test Equipment 自动测试设备•AUWo见Authorized Unpriced Work•Auxiliary Ground Equipment 辅助场地设备•Availability 可用性•Average Outgoing Quality ("AOQ") 平均出厂质量•Average Outgoing Quality Limit ("AOQL") 平均出厂质量限度•Average Sample Size Curve 平均样本规模曲线•Avoidance 避免•Award 授予•Award Fee 奖金•Award Letter 中标函[编辑]B•BAC 完工预算•Budget at Completion•Baseline at Completion•Back Charge 逆向计费•Backcharge 逆向收费•Backward Pass 倒推法/反向计算•Bad Debts 坏帐•Balance 余额权衡•Balanced Matrix 平衡矩阵•Balanced Scorecard平衡记分卡•Balanced Scorecard Approach ("BSA") 平衡记分卡方法•Bank 储备•Banking 储备•Bar Chart 横道图•Bargaining 讨价还价交涉•Bargaining Power 讨价还价权力交涉权力•Barriers 障碍•Base 基础基数•Baseline 基线基准•Baseline at Completion ("BAC") 完成/完工基线•Baseline Concept 基线概念•Baseline Control 基线控制•Baseline Cost 基线成本•Baseline Dates 基线日期•Baseline Finish Date 基线完成日期•Baseline Management 基线管理•Baseline Plan 基线计划基准计划•Baseline Review 基线评审•Baseline Schedule 基线进度计划•Baseline Start Date 基线开始日期•Baseline, budget 基线预算•Baseline, business 基线商业•Baseline, cost estimate 基线费用估算•Baseline, technical 基线技术•Basis of Estimate 估算根据•Batch 批量•Batch Operation 批运行/批处理•BATNA•Best Alternative to Negotiated Agreement•BCM•Business Change Manager•BCWP•Budgeted Cost of Work Performed•BCWS•Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled•BEC•Elapsed Cost•Behavior 行为/反应•Behavior Analysis 行为分析•Benchmark 基准•Benchmarking标竿管理•Beneficial Occupancy/Use 有益的占用/使用•Benefits 效益•Benefits Framework 效益框架•Benefits Management 效益管理•Benefits Management Plan 效益管理计划•Benefits Management Regime 效益管理制度•Benefits Profiles 效益简述•Benefits Realization Phase 效益实现阶段•Best Alternative to Negotiated Agreement ("BATNA") 协议外最佳方案•BATNA•Best and Final Contract Offer 最佳及最终合同报价•Best and Final Offer 最佳及最终报价•Best Efforts Contract 最大努力合同•Best Practices 最佳实践•Best value 最佳值•Beta Distribution 贝塔发布•Beta Test 贝塔测试•Beta testing 贝塔测试•Bid 投标•Bid Analysis 投标分析•Bid Bond投标保证金•Bid Cost Considerations 投标成本补偿费•Bid document.nbspPreparation 招标文件准备•Bid document.招标文件•Bid Evaluation 评标•Bid List 投标人清单•Bid Package 标段标块•Bid Protests 投标抗议/拒付•Bid Qualifications 投标资质•Bid Response 投标响应•Bid Technical Consideration 投标技术因素•Bid Time Consideration 投标中的时间因素•Bid/No Bid Decision 投标/不投标决策•Bidder 投标人•Bidders Conference 投标人会议•Bidders List 投标人名单•Bidders Source Selection 投标人来源选择•Bidding 投标•Bidding Strategy 投标策略•Bill 帐单•Bill of Materials 材料清单•Bills of Materials 材料清单•Blanket Purchase Agreement ("BPA") 一揽子采购协议BPA •Blueprint 蓝图/计划设计图•Board 委员会•Boiler Plate 样板文件•Bona Fide 真诚真实•Bond 担保•Bonus 奖金•Bonus Schemes 奖励计划•Booking Rates 预提费率•BOOT•Build, Own, Operate, Transfer•Bottom Up Cost Estimate 自下而上成本估算•Bottom Up Cost Estimating 自下而上成本估算•Bottom Up Estimating 自下而上估算•Boundary 边界•BPA•Blanket Purchase Agreement•BPR•Business Process Reengineering •Brainstorming 头脑风暴法•Branching Logic 分支逻辑关系•Breach of Contract 违约•Breadboarding 实验模型•Break Even 盈亏平衡•Breakdown 分解•Breakdown Structure 分解结构•Break-Even Chart 盈亏平衡图•Break-Even Charts 盈亏平衡图•Break-Even Point 盈亏平衡点•Bribe 贿赂•BSA•Balanced Scorecard Approach•Buck Passing 完全通过/推卸责任•Budget 预算•Budget at Completion ("BAC") 完工预算BAC•Budget Cost 预算成本•Budget Costs 预算成本预算费用•Budget Decrement 预算消耗•Budget Element 预算要素•Budget Estimate 预算估算•Budget Presentation 预算介绍•Budget Revision 预算修订•Budget Unit 预算单位•Budgetary Control预算性控制•Budgeted 已安排预算的•Budgeted Cost of Work Performed ("BCWP") 已完工作预算成本BCWP•Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled ("BCWS") 计划工作的预算成本•Budgeting 制定预算•Budgeting & Cost Management 预算制定与成本管理•Build 建设构造•Build, Own, Operate, Transfer ("BOOT") 建造拥有经营转让•Buildability 建造能力•Building 建筑物•Building Professionalism 建设专业化•Build-to document.tion 建成文档•Built-in Test Equipment 内置测试设备•Bulk Material 大宗材料•Burden 间接费用负担•Burden of Proof 举证费•Bureaucracy 官僚制度•Burn Rate 消耗速度•Burst Node 分支点•Business Actor 业务参与者/角色•Business Appraisal 商业评估•Business Area 业务领域•Business Assurance 商业保证•Business Assurance Coordinator 商业保证协调人•Business Case 商业案例•Business Change Manager ("BCM") 商业变更经理BCM •Business Creation 商业创新•Business Engineering 商业工程•Business Imperative 商业需要•Business Improvement 业务改进•Business Manager 商务经理商业经理•Business Modeling 业务建模•Business Needs 商业需求•Business Objectives 商业目标•Business Operations 业务运作•Business Process 业务流程•Business Process Engineering 业务流程工程•Business Process Reengineering ("BPR") 业务流程重组•Business Processes 业务流程•Business Risk 商业风险•Business Rule 商业规则•Business Transition Plan 业务转换计划•Business Unit 业务单位•Buyer 买方•Buyer's Market 买方市场•Buy-In 支持认同买进•Bypassing 回避[编辑]C•C/SCSC•Cost/Schedule Control System Criteria•C/SSR•Cost/Schedule Status Report•CA•Control Account•CAD•Computer Aided Drafting•Computer Aided Design•Calculate Schedule 估算进度安排•Calculation 计算•Calendar 日历•Calendar File 日历文件•Calendar Range 日历范围•Calendar Start Date 日历开始日期•Calendar Unit 日历单位•Calendar, Software 日历软件•Calendars 日历集•Calibration 校准•CAM•Cost Account Manager•Computer Aided Manufacturing •Control Account Manager•CAP•Cost Account Plan•Control Account Plan•Capability 能力•Capability Survey 能力调查•Capital 资本•Capital Appropriation 资本划拨•Capital Asset 资本资产•Capital Cost 资本成本•Capital Employed 占用的资本•Capital Expansion Projects 资本扩展项目•Capital Goods Project 资本货物项目•Capital Property 资本财产•CAR•Capital Appropriation Request •Cards-on-the-wall Planning 墙卡规划法•Career 职业•Career Path Planning 职业路线规划•Career Planning职业规划•Career Path Planning.•Carryover Type 1 结转类型1•Carryover Type 2 结转类型2•Cascade Chart 层叠图•CASEo Computer Aided Software Engineeringo Computer Aided System Engineering •Cash现金•Cash Flow 现金流•Cash Flow Analysis 现金流分析•Cash Flow Management 现金流管理•Cash Flow, Net 现金流净值•Cash In 现金流入•Cash Out 现金支出•Catalyst 催化者•Catch-up Alternatives 赶上计划的备选方案•Causation 起因•Cause 动因•CBD•Component-Based Development•CBS•Cost Breakdown Structure•CCB•Change Control Board•CCDR•Contractor Cost Data Report•CDR•Critical Design Review•Central Processing Unit (CPU) 中央处理单元•Centralized 集中的•Certain 确定的•Certainty.•Certainty 确定性•Certificate of Conformance 一致性认证•Certification 认证•Chain 链•Challenge 挑战•Champion 推动者支持者•Change 变更变化变革•Change Control 变更控制•Change Control Board (CCB) 变更管理委员会•Change document.tion 变更文档•Change in Scope 工作范围变化•Change Log 变更日志•Change Management 变更管理•Change Management Plan 变更管理计划•Change Notice 变更通知•Change Order 变更通知单•Changed Conditions 变更的条款•Characteristic 特性•Chart 图表•Chart of Accounts 会计科目表•Chart Room 图表室•Charter 章程•Checking 检查•Checklist 检查清单•Checkpoint 检查点•Checkpoints 检查点集•Chief Executive Officer首席执行官•Child 子项•Child Activity 子活动•CI•Configuration Item•Claim 索赔•Clarification 澄清•Class 类•Classes 类•Classification 分类•Classification of Defects 缺陷的分类•Clearance Number 净空数•Client 客户•Client Environment 客户环境•Client Quality Services 客户质量服务•Closed Projects 已收尾的项目•Closeout 收尾•Closeout Report 收尾报告•Closeout, phase 收尾阶段•Closing 终止•Closure 收尾•CM•Configuration Management •Construction Management •Coaching 教练•Code 代码•Code and Unit Test 编码和单元测试•Code of Accounts 帐目编码•Coding 编码•Collaboration 协作•Collapsing 折叠•Collective 集体的•Combative 好战的•Commercial 商务的•Commercial Item Description 商务描述•Commission and Handover 委托和移交•Commissioning 试运行•Commissions and Bonuses 酬金和奖金•Commit 提交•Commitment 承诺义务•Commitment document.nbsp 承诺文件•Commitment Estimate•Commitment Package 承诺包•Commitment to Objectives 对目标的承诺•Committed Cost 已承担成本已承付成本•Committed Costs 已承诺费用•Common Carrier 公众运营商•Communicating With Groups 与团队的沟通•Communicating With Individuals 与个人的沟通•Communication 沟通•Communication Channels 沟通渠道•Communication Plan, Strategic 沟通计划策略性的•Communication Plan, Tactical 沟通计划--战术性的•Communication Room 交流室•Communications Management 沟通管理•Communications Plan 沟通计划•Communications Planning 沟通规划编制•Community 社团•Company 公司•Comparison 对比•Compatibility 兼容性•Compensation 补偿•Compensation and Evaluation 补偿和评价•Competence 能力•Competency 能力•Competition 竞争•Competitive:竞争的•Compile 编译•Compile Time 编译时•Complete 完成•Completed Activity 已完成的活动•Completed Units 完工单元•Completion 完工•Completion Date 完成日期•Complex 复杂的•Component 构件组件•Component Integration and Test 组件集成和测试•Component-Based Development ("CBD") 基于构件的开发•Components 组件•Compound Risk 复合风险•Compromise 折衷•Compromising, in negotiating 折衷谈判•Computer 计算机•Computer Aided Design (CAD) 计算机辅助设计•Computer Aided Drafting (CAD) 计算机辅助制图•Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) 计算机辅助制造•Computer Cost Applications 计算机化的成本管理应用•Computer Hardware 计算机硬件•Computer Modeling 计算机建模•Computer Program Configuration Item 计算机程序配置项•Computer Software 计算机软件•Computer Software Component 计算机软件组件•Computer Software Configuration Item (CSCI) 计算机软件配置项•Computer Software document.tion 计算机软件文档•Computer Software Unit 计算机软件单元•Computer-Aided 计算机辅助的•Computerized Information Storage, Reference and Retrieval 计算机化的信息存储定位和检索•Concept 概念•Concept Definition document.概念定义文档•Concept Phase 概念阶段•Concept Study 概念研究•Conception Phase 概念形成阶段•Conceptual 概念性的•Conceptual Budgeting 概念性预算•Conceptual Design 概念性设计•Conceptual Development 概念性开发•Conceptual Project Planning 概念性项目计划•Concession 让步•Concession Making, in negotiating 谈判中的让步•Conciliatory 调和的•Concluding 终决的•Conclusions 结论•Concurrency 并发性•Concurrent 并发事件•Concurrent Delays 并行延迟•Concurrent Engineering 并行工程•Concurrent Tasks 并行任务•Conditional Risk 条件风险•Conditions 条件条款•Conducting 执行•Confidence Level 信心等级•Configuration 配置•Configuration Audit 配置审核•Configuration Breakdown 配置分解•Configuration Control 配置控制•Configuration Control Board 配置控制委员会•Configuration Identification 配置识别•Configuration Item Acceptance Review 配置项验收评审•Configuration Item Verification 配置项验证•Configuration Item Verification Procedures 配置项验证程序•Configuration Management 配置管理•Configuration Management Board 配置管理委员会•Configuration Relationships 配置关系•Configuration Status Accounting 配置状态统计•Conflict 冲突•Conflict Management 冲突管理•Conflict Resolution 冲突解决方案•Conformance to Requirements 与需求的一致性•Confrontation 积极面对•Consensus 一致同意•Consensus Decision Process 集体决策过程•Consent 同意•Consequences 后果•Consideration 对价•Considerations 对价需要考虑的事项•Consolidate 合并•Consortium 联盟•Constituents 涉众•Constraint 约束条件•Constraint, project constraint 约束条件对项目的约束•Constraints 约束条件•Constructability 施工能力•Construction 施工构造建造建筑•Construction Contractor 施工承包商•Construction Cost 施工成本•Construction Management ("CM") 施工管理•Construction Manager 施工经理•Construction Stage 施工阶段•Construction Work 施工工作•Construction-Oriented 以施工为导向的•Constructive Challenge 建设性质询•Constructive Change 建设性变更•Consultant 咨询顾问•Consulting 咨询•Consumable Resource 可消耗资源•Consumables 消费性物资•Contemplated Change Notice 预期变更通知•Contending, in negotiating 争论在谈判中•Content 内容•Content Type 内容类型•Context 背景•Contingencies 不可预见费应急费用•Contingency 不可预见费应急费用•Contingency Allowance 应急补助•Contingency Budget Procedure 不可预见费用预算程序•Contingency Plan 意外事件计划•Contract Package 合同包•Contract Performance Control 合同履行控制•Contract Plan 合同计划•Contract Pre-award Meetings 合同预授予会议•Contract Quality Requirements 合同质量要求•Contract Requirements 合同要求•Contract Risk 合同风险•Contract Risk Analysis 合同风险分析•Contract Signing 合同签署•Contract Strategy 合同战略•Contract Target Cost (CTC) 合同目标成本•Contract Target Price (CTP) 合同目标价格•Contract Type 合同分类•Contract Types 合同类型•Contract Work Breakdown Structure (CWBS) 合同工作分解结构•Contract/Procurement Management 合同/采购管理•Contracting 签订合同•Contractor 承包商•Contractor Claims Release 承包商索赔豁免•Contractor Cost Data Report (CCDR) 承包商成本数据报告•Contractor Evaluation 承包商评估•Contractor Furnished Equipment 承包商供应的设备•Contractor Project Office 承包商项目办公室•Contractor Short Listing 承包商短列表•Contractor's Performance Evaluation 承包商的绩效评价•Contractual 合同的•Contractual Conditions 合同条款•Contractual/Legal Requirements 合同的/法律上的要求•Contributed value 贡献价值•Contribution Analysis 贡献分析•Control 控制•Control Account (CA) 控制帐目•Control Account Manager (CAM) 控制帐目经理•Control Account Plan (CAP) 控制帐目计划•Control and Coordination 控制和协调•Control Chart 控制表•Control Cycle 控制周期•Control Gate 控制关口控制关卡•Control Loop 控制回路•Control Point 控制点•Control Requirements 控制必要条件要求•Control System 控制系统•Control Theory 控制论•Controllable Risks 可控风险•Controlling 控制o参看Project Control•Controlling Relationship 控制关系•Coordinated Matrix 协调型的矩阵•Coordination 协调•Coordinator 协调员•Corporate 公司•Corporate Administration and Finance 公司行政和财务•Corporate Budget. 公司预算•Corporate Business Life Cycle 公司商务生命周期•Corporate Constraints 公司限制因素•Corporate Data Bank 公司数据库•Corporate Management 公司管理•Corporate Memory 公司记忆库•Corporate Philosophy 公司价值体系, 公司哲学•Corporate Planning 公司计划编制•Corporate Project Management 公司项目管理•Corporate Project Strategy 公司项目战略•Corporate Quality Standards 公司质量标准•Corporate Resources 公司资源•Corporate Responsibility Matrix 公司责任矩阵•Corporate Standards 公司标准•Corporate Supervision 公司监管•Corporation 公司•Correction 纠正•Corrective Action 纠正措施•Correlation 相关性•Cost 成本•Cost Account 成本帐目•Cost Account Breakdown 成本帐目分解•Cost Account Manager (CAM) 成本帐目经理•Cost Account Plan (CAP) 成本帐目计划•Cost Accumulation Methods 成本累加方法•Cost Analysis 成本分析•Cost Applications 成本应用•Cost Avoidance 成本规避•Cost Baseline 成本基线•Cost Benefit 成本效益•Cost Benefit Analysis 成本效益分析•Cost Breakdown Structure 成本分解结构•Cost Budgeting 成本预算•Cost Ceiling 封顶成本成本上限•Cost Ceiling Bracket 成本上限范围•Cost Center 成本中心•Cost Check 成本检查•Cost Classes 成本类别•Cost Code 成本代码•Cost Codes 成本代码•Cost Control 成本控制•Cost Control Point 成本控制点•Cost Control System 成本控制系统•Cost Curve 成本曲线•Cost Distribution 成本分摊•Cost Effective 成本效率成本有效的•Cost Element 成本元素•Cost Engineering 成本工程•Cost Envelope 成本区域•Cost Estimate 成本估算•Cost Estimate Classification System 成本估算分类系统•Cost Estimating 成本估算•Cost Estimating Relationship 成本估算关系•Cost Forecast 成本预测•Cost Forecasting 成本预测•Cost Growth 成本增长•Cost Incurred 已发生成本•Cost Index 成本指数•Cost Indices 成本指数表•Cost Input 成本投入•Cost Management 成本管理•Cost Model 成本模型•Cost of Money 资金成本•Cost of Quality 质量成本•Cost Overrun 成本超支•Cost Performance Baseline 成本绩效基线•Cost Performance Index (CPI) 成本绩效指数•Cost Performance Indicator (CPI) 成本绩效指数•Cost Performance Measurement Baseline 成本绩效度量基线•Cost Performance Ratio (CPR) 成本绩效比率•Cost Performance Report (CPR) 成本绩效报告•Cost Plan 成本计划•Cost Plus 成本补偿•Cost Plus Fixed Fee Contract ("CPFF") 成本加固定费用合同•Cost Plus Incentive Fee Contract ("CPIFC") 成本加奖励费用合同•Cost Plus Percentage of Cost Contract ("CPPC") 成本加成本百分比合同•Cost Reimbursable Contract 成本补偿合同费用可偿还合同•Cost Reimbursement 成本补偿•Cost Reimbursement Type Contracts 成本补偿型合同•Cost Reviews 成本评审•Cost Savings 成本节约•Cost Sharing Contract 成本共享合同•Cost Status 成本状态•Cost to Complete 竣工尚需成本•Cost to Complete Forecast 竣工所需成本预测•Cost Types 成本类型•Cost Variance ("CV") 成本偏差•Cost/Schedule Status Report ("C/SSR") 成本/进度状态报告•Cost-Benefit Analysis 成本效益分析•Costed Work Breakdown Structure 带成本信息的工作分解结构•Cost-Effectiveness 成本效果分析法•Costing 成本核算•Costing Systems 成本核算系统•Cost-Time Resource Sheet (CTR) 成本时间资源表•Counseling 指导•Countermeasures 对策•CPFFCo Cost Plus Fixed Fee Contract•CPIo Cost Performance Indexo Cost Performance Indicator•CPIF 成本加奖励费用合同o Cost Plus Incentive Fee Contract•CPIFCo Cost Plus Incentive Fee Contract•CPMo Critical Path Method•CPNo Critical Path Network•CPPCo Cost Plus Percentage of Cost Contract •CPRo Cost Performance Ratioo Cost Performance Report•CPUo Central Processing Unit•CRo Change Request•Craft 技艺•Crash Costs 赶工成本•Crash Duration 赶工工期•Crashing 赶工•Creativity 创造力•Credit 赊欠信誉•Credited Resource 已授予的资源•Crisis 危机•Criteria 标准指标•Criterion 标准指标•Critical 关键的•Critical Activity 关键活动•Critical Chain 关键链•Critical Defect 关键性缺陷•Critical Defective 有关键缺陷的产品•Critical Design Review 关键设计评审•Critical Event 关键事件•Critical Factors 关键因素•Critical Path 关键路径•Critical Path Analysis 关键路径分析•Critical Path Method (CPM) 关键路径法•Critical Path Network (CPN) 关键路径网络图•Critical Performance Indicator 关键绩效指标•Critical Ratio 临界比关键比率•Critical Sequence 关键工序•Critical Sequence Analysis 关键工序分析•Critical Subcontractor 关键分包商•Critical Success Factors (CSF) 关键的成功因素•Critical Task 关键任务•Critical Work Item 关键工作项•Criticality Index 关键指数•Cross Organizational 交叉型组织跨组织的•Cross References 交叉参照•Cross-Stage Plan 交叉阶段计划•CSCIo Computer Software Configuration Item •CSFo Critical Success Factors•CTCo Contract Target Cost•CTPo Contract Target Price•CTRo Cost-Time Resource Sheet•Culture 文化•Culture, organizational 文化组织文化•Cumulative Cost-to-Date 到目前为止的累计成本•Cumulative S Curve 累计S 曲线•Currency Conversion 货币兑换•Current Budget 当前预算•Current Date Line 当前日期线•Current Finish Date 当前完成日期•Current FY Budget Allocation 当前财政年的预算分配•Current Start Date 当前开始日期•Current Status 当前状态•Current Year 当年•Custom Duty and Tax 海关关税•Customer 客户•Customer Acceptance Criteria 客户验收标准•Customer Furnished Equipment 客户提供的设备•Customer Perspective 客户观点•Customer/Client Personnel 客户方的职员•Cutoff Date 移交日期•Cutover 移交•CV•Cost Variance•CWBSo Contract Work Breakdown Structure •Cybernetics 控制论•Cycle 周期•Cycle Time 周期[编辑]D•Damages 损害赔偿金•Dangle 悬空活动•Data 数据•Data Application 数据应用•Data Collection 数据收集•Data Date ("DD") 数据日期•Data Entry Clerk 数据录入员•Data Item Description ("DID") 工作项描述•Data Processing 数据处理•Data Refinements 数据改进•Data Type 数据类型•Data Structure Organization 数据结构组织•Database 数据库•Database Administrator ("DBA") 数据库管理员•Database Management System ("DBMS") 数据库管理系统•Date of Acceptance 验收日期•Day Work Account 日常工作帐户•DBAo”Database Administrator"•DBMo”Dynamic Baseline Model"•DBMSo”Database Management System"•DCEo”Distributed Computing Environment" •DCFo”Discounted Cash Flow"•DDo”Data Date"•Deactivation Plan 惰性化计划•Deactivation Procedures 惰性化流程•Debriefing 投标反馈听取情况汇报情况•Decentralized 分散的•Decision 决策•Decision document.tion 决策文档•Decision Event 决策事件•Decision Making 制定决策•Decision Making Process 决策过程•Decision Support System 决策支持系统•Decision Theory 决策论•Decision Tree 决策树•Decision Trees 决策树组•Decomposing 分解•Decomposition 分解•Default 违约•Default values 默认值•Defect 缺陷•Defective 缺陷产品•Defects-Per-Hundred-Units 每百个单元有缺陷的数量•Deficiency 缺陷•Deficiency List 缺陷清单•Definition 定义•Definition Phase 定义阶段•Definitive 确定性的•Definitive Estimate 确定性估算•Deflection 风险转移•Degradation 降级•Delay 延期•Delay, compensable 补偿性延期•Delaying Resource 资源延期•Delegating 授权•Delegation 授权•Deliberate Decision Event 预先准备的决策事件•Deliverable 可交付成果,可交付物•Deliverable Breakdown Structure 可交付物分解结构•Deliverable Deadline 可交付物的终止期限•Deliverables 可交付成果可交付物•Deliverables Management 交付物管理•Delivery 交付•Delphi Technique德尔菲法•Demonstrate 演示证明•Demonstrated 已证明的•Demonstrated Past Experience 已证明的过去经验•Demonstration 演示•Demonstration Review 演示评审•Department 部门•Departmental Budget 部门预算•Dependability 可靠性•Dependencies 依赖关系•Dependency 活动之间的依赖关系•Dependency Arrow 关系箭线•Dependency Diagram 网络图前导网络图•Dependency Links 依赖关系•Dependency Management 依赖关系管理•Deployment 部署•Deployment Lessons Learned document.nbsp 部署的经验教训文档•Deployment Plan 部署计划•Deployment Procedures 部署流程•Deployment Readiness Review 部署准备评审•Deployment View 部署视图•Depreciation 折旧•Descriptive 描述性的•Design 设计•Design & Development Phase 设计和开发阶段•Design Alternatives 设计备选方案•Design Appraisal 设计评估•Design Authority 设计权威•Design Baseline 基准设计•Design Bid Build 设计阶段投标的建立•Design Brief 设计大纲•Design Build 设计的建立包括设计和构造•Design Concept 设计概念•Design Contingency 设计应急费用•Design Contract 设计合同•Design Control 设计控制•Design Development 设计开发•Design Management 设计管理•Design Management Plan 设计管理计划•Design Model 设计模型•Design of Experiment试验设计•Design Package 设计包•Design Review 设计评审•Design Subsystem 设计子系统•Design Time 设计时间•Design to Budget 按预算设计•Design to Cost 按成本设计•Design-to Specifications 按规范设计•Desirable Logic 合意逻辑•Detail document.tion 详细的文档•Detail Schedule 详细的进度安排•Detailed Design 详细设计•Detailed Design Stage 详细设计阶段•Detailed Engineering 详细工程•Detailed Planning 详细计划•Detailed Plans 详细的计划•Detailed Resource Plan 详细的资源计划•Detailed Schedule 详细的进度安排•Detailed Technical Plan 详细的技术计划•Determination 决定决心•Determine Least Cost for Maximum Results 确定可以获得最大收获的最小成本•Deterministic 确定性的•Deterministic Network 确定的网络图•Developed Country 发达国家•Developer 开发人员•Developing Country 发展中国家•Development 开发•Development case 开发案例•Development Phase 开发阶段•Development Plan 开发计划•Development process 开发过程•Deviation 偏差•Deviation Permit 允许偏差•Diagram 图•DIDo”Data Item Description" •Differences 偏差差异•Differentials 差值•Differing Site Conditions 不同的现场环境•Direct Cost 直接成本•Direct Cost Contingency 直接成本应急费用•Direct Costs 直接成本•Direct Labor 直接人工•Direct Project Costs 直接项目成本费用•Directing 指挥•Direction 指导•Directive 指示•Director 主管总监•Discipline 学科•Discipline Maintenance 规矩的维护•Discontinuous Activity 非连续的活动•Discontinuous Processing 非连续的过程•Discount Rate贴现率折现率•Discounted Cash Flow ("DCF") 折现现金流•Discounting 折现•Discrete Effort 离散工作•Discrete Milestone 离散里程碑•Discrete Task 离散任务•Discrimination 歧视•Discussion 讨论•Display 显示•Disposal of Materials 材料处置•Dispute 辩论•Disruption 破坏•Disruptive 破坏性的•Dissemination 分发•Distinguishing Constraint 区分性的约束。

ESSENCE OF PMBOK & PMP EXAM PMBOK及PMP考试精要(考试串讲教材)PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系 (2)PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期及过程组 (10)SCOPE范围管理 (18)HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源管理 (21)COMMUNICATIONS沟通管理 (25)TIME时间管理 (29)COST成本管理 (33)RISK风险管理 (38)QUALITY质量管理 (40)PROCUREMENT采购管理 (40)INTEGRATION整体管理 (19)PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES职业道德 (19)POSSIBLE EXAM QUESTIONS考点 (20)PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组Project Scope Management项目范围管理- processes required to ensure that the project includes only the work required to complete the project successfully.此过程必须确保项目只包括能保证项目成功完成的工作Management by Objective (MBO)基于目标的管理–determining company’s objective and how the project fits into them. MBO focuses on the goals of an activity rather than the activity itself(manager is responsible for results rather than performing certain activities)决定公司目标及项目如何满足该目标。

ESSENCE OF PMBOK & PMP EXAMPMBOK及PMP考试精要(考试串讲教材)1PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系 (2)2PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组 (18)3SCOPE范围 (20)4HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源 (22)5COMMUNICATIONS沟通 (26)6TIME时间 (29)7COST (32)8RISK风险 (37)9QUALITY (39)10PROCUREMENT采购 (43)11INTEGRATION综合 (46)12PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES专业职责 (47)13POSSIBLE EXAM QUESTIONS考点 (48)具备的。
任何在工作分解结构中被遗漏的需要被添加进来。
第一层是项目生命周期(不是产品生命周期)。
工作分解结构由项目团队产生,它用于确定所有工作都被覆盖到。
它提供对于项目估算的基础并帮助组织工作。
它组织并定义整个项目范围。
定义项目的范围基线。
The 3 most common types of WBS are system/sub systems, life-cycle phasing and organizational工作分解结构最常见的三种形式是系统/子系统,生命周期方式,组织的分解结构WBS Dictionary 工作分解结构字典– Defines each item in the WBS, including description of the work packages and other planning info such as schedule dates, cost budgets and staff assignments..定义工作分解结构中的所有元素,包括工作包描述和其他计划编制信息如进度计划日期,成本预算和人员安排。

PMP考试最新内容大纲(中英文对照版)
为了让项目管理专业人士(PMP)适应专业发展的变化,PMI将在2016年1月12日对PMP考试的内容进行变化。
这些变化将在中国区2016年3月PMP考试中体现。
2015年12月考试不受影响。
此次变化是基于PMI对项目管理专业人士的角色描述研究(RDS),研究通过对全球范围内的PMP认证持有者进行问卷调查,确认了领域、任务、知识、技能版块的内容更新。
RDS捕捉来自各行业、各工作岗位、各地区的项目管理实践者的视角,作为PMP考试的基础,以确保其正确性和相关性。
2015年5月初,PMI发布了最新PMP考试内容大纲英文版。
PMP考试大纲主要变化:
PMP的五大实践领域保持不变。
然而,各领域内的任务则被修改、添加或删除。
以下是对此次新增内容的概述:
领域1启动项目,增加了三个任务——任务2、任务7、任务8j
领域2项目计划,增加了一个任务——任务13
领域3项目执行,增加了两个任务——任务6、任务7
领域4项目监视与控制,增加了两个任务——任务6、任务7
领域5项目结尾,没有新增任务。

ESSENCE OF PMBOK&PMP EXAMPMBOK及PMP考试精要(考试串讲教材)PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系 (2)PROJECT LIFE CYCLE/PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期及过程组 (10)SCOPE范围管理 (13)HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源管理 (14)COMMUNICATIONS沟通管理 (18)TIME时间管理 (20)COST成本管理 (22)RISK风险管理 (25)QUALITY质量管理 (27)PROCUREMENT采购管理 (27)INTEGRATION整体管理 (19)PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES职业道德 (19)POSSIBLE EXAM QUESTIONS考点 (20)PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系KnowledgeAreas知识体系Primary Inputs输入Tools&Techniques工具及技术Primary Outputs输出INTEGRATION整体制定项目章程Develop Project Charter1.合同(如果适用)Contract(When applicable)2.项目工作说明书Project statement of work3.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程资产Organizational process assets1.项目选择方法Project selectionmethods2.项目管理方法论Projectmanagement methodology3.项目管理信息系统Projectmanagement information system4.专家判断Expert judgment1.项目章程Project charter制定项目初步范围说明书1.项目章程Project charter2.项目工作说明书Project statement of work3.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程资产Organizational process assets1.项目管理方法系Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Projectmanagement information system3.专家判断Expert judgment1.项目初步范围说明书Preliminary project scopestatement制定项目管理计划Develop Projectmanageme nt Plan1.项目初步范围说明书Preliminary projectscope statement2.项目管理各过程Project managementprocesses3.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程生产Organizational process assets1.项目管理方法系Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Projectmanagement information system3.专家判断Expert judgment1.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan指导与管理项目执行Direct and ManageProject Execution1.项目管理计划Progece management plan2.批准的纠正措施Approved corrective actions3.批准的预防措施Approved preventive actions4.批准的变更申请Approved change requests5.批准的缺陷补救Approved defect repair6.确认的缺陷补救Validated defect repair7.行政收尾程序Administrative closureprocedure1.项目管理方法系Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Projectmanagement information system1.可交付成果Deliverables2.请求的变更Requestedchanges3.实施的变更请求Implementdechange requests4.实施的纠正措施Implementdecorrective actions5.实施的预防措施Implementdepreventive actions6.实施的缺陷补救Implementdedefect repair7.工作绩效信息Workperformance information监控项目工作Monitor and Control Project Work 1.项目管理计划Progece management plan2.工作绩效信息Work performance information3.否决的变更请求Rejected change requests1.项目管理方法系Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Projectmanagement information system3.实现价值技术Eamed valuetechnique(EVT)4.专家判断Expert judgment1.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action2.推荐的预防措施Recommended preventiveaction3.预测Forecasts4.推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defect repair5.请求的变更Requestedchanges整体变更控制Integrated Change Control 1.项目管理计划Progece management plan2.请求的变更Requested changes3.工作绩效信息Work performance information4.推荐的纠正措施Recommended correctiveaction5.推荐的预防措施Recommended preventiveaction6.推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defect repair7.可交付成果Deliverables1.项目管理方法系Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Projectmanagement information system3.专家判断Expert judgment1.批准的变更申请Approvedchange requests2.否决的变更请求Rejectedchange requests3.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates)4.项目范围说明书(更新)Projectscope statement(updates)5.批准的纠正措施Approvedcorrective actions6.批准的预防措施Approved preventive actions7.批准的缺陷补救Approved defect repair8.确认的缺陷补救Validated defect repair9.可交付成果Deliverables项目收尾Close Project1.项目管理计划Progece management plan2.合同文件Contract documentation3.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程资产Organizational process assets5.工作绩效信息Work performance information6.可交付成果Deliverables1.项目管理方法系Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Projectmanagement information system3.专家判断Expert judgment1.行政收尾程序Administrativeclosure procedure2.合同收尾程序Contractclosure procedure3.最终产品,服务或成果Finalproduct,service or result4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)SCOPE范围范围规划 1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets3.项目章程Project charter4.项目初步范围说明书Preliminary projectscope statement5.项目管理计划Project management plan 1.专家判断Expert judgment2.样板,表格与标准Templates,forms,standards1.项目范围管理计划Projectscope management plan范围定义 1.组织过程资产Organizational process assets2.项目章程Project charter3.项目初步范围说明书Preliminary projectscope statement4.项目范围管理计划Project scopemanagement plan5.批准的变更申请Approved change requests1.产品分析Product analysis2.其他方案识别Alternativesidentification3.专家判断Expert judgment4.利害关系者分析Stakeholderanalysis1.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement2.请求的变更Requestedchanges3.项目范围管理计划Projectscope management plan制作工作分解结构Create WBS1.组织过程资产Organizational process assets2.项目范围说明书Project scope statement3.项目范围管理计划Project scopemanagement plan4.批准的变更申请Approved change requests1.工作分解结构模板Workbreakdown structure templates2.分解Decomposition1.项目范围说明书(更新)Projectscope statement(updates)_2.工作分解结构Workbreakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表WBSdictionary4.范围基准Scope baseline5.项目范围管理计划(更新)Project scope managementplan(updates)6.请求的变更RequestedchangesScope Verification 范围核实1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement2.工作分解结构词汇表WBS dictionary3.项目范围管理计划Project scopemanagement plan4.可交付成果Deliverables1.检查Inspection 1.验收的可交付成果Accepteddeliverables2.请求的变更Requestedchanges3.推荐的纠正措施Recommended correctiveactions范围控制Scope Control1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement2.工作分解结构Work breakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表WBS dictionary4.项目范围管理计划Project scopemanagement plan5.绩效报告Performance reports6.批准的变更申请Approved change requests7.工作绩效信息Work performance information1.变更控制系统Change controlsystem2.偏差分析Variance analysis3.补充规划Replanning4.配置管理系统Configurationmanagement system1.项目范围说明书(更新)Projectscope statement(updates)2.工作分解结构(更新)Workbreakdown structure(updates)3.工作分解结构词汇表(更新)WBS dictionary(updates)4.范围基准(更新)Scopebaseline(updates)5.请求的变更Requestedchanges6.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action7.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)8.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates) TIME进度活动定义Activity Definition 1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.工作分解结构Work breakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表WBS clictionary6.项目管理计划Progece management plan1.分解Decomposition2.样板Templates3.滚动式规划Rolling waveplanning4.专家判断Expert judgment5.规划组成部分Planningcomponet1.活动清单Activity list2.活动属性Activity attributes3.里程碑清单Milestone list4.请求的变更Requestedchanges活动排序Activity Sequencin g 1.项目范围说明书Project scope statament2.活动清单Activity list3.活动属性Activity attributes4.里程碑清单Milestons list5.批准的变更请求Approved change requesta1.紧前关系绘图法(PDM)Precedence DiagrammingMethod(PDM)2.箭线绘图法(ADM)ArrowDiagramming Method(ADM)3.进度网络样板Schedulenetwork tempiates4.确定依赖关系Dependencydetermination5.利用时间提前量与滞后量Applying leads and lags1.项目进度网络图Projectschedule network diagrams2.活动清单(更新)Activity list(updates)3.活动属性(更新)Activityattributes(updates)4.请求的变更Requesaedchanges活动资源估算Activity Resource Estimating 1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets3.活动清单Activity list4.活动属性Activity attributes5.资源可利用情况Resouce availability6.项目管理计划Project management l1.专家判断Expert judgment2.多方案分析Alternatives analysis3.出版的估算数据Publishedestimating data4.项目管理软件Projectmanagement sortware5.自上而下的估算Bottomestimating1.活动资源要求Activity resourcerequirements2.活动属性(更新)Activityattributes(updates)3.资源分解结构Resourcebreakdown structure4.资源日历(更新)Resourcecalendars5.请求的变更Requestedchanges活动持续时间估算Activity DurationEstimating1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets3.项目范围说明书Project scops statement4.活动清单Activity list5.活动属性Activity attributes6.活动资源要求Activity resource requirements7.资源日历Resource calendars8.项目管理计划Project management plan●风险登记册Risk register●活动费用估算Activity cost estimates1.专家判断Expert judgment2.类比估算Analogous estimating3.参数估算Parametric estimating4.三点估算Three-point estimates5.后备分析Reserve analysis1.活动持续时间估算Activityduration estimates2.活动属性Activityattributes(updates)制定进度表Schedule Developme nt1.组织过程资产Organizational process assets2.项目范围说明书Project scope statement3.活动清单Activity list4.活动属性Activity attributes5.项目进度网络图Project schedule networkdiagrams6.活动资源要求Activity resource requirements7.资源日历Resource calendars8.活动持续时间估算Activity duration estimates9.项目管理计划Project management plan1.进度网络分析Schedulenetwork analysisi2.关键路线法Critical pathmethod3.进度压缩Schsdulecompression4.假设情景分析What-if scenarioanalysis5.资源平衡Resource leveling6.关键链法Critical chainmethod1.项目进度表Project schedule2.进度模型数据Schedulemodel data3.进度基准Schedule baseline4.资源要求Resourcerequirements(updates)5.活动属性(更新)Activityattributes(updates)6.项目日历(更新)Projectcalendar●风险登记册Risk register7.项目管理软件Projectmanagement software8.应用日历Applying calendars9.调整时间提前滞后量Adjustingleads and lags10.进度模型Schedule model 7.请求的变更Requesaed changes8.项目管理计划(更新)Project management plan(updates)●进度管理计划(更新) Schedule managementplan(updates)进度控制Schedule Control 1.进度管理计划schedule management plan2.进度基准Schedule baseline3.绩效报告Performance reports4.批准的变更要求Approved change requests1.进度报告Progress reporting2.进度变更控制系统Schedulechange control system3.绩效衡量Performancemeasurement4.项目管理软件Projectmanagement software5.偏差分析Variance analysisi6.进度比较横道图Schedulecomparison bar chars1.进度模型数据(更新)Schedulemodel data(updates)2.进度基准(更新)Schedulebaseline(updates)3.绩效衡量Performancemeasurements4.请求的变更Requesaedchanges5.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action6.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)7.活动清单(更新)Activitylist(updates)8.活动属性(更新)Activityattributes(updates)9.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates)COST费用费用估算Cost Estimating 1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.工作分解结构Work breakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表WBS dictionary6.项目管理计划Progece management plan●进度管理计划Schedule management plan●人员配备管理计划Staffing managementplan●风险登记册Risk registor1.类比估算Analogous estimating2.确定资源费率Determineresource cost rates3.自上而下估算Bottom-upestimating4.参数估算Parametric estimating5.项目管理软件Projectmanagement software6.供货商投标分析Vendor bidanalysis7.准备金分析Reserve analysis8.质量成本Cost of quality1.活动费用估算Activity costestimates2.活动费用估算支持细节Activity cost estimatesupporting detall3.请求的变更Requestedchanges4.费用管理计划(更新)Costmanagement plan(updates)费用预算Cost Budgeting 1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement2.工作分解结构Work breakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表WBS dictionary4.活动费用估算Activity cost estimates5.活动费用估算支持细节Activity cost estimatesupporting detall6.项目进度Project schedule7.资源日历Resource calendars8.合同Contract9.费用管理计划Cost management plan1.费用汇总Cost aggregation2.储备基金分析Reserve analysis3.参数估算Parametric esrimating4.资金限制平衡Funding limitreconciliation1.费用基准Cost baseline2.项目资金要求Project fundingrequirements3.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates)4.请求的变更Requestedchanges费用控制Cost Control 1.费用基准Cost baseline2.项目资金要求Project funding requirements3.绩效报告Performance reports4.工作绩效信息Work performance information5.批准的变更申请Approved change requests6.项目管理计划Project management plan1.费用变更控制系统Cost changecontrol system2.绩效衡量分析Performancemeasurements analysis3.预测Forecasting4.项目绩效审核Projectperformance reviews5.项目管理软件Projectmanagement software6.偏差管理Variancemanagement1.费用估算(更新)Costestimates(update)2.费用基准(更新)Costbaseline(update)3.绩效衡量Performancemeasurements4.预测完工5.请求的变更Requestedchanges6.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action7.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)8.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates) RISK风险风险管理规划Risk Manageme nt Planning1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.项目管理计划Progece management plan1.规则会议和分析Planningmeeting and analysis1.风险管理计划RiskManagement Plan风险识别Risk Identificatio n1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程生产Organizational process assets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.风险管理计划Risk Management Plan5.项目管理计划Project management plan1.文件审查Documentationreviews2.信息搜索技术Informationgathering techniques3.核对表分析Checklist analysis4.假设分析Assumptions analysis5.图解技术Diagiammingtechniques1.风险登记册Risk registerQualitative Risk Analysisi 风险定性分析1.组织过程生产Organizational process assets2.项目范围说明书Project scope statement3.风险管理计划Risk Management Plan4.风险登记册Risk register1.风险概率与影响评估Riskprobability and impactassessment2.概率和影响矩阵Probablity andimpact matrix3.风险数据质量评估Risk dataquality assessment4.风险分类Risk categorization5.风险紧迫性评估Risk urgencyassessment1.风险登记册(更新)Riskregister(updates)定量风险分析Quantitativ e RiskAnalysis1.组织过程生产Organizational process assets2.项目范围说明书Project scope statement3.风险管理计划Risk Management Plan4.风险登记册Risk register5.项目管理计划Project management plan●项目进度管理计划Project schedulemanagement plan●项目费用管理计划Project cost managementplan1.数据收集和表示技术Datagathering and representationtechniques2.定量风险分析和模型技术Quantitative risk analysis andmodeling techniques1.风险登记册(更新)Riskregister(updates)风险应对规划Risk Response Planning 1.风险管理计划Risk Management Plan2.风险登记册Risk register1.消极风险或威胁的应对策略Strategies for negative risk orthreats2.积极风险或机会的应对策略Strategies for positive risk oropportunities3.威胁或机会的应对策略Strategies for both threats andopprtunities4.应急应对策略Contingentresponse strategy1.风险登记册(更新)Riskregister(updates)2.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates)3.与风险有关的合同协议Risk-related contractual agreements风险监控Risk Monitoring and Control 1.风险管理计划Risk Management Plan2.风险登记册Risk register3.批准的变更申请Approved change requests4.工作绩效信息Work performance information5.绩效报告Performance reports1.风险再评估Risk reassessment2.风险审计Risk audits3.变差和趋势分析Variance andtrend analysis4.技术绩效分析Technicalperformance measurement5.储备金分析Reserve analysis1.风险登记册(更新)Riskregister(updates)2.请求的变更Requestedchanges3.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action4.推荐的预防措施6.状态审查会Status meetings Recommended preventiveaction5.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)6.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates) QUALITY质量质量规划Quality Planning 1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.项目管理计划Progece management plan1.成本效益分析Cost-benefitanalysis2.基准对照Benchmarking3.试验设计Design ofexperiments5.质量成本(COQ)Cost of quality(COQ)6.其他质量规划工具Additionalquality planning tools1.质量管理计划Qualitymanagement plan2.质量测量指标Quality metrics3.质量核对表Qualitychecklists4.过程改进计划Processimprovement plan5.质量基准Quality baseline6.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates)实施质量保证Perform Quality Assurance 1.质量管理计划Quality management plan2.质量测量指标Quality metrics3.过程改进计划Process improvement plan4.工作绩效信息Work performance information5.批准的变更申请Approved change requests6.质量控制衡量Quality control measurnments7.实施的变更请求Implementde changerequests8.实施的纠正措施Implementde correctiveactions9.实施的缺陷补救Implementde defect repair10.实施的预防措施Implementde preventiveactions1.质量规划工具与技术Qualityplanning tools and techniques2.质量审计Quality audits3.过程分析Process analysis4.质量控制工具与技术Qualitycontrol tools and techniques1.请求的变更Requestedchanges2.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action3.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)4.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates)实施质量监控Perform Quality Control 1.质量管理计划Quality management plan2.质量测量指标Quality metrics3.质量核对表Quality checklists4.组织过程资产Organizational process assets5.工作绩效信息Work performance information6.批准的变更请求Approved change requests7.可交付成果Deliverables1.因果图Cause and effectdiagram2.控制图Control charts3.流程图Flowcharting4.直方图Histogram5.帕雷托图Pareto chart6.趋势图Run chart7.散点图Scatter diagram8,统计抽样Statistical sampling9.检查Inspection10.缺陷补救审查Defect repairreview1.质量控制衡量Quality controlmeasurnments2.确认的缺陷补救Validateddefect repair3.质量基准(更新)Qualitybaseline(updates)4.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action5.推荐的预防措施Recommended preventiveaction6.请求的变更Requestedchanges7.推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defect repair8.组织过程资产Organizationalprocess assets9.确认的可交付成果Validateddeliverables10.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates)HUMAN RESOURCE 人力资源人力资源规划1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets1.组织机构图和岗位描述Organization charts and positiondescriptions1.角色与职责roles andresponsibilities2.项目组织图Projece3.项目管理计划Progece management plan●活动资源需求Activity resource requirements 2.交际Networking3.组织理论Organization theoryorganization chares3.人员配备管理计划Staffinfmanagement plan项目团队组建Acquire Project Team1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets3.角色与职责roles and responsibilities4.项目组织图Projece organization chares5.人员配备管理计划Staffinf management plan招聘惯例1.预分派Pre-assignment2.谈判Negotiation3.招募Acquisition4.虚拟团队Virtual teams1.项目人员分派到位Projectstaff assignments2.资源可利用情况Resourceavailability3.人员配备管理计划(更新)Staffinf managementplan(updates)项目团队建设Develop Project Team 1.项目人员分派Project staff assignments2.人员配备管理计划Staffinf management plan3.资源可利用情况Resource availability1.通用管理技能Generalmanagement skills2.培训Training3.团队建设活动Team-buildingactivities4.规则Ground rules5.集中办公Co-location6.奖励与表彰Recognition andrewards1.团队绩效评估Teamperformance assessment项目团队管理Manage Project Team 1.组织过程资产Organizational process assets2.项目人员分派Project staff assignments3.角色与职责roles and responsibilities4.项目组织图Projece organization chares5.人员配备管理计划Staffinf management plan6.团队绩效考核Team performanceassessment7.工作绩效信息Work performance information8.绩效报告Performance reports1.观察与交谈Observation andconversation2.项目绩效评估Projectperformance appraisals3.冲突管理Conflict management4.问题登记薄Lssue log1.请求的变更Requestedchanges2.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action3.推荐的预防措施Recommended preventiveaction4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates)COMMUNIC ATIONS沟通Communicati ons Planning 沟通规划1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmental factors2.组织过程生产Organizational process assets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.项目管理计划Progece management plan●制约因素Constraints●假设Assumptions1.沟通需求分析Communicationsrequirements analysls2.沟通技术Communicationstechnology1.沟通管理计划Communications managementplanInformation Distribution 信息发布1.沟通管理计划Communications managementplan1.沟通技能Communications skills2.信息收集和检索系统Informationgathering and retrieval system3.信息发布系统Informationdistribution methods4.经验教训总结过程Lessonslearned process1.组织过程生产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)2.请求的变更RequestedchangesPerformance Reporting绩效报告1.工作绩效信息Work performance information2.绩效衡量Performance measurements3.完工预测Forecasted completion4.质量控制衡量Quality control measurnments5.项目管理计划Project management plan●绩效衡量分析Performance measurementsbaseline6.批准的变更申请Approved change requests7.可交付成果Deliverables1.信息演示工具Informationpresentation tools2.绩效信息收集和汇总Performance informationgathering and compilation3.状态审查会Status reviewmeetings4.工时汇报系统Time reportingsystems5.费用汇报系统Cost reportingsystems1.绩效报告Performance reports2.预测Forecasts3.请求的变更Requestedchanges4.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action5.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)利害关系者管理Manage Stakeholders 1.沟通管理计划Communications managementplan2.组织过程资产Organizational process assets1.沟通方法Communicationsmethods2.问题登记薄lssue logs1.问题得以解决Resolved issues2.批准的变更申请Approvedchange requests3.批准的纠正措施Approvedcorrective action4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新)Projectmanagement plan(updates)PROCUREM ENT采购采购规划Plan Purchases and Acquisition s1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程生产Organizational process assets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.工作分解结构Work breakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表WBS clictionary6.项目管理计划Progece management plan●风险登记册Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议Risk-relatedcontractual agreements●资源要求Resource requirements●项目进度计划Project schedule●活动费用估算Activity cost estimate●费用基准Cost baseline1.自制或外购分析Make-or-buyanalysls2.专家判断Expert judgment3.合同类型Contract types1.采购管理计划Procurementmanagement plan2.合同工作说明书Contractstatement of work3.自制或外购决策Maker-or-buychanges4.请求的变更Requestedchanges发包规划Plan Contractin g 1.采购管理计划Procurement management plan2.合同工作说明书Contract statement of work3.自制或外购决策Maker-or-buy changes4.项目管理计划Project management plan●风险登记册Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议Risk-relatedcontractual agreements●资源要求Resource requirements●项目进度计划Project schedule●活动费用估算Activity cost estimate●费用基准Cost baseline1.标准表格Standard forms2.专家判断Expert Judgment1.采购文件Procurementdocuments2.评估标准Evaluation criteria3.合同工作说明书(更新)Contract statement ofwork(updates)询价Request Seller Responses 1.组织过程资产Organizational process assets2.采购管理计划Procurement management plan3.采购文件Procurement documents1.招标人会议Bldder conferences2.刊登广告Advertising3.制定合格卖方清单Developqualifid sellers list1.合格卖方清单Qualified sellerslist2.采购文件包Procurementdocument package3.建议书Proposals卖方选择Select Sellers 1.组织过程资产Organizational process assets2.采购管理计划Procurement management plan3.评估标准Evaluation criteria4.采购文件包Procurement document package5.建议书Proposals6.合格卖方清单Qualified sellers list7.项目管理计划Project management plan●风险登记册Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议Risk-relatedcontractual agreements1.加权系统Weighting system2.独立估算Independentestimates3.筛选系统Screening system4.合同谈判negotiation5.卖方评级系统Seller ratingsystens6.专家判断Expert judgment7.建议书评估技术Proposalevaluation techniques1.选中的卖方Selected sellers2.合同Contract3.合同管理计划Contractmanagement plan4.资源可利用情况Resourceavailability5.采购管理计划(更新)Procurement managementplan(updates)6.请求的变更Requestedchanges合同管理Contract Administrat ion 1.合同Contract2.合同管理计划Contract management plan3.选中的卖方Selected sellers4.绩效报告Performance reports5.批准的变更申请Approved change requests6.工作绩效信息Work performance information1.合同变更控制系统Contractchange control system2.买方进行的绩效审核Buyer-conducted per-formance review3.检验和审计Inspections andaudits1.合同文件Contractdocumentation2.请求的变更Requestedchanges3.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action4.绩效报告Performance reporting5.支付系统Payment system6.索赔管理Claims administration7.合同档案管理系统Records management system8.信息技术Information technology4.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational processassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新)Project management plan(updates)●采购管理计划Procurement management plan●合同管理计划Contract management plan合同收尾Contract Closure 1.采购管理计划Procurement management plan2.合同管理计划Contract management plan3.合同文件Contract documentation4.合同收尾程序Contract closure procedure1.采购审计Procurement audits2.合同档案管理系统Recordsmanagement system1.合同收尾Contract closures2.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)PROJECT LIFE CYCLE/PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组INITIATION启动(Concept)PLANNING计划(Development)EXECUTION执行(Implementation)CONTROL控制CLOSE-OUT结束(Termination)(Finishing)Select project选择项目Create Scope Statement&scopemanagement plan创建范围说明和范围管理计划Execute theproject plan执行项目计划Integratedchange control综合变更控制Procurement audits采购审计Determine project objectives确定项目目标Determine project team组织计划编制Manage projectprogress管理项目进程Projectperformancereporting项目绩效报告Product verification产品确认Determine high level deliverables,time&cost estimates确定主要可交付物、时间及成本估计Create WBS创建工作分解结构Complete workpackages or tasks完成工作包或任务Performancereporting绩效报告Formal acceptance正式接收Determine high level constraints& assumptions高级别的限制和约束Finalize the team&createresource management plan人员获取及创建资源管理计划Distributeinformation信息发布Scope changecontrol范围变更控制Lessons learned经验教训Determine business need 确定业务需求Create WBS dictionary创建工作分解结构字典Quality assurance质量保证Quality control质量控制Update records更新记录Develop product descriptionDefine responsibilities of the project manager确定项目管理者责任Create Network Diagram创建网络图Teamdevelopment团队发展Risk monitoring&control风险监控Archive records文档记录Determine high-level resource requirements 制定高水平资源需求Estimate time&costs估算时间及成本Progressmeetings状态评审Schedule control计划控制Release resources人员遣散Finalize project charter 制订项目章程Determine Critical path确定关键路径Cost control成本控制Develop Schedule&schedulemanagement plan制定进度及进度管理计划Scopeverification范围确认Develop Budget制定预算Manage byexception to theproject plan对项目进行中的突发事件进行管理Create CommunicationsManagement Plan创建沟通管理计划Ensurecompliance withplans确保按计划进行Create Quality Management Plan创建质量管理计划Reassess plans补充计划Risk management planning,identification,qualification,quantification&response planning风险管理计划,识别、定性、定量分析及应对计划编制Take correctiveaction纠正措施Create procurement managementplan创建采购管理计划Create stakeholder managementplan创建对发起人或干系人的管理计划Create project control plan创建项目控制计划Develop formal project plan制定正式项目计划Gain formal project plan approval 获取对项目计划的正式许可Hold kickoff meeting项目动员大会Overall 整体Influencing theorganization组织机构的影响Leading领导Solvingproblems解决问题Negotiating谈判Communicating沟通Holdingmeetings召开会议Stakeholdermanagement干系人管理SCOPE范围Project Scope Management项目范围管理-processes required to ensure that the project includes only the work required to complete the project successfully.此过程必须确保项目只包括能保证项目成功完成的工作Management by Objective(MBO)基于目标的管理–determining company’s objective and how the project fits into them.MBO focuses on the goals of an activity rather than the activity itself(manager is responsible for results rather than performing certain activities)决定公司目标及项目如何满足该目标。

项目管理PMP关键概念(中英文对照)1. 项目(Project)项目是指为创造独特的产品、服务或结果而进行的临时性工作。
是指为创造独特的产品、服务或结果而进行的临时性工作。
A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.2. 项目经理(Project Manager)项目经理是负责项目实施和项目团队管理的人员。
是负责项目实施和项目团队管理的人员。
A project manager is the person responsible for project implementation and the management of the project team.project manager is the person responsible for project implementation and the management of the project team.3. 里程碑(Milestone)里程碑是对项目进展的重要标志性事件或状况的描述。
是对项目进展的重要标志性事件或状况的描述。
A milestone is a significant event or condition in the project that marks a major project estone is a significant event or condition in the project that marks a major project progress.4. 范围(Scope)范围是指项目工作的所有产品、服务和结果的总体描述和界定。

项目管理PMP实践指南(中英文对照)指南简介本指南旨在提供项目管理专业人员在PMP认证考试与实际项目管理中的实践指导。
以下是一些关键领域和技巧,有助于项目管理工作的顺利进行。
项目定义与规划- 项目目标的明确定义对于项目的成功至关重要。
项目经理应与相关利益方交流,确保他们对项目目标和交付物有清晰的认识。
- 在项目规划阶段,项目经理应制定详细的项目计划,明确任务分工、资源需求和里程碑。
- 确定项目风险并制定应对策略是项目规划的重要环节。
项目经理应与团队成员一起分析潜在风险,并制定相应的风险管理计划。
项目执行与监控- 项目经理要确保项目团队按照项目计划执行任务,并及时进行进度监控。
这包括定期的会议和报告,以及与团队成员的有效沟通。
- 项目经理应关注项目进展和风险情况,并及时采取措施解决问题。
在问题出现时,项目经理应调整项目计划,并与相关利益方沟通。
- 项目经理应确保项目交付物的质量符合预期。
这包括对成果进行评估和验证,以及与相关利益方进行验收。
项目收尾与总结- 项目收尾阶段是项目交付的关键节点。
项目经理应进行项目总结和评估,并与相关利益方一起审查项目的成果和经验教训。
- 项目经理应制定项目收尾报告,并对项目团队成员进行表彰和激励。
- 项目经理还应与相关利益方进行项目闭环交流,以获取反馈和改进建议。
结论本指南提供了项目管理专业人员在PMP认证考试和实际项目管理中的实践指导。
只有通过规范的项目定义与规划、有效的项目执行与监控,以及详细的项目收尾与总结,项目管理工作才能够取得成功。
---IntroductionThis guide aims to provide practical guidance for project management professionals in PMP certification exams and real-world project management. The following are key areas and skills that contribute to successful project management.Project Definition and Planning- During the project planning phase, project managers should develop detailed project plans that outline task allocation, resource requirements, and milestones.- Identifying project risks and developing response strategies is an important aspect of project planning. Project managers should analyze potential risks together with team members and develop risk management plans accordingly.Project Execution and Monitoring- Project managers should ensure the quality of project deliverables meets expectations. This includes evaluating and verifying deliverables and conducting acceptance with relevant stakeholders.Project Closure and Lessons Learned- Project managers should prepare project closure reports and recognize and motivate project team members.ConclusionThis guide provides practical guidance for project management professionals in PMP certification exams and real-world project management. Only through proper project definition and planning, effective project execution and monitoring, and thorough project closure and lessons learned can successful project management be achieved.。

ESSENCE OF PMBOK & PMP EXAMPMBOK及PMP考试精要(考试串讲教材)1PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系.............................................. 错误!未定义书签。
2PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组 ...... 错误!未定义书签。
3SCOPE范围 ....................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
4HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源.............................................................................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。
5COMMUNICATIONS沟通...................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
6TIME时间 ......................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
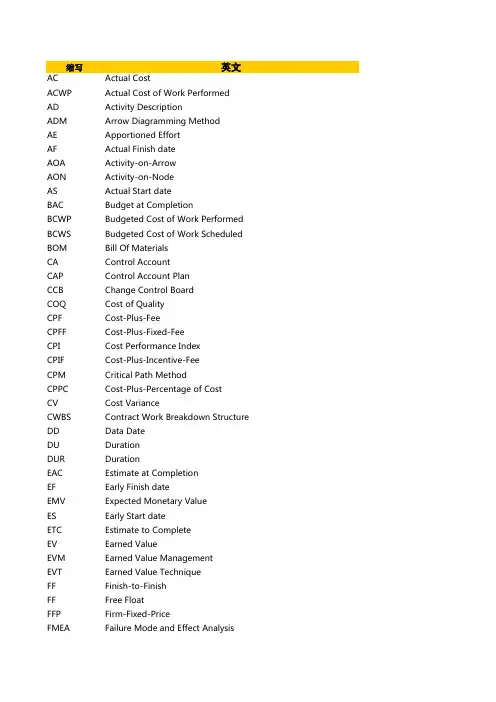
E S S E N C E OF P M B O K&P M P E X A MPMBOK及PMP考试精要(考试串讲教材)1PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系................................................................................ 2PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组 .. (1)3SCOPE范围 (2)4HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源 (2)5COMMUNICATIONS沟通 (2)6TIME时间 (2)7COST (3)8RISK风险 (3)9QUALITY (3)10PROCUREMENT采购 (4)11INTEGRATION综合 (4)12PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES专业职责 (4)13POSSIBLE EXAM QUESTIONS考点 (4)1PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系Knowledge Areas 知识体系Primary Inputs输入Tools & Techniques工具及技术Primary Outputs输出INTEGRATION整体制定项目章程Develop Project Charter1.合同(如果适用)Contract(When applicable)2.项目工作说明书 Projectstatement of work3.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors4.组织过程资产Organizational processassets1.项目选择方法Projectselection methods2.项目管理方法论 Projectmanagement methodology3.项目管理信息系统Project managementinformation system4.专家判断Expertjudgment1.项目章程Projectcharter制定项目初步范围说明书1.项目章程 Project charter2.项目工作说明书 Projectstatement of work3.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors4.组织过程资产Organizational processassets1.项目管理方法系 Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Project managementinformation system3.专家判断Expertjudgment1.项目初步范围说明书Preliminaryproject scopestatement制定项目管理计划Develop Project management Plan1.项目初步范围说明书Preliminary project scopestatement2.项目管理各过程 Projectmanagement processes3.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors4.组织过程生产Organizational processassets1.项目管理方法系 Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Project managementinformation system3.专家判断Expertjudgment1.项目管理计划Progece managementplan指导与管理项目执行Direct and Manage Project Execution1.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan2.批准的纠正措施 Approvedcorrective actions3.批准的预防措施 Approvedpreventive actions4.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests5.批准的缺陷补救 Approveddefect repair6.确认的缺陷补救 Validateddefect repair7.行政收尾程序Administrative closureprocedure1.项目管理方法系 Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Project managementinformation system1.可交付成果Deliverables2.请求的变更Requested changes3.实施的变更请求Implementde changerequests4.实施的纠正措施Implementdecorrective actions5.实施的预防措施Implementdepreventive actions6.实施的缺陷补救Implementde defectrepair7.工作绩效信息Work performanceinformation监控项目工作Monitor and1.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan1.项目管理方法系 Projectmanagement methodology1.推荐的纠正措施RecommendedControl Project Work2. 工作绩效信息Workperformance information3.否决的变更请求 Rejectedchange requests2.项目管理信息系统Project managementinformation system3.实现价值技术Eamedvalue technique(EVT)4.专家判断Expertjudgmentcorrective action2.推荐的预防措施Recommendedpreventive action3.预测 Forecasts4.推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defectrepair5.请求的变更Requested changes整体变更控制Integrated Change Control 1.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan2.请求的变更Requestedchanges3.工作绩效信息Workperformance information4.推荐的纠正措施Recommended correctiveaction5.推荐的预防措施Recommended preventiveaction6.推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defect repair7.可交付成果 Deliverables1.项目管理方法系 Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Project managementinformation system3.专家判断Expertjudgment1.批准的变更申请Approved changerequests2.否决的变更请求Rejected changerequests3.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)4.项目范围说明书(更新) Projectscopestatement(updates)5.批准的纠正措施Approved correctiveactions6.批准的预防措施Approved preventiveactions7.批准的缺陷补救Approved defectrepair8.确认的缺陷补救Validated defectrepair9.可交付成果Deliverables项目收尾Close Project1.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan2.合同文件Contractdocumentation3.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors4.组织过程资产Organizational processassets5.工作绩效信息Workperformance information6.可交付成果 Deliverables1.项目管理方法系 Projectmanagement methodology2.项目管理信息系统Project managementinformation system3.专家判断Expertjudgment1.行政收尾程序Administrativeclosure procedure2.合同收尾程序Contract closureprocedure3.最终产品,服务或成果Finalproduct,service orresult4.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)SCOPE范围范围规划Scope Planning1.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.项目章程 Project charter4.项目初步范围说明书Preliminary project scopestatement5.项目管理计划Projectmanagement plan1.专家判断 Expert judgment2.样板,表格与标准Templates,forms,standards1.项目范围管理计划Project scopemanagement plan范围定义 Scope Definition1.组织过程资产Organizational processassets2.项目章程 Project charter3.项目初步范围说明书Preliminary project scopestatement4.项目范围管理计划 Projectscope management plan5.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests1.产品分析Productanalysis2.其他方案识别Alternativesidentification3.专家判断Expertjudgment4.利害关系者分析Stakeholder analysis1.项目范围说明书Project scopestatement2.请求的变更Requested changes3.项目范围管理计划Project scopemanagement plan制作工作分解结构Create WBS1.组织过程资产Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement3.项目范围管理计划 Projectscope management plan4.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests1.工作分解结构模板Workbreakdown structuretemplates2.分解 Decomposition1.项目范围说明书(更新) Projectscopestatement(updates)_2.工作分解结构Work breakdownstructure3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary4.范围基准Scopebaseline5.项目范围管理计划(更新) Projectscope managementplan(updates)6.请求的变更Requested changesScope Verification范围核实1.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement2.工作分解结构词汇表 WBSdictionary3.项目范围管理计划 Projectscope management plan4.可交付成果 Deliverables1.检查 Inspection 1.验收的可交付成果Accepteddeliverables2.请求的变更Requested changes3. 推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective actions范围控制Scope Control1.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement2.工作分解结构Work1.变更控制系统Changecontrol system2.偏差分析Variance1.项目范围说明书(更新) Projectscopebreakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary4.项目范围管理计划 Project scope management plan5.绩效报告Performance reports6.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests7.工作绩效信息Work performance information analysis3.补充规划 Replanning4.配置管理系统Configuration managementsystemstatement(updates)2.工作分解结构(更新) Work breakdownstructure(updates)3.工作分解结构词汇表(更新) WBSdictionary(updates)4.范围基准(更新)Scopebaseline(updates)5.请求的变更Requested changes6.推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective action7.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)8.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)TIME进度活动定义Activity Definition 1.事业环境因素Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement4.工作分解结构Workbreakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表WBSclictionary6.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan1.分解 Decomposition2.样板 Templates3.滚动式规划 Rolling waveplanning4.专家判断 Expert judgment5.规划组成部分Planningcomponet1.活动清单Activitylist2.活动属性 Activityattributes3.里程碑清单Milestone list4.请求的变更Requested changes活动排序Activity Sequencing 1.项目范围说明书Projectscope statament2.活动清单 Activity list3.活动属性Activityattributes4.里程碑清单Milestonslist5.批准的变更请求 Approvedchange requesta1.紧前关系绘图法(PDM)Precedence DiagrammingMethod(PDM)2.箭线绘图法(ADM) ArrowDiagramming Method(ADM)3.进度网络样板Schedulenetwork tempiates4.确定依赖关系 Dependencydetermination5.利用时间提前量与滞后量Applying leads and lags1.项目进度网络图Project schedulenetwork diagrams2.活动清单(更新)Activity list(updates)3.活动属性(更新)Activityattributes(updates)4.请求的变更Requesaed changes活动资源估算Activity Resource 1.事业环境因素Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程资产1.专家判断 Expert judgment2.多方案分析 Alternativesanalysis1.活动资源要求Activity resourcerequirementsEstimating Organizational processassets3.活动清单Activity list4.活动属性Activityattributes5.资源可利用情况Resouceavailability6.项目管理计划Projectmanagement l 3.出版的估算数据 Publishedestimating data4.项目管理软件Projectmanagement sortware5.自上而下的估算Bottomestimating2.活动属性(更新)Activityattributes(updates)3.资源分解结构Resource breakdownstructure4.资源日历(更新)Resourcecalendars5.请求的变更Requested changes活动持续时间估算Activity Duration Estimating1.事业环境因素Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Projectscops statement4.活动清单 Activity list5.活动属性Activityattributes6.活动资源要求Activityresource requirements7.资源日历Resourcecalendars8.项目管理计划Projectmanagement plan●风险登记册Riskregister●活动费用估算 Activitycost estimates1.专家判断Expertjudgment2.类比估算Analogousestimating3.参数估算Parametricestimating4.三点估算Three-pointestimates5.后备分析Reserveanalysis1.活动持续时间估算Activity durationestimates2.活动属性Activityattributes(updates)制定进度表Schedule Development1.组织过程资产Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement3.活动清单 Activity list4.活动属性Activityattributes5.项目进度网络图 Projectschedule network diagrams6.活动资源要求Activityresource requirements7.资源日历Resourcecalendars8.活动持续时间估算Activity duration estimates9.项目管理计划Projectmanagement plan●风险登记册Riskregister1.进度网络分析 Schedulenetwork analysisi2.关键路线法Criticalpath method3.进度压缩Schsdulecompression4.假设情景分析What-ifscenario analysis5.资源平衡Resourceleveling6.关键链法Criticalchain method7.项目管理软件Projectmanagement software8.应用日历Applyingcalendars9.调整时间提前滞后量Adjusting leads and lags10.进度模型Schedulemodel1.项目进度表Project schedule2.进度模型数据Schedule model data3.进度基准Schedule baseline4.资源要求Resourcerequirements(updates)5.活动属性(更新)Activityattributes(updates)6.项目日历(更新)Project calendar7.请求的变更Requesaed changes8.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)●进度管理计划(更新) Schedule managementplan(updates)进度控制 Schedule Control 1.进度管理计划schedulemanagement plan2.进度基准Schedulebaseline3.绩效报告Performancereports4.批准的变更要求 Approvedchange requests1.进度报告Progressreporting2.进度变更控制系统Schedule change controlsystem3.绩效衡量Performancemeasurement4.项目管理软件Projectmanagement software5.偏差分析Varianceanalysisi6.进度比较横道图 Schedulecomparison bar chars1. 进度模型数据(更新) Schedule modeldata(updates)2. 进度基准(更新)Schedulebaseline(updates)3. 绩效衡量Performancemeasurements4. 请求的变更Requesaed changes5.推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective action6.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)7.活动清单(更新)Activitylist(updates)8.活动属性(更新)Activityattributes(updates)9.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)COST费用费用估算Cost Estimating 1.事业环境因素Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement4. 工作分解结构Workbreakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBSdictionary6.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan●进度管理计划Schedulemanagement plan●人员配备管理计划Staffing management plan●风险登记册Risk1.类比估算Analogousestimating2.确定资源费率 Determineresource cost rates3.自上而下估算 Bottom-upestimating4.参数估算Parametricestimating5.项目管理软件Projectmanagement software6.供货商投标分析Vendorbid analysis7.准备金分析Reserveanalysis8.质量成本Cost ofquality1.活动费用估算Activity costestimates2.活动费用估算支持细节Activitycost estimatesupportingdetall3.请求的变更Requested changes4.费用管理计划(更新) Cost managementplan(updates)registor费用预算Cost Budgeting 1.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement2.工作分解结构Workbreakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBSdictionary4.活动费用估算Activitycost estimates5.活动费用估算支持细节Activity cost estimatesupporting detall6.项目进度Projectschedule7.资源日历Resourcecalendars8.合同 Contract9.费用管理计划Costmanagement plan1.费用汇总Costaggregation2.储备基金分析Reserveanalysis3.参数估算Parametricesrimating4.资金限制平衡Fundinglimit reconciliation1.费用基准Costbaseline2.项目资金要求Project fundingrequirements3.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)4.请求的变更Requested changes费用控制Cost Control 1.费用基准 Cost baseline2.项目资金要求Projectfunding requirements3.绩效报告Performancereports4.工作绩效信息Workperformance information5.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests6.项目管理计划Projectmanagement plan1.费用变更控制系统Costchange control system2.绩效衡量分析Performance measurementsanalysis3.预测 Forecasting4.项目绩效审核Projectperformance reviews5.项目管理软件Projectmanagement software6.偏差管理Variancemanagement1.费用估算(更新)Costestimates(update)2.费用基准(更新)Costbaseline(update)3.绩效衡量Performancemeasurements4.预测完工5.请求的变更Requested changes6.推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective action7.组织过程资产(更新)Organizationalprocessassets(updates)8.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)RISK风险风险管理规划Risk Management Planning1.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Projectscope statement1.规则会议和分析 Planningmeeting and analysis1.风险管理计划Risk ManagementPlan4.项目管理计划Progece management plan风险识别Risk Identification1.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程生产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Projectscope statement4. 风险管理计划RiskManagement Plan5. 项目管理计划Projectmanagement plan1.文件审查 Documentationreviews2.信息搜索技术Information gatheringtechniques3.核对表分析Checklistanalysis4.假设分析Assumptionsanalysis5.图解技术Diagiammingtechniques1.风险登记册RiskregisterQualitative Risk Analysisi 风险定性分析1.组织过程生产Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书 Projectscope statement3. 风险管理计划RiskManagement Plan4. 风险登记册Riskregister1.风险概率与影响评估 Riskprobability and impactassessment2.概率和影响矩阵Probablity and impactmatrix3.风险数据质量评估 Riskdata quality assessment4.风险分类Riskcategorization5.风险紧迫性评估Riskurgency assessment1.风险登记册(更新)Riskregister(updates)定量风险分析Quantitative Risk Analysis1.组织过程生产Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书 Projectscope statement3. 风险管理计划RiskManagement Plan4. 风险登记册Riskregister5. 项目管理计划Projectmanagement plan●项目进度管理计划Project schedulemanagement plan●项目费用管理计划Project cost managementplan1.数据收集和表示技术 Datagathering andrepresentationtechniques2.定量风险分析和模型技术Quantitative riskanalysis and modelingtechniques1.风险登记册(更新)Riskregister(updates)风险应对规划Risk Response Planning 1.风险管理计划RiskManagement Plan2.风险登记册 Risk register1.消极风险或威胁的应对策略Strategies for negativerisk or threats2.积极风险或机会的应对策略Strategies forpositive risk oropportunities3.威胁或机会的应对策略Strategies for boththreats and1.风险登记册(更新)Riskregister(updates)2.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)3.与风险有关的合同协议Risk-relatedcontractualopprtunities4.应急应对策略 Contingentresponse strategyagreements风险监控Risk Monitoring and Control1.风险管理计划RiskManagement Plan2.风险登记册 Risk register3.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests4.工作绩效信息Workperformance information5.绩效报告Performancereports1.风险再评估Riskreassessment2.风险审计 Risk audits3.变差和趋势分析 Varianceand trend analysis4.技术绩效分析 Technicalperformance measurement5.储备金分析Reserveanalysis6.状态审查会Statusmeetings1.风险登记册(更新)Riskregister(updates)2.请求的变更Requested changes3.推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective action4.推荐的预防措施Recommendedpreventive action5.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)6.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)QUALITY质量质量规划Quality Planning 1.事业环境因素Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement4.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan1.成本效益分析Cost-benefit analysis2.基准对照 Benchmarking3.试验设计Design ofexperiments5.质量成本(COQ) Cost ofquality (COQ)6.其他质量规划工具Additional qualityplanning tools1.质量管理计划Quality managementplan2.质量测量指标Quality metrics3.质量核对表Qualitychecklists4.过程改进计划Process improvementplan5.质量基准 Qualitybaseline6.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)实施质量保证Perform Quality Assurance 1.质量管理计划Qualitymanagement plan2.质量测量指标Qualitymetrics3.过程改进计划Processimprovement plan4.工作绩效信息Workperformance information5.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests6.质量控制衡量Quality1.质量规划工具与技术Quality planning tools andtechniques2.质量审计 Quality audits3.过程分析Processanalysis4.质量控制工具与技术Quality control tools andtechniques1.请求的变更Requested changes2.推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective action3.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)4.项目管理计划(更新) Projectcontrol measurnments7.实施的变更请求Implementde change requests 8.实施的纠正措施Implementde corrective actions9.实施的缺陷补救Implementde defect repair 10.实施的预防措施Implementde preventive actions management plan(updates)实施质量监控Perform Quality Control 1.质量管理计划Qualitymanagement plan2.质量测量指标Qualitymetrics3.质量核对表Quality checklists4.组织过程资产Organizational processassets5.工作绩效信息Workperformance information6.批准的变更请求 Approvedchange requests7.可交付成果 Deliverables1.因果图 Cause and effectdiagram2.控制图 Control charts3.流程图 Flowcharting4.直方图 Histogram5.帕雷托图 Pareto chart6.趋势图 Run chart7.散点图 Scatter diagram8,统计抽样Statisticalsampling9.检查 Inspection10.缺陷补救审查Defectrepair review1.质量控制衡量Quality controlmeasurnments2.确认的缺陷补救Validated defectrepair3.质量基准(更新)Qualitybaseline(updates)4.推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective action5.推荐的预防措施Recommendedpreventive action6.请求的变更Requested changes7.推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defectrepair8.组织过程资产Organizationalprocess assets9.确认的可交付成果Validateddeliverables10.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源人力资源规划 1.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan●活动资源需求 Activity 1.组织机构图和岗位描述Organization charts andposition descriptions2.交际 Networking3.组织理论Organizationtheory1.角色与职责 rolesandresponsibilities2.项目组织图Projeceorganization chares3.人员配备管理计划Staffinf managementresource requirements plan项目团队组建Acquire Project Team1.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.角色与职责roles andresponsibilities4.项目组织图Projeceorganization chares5.人员配备管理计划Staffinf management plan招聘惯例1.预分派 Pre-assignment2.谈判 Negotiation3.招募 Acquisition4.虚拟团队Virtual teams1.项目人员分派到位Project staffassignments2.资源可利用情况Resourceavailability3.人员配备管理计划(更新) Staffinfmanagementplan(updates)项目团队建设Develop Project Team 1.项目人员分派Projectstaff assignments2.人员配备管理计划Staffinf management plan3.资源可利用情况 Resourceavailability1.通用管理技能Generalmanagement skills2.培训 Training3.团队建设活动Team-building activities4.规则 Ground rules5.集中办公 Co-location6.奖励与表彰 Recognitionand rewards1.团队绩效评估Team performanceassessment项目团队管理Manage Project Team 1.组织过程资产Organizational processassets2.项目人员分派Projectstaff assignments3.角色与职责roles andresponsibilities4.项目组织图Projeceorganization chares5.人员配备管理计划Staffinf management plan6.团队绩效考核Teamperformance assessment7.工作绩效信息Workperformance information8.绩效报告Performancereports1.观察与交谈 Observationand conversation2.项目绩效评估Projectperformance appraisals3.冲突管理Conflictmanagement4.问题登记薄 Lssue log1.请求的变更Requested changes2.推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective action3.推荐的预防措施Recommendedpreventive action4.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)COMMUNICATIONS沟通Communications Planning沟通规划1.事业环境因素Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程生产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement4.项目管理计划Progecemanagement plan●制约因素 Constraints1.沟通需求分析Communicationsrequirements analysls2.沟通技术 Communicationstechnology1.沟通管理计划Communicationsmanagement plan●假设 AssumptionsInformation Distribution信息发布1. 沟通管理计划Communications managementplan1.沟通技能 Communicationsskills2.信息收集和检索系统Information gathering andretrieval system3.信息发布系统 Informationdistribution methods4.经验教训总结过程 Lessonslearned process1. 组织过程生产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)2. 请求的变更Requested changesPerformance Reporting绩效报告1.工作绩效信息Workperformance information2.绩效衡量Performancemeasurements3.完工预测Forecastedcompletion4.质量控制衡量Qualitycontrol measurnments5.项目管理计划Projectmanagement plan●绩效衡量分析Performance measurementsbaseline6.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests7.可交付成果 Deliverables1.信息演示工具 Informationpresentation tools2.绩效信息收集和汇总Performance informationgathering and compilation3.状态审查会 Status reviewmeetings4.工时汇报系统Timereporting systems5.费用汇报系统Costreporting systems1.绩效报告Performance reports2.预测 Forecasts3.请求的变更Requested changes4.推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective action5.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)利害关系者管理Manage Stakeholders 1.沟通管理计划Communications managementplan2. 组织过程资产Organizational processassets1.沟通方法 Communicationsmethods2.问题登记薄 lssue logs1.问题得以解决Resolved issues2.批准的变更申请Approved changerequests3.批准的纠正措施Approved correctiveaction4.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)PROCUREMENT采购采购规划Plan Purchases and Acquisitions1.事业环境因素 Enterpriseenvironmental factors2.组织过程生产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement4.工作分解结构Work1.自制或外购分析 Make-or-buy analysls2.专家判断Expertjudgment3.合同类型 Contract types1.采购管理计划Procurementmanagement plan2.合同工作说明书Contract statementof work3.自制或外购决策Maker-or-buybreakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS clictionary6.项目管理计划Progece management plan●风险登记册Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议Risk-relatedcontractualagreements●资源要求Resourcerequirements●项目进度计划 Project schedule●活动费用估算 Activity cost estimate●费用基准Cost baseline changes4.请求的变更Requested changes发包规划Plan Contracting1.采购管理计划 Procurementmanagement plan2.合同工作说明书 Contractstatement of work3.自制或外购决策 Maker-or-buy changes4.项目管理计划Projectmanagement plan●风险登记册Riskregister●与风险有关的合同协议Risk-relatedcontractualagreements●资源要求Resourcerequirements●项目进度计划Projectschedule●活动费用估算 Activitycost estimate●费用基准 Cost baseline1.标准表格 Standard forms2.专家判断ExpertJudgment1.采购文件Procurementdocuments2.评估标准Evaluation criteria3.合同工作说明书(更新) Contractstatement ofwork(updates)询价Request Seller Responses1.组织过程资产Organizational processassets2.采购管理计划 Procurementmanagement plan3.采购文件Procurementdocuments1.招标人会议Bldderconferences2.刊登广告 Advertising3.制定合格卖方清单Develop qualifid sellerslist1.合格卖方清单Qualified sellerslist2.采购文件包Procurementdocument package3.建议书 Proposals卖方选择Select Sellers1.组织过程资产Organizational processassets2.采购管理计划 Procurementmanagement plan1.加权系统Weightingsystem2.独立估算Independentestimates3.筛选系统Screening1.选中的卖方Selected sellers2.合同 Contract3.合同管理计划Contract management3.评估标准Evaluation criteria4.采购文件包Procurement document package5.建议书 Proposals6.合格卖方清单Qualified sellers list7.项目管理计划Project management plan●风险登记册Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议Risk-relatedcontractualagreements system4.合同谈判negotiation5.卖方评级系统Sellerrating systens6.专家判断Expertjudgment7.建议书评估技术 Proposalevaluation techniquesplan4.资源可利用情况Resourceavailability5.采购管理计划(更新) Procurementmanagementplan(updates)6.请求的变更Requested changes合同管理Contract Administration 1.合同 Contract2.合同管理计划Contractmanagement plan3.选中的卖方Selectedsellers4.绩效报告Performancereports5.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests6.工作绩效信息Workperformance information1.合同变更控制系统Contract change controlsystem2.买方进行的绩效审核Buyer-conducted per-formance review3.检验和审计 Inspectionsand audits4.绩效报告Performancereporting5.支付系统 Payment system6.索赔管理Claimsadministration7.合同档案管理系统Records management system8.信息技术Informationtechnology1.合同文件Contractdocumentation2.请求的变更Requested changes3.推荐的纠正措施Recommendedcorrective action4.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagementplan(updates)●采购管理计划Procurementmanagement plan●合同管理计划Contract managementplan合同收尾Contract Closure1.采购管理计划 Procurementmanagement plan2.合同管理计划Contractmanagement plan3.合同文件Contractdocumentation4.合同收尾程序Contractclosure procedure1.采购审计Procurementaudits2.合同档案管理系统Records management system1.合同收尾Contractclosures2.组织过程资产(更新) Organizationalprocessassets(updates)2PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组INITIATION启动(Concept)PLANNING计划(Development)EXECUTION 执行(Implementation)CONTROL控制CLOSE-OUT结束(Termination)(Finishing)Select project选择项目Create Scope Statement &scope management plan创建范围说明和范围管理计划Execute theproject plan执行项目计划Integratedchangecontrol综合Procurementaudits采购审计变更控制Determine project objectives确定项目目标Determine project team组织计划编制Manage projectprogress管理项目进程Projectperformancereporting项目绩效报告Productverification产品确认Determine high level deliverables, time & cost estimates确定主要可交付物、时间及成本估计Create WBS创建工作分解结构Complete workpackages ortasks完成工作包或任务Performancereporting绩效报告Formalacceptance正式接收Determine high level constraints & assumptions高级别的限制和约束Finalize the team & createresource management plan人员获取及创建资源管理计划Distributeinformation信息发布Scope changecontrol范围变更控制Lessons learned经验教训Determine business need确定业务需求Create WBS dictionary创建工作分解结构字典Qualityassurance质量保证Qualitycontrol质量控制Update records更新记录Develop product descriptionDefine responsibilities of the project manager 确定项目管理者责任Create Network Diagram创建网络图Teamdevelopment团队发展Riskmonitoring &control风险监控Archive records文档记录Determine high-level resource requirements制定高水平资源需求Estimate time & costs估算时间及成本Progressmeetings状态评审Schedulecontrol计划控制Releaseresources人员遣散Finalize project charter制订项目章程Determine Critical path确定关键路径Cost control成本控制Develop Schedule &schedule management plan制定进度及进度管理计划Scopeverification范围确认Develop Budget制定预算Manage byexception tothe projectplan对项目进行中的突发事件进行管理Create CommunicationsManagement Plan创建沟通管理计划Ensurecompliancewith plans确保按计划进行Create Quality ManagementPlan创建质量管理计划Reassessplans补充计划Risk management planning,identification,qualification,quantification & responseTakecorrectiveaction纠正措施。
ESSENCE OF PMBOK & PMP EXAMPMBOK及PMP考试精要(考试串讲教材)PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系 (2)PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期及过程组 (10)SCOPE范围管理 (12)HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源管理 (14)COMMUNICATIONS沟通管理 (18)TIME时间管理 (21)COST成本管理 (25)RISK风险管理 (29)QUALITY质量管理 (31)PROCUREMENT采购管理 (31)INTEGRATION整体管理 (19)PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES职业道德 (19)POSSIBLE EXAM QUESTIONS考点 (20)PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系Knowledge Areas知识体系Primary Inputs输入Tools & Techniques工具及技术Primary Outputs输出INTEGRATION整体制定项目章程 Develop Project Charter1.合同(如果适用) Contract(Whenapplicable)2.项目工作说明书 Project statement ofwork3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets1.项目选择方法 Project selectionmethods2.项目管理方法论 Project managementmethodology3.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system4.专家判断 Expert judgment1.项目章程 Project charter制定项目初步范围说明书 1.项目章程 Project charter2.项目工作说明书 Project statement ofwork3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.专家判断 Expert judgment1.项目初步范围说明书Preliminary project scopestatement制定项目管理计划Develop Project management Plan1.项目初步范围说明书 Preliminaryproject scope statement2.项目管理各过程 Project managementprocesses3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.专家判断 Expert judgment1.项目管理计划 Progecemanagement plan指导与管理项目执行 Direct and Manage Project Execution1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan2.批准的纠正措施 Approved correctiveactions3.批准的预防措施 Approved preventiveactions4.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests5.批准的缺陷补救 Approved defect repair6.确认的缺陷补救 Validated defectrepair7.行政收尾程序 Administrative closureprocedure1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system1.可交付成果 Deliverables2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3.实施的变更请求 Implementdechange requests4.实施的纠正措施 Implementdecorrective actions5.实施的预防措施 Implementdepreventive actions6.实施的缺陷补救 Implementdedefect repair7.工作绩效信息 Workperformance information监控项目工作 Monitor and Control Project Work1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan2. 工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation3.否决的变更请求 Rejected changerequests1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.实现价值技术 Eamed valuetechnique(EVT)4.专家判断 Expert judgment1.推荐的纠正措施 Recommendedcorrective action2.推荐的预防措施 Recommendedpreventive action3.预测 Forecasts4.推荐的缺陷补救 Recommendeddefect repair5.请求的变更 Requestedchanges整体变更控制 Integrated Change Control 1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan2.请求的变更 Requested changes3.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation4.推荐的纠正措施 Recommended correctiveaction5.推荐的预防措施 Recommended preventiveaction6.推荐的缺陷补救 Recommended defectrepair7.可交付成果 Deliverables1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.专家判断 Expert judgment1.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests2.否决的变更请求 Rejectedchange requests3.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)4.项目范围说明书(更新)Project scopestatement(updates)5.批准的纠正措施 Approvedcorrective actions6.批准的预防措施 Approvedpreventive actions7.批准的缺陷补救 Approveddefect repair8.确认的缺陷补救 Validateddefect repair9.可交付成果 Deliverables项目收尾 Close Project 1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan2.合同文件 Contract documentation3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets5.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation6.可交付成果 Deliverables1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.专家判断 Expert judgment1.行政收尾程序 Administrativeclosure procedure2.合同收尾程序 Contractclosure procedure3.最终产品,服务或成果 Finalproduct,service or result4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)SCOPE范围范围规划 Scope Planning 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目章程 Project charter4.项目初步范围说明书 Preliminaryproject scope statement5.项目管理计划 Project management plan 1.专家判断 Expert judgment2.样板,表格与标准Templates,forms,standards1.项目范围管理计划 Projectscope management plan范围定义 Scope Definition1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.项目章程 Project charter3.项目初步范围说明书 Preliminaryproject scope statement4.项目范围管理计划 Project scopemanagement plan5.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests1.产品分析 Product analysis2.其他方案识别 Alternativesidentification3.专家判断 Expert judgment4.利害关系者分析 Stakeholder analysis1.项目范围说明书Projectscope statement2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3.项目范围管理计划 Projectscope management plan制作工作分解结构 Create WBS1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书 Project scopestatement3.项目范围管理计划 Project scopemanagement plan4.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests1.工作分解结构模板 Work breakdownstructure templates2.分解 Decomposition1.项目范围说明书(更新)Project scopestatement(updates)_2.工作分解结构 Workbreakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBSdictionary4.范围基准 Scope baseline5.项目范围管理计划(更新)Project scope managementplan(updates)6.请求的变更 RequestedchangesScope Verification范围核实1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement2.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary3.项目范围管理计划 Project scopemanagement plan4.可交付成果 Deliverables1.检查 Inspection 1.验收的可交付成果 Accepteddeliverables2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3. 推荐的纠正措施Recommended correctiveactions范围控制 Scope Control 1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement2.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary4.项目范围管理计划 Project scopemanagement plan5.绩效报告 Performance reports6.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests7.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation 1.变更控制系统 Change control system2.偏差分析 Variance analysis3.补充规划 Replanning4.配置管理系统 Configurationmanagement system1.项目范围说明书(更新)Project scopestatement(updates)2.工作分解结构(更新) Workbreakdown structure(updates)3.工作分解结构词汇表(更新)WBS dictionary(updates)4.范围基准(更新) Scopebaseline(updates)5.请求的变更 Requestedchanges6.推荐的纠正措施 Recommendedcorrective action7.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)8.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)TIME进度活动定义 Activity Definition 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement4.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS clictionary6.项目管理计划 Progece management plan1.分解 Decomposition2.样板 Templates3.滚动式规划 Rolling wave planning4.专家判断 Expert judgment5.规划组成部分 Planning componet1.活动清单Activity list2.活动属性 Activityattributes3.里程碑清单 Milestone list4.请求的变更 Requestedchanges活动排序 Activity Sequencing 1.项目范围说明书 Project scopestatament2.活动清单 Activity list3.活动属性 Activity attributes4.里程碑清单 Milestons list5.批准的变更请求 Approved changerequesta1.紧前关系绘图法(PDM) PrecedenceDiagramming Method(PDM)2.箭线绘图法(ADM) Arrow DiagrammingMethod(ADM)3.进度网络样板 Schedule networktempiates4.确定依赖关系 Dependencydetermination5.利用时间提前量与滞后量 Applyingleads and lags1.项目进度网络图 Projectschedule network diagrams2.活动清单(更新) Activitylist (updates)3.活动属性(更新) Activityattributes(updates)4.请求的变更 Requesaedchanges活动资源估算Activity Resource Estimating 1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.活动清单Activity list4.活动属性Activity attributes5.资源可利用情况 Resouce availability6.项目管理计划Project management l1.专家判断 Expert judgment2.多方案分析 Alternatives analysis3.出版的估算数据 Published estimatingdata4.项目管理软件 Project managementsortware5.自上而下的估算 Bottom estimating1.活动资源要求 Activityresource requirements2.活动属性(更新) Activityattributes(updates)3.资源分解结构 Resourcebreakdown structure4.资源日历(更新)Resourcecalendars5.请求的变更 Requestedchanges活动持续时间估算Activity Duration Estimating1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Project scopsstatement4.活动清单 Activity list5.活动属性 Activity attributes6.活动资源要求 Activity resourcerequirements7.资源日历 Resource calendars8.项目管理计划 Project management plan●风险登记册 Risk register●活动费用估算 Activity costestimates1.专家判断 Expert judgment2.类比估算 Analogous estimating3.参数估算 Parametric estimating4.三点估算 Three-point estimates5.后备分析 Reserve analysis1.活动持续时间估算 Activityduration estimates2.活动属性 Activityattributes(updates)制定进度表Schedule Development1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书Project scopestatement3.活动清单 Activity list4.活动属性 Activity attributes5.项目进度网络图 Project schedulenetwork diagrams6.活动资源要求 Activity resourcerequirements7.资源日历 Resource calendars8.活动持续时间估算 Activity durationestimates9.项目管理计划 Project management plan●风险登记册 Risk register1.进度网络分析 Schedule networkanalysisi2.关键路线法 Critical path method3.进度压缩 Schsdule compression4.假设情景分析What-if scenarioanalysis5.资源平衡 Resource leveling6.关键链法 Critical chain method7.项目管理软件 Project managementsoftware8.应用日历 Applying calendars9.调整时间提前滞后量 Adjusting leadsand lags10.进度模型 Schedule model1.项目进度表 Projectschedule2.进度模型数据 Schedulemodel data3.进度基准 Schedule baseline4.资源要求 Resourcerequirements(updates)5.活动属性(更新) Activityattributes(updates)6.项目日历(更新)Projectcalendar7.请求的变更 Requesaedchanges8.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)●进度管理计划(更新)Schedule managementplan(updates)进度控制 Schedule Control 1.进度管理计划 schedule management plan2.进度基准 Schedule baseline3.绩效报告 Performance reports4.批准的变更要求 Approved changerequests 1.进度报告 Progress reporting2.进度变更控制系统 Schedule changecontrol system3.绩效衡量 Performance measurement4.项目管理软件 Project management1. 进度模型数据(更新)Schedule model data(updates)2. 进度基准(更新) Schedulebaseline(updates)3. 绩效衡量 Performancesoftware5.偏差分析 Variance analysisi6.进度比较横道图 Schedule comparison bar chars measurements4. 请求的变更 Requesaed changes5.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action6.组织过程资产(更新) Organizational process assets(updates)7.活动清单(更新) Activitylist(updates)8.活动属性(更新) Activity attributes(updates)9.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates)COST费用费用估算Cost Estimating 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4. 工作分解结构 Work breakdownstructure5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary6.项目管理计划 Progece management plan●进度管理计划 Schedule managementplan●人员配备管理计划Staffing managementplan●风险登记册 Risk registor1.类比估算 Analogous estimating2.确定资源费率 Determine resource costrates3.自上而下估算 Bottom-up estimating4.参数估算 Parametric estimating5.项目管理软件 Project managementsoftware6.供货商投标分析 Vendor bid analysis7.准备金分析 Reserve analysis8.质量成本 Cost of quality1.活动费用估算 Activity costestimates2.活动费用估算支持细节Activity cost estimatesupporting detall3.请求的变更 Requestedchanges4.费用管理计划(更新) Costmanagement plan(updates)费用预算 Cost Budgeting 1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement2.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary4.活动费用估算 Activity cost estimates5.活动费用估算支持细节 Activity costestimate supporting detall6.项目进度 Project schedule7.资源日历 Resource calendars8.合同 Contract9.费用管理计划 Cost management plan 1.费用汇总 Cost aggregation2.储备基金分析 Reserve analysis3.参数估算 Parametric esrimating4.资金限制平衡 Funding limitreconciliation1.费用基准 Cost baseline2.项目资金要求 Projectfunding requirements3.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)4.请求的变更 Requestedchanges费用控制Cost Control 1.费用基准 Cost baseline2.项目资金要求 Project fundingrequirements3.绩效报告 Performance reports4.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation5.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests6.项目管理计划 Project management plan 1.费用变更控制系统 Cost change controlsystem2.绩效衡量分析 Performancemeasurements analysis3.预测 Forecasting4.项目绩效审核 Project performancereviews5.项目管理软件 Project managementsoftware6.偏差管理 Variance management1.费用估算(更新) Costestimates(update)2.费用基准(更新) Costbaseline(update)3.绩效衡量 Performancemeasurements4.预测完工5.请求的变更 Requestedchanges6.推荐的纠正措施 Recommendedcorrective action7.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)8.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)RISK风险风险管理规划 Risk Management Planning1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Project scopestatement4.项目管理计划 Progece management plan1.规则会议和分析 Planning meeting andanalysis1.风险管理计划 RiskManagement Plan风险识别Risk Identification1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors1.文件审查 Documentation reviews2.信息搜索技术 Information gathering1.风险登记册 Risk register2.组织过程生产 Organizational process assets3.项目范围说明书 Project scopestatement4. 风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan5. 项目管理计划 Project management plan techniques3.核对表分析 Checklist analysis4.假设分析 Assumptions analysis5.图解技术 Diagiamming techniquesQualitative Risk Analysisi风险定性分析1.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书 Project scopestatement3. 风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan4. 风险登记册 Risk register1.风险概率与影响评估 Risk probabilityand impact assessment2.概率和影响矩阵 Probablity and impactmatrix3.风险数据质量评估 Risk data qualityassessment4.风险分类 Risk categorization5.风险紧迫性评估 Risk urgencyassessment1.风险登记册(更新) Riskregister(updates)定量风险分析Quantitative Risk Analysis1.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书 Project scopestatement3. 风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan4. 风险登记册 Risk register5. 项目管理计划 Project management plan●项目进度管理计划 Project schedulemanagement plan●项目费用管理计划 Project costmanagement plan1.数据收集和表示技术 Data gathering andrepresentation techniques2.定量风险分析和模型技术 Quantitativerisk analysis and modelingtechniques1.风险登记册(更新) Riskregister(updates)风险应对规划 Risk Response Planning 1.风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan2.风险登记册 Risk register1.消极风险或威胁的应对策略 Strategiesfor negative risk or threats2.积极风险或机会的应对策略 Strategiesfor positive risk or opportunities3.威胁或机会的应对策略 Strategies forboth threats and opprtunities4.应急应对策略 Contingent responsestrategy1.风险登记册(更新) Riskregister(updates)2.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)3.与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-related contractualagreements风险监控 Risk Monitoring and Control1.风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan2.风险登记册 Risk register3.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests4.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation5.绩效报告 Performance reports1.风险再评估 Risk reassessment2.风险审计 Risk audits3.变差和趋势分析 Variance and trendanalysis4.技术绩效分析 Technical performancemeasurement5.储备金分析Reserve analysis6.状态审查会 Status meetings1.风险登记册(更新) Riskregister(updates)2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3.推荐的纠正措施 Recommendedcorrective action4.推荐的预防措施 Recommendedpreventive action5.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)6.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)QUALITY质量质量规划 Quality Planning 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.项目管理计划 Progece management plan1.成本效益分析 Cost-benefit analysis2.基准对照 Benchmarking3.试验设计 Design of experiments5.质量成本(COQ) Cost of quality (COQ)6.其他质量规划工具 Additional qualityplanning tools1.质量管理计划 Qualitymanagement plan2.质量测量指标 Qualitymetrics3.质量核对表Qualitychecklists4.过程改进计划 Processimprovement plan5.质量基准 Quality baseline6.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)实施质量保证Perform Quality Assurance 1.质量管理计划 Quality management plan2.质量测量指标 Quality metrics3.过程改进计划 Process improvement plan4.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation5.批准的变更申请 Approved change1.质量规划工具与技术 Quality planningtools and techniques2.质量审计 Quality audits3.过程分析 Process analysis4.质量控制工具与技术 Quality controltools and techniques1.请求的变更 Requestedchanges2.推荐的纠正措施 Recommendedcorrective action3.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processrequests6.质量控制衡量 Quality control measurnments7.实施的变更请求 Implementde change requests8.实施的纠正措施 Implementde corrective actions9.实施的缺陷补救 Implementde defect repair10.实施的预防措施 Implementde preventive actions assets(updates)4.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates)实施质量监控 Perform Quality Control 1.质量管理计划 Quality management plan2.质量测量指标 Quality metrics3.质量核对表Quality checklists4.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets5.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation6.批准的变更请求 Approved changerequests7.可交付成果 Deliverables1.因果图 Cause and effect diagram2.控制图 Control charts3.流程图 Flowcharting4.直方图 Histogram5.帕雷托图 Pareto chart6.趋势图 Run chart7.散点图 Scatter diagram8,统计抽样 Statistical sampling9.检查 Inspection10.缺陷补救审查 Defect repair review1.质量控制衡量 Qualitycontrol measurnments2.确认的缺陷补救 Validateddefect repair3.质量基准(更新) Qualitybaseline(updates)4.推荐的纠正措施 Recommendedcorrective action5.推荐的预防措施 Recommendedpreventive action6.请求的变更 Requestedchanges7.推荐的缺陷补救 Recommendeddefect repair8.组织过程资产Organizational process assets9.确认的可交付成果 Validateddeliverables10.项目管理计划(更新)Project managementplan(updates)HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源人力资源规划 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目管理计划 Progece management plan●活动资源需求 Activity resourcerequirements 1.组织机构图和岗位描述 Organizationcharts and position descriptions2.交际 Networking3.组织理论 Organization theory1.角色与职责 roles andresponsibilities2.项目组织图 Projeceorganization chares3.人员配备管理计划 Staffinfmanagement plan项目团队组建 Acquire Project Team1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.角色与职责 roles and responsibilities4.项目组织图 Projece organizationchares5.人员配备管理计划 Staffinf managementplan招聘惯例1.预分派 Pre-assignment2.谈判 Negotiation3.招募 Acquisition4.虚拟团队Virtual teams1.项目人员分派到位 Projectstaff assignments2.资源可利用情况 Resourceavailability3.人员配备管理计划(更新)Staffinf managementplan(updates)项目团队建设 Develop Project Team 1.项目人员分派 Project staff assignments2.人员配备管理计划 Staffinf managementplan3.资源可利用情况 Resource availability1.通用管理技能 General managementskills2.培训 Training3.团队建设活动 Team-buildingactivities4.规则 Ground rules5.集中办公 Co-location6.奖励与表彰 Recognition and rewards1.团队绩效评估 Teamperformance assessment项目团队管理 Manage Project Team 1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.项目人员分派 Project staffassignments3.角色与职责 roles and responsibilities4.项目组织图 Projece organizationchares5.人员配备管理计划 Staffinf managementplan1.观察与交谈 Observation andconversation2.项目绩效评估 Project performanceappraisals3.冲突管理 Conflict management4.问题登记薄 Lssue log1.请求的变更 Requestedchanges2.推荐的纠正措施 Recommendedcorrective action3.推荐的预防措施 Recommendedpreventive action4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)6.团队绩效考核 Team performance assessment7.工作绩效信息 Work performance information8.绩效报告 Performance reports5.项目管理计划(更新) Project management plan(updates)COMMUNICATIONS沟通Communications Planning 沟通规划1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.项目管理计划 Progece management plan●制约因素 Constraints●假设 Assumptions1.沟通需求分析 Communicationsrequirements analysls2.沟通技术 Communications technology1.沟通管理计划 Communicationsmanagement planInformation Distribution 信息发布1. 沟通管理计划 Communicationsmanagement plan1.沟通技能 Communications skills2.信息收集和检索系统 Informationgathering and retrieval system3.信息发布系统 Information distributionmethods4.经验教训总结过程 Lessons learnedprocess1. 组织过程生产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)2. 请求的变更 RequestedchangesPerformance Reporting绩效报告1.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation2.绩效衡量 Performance measurements3.完工预测 Forecasted completion4.质量控制衡量 Quality controlmeasurnments5.项目管理计划 Project management plan●绩效衡量分析 Performancemeasurements baseline6.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests7.可交付成果 Deliverables1.信息演示工具 Information presentationtools2.绩效信息收集和汇总 Performanceinformation gathering and compilation3.状态审查会 Status review meetings4.工时汇报系统Time reporting systems5.费用汇报系统Cost reporting systems1.绩效报告 Performancereports2.预测 Forecasts3.请求的变更 Requestedchanges4.推荐的纠正措施 Recommendedcorrective action5.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)利害关系者管理 Manage Stakeholders 1.沟通管理计划 Communications managementplan2. 组织过程资产 Organizational processassets1.沟通方法 Communications methods2.问题登记薄 lssue logs1.问题得以解决Resolvedissues2.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests3.批准的纠正措施 Approvedcorrective action4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)PROCUREMENT采购采购规划 Plan Purchases and Acquisitions1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS clictionary6.项目管理计划 Progece management plan●风险登记册 Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-relatedcontractual agreements●资源要求 Resource requirements●项目进度计划 Project schedule●活动费用估算 Activity costestimate●费用基准 Cost baseline1.自制或外购分析 Make-or-buy analysls2.专家判断 Expert judgment3.合同类型 Contract types1.采购管理计划 Procurementmanagement plan2.合同工作说明书 Contractstatement of work3.自制或外购决策 Maker-or-buychanges4.请求的变更 Requestedchanges发包规划 Plan 1.采购管理计划 Procurement management 1.标准表格 Standard forms 1.采购文件 ProcurementContracting plan2.合同工作说明书 Contract statement ofwork3.自制或外购决策 Maker-or-buy changes4.项目管理计划 Project management plan●风险登记册 Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-relatedcontractual agreements●资源要求 Resource requirements●项目进度计划 Project schedule●活动费用估算 Activity cost estimate●费用基准 Cost baseline 2.专家判断 Expert Judgment documents2.评估标准 Evaluationcriteria3.合同工作说明书(更新)Contract statement ofwork(updates)询价Request Seller Responses1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.采购管理计划 Procurement managementplan3.采购文件 Procurement documents1.招标人会议 Bldder conferences2.刊登广告 Advertising3.制定合格卖方清单 Develop qualifidsellers list1.合格卖方清单 Qualifiedsellers list2.采购文件包 Procurementdocument package3.建议书 Proposals卖方选择Select Sellers 1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.采购管理计划 Procurement managementplan3.评估标准 Evaluation criteria4.采购文件包 Procurement documentpackage5.建议书 Proposals6.合格卖方清单 Qualified sellers list7.项目管理计划 Project management plan●风险登记册 Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-relatedcontractualagreements 1.加权系统 Weighting system2.独立估算 Independent estimates3.筛选系统 Screening system4.合同谈判 negotiation5.卖方评级系统 Seller rating systens6.专家判断 Expert judgment7.建议书评估技术 Proposal evaluationtechniques1.选中的卖方 Selected sellers2.合同 Contract3.合同管理计划 Contractmanagement plan4.资源可利用情况 Resourceavailability5.采购管理计划(更新)Procurement managementplan(updates)6.请求的变更 Requestedchanges合同管理 Contract Administration 1.合同 Contract2.合同管理计划 Contract management plan3.选中的卖方 Selected sellers4.绩效报告 Performance reports5.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests6.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation1.合同变更控制系统 Contract changecontrol system2.买方进行的绩效审核 Buyer-conductedper-formance review3.检验和审计 Inspections and audits4.绩效报告 Performance reporting5.支付系统 Payment system6.索赔管理 Claims administration7.合同档案管理系统 Records managementsystem8.信息技术 Information technology1.合同文件 Contractdocumentation2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3.推荐的纠正措施 Recommendedcorrective action4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)●采购管理计划 Procurementmanagement plan●合同管理计划 Contractmanagement plan合同收尾 Contract Closure1.采购管理计划 Procurement managementplan2.合同管理计划 Contract management plan3.合同文件 Contract documentation4.合同收尾程序 Contract closureprocedure1.采购审计 Procurement audits2.合同档案管理系统 Records managementsystem1.合同收尾Contract closures2.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组INITIATION启动(Concept)PLANNING计划(Development)EXECUTION 执行(Implementation)CONTROL控制CLOSE-OUT结束(Termination)(Finishing)Select project选择项目Create Scope Statement &scope management plan创建范围说明和范围管理计划Execute theproject plan执行项目计划Integratedchangecontrol综合变更控制Procurementaudits采购审计Determine project objectives确定项目目标Determine project team组织计划编制Manage projectprogress管理项目进程Projectperformancereporting项目绩效报告Productverification产品确认Determine highlevel deliverables, time & cost estimates确定主要可交付物、时间及成本估计Create WBS创建工作分解结构Complete workpackages ortasks完成工作包或任务Performancereporting绩效报告Formalacceptance正式接收Determine highlevel constraints & assumptions高级别的限制和约束Finalize the team & createresource management plan人员获取及创建资源管理计划Distributeinformation信息发布Scope changecontrol范围变更控制Lessons learned经验教训Determine business need确定业务需求Create WBS dictionary创建工作分解结构字典Qualityassurance质量保证Qualitycontrol质量控制Update records更新记录Develop product descriptionDefine responsibilities of the project manager 确定项目管理者责任Create Network Diagram创建网络图Teamdevelopment团队发展Riskmonitoring &control风险监控Archive records文档记录Determine high-level resource requirements制定高水平资源需求Estimate time & costs估算时间及成本Progressmeetings状态评审Schedulecontrol计划控制Releaseresources人员遣散Finalize project charter制订项目章程Determine Critical path确定关键路径Cost control成本控制Develop Schedule &schedule management plan制定进度及进度管理计划Scopeverification范围确认Develop Budget制定预算Manage byexception tothe projectplan对项目进行中的突发事件进行管理Create Communications Management Plan创建沟通管理计划Ensure compliance with plans确保按计划进行Create Quality Management Plan创建质量管理计划Reassess plans补充计划Risk management planning, identification, qualification, quantification & response planning风险管理计划,识别、定性、定量分析及应对计划编制Take corrective action纠正措施Create procurement management plan创建采购管理计划Create stakeholder management plan创建对发起人或干系人的管理计划Create project control plan创建项目控制计划Develop formal project plan制定正式项目计划Gain formal project plan approval获取对项目计划的正式许可Hold kickoff meeting项目动员大会Overall 整体Influencingtheorganization组织机构的影响Leading领导Solvingproblems解决问题Negotiating谈判Communicating沟通Holdingmeetings召开会议Stakeholdermanagement干系人管理。
ESSENCE OF PMBOK & PMP EXAMPMBOK及PMP考试精要(考试串讲教材)1PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系 (2)2PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组 (18)3SCOPE范围 (20)4HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源 (22)5COMMUNICATIONS沟通 (26)6TIME时间 (29)7COST (32)8RISK风险 (37)9QUALITY (39)10PROCUREMENT采购 (43)11INTEGRATION综合 (46)12PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES专业职责 (47)13POSSIBLE EXAM QUESTIONS考点 (48)1 PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系2PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组3SCOPE范围Project Scope Management项目范围管理- processes required to ensure that the project includes only the work required to complete the project successfully.此过程必须确保项目只包括能保证项目成功完成的工作Management by Objective (MBO)基于目标的管理–determining company’s objective and how the project fits into them. MBO focuses on the goals of an activity rather than the activity itself (manager is responsible for results rather than performing certain activities)决定公司目标及项目如何满足该目标。
ESSENCE OF PMBOK & PMP EXAMPMBOK及PMP考试精要(考试串讲教材)PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系 (2)PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期及过程组 (10)SCOPE范围管理 (10)HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源管理 (11)COMMUNICATIONS沟通管理 (14)TIME时间管理 (16)COST成本管理 (17)RISK风险管理 (20)QUALITY质量管理 (22)PROCUREMENT采购管理 (22)INTEGRATION整体管理 (19)PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES职业道德 (19)POSSIBLE EXAM QUESTIONS考点 (20)PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系Knowledge Areas知识体系Primary Inputs输入Tools & Techniques工具及技术Primary Outputs输出INTEGRATION整体制定项目章程 Develop Project Charter1.合同(如果适用) Contract(When applicable)2.项目工作说明书 Project statement of work3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets1.项目选择方法 Project selection methods2.项目管理方法论 Project managementmethodology3.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system4.专家判断 Expert judgment1.项目章程 Project charter制定项目初步范围说明书 1.项目章程 Project charter2.项目工作说明书 Project statement of work3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.专家判断 Expert judgment1.项目初步范围说明书Preliminary project scopestatement制定项目管理计划Develop Project management Plan1.项目初步范围说明书 Preliminary projectscope statement2.项目管理各过程 Project managementprocesses3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.专家判断 Expert judgment1.项目管理计划 Progecemanagement plan指导与管理项目执行 Direct and Manage Project Execution1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan2.批准的纠正措施 Approved correctiveactions3.批准的预防措施 Approved preventiveactions4.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests5.批准的缺陷补救 Approved defect repair6.确认的缺陷补救 Validated defect repair7.行政收尾程序 Administrative closureprocedure1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system1.可交付成果 Deliverables2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3.实施的变更请求 Implementdechange requests4.实施的纠正措施 Implementdecorrective actions5.实施的预防措施 Implementdepreventive actions6.实施的缺陷补救 Implementdedefect repair7.工作绩效信息 Workperformance information监控项目工作 Monitor and Control Project Work1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan2. 工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation3.否决的变更请求 Rejected change requests1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.实现价值技术 Eamed valuetechnique(EVT)4.专家判断 Expert judgment1.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action2.推荐的预防措施Recommended preventive action3.预测 Forecasts4.推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defect repair5.请求的变更 Requestedchanges整体变更控制 Integrated Change Control 1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan2.请求的变更 Requested changes3.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation4.推荐的纠正措施 Recommended correctiveaction5.推荐的预防措施 Recommended preventiveaction6.推荐的缺陷补救 Recommended defectrepair7.可交付成果 Deliverables1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.专家判断 Expert judgment1.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests2.否决的变更请求 Rejectedchange requests3.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)4.项目范围说明书(更新) Projectscope statement(updates)5.批准的纠正措施 Approvedcorrective actions6.批准的预防措施 Approvedpreventive actions7.批准的缺陷补救 Approveddefect repair8.确认的缺陷补救 Validateddefect repair9.可交付成果 Deliverables项目收尾 Close Project 1.项目管理计划 Progece management plan2.合同文件 Contract documentation3.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors4.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets5.工作绩效信息 Work performance1.项目管理方法系 Project managementmethodology2.项目管理信息系统 Project managementinformation system3.专家判断 Expert judgment1.行政收尾程序 Administrativeclosure procedure2.合同收尾程序 Contractclosure procedure3.最终产品,服务或成果 Finalproduct,service or result4.组织过程资产(更新)information6.可交付成果 Deliverables Organizational process assets(updates)SCOPE范围范围规划 Scope Planning 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目章程 Project charter4.项目初步范围说明书 Preliminary projectscope statement5.项目管理计划 Project management plan 1.专家判断 Expert judgment2.样板,表格与标准Templates,forms,standards1.项目范围管理计划 Projectscope management plan范围定义 Scope Definition 1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.项目章程 Project charter3.项目初步范围说明书 Preliminary projectscope statement4.项目范围管理计划 Project scopemanagement plan5.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests 1.产品分析 Product analysis2.其他方案识别 Alternatives identification3.专家判断 Expert judgment4.利害关系者分析 Stakeholder analysis1.项目范围说明书Project scopestatement2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3.项目范围管理计划 Projectscope management plan制作工作分解结构 Create WBS1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement3.项目范围管理计划 Project scopemanagement plan4.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests1.工作分解结构模板 Work breakdownstructure templates2.分解 Decomposition1.项目范围说明书(更新) Projectscope statement(updates)_2.工作分解结构 Workbreakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBSdictionary4.范围基准 Scope baseline5.项目范围管理计划(更新)Project scope managementplan(updates)6.请求的变更 RequestedchangesScope Verification范围核实1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement2.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary3.项目范围管理计划 Project scopemanagement plan4.可交付成果 Deliverables1.检查 Inspection 1.验收的可交付成果 Accepteddeliverables2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3. 推荐的纠正措施Recommended correctiveactions范围控制 Scope Control 1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement2.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary4.项目范围管理计划 Project scopemanagement plan5.绩效报告 Performance reports6.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests7.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation 1.变更控制系统 Change control system2.偏差分析 Variance analysis3.补充规划 Replanning4.配置管理系统 Configuration managementsystem1.项目范围说明书(更新) Projectscope statement(updates)2.工作分解结构(更新) Workbreakdown structure(updates)3.工作分解结构词汇表(更新)WBS dictionary(updates)4.范围基准(更新) Scopebaseline(updates)5.请求的变更 Requestedchanges6.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action7.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)8.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)TIME进度活动定义 Activity Definition 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement4.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS clictionary6.项目管理计划 Progece management plan1.分解 Decomposition2.样板 Templates3.滚动式规划 Rolling wave planning4.专家判断 Expert judgment5.规划组成部分 Planning componet1.活动清单Activity list2.活动属性 Activity attributes3.里程碑清单 Milestone list4.请求的变更 Requestedchanges活动排序 Activity Sequencing 1.项目范围说明书 Project scope statament2.活动清单 Activity list3.活动属性 Activity attributes4.里程碑清单 Milestons list1.紧前关系绘图法(PDM) PrecedenceDiagramming Method(PDM)2.箭线绘图法(ADM) Arrow DiagrammingMethod(ADM)1.项目进度网络图 Projectschedule network diagrams2.活动清单(更新) Activity list(updates)5.批准的变更请求 Approved change requesta 3.进度网络样板 Schedule networktempiates4.确定依赖关系 Dependency determination5.利用时间提前量与滞后量 Applying leadsand lags3.活动属性(更新) Activityattributes(updates)4.请求的变更 Requesaedchanges活动资源估算Activity Resource Estimating 1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.活动清单Activity list4.活动属性Activity attributes5.资源可利用情况 Resouce availability6.项目管理计划Project management l1.专家判断 Expert judgment2.多方案分析 Alternatives analysis3.出版的估算数据 Published estimating data4.项目管理软件 Project managementsortware5.自上而下的估算 Bottom estimating1.活动资源要求 Activity resourcerequirements2.活动属性(更新) Activityattributes(updates)3.资源分解结构 Resourcebreakdown structure4.资源日历(更新)Resourcecalendars5.请求的变更 Requestedchanges活动持续时间估算Activity Duration Estimating1.事业环境因素Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Project scops statement4.活动清单 Activity list5.活动属性 Activity attributes6.活动资源要求 Activity resourcerequirements7.资源日历 Resource calendars8.项目管理计划 Project management plan●风险登记册 Risk register●活动费用估算 Activity cost estimates1.专家判断 Expert judgment2.类比估算 Analogous estimating3.参数估算 Parametric estimating4.三点估算 Three-point estimates5.后备分析 Reserve analysis1.活动持续时间估算 Activityduration estimates2.活动属性 Activityattributes(updates)制定进度表Schedule Development1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书Project scope statement3.活动清单 Activity list4.活动属性 Activity attributes5.项目进度网络图 Project schedule networkdiagrams6.活动资源要求 Activity resourcerequirements7.资源日历 Resource calendars8.活动持续时间估算 Activity durationestimates9.项目管理计划 Project management plan●风险登记册 Risk register1.进度网络分析 Schedule networkanalysisi2.关键路线法 Critical path method3.进度压缩 Schsdule compression4.假设情景分析What-if scenario analysis5.资源平衡 Resource leveling6.关键链法 Critical chain method7.项目管理软件 Project managementsoftware8.应用日历 Applying calendars9.调整时间提前滞后量 Adjusting leadsand lags10.进度模型 Schedule model1.项目进度表 Project schedule2.进度模型数据 Schedule modeldata3.进度基准 Schedule baseline4.资源要求 Resourcerequirements(updates)5.活动属性(更新) Activityattributes(updates)6.项目日历(更新)Projectcalendar7.请求的变更 Requesaedchanges8.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)●进度管理计划(更新)Schedule managementplan(updates)进度控制 Schedule Control 1.进度管理计划 schedule management plan2.进度基准 Schedule baseline3.绩效报告 Performance reports4.批准的变更要求 Approved change requests 1.进度报告 Progress reporting2.进度变更控制系统 Schedule changecontrol system3.绩效衡量 Performance measurement4.项目管理软件 Project managementsoftware5.偏差分析 Variance analysisi6.进度比较横道图 Schedule comparisonbar chars1. 进度模型数据(更新) Schedulemodel data(updates)2. 进度基准(更新) Schedulebaseline(updates)3. 绩效衡量 Performancemeasurements4. 请求的变更 Requesaedchanges5.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action6.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)7.活动清单(更新) Activitylist(updates)8.活动属性(更新) Activityattributes(updates)9.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)COST费用费用估算Cost Estimating 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4. 工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure1.类比估算 Analogous estimating2.确定资源费率 Determine resource costrates3.自上而下估算 Bottom-up estimating4.参数估算 Parametric estimating5.项目管理软件 Project management1.活动费用估算 Activity costestimates2.活动费用估算支持细节 Activitycost estimate supportingdetall3.请求的变更 Requested5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary6.项目管理计划 Progece management plan●进度管理计划 Schedule management plan●人员配备管理计划Staffing management plan●风险登记册 Risk registor software6.供货商投标分析 Vendor bid analysis7.准备金分析 Reserve analysis8.质量成本 Cost of qualitychanges4.费用管理计划(更新) Costmanagement plan(updates)费用预算 Cost Budgeting 1.项目范围说明书Project scope statement2.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure3.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS dictionary4.活动费用估算 Activity cost estimates5.活动费用估算支持细节 Activity costestimate supporting detall6.项目进度 Project schedule7.资源日历 Resource calendars8.合同 Contract9.费用管理计划 Cost management plan 1.费用汇总 Cost aggregation2.储备基金分析 Reserve analysis3.参数估算 Parametric esrimating4.资金限制平衡 Funding limit reconciliation1.费用基准 Cost baseline2.项目资金要求 Project fundingrequirements3.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)4.请求的变更 Requestedchanges费用控制Cost Control 1.费用基准 Cost baseline2.项目资金要求 Project funding requirements3.绩效报告 Performance reports4.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation5.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests6.项目管理计划 Project management plan 1.费用变更控制系统 Cost change controlsystem2.绩效衡量分析 Performancemeasurements analysis3.预测 Forecasting4.项目绩效审核 Project performancereviews5.项目管理软件 Project managementsoftware6.偏差管理 Variance management1.费用估算(更新) Costestimates(update)2.费用基准(更新) Costbaseline(update)3.绩效衡量 Performancemeasurements4.预测完工5.请求的变更 Requestedchanges6.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action7.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)8.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)RISK风险风险管理规划 Risk Management Planning1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement4.项目管理计划 Progece management plan1.规则会议和分析 Planning meeting andanalysis1.风险管理计划 RiskManagement Plan风险识别Risk Identification1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement4. 风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan5. 项目管理计划 Project management plan1.文件审查 Documentation reviews2.信息搜索技术 Information gatheringtechniques3.核对表分析 Checklist analysis4.假设分析 Assumptions analysis5.图解技术 Diagiamming techniques1.风险登记册 Risk registerQualitative Risk Analysisi 风险定性分析1.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement3. 风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan4. 风险登记册 Risk register1.风险概率与影响评估 Risk probability andimpact assessment2.概率和影响矩阵 Probablity and impactmatrix3.风险数据质量评估 Risk data qualityassessment4.风险分类 Risk categorization5.风险紧迫性评估 Risk urgencyassessment1.风险登记册(更新) Riskregister(updates)定量风险分析 Quantitative Risk Analysis1.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets2.项目范围说明书 Project scope statement3. 风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan4. 风险登记册 Risk register5. 项目管理计划 Project management plan●项目进度管理计划 Project schedulemanagement plan●项目费用管理计划 Project costmanagement plan1.数据收集和表示技术 Data gathering andrepresentation techniques2.定量风险分析和模型技术 Quantitative riskanalysis and modeling techniques1.风险登记册(更新) Riskregister(updates)风险应对规划 Risk Response Planning 1.风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan2.风险登记册 Risk register1.消极风险或威胁的应对策略 Strategies fornegative risk or threats2.积极风险或机会的应对策略 Strategies for1.风险登记册(更新) Riskregister(updates)2.项目管理计划(更新) Projectpositive risk or opportunities3.威胁或机会的应对策略 Strategies for boththreats and opprtunities4.应急应对策略 Contingent response strategy management plan(updates)3.与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-related contractual agreements风险监控 Risk Monitoring and Control1.风险管理计划 Risk Management Plan2.风险登记册 Risk register3.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests4.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation5.绩效报告 Performance reports1.风险再评估 Risk reassessment2.风险审计 Risk audits3.变差和趋势分析 Variance and trendanalysis4.技术绩效分析 Technical performancemeasurement5.储备金分析Reserve analysis6.状态审查会 Status meetings1.风险登记册(更新) Riskregister(updates)2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action4.推荐的预防措施Recommended preventive action5.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)6.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)QUALITY质量质量规划 Quality Planning 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.项目管理计划 Progece management plan 1.成本效益分析 Cost-benefit analysis2.基准对照 Benchmarking3.试验设计 Design of experiments5.质量成本(COQ) Cost of quality (COQ)6.其他质量规划工具 Additional qualityplanning tools1.质量管理计划 Qualitymanagement plan2.质量测量指标 Quality metrics3.质量核对表Qualitychecklists4.过程改进计划 Processimprovement plan5.质量基准 Quality baseline6.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)实施质量保证Perform Quality Assurance 1.质量管理计划 Quality management plan2.质量测量指标 Quality metrics3.过程改进计划 Process improvement plan4.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation5.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests6.质量控制衡量 Quality controlmeasurnments7.实施的变更请求 Implementde changerequests8.实施的纠正措施 Implementde correctiveactions9.实施的缺陷补救 Implementde defect repair10.实施的预防措施 Implementde preventiveactions1.质量规划工具与技术 Quality planningtools and techniques2.质量审计 Quality audits3.过程分析 Process analysis4.质量控制工具与技术 Quality control toolsand techniques1.请求的变更 Requestedchanges2.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action3.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)4.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)实施质量监控 Perform Quality Control 1.质量管理计划 Quality management plan2.质量测量指标 Quality metrics3.质量核对表Quality checklists4.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets5.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation6.批准的变更请求 Approved change requests7.可交付成果 Deliverables1.因果图 Cause and effect diagram2.控制图 Control charts3.流程图 Flowcharting4.直方图 Histogram5.帕雷托图 Pareto chart6.趋势图 Run chart7.散点图 Scatter diagram8,统计抽样 Statistical sampling9.检查 Inspection10.缺陷补救审查 Defect repair review1.质量控制衡量 Quality controlmeasurnments2.确认的缺陷补救 Validateddefect repair3.质量基准(更新) Qualitybaseline(updates)4.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action5.推荐的预防措施Recommended preventive action6.请求的变更 Requestedchanges7.推荐的缺陷补救Recommended defect repair8.组织过程资产 Organizationalprocess assets9.确认的可交付成果 Validateddeliverables10.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源人力资源规划 1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets 1.组织机构图和岗位描述 Organizationcharts and position descriptions2.交际 Networking3.组织理论 Organization theory1.角色与职责 roles andresponsibilities2.项目组织图 Projeceorganization chares3.项目管理计划 Progece management plan●活动资源需求 Activity resource requirements 3.人员配备管理计划 Staffinf management plan项目团队组建 Acquire Project Team1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets3.角色与职责 roles and responsibilities4.项目组织图 Projece organization chares5.人员配备管理计划 Staffinf managementplan招聘惯例1.预分派 Pre-assignment2.谈判 Negotiation3.招募 Acquisition4.虚拟团队Virtual teams1.项目人员分派到位 Projectstaff assignments2.资源可利用情况 Resourceavailability3.人员配备管理计划(更新)Staffinf managementplan(updates)项目团队建设 Develop Project Team 1.项目人员分派 Project staff assignments2.人员配备管理计划 Staffinf managementplan3.资源可利用情况 Resource availability1.通用管理技能 General management skills2.培训 Training3.团队建设活动 Team-building activities4.规则 Ground rules5.集中办公 Co-location6.奖励与表彰 Recognition and rewards1.团队绩效评估 Teamperformance assessment项目团队管理 Manage Project Team 1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.项目人员分派 Project staff assignments3.角色与职责 roles and responsibilities4.项目组织图 Projece organization chares5.人员配备管理计划 Staffinf managementplan6.团队绩效考核 Team performanceassessment7.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation8.绩效报告 Performance reports1.观察与交谈 Observation and conversation2.项目绩效评估 Project performanceappraisals3.冲突管理 Conflict management4.问题登记薄 Lssue log1.请求的变更 Requestedchanges2.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action3.推荐的预防措施Recommended preventive action4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)COMMUNICATIONS沟通Communications Planning 沟通规划1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.项目管理计划 Progece management plan●制约因素 Constraints●假设 Assumptions1.沟通需求分析 Communicationsrequirements analysls2.沟通技术 Communications technology1.沟通管理计划 Communicationsmanagement planInformation Distribution信息发布1. 沟通管理计划 Communicationsmanagement plan1.沟通技能 Communications skills2.信息收集和检索系统 Information gatheringand retrieval system3.信息发布系统 Information distributionmethods4.经验教训总结过程 Lessons learnedprocess1. 组织过程生产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)2. 请求的变更 RequestedchangesPerformance Reporting绩效报告1.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation2.绩效衡量 Performance measurements3.完工预测 Forecasted completion4.质量控制衡量 Quality controlmeasurnments5.项目管理计划 Project management plan●绩效衡量分析 Performancemeasurements baseline6.批准的变更申请 Approved change requests7.可交付成果 Deliverables1.信息演示工具 Information presentationtools2.绩效信息收集和汇总 Performanceinformation gathering and compilation3.状态审查会 Status review meetings4.工时汇报系统Time reporting systems5.费用汇报系统Cost reporting systems1.绩效报告 Performance reports2.预测 Forecasts3.请求的变更 Requestedchanges4.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action5.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)利害关系者管理 Manage Stakeholders 1.沟通管理计划 Communicationsmanagement plan2. 组织过程资产 Organizational processassets1.沟通方法 Communications methods2.问题登记薄 lssue logs1.问题得以解决Resolved issues2.批准的变更申请 Approvedchange requests3.批准的纠正措施 Approvedcorrective action4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)PROCUREMENT采购采购规划 Plan Purchases and Acquisitions1.事业环境因素 Enterprise environmentalfactors2.组织过程生产 Organizational processassets3.项目范围说明书Project scope statement4.工作分解结构 Work breakdown structure5.工作分解结构词汇表 WBS clictionary6.项目管理计划 Progece management plan●风险登记册 Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-relatedcontractual agreements●资源要求 Resource requirements●项目进度计划 Project schedule●活动费用估算 Activity cost estimate●费用基准 Cost baseline1.自制或外购分析 Make-or-buy analysls2.专家判断 Expert judgment3.合同类型 Contract types1.采购管理计划 Procurementmanagement plan2.合同工作说明书 Contractstatement of work3.自制或外购决策 Maker-or-buychanges4.请求的变更 Requestedchanges发包规划 Plan Contracting 1.采购管理计划 Procurement managementplan2.合同工作说明书 Contract statement ofwork3.自制或外购决策 Maker-or-buy changes4.项目管理计划 Project management plan●风险登记册 Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-relatedcontractual agreements●资源要求 Resource requirements●项目进度计划 Project schedule●活动费用估算 Activity cost estimate●费用基准 Cost baseline 1.标准表格 Standard forms2.专家判断 Expert Judgment1.采购文件 Procurementdocuments2.评估标准 Evaluation criteria3.合同工作说明书(更新)Contract statement ofwork(updates)询价Request Seller Responses1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.采购管理计划 Procurement managementplan3.采购文件 Procurement documents1.招标人会议 Bldder conferences2.刊登广告 Advertising3.制定合格卖方清单 Develop qualifid sellerslist1.合格卖方清单 Qualified sellerslist2.采购文件包 Procurementdocument package3.建议书 Proposals卖方选择Select Sellers 1.组织过程资产 Organizational processassets2.采购管理计划 Procurement managementplan3.评估标准 Evaluation criteria4.采购文件包 Procurement documentpackage5.建议书 Proposals6.合格卖方清单 Qualified sellers list7.项目管理计划 Project management plan●风险登记册 Risk register●与风险有关的合同协议 Risk-relatedcontractualagreements 1.加权系统 Weighting system2.独立估算 Independent estimates3.筛选系统 Screening system4.合同谈判 negotiation5.卖方评级系统 Seller rating systens6.专家判断 Expert judgment7.建议书评估技术 Proposal evaluationtechniques1.选中的卖方 Selected sellers2.合同 Contract3.合同管理计划 Contractmanagement plan4.资源可利用情况 Resourceavailability5.采购管理计划(更新)Procurement managementplan(updates)6.请求的变更 Requestedchanges合同管理 Contract Administration 1.合同 Contract2.合同管理计划 Contract management plan3.选中的卖方 Selected sellers4.绩效报告 Performance reports5.批准的变更申请 Approved changerequests6.工作绩效信息 Work performanceinformation1.合同变更控制系统 Contract changecontrol system2.买方进行的绩效审核 Buyer-conductedper-formance review3.检验和审计 Inspections and audits4.绩效报告 Performance reporting5.支付系统 Payment system6.索赔管理 Claims administration7.合同档案管理系统 Records managementsystem8.信息技术 Information technology1.合同文件 Contractdocumentation2.请求的变更 Requestedchanges3.推荐的纠正措施Recommended corrective action4.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)5.项目管理计划(更新) Projectmanagement plan(updates)●采购管理计划 Procurementmanagement plan●合同管理计划 Contractmanagement plan合同收尾 Contract Closure1.采购管理计划 Procurement managementplan2.合同管理计划 Contract management plan3.合同文件 Contract documentation4.合同收尾程序 Contract closure procedure1.采购审计 Procurement audits2.合同档案管理系统 Records managementsystem1.合同收尾Contract closures2.组织过程资产(更新)Organizational processassets(updates)PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期和项目管理过程组INITIATION启动(Concept)PLANNING计划(Development)EXECUTION 执行(Implementation)CONTROL控制CLOSE-OUT结束(Termination)(Finishing)Select project选择项目Create Scope Statement & scopemanagement plan创建范围说明和范围管理计划Execute the projectplan执行项目计划Integrated changecontrol综合变更控制Procurement audits采购审计Determine project objectives 确定项目目标Determine project team组织计划编制Manage projectprogress管理项目进程Projectperformancereporting项目绩效报告Product verification产品确认Determine high level deliverables, time & cost estimates确定主要可交付物、时间及成本估计Create WBS创建工作分解结构Complete workpackages or tasks完成工作包或任务Performancereporting绩效报告Formal acceptance正式接收Determine high level constraints & assumptions 高级别的限制和约束Finalize the team & create resourcemanagement plan人员获取及创建资源管理计划Distributeinformation信息发布Scope changecontrol范围变更控制Lessons learned经验教训Determine business need 确定业务需求Create WBS dictionary创建工作分解结构字典Quality assurance质量保证Quality control质量控制Update records更新记录Develop product descriptionDefine responsibilities of the project manager确定项目管理者责任Create Network Diagram创建网络图Team development团队发展Risk monitoring &control风险监控Archive records文档记录Determine high-level resource requirements 制定高水平资源需求Estimate time & costs估算时间及成本Progress meetings状态评审Schedule control计划控制Release resources人员遣散Finalize project charter 制订项目章程Determine Critical path确定关键路径Cost control成本控制Develop Schedule & schedulemanagement plan制定进度及进度管理计划Scope verification范围确认Develop Budget制定预算Manage byexception to theproject plan对项目进行中的突发事件进行管理Create Communications ManagementPlan创建沟通管理计划Ensure compliancewith plans确保按计划进行Create Quality Management Plan创建质量管理计划Reassess plans补充计划Risk management planning,identification, qualification,quantification & response planning风险管理计划,识别、定性、定量分析及应对计划编制Take correctiveaction纠正措施Create procurement management plan创建采购管理计划Create stakeholder management plan创建对发起人或干系人的管理计划Create project control plan创建项目控制计划Develop formal project plan制定正式项目计划Gain formal project plan approval获取对项目计划的正式许可Hold kickoff meeting项目动员大会Overall 整体Influencing theorganization组织机构的影响Leading领导Solvingproblems解决问题Negotiating谈判Communicating沟通Holdingmeetings召开会议Stakeholdermanagement干系人管理。
ESSENCE OF PMBOK & PMP EXAMPMBOK及PMP考试精要(考试串讲教材)PROJECT MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREAS项目管理知识体系1PROJECT LIFE CYCLE / PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS GROUPS项目生命周期及过程组10 SCOPEX围管理9HUMAN RESOURCE人力资源管理11MUNICATIONS沟通管理13TIME时间管理15COST成本管理17RISK风险管理20QUALITY质量管理21PROCUREMENT采购管理21INTEGRATION整体管理19PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES职业道德19POSSIBLE EXAM QUESTIONS考点20Project Scope Management项目X围管理- processes required to ensure that the project includes only the work required to plete the project successfully.此过程必须确保项目只包括能保证项目成功完成的工作Management by Objective (MBO)基于目标的管理–determining pany’s objective and how the project fits into them. MBO focuses on the goals of an activity rather than the activity itself (manager is responsible for results rather than performing certain activities)决定公司目标及项目如何满足该目标。
MBO关注于活动的目标而不仅仅是活动本身(管理者对绩效结果而不仅仅是某项活动负责)Project Scope项目X围- the work that must be done in order to deliver a product; pletion is measured against the project plan.为交付产品而必须完成的工作,通过计划来评价。
Product Scope产品X围 - features and functions that are to be included in a product; pletion is measured against the requirements.产品或服务所包含的特征或性能,通过需求来评价。
Design ScopeX围计划编制– contain the detailed project requirements (used for FP contract)包含详细的项目要求(用于固定价合同)Scope DefinitionX围定义– subdividing major project deliverables.细分主要项目可交付成果Deposing分解– subdividing project work packages into smaller, more manageable ponents (activities/action steps). The heuristic (rule of thumb) used in project deposition is 80 hours. 将项目分解为更小的更易管理的工作包(活动或工作步骤)。
首选的项目分解原则(大拇指原则)为80小时Scope Management PlanX围管理计划 - describes how scope will be managed and how changes will be integrated into project; also includes assessment of expected stability of project scope. (e.g. project manager would refer to the Scope Management Plan to make a change)描述项目X 围如何被管理及项目X围变更如何被集成到项目中去,也包括对项目X围预测稳定性的评估。
(例如,项目管理者应依据X围管理计划去进行变更)Stakeholder Management干系人管理– the project manager must identify the stakeholders, determine their needs and expectations, then manage and influence expectations to ensure project success.项目管理者必须识别干系人,确定他们的需求及期望,管理并影响这些期望以确保项目成功。
Configuration Management配置管理- a meansof monitoring and controlling emerging project scope against the scope baseline; its purpose is to control change throughout the project. It is any documented procedures used to apply technical and administrative direction and surveillance to audit the items and system to verify conformance requirements. . It documents the physical characteristics of formal project documents and steps required to control changes to them (e.g. would be used by a customer who wishes to expand the project scope after the performancemeasurement baseline has been established). When more than one individual has sign a Charter, you have to be concerned with peting needs and requirements impacting your efforts on configuration management一种对基于X围基线所形成项目X围的监控方法;它的用途是控制项目的全部变更。
配置管理是任何成文的程序,这些程序对工作项和系统进行技术和行政的指挥与监督,通过审计证实其与要求相一致。
识别一个工作项或系统的物理特性和功能特性并形成文档,控制对这些特性所做的任何变更(例如:应用于那些希望在绩效测量基线被建立之后扩大项目X 围的客户)当多于一个个体签署协议,你必须关注于与配置管理WBS工作分解结构 - subdividing project deliverables into smaller, more manageable ponents. It is a deliverable-oriented grouping of project elements that organizes and defines the total scope of the project. It is a munication tool and it describes what needs to be done and what skills are required.Anything missing in the WBS should be added. The 1st level should be the project life-cycle (not product). The WBS is created by the team (helps to get buy-in) and it is used to make certain that all the work is covered. It provides a basis for estimating the project and helps to organize the work.Its purpose is to include the total project scope of all the work that must be done to plete the project. Defines the project’s scope baseline. 将项目可交付成果分解为更小的更易管理的单元。
以可交付成果为导向对项目元素的分组。
它是一个沟通工具,描述什么必须去做什么技术是必须具备的。
任何在工作分解结构中被遗漏的需要被添加进来。
第一层是项目生命周期(不是产品生命周期)。
工作分解结构由项目团队产生,它用于确定所有工作都被覆盖到。
它提供对于项目估算的基础并帮助组织工作。
它组织并定义整个项目X围。
定义项目的X围基线。
The 3 most mon types of WBS are system/sub systems, life-cycle phasing and organizational工作分解结构最常见的三种形式是系统/子系统,生命周期方式,组织的分解结构WBS Dictionary 工作分解结构字典–Defines each item in the WBS, including description of the work packages and other planning info such as schedule dates, cost budgets and staff assignments..定义工作分解结构中的所有元素,包括工作包描述和其他计划编制信息如进度计划日期,成本预算和人员安排。
Scope StatementX围说明 - a documented description of the objectives, work content, deliverables, and end product; it includes a description of project assumptions and constraints. Provides stakeholders with a mon understanding of the scope of the project and is a source of reference for making future project decisions.目标,工作内容,可交付成果,最终产品的备有证明文件的描述;它包括对项目的约束和假设的描述。