二向应力状态分析
- 格式:doc
- 大小:114.00 KB
- 文档页数:15



第七章 应力状态及应变状态分析第一节 概 述在第一章中将应力定义为内力的集度或单位面积的内力值。
应力又分正应力σ和剪应力τ两种。
前面各章的知识表明,受力杆件中任一点的应力是随截面位置及点的位置的不同而不同,如7-1(a )中a 、b 两点分别在两个截面上,其应力是不同的。
同一截面上的各点,如图7-1(b )中b 、c 两点的应力一般情况下也是不同的。
同一点不同方向的应力也是不同的。
过一点各个方向上的应力情况称为该点的应力状态....,应力状态分析就是要研究杆件中某一点(特别是危险点)各个方向上的应力之间的关系,确定该点处的最大正应力和最大剪应力,为强度计算提供重要依据。
研究应力状态的方法是过杆件中的任一点取出一个微小的六面体——单元..体.。
如图7-1(a )中过a 点取出的单元体放大如图7-2所示。
单元体三个方向的边长很小且趋于零,则该单元体代表一点,即a 点,互相平行的平面上的正应力相等,剪应力也相等。
杆件在任意荷载作用下,从中所取出的单元体表面上一般既有正应为又有剪应力,如图7-2所示。
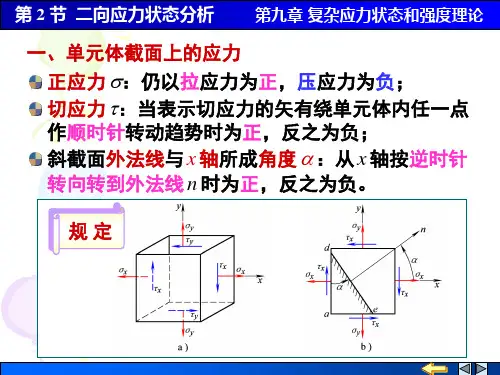
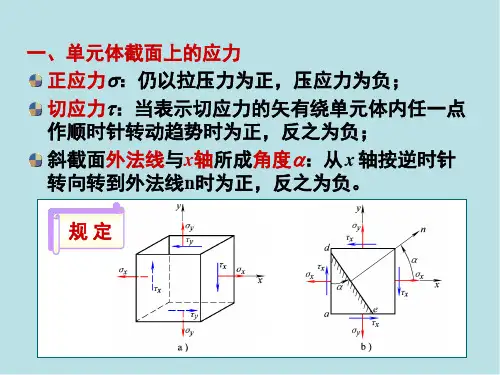
当图7-2所示的单元体各面上的,0,0,0,0,0,0======zy zx yx yz xz xy ττττττ 即六个面上均没有剪应力作用时,这种面叫做特殊平面,并定义为主平面...。
该主(a)(b)图7-1各点的应力情况平面上作用的正应力称为主应力...,用,,,321σσσ表示(,321σσσ≥≥),如图7-3所示。
各面均为主平面的单元体,称为主单元体....。
三个主应力中若有两个等于零一个不等于零,该单元体称为单向应力状态......,如图7-4(a );三个主应力中有一个等于零,两个不等于零,该单元体称为二向应...力状态...,如图7-4(b );三个主应力均不等于零,该单元体称为三向应力状态......,如7-3。
单向应力状态和二向应力状态属平面应力状态,三向应力状态属空间应力状.....态.。




二向等拉应力状态二向等拉应力状态引言在工程设计和实际应用中,结构件的受力状态是非常重要的。
其中,二向等拉应力状态是一种常见的受力状态,其特点是在两个方向上都存在同样大小的拉力。
本文将深入探讨二向等拉应力状态的概念、特点、计算方法以及在实际应用中的注意事项。
概念二向等拉应力状态指的是,在一个平面内,某一结构件或零件同时受到两个方向上同样大小的拉力作用。
这种受力状态也称为“正交拉伸”或“均匀张伸”。
特点1. 拉伸方向相互垂直:在二向等拉应力状态下,两个方向上的拉伸相互垂直,即使其中一个方向上出现了变形或破坏,也不会影响到另一个方向。
2. 可以通过简单计算确定最大应力值:由于该受力状态下两个方向上的应力相同且相互垂直,因此可以通过简单计算确定最大应力值。
3. 适用范围广泛:由于该受力状态具有均匀性和对称性,在实际工程中广泛适用于各种结构件和零件的设计和制造。
计算方法在二向等拉应力状态下,最大应力值可以通过以下公式进行计算:σ = F / A其中,σ为应力值,F为作用于结构件上的拉力大小,A为结构件横截面积大小。
由于该受力状态下两个方向上的应力相同且相互垂直,因此在计算时只需考虑其中一个方向即可。
注意事项1. 结构件需要具有对称性:由于该受力状态具有对称性,因此结构件需要具有对称性才能保证两个方向上的拉伸大小相同。
2. 结构件需要足够强度:在实际应用中,结构件需要具有足够的强度才能承受两个方向上的拉伸力。
3. 避免过度设计:由于该受力状态下可以通过简单计算确定最大应力值,因此在设计时要避免过度设计,否则会造成资源浪费和成本增加。
4. 注意材料特性:不同材料的特性不同,在实际应用中需要根据材料特性进行合理选择和使用。
结论二向等拉应力状态是一种常见的受力状态,在工程设计和实际应用中广泛适用。
其特点是拉伸方向相互垂直、可以通过简单计算确定最大应力值、适用范围广泛等。
在实际应用中需要注意结构件的对称性、足够强度、避免过度设计以及材料特性等问题。

一般二向应力状态下求解主应力方法1.引言二向应力状态是指材料在受力情况下同时受到两个不同方向的应力作用。
在工程实践中,很多材料都会出现二向应力状态,因此如何准确求解在这种情况下的主应力是非常重要的。
本文将介绍一般二向应力状态下求解主应力的方法。
2.二向应力状态的概念在材料受力的情况下,如果同时存在两个不同方向的应力作用,就形成了二向应力状态。
一般来说,二向应力状态可以分为各向同性的和各向异性的两种情况。
各向同性是指材料在各个方向上的性能均相同,而各向异性则是指材料在不同方向上的性能存在差异。
在工程实践中,需要根据具体情况来判断材料的二向应力状态,以便正确求解主应力。
3.一般二向应力状态下求解主应力方法一般二向应力状态下求解主应力的方法可以分为数学方法和实验方法两种。
3.1 数学方法数学方法是通过数学推导和计算来求解主应力的方法。
在一般二向应力状态下,可以采用坐标变换的方法将二向应力状态转化为主应力状态。
具体步骤如下:(1)确定材料受力情况并获取二向应力状态的数值;(2)根据材料的各向同性或各向异性特点,选择合适的坐标系,进行坐标变换;(3)利用坐标变换后的应力矩阵,通过数学运算求解出主应力的数值。
3.2 实验方法实验方法是通过实验手段来求解主应力的方法。
在一般二向应力状态下,可以采用应变片法或光栅法来进行主应力的实验测量。
具体步骤如下:(1)利用应变片或光栅在材料表面进行应力测量;(2)根据实验测量结果,计算出主应力的数值。
4.应用举例为了更好地理解一般二向应力状态下求解主应力的方法,我们可以举一个具体的应用例子。
某种材料同时受到水平和垂直方向的应力作用,需要求解主应力。
可以采用数学方法进行坐标变换,将二向应力状态转化为主应力状态,再通过数学计算求解主应力的数值。
5.总结一般二向应力状态下求解主应力是工程实践中的重要课题。
通过数学方法和实验方法的结合,可以准确求解出材料在二向应力状态下的主应力,为工程设计和材料应用提供重要依据。
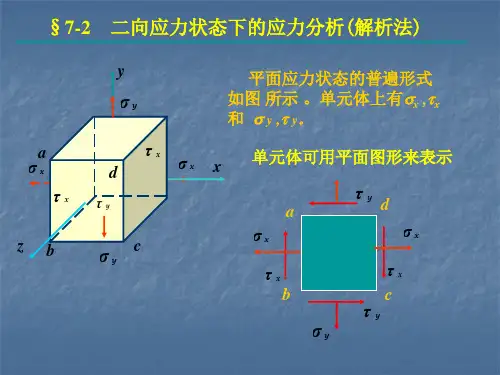
二向应力状态分析的解析法二向应力状态分析的解析法[知识回顾]基本变形下的强度条件:(板书)FNmax1、拉压 ,,,[,]maxA 正应力强度条件Mmax2、弯曲 ,,,[,]maxW*FSsz ,,,[,]maxbIz3、扭转剪应力强度条件T,,,[,]max Wt[教学导入]特点:以上强度条件考虑了危险点上只有正应力或只有剪应力的情况,即单向应力状态;当考虑的点上既有正应力又有剪应力时,就不能用单向应力状态理论来建立强度条件,需要用强度理论来建立强度条件[新课教学]材料力学教案力学教研室于月民二向应力状态分析的解析法一、应力状态的概述(一)一点处的应力状态(ppt)1、不同截面上,各点的应力不同F2F ,,,,12AA2、横截面上正应力分析和切应力分析的结果表明:同一横截面上,不同点的应力各不相同,此即应力的点的概念。
3、F横截面上: ,,,,0AF22,,cos,,,cos,,斜截面上: A,F,,sin2,,sin2,, 2A2同一点在不同方位截面上,它的应力也是各不相同的,此即应力的面的概念。
点的应力状态:(State of the Stresses of a Given Point)通过受力构件内某一点的不同方向面上的应力的集合,称之为这一点的应力状态1材料力学教案力学教研室于月民 (二)点的应力状态的表示(板书)1、单元体:围绕所考查的点,取三方向上尺寸无穷小的正六面体。
特点:1、各面上应力均匀分布2、相互平行的面上应力值相等如:轴向拉伸杆中过A取单元体,1)横、纵取F左右二面是杆横截面的一部分: ,,xA,,0上下和前后面都平行轴线:2)若与横纵成α角截取四个侧面与轴线即不平行也不垂直是斜截面,其上有正应力和剪应力2,,,cos,,x,x ,,sin2,,2由此可见:单元体的应力状态实质上代表一个点的应力状态,研究研究过一点的不同截面上应力变化情况,就是应力分析的内容。
取单元体的方位不同,表示出的形态不同,但二者等价。
二向应力状态分析程序代码function varargout = erxyl(varargin)% ERXYL M-file for erxyl.fig% ERXYL, by itself, creates a new ERXYL or raises the existing% singleton*.%% H = ERXYL returns the handle to a new ERXYL or the handle to% the existing singleton*.%% ERXYL('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local % function named CALLBACK in ERXYL.M with the given input arguments. %% ERXYL('Property','Value',...) creates a new ERXYL or raises the % existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are% applied to the GUI before erxyl_OpeningFcn gets called. An% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application% stop. All inputs are passed to erxyl_OpeningFcn via varargin.%% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one% instance to run (singleton)".%% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES% Edit the above text to modify the response to help erxyl% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 05-Jan-2011 17:46:09% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDITgui_Singleton = 1;gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...'gui_OpeningFcn', @erxyl_OpeningFcn, ...'gui_OutputFcn', @erxyl_OutputFcn, ...'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...'gui_Callback', []);if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});endif nargout[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:}); elsegui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});end% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT% --- Executes just before erxyl is made visible.function erxyl_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.% hObject handle to figure% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% varargin command line arguments to erxyl (see VARARGIN)% Choose default command line output for erxylhandles.output = hObject;% Update handles structureguidata(hObject, handles);% UIWAIT makes erxyl wait for user response (see UIRESUME)% uiwait(handles.figure1);% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line. function varargout = erxyl_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles) % varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT); % hObject handle to figure% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Get default command line output from handles structurevarargout{1} = handles.output;function edit1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)handles.X=str2double(get(hObject,'String'));guidata(hObject,handles);% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit1 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit1 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)handles.T=str2double(get(hObject,'String'));guidata(hObject,handles);% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit2 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit2 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');function edit3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)handles.Y=str2double(get(hObject,'String'));guidata(hObject,handles);% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit3 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit3 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)handles.A=str2double(get(hObject,'String'));guidata(hObject,handles);% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit4 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit4 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.function edit4_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit5 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit5 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit5 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit5_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit5 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit6 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit6 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit6 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit6_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit6 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit7 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit7 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit7 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit7_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit7 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit8_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit8 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit8 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit8 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit8_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit8 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit9_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit9 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit9 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit9 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit9_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit9 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit10_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit10 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit10 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit10 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit10_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit10 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit11_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit11 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit11 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit11 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit11_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit11 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit12_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit12 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit12 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit12 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit12_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit12 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit13_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit13 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit13 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit13 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit13_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit13 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');endfunction edit14_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit14 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit14 as text% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit14 as a double% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties. function edit14_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)% hObject handle to edit14 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.% See ISPC and COMPUTER.if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'),get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');end% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.%显示应力圆,蓝线代表斜截面上应力,绿线代表主切应力,水平黑线代表主应力function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)R=(((handles.X-handles.Y)/2)^2+handles.T^2)^(1/2);x1=-100:100;y1=0*x1;y2=-100:100;x2=0*y2;a=0:1/1000000:2*pi;x=(handles.X+handles.Y)/2+sin(a)*R;y=cos(a)*R;xx=(handles.X+handles.Y)/2+(handles.X-handles.Y)/2*cos(2*handles.A)+h andles.T*sin(2*handles.A);tt=handles.T*cos(2*handles.A)-((handles.X-handles.Y)/2)*sin(2*handles .A);aa=[(handles.X+handles.Y)/2,xx];bb=[0,tt];xmax=(handles.X+handles.Y)/2+(((handles.X-handles.Y)/2)^2+handles.T^2 )^(1/2);xmin=(handles.X+handles.Y)/2-(((handles.X-handles.Y)/2)^2+handles.T^2 )^(1/2);tmax=(xmax-xmin)/2;tmin=-tmax;MM=[(handles.X+handles.Y)/2,(handles.X+handles.Y)/2];NN=[tmax,tmin];plot(x1,y1,'black',x2,y2,'black',x,y,'black',aa,bb,'b-',MM,NN,'g-','L ineWidth',1.5);title('Ó¦ Á¦ Ô²');% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.%显示计算结果function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)x1=(handles.X+handles.Y)/2+(handles.X-handles.Y)/2*cos(2*handles.A)+h andles.T*sin(2*handles.A);t1=handles.T*cos(2*handles.A)-((handles.X-handles.Y)/2)*sin(2*handles .A);xmax=(handles.X+handles.Y)/2+(((handles.X-handles.Y)/2)^2+handles.T^2 )^(1/2);xmin=(handles.X+handles.Y)/2-(((handles.X-handles.Y)/2)^2+handles.T^2 )^(1/2);tmax=(xmax-xmin)/2;tmin=-tmax;Tmax=num2str(tmax);Tmin=num2str(tmin);Xmax=num2str(xmax);Xmin=num2str(xmin);T1=num2str(t1);X1=num2str(x1);set(handles.edit5,'String',X1);set(handles.edit6,'String',T1);set(handles.edit7,'String',Xmax);set(handles.edit8,'String',Xmin);set(handles.edit11,'String',Tmax);set(handles.edit12,'String',Tmin);dA=2*handles.T/(handles.X-handles.Y);A=atan(dA);judge1=(handles.X+handles.Y)/2+(handles.X-handles.Y)/2*cos(A)+handles .T*sin(A);judge2=(handles.X+handles.Y)/2+(handles.X-handles.Y)/2*cos(A+pi)+hand les.T*sin(A+pi);AA1=num2str(A/2);AA2=num2str((pi+A)/2);if judge1>=judge2set(handles.edit9,'String',AA1);set(handles.edit10,'String',AA2);set(handles.edit13,'String',num2str(A/2-pi/4));set(handles.edit14,'String',num2str(A/2+pi/4));elseset(handles.edit9,'String',AA2);set(handles.edit10,'String',AA1);set(handles.edit13,'String',num2str((pi+A)/2-pi/4));set(handles.edit14,'String',num2str((pi+A)/2+pi/4));end% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)运行截图程序说明本程序运行方式:将m代码在matlab中打开,点击运行符号即可(不要用fig文件运行)。