高中化学竞赛辅导无机化学16.2配位化合物的同分异构现象知识点素材
- 格式:doc
- 大小:6.26 MB
- 文档页数:8

高一化学同分异构体知识点同分异构体是指分子式相同、结构不同的有机化合物。
同分异构体存在于有机化合物的世界中,它们具有相同的分子式,但是它们的结构不同,因此,它们的化学性质和物理性质也存在差别。
同分异构体的研究对于深化我们对有机化合物结构与性质的认识,具有重要的科学意义和应用价值。
下面,我将为大家介绍高一化学课程中关于同分异构体的重要知识点。
一、同分异构体的分类1. 构造同分异构体:它们的分子式相同,但是化学式相同的原子按照不同的顺序相连。
2. 空间同分异构体:它们的分子式相同,但是化学式相同的原子在空间中的排列方式不同。
二、构造同分异构体1. 键式同分异构体:它们的原子通过键的连接方式不同而构成,如异构烷烃和环烷烃。
2. 位置同分异构体:它们的化学式中相同的原子或原子团在主链上的位置不同,如卤代烷烃。
3. 功能同分异构体:它们的化学式中相同的原子或原子团发生了功能性基团的改变,如醛和酮、酸和酯、醇和醚等。
4. 顺反异构体:它们的空间中相同的原子或原子团与其他部分的位置关系不同,如烯烃的顺反异构体。
三、空间同分异构体1. 光学异构体:它们的分子式相同,但是它们在空间中的结构是镜像对称的,无法重合,如手性分子。
2. 几何异构体:它们的分子式相同,但是它们在空间中的结构是由于双键的构象不同而导致的,如具有顺式和反式结构的烯烃。
四、同分异构体的性质和应用1. 密度和沸点的差异:由于结构的不同,同分异构体的密度和沸点也存在差异。
2. 光学活性:光学异构体是具有光学旋光性质的,可以将普通光线分解为左旋光和右旋光。
3. 药物活性:同分异构体的结构不同,其生物活性也不同,对于药物的研发和制造具有重要的指导意义。
同分异构体的研究对于我们深入了解有机化合物的特性和性质具有重要意义,通过对同分异构体的研究,可以为有机合成的优化和新药物的研发提供理论基础和指导。
在高一化学课程中,我们需要掌握同分异构体的分类方法、构造特点以及相关的性质和应用知识,为以后的学习和科学研究打下坚实的基础。

高考有机化学二轮复习同分异构体书写知识点同分异构现象:化合物具有相同的分子式,但因结构不同而产生了性质上的差异的现象。
同分异构体:分子式相同,结构不同的化合物互称为同分异构体。
1.同分异构体的类别(1)碳链异构:碳骨架不同引起的异构。
(5)对映异构(旋光异构):互为实物与镜像而不可重叠的立体异构体,称为对映异构体(称为对映体),对映异构体都有旋光性,其中一个是左旋的,一个是右旋的,所以对映异构体又称为旋光异构体。
手性碳:与4个不同的原子或原子团相连的碳原子。
(6)构象异构:由于有机分子中σ键可以自由旋转,使分子中的原子或基团在空间产生不同的排列,这种特定的排列形式称为构象。
由单链旋转而产生的异构体称为构象异构体或旋转异构体。
2.同分异构体数目的判断方法一般按碳链异构?位置异构?官能团异构的顺序书写。
(1)记忆法记住一些常见有机物异构体数目。
例如:①凡只含一个碳原子的分子均无异构体;②乙烷、丙烷、乙烯、丙烯、乙炔、丙炔无异构体;③4个碳原子的烷烃有2种异构体,5个碳原子的烷烃有3种异构体,6个碳原子的烷烃有5种异构体。
④苯环上有两个取代基,苯环上的位置有邻、间、对3种。
⑤苯环上有三个取代基。
若三个取代基相同,则有3种结构:若三个取代基中有2个相同,则有6种结构:若三个取代基均不相同,则有10种结构:(2)基元法①丙基的结构有2种[CH2CH2CH3、CH(CH3)2],则丙醇(C3H7OH)、丁醛(C3H7CHO)、丁酸(C3H7COOH)有2种同分异构体。
②丁基的结构有4种,则一氯丁烷(C4H9Cl)、丁醇(C4H9OH)、戊醛(C4H9CHO)、戊酸(C4H9COOH)有4种同分异构体。
③戊基的结构有8种,则一氯戊烷(C5H11Cl)、戊醇(C5H11OH)、己醛(C5H11CHO)、己酸(C5H11COOH)有8种同分异构体。
(3)先定后动法分析二元取代物的方法,如分析C3H6Cl2的同分异构体,先固定其中一个Cl的位置,移动另外一个Cl,从而得到其同分异构体,共四种。

高中化学竞赛专题辅导化学竞赛作为一项高校选拔优秀化学学子的重要途径,对参赛学生的知识储备和实验技能要求颇高。
在备战化学竞赛的过程中,专题辅导显得尤为关键。
本文将针对高中化学竞赛专题辅导进行详细介绍和分析,帮助学生提高竞赛成绩。
一、基础知识梳理在准备化学竞赛的过程中,首先需要对化学基础知识进行梳理和扎实掌握。
高中化学的基础知识包括无机化学、有机化学、物理化学等多个方面,学生需要逐一进行系统复习和强化。
特别是一些常见的基础概念、化学方程式、反应机理等内容,是竞赛中常考的知识点,因此要特别重视。
二、实验技能训练化学竞赛中的实验环节占据着重要的位置,学生需要具备一定的实验技能才能有效完成实验操作和数据处理。
因此,专题辅导中应当加强实验技能的训练和提高。
可以通过模拟实验、实验训练等方式,让学生熟悉实验仪器的使用和实验方法的操作步骤,为竞赛实验做好准备。
三、解题技巧培养化学竞赛中的解题技巧至关重要,考查的不仅是学生的知识储备,更重要的是解决问题的思维方式和策略。
在专题辅导中,应当重点培养学生的解题技巧,包括化学题型的分析方法、解题思路的拓展、答题技巧的提升等。
只有掌握了一定的解题技巧,学生才能更好地在竞赛中脱颖而出。
四、模拟竞赛演练为了更好地适应竞赛的紧张氛围和题型要求,学生需要进行大量的模拟竞赛演练。
在专题辅导中,可以安排定期的模拟竞赛,让学生身临其境地感受竞赛的氛围,检验自己的学习成果。
通过模拟竞赛的演练,学生可以及时发现自身存在的问题,并加以针对性地提高和改进。
五、总结反思与备考调整在专题辅导的过程中,学生要养成总结反思的好习惯,及时总结每次学习和模拟竞赛的经验教训,发现弱点并加以改进。
同时,根据总结的结果和教师的指导建议,调整备考策略和学习计划,及时进行补充和强化。
只有不断总结反思,不断调整备考方向,才能最终取得好成绩。
综上所述,高中化学竞赛专题辅导是一个系统性的过程,需要学生和教师齐心协力,共同努力。


高考化学同分异构体的知识点一、有机物的同分异构体1. 同分异构体的概念化合物具有相同的分子式,但具有不同结构的现象,叫做同分异构现象。
具有同分异构现象的化合物互称为同分异构体。
2. 同系物、同分异构体、同素异形体和同位素的比较①分子式相同则相对分子质量必然相同,但相对分子质量相同而分子式不一定相同。
如:H3PO4与H2SO4、C2H6O与CH2O2的相对分子质量相同,但分子式不同。
最简式相同的化合物不一定是同分异构体,如:HCHO、CH3COOH、HCOOCH3、C6H12O6的最简式相同,但分子式不同。
②分子结构不同是由分子里原子或原子团的排列方式不同而引起的,如:CH3CH2OH和CH3OCH3、CH3CH2CHO和CH3COCH3等。
③同分异构现象在有机化合物中广泛存在,既存在于同类有机物中,又存在于某些不同类有机物中,如:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3、CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH3、C(CH3)4;CH3COOH、HCOOCH3。
同分异构现象在某些无机化合物中也存在,如:CO(NH2)2与NH4OCN、HOCN(氰酸)和HNCO(异氰酸)。
④化合物的分子组成、分子结构越简单,同分异构现象越弱。
反之,化合物的分子组成、分子结构越复杂,同分异构现象越强。
如甲烷、乙烷、丙烷等均无同分异构现象,而丁烷、戊烷的同分异构体分别为2种、3种。
⑤同分异构体之间的化学性质可能相同也可能不同,但它们的物理性质一定不同。
各同分异构体中,分子里支链越多,熔沸点一般越低。
二. 同分异构体的类型绝大多数有机物普遍存在同分异构现象,高中阶段的同分异构现象主要有4种情况。
即碳链异构、官能团位置异构、官能团类别异构和顺反异构。
1. 碳链异构碳链异构是指由于碳原子的连接次序不同引起的异构,如,正丁烷与异丁烷。
由于烷烃分子中没有官能团,所以烷烃不存在官能团位置异构和官能团类别异构,而只有碳链异构。
再如,CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO(戊醛)与(CH3)2CHCH2CHO(2-甲基丁醛)也属于碳链异构。

高三化学同分异构体专题复习(一)【高考趋向】同分异构体的对象是化合物,属于同分异构体的物质必须化学式相同,结构不同,因而性质不同。
具有“五同一异”,即同分子式、同最简式、同元素、同相对原子式量、同质量分数、结构不同。
同分异构体的书写及数目确定是高考的必考点,通常有两种考查形式:一是以选择题的形式考查同分异构体的数目;二是以非选择题的形式考查某些具有特定结构的同分异构体。
【基础回顾】一、同分异构体的书写同分异构体主要有碳链异构;(官能团)位置异构;(官能团)类别异构等。
1. 碳链异构:碳链不同而产生的异构现象。
如CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO(戊醛)与(CH3)2CHCH2CHO(2-甲基丁醛)。
在碳链异构中首先必须掌握对等效氢原子(有机物分子中位置等同的氢)的判断:(1)连在同一个碳原子上的氢原子是等效的;(2)连在同一个碳原子上的甲基上的氢原子是等效的;(3)处于对称位置或镜面对称位置的碳原子上连接的氢原子是等效的。
如其次,书写的方法好顺序为:(1)缩碳法:先将所给出的碳原子写成一条长链,在此基础上依次减碳;(2)先整后散:这一句话包含两层意思,一是取下来的碳原子若有两个,则为一个CH3CH2-,或者两个CH3-,其他与此类推。
二是若有两个取代基时,先将两个取代基连接在一个主链碳原子上,然后再分开连在不同的碳原子上。
(3)由边到心(或由心到边):若取下来的为一个取代基,则在等效氢的前提下,在主链碳上的连接方式为,从两边到中心(或从中心到两边)。
(4)定一变一:若有两个取代基要将其分开连在不同的碳原子上,首先将一个取代基定位,再变动另一个取代基。
2.位置异构:由于官能团在碳链或碳环上的位置不同而产生的异构现象。
如,CH2=CHCH2CH3和CH3CH=CHCH3; CH3CH2CH2COH(1-丙醇)CH3CH(OH)CH3(2-丙醇)。
3.官能团异构:由于官能团的种类不同而产生的异构现象。
官能团的种类主要有以下几种,烯烃~环烷烃,二烯烃~炔烃,饱和一元醇~醚,饱和一元醛~酮,饱和一元羧酸~酯,芳香醇~芳香醚~酚,硝基化合物~氨基酸,葡萄糖~果糖,蔗糖~麦芽糖。
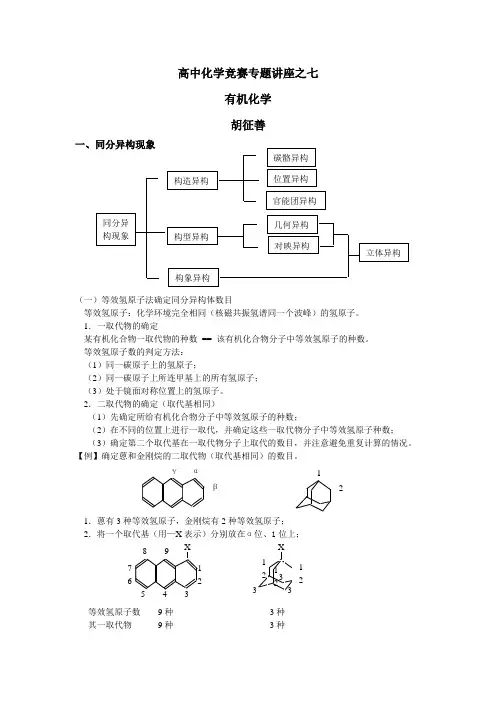
高中化学竞赛专题讲座之七有机化学胡征善一、同分异构现象(一)等效氢原子法确定同分异构体数目等效氢原子:化学环境完全相同(核磁共振氢谱同一个波峰)的氢原子。
1.一取代物的确定某有机化合物一取代物的种数== 该有机化合物分子中等效氢原子的种数。
等效氢原子数的判定方法:(1)同一碳原子上的氢原子;(2)同一碳原子上所连甲基上的所有氢原子;(3)处于镜面对称位置上的氢原子。
2.二取代物的确定(取代基相同)(1)先确定所给有机化合物分子中等效氢原子的种数;(2)在不同的位置上进行一取代,并确定这些一取代物分子中等效氢原子种数;(3)确定第二个取代基在一取代物分子上取代的数目,并注意避免重复计算的情况。
1.蒽有3种等效氢原子,金刚烷有2种等效氢原子;21位上;X等效氢原子数9种3种其一取代物9种3种1212 33 31212然后将—X 分别放在β位、2位(为了避免重复,另一取代基不能再连在α位、1位)上;3种最后将—X 分别放在γ位(为了避免重复,另一取代基不能再连在α位、β位)上;其一取代物 1种 所以:蒽的二取代物(取代基相同)有9+5+1==16种同分异构体;金刚烷的二取代物(取代基相同)有3+3 == 6种。
若考虑顺反异构,金刚烷还另加2种顺反(几何)异构体: 顺式 反式同理可求:苯、萘、蒽、并四苯、并五苯……二取代物(取代基相同)的同分异构体数目有: ② 当苯环数为偶数时1.原子次序(1)原子:原子序数大的排在前面,同位素质量数大的优先。
几种常见原子的优先次序为:I >Br >Cl >S >P >O >N >C >D >H(2)饱和基团:如果第一个原子序数相同,则比较第二个原子的原子序数,依次类推。
常见的烃基优先次序为:(CH 3)3C —>(CH 3)2CH —>CH 3CH 2—>CH 3—(3)不饱和基团:将双键或三键拆开,如: C=O C —O 再依(2)作比较。
故O—X 2 1 22 3 2 H X H X H X X H HX H X H X X H有:—C CH >—CH=CH 2>(CH 3)2CH — 2.某些有机化合物的命名(1)几何异构A .当双键(或环)碳原子的每个碳原子上所连2个基团不相同时,可用顺反表示。


同分异构体
高乃群高级教师
1几何异构体:因双键或成环碳原子的单键不能自由旋转而引起的异构体称为几何异构体,也称为顺反异构体。
2互变异构体:因分子中某一原子在两个位置迅速移动而产生的官能团异构体称为互变异构体。
互变异构体是一种特殊的官能团异构体。
3立体异构体:分子中原子或原子团互相连接次序相同、但空间排列不同而引起的异构体称为立体异构体。
4同分异构体:分子式相同而结构不同的化合物称为同分异构体,也称为结构异构体。
5同分异构现象:分子式相同而结构不同的现象称为同分异构现象。
6价键异构体:因分子中某些价键的分布发生了改变,与此同时也改变了分子的几何形状,从而引起的异构体称为价键异构体。
7位置异构体:官能团在碳链或碳环上的位置不同而产生的异构体称为位置异构体。
8构型异构体:因键长、键角、分子内有双键、有环等原因引起的立体异构体称为构型异构体。
一般来讲,构型异构体之间不能或很难互相转换。
9官能团异构体:因分子中所含官能团的种类不同所产生的异构体称为官能团异构体。
10构造异构体:因分子中原子的连结次序不同或者键合性质不同引起的异构体称为构造异构体。
11构象异构体:仅由于单键的旋转而引起的立体异构体称为构象异构体。
有时也称为旋转异构体。
由于旋转的角度可以是任意的,单键旋转360˚可以产生无数个构象异构体。
通常以稳定的有限几种构象来代表它们。
12旋光异构体:因分子中没有反轴对称性而引起的具有不同旋光性能的立体异构体称为旋光异构体。
13碳架异构体:因碳架不同产生的异构体称为碳架异构体。
第十六章 配位化合物Chapter 16 The Coordination Compounds最早的配合物是偶然、孤立地发现的,它可以追溯到1693年发现的铜氨配合物,1704年发现的普鲁士蓝以及1760年发现的氯铂酸钾等配合物。
配位化学作为化学学科的一个重要分支是从1793年法国化学家Tassaert 无意中发现CoCl ·6NH 3开始的。
B.M.Tassaert 是一位分析化学家。
他在从事钴的重量分析的研究过程中,偶因NaOH 用完而用NH 3·H 2O 代替加入到CoCl 2(aq)中。
他本想用NH 3·H 2O 沉淀Co 2+,再灼烧得到CoO ,恒重后测定钴的含量。
但结果发现加入过量氨水后,得不到Co(OH)2沉淀,因而无法称重,次日又析出了橙黄色晶体。
分析其组成为:CoCl 3·6NH 3。
配位化学的近代研究始于两位精明的化学家 −− A. Werner 和 S. M. Jogensen 。
他们不仅有精湛的实验技术,而且有厚实的理论基础。
特别是从1891年开始,时年25岁在瑞士苏黎士大学学习的Werner 提出的配合物理论:1.提出主价(primary valence )和副价(second valence ),相当于现代术语的氧化数和配位数;又指出了配合物有内界(inner )和外界(outer )。
2.在任何直接测定分子结构的实验方法发明之前很长一段时间,他指出了一些配合物的正确的几何构型。
其方法是沿用有机化学家计算苯取代物的同分异构体数目来推测结构。
例:W erner 认为[Co(NH 3)4Cl 2]+的构型及其异构体的关系如下:化学式 平面六边形三角棱柱八面体 实验 [Co(NH 3)4Cl 2]+3322Werner 合成出[Co(NH 3)4Cl 2]Cl 的异构体只有两种,而仅有八面体才是两种几何异构体,故[Co(NH 3)4Cl 2]+的几何构型构是八面体。
重难点六同分异构现象和同分异构体【要点解读】一、同分异构现象与同分异构体1)同分异构现象:化合物具有相同的分子式但不同结构的现象.2)同分异构体:具有同分异构现象的化合物互称为同分异构体.3)异构类型:(1)碳链异构(如丁烷与异丁烷)(2)官能团异构(如乙醇和甲醚)常见的官能团异构:组成通式可能的类别典型实例C n H2n烯烃、环烷烃CH2=CHCH3与C n H2n-2炔烃、二烯烃CH≡C-CH2CH3与CH2=CHCH=CH2C n H2n+2O饱和一元醇、醚C2H5OH与CH3OCH3C n H2n O 醛、酮、烯醇、环醚、环醇CH3CH2CHO、CH3COCH3、CH=CHCH2OH与C n H2n O2羧酸、酯、羟基醛CH3COOH、HCOOCH3与HO-CH3-CHO C n H2n-6O酚、芳香醇、芳香醚C n H2n+1NO2硝基烷、氨基酸CH3CH2-NO2与H2NCH2-COOHC n(H2O)m单糖或二糖葡萄糖与果糖(C6H12O6)、蔗糖与麦芽糖(C12H22O11) (3)位置异构(如1-丁烯和2-丁烯)4)同分异构体的书写规律:书写时,要尽量把主链写直,不要写得扭七歪八的,以免干扰自己的视觉;思维一定要有序,可按下列顺序考虑:①主链由长到短,支链由整到散,位置由心到边,排列邻、间、对.②按照碳链异构→位置异构→官能团异构的顺序书写,也可按官能团异构→碳链异构→位置异构的顺序书写,不管按哪种方法书写都必须防止漏写和重写.(烯烃要注意“顺反异构”是否写的信息啊)③若遇到苯环上有三个取代基时,可先定两个的位置关系是邻或间或对,然后再对第三个取代基依次进行定位,同时要注意哪些是与前面重复的.5)同分异构体数目的判断方法:(1)记忆法:记住已掌握的常见的异构体数.例如:①凡只含一个碳原子的分子均无异构;②丁烷、丁炔、丙基、丙醇有2种;③戊烷、戊炔有3种;④丁基、丁烯(包括顺反异构)、C8H10(芳烃)有4种;⑤己烷、C7H8O(含苯环)有5种;⑥C8H8O2的芳香酯有6种;⑦戊基、C9H12(芳烃)有8种.(2)基元法例如:丁基有4种,丁醇、戊醛、戊酸都有4种(3)替代法例如:二氯苯C6H4C l2有3种,四氯苯也为3种(将H替代Cl);又如:CH4的一氯代物只有一种,新戊烷C(CH3)4的一氯代物也只有一种.【称互补规律】(4)对称法(又称等效氢法) 等效氢法的判断可按下列三点进行:①同一碳原子上的氢原子是等效的;②同一碳原子所连甲基上的氢原子是等效的;③处于镜面对称位置上的氢原子是等效的(相当于平面成像时,物与像的关系)。
【高中化学】高中化学知识点:同分异构体同分异构现象和同分异构体:1.概念:化合物具有相同的分子式.但结构小同,因而产生了性质上的差异,这种现象叫同分异构现象。
具有同分异构现象的化合物互为同分异构体。
2.同分异构体的基本类型(1)碳链异构:指的是分子中碳骨架不同而产生的同分异构现象。
如所有的烷烃异构都属于碳链异构。
(2)边线异构:所指的就是分子中官能团边线相同而产生的同分异构现象。
如l一丁烯与2一丁烯、l一丙醇与2一丙醇、邻二甲苯与间二甲苯及对二甲苯。
(3)官能团异构:指的是有机物分子式相同,但具有不同官能团的同分异构体的现象。
常见的官能团异构关系如下表所示:(4)顺反异构:由于碳碳双键无法转动而引致分子中原子或原子团在空间的排序方式相同所产生的异构现象。
两个相同的原子或原子团排序在双键的同一侧的称作双键结构;两个相同的原子或原子团排序在双键的两侧的称作反式结构。
例如同分异构体的写法:1.烷烃的同分异构体的读法烷烃只存有碳链异构,其书写技巧通常使用“减碳法”,可以归纳为“两特别注意,四句话”。
(1)两注意:①选择最长的碳链为主链;②找出主链的中心对称线。
(2)四句话:主链由短至长、支链由Marciac贫,边线由心到边,轨域邻、间、对。
例如,c6h14的同分异构体可按此法完整写出(为了简便,在所写结构式中删去了氢原子):2.烯烃的同分异构体的读法分子共同组成合乎cnh2n的烃除烯烃外,除了环烷烃(n≥3),并且烯烃中双键的边线相同则结构相同,有的烯烃还存有顺反异构,所以烯烃的同分异构体比烷烃繁杂得多。
以c5h10为基准表明同分异构体的读法:共有5种烯烃,其中(2)还存在顺反异构体,5种环烷烃,共计11种。
3.苯的同系物的同分异构体的读法由于苯环上的侧链边线相同,可以构成多种同分异构体。
以c8h10为基准写下其属苯的同系物的同分异构体:判断同分异构体数目的方法:1.碳链异构和边线异构:先切除官能团,书写最久碳链,移动官能团的边线;再逐渐增加碳数,移动官能团的边线。
§16-2 配位化合物的同分异构现象The Isomerism of Complexes一、总论:1.Definition:凡是化学组成相同的若干配合物,因原子间的连接方式或空间排列方式的不同而引起的结构和性质不同的现象,称为配合物的同分异构现象(isomerism)。
2.Classification(1) 化学结构异构现象(chemical structure isomerism):化学组成相同,原子间的连接方式不同而引起的异构现象,称为化学结构异构现象。
例如:[Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+和 [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]2+(2) 立体异构现象(stereo isomerism):化学组成相同,空间排列不同而引起的异构现象,称为立体异构现象。
例如:Pt(NH3)2Cl2cis–二氯·二氨合铂(II)trans - 二氯·二氨合铂(II)二、化学结构异构现象,大致分为五类:Ionization isomerism, Hydrate isomerism, Linkage isomerism, Coordination isomerism,Polymerization isomerism. 1.Ionization isomerism(1) Two coordination compounds which differ in the distribution of ionsbetween those directly coordinated and counter-ions present in the crystal lattice are called ionization isomers.(2) e.g. [Cr(NH 3)5Br]SO 4 and [Cr(NH 3)5SO 4]Br 2.Hydrate isomerism (Solvent isomerism)(1) Hydrate isomerism is similar to ionization isomerism except that anuncharged ligand changes from being coordinated to a free-lattice position whilst another ligand moves in the opposite sense.(2) e.g. [Cr(H 2O)6]Cl 3 ,[Cr(H 2O)5Cl]Cl 2·H 2O ,[Cr(H 2O)4Cl 2]Cl ·2H 2O 3.Linkage isomerism(1) The first example of this type of isomerism was provided by J φrgensen,W erner’scontemporary. His method of preparation was as follows :A"solution "Cl]Cl )[Co(NH 23N aN O H ClN H 253−−−→−−−→−−−→− red Co(ONO)]Cl )[(NH A"solution "253cold in stand let −−−−−→− yellow )]Cl Co(NO )[(NH A"solution "2253H Cl conc heat −−−→−−−→−⋅(2) It deals with a few ligands (ambidenatate) that are capable of bondingthrough are type of donor atom in one situation not a different atom in another complex. Some authors refer to this type of isomerism as “structura l i somerism” but inasmuch as all isomerism is basically “structural” , the term linkage isomerism is preferable.(3) e.g. +252SCN]O)[Cr(H and +252NCS]O)Cr(H [ +]SSO )Co(NH [353 and +S]OSO )[Co(NH 253 4.Coordination isomerism(1) This may occur only when the cation and anion of a salt are bothcomplexes, the two isomers differing in the distribution of ligands between the cation and anion(2) e.g. ]Cr(Ox)][)Co(NH [363 and ]][Co(Ox))[Cr(NH 363 ]][Cr(SCN))[Cr(NH 663 and](SCN))][Cr(NH (SCN))[Cr(NH 423243]PtCl ][)[Pt(NH 643 and ]][PtCl Cl )[Pt(NH 4243(3) Coordination position isomerismIn this form of isomerism the distribution of ligands between two coordination centers differs e.g. and5.Polymerization isomerism(1) Strictly speaking, polymerization isomerism, in which n varies in thecomplex [ML m ]n is not isomerism. It is included in this list because it represents on additional way in which an empirical formula may give incomplete information about the nature of a complex.(2) For example, all members of the following series are polymerization isomers:])(NO )[Co(NH 3233 1=n ])Co(NO ][)Co(NH [62632=n ])(NO )][Co(NH )(NO )Co(NH [42232243 2=n24223253])(NO ))][Co(NH (NO )Co(NH [ 3=n 3422363])(NO )][Co(NH )Co(NH [ 4=n 2623253])Co(NO [)](NO )Co(NH [ 5=n三、立体异构现象 (Stereo Isomerism ) 1.几何异构现象 (Geometrical isomerism )(1) 配合物的配位数与几何构型的关系 (The relationship betweencoordination number of complexes and geometrical structure.)a .两配位:直线型 (linear) +23)Ag(NH 、-2CuClb .三配位:平面三角型 (triangle) -][HgI 3c .四配位:平面四方 (square planar) -24PtCl ; 正四面体 (tetrahedron)-24Zn(CN)d .五配位:三角双锥 (trigonal bipyramid) +])[Co(NCCH 53、+I]Cu(dipy)[2四方锥 (square pyramid) ][VO(acac)2e .六配位:正八面体 (octahed ron) 6SF 、-6PCl三棱柱 (trigonal prism) ])ph C [Re(S 3222f .七配位:五角双锥 (pentagonal bipyramid) ][ZrF Na 73带帽三棱柱 (the one-face centred trigonal prism) ][ZrF )(NH 734带帽八面体 (the one-face centred octahedron)g .八配位:立方体 (cube) 88H C (立方烷)四方反棱柱(square anti prism ) ]Zr(acac)[4 十二面体(dodecahedron ) 44[Zr(ox)]-[ (NH 3)4Co OO Co(NH 3)2Cl 2 ]2+HH[ Cl(NH 3)3Co O O Co(NH 3)3Cl ]2+HH我们将讨论四、五、六配位配合物的几何异构现象(2) 决定配合物几何异构体数目的因素:a .空间构型:例如正四面体几何构型不存在几何异构体。
这是因为正四面体的四个顶点是等价的。
空间构型中等价点越多,几何异构体越少。
b .配体种类:在配合物中配体种类越多,几何异构体越多。
例如,八面体配合物:Ma 6(一种),Mabcdef (15种) (a 、b 、c 、d 、e 、f 为单齿配体) c .配体的齿数:双齿配体的两个配位原子只能放置在结构中的邻位位置上,不能放置在对位位置上(跨度大,环中张力太大),即: d .多齿配体中配位原子的种类(及环境):种类越多, 环境越复杂,几何异构体越多。
(3) 几种常见配位数的配合物的几何异构现象 a .四配位:(i) 正四面体:不存在几何异构体(ii) 平面四方:M — 中心体,— 双齿配体 ,a, b, c — 单齿配体。
-cis -trans b .五配位:c .六配位:只讨论正八面体几何构型: +]Cl )[Co(NH 243]O)(H RuCl [323-cis -t r a n s -fac -mer(4) 确定几何异构体的方法 −− 直接图示法a .只有单齿配体的配合物 以Ma 2cdef 为例 (9种): 第一步,先确定相同单齿配体的位置M O O C COO NH 3CoNH 3H 3N Cl H 3N Cl Co Cl H 3N NH 33H 3N Cl Ru OH 2H 2O Cl H 2O OH 2Ru OH 2Cl Cl OH 2Cl M aa① ②第二步,再确定其他配体的位置 ① (6种): ② (3种):b .既有单齿配体,又有双齿配体的配合物 以M(AB)2ef 为例 (6种) 第一步,先固定双齿的位置②第二步,确定双齿配体中配位原子的位置.①②第三步,最后确定单齿配体的位置.2.配合物的光学异构现象(Optical isomerism of coordination compounds )(1) 光学异构体定义a .手性分子(chiral molecular ):当两个分子的对称性互为人的左右手的对称关系,即为镜面对称关系,但它们不能相互重合,则称这两个分子为手性分子,手性分子也称一对对映体(enantiomer )。