蔡氏电路的建模_仿真及混沌稳定岛图的研究_刘孝贤
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:273.23 KB
- 文档页数:8

蔡氏电路的Matlab混沌仿真研究班级:姓名:学号:摘要本文首先介绍非线性系统中的混沌现象,并从理论分析与仿真计算两个方面细致研究了非线性电路中典型混沌电路,即蔡氏电路反映出的非线性性质。
通过改变蔡氏电路中元件的参数,进而产生多种类型混沌现象。
最后利用软件对蔡氏电路的非线性微分方程组进行编程仿真,实现了双涡旋和单涡旋状态下的同步,并准确地观察到混沌吸引子的行为特征。
关键词:混沌;蔡氏电路;MATLAB仿真AbstractThis paper introduces the chaos phenomenon in nonlinear circuits. Chua’s circuit was a typical chaos circuit, thus theoretical analysis and simulation was made to research it. Many kinds of chaos phenomenon on would generate as long as one component parameter was altered in Chua’s circuit.On the platform of Matlab, mathematical model of Chua’s circuit was programmed and simulated to acquire the synchronization of dual and single cochlear volume. Meanwhile, behavioral characteristics of chaos attractor were observed.Key words:chaos phenomenon;Chua’s circuit;Simulation1、引言混沌理论的基本思想起源于20世纪初,完善于20世纪60年代后,发展壮大于20世纪80年代,被认为是继相对论、量子力学之后,人类认识世界和改造世界的最富有创造性的科学领域第三次大革命。
![蔡氏电路毕业设计论文[管理资料]](https://uimg.taocdn.com/99f3b0bf2b160b4e777fcf9b.webp)
目录前言 (4)第一章混沌学基本理论 (4) (5)混沌的定义 (5)混沌的主要特征 (6)混沌的意义 (7)混沌的发展与前景展望 (7)蔡氏电路简介 (8)软件介绍 (8)第二章蔡氏电路理论分析 (10)蔡氏电路构成及蔡氏二极管 (10)蔡氏电路的数学模型 (14) (14)平衡点及稳定性 (15)第三章蔡氏电路的电路实验 (19)典型蔡氏电路仿真 (19)振荡吸收器 (23)等效电感 (31)第四章结束语 (34)第五章总结与心得 (36)参考文献 (39)致谢 (40)附录 (41)蔡氏电路混沌特性的实验研究摘要:混沌现象是一种确定性的非线性运动,在非线性控制领域,混沌控制的研究受到人们越来越多的关注。
典型蔡氏电路结构简单,但有复杂的混沌动力学特征,因而在混沌控制领域中成为研究的重要对象。
本次设计简单介绍了混沌学基本理论,从理论分析和仿真实验两个角度分别研究Chua's Circuit的混沌行为,用Multisim 软件对电路进行仿真实验,通过改变参数,得到了系统各周期的相轨图,并对实验中遇到的现象进行简单的讨论,将蔡氏电路与一个线性二阶电路耦合,得到了更加丰富的混沌行为。
由于普通蔡氏电路在产生混沌现象时,其元件参数可调范围很小,且对初始条件极为敏感,不易于搭建实验电路。
所以引入了电感等效电路,在本文的最后将蔡氏电路中的电感用等效电路替代,从而实现了无感蔡氏电路。
关键词:混沌;蔡氏电路;Multisim;振荡吸收器;等效电感Experimental Study of Chua's Circuit ChaoticAbstract:Chaos is a deterministic non-linear movement, in the field of nonlinear control, chaotic control get more and more attention by people. Typical Chua's circuit is simple, but complex and chaotic dynamics characteristics, so become an important research object in the field of chaos control . The design simple introduced the basic theory of chaos, study the chaotic behavior of Chua's Circuit from two angles of the theoretical analysis and experimental with Multisim circuit simulation software, by changing the parameters, get each cycle tracks phase diagram of the system, simple discuss the experimental phenomena encountered, couple the second-order Chua's circuit with a linear circuit ("oscillation absorber"), get even more chaotic behavior of the rich. As the general chaos in Chua's circuit in the production, its range of component parameters adjustable is very small, and extremely sensitive to initialconditions, hard to set up experimental circuit. Therefore introduce the inductor equivalent circuit, in this final, change the inductor of Chua's circuit with the equivalent circuit, thus achieving non- inductor of Chua's circuit.Key words:chaos; Chua's circuit; Multisim; vibration absorber; equivalent inductance前言“1979年12月,洛伦兹在华盛顿的美国科学促进会的一次讲演中提出:一只蝴蝶在巴西扇动翅膀,有可能会在美国的德克萨斯引起一场龙卷风。

仿真蔡氏电路混沌效应的教学讨论
蔡氏电路是一种混沌系统,其混沌现象在模拟电路领域非常重要。
仿真蔡氏电路的混沌效应,是电路仿真教学中的一个重要课题。
首先,混沌效应的探究是基于学生对混沌学理论的掌握和电路
仿真工具的运用。
因此,在教学过程中,应先向学生介绍混沌现象
和蔡氏电路的基本原理,让学生理解混沌是一种非周期性且不可预
测的现象,而蔡氏电路是一种具有三个不同周期的振荡器。
接着,教师可以使用仿真软件(如Multisim或LTSpice)进行
电路仿真,让学生通过仿真实验的方式来观察混沌效应。
学生可以
通过改变电路元件的参数(如电容、电阻等)来观察混沌效应的变化。
同时,学生也能够通过仿真实验来了解混沌系统的稳定性和可
控性。
在教学过程中,教师可以提供一些课堂讨论或小组讨论的环节,让学生可以对混沌效应进行深入的探究和分析。
例如,让学生讨论
如何通过改变蔡氏电路中的元件来改变电路的混沌状态,或者讨论
混沌现象在日常生活中的应用。
最后,在教学结束后,教师可以要求学生进行实验报告的书写,来总结混沌电路的基本原理、仿真过程、结果分析以及对混沌现象
的理解和探究。
通过这种方式,学生能够获得更深入的学习和理解,也能够提高其电路仿真和实验技能。
仿真蔡氏电路的混沌效应是电路仿真教学中一个重要的课题,
通过深入的探讨和分析,将有助于学生加深对混沌系统的理解和掌
握,提高其仿真和实验技能,也有助于学生将所学知识转化为现实应用。


蔡氏电路及混沌现象研究一、引言在非线性电路中蔡氏电路是迄今为止产生复杂动力学行为的最为有效和较为简单的电路之一。
混沌(chaos)现象的研究是非线性系统理论研究中的前沿课题之一,混沌现象普遍存在物理、化学、生物学,以及社会科学等等各个学科领域中,是在确定性系统中出现的一种貌似无规则、类似随机的现象,是非线性动力学系统特有的一种运[1]。
动形式。
蔡氏电路是一个能产生混沌现象的最简单三阶自治电路1983年,美籍华裔科学家蔡少棠教授首次提出了著名的蔡氏电路(chua's circuit)。
它是历史上第一例用电子电路来证实混沌现象的电路,也是迄今为止在非线性电路中产生复杂动力学行为的最为有效和较为简单的电路之一。
通过改变蔡氏电路的拓扑结构或电路参数,可以产生倍周期分叉、单涡卷、周期3、双涡卷吸引子、多涡卷吸引子等十分丰富的混沌现象。
因此,蔡氏电路开启了混沌电子学的大门,人们已围绕它开展了混沌机理的探索、混沌在保密通信中的应用研究,并取得了一系列丰硕的成果。
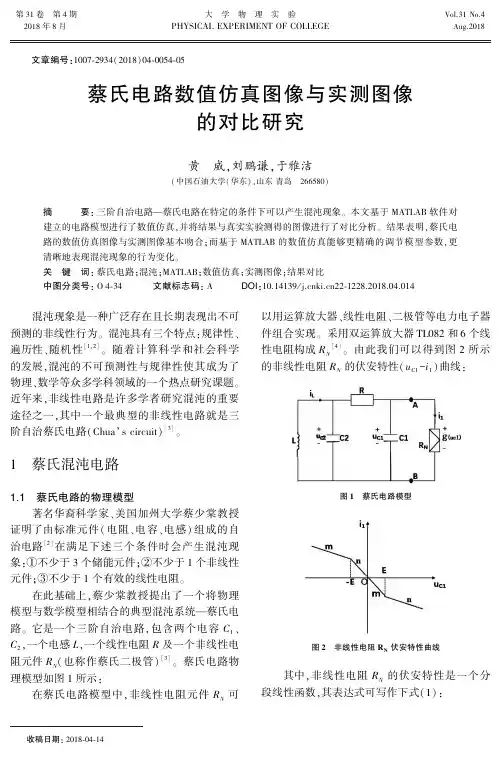
图1(a)是蔡氏电路的电路拓扑图,它是一个三阶电路,有两个电容、一个电感、一个线性电阻,并含有一个非线性电阻元件N,它R的伏一安特性曲线如图1 (b)所示,是一个分段线性函数,中间一段呈现负电阻的特征,它可以用开关电源等电子电路来实现。
.考虑图1(a)的电路,非线性电阻的伏安特性曲线由图1(b)给出。
蔡氏电路的动力学特性由下列各式描述:其中v,v和i分别是C,C两端的电压以及流过£的电流,21c1Lc2g(vc1)是图(6)所示的分段线性化函数,G=1/R。
该电路描述可以写成无量纲的形式(即下面的正规化状态方程):其中,α和α是非线性函数,满足如下方程:)·K(是参数,21.其中m和m是参数。
给定适当的参数,该系统表现出混沌行为。
10方程(2)是非线性的微分方程组,一般需要用四阶龙格一库塔算法这样的数值方法求解。
其算法思想如下:基于Tavlor级数展开的方法,利用f在某些点处函数值的线性组合构造差分方程,从而避免高阶导数的计算。

对于仿真蔡氏电路混沌效应的教学讨论物理实验中混沌实验是启迪大学生探索自然界非线性动力学的重要途径。
传统的混沌实验仪器往往受到场地、设备和操作等的局限,不能很好的培养学生分析问题和解决问题能力。
本文结合蔡氏电路的原理,阐述如何实现非线性现象中倍周期分岔相图的数值模拟;并指出以上过程中实现培养学生兴趣、动手能力和创新意识的注意事项,为大学物理实验教学改革提供新思路。
:混沌效应,蔡氏电路,仿真,注意事项,教学讨论大学物理实验中混沌实验有助于提高学生的学习主动性、积极性,激发学生的学习兴趣。
但由于传统的混沌实验仪器(蔡氏电路)往往受到场地、设备和操作等的局限,不能很好的培养学生分析问题和解决问题能力。
因此,利用软件仿真混沌实验提高实验教学质量摆在了物理实验教学工作者的面前。
目前有很多人对混沌仿真实验进行着有意义的讨论与实践。
高英俊[1]等人认为混沌中利用仿真中可以结合专业特点, 适当延伸到声学混沌, 光学湍流等,实现有效教学。
张建忠[2]认为利用Matlab数值模拟观察李萨如图形能让学生理性地理解非线性混沌现象,并可以指导学生在实验中更加有效地调节非线性电路混沌仪。
苗明川[3]等人认为仿真混沌实验可以让学生既了解了混沌的概念, 又能掌握数据处理、电脑编程等方面的知识,又增加了学习兴趣。
由最近的研究进展可以看出,尽管很多大学物理实验教学者认识到仿真混沌实验在提高学习兴趣,培养对混沌的认识有重要作用。
然而,对于如何在培养学生认识非线性动力学的过程中注意事项,提高大学生的独立思考能力以及创新能力方面探讨较少。
本文结合蔡氏电路的原理,阐述如何通过Matlab软件实现非线性现象中倍周期分岔相图的数值模拟。
并指出以上过程中实现培养学生动手能力和创新意识的注意事项,为大学物理实验教学改革提供新思路。
1蔡氏电路模型、仿真原理以及结果三阶蔡氏电路模型如图1所示,其中R为有源非线性电阻,其伏安特性如图2所示,Ga为中间线段斜率,Gb为两段直线斜率。

Stabilization of unstable equilibria of chaotic systemsand its applications to Chua’s circuitAbstractBased on the ergodicity of chaos and the state PI regulator approach, a new method was proposed for stabilizing unstable equilibria and for tracking set point targets for a class of chaotic systems with nonlinearities satisfying a specific condition.A criterion was derived for designing the controller gains, in which control parameters could be selected by solving a Lyapunov matrix inequality. In particular, for piecewise linear chaotic systems, such as Chua’s circuit, the control parameters can be selected via the pole placement technique in linear control theory. More importantly, this method has high robustness to system parametric variations and strong rejection to external constant disturbances. For verification and demonstration, the design method is applied to the chaotic Chua’s circuit, showing satisfactory simulation results.Key words: Chua’s circuit; unstable equilibrium point; stabilization; P I regulator1.IntroductionIn the past decade, much attention has been paid to chaos control, and many methods have been proposed for suppressing chaos[1,2]. For instance, the delayed feedback control (DFC) method[3]is based on the difference between the current system output and the time_delayed output signals, which does not require any knowledge of the target points.However, this approach in general cannot specify the target setting point and is subject to the so_called odd number eigenvalue limitation[4~6]. On the other hand, the OGY method[7],which is a local control scheme, and the methods[8,9]that are based on precise state feedback control usually fail with system parameters variation and are inconvenient for practical engineering systems. In this paper, based on the ergodicity of chaos and state PIregulator approach[10], a feedback control design method is proposed for stabilizing unstable equilibria and for set-point tracking for a class of chaotic systems with nonlinearities satisfying a specific condition. The proposed method combines a state feedback and an integral of the difference between the target output and the current output signals. The output signal is a simple function (e.g., linear combination) of the state variables of the chaotic system. In particular, if a suitable linear combination is selected and used as the output feedback, the target output signal can become zero, and then no information about the target equilibrium is needed in the integral part of the controller. Moreover, this control method has satisfactory control performance and robustness. It will also be demonstrated that this control method can reject external bounded constant-disturbances asymptotically. Based on the Lyapunov stabilization theory, a criterion is derived for choosing the proportional and integral gains. The control parameters can be selected via solving aLyapunov matrix inequality. In particular, for piece-wise linear chaotic systems, such as Chua’s circuit, the control parameters can be chosen via the pole placement technique in linear control theory2. Working with Chaos: Building the circuitThe hardest part in building the circuit is getting the correct value of the inductance (电感). I used a simple RL filter to tune the inductance. I used a known R and applied a sinusoid at the input. Since I know the frequency and amplitude of the sinusoid, I can use the frequency response of the circuit to obtain the value of the inductance I want. In order to measure the series resistance of the inductor, use a simple ohm-meter. I even used an ohm-meter to figure out across which pins in the T1105 is the coil actually connected. Screenshots:3. Other possible component values for Chua's circuitThe list below shows some other possible component values for Chua's circuit. Please note that the nonlinear resistor (Chua Diode) is the same as shown in the schematic from the Simulation section. You can refer to the schematic shown at the banner on top of the page.①L=8mH, C2=47nF, C1=3nF, R=1.85k②L=18mH, C2=50nF, C1=4.7nF, R=2.1k4 Stabilizing unstable equilibria of a class of chaotic systems Consider a controlled chaotic system of the form =.x Ax+g(x)+u (1) Where n R x ∈is the state vector, n R u ∈ is the control input to be designed, A ∈×a constant matrix, and g(x) is a continuous nonlinear function satisfying the following condition[11]: ⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-=-~,~~)()(x x M x g x g x x (2) where ~,x x M is a bounded matrix that depends on both x and ~x . Remark1 Many chaotic systems can be described by (1) and (2), such as the classic Chua’s circuit[12],the modified Chua’s circuit with a sine function, the modified Chua’s circuit with nonlinear quadratic function x | x |[13],and the MLC circuit.Let s x be an unstable equilibrium of (1) when u =0,that is,0)(=+s s x g Ax (3)The objective is to design a controller u such that the states of system (1) are stabilized to s x , which is a constant vector independent of time. Later, the objective will also be extended to tracking a constant set point. According to the state PIregulator theory, a controller is constructed as follows:)])()(([0τλd y y k x x K B u t s s ⎰-+-= (4)Where B ∈1⨯n R is a constant gain matrix, K ∈1⨯n R is the proportional state feedback gain vector, k ∈R s the integral gain, y = Cx is the output with a constant matrix C ∈1⨯n R ,s s Cx y = is the observation of the target equilibrium s x ,andWhere x Ω denotes the neighborhood of the unstable equilibrium s xRemark2 Because of the ergodicity of chaos, the trajectory will visit or access Ωx sat times. When the trajectory accesses x Ω, the controller (4) is turned on, and the trajectory will converge to s x asymptotically under the controller (4), in which the control parameters will be chosen to ensure the error dynamic system is asymptotically stable, as further described below.Remark3 In control law (4), if we choose r y s = , where is a constant set point for tracking, then the output y can track this set point asymptotically.Remark 4 If there exists an external bounded constant disturbance w, whose value is unknown but bounded, in the system (1), then we can easily prove that the chaotic system can be stabilized at the targeted unstable equilibrium point by using the similar procedure above.5. Applications of ChaosBelieve it or not, there are tons of applications for Chaos. Here are a few: The stock market (finance) ,Power systems (electrical engineering) ,Population Dynamics (biology) ,Communication Systems (electrical engineering) There are also very interesting chaotic processes in the human brain. Here are two excellent papers by French scientists on this topic (pubmed links to both articles):Conclusion and discussion In this paper, a new method for stabilizing unstable equilibria has been developed for a class of chaotic systems based on the state PI regulator method.. The proposed method is robust to a certain level of external disturbances as well as system parameters variation. Based on the Lyapunov stabilization theory, a precise criterion is derived to accomplish the stabilization of the target unstable equilibria of the chaotic system. The control parameters can be selected via solving a Lyapunov matrix inequality. Particularly, for piece wise linear chaotic systems such as Chua’s circuit, they can be selected via the simple pole placement technique. This new design method is better than the state feedback control method in the sense that even the given.出处:Control Theory & Applications 2003.V ol.20.No.5摘要基于混沌系统的遍历性和状态PI调节器理论,提出一类混沌系统不稳定平衡点的镇定和设定点跟踪新方法,给出用于控制器参数设计的Lyapunov矩阵不等式.对于分段线性混沌系统,如蔡氏电路,可通过控制理论中的极点配置技术来设计控制器参数.该方法对系统参数变化具有很强的鲁棒性,能够消除外部定值扰动.将该方法用于蔡氏混沌电路不稳定平衡点的镇定,取得了满意的结果.关键词:混沌系统蔡氏电路;不稳定平衡点;镇定; PI调节器1.简介在过去的十年中,混沌控制受到了很大重视,提出了许多控制混沌的方法。


引言混沌研究最先起源于Lorenz研究天气预报时用到的三个动力学方程.后来的研究表明,无论是复杂系统,如气象系统、太阳系,还是简单系统,如钟摆、滴水龙头等,皆因存在着内在随机性而出现类似无轨,但实际是非周期有序运动,即混沌现象.现在混沌研究涉及的领域包括数学、物理学、生物学、化学、天文学、经济学及工程技术的众多学科,并对这些学科的发展产生了深远影响.随着计算机和计算科学的快速发展,混沌现象及其应用研究已成为自然科学技术和社会科学研究领域的一个热点。
而非线性电路是混沌及混沌同步应用研究的重要途径之一。
其中一个最典型的电路是三阶自治蔡氏电路,这个电路是由加州大学伯克利分校的蔡少棠首先发起研究的。
在这个电路中观察到了混沌吸引子。
蔡氏电路是能产生混沌行为最简单的自治电路,所有应该从三阶自治常微分方程描述的系统中得到的分岔和混沌现象都能够在蔡氏电路中通过计算机仿真和示波器观察到。
蔡氏电路虽然简单,但其中蕴含着丰富和复杂的非线性现象。
不须改变电路系统结构,只调整控制参数R,就能获得电路系统不同状态的响应输出信号[1]。
该文对产生混沌现象的蔡氏电路进行了研究,建立了数学模型,分析了产生混沌的原因,并根据建立的数学模型,利用MATLAB进行了仿真研究,仿真结果表明在一定的条件下该电路能够出现混沌双涡卷吸引子和稳定周期轨道。
+1 混沌学概述1.1混沌与非线性科学混沌学于上世纪六十年代初在美国兴起。
它是非线性系统中存在的一种普遍现象,也是非线性系统所特有的一种复杂状态。
所以我在论文中研究的蔡氏电路必然是一个非线性系统,确切地说是一个非线性动力系统。
从函数构造的角度来说,非线性系统要比“线性系统”更多、更普遍。
“线性系统”与“非线性系统”的不同之处至少有两个方面。
第一:线性系统可以使用叠加原理,而非线性系统则不能。
第二:(也就是最本质的)非线性系统对初值极敏感,而线性系统则不然。
1.2混沌的含义混沌到目前为止,还没有一个统一的、有足够数学定理支持的、普遍适用和完美的混沌理论,所以只能通过混沌系统所表现出的一些普遍现象总结归纳出其所谓的本质。
模电期末论文《蔡氏电路混沌特性的研究》2009013157模电期末论文——关于蔡氏电路混沌现象的研究2009013157 生医9 王颖奇*所有仿真结果均于2010年12月24日完成在上学期的大学物理教材中,混沌现象就曾经被老师提起。
书中介绍,混沌现象是指发生在确定性系统中的貌似随机的不规则运动,一个确定性理论描述的系统,其行为却表现为不确定性一不可重复、不可预测,这就是混沌现象。
进一步研究表明,混沌是非线性动力系统的固有特性,是非线性系统普遍存在的现象。
牛顿确定性理论能够充分处理的多为线性系统,而线性系统大多是由非线性系统简化来的。
因此,在现实生活和实际工程技术问题中,混沌是无处不在的。
“ 混沌”是近代非常引人注目的热点研究,它掀起了继相对论和量子力学以来基础科学的第三次革命。
科学中的混沌概念不同于古典哲学和日常语言中的理解,简单地说,混沌是一种确定系统中出现的无规则的运动。
混沌理论所研究的是非线性动力学混沌,目的是要揭示貌似随机的现象背后可能隐藏的简单规律,以求发现一大类复杂问题普遍遵循的共同规律。
那么这种现象在电路有什么应用呢?传统上,人们把信号分为两大类:确定性信号这种信号所有时刻的波形都是确定的;随机过程它的波形由概率分布确定。
然而,这样的分类忽略了另一类极为重要的信号——混沌信号。
混沌信号的波形是非常不规则的,表面上看来就象噪声,但实际上它却是由确定性的规则所产生的,这种规则有时是很简单的。
正是这种简单的规则产生出复杂的波形激发了人们对它极大的兴趣。
在图(1-2)中,我们向大家展示了由Logistic映射所生成的混沌信号与白噪声信号,从表面上我们是无法判断出噪声与混沌的。
让人兴奋的是:实践证明,在大量的物理系统和自然系统中都存在着混沌信号!虽然,混沌现象的出现使我们无法对系统的长期行为进行预测,但是我们完全可以利用混沌的规律对系统进行短期的行为预测,这样比传统的统计学方法更加有效。
在工程学中,混沌现象主要有以下两方面的应用。
·实验技术·一种蔡氏混沌电路实验设计刘 恒,刘远林,吴朝阳,孙亚坤,刘 泽(南京信息工程大学 电子与信息工程学院,南京 210044)摘要:分立器件构成的混沌电路的响应受电路参数及储能元件初始状态影响,电感元件参数的不稳定带来电路混沌的不可控问题。
该论文在介绍蔡氏混沌电路动力学原理的基础上,利用模拟电感代替无源独立电感,并进行了基于Multisim 软件的仿真,得到了改进的蔡氏电路的相轨迹图。
利用单面板腐蚀制作了实验电路,实验结果与仿真结果一致,验证了模拟电感的有效性。
改进的混沌电路可作为电路实验的拓展教学案例,提高学生学习电路与电子工艺课程的积极性,同时也可以增强学生对混沌理论的理解。
关 键 词:蔡氏电路;混沌;模拟电感;仿真中图分类号:TN911.71 文献标志码:A DOI: 10.12179/1672-4550.20200087Experimental Design of A Chua’s Chaotic CircuitLIU Heng, LIU Yuanlin, WU Zhaoyang, SUN Yakun, LIU Ze(College of Electronic & Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing 210044, China )Abstract: Due to the response of chaotic circuit composed of discrete devices is affected by circuit parameters and the initial state of energy storage elements, the instability of inductance parameters may bring uncontrollable problem of circuit chaos. On the basis of introducing the dynamic principle of Chua’s chaotic circuit, this paper uses simulated inductor to replace the passive independent inductor, carries out the simulation based on Multisim software, and obtains the phase trajectory diagram of the improved Chua’s circuit. The experimental circuit, fabricated by single panel etching process, achieves the same experimental results with the simulation results, thus verifying the effectiveness of the simulated inductor. The improved chaotic circuit can be used as an expanded teaching case of circuit experiment to improve students’ enthusiasm in learning circuit and electronic technology courses, thereby enhancing their understanding of chaotic theory.Key words: Chua’s circuit; chaos; stimulated inductor; simulation近年来,混沌在非线性科学、信息科学、保密通信以及其他工程领域获得了广泛的应用,已成为非线性电路与系统的一个热点研究课题[1−2]。
引言混沌研究最先起源于 Lorenz研究天气预报时用到的三个动力学方程.后来的研究表明,无论是复杂系统,如气象系统、太阳系,还是简单系统,如钟摆、滴水龙头等,皆因存在着内在随机性而出现类似无轨,但实际是非周期有序运动,即混沌现象.现在混沌研究涉及的领域包括数学、物理学、生物学、化学、天文学、经济学及工程技术的众多学科,并对这些学科的发展产生了深远影响.随着计算机和计算科学的快速发展,混沌现象及其应用研究已成为自然科学技术和社会科学研究领域的一个热点。
而非线性电路是混沌及混沌同步应用研究的重要途径之一。
其中一个最典型的电路是三阶自治蔡氏电路,这个电路是由加州大学伯克利分校的蔡少棠首先发起研究的。
在这个电路中观察到了混沌吸引子。
蔡氏电路是能产生混沌行为最简单的自治电路,所有应该从三阶自治常微分方程描述的系统中得到的分岔和混沌现象都能够在蔡氏电路中通过计算机仿真和示波器观察到。
蔡氏电路虽然简单,但其中蕴含着丰富和复杂的非线性现象。
不须改变电路系统结构,只调整控制参数R,就能获得电路系统不同状态的响应输出信号[1]。
该文对产生混沌现象的蔡氏电路进行了研究,建立了数学模型,分析了产生混沌的原因,并根据建立的数学模型,利用MATLAB进行了仿真研究,仿真结果表明在一定的条件下该电路能够出现混沌双涡卷吸引子和稳定周期轨道。
+1 混沌学概述1.1混沌与非线性科学混沌学于上世纪六十年代初在美国兴起。
它是非线性系统中存在的一种普遍现象,也是非线性系统所特有的一种复杂状态。
所以我在论文中研究的蔡氏电路必然是一个非线性系统,确切地说是一个非线性动力系统。
从函数构造的角度来说,非线性系统要比“线性系统”更多、更普遍。
“线性系统”与“非线性系统”的不同之处至少有两个方面。
第一:线性系统可以使用叠加原理,而非线性系统则不能。
第二:(也就是最本质的)非线性系统对初值极敏感,而线性系统则不然。
1.2混沌的含义混沌到目前为止,还没有一个统一的、有足够数学定理支持的、普遍适用和完美的混沌理论,所以只能通过混沌系统所表现出的一些普遍现象总结归纳出其所谓的本质。
基于MATLAB的蔡氏混沌非线性电路的仿真研究作者:王玮刘亦萍来源:《科技视界》2013年第33期【摘要】混沌现象存在于自然界各个领域,在现代科学与工程学领域的应用也十分广泛。
通过对混沌现象及其特征,产生的机理和条件的研究,并从理论分析与MATLAB仿真两个角度分别研究了蔡氏混沌电路的演化过程和混沌电路状态,进而构造出符合三阶混沌系统的非线性电路和数学模型。
研究结果表明,蔡氏混沌非线性电路中元件参数影响电路混沌状态的演化,仿真数据与理论分析结论一致,随着线性电阻阻值的减小电路状态大致经历:稳定态,周期态,混沌态,负阻尼振荡态。
【关键词】混沌现象;非线性电路;蔡氏混沌电路;MATLAB仿真Simulation Study of Chua’s Nonlinear Circuit Based on MATLABWANG Wei LIU Yi-Ping(School of Electronic and Electric Engineering, Shanghai Second Polytechnic University,Shanghai 201209,China)【Abstract】Chaos exists in nature in various fields, in the field of modern science and engineering applications are very extensive. Through the chaos and its characteristics, the production mechanism and conditions of the study and theoretical analysis and MATLAB simulation from two angles were investigated chaotic circuit evolution and chaos circuit state, and thus construct a third-order chaotic systems with non-compliance linear circuits and mathematical models. The results show that non-linear circuit element Chua circuit parameters that affect the evolution of the chaotic state, the simulation data and theoretical analysis conclusion consistent with the decrease of the linear resistor circuit state generally experience: steady state, periodic state, chaotic state, negative damping oscillation state.【Key words】Chaos; Nonlinear circuits; Chaotic circuit; MATLAB simulation0 引言混沌现象是一种普遍存在的非线性现象,随着计算机水平的快速发展,混沌现象及其应用研究已成为自然科学和社会科学研究领域的一个热点[1-2]。