一维CFD模拟仿真设计
- 格式:doc
- 大小:197.00 KB
- 文档页数:18

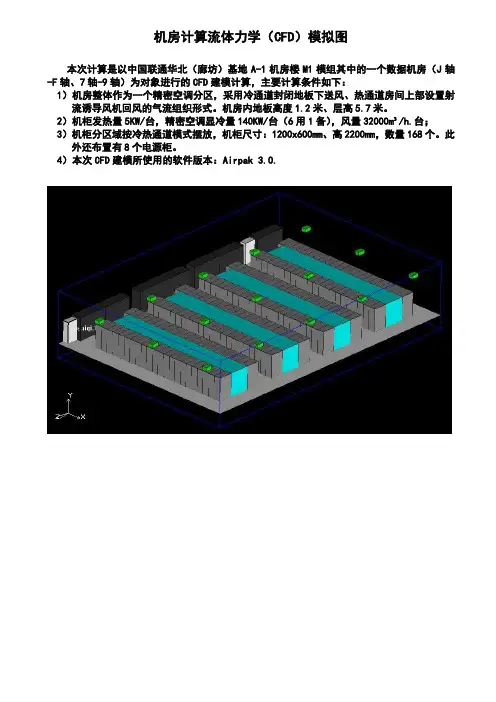
机房计算流体力学(CFD)模拟图
本次计算是以中国联通华北(廊坊)基地A-1机房楼M1模组其中的一个数据机房(J轴-F轴、7轴-9轴)为对象进行的CFD建模计算,主要计算条件如下:
1)机房整体作为一个精密空调分区,采用冷通道封闭地板下送风、热通道房间上部设置射流诱导风机回风的气流组织形式。
机房内地板高度1.2米、层高5.7米。
2)机柜发热量5KW/台,精密空调显冷量140KW/台(6用1备),风量32000m³/h.台;
3)机柜分区域按冷热通道模式摆放,机柜尺寸:1200x600mm、高2200mm,数量168个。
此外还布置有8个电源柜。
4)本次CFD建模所使用的软件版本:Airpak 3.0.
一、CFD模拟温度场计算结果:(1)地板上高度0.5米高度温度场分布
(2)地板上高度1.0米高度温度场分布
(3)地板上高度1.8米高度温度场分布
(4)地板上X轴向温度场分布
三、CFD 计算结果表明:机柜冷通道封闭,其温度场分布均匀,无局部过热情况出现。
冷量得到有效管理,避免了气流短路,效率高从而更为节能。

0引言弹道修正引信技术将引信的功能从安全控制、炸点控制和起爆控制拓宽到命中点控制,使引信不仅控制对目标实施有效的毁伤,而且还控制对目标的命中精度。
也就是说,弹道修正引信不仅具有传统引信系统保证弹药安全和控制战斗部起爆的功能,还具有感知及辨识弹道环境和修正弹道的功能。
它通过对弹丸实际弹道环境的辨识,预估弹道偏差,迅速产生弹道修正指令并传输给相应的执行机构,以达到对无控弹药的弹道修正。
发射后,炮弹即不受地面控制,因此抗干扰能力较强。
本文探讨的迫击炮一维弹道修正引信的基本目的是在不增加士兵后勤负担的情况下,提高步兵迫击炮间接射击的有效性。
一维弹道修正模块使之成为一个灵巧武器,能减小射程误差,提高其打击毁伤效率。
1一维弹道修正模块设计引信对弹道修正模块在各方面有严格的要求和限制,具体如下:(1)弹道修正模块必须在系统通过测量、计算得到的不定时刻t起,通过某种方式显著增加引信在飞行中所受的空气阻力;(2)在t时刻之前,弹道修正模块的附加不应对原弹道特性产生显著影响;(3)由于现实条件限制,引信提供给修正模块的最大空间仅为17 cm3,因此空间利用率愈高愈好;(4)目前技术条件下,引信无法为修正模块提供过多电能,以带动电机等耗能设备;(5)弹丸在飞行过程中不作任何旋转运动,不能提供任何大小的离心力。
基于以上要求,本设计选取可以存储能量的扭转弹簧作为机构打开的动力源。
如图1所示:8个叶片分别受起始角为0°,自然角为108°扭转弹簧作用;固定盘受起始角为0°,自然角为17.5°的扭转弹簧作用。
控制装置在一定时刻释放桨式叶片,通过增大飞行装置与空气的接触面积达到增大空气阻力的目的。
其工作过程如下:机构张开前,8个叶片紧贴飞行装置圆锥状外表面,以尽可能减小对飞行装置原飞行特性的影响。
固定盘由固定销固定于起始位置,其8个支爪则分别抵于8个叶片的底部,从而固定了叶片。
系统发出张开指令后,控制装置引爆微型雷管,利用其爆炸产生的能量拔出固定销,释放固定盘。


一.介绍1.什么是CFD?简单地说,CFD就是利用计算机求解流体流动的各种守恒控制偏微分方程组的技术,这其中将涉及流体力学(尤其是湍流力学)、计算方法乃至计算机图形处理等技术。
因问题的不同,CFD技术也会有所差别,如可压缩气体的亚音速流动、不可压缩气体的低速流动等。
对于暖通空调领域内的流动问题,多为低速流动,流速在10m/s以下;流体温度或密度变化不大,故可将其看作不可压缩流动,不必考虑可压缩流体高速流动下的激波等复杂现象。
从此角度而言,此应用范围内的CFD和数值传热学NHT(Numerical Heat Transfer)等同。
另外,暖通空调领域内的流体流动多为湍流流动,这又给解决实际问题带来很大的困难。
由于湍流现象至今没有完全得到解决,目前HVAC内的一些湍流现象主要依靠湍流半经验理论来解决。
总体而言,CFD通常包含如下几个主要环节:建立数学物理模型、数值算法求解、结果可视化。
2.建立模型建立数学物理模型是对所研究的流动问题进行数学描述,对于暖通空调工程领域的流动问题而言,通常是不可压流体的粘性流体流动的控制微分方程。
另外,由于暖通空调领域的流体流动基本为湍流流动,所以要结合湍流模型才能构成对所关心问题的完整描述,便于数值求解。
如下式为粘性流体流动的通用控制微分方程,随着其中的变量f的不同,如f代表速度、焓以及湍流参数等物理量时,上式代表流体流动的动量守恒方程、能量守恒方程以及湍流动能和湍流动能耗散率方程。
基于该方程,即可求解工程中关心的流场速度、温度、浓度等物理量分布。
3.数值算法上述的各微分方程相互耦合,具有很强的非线性特征,目前只能利用数值方法进行求解。
这就需要对实际问题的求解区域进行离散。
数值方法中常用的离散形式有:有限容积,有限差分,有限元。
目前这三种方法在暖通空调工程领域的CFD技术中均有应用。
总体而言,对于暖通空调领域中的低速,不可压流动和传热问题,采用有限容积法进行离散的情形较多。

车辆冷却风道的一维CFD仿真研究 One Dimensional CFD Simulation Study for WindTunnel of Vehicle韩恺 赵长禄(北京理工大学机械与车辆学院军用车辆动力系统技术国防重点学科实验室)摘 要: 本文利用GT-Suite软件的Cool3D模块和GT-Cool模块离散了车辆冷却风道的3D模型,并采用边界耦合法建立了特殊冷却风道的一维CFD仿真模型。
在此基础上,利用主要部件的性能试验数据建立了某装甲车辆冷却系统模型,研究环境温度和散热器高度变化时对冷却风道主要设计参数之间的影响。
仿真结果为冷却风道的设计提供了理论依据。
关键词:车辆; Cool3D; 冷却风道; 一维CFDAbstract: 3D model of wind tunnel of vehicle is discrete by Cool3D module and GT-Cool module of GT-Suite Software, and One Dimensional CFD simulation model of special wind tunnel is built up by boundary coupling method.On the basis, the cooling system simulation model of the armored vehicle is created by utilizing performance experimental data of main components, and the main design parameters of the wind tunnel versus environment temperature and radiator high is investigated. Simulation results provide theory instruction for design of wind tunnel.Key words: Vehicle; Cool3D; Wind Tunnel; One Dimensional CFD1 引言冷却空气从进入车辆到从车辆排出的全流程所掠过的腔道,称为冷却风道【1】。

第2期(总第229期) 2017年4月车用发动机VEHICLEENGINENo .2(Serial No .229)Apr .2017基于一维-三维耦合仿真的进气系统优化方法董江峰\孙淑慧2,仲蕾s 陈晋兵s 王尚学\牛海杰1(1.中国北方发动机研究所(天津),天津 300400; 2.天津市热电设计院有限公司,天津 300000 )摘要:提出了基于一维-三维耦合仿真的进气系统优化方法,此方法兼具CFD 对进气系统三维流动特性准确描述与一维仿真对内燃机进气系统全局控制的优点。
建立了进气歧管三维模型,采用GT-Power 软件进行缸内工作过程模型仿真,根据试验数据标定仿真模型。
通过一维-三维耦合仿真计算得到进气歧管各转速下的流动参数, 以此作为CFD 仿真的边界条件,优化进气歧管的结构参数。
通过整机试验对进气歧管流动性能进行了验证。
试验结果表明,该方法能够较好地指导进气歧管设计。
关键词:内燃机;仿真;进气歧管;进气均勻性DOI : 10.3969/j .issn .l 001-2222.2017.02.010中图分类号:TK 413.44 文献标志码:B文章编号:1001-2222(2017)02-0056-06油气混合的质量对发动机燃烧过程及整机性能 有着十分重要的影响,而进排气系统设计的优劣会 影响其流动特性,进而影响油气混合质量。
为提高 各缸进气均匀性,降低流通阻力,需要对进气歧管的 结构进行优化,在满足各缸进气均匀性的条件下,尽 可能减小流通阻力,增加进气量,从而增加有效功的 循环输出量,提高柴油机功率密度,同时满足排放法 规要求,这些在工程应用中也是重要的内容〜5]。
国内外在发动机进气系统的流动特性研究方面做了很多工作。
Hoong T T o h 等研究了进气歧管 几何结构对内燃机缸内气体流动的影响规律[6] ;Cui Y 等以整个进气系统作为研究对象,研究了多缸发 动机中间气缸与其他气缸的流量及总压变化[7] ;Y . L.Q i 等研究了在进气冲程时进气门上游漩涡对缸 内流动的影响规律,揭示了滚流率和充量系数的提 高途径[8];蓝志宝等应用C FD 方法进行了进气歧管 的开发研究[9# ;王文、王兴海等对进排气压力波对 缸内燃烧的影响规律进行了试验研究[11_12]。

CFD 数值模拟原理课程总结随着近代科学技术的进步,在绝大部分的研究领域内,人们对常见现象的理论研究已达到了一个崭新的境界,如力学、新材料设计的超分子建筑学、统计物理学、流体力学、传热学、化学反应流等。
与此同时,这些数学物理方程、理论模型或经验模型,在大量的实验研究及工程应用中得到证实。
为了在实际工程运用中能更加直观简洁的描述流体在流场中的流动情况,CFX 软件系列中的CFD ,PRO-E 等软件就能系统的解决流体的数值模拟问题。
CFD 的基本理论基础与流体力学理论基础相似,质量守恒方程,动量守恒方程(牛顿运动定律)和能量守恒方程(热力学第一定律)是CFD 理论的基石和核心。
以下为粘性流体流动的基本方程组:(1)连续性方程: (2)动量方程:(3)能量方程:(4)质量组分分数方程:在粘性流体流动的系统中,以上四个方程构成的方程组是叩开理论流体力学实际问题的基础,同时在CFD 软件运用开发过程中起着理论核心的作用。
二、网格计算中的对流——扩散方程的差分格式分析网格计算中的基本物理概念(1)节点:需要求解未知物理量的空间几何位置;(2)控制容积:空间实体的面积或体积;(3)界面:控制容积之间的分界面;(4)网格线:连接各节点之间的连线。
对于均匀网格,内节点与外节点在区域内的分布趋于一致,仅在坐标轴方向错位半个网格空间;对于不均匀网格计算,内节点永远在控制容积中心,而外节点的界面永远位于两相邻点的中间位置。
在实际工程运算中,内节点网格计算处理特变物理现象比较容易,外节点状态。
由能量守恒微分方程可以推出差分方程,根据工程应用数学所学知识,运用Taylor 展开得到差分方程。
在均匀的网格中,对一维方程,采用不同的离散形式,可以得到相同的差分方程。
但是,这不是普遍现象。
一般情况下,有差别,计算结果的准确度也不有差别。
运用Taylor 展开易于进行数学分析,其缺点是物理概念不清,计算()()0=⋅∇+i i i i i t u ρε∂ρε∂()()()i g s i i i i i i i i i Sc P t +-+∇-=⋅∇+u u u u u βερε∂ρε∂()()()i g s i i i i i i i i i Sc P t+-+∇-=⋅∇+u u u u u βερε∂ρε∂()()()()∑∑==-+-=∇Γ-⋅∇+Np j ik ji jk ij Np j ik i jk j k ij ik i ik ik i i i ik i i Y m Y m Y Y Y Y t Y 11ρρβαρα∂ρα∂u的结果可能违背基本的物理定律。



CFD模拟仿真理论知识:流体仿真应用
本文将介绍CFD(Computational Fluid Dynamics,计算流体动力学)模拟仿真理论知识的原理、方法和应用。
通过本文对CFD的深入理解,并了解如何运用这一理论解决实际问题。
一、CFD模拟仿真理论知识概述
CFD是一种通过计算机模拟和分析流体流动、传热、化学反应等自然现象的学科。
它广泛应用于航空航天、能源、建筑、环境科学、生物医学等领域。
CFD模拟仿真理论知识是CFD的核心,它包括流体动力学基本原理、数值计算方法和计算机程序设计等。
二、CFD模拟仿真基本原理和方法
1.基本原理:CFD基于牛顿第二定律和连续介质假设,通过数值方法求解流体控制方程,如Navier-Stokes方程,以获得流场的定量描述。
2.数值计算方法:常用的CFD数值计算方法包括有限差分法(Finite Difference Method,FDM)、有限元法(Finite Element Method,FEM)、有限体积法(Finite V olume Method,FVM)等。
这些方法将连续的流体流动问题离散为一系列离散点上的数值计算问题,通过求解这些离散点上的数值,得到流场的近似解。
3.计算机程序设计:为了实现CFD模拟仿真的自动化,我们需要编写计算机程序。
常用的编程语言包括Fortran、C++、Python等。
程序应包含建模、离散化、求解和后处理等步骤。
三、CFD模拟仿真难点与挑战。
【干货】本号CFD仿真干货锦集1.Fluent仿真案例2.ANSYS Meshing网格教程3.CFX仿真案例4.CFD前、后处理教程5.CFD技巧6.流体与仪器提示:点击标题,即可跳转到相应文章。
一、Fluent仿真案例1.Fluent声学模型CAA仿真实例-喷嘴噪音2.Fluent仿真燃烧器内甲烷和空气的燃烧3.Fluent欧拉多相流+MRF旋转仿真-气液喷射搅拌器4.Fluent多相流Mixture模型仿真-鼓泡塔反应器的流场5.Fluent的DEM+DDPM模型实例-鼓泡流化床6.Fluent凝固/融解模型实例-液态金属冷却抽出7.Fluent热辐射DO模型实例-汽车车头灯8.Fluent多孔介质模型实例-催化转换器9.Fluent DPM+PDF燃烧仿真实例-液体燃料喷射燃烧10.Fluent可压缩外部流动仿真实例-2D飞机翼型11.Fluent旋转机械MRF仿真实例-旋转搅拌混合器12.Fluent热流耦合仿真实例-风冷发热芯片13.Fluent层流仿真实例-细长管内流动二、ANSYS Meshing网格教程1.ANSYS meshing 网格划分之 - 入门1 - 3D几何边界命名2.ANSYS meshing 网格划分之 - 入门2 - 2D冷热水管几何边界命名3.ANSYS meshing 网格划分之 - 入门3 - 总体网格控制参数详解(上)4.ANSYS meshing 网格划分之 - 入门4 - 总体网格控制参数详解(中)5.ANSYS meshing 网格划分之 - 入门5 - 总体网格控制参数详解(下)6.ANSYS meshing 网格划分之 - 上手1 - 3D tube网格划分7.ANSYS meshing 网格划分之 - 上手2 - 2D冷热水管网格划分三、CFX仿真案例1.手把手教你ANSYS CFX仿真多相流VOF模型-以水池排水为例2.手把手教你ANSYS CFX 模拟气体辐射流动换热3.手把手教你如何用ANSYS CFX仿真流场,以混合器示例4.ANSYS CFX有几种边界条件?该如何选用?四、CFD前、后处理教程1.Fluent的数据如何导入Matlab中进行后处理2.ICEM划分非结构网格,如何提高网格质量?3.教你如何玩转ANSYS CFD-Post后处理模4.教你如何用ANSYS Workbench提取复杂流道5.教你如何用SolidWorks提取复杂装配体的流道五、CFD技巧1.Fluent求解设置中的网格Gradient梯度离散方法选择2.Fluent背景色如何修改3.FLUENT中水-水蒸汽蒸发过程UDF程序及其解释4.FLUENT帮助文件中UDF宏定义实例集锦5.Fluent非稳态计算过程时间步长的设置6.FLUENT中燃烧模拟计算的步骤和原则7.k-ε(epsilon)模型中的K和ε物理意义8.9.Fluent壁面粗糙度的设置10.Fluent仿真中湍流参数的设置11.Fluent的DPM模型中5种颗粒类型,你懂选择吗12.Fluent中离散相DPM模型稳态设置和非稳态设置的区别13.用心整理的一份关于Fluent多相流模型的应用、限制和选择14.谈谈Fluent残差图中continuity不收敛如何处理15.关于在fluent中如何设置边界层随体动的设置方法16.给你全面讲解UDF在Fluent中的应用,你了解UDF吗17.Fluent提供了9个湍流模型,教你如何选择18.用一个例子告诉你,多面体网格在Fluent仿真中的优势六、流体与仪器1.10个目前流行的CFD仿真软件,你了解几个?2.目前流行的CFD网格划分软件,你了解几个?3.一文带你全面了解流体力学是个什么专业4.谈谈常见的几种CFD算法-FVM FDM FEM MPS SPH LBM究竟有什么区别5.为什么流体N-S方程在物理学中最难解的6.CFD工程仿真中基本用到湍流模型,你真的深入了解过湍流吗7.一文带你了解计算流体力学CFD及其应用领域8.流线型-流体力学中的漂亮杰作9.计算流体力学(CFD)理论基础概述10.Fluent中湍流计算中近壁处理对网格的要求,即传说中的Y+值(上)11.Fluent中湍流计算中近壁处理对网格的要求,即传说中的Y+值(下)12.Fluent中壁面函数和粗糙度13.层流技术在飞机上的研究和应用14.一文带你了解流体力学的流动显示与测量技术15.魔性的磁流体16.流体,也可以很文艺!当流体碰上设计,火花就来了17.懂流体力学的画家,才是一个好画家——文森特·梵高18.13种液压阀的动画,再也不用担心选错阀门了19.都是啤酒,为什么黑啤气泡却往下走的?流体力学告诉你20.慢镜头播放你所不了解的“流体力学”21.9种常用流量计的基础知识和比较22.多相流的流量测量方法及其仪器23.计算流体力学(CFD)的有内涵的故事,值得一看24.聊聊流体力学中的雷诺数25.湍流减阻-被 NASA 列为 21世纪的航空关键技术之一26.星空中的湍流27.有关流体的专业词汇大全,收藏这一份就够了28.纳米流体及其应用29.CFD技术和CFD软件有何区别30.流体力学中大名鼎鼎的伯努利方程在实际生活有何应用31.神奇的非牛顿流体,遇强则强,遇弱则弱32.风洞实验室你了解多少?中国有几个?。
CFD simulation in Laval nozzleSIAE 090441313AbstractWe aim to simulate the quasi one dimension flow in the Laval nozzle based on CFD computation in this paper .We consider the change of the temperature ,the pressure ,the density and the speed of the flow to study the flow.The analytic solution of the flow in the Laval nozzle is provided when the input velocity is supersonic.We use the Mac-Cormack Explicit Difference Scheme to slove the question.Key words :Laval nozzle ,CFD,throat narrow.ContentsAbstract .................................................. . (1)Introduction .............................................. .. (2)Simulation of one-dimensional steady flow (3)Basisequations ................................................. (3)Dimensionless .......................................... . (10)Mac -Cormack Explicit Difference Scheme (11)Boundaryconditions ................................................ (13)Reference .............................................. (13)Annex .................................................. .. (14)IntroductionLaval nozzle is the most commonly used components of rocket engines and aero-engine, constituted by two tapered tube, one shrink tube, another expansion tube.Laval nozzle is an important part of the thrust chamber. The first half of the nozzle from large to small contraction to a narrow throat to the middle. Narrow throat and then expandoutwards from small to big to the end. The gas in the rocket body by the front half of the high pressure into the nozzle, through the narrow throat to escape by the rear half. This architecture allows the speed of the air flow changes due to changes in the jet cross-sectional area, the airflow from subsonic to the speed of sound, until accelerated to transonic. So, people flared nozzle called transonic nozzle. Since it was invented by the Swedish Laval, also known as Laval nozzle. Analysis of the principle of the Laval nozzle. The rocket engines of the gas flow in the combustion chamber under pressure, after the backward movement of the nozzle into the nozzle . At this stage, the gas movement follow the principle of "the fluid moves in the tube , the small cross-section at the flow rate large sectional large flow velocity", thus accelerating airflow.Laval nozzleWhen you reach the narrow throat, the flow rate has exceededthe speed of sound. Transonic fluid movement they no longer follow the principle of "cross-section at small velocity, at a flow rate of small cross-section large", but on the contrary the larger cross-sectional flow faster. The gas flow speed is further accelerated to 2-3 km / sec,equivalent to 7-8 times the speed of sound, thus creating a great thrust. The Laval nozzle fact played the role of a "flow rate Enlargement Device". In fact, not just rocket engines, missile nozzle is this horn shape, so the Laval nozzle weapons has a very wide range of applications.Simulation of one-dimensional steady flow1.Basis equationsAs we know,Laval nozzle is a zooming nozzle flow channel to narrow further expansion.Allows the airflow to further accelerate to reach the speed of sound at the throat into a supersonic flow.Now,we want to simulate the quasione-dimension flowing.Firstly,we will analysis on theory.The flow is isentropic,so we can apply the following equations.(1)Continuity equation:In the flow, we need to consider the following physical quantities.The pression ,the temperature ,the speed of the fluid and the cross-section .They are respectively represented by P,T,u,A. We apply the conservation of the mass.we will obtain this equation.))()((du u dA A d uA +++=ρρρAnd then we get=++ρρd u du A dA(2)Equation of momentum(in the direction of the axis) According to the theory of momentum:dAdP P dA A dP P PA uAu du u uA )2())(()(++++-=-+ρρThe simplification of this equation isdP udu -=ρ(3)Energy equation)2(2=+=+=udu dh v h d dh tIdeal gas equation of stateRTMP ρ=R is ideal gas constant,R=8.314J/g/K. M is the masse per mole.(4)The equation of ThermodynamicsP dPRT dT C dP T V T dT C dS dT C dh VdP dh TdS P e h PdV de dS p p p -=-=⇒=-=+=+=;,;V ,T Because the flow is isentropic,sodS=0And we use the equation of momentum,we have1)(T P -∆=∆=∆γγT RC p)(Combine with others equations,we result withRTγ=2uWe called u the speed of sound,we noted a.RTγ=2aWe apply the continuity equation)1(A dA 22-=a uWe defined the Mach numbera u =MIf we have the relation as)48.0tanh(347.0398.1A -+=xWe have the figure ○1Sou du M A A )1(d 2-= M>1,supersonic If dA<0,we have du>0. If dA>0,we have du<0. M<1,subsonicIf dA<0,we have du>0. If dA>0,we have du<0.This is the reason why this architecture allows the speed of the air flow changes due to changes in the jet cross-sectional area, the airflow from subsonic to the speed of sound, until accelerated to transonic.We have the consequence as followsPAMRTMAMP T R t tγγγγγ=-+⋅=-+)1(212)2111(m&1)211(;)211(T 22--+=-+=γγγγM P P M T ttThen we replace P and T in this equation.The consequence will become122)211(211m--+⋅-+=γγγγγM AMP T M Rt t&To simplify)1(212)2111(m-+-+=γγγγMAM T P R tt &In this equation,the variable is the much number,as the speed of the flow is from subsonic to supersonic ,so we can suppose that there exist a critical section where M equal to 1.Then)1(212)21211(1-+*+-+=γγγγMM AAFigure ○2This section is called narrow throat.The same method,we can obtain121122)21121()21121(21121-*-**-++=-++=-++=γγγγγρργγγγM M P PM T TFigure ○3We know the section in narrow throat is minimum.])2111)()1())1(2)1(()111[()(1)1(212)1(212+-+-+++-⋅-+-+-+=γγγγγγγγγγMM M M K AmdM d &we can judge that the function attains the maximum or not)1(212)2111()(f -+-+=γγγMM M2 DimensionlessCombining CFD with one-dimension flow theory,we make the variables dimensionless.According to the condition initial which is given .We note0'0''0'0'0'u lt t A A A lx x u u u T T T ======ρρρWe use the variable dimensionless to represent theequations.And the equations have the following changes (1)Continuity equation'''''''''''''''''''''''ln t 0t x v x A v x v xv x A A v x v ∂∂-∂∂-∂∂-=∂∂⇒=∂∂+∂∂+∂∂+∂∂ρρρρρρρρ‘‘ (2)Equation of momentum)(1v '''''''''''x T x T x v v t ∂∂+∂∂-∂∂-=∂∂ρργ (3)Energy equation)ln ()1(T '''''''''''x A v x v T x T v t ∂∂+∂∂--∂∂-=∂∂γ3.Mac-Cormack Explicit Difference SchemeThen we use the Mac-Cormack Explicit Difference Scheme,theprincipal of this theory is using the surrounding points to present differential parts of a point and we consider the question with one dimension.The distance between two points is h.0222003022200103013003320022000)(2)()(2)()()(!31)()(!21))((f f(x)x f h x f h f f x f h x f h f f hx x hx x x x xf x x x f x f x x ∂∂+∂∂-=∂∂+∂∂+=-=+=-∂∂+-∂∂+∂∂-+≈So we can use two points adjacent to present the differential parts.20310223102)(2)(h f f f x f hf f x f -+=∂∂-=∂∂Using this method,we make an estimation and correct the error. Estimationx nA A v x v v x v t i i t i t i t i t i t i t i t i t i t i ∆-⋅-∆-⋅-∆--=∂∂+++111ln )(ρρρρρ correct the errorx v t t t i t t i t t i t t i ∆--=∂∂∆+-∆+∆+∆+1)(ρρρIntermediate valuet t t i t i t t i ∆∂∂+=∆+)(ρρρ Then the equation has the following change))()((21)(t ti ti av t t t ∆+∂∂+∂∂=∂∂ρρρAt the moment t ,we will know the value in the whole plan . And we define).....,,,,min(54321t N t t t t t ii ii t t t t t t t a v x c t ∆∆∆∆∆∆=∆+∆=∆4.Boundary conditionsHyperbola equation has two characteristics lines.When one of the characteristics lines enter the flow zone .We admit a parameter to be fixed ,otherwise when one of the characteristics go out the flow zone ,we admit a parameter to be a variable depends the time.Applying this theory ,we can determine the boundary conditions.Reference :[1]章利特,高铁瑜,夏庆锋,徐廷相.拉瓦尔喷管的准一维定常流动.中国科技论文在线。
流体动力学中的一维流动模拟引言流体动力学是研究流体力学和固体力学中流体的运动和力学性质的一个分支学科。
在很多实际应用中,对流体流动的模拟和分析是非常重要的。
在这方面,一维流动模拟是一个重要的工具,它可以帮助工程师和科学家更好地理解和预测流体的行为。
本文将介绍一维流动模拟的基本原理和方法。
一维流动模拟的基本原理一维流动模拟是基于一维流动方程组进行求解的。
一维流动方程组是由质量守恒方程和动量守恒方程组成的。
质量守恒方程描述了流体在流动过程中质量的守恒,动量守恒方程描述了流体在流动过程中动量的守恒。
质量守恒方程质量守恒方程可以用连续性方程来表示:$$\\frac{\\partial \\rho}{\\partial t} + \\frac{\\partial(\\rho v)}{\\partial x} = 0$$其中,$\\rho$是流体的密度,v是流体的速度,x是流体流动的坐标。
这个方程描述了流体质量随时间和空间的变化关系。
动量守恒方程动量守恒方程可以用动量守恒方程来表示:$$\\frac{\\partial (\\rho v)}{\\partial t} + \\frac{\\partial(\\rhov^2)}{\\partial x} = -\\frac{\\partial p}{\\partial x} + \\frac{\\partial}{\\partialx}\\left(\\mu \\frac{\\partial v}{\\partial x}\\right)$$其中,p是流体的压力,$\\mu$是流体的动力粘度。
这个方程描述了流体动量随时间和空间的变化关系。
一维流动模拟的方法一维流动模拟可以通过求解一维流动方程组来实现。
常用的求解方法包括有限差分法和有限元法。
有限差分法有限差分法是一种基于差分逼近的数值求解方法。
它将空间和时间离散化,将连续的一维流动方程组转化为离散的代数方程组。
CFD simulation in Laval nozzleSIAE 090441313AbstractWe aim to simulate the quasi one dimension flow in the Laval nozzle based on CFD computation in this paper .We consider the change of the temperature ,the pressure ,the density and the speed of the flow to study the flow.The analytic solution of the flow in the Laval nozzle is provided when the input velocity is supersonic.We use the Mac-Cormack Explicit Difference Scheme to slove the question.Key words :Laval nozzle ,CFD,throat narrow.ContentsAbstract .................................................. . (1)Introduction .............................................. .. (2)Simulation of one-dimensional steady flow (3)Basisequations ................................................. (3)Dimensionless .......................................... . (10)Mac -Cormack Explicit Difference Scheme (11)Boundaryconditions ................................................ (13)Reference .............................................. (13)Annex .................................................. .. (14)IntroductionLaval nozzle is the most commonly used components of rocket engines and aero-engine, constituted by two tapered tube, one shrink tube, another expansion tube.Laval nozzle is an important part of the thrust chamber. The first half of the nozzle from large to small contraction to a narrow throat to the middle. Narrow throat and then expandoutwards from small to big to the end. The gas in the rocket body by the front half of the high pressure into the nozzle, through the narrow throat to escape by the rear half. This architecture allows the speed of the air flow changes due to changes in the jet cross-sectional area, the airflow from subsonic to the speed of sound, until accelerated to transonic. So, people flared nozzle called transonic nozzle. Since it was invented by the Swedish Laval, also known as Laval nozzle. Analysis of the principle of the Laval nozzle. The rocket engines of the gas flow in the combustion chamber under pressure, after the backward movement of the nozzle into the nozzle . At this stage, the gas movement follow the principle of "the fluid moves in the tube , the small cross-section at the flow rate large sectional large flow velocity", thus accelerating airflow.Laval nozzleWhen you reach the narrow throat, the flow rate has exceededthe speed of sound. Transonic fluid movement they no longer follow the principle of "cross-section at small velocity, at a flow rate of small cross-section large", but on the contrary the larger cross-sectional flow faster. The gas flow speed is further accelerated to 2-3 km / sec,equivalent to 7-8 times the speed of sound, thus creating a great thrust. The Laval nozzle fact played the role of a "flow rate Enlargement Device". In fact, not just rocket engines, missile nozzle is this horn shape, so the Laval nozzle weapons has a very wide range of applications.Simulation of one-dimensional steady flow1.Basis equationsAs we know,Laval nozzle is a zooming nozzle flow channel to narrow further expansion.Allows the airflow to further accelerate to reach the speed of sound at the throat into a supersonic flow.Now,we want to simulate the quasione-dimension flowing.Firstly,we will analysis on theory.The flow is isentropic,so we can apply the following equations.(1)Continuity equation:In the flow, we need to consider the following physical quantities.The pression ,the temperature ,the speed of the fluid and the cross-section .They are respectively represented by P,T,u,A. We apply the conservation of the mass.we will obtain this equation.))()((du u dA A d uA +++=ρρρAnd then we get=++ρρd u du A dA(2)Equation of momentum(in the direction of the axis) According to the theory of momentum:dAdP P dA A dP P PA uAu du u uA )2())(()(++++-=-+ρρThe simplification of this equation isdP udu -=ρ(3)Energy equation)2(2=+=+=udu dh v h d dh tIdeal gas equation of stateRTMP ρ=R is ideal gas constant,R=8.314J/g/K. M is the masse per mole.(4)The equation of ThermodynamicsP dPRT dT C dP T V T dT C dS dT C dh VdP dh TdS P e h PdV de dS p p p -=-=⇒=-=+=+=;,;V ,T Because the flow is isentropic,sodS=0And we use the equation of momentum,we have1)(T P -∆=∆=∆γγT RC p)(Combine with others equations,we result withRTγ=2uWe called u the speed of sound,we noted a.RTγ=2aWe apply the continuity equation)1(A dA 22-=a uWe defined the Mach numbera u =MIf we have the relation as)48.0tanh(347.0398.1A -+=xWe have the figure ○1Sou du M A A )1(d 2-= M>1,supersonic If dA<0,we have du>0. If dA>0,we have du<0. M<1,subsonicIf dA<0,we have du>0. If dA>0,we have du<0.This is the reason why this architecture allows the speed of the air flow changes due to changes in the jet cross-sectional area, the airflow from subsonic to the speed of sound, until accelerated to transonic.We have the consequence as followsPAMRTMAMP T R t tγγγγγ=-+⋅=-+)1(212)2111(m&1)211(;)211(T 22--+=-+=γγγγM P P M T ttThen we replace P and T in this equation.The consequence will become122)211(211m--+⋅-+=γγγγγM AMP T M Rt t&To simplify)1(212)2111(m-+-+=γγγγMAM T P R tt &In this equation,the variable is the much number,as the speed of the flow is from subsonic to supersonic ,so we can suppose that there exist a critical section where M equal to 1.Then)1(212)21211(1-+*+-+=γγγγMM AAFigure ○2This section is called narrow throat.The same method,we can obtain121122)21121()21121(21121-*-**-++=-++=-++=γγγγγρργγγγM M P PM T TFigure ○3We know the section in narrow throat is minimum.])2111)()1())1(2)1(()111[()(1)1(212)1(212+-+-+++-⋅-+-+-+=γγγγγγγγγγMM M M K AmdM d &we can judge that the function attains the maximum or not)1(212)2111()(f -+-+=γγγMM M2 DimensionlessCombining CFD with one-dimension flow theory,we make the variables dimensionless.According to the condition initial which is given .We note0'0''0'0'0'u lt t A A A lx x u u u T T T ======ρρρWe use the variable dimensionless to represent theequations.And the equations have the following changes (1)Continuity equation'''''''''''''''''''''''ln t 0t x v x A v x v xv x A A v x v ∂∂-∂∂-∂∂-=∂∂⇒=∂∂+∂∂+∂∂+∂∂ρρρρρρρρ‘‘ (2)Equation of momentum)(1v '''''''''''x T x T x v v t ∂∂+∂∂-∂∂-=∂∂ρργ (3)Energy equation)ln ()1(T '''''''''''x A v x v T x T v t ∂∂+∂∂--∂∂-=∂∂γ3.Mac-Cormack Explicit Difference SchemeThen we use the Mac-Cormack Explicit Difference Scheme,theprincipal of this theory is using the surrounding points to present differential parts of a point and we consider the question with one dimension.The distance between two points is h.0222003022200103013003320022000)(2)()(2)()()(!31)()(!21))((f f(x)x f h x f h f f x f h x f h f f hx x hx x x x xf x x x f x f x x ∂∂+∂∂-=∂∂+∂∂+=-=+=-∂∂+-∂∂+∂∂-+≈So we can use two points adjacent to present the differential parts.20310223102)(2)(h f f f x f hf f x f -+=∂∂-=∂∂Using this method,we make an estimation and correct the error. Estimationx nA A v x v v x v t i i t i t i t i t i t i t i t i t i t i ∆-⋅-∆-⋅-∆--=∂∂+++111ln )(ρρρρρ correct the errorx v t t t i t t i t t i t t i ∆--=∂∂∆+-∆+∆+∆+1)(ρρρIntermediate valuet t t i t i t t i ∆∂∂+=∆+)(ρρρ Then the equation has the following change))()((21)(t ti ti av t t t ∆+∂∂+∂∂=∂∂ρρρAt the moment t ,we will know the value in the whole plan . And we define).....,,,,min(54321t N t t t t t ii ii t t t t t t t a v x c t ∆∆∆∆∆∆=∆+∆=∆4.Boundary conditionsHyperbola equation has two characteristics lines.When one of the characteristics lines enter the flow zone .We admit a parameter to be fixed ,otherwise when one of the characteristics go out the flow zone ,we admit a parameter to be a variable depends the time.Applying this theory ,we can determine the boundary conditions.Reference :[1]章利特,高铁瑜,夏庆锋,徐廷相.拉瓦尔喷管的准一维定常流动.中国科技论文在线。