红外线通讯协议 V1.1
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:79.10 KB
- 文档页数:13

电子报/2006年/7月/16日/第013版资料(开发)常用红外遥控信号传输协议详解(一)四川杨叶珍编者按:红外遥控器应用非常广泛,但由于各个厂家设计的遥控器种类各异,因而针对各类不同电子产品,采用的红外遥控器也就不完全相同,除了遥控器本身的造型外,起决定因素的是红外遥控信号传输协议。
目前,多数电子设计人员在设计产品遥控部分时,大多采用现成的遥控套件,或依靠现成的红外遥控接收程序,直接进行应用。
这一切原因,源于大多电子设计工程师难以了解到更多的红外遥控信号传输协议,故此仅能“照搬”制作。
本文(将分3期连续)介绍常见的8种红外遥控信号传输协议,这些协议是非常实用的,不仅是一套全面的红外遥控协议概念,更便于掌握和选择设计更优异的红外遥控产品。
常用的红外线信号传输协议有ITT协议、NEC协议、Nokia NRC协议、Sharp协议、Philips RC -5协议、Philips RC-6协议,Philips RECS-80协议,以及Sony SIRC协议等,下面分别进行介绍。
一、ITT协议ITT是最早的一种红外线传输协议。
该协议没有象其他协议那样使用载波频率传输红外线信号,而是用宽度为10μs的14个脉冲进行遥控命令的传送,通过改变脉冲的间距对命令进行编码。
用ITT协议传输数据非常可靠,而且功耗极低。
在欧洲,包括ITT(国际电话电报公司)、Greatz、Schaub-Lorenz、Fin-lux、Nokia等在内的很多公司均采用此协议做用户电子标签。
1.主要特性:每条信息只有14个非常窄的脉冲(脉宽10μs),不对信号进行调制;采用脉冲距离编码;电池寿命极长;4位地址码、6位命令码;带时间自校准,发送器中可使用RC振荡器;通信速度快,发送一条信息只需1.7ms~2.7ms;应用该协议的器件生产厂家有Intermetal、Micronas 等。
2.协议:14个脉冲传送1条红外信息,每个脉冲宽10μs,用三种不同的脉冲周期来区别每位所表达的内容:100μs表示二进制的“0”,200μs表示“1”, 300μs表示预备脉冲或结束脉冲。



第五章总结与期望摘要红外无线通信,通常又叫红外光通信,是利用红外线传送信息的一种通信方式。
红外线通信所传输的内容是多样的,可以是音频信号,也可以是视频信号。
利用红外线,可以构成无绳电话及无线耳机系统。
红外线的传输距离不远,一般在十米以内,但可以避免频谱占用,信号失真等电气指标较易处理,应用于普通的办公室和家庭等场合应该已经可以满足要求。
红外线的应用范围很广,电视机、空调、微波炉等凡涉及到遥控的家电,一般均采用红外线来作为信号传输的载体。
本次设计的红外无线通信系统主要是传递音频信号。
该系统是由发射模块和接收模块组成。
发射模块的输入与音响设备相连接,从音响设备输出的音频信号调制红外光以后,由红外光发射机将调制的红外光向空间发射。
红外无线系统的接收部分将接收到的已调制红外光进行解调,还原出音频信号,然后送到扬声器发出声音。
本次设计的电路系统具有实用、成本低廉、使用方便的优点。
关键词红外线、发射、接收、调制、解调目录中文摘要 (Ⅰ)英文摘要 (Ⅱ)0 引言1 红外发射系统1.1 红外发射系统组成框图1.2 红外发射系统的工作原理分析1.2.1 直流稳压电源..............................................1.2.2 音频放大电路..............................................1.2.3 高频振荡电路..............................................1.2.4 高频放大电路..............................................1.2.5 频率调制电路..............................................1.2.6 高频功放电路..............................................1.2.7 红外发射电路..............................................2 红外接收系统2.1 红外接收系统的组成框图2.2 红外接收系统的工作原理分析2.2.1 直流稳压电源.................................................2.2.2 红外接收电路.................................................2.2.3 高频放大电路.................................................2.2.4 频率解调电路.................................................2.2.5 音频功放电路.................................................2.2.6 扬声器.......................................................3 红外通信系统的仿真3.1 仿真软件的介绍3.2 仿真调试4.安装、焊接、调试及性能分析5.结论6.致谢7.参考文献0 引言随着计算机与通信技术的飞速发展,计算机通信得到广泛应用,硬件技术可谓是日新月异,其总体趋势向着高集成度、高稳定性、高速和高性价比方向发展。

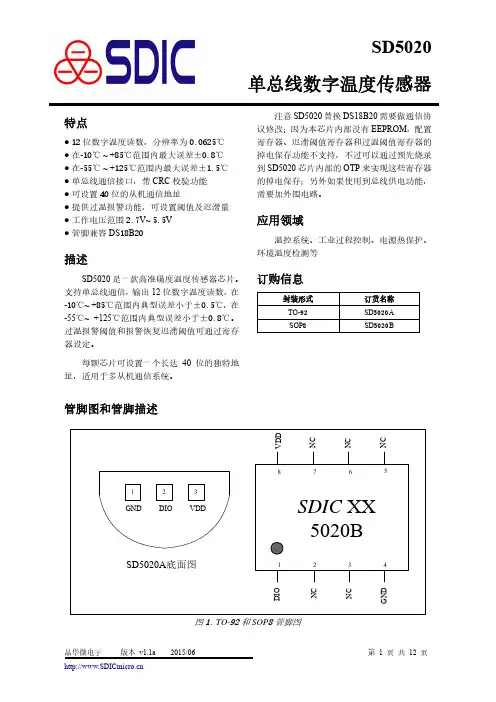
SD5020单总线数字温度传感器特点● 12位数字温度读数,分辨率为0.0625℃ ● 在-10℃ ~ +85℃范围内最大误差±0.8℃ ● 在-55℃ ~ +125℃范围内最大误差±1.5℃ ● 单总线通信接口,带CRC 校验功能 ● 可设置40位的从机通信地址● 提供过温报警功能,可设置阈值及迟滞量 ● 工作电压范围2.7V~ 5.5V ● 管脚兼容DS 18B 20描述SD5020是一款高准确度温度传感器芯片。
支持单总线通信,输出12位数字温度读数,在-10℃~ +85℃范围内典型误差小于±0.5℃,在-55℃~ +125℃范围内典型误差小于±0.8℃。
过温报警阈值和报警恢复迟滞阈值可通过寄存器设定。
每颗芯片可设置一个长达40位的独特地址,适用于多从机通信系统。
注意SD5020替换DS18B20需要做通信协议修改;因为本芯片内部没有EEPROM ,配置寄存器、迟滞阈值寄存器和过温阈值寄存器的掉电保存功能不支持,不过可以通过预先烧录到SD5020芯片内部的OTP 来实现这些寄存器的掉电保存;另外如果使用到总线供电功能,需要加外围电路。
应用领域温控系统、工业过程控制、电源热保护、环境温度检测等订购信息封装形式 订货名称 TO-92 SD 5020A SOP 8SD 5020B管脚图和管脚描述图1. TO-92和SOP 8管脚图表1. 管脚描述序号管脚名称属性管脚描述SD 5020A (TO-92)SD 5020B (SOP 8)21 DIO 输入/输出 开漏端口,单总线数据通信口-- 2--3,5--7NC -- 悬空 1 4 GND 地 地38VDD电源电源功能描述图2. 功能框图图2是SD 5020的功能模块框图。
SD 5020是一个单总线通信的数字温度传感器,DIO 管脚需要外接一个上拉电阻。
每一颗芯片内都设置了独特的40位从机地址,适合多从机通信。

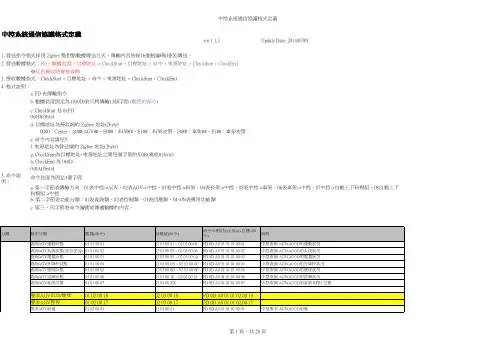
ver 1.1.3Update Date: 2014/07/01※紅色接收時會被省略c. CheckStart 為 0xFD 0x0D(2byte)h. CheckEnd 為 0x0D 0x0A(2byte)5. 命令說明:命令長度為固定4個字節b . 第二字節表功能分類:01表查詢類、02表控制類、03表回應類、04~0N表專用功能類中控系統通信協議格式定義b. 數據長度固定為 (0x0D)表示將傳輸13個字節 (藍色的部分)e. 命令內容請見5.d. 目標地址為接收端的 Zigbee 地址(2byte)1. 發送指令格式採用 Zigbee 點對點數據傳送方式,傳輸內容皆採16進制編碼(HEX)傳送。
3. 接收數據格式:CheckStart + 目標地址 + 命令 + 來源地址 + CheckSum + CheckEnd f. 來源地址為發送端的 Zigbee 地址(2byte) 0000:Center、A0##:AGV##、E0##:料架##、E1##:料架皮帶、F0##:車架##、F1##:車架皮帶c. 第三、四字節表命令編號或傳遞數據的內容。
4. 格式說明:a. FD 表傳輸指令g. CheckSum為目標地址~來源地址之間每個字節的XOR(異或)(1byte)a. 第一字節表傳輸方向:01表中控->AGV、02表AGV->中控、03表中控->料架、04表料架->中控、05表中控->車架、06表車架->中控、07中控->自動上下料模組、08自動上下料模組->中控2. 發送數據格式:FD + 數據長度 + 目標地址 + CheckStart + 目標地址 + 命令 + 來源地址 + CheckSum + CheckEnd。

红外通信标准是一种无线通信技术标准,它利用红外线进行数据传输。
红外通信标准被广泛应用于各种设备之间的短距离通信,如手机、PDA、笔记本电脑等。
红外通信标准的主要优点是传输速度快、成本低廉、易于实现。
由于红外线在空气中的传播速度非常快,因此红外通信可以实现高速数据传输,适用于需要快速传输大量数据的场景。
此外,红外通信设备的成本相对较低,使得这种技术在许多消费电子产品中得到了广泛应用。
然而,红外通信也存在一些局限性。
首先,红外线在传输过程中容易受到环境光线的影响,导致信号干扰和传输距离受限。
其次,红外通信需要设备之间保持一定的对准角度和距离,对使用者的操作要求较高。
总之,红外通信标准作为一种成熟的无线通信技术,在许多领域发挥着重要作用。
随着技术的不断发展,未来红外通信有望实现更高的传输速度和更稳定的性能,以满足不断增长的无线通信需求。
红外通信原理——NEC红外协议IDEA 2012年8月4日星期六红外线遥控是目前使用最广泛的一种通信和遥控手段。
由于红外线遥控装置具有体积小、功耗低、功能强、成本低等特点,因而,继彩电、录像机之后,在录音机、音响设备、空凋机以及玩具等其它小型电器装置上也纷纷采用红外线遥控。
工业设备中,在高压、辐射、有毒气体、粉尘等环境下,采用红外线遥控不仅完全可靠而且能有效地隔离电气干扰。
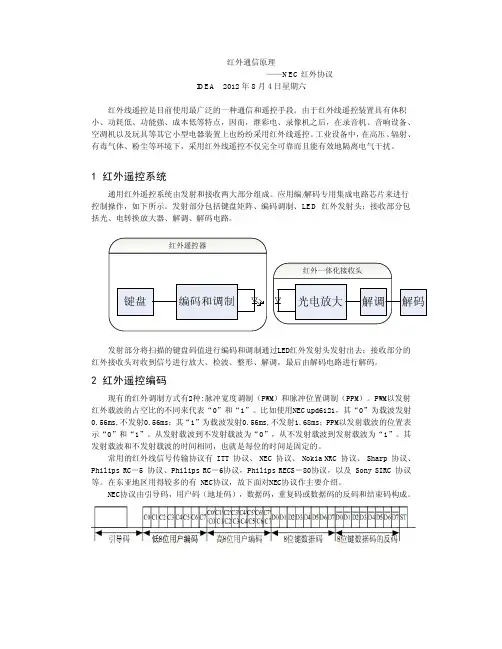
1 红外遥控系统通用红外遥控系统由发射和接收两大部分组成。
应用编/解码专用集成电路芯片来进行控制操作,如下所示。
发射部分包括键盘矩阵、编码调制、LED 红外发射头;接收部分包括光、电转换放大器、解调、解码电路。
发射部分将扫描的键盘码值进行编码和调制通过LED红外发射头发射出去;接收部分的红外接收头对收到信号进行放大、检波、整形、解调,最后由解码电路进行解码。
2 红外遥控编码现有的红外调制方式有2种:脉冲宽度调制(PWM)和脉冲位置调制(PPM)。
PWM以发射红外载波的占空比的不同来代表“0”和“1”。
比如使用NEC upd6121,其“0”为载波发射0.56ms,不发射0.56ms;其“1”为载波发射0.56ms,不发射1.68ms;PPM以发射载波的位置表示“0”和“1”。
从发射载波到不发射载波为“0”,从不发射载波到发射载波为“1”。
其发射载波和不发射载波的时间相同,也就是每位的时间是固定的。
常用的红外线信号传输协议有 ITT 协议、 NEC 协议、 Nokia NRC 协议、 Sharp 协议、Philips RC-5 协议、Philips RC-6协议,Philips RECS-80协议,以及 Sony SIRC 协议等。
在东亚地区用得较多的有 NEC协议,故下面对NEC协议作主要介绍。
NEC协议由引导码,用户码(地址码),数据码,重复码或数据码的反码和结束码构成。
①引导码由一个9ms的载波波形和4.5ms的关断时间(低电平)构成;②地址码共16bits,低8位在前,高8位在后。

1376.1-2013版规约与376.1-2009版规约差异分析V1.12014年1月目录目录I第1章概述 (2)1.1背景 (2)1.2目的 (2)第2章规约变更内容 (3)2.1帧格式变更 (3)2.1.1功能码 (3)2.1.2帧序列域SEQ (3)2.1.3数据单元标识 (4)2.1.4附加信息域AUX (4)2.2报文应用及数据结构变更 (5)2.2.1确认/否认(AFN=00H) (5)2.2.2链路接口检测(AFN=02H) (5)2.2.3设置参数(AFN=04H) (6)2.2.4控制命令(AFN=05H) (11)2.2.5身份认证及密钥协商(AFN=06H) (12)2.2.6请求终端配置及信息(AFN=09H) (19)2.2.7请求1类数据(AFN=0CH) (21)2.2.8请求2类数据(AFN=0DH) (29)2.2.9请求3类数据(AFN=0EH) (38)2.2.10文件传输(AFN=0FH) (42)2.2.11数据转发(AFN=10H) (44)第3章与重庆规约扩展冲突 ..................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
3.1控制命令(AFN=05H)...................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
3.1.1下行报文..................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
第1章概述1.1背景国家电网公司在2013年颁布了Q/GDW1376—2013《电力用户用电信息采集系统通信协议》。
该协议是根据《关于下达2012年度国家电网公司技术标准制(修)订计划的通知》(国家电网科[2012]66号)的要求,对Q/GDW 376—2009《电力用户用电信息采集系统通信协议》的修订。
红外光通信装置的设计吴守霞;彭琳茹【摘要】以LM386和红外光收发对管为核心元件,通过红外光定向传输语音信号,并具有环境温度实时检测功能.该设计中,音频信号经过发射电路转换为光强变化的红外光信号,接收电路接收到红外光,经LM386集成音频运放处理通过扬声器还原成声音.由DS18B20采集环境温度,经单片机STC12C5A60S2数据编码后发射,接收电路接收的红外光信号,经单片机解码后通过LCD液晶显示实时温度.【期刊名称】《工业仪表与自动化装置》【年(卷),期】2015(000)006【总页数】4页(P97-99,104)【关键词】红外光;通信;发射;接收【作者】吴守霞;彭琳茹【作者单位】兰州工业学院电子信息工程学院,兰州730050;兰州工业学院电子信息工程学院,兰州730050【正文语种】中文【中图分类】TN929.10 引言红外光通信是利用红外光传输数据,是一种短距离自由空间光通信方式,因其频带宽、抗干扰性强、发射功率小,适应于低成本的通信方式。
该文设计的红外光通信装置以红外发光管来定向传输语音信号,能够近距离传输频率为300~3400 Hz的语音信号,接收的声音应无明显失真;当发送端输入的语音信号改为800 Hz单音信号时,在8Ω电阻负载上,接收装置的输出电压有效值不小于0.4 V;增加一路数字信道能够传输环境温度,并在接收端显示。
1 系统设计方案1.1 基础部分方案论证与比较方案一:通过单片机实现语音信号的红外光传输。
该方案信号发射部分由信号调理电路、信号处理电路、发射电路组成,信号接收部分由调制解调电路和音频处理电路组成。
由于红外光接收管采样速率的限制,连续的声音信号将会产生严重失真,故放弃此方案。
但是该文方案中的温度信号传输采用方案一的方法。
方案二:采用LM386音频集成运放实现声音信号的红外光传输。
发射电路部分由模拟电路组成,红外光发射管发出红外光随音频信号的变化而变化,通过红外光传输声音信号。
全电子式多功能三相交流电能表数据通信协议(V1.0/V2.0/V2.1/ V3.0/V4.0/ V4.1)(适用于RS-485/RS-232)(威胜集团)湖南威胜电子有限公司HUNAN WEISHENG ELECTRONICS CO.,L TD.WEISHENG GROUP CORP.二零零零年六月全电子式多功能三相交流电能表数据通信协议(V1.0/V2.0/V2.1/ V3.0/V4.0/ V4.1)(适用于RS-485/RS-232)随着威胜全电子式多功能三相交流电能表在国内的广泛使用,以及当前各地建设现代化用电管理系统的迫切要求,越来越多的用户和厂家在充分肯定威胜电表高精度、高可靠性和功能完善的同时,也对电表的数据通信接口提出了一些建议和要求。
为进一步完善威胜全电子式多功能三相交流电能表数据通信接口的技术要求,提高电表数据通信接口的可靠性和通信效率,增加通过通信接口可进行上/下装数据内容,本公司在兼容原通信协议(技术要求)的基础上,特对通信协议(技术要求)进行了系统补充和完善。
本协议以电力负荷管理终端与电表进行数据通信为例进行说明,但不限于此。
本协议是所有通信内容的全集,当用户在具体使用本协议时,请仔细确认电表的通信软件版本、功能、型号等有关说明,以确定实际适用的子集。
本协议所有版本向上兼容,高版本协议内容包含低版本协议内容。
协议按《标志字节》升序排序。
本协议于1997年1月制定含V1.0、V2.0、V3.0的通信协议,并根据我公司通信型电子式电能表的发展,于1998年11月制定V4.0通信协议,于1999年1月制定V4.1通信协议,于2000年05月制定V2.1通信协议。
V1.0版协议为基本内容,并且参数设置命令无密码保护。
V2.0版协议在V1.0的内容上增加标有“V20☆”符号的内容,分参数设置命令有密码保护和无密码保护两大类。
V2.1版协议在V2.0版协议基础上增加标注“V21▴”符号的内容,为DTSD341-3型表威胜协议。
红外通信标准红外通信是一种无线通信技术,利用红外光来实现传输信息。
它在日常生活中得到广泛应用,例如遥控器、红外耳机、红外数据传输等。
为了确保不同设备之间的兼容性,红外通信标准的制定变得尤为重要。
下面是一些与红外通信标准相关的内容。
1. 红外通信标准的定义和分类:- 红外通信标准是针对红外通信技术制定的规范,用于确保不同设备之间的互操作性。
- 红外通信标准可以根据不同的应用领域进行分类,例如红外遥控、红外通信、红外数据传输等。
2. 红外通信标准的国际组织:- 国际电信联盟(ITU)是一个重要的国际组织,它发布了一系列关于红外通信的标准。
- 例如ITU-T H.610是关于树莓派红外遥控器编码的标准,ITU-T H.610.1是关于红外通信设备的通信速率的标准。
3. 红外通信标准的制定过程:- 红外通信标准的制定过程通常由国际组织、行业协会、技术委员会等机构来组织。
- 制定红外通信标准需要考虑技术可行性、兼容性、安全性等因素,并通过一系列的测试和验证来确保标准的质量和可靠性。
4. 红外通信标准的主要内容:- 红外通信标准通常包括红外通信协议、红外编码解码方法、通信速率、通信距离等方面的内容。
- 红外通信协议用于定义通信的格式和数据交换过程,例如红外遥控通常使用的NEC协议。
- 红外编码解码方法用于将信息编码成红外脉冲信号,并将接收到的红外信号解码成原始信息。
- 通信速率和通信距离是红外通信标准中关键的参数,不同的应用场景需要不同的速率和距离支持。
5. 红外通信标准的应用举例:- 红外遥控是红外通信的常见应用之一,它使用特定的红外编码协议来实现设备的控制。
- 红外通信还广泛应用于电脑配件,例如红外鼠标、红外键盘等,用于实现与计算机的无线连接。
- 红外数据传输则用于实现设备之间的数据交换,例如红外数据传输接口(IrDA)标准被广泛应用于移动设备、摄像机等。
6. 红外通信标准的发展趋势:- 随着无线通信技术的不断发展,红外通信标准也在不断演进和更新。
出入口相机HTTP通信协议V1.2修改记录目录修改记录 (1)一.协议概述 (3)二.相机端配置说明 (4)三.数据类型定义 (6)四.车牌识别结果交互数据内容说明 (8)五.IO输入触发交互数据内容说明 (11)六.串口输入交互数据内容说明 (12)七.心跳交互数据内容说明 (14)八.白名单查询,交互数据内容说明 (16)九.白名单添加,交互数据内容说明 (17)十.删除全部白名单,交互数据内容说明 (19)十一删除指定白名单,交互数据内容说明 (20)一.协议概述相机端基于HTTP V1.1 版本。
这种方式需要用户建立一个HTTP服务器,同时将这台HTTP服务器的地址配置给一体机。
当一体机有识别结果后(或者其他需要推送的内容时),就会往指定的地址发HTTP命令。
数据交互内容采用JSON格式,区分大小写。
二.相机端配置说明三.数据类型定义1.车牌颜色宏定义E_PlateColortypedef enum{UNKNOWN_PLATE = 0,BLUE_PLATE, /*蓝牌*/YELLOW_PLATE, /*黄牌*/WHITE_PLATE,/* 白牌*/BLACK_PLATE, /*黑牌*/GREEN_PLATE, /*绿牌*/YELLOW_GREEN_PLATE, /*黄绿牌*/BLACK_PLATE_OTHER}E_PlateColor;2.车牌类型宏定义ITS_PlateTypetypedef enum{PLATE_TYPE_NULL=0, //未知PLATE_TYPE_BLUE, //普通蓝牌PLATE_TYPE_BLACK, //普通黑牌PLATE_TYPE_YELL, //普通黄牌PLATE_TYPE_YELL2, //双层黄牌PLATE_TYPE_POL, //警察车牌PLATE_TYPE_APOL, //武警车牌PLATE_TYPE_APOL2, //双层武警PLATE_TYPE_ARM, //单层军牌PLATE_TYPE_ARM2, //双层军牌PLATE_TYPE_INDI, //个性车牌PLATE_TYPE_NEWN, //新能源小车牌PLATE_TYPE_NEWN1, //新能源大车牌PLATE_TYPE_EMB, //大使馆车牌PLATE_TYPE_CON, //领事馆车牌PLATE_TYPE_MIN, //民航车牌}ITS_PlateType;3.车型宏定义E_VehiclSiezetypedef enum{UNKNOWN_SIZE,LARGE_VEHICLE, /*大型车*/MIDDLE_VEHICLE, /*中型车*/SMALL_VEHICLE, /*小型车*/ }E_VehiclSieze;4.触发方式定义E_SnapModetypedef enum{SNAP_MODE_UNKNOW = 0,SNAP_MODE_MANUAL, /*手动*/SNAP_MODE_VIDEO, /*视频*/SNAP_MODE_LOOP, /*线圈*/SNAP_MODE_MAX,}E_SnapMode;四.车牌识别结果交互数据内容说明1.相机端请求数据内容{"AlarmInfoPlate" : {"channel" : 0,"deviceName" : "default","ipaddr" : "192.168.0.100","result" : {"PlateResult" : {"bright" : 0,"carBright" : 0,"carColor" : 0,"colorType" : 0,"colorValue" : 0,"confidence" : 0,"direction" : 0,"license" : "_无_","location" : {"RECT" : {"left" : 0,"top" : 0,"right" : 0,"bottom" : 0}},"timeStamp" : {"Timeval" : {"sec" : 1441815171,"usec" : 0}},"timeUsed" : 0,"triggerType" : 1,"type" : 0}},"serialno" : "e10b2d6c8c07b422361457935b518642"}}2.HTTP服务器应答数据内容{"Response_AlarmInfoPlate":{"info":"ok","content":"retransfer_stop","is_pay":"true","serialData":[{"serialChannel":0,"data":"MTEyMzQ1Njc4OQ==","dataLen":10},{"serialChannel":1,"data":"MTEyMzQ1Njc4OQ==","dataLen":10}]}}五.IO输入触发交互数据内容说明1.相机端请求数据内容{"AlarmGioIn" : {"deviceName" : "default","ipaddr" : "192.168.0.100","result" : {"TriggerResult" :{"source" : 0,"value" : 0}},"serialno" : "e10b2d6c8c07b422361457935b518642"}}2.HTTP服务器应答数据内容回复数据无六.串口输入交互数据内容说明1.相机端请求数据内容{"SerialData":{"channel":0,"serialno":"e10b2d6c8c07b422361457935b518642","ipaddr":"192.168.0.100","serialChannel":0,"data":"MTEyMzQ1Njc4OQ==","dataLen":10}}2.HTTP服务器应答数据内容{"Response_SerialData":{"info":"","serialData":[{"serialChannel":0,"data":"MTEyMzQ1Njc4OQ==","dataLen":10},{"serialChannel":1,"data":"MTEyMzQ1Njc4OQ==","dataLen":10}]}}七.心跳交互数据内容说明1.相机端请求数据内容{"Heartbeat":{"countid":1,"timeStamp" :{"Timeval" : {"sec" : 1441815171,"usec" : 0}},"serialno" : "e10b2d6c8c07b422361457935b518642"}}2.HTTP服务器应答数据内容回复数据无或者回复下面内容{"Response_Heartbeat":{"info":"ok","serialData":[{"serialChannel":0,"data":"MTEyMzQ1Njc4OQ==","dataLen":10},{"serialChannel":1,"data":"MTEyMzQ1Njc4OQ==","dataLen":10}],"shutoff":"ok","snapnow":"yes"}}八.白名单查询,交互数据内容说明说明:HTTP交互流程是基于一个请求一个应答的。
PMAC®802低压电动机保护控制器MODBUS串行通信协议V1.0ZHUHAI PILOT TECHNOLOGY Co.,Ltd珠海派诺科技股份有限公司目录第一章简介 (3)1.1 串行通讯协议的目的 (3)1.2 MODBUS通讯协议的版本 (3)第二章PMAC®802-MODBUS 串行通信协议详细说明 (3)2.1 PMAC®802-MODBUS协议基本规则 (3)2.2 传送模式 (3)2.3 MODBUS包裹结构描述 (3)2.4 网络时间考虑 (4)2.5 异常响应 (4)2.6 广播命令 (5)第三章通讯包裹 (5)3.1 读寄存器(功能码03) (5)3.2 写寄存器(功能码16) (5)第四章计算CRC-16 (6)第五章PMAC®802寄存器说明 (7)5.1实时数据寄存器 (7)5.2 设备参数寄存器 (12)5.3 保护整定参数寄存器 (14)5.4 控制寄存器 (17)5.5 故障记录寄存器 (17)5.6 时钟寄存器 (18)5.7 欠压重启动功能寄存器 (18)第一章简介通信协议详细地描述了PMAC®802在MODBUS通讯模式下的输入和输出命令、信息和资料,以便第三方使用和开发。
1.1 串行通讯协议的目的通信协议的作用使信息和资料在上位机(主站)和PMAC®802之间有效地传递,它包括:1)允许主站访问和设定所接PMAC®802的全部设置参数;2)允许访问PMAC®802的所有测量资料和事件纪录。
1.2 MODBUS通讯协议的版本该通讯协议适用于本公司已经出厂的所有各种版本的PMAC®802仪表,对于日后的系列若有改动会加以特别说明。
第二章PMAC®802-MODBUS 串行通信协议详细说明2.1 PMAC®802-MODBUS协议基本规则以下规则确定在RS485(或者RS232C)回路控制器和其它RS485串行通信回路中设备的通信规则:1)所有RS485回路通信应遵照主/从方式。
Infrared Data AssociationPlug and Play ExtensionstoLink Management Protocol
Version 1.1Monday, January 08, 1996Intel CorporationMicrosoft Corporation Plug and Play with IR devices2
1. IntroductionThere are two scenarios in IR device inter-operability:
• Communication between a host (PC) and a peripheral.• Communication between two hosts.
The differentiating feature in the two scenarios is that in the first case, an IR peripheral is logicallya part of the host (as far as the user is concerned), while in the other, the two hosts are logicallyindependent units. There are Plug and Play issues in both cases.
ScopeThe software layers proposed by IrDA enable two IR devices to communicate with each other.Communication capability alone does not imply Plug and Play. This document focuses on Plugand Play issues pertaining to host and peripheral inter-operability. This document does not addressPlug and Play issues supporting the physical infrared provider. The physical infrared provider issimilar to any other physical device and PnP issues of this device are addressed in the standard PnPworld.
The above diagram illustrates the software stack on a typical IrDA approved PnP compatibledevice. The stack pictured on the left portrays a PnP ready OS and the layers required to support a
Diagram of software layers required for a COMM Device.PhysicalIR Provider
Device PersonalityCOMM, LPT, PPP, WinSock
IrLAP/IrLMP Protocol Stack
PnP
Extensions
ôPhysicalIR Provider
COMM Personality IrLMPIrLAP
PnP
Extensions
ô Plug and Play with IR devices3
general IrDA PnP implementation. The stack on the right depicts an IrDA approved device whichonly needs software enough to support it’s own device.
Plug and Play issues between two hosts will be addressed at a later time. Currently, we do notaddress Plug and Play with IR peripherals needed at boot, for example, a keyboard.
References[EISA]EISA specification version 3.12[WinID]Windows Generic Device ID specification[PnP]Plug and Play Device Driver Developer's Guide[IrLAP]Infrared Data Association Link Access Protocol[IrLMP]Infrared Data Association Link Management Protocol Plug and Play with IR devices4
2. TerminologyDevice IDA Device ID is an uncompressed EISA Device ID.EISA Device IDAn EISA device ID is a seven character field consisting of a three-character manufacturer code, a three-character hexadecimal productidentifier and a one character hexadecimal revision number.HostIn the context of this document, a host is the entity that has discoveredan IR device.IASInformation Access Service. This is an information service that mustbe provided by every IrDA device. The information available via theIAS contains a description of the services being offered by an IrDAdevice to other IrDA devices.IAPInformation Access Protocol, IrLMP defined function set required toaccess the IAS data.IrDAInfrared Data Association. The Standards body responsible forinfrared PC standards.IrLAPInfrared Link Access ProtocolInitiatorStation performing the IrLAP discovery procedure.IrLMPInfrared Link Management ProtocolLSAPLink Service Access PointIR DeviceAn IR entity that responds to the XID discovery process.IR PeripheralAn IR device that provides one or more peripheral functions to a hostvia an IR connection.Multi-function DeviceA peripheral device that supports more than one logical function. Forexample a device that provides modem access plus printer services.PeripheralA device external to a Host that provides a specific function to thathost.Windows Device IDA Windows Device ID is a PnP Device ID. This list of PnP deviceID’s is currently maintained by Microsoft.ResponderA station that responds to an IrLAP discovery procedure. Plug and Play with IR devices5
3. Plug and Play IssuesMany PnP add-in device issues are not relevant for IR devices. IR devices have no need tocontend for physical resources such as IRQ’s and IO mappings. However, the IrLAP physicalcommunication device is a standard PnP device consuming physical resources. IR peripherals doneed a mechanism for device identification.
For transparency and ease-of-use reasons, connecting to an IR peripheral must be logically similarto connecting to a physically attached peripheral. Once discovered and integrated, the IRperipheral should appear in the host’s view of the underlying hardware. In a like manner, when theuser removes the peripheral, it should be removed from the host’s view. In current Microsoftproducts, this view typically appears in the Registry.