电子专业中英文翻译
- 格式:doc
- 大小:626.00 KB
- 文档页数:15
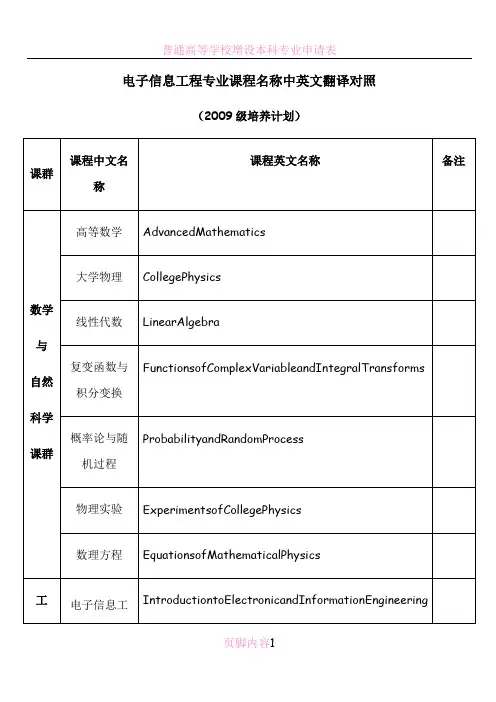


The report concludesThe report mainly collected from the power transmission and power system requirements related to the content of these twoareas, and analyze, to understand some of the relevant knowledge.Page2 Electrical Energy Transmission(电能输送)1 English textFrom reference 1Growing populations and industrializing countries create huge needs for electrical energy. Unfortunately, electricity is not alwaysused in the same place that it is produced, meaning long-distance transmission lines and distribution systems are necessary. Buttransmitting electricity over distance and via networks involves energy loss.So, with growing demand comes the need to minimize this loss to achieve two main goals: reduce resource consumption whiledelivering more power to users. Reducing consumption can be done in at least two ways: deliver electrical energy more efficientlyand change consumer habits.Transmission and distribution of electrical energy require cables and power transformers, which create three types of energy loss:the Joule effect, where energy is lost as heat in the conductor (a copper wire, for example); magnetic losses, where energy dissipates into a magnetic field;the dielectric effect, where energy is absorbed in the insulating material.The Joule effect in transmission cables accounts for losses of about 2.5 % while the losses in transformers range between 1 % and2 % (depending on the type and ratings of the transformer). So, saving just 1 % on the electrical energy produced by a powerplant of 1 000 megawatts means transmitting 10 MW more to consumers, which is far from negligible: with the same energy we cansupply 1 000 - 2 000 more homes.Changing consumer habits involves awareness-raising programmers, often undertaken by governments or activist groups. Simplethings, such as turning off lights in unoccupied rooms, or switching off the television at night (not just putting it into standbymode), or setting tasks such as laundry for non-peak hours are but a few examples among the myriad of possibilities.On the energy production side, building more efficient transmission and distribution systems is another way to go about it. Highefficiency transformers, superconducting transformers and high temperature superconductors are new technologies which promisemuch in terms of electrical energy efficiency and at the same time, new techniques are being studied. These include direct currentand ultra high voltage transmission in both alternating current and direct current modes. Keywords: electrical energy transmissionFrom reference 2Disturbing loads like arc furnaces and thyristor rectifiers draw fluctuating and harmonic currents from the utility grid. These nonsinusoidal currents cause a voltage drop across the finite internal grid impedance, and the voltage waveform in the vicinity becomesdistorted. Hence, the normal operation of sensitive consumers is jeopardized.Active filters are a means to improve the power quality in distribution networks. In order to reduce the injection of non sinusoidalload currents shunt active filters are connnected in parallel to disturbing loads (Fig. 1). The active filter investigated in this projectconsists of a PWM controlled three-level VSI with a DC link capacitor.The VSI is connected to the point of common coupling via atransformer. The configuration is identical with an advanced static var compensator.The purpose of the active filter is to compensate transient and harmonic components of the load current so that only fundamentalfrequency components remain in the grid current. Additionally, the active filter may provide the reactive power consumed by theload. The control principle for the active filter is rather straightforward: The load current ismeasured, the fundamental activecomponent is removed from the measurement, and the result is used as the reference for the VSI output current.In the low voltage grid, active filters may use inverters based on IGBTs with switching frequencies of 10 kHz or more. The harmonicsproduced by those inverters are easily suppressed with small passive filters. The VSI can be regarded nearly as an ideally controllablevoltage source. Inmedium voltage applications with power ratings of several MV A, however, the switching frequen cy of today’s VSIsis limited to some hundred Hertz. Modern high power IGCTs can operate at around 1 kHz. Therefore, large passive filters are neededin order to remove the current ripple generated by the VSI. Furthermore, in fast control schemes the VSI no longer represents anideal voltage source because the PWM modulator produces a considerable dead-time. In this project a fast dead-beat algorithm forPWM operated VSIs is developed [1].This algorithm improves the load current tracking performance and the stability of the activefilter. Normally, for a harmonics free current measurement the VSI currentwould be sampled synchronously with the tips of the triangular carriers. Here, the current acquisition is shifted in order to minimizethe delays in the control loop. The harmonics now included in themeasurement can be calculated and subtracted from the VSIcurrent. Thus, an instantaneous current estimation free of harmonics is obtained.Keywords: active filtersFrom reference 3This report provides background information on electric power transmission and related policy issues. Proposals for changing federaltransmission policy before the 111th Congress include S. 539, the Clean Renewable Energy and Economic Development Act,introduced on March 5, 2009; and the March 9, 2009, majority staff transmission siting draft of the Senate Energy and NaturalResources Committee. The policy issues identified and discussed in this report include:Federal Transmission Planning: several current proposals call for the federal government to sponsor and supervise large scale, on-going transmission planning programs. Issues for Congress to consider are the objectives of the planning process (e.g., a focus onsupporting the development of renewable power or on a broader set of transmission goals), determining how much authority newinterconnection-wide planning entities should be granted, the degree to which transmission planning needs to consider non-transmission solutions to power market needs, what resources theexecutive agencies will need to oversee the planning process, and whether the benefits for projects included in the transmissionplans (e.g., a federal permitting option) will motivate developers to add unnecessary features and costs to qualify proposals for theplan.Permitting of Transmission Lines: a contentious issue is whether the federal government should assume from the states the primaryrole in permitting new transmission lines. Related issues include whether Congress should view management and expansion of thegrid as primarily a state or national issue, whether national authority over grid reliability (which Congress established in the EnergyPolicy Act of 2005) can be effectively exercised without federal authority over permitting, if it is important to accelerate theconstruction of new transmission lines (which is one of the assumed benefits of federal permitting), and whether the executiveagencies are equipped to take on the task of permitting transmission lines.Transmission Line Funding and Cost Allocation: the primary issues are whether the the federal government should help pay for newtransmission lines, and if Congress should establish a national standard for allocating the costs of interstate transmission lines toratepayers.Transmission Modernization and the Smart Grid: issues include the need for Congressional oversight of existing federal smart gridresearch, development, demonstration, and grant programs; and oversight over whether the smart grid is actually proving to be agood investment for taxpayers and ratepayers.Transmission System Reliability: it is not clear whether Congress and the executive branch have the information needed to evaluatethe reliability of the transmission system. Congress may also want to review whether the power industry is striking the right balancebetween modernization and new construction as a means of enhancing transmission reliability, and whether the reliability standardsbeing developed for the transmission system are appropriate for a rapidly changing power system. Keywords: electric power transmissionPage3 Requirements of an Electric Supply System(供电系统需求)1 English textFrom reference1Connections to external 330 kV power grids are provided using an open 330 kV switchyard. The plant is connected to theLithuanian power grid using two transmission lines L-454 and L-453, 330 kV each, to the Belorussian power grid using threetransmission lines L-450, L-452 and L-705, and to the Latvian power grid using one transmission line L-451.Connections to external power grids at 110 kV are provided using the first section of the open 110 kV switchyard. The plant isconnected to the Lithuanian power grid using one transmission line “Zarasai” 110 kV, and to the Latvian power grid using onetransmission line L-632.Connections between the open switchyards at 330 kV and 110 kV are established using two coupling autotransformers AT-1 andAT-2, types ATDCTN- 200000/330. Power of each autotransformer is equal to 200 MV×A. The autotransformers have a device forvoltage regulation under load. The device type is RNOA-110/1000. 15 positions are provided to regulate voltage in a range (115 ±6) kV.The open 330 kV switchyard is designed using "4/3" principle (four circuit breakers per three connections) and consists of twosections. Circuit breakers are placed in two rows. The first section of the open switchyard 110 kV is designed using “Double systemof buses with bypass” structure. The second section of open switchyard 110 kV is connected to the first section through twocircuit breakers C101 and C102. The second section has the same design as the first one. The following transmission lines areconnected to the second section: L-Vidzy, L-Opsa, L-Statyba, LDuk Ötas. These transmission lines are intended for district powersupplies, so they are not essential for electric power supply for the plant in-house operation.Air circuit breakers of VNV-330/3150A type are used in the open 330 kV switchyard. Air circuit breakers of VVBK-110B-50/3150U1type are used in open switchyard 110 kV. To supply power loads on voltage level 330 kV and 110 kV, aerial transmission lines areused. Electrical connections of external grids 110 and 330 kV are presented in Fig. 8.1. Keywords: transmission linesFrom reference 2AbstractThis paper addresses sustainability criteria and the associated indicators allowing operationalization of the sustainability concept in the context of electricity supply. The criteria and indicators cover economic,environmental and social aspects. Some selected results from environmental analysis, risk assessment and economic studies areshown. These studies are supported by the extensive databases developed in this work. The applications of multi-criteria analysisdemonstrate the use of a framework that allows decision-makers to simultaneously address the often conflicting socio-economic andecological criteria. “EnergyGame”, the communication-oriented software recently developed by the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI),provides the opportunity to integrate the central knowledge-based results with subjective value judgments. In this way a sensitivitymap of technology choices can be constructed in an interactive manner. Accommodation of a range of perspectives expressed inthe energy debate, including the concept of sustainable development, may lead to different internal rankings of the options butsome patterns appear to be relatively robust.IntroductionThe public, opinion leaders and decision-makers ask for clear answers on issues concerning the energy sector and electricitygeneration in particular. Is it feasible to phase out nuclear power in countries extensively relying on nuclear electricity supply andsimultaneously reduce greenhouse gas emissions? What are the environmental and economic implications of enhanced uses ofcogeneration systems, renewable sources and heat pumps? How do the various energy carriers compare with respect to accidentrisks? How would internalization of external costs affect the relative competitiveness of the various means of electricity production?What can we expect from the prospective technological advancements during the next two or three decades? Which systems orenergy mixes come closest to the ideal of being cheap, environmentally clean, reliable and at the same time exhibit low accidentrisks?How can we evaluate and rank the current and future energy supply options with respect to their performance on specificsustainability criteria?The Swiss GaBE Project on “Comprehensive Assessment of Energy Systems” provides answers to many issues in the Swiss andinternational energy arena. A systematic, multidisciplinary, bottom-up methodology for the assessment of energy systems, has beenestablished and implemented. It covers environmental analysis, risk assessment and economic studies, which are supported by theextensive databases developed in this work. One of the analysis products are aggregated indicators associated with the varioussustainability criteria, thus allowing a practical operationalization of the sustainability concept. Apart from technical and economicaspects an integrated approach needs to consider also social preferences, which may be done in the framework of multi-criteriaanalysis.Keywords: criteria indicatorsFrom reference 3Mobility of persons and goods is an essential component of the competitiveness of European industry and services as well as anessential citizen right. The goal of the EU's sustainable transport policy is to ensure that our transport systems meet society'seconomic, social and environmental needs.The transport sector is responsible for about 30% of the total final energy consumption and for about 25% of the total CO2emissions. In particular the contribution of road transport is very high (around 80% and 70% respectively). These simple data shedlight on the necessity to move towards a more sustainable transportation system, but also suggest that a technological/systemicrevolution in the field will positively impact the overall world’s sustainable development.From a technological point of view, a lower dependency from not renewable energy sources (i.e. fuel oil) of the road transport isthe main anticipated change. In particular electric engines possibly represent the natural vehicle evolution in this direction. Indeedthey have much higher energy efficiency (around three times that of internal combustion engines, ICE) and do not produce anykind of tailpipe emissions. How the electricity will be supplied to the vehicles is still unpredictable due to the too many existinguncertainties on the future development, but the electrification of the drive train will contribute to having alternative energy pathsto reduce the nearly total dependency on crude oil. In particular, vehicle range and performances allowed by the differentpossibilities will play a key role on the debate.At the moment a great attention is attracted by electric vehicles, both hybrid and not, that will allow users to recharge theirvehicles directly at home. This kind of vehicle can represent a real future alternative to the ICE vehicles in particular for whatconcerns the daily commuting trips (whose range is quite low). It is therefore important to understand what might be the impacton the electric supply system capabilities of this recharging activity.In this light the present study carries out an analysis of this impact for the Province of Milan (of particular relevant due the very highdaily commuting trips) at a 2030 time horizon. Key issue of the analysis is the estimation of a potential market share evolution for theelectric vehicles. The results obtained show that even with a very high future market penetration the impact of the vehicles on theannual energy consumption will be quite negligible. On the contrary they also show that without an appropriate regulation (e.g. theintelligent integration of electric vehicles into the existing power grid as decentralised and flexible energy storage), they couldheavily impact on the daily electric power requirements.Keywords: electric vehicles报告总结本次报告主要从网上收集了电能输送和供电系统的需求这两个方面的相关内容,并对其进行了分析,了解了一些相关知识。

电子行业英语A1.Analog 模拟相似物2.A/D Analog to Digital 模-数转换3.AAC Advanced Audio Coding 高级音频编码4.ABB Automatic Black Balance 自动黑平衡5.ABC American Broadcasting Company 美国广播公司6.Automatic Bass Compensation 自动低音补偿7.Automatic Brightness Control 自动亮度控制8.ABL Automatic Black Level 自动黑电平9.ABLC Automatic Brightness Limiter Circuit 自动亮度限制电路10.ABU Asian Broadcasting Union 亚洲广播联盟亚广联11.ABS American Bureau of Standard 美国标准局12.AC Access Conditions 接入条件13.Audio Center 音频中心14.ACA Adjacent Channel Attenuation 邻频道衰减15.ACC Automatic Centering Control 自动中心控制16.Automatic Chroma Control 自动色度增益控制17.ACK Automatic Chroma Killer 自动消色器18.ACP Additive Colour Process 加色法19.ACS Access Control System 接入控制系统20.Advanced Communication Service 高级通信业务21.Area Communication System 区域通信系统22.ADC Analog to Digital Converter 模-数转换器23.Automatic Degaussing Circuit 自动消磁电路24.ADL Acoustic Delay Line 声延迟线25.ADS Audio Distribution System 音频分配系统26.AE Audio Erasing 音频(声音擦除27.AEF Automatic Editing Function 自动编辑功能28.AES Audio Engineering Society 音频工程协会29.AF Audio Frequency 音频30.AFA Audio Frequency Amplifier 音频放大器31.AFC Automatic Frequency Coder 音频编码器32.Automatic Frequency Control 自动频率控制33.AFT Automatic Fine Tuning 自动微调34.Automatic Frequency Track 自动频率跟踪35.Automatic Frequency Trim 自动额率微调36.AGC Automatic Gain Control 自动增益控制37.AI Artificial Intelligence 人工智能38.ALM Audio-Level Meter 音频电平表39.AM Amplitude Modulation 调幅40.AMS Automatic Music Sensor 自动音乐传感装置41.ANC Automatic Noise Canceller 自动噪声消除器42.ANT antenna 天线43.AO Analog Output 模拟输出44.APS Automatic Program Search 自动节目搜索45.APPS Automatic Program Pause System 自动节目暂停系统46.APSS Automatic Program Search System 自动节目搜索系统47.AR Audio Response 音频响应48.ARC Automatic Remote Control 自动遥控49.ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange 美国信息交换标准50.AST Automatic Scanning Tracking 自动扫描跟踪51.ATC Automatic Timing Control 自动定时控制52.Automatic Tone Correction 自动音频校正53.ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode 异步传输模式54.ATF Automatic Track Finding 自动寻迹55.ATS Automatic Test System 自动测试系统56.ATSC Advanced Television Systems Committee 美国高级电视制式委员会57.AVC Automatic Volume Control 自动音量控制58.AVR Automatic Voltage Regulator 自动稳压器59.AWB Automatic White Balance 自动白平衡60.AZC Automatic Zooming Control 自动变焦控制61.AZS Automatic Zero Setting 自动调零B1.BA Branch Amplifier 分支放大器2.Buffer Amplifier 缓冲放大器3.BAC Binary-Analog Conversion 二进制模拟转换4.BB Black Burst 黑场信号5.BBC British Broadcasting Corporation 英国广播公司6.BBI Beijing Broadcasting Institute 北京广播学院7.BC Binary Code 二进制码8.Balanced Current 平衡电流9.Broadcast Control 广播控制10.BCT Bandwidth Compression Technique 带宽压缩技术11.BDB Bi-directional Data Bus 双向数据总线12.BER Basic Encoding Rules 基本编码规则13.Bit Error Rate 比特误码率14.BF Burst Flag 色同步旗脉冲15.BFA Bare Fiber Adapter 裸光纤适配器16.Brillouin Fiber Amplifier 布里渊光纤放大器17.BM Background Music 背景音乐18.BIOS Basic Input/Output System 基本输入输出系统19.B-ISDN Broadband-ISDN 宽带综合业务数据网20.BIU Basic Information Unit 基本信息单元21.Bus Interface Unit 总线接口单元22.BM Bi-phase Modulation 双相调制23.BML Business Management Layer 商务管理层24.BN Backbone Network 主干网25.BNT Broadband Network Termination 宽带网络终端设备26.BO Bus Out 总线输出27.BPG Basic Pulse Generator 基准脉冲发生器28.BPS Band Pitch Shift 分频段变调节器29.BSI British Standard Institute 英国标准学会30.BSS Broadcast Satellite Service 广播卫星业务31.BT Block Terminal 分线盒、分组终端32.British Telecom 英国电信33.BTA Broadband Terminal Adapter 宽带终端适配器34.Broadcasting Technology Association (***广播技术协会35.BTL Balanced Transformer-Less 桥式推挽放大电路36.BTS Broadcast Technical Standard 广播技术标准37.BTU Basic Transmission Unit 基本传输单元38.BVU Broadcasting Video Unit 广播视频型(一种3/4英寸带录像机记录格式39.BW BandWidth 带宽40.BWTV Black and White Television 黑白电视C1.CA Conditional Access 条件接收2.CAC Conditional Access Control 条件接收控制3.CAL Continuity Accept Limit 连续性接受极限4.CAS Conditional Access System 条件接收系统5.Conditional Access Sub-system 条件接收子系统6.CATV Cable Television 有线电视,电缆电视munity Antenna Television 共用天线电视8.CAV Constant Angular Velocity 恒角速度9.CBC Canadian Broadcasting Corporation 加拿大广播公司10.CBS Columbia Broadcasting System 美国哥伦比亚广播公司 Concentric Cable 同轴电缆G Chinese Character Generator 中文字幕发生器IR International Radio Consultative Committee 国际无线电咨询委员会ITT International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee 国际电话电报咨询委员会R Central Control Room 中心控制室TV China Central Television 中国中央电视台17.Close-Circuit Television 闭路电视S Center Central System 中心控制系统U Camera Control Unit 摄像机控制器W Counter Clock-Wise 反时针方向21.CD Compact Disc 激光唱片22.CDA Current Dumping Amplifier 电流放大器23.CD-E Compact Disc Erasable 可抹式激光唱片24.CDFM Compact Disc File Manager 光盘文件管理程序25.CDPG Compact-Disc Plus Graphic 带有静止图像的CD唱盘26.CD-ROM Compact Disc-Read Only Memory 只读式紧凑光盘27.CETV China Educational Television 中国教育电视台28.CF Color Framing 彩色成帧29.CGA Color Graphics Adapter 彩色图形显示卡30.CI Common Interface 通用接口31.CIE Chinese Institute of Electronics 中国电子学会32.CII China Information Infrastructure 中国信息基础设施33.CIF Common Intermediate Format 通用中间格式34.CIS Chinese Industrial Standard 中国工业标准35.CLV Constant Linear Velocity 恒定线速度36.CM Colour Monitor 色监视器37.CMTS Cable Modem Termination System 线缆调制解调器终端系统R Carrier-to-Noise Ratio 载噪比39.CON Console 操纵台40.Controller 控制器41.CPB Corporation of Public Broadcasting 美国公共广播公司42.CPU Central Processing Unit 中央处理单元43.CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check 循环冗余校验44.CRCC CRI Cyclic Redundancy Check Code 循环冗余校验码45.CROM China Radio International 中国国际广播电台46.CRT Control Read Only Memory 控制只读存储器47.CS Cathode-Ray Tube 阴极射线管48.CSC Communication Satellite 通信卫星49.CSS Color Sub-carrier 彩色副载波50.Center Storage Server 中央存储服务器51.Content Scrambling System 内容加扰系统52.CSU Channel Service Unit 信道业务单元53.CT Color Temperature 色温54.CTC Cassette Tape Controller 盒式磁带控制器55.Channel Traffic Control 通道通信量控制56.Counter Timer Circuit 计数器定时器电路57.Counter Timer Control 计数器定时器控制58.CTE Cable Termination Equipment 线缆终端设备59.Customer Terminal Equipment 用户终端设备60.CTV Color Television 彩色电视61.CVD China Video Disc 中国数字视盘62.CW Carrie Wave 载波D1.DAB Digital Audio Broadcasting 数字音频广播2.DASH Digital Audio Stationary Head 数字音频静止磁头3.DAT Digital Audio Tape 数字音频磁带4.DBMS Data Base Management System 数据库管理系统5.DBS Direct Broadcast Satellite 直播卫星6.DCC Digital Compact Cassette 数字小型盒带7.Dynamic Contrast Control 动态对比度控制8.DCT Digital Component Technology 数字分量技术9.Discrete Cosine Transform 离散余弦变换10.DCTV Digital Color Television 数字彩色电视11.DD Direct Drive 直接驱动12.DDC Direct Digital Control 直接数字控制13.DDE Dynamic Data Exchange 动态数据交换14.DDM Data Display Monitor 数据显示监视器15.DES Data Elementary Stream 数据基本码流16.Data Encryption Standard 美国数据加密标准17.DF Dispersion Flattened 色散平坦光纤18.DG Differential Gain 微分增益19.DI Digital Interface 数字接口20.DITEC Digital Television Camera 数字电视摄像机21.DL Delay Line 延时线22.DLD Dynamic Linear Drive 动态线性驱动23.DM Delta Modulation 增量调制24.Digital Modulation 数字调制25.DMB Digital Multimedia Broadcasting 数字多媒体广播26.DMC Dynamic Motion Control 动态控制27.DME Digital Multiple Effect 数字多功能特技28.DMS Digital Mastering System 数字主系统29.DN Data Network 数据网络30.DNG Digital News Gathering 数字新闻采集31.DNR Digital Noise Reducer 数字式降噪器32.DOB Data Output Bus 数据输出总线33.DOCSIS Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications 有线数据传输业务接口规范34.DOC Drop Out Compensation 失落补偿35.DOS Disc Operating System 磁盘操作系统36.DP Differential Phase 微分相位37.Data Pulse 数据脉冲38.DPCM Differential Pulse Code Modulation 差值脉冲编码调制39.DPL Dolby Pro Logic 杜比定向逻辑40.DSB Digital Satellite Broadcasting 数字卫星广播41.DSC Digital Studio Control 数字演播室控制42.DSD Dolby Surround Digital 杜比数字环绕声43.DSE Digital Special Effect 数字特技44.DSK Down-Stream Key 下游键45.DSP Digital Signal Processing 数字信号处理46.Digital Sound Processor 数字声音处理器47.DSS Digital Satellite System 数字卫星系统48.DT Digital Technique 数字技术49.Digital Television 数字电视50.Data Terminal 数据终端51.Data Transmission 数据传输52.DTB Digital Terrestrial Broadcasting 数字地面广播53.DTBC Digital Time-Base Corrector 数字时基校正器54.DTC Digital Television Camera 数字电视摄像机55.DTS Digital Theater System 数字影院系统56.Digital Tuning System 数字调谐系统57.Digital Television Standard 数字电视标准58.DVB Digital Video Broadcasting 数字视频广播59.DVC Digital Video Compression 数字视频压缩60.DVE Digital Video Effect 数字视频特技61.DVS Desktop Video Studio 桌上视频演播(系统62.DVTR Digital Video Tape Recorder 数字磁带录像机E1.EA Extension Amplifier 延长放大器2.EB Electron Beam 电子束3.EBS Emergency Broadcasting System 紧急广播系统4.EBU European Broadcasting Union 欧洲广播联盟5.EC Error Correction 误差校正6.ECN Emergency Communications Network 应急通信网络7.ECS European Communication Satellite 欧洲通信卫星8.EDC Error Detection Code 错误检测码9.EDE Electronic Data Exchange 电子数据交换10.EDF Erbium-Doped Fiber 掺饵光纤11.EDFA Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier 掺饵光纤放大器12.EDL Edit Decision List 编辑点清单13.EDTV Extended Definition Television 扩展清晰度电视14.EE Error Excepted 允许误差15.EFM Eight to Fourteen Modulation 8-14调制16.EFP Electronic Field Production 电子现场节目制作17.EH Ethernet Hosts 以太网主机18.EIN Equivalent Input Noise 等效输入噪声19.EIS Electronic Information System 电子信息系统20.EISA Extended Industrial Standard Architecture 扩展工业标准总线21.EL Electro-Luminescent 场致发光22.EM Error Monitoring 误码监测23.EN End Node 末端节点24.ENG Electronic News Gathering 电子新闻采集25.EOT End of Tape 带尾26.EP Edit Point 编辑点27.Error Protocol 错误协议28.EPG Electronic Program Guides 电子节目指南29.EPS Emergency Power Supply 应急电源30.ERP Effective Radiated Power 有效辐射功率31.ES Elementary Stream 基本码流32.End System 终端系统33.ESA European Space Agency 欧洲空间局34.ETV Education Television 教育电视35.ETV Enhanced Television 增强电视F1.FA Facial Animation 面部动画2.FABM Fiber Amplifier Booster Module 光纤放大器增强模块3.Fiber Access System 光纤接入系统4.Frequency Changer 变频器5.FC Fiber Channel 光纤通道6.Film Composer 电影编辑系统9.FCC Federal Communications Commission 美国联邦通信委员会10.FD Frequency Divider 分频器11.FD Fiber Duct 光纤管道12.FDCT Forward Discrete Cosine Transform 离散余弦正变换13.FDDI Fiber Distributed Data Interface 分布式光纤数据接口14.FDM Frequency-Division Multiplexing 频分复用15.FDP Fiber Distribution Point 光纤分配点16.FE Front End 前端17.FE Framing Error 成帧误差18.FF Fast Forward 快进19.FG Frequency Generator 频率发生器20.FH Frequency Hopping 跳频21.FIT Frame-Interline Transfer 帧一行间转移22.FN Fiber Node 光纤节点23.FOA Fiber Optic Amplifier 光纤放大器24.FOC Fiber Optic Cable 光缆25.FOC Fiber Optic Communications 光纤通信26.FOC Fiber Optic Coupler 光纤耦合器27.FOM Fiber Optic Modem 光纤调制解调器28.Fiber Optic Net 光纤网29.Factor of Safety 安全系数30.Fiber Optic Trunk Cable 光缆干线31.Frame Scan 帧扫描32.Frame Store 帧存储器33.Frame Synchro 帧同步机34.France Telecom 法国电信35.FTP File Transfer Protocol 文件传输协议36.FTTB Fiber-To-The-Building 光纤到楼37.FTTC Fiber-To-The-Curb 光纤到路边38.FTTH Fiber-To-The-Home 光纤到家39.FTTN Fiber-To-The-Node 光纤到节点40.FTTO Fiber-To-The-Office 光纤到办公室G1.GA General Average 总平均值2.GB Gain Bandwidth 增益带宽3.GFC Generic Flow Control 一般流量控制4.GMT Greenwich Mean Time 格林威治标准时间5.Ground 接地6.GPC General Purpose Computer 通用接口7.GPIB General Purpose Interface Bus 通用接口总线8.GPS Global Positioning Satellite 全球定位卫星9.GPS Global Positioning System 全球定位系统10.GSM Global System for Mobile Communication 全球移动通信系统11.GVFS General Video File Server 通用视频文件服务器H1.HA Head Amplifier 前置放大器2.HB Head Bus 前端总线3.HC Hierarchical Coding 分层编码4.HCT Home Communication Terminal 家庭通信终端5.HD High Definition 高清晰度6.HD Horizontal Drive 水平驱动脉冲7.HDM High Density Modulation 高密度调制8.HDTV High Definition Television 高清晰度电视9.HDVS High Definition Video System 高清晰度视频系统10.HF High Frequency 高频11.HFC Hybrid Fiber Coaxial 光纤同轴电缆混合网12.HFCT Hybrid Fiber Concentric Twisted Pair Wire 混合光纤同轴双绞线13.HIS Home Information System 家庭信息系统14.HF High-Fidelity 高保真度15.HPA High Power Amplifier 大功率放大器16.HPF High-Pass Filter 高通滤波器17.HQAD High Quality Audio Disc 高品位音频光盘18.HS Horizon Scanner 水平扫描19.HSCS High Speed Camera System 高速摄像机系统20.HSC High Speed Channel 高速信道21.HDB High Speed Data Broadcast 高速数据广播22.HT High Tension 高压23.HTT Home Television Theatre 家庭电视影院24.HTTP Hyper Text Transmission Protocol 超文本传输协议25.HTU Home Terminal Unit 家庭终端单元I1.IA Information Access 信息存取2.IB International Broadcasting 国际广播3.IB Interface Bus 接口总线4.IB Internal Bus 内部总线5.IBC Integrated Broadband Communication 综合宽带通信6.IBC International Broadcasting Center 国际广播中心7.IBC International Broadcasting Convention 欧洲国际广播会议8.IBG Inter Block Gap 字组间隔9.IC Integrated Circuit 集成电路10.IDC Inverse Discrete Cosine Transform 离散余弦逆变换11.IF Intermediate Frequency 中频12.IM Interface Module 接口模块13.IMTV Interactive Multimedia Television 交互式多媒体电视14.IN Integrated Network 综合网 Integrated Network Using Fiber Optics 光纤综合网16.INS Information Network System 信息网络系统17.IOCS Input-Output Control System 输入/输出控制系统18.IOD Information On Demand 点播信息19.Input Power 输入功率20.IP Internet Protocol 因特网协议21.IPC Information Processing Center 信息处理中心22.IPD Interactive Program Directory 交互式节目指南23.IPDC International Press Telecommunication Council 国际新闻通信委员会24.IRD Integrated Receiver/Decoder 综合接收机/解码器25.IS Information Superhighway 信息高速公路26.IS Interactive Service 交互业务27.IS International Standard 国际标准28.ISA Industry Standard Architecture 工业标准总线29.Integrated Service Analog Network 综合业务模拟网30.ISAN International Standard Audiovisual Number 国际标准音视频编号31.ISO International Standards Organization 国际标准化组织32.ISRC International Standard Recording Code 国际标准记录码33.ISSI Inter-Switching System Interface 交换机间系统接口34.IT Interline Transfer 行间转移35.ITS Insertion Test Signal 插入测试信号36.ITS Intelligent Traffic System 智能交通系统37.ITS International Telecommunication Service 国际电信业务38.ITU International Telecommunications Union 国际电信联盟39.ITV Industrial Television 工业电视40.ITV Interactive Television 交互式电视41.IU Information Unit 信息单元42.IVCS Intelligent Video Conferencing System 智能视频会议系统43.IVDS Interactive Video Data Service 交互视频数据业务44.IVO Interactive Video On Demand 交互点播电视45.IVS Interactive Video System 交互视频系统J1.JB Junction Box 接线盒2.JCTA Japan Cable Television Association ***有线电视协会3.JPEG Joint Photographic Experts Group 联合图片专家组4.JSB Japan Satellite Broadcasting Inc ***广播卫星公司Keyboard 键盘LN Local Area Network 局域网2.LBC Low Bit-rate Coding 低码率编码3.LC Lossless Coding 无损编码4.LCD Liquid Crystal Display 液晶显示器5.LCD Light Coupled Device 光耦合器件6.LD Laser Diode 激光二极管7.LDT Low Definition Television 低分辨率数字电视8.LED Light-Emitting Diode 发光二极管9.LF Low Frequency 低频10.LFR Low Frequency Response 低频响应11.LFE Low Frequency Oscillator 低频振荡器12.LI Level Indicator 电平指示器13.LMDS Local Microwave Distribution System 本地微波分配系统14.LNA Low Noise Amplifier 低噪声放大器15.LO Local Oscillator 本地振荡器16.LPF Low Pass Filter 低通滤波器17.LRC Longitudinal Redundancy Checking 纵向冗余校验18.LS Light Source 光源19.LSD Large Screen Display 大屏幕显示器20.LSIC Large Scale Integrated Circuit 大规模集成电路21.LSN Local Supervision Network 本地监测网22.LTC Longitudinal Time Code 纵向时间码23.LVD Laser Vision Disc 激光电视唱片24.LVRS Laser Video Recording System 激光视盘录制系统1.MAC Multiplexed Analog Components 复用模拟分量2.MAN Metropolitan Area Network 都市网3.MAPI Multimedia Application Programming Interface 多媒体应用编程接口4.MAT Master Antenna Television 共用天线电视5.MC Main Control 主控6.Media Composer 非线性媒体编辑系统7.MD Motion Compensation 运动补偿8.MC Multimedia Communication 多媒体通信9.MCI Media Control Interface 媒体控制接口10.MCPC Multi-Channel Per Carrier 多路单载波11.MCR Master Control Room 主控制室12.MCR Mobile Control Room 转播车,移动控制室13.MD Magnetic Drum 磁鼓14.MDM Multimedia Data Management 多媒体数据管理15.MDOP Multimedia Data Operation Platform 多媒体数据操作平台16.MF Medium Frequency 中频16.Microphone 传声器,话筒17.MIDI Musical Instrument Digital Interface 乐器数字接口18.MMDS Multi-Channel Microwave Distribution System 微波多点分配系统19.MAD Modulator And Demodulator 调制解调器20.MOL Maximum Output Level 最大输出电平21.Monitor 监视器,监听器。

电路的基本概念及定律电源source电压源voltage source电流源current source理想电压源ideal voltage source理想电流源ideal current source伏安特性volt-ampere characteristic电动势electromotive force电压voltage电流current电位potential电位差potential difference欧姆Ohm伏特Volt安培Ampere瓦特Watt焦耳Joule电路circuit电路元件circuit element电阻resistance电阻器resistor电感inductance电感器inductor电容capacitance电容器capacitor电路模型circuit model参考方向reference direction参考电位reference potential欧姆定律Ohm’s law基尔霍夫定律Kirchhoff’s law基尔霍夫电压定律Kirchhoff’s voltage law(KVL)基尔霍夫电流定律Kirchhoff’s current law(KCL)结点node支路branch回路loop网孔mesh支路电流法branch current analysis网孔电流法mesh current analysis结点电位法node voltage analysis电源变换source transformations叠加原理superposition theorem网络network无源二端网络passive two-terminal network有源二端网络active two-terminal network 戴维宁定理Thevenin’s theorem诺顿定理Norton’s theorem开路(断路)open circuit短路short circuit开路电压open-circuit voltage短路电流short-circuit current交流电路直流电路direct current circuit (dc)交流电路alternating current circuit (ac)正弦交流电路sinusoidal a-c circuit平均值average value有效值effective value均方根值root-mean-squire value (rms)瞬时值instantaneous value电抗reactance感抗inductive reactance容抗capacitive reactance法拉Farad亨利Henry阻抗impedance复数阻抗complex impedance相位phase初相位initial phase相位差phase difference相位领先phase lead相位落后phase lag倒相,反相phase inversion频率frequency角频率angular frequency赫兹Hertz相量phasor相量图phasor diagram有功功率active power无功功率reactive power视在功率apparent power功率因数power factor功率因数补偿power-factor compensation串联谐振series resonance并联谐振parallel resonance谐振频率resonance frequency频率特性frequency characteristic幅频特性amplitude-frequency response characteristic 相频特性phase-frequency response characteristic截止频率cutoff frequency品质因数quality factor通频带pass-band带宽bandwidth (BW)滤波器filter一阶滤波器first-order filter二阶滤波器second-order filter低通滤波器low-pass filter高通滤波器high-pass filter带通滤波器band-pass filter带阻滤波器band-stop filter转移函数transfer function波特图Bode diagram傅立叶级数Fourier series三相电路三相电路three-phase circuit三相电源three-phase source对称三相电源symmetrical three-phase source对称三相负载symmetrical three-phase load相电压phase voltage相电流phase current线电压line voltage线电流line current三相三线制three-phase three-wire system三相四线制three-phase four-wire system三相功率three-phase power星形连接star connection(Y-connection)三角形连接triangular connection(D- connection ,delta connection)中线neutral line电路的暂态过程分析暂态transient state稳态steady state暂态过程,暂态响应transient response换路定理low of switch一阶电路first-order circuit三要素法three-factor method时间常数time constant积分电路integrating circuit微分电路differentiating circuit磁路与变压器磁场magnetic field磁通flux磁路magnetic circuit磁感应强度flux density磁通势magnetomotive force磁阻reluctance电动机直流电动机dc motor交流电动机ac motor异步电动机asynchronous motor同步电动机synchronous motor三相异步电动机three-phase asynchronous motor 单相异步电动机single-phase asynchronous motor 旋转磁场rotating magnetic field定子stator转子rotor转差率slip起动电流starting current起动转矩starting torque额定电压rated voltage额定电流rated current额定功率rated power机械特性mechanical characteristic继电器-接触器控制按钮button熔断器fuse开关switch行程开关travel switch继电器relay接触器contactor常开(动合)触点normally open contact常闭(动断)触点normally closed contact时间继电器time relay热继电器thermal overload relay中间继电器intermediate relay可编程控制器(PLC)可编程控制器programmable logic controller语句表statement list梯形图ladder diagram半导体器件本征半导体intrinsic semiconductor掺杂半导体doped semiconductorP型半导体P-type semiconductorN型半导体N--type semiconductor自由电子free electron空穴hole载流子carriersPN结PN junction扩散diffusion漂移drift二极管diode硅二极管silicon diode锗二极管germanium diode阳极anode阴极cathode发光二极管light-emitting diode (LED)光电二极管photodiode稳压二极管Zener diode晶体管(三极管)transistorPNP型晶体管PNP transistorNPN型晶体管NPN transistor发射极emitter集电极collector基极base电流放大系数current amplification coefficient场效应管field-effect transistor (FET)P沟道p-channelN沟道n-channel结型场效应管junction FET(JFET)金属氧化物半导体metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) 耗尽型MOS场效应管depletion mode MOSFET (D-MOSFET)增强型MOS场效应管enhancement mode MOSFET (E-MOSFET)源极source栅极grid漏极drain跨导transconductance夹断电压pinch-off voltage热敏电阻thermistor开路open短路shorted基本放大器放大器amplifier 正向偏置forward bias反向偏置backward bias静态工作点quiescent point (Q-point)等效电路equivalent circuit电压放大倍数voltage gain总的电压放大倍数overall voltage gain饱和saturation截止cut-off放大区amplifier region饱和区saturation region截止区cut-off region失真distortion饱和失真saturation distortion截止失真cut-off distortion零点漂移zero drift正反馈positive feedback负反馈negative feedback串联负反馈series negative feedback并联负反馈parallel negative feedback共射极放大器common-emitter amplifier射极跟随器emitter-follower共源极放大器common-source amplifier共漏极放大器common-drain amplifier多级放大器multistage amplifier阻容耦合放大器resistance-capacitance coupled amplifier直接耦合放大器direct- coupled amplifier输入电阻input resistance输出电阻output resistance负载电阻load resistance动态电阻dynamic resistance负载电流load current旁路电容bypass capacitor耦合电容coupled capacitor直流通路direct current path交流通路alternating current path直流分量direct current component交流分量alternating current component变阻器(电位器)rheostat电阻(器)resistor电阻(值)resistance电容(器)capacitor电容(量)capacitance电感(器,线圈)inductor电感(量),感应系数inductance正弦电压sinusoidal voltage集成运算放大器及应用差动放大器differential amplifier运算放大器operational amplifier(op-amp)失调电压offset voltage失调电流offset current共模信号common-mode signal差模信号different-mode signal共模抑制比common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) 积分电路integrator(circuit)微分电路differentiator(circuit)有源滤波器active filter低通滤波器low-pass filter高通滤波器high-pass filter带通滤波器band-pass filter带阻滤波器band-stop filter波特沃斯滤波器Butterworth filter切比雪夫滤波器Chebyshev filter贝塞尔滤波器Bessel filter截止频率cut-off frequency上限截止频率upper cut-off frequency下限截止频率lower cut-off frequency中心频率center frequency带宽Bandwidth开环增益open-loop gain闭环增益closed-loop gain共模增益common-mode gain输入阻抗input impedance电压跟随器voltage-follower电压源voltage source电流源current source单位增益带宽unity-gain bandwidth频率响应frequency response频响特性(曲线)response characteristic波特图the Bode plot稳定性stability补偿compensation比较器comparator迟滞比较器hysteresis comparator阶跃输入电压step input voltage仪表放大器instrumentation amplifier隔离放大器isolation amplifier对数放大器log amplifier 反对数放大器antilog amplifier反馈通道feedback path反向漏电流reverse leakage current相位phase相移phase shift锁相环phase-locked loop(PLL)锁相环相位监测器PLL phase detector和频sum frequency差频difference frequency波形发生电路振荡器oscillatorRC振荡器RC oscillatorLC振荡器LC oscillator正弦波振荡器sinusoidal oscillator三角波发生器triangular wave generator方波发生器square wave generator幅度magnitude电平level饱和输出电平(电压)saturated output level功率放大器功率放大器power amplifier交越失真cross-over distortion甲类功率放大器class A power amplifier乙类推挽功率放大器class B push-pull power amplifier OTL功率放大器output transformerless power amplifier OCL功率放大器output capacitorless power amplifier 直流稳压电源半波整流full-wave rectifier全波整流half-wave rectifier电感滤波器inductor filter电容滤波器capacitor filter串联型稳压电源series (voltage) regulator开关型稳压电源switching (voltage) regulator集成稳压器IC (voltage) regulator晶闸管及可控整流电路晶闸管thyristor单结晶体管unijunction transistor(UJT)可控整流controlled rectifier可控硅silicon-controlled rectifier峰点peak point谷点valley point控制角controlling angle导通角turn-on angle门电路与逻辑代数二进制binary二进制数binary number十进制decimal十六进制hexadecimal二-十进制binary coded decimal (BCD)门电路gate三态门tri-state gate与门AND gate或门OR gate非门NOT gate与非门NAND gate或非门NOR gate异或门exclusive-OR gate反相器inverter布尔代数Boolean algebra真值表truth table卡诺图the Karnaugh map逻辑函数logic function逻辑表达式logic expression组合逻辑电路组合逻辑电路combination logic circuit译码器decoder编码器coder比较器comparator半加器half-adder全加器full-adder七段显示器seven-segment display时序逻辑电路时序逻辑电路sequential logic circuitR-S 触发器R-S flip-flopD触发器D flip-flopJ-K触发器J-K flip-flop主从型触发器master-slave flip-flop置位set复位reset直接置位端direct-set terminal直接复位端direct-reset terminal寄存器register移位寄存器shift register双向移位寄存器bidirectional shift register 计数器counter同步计数器synchronous counter异步计数器asynchronous counter 加法计数器adding counter减法计数器subtracting counter定时器timer清除(清0)clear载入load时钟脉冲clock pulse触发脉冲trigger pulse上升沿positive edge下降沿negative edge时序图timing diagram波形图waveform脉冲波形的产生与整形单稳态触发器monostable flip-flop双稳态触发器bistable flip-flop无稳态振荡器astable oscillator晶体crystal555定时器555 timer模拟信号与数字信号的相互转换模拟信号analog signal数字信号digital signalAD转换器analog -digital converter (ADC)DA转换器digital-analog converter (DAC)半导体存储器只读存储器read-only memory(ROM)随机存取存储器random-access memory(RAM)可编程ROM programmable ROM(PROM)。

汽车电子系统中英文对照外文翻译文献汽车电子系统中英文对照外文翻译文献1汽车电子系统中英文对照外文翻译文献(文档含英文原文和中文翻译)The Changing Automotive Environment: High-Temperature ElectronicsR. Wayne Johnson, Fellow, IEEE, John L. Evans, Peter Jacobsen, James R. (Rick) Thompson, and Mark ChristopherAbstract —The underhood automotive environment is harsh and current trends in the automotive electronics industry will be pushing the temperatureenvelope for electronic components. The desire to place engine control unitson the engine and transmission control units either on or in the transmissionwill push the ambient temperature above 125125℃℃.However, extreme cost pressures,increasing reliability demands (10 year/241 350 km) and the cost of field failures (recalls, liability, customer loyalty) will make the shift to higher temperatures occur incrementally. The coolest spots on engine and in the transmission will be used. These large bodies do provide considerableheat sinking to reduce temperature rise due to power dissipation in the controlunit. The majority of near term applications will be at 150 ℃ or less andthese will be worst case temperatures, not nominal. The transition toX-by-wire technology, replacing mechanical and hydraulic systems with electromechanical systems will require more power electronics. Integrationof power transistors and smart power devices into the electromechanical℃ to 200℃ . Hybridactuator will require power devices to operate at 175electric vehicles and fuel cell vehicles will also drive the demand for higher temperature power electronics. In the case of hybrid electric and fuel cell vehicles, the high temperature will be due to power dissipation. Thealternates to high-temperature devices are thermal management systems which add weight and cost. Finally, the number of sensors in vehicles is increasingas more electrically controlled systems are added. Many of these sensors mustwork in high-temperature environments. The harshest applications are exhaustgas sensors and cylinder pressure or combustion sensors. High-temperature electronics use in automotive systems will continue to grow, but it will be gradual as cost and reliability issues are addressed. This paper examines themotivation for higher temperature operation,the packaging limitations evenat 125 C with newer package styles and concludes with a review of challenge at both the semiconductor device and packaging level as temperatures push beyond 125 ℃.Index Terms—Automotive, extreme-environment electronics.I. INTRODUCTIONI N 1977, the average automobile contained $110 worth of electronics [1]. By 2003 the electronics content was $1510 per vehicle and is expected to reach$2285 in 2013 [2].The turning point in automotive electronics was governmentTABLE IMAJOR AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONIC SYSTEMSTABLE IIAUTOMOTIVETEMPERATUREEXTREMES(DELPHIDELCOELECTRONIC SYSTEMS) [3]regulation in the 1970s mandating emissions control and fuel economy. The complex fuel control required could not be accomplished using traditional mechanical systems. These government regulations coupled with increasing semiconductor computing power at decreasing cost have led to an ever increasing array of automotive electronics. Automotive electronics can be divided into five major categories as shown in Table I.The operating temperature of the electronics is a function of location, power dissipation by the electronics, and the thermal design. The automotive electronics industry defines high-temperature electronics as electronics operating above 125 ℃. However, the actual temperature for various electronics mounting locations varies considerably. Delphi Delco Electronic Systems recently published the typical continuous maximum temperatures as reproduced in Table II [3]. The corresponding underhood temperatures are shown in Fig. 1. The authors note that typical junction temperatures for integrated circuits are 10 ℃to15℃ higher than ambient or baseplate temperature, while power devices can reach 25 ℃ higher. At-engine temperatures of 125℃ peak can be maintained by placing the electronics on theintake manifold.Fig. 1. Engine compartment thermal profile (Delphi Delco Electronic Systems) [3].TABLE III THEAUTOMOTIVEENVIRONMENT(GENERALMOTORS ANDDELPHIDELCO ELECTRONICSYSTEMS) [4]TABLE IV REQUIREDOPERATIONTEMPERATURE FORAUTOMOTIVEELECTRONIC SYSTEMS(TOYOTAMOTORCORP. [5]TABLE VMECHA TRONICMAXIMUMTEMPERA TURERANGES(DAIMLERCHRYSLER,EA TONCORPORA TION, ANDAUBURNUNIVERSITY) [6]Fig. 2. Automotive temperatures and related systems (DaimlerChrysler) [8].automotive electronic systems [8]. Fig. 3 shows an actual measured transmission transmission temperature temperature temperature profile profile profile during during during normal normal normal and and excessive excessive driving drivingconditions [8]. Power braking is a commonly used test condition where the brakes are applied and the engine is revved with the transmission in gear.A similar real-world situation would be applying throttle with the emergencybrake applied. Note that when the temperature reached 135135℃℃,the over temperature light came on and at the peak temperature of 145145℃℃,the transmission was beginning to smell of burnt transmission fluid.TABLE VI2002I NTERNA TIONAL T ECHNOLOGY R OADMAPFOR S EMICONDUCTORS A MBI ENTOPERA TINGTEMPERA TURES FORHARSHENVIRONMENTS (AUTOMOTIVE) [9]The 2002 update to the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS) did not reflect the need for higher operating temperatures for complex integrated circuits, but did recognize increasing temperature requirements for power and linear devices as shown in Table VI [9]. Higher temperature power devices (diodes and transistors) will be used for the power section of power converters and motor drives for electromechanical actuators. Higher temperature linear devices will be used for analog control of power converters and for amplification and some signal processing of sensor outputs prior to transmission to the control units. It should be noted that at the maximum rated temperature for a power device, the power handling capability is derated to zero. Thus, a 200℃ rated power transistor in a 200℃ environment would have zero current carrying capability. Thus, the actual operating environments must be lower than the maximum rating.In the 2003 edition of the ITRS, the maximum junction temperatures identified forharsh-environment complex integrated circuits was raised to 150℃through 2018 [9]. Theambient operating temperature extreme for harsh-environment complex integrated circuits was defined as 40℃to 125℃ through 2009, increasing to 40℃to 150℃for 2010 and beyond. Power/linear devices were not separately listed in 2003.The ITRS is consistent with the current automotive high-temperature limitations. Delphi Delco Electronic Systems offers two production engine controllers (one on ceramic and one on thin laminate) for direct mounting on the engine. These controllers are rated for operation over the temperature range of 40℃to 125℃. The ECU must be mounted on the coolest spot on the engine. The packaging technology is consistent with 140℃ operation, but the ECU is limited by semiconductor and capacitor technologies to 125℃.The future projections in the ITRS are not consistent with the desire to place controllers on-engine or in-transmission. It will not always be possible to use the coolest location for mounting control units. Delphi Delco Electronics Systems has developed an in-transmission controller for use in an ambient temperature of 140℃[10] using ceramic substrate technology. DaimlerChrysler is also designing an in-transmission controller for usewith a maximum ambient temperature of 150℃ (Figs. 4 and 5) [11].II. MECHATRONICSMechatronics, or the integration of electrical and mechanical systems offers a number ofadvantages in automotive assembly. Integration of the engine controller with the engine allows pretest of the engine as a complete system prior to vehicle assembly. Likewise with the integration of the transmission controller and the transmission, pretesting and tuning to account for machining variations can be performed at the transmission factory prior to shipment to the automobile assembly site. In addition, most of the wires connecting to a transmission controller run to the solenoid pack inside the transmission. Integration of the controller into the transmission reduces the wiring harness requirements at the automobile assembly level.Fig. 4. Prototype DaimlerChrysler ceramic transmission controller [11]Fig. 5. DaimlerChrysler in-transmission module [11].The trend in automotive design is to distribute control with network communications. As the industry moves to more X-by-wire systems, this trend will continue. Automotivefinalassembly plants assemble subsystems and components supplied by numerous vendors to build the vehicle. Complete mechatronic subsystems simplify the design, integration, management, inventory control, and assembly of vehicles. As discussed in the previous section, higher temperature electronics will be required to meet future mechatronic designs.III. PACKAGINGCHALLENGES AT125℃Trends in electronics packaging, driven by computer and portable products are resulting in packages which will not meet underhood automotive requirements at 125℃. Most notable are leadless and area array packages such as small ball grid arrays (BGAs) and quadflatpacks no-lead (QFNs). Fig. 6 shows the thermal cycle test 40 ℃to 125℃ results for two sizes of QFN from two suppliers [12]. A typical requirement is for the product to survive 2000–2500 thermal cycles with<1% failure for underhood applications. Smaller I/O QFNs have been found to meet the requirements.Fig. 7 presents the thermal cycle results for BGAs of various body sizes [13]. The die size in the BGA remained constant (8.6 *8.6 mm). As the body size decreases so does the reliability. Only the 23-mm BGA meets the requirements. The 15-mm BGA with the 0.56-mm-thick BT substrate nearly meets the minimum requirements. However, the industry trend is to use thinner BT substrates (0.38 mm) for BGA packages.One solution to increasing the thermal cycle performance of smaller BGAs is to use underfill. Capillary underfill was dispensed and cured after reflow assembly of the BGA. Fig. 8 shows a Weibull plot of the thermal cycle data for the 15-mm BGAs with four different underfills. Underfill UF1 had no failures after 5500 cycles and is, therefore, not plotted. Underfill, therefore, provides a viable approach to meeting underhood automotive requirements with smaller BGAs, but adds process steps, time, and cost to the electronics assembly process.Since portable and computer products dominate the electronics market, the packages developed for these applications are replacing traditional packages such as QFPs for new devices. The automotive electronics industry will have to continuedeveloping assembly approaches such as underfill just to use these new packages in current underhood applications.IV. TECHNOLOGY CHALLENGES ABOVE125 ℃The technical challenges for high-temperature automotive applications are interrelated, but can be divided into semiconductors, passives, substrates,interconnections, and housings/connectors. Industries such as oil well logging have successfully fielded high-temperature electronics operating at 200℃ and above. However, automotive electronics are further constrained by high-volume production, low cost, and long-term reliability requirements. The typical operating life for oil well logging electronics may only be 1000 h, production volumes are in the range of 10s or 100s and, while cost is a concern, it is not a dominant issue. In the following paragraphs, the technical challenges for high-temperature automotive electronics are discussed.Semiconductors: The maximum rated ambient temperature for most silicon basedintegrated circuits is 85℃, which is sufficient for consumer, portable, and computing product applications. Devices for military and automotive applications are typically rated to 125℃. A few integrated circuits are rated to 150℃, particularly for power supply controllers and a few automotive applications. Finally, many power semiconductor devices are derated to zero power handling capability at 200℃.Nelmset al.and Johnsonet al.have shown that power insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) and metal–oxide–semiconductorfield-effect transistors (MOSFETs) can be used at 200℃[14], [15]. The primary limitations of these power transistors at the higher temperatures are the packaging (the glass transition temperature of common molding compounds is in the 180℃ to 200℃range) and the electrical stress on the transistor during hard switching.A number of factors limit the use of silicon at high temperatures. First, with a bandgap of 1.12 eV, the silicon p-n junction becomes intrinsic at high temperature (225℃ to 400℃depending on doping levels). The intrinsic carrier concentration is given by (1)As the temperature increases, the intrinsic carrier concentration increases. When the intrinsic carrier concentration nears the doping concentration level, p-n junctions behave as resistors, not diodes, and transistors lose their switching characteristics. One approach used in high-temperature integrated circuit design is to increase the doping levels, which increases the temperature at which the device becomes intrinsic. However, increasing the doping levels decreases the depletion widths, resulting in higher electricfields within the device that can lead to breakdown.A second problem is the increase in leakage current through a reverse-biased p-n junction with increasing temperature. Reverse-biased p-n junctions are commonly used in IC design to provide isolation between devices. The saturation current (I,the ideal reverse-bias current of the junction) is proportional to the square of the intrinsic carrier concentrationwhere Ego=bandgap energy atT= 0KThe leakage current approximately doubles for each 10℃rise in junction temperature. Increased junction leakage currents increase power dissipation within the device and can lead to latch-up of the parasitic p-n-p-n structure in complimentary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) devices. Epitaxial-CMOS (epi-CMOS) has been developed to improve latch-up resistance as the device dimensions are decreased due to scaling and provides improved high-temperature performance compared to bulk CMOS.Silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology replaces reverse-biased p-n junctions with insulators, typically SiO2 , reducing the leakage currents and extending the operating range of silicon above 200℃. At present, SOI devices are more expensive than conventional p-njunction isolated devices. This is in part due to the limited use of SOI technology. With the continued scaling of device dimensions, SOI is being used in some high-performance applications and the increasing volume may help to eventually lower the cost.Other device performance issues at higher temperatures include gate threshold voltage shifts, decreased noise margin, decreased switching speed, decreased mobility, decreased gain-bandwidth product, and increased amplifier input–offset voltage [16]. Leakage currents also increase for insulators with increasing temperature. This results in increased gate leakage currents, and increased leakage of charge stored in memory cells (data loss). For dynamic memory, the increased leakage currents require faster refresh rates. For nonvolatile memory, the leakage limits the life of the stored data, a particular issue for FLASH memory used in microcontrollers and automotive electronics modules.Beyond the electrical performance of the device, the device reliability must also be considered. Electromigration of the aluminum metallization is a major concern. Electromigration is the movement of the metal atoms due to their bombardment by electrons (current flow). Electromigration results in the formation of hillocks and voids in the conductor traces. The mean time to failure (MTTF) for electromigration is related to the current density (J)and temperature(T) as shown in (3)The exact rate of electromigration and resulting time to failure is a function of the aluminum microstructure. Addition of copper to the aluminum increases electromigration resistance. The trend in the industry to replace aluminum with copper will improve the electromigration resistance by up to three orders of magnitude [17].Time dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB) is a second reliability concern. Time to failure due to TDDB decreases with increasing temperature. Oxide defects, including pinholes, asperities at the Si–SiO2 interface and localized changes in chemical structure that reduce the barrier height or increase the charge trapping are common sources of early failure [18]. Breakdown can also occur due to hole trapping (Fowler–Nordheim tunneling). The holes can collect at weak spots in the Si–SiO2 interface, increasing the electricfield locally and leading to breakdown [18]. The temperature dependence of time-to-breakdown(tBD) can be expressed as [18]Values reported for Etbd vary in the literature due to its dependence on the oxidefield and the oxide quality. Furthermore, the activation energy increases with breakdown time [18].With proper high-temperature design, junction isolated silicon integrated circuits can be used to junction temperatures of 150℃ to 165℃, epi-CMOS can extend the range to 225℃to 250℃ and SOI can be used to 250℃ to 280℃ [16, pp. 224]. High-temperature, nonvolatile memory remains an issue.For temperatures beyond the limits of silicon, silicon carbidebased semiconductors are being developed. The bandgap of SiC ranges from 2.75–3.1 depending on the polytype. SiC has lower leakage currents and higher electric field strength than Si. Due to its wider bandgap, SiC can be used as a semiconductor device at temperatures over 600℃. Theprimary focus of SiC device research is currently for power devices. SiC power devices may eventuallyfind application as power devices in braking systems and direct fuel injection. High-temperature sensors have also been fabricated with SiC. Berget al.have demonstrated a SiCbased sensor for cylinder pressure in combustion engines [19] at up to 350℃ and Casadyet al.[20] have shown a SiC-based temperature sensor for use to 500℃. At present, the wafer size, cost, and device yield have made SiC devices too expensive for general automotive use. Most SiC devices are discrete, as the level of integration achieved in SiC to date is low.Passives: Thick and thin-film chip resistors are typically rated to 125 ℃. Naefeet al.[21] and Salmonet al.[22] have shown that thick-film resistors can be used at temperatures above 200℃ if the allowable absolute tolerance is 5% or greater. The resistors studied were specifically formulated with a higher softening point glass. The minimum resistance as afunction of temperature was shifted from 25℃to 150℃to minimize the temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) over the temperature range to 300℃. TaN and NiCr thin-film resistors have been shown to have less than 1% drift after 1000 h at 200℃ [23]. Thus, for tighter tolerance applications, thin-film chip resistors are preferred. Wire wound resistors provide a high-temperature option for higher power dissipation levels [21].High-temperature capacitors present more of a challenge. For low-value capacitors, negative-positive-zero (NPO) ceramic and MOS capacitors provide low-temperature coefficient of capacitance (TCC) to 200℃. NPO ceramic capacitorshave been demonstrated to 500℃ [24]. Higher dielectric constant ceramics (X7R, X8R, X9U), used to achieve the high volumetric efficiency necessary for larger capacitor values, exhibit a significant capacitance decrease above the Curie temperature, which is typically between 125℃ to 150℃. As the temperature increases, the leakage current increases, the dissipation factor increases, and the breakdown strength decreases. Increasing the dielectric tape thickness to increase breakdown strength reduces the capacitance and is a tradeoff. X7R ceramic capacitors have been shown to be stable when stored at 200℃ [23]. X9U chip capacitors are commercially available for use to 200 C, but there is a significant decrease in capacitance above 150℃.Consideration must also be given to the capacitor electrodes and terminations. Ni is now being substituted for Ag and PdAg to lower capacitor cost. The impact of this change on hightemperature reliability must be evaluated. The surface finish for ceramic capacitor terminations is typically Sn. The melting point of the Sn (232℃) and its interaction with potential solders/brazes must also be considered. Alternate surfacefinishes may be required.For higher value, low-voltage requirements, wet tantalum capacitors show reasonable behavior at 200℃ if the hermetic seal does not lose integrity [23]. Aluminum electrolytics are also available for use to 150℃. Mica paper (260℃) and Teflonfilm (200℃) capacitors can provide higher voltage capability, but are large and bulky [25]. High-temperature capacitors are relatively expensive. V capacitors are relatively expensive. Volumetrically efficient, high-voltage, highcapacitance, olumetrically efficient, high-voltage, highcapacitance, high-temperature and low-cost capacitors are still needed.Standard transformers and inductor cores with copper wire and teflon insulation are suitable for operation to 200℃. For higher temperature operation, the magnetic core, the conductor metal (Ni instead of Cu) and insulator must be selected to be compatible with the higher temperatures [16, pp. 651–652] Specially designed transformers can be used to 450℃ to 500℃, however, they are limited in operating frequency.Crystals are required for clock frequency generation for microcontrollers. Crystals with acceptable frequency shift over the temperature range from 55℃to 200℃ have been demonstrated [22]. However, the selection of packaging materials and assembly process for the crystal are key to high-temperature performance and reliability. For example, epoxies used in assembly must be compatible with 200℃ operation.Substrates: Thick-film substrates with gold metallization have been used in circuits to 500℃ [21], [23]. Palladium silver, platinum silver, and silver conductors are morecommonly used in automotive hybrids for reduced cost. Silver migration has been observed with an unpassivated PdAg thick-film conductor under bias at 300℃ [21]. The time-to-failure needs to be examined as a function of temperature and bias voltage with and without passivation. Low-temperature cofired ceramic (LTCC) and high-temperature cofired ceramic (HTCC) are also suitable for high-temperature automotive applications. Embedded resistors are standard to thick-film hybrids, LTCC, and some HTCC technologies. As previously mentioned, thick-film resistors have been demonstrated at temperatures 200℃. Dielectric tapes for embedded capacitors have also been developed for LTCC and HTCC. However, these embedded capacitors have not been characterized for high-temperature use.High-Tg laminates are also available for fabrication of hightemperature printed wiring boards. Cyanate esters [Tg=250℃by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)], polyimide (260℃by DSC), and liquid crystal polymers(Tm>280℃)provide options for use to 200℃. Cyanate ester boards have been used successfully in test vehicles at 175℃, but failed when exposed to 250℃ [26]. The higher coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the laminate substrates compared to the ceramics must be considered in the selection of component attachment materials. The temperature limits of the laminates with respect to assembly temperatures must also be carefully considered. Work is ongoing to develop and implement embedded resistor and capacitor technology for laminate substrates for conventional temperature ranges. This technology has not been extended to high-temperature applications.One method many manufacturers are using to address the higher temperatures whilemaintaining lower cost is the use of laminate substrates attached to metal. The typical design involves the use of higher Tg( +140℃ and above) laminate substrates attached to an aluminum plate (approximately 2.54-mm thick) using a sheet or liquid adhesive. To assist in thermal performance, the laminate substrate is often thinner (0.76 mm) than traditional automotive substrates for under-the-hood applications. While this design provides improved thermal performance, the attachment of the laminate to aluminum increases the CTE for the overall substrates. The resultant CTE is very dependent on the ability of the attachment material to decouple the CTE between the laminate substrate and the metal backing. However, regardless of the attachment material used, the combination of the laminate and metal will increase the CTE of the overall substrate above that of a stand-alone laminate substrate. This impact can be quite significant in the reliability performance for components with low CTE values (such as ceramic chip resistors). Fig. 9 illustrates the impact of two laminate-to-metal attachment options compared to standard laminate substrates [27], [28]. The reliability data presented is for 2512 ceramic chip resistors attached to a 0.79-mm-thick laminate substrate attached to aluminum using two attachment materials. Notice that while one material significantly outperforms the other, both are less reliable than the same chip resistor attached to laminate without metal backing.This decrease in reliability is also exhibited on small ball grid array (BGA) packages. Fig. 10 shows the reliability of a 15-mm BGA package attached to laminate compared to the same package attached to a laminate substrate with metal backing [27], [28]. The attachment material used for the metal-backed substrate was the best material selected from previous testing. Notice again that the metal-backed substrate deteriorates the reliability. This reliability deterioration is of particular concern since many IC packages used for automotive applications are ball grid array packages and the packaging trend is for reduced packaging size. These packaging trends make the use of metal-backed substrates difficult for next generation products.One potential solution to the above reliability concern is the use of encapsulants and underfills. Fig. 11 illustrates how conformal coating can improve component reliability for surface mount chip resistors [27], [28]. Notice that the reliability varies greatly depending on material composition. However, for components which meet a marginal level of reliability, conformal coatings may assist the design in meeting the target reliability requirements. The same scenario can be found for BGA underfills. Typical underfill materials may extend the component life by a factor of two or more. For marginal IC packages, this enhancement may provide enough reliability improvement toall the designs to meet under-the-hood requirements. Unfortunately, the improvements provided byencapsulants and underfills increase the material cost and adds one or more manufacturing processes for material dispense and cure.Interconnections: Methods of mechanical and electrical interconnection of the active and passive components to the board include chip and wire,flip-chip, and soldering of packaged parts. In chip and wire assembly, epoxy die-attach materials can beused to 165℃ [29]. Polyimide and silicone die-attach materials can be used to 200℃. For higher temperatures, SnPb ( >90Pb), AuGe, AuSi, AuSn, and AuIn have been used. However,with the exception of SnPb, these are hard brazes and with increasing die size, CTE mismatches between the die and the substrate will lead to cracking with thermal。

一、根据英文单词,写出中文意义(每个 1 分,共 15分)第一组1.alternator2. semiconductor3. impedance4. charge5. inductor6. dielectrics7.oscillator8.emitter9.amplifier 10.wavelength 11.capacitor 12.resistance 13.insulator 14.conductor 15.formula1交流发电机、2半导体、3阻抗、4电荷、5电感、6电介质、7振荡器 8发射器、9放大器、10波长、11电容、12电阻、13绝缘体、14导体、 15公式第二组1.generator2.cross-section3.current flow4.cycle5.terminallivolt7.microvolt8.neutral state 9.electric field 10.magnetic field 11.root-mean-sqare 12.peak value 13.instantaneous value 14.peak-to-peak value 15.three-phase AC发电机横截面电流周期终端毫伏微伏中性状态电场磁场均方根峰值瞬时值峰峰值三相交流电第三组1、sine wave 正弦波2、positive direction 正向3、negative direction 负向4、trigonometric fuction 三角函数5、effective value 有效值6、battery 电池7、voltmeter 电压表8、ammeter 电流表9、Ohm’s Law 欧姆定律 10、series circuit 串联电路 11、parallel circuit 并联电路 12、 series resistance 串联电阻 13、equal value resistor 等值电阻 14、compound circuit 复合电路 15、electromagnet 电磁铁第四组parallel branch 并联分支 lowest common multiple 最小公倍数 series-parallel 串并联 diode 二极管 transistor 晶体管 physics types 物理模型 carbon family 碳族outer electron 外层电子 perodici table 元素周期表 positive charge 正电荷PN junction PN结number system 数字系统compound circuit 复合电路 N region第五组numerical value 数字值binary system 二进制系统decimal value 十进制programmable controller 可编程编码控制器 switch 开关 conversion of number 数字转换 laptop 手提电脑 truth table 真值表 inverter switch 转向开关 pull-up resistor 牵引电阻 Very Large Scale Integration 超大规模集成电路 linear speed 线速度external force 外力 acceleration 加速度第六组1.permanent magnet2. south pole3. magnetic lines4. DC motors5. electromotive force6. closed-loop7. controller8. feedback9. disturbance 10. over time 11. self-regulation12. dead time 13. sampling period 14. external force 15. acceleration永久磁铁南极磁力线直流电动机电动势闭环控制器反馈干扰超时自调整死区采样周期外力加速度第七组1.series resonance2. rectifier3. amplifier4. voltage divider5. end-to-end6.equivalent circuit7.oscillator8.emitter9.amplifier 10.wavelength11.capacitor 12.resistance 13.insulator 14.conductor 15.formula串联谐振整流器放大器分压器首尾相连等效电路7振荡器 8发射器、9放大器、10波长、11电容、12电阻、13绝缘体、14导体、 15公式第八组1. neutral state2. Alternator3. magnetic lines4. Effective value5. counter electromotive force6. Root-mean-square7. equation root8. feedback9. disturbance 10. over time11. self-regulation 12. dead time 13. sampling period 14. external force 15. acceleration中性状态南极磁力线有效值反电动势均方值(均方根)方程根反馈干扰超时自调整死区采样周期外力加速度第九组1.alternator2. semiconductor3. impedance4. charge5. inductor6. dielectrics7.oscillator8. feedback9. disturbance 10. over time 11. self-regulation 12. dead time 13. sampling period 14. external force 15. acceleration1交流发电机、2半导体、3阻抗、4电荷、5电感、6电介质、7振荡器反馈干扰超时自调整死区采样周期外力加速度第十组1. open-loop2. controller3. feedback4. disturbance5. over time6. self-regulation7. dead time8.emitter9.amplifier 10.wavelength11.capacitor 12.resistance 13.insulator 14.conductor 15.formula1开环 2控制器 3反馈 4干扰 5超时 6自调整 7死区8发射器、9放大器、10波长、11电容、12电阻、13绝缘体、14导体、 15公式。

FanE『翻译中国』--- E时代的翻译! 中国人的翻译! 选择效应 selective photoelectric effect 选择性光电效应 self irradiation effect 自辐照效应 self scattering effect 自散射效应 self-bias cut-off effect 自偏截止效应; 自偏压截止效应 self-biasing effect 自偏压效应self-cleaning effect 自行清洁作用 self-demagnetization effect of tape 磁带自去磁效应 self-right effect 自动回正作用self-righting effect 自动回正作用 self-shielding effect 自屏蔽效应 self-stabilizing effect in braking 汽车制动自稳效应self-traping effect 光束自陷效应 self-trapping effect 自陷效应 sensible cooling effect 显热冷却效果 sensitizing effect 敏化效应 sensitlzing effect 敏感效应 separate efficiency 分部效率 separating efficiency 分离效率; 分离总效率separation effect 分离效应 separation efficiency 分离效率; 分选效率 separation fluid effect 脱流效应 serous effusion 浆液性渗出物; 浆液性渗漏液 service efficiency 使用效率setting effect 凝固效应 Sewell Wright effect 赖特氏效应shadow effect 屏蔽效应; 荫影效应; 阴影效应 shallow water effect 浅水效应 shaped-charge effect 锥形装药聚能效应shearing effect 剪切效应 sheath effects 外皮效应 shell effect 外壳效应 shield effectiveness 屏蔽效率 shielding effect 屏蔽效应; 屏蔽作用 shift effect hypothesis 移动效应假设 shoaling effect 滩浅影响 shock effect 冲击效应; 冲击影响; 震动作用 shock metamorphic effect 冲击变质效应 shock stall effect 激波离体效应 short-term effect 短期效应; 短时效应;近期效应 shot effect 散弹效应; 散粒效应; 散粒噪声 shoulder effect (由肩颈现象而产生的作用) 肩颈效应 Shpol'skii effect 施伯斯基效应 shunting effect 分流作用; 分路效应 shutter efficiency 快门光学有效系数 side effect 副作业; 次要的影响side-band effect 旁带效应 sieve effect 筛分效应 sign of pericardial effusion 心包积液症 signal effect 信号效果silhouette effect 侧影效果 silicon field-effect transistor 硅场效应晶体管 Silsbee effect 西尔斯比效应 singing effect 振鸣作用 singing stovepipe effect 火炉烟囱振鸣效应 single effect 单向作用; 单效 single effect evaporator 单效蒸发器single-effect distillator 单效蒸馏器 sink effect 吸收效应sink-efficiency 散热器效率 size effect 尺寸效应; 截面因数skin effect 趋肤效应; 皮层效应; 表面效应; 表皮效应; 集肤效应 skin effect rotor 深槽式转子 skin effect winding 深槽式绕组 skin-effect attenuation 趋肤衰减 skin-friction effect 表面摩擦效应 skip effect 跳越效应 sky-wave effect 天波效应slack effective 迟效的化肥或农药 slight effect 轻度影响 slot effect 槽效应; 齿槽效应 slot field-effect transistor 沟道场效应晶体管 slow motion effecf 慢动作效果 smearing effect 涂污效应; 拖尾效应; 模糊效应 smoke effect 烟幕作用 smoke removal efficiency 烟雾滤除效率 smoothing effect 平滑作用snob effect 逆反效应 Snoek effect 斯诺克效应 snowplough effect 雪犁效应 snowplow effect 雪犁效应 solar cycle effect 太阳周效应 solar flare effects 太阳耀斑效应 solubilityeffect 溶解效应 solution effect 溶解作用 solvent effect 溶剂效应 solvent efficiency 溶剂效率 solvent isotope effect 溶剂同位素效应 somatic effects 躯体效应 somatic efferent cranial nerve 躯体传出脑神经 somatic position effect 体细胞位置效应sound disturbance effects 声干扰效应 sound effect filter 声响效果滤波器 sound effects 音响效果 source bias effect 源偏压效应 source efficiency 源效率; 光源效率 source output efficiency 源输出效率 source-coupling efficiency 光源耦合效率 space-charge effect 空间电荷效应 spalling effect 剥落作用; 激冷激热效应 spatial degeneracy effect 空间简并效应 speaker efficiency 扬声器效率 special effect 特殊效果 special effect generator 特技信号发生器 special effects 特技效果 specially good effect 特效 specific efficiency 比效率 specific ion effect 专性离子效应 specific melting efficiency 比熔化效率specific toxic effect 特异毒害作用; 专性毒害作物 speckle effect 斑纹效应; 散斑效应 spectral luminous efficacy 光谱光视效能 spectral luminous efficiency 光谱发光效率; 光谱光视效率; 发光度函数 speculative efficiency hypothesis 投机效率假说 speed effect 速度效应 speed(-)up effect 增速效应 spheric wave proximity effect 球面波近场效应 spillover effect 超溢效果 spillover efficiency 溢流效率 spin effect 自旋效应 spiral effect of slipstream 滑流螺旋效应 spite effect 泄愤效应split screen effect 分画面特技 sport efficiency 运动效率spread effect 波及效果 spreading effect 扩散效应sprocket-hole effect 片孔效应 squeeze effect 挤压效应stabilization efficiency 稳定效率 stabilizing effect 稳定效应 stable effluent 稳定排液 stage efficiency 分段效率; 级效率 stage-lighting effect 舞台灯光效果; 舞台照明效应 staging effective data rate 阶梯有效数据传输率; 登台数据有效率standard effective temperature (SET) 标准有效温度 Stark effect 斯塔克谱线磁裂效应; 斯塔克效应 starting effort 起动力 starting tractive effort 起动牵引力 static effect of conjugation 静态共轭效应; 静态共轭效应 static efficiency 静电效率; 静电效率; 静态效率; 静态效率 static inductive effect 静态诱导效应; 静态诱导效应 station efficiency 电站效率statistical efficiency 统计有效性 steadying effect 稳定效应; 旋转质量惯性 steam efficiency 蒸汽效率 steering effort 转向力 steering-wheel (rim) effort 转向盘操纵力 stem effect 支柄影响 step recovery effect harmonic generator 阶跃恢复效应谐波发生器 step recovery effect pulse sharpener 阶跃恢复效应脉冲整形器 stereo effect 立体声效应 stereoscopic effect 立体效果; 立体效应; 体视效应 steric effect 位阻效应Stiles-Crawfood effect 斯太耳斯-克劳福德效应 stimulated Brillouin effect 受激布里渊效应 stimulated Raman effect 受激喇曼效应 stimulated Rayleigh effect 受激瑞利效应 stochastic effect 随机效应 stochastic effects 随机效应 stock-removing efficiency 切削效率 stopping effect 抑制效应 storage effect 储能效应; 累积效应 storage efficiency 存储效率 strain hardening effect 应变硬化效应 stray-capacity effect 杂散电容效应 stray-field effect 杂散场效应 strength efficiency 强力利用率 strengthening effect 强化效应 stress effect 应力效应stress-softening effect 应力软化效应 stretching effect 拉伸效应 striated effect 成纹效应 string efficiency 串效率stroboscopic effect 频闪效应 strong interaction effect 强相互作用效应 strong renormalization effect 强重正化效应structural effects index 结构影响指数 subacuteeffusion-constrictive pericarditis 亚急性渗液缩窄性心包炎sublethal effect 亚致死效应 subsequent effects of fertilizer 肥料残效 subsonic effuser 亚音速喷管 substituting effect 取代效应 substitution effect 替代效果; 替代效应 suction effect 吸气作用 sugar mill effluent 糖厂流出水 sun effect (通过窗户和结构材料传入室内的太阳能) 日照得热量 super-relativistic effect 极端相对论性效应 superconductive tunnel effect 超导隧道效应 superimposed effect 叠加效应 superperiod effect 超周期效应 supplementary effect 互补作用 surface effect 表面效应surface photoelectric effect 表面光电效应 surface-effect vehicle 表面效应运载工具; 气垫艇 surge effect 涌浪效应suspension effect 悬浮作用; 悬液效应 suspension roll geometry effect 悬挂系统侧倾效应 Suzuki effect 铃木秀茨效应sweep efficiency 波及系数 sweep-out effect 扫出效应synchronous effect 同步作用 system effectiveness 系统效率; 系统有效性 system efficiency 系统效率 system performance effectiveness 系统性能有效度 systemic effect 全身效应 T effector cell 效应性T细胞 tactical efficiency 战斗力 tail effect 尾端效应 tare effect 支架效应 tautomeric effect 互变效应 tax effect 课税效果; 课税影响 tax effort 课征效率Taylor effect 泰勒效应 technical efficiency 技术效率temperature effect 温度效应; 温度影响 temperature efficiency 温度效率 temperature-efficiency index 温度有效指数; 温效指数 tensor-tensor effect 张量张量效应 terms-of-trade effect 贸易条件效果 test for metabolic effect of thyroid hormone 甲状腺激素代谢效应试验 tetrad effect 四素组效应 texturing effect 变形效应 theoretical volumetric efficiency 理论容积效率 theory of human effectiveness 人的有效性理论 therapeutic effectiveness 疗效 therapeutic efficacy 治疗效能 thermal broadening effect 热增宽效应 thermal cycle efficiency 热循环效率 thermal effect 热骚动 thermal effectiveness 热处理效果thermal efficiency 热效率; 温度效率 thermal efficiency ratio 热效率比 thermal effusion 热隙透 thermal feedback effect 热隙透效应 thermal lens effect 热透效应 thermal pinch effect 热箍缩效应 thermal rod effect 热棒效应 thermal sensitive effect 热敏效应 thermal shock effect 热冲击影响 thermal skin effect 热趋肤效应 thermal-efficiency index 温度效率指数thermal-efficiency ratio 温度效率比 thermionic effect 热离子效应 thermo-optic effect 热光效应 thermo-resistive effect 温阻效应 thermoacoustic effect 光声效应 thermochemical isotope effect 热化学同位素效应 thermochromatic effect 热色效应thermodynamic efficiency 热力效率; 热力学效率 thermoelastic effect 热弹效应; 热弹性效应 thermoelectric (al) heterogeneous effect 热电非均匀效应 thermoelectric effect 温差电效应; 热电效应 thermoelectrical effect 热电效应thermoelectronic effect 热电子效应 thermohydraulic effect 热水力学效应 thermolens effect 热透效应 thermomagnetic effect 热磁效应 thermomechanical effect 热机械效应 thixotropic effect 触变效应 Thomson effect 汤姆逊热电效应; 汤姆逊效应;同质热电效应 Thornthwaite precipitation effectiveness index 桑斯威特降水效率指数 three-dimension effect 立体感three-dimensional effect 三维效应; 立体效果; 空间效应threshold effect 阈作用 throw-off effect 断开效应 tidal effect 潮汐效应; 潮汐影响 tidal efficiency 潮汐效率 time dilation effect 时钟变慢 time effect 时间效应 time efficiency 时间效率 time-dependent effect 含时效应time-dependent lensingn effect 时间相关透镜效应 tip effect 末端效应 tissue growth efficiency 组织生长效率 topographic curl effect 地形旋度效应 topographic(al) effect 地形影响torpedo effective range indicator 鱼雷有效距离指示仪 torque efficiency 转矩效率; 机械效率 total (combined) efficiency 总效率 total cooling effect 总冷却效果 total efficiency 全效率total head efficiency 总压头效率 total lumen efficiency 总流明效率 total resolution efficiency 总分辨效率 towing efficiency 拖带效率 toxic effect 毒效 tractive efficiency 牵引效率 tractive effort 牵引效力; 牵引作用 trade creation effect 增加贸易作用 trade diversion effect 转移贸易作用trade diverting effect 贸易转向效果 trans-effect 反式效应transchannel effect 传递通道效应 transcolumn effect 传递柱效应 transfer efficiency 转换效率; 转移效率; 传递效率; 合金过渡系数 transferred electron effect 迁移电子效应 transformerefficiency 变压器效率 transient effect 瞬态效应; 暂态效应transient radiation effects (TRE) 瞬时辐照效应transient-response efficiency 瞬变负荷效率 transit time effect 切换时间效应; 渡越时间效应 transition effect 过渡效应 transmission efficiency 传递效率; 传动效率; 传输效率; 传送效率; 通话效率 transmission efficiency measuring set 传输效率测量器 transmission-line efficiency 传输线效率transmitting efficiency 发送效率 transonic effect 跨声速效应transparticle effect 传递颗粒效应 transpiration effection leaching fractions 蒸腾对淋溶等级的作用 transpiration efficiency 蒸腾效率 transponder reply efficiency 应答器的应答效率 transport efficiency 迁移效率 transverse Doppler effect 横向多普勒效应 transverse magnetic field effect 横向磁场效应 transverse piezoelectric effect 横压电效应 trap effect 陷阱效应 traumatic subdural effusion 外伤性硬脑膜下积液 trawling efficiency 拖曳效率 tray efficiency 板效率 trend effect 趋势效果 triboelectric effect 摩擦带电效应; 摩电效应trick effects 特技效果 trickling-down effect 浸透效应trigger effect 触发效应 triode field-effect transistor 三极场效应晶体管 triple effect 三效 triple effect evaporation 三效蒸发 triple effect evaporator 三效蒸发器 triplet-state effect 三重态效应 tube efficiency 电子管效率 tumorouspleural effusion 肿瘤性胸膜渗液 tunnel effect element 隧道效应元件 turbine efficiency 涡轮机效率; 水轮机效率 turning effect 转动效应 turning effort 旋转作用; 回转力 twelve principles of efficiency 效率十二原则 twist effect 扭曲效应two-effect evaporator system 双级蒸发装置 Tyndall effect 廷德尔氏效应; 丁达尔效应 ultrasonic Doppler effect 超声多普勒效应 ultrasonic effect 超声效应 Umkehr effect 逆转效应unchoking effect 消扼流作用; 去扼流作用 unequal irradiation effect 不等辐射效应 unequal quantization effect 不等量子化效应 unipolar field effect transistor 单极场效应晶体管unipolar field effect type transistor 单极场效应型晶体管 unit efficiency 装置效率; 分部效率; 机组效率 universal effective set 全有效集 unpaired-spin effect 不成对自旋效应 untoward effect 不良反应 untreated effluent 未处理废水 upward substitution effect 向上替代影响 upwind effect 上吹效应 ul effect 有效作用 ul efficiency 有效功率 user effort 用户花费valence effect 价效应 valve effect 阀效应; 单向导电性 valve microphonic effect 电子管颤噪效应 valve-point internal efficiency 阀点内效率 vane efficiency 叶片效率 vanity effect (被调查者的) 虚荣心影响 vapo(u)rization efficiency 蒸发效率vaporization efficency 汽化效率 vapour effects 蒸气效力vapour pressure isotope effect (VPIE) 蒸汽压同位素效应variegated position effect 花斑型位置效应 vector effect 媒介作用 vectorial photoelectric effect 矢量光电效应 vehicleroll effect 汽车横摇效应 velocity-modulating effect 速度调制效应 Venturi effect 文丘里效应 vibration effect 振动效应vignetting effects 渐晕效应 Villard effect 维拉德效应Villari effect 维拉里效应 Viogt effect 佛克脱效应 visceral effector 脏器效应器 viscoelastic cross effect 粘弹性横向效应viscosity effect 粘度效应 viscous effect 粘滞作用 visual effect 视觉效应 visual efficiency 视觉效率 visual Herschel effect 赫歇尔效应 Vogel-Colson-Russell effect 罗素效应 void effect 空穴效应 Voigt effect 福格特效应 Volta effect 伏打效应 voltage efficiency 电压效率 voltage of microphonic effect 颤噪电压 voltage saturation effect 电压饱和效应voltage-sensitive effect 压敏效应 voltaic effect 伏打效应volume effect 体积效应 volume efficiency 体积效率; 容量系数; 声量效率 volume electrostrictive effect 体积电致伸缩效应volume magnetostrictive effect 体积磁致伸缩效应 volume photoelectric effect 体光电效应 volumetric effect 体积效应volumetric efficiency 容积效率; 容量系数; 容量效率; 充气效率 volumetric efficiency capa 容积效率 vortex-interference effect 涡流干扰效应 wake efficiency 尾流效率 wall effect 壁效应; 器壁效应; 畴壁效应; 管壁效应 warping effect 翘曲作用washery effluent 洗矿厂泄出水 washing efficiency 洗选效率waste effluent flume 废水沟 watt-hour efficiency 瓦-时效率; 瓦时效率 wave efficiency 波动高峰; 波动效率 wave-particle resonant effect 波粒共振效应 wave-scattering effect 波散效应wave-wave resonant effect 波波共振效应 waveguide effective thickness 波导有效厚度 wavelength effect 波长效应 wealth effect 财富效应 weapon effect 武器效应 Webb effect 威布效应wedging effect 楔入效应 t effect 纬面花纹 Weigert effect 魏格特效应 weight distribution effect (汽车的) 载荷分配效应weight distribution steer effect (汽车的) 载荷分配偏向效应weight efficiency 重量效率 weightlessness effect 失重效应Weissenberg effect (即粘弹性交叉效应) 韦森堡效应 welfare effects 福利效应 Wertheim effect 威德曼效应 wet end efficiency 湿部效率 wet plate efficiency 湿板效率 wet-memory effect 湿定形效应 whirlpool effect 旋涡效应 whispering gallery effect 耳语廊效应 white fishes effect 银鱼效应 Wien effect 威恩效应; 维恩效应 wiggle effect 失常效应 Wigner effect 维格纳效应 wild effect 不稳定现象 Wilson effect 威尔逊效应 Wilson-Bappu effect 威尔逊-巴普效应 Winslow effect 温斯洛效应 wiping effect 擦浆效果; 拭擦效应 wire rope efficiency 钢丝绳效率 wobbling effect 颤动效应 Wood effect 伍德效应 work efficiency 工效; 劳动效率 worked efficiency 工作效率 working (machining) efficiency 加工效率 wound effect 伤口效应 yearly efficiency 年效率 Yigong San powder with marveous Effect 异功散 Zeeman effect 塞曼效应 Zeeman effect frequency stabilization 塞曼效应稳频 Zener effect 齐纳效应Zener efficiency 齐纳效应 zero gravity effect 失重效应Ziehen effect 离子牵制效应 zymotic efficiency 发酵效应zymotic efficiency of soil 土壤发酵效应 ractivity effect 空气折射率效应 egg cleaner 洗蛋机; 蛋品清洗机 egg coal 蛋级烟煤块 egg coke 小块焦炭 egg collecting trough 集蛋 egg collection 集蛋 egg collection conveyer 集蛋输送器 egg collection vehicle 蛋品收集车 egg covering 卵膜 egg culture 卵培养 egg culture-medium 鸡蛋培养基 egg cup 蛋杯 egg dry cleaning machine 蛋品干式清洁机 egg end 半球形末端板 egg ended boiler 蛋形端锅炉 egg follicle 卵包 egg formation 蛋的形成 egg grader 蛋分级器; 蛋品分级机; 蛋品分级器; 鸡蛋分级机 egg grading machine 蛋分级机 egg inoculation 鸡胚接种 egg insulator 蛋形绝缘子; 拉线绝缘子 egg laying 产卵 egg laying performance 产蛋能力 egg mass 卵块 egg medium 鸡蛋培养基 egg membrane 卵膜 egg mother cell 卵母细胞 egg moulding 卵圆饰egg nucleus 卵核 egg or meat type 蛋用型或肉用型 egg parasite 卵蜂 egg plant Jun glaze 茄均釉 egg plum 卵形李 egg pod 卵荚egg pouch 卵鞘 egg powder 蛋粉 egg production 产蛋量 egg pulp全蛋液 egg record card 产蛋记录卡片 egg roll making machine 蛋卷机 egg shape 蛋型 egg shaped kiln 蛋形窑 egg shell 蛋壳; 卵壳 egg shell china 薄胎瓷 egg shell lampshade 皮灯 egg shell porcelain 薄胎瓷 egg size 蛋重 egg sleeker 蛋型墁刀; 蛋形墁刀; 小型圆角光子 egg spoon 蛋匙 egg tempera 蛋青画 egg tester 照蛋灯 egg transfer 卵移植; 受精卵移植 egg tree 蛋树果 egg tubercle 虫卵结节; 卵结节 egg turner 翻蛋器 egg turning (孵化器中) 翻蛋 egg type 蛋用型 egg washer 洗蛋机egg washing machine 蛋品清洗机 egg weight 蛋重 egg white 卵白; 卵清 egg white glaze 乳白釉 egg yolk 蛋黄egg-biscuit-roll machine 蛋卷机 egg-breaking machine 打蛋机egg-breaking plant 打蛋厂 egg-chamber 卵室 egg-collecting line 集蛋传送带 egg-feed ratio 产蛋饲料报酬 egg-globulin 卵球蛋白 egg-holding 蛋的保存 egg-incubation 蚕卵孵化egg-laying test 产蛋性能测定 egg-pair 双蛋 egg-peritonitis 禽卵巢腹膜炎 egg-shaped cup saucer 蛋形杯碟 egg-shaped ornament 卵形饰 egg-shaped sewer 卵形下水道 egg-shell china 蛋壳瓷 egg-shell finish 蛋壳状加工 egg-shell glaze 蛋壳釉egg-shell gloss 蛋壳光 egg-shell meal 蛋壳粉 egg-shell painting 彩绘蛋 egg-shell paper 光厚绘图纸 egg-shell porcelain 蛋壳瓷 egg-shell pottery 蛋壳陶 egg-shelling (釉面缺陷) 蛋壳状釉面 egg-shelling glaze 蛋壳釉 egg-whitesyndrome 卵白综合征 egg-yolk citrate diluent 卵黄柠檬酸稀释液 egg-yolk phosphate diluent 卵黄磷酸酸盐稀释液 eggcrate canopy 格片挑棚 eggcrate ceiling 格片顶棚 eggcrate diffuser 格片散光罩 eggcrate louver 格片百叶窗 eggcrate overhang 格片挑棚 eggcrate type louver 格片百叶窗 eggcrate type shading device 格片遮阳装置 Eggert's test 埃杰特快速定碳试验Eggertz's method 埃格茨法 eggplant 茄子 eggplant phomopsis rot 茄褐纹病 eggplant purple 茄皮紫 eggs per gram 每克卵数eglantine 苯己酸异丁酯; 苯甲酸异丁酯 eglestonite 褐氯汞矿Egnell's law 伊格尼尔定律 ego 自我 ego involvement 自我投入ego-defence mechanisms 自我防御机制 ego-defense 保护自我ego-enhancement 提高自我 ego-ideal 自我理想 egocentric 自我中心的 egomania 自尊癖; 利己狂 egophony 羊鸣音; 羊音 egress 溢出; 出口; 出食; 终切 egress of heat 放热 egress pressure 出口压力 egueite 球磷钙铁矿 eguiphase zone 等相带 Egyptain millet 黑黍 Egyptian blue 埃及蓝 Egyptian chlorosis 埃及萎黄病 Egyptian clovet 埃及三叶草 Egyptian corn 埃及高粱Egyptian cotton 埃及棉 Egyptian flax 埃及亚麻 Egyptian General Petroleum Corp. 埃及石油总公司 Egyptian henna 散沫花Egyptian intestinal fluke 埃及肠吸虫 Egyptian jasper 埃及碧玉 Egyptian kidney bean 埃及云豆 Egyptian lace 埃及花边Egyptian lupin 埃及羽扇豆 Egyptian splenomegaly 曼森氏血吸虫病性脾大 Egyptian wind 埃及风 Egyptianized clay 埃及的粘土electric egg mixer 电动打蛋机 exhaust pressure modulated EGR valve FanE『翻译中国』--- E时代的翻译! 中国人的翻译!silica glass structure 石英玻璃结构Silicom Ltd. Silicom 公司 companysilicon 硅 Sisilicon 硅silicon avalanche rectifier 硅雪崩整流器silicon band gap 硅禁带宽度silicon bilateral switch 硅双通开关 SBSsilicon bilateral switch 硅双向开关silicon carbide 碳化硅silicon carbide acceptor 碳化硅受主silicon carbide band gap 碳化硅禁带宽度silicon carbide decomposition 碳化硅施主silicon carbide donor 碳化硅的分解silicon carbide electron mobility 碳化硅的电子迁移率silicon carbide hole mobility 碳化硅空穴迁移率silicon carbide lamp 碳化硅发光管碳化硅灯silicon carbide luminescence 碳化硅发光silicon carbide polytype 碳化硅的多种类型silicon chip 硅芯片Silicon Composers, Inc. 硅制造公司 companysilicon crystal 硅晶体silicon crystal acceptor 硅晶体受主silicon crystal donor 硅晶体施主silicon diode 硅二极管silicon diode array tube 硅二极管阵列管silicon dioxide 二氧化硅silicon electron mobility 硅的电子迁移率silicon EPD etch 硅EPD腐蚀法silicon epitaxy 硅外延silicon evaporation 硅蒸发silicon evaporation process 硅蒸发工艺silicon gate 硅栅silicon gate MOS 硅栅金属氧化物半导体Silicon General 硅通用 companysilicon germanium compound 锗-硅合金silicon hole mobility 硅的空穴迁移率silicon integrated circuit 硅集成电路 SICSilicon Integrated Systems Corporation 硅集成系统公司公司 companysilicon melting point 硅熔点silicon monolithic integrated circuit 硅单片集成电路silicon monoxide 一氧化硅silicon monoxide source 一氧化硅源silicon MOS transistor 硅金属氧化物半导体晶体管silicon nitride 氮化硅silicon nitride passivation 氮化硅钝化silicon on sapphire 硅-蓝宝石工艺,蓝宝石上外延硅silicon on sapphire system 蓝宝石外延硅系统silicon oxidation relationship 硅氧化关系式silicon oxide 氧化硅silicon oxide absorption peak 硅氧化物吸收峰silicon oxide growth 硅氧化物生长silicon photocell 硅光电池silicon planar transistor 硅平面晶体管silicon precision alloy transistor 硅精密合金晶体管 SPC silicon PROM fuse 硅可编程序只读存储器熔丝silicon rectifier 硅整流器silicon rectifier diode 硅整流二极管silicon rectifying bridge 硅整流桥组silicon rectifying cell 硅整流元件silicon resistor 硅电阻silicon solar cell 硅太阳能电池silicon source 硅源silicon steel 硅钢Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. 硅存储科技公司 company silicon sublimation 硅升华silicon sublimation process 硅升华工艺silicon substrate 硅衬底silicon symmetrical switch 硅对称开关Silicon Systems 硅系统 companysilicon tetrabromide process 四溴化硅工人艺silicon tetrahalide 硅的卤化物silicon thyristor 硅闸流管silicon transistor 硅晶体管silicon unilateral switch 硅单向开关silicon wafer 硅圆片silicon warpage 翘曲Silicon-controlled rectifier 硅控整流器silicon-controlled rectifier 晶闸管整流器 SCR silicon-controlled rectifier 晶闸管整流器silicon-controlled switch 晶闸管开关silicone 硅酮silicone heat-sink compound 硅酮散热化合物silicone-assisted photoresist 硅酮助光致故醇Siliconix Inc. Siliconix companysilicon-on-insulator 绝缘体衬底硅 SOLsilk screen method 丝网印制法silk-covered wire 丝包线silver 银silver migration 银迁移silver solder 银焊料silver spraying 银喷镀silver-bonded diode 银键二极管silvered mica capacitor 镀银云母电容器silver-plated copper 镀银铜 SPCsilverstat regulator 银接触型调压器similarity measure 相似性测度simple arithmetic expression 简单算术表达式 SAE simple arithmetic expression 简单算术表达式 SAE simple buffering 简单缓冲simple electronic computer 简便式电子计算机 SEC simple harmonic current 简谐波电流simple harmonic electromotive force 简谐电动势simple loop of bubble 磁泡简单环simple name 简单名simple programming language 简单程序设计语言 SPL simple scanning 简单扫描simple sound source 单声源simple steady state vibration 单稳态振动simple target 单目标Simple Technologies Simple 科技 companysimple tone 单音,纯音simplex 单工,单路,单向 SPXsimplex 单工,单向simplex channel 单向通道simplex coil 单工线圈simplex mode 单工方式simplex operation 单工运用simplex system 单工系统simplex transmission 单工传输simplexes circuit 单工电路simplicity 简明性simplified computer code 计算机简化码 SCCSimtek Corporation Simtek 公司 companysimulate 模拟,仿真simulate assembler 模拟编辑机simulated BOMADC program BOMADC模拟程序 SBPsimulated input processor 模拟输入处理程序 SIP simulated linguistic computer 模拟语言计算机 SLC simulated network analysis program 模拟网络分析程序 SNAP simulated operating procedure 模拟操作过程 SOP simulated output program 模拟输出程序 SOPsimulated-field-effect tetrode 仿场效应四极管simulation 模拟simulation 模拟simulation analysis and modeling 模拟分析与模型化 SAAM simulation analysis and modeling 模拟分析与模型化 SAAM simulation data subsystem 模拟数据子系统 SDS simulation equipment 模拟设备simulation input tape 模拟输入带 SITsimulation language 模拟语言simulation oriented language 面向模拟的语言 SOL simulation programming language 模拟程序设计语言 SPL simulation programming language 模拟处理simulation software 模拟程序设计语言simulator 模拟器,模拟程序simulator 模拟器,模拟程序 Simsimulator 模拟器,模拟程序 Smsimulator 模拟器,模拟程序 Smlsimulator 模拟软件simulator program 模拟程序simulator software program 模拟器软件程序,模拟程序软件simulator/debug utility 模拟器,模拟软件simulcast 同时联播simulcasting 同时联播simultaneity 同时性simultaneous 同时的simultaneous access 同时存取simultaneous computer 同时操作计算机simultaneous I/O bus interface 同时输入/输出总线接口simultaneous input-output 同时输入输出simultaneous lobing 同时扫掠simultaneous operation 同时操作simultaneous sampling 同时采样 SSsimultaneous track processor 并行轨道处理机 STP simultaneous transmission 同时传输simultaneous voice/data 语声/数据同时传送 SVDsine 正弦sine galvanometer 正弦电流计sine low 正弦律sine potentiometer 正弦电位计sine wave 正弦波sine wave modulated jamming 正弦调制干扰sine-cosine 正弦-余弦 SCsinging 啸声,振鸣singing point 振鸣点singing stovepipe effect 炉管唱歌效应single 单个的,单一的 Sgl.single 单一的,单个的 SNIsingle access computer 单存取计算机 SACsingle access computer 半存取计算机 SACsingle address 单地址single address code 单地址码single address instruction 单地址指令single address machine 单地址计算机single address message 单地址信息single agent approach 单模块法single amplitude 单幅度single anode tube 单阳极管single axis gyro 单轴回转仪single board computer 单板计算机 SBCsingle board computer 单板计算机single board computer controller 单板计算机控制器single bus operation 单总线操作single button carbon microphone 单钮式炭粒话筒single call 单呼 SCsingle capstan tape drive 单主动轮磁带机single channel 单通道single channel communications controller 单信道通信控制器 SCCsingle channel simplex 单通道单向通道single chip microcomputer 单片微型计算机single chip modem 单片调制解调器single chip processor 单片处理机single circuit 单工线路single column pence coding 单列十二进制编码single conversion receiver 一次变频接收机single crystal TFT material 单晶薄膜晶体管材料single crystalgrowing furnace 单晶炉Single Cycle Execute 执行单行 SCEsingle degree of freedom system 单自由度系统single density format 单密度格式single dial control 拨号法统调single diffused junction transistor 单扩散结晶体管single domain particle 单畴颗粒single ended pushpull circuit 单端推挽电路 SEPPCsingle error 单个错误single frequency 单频 SFsingle frequency duplex 单频双工制single frequency simplex 单频单工制single grip terminal 单夹端single gun color tube 单枪彩色管single harmonic distortion 单谐波失真single heterojunction laser 单异质结激光器single hop 单跳single hop propagation 一次反射传播single in-line memory module 单列存储器模块 SIMM single inline package 单排引线插件,单插入式管single in-line package 单列直插式封装 SIPsingle instruction execute 单指令执行 SIEsingle instruction format 单一指令格式single instruction-multiple data 单指令多数据 SIMD single instruction-single data 单指令单数据 SRSD single line diagram 单线方框图single line repeater 单线中继器single pass 单遍,一次通过single phase synchronous generator 单相同步发电机single phasing 单相工作single point grounding 单点接地single pole 单极single pole double throw 单刀双掷single precision 单精度single program initiation 单个程序启动 SPIsingle punch 单穿孔single quote mark 单引号single rail 单轨single sampling plan 一次取样方式single setup 单一编排single sheet feeding 单页馈送single shield solid enclosure 单屏蔽固体罩single side band 单边带 SSBsingle signal receiver 单信号接收机single signal reception 单信号接收single stage interconnection cetwork 单极互连网络single step 单步 SSsingle sweep 单扫描single vertical key 单垂直键single-access single-distribution 单存取单分配 SASD single-channel per carrier 每载波单信道 SC/Csingle-channel simplex 单路单工 SCSsingle-chip microcomputer 单片微计算机 SCMsingle-dilution source 单稀释源single-ended 单端single-ended input 单端输入single-ended input impedance 单端输入阻抗single-ended input voltage 单端输入电压single-ended output 单端输出single-ended output voltage 单端输出电压single-ended tube 单端电子管single-ended voltage gain 单端电压增益single-in-line package 单列直插式封装single-phase 单相 SPsingle-polarity pulse 单极性脉冲single-pole 单极 SPsingle-pole double-throw 单刀双掷 SPDTsingle-pole single-throw 单刀单掷 SPSTsingle-pole single-throw 单刀单掷single-pole-piece magnetic head 单极片磁头single-short multivibrator 单稳多谐振荡器 SSsingle-shot blocking oscillator 单稳阻塞振荡器single-shot multivibrator 单稳多谐振荡器single-shot trigger circuit 单稳触发电路single-sideband filter 单边频带滤波器single-sideband modulation 单边频带调制single-sideband suppressed carrier 抑制载波的单边频带single-sideband system 单边频带制single-sideband transmission 单边频带传输single-sideband transmitter 单边频带发射机single-sided diskette 单面软磁盘single-sided double-density diskette 单面倍密度软磁盘single-sided minidiskette 单面小型软磁盘single-step 单步,一步single-step debug 单步调试single-step debugging 单步调试single-step operation 单步操作single-stub tuner 单短路线调谐器single-stud transformer 单短路线变换器single-throw 单掷single-throw circuit breaker 单掷断路器single-throw switch 单掷开关single-tone keying 单音键控single-track magnetic system 单迹磁记录系统single-track recorder 单迹录音机single-tube diffusion furnace 单管扩散炉single-tuned amplifier 单调谐放大器single-tuned circuit 单调谐电路single-turn film head 单匝薄膜磁头single-turn potentiometer 单圈电位器single-unit semiconductor device 单元半导体器件single-valued-current D/A decoder 单值电流数/模译码器single-wire line 单线线路single-word instruction 单字指令single-wound resistor 单层线绕电阻器singular set 奇异系,无首系sink 转接器,接收器,散热器,吸收sink load 耗散负载sinker 下向扩展sinker diffusion 槽扩散sinter 烧结,热压结,结块sintering 烧结sinusoid 正弦曲线,正弦波sinusoidal 正弦的sinusoidal electromagnetic wave 正弦电磁波sinusoidal field 正弦场sinusoidal frequency divider 正弦分频器sinusoidal light wave 正弦光波sinusoidal quantity 正弦变量sinusoidal vibration 正弦振动sinusoidal wave 正弦波Sipex Corporation Sipex 公司 company。
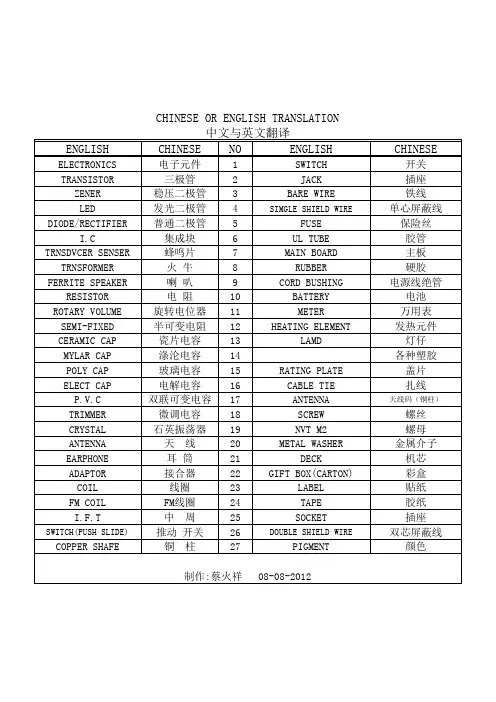


English translationThe E- Behind EverythingElectricity and magnetism run nearly everything we plug in or turn on. Although it’s something we take for granted, it has taken hundreds of years of experimentation and research to reach the point where we flick a switch and the lights go on.People knew about electricity for a long time. Ancient Greeks noticed that if they rubbed a piece of amber, feathers would stick to it. You’ve experienced a similar thing if you’ve ever had your hair stick up straight after you combed it, or had your socks stick together when you removed them from the drier. This is called static electricity, but back then nobody knew how to explain it or what to do with it.Experiments using friction to generate static electricity led to machines that could produce large amounts of static electricity on demand. In 1660 German Otto von made the first electrostatic generator with a ball of sulfur and some cloth. The ball symbolized the earth, and he believed that this little replica of the e arth would shed part of its electric “soul” when rubbed. It worked, and now scientists could study electric shocks and sparks whenever they wanted.As scientists continued to study electricity, they began thinking of it as an invisible fluid and tried to capture and store it. One of the first to do this was Pieter van, Holland. In 1746 he wrapped a water-filled jar with metal foil and discovered that this simple device could store the energy produced by an electrostatic generator. This device became known as the jar. were very important in other people’s experiments, such as Benjamin Franklin’s famous kite experiment. Many people suspected that lightning and static electricity were the same thing, since both crackled and produced bright sparks. In 1752 Franklin attached a key to a kite and flew it in a storm-threatened sky. (NOTE that Franklin did not fly a kite in an actual storm. NEVER do that!) When a thundercloud moved by, the key sparked. This spark charged the jars and proved that lightning was really electricity. Like many experimenters and scientists Franklin used one discovery to make another. Franklin was not the only scientist inspired to conduct experiments with electricity. In the 1780s, the Italian scientist Luigi m ade a dead frog’s leg move by means of an electric current. called this “animal electricity.” He thought that the wet animal tissue generated electricity when it came in contact with metal probes. He even suggested that the soul was actually Italian Alessandro Volta was skeptical of con clusions. In 1799 he discovered that it wasn’t animal tissue alone producing the electric current at all. Volta believed that the current was actually caused by the interaction of water and chemicals in the animal tissue with the metal probes. Volta stacked metal disks separated by layers of cardboard soaked in salt water. This so-called voltaic pile produced an electric current without needing to be charged like a jar. This invention is still around today, but we call it the battery.Volta’s pile was a lot different from the batteries you put in your Discman. It was big, ugly, and messy, but it worked, making Volta the first person to generate electricity with a chemical reaction. His work was so important that the term volt—the unit of electrical tension or pr—is named in his honor. As for Galvani, although he was proven wrong, his work stimulated research on electricity and the body. That research eventually proved that nerves do carry electrical impulses, an important medical discovery. Like electricity, magnetism was baffling to the earliest researchers. Today manufactured magnets are common, but in earlier timesthe only available magnets were rare and mysterious rocks with an unexplainable attraction for bits of iron. Explanations of the way they work sound strange today. For example, in the 1600, English doctor William Gilbert published a book on magnetism. He thought that these strange substances, called “lodestones,” had a soul that accounted for the attraction of a lodestone to iron and steel. The only real use for lodestones was to make compasses, and many thought the compass needle’s movement was in response to its attraction to the earth’s “soul.” By 1800, after many years of study, scientists began wondering if these two mysterious forces—electricity and magnetism—were related. In 1820 Danish physicist Hans Oersted showed that whenever an electric current flows through a wire, it produces a magnetic field around the wire. French mathematician André-Marie used algebra to come up with a mathematical formula to describe this relationship between electricity and magnetism. He was one of the first to develop measuring techniques for electricity. The unit for current, the ampere, abbreviated as amp or as A, is named in his honor. Groundbreaking experiments in electromagnetism were conducted by British scientist Michael Faraday. He showed that when you move a loop of a wire in a magnetic field, a little bit of current flows through the loop for just a moment. This is called induction. Faraday constructed a different version of it called the induction ring. In later years, engineers would use the principle of the induction ring to build electrical transformers, which are used today in thousands of electrical and electronic devices. Faraday also invented a machine that kept a loop of wire rotating near a magnet continuously. By touching two wires to the rotating loop, he could detect the small flow electric current. This machine used induction to produce a flow of current as long as it was in motion, and so it was an electromagnetic generator. However, the amount of electricity it produced was very tiny. There was still another use for induction. Faraday also created a tiny electric motor—too small to do the work of a steam engine but still quite promising. For thousands of years electricity and magnetism were subjects of interest only to experimenters and scientists. Nobody thought of a practical way of using electricity before the 1800s and it was of little interest to most people. But by Faraday’s time invento rs and engineers were gearing up to transform scientific concepts into practical machines.Telegraphs and TelephonesOne of the most important ways that electricity and magnetism have been put to use is making communication faster and easier. In this day o f instant messaging, cell phones, and pagers, it’s hard to imagine a time when messages had to be written and might spend weeks or even months reaching their destination. They had to be carried great distances by ships, wagon, or even by horseback—you coul dn’t just call somebody up to say hello. That all changed when inventors began using electricity and magnetism to find better ways for people to talk to each other. The telegraph was first conceived of in the 1700s, but few people pursued it. By the 1830s, however, advancements in the field of electromagnetism, such as those made by Alessandro Volta and Joseph Henry, created new interest in electromagnetic communication. In 1837, English scientist Charles Wheatstone opened the first com telegraph line between London and Camden Town, a distance of 1.5 miles. Building on, Samuel Morse, an American artist and inventor, designed a line to connect Washington, DC and Baltimore, Maryland in 1844. Morse’s telegraph was a simple device that used a battery, a switch, and a small electromagnet, but it allowed people miles apart to communicate instantly. Although Morse is often credited with inventing the telegraph, his greatest contribution was actually Morse, a special language designed for the telegraph. Morse'scommercialization of the telegraph spread the technology quickly. In 1861 California was connected to the rest of the United States with the first transcontinental telegraph line. Five years later, engineers found a way of spanning the Atlantic Ocean with telegraph lines, thus connecting the United States and Europe. This was an enormous and challenging job. To do it engineers had to use a huge ship called The Great Eastern to lay the cable across the ocean. It was the only ship with enough room to store all that cable. The world was connected by wire before the nation was connected by rail—the transcontinental railroad wasn’t completed until 1869! The telegraph was the key to fast, efficient railroad service. The railroads and the telegraph expanded side-by-side, crisscrossing every continent, except Anta, in the late 1800s. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, telegraphy became a very lucrative business for companies such as Western Union. It also provided women with new career options. As convenient as the telegraph was, people dreamt of hearing the voices of loved ones who lived far away. Pretty soon, another instrument to communicate across distances was invented. Alexander Graham Bell, a teacher and inventor, worked with the deaf and became fascinated with studying sound. In 1875, Bell discovered a way to convert sound waves to an undulating current that could be carried along wires. This helped him invent the telephone. The first phone conversation was an inadvertent one between Bell and Watson, his ass istant in the next room. After spilling some acid, Bell said “Mr. Watson, come here.I want you.” He patented his device the same year. Early phone service wasn’t as portable and convenient as today’s. At first, telephones we connected in pairs. You could call only one person, and they could only call you. The telephone exchange changed all that. The first exchange was in New Haven, Connecticut in 1878. It allowed people who subscribed to it to call one another. Operators had to connect the calls, but in 1891 an automatic exchange was invented. Some problems had to be solved, though, before long-distance telephoning could work. The main one was that the signal weakened with distance, disappearing if the telephone lines were too long. A solution was found in 1912 with a way to amplify electrical signals, and transcontinental phone calls were possible. A test took place in 1914, and the next year, Bell, who was in New York, called Watson, who was in San Francisco. He said the same thing he had said during the first phone conversation. Watson’s answer? “It will take me five days to get there now!”Plc development1.1 MotivationProgrammable Logic Controllers (PLC), a computing device invented by Richard E. Morley in 1968, have been widely used in industry including manufacturing systems, transportation systems, chemical process facilities, and many others. At that time, the PLC replaced the hardwired logic with soft-wired logic or so-called relay ladder logic (RLL), a programming language visually resembling the hardwired logic, and reduced thereby the configuration time from 6 months down to 6 days [Moody and Morley, 1999].Although PC based control has started to come into place, PLC based control will remain the technique to which the majority of industrial applications will adhere due to its higher performance, lower price, and superior reliability in harsh environments. Moreover, according to a study on the PLC market of Frost and Sullivan [1995], an increase of the annual sales volume to 15 million PLCs per year with the hardware value of more than 8 billion US dollars has been predicted, though the prices of computing hardware is steadily dropping. The inventor of the PLC, Richard E Morley, fairly considers the PLC market as a 5-billion industry at the present time.Though PLCs are widely used in industrial practice, the programming of PLC based control systems is still very much relying on trial-and-error. Alike software engineering, PLC software design is facing the software dilemma or crisis in a similar way. Morley himself emphasized this aspect most forcefully by indicating [Moody and Morley, 1999, p. 110]:`If houses were built like software projects, a single woodpecker could destroy civilization.” Particularly, practical problems in PLC programming are to eliminate software bugs and to reduce the maintenance costs of old ladder logic programs. Though the hardware costs of PLCs are dropping continuously, reducing the scan time of the ladder logic is still an issue in industry so that low-cost PLCs can be used.In general, the productivity in generating PLC is far behind compared to other domains, for instance, VLSI design, where efficient computer aided design tools are in practice. Existent software engineering methodologies are not necessarily applicable to the PLC based software design because PLC-programming requires a simultaneous consideration of hardware and software. The software design becomes, thereby, more and more the major cost driver. In many industrial design projects, more than SO0/a of the manpower allocated for the control system design and installation is scheduled for testing and debugging PLC programs [Rockwell, 1999].In addition, current PLC based control systems are not properly designed to support the growing demand for flexibility and reconfigurability of manufacturing systems. A further problem, impelling the need for a systematic design methodology, is the increasing software complexity in large-scale projects.1.2 Objective and Significance of the ThesisThe objective of this thesis is to develop a systematic software design methodology for PLC operated automation systems. The design methodology involves high-level description based on state transition models that treat automation control systems as discrete event systems, a stepwise design process, and set of design rules providing guidance and measurements to achieve a successful design. The tangible outcome of this research is to find a way to reduce the uncertainty in managing the control software development process, that is, reducing programming and debugging time and their variation, increasing flexibility of the automation systems, and enabling software reusability through modularity. The goal is to overcome shortcomings of current programming strategies that are based on the experience of the individual software developer.A systematic approach to designing PLC software can overcome deficiencies in the traditional way of programming manufacturing control systems, and can have wide ramifications in several industrial applications. Automation control systems are modeled by formal languages or, equivalently, by state machines. Formal representations provide a high-level description of the behavior of the system to be controlled. State machines can be analytically evaluated as to whether or not they meet the desired goals. Secondly, a state machine description provides a structured representation to convey the logical requirements and constraints such as detailed safety rules. Thirdly, well-defined control systems design outcomes are conducive to automatic code generation- An ability to produce control software executable on commercial distinct logic controllers can reduce programming lead-time and labor cost. In particular, the thesis is relevant with respect to the following aspects.Customer-Driven ManufacturingIn modern manufacturing, systems are characterized by product and process innovation, become customer-driven and thus have to respond quickly to changing system requirements. A majorchallenge is therefore to provide enabling technologies that can economically reconfigure automation control systems in response to changing needs and new opportunities. Design and operational knowledge can be reused in real-time, therefore, giving a significant competitive edge in industrial practice.Higher Degree of Design Automation and Software QualityStudies have shown that programming methodologies in automation systems have not been able to match rapid increase in use of computing resources. For instance, the programming of PLCs still relies on a conventional programming style with ladder logic diagrams. As a result, the delays and resources in programming are a major stumbling stone for the progress of manufacturing industry. Testing and debugging may consume over 50% of the manpower allocated for the PLC program design. Standards [IEC 60848, 1999; IEC-61131-3, 1993; IEC 61499, 1998; ISO 15745-1, 1999] have been formed to fix and disseminate state-of-the-art design methods, but they normally cannot participate in advancing the knowledge of efficient program and system design.A systematic approach will increase the level of design automation through reusing existing software components, and will provide methods to make large-scale system design manageable. Likewise, it will improve software quality and reliability and will be relevant to systems high security standards, especially those having hazardous impact on the environment such as airport control, and public railroads.System ComplexityThe software industry is regarded as a performance destructor and complexity generator. Steadily shrinking hardware prices spoils the need for software performance in terms of code optimization and efficiency. The result is that massive and less efficient software code on one hand outpaces the gains in hardware performance on the other hand. Secondly, software proliferates into complexity of unmanageable dimensions; software redesign and maintenance-essential in modern automation systems-becomes nearly impossible. Particularly, PLC programs have evolved from a couple lines of code 25 years ago to thousands of lines of code with a similar number of 1/O points. Increased safety, for instance new policies on fire protection, and the flexibility of modern automation systems add complexity to the program design process. Consequently, the life-cycle cost of software is a permanently growing fraction of the total cost. 80-90% of these costs are going into software maintenance, debugging, adaptation and expansion to meet changing needs [Simmons et al., 1998].Design Theory DevelopmentToday, the primary focus of most design research is based on mechanical or electrical products. One of the by-products of this proposed research is to enhance our fundamental understanding of design theory and methodology by extending it to the field of engineering systems design. A system design theory for large-scale and complex system is not yet fully developed. Particularly, the question of how to simplify a complicated or complex design task has not been tackled in a scientific way. Furthermore, building a bridge between design theory and the latest epistemological outcomes of formal representations in computer sciences and operations research, such as discrete event system modeling, can advance future development in engineering design. Application in Logical Hardware DesignFrom a logical perspective, PLC software design is similar to the hardware design of integrated circuits. Modern VLSI designs are extremely complex with several million parts and a product development time of 3 years [Whitney, 1996]. The design process is normally separated into acomponent design and a system design stage. At component design stage, single functions are designed and verified. At system design stage, components are aggregated and the whole system behavior and functionality is tested through simulation. In general, a complete verification is impossible. Hence, a systematic approach as exemplified for the PLC program design may impact the logical hardware design.1.3 Structure of the ThesisFigure 1.1 illustrates the outline of the following thesis. Chapter 2 clarifies the major challenges and research issues, and discourses the relevant background and terminology. It will be argued that a systematic design of PLC software can contribute to higher flexibility and reconfigurability of manufacturing systems. The important issue of how to deal with complexity in engineering design with respect to designing and operating a system will be debated. The research approach applied in this thesis is introduced starting from a discussion of design theory and methodology and what can be learnt from that field.Chapter 3 covers the state-of-the-art of control technology and the current practice in designing and programming PLC software. The influences of electrical and software engineering are revealed as well as the potentially applicable methods from computer science are discussed. Pros and cons are evaluated and will lead to the conclusion that a new methodology is required that suffices the increasing complexity of PLC software design.Chapter 4 represents the main body of the thesis and captures the essential features of the design methodology. Though design theory is regarded as being in a pre- scientific stage it has advanced in mechanical, software and system engineering with respect to a number of proposed design models and their evaluation throughout real-world examples. Based on a literature review in Chapter 2 and 3 potential applicable design concepts and approaches are selected and applied to context of PLC software design. Axiomatic design is chosen as underlying design concept since it provides guidance for the designer without restriction to a particular design context. To advance the design concept to PLC software design, a formal notation based on statechart formalism is introduced. Furthermore, a design process is developed that arranges the activities needed in a sequential order and shows the related design outcomes.In Chapter 5, a number of case studies are given to demonstrate the applicability of the developed design methodology. The examples are derived from a complex reference system, a flexible assembly system. The achieved insights are evaluated in a concluding paragraph.Chapter 6 presents the developed computerized design tool for PLC software design on a conceptual level. The software is written in Visual Basic by using ActiveX controls to provide modularity and reuse in a web-based collaborative programming environment. Main components of the PLC software are modeling editors for the structural (modular) and the behavioral design, a layout specification interface and a simulation engine that can validate the developed model. Chapter 7 is concluding this thesis. It addresses the achievements with respect to the research objectives and questions. A critical evaluation is given alongside with an outlook for future research issues.电力的故事当我们插上电源,打开旋钮,电和磁差不多在每样东西上都运行着,今天我们知道这是什么,这一些花了人们上百年时间的实验和研究来达到这一点—当我们按下按钮时,光亮已经开始,人们对电的了解已经有很长一段时间了.古希腊人注意到,摩擦一块琥珀,羽毛将能被吸住.你已经经历过相类似的事情,当你梳头时,头发将垂直竖起,当你从干燥机中拿袜子时,袜子也会粘在一起.这被称作静电.但是在以前人们不知道如何解释此类现象或如何应用这种现象,使用摩擦产生的静电来带动机器的实验可以产生大量所需要的静电.在1660年,德国人Otto von Guericke用一个硫磺球和一些布制造了第一台静电发电机.硫磺球象征大地,他深信这种小型地球复制品被摩擦时将流出电的灵魂,他成功了,现在的科学家可以在任何想要的时候来研究电击和电火花.随着科学家们持续对电的研究,他们开始认为它以一种看不见的方式流动,并试图去捕获并储存.第一次去做这项研究的是荷兰Leyden的Pieter van Musschenbroek.1746,他用一个金属箔片包一个装满水的罐子,发现这种简单的设备能储存由静电发电机产生的能量.这个设备后来著名的莱顿瓶.莱顿瓶在其他人的实验中有非常重要的作用.如Benjamin Franklin著名的风筝实验.许多人认为闪电和静电是同一种东西,由于双方碰撞产生明亮的电火花.1752年, Franklin将一把钥匙绑在风筝上,在一个暴风即将来临的天气里放飞(请记住Franklin不是在一个真正的暴风寸中放飞的,永远不要这样做),当一块雷雨云经过时,钥匙被闪电击中,闪电充满莱顿瓶,由此证明闪电实际也是一种电力.同其他实验人和科学家一样, Franklin用一个发现来做另外一个. Franklin并不是唯一的在电力实验方面灵光突现的科学家.18世纪80年代,意大利的科学家Luigi Galvani用电流让一只切断的青蛙的腿移动. Galvani称之为生物电.他认为当潮湿的动物组织同金属探测针接触时产生电能.他甚至大胆预测精神也是一种电能。
电子专业中英文翻译电子专业中英文翻译是在电子工程学科中进行的一项重要工作,在国际交流和合作中发挥着不可替代的作用。
随着信息技术的快速发展,电子专业所涉及到的课程和知识点日益增多,涵盖广泛,因此在进行翻译时也需要对相关的专业词汇和术语进行深入了解和分析。
电子专业中英文翻译的难点在于词汇和术语的特殊性。
例如,电子线路板的英文表述为“printed circuit board”,其中“printed”和“circuit”两个词汇均用于表示电路板的性质和组成,但是在中文中往往直接使用“PCB”进行称呼。
此类现象在专业术语中更为普遍,涉及到电路、元器件、高频、通信、控制以及计算机等多个方面的内容。
因此,翻译人员需要准确理解各种专业词汇,加强与领域专家的沟通和交流,并及时更新和修订相关的专业术语库和词汇表。
在电子专业中英文翻译中,除了词汇和术语的翻译外,还需要充分考虑语境和句式的处理。
在翻译时需要对原文进行整体认识,理解文章中的主旨和具体意义。
例如,文章中出现的一些缩写和首字母缩写,不仅仅是简单的表述,而且与文章的内容有着密切的联系,同时也体现了该领域的专业性和发展趋势。
此外,英文和中文的语序和表达方式也有所不同,在翻译时需要根据具体的语境和句式进行灵活处理,确保翻译准确、流畅和自然。
为了有效地进行电子专业中英文翻译,翻译人员需要具备一定的专业知识和技能。
首先,翻译人员需要具备扎实的英语语言基础,包括英语语法、词汇和听说读写能力等方面的技能。
其次,需要对电子专业的相关知识有一定的了解和掌握,熟悉电子工程的基本原理和最新技术发展趋势。
最后,需要具备翻译技能,包括较强的独立思考、分析和处理能力,以及对翻译工具和软件的熟练应用和管理能力。
总之,电子专业中英文翻译是一项复杂而重要的工作,需要翻译人员具备扎实的英语和专业知识背景,同时还需要精通翻译技能和熟练应用现代化工具和技术。
只有通过不断学习和积累经验,并与相关领域专家充分交流和合作,才能够达到翻译的精确、准确和高效。
AC(alternating current) 交流(电)A/D(analog to digital) 模拟/数字转换ADC(analog to digital convertor) 模拟/数字转换器ADM(adaptive delta modulation) 自适应增量调制ADPCM(adaptive differential pulse code modulation) 自适应差分脉冲编码调制ALU(arithmetic logic unit) 算术逻辑单元ASCII(American standard code for informationinterchange) 美国信息交换标准码A V(audio visual) 声视,视听BCD(binary coded decimal) 二进制编码的十进制数BCR(bi-directional controlled rectifier)双向晶闸管BCR(buffer courtier reset) 缓冲计数器BZ(buzzer) 蜂鸣器,蜂音器C(capacitance,capacitor) 电容量,电容器CATV(cable television) 电缆电视CCD(charge-coupled device) 电荷耦合器件CCTV(closed-circuit television) 闭路电视CMOS(complementary) 互补MOSCPU(central processing unit)**处理单元CS(control signal) 控制信号D(diode) 二极管DAST(direct analog store technology) 直接模拟存储技术DC(direct current) 直流DIP(dual in-line package) 双列直插封装DP(dial pulse) 拨号脉冲DRAM(dynamic random access memory) 动态随机存储器DTL(diode-transistor logic) 二极管晶体管逻辑DUT(device under test) 被测器件DVM(digital voltmeter) 数字电压表ECG(electrocardiograph) 心电图ECL(emitter coupled logic) 射极耦合逻辑EDI(electronic data interchange) 电子/download/EPROMshuju/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>数据交换EIA(Electronic Industries Association) 电子工业联合会EOC(end of conversion) 转换结束EPROM(erasable programmable read only memory) 可擦可编程只读存储器EEPROM(electrically EPROM) 电可擦可编程只读存储器ESD(electro-static discharge) 静电放电FET(field-effect transistor) 场效应晶体管FS(full scale) 满量程F/V(frequency to voltage convertor) 频率/电压转换FM(frequency modulation) 调频FSK(frequency shift keying) 频移键控FSM(field strength meter) 场强计FST(fast switching shyster) 快速晶闸管FT(fixed time) 固定时间FU(fuse unit) 保险丝装置FWD(forward) 正向的GAL(generic array logic) 通用阵列逻辑GND(ground) 接地,地线GTO(Sate turn off thruster) 门极可关断晶体管HART(highway addressable remote transducer) 可寻址远程传感器/download/EPROMshuju/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>数据公路HCMOS(high density COMS) 高密度互补金属氧化物半导体(器件)HF(high frequency) 高频HTL(high threshold logic) 高阈值逻辑电路HTS(heat temperature sensor) 热温度传感器IC(integrated circuit) 集成电路ID(international data) 国际/download/EPROMshuju/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>数据IGBT(insulated gate bipolar transistor) 绝缘栅双极型晶体管IGFET(insulated gate field effect transistor) 绝缘栅场效应晶体管I/O(input/output) 输入/输出I/V(current to voltage convertor) 电流-电压变换器IPM(incidental phase modulation) 附带的相位调制IPM(intelligent power module) 智能功率模块IR(infrared radiation) 红外辐射IRQ(interrupt request) 中断请求JFET(junction field effect transistor) 结型场效应晶体管LAS(light activated switch)光敏开关LASCS(light activated silicon controlled switch) 光控可控硅开关LCD(liquid crystal display) 液晶显示器LDR(light dependent resistor) 光敏电阻LED(light emitting diode) 发光二极管LRC(longitudinal redundancy check) 纵向冗余(码)校验LSB(least significant bit) 最低有效位LSI(1arge scale integration) 大规模集成电路M(motor) 电动机MCT(MOS controlled gyrator) 场控晶闸管MIC(microphone) 话筒,微音器,麦克风min(minute) 分MOS(metal oxide semiconductor)金属氧化物半导体MOSFET(metal oxide semiconductor FET) 金属氧化物半导体场效应晶体管N(negative) 负NMOS(N-channel metal oxide semiconductor FET) N沟道MOSFETNTC(negative temperature coefficient) 负温度系数OC(over current) 过电流OCB(overload circuit breaker) 过载断路器OCS(optical communication system) 光通讯系统OR(type of logic circuit) 或逻辑电路OV(over voltage) 过电压P(pressure) 压力FAM(pulse amplitude modulation) 脉冲幅度调制PC(pulse code) 脉冲码PCM(pulse code modulation) 脉冲编码调制PDM(pulse duration modulation) 脉冲宽度调制PF(power factor) 功率因数PFM(pulse frequency modulation) 脉冲频率调制PG(pulse generator) 脉冲发生器PGM(programmable) 编程信号PI(proportional-integral(controller)) 比例积分(控制器)PID(proportional-integral-differential(controller))比例积分微分(控制器)PIN(positive intrinsic-negative) 光电二极管PIO(parallel input output) 并行输入输出PLD(phase-locked detector) 同相检波PLD(phase-locked discriminator) 锁相解调器PLL(phase-locked loop) 锁相环路PMOS(P-channel metal oxide semiconductor FET) P沟道MOSFETP-P(peak-to-peak) 峰--峰PPM(pulse phase modulation) 脉冲相位洲制PRD(piezoelectric radiation detector) 热电辐射控测器PROM(programmable read only memory) 可编只读程存储器PRT(platinum resistance thermometer) 铂电阻温度计PRT(pulse recurrent time) 脉冲周期时间PUT(programmable unijunction transistor) 可编程单结晶体管PWM(pulse width modulation) 脉宽调制R(resistance,resistor) 电阻,电阻器RAM(random access memory) 随机存储器RCT(reverse conducting thyristor) 逆导晶闸管REF(reference) 参考,基准REV(reverse) 反转R/F(radio frequency) 射频RGB(red/green/blue) 红绿蓝ROM(read only memory) 只读存储器RP(resistance potentiometer) 电位器RST(reset) 复位信号RT(resistor with inherent variability dependent) 热敏电阻RTD(resistance temperature detector) 电阻温度传感器RTL(resistor transistor logic) 电阻晶体管逻辑(电路)RV(resistor with inherent variability dependent on the voltage) 压敏电阻器SA(switching assembly) 开关组件SBS(silicon bi-directional switch) 硅双向开关,双向硅开关SCR(silicon controlled rectifier) 可控硅整流器SCS(safety control switch) 安全控制开关SCS(silicon controlled switch) 可控硅开关SCS(speed control system) 速度控制系统SCS(supply control system) 电源控制系统SG(spark gap) 放电器)SIT(static induction transformer) 静电感应晶体管SITH(static induction thyristor) 静电感应晶闸管SP(shift pulse) 移位脉冲SPI(serial peripheral interface) 串行外围接口SR(sample realy,saturable reactor) 取样继电器,饱和电抗器SR(silicon rectifier) 硅整流器SRAM(static random access memory) 静态随机存储器SSR(solid-state relay) 固体继电器SSR(switching select repeater) 中断器开关选择器SSS(silicon symmetrical switch) 硅对称开关,双向可控硅SSW(synchro-switch) 同步开关ST(start) 启动ST(starter) 启动器STB(strobe) 闸门,选通脉冲T(transistor) 晶体管,晶闸管TACH(tachometer) 转速计,转速表TP(temperature probe) 温度传感器TRIAC(triodes AC switch) 三极管交流开关TTL(transistor-transistor logic) 晶体管一晶体管逻辑TV(television) 电视UART(universal asynchronous receiver transmitter) 通用异步收发器VCO(voltage controlled oscillator) 压控振荡器VD(video decoders) /movie/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>视频译码器VDR(voltage dependent resistor) 压敏电阻VF(video frequency) /movie/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>视频V/F(voltage-to-frequency) 电压/频率转换V/I(voltage to current convertor) 电压-电流变换器VM(voltmeter) 电压表VS(vacuum switch) 电子开关VT(visual telephone) 电视电话VT(video terminal) /movie/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>视频终端AC(alternating current) 交流(电)A/D(analog to digital) 模拟/数字转换ADC(analog to digital convertor) 模拟/数字转换器ADM(adaptive delta modulation) 自适应增量调制ADPCM(adaptive differential pulse code modulation) 自适应差分脉冲编码调制ALU(arithmetic logic unit) 算术逻辑单元ASCII(American standard code for informationinterchange) 美国信息交换标准码A V(audio visual) 声视,视听BCD(binary coded decimal) 二进制编码的十进制数BCR(bi-directional controlled rectifier)双向晶闸管BCR(buffer courtier reset) 缓冲计数器BZ(buzzer) 蜂鸣器,蜂音器C(capacitance,capacitor) 电容量,电容器CATV(cable television) 电缆电视CCD(charge-coupled device) 电荷耦合器件CCTV(closed-circuit television) 闭路电视CMOS(complementary) 互补MOSCPU(central processing unit)**处理单元CS(control signal) 控制信号D(diode) 二极管DAST(direct analog store technology) 直接模拟存储技术DC(direct current) 直流DIP(dual in-line package) 双列直插封装DP(dial pulse) 拨号脉冲DRAM(dynamic random access memory) 动态随机存储器DTL(diode-transistor logic) 二极管晶体管逻辑DUT(device under test) 被测器件DVM(digital voltmeter) 数字电压表ECG(electrocardiograph) 心电图ECL(emitter coupled logic) 射极耦合逻辑EDI(electronic data interchange) 电子/download/EPROMshuju/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>数据交换EIA(Electronic Industries Association) 电子工业联合会EOC(end of conversion) 转换结束EPROM(erasable programmable read only memory) 可擦可编程只读存储器EEPROM(electrically EPROM) 电可擦可编程只读存储器ESD(electro-static discharge) 静电放电FET(field-effect transistor) 场效应晶体管FS(full scale) 满量程F/V(frequency to voltage convertor) 频率/电压转换FM(frequency modulation) 调频FSK(frequency shift keying) 频移键控FSM(field strength meter) 场强计FST(fast switching shyster) 快速晶闸管FT(fixed time) 固定时间FU(fuse unit) 保险丝装置FWD(forward) 正向的GAL(generic array logic) 通用阵列逻辑GND(ground) 接地,地线GTO(Sate turn off thruster) 门极可关断晶体管HART(highway addressable remote transducer) 可寻址远程传感器/download/EPROMshuju/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>数据公路HCMOS(high density COMS) 高密度互补金属氧化物半导体(器件)HF(high frequency) 高频HTL(high threshold logic) 高阈值逻辑电路HTS(heat temperature sensor) 热温度传感器IC(integrated circuit) 集成电路ID(international data) 国际/download/EPROMshuju/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>数据IGBT(insulated gate bipolar transistor) 绝缘栅双极型晶体管IGFET(insulated gate field effect transistor) 绝缘栅场效应晶体管I/O(input/output) 输入/输出I/V(current to voltage convertor) 电流-电压变换器IPM(incidental phase modulation) 附带的相位调制IPM(intelligent power module) 智能功率模块IR(infrared radiation) 红外辐射IRQ(interrupt request) 中断请求JFET(junction field effect transistor) 结型场效应晶体管LAS(light activated switch)光敏开关LASCS(light activated silicon controlled switch) 光控可控硅开关LCD(liquid crystal display) 液晶显示器LDR(light dependent resistor) 光敏电阻LED(light emitting diode) 发光二极管LRC(longitudinal redundancy check) 纵向冗余(码)校验LSB(least significant bit) 最低有效位LSI(1arge scale integration) 大规模集成电路M(motor) 电动机MCT(MOS controlled gyrator) 场控晶闸管MIC(microphone) 话筒,微音器,麦克风min(minute) 分MOS(metal oxide semiconductor)金属氧化物半导体MOSFET(metal oxide semiconductor FET) 金属氧化物半导体场效应晶体管N(negative) 负NMOS(N-channel metal oxide semiconductor FET) N沟道MOSFETNTC(negative temperature coefficient) 负温度系数OC(over current) 过电流OCB(overload circuit breaker) 过载断路器OCS(optical communication system) 光通讯系统OR(type of logic circuit) 或逻辑电路OV(over voltage) 过电压P(pressure) 压力FAM(pulse amplitude modulation) 脉冲幅度调制PC(pulse code) 脉冲码PCM(pulse code modulation) 脉冲编码调制PDM(pulse duration modulation) 脉冲宽度调制PF(power factor) 功率因数PFM(pulse frequency modulation) 脉冲频率调制PG(pulse generator) 脉冲发生器PGM(programmable) 编程信号PI(proportional-integral(controller)) 比例积分(控制器)PID(proportional-integral-differential(controller))比例积分微分(控制器)PIN(positive intrinsic-negative) 光电二极管PIO(parallel input output) 并行输入输出PLD(phase-locked detector) 同相检波PLD(phase-locked discriminator) 锁相解调器PLL(phase-locked loop) 锁相环路PMOS(P-channel metal oxide semiconductor FET) P沟道MOSFETP-P(peak-to-peak) 峰--峰PPM(pulse phase modulation) 脉冲相位洲制PRD(piezoelectric radiation detector) 热电辐射控测器PROM(programmable read only memory) 可编只读程存储器PRT(platinum resistance thermometer) 铂电阻温度计PRT(pulse recurrent time) 脉冲周期时间PUT(programmable unijunction transistor) 可编程单结晶体管PWM(pulse width modulation) 脉宽调制R(resistance,resistor) 电阻,电阻器RAM(random access memory) 随机存储器RCT(reverse conducting thyristor) 逆导晶闸管REF(reference) 参考,基准REV(reverse) 反转R/F(radio frequency) 射频RGB(red/green/blue) 红绿蓝ROM(read only memory) 只读存储器RP(resistance potentiometer) 电位器RST(reset) 复位信号RT(resistor with inherent variability dependent) 热敏电阻RTD(resistance temperature detector) 电阻温度传感器RTL(resistor transistor logic) 电阻晶体管逻辑(电路)RV(resistor with inherent variability dependent on the voltage) 压敏电阻器SA(switching assembly) 开关组件SBS(silicon bi-directional switch) 硅双向开关,双向硅开关SCR(silicon controlled rectifier) 可控硅整流器SCS(safety control switch) 安全控制开关SCS(silicon controlled switch) 可控硅开关SCS(speed control system) 速度控制系统SCS(supply control system) 电源控制系统SG(spark gap) 放电器SIT(static induction transformer) 静电感应晶体管SITH(static induction thyristor) 静电感应晶闸管SP(shift pulse) 移位脉冲SPI(serial peripheral interface) 串行外围接口SR(sample realy,saturable reactor) 取样继电器,饱和电抗器SR(silicon rectifier) 硅整流器SRAM(static random access memory) 静态随机存储器SSR(solid-state relay) 固体继电器SSR(switching select repeater) 中断器开关选择器SSS(silicon symmetrical switch) 硅对称开关,双向可控硅SSW(synchro-switch) 同步开关ST(start) 启动ST(starter) 启动器STB(strobe) 闸门,选通脉冲T(transistor) 晶体管,晶闸管TACH(tachometer) 转速计,转速表TP(temperature probe) 温度传感器TRIAC(triodes AC switch) 三极管交流开关TTL(transistor-transistor logic) 晶体管一晶体管逻辑TV(television) 电视UART(universal asynchronous receiver transmitter) 通用异步收发器VCO(voltage controlled oscillator) 压控振荡器VD(video decoders) /movie/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>视频译码器VDR(voltage dependent resistor) 压敏电阻VF(video frequency) /movie/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>视频V/F(voltage-to-frequency) 电压/频率转换V/I(voltage to current convertor) 电压-电流变换器VM(voltmeter) 电压表VS(vacuum switch) 电子开关VT(visual telephone) 电视电话VT(video terminal) /movie/' target='_blank' class='infotextkey'>视频终端。
电子类文献中英文翻译发电机Electricity is the backbone of modern society, and it is generated by using various methods, with one of the most common ways being through the use of generators. This article explores the concept of generators and their role in electricity production.GeneratorA generator is a device that transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which was discovered by Michael Faraday in the early 19th century. A generator consists of two parts: the rotor and the stator. The rotor is the rotating part of the generator, while the stator is the stationary part. The two parts are separated by an air gap.When the rotor rotates inside the stator, it produces a magnetic field that cuts across the wires in the stator. This creates an electric current. The amount of electric current generated by the generator depends on the speed of the rotor and the number of wire turns in the stator.Types of GeneratorsThere are two main types of generators: AC generators and DC generators. AC generators generate alternating current, while DC generators generate direct current.AC GeneratorsAC generators are the most common type of generators used in modern society. They produce electrical power by rotating a coil of wire around a magnetic field. This creates a changing magnetic field, which induces a current in the coil. The current flows back and forth at a set frequency, resulting in an alternating current.The advantage of AC generators is that the voltage and frequency can be easily controlled. This makes it possible to build large power plants that can produce electricity at high voltage and transmit it over long distances.DC GeneratorsDC generators are less common than AC generators, but they are still used in some applications. They generate a constant DC voltage by rotating a coil of wire around a magnetic field. The voltage produced by a DC generator is proportional to the speed of the rotor and the number of wire turns in the coil.The main disadvantage of DC generators is that the voltage cannot be easily changed. This makes them unsuitable for large power plants and long-distance transmission.ConclusionGenerators play a vital role in the production of electricity, and the development of more efficient and effective generators has greatly improved the quality of life for people all over the world. The ability to generate electricity has enabled people to access a wide range of electronic devices that improve communication, enable faster transportation, and enhance safety and security. As technology continues to advance, the generators of the future will undoubtedly become even more efficient and effective, providing sustainable, reliable, and affordable energy for generations to come.。
电子专业英文求职信带翻译[Your Name][Your Address][City, State ZIP Code][Email Address][Phone Number][Date][Hiring Manager's Name][Company Name][Company Address][City, State ZIP Code]Dear Hiring Manager,I am writing to express my interest in the Electrical Engineering position at [Company Name] as advertised on [where you found the job posting]. With a Bachelor's degree in Electrical Engineering from [University Name], strong technical skills, and hands-on experience in the field, I am confident in my ability to contribute to your team and help drive innovation in your company. During my time at [University Name], I gained a solid foundation in electrical engineering principles and developed strong problem-solving skills through various projects and internships. I also honed my technical skills by working on projects such as designing and implementing electronic circuits, programming microcontrollers, and troubleshooting electrical systems. Additionally, I have a solid understanding of programming languages such as C, Java, and MATLAB, which have been instrumental in my ability to analyzeand solve complex technical problems.One of the highlights of my academic career was my involvement in a research project on renewable energy systems, where I worked with a team to design and implement a solar power system for a rural community in need of sustainable energy solutions. This experience not only enhanced my technical skills but also gave me a deeper appreciation for the impact that electrical engineering can have on improving people's lives.In addition to my academic achievements, I have also completed internships at [Company Name] and [Company Name], where I gained practical experience in designing, testing, and troubleshooting electrical systems. These experiences have equipped me with the hands-on skills necessary to excel in a fast-paced engineering environment and have given me a solid foundation in project management, teamwork, and communication.I am particularly excited about the opportunity to work at [Company Name] because of your commitment to innovation and your focus on developing cutting-edge technologies. I am confident that my strong technical skills, passion for electrical engineering, and ability to work collaboratively with multidisciplinary teams make me a strong fit for this role.Thank you for considering my application. I am excited about the opportunity to contribute to your team and help drive the success of [Company Name]. I look forward to the possibility of discussing my application with you further.Sincerely,[Your Name][Translation]亲爱的招聘经理,我写信是为了表达我对贵公司电气工程职位的兴趣,这个职位是在[您在哪里找到职位广告]上广告的。
基于单片机控制的光收发器设计1 引言在“三网合一”的推动下,光纤到户等光纤接入方案的应用日益广泛。
在光进铜退的呼声下,光网络迅速发展。
光收发器在光通信中起到光电、电光转换的作用,是光通信必不可少的器件。
由于涉及到高速电路设计、精密机械加工和光学设计,光收发器的成本占据了光纤通信系统和的重要部分,而较高的光收发器价格成了制约光纤接入推广的瓶颈。
进一步降低光收发器的成本将有利于光接入的应用推广,加快光进铜退的步伐。
光收发器主要由电路部分、光发送组件和光接收组件组成。
其中电路部分又包括激光驱动、光接收信号放大和控制部分。
目前市场上的光收发器的电路部分使用的是三个专用芯片。
一直有公司在研究把激光驱动和接收信号放大电路集成在一个器件上,控制器使用普通的嵌入式处理器的方案。
由于只使用一个专用芯片和一个通用芯片,这样就可以大幅降低电路部分的成本。
PHYWORKS 公司研制的PHY1076芯片就是一款这样的芯片。
它主要针对1.25Gbps到2.5Gbps的光收发器,具有外围电路简单,控制电路只需要普通的8位单片机就可以实现的特点。
本文主要研究了PHY1076 的性能,选择了ATMEL 公司的ATMEGA88 单片机进行控制,设计出光收发器样品,并进行了性能测试,最终成功设计了1.25G 光收发器。
2光收发器设计方案及工作原理讨论光收发器在发展的过程中,有许多种不同的外形封装。
SFP(小型化可热插拔光收发一体模块)是目前在5Gbps以下速率中最先进的一种封装形式,具有小型化、可热插拔、功耗小、系统可集成度高以及能够进行数字诊断功能等特点。
本设计中使用激光驱动电路和光接收放大电路集成的PHY1076 作为专用芯片,使用ATMEL 的AVR 单片机ATMEGA88 进行控制和实现DDM功能,加上相应的TOSA(光发射组件),ROSA(光接收组件)和结构件,设计了一款工作在1.25Gbps传输距离为10km 的SFP 光收发器。
系统方框图如图1所示:图 1光纤收发器的内部结构图1) 发射部分工作原理:系统的串行数据信号从TX+/-端以差分信号形式输入到PHY1706 的激光器驱动部分。
驱动电路进行放大处理后,转换成差分调制电流信号加载到TOSA(光发射组件)上,控制TOSA中的激光器发出光脉冲,耦合入光纤发送到远端。
2)接收部分工作原理:光脉冲信号输入到ROSA(光接收组件),ROSA将光脉冲信号转换成差分电压信号输出到PHY1076的限幅放大部分。
该信号经过限幅放大处理后,从PHY1076的RX+/-端输出差分电压串行数字信号。
3) 控制及DDM 部分:PHY1076 是一款模拟数字混合芯片,其内部包括多个模数(A/D)、数模转换(D/A)器。
发射和接收通路上的参数都是通过ADC 转换成数字量存入状态寄存器进行监视,通过DAC把设置寄存器的值转换成模拟量来进行控制的。
这些寄存器都可以由外部控制器进行读取和设置。
DDM(Digital Diagnostic Monitor),数字诊断和监控是指的光纤收发器能够对发射功率(Tx_power),接收功率(Rx_power),激光器偏置电流(Ibias),工作电压(Vcc),模块内部温度(Temperature)这些参数进行实时监视,并能够在各项参数超过设定值时设置报警标志位的功能。
PHY1076内部集成的ADC 能够对发射功率、接收功率和偏置电流进行监测。
工作电压和温度传感则需要另外ADC进行转换。
而所有这些报警的实现则需要外部控制器来实现。
ATMEL 公司的AVR单片机ATMEGA88 是一款8 位单片机,内部集成FLASH、RAM、EEPROM、内部时钟和ADC。
无需任何外围电路即可构成系统,支持在线编程下载和单步调试。
系统设计和软件调试都很方便。
集成硬件I2C模块,可直接对外提供符合SFP-MSA 规范要求的外部I2C 接口。
而且此单片机是一款在家电和工业控制领域使用广泛的芯片,用量大,性能稳定可靠,价格低。
本设计选用此芯片控制PHY1076的工作参数和实现DDM功能。
3 关键参数控制和实现在光纤通信系统中,发射光脉冲的平均光功率和消光比是两个非常重要的参数。
根据传输距离不同,需要设定不同的值。
对具体某一个光收发器则希望其发光功率和消光比能够长期维持在一定范围内。
要维持稳定的光功率则需要使用APC(自动功率控制)电路。
又由于激光器的温度特性和老化特性,其发光效率会变化,所以又需要进行温度补偿。
消光比的自动控制则需要根据温度变化而实时的调整调制电流的大小。
早期的光收发器中,大都使用专用模拟器件,所以要实现功率APC、温度补偿和消光比自动控制都非常困难,或者很难得到满意的效果。
PHY1076是一个模数混合器件,其高速通道部分使用模拟设计,而其功率控制、调制电流则是使用寄存器进行的。
从而只要外部控制器能够监测温度,就能根据温度调整寄存器的值,达到自动更改输出功率和调制电流,使功率和消光比维持在一定得范围内的目的。
1) 平均光功率的控制实现:PHY1076 内部APC电路如图2所示。
TOSA 内部集成了一个激光发射二极管和一个光电感应二极管。
激光器的发光功率与电流成正比,激光器的阴极接到PHY1076的Laser_bias引脚。
PHY1076内部功率设置寄存器的数据直接输入到DAC,DAC 产生一个模拟电压输出控制压控电流源的输出电流,此电流源输出电流经过电感耦合后给激光器的提供直流偏置电流。
因此修改功率设置寄存器的值就可以直接修改激光器的输出光功率。
光电感应二极管的反向漏电流与激光器的发射功率成正比。
该电流从MPD引脚接入PHY1076内部,经过放大和转换成电压信号后,作为负反馈信号引入到压控电流源的控制端,起到自动功率控制的作用。
但是APC 能够控制的功率变化范围是有限的。
当温度变大时,由于激光器的发光效率降低,APC将不能提供足够大的电流来保持功率稳定。
此时就需要调节功率设置寄存器的值来获得更大的偏置电流以保持功率稳定。
本设计中是通过外接单片机来根据温度进行寄存器设置,达到温度补偿的目的。
图2 APC 工作原理图2) 消光比控制的实现:PHY1076内部调制电流控制电路如图3 所示。
消光比在光纤通信系统中定义为发送数据为1 时与发送0 时的光功率的比值。
其值的大小会影响通信系统的误码率,因此需要控制在一定范围内。
在使用交流耦合的调制激光器的电路中,平均发射功率受直流偏置电流影响,消光比的大小受调制电流的影响。
在PHY1076 的内部,激光器的调制电流由专门的寄存器进行设置后,经过模数转换器(DAC)输出控制电压,进而控制输出调制电流的大小。
因此适当设置该寄存器的值就可以得到理想的消光比。
由于没有办法检测工作中消光比的大小,因此无法引入反馈电路实现消光比自动控制。
比较可行的办法是寻找消光比与温度变化的统计规律,然后通过外部控制器依规律进行温度补偿。
图3调制电流控制原理图3)ATMEGA88 的控制算法分析和DDM 实现:从上面的分析可以看出,光收发器的关键参数平均发射功率和消光比都是通过对PHY1076的内部寄存器的设置来控制的,而PHY1076提供I2C 接口进行访问。
本设计中,使用ATMEGA88 单片机进行控制。
ATMEGA88 单片机内部有一个标准的硬件I2C接口,可以用来为系统设备提供SFP-MSA(SFP多源协议)要求的对外I2C。
为了与PHY1076进行通信,本设计中用软件模拟了一个I2C 接口。
单片机的主要工作内容包括:为功率控制提供温度补偿功能;为消光比提供自动控制功能;设置PHY1076 的接收放大部分的一些工作参数;对PHY1076进行初始化;提供DDM 功能和记录产品信息。
ATMEGE88 与PHY1076的连接如图4所示。
SCL图4ATMEGA88 与PHY1076连接图激光器的发光效率和阈值电流与环境温度成反比,即当环境温度升高时,激光器的发光效率会降低,阈值电流会升高。
为了达到输出光功率和消光比的稳定性,就要根据温度变化来响应调节激光器的偏置电流和调制电流。
本设计中采用查表法来设置偏置和调制电流。
具体就是建立两个数据表,功率设置表和调制电流设置表,每个值对应一段温度下的功率设置寄存器的值。
如图4 所示,调制电流设置表为80 个字节,每两摄氏度占一个字节;功率设置表占用40 个字节,每4 摄氏度占用一个字节;温度范围都是-40~120℃,满足工业温度的要求。
给单片机外接一个温度传感器,单片机通过模数转换器把温度传感器送来的电压转换成温度值,然后根据温度查表,找到对应的数据,把数据分别送往PHY1076 的功率设置寄存器和调制电流设置寄存器,调整激光器的偏置电流和调制电流,由此调整输出光功率和消光比。
数据表的数值确定则使用测试的方法得出。
在收发器的调试过程中,对样品在每个温度下的输出眼图进行测试,并修改对应温度下的数据,使得光收发器的输出光眼图、光功率和消光比满足要求。
最后把这些数据保存到温度查找表中,并同时保存到ATMEGA88 内部的EEPROM 中。
收发器在实际的应用环境下,重新加电后,就先从EEPROM 中把数据加载到RAM区,然后就可以在全温度范围内稳定平均输出光功率和消光比。
4设计结果及测试分析本设计根据以上讨论的方案,选择PHY1076专用芯片和ATMEGA88 单片机,外加适当的外围电路设计电路板,把TOSA、ROSA焊接到一起装入定制外壳,实现了一款1.25Gbps 的SFP光收发器。
调试PHY1076 内部寄存器使光收发器各项参数符合802.3z协议中对10km 千兆以太网光接口的要求。
同时设计的上位机调试软件对ATMEGA88 的温度查找表进行调试,确定了具体每个温度下的值。
由此完成了整个光收发器的设计工作。
然后对光收发器在低温,常温,高温三种环境下的所有参数进行测试。
结果如表1 所示。
表1光收发器的参数测试结果从表中可以看出。
激光器的输出光功率和消光比都在参数要求范围内,且变化小。
测试了各个温度下的眼图,发现光收发器在低温,常温,低温下的性能都比较好。
由于温度变高时需要提供较大的调制电流,因此信号的下冲比较明显,表现在眼图中就是在眼图中的“0”信号出现轻微双眼线。
但总体上模板测试余量都大于40%。
由此验证了此设计方案的可行性和正确性。
5 总结经过方案讨论、硬件设计、软件设计和样品调试、测试。
最终成功设计了1.25GSFP 单芯片SFP 光收发器。
此方案的特点是把激光驱动和接收放大部分集成在一起,使用了普通单片机进行控制,理论上能够降低了产品的成本和提高生产效率。
由于此方案是一个新的方案,技术成熟度有待提高,系统兼容性和市场应用的潜在问题有待验证。
加上用量的关系,其成本的优势也体现不出很大的优势。