Radware+AppDirector配置手册-2015
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:4.52 MB
- 文档页数:31

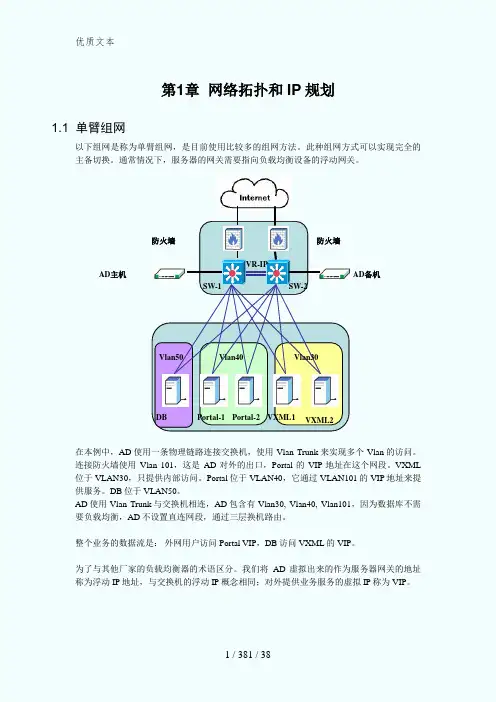
第1章 网络拓扑和IP 规划1.1 单臂组网以下组网是称为单臂组网,是目前使用比较多的组网方法。
此种组网方式可以实现完全的主备切换。
通常情况下,服务器的网关需要指向负载均衡设备的浮动网关。
在本例中,AD 使用一条物理链路连接交换机,使用Vlan Trunk 来实现多个Vlan 的访问。
连接防火墙使用Vlan 101,这是AD 对外的出口,Portal 的VIP 地址在这个网段。
VXML 位于VLAN30,只提供内部访问。
Portal 位于VLAN40,它通过VLAN101的VIP 地址来提供服务。
DB 位于VLAN50。
AD 使用Vlan Trunk 与交换机相连,AD 包含有Vlan30, Vlan40, Vlan101,因为数据库不需要负载均衡,AD 不设置直连网段,通过三层换机路由。
整个业务的数据流是: 外网用户访问Portal VIP ,DB 访问VXML 的VIP 。
为了与其他厂家的负载均衡器的术语区分。
我们将AD 虚拟出来的作为服务器网关的地址称为浮动IP 地址,与交换机的浮动IP 概念相同;对外提供业务服务的虚拟IP 称为VIP 。
AD 主机DB VXML1VXML2SW-1SW-2VR-IPAD 备机防火墙Portal-1 Portal-2 防火墙Vlan50 Vlan40 Vlan301.2 VLAN划分与地址分配1.2.1 VLAN30说明:VXML也需要使用RADWARE进行负荷分担,但不向Internet开放,因此要将其划分在另外一个独立的VLAN30中网段:172.168.1.64~172.168.1.79 掩码:255.255.255.240 28 网元IP地址浮动IP地址网关VLAN 备注S5624-3 172.168.1.65/28172.168.1.67N/A 30 管理用S5624-4 172.168.1.66/28 N/A 30 管理用AD-1 172.168.1.76/28172.168.1.78 N/A30AD-2 172.168.1.77/28 30VXML-1 FABRIC 1/2: 172.168.1.71/28VIP: 172.168.1.79 172.168.1.7830 BondingVXML-2 FABRIC 1/2: 172.168.1.72/28 30 Bonding1.2.2 VLAN40说明:Portal也需要使用RADWARE进行负荷分担,对Internet开放,因此要将其划分在另外一个独立的VLAN40中网段:172.168.1.80~172.168.1.95 掩码:255.255.255.240 28 网元IP地址浮动IP 网关VLAN 备注S5624-3 172.168.1.87/28172.168.1.89/28 N/A 40 管理用S5624-4 172.168.1.88/28 N/A 40 管理用AD-1 172.168.1.88/28172.168.1.90 N/A 40AD-2 172.168.1.89/28 40PORTAL-1 FABRIC 1/2: 172.168.1.81/28N/A 172.168.1.90 40 BondingPORTAL-2 FABRIC 1/2: 172.168.1.82/28 40 Bonding1.2.3 VLAN101RADWARE External网段与E200互连VLAN网段:172.168.1.112~172.168.1.127 掩码:255.255.255.240 28网元IP地址浮动IP地址网关VLAN 备注S5624-3 172.168.1.113/28172.168.1.124N/A 101 管理用S5624-4 172.168.1.114/28 N/A 101 管理用AD-1-1 172.168.1.116/28 172.168.1.118VIP: 172.168.1.119 172.168.1.124101PortalExternalAD-2-1 172.168.1.117/28 101第2章 AppDirector基本配置2.1 主机初始化配置2.1.1 配置VLAN Tag某些场景中,AD只使用一条千兆端口连接交换机,使用802.1Q Vlan Trunk方式连接,同时将内部Vlan与外部Vlan在一根链路上跑。

Radware AppDirector负载均衡器配置指导书目录第1章 AppDirector组网和配置流程 (1)单臂组网 (1)配置负载均衡的基本流程 (2)第2章 Radware连接 (2)通过console连接Radware设备 ...................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
通过telnet连接Radware设备.......................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
登录radware设备............................................................................................ 错误!未定义书签。
确认当前设备的版本 (2)查看当前设备的License (7)通过WEB界面对设备进行管理 (8)第3章网络层配置 (9)3.1 Vlan划分 (11)定义IP地址 (13)3.3 Routing Table (14)3.4 Farm 管理 (15)服务器管理 (19)3.6 L4 Policy管理 (21)3.7 Cookie会话保持 (22)3.8 NAT配置 (24)双机配置 (27)保存配置文件 (31)恢复配置文件 (32)3.12 SNMP的字串管理 (33)用户名和密码管理 (35)第4章命令行基本配置 (36)设备 (36)管理 (36)全局表项 (37)命令行网络配置 (37)物理端口 (37)4.4.2 VLAN (37)4.4.3 Interface (38)路由和默认网关 (38)命令行负载均衡配置 (39)4.5.1 Farm配置 (39)服务器配置 (40)第5章命令行维护命令 (41)查看接口地址 (41)查看路由表 (41)查看CPU (42)查看服务器的连接用户数 (42)查看AppDirector的会话表 (42)查看AppDirector的动态Cookie表 (43)查看AppDirector的命令全部配置 (44)关键词:摘要:按照常见的配置步骤,本文对Radware AppDirector负载均衡器设备配置进行说明缩略语清单:参考资料清单第1章 AppDirector 组网和配置流程AppDirector 在使用中都是采用双机主备方式工作,其对应的组网依据不同的方式分为单臂组网双臂组网和三角传输方式组网,下面依次做详细介绍。



Radware配置手册AppDirector配置指导书二○○六年四月目录说明 (3)1Radware WSD设备配置步骤 (4)1.1登陆WSD设备 (4)1.2配置WSD设备 (4)2Radware WSD设备的登陆 (4)2.1radware WSD和电脑的连接: (4)2.2定义radware WSD Console参数: (4)2.3初始化,清配置: (5)2.4配置WSD的管理口地址: (5)2.5登录Radware设备 (6)3Radware WSD 配置 (7)3.1网络结构图 (7)3.2配置过程 (8)3.2.1WSD (8)3.2.1.1划分VLAN和配置IP地址 (8)3.2.1.2配置默认路由 (9)3.2.1.3配置Farm T able (10)3.2.1.4把服务器地址加入到Farm Table中 (11)3.2.1.5配置VIP地址 (13)3.2.1.6配置健康检查Health Monitoring (14)3.2.1.6.1启用health monitoring功能 (15)3.2.1.6.2配置check table (15)3.2.1.6.3将定义的健康检查方式绑定到相应的server上 (16) 3.2.1.7配置Tuning (17)3.2.1.8配置client NAT (18)3.3其他配置 (21)3.3.1Syslog (23)3.3.2Telnet (24)3.3.3WEB管理 (24)3.3.4安全管理 (25)版本注释:版本 1.0 2006-3-6 创建说明Software Version: 1.01.01A (build 8ca06c)。
只有该版本支持对服务器的多端口的负载均衡功能。
1Radware WSD设备配置步骤1.1登陆WSD设备1.2配置WSD设备2 Radware WSD设备的登陆2.1radware WSD和电脑的连接:2.2定义radware WSD Console参数:2.3初始化,清配置:Power on Radware device,在3秒内按任意键“Press any key to stop auto-boot... ”3> ?- print this list@ - boot (load and go)e - print fatal exceptionw - download via xmodemq - erase configuration from flash(每次升级以前必须做) u - download to secondary boot via xmodemr - clear Log file>q0(清空原有配置参数,恢复缺省值)>q1(清空原有配置参数,恢复缺省值)>@(设备重启)2.4配置WSD的管理口地址:StartUp Configuration0. Exit1. IP address2. IP subnet mask3. Port number4. Default router IP address5. RIP version6. OSPF enable7. OSPF area ID8. NMS IP address9. Community name10. Configuration file name Enter your choice: 1Enter ip address: 192.168.1.100Enter your choice: 2Enter ip subnet mask: 255.255.255.0Enter your choice: 3Enter ifIndex: 16Continue with the new configuration (Y/N) ?y 注:1、选择访问模式的时候记得选Yes2、及时修改用户名和密码3、修改SNMP参数2.5登录Radware设备>Login: radware>password : radware3 Radware WSD 配置3.1网络结构图实现目的:对外提供服务的vip地址为198.93.1.20,端口为80 VIP198.93.1.20:80 ->198.93.1.13:80->198.93.1.13:81->198.93.1.13:21->198.93.1.14:80->198.93.1.14:81->198.93.1.14:21对外提供服务的vip地址为198.93.1.20,端口为21:VIP 198.93.1.20:21 ->198.93.1.10:21对外提供服务的vip地址为198.93.1.20,端口为8080:VIP 198.93.1.20:8080 ->198.216.1.57:80803.2配置过程3.2.1 WSD3.2.1.1划分VLAN和配置IP地址Open “ip Interface Parameters”3.2.1.2配置默认路由Open“Route>Routing Table”3.2.1.3配置Farm T able注意事项:在farm table中的配置中,需要特别注意session mode 对于C/S架构的应用,需要将session mode设置成为sps或eps的方式。

AppDirector配置指导书高级健康检查_1对1对多的服务器备份配置1 网络结构图1VIP 192.168.0.32 --->192.168.0.33--->192.168.0.34--->192.168.0.35 --->192.168.0.362、对服务器192.168.0.33 192.168.0.34 192.168.0.35和192.168.0.36做高级健康检查,当192.168.0.33故障宕机时,192.168.0.34才启用。
当192.168.0.33和34都故障宕机时,192.168.0.35才启用。
当192.168.0.33和34 35都故障宕机时,192.168.0.36才启用。
也就是说每次只有一台服务器启用。
即达到1对1对多的服务器备份功能。
实现方法:1、 健康检查的算法采用反转策略和逻辑运算2、 33启用的条件,对于33up3、 34启用的条件,对于33up 反转 对于34up4、 35启用的条件,对于33up 反转 对于34反转 对于34upRouterAD-backupWeb Server1 192.168.0.33 Web Server2 192.168.0.34 Web Server3 192.168.0.35 Web Server4 192.168.0.365、36启用的条件,对于33up反转对于34反转对于35反转对34up6、建立不同的group,采用and逻辑运算2配置高级健康检查Health Monitoring高级健康检查是通过一个单独的健康检查模块来实现,它对服务器的健康检查功能比基于连接的健康检查功能强,且能够实现更为复杂的健康检查方法。
2.1全局参数配置如果用高级健康检查,就没有必要在启用farm中的基于连接的健康检查,需要在配置高级健康检查的farm中的Connectivity Check Method选项选择No checks然后点击Health Monitoring->Global Parameters在Health Monitoring Status选项中选择Use Health Monitoring即可,表示启用高级健康检查的功能。


Radware 双机同步配置指导书VRRP2009.2Revision record 修订记录Date 日期RevisionVersion修订版本CRID CR号SectionNumber修改章节Change Description修改描述Author作者2009-2-26 1.00 初稿完成刘庆明Table of Contents 目录第1章VRRP主机配置 (6)1.1 配置IP和路由. (6)1.1.1 IP地址配置 (6)1.1.2 路由配置 (7)1.2 全局配置开启VRRP (8)1.3 配置VR (Virtual Router) (9)第2章业务配置(略) (12)第3章VRRP后续配置 (12)3.1 检查Associated IP配置. (12)3.2 启用VR (13)第4章备机VRRP配置: (15)4.1 备机初使化配置 (15)4.1.1 IP地址配置 (15)4.1.2 路由配置 (16)4.2 全局配置开启VRRP (17)4.3 配置VR (Virtual Router) (18)第5章同步配置: (20)5.1 安装APSolute Insite软件 (20)5.2 运行APSolute Insite软件 (25)5.2.1 登录软件 (25)5.2.2 添加AD主设备 (26)5.2.3 添加AD备机 (28)5.3 同步配置 (31)5.3.1 重启备机 (33)5.4 启用备机的VR (34)Radware 双机同步配置指导书关键词:摘要:缩略语清单:AS Application SwitchAD AppDirectorVRRP Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol图例说明:创建,创建一个新的条目删除,删除选定的条目选择,在删除条目前必须先选择设置,设置后生效放弃,放弃当前的改动帮助,在工作站可以连接Internet的情况下,可以去Radware网站获取当前配置的详细帮助后退前进刷新页面第1章VRRP主机配置使用VRRP冗余方式时配置如下参数。

(初稿)Radware负载均衡设备主要参数配置说明2007年10月radware北京代表处目录一、基本配置 (3)1.1 Tuning配置 (3)1.2 802.1q配置 (4)1.2 IP配置 (6)1.3 路由配置 (7)二、四层配置 (8)2.1 farm 配置 (8)2.2 servers配置 (10)2.3 Client NAT配置 (11)2.4 Layer 4 Policy配置 (16)三、对服务器健康检查 (18)3.1 基于连接的健康检查 (19)3.2 高级健康检查 (21)四、常用系统命令 (25)一、基本配置Radware负载均衡设备的配置主要包括基本配置、四层配置和对服务器健康检查配置。
注:本文档内容,用红色标注的字体请关注。
1.1 Tuning配置Rradware设备tuning table的值是设备工作的环境变量,在做完简单初始化后建议调整tuning值的大小。
调整完tuning table后,强烈建议,一定要做memory check,系统提示没有内存溢出,才能重新启动设备,如果系统提示内存溢出,说明某些表的空间调大了,需要把相应的表调小,然后,在做memory check,直到没有内存溢出提示后,重启设备,使配置生效。
点击service->tuning->device 配置相应的环境参数,Tuning for AppDirector AS2 AS4缺省值最大值建议值缺省值最大值建议值Bridge Forwarding Table: 1,02432,76732,7671,02432,76732,767 IP Forwarding Table: 32,768262,144256,00032,768262,144256,000 ARP Forwarding Table: 1,02432,7679,0001,02432,7679,000 Client Table: 65,536537,000400,00065,5361,396,685800,000 Routing Table: 51232,76751251232,767512在做一般的配置时主要调整的参数如下:Bridge Forwarding Table、IP Forwarding Table、ARP Forwarding Table、Client Table等。
Radware配置手册目录一. Radware连接 (4)1.1 console连接 (4)1 .2 初始化 (4)1.3登录radware设备 (6)1.4通过WEB界面对设备进行管理 (7)二.网络层配置 (8)2.1配置IP地址 (8)2.2 Vlan划分 (8)2.3 Routing Table (10)三 Farm 管理 (12)四服务器管理 (15)五 Super Farm IP管理 (17)六 Cookie会话保持 (19)七 NAT配置 (21)八双机配置 (24)九其他配置(可选) (28)9.1 保存配置文件 (28)9.2 恢复配置文件 (29)9.3 用户名和密码管理 (30)9.4 Syslog (30)9.5 Telnet (31)9.6 WEB管理 (31)9.7 安全管理 (32)十命令行网络配置 (33)10.1 更改设备名称 (33)10.2 物理端口 (33)10.3 VLAN (33)10.4 Interface (34)十一命令行维护命令 (35)11.1 查看接口地址 (35)11.2 查看路由表 (35)11.3 查看CPU (35)11.4 查看WSD的全部配置 (36)11.5 查看当前设备的版本信息 (36)11.6 查看当前设备的License (36)11.7 查看端口流量 (36)11.8 查看2层端口状态 (36)11.9 显示日志信息 (36)一. Radware连接1.1 console连接通过console连接Radware设备radware AppDirector和电脑的连接:Console各参数如下:Bits per second: 19200Data bits: 8Parity: NoneStop bits: 1Flow Control: None1 .2 初始化给设备加电,在3秒内按任意键CPU: RadWare BOOMER - MPC740/750Active boot: 1DRAM size: 256MFlash size: 16MAltera version: 24BSP version: 6.00Creation date: Oct 11 2005, 16:34:37Press any key to stop auto-boot...3>> ?- print this list@ - boot (load and go)e - print fatal exceptionw - download via xmodema - print installed applications listi - set active applicationu - download to secondary boot via xmodem x - extract from an archive>q0(清空原有配置参数,恢复缺省值)>q1(清空原有配置参数,恢复缺省值)Q是隐含命令,防止用户误删除配置.> q0Erasing configuration ...Erasing Network Section ...done> q1Erasing configuration ...fl:/ - Volume is OKconfig file is not foundErasing Network Section ...done>@(设备重启)1.3登录radware设备在“>”提示符下,输入login命令,并接照提示输入正确的用户名及口令即可登录.>LoginUsername:radwarePassword:: ******如果登录成功,提示符将变为“#”说明:(1) 如果Console显示中存在乱码,请输入如下命令#manage terminal grid-mode set disable。
Radware AppDirector负载均衡器指导书Radware AppDirector负载均衡器开局指导书拟制:日期:审核:日期:审核:日期:2006-11-30批准:日期:2006-11-30Radware AppDirector负载均衡器指导书目录第1章Radware AppDirector产品11.1AppDirector产品介绍1第2章Radware连接12.1通过console连接Radware设备12.2通过telnet连接Radware设备12.3登录radware设备22.4确认当前设备的版本22.5查看当前设备的License32.6通过WEB界面对设备进行管理3第3章网络层配置43.1Vlan划分43.2定义IP地址63.3Routing Table73.4Farm管理83.5服务器管理123.6L4Policy管理143.7Cookie会话保持153.8NAT配置173.9双机配置203.10保存配置文件253.11恢复配置文件263.12SNMP的字串管理273.13用户名和密码管理29第4章命令行基本配置314.1设备314.2管理314.3全局表项314.4命令行网络配置324.4.1物理端口324.4.2VLAN324.4.3Interface33Radware AppDirector负载均衡器指导书4.4.4路由和默认网关334.5命令行负载均衡配置334.5.1Farm配置334.5.2服务器配置35第5章命令行维护命令365.1查看接口地址365.2查看路由表365.3查看CPU365.4查看服务器的连接用户数375.5查看AppDirector的会话表375.6查看AppDirector的动态Cookie表385.7查看AppDirector的命令全部配置39第6章AppDirector组网406.1直连组网406.2单臂组网41Radware AppDirector负载均衡器指导书关键词:摘要:按照常见的配置步骤,本文对Radware AppDirector负载均衡器设备配置进行说明缩略语清单:参考资料清单:Radware AppDirector负载均衡器指导书第1章Radware AppDirector产品1.1AppDirector产品介绍AppDirector产品有一系列产品,从低端到高端产品分别是AD200/202、AD1000、AD3020和AD6000,对应的产品相关指标分别如下,对于AppDirector产品而言处理的关键在于处理流量的大小。
Radware AppDirector CLI 命令行配置手册Radware China2007-3-19刘庆明Ver1.0本文是Radware AppDirector的快速配置手册,不包括Radware CLI的所有详细说明,旨在为用户提供一个快速的配置介绍。
本文档基于AppDirector AS2 1.01.03。
本文档是根据配置的顺序来组织的,请用户按照文档的顺序来配置AppDirector。
一般情况下,配置按照网络分层协议由低到高来进行,即先进行物理层和数据链路层的配置,然后是网络层的配置,最后才是4-7层负载均衡的配置。
如果未标明是主用设备还是备用设备,则主备配置是相同的,主备设备都需要配置。
首先通过Console口进行初始化配置,配置好必要的管理IP,然后通过Telnet登录AppDirector。
以下所有的命令均通过Telnet或SSH操作。
Console口主要用来观察输出和排错,千万不要用来粘贴命令,切记!!!1基本配置系统默认使用英文的制表符,会与中文系统的内码冲突,所以最好先关闭制表符的输出。
AppDirector-OA#net ipInterface Table哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪穆哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪穆哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪穆哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪IP Address 砃etwork Mask 矷f Number 砎lanTag哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪呐哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪呐哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪呐哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪2.2.2.1 ?55.255.255.0 ? ?哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪呐哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪呐哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪呐哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪3.3.3.1 ?55.255.255.0 ? ?哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪牧哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪牧哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪牧哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪哪AppDirector-OA#manage terminal grid-mode set disDisplay of ascii graphics characters: disabledAppDirector-OA#net ipInterface TableIP Address Network Mask If Number VlanTag2.2.2.1 255.255.255.0 2 03.3.3.1 255.255.255.0 3 01.1设备以下两条命令是用来标识AppDirector设备的,给它们取个好记的名字;设置命令提示符,让你知道现在正登录在哪台设备上,当设备多的时候,尤其是多设备冗余时。
1.1.1 双机配置1.进入AppDirector→Redundancy → Global ParametersIP Redundancy Admin Status: 选择VRRP,彩铃业务中我们一般采用VRRP双机方式。
Interface Grouping: 选择enable,表示在一个端口出现问题的时候进行整体设备切换2.配置VRRP的Vitural Router进入AppDirector→Redundancy →VRRP→Virtual Routers++If index :选择实际物理端口,如图内部VLAN 使用端口2VR ID :Virtual Router 的编号,可以和端口号设成一致,方便识别。
Admin status :选择up ,可以管理。
Priority :主备机的优先级,数值高表示主机,要求在255以下,建议主机配成254,备机用默认的100Primary IP :端口的实际IP 地址内部Vlan 和外部Vlan 都需要进行设置。
说明:关于VR (Virtual Router),第一次配置状态是Down的,在没有配置Associated IP的时候,VR是不能UP的。
只有在配置完主备设备的Associated IP,并且内容一致的时候,才能将VR的状态设置为up。
VRRP就开始工作了。
3.配置VRRP的Vitural IP Interface (浮动IP)进入AppDirector > Layer 4 Farm Selection >Layer 4 Policy Table将内部Vlan和外部Vlan的浮动IP添加到L4 Policy table中其中L4 Protocol选择anyApplication:选择Virtual IP Interface4.配置VRRP的Associated IP进入AppDirector > Redundancy > VRRP > Associated IP配置相关联的IP地址,包括所有的Farm的Virtual IP和Virtaual IP Interface,即所有主备机上相同的,属于radware的IP 地址都需要进行配置++上述配置主备机都需要配置。
radvd配置手册radvd.conf - Linux man page 收藏Nameradvd.conf - configuration file of the router advertisement daemon radvdDescriptionThis file describes the information which is included in the router advertisement (RA) of a specific interface.The file contains one or more interface definitions of the form:interface name {list of interface specific optionslist of prefix definitionslist of route definitions};All the possible interface specific options are detailed below. Each option has to be terminated by a semicolon.Prefix definitions are of the form:prefix prefix/length {list of prefix specific options};Prefix can be network prefix or the address of the inferface. The address of interface should be used when using Mobile IPv6 extensions.All the possible prefix specific options are described below. Each option has to be terminated by a semicolon.Decimal values are allowed only for MinDelayBetweenRAs, MaxRtrAdvInterval and MinRtrAdvInterval. Decimal values should be used only when using Mobile IPv6 extensions.Route definitions are of the form:route prefix/length {list of route specific options};The prefix of a route definition should be network prefix; it can be used to advertise more specific routes to the hosts.Interface Specific OptionsIgnoreIfMissing on |offA flag indicating whether or not the interface is ignored if it does not exist. This is useful for dynamic interfaces which are not active when radvd starts, but for which you want to already have configuration -- and when they become active, you send HUP signal to radvd to activate them.Default: offAdvSendAdvert on |offA flag indicating whether or not the router sends periodic router advertisements and responds to router solicitations.This option no longer has to be specified first, but it needsto be on to enable advertisement on this interface.Default:offUnicastOnly on |offIndicates that the interface link type only supports unicast. This will prevent unsolicited advertisements from being sent, and will cause solicited advertisements to be unicast to the soliciting node. This option is necessary for non-broadcast, multiple-access links, such as ISATAP.Default: offMaxRtrAdvInterval secondsThe maximum time allowed between sending unsolicited multicast router advertisements from the interface, in seconds.Must be no less than 4 seconds and no greater than 1800 seconds.Minimum when using Mobile IPv6 extensions: 0.07.For values less than 0.2 seconds, 0.02 seconds is added to account for scheduling granularities as specified in RFC3775.Default: 600 secondsMinRtrAdvInterval secondsThe minimum time allowed between sending unsolicited multicast router advertisements from the interface, in seconds.Must be no less than 3 seconds and no greater than 0.75 * MaxRtrAdvInterval.Minimum when using Mobile IPv6 extensions: 0.03.Default: 0.33 * MaxRtrAdvIntervalMinDelayBetweenRAs secondsThe minimum time allowed between sending multicast router advertisements from the interface, in seconds.This applies to solicited multicast RAs. This is defined as the protocol constant MIN_DELAY_BETWEEN_RAS in RFC2461. MIPv6 redefines this parameter to have a minimum of 0.03 seconds.Minimum when using Mobile IPv6 extensions: 0.03.Default: 3AdvManagedFlag on |offWhen set, hosts use the administered (stateful) protocol for address autoconfiguration in addition to any addresses autoconfigured using stateless address autoconfiguration. The use of this flag is described in RFC 2462.Default: offAdvOtherConfigFlag on |offWhen set, hosts use the administered (stateful) protocol for autoconfiguration of other (non-address) information. The use of this flag is described in RFC 2462.Default: offAdvLinkMTU integerThe MTU option is used in router advertisement messages to insure that all nodes on a link use the same MTU value in those cases where the link MTU is not well known.If specified, i.e. not 0, must not be smaller than 1280 and not greater than the maximum MTU allowed for this link (e.g. ethernet has a maximum MTU of 1500. See RFC 2464).Default: 0AdvReachableTime millisecondsThe time, in milliseconds, that a node assumes a neighbor is reachable after having received a reachability confirmation. Used by the Neighbor Unreachability Detection algorithm (see Section 7.3 of RFC 2461). A value of zero means unspecified (by this router).Must be no greater than 3,600,000 milliseconds (1 hour).Default: 0AdvRetransTimer millisecondsThe time, in milliseconds, between retransmitted NeighborSolicitation messages. Used by address resolution and the Neighbor Unreachability Detection algorithm (see Sections 7.2 and 7.3 of RFC 2461). A value of zero means unspecified (by this router).Default:AdvCurHopLimit integerThe default value that should be placed in the Hop Count field of the IP header for outgoing (unicast) IP packets. The value should be set to the current diameter of the Internet. The value zero means unspecified (by this router).Default: 64AdvDefaultLifetime secondsThe lifetime associated with the default router in units of seconds. The maximum value corresponds to 18.2 hours. A lifetime of 0 indicates that the router is not a default router and should not appear on the default router list. The router lifetime applies only to the router's usefulness as a default router; it does not apply to information contained in other message fields or options. Options that need time limits for their information include their own lifetime fields.Must be either zero or between MaxRtrAdvInterval and 9000 seconds.Default: 3 * MaxRtrAdvInterval (Minimum 1 second).AdvDefaultPreference low |medium |highThe preference associated with the default router, as either "low", "medium", or "high".Default: mediumAdvSourceLLAddress on |offWhen set, the link-layer address of the outgoing interface is included in the RA.Default: onAdvHomeAgentFlag on |offWhen set, indicates that sending router is able to serve as Mobile IPv6 Home Agent. When set, minimum limits specified by Mobile IPv6 are used for MinRtrAdvInterval and MaxRtrAdvInterval.Default: offAdvHomeAgentInfo on |offWhen set, Home Agent Information Option (specified by Mobile IPv6) is included in Router Advertisements. AdvHomeAgentFlag must also be set when using this option.Default: offHomeAgentLifetime secondsThe length of time in seconds (relative to the time the packet is sent) that the router is offering Mobile IPv6 Home Agent services. A value 0 must not be used. The maximum lifetime is 65520 seconds (18.2 hours). This option is ignored, if AdvHomeAgentInfo is not set.If both HomeAgentLifetime and HomeAgentPreference are set to their default values, Home Agent Information Option will not be sent.Default:AdvDefaultLifetimeHomeAgentPreference integerThe preference for the Home Agent sending this Router Advertisement. Values greater than 0 indicate more preferable Home Agent, values less than 0 indicate less preferable Home Agent. This option is ignored, if AdvHomeAgentInfo is not set.If both HomeAgentLifetime and HomeAgentPreference are set to their default values, Home Agent Information Option will not be sent.Default: 0AdvMobRtrSupportFlag on |offWhen set, the Home Agent signals it supports Mobile Router registrations (specified by NEMO Basic). AdvHomeAgentInfomust also be set when using this option.Default: offAdvIntervalOpt on |offWhen set, Advertisement Interval Option (specified by Mobile IPv6) is included in Router Advertisements. When set, minimum limits specified by Mobile IPv6 are used for MinRtrAdvInterval and MaxRtrAdvInterval.The advertisement interval is based on the configured MaxRtrAdvInterval parameter except where this is less than 200ms. In this case, the advertised interval is ( MaxRtrAdvInterval + 20ms ).Default:offPrefix Specific OptionsAdvOnLink on |offWhen set, indicates that this prefix can be used for on-link determination. When not set the advertisement makes no statement about on-link or off-link properties of the prefix. For instance, the prefix might be used for address configuration with some of the addresses belonging to the prefix being on-link and others being off-link.Default: onAdvAutonomous on |offWhen set, indicates that this prefix can be used for autonomous address configuration as specified in RFC 2462.Default: onAdvRouterAddr on |offWhen set, indicates that the address of interface is sent instead of network prefix, as is required by Mobile IPv6. When set, minimum limits specified by Mobile IPv6 are used for MinRtrAdvInterval and MaxRtrAdvInterval.Default: offAdvValidLifetime seconds|infinityThe length of time in seconds (relative to the time the packet is sent) that the prefix is valid for the purpose of on-link determination. The symbolic value infinity represents infinity (i.e.a value of all one bits (0xffffffff)). The valid lifetime is also used by RFC 2462.Default: 2592000 seconds (30 days)AdvPreferredLifetime seconds|infinityThe length of time in seconds (relative to the time the packet is sent) that addresses generated from the prefix via stateless address autoconfiguration remain preferred. The symbolic value infinity represents infinity (i.e. a value of all one bits (0xffffffff)). See RFC 2462.Default: 604800 seconds (7 days)Base6to4Interface nameIf this option is specified, this prefix will be combined with the IPv4 address of interface name to produce a valid 6to4 prefix. The first 16 bits of this prefix will be replaced by 2002 and the next 32 bits of this prefix will be replaced by the IPv4 address assigned to interface name at configuration time. The remaining 80 bits of the prefix (including the SLA ID) will be advertised as specified in the configuration file. See the next section for an example.If interface name is not available at configuration time, a warning will be written to the log and this prefix will be disabled until radvd is reconfigured.This option enables systems with dynamic IPv4 addresses to update their advertised 6to4 prefixes simply by restarting radvd or sending a SIGHUP signal to cause radvd to reconfigure itself.Note that 6to4 prefixes derived from dynamically-assigned IPv4 addresses should be advertised with a significantly shorter lifetime (see the AdvValidLifetime and AdvPreferredLifetime options).For more information on 6to4, see RFC 3056.Default: 6to4 is not usedRoute Specific OptionsAdvRouteLifetime seconds|infinityThe lifetime associated with the route in units of seconds. The symbolic value infinity represents infinity (i.e. a value of all one bits (0xffffffff)).Default: 3 * MaxRtrAdvIntervalAdvRoutePreference low |medium |highThe preference associated with the default router, as either "low", "medium", or "high".Default: mediumExamplesinterface eth0{AdvSendAdvert on;prefix 2001:db8:0:1::/64{AdvOnLink on;AdvAutonomous on;};};It says that router advertisement daemon should advertise (AdvSendAdvert on;) the prefix 2001:db8:0:1:: which has a lenght of 64 on the interface eth0. Also the prefix should be marked as autonomous (AdvAutonomous on;) and as on-link (AdvOnLink on;). All the other options are left on their default values.To support movement detection of Mobile IPv6 MobileNodes, the address of interface should be used instead of network prefix:interface eth0{AdvSendAdvert on;prefix 2001:db8:0:1::4/64{AdvOnLink on;AdvAutonomous on;AdvRouterAddr on;};};For 6to4 support, include the Base6to4Interface option in each prefix section. When using a dynamic IPv4 address, set small prefix lifetimes to prevent hosts from retaining unreachable prefixes after a new IPv4 address has been assigned. When advertising to on a dynamic interface (e.g., Bluetooth), skip the interface if it is not active yet.interface bnep0{IgnoreIfMissing on;AdvSendAdvert on;# Advertise at least every 30 secondsMaxRtrAdvInterval 30;prefix 0:0:0:5678::/64{AdvOnLink on;AdvAutonomous on;Base6to4Interface ppp0;# Very short lifetimes for dynamic addressesAdvValidLifetime 300;AdvPreferredLifetime 120;};};Since 6to4 is enabled, the prefix will be advertised as 2002:WWXX:YYZZ:5678::/64, where WW.XX.YY.ZZ is the IPv4 address of ppp0 at configuration time. (IPv6 addresses are written in hexadecimal whereas IPv4 addresses are written in decimal, so the IPv4 address WW.XX.YY.ZZ in the 6to4 prefix will be represented in hex.)In this specific case, the configuration scripts should send HUP signal to radvd when taking bnep0 up or down to notify about the status.Files/usr/sbin/radvd/etc/radvd.conf/var/run/radvd/radvd.pid/var/log/radvd.logCreditThe description of the different flags and variables is in large parts taken from RFC 2461.RfcsNarten, T., E. Nordmark, W. Simpson, "Neighbor Discovery for IP Version 6 (IPv6)", RFC 2461, December 1998Thomson, S., and T. Narten, "IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration", RFC 2462, December 1998.Deering, S., and R. Hinden, "IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture", RFC 3513, April 2003.Conta, A., and S. Deering, "Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMPv6) for the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6)", RFC 2463, December 1998.Crawford, M., "Transmission of IPv6 Packets over Ethernet Networks", RFC 2464, December 1998.Carpenter B., K. Moore, "Connection of IPv6 Domains via IPv4 Clouds", RFC 3056, February 2001. (6to4 specification)Draves, R., D. Thaler, "Default Router Preferences and More-Specific Routes", RFC 4191, November 2005.Johnson, D., Perkins, C., and J. Arkko, "Mobility Support in IPv6", RFC 3775, June 2004.Devarapalli, V., Wakikawa, R., Petrescu, A., and P. Thubert "Network Mobility (NEMO) Basic Support Protocol", RFC 3963, January 2005.本文来自CSDN博客,转载请标明出处:/doc/8f2468308.html,/fengyv/archive/2011/05/ 10/6408618.aspxvi /etc/systcl.confnet.ipv4.ip_forward = 1net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 1 systcl -p。