20120524_天清异常流量检测系统ADM-Detector配置培训文档 V3.6.3.1
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:5.44 MB
- 文档页数:34





天馈线分析仪SiteMaster操作指导书----------------------- Page 1----------------------- Site Master天馈线分析仪操作培训2004年1月Slide 1 of 33----------------------- Page 2----------------------- 内容传输线和天线(天馈线)简介天馈线测量基础测试设备(方法)和比较操作培训故障分析测验参考文献Slide 2 of 33----------------------- Page 3----------------------- 内容传输线和天线(天馈线)简介天馈线测量基础测试设备(方法)和比较操作培训故障分析测验参考文献Slide 3 of 33----------------------- Page 4----------------------- 传输线和天线(天馈线)简介Slide 4 of 33----------------------- Page 5----------------------- 传输线和天线(天馈线)简介天馈线系统组成和性能安装质量Slide 5 of 33----------------------- Page 6----------------------- 天馈线系统组成和性能哪些因素影响系统品质?传输线和天线系统有许多特性能够而且确实影响射频信号的质量。
o 射频信号的频率o 传输线的类型o 传输线的长度o 电缆的类型o 电缆的尺寸o 连接器o 天线o 安装的质量Slide 6 of 33----------------------- Page 7----------------------- 天馈线系统组成和性能频率频率如何影响性能?传输线传输线的类型如何影响您的系统?传输线的长度如何影响您的系统?我们如何选择正确的传输线?电缆电缆类型如何影响您的系统?电缆尺寸如何影响您的系统?我们如何选择正确的电缆?连接器使用目的和安装质量对系统的影响?面对众多连接器我们如何选择?天线天线类型如何影响您的系统?我们如何选择合适的天线?Slide 7 of 33----------------------- Page 8----------------------- 天馈线系统组成和性能频率频率如何影响性能?频率越高,损耗越大。


5th International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Computing Technology (ICMMCT 2017)An Abnormal Traffic Cleaning SystemYang Li1,a,*, Yanlian Zhang2,b1DIGITAL CHINA(CHINA)LIMITED, Beijing, China2 China Flight test establishment , Xi’an 710089,China,a,*********************Keywords: Abnormal Traffic, Cleaning, Detection, Traffic Re-injectionAbstract.Abnormal traffic cleaning system is proposed, which includes a cleaning platform, a detection platform and a management platform. The cleaning platform is mainly deployed through the bypass to guide the flow of the attacked object to the cleaning equipment. According to the protection strategy, the attack traffic is cleaned and normal traffic, the detection platform complete the detection of traffic for the attack, the management platform to provide cleaning equipment, testing equipment, state monitoring. The system can effectively clean the abnormal traffic and improve the security of the network.1.IntroductionWith the development of network technology and network economy, the importance of network to enterprises and individuals is increasing. At the same time, the network security vulnerabilities are also being increased, the importance of network security issues is also growing. In the metropolitan area network side for enterprise customers to carry out traffic cleaning services to achieve the defences of DDoS attacks, can meet the dual needs of customers. The traffic cleaning service is a kind of network security service for the government and enterprise customers who rent the IDC service and monitor, alarm and protect against the DOS /DDOS attack.2. Architecture of Traffic Cleaning SystemAbnormal traffic cleaning system includes cleaning platform, detecting platform and management platform. These parts of the function may be implemented by a device, or each part of the function realize by a single device.The cleaning platform is mainly deployed through the bypass. It uses the routing protocol to route the attacked objects from the routing device to the cleaning device. According to the protection strategy, the abnormal traffic can be distinguished from the normal traffic to realize the cleaning of the attack traffic and the return of the normal traffic. And feedback the cleaning results to the management platform for unified management and presentation.The detection platform can use splitting, mirroring, or traffic information collection, and can detect the attack traffic based on the traffic baseline policy. After the test platform runs for a period of time in the network, it can form a set of traffic distribution similar to the actual network according to the traffic situation in the actual network. The automatic learning generation or manual configuration forms the traffic baseline. When an attack is detected, an alarm is generated to the management platform.Management platform provide cleaning equipment, testing equipment, state monitoring, and unified policy management, user management, device management and other functions, to provide users with cleaning statements query portal, can send and receive instructions to achieve linkage with other platforms.Traffic cleaning system can interact with external detection alarm system, unified scheduling platform; form a multi-level traffic cleaning system.Figure 1 architecture of traffic cleaning system3.Traffic Cleaning Function3.1 Traffic CleaningSupport clean typical traffic-based attacks, the cleaning of the attack types should include: Syn flood, ICMP flood, UDP flood, Ack flood, TCP connections flooded, DNS flood, HTTP post flood, Https flood. Support clean typical reflection attacks, including at least DNS reply flood, NTP flood and so on.Support cleaning of application-level non-traffic-based attacks, at least should include HTTP slow request attacks, CC attacks. Supports common DOS attack packet cleaning, include Smurf, Land, deformity package, and TearDrop.3.2 Cleaning limitAccording to the user policy, it is defined that when the total traffic rate of the protection object exceeds a certain threshold value, random discarding is carried out, and the flow rate after cleaning is limited below the threshold value.3.3 Black hole cleaningIt is recommended to use the route traction command to implement the black hole policy when the total traffic rate exceeds a certain threshold. This tells the neighbour router to directly flood all the traffic. Black hole routing instructions should support the use of BGP protocol.3.4 Cleaning featureAccording to the characteristics of the attack (such as IP header, TCP header, TCP payload, UDP header and UDP payload, source port, destination port, etc.) to define the precise filtering policy, support the analysis of typical protocol fields, and apply the attack feature to the protection object .3.5 Protection strategyProtection policy for the protection object should be configured. The protection objects should be distinguished by IP addresses. A default protection object policy should be supported to support the creation of a unified protection policy (the default protection policy) for protected objects that do not have explicit IP protection.The protection strategy should include the following:●Support the defence flow threshold and rate of a specific protocol●Support the use of specific cleaning algorithm (including whether the source calibration, etc.)●Support the cleaning strategy when exceeding the protection threshold (traffic rate limit, sub-protocol speed limit, black hole routing, etc.)●Configure the cleaning features of specific attack packets●Supports IP address blacklist function based on attack source geographic information (optional), and blacklist IP address traffic directly intercepts.3.6 Traffic tractionThe traffic cleaning device has a neighbour relationship with the router, and dynamically sends a route advertisement to the upstream (neighbour) router to dynamically draw the traffic of the protected object to the cleaning device. The traffic clean-up platform support dynamic routing traction using the BGP-4 protocol. Traffic cleaning and draining can support OSPF, IS-IS, MPLS LSP, MPLS VPN and other forms of traffic traction requirements.Traffic tracing supports specifying a traffic traction policy for each protection object. It supports setting the mask length for different bits in traffic advertisement for protection objects. The BGP peering policy support the configuration of BGP community, AS path, and other basic attributes. And can configure route-map, prefix-list, and other route filtering modes.The cleaning platform support BGP route advertisements with different attribute parameters for different neighbouring routers. The router can advertise only a route advertisement to a specific neighbour router (not all neighbour routers) to cooperate with the router in the network.3.7 Traffic injectedThe traffic injected through policy routing, MPLS VPN, MPLS LSP, GRE, and Layer 2 injection will be injected into the network.3.8 Traffic balanceDiversion and re-injection of two-way links should be supported through link aggregation, equivalent routing and other forms of drainage, re-injection flow load sharing.3.9 Cleaning source authenticationThe source IP address of the specified attack type should be authenticated according to the user protection policy. The IP address of the source IP address to be authenticated should be used as the source authentication whitelist. No longer need to perform source authentication. The whitelist should have a certain aging time.The number of IP addresses of the whitelist entries must be selected according to the deployment requirements. The total number of whitelist entries should be at least 100,000.4.Detection functionThe detection device support traffic detection by means of one or more means based on traffic information or per packet detection.●Data flow based detection: Supports the analysis of the data flow in the traffic, the acquisitionformat should support a variety of protocol formats, including Netflow V5/V9, Netstream and other protocols, while supporting IPv4 and IPv6 traffic detection.●DPI based traffic detection: Supports packet-by-packet traffic analysis to detect abnormaltraffic events in the network. Supports detection of traffic packets based on detection thresholds, detection features, and so on.●Dynamic baseline learning: The detection equipment supports the dynamic baseline learningtask. It should support dynamic baseline learning at a specified time, support dynamic baseline automatic generation, and support manual adjustment and confirmation of thresholds for dynamic learning.●Attack event Alarm :Alarm event list Including the alarm ID, alarm type, alarm cause,severity, IP address and port to be attacked, the source IP address of the attack, and the source IP address of the attack source, Start time and so on.5.Management functionLogin Management: B/S mode should support the user login management, multi-user landing at the same time, to support more than one login account or only single sign-on. Support mandatory toenable https, support the management of IP address restrictions, the command line should support SSH. RADIUS-based authentication should be supported.User management: It should support a unified operation and maintenance management portal and user service portal capabilities, the system should support the creation of sub-domain for the user to achieve management of the sub-domain management.Protection object management: The protection object is configured by IP address. It should be configured through IP address. It can be configured by IP address segment plus mask. Supports the object protection strategy of the bulk application, protection object (group) number of not less than 1000.Device management: support the management of the device group, and to add, delete and modify the devices in the group. The defence group can be built and the protection strategy of the protection object can be unified. The import and export of device configuration information should be supported.6.Performance requirementsSingle Device Throughput: The throughput of a device should meet the throughput requirements according to the actual requirements in different deployment environments. Packet flooding, DNS flood, ICMP flood, UDP flood, mixed flood, HTTP Get Flood, and so on.Equipment cleaning accuracy: cleaning specifications 90% load, normal traffic and mixed attack traffic according to 1: 9 ratio, the normal business packet loss rate should not be higher than one thousandth, attack traffic leakage blocking rate should not be high One percent.Cleaning delay requirements: cleaning specifications 90% load conditions, the forwarding delay of not more than 80us.Reliability Requirement: The overall reliability of the system should reach 99.999% (software and hardware), that is, the system may not interrupt more than 5.26 minutes during the continuous operation for 1 year.7.External interfaceCleaning system external interface support the establishment of a trusted channel interface to meet the security requirements of transmission, support for domestic encryption algorithm.Interface between the cleaning system and the third-party detection equipment: The attacking alarm reported by the third-party detection platform Syslog should be supported. The protocol and format of the Syslog interface meet the requirements of RFC3164.Management system interface with the external dispatch platform include: data reporting interface: to support the cleaning task start / end of the report, reporting the status of cleaning tasks changes. support the cleaning log, traffic log regularly reported, reported cleaning data, traffic data to the scheduling platform. Can support the cleaning capacity is insufficient cleaning business alarm report. Command issuance interface: It can support the protection strategy and drainage policy of cleaning protection object issued by external management platform. Can support the external platform issued the task of cleaning tasks, scheduling cleaning equipment for cleaning, stop cleaning and other operations.8.ConclusionsAn abnormal traffic cleaning system is proposed in this paper, the architecture of the system is provided, which includes a cleaning platform, a detection platform and a management platform. And this system can improve the security of traffic.References[1] Francesco Gargiulo; Carlo Sansone, (2010) Improving Performance of Network TrafficClassification Systems by Cleaning Training Data, 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2768 - 2771[2] Byoung-Koo Kim; Dong-Ho Kang, (2016)Abnormal traffic filtering mechanism for protecting ICS networks 2016 18th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, 436 – 440[3] Sergey Ageev; Yan Kopchak,(2015) Abnormal traffic detection in networks of the Internet of things based on fuzzy logical inference, 2015 XVIII International Conference on Soft Computing and Measurements (SCM), 5 - 8[4] Tianshu Wu; Kunqing Xie ,(2012) A online boosting approach for traffic flow forecasting under abnormal conditions2012 9th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, 2555 – 2559[5] Ayman Mohammad Bahaa-Eldin ,(2011)Time series analysis based models for network abnormal traffic detection The 2011 International Conference on Computer Engineering & Systems, 64 - 70。

Commvault数据管理系统日常运维手册XXXXXXXX2016年8月注意事项本报告中的观点和决定都不代表任何官方立场。
它仅用于交流技术信息。
本文中所有内容均属本地航空和Commvault的商业秘密。
未经允许,不得作任何形式的复制和传播。
目录目录 (3)1环境说明 (5)1.1CommServe & MA (5)1.2客户端 (5)1.3License (5)1.4架构拓扑 (5)1.5系统说明 (5)2软件使用说明 (7)2.1登陆CommCell管理控制台 (7)2.1.1通过本地CommCell登陆控制台 (7)2.1.2远程登陆CommCell (8)2.2访问Web Console (9)2.3服务及进程管理 (10)2.3.1Windows平台启动/停止服务 (10)2.4通用进程管理 (11)2.4.1CommServer 上的进程 (11)2.4.2MediaAgent 上的进程 (11)2.4.3客户端上的进程 (12)2.5CommCell管理界面说明 (12)2.5.1CommCell管理界面布局 (12)2.5.2查看计算机组或者计算机详情 (12)2.5.3合理布局多个窗体 (13)3管理存储资源 (15)3.1管理磁盘库 (15)3.1.1检查磁盘库状态 (15)3.1.2检查磁盘库装载路径 (17)3.1.3磁盘库临时释放空间 (19)3.2管理介质服务器 (22)3.2.1MediaAgent状态 (22)3.2.2IndexCache管理 (23)4日常维护监控 (25)4.1查看客户端状态 (25)4.1.1客户端检查连接 (25)4.1.2报表检查 (25)4.2查看客户端计划 (26)4.2.1客户端级别作业计划. (26)4.2.2CommCell级别作业计划. (27)4.2.3报表查看作业计划 (27)4.3管理作业任务 (28)4.3.1管理当前作业 (28)4.3.2管理历史作业 (30)4.4管理客户端属性 (33)5故障处理 (36)5.1查看作业日志 (36)5.2查看客户端日志 (37)5.3收集发送日志 (39)5.4报修流程 (41)1环境说明1.1CommServe & MAxmncvserver 11.2.80.16 本地生产commservexmncvserverbak 11.2.80.17 本地standby commservexmncvma1 11.2.80.32 本地MediaAgent1.2客户端1.3License1.4架构拓扑CSVcenter Vcenter1.5系统说明本地:mservea)主CS:单机,生产CommServe,DR备份到备节点主机的共享文件夹中b)备用CS:单机,主CS出现问题后,使用DR备份进行恢复2.Web Servera)位于CS上,用于Web Console3.Web Consolea)位于CS4.MediaAgenta)本地MA,用于备份本地的数据b)同时作为VSA,备份本地的VMware5.Clienta)本地客户生产机,备份数据源b)Virtual Center异地(未实施):1.MediaAgenta)异地MA,用于备份异地的数据b)同时作为VSA,备份异地的VMwarec)同时作为Proxy,负责异地客户端与本地CS之间的通信2.Clienta)异地客户生产机,备份数据源b)Virtual Center2软件使用说明2.1登陆CommCell管理控制台2.1.1通过本地CommCell登陆控制台本地CommCell管理是指通过Windows 远程桌面连接到CommServe主机,然后直接通过本地CommCell GUI登陆管理控制台。

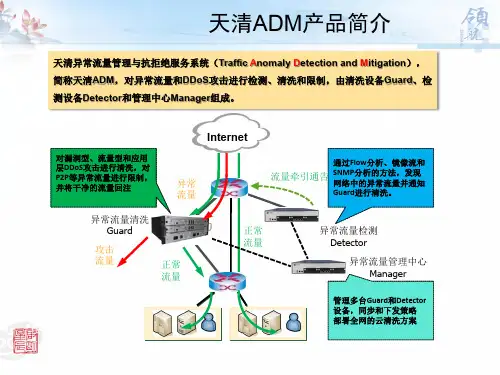
天清异常流量清洗系统A D M-G u a r d W e b管理用户手册北京启明星辰信息安全技术有限公司Beijing Venustech Cybervision Co., Ltd二零一二年五月版权声明北京启明星辰信息安全技术有限公司版权所有,并保留对本文档及本声明的最终解释权和修改权。
本文档中出现的任何文字叙述、文档格式、插图、照片、方法、过程等内容,除另有特别注明外,其著作权或其他相关权利均属于北京启明星辰信息安全技术有限公司。
未经北京启明星辰信息安全技术有限公司书面同意,任何人不得以任何方式或形式对本手册内的任何部分进行复制、摘录、备份、修改、传播、翻译成其它语言、将其全部或部分用于商业用途。
免责条款本文档依据现有信息制作,其内容如有更改,恕不另行通知。
北京启明星辰信息安全技术有限公司在编写该文档的时候已尽最大努力保证其内容准确可靠,但北京启明星辰信息安全技术有限公司不对本文档中的遗漏、不准确、或错误导致的损失和损害承担责任。
信息反馈如有任何宝贵意见,请反馈:信箱:北京市海淀区东北旺西路8号中关村软件园21号楼启明星辰大厦邮编:100193 电话:************传真:************您可以访问启明星辰网站:获得最新技术和产品信息。
目录第1章前言 (9)1.1 导言 (9)1.2 本书适用对象 (9)1.3 本书适合的产品 (9)1.4 手册章节组织 (9)1.5 相关参考手册 (10)第2章如何开始 (11)2.1 概述 (11)2.1.1 产品特点 (11)2.1.2 主要功能 (11)2.1.3 硬件描述 (13)2.1.4 软件描述 (15)2.1.5 附带软件描述 (16)2.2 拆箱检查 (16)2.3 安装 (16)2.3.1 检查安装场所 (16)2.3.2 安装 (17)2.3.3 网络连接 (17)2.4 配置管理方法 (17)2.4.1 网络接口WEB配置 (17)2.4.2 网络接口CLI配置 (17)2.4.3 本地串口CLI配置 (18)2.5 登录管理界面 (18)2.5.1 登录方法 (18)2.5.2 证书认证 (19)2.5.3 登录过程 (19)2.5.4 一般配置过程 (20)2.5.5 退出登录 (20)第3章系统管理 (22)3.1 系统信息 (22)3.1.1 版本信息 (22)3.1.2 License信息 (22)3.1.3 设备名称 (23)3.1.4 日期时间 (23)3.2 系统服务 (25)3.2.1 本地服务 (25)3.2.2 SSH服务 (26)3.2.3 Telnet服务 (28)3.2.4 SNMP配置 (29)3.2.5 WebUI超时 (31)3.3 配置管理 (31)3.3.2 存储设备管理 (32)3.3.3 当前配置查看 (33)3.4 维护升级 (33)3.4.1 系统升级 (33)3.4.2 License升级 (35)3.4.3 特征库升级 (35)3.5 证书管理 (36)3.5.1 导入证书 (36)3.5.2 本地证书 (37)3.5.3 CA中心 (42)3.6 集中管理 (45)3.7 批处理工具 (45)第4章网络管理 (46)4.1 网络接口 (46)4.1.1 接口IP地址 (46)4.1.2 接口配置 (51)4.2 ARP (56)4.2.1 静态ARP (56)4.2.2 ARP查看 (58)4.2.3 免费ARP (58)4.3 路由 (59)4.3.1 静态路由 (59)4.3.2 OSPF (62)4.3.3 智能路由 (65)4.3.4 路由表信息 (71)4.3.5 ISIS (71)4.4 DNS设置 (73)4.5 DHCP (74)4.5.1 服务器配置 (74)4.5.2 地址池配置 (75)4.5.3 DHCP中继 (78)第5章IPv6 (80)5.1 网络管理 (80)5.1.1 地址配置 (80)5.1.2 邻居配置 (81)5.1.3 服务段前缀 (81)5.1.4 自动配置 (82)5.1.5 静态路由 (82)5.2 资源定义 (83)5.2.1 地址 (83)5.2.2 服务 (85)5.2.3时间 (90)5.3 防火墙 (97)5.3.1 包过滤 (97)5.3.2 默认过滤策略 (97)5.4 流量牵引 (98)5.4.1 BGP牵引 (98)5.4.2 OSPF (109)5.5 流量分析 (110)5.5.1 自学习配置 (110)5.5.2 自学习管理 (112)5.6 流量清洗 (113)5.6.1 攻击处理方式 (113)5.6.2 日志采样 (114)5.6.3 DNS防护 (114)5.6.4 高级型攻击 (120)5.6.5 自定义特征 (124)5.7 流量统计 (126)5.7.1 事件统计 (126)5.7.2 攻击类型TOP5 (126)5.7.3 攻击来源TOP5 (127)5.7.4 攻击目的TOP5 (127)5.7.5 攻击流量统计 (128)5.7.6 保护域流量统计 (128)第6章虚拟网关 (130)6.1 网关管理 (130)6.1.1 虚拟网关划分 (130)6.1.2 接口归属查看 (132)6.2 全局资源 (132)6.2.1 地址 (132)6.2.2 服务 (137)6.2.3 时间 (142)6.2.4 应用协议 (145)6.2.5 包分类 (146)6.3 全局策略 (150)6.3.1 包过滤 (150)6.3.2 DNAT策略 (151)6.3.3 SNAT策略 (152)6.3.4 长连接 (154)第7章资源定义 (156)7.1 地址 (156)7.1.1 地址列表 (156)7.1.2 地址池 (157)7.1.3 地址组 (158)7.2 服务 (161)7.2.1 服务对象定义 (161)7.2.2 ICMP服务 (162)7.2.3 基本服务 (162)7.2.4 服务组 (164)7.2.5 ALG定义 (165)7.3 时间 (166)7.3.1 时间列表 (167)7.3.2 时间组 (168)7.4 应用协议 (169)7.4.1 应用协议 (169)7.4.2 应用协议组 (170)7.5 包分类 (170)第8章流量牵引 (174)8.1 BGP牵引 (174)8.1.1 BGP本地配置 (174)8.1.2 BGP邻居配置 (175)8.1.3 访问控制链表 (177)8.1.4 路由映射 (179)8.1.5 路由牵引配置 (181)8.2 OSPF (183)8.2.1 配置路由重分发 (183)8.2.2 启动、停止OSPF功能 (184)8.2.3 修改路由器ID (184)8.2.4 设置区域 (184)8.2.5 设置网络 (184)8.2.6 设置网络接口认证 (185)第9章流量分析 (186)9.1 自学习配置 (186)9.1.1 学习配置 (186)9.1.2 学习过程 (188)9.2 自学习管理 (188)9.2.1 学习结果 (188)9.2.2 学习曲线 (189)9.2.3 应用查看 (190)第10章流量清洗 (191)10.1 攻击处理方式 (191)10.2 日志采样 (191)10.3 攻击证据提取 (191)10.3.1 攻击证据提取 (191)10.3.2 捉包分析取证 (192)10.4 DNS防护 (193)10.4.2 域名访问限制 (195)10.4.3 DNS攻击保护 (197)10.4.4 域名长度参数 (199)10.5 基本型攻击 (199)10.6 高级型攻击 (200)10.7 自定义特征 (206)10.7.1 TCP (206)10.7.2 UDP (207)10.7.3 ICMP (207)10.7.4 自定义特征开启配置 (208)第11章流量回注 (209)11.1 接口转发 (209)11.2 启动GRE (211)11.3 隧道配置 (211)第12章流量统计 (213)12.1 事件统计 (213)12.1.1 开启统计 (213)12.1.2 事件统计 (213)12.2 攻击类型TOP5 (213)12.3 攻击来源TOP5 (214)12.4 攻击目的TOP5 (214)12.5 攻击流量统计 (215)12.5.1 即时流量统计 (215)12.5.2 异常流量统计 (215)12.6 保护域流量统计 (215)12.6.1 牵引流量统计 (215)12.6.2 清洗流量统计 (216)第13章防火墙 (217)13.1 包过滤 (217)13.1.1 默认过滤策略 (218)13.2 DNAT策略 (218)13.3 SNAT策略 (220)13.4 二层协议 (221)13.5 地址绑定 (222)13.6 服务器探测 (229)第14章会话管理 (232)14.1 会话配置 (232)14.2 长连接 (232)14.3 会话日志 (233)14.4 会话状态 (233)14.5 同步选项配置 (234)第15章带宽管理 (235)15.1 基于管道的带宽管理 (235)15.1.1 配置中心 (235)15.1.2 管道管理 (235)15.1.3 IP型策略管理 (236)15.1.4 动作管理 (237)15.2 基于接口的带宽管理 (238)15.2.1 物理限速 (238)15.2.2 QoS标签 (240)15.2.3 IPQoS (241)15.2.4 流量监管 (243)15.2.5 流量整形 (246)15.2.6 拥塞管理 (249)15.3 流量优化 (268)15.3.1 带宽借用 (268)15.3.2 流量建模 (271)第16章高可用性 (273)16.1 节点配置 (274)16.2 工作模式 (275)16.3 查看状态 (277)第17章应用安全 (278)17.1 DNS应用防火墙 (278)17.1.1 基本配置 (278)17.1.2 自定义域名监测 (279)17.1.3 静态域名表 (279)17.1.4 域名黑名单 (280)17.1.5 QPS信息 (282)17.1.6 重定向统计 (282)17.2 缓存感染监测 (283)17.2.1 缓存感染监测配置 (283)17.2.2 缓存感染实时监测统计 (283)17.2.3 缓存感染历史监测统计 (284)第18章应用识别 (285)18.1 特征策略 (285)18.2 策略应用 (288)18.3 统计图表 (290)18.4 日志采样 (290)第19章用户认证 (291)19.1 本地用户 (291)19.2 AAA认证 (292)19.2.1 认证服务器 (293)19.2.2 登录用户 (294)19.2.3 在线Portal用户 (294)19.2.4 Portal用户组 (294)19.2.5 Portal服务器 (296)第20章日志信息 (298)20.1 日志配置 (298)20.1.1 日志服务器 (298)20.1.2 终端信息控制 (298)20.1.3 信息终端 (299)20.1.4 U盘日志输出 (301)20.2 日志查看 (301)20.2.1 日志查看 (301)20.2.2 管理日志 (302)20.2.3 会话日志 (302)20.2.4 抗攻击日志 (302)20.2.5 流量牵引日志 (303)20.2.6 云安全日志 (303)20.3 邮件报警 (303)20.3.1 邮件报警 (304)20.3.2 邮件测试 (306)第21章流量可视 (308)21.1 统计配置 (308)21.2 网络概览 (309)21.3 接口统计 (309)21.4 应用统计 (310)21.5 会话统计 (312)21.6 IP统计 (313)21.7 自定义统计 (313)第22章系统监控 (316)22.1 CPU监控 (316)22.2 内存监控 (316)22.3 接口流量统计 (317)第23章在线支持 (318)23.1 技术支持 (318)23.2 关于 (318)第1章前言1.1 导言《天清异常流清洗系统ADM-Guard Web管理用户手册》是启明星辰天清异常流量管理与抗拒绝服务系统(天清ADM)管理员手册中的一本。

异常流量清洗技术规范书二O一三年五月目次1 主设备需求 (1)1.1 本期工程主设备配置表 (1)2 总体要求 (1)2.1 硬件设备要求 (1)2.2 软件系统要求 (2)2.3 电源及节能环保要求 (3)2.4 卖方应提供的工程资料 (4)3 主设备技术规范 (5)3.1 流量清洗设备 (5)3.2 流量检测设备 (7)1 主设备需求下表中规格为本期主设备之最低要求,卖方可更换设备品牌、型号等,但卖方提供的设备性能应超过或相当于下表所列设备性能,满足本项目需求。
1.1 本期工程主设备配置表2 总体要求2.1 硬件设备要求(1)卖方提供的所有设备必须是最新且成熟的产品,并保证所提供产品的数量、质量,特别是接口的兼容性。
卖方应对所采用的硬件系统进行详细的功能及性能说明。
(2)设备主要模块(包括电源、风扇、控制引擎、旁路模块等)配置冗余度为1+1,易于扩容和维护。
(3)系统应采用模块化的硬件结构,便于扩充,并能容纳新业务和新数据。
(4)主要设备能在不中断通信的情况下,可带电进行印刷电路板的插拔操作。
(5)卖方提供的设备要选用世界上高质量的元器件,生产过程中进行严格质量控制,出厂前要经买方人员严格测试和检查,确保设备长期稳定、可靠地运行。
(6)卖方应提供设备的具体电磁兼容指标、测试方法和测试数据。
(7)卖方提供的设备应支持不同业务处理板的混插,提高插槽的通用性和灵活性。
(8)设备应具有网络故障和硬件故障告警功能。
(9)当软件升级时,应不影响硬件结构。
(10)对主控模块的要求:主控模块应具有软硬件故障告警功能。
主控模块应有冗余度,保证其安全可靠。
主控模块应具备自动诊断功能以及负荷控制措施。
主控模块应具备故障自动切换功能,在切换过程中不影响用户业务的连续性。
(11)设备应提供过流、过压、过热保护措施。
(12)设备应具有良好的散热性能,并要求卖方对设备的散热方式及原理进行分析。
(13)环境及设备技术参数要求卖方应详细提供设备对温湿度等环境的技术要求指标,并满足工作温度:0~40℃;工作湿度:5%~95%(非凝结)。
启明星辰天清汉马集中管理中心用户使用手册北京启明星辰信息安全技术有限公司2014年9月目录第一章前言 (4)1.1导言 (4)1.2适用对象 (5)1.3适合产品 (5)第二章如何开始 (6)1.4概述 (6)1.4.1产品特点 (6)1.4.2软件描述 (6)1.4.3主要功能 (7)1.4.4License控制 (7)1.5进入系统 (8)1.5.1登录 (8)1.5.2界面主框架 (8)第三章系统主页 (9)1.6概述 (9)1.6.1安全等级 (9)1.6.224小时安全趋势 (10)1.6.3系统状态 (10)1.6.4设备探测 (10)1.7安全概览图 (11)1.8安全设备分析 (11)1.9实时告警 (13)1.10攻击拓扑 (14)第四章资产管理 (14)1.11设备管理 (14)1.11.1网络拓扑管理 (15)1.11.2设备信息读取 (17)1.11.3设备基本信息查看 (18)1.11.4设备管理配置 (19)1.11.5节点管理 (19)1.11.6级联管理 (21)1.12策略管理 (21)1.12.1策略管理工具栏 (23)1.13VPN管理 (23)1.13.1IKE策略 (23)1.13.2IPSec策略 (24)1.13.3策略模板 (24)1.13.4VPN策略向导 (24)1.13.5VPN隧道监控 (24)1.14.1单个设备监控 (25)1.14.2设备集中监控 (26)1.14.3监控任务管理 (26)1.15升级管理 (27)1.15.1设备升级包管理 (27)1.15.2设备升级管理 (27)第五章事件管理 (28)1.16实时监控 (28)1.17安全日志查询 (29)1.18设备日志查询 (31)1.19系统日志查询 (31)第六章报表管理 (32)1.20概述 (32)1.20.1功能简介 (32)1.20.2功能分类 (32)1.21功能介绍 (33)1.21.1功能首页 (33)1.21.2安全事件特征报表 (34)1.21.3设备报表 (41)1.21.4定时报表 (42)1.21.5自定义报表 (44)第七章安全态势 (44)1.22概述 (44)1.22.1功能简介 (44)第八章工单管理 (46)1.23概述 (46)1.23.1新增工单 (46)1.23.2查询工单 (47)1.23.3修改及删除工单 (48)第九章知识库管理 (48)第十章威胁响应 (49)1.24概述 (49)1.24.1短信告警 (50)1.24.2声音告警 (50)1.24.3邮件告警 (51)1.24.4响应记录查询 (51)1.25管理配置 (53)1.25.1服务器状态 (53)1.25.2设备发现列表 (53)1.25.4系统日志 (55)1.25.5系统参数配置 (56)1.25.6系统维护 (57)1.26日志维护 (58)1.26.1日志备份与删除 (58)1.26.2日志恢复 (59)1.27事件服务器管理 (61)第十二章权限配置 (61)1.28用户管理 (61)1.28.1添加用户 (62)1.28.2修改用户信息 (62)1.28.3修改密码 (63)1.28.4删除用户 (64)1.29角色管理 (64)1.29.1添加角色 (64)1.29.2修改角色 (65)1.29.3删除角色 (65)1.30在线用户列表 (65)第十三章帮助 (66)1.31帮助中心 (67)1.31.1帮助文档 (67)1.31.2FAQ (67)1.31.3联系支持中心 (67)1.31.4生成支持文件 (67)1.32配置实用工具 (68)1.32.1ping测试 (68)1.32.2snmp测试 (68)第一章前言1.1 导言《启明星辰天清汉马集中管理中心用户帮助手册》是启明星辰天清汉马集中管理中心(VenusManager)管理员的用户帮助文档。
网络安全管理中的异常流量检测与防御引言:现代社会中,网络已经成为世界各个领域中不可或缺的组成部分。
然而,随着互联网的蓬勃发展,网络安全问题也日益突出。
恶意攻击者利用各种方式进行网络攻击,其中一种常见的攻击手段就是通过异常流量攻击来破坏网络安全。
因此,异常流量检测与防御成为了网络安全管理中的重要环节。
一、异常流量的定义和分类异常流量指的是网络中与正常流量不一致的数据包或数据流,并且可能具有危害性的网络信息。
根据异常流量产生的原因和形式,可以将其分为分布式拒绝服务攻击(DDoS攻击)、入侵检测系统报警、带宽超载等类型。
1. DDoS攻击DDoS攻击(Distributed Denial of Service attack)是指通过利用多个计算机同时发送大量请求,使目标服务器或网络资源无法正常工作的攻击行为。
这种攻击方式主要通过控制大量的僵尸主机,将海量的数据流量集中发向目标服务器,从而导致网络拥堵,正常用户无法访问网站或服务。
2. 入侵检测系统报警一些入侵检测系统(Intrusion Detection Systems)通过监测网络中的流量和数据包,来检测是否存在安全漏洞和异常事件。
当系统检测到异常流量或疑似入侵行为时,会发出报警信息,以便管理员及时采取相应的防御措施。
3. 带宽超载带宽超载是指某个或某些网络流量较大的节点所引起的网络拥堵现象。
当某个节点的流量超过其带宽容量时,会导致该节点丢包严重或网络延迟较大,从而影响整个网络的正常运行。
二、异常流量检测的技术与方法为了保护网络安全,检测和防御异常流量是至关重要的。
以下是一些常用的异常流量检测技术与方法:1. 基于特征的检测基于特征的检测方法使用预定义的特征库和数据模型,通过比对流量数据与正常行为的差异来识别异常流量。
这种方法通过监控网络流量中的不正常模式或行为进行异常检测,并及时采取措施来保护网络。
2. 流量分析与建模流量分析与建模是一种通过统计分析、流量模型和算法来分析网络流量数据的方法。
数字化时代的来临使得网络安全问题日益突出,其中异常流量检测与防御成为了网络安全管理中的重要环节。
异常流量指的是网络中与正常使用模式不相符的数据流量,这些异常流量往往是攻击者入侵、病毒传播或者其他恶意活动的表现。
如何有效地检测异常流量并及时采取相应防御措施成为了保障网络安全的关键。
一、异常流量的检测方法目前,常用的异常流量检测方法主要有基于规则的方法和基于机器学习的方法。
基于规则的方法是根据网络行为的特征制定出一系列规则,通过检查网络数据流是否符合规则来识别异常流量。
这种方法适用于一些已知攻击模式的检测,但对于新型攻击往往无法准确地识别异常流量。
基于机器学习的方法通过分析大量的网络数据,构建模型来识别异常流量。
这种方法不依赖于预先定义的规则,可以自动学习和适应网络环境的变化,具有较高的检测准确性和适应性。
目前比较常用的机器学习算法包括支持向量机(SVM)、神经网络(NN)和随机森林(RF)等。
二、异常流量的防御策略一旦异常流量被检测到,及时采取防御措施至关重要。
以下是几种常见的异常流量防御策略:1.入侵检测系统(IDS):IDS可以根据网络流量中的异常行为识别出潜在的攻击,并通过警报或日志记录等方式通知管理员。
IDS可以分为主机型IDS和网络型IDS,前者通过监控主机上的活动来检测异常流量,后者通过监控网络上的数据流来检测异常。
2.入侵防御系统(IPS):IPS是在IDS基础上进一步加强的防御系统,不仅可以检测异常流量,还可以及时采取防御措施,如封锁攻击源IP、阻断攻击流量等。
3.反射放大攻击防御:反射放大攻击是一种常见的DDoS(分布式拒绝服务)攻击方式,攻击者通过伪造目标IP地址向一个支持放大的服务发送请求,使得服务响应的数据包中包含更多数据,进而导致目标地址被淹没。
防御反射放大攻击可以通过对网络流量进行过滤和限制来减轻攻击影响。
4.网络流量清洗:网络流量清洗是指将网络流量经过清洗系统进行过滤,过滤掉异常流量,只保留正常的用户请求流量。
网络安全管理中的异常流量检测与防御引言:如今,互联网已成为人们生活中不可或缺的一部分。
然而,与此同时,网络安全问题也逐渐凸显出来。
在网络安全管理中,异常流量检测与防御技术扮演着关键角色。
本文旨在探讨这一技术在网络安全中的重要性和应对方法。
I. 异常流量的概念和分类异常流量指的是与正常网络流量不符的数据传输行为。
其特征包括传输速度异常、数据量异常、协议异常等。
根据异常流量的来源和性质,可以将其分为外部异常流量和内部异常流量。
外部异常流量主要来自于网络中的恶意攻击,如DDoS攻击、恶意软件传播等。
而内部异常流量主要与网络设备的故障、恶意员工操作等有关。
II. 异常流量检测技术为了及时发现和阻止异常流量,网络管理员采用了多种检测技术。
其中,流量分析技术是最常用的一种。
它通过对网络数据包进行分析,识别出异常流量的特征。
另外,信号处理技术也被广泛应用于异常流量检测。
它通过对网络信号进行采集和处理,识别出信号中的异常行为。
此外,机器学习技术也被引入异常流量检测中。
基于大数据分析和模式识别的机器学习算法,可以快速识别和分类各类异常流量。
III. 异常流量防御方法对恶意攻击和异常流量进行防御是网络安全管理的关键任务之一。
首先,网络管理员可以通过强化网络设备的安全设置,提高网络的基础安全防护能力。
其次,建立完善的流量监测和分析系统,实时监控和分析网络流量,及时发现和应对异常行为。
此外,网络管理员还可以部署入侵检测和防火墙系统,对网络流量进行实时过滤和阻断,以防止恶意攻击和异常流量的传播。
IV. 异常流量检测与防御的挑战尽管异常流量检测与防御技术的发展日新月异,但仍然面临着一些挑战。
首先,网络流量量大,传输速度快,这给异常流量的检测和防御带来了困难。
其次,网络攻击手段不断更新,攻击者采取了更加隐蔽和复杂的方式进行攻击,使得异常流量的识别和防御变得更加困难。
再者,个人信息泄露和网络攻击行为频繁发生,这给网络安全带来了更大的挑战。
启明星辰网站安全监测系统维护手册目录1.网站安全监测系统默认用户名密码及接口地址 (3)1.1.网站安全监测系统web界面 (3)1.2.系统默认接口地址 (3)1.3.密码重置 (3)2.虚拟机版安装常见问题 (3)2.1.启动虚拟机报错规范一致性或虚拟机硬件合规检查 (3)2.2.启动虚拟机时inter VT为启用报错 (4)2.3.无法启动报错vmsvc (4)3.无法登陆界面 (6)3.1.检查虚拟机和物理机是否可以ping通。
(6)3.2.检查虚拟机的ip是否生效 (7)3.3.检查虚拟机接口是否RUNNING (7)3.4.关掉物理机防火墙 (8)4.授权问题 (8)4.1.授权申请 (8)4.2.授权格式 (8)5.抓包方法 (8)6.网站安全监测系统的登录扫描 (9)6.1.添加cookies、设置User_Agent扫描站点 (9)6.2.BASIC、NTLM认证 (9)7.无法登录到web系统中 (10)1.网站安全监测系统默认用户名密码及接口地址1.1.网站安全监测系统web界面启明版本:root/Venustech60admin/Venustech60网御版本:root/Leadsec60admin/Leadsec601.2.系统默认接口地址接口IP为10.0.0.1/241.3.密码重置系统admin忘记密码之后,可以使用root账号登陆进行密码修改。
如果忘记root账号和密码,请联系产品线专家进行密码修改。
2.虚拟机版安装常见问题2.1.启动虚拟机报错规范一致性或虚拟机硬件合规检查此报错的原因一般为下载的解压出来的文件不完整,务必下载两个压缩包并放在同一级目录解压。
解决办法1、选择重试,如果还是不行,重新解压导入。
2.2.启动虚拟机时inter VT为启用报错原因是如果主机是32位操作系统,使用vmware导入64位网站安全监测系统虚拟机,且主机BIOS中默认inter VT 是disable的状态,这样就会造成虚拟机开机报错。