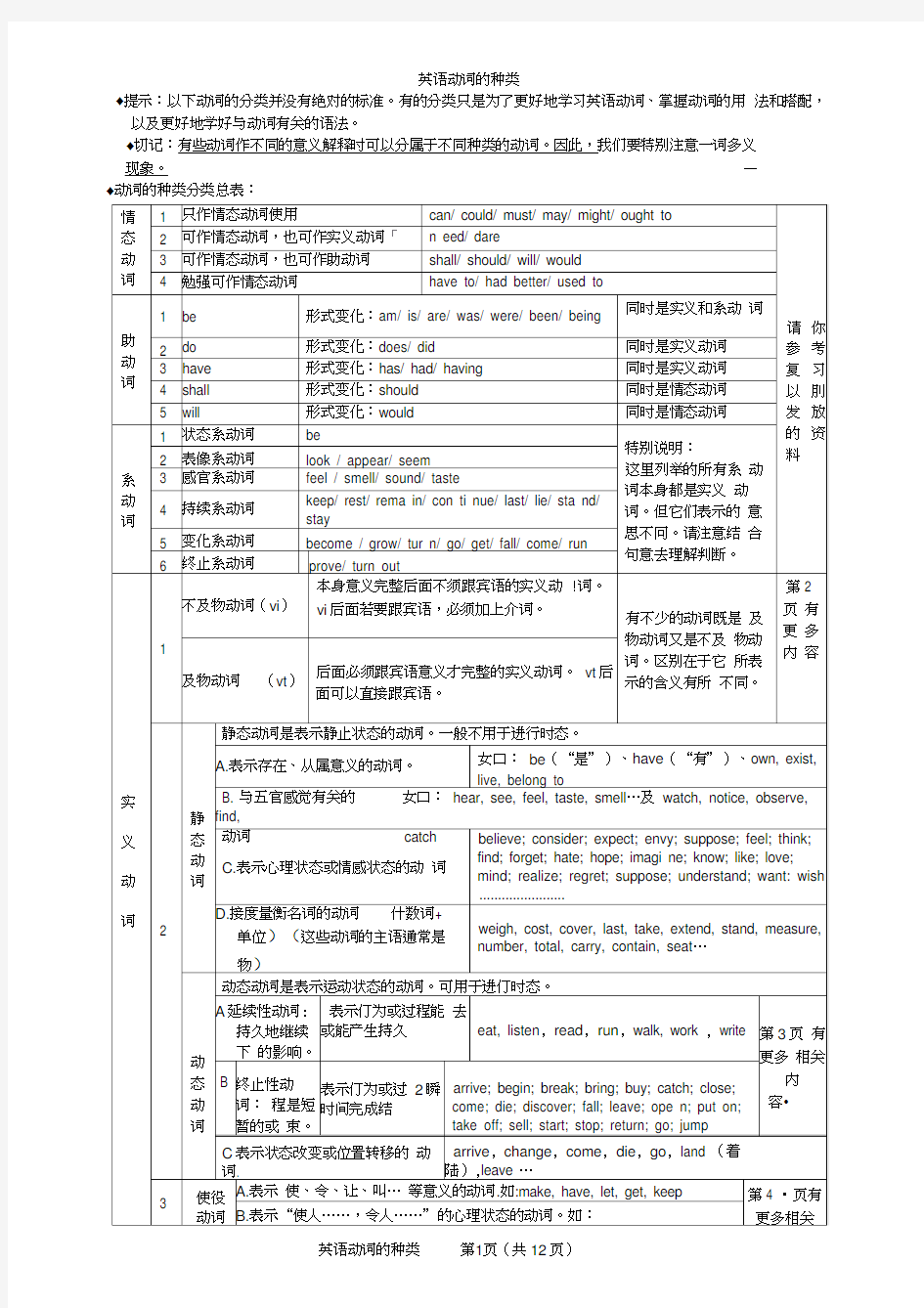

英语动词的种类
?提示:以下动词的分类并没有绝对的标准。有的分类只是为了更好地学习英语动词、掌握动词的用法和搭配,以及更好地学好与动词有关的语法。
?切记:有些动词作不同的意义解释时可以分属于不同种类的动词。因此,我们要特别注意一词多义
现象。—
?动词的种类分类总表:
3.终止性动词的完成时态,表示动作的完成并
产生了影响与结果。但一般不能与表示延续的时间段短语“for…”或
“since…”以及“ How long…"连用,终止性动词否定式除外。He has joined the League.他已经入团。T He has bee n a League member for three years. T He has bee n in the League for three years.
The old man died 4 years ago.
T The old man has bee n dead for 4 years. T It is 4 years since the old man died.
T Four years has passed since the old man died.
I bought the book 5 days ago. T I have had the book for 5 days.
4?注意句型(1):
“It is +—段时间+ si nee从句什终止性动词的过去时)”
“一段时间+ has passed+ si nee 从句(+ 终止性动词的过去时)”:
句子的含义是:“自从…起,有……侈长的时间)”。
如果在since从句中的谓语动词是延续性动词的现在完成时,那么与其一般过去时的含义就完全相反了。注意比较理解
I have bee n at school since I have bee n ill. 我生病以来一直在学校里。
I have bee n at school since I was
ill. 我病愈以来一直在学校里。
It' s 4 years since Mr Li smoked. 李
先生吸烟已有四年了
5.注意句型(2):
“not +终止性动词+ until/till ... ”意为“直到……才……”。
“延续性动词+ until /till…”
表示:“…一直延续到….”It is four mon ths since my elder sister went to Britain.我姐姐去英国已有四个月了。
More than three years has passed since Mary came to Chi na. 玛丽来中国已有三年多了
I will not go to bed until I finish drawing the picture tonight.今天晚上直到我画完画,我才上床睡觉。
I won 'leave till my parents come back. 我将呆在家里直到我父母回来。言外之意是,我父母不回来,我就一直呆在家里,我父母回来后我就离开家。
I didn 'receive the notice until last evening. 直到昨天晚上我才收到通知。言外之意是,昨天晚上前我一直没有接到通知。
We worked until 11:00 yesterday evening.我们昨天晚上一直工作到11点。
1 ?实义动词
实义动词是指具有完整意义,可以单独作谓语的动词,主要表示主语的动作、状态和品质。实义动词也可与助动词相结合表示更加复杂的动词意义。实义动词主要包括及物动词和不及物动词两类。
(1)不及物动词
不及物动词指的是后面不能跟宾语的动词。在英语中大多数动词既可作及物动词,又可作不及物
动词。纯不及物动词很少。常见的不及物动词有:
apologize 道歉
come 来appear 出现
go 去arrive 至U 达
waIk 走 die 死
faII 掉
fIow 流淌
happen 发生 rise 升起、站起 stay 呆、留 sit 坐 Iie 躺
sta nd 站 cry 哭
swim
游泳 e.g. Let's go.我们走吧!
(2 )及物动词
能跟宾语的动词称为及物动词。可分为跟单宾语的及物动词、跟双宾语的及物动词、跟复合结构 的及物动词等。 ①常见的只跟单宾语的及物动词
accept 接受 borrow 借 bury 埋
cover 覆盖 defeat 挫败 discover 发现 enjoy 喜欢 excite 使激动 in terest 使感兴趣 pIease 使咼兴 put 放
worry 担心 surprise 使凉讶
forget 忘记
guess 猜测
love 热爱 use 运用
e.g.Don ' t forget to wake me up at six tomorrow morning. 别忘了明天早晨六点叫醒我。
You can borrow one book at a time from the library. 在图书馆一次只能借一本书。 ②常见的跟双宾语的及物动词
A ?指人的间接宾语在指物的直接宾语后面需加 to 的动词: bring 带来 give 给 hand 递 pass 递
pay 付款 post 寄 promise 答应 read 读 return 返还 seII 卖 show 表现 teach 教
teII 告诉
wish 祝愿
offer
提供 e.g.I returned him the storybook.(可变为 I returned the storybook to him.) 我已把故事书还给他了。 B ?指人的间接宾语在指物的直接宾语后需加 for 的动词:
buy 买 choose 选择 draw 画 find 发现 keep 保持 make 使 order 点菜
pai nt 油漆
save 救护 e.g.I ' II find you another chance.(可变为 I ' II find another chanee for you.) 我会再给你找机会的。 C ?指人的间接宾语在指物的直接宾语后既可加 to 也可加for 的动词: do 做
play 表演
read 读
get 得到 si ng 唱歌 bring 带来
e.g.I ' II get you some tea.(可变为 I ' II get some tea to/for you.) 我给你取些茶。 ③常见的跟宾语补足语的及物动词
A . beIieve 相信 find 发现 keep 使保持 make 使 set 使 cut 切 decIare 宣布 可跟形容词或形容词短语作宾补的动词有 drive 驱赶;使 get 使 Ieave 留下 push 推 con sider 认为
dye 染
imagi ne 想象 judge 判断 pai nt 漆 e.g.We aII beIieve him hon est and kind. 我们都相信他诚实、善良。
注意:这类动词只跟一个宾语意义上不完整,宾语后必须再加上一个成分 完整。
(宾语补足语),其意义方可
B ?可跟名词短语作宾补的动词有: caII 叫 name 命名
make 使变为
英语动词的种类
第6页(共12页)
我无法使所有听众都能听见我。
H .可跟as/for 等引起的介词短语作宾补的动词有: regard 看做 con sider 认为 choose 选为
use 当作.... 用
keep 把 ..... 当作
e.g. You can keep this book as your own. 你可以留着这本书自己用。 She is con sidered as the best dancer.她被认为是最好的舞蹈演员。 I .可跟副词作宾补的动词有: ask 叫、让
get 使
find 发现
wish 祝愿 con sider 认为 keep 使 choose 选择
e.g.We con sider him a stra nge pers on. 我们认为他是一个奇怪的人。
C .可跟带to 不定式结构作宾补的动词有: advise 建议
allow 允许 expect 期望
in vite 邀请
order 命令 tell 告诉 wish 希望 warn 警告
e.g.Mother often tells me to make friends carefully. 妈妈经常告诫我交朋友要小心。
D .可跟"to be+名词或形容词作宾补”的动词有:
believe 认为
feel 感觉 imagine 想象 suppose
猜测 prove 证明 consider 认为
find 发现 know 知道 un dersta nd 理解 declare 宣布
e.g .I believe what you said to be true. 我相信你所说的是真的。
注意:这些结构中的 to be 也可省略。 E. 可跟不带to 的不定式作宾补的动词有:
have 使 let 让 no tice 注意 watch 注意看 liste n to 听
discover 发现
make 使 see 看见 feel 感觉 look at 看 observe 观察
find 找到 elect ask 要求 get 使 teach 教
注意:我们通常给学生讲的原则是记住这些词后加动词原形。 e.g. What made you think of that? 什么使你想起那件事的?
Paul doesn ' t have to be made to learn. 保罗不必被逼着学习。 F. 可用-ing 形式作宾补的动词有:
选举
see 看见 hear 听见 keep 使
catch 抓住 find 发现 have 让 watch 注意看
smell 闻到 look at 看 liste n to 听 observe 观察 discover 发现
get 使 have 使
e.g. Can you hear some one play ing the pia no next door? 你能听见隔壁有人弹钢琴吗 ?(v.-ing 形式作宾
补)
The boy was last seen playing by the riverside.(v.-ing 人们最后一次看见这小男孩时他在河边玩耍。
G .可跟-ed 形式作宾补的动词有: have
使 get find 发现 feel hear 听见 thi nk
e.g. I could n
形式作主补 使 感觉
认为 't make myself heard by all the listeners. make 使 see 看见 watch 注意看
let 让drive 开车送show 领see 看见invite 邀请order 命令
e.g. Can I ask Bob in?我可以让鲍勃进来吗?
Show the visitor in, please.请把客人带进来。
J可跟介词短语作宾补的动词有:
have 使find 发现hear 听见get 使make 使feel 感觉see 看见notice 注意到keep 保持
e.g. Don' t have children at home all day. Give them time to play outdoors. 不要让孩子老呆在家里,给他们出外玩耍的时间。
Keep all these books on the shelf and take them whe n n ecessary. 把所有的书放在书架上,用时随时拿。
3 助动词协助主要动词构成谓语动词的词叫做助动词,其自身没有词义,不可单独使用。它与其他词一
注意 现在,尤其是在口语中,will 常用于第二、三人称,但shall 只用于第一人称,如 用于第二、三人称,就失去了助动词含义,已变成情态动词。
He shall come.
他必须来。(shall 有命令的意味) 4.情态动词
情态动词基本用法一览表
构成聽何旬
TOEFL?探揑通述托植考
试吗?
do
'"do —n?i"构电否
定旬
Ln the many students
diiin't know thr- impnnancr of
吕gh*h.过去.许藩学生 下丹道吏厝的車畫性“
don't 构成否定祈
憧可
Don't be $0
通m-tn 】打山町
-
别辻么心来生馬
shall
will
作为朋渤词与动 词原形一起构战 一股將来时
should 为 shall 的
过去式.后聂动词 原形构成谊去将 来时.
貝用于第一
I telephoned him yesterday
to
whftt I should do n^xt
Wuek.我昨天给他打电运问
should
人 : would 为
英下周要干什么
would
will 的过去式,后 He said he would cOme to
接动词匣形掏成 my birthday p*rty,他说他要
过去熾来时.用于 来养加我的生日聚会。
第二、三人称
Vo you want to pass the
I shall study harder at Eng I 怡
扎我特更加努力学习英 He will go to Hainan during the Spring Festival.春节期 间他要
占禅南■>
t
“情态动词不定式进行式”和“情态动词不定式完成式”用法一览表
动词概述 一、实义动词 ■①及物动词与不及物动词 根据后面是否带宾语,行为动词又可分为及物动词和不及物动词,及物动词。Vt. vi . They study hard. I know them well. 注:有的动词既可作及物动词,也可用作不及物动词。如: She sings very well. She sang an English song just now. 英语里有不少实义动词可以兼作及物动词和不及物动词。兼作及物动词和不及物动词时,____不变。试比较: Shall I begin at once? She began working as a librarian after she left school. When did they leave Chicago?They left last week. 短语: ■②动态动词和静态动词 动态动词表示动作,如give, take, work, run等;静态动词表示感觉、情感、内心世界、相互关系等,如know, exist, be, have, appear, prove, concern, hate, dislike, like, love, surprise, include, depend on, belong to, guess, suppose,imagine, believe, doubt, admire, envy等。 ■③延续性动词和非延续性动词 根据动作是否延续,行为动词又分为延续性动词和非延续性动词。如rain, live, work, learn等是延续性动词,go, come, leave, start, arrive, join, finish, end等是非延续性动词。 注:非延续性动词在肯定句中通常不与表示时间段连用的for短语连用。如:[译]他离开这里三天了。 [误]He has left here for three days. [正]He has been away from here for three days. [正]He left here three days ago. [正]It’s three days since he left. ■④限定动词与非限定动词
时态是英语谓语动词的一种形式,表示动作发生的时间和所处的状态.英语中的时态是通 过动词形式本身的变化来实现的.英语有16种时态,但中学阶段较常用的有十种:一般现在时,一般过去时,一般将来时,过去将来时,现在进行时,过去进行时,将来进行时,过去完成时,英在完成时和现在完成进行时. 1.一般现在时的用法 1) 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频腮度的时间状语连用。时间状语: every..., sometimes, at..., on Sunday。例如: I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。 2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。例如: The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。 Shanghai lies in the east of China. 上海位于中国东部。 3) 表示格言或警句。例如: Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。 注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。 例:Columbus proved that the earth is round. 哥伦布证实了地球是圆的。 4) 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。例如: I don't want so much. 我不要那么多。 Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 安英语写得不错,讲的可不行。 比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup. 把糖放入杯子。 I am doing my homework now. 我正在做功课。 第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。
表格式一般现在时态和语态 2. Jenny (has) a good friend? 3. Brian (not live) in China. 4. Li Ming with me (be) in Beijing. 5. If it (not rain)tomorrow, we will go to the park. 6. Our teacher said that the earth (go)around the sun yesterday. 7.He (help)the old man every week . 8.The old man (help)by him every week. 9.The building (visit) by many people every year.
一一般现在时 (一)定义:主要用来表示人、事物的现在状况和特点;表示经常或习惯性的动作, 句子中常有often, always, from time to time 等时间状语;表示客观规律和永恒真理等 He usually goes to work at 7 o’clock every morning. The earth goes around the sun. Guangzhou is situated in the south of China. (二)标志词: always, usually, often, sometimes, hardly ever,every week (day, year, month…), once /twice a week, on Sundays, (三)谓语动词构成: 1 be动词的一般现在时:am is are("是",“在”) 2 当谓语动词是行为动词的时候: (1)当主语不是第三人称单数的时候,一般现在时用行为动词的原形 (2)主语是he,she,it等第三人称单数(除去I,you以外的任何一个单数的名词或者代词),动词要变形加s或es. (温馨提示:动词变形要符合两个条件:1,主语是三单,2,句子是肯定句) (四).基本结构: 1,肯定句:主语+谓语(+其他的) He loves sports. Jane is an outgoing girl. (主语He是三单,又是肯定句,所以谓语动词发生变形,加上了s) Tom and Tim both have medium height. He has a big mouth. We like the dog very much. 2,否定句:主语+don’t或者doesn’t+动词原形+其他(在be或者后面加上do does) Candy doesn’t do her housework every day. We don’t dance . He isn’t a worker. 3,一般疑问句:Do (Does)+主语+动词原形+其他?(把be或者do does 提到主语的前面)Does she like English? Yes,she does. No,she doesn’t. Do you swim in summer? Are you a teacher? 4,特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句Where does Tom come from? (五) 一般现在时态用法 (1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与这样的时间状语连用: eg: We always help each other. It often snows in winter. I get up early every morning. (2)表示主语现在的特征、性格、能力等。 eg: He loves sports. Jane is an outgoing girl. Tom and Tim both have medium height. (3)表示客观、普遍真理 eg: Two and four makes six. Water boils at 100℃The moon moves round the earth。The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. (4)表示格言或警句中。Pride goes before a fall.骄者必败。 (六)一般现在时态的考点:
一.动词概述 注:英语行为动词也可以分为及物动词和不及物动词。及物动词是必须带宾语的动词。可以分为两类:(1)及物动词+宾语(2)及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语 My mother bought me a gift. (可以接双宾语的词有:give, teach, buy, l end, find, hand, l eave, sell, show, read, pay, make, offer, buil d, pass, bring, cook等 不及物动词不需要跟宾语,本身意义完整。有些不及物动词加上介词后变成及物性短语动词,后跟宾语。She did not reply to my l etter。 英语中接双宾语的动词 award sb. sth. = award sth. to sb. 颁奖给某人 bring sb. sth. = bring sth. to sb. 把某物带给某人 hand sb. sth. =hand sth. to sb. 把某物递给某人 lend sb. sth. = lend sth. to sb. 把某物借给某人 mail sb. sth. = mail sth. to sb. 把某物寄给某人 offer sb. sth. = offer sth. to sb. 将某物给某人 owe sb. sth. = owe sth. to sb. 欠某人某物 pass sb. sth. = pass sth. to sb. 把某物递给某人 pay sb. sth. = pay sth. to sb. 付给某人某物(钱) post sb. sth. = post sth. to sb. 把某物寄给某人 read sb. sth. = read sth. to sb. 把某物读给某人听 return sb.sth. = return sth. to sb. 把某物还给某人 send sb. sth. = send sth. to sb. 把某物送给某人 sell sb. sth. = sell sth. to sb. 把某物卖给某人 serve sb. sth. = serve sth. to sb. 拿某物招待某人 show sb. sth. = show sth. to sb. 拿某物给某人看 take sb. sth. = take sth. to sb. 把某物拿给某人 teach sb. sth. = teach sth. to sb. 教某人某物 tell sb. sth. = tell sth. to sb. 告诉某人某情况 throw sb. sth. = throw sth. to sb. 把某物扔给某人 write sb. sth. = write sth. to sb. 给某人写信 2、双宾语易位时需借助介词for的常用动词 book sb. sth. = book sth. for sb. 为某人预定某物 buy sb. sth. = buy sth. for sb. 为某人买某物 choose sb. sth. = choose sth. for sb. 为某人选某物 cook sb. sth. = cook sth. for sb. 为某人煮某物
动词学案 Class:Name: ◆Teaching Aims: ★To learn the classifications of the verbs. ★To master their usage through cooperation and exploration. ◆Teaching Procedures: 一、动词的分类 1. 实义动词 实义动词时能独立作谓语的动词。根据动词在句子中是否可以接宾语,可以把实义动词分为 __________动词和_________动词两种类型。按其持续性可分为_____________动词和___________动词。(1)及物动词 及物动词本身意义不完整,需要接宾语才能使其意思完整。 ①动词+宾语 My brother is ________ ______ ________(fly)on the playground. ②动词+宾语+宾补 The teacher made his students___________(happiness) by doing some games. 翻译:We call English teacher Zhang Sir. ____________________________________________________ 注意:带省略to的不定式或现在分词作宾补的动词有:make, let, see, watch, notice, hear等。 ③动词+双宾语 My mother gives me a new bike. 注意:有些间接宾语(人)放在直接宾语(事物)之后时,间接宾语前要加to。常用的此类词有bring、give、hand、pass、pay、post、return、sell、show、teach、tell、throw、lend等。 Hand me that book, please. = Hand____________________________________. 有些间接宾语(人)放在直接宾语(事物)之后时,间接宾语前要加for。常用的此类词有buy、choose、cook、draw、book、find、get、make、order等。 My mom bought me a nice backpack. = My mom________________________________________. (2)不及物动词 不及物动词一般不可以接宾语,但是有些不及物动词与一些介词、副词等词搭配在一起构成短语动词,它的作用等于一个及物动词。请在横线上加上适当的介词! ①We arrived______ the station at five. ②He turned _______ the light when he left. ③He takes pride_______ doing a job well. 注意:有些动词既可作及物动词也可作不及物动词。常用的此类动词有turn、open、close、start、change、drive、play、meet、win、study等。 The girl turned her head and smiled. 这个女孩子转过头笑一笑。
高中英语时态语态讲解 1、一般现在时主要用来表示人、事物的现在状况和特点;表示经常或习惯性的动作;表示客观规律和永恒真理;按照计划安排好了将要发生的动作(一般指时 刻表)等 He usually goes to w ork at 7 o’clock every morning. The train to Shanghai leaves at 7am. 考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。如:I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 考点二:在时间、方式、让步和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, once, the moment/the minute, the day; 条件:if, unless, provided. If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon. 只要他努力工作,我不介意他什么时候做完试验。 2、现在进行时 表说话时或目前一段时间内正在进行的活动;或表感情色彩,加强语气。与频率副词,如always,constantly,continually,again等连用表示说话人的某种感情色彩(赞叹、厌烦、埋怨等)。 We are having English class. The house is being built these days. The little boy is always making trouble. 考点一:在时间状语或条件状语从句中表示将来正在进行的动作。Look out when you are crossing the street. Don't wake him up if he is still sleeping at 7 tomorrow morning. 考点二:表示在最近按计划或安排要进行的动作(这时多有表示将来的时间状语)。 Marry is leaving on Friday. 3、现在完成时 (1)非延续动作:动作发生在过去,对现在有影响。(2)延续性动作:动作和状态的持续。现在完成时有一些标志性的时间状语: 考点一:for + 时间段;since + 时间点 They have lived in Beijing for five years. They have lived in Beijing since 1995. 考点二:常见的不确定的时间状语:lately; recently, just, already, yet, up to now; till now; so far, these days, Has it stopped raining yet ? 考点三:在表示“最近几世纪/ 年/ 月以来……”时间状语中,谓语动词用现在完成时。 in the past;over the past; during the last等 考点四:表示“第几次做某事,”或在“It is the best (worst, most interesting ) +名词+that” 后面,主句是一般现在时态时,从句用现在完成时。 This is my first time that I have visited China. This is the most interesting film I have ever seen. 4.一般过去时 表在过去某个特定时间发生且完成的动作,或过去习惯性动作,不强调对现在的影响,只说明过去。常跟明确的过去时间连用, 注意: 考点一:used to + do,表示过去经常但现在已不再维持的习惯动作。 be/become/get used to + doing,表示习惯于 He used to smoke a lot. He has got used to getting up early. 考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替过去将来时。 He promised to buy me a computer if he got a raise 5. 过去进行时
英语动词分类大全(附练习) 十大词类2010-11-01 08:23:01 阅读1174 评论6 字号:大中小订阅 一、什么是动词 动词是用来表示主语做什么(即行为动词),或表示主语是什么或怎么 样(即状态动词)的词,例如: The boy runs fast.(这个男孩跑得快。)runs表示主语的行为 He is a boy.(他是个男孩。)is与后面的表语a boy表示主语的状态 二、动词的分类 动词可以按照含义及它们在句中的作用分成四类,即行为动词(也称实义动词)、连系动词、助动词和情态动词。 (一)行为动词 行为动词(实义动词)是表示行为、动作或状态的词。它的词义完整, 可以单独作谓语。例如: I live in Beijing with my mother.(我和我妈妈住在北京。)live,住 It has a round face.(它有一张圆脸。)has,有 (二)连系动词 连系动词是表示主语“是什么”或“怎么样”的词,它虽有词义,但不完整,所以不能单独作谓语,必须跟表语一起构成合成谓语,例如: We are in Grade Two this year.(今年我们在两年级。)are,是are 这个词的词义“是”在句子中常常不译出。 连系动词可具体分为三类:
1、表示“是”的动词be。这个词在不同的主语后面和不同的时态中有不同的形式,is,am,are,was,were,have/has been等要特别予以 注意。例如: He is a teacher.(他是个教师。) He was a soldier two years ago.(两年前他是个士兵。) We are Chinese.(我们是中国人。) 2、表示“感觉”的词,如look(看起来),feel(觉得,摸起来),smell (闻起来),sound(听起来),taste(尝起来)等,例如: She looked tired.(她看一去很疲劳。) I feel ill.(我觉得不舒服。) Cotton feels soft.(棉花摸起来很软。) The story sounds interesting.(这个故事听起来很有趣。)The flowers smell sweet.(这些花闻起来很香。) The mixture tasted horrible.(这药水太难喝了。) 3、表示“变”、“变成”的意思的词,如become, get, grow, turn, 都解释 为“变”、“变得”,例如: She became a college student.(她成了一名大学生。) He feels sick. His face turns white.(他感到不舒服,他的脸色变苍白 了。) The weather gets warmer and the days get longer when spring comes. (春天来了,天气变得暖和些了,白天也变得较长些了。) He grew old.(他老了。) [难点解释]
动词的时态和语态用法详解 在英语中,不同时间里发生的动作或存在的状态需要用动词的不同形式表示出来,动词的这种不同 形式就构成了动词的时态。 英语中的时态按动作发生时间分为现在时态、过去时态、将来时态 二、常见时态的基本用法 1. 一般现在时:一般现在时是描述现在或经常性的动作性质或状态的时态。常和表示频率、时间的副词 (短语) always, every time, now and the n, occasi on ally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually 连用。 1) 表示经常性或习惯性的动作。 We have three meals a day. 2) 表示客观事实、真理和自然现象。 Kno wledge is power. 3)表示现在的情况或状态。 I live in Beiji ng. 4)表示已经“列入日程”的将来的事件,尤其指计划中的和安排好的将来的动作,这些动词往往表示“出 发,到达”等含义 的词, 女口, arrive, begin, go, leave, start, stay 等。 The train arrives at 10:30. There's ple nty of time. 。 考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。 如: I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, on ce, the mome nt/the minu te, the day; 条件:if, uni ess, provided. If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon. 考点三:在 make sure (certain), see to it, mind, care, matter 替一般将来时。 So long as he works hard, I don ' t mind when he finish 考点四:在 the more …the more …(越 ..................... 越 ... )句型中 在时。 The harder you study, the better results you will get. 2. 一般过去时:一般过去时表示过去发生的动作、存在的状态,或反复发生的动作,句中一般都有表示 过去具体时间的时间 状语。 1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或状态。 此时与表示过去的时间状语连用, 如yesterday, last week, an hour ago, the other day, in 1998 等。 +宾语从句,从句用一般现在时代 es the experime nt. ,若主句是一般将来时,从句通常用一般现
一、选择题 1.Karen and Helen _______ my brother's friends. I know _______. A.is; her B.are; them C.are; her D.is; them 2.Kay looked _________ at the guests who said that the food she cooked tasted _________. A.happily; wonderfully B.happily; wonderful C.happy; wonderful D.happy; wonderfully 3.I don’t have a baseball, but Alan A.do B.does C.have D.has 4.—Listen! I can hear someone __________ for help. —Is there __________? A.calling; anything wrong B.call; anything wrong C.calling; wrong anything D.call; wrong anything 5.Our school basketball team ________ in the final of the basketball competition. Another team from No.5 Middle School ________ doing very well too. A.is; isn’t B.are; aren’t C.is; are D.are; is 6.—Why ______ you so busy these days? —Because they arrived ______ London ______ the morning of July1. A.are; in , in B.are; in , on C.do; on , in D.do; at , on 7.A number of visitors ________visiting our school. The number of them________ about 180. A.is;are B.are; is C.is; is D.are; are 8.—William, your hat _______ nice. —Thanks. A.buys B.looks C.finds 9.This is a photo of my grandpa. He young A.looks B.feels C.sounds D.hears 10.Lily and Lucy _______ their mother. They have big eyes and yellow hair. A.like both B.both are like C.both like D.are both like 11.—He’s never been late for school. —________________. A.So have I B.So am I C.Neither have I D.Nor am I 12.In the past he often made his sister____, but now he is often made ___by his sister. A.to cry; to cry B.cry; cry C.to cry; cry D.cry; to cry 13.This my sister and those my brothers. A.is, is B.are, are C.is, are 14.— Tom in the library? —Yes,and his friends Eric and Dale in the library,too. A.Is;are B.Is;is C.Are;is
高考英语热点动词十五类 动词是英语中最活跃的词类,是句子的核心成分。此外,英语动词的变化较多,形式颇为复杂,是英语学习的难点之一。历届高考英语试题常把动词作为测试的重点,在单项填空题中所占比例在50%以上。笔者通过对近十年来的高考英语试题进行分析,归纳常考动词十五类,供大家参考。 一、连系动词类 连系动词按其所表示的意义可分为以下四种: 1.变化类表事物发展变化的过程,如become, go, turn, grow, get, fall等。 2.感觉类表人体部位的感受,如feel, smell, taste, look, sound等。 3.状态类表事物所处的状态,如keep, come, run, remain, stand, lie, stay, prove等。 4.外表特征类表外表给人的印象,如appear, seem, look等。 连系动词的作用是后接形容词或相当于形容词的结构作表语。除了少数几个(如feel, get, become, grow等)外,不用于进行时态和被动结构。例如: The mixture is tasted terrible.(误) The mixture tastes terrible(正) Jim pretended to be falling asleep when his mother came in.(误) Jim pretended to fall /be asleep when his mother came in.(正) I'm feeling much better than ever before. It was getting darker and darker. Besides, a cold rain began to fall. 【高考例题】 (1) ---Do you like the material? ---Yes, it ____ very soft. (NMET94) A. is feeling B. felt C. feels D. is felt (2) Why don't you put the meat in the fridge? It will ____ fresh for several days. (NMET 03) A. be stayed B. stay C. be staying D. have stayed (3) The pilot asked all the passengers on board to remain ____ as the plane was making a landing. (04春季高考上海卷) A. seat B. seating C. seated D. to be seating (4) Be careful when you cross this very busy street. If not, you may ____ run over by a car. (02高考北京卷) A. have B. get C. become D. turn (5) Happy birthday, Alice. So you have ____ twenty-one already. (04天津卷)
1、一般现在时主要用来表示人、事物的现在状况和特点;表示经常或习惯性的动作,句子中常有often, always, from time to time 等时间状语;表示客观规律和永恒真理等。He usually goes to w ork at 7 o’clock every morning. The earth goes around the sun. Guangzhou is situated in the south of China. 考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。如:I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, once, the moment/the minute, the day; 条件:if, unless, provided. If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon. 考点三:在make sure (certain), see to it, mind, care, matter +宾语从句,从句用一般现在时代替一般将来时。 So long as he works hard, I don’t mind when he finishes the experiment. 只要他努力工作,我不介意他什么时候做完试验。 考点四:在the more… the more … (越……越……) 句型中, 若主句是一般将来时, 从句通常用一般现在时。 The harder you study, the better results you will get. 2、现在进行时 表说话时或目前一段时间内正在进行的活动:或表感情色彩,加强语气。与频率副词,如always,constantly,continually,again等连用表示说话人的某种感情色彩(赞叹、厌烦、埋怨等)。
英语动词分类大全(附练习) 一、什么是动词 动词是用来表示主语做什么(即行为动词),或表示主语是什么或怎么样(即状态动词)的词,例如: The boy runs fast.(这个男孩跑得快。)runs表示主语的行为He is a boy.(他是个男孩。)is与后面的表语a boy表示主语的状态 二、动词的分类 动词可以按照含义及它们在句中的作用分成四类,即行为动词(也称实义动词)、连系动词、助动词和情态动词。(一)行为动词 行为动词(实义动词)是表示行为、动作或状态的词。它的词义完整,可以单独作谓语。例如: I live in Beijing with my mother.(我和我妈妈住在北京。)live,住
It has a round face.(它有一张圆脸。)has,有 (二)连系动词 连系动词是表示主语“是什么”或“怎么样”的词,它虽有词义,但不完整,所以不能单独作谓语,必须跟表语一起构成合成谓语,例如: We are in Grade Two this year.(今年我们在两年级。)are,是 are 这个词的词义“是”在句子中常常不译出。 连系动词可具体分为三类: 1、表示“是”的动词be。这个词在不同的主语后面和不同的时态中有不同的形式,is,am,are,was,were,have/has been 等要特别予以注意。例如: He is a teacher.(他是个教师。) He was a soldier two years ago.(两年前他是个士兵。) We are Chinese.(我们是中国人。) 2、表示“感觉”的词,如look(看起来),feel(觉得,摸起来),smell(闻起来),sound(听起来),taste(尝起来)等,例如: She looked tired.(她看一去很疲劳。) I feel ill.(我觉得不舒服。) Cotton feels soft.(棉花摸起来很软。) The story sounds interesting.(这个故事听起来很有趣。)
动词 定义: 动词是表示动作或状态的词。例如:work,工作, study,学习,eat 吃。 动词的分类:动词有两种分类方法。 1)限定动词和非限定动词。 限定动词在句中作谓语,有人称和数的变化。非限定动词有动词不定式,动名词和分词三种。在句中不能单独作谓语,没有人称和数的变化。 2)实义动词,连系动词,情态动词和助动词。 实义动词有完整的词义,并能单独作谓语,实义动词又可分为及物动词和不及物动词。例如: study 学习, reach 到达, see 看见, rise 升起。 连系动词在句中作谓语动词,后面跟表语。连系动词有be, seem, look, become, get, grow, feel, appear, remain, turn。 情态动词表示能力,义务,必要,猜测等说话人的语气或情态。情态动词只能和动词原形一起构成谓语动词。情态动词有can, will, have, be, should, do, would, 等。 助动词只能和主要动词一起构成各种时态,语态和语气等动词形式。 do, shall, will, have, has. 动词的基本形式: 英语动词有四种基本形式:动词原形,过去式,过去分词和现在分词。这四种动词形式和助动词一起构成动词的时态,语态和语气。 动词的原形。就是词典中所给的形式。例如:be, have, buy, sit. 动词过去式和过去分词的构成有规则的和不规则的两种形式。规则动词的过去式和过去分词,由在原形动词的后面加词尾-ed 构成。 work - worked - worked 不规则动词的过去式和过去分词的形式是不规则的,须要一一记忆。 go - went - gone do - did - done 动词的现在分词由动词原形加-ing 构成。构成方法如下: 1)一般情况在动词原形后加-ing 。 go---going stand---standing 2)以不发音的 e 结尾的动词,去掉 e ,再加-ing. 动词是闭音节的单音节词,或是以重读闭音节结尾的多音节词,而末尾只有一辅音字母时,这个辅音字母须双写,然后再加ing。 arrive- arriving get- getting 3)少数几个以-ie 结尾的动词,须将ie 变成y ,再加ing.例如:die--dying lie--lying。动词的时态: 英语动词的时态是一种动词的形式。不同的动词时态用以表示不同的时间和方式。共有十六种时态。 一般现在时: 一般现在时表示经常发生的习惯性的动作或目前所处的状态。 We go to school every day. 我们每天去学校。 The students study very hard. 学生们学习很努力。 She has a dictionary. 她有一本词典。
人教版英语英语动词的时态的用法大全含答案解析百度文库 一、初中英语动词的时态 1.Hong Kong __________to China for 20 years. I ________there for 2 weeks next year. A.has returned; will stay B.has been back; will stay C.has been back; have stayed D.has returned; have stayed 【答案】B 【解析】 【详解】 句意:香港回归中国已有20年。明年我将在那里呆两周。考查动词时态辨析。for 20 years 是一段时间,需和持续性动词连用;return返回,终止性动词,可排除AD两项。next year 明年,用于一般将来时,可排除C项。根据句意结构和语境,可知选B。 2.--- I went to see you last night, but you weren’t in. Where were you then? ---I _______ a walk by the river. A.had B.was having C.have had D.have 【答案】B 【解析】 【详解】 句意:——昨晚我去看你了,但你不在。那时你在哪里?——我在河边散步。由上文中“Where were you then?”可知,问句是询问“昨天晚上当我去看望你的时候,你正在哪里?”此句表达的是过去正在发生的事情,要用过去进行时态。故答案为B。 3.–Don’t worry! I’m sure your son will arrive safely. -- But if he ______, what can I do? It’s getting dark and it’s going to rain. A.won’t come B.doesn’t come C.isn’t coming D.wouldn’t come 【答案】B 【解析】 【详解】 句意“-不要担心,我确信你的儿子将会安全到达。-但是如果他没到,我该如何做?现在天要黑了,而且要下雨了”。根据句意可知,此处的if译为“如果”,且主句表示将来,从句用一般现在时,且从句谓语为实意动词,故选B。 4.— Why did so many people get hurt in the earthquake? —Don’t you know? People when it happened that night. A.slept B.have slept C.sleep D.were sleeping 【答案】D 【解析】句意:-为什么这么多人在地震中受伤? -你不知道吗?当晚发生的时候,人们都在睡觉。 由句子when it happened that night.可知是过去时,因此主句用过去时。排除B/C。再根据