
课程教案
课程名称:口译与听力学院:外国语
系别:英语
授课人:徐熙
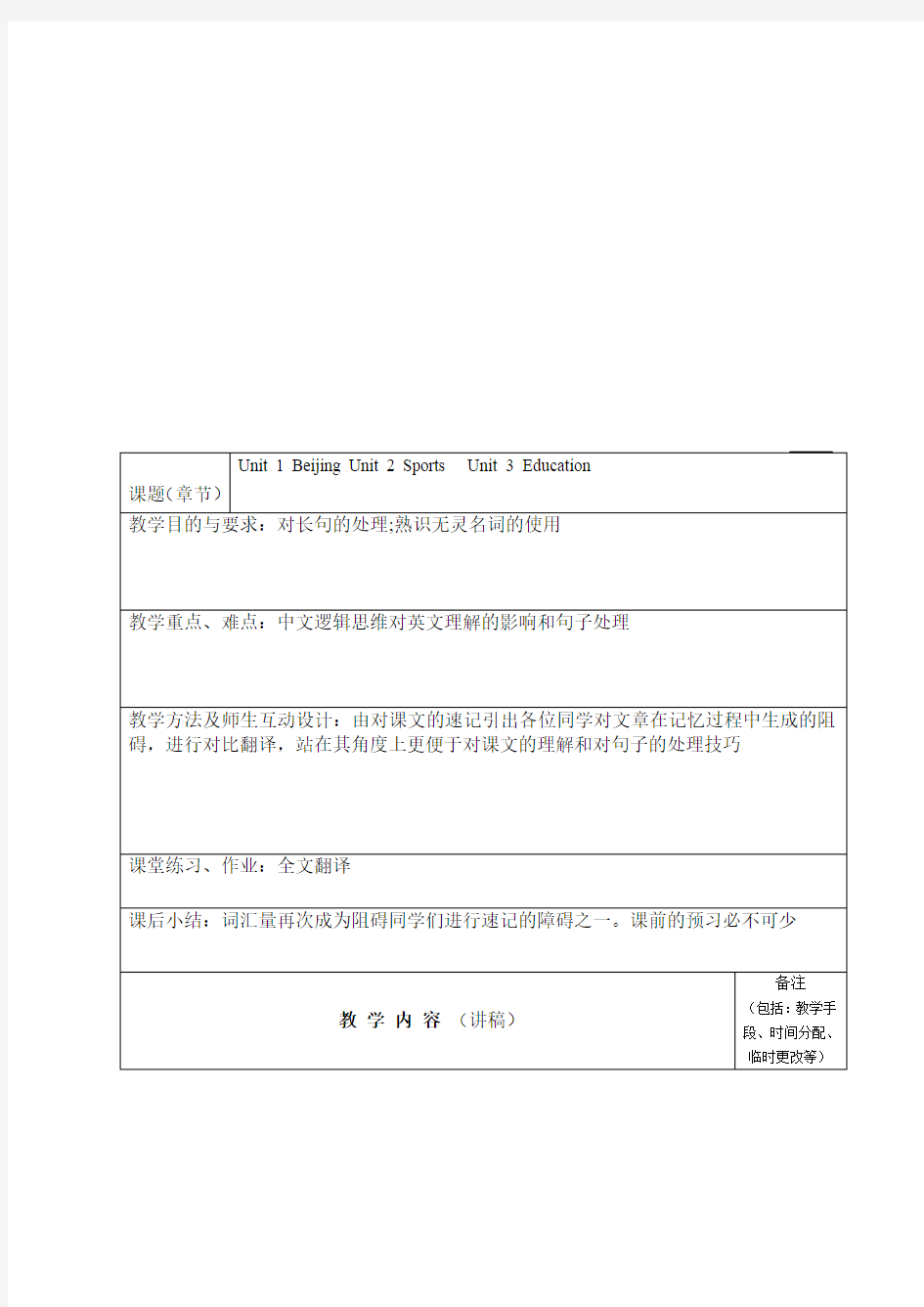
课题(章节)
Unit 1 Beijing Unit 2 Sports Unit 3 Education
教学目的与要求:对长句的处理;熟识无灵名词的使用
教学重点、难点:中文逻辑思维对英文理解的影响和句子处理
教学方法及师生互动设计:由对课文的速记引出各位同学对文章在记忆过程中生成的阻碍,进行对比翻译,站在其角度上更便于对课文的理解和对句子的处理技巧
课堂练习、作业:全文翻译
课后小结:词汇量再次成为阻碍同学们进行速记的障碍之一。课前的预习必不可少
教学内容(讲稿)
备注
(包括:教学手段、时间分配、临时更改等)
1.When the founding of the People's Republic of China was officially proclaimed on October 1st, 1949, Beijing became its capital. 中华人民共和国在1949 年10 月1 日正式宣布成立,从那时起,北京就是其首都。explanation: (
1)副词officially 通常包含两层词义,一是当“官方”来讲,二是“正式”的意思,副词在具体语言环境下的翻译,是和语言环境密切相关的,并且有时需要对句子的语序进行调整,有时需要对词性进行转换。(
2)由When 引导的状语从句,在译文中并没有遵循原句英语的语序,而是把其拆分成两相相对独立的语言单位,并把时间状语译成“从那时起” 。
2.There has been a settlement on its site for over 3,000 years. 这里(有人)定居(的历史)已逾3000 年。英语重客观,汉语重主观,所以,在对英语中的“there be”结构进行翻译时,一般通过增加词汇、词性转译和调整语序的方式,将其译成符合汉语表达习惯的句式(人做主语)。因而,上句也可译成:(人们)定居在这里的历史已有3000 多年了。
3.The late 1950s saw the construction of a number of important building.... 二十世纪五十年代末,许多重要建筑拔地而起…… 非生命名词做主语,是英语中非常常见的句式,对这类结构的翻译不可拘泥于英语的句式,不然,译文会违背汉语的表达原则,显得不伦不类。对这类结构的翻译,一般是将英语中的主语(非生命名词)译成汉语中的状语或是宾语。例:His absence puts off the meeting. 因为他缺席,会议延期。
4.Covering 273 ha., the main structure of the Temple of Heaven include...... 占地273 公顷,天坛的主体结构包括…… (
1)现在分词短语做状语的英语句子翻译成汉语时,要根据分词短语所做的状语的不同类别,加上适当的关联词,如表示原因的,表示让步的,表示条件的等等。例:
1.Weather permitting, we will start tommorrow. (如果)天气允许,我们明天开始。
2.Being late, I was punished. (因为)迟到,我受到了惩罚。(
2)“cover”一词词义较为广泛,常见的用法有“占用”“覆盖”和“含盖”等意思。、The money which our company gives you will cover your traveling expense. 我们公司给你的钱也将含盖你的差旅费。Unit 2 Sports
1.The founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949 brought about fundamental changes to the field of sports and the skills of Chinese athletes improved quickly. 随着1949 年中华人民共和国的成立,中国体育迎来了根本性的变化,体育健儿的竞技水平也在迅速提高。如果把本句译为:1949 年中华人民共和国的成立给中国体育带来根本性的变化,体育健儿的竞技水平也迅速提高,就显得头重脚轻,语流不畅。我们在处理这一问题时,把英语中的主语翻译成汉语中的状语,这样就流畅自然了许多。这样的处理方式,还是根源于非生命名词做主语的翻译技巧。
2.The athletic progress of New China is rooted in mass participation. 新中国体育的进步是以广泛的群众参与为基础的。或是:群众的广泛参与为新中国的体育进步奠定了基础。将非生命名词的主语翻译成汉语句子中的宾语。另外:be rooted in 不宜翻译成“扎根于” 。
3.Literally meaning"breathing exercises",qigong was mentioned in records in China dating as far back as 3,000 years ago. 气功,字面意思为“气息锻炼” ,其在中国史料中
的记载可以追溯到三千年前。(
1)“字面意思为……” ,这是在口译中经常会出现的字眼,尤其是在汉译英中,用来解释一些直接译为拼音的、中国所特有的、用单词或短语无法翻译清楚的典故和俚语,来源于寓言故事的成语,或是需要补充说明的字眼上。例:
1.双喜临门literally means "double happiness fall on before the door"
2."狮子头"literally means "lion's head" is a large pork ball (
2)date back, 译为“追溯”既显得有文采,也遵循了口译的三原则。
4.It has been suggested that China adopt the English professional soccer system, under which players are selected for the national team from the clubs. 有人提议中国应该采取英国职业足球体系,从各个俱乐部中选拔国家队球员。英译中的It is+V(e)d+that 从句的结构,在翻译成汉语时,往往采取两种处理方式,一是译为“据……” ,如:“据说”“据报道”等;二是译为“有人……” 、,如:“有人提议”“有人设、想”等。例1:it is supposed that all the senior should be cared in the family. 例2:It is expected that U.S. should take more responsibility in struggling with global
poverty. Unit 3 Education
1.The guidelines for China's education are:education must serve the needs of socialist modernization, be integrated with productive labor, and train builders and successors who are well developed morally, intellectually, and physically. 中国的教育方针是,“教育必须为社会主义现代化建设服务,必须与生产劳动相结合,培养德、智、体全面发展的社会主义事业的建设者和接班人” 。英语当中的副词一般来讲信息承载量都比较大,但并不是所有的副词都是那样,相反,有一些副词在翻译的时候却要“简洁化” ,如上句中的morally,intellectually 和physically. 例:Morning exercise does good to us physically and mentally. 晨练对我们的身心都有好处。
2.That's to say, in these poverty-stricken counties food and clothing are still the primary concern of the population. 也就是说,在这些贫困县,人们最关注的事情还是衣服和食物。Poverty-stricken counties 一个具有强烈中国特色的词汇,对其的学习要做到举一反三,贫困地区,贫困家庭,贫困生等的翻译也就顺理成章啦。
3.中山大学师资力量雄厚。其中教授、副教授700 余人,讲师650 人,助教400
人。Zhongshan University has a strong teaching staff,with over 700 professors and assocaite professors, 650 lecturers, and some 400 assistants and instructors. 在汉译英中,汉语中表示细节解释或是伴随说明的部分,在译成英语时,往往不翻译成相对独立的语言单位,而是用短语来表达,最常见的结构是介词短语(with, including)和分词
短语。例:
1.With the company of her sister, Mary goes to hospital.
https://www.doczj.com/doc/cc6431664.html,panied by her sister,Mary goes to hospital.
1.Step 1,to double China's GNP of 1980 in 10 years with chief aim of providing adequate food and clothing for the Chinese people.第一步,用十年时间,实现国民生产总值比1980 年翻一翻,基本解决人民的温饱问题。
2.China is a country with a population of over
1.1 billion people of whom over 800 million live in
the rual areas. 中国是一个拥有十一亿人口的大国,其中八亿是农民。
3.Reform in China does not mean a change of the socialist system but its improvement and development. 中国的改革不是要改变社会主义制度,而是其的(自
我)完善和(自我)发展。(
1)does not mean 不是意味着,但我们在翻译的时候,不能照章直译,要考虑全
局,本着“既能够表达清楚意思,又要足够的简洁” 。(2)its improvement and development 自我完善和自我发展,口译时,有时为了表达更加完整和清晰,需要添加词汇来达到这一目的。
4.Economic development has been the top priority of the Chinese government. China
has only 7% of the world's total cultivated land and yet has 22% of world's total population. 经济发展是中国政府的第一要务。中国用世界7%的耕地养活了世界
22%的人口。
5.The Third Plenary Session of the 11th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China held at the end of 1978 marked the dawn of a new era of reform in China. 1978 年召开十一届三中全会开辟了中国改革的新纪元。(
1)The Third Plenary Session of the 11th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China 全译为“中国共产党第十一届中央委员会第三次全体会议” ,在这里我们把其译成“十一届三中全会”是符合题目的要求的。(
2)Marked the dawn of a new era 字面意思为“标志着新纪元的开始” ,我们采取
“转译”的手段,使译文更为简洁,更符合汉语的表达习惯。
6.Over the past 40 years China's light industry has developed from a backward,
workshop-based handicraft industry with a limited variety of products into a modern, mechanized industry. 在过去的四十年中,中国轻工业从一个以手工劳动为基础,产品相对单一、落后的作坊式生产行业成长为现代的、机械化的产业。
7.The industry now shoulders the task of supplying the Chinese market, earning foreign currency through exports and accumulating capital for the production of goods
worth a total of 25
64.1 billion Yuan. 工业肩负着市场供应,出口创汇的重任,同时,也为生产积
累资金两万五千六百四十五亿元。(
1)英语中的后置定语往往是从句或是短语,相对信息承载量较大,在翻译的时候,要尽可能地使其简洁,如果在译文中,放在定语的位置上不合适,显得累赘,就要考虑分句翻译,译成并列结构或是状语。(
2)英语中带有小数点的数字,在译成汉语时,不一定要把小数点译出来。要视情况而定,特别是数值较大的时候,反之亦然。
8.Agriculture-the Foundation of China's Economic Development, social stability and self-reliance. In the final analysis, rural problems are the fundamental problems addressed by the Chinese revolution and subsequent construction. Without the stability and development in the countryside, there can never be social stability and progress. Without the modernization of the agriculture sector, the rest of the national economy can not modernize. 农业是中国经济发展、社会稳定、自力更生的基础。总之,农村问题是中国革命和建设的基本问题。没有农村的稳定,就没有全社会的稳定;没有农民的富裕,就没有全民族的繁荣;没有农业的现代化,就没有整个国民经济的现代化。
1.In the final analysis-总之,subsequent--?
2.否定结构的肯定翻译,也是一种常见的处理长句的方法。
9.This means that farm production can be contracted by individual households, while
investment,
water management, electricity, chemical fertilizers and irrigation equipment can still be handled in a unified way. 这就意味着农业生产可以承包到户、分户经营;而投资建设、水力电力、化肥农药、灌溉设备还是由集体统一管理。英语当中的被动语态在译成
汉语的时候,不一定也要遵照原句,必须翻译成被动语态,事实上,汉语中,被动语态的应用是很少的,如果在不影响句子的基本含义,又符合汉语的表达习惯,我
们在英译汉的时候,被动结构主动化。
10.Introduced by the State Science and Technology Commission in 1986, the Spark
Plan aims to popularize and carry out science and technology projects to increase
production capacity of township enterprises and train managers and technological personnel for rural areas. 由国家科学技术委员会在1986 年提出的“星火计划” 目的在于在乡镇企业中普及贯彻科技,方案,依次来提升其生产能力,同时也为农村地
区培养管理者和技术人员。
1.一些比较长的状语形式,可以翻译成定语,如上句中的过去分词式的状语,就是这样处理的,同样,比较长的定语也可以处理为状语,前提是保证句子的基本含
义没有任何改变。
2.谓语动词的“名词化”适用于句子的宾主较大的情况,如上句中的aims to. Unit
Seven Foreign Trade and Special Economic Zone
1.Foreign economic relations and trade, guided by the policies of reform and opening to the outside world, have developed rapidly and great achievements have been made. 对外经济关系和贸易迅速发展并取得了重大成就,这是受改革和对外开放政策的影响的。在翻译包含较长的状语的英语句子时,无论状语在什么位置,在译成汉语时,一般是先译状语,再译句子的其它成分。故而,上句还可以译为“受改革和对外开放政策的影响,对外经济关系和贸易迅速发展并取得了重大成就” 。另外,在翻译由by 引进的短语的时候,有时也可以将其处理为译文中的“外位”成分。
2.By utilizing foreign capital, China has improved its energy resources, transport and telecommunications facilities and raw material industry and has technically transformed a number of old enterprises. 通过利用外资,中国改善了其能源、交通、通讯设施和原材料加工,并且对一些老企业进行了技术改造。本句翻译的难点在于“对个别专业领域的词汇的处理”“副词做状语时的转译”ra w material
学生反馈
学生反馈意见解决办法
词汇量匮乏建议使用TOFEL10000词汇一书
英语教学设计 名称形容词、副词的比较级 科目英语教学对象学生提供者邓海英 课时第2课时 一、教学内容分析 (1)语法课比较乏味,要以灵活的形式教授 (2)需要反复练习,学生能运用比较级对事物进行比较 (3)本课运用一些明星图片对比,进行一些比较级的练习,体会比较的应用 二、教学目标(知识,技能,情感态度、价值观) 1、熟练掌握形容词、副词的比较级的变化规则。 2、熟练准确应用提到对比双方时,在比较级后用than, 例如It's smaller than the blue one 3、熟练运用所学知识。用所学知识表扬自己。 三、教学策略选择与设计 1.教师运用网络媒体给学生创造一个学习的空间,让同学们自己通过合作探究,自学掌握形容词的比较级。 2.课堂上提出比较话题,让学生回答。 五、教学环境及资源准备 1.本课教材:八年级英语课本 2.教学环境:微机室
六、教学过程 一、师生问候:Hello! Everyone! 问:What's the weather like today?How about yesterday ? 回答:cold\colder\ 或者warm\warmer 通过观察图片引出本课的知识点:比较级 二、呈现新课:(以网页形式展现形容词比较级的变化规则) 1. 构成的规则变化及单词举例 (1)一般在单音节词尾加-er 或-est (2)以e结尾的单词只在词尾加-r或-st (3)只有一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节单词, 先双写这个辅音字母, 再加-er或-est (4 以“辅音字母+ y”结尾的单词,先改y为i, 再加-er或-est。 (5)除early 外,以ly结尾的单词,一般在词前加more / most (6)多音节词和部分双音节词在词前加more或the most。 2. 构成不规则变化的单词good / well –better –best ill / bad / badly –worse –worst many / much –more –most little –less –least 指路程更远far –farther –farthest 指意义深远或进一步far –further –furthest 指年龄大小old –older –oldest 指家庭成员长幼old –elder –eldest
一.商务职衔 1.总裁/会长/理事长President 2.董事会主席/董事长Chairman (board of directors) 3.董事Director 4.执行董事Executive Director 5.总干事Director-General 6.理事Trustee/Council Member 7.总监/主任Director 8.经理Manager 9.总经理General Manager 99(GM) 10.副总经理Assistant General Manager 11.总经理助理General Manager Assistant 12.公关部经理PR (Public Relations)Manager 13.销售部经理Sales Manager 14.营业经理Business Manager 15.市场部经理Marketing Manager 16.生产部经理Production Manager 17.研发部经理R&D (Research and Development) Manager 18.厂长Factory Managing Director 19.车间主任Workshop Manager 20.高级工程师Senior Engineer 21.工程师Engineer
22.助理工程师Assistant Engineer 23.首席执行官/总裁C.E.O (Chief Executive Officer) 24.首席财务官/财务总监C.F.O (Chief Financial Officer) 25.财务主管Financial Controller 26.高级会计师Senior Accountant 27.会计师Accountant 28.助理会计师Assistant Accountant 29.注册会计师CPA (Certified Public Accountant) 30.会计员Treasurer 31.出纳员Teller 32.首席信息官/咨讯总监C.I.O (Chief Information Officer) 33.首席营运官/运营总监C.O.O (Chief Operation Officer) 34.技术员Technician 35.程序员Programmer 36.设计师Designer 37.机械师Mechanic 38.化验员Chemical Analyst 39.质检员Quality Inspector 40.推销员Salesman/Salesperson 41.采购员Purchaser 42.部长Minister 43.副部长Vice-Minister
一、 教材分析 :Analysis of the Teaching material 二、教学目标:Teaching alms and demands: 三、教学重难点 :Teaching keys and difficulties: 四、教学方法 :Teaching methods: 五、教学工具 :Teaching aids : 六、教学过程:Teaching procedures: 七、板书设计 : Blackboard Design. 八 教学评价与反思 一份正规的高中英语教案主要应该包含上面的八个要点,也是作为一份教案应该具有 的基本格式。 课题: 《My name ’s Gina! 》教学设计 科目: 英语 教学对象: 初一( 3)班: 1 课时 提供者:单位: 江 西南 昌经开中学 一、教学内容分析 该 部分学 习内容贴近学生的生活,谈 论 的主题 是 结 交 生在轻松、愉快的学习氛围中熟识新伙。 二、教学目标 采用 Practicing, Listening for specific information 和 Role playing 的学习策略,使学生学会打招呼和介绍自 己、 询问他人姓名的基本句型 What's your/his/her name ?My/His/Her name is ? 。 ”培养学生结交新朋友的 能力。 三、学习者特征分析 1
本单元的主题是熟识新伙伴,同时引导学生采用 Practicing, Listening for specific information 和 Role playing 的学习策略,学习一些新词汇,掌握一些重点句型,在小组合作学习的过程中,进一步促进学生 之间的相互了解。 四 、 教 学策与设计 采用 Practicing, Listening for specific information 和 Role playing 的学习策略,使学生学会 打招呼和介绍自己、询问他人姓名的基本句型 What's your/his/her name ?My/His/Her name is ? 。” 培养学生结交新朋友的能采用 Practicing, Listening for specific information 和 Role playing 的 学习策略,使学生学会打招呼和介绍自己、询问他人姓名的基本句型 What's your/his/her name ? My/His/Her name is ? 。”培养学生结交新朋友的能力。 五、教学重点及难点 specific information Role playing 六、教学过程、 教学 找出在预备篇中所学的单词,学习打招 利用插图或实物卡片让学生找出在预备篇 呼和介绍自己、询问他人姓名的基本句型 中所学的单词, 然后教师引导学习打招呼和 介绍自己、询问他人姓名的基本句型 “What ’ s your/his/her name? My/His/Her name is ? "---What's your /his /he name? My/His/Her name is ? ”. 熟练掌握句型 2.让学生听对话,练习对话并模仿对话,结 2.练习对话并模仿对话,结识班级的其他同 识班级的其他同学 学。 一 1、播放 2a 部分的录音让学生听, 引导学生通过 1.通过听对话熟悉人名 "Ton 》Tom 听对话熟悉人名 "Tony TomJenny Bob Bruce Jim" , Jenny Bob Bruce Jim" ,完成 2a, 2b 部分 完成 2a,2b 部分的教学任务。 的教学任务。 2. 引导学生重复他们所听到的, 模仿对话结识班级 的其他同学,完成 2c 部分的
《英语口译》课程标准 课程名称:英语口译 课程类别:专业必修课 教学学时:32(理论)+32(实践) 课程学分: 4 先行课程:高级英语听力,英语视听说,基础英语等 适用专业:英语专业 参考教材:1、《英语口译实务》,外文出版社,2009年1月(主编:梅德明) 2、《实战口译》,外语教学与研究出版社,2004年9月(主编:林超伦) 3、《英语中级口译证书考试:中级口译教程(第4版)》,上海外语教育出版社,2014年3月(主编:梅德明) 4、《英语中级口译证书考试:中级听力教程(第4版)》,上海外语教育出版社,2014年3月(主编:周国强) 一、课程性质 《英语口译》是英语专业三年级翻译系列课程中的一门必修课,也是英语专业的核心课,着重口头翻译训练。口译是一项实践性很强的语言交际活动,通过口头表达形式,将所感知和理解的信息准确而又快速地由一种语言形式转化成另一种语言形式,进而达到完整并及时传递交流信息之目的的交际行为,是现代社会跨文化,跨民族交往的一种基本沟通方式。表面上看,它似乎是一种被动,单一,机械性的语言传达活动,其实不然,它是一种集语言信息,语境信息,文化信息,心理信息等于一体的综合交际活动,是一种综合运用视,听,说,写,读等知识和技能的语言操作活动。准确、流利是衡量口译优劣的两条基本标准。 本课程旨在帮助学生掌握与专业相关主题的有关词语、表达方式及句型;让学生更好地了解中国的基本国策及国情,同时也能了解其它国家的历史、政治、经济、文化等概况。本课程要求学生具有扎实的双语基本功,了解口译活动的基本过程,口译过程中大脑的反应,对笔记的要求,各类句式的处理,各类意外情况的处置,以及基本的社交礼仪(着装,提前到场,文具准备)等。本课程以英汉互为口译为主,培养学生掌握口译的基本理论和专题连续传译的技能,帮助学生掌握口译记忆方法,口头概述,口译笔记,及公众演讲技巧以求学生能较准确、流畅地进行汉英对译。 二、课程目标 本课程的授课对象是英语专业学生,属英语类专业技能课。学生通过学习该课程掌握良好的口语水平和娴熟的口译技能。通过该课程的学习,学生能了解口译基本理论,掌握口译技巧,并运用到不同情景的口译实践当中,可从事一般的生活翻译,陪同翻译,涉外导游以及外事接待等翻译工作。 (一)专业能力目标: 在对语言理解和运用方面,以英语录音、录像、电影电视、多媒体教学片的形式进行教学,通过观赏英文电影、电视、多媒体教学片等,使学生能够增加对语境和语用场合了解;能较好地复述所观看的故事情节,讲述自己的理解和分析,具备用英语讲述和组织语言的能力;能针对特定语境和语用场合中的若干话题,进行模仿、对话、讨论等,具备用英语解决实际问题的能力、较强的上口能力和正确的语音、语调和较快的语速。经过系统
UNIT 5 第五单元 来源:口译-学院精品课程作者:Jay J Yang STENOGRAPHY (II) 口译笔记技巧(二) Unit Objective (单元目标) After reading this unit you should ☆ understand the structure of stenographic notes. ☆ master the two major types of stenography. Warm-up (准备) 1. Two students are requested to sit at the Interpreting Desk or Booth, acting as interpreters of the class. Their performance is evaluated and graded by instructor. 2.One or Two students are asked to present a piece of news or a weather forecast of the week. Theory of Interpretation (口译理论) 口译笔记的结构:纵向分页、横向分段、阶梯排列、条列记录。 口译笔记的符号:符号的利用与创新、古英语缩写法、常用缩写词。 Memoria Technica (记忆法) Listen to the following passage, “Dutch Treat”, and try to catch the key words and details, then retell them in your own words: Dutch Treat The phrase “Dutch Treat” can sometimes pull you out of a group of four and had an expensive diner. Well, the waiter brings the check shortly after you have offered to pay for the diner. You look at the check and shocked at the total cost. Whew! Slowly you pick up the check, but the only other man in the group says: “Just a minute. Let me take it.” Off course, he does not mean it, and feels safe in making the offer because you have already agreed to pay the check.. You both struggle,
一、教材分析:Analysis of the Teaching material 二、教学目标:Teaching alms and demands: 三、教学重难点:Teaching keys and difficulties: 四、教学方法:Teaching methods: 五、教学工具:Teaching aids: 六、教学过程:Teaching procedures: 七、板书设计:Blackboard Design. 八教学评价与反思 一份正规的高中英语教案主要应该包含上面的八个要点,也是作为一份教案应该具有的基本格式。
《Making Apologies》说课稿 关于课文 本篇课文选自中等职业技术学校教材《基础英语》第一册。 教学目标和要求 本课是第2课时,教学目标主要是对课文中的对话进行阅读、巩固和拓展。要求通过学习,学生能达到以下要求: 1.知识目标
能够牢固掌握好课文对话中的重点词汇词组;阅读对话并且根据提示完成对话,运用已经学会知识让学生分角色进行口语练习,特别要求记忆Sarah所说的话并能当堂表演对话。能够拓展对话,根据图片内容创作一段对话。 2.能力目标 能够独立阅读课文对话,能够正确理解课文对话并根据提示完成对话,能够用英语表达歉意和接受道歉并学会为工作中所犯的错误致歉。能够拓展对话,完成看图说话并把每张图片的对话内容连在一起形成一段对话。 3.情感目标 通过小组讨论,培养同学们的交际能力和团队合作精神; 不同的教学目标和要求 A. 对于基础相对好的同学,能够阅读对话并且根据提示完成对话,运用已经学会知识让学生分角色进行口语练习,能当堂表演对话,能够拓展对话,根据图片内容创作一段对话。 B. 对于基础中等的同学,能够完成课文对话,分角色进行口语练习,能当堂表演对话。 C. 程度较弱的同学,要求能够熟练掌握课文中的生词和词组,能够正确完成课文对话。 教学重点 英语道歉和接受道歉的词汇及表达;学习英语在工作中犯错误的表达;根据提示完成对话;表演对话; 教学难点 根据提示完成对话,表演对话,拓展对话,根据图片创作对话。
《口译》教学大纲 英文名称:Interpretation 一、课程目标 1. 课程性质:《口译》为英语专业学科基础课程的后续课程,为英语专业本科四年级必修课程。口译活动是集听、说、读、写、记为一体的复杂言语交际活动,因而必须以精读、泛读、听力、口语等课程为基础,在掌握这些课程所传授的技巧的基础上才能顺畅完成教学任务,是培养英语专业学生的综合语言能力的课程。此外,口译课涉及内容大多与现实生活的方方面面相关,因此除了注重词汇、句式积累,该课程注重学生的知识面拓展,努力提高学生的语言综合及运用能力,该课程将为社会培养基础实用人才。 2.教学方法:课堂教学为主,课后练习为辅 3.课程学习目标和基本要求 《口译》课旨在通过讲授口译基本及其和逻辑推理能力训练,并结合口译实践,拓宽学生知识面,培养学生跨文化交际能力、口译相关及其的这运用能力、认知、推理能力及相应的心理素质。 课堂教学应以学生为主体,教师为主导,改变以教师为中心的教学模式。注重培养学生的学习能力,学习兴趣和语言应用能力。在教学中开展以任务为中心,形式多样的教学活动。教师更多采用采用启发式,讨论式,发现式和研究式等教学方法,充分调动学生的学习积极性和主动性。在精心组织课堂教学的同时,结合口译技巧教学部分开展丰富多彩的课内外实践活动,如英语讲演,辩论,田野采集等方式,并积极探索利用现代化的语言教学手段丰富课堂教学内容。 4.课程学时:36学时 5.课程学分:3学分 6.课程类型:学科专业课 7.考核方式:考试 8.适用专业与年级:英语专业本科四年级 二、课程结构 Chapter One A brief introduction to Interpretation(学时数: 2) 知识点:1) the history of interpretation 2) the criteria of interpretation 3)the process of interpretation 4)the patterns of interpretation 重点:the history of interpretation; the criteria of interpretation; the process of interpretation; the patterns of interpretation, etc 难点:interpretation skills, the cultural elements in interpretation Chapter Two Ceremonial interpretation and public speeches skills(学时数: 4)
教案 第3次课2学时章节无笔记陪同口译(1)欢迎光临&景点游玩Welcome& Tourism unit 1&3 教学目的和要求Teaching Aims: After this lecture, the students should 1. Know how to receive western guests at the airport. 2. Know how to tour around the scenic spots with the western guests. 3. Master some common words and expressions about reception and tourism. 教学重点难点Difficult Points: 1. How to receive western guests at the airport. 2. How to introduce the famous scenic spots for the guests. 教学进程 (含章节教学内容、学时分配、教学方法、帮助手段)I. Lead-in Part:(20’) A. In this part, the teacher aims to tell students how to make preparations before the interpreting. 1. Why should we do preparations before the interpreting? (Answers: interpreting includes various kinds of areas, such as economy, politics, technology, culture, etc., therefore, the interpreter should be Jack of all trades.) 2. How to do preparation before the interpreting? (Answers: (1) Collect the background information of the speaker and the topic. (2) Prepare for the professional words and expressions of the topic. (3) Communicate with the speaker. (4) Have good psychological qualities. B. professional words and expressions of the topic (1) welcome
v1.0 可编辑可修改 &Punshiment 罪与罚 盗窃类 Stealing/theftCar theft (偷车), ID Card theft(intelligent crime智能犯罪)Pickpocket 扒手Shoplifter 顺手牵羊者Burglar 入室盗窃,窃贼—burglary Break-in 入室盗窃 攻击类 Attack 攻击Assault 袭击Mugging 背后袭击 Rape 强奸 抢劫类 Robbery 抢劫Hijack 劫持Hostage 人质Kidnapping/Abduction 绑架 Juvenile青少年类 School/Campus violence 校园暴力Bully 欺负Juvenile Delinquency 青少年犯罪Drug addiction/abuse 吸毒Drug trafficking 贩毒Cheating 作弊Academic Plagiarism 学术剽窃Copy 抄袭Corporal Punishment 体罚Spank 打屁股 Slap 抽耳光 经济类 Corruption 腐败Bribery 贿赂 Fraud, Scam 诈骗 公路交通类 Speeding 超速驾驶Drunken driving 醉酒驾车Reckless driving 鲁莽驾车Fine, Ticket 罚款 Parking 停车 罪犯 Delinquent Offender Criminal 商业 Smuggling 走私Smuggled goods 水货Cheap copy/copycat 山寨Piracy 盗版
v1.0 可编辑可修改 Swindle 骗财 Law & Order 法制类 Law Enforcement 执法 Law-abiding citizen 守法公民 Punishment惩罚类 Capital punishment 死刑Life imprisonment 终生监禁Jailed / Behind bars 入狱,铁窗生涯Prison/Jail break 越狱Penalty 惩罚Execution 处死Community Service 社区服务Deportation 驱逐出境 Extradition 引渡 Court法庭类 Judge 法官Supreme Court 最高法院Attorney 辩护律师Lawyer 律师Barrister (英)高级律师Defendant 被告Prosecutor 检察官Sue 起诉Lawsuit 诉讼Jury 陪审团Innocent 无罪Guilty 有罪Be sentenced to…被判…Trail 审判,试验Evidence 证据Forensic medicine 法医Investigation 调查Interrogation 审问Police Department 警察局Witness 目击证人Jurisdiction 裁判权,审判权Criminal Justice System 犯罪司法系统 健康类词汇合集 WHO-World Health Organization 世界卫生组织 Epidemic; Pandemic; Endemic 流行病 Plague 瘟疫 Disease; illness 疾病 Ailment 小病Bird flu; Avian flu 禽流感 Influenza (flu) 流感 Foot & Mouth Disease 口蹄疫 Mad Cow Disease 疯牛病SARS 非典Swine flu 猪流感 AIDS 艾滋病 Virus 病毒 Bacteria; Fungus 细菌 饮食健康 Calorie 卡路里,食物热量 Diet 节食Blood sugar 血糖 blood pressure 血压Cholesterol 胆固醇 Fiber 纤维 Calcium 钙 Vitamin 维生素 Fruit sugar; fructose 果糖 Glucose 麦芽糖Nutrition 营养
《口译2》课程教学大纲 课程代码:070141032 课程英文名称:Interpretation 2 课程总学时:16 讲课:16 实验:0 上机:0 适用专业:英语 大纲编写(修订)时间:2017. 10 一、大纲使用说明 (一)课程的地位及教学目标 本课程为英语专业第六学期口译课,为英语专业三年级的主要课程,是一门综合性的英语知识与技能课,主要讲授口译基础知识,训练包括听、说、读、记、译在内的口译能力;帮助学生建立合理的知识结构和获得运用英语语言的基本能力;提高学生的听、说、译等综合能力;为高级英语和其他专业课的学习打下坚固的基础。 (二)知识、能力及技能方面的基本要求 本课程主要讲授口译基础知识,对学生进行全面、严格的听、说、读、记、译基本技能训练,培养学生实际运用语言的能力,即:正确、自然、流畅地运用本阶段所学的语言,恰当、灵活地予以使用。并通过基础训练与实例讲解分析,使学生逐步提高口译能力,了解英语各种问题的表达方式和特点,扩大词汇量和熟悉英语常用句型。同时,培养学生养成良好的学习作风和正确的学习方法,提高学生的逻辑思维能力和独立工作的能力,丰富学生社会文化知识,增强学生对文化差异的敏感性。 (三)实施说明 本课程为英语专业本科生第六学期课程,共计16学时。改变过去以教师为中心的课堂模式,展开形式多样的教学活动,鼓励学生成为课堂主体,培养学生的学习能力和研究能力。采用启发式、讨论式、发现式和研究式的教学方法,激发学生的学习动机。引导学生主动积极地利用现有图书资料和网上信息获得知识,掌握查阅文献、检索资料的基本方法。 (四)对先修课的要求 无 (五)对习题课、实验环节的要求 各类原版英文视听材料为基本,使学生达到在一般及个别专业翻译场合能胜任外事翻译。专业八级以上难度的段落及篇章。 (六)课程考核方式 1. 考核方式:考查 2. 考核目标:在考核学生对口译基础知识掌握的基础上,重点考核学生具体场合口译能力。 3. 成绩构成:本课程的总成绩由两部分构成:平时考核(包括出勤、课堂表现等)占30%;小测验、作业占70%。 (七)主要参考书目: 《高级口译教程》,梅德明、戴炜栋编,上海外语教育出版社,2010 《口译教程》,梅德明编,上海外语教育出版社,2008 《翻译精要》,陈定安编,中国青年出版社,2004 《翻译变体研究》,黄忠廉编,中国对外翻译出版公司,2000 《轻松掌握英语翻译》,马光编,中国书籍出版社,2002
口译教学案例 模块I.口译概述 Purpose of offering interpretation course: 1. General purpose: On some occasions to some degree students can better serve as interpreters. 2. Requirement of Students: a. conquering words & phrases in different fields b. mastering some interpreting skills c. improving listening ability, oral English & Chinese d. enhancing transferring ability of different codes e. strengthening memory of information & responding speed Definition of Interpreting: Interpreting is a service activity with a communication function. (Gile) It is usually a face-to-face communicative act. ●Way of communication ●Communicating through sounds ●Rendering from one language into another keeping the meaning intact ● A task-based activity cutting across receptive and productive skills Types of interpretation: Classification on nature: ●Conference Interpretation 会议口译 ●Personal/Escort Interpretation 随行口译 ●Liaison Interpretation 联络口译 Classification on operation form: ●alternating interpretation (交替口译) ●consecutive interpretation (CI) (连续/逐步口译) ●simultaneous interpretation (SI)(同声传译) ●whispering interpretation (耳语翻译) ●sight/on-sight interpretation (视阅翻译/视译) General Interpretation process Accepted in Classroom Practice: I. Lead-in Activities 导入活动 II. Interpretation Practice on Different Topics 不同话题口译 III. Other Classroom Activities 其它活动 IV. After-class Assignment 作业布置 模块II.口译技巧 1. Interpreting similar word orders 顺句驱动 根据源语的句子顺序,把整个句子切分成多个信息单位或意群单位,再用连接词把这些单位连接起来,译出整体的意思。 顺句驱动的优点:减轻记忆的压力 e.g. 所有人//都可以借助互联网资源//来学习,不论他们是哪个民族、//何种性别、//何种肤色、//
Chapter 3 Cohesive clues in interpreting I Teaching objectives: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to: 1.identify key information through cohesive clues 2.master key words, expressions and sentences on economy 3. improve interpreting skills and practice II Key points:the ability to identify key information with cohesive devices III Teaching Allotment:2 periods IV Teaching Methods:communicative approach; audio-lingual approach V Teaching Procedures: 1.Dialogue interpreting (10 mins) Performers: Group 2 Interpreter: 李子莹 2.Interpreting skills (10 mins) (1) In English, there are a large quantity of lexical, grammatical and logical connectors that help to form cohesion in a discourse. When it comes to listening, paying special attention to cohesive devices is also very essential for better understanding. (2) Please be familiar with the linking words on P26. 3.Practices: Dialogue & passage interpreting (70 mins) (1) 开幕式主持词 V ocabulary: 阁下His/Her/Your Excellency 东盟ASEAN (Association of South-East Asia Nations) 中国—东盟博览会China-ASEAN Expo 同舟共济to cross the river in the same boat 参会客商business participants "10+1"自贸区"Ten plus One" Free Trade Area 轮值主席rotating president 远见卓识great vision 源远流长have a long standing 感受have a touch of 邻邦友谊friendly neighborhood 剪彩to cut the ribbon for ... 广西壮族自治区主席Govenor of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region 东道主host
UNIT 2 第二单元教案 来源:口译-学院精品课程作者:Jay J Yang Memoria Technica (II) 口译记忆(二) Unit Objective (单元目标) After reading this unit you should ☆ understand the process of memorization. ☆ master the “Memoria Technica”. Warm-up (准备) 1. Two students are requested to sit at the Interpreting Desk or Booth, acting as interpretors of the class. Their performance is evaluated and graded by instructor. 2.One or Two students are asked to present a piece of news or a weather forecast of the week. Theory of Interpretation II (口译理论二) 口译记忆过程:源语信息编码+信息存储+信息提取+译语信息解码 口译记忆方法:源语复述;总结概括;逻辑整理;影子练习。 Memoria T echnica (记忆法) Listen to the following sentences, and try to catch the key words and details, then repeat as accurately as possible: A. Two sentences repeating:: Sentences from Textbook Unit One as a part of review: 1.20 years ago, almost to the day, President Ronald Reagan spoke at this university and expressed the essence of economic and political freedom. https://www.doczj.com/doc/cc6431664.html,pared to President N ixon’s, or even President reagon’s day, many Chinese citizens are now freer to make their own ways of life ---- to choose carers, to aquire property, and to travel. 3.China’s economic success has also come about through far greater integration into the world economy. In the last decades, your country has
.. 初中英语教学设计 教材分析: 在课改的背景下,本套教材避免了传统课程的缺点,强调了学生的兴趣、经验等,能结合实际,贴近生活,插图生动活泼,重视了学生的情感。本节课我强调英语课程要从学生的学习兴趣、生活经验和认知水平出发,倡导体验、实践、参与、合作与交流的学习方式和任务型的教学途径,发展学生的综合语言运用能力。 设计理念: 以听说训练为主线,通过看、听、说、演练、唱、动手操 作等一系列教学活动,使学生获得最基本的英语听说能力,并在教学中充分激发学生强烈的学习愿望,在注重学生知识能力发展的同时,特别强调学生人格的发展和思维的发展。 设计特色: 强调学生自主学习,培养学生学习英语的习惯。如:预习作业的设计――选择一个你最喜欢的国家(如:英国、美国、日本、法国、澳大利亚等),收集查找相关资料,如:它的国旗、国名、人民、语言、著名人物等,并能用英语做简单介绍。教案流程图: Free talk Learning new words Presentation Say a rhyme Learning new sentences Summary Talking
板书设计: Unit 9 The English Club Lesson 1 W here are you from? I’m from … . I’m … . 教学反思: 1、本课力求通过一系列贴近小学生生活实际的生动活泼的教学设计,激发学生学习英语的兴趣,培养学生自主学习以及团结合作的能力,使学生初步形成该话题的会话能力。 2、教学过程中根据学生的心理和生理特征,采用游戏与教学相结合的方法,同时积极鼓励学生进行情景交际,让学生在教师的指导下通过感知、体验、实践、参与和合作等方式实现人物的目标,感受成功。 3、教学过程中注重环节与环节之间的有机联系,精心设计,努力导入自然,做到环环相扣,步步为营,使学生真正做到学以致用。
《英语口译》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息: 课程代码D0111007 D0111005 课程名称英语口译 课程性质英语专业选修课 适用专业英语专业(含各方向) 开课学期秋季学期 总学时34 先修课程:综合英语1-4 英语听力1-4 英语口语1-4 英语语法翻译理论与实践1-2 英语词汇学跨文化交际学英语语法英国文学美国文学英语语言学英文报刊阅读高级英语1-2 英语国家社会与 文化1-2 平行课程:英语测试英语论文写作教育科学研究方法基础教育英语新教材分析英语教师职业技能商务英语写作商务英语翻译导游业务模拟导游 后续课程:无 课程简介: 口译课是为高年级学生开设的英语基本技能课程。通过讲授口译基本理论、口译背景知识和口译基本技巧训练,使学生掌握口译的基本理论和专题连续传译的基本技能,初步学会口译记忆方法、口头概述、口译笔记及公众演讲等口译技巧,能够基本准确、流畅地进行汉英双语对译。 推荐教材:《口译教程》(雷天放,陈菁主编。新世纪高等院校英语专业本科生系列教材,上海外语教育出版社,2006。) 参考书目: 1、钟述孔,《实用口译手册》,中国对外翻译出版公司,1991. 2、吴冰,《汉译英口译教程》,外语与教学研究出版社,1995. 3. 冯建忠,《实用英语口译教程》,译林出版社2002.3 4、林超伦,《实战口译》,外语教学与研究出版社, 2004.9 5、仲伟合,《英语口译教程》,高等教育出版社,2006.1 6、 CHINA DAILY, CHINA TODAY, VOA,BBC,CRI,CCTV-9 等。 二、课程总目标 本课程旨在进一步加强英语专业高年级学生听、说、读、译等基本外语能力,并通过英语口译基本理论知识、基本技巧、口译背景知识的讲解和各种题材的口译练习,使学生初步了解口译的基本理论和基本方法,了解常用题材口译要运用到的词语、表达方式等,了解口译记忆方法、口头概述、口译笔记及公众演讲技巧,提高学生综合运用母语和外语的能力,使学生能够基本胜任一般性口头翻译工作;同时结合各项专题口译知识学习,扩大学生知识面,培养工作应变能力,开拓职业合作精神,为社会培养复合型外语人才。在课程结束时,学生对外事联络陪同口译工作有初步的了解,并能基本胜任这项工作。 三、理论教学内容与目标 课程主要以介绍基本口译技巧为主线,技巧主要包括:信息听辩、口译记忆、逻辑分析、口译笔记、公众演讲、数字口译、应对策略等。口译技巧训练不仅能培养从事口译工作所需要的技能,良好的逻辑思维能力、快速的语言组织和表达以及出色的公众演讲技巧,同时也是学生毕业后胜任实际工作的有利条件。