供应链管理 第三版 Unit3 习题与答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:91.00 KB
- 文档页数:15
![供应链管理(第三版)习题 (9)[5页]](https://uimg.taocdn.com/17b7071cfe00bed5b9f3f90f76c66137ee064f23.webp)
第四章供应链的运作(一)判断题(1)供应链的库存水平越高,其对市场的响应速度就越慢,客户的满意度就越低。
( F )(2)在进货总数不变的情况下,增加订货次数,会减少库存成本。
(T )(3)安全库存是用来满足不可预知的突发需求的,如果需求是确定的,就不需要安全库存。
(T )(4)如果面对的是那些以价格作为主要决策依据的客户,可以通过低成本的运输方式来提高产品价格,这时响应速度就处于次要位置。
(F )(5)运输速度越快,运输成本就越高,但对市场的响应速度快。
(T )(6)在供应链协同中,战术协同处于承上启下的位置,是供应链协同管理的中心问题。
(T )(7)供应链节点企业的减少,主体利益的矛盾性和供应链环节的不确定性,导致供应链协同很困难。
( F )(8)供应链所有权的分散使供应链运作变得很容易。
( F )(9)电子供应链的实施,能够降低存货水平,但不能缩短交易时间。
( F )(10)供应链的维持需要各节点企业相互信任、相互合作、信息共享。
(T )(二)单选题1、业务流程再造的英文缩写是(C )。
A、ERPB、CRMC、BPRD、EDI2、利用(B ),在淡季进行大量库存,为无法提供满足全部产品的旺季需求做储备。
A、周转库存B、季节库存C、安全库存D、循环库存3、( D )是供应链运营中最大的驱动要素。
A、库存B、运输C、设施D、信息4、供应链运营的制约因素有(C )。
A、库存B、设施C、产品种类的增加D、运输5、供给和需求的缓冲作用是通过调节(A )来实现的。
A、库存储备B、设备C、运输D、物流(二)多选题1、供应链运营的四个主要动力因素(ABCD ),这些因素相互作用,决定了供应链的获利水平和对市场的响应速度。
A、库存B、运输C、设备D、信息E、供应链环节增多2、供应链运营的制约因素包括(ABCDE )A、产品种类飞速膨胀B、产品生命周期缩短C、顾客需求不断增加D、供应链的复杂性和变化性E、业务外包导致供应链环节的增加3、供应链运营模式有(ABC )。

供应链(S C)第一章1、供应链:生产及流通过程中,设计将产品或服务提供给最终用户的上游和下游企业所形成的网链结构2、供应链特征:复杂性动态性交叉性面向客户需求3 、供应链类型:1)稳定SC的和动态的SC 2)平衡SC的和倾斜的 SC3)有效性SC和反应性SC4、使用环节法分析供应链流程:1)顾客订购环节(顾客抵达,顾客订单递交,顾客订货接收,顾客订单完成) 2)补充库存环节(零售订货的发起,零售订单的递交,零售订单的完成,零售订货的接收)3)生产环节(订单到达,生产安排,生产和运输,订货5、接收)4)原料获取环节5、推拉法分析供应链流程:依据相对于顾客需求的执行顺序,供应链上的所有流程可以分为两类:推动流程和拉动流程。
对顾客订单的反应启动拉动流程;对顾客订购预期的反应启动推动流程。
在拉动流程执行过程中,需求是已知的、确定的;而在推动流程执行过程中,需求是未知的,因此必须进行预测。
由于拉动流程是对顾客需求的反应,因而也可以被视为反应性流程;相应地,推动流程可以被视为推测性流程。
供应链上的推/拉边界将推动流程和拉动流程区别开来。
在戴尔公司,个人计算机组装线的起点就是推/拉边界。
个人计算机组装前的所有流程是推动流程,而所有组装过程中和此后的所有流程均是对顾客需求的反应,因而是拉动流程。
6 、供应链管理(SCM):利用计算机网络技术全面规划供应链中的商流、物流、信息流,并进行组织、协调与控制。
7 、SCM内涵:1)信息管理 2)客户管理 3)库存管理 4)关系管理 5)风险管理8、 SCM特点:(一)与传统管理方法相比较的特点: 1)以客户为中心2)跨企业的贸易伙伴之间密切合作、共享利益和共担风险 3)集成化管理4)供应链管理是对物流的一体化管理(二)与物流管理相比较的特点1)供应链管理的互动特性2)供应链管理成为物流的高级形态 3 )供应链管理决策的发展 4)供应链管理的协商机制 5)供应链管理强调组织外部一体化6)供应链管理对共同价值的依赖性7)供应链管理是“外源”整合组织 8)供应链管理是一个动态的响应系统9 、SCM的目标: 1)总成本最低化 2)客户服务最优化 3)总库存成本最小化4)总周期最短化5)物流质量最优化第二章1 、建树价值链的九种价值活动分为哪两类,分别包含哪些内容一)基本活动:内部物流生产作业外部物流市场和销售服务二)辅助活动:采购技术开发人力资源管理企业基础设施2 、价值分析的主要内容:1)识别价值活动 2)确定活动类型每种基本和辅助活动由三种类型:直接活动简介活动质量保证3、核心竞争力形成过程:1)锁定目标。

供应链管理习题答案供应链管理习题答案供应链管理是现代企业运营中至关重要的一环。
它涉及到从原材料采购到最终产品交付的整个流程,包括供应商选择、物流运输、库存管理等各个环节。
在实践中,供应链管理面临着各种挑战和问题,需要通过有效的策略和方法来解决。
下面将针对几个供应链管理习题给出相应的答案和解析。
习题一:如何选择供应商?答案:选择供应商是供应链管理中关键的一步。
首先,企业应该明确自己的需求和要求,包括质量、价格、交货时间等方面。
然后,通过市场调研和供应商评估,筛选出符合要求的候选供应商。
最后,通过实地考察和合同谈判,选择最合适的供应商。
习题二:如何优化物流运输?答案:物流运输是供应链管理中的一个重要环节。
为了优化物流运输,企业可以采取以下策略。
首先,合理规划物流网络,选择合适的仓储和配送中心。
其次,优化运输路线,减少运输时间和成本。
再次,使用信息技术来跟踪和管理货物的运输过程,提高运输效率和准确性。
习题三:如何管理库存?答案:库存管理是供应链管理中的一个重要环节。
有效的库存管理可以降低成本,提高客户满意度。
为了管理库存,企业可以采取以下措施。
首先,建立准确的需求预测模型,避免库存过剩或缺货。
其次,优化订货策略,合理控制订货量和订货时间。
再次,使用先进的库存管理技术,如ABC分类法和定期盘点等,提高库存管理效率。
习题四:如何应对供应链风险?答案:供应链管理面临各种风险,如自然灾害、供应商倒闭等。
为了应对供应链风险,企业可以采取以下策略。
首先,建立供应链风险管理体系,包括风险评估、风险监控和风险应对等方面。
其次,与供应商建立紧密的合作关系,共同应对风险。
再次,建立备份供应商和备用物流渠道,以应对突发情况。
习题五:如何评估供应链绩效?答案:评估供应链绩效是衡量供应链管理效果的重要指标。
为了评估供应链绩效,企业可以采取以下方法。
首先,建立供应链绩效指标体系,包括交货时间、库存周转率、客户满意度等方面。
其次,收集和分析相关数据,进行绩效评估和比较。

南财大《供应链管理》练习题和答案----359c2ef9-6eac-11ec-a83e-7cb59b590d7d供应链管理1总分:100考试时间:100分钟一、单项选择题1.物流的概念最早由()提出。
(正确答案:B,答案:a)a、a.日本b、 b.美国c、c.德国d、 d.荷兰2、物流的英文名称是()。
(正确答案:a,答题答案:a)a、 a.物流?b、b.logsticsc、 c.物流d、d.logistc3.配送是指物流系统中的()要素。
(正确答案:C,答案:C)a、a.运输b、 b.采购c、c.配送d、 d.仓储4、供应链管理与物流管理之间的关系是()。
(正确答案:c,答题答案:b)a、 a.物流管理和供应链管理之间没有关系。
b、b.物流管理包含供应链管理c、 c.供应链管理包含物流管理,物流管理师供应链管理中的一部分。
d、d.供应链管理是物流管理的低级阶段。
5.企业物流是货物的实际流动。
(正确答案:B,答案:D)a、a.企业外部b、 b.内部和外部c、c.企业自身d、 d.企业内部6、供应商的选择、订货模式的决定、生产物料计划等被称为()。
(正确答案:a,答题答案例:a)a、a.供应物流b、 b.生产物流c、c.销售物流d、 d.内部物流7、物流运输服务具有无形性、不可存储性以及()。
(正确答案:d,答题答案:c)a、 a.独立性b、b.公平性c、 c.所有权转让的特点d、d.生产消费不可分离性8.()运输特别适合短距离和高价值产品的配送。
这种运输方式不仅可以进行直接运输,还可以作为其他运输方式的接送方式。
(正确答案:B,答案:B)a、a.铁路运输b、 b.公路运输c、c.水路运输d、 d.空运9、运输规模越大,运输商品所花费的()越小。
(正确答案:d,答题答案:d)a、 a.固定成本b、b.变动成本c、 c.共同费用d、d.单位成本10.以下关于物流活动的陈述不正确()。
(正确答案:A,答案:A)a、a.工业包装的目的是为了促进销售,讲究包装外形美观,装潢富于吸引力。

供应链运作管理部分习题库一、单项选择题1.()是生产及流通过程中,为了将产品或服务交付给最终用户,由上游与下游企业共同建立的网链状组织。
AA.供应链 B.合作伙伴 C.联盟组织 D.供应链管理2. 供应链管理的英文简写为:()。
CA. SSTB. SCC. SCMD. CIMS3. 供应链管理目的:()。
AA. 既提高服务水平又降低物流总成本B. 在于提高服务水平C. 在于降低物流总成本D. 以上答案都不是4. 供应链特征中不包含的因素有( C )。
A.动态性 B.面向用户需求C.静态性 D.交叉性5. 供应链不仅是一条连接供应商到用户的物料链、信息链、资金链,而且是一条( )。
DA.加工链 B.运输链C.分销链 D.增值链6. 商流是货物所有权的转移过程,是在供货商与消费者之间进行的( )流动。
AA.双向 B.价值C.单向 D.信息7. 供应链是一个网链结构,由围绕( )的供应商、供应商的供应商和用户、用户的用户组成。
DA.主要 B.最终用户C.一级 D.核心企业8. 以最低的成本将原材料转化成零部件和成品,并尽量控制供应链中的库存和运输成本,这种供应链属()。
CA. 平衡的供应链B. 反应型供应链C. 有效型供应链D. 稳定的供应链9. 选择恰当的供应链战略对企业发展非常重要,在客户市场需求稳定,且生产的产品相对成熟的情况下,哪种供应链更能发挥竞争优势:()。
DA. 响应型供应链B. 拉动式供应链C. 动态的供应链D. 效率型供应链10. 基于相对稳定、单一的市场需求而形成的供应链,我们称为()。
AA. 稳定的供应链B. 动态的供应链C. 平衡的供应链D. 倾斜的供应链11. 在市场变化加剧情况下,若供应链成本增加,库存增加、浪费增加时,企业不能在最优状态下运作,此时的供应链是:()。
DA. 稳定供应链B. 反应供应链C. 平衡供应链D. 倾斜供应链12. 当企业订购的产品数量大、竞争激烈时,合作伙伴选择最适宜的方法是()。

供应链管理-第三版-Unit1-习题与答案Chapter 1Understanding the Supply ChainTrue/False1. A supply chain includes only the organizations directly involved insupplying components needed for manufacturing.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate2. A supply chain consists of all parties involved, directly or indirectly,in fulfilling a customer request.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate3. A supply chain could be more accurately described as a supply network orsupply web.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate4. The objective of every supply chain is to maximize the overall valuegenerated.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy5. The objective of every supply chain is to maximize the value generatedfor the manufacturing component of the supply chain.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate6. Every supply chain must include all 5 stages.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy7. The cycle view of a supply chain holds that the processes in a supplychain are divided into a series of activities performed at the interface between successive stages. Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate8. The cycle view of a supply chain holds that the processes in a supplychain are divided into 2 categories depending on whether they areinitiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate9. The push/pull view of a supply chain holds that the processes in asupply chain are divided into 2 categories depending on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy10. The push/pull view of a supply chain holds that the processes in asupply chain are divided into a series of activities performed at theinterface between successive stages.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy11. The objective of the customer arrival process is to maximize theconversion of customer arrivals to customer orders.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate12. The objective of the customer arrival process is to ensure that ordersare quickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affectedsupply chain processes.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate13. The objective of customer order entry is to ensure that orders arequickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affected supply chain processes.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate14. The objective of customer order entry is to maintain a record of productreceipt and complete payment.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Hard15. The replenishment cycle occurs at the retailer/distributor interface.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Hard16. The replenishment cycle occurs at the distributor/manufacturer interface.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Hard17. The replenishment cycle is initiated when a supermarket runs out ofstock of a particular item.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Hard18. The replenishment cycle is initiated when customers load items intendedfor purchase into their carts.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Hard19. The manufacturing cycle occurs at the distributor/manufacturer interface.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate20. The manufacturing cycle occurs at the manufacturer/supplier interface.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate21. The production scheduling process in the manufacturing cycle is similarto the order entry process in the replenishment cycle.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Hard22. The production scheduling process in the manufacturing cycle is similarto the order fulfillment process in the replenishment cycle.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Hard23. The procurement cycle occurs at the manufacturer/supplier interface.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy24. The procurement cycle occurs at the retailer/distributor interface.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy25. The cycle view of the supply chain is useful when consideringoperational decisions, because it specifies the roles andresponsibilities of each member of the supply chain.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate26. The cycle view of the supply chain is useful when consideringoperational decisions, because it categorizes processes based on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate27. The push/pull view of the supply chain is useful when consideringstrategic decisions relating to supply chain design, because itcategorizes processes based on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders. Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate28. The push/pull view of the supply chain is useful when consideringstrategic decisions relating to supply chain design, because itspecifies the roles and responsibilities of each member of the supplychain.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate29. Pull processes may also be referred to as reactive processes.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy30. Pull processes may also be referred to as speculative processes.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy31. Push processes may also be referred to as speculative processes.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy32. Push processes may also be referred to as reactive processes.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy33. All supply chain activities within a firm belong to one of three macroprocesses – CRM, ISCM and SRM.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy34. There is a close connection between the design and management of supplychain flows and the success of a supply chain.Answer: TrueDifficulty: EasyMultiple Choice1. Which of the following is not a stage within a typical supply chain?a. Customersb. Retailersc. Wholesalers/Distributorsd. Manufacturerse. All of the above are stages within a typical supply chain. Answer: eDifficulty: Easy2. Which of the following is not a stage within a typical supply chain?a. Customersb. Retailersc. Wholesalers/Distributorsd. Merchandiserse. Component/Raw material suppliersAnswer: dDifficulty: Easy3. Supply chain profitability isa. not correlated to the value generated by the various stages ofthe supply chain.b. the total profit to be shared across all supply chain stages.c. the difference between the revenue generated from the customer and the overall cost across the supply chain.d. the total revenue generated by the distributor stage of thesupply chain.e. b and c onlyAnswer: eDifficulty: Difficult4. Successful supply chain management requires which of the following decision phases?a. supply chain strategy/designb. supply chain planningc. supply chain operationd. all of the abovee. a and b onlyAnswer: dDifficulty: Moderate5. The decision phases in a supply chain includea. production scheduling.b. customer relationship management.c. supply chain operation.d. supply chain orientation.e. all of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Moderate6. The cycle view of a supply chain holds thata. the processes in a supply chain are divided into 2 categories.b. the processes in a supply chain are divided into a series of activities performed at the interface between successive stages.c. all processes in a supply chain are initiated in response to a customer order.d. all processes in a supply chain are performed in anticipation of customer orders.e. None of the above are true.Answer: bDifficulty: Moderate7. The push/pull view of a supply chain holds thata. the processes in a supply chain are divided into a series of activities performed at the interface between successive stages.b. all processes in a supply chain are initiated in response to a customer order.c. all response in a supply chain are performed in anticipation of customer orders.d. the processes in a supply chain are divided into 2 categories depending on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.e. None of the above are true.Answer: dDifficulty: Moderate8. Which of the following is not a cycle in the supply chain cycle view?a. Analysis cycleb. Customer order cyclec. Replenishment cycled. Manufacturing cyclee. Procurement cycleAnswer: aDifficulty: Moderate9. Which of the following is not a cycle in the supply chain cycle view?a. Customer order cycleb. Replenishment cyclec. Manufacturing cycled. Procurement cyclee. All of the above are part of the supply chain cycle view.Answer: eDifficulty: Moderate10. The customer order cycle occurs at thea. customer/retailer interface.b. retailer/distributor interface.c. distributor/manufacturer interface.d. manufacturer/supplier interface.e. none of the aboveAnswer: aDifficulty: Easy11. Which of the following is not a process in the customer order cycle?a. Customer arrivalb. Customer qualificationc. Customer order entryd. Customer order fulfillmente. Customer order receivingAnswer: bDifficulty: Moderate12. Customer arrival refers toa. the point in time when the customer has access to choices and makes a decision regarding a purchase.b. the customer informing the retailer of what they want to purchase and the retailer allocating product to the customer.c. the process where product is prepared and sent to the customer.d. the process where the customer receives the product and takesownership.e. none of the aboveAnswer: aDifficulty: Moderate13. The objective of the customer arrival process is toa. get the correct orders to customers by the promised due date at the lowest possible cost.b. maintain a record of product receipt and complete payment.c. maximize the conversion of customer arrivals to customer orders.d. ensure that orders are quickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affected supply chain processes.e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Easy14. Customer order entry isa. the point in time when the customer has access to choices and makes a decision regarding a purchase.b. the customer informing the retailer of what they want to purchase and the retailer allocating product to the customer.c. the process where product is prepared and sent to the customer.d. the process where the customer receives the product and takes ownership.e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Moderate15. The objective of customer order entry is toa. get the correct orders to customers by the promised due date at the lowest possible cost.b. maintain a record of product receipt and complete payment.c. maximize the conversion of customer arrivals to customer orders.d. ensure that orders are quickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affected supply chain processes.e. none of the aboveAnswer: dDifficulty: Easy16. Customer order fulfillment refers toa. the point in time when the customer has access to choices and makes a decision regarding a purchase.b. the customer informing the retailer of what they want to purchase and the retailer allocating product to the customer.c. the process where product is prepared and sent to the customer.d. the process where the customer receives the product and takes ownership.e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Moderate17. The objective of customer order fulfillment is toa. get the correct orders to customers by the promised due date at the lowest possible cost.b. maintain a record of product receipt and complete payment.c. maximize the conversion of customer arrivals to customer orders.d. ensure that orders are quickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affected supply chain processes.e. none of the aboveAnswer: aDifficulty: Easy18. Customer order receiving isa. the point in time when the customer has access to choices and makes a decision regarding a purchase.b. the customer informing the retailer of what they want to purchase and the retailer allocates product to the customer.c. the process where product is prepared and sent to the customer.d. the process where the customer receives the product and takes ownership.e. none of the aboveAnswer: dDifficulty: Moderate19. The replenishment cycle occurs at thea. customer/retailer interface.b. retailer/distributor interface.c. distributor/manufacturer interface.d. manufacturer/supplier interface.e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Easy20. The processes involved in the replenishment cycle includea. retail order receiving.b. retail order entry.c. retail order trigger.d. retail order fulfillment.e. all of the aboveAnswer: eDifficulty: Moderate21. The processes included in the replenishment cycle include all of the following excepta. retail order receiving.b. retail order entry.c. retail order trigger.d. retail order fulfillment.e. none of the aboveAnswer: eDifficulty: Moderate22. The processes included in the replenishment cycle includea. order arrival.b. production scheduling.c. retail trigger.d. manufacturing.e. receiving.Answer: cDifficulty: Moderate23. The replenishment cycle is initiated whena. the customer walks into the supermarket.b. the customer calls a mail order telemarketing center.c. customers load items intended for purchase into their carts.d. a supermarket runs out of stock of a particular item.e. a product is received into stock at a store.Answer: dDifficulty: Hard24. The manufacturing cycle occurs at thea. customer/retailer interface.b. retailer/distributor interface.c. distributor/manufacturer interface.d. manufacturer/supplier interface.e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Easy25. The processes involved in the manufacturing cycle includea. receiving.b. manufacturing and shipping.c. production scheduling.d. order arrival.e. all of the aboveAnswer: eDifficulty: Moderate26. The processes involved in the manufacturing cycle includea. order trigger.b. production scheduling.c. order fulfillment.d. order entry.e. manufacturing order analysis.Answer: bDifficulty: Moderate27. The production scheduling process in the manufacturing cycle is similar to thea. order receiving process in the replenishment cycle.b. order fulfillment process in the replenishment cycle.c. order entry process in the replenishment cycle.d. order trigger process in the replenishment cycle.e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Hard28. The manufacturing and shipping process in the manufacturing cycle is equivalent to thea. order receiving process in the replenishment cycle.b. order fulfillment process in the replenishment cycle.c. order entry process in the replenishment cycle.d. order trigger process in the replenishment cycle.e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Hard29. The procurement cycle occurs at thea. customer/retailer interface.b. retailer/distributor interface.c. distributor/manufacturer interface.d. manufacturer/supplier interface.e. none of the aboveAnswer: dDifficulty: Easy30. The relationship between the manufacturer and supplier during the procurement cycle is very similar to the relationship betweena. customer and retailer.b. retailer and distributor.c. retailer and manufacturer.d. distributor and manufacturer.e. manufacturer and customer.Answer: dDifficulty: Moderate31. The cycle view of the supply chain is useful when considering operational decisions, becausea. it categorizes processes based on whether they are initiated inresponse to or in anticipation of customer orders.b. it specifies the roles and responsibilities of each member of the supply chain.c. processes are identified as either reactive or speculative.d. it focuses on processes that are external to the firm.e. it focuses on processes that are internal to the firm.Answer: bDifficulty: Hard32. The push/pull view of the supply chain is useful when considering strategic decisions relating to supply chain design, becausea. it categorizes processes based on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.b. it specifies the roles and responsibilities of each member of the supply chain.c. it clearly defines the processes involved and the owners of each process.d. it focuses on processes that are external to the firm.e. it focuses on processes that are internal to the firm.Answer: aDifficulty: Hard33. Which of the following statements about pull processes is accurate?a. May also be referred to as speculative processes.b. Execution is initiated in anticipation of customer orders.c. At the time of execution, demand must be forecast.d. May also be referred to as reactive processes.e. None of the above are accurate.Answer: dDifficulty: Easy34. Which of the following is not an accurate statement about pull processes?a. May also be referred to as speculative processes.b. Execution is initiated in response to a customer order.c. At the time of execution, demand is known with certainty.d. May also be referred to as reactive processes.e. All of the above are accurate.Answer: aDifficulty: Easy35. Which of the following statements about push processes is accurate?a. May also be referred to as speculative processes.b. Execution is initiated in response to customer orders.c. At the time of execution, demand is known with certainty.d. May also be referred to as reactive processes.e. None of the above are accurate.Answer: aDifficulty: Easy36. Which of the following is not an accurate statement about push processes?a. May also be referred to as speculative processes.b. Execution is initiated in anticipation of customer orders.c. At the time of execution, demand must be forecast.d. May also be referred to as reactive processes.e. All of the above are accurate.Answer: dDifficulty: Easy37. Supply chain macro processes include which of the following?a. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)b. Internal Supply Chain Management (ISCM)c. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)d. all of the abovee. none of the aboveAnswer: dDifficulty: Easy38. Supply chain macro processes include which of the following?a. Internal Relationship Management (IRM)b. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)c. External Relationship Management (ERM)d. Supply Chain Relationship Management (SCRM)e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Moderate39. Supply chain macro processes include which of the following?a. Internal Relationship Management (IRM)b. External Relationship Management (ERM)c. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)d. Supply Chain Relationship Management (SCRM)e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Moderate40. Activities involved in the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) macro process includea. planning of internal production and storage.b. order fulfillment.c. marketing.d. supply planning.e. demand planning.Answer: cDifficulty: Hard41. Activities involved in the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) macro process include all of the following excepta. demand planning.b. marketing.c. sales.d. order management.e. call center management.Answer: aDifficulty: Hard42. Activities involved in the Internal Supply Chain Management (ISCM) macro process includea. marketing.b. order fulfillment.c. sales.d. order management.e. call center management.Answer: bDifficulty: Hard43. Activities involved in the Internal Supply Chain Management (ISCM) macro process include all of the following excepta. planning of internal production and storage.b. order fulfillment.c. supply planning.d. demand planning.e. order management.Answer: eDifficulty: Hard44. Activities involved in the Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) macro process includea. planning of internal production and storage.b. order fulfillment.c. supply planning.d. supplier evaluation and selection.e. order management.Answer: dDifficulty: Moderate45. Activities involved in the Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) macro process include all of the following excepta. negotiation of supply terms.b. design collaboration.c. supply planning.d. supplier evaluation and selection.e. supply collaboration.Answer: cDifficulty: Hard46. The phenomenal success of 7-Eleven Japan is attributed toa. being in the right place at the right time.b. its supply chain design and management ability.c. having 9000 locations.d. serving fresh food.e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Moderate47. A key issue facing Toyota isa. developing an internet marketing system.b. whether to specialize in a particular market.c. design of its global production and distribution network.d. how to implement model changes.e. all of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: HardEssay/Problems1. Explain the 3 decision phases (categories) that must be made in asuccessful supply chain.Answer: The 3 decision phases that occur within a supply chain aresupply chain strategy (or design), supply chain planning and supplychain operation. Decisions relate to the flow of information, productand funds. The difference between categories depends upon the frequency of each decision and the time frame over which it has an impact. During the supply chain strategy phase, a company determines what the chain’s configurations will be, how resources will be allocated, and whatprocesses each stage will perform. This will establish the structure of the supply chain for several years. Supply chain planning deals withdecisions with a time frame from 3 months up to a year. The planning。

商学院《供应链管理》三习题库(课程学分:3学分)物流管理系:方智勇第1章供应链概述一、预习题:(一)案例分析题阅读P1导入案例:沃尔玛神话般成功的关键----高效的供应链管理思考题:(1) 总体而言,沃尔玛的成功要素有哪些?(2) 沃尔玛高效的供应链管理表现在哪些方面?(二)简答题1、简述供应链的结构属性。
2、简述供应链节点属性的内容。
3、何谓供应链管理?4、供应链管理的本质是什么?5、供应链管理的目标是什么?6、供应链管理的核心功能有哪些?7、供应链管理的延伸功能有哪些?8、简述供应链计划的内容。
9、举例说明供应链流动路径。
二、练习题(一)单选题1.在产品供应链中既包括物料的流动,又包括()的流动。
A. 信息和成本B. 资金和信息C. 人员和设备D. 资金和设备2. 根据CSCMP的定义,供应链管理与企业物流管理的根本区别在于()。
A. 利润的最大化B. 不确定性C. 跨组织特性D. 满足客户需求3.供应链的主要成员包括:原料供应商、产品生产商、批发商、零售商和()。
A. 运输企业B. 提供生产设备的企业C. 提供贷款的银行D. 物流服务提供商4. 在维持同样客户服务水平的情况下,增加网络设施数目,将会导致库存水平的()。
A. 增加B. 下降C. 先增加后下降D. 没有明显变化(二)判断题1、供应链的水平结构是指供应链的层次数目。
2、供应链的垂直结构是指每一层所包含的供应商数目或客户的数目。
3、供应链的需求端说明了需求的来源。
4、供应链的供应端表示供应的来源,称为供应链的下游。
5、供应链的核心功能包括向上下游延伸的功能。
6、因为运作决策时长期的,所以需求信息的不确定性较低。
7、供应链的次要成员是指仅仅提供资源、知识或主要成员提供协助的企业。
8、供应链的每个节点包括库存、资源和技术等三个要素。
9、流动路径和节点构成了实体供应链的网络。
10、长期战略决策介于供应链计划和运作管理之间。
三、复习题(一)简答题1、供应链网络规模如何刻画?2、供应链管理的主要功能有哪些?3、简述供应链结构的一般形式。

供应链管理师三级实操考试题库1. 供应链管理中,如何进行供应商的初步筛选?A. 完全依据价格B. 依据供应商的规模C. 综合考虑供应商的质量、价格、交货时间等因素D. 仅考虑供应商的地理位置【答案】C2. 在供应链中,如何降低库存成本?A. 减少安全库存B. 增加订购批量C. 提高运输效率D. 定期进行库存盘点【答案】A3. 供应链中的牛鞭效应是什么?A. 需求信息在供应链中的传递过程中逐渐放大B. 供应信息在供应链中的传递过程中逐渐放大C. 库存在供应链中的分布不均匀D. 运输成本在供应链中的波动【答案】A4. 以下哪个不属于供应链管理的主要环节?A. 采购B. 生产C. 销售与营销D. 人力资源管理【答案】D5. 如何制定供应链中的运输计划?A. 仅考虑运输成本B. 仅考虑运输时间C. 综合考虑运输成本、时间、服务质量等因素D. 依据供应商的偏好【答案】C6. 供应链风险管理中,以下哪个措施不正确?A. 选择多家供应商以降低供应风险B. 增加库存以应对需求波动C. 定期进行供应链审计D. 忽视市场变化,保持原有供应链结构【答案】D7. 在供应链协调中,如何解决供应链各方之间的利益冲突?A. 强化市场竞争B. 建立合作伙伴关系C. 提高供应链透明度D. 增加供应链环节【答案】B8. 供应链中的VMI(Vendor Managed Inventory)系统是什么?A. 一种由供应商负责管理的库存系统B. 一种由分销商负责管理的库存系统C. 一种由零售商负责管理的库存系统D. 一种由第三方物流公司负责管理的库存系统【答案】A9. 供应链中的ERP(Enterprise Resource Planning)系统主要功能是什么?A. 仅用于财务管理和人力资源管理B. 仅用于生产管理和库存管理C. 集成企业内部各部门的信息系统,实现资源优化配置D. 仅用于销售管理和客户关系管理【答案】C10. 在供应链管理中,以下哪个指标不属于衡量供应链绩效的关键指标?A. 订单履行率B. 库存周转率C. 供应链总成本D. 员工满意度【答案】D。

供应链管理-第三版-Unit1-习题与答案Chapter 1Understanding the Supply ChainTrue/False1. A supply chain includes only the organizations directly involved insupplying components needed for manufacturing.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate2. A supply chain consists of all parties involved, directly or indirectly,in fulfilling a customer request.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate3. A supply chain could be more accurately described as a supply network orsupply web.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate4. The objective of every supply chain is to maximize the overall valuegenerated.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy5. The objective of every supply chain is to maximize the value generatedfor the manufacturing component of the supply chain.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate6. Every supply chain must include all 5 stages.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy7. The cycle view of a supply chain holds that the processes in a supplychain are divided into a series of activities performed at the interface between successive stages. Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate8. The cycle view of a supply chain holds that the processes in a supplychain are divided into 2 categories depending on whether they areinitiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate9. The push/pull view of a supply chain holds that the processes in asupply chain are divided into 2 categories depending on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy10. The push/pull view of a supply chain holds that the processes in asupply chain are divided into a series of activities performed at theinterface between successive stages.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy11. The objective of the customer arrival process is to maximize theconversion of customer arrivals to customer orders.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate12. The objective of the customer arrival process is to ensure that ordersare quickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affectedsupply chain processes.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate13. The objective of customer order entry is to ensure that orders arequickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affected supply chain processes.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate14. The objective of customer order entry is to maintain a record of productreceipt and complete payment.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Hard15. The replenishment cycle occurs at the retailer/distributor interface.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Hard16. The replenishment cycle occurs at the distributor/manufacturer interface.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Hard17. The replenishment cycle is initiated when a supermarket runs out ofstock of a particular item.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Hard18. The replenishment cycle is initiated when customers load items intendedfor purchase into their carts.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Hard19. The manufacturing cycle occurs at the distributor/manufacturer interface.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate20. The manufacturing cycle occurs at the manufacturer/supplier interface.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate21. The production scheduling process in the manufacturing cycle is similarto the order entry process in the replenishment cycle.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Hard22. The production scheduling process in the manufacturing cycle is similarto the order fulfillment process in the replenishment cycle.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Hard23. The procurement cycle occurs at the manufacturer/supplier interface.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy24. The procurement cycle occurs at the retailer/distributor interface.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy25. The cycle view of the supply chain is useful when consideringoperational decisions, because it specifies the roles andresponsibilities of each member of the supply chain.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate26. The cycle view of the supply chain is useful when consideringoperational decisions, because it categorizes processes based on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate27. The push/pull view of the supply chain is useful when consideringstrategic decisions relating to supply chain design, because itcategorizes processes based on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders. Answer: TrueDifficulty: Moderate28. The push/pull view of the supply chain is useful when consideringstrategic decisions relating to supply chain design, because itspecifies the roles and responsibilities of each member of the supplychain.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Moderate29. Pull processes may also be referred to as reactive processes.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy30. Pull processes may also be referred to as speculative processes.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy31. Push processes may also be referred to as speculative processes.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy32. Push processes may also be referred to as reactive processes.Answer: FalseDifficulty: Easy33. All supply chain activities within a firm belong to one of three macroprocesses – CRM, ISCM and SRM.Answer: TrueDifficulty: Easy34. There is a close connection between the design and management of supplychain flows and the success of a supply chain.Answer: TrueDifficulty: EasyMultiple Choice1. Which of the following is not a stage within a typical supply chain?a. Customersb. Retailersc. Wholesalers/Distributorsd. Manufacturerse. All of the above are stages within a typical supply chain. Answer: eDifficulty: Easy2. Which of the following is not a stage within a typical supply chain?a. Customersb. Retailersc. Wholesalers/Distributorsd. Merchandiserse. Component/Raw material suppliersAnswer: dDifficulty: Easy3. Supply chain profitability isa. not correlated to the value generated by the various stages ofthe supply chain.b. the total profit to be shared across all supply chain stages.c. the difference between the revenue generated from the customer and the overall cost across the supply chain.d. the total revenue generated by the distributor stage of thesupply chain.e. b and c onlyAnswer: eDifficulty: Difficult4. Successful supply chain management requires which of the following decision phases?a. supply chain strategy/designb. supply chain planningc. supply chain operationd. all of the abovee. a and b onlyAnswer: dDifficulty: Moderate5. The decision phases in a supply chain includea. production scheduling.b. customer relationship management.c. supply chain operation.d. supply chain orientation.e. all of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Moderate6. The cycle view of a supply chain holds thata. the processes in a supply chain are divided into 2 categories.b. the processes in a supply chain are divided into a series of activities performed at the interface between successive stages.c. all processes in a supply chain are initiated in response to a customer order.d. all processes in a supply chain are performed in anticipation of customer orders.e. None of the above are true.Answer: bDifficulty: Moderate7. The push/pull view of a supply chain holds thata. the processes in a supply chain are divided into a series of activities performed at the interface between successive stages.b. all processes in a supply chain are initiated in response to a customer order.c. all response in a supply chain are performed in anticipation of customer orders.d. the processes in a supply chain are divided into 2 categories depending on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.e. None of the above are true.Answer: dDifficulty: Moderate8. Which of the following is not a cycle in the supply chain cycle view?a. Analysis cycleb. Customer order cyclec. Replenishment cycled. Manufacturing cyclee. Procurement cycleAnswer: aDifficulty: Moderate9. Which of the following is not a cycle in the supply chain cycle view?a. Customer order cycleb. Replenishment cyclec. Manufacturing cycled. Procurement cyclee. All of the above are part of the supply chain cycle view.Answer: eDifficulty: Moderate10. The customer order cycle occurs at thea. customer/retailer interface.b. retailer/distributor interface.c. distributor/manufacturer interface.d. manufacturer/supplier interface.e. none of the aboveAnswer: aDifficulty: Easy11. Which of the following is not a process in the customer order cycle?a. Customer arrivalb. Customer qualificationc. Customer order entryd. Customer order fulfillmente. Customer order receivingAnswer: bDifficulty: Moderate12. Customer arrival refers toa. the point in time when the customer has access to choices and makes a decision regarding a purchase.b. the customer informing the retailer of what they want to purchase and the retailer allocating product to the customer.c. the process where product is prepared and sent to the customer.d. the process where the customer receives the product and takesownership.e. none of the aboveAnswer: aDifficulty: Moderate13. The objective of the customer arrival process is toa. get the correct orders to customers by the promised due date at the lowest possible cost.b. maintain a record of product receipt and complete payment.c. maximize the conversion of customer arrivals to customer orders.d. ensure that orders are quickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affected supply chain processes.e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Easy14. Customer order entry isa. the point in time when the customer has access to choices and makes a decision regarding a purchase.b. the customer informing the retailer of what they want to purchase and the retailer allocating product to the customer.c. the process where product is prepared and sent to the customer.d. the process where the customer receives the product and takes ownership.e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Moderate15. The objective of customer order entry is toa. get the correct orders to customers by the promised due date at the lowest possible cost.b. maintain a record of product receipt and complete payment.c. maximize the conversion of customer arrivals to customer orders.d. ensure that orders are quickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affected supply chain processes.e. none of the aboveAnswer: dDifficulty: Easy16. Customer order fulfillment refers toa. the point in time when the customer has access to choices and makes a decision regarding a purchase.b. the customer informing the retailer of what they want to purchase and the retailer allocating product to the customer.c. the process where product is prepared and sent to the customer.d. the process where the customer receives the product and takes ownership.e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Moderate17. The objective of customer order fulfillment is toa. get the correct orders to customers by the promised due date at the lowest possible cost.b. maintain a record of product receipt and complete payment.c. maximize the conversion of customer arrivals to customer orders.d. ensure that orders are quickly and accurately entered and communicated to other affected supply chain processes.e. none of the aboveAnswer: aDifficulty: Easy18. Customer order receiving isa. the point in time when the customer has access to choices and makes a decision regarding a purchase.b. the customer informing the retailer of what they want to purchase and the retailer allocates product to the customer.c. the process where product is prepared and sent to the customer.d. the process where the customer receives the product and takes ownership.e. none of the aboveAnswer: dDifficulty: Moderate19. The replenishment cycle occurs at thea. customer/retailer interface.b. retailer/distributor interface.c. distributor/manufacturer interface.d. manufacturer/supplier interface.e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Easy20. The processes involved in the replenishment cycle includea. retail order receiving.b. retail order entry.c. retail order trigger.d. retail order fulfillment.e. all of the aboveAnswer: eDifficulty: Moderate21. The processes included in the replenishment cycle include all of the following excepta. retail order receiving.b. retail order entry.c. retail order trigger.d. retail order fulfillment.e. none of the aboveAnswer: eDifficulty: Moderate22. The processes included in the replenishment cycle includea. order arrival.b. production scheduling.c. retail trigger.d. manufacturing.e. receiving.Answer: cDifficulty: Moderate23. The replenishment cycle is initiated whena. the customer walks into the supermarket.b. the customer calls a mail order telemarketing center.c. customers load items intended for purchase into their carts.d. a supermarket runs out of stock of a particular item.e. a product is received into stock at a store.Answer: dDifficulty: Hard24. The manufacturing cycle occurs at thea. customer/retailer interface.b. retailer/distributor interface.c. distributor/manufacturer interface.d. manufacturer/supplier interface.e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Easy25. The processes involved in the manufacturing cycle includea. receiving.b. manufacturing and shipping.c. production scheduling.d. order arrival.e. all of the aboveAnswer: eDifficulty: Moderate26. The processes involved in the manufacturing cycle includea. order trigger.b. production scheduling.c. order fulfillment.d. order entry.e. manufacturing order analysis.Answer: bDifficulty: Moderate27. The production scheduling process in the manufacturing cycle is similar to thea. order receiving process in the replenishment cycle.b. order fulfillment process in the replenishment cycle.c. order entry process in the replenishment cycle.d. order trigger process in the replenishment cycle.e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Hard28. The manufacturing and shipping process in the manufacturing cycle is equivalent to thea. order receiving process in the replenishment cycle.b. order fulfillment process in the replenishment cycle.c. order entry process in the replenishment cycle.d. order trigger process in the replenishment cycle.e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Hard29. The procurement cycle occurs at thea. customer/retailer interface.b. retailer/distributor interface.c. distributor/manufacturer interface.d. manufacturer/supplier interface.e. none of the aboveAnswer: dDifficulty: Easy30. The relationship between the manufacturer and supplier during the procurement cycle is very similar to the relationship betweena. customer and retailer.b. retailer and distributor.c. retailer and manufacturer.d. distributor and manufacturer.e. manufacturer and customer.Answer: dDifficulty: Moderate31. The cycle view of the supply chain is useful when considering operational decisions, becausea. it categorizes processes based on whether they are initiated inresponse to or in anticipation of customer orders.b. it specifies the roles and responsibilities of each member of the supply chain.c. processes are identified as either reactive or speculative.d. it focuses on processes that are external to the firm.e. it focuses on processes that are internal to the firm.Answer: bDifficulty: Hard32. The push/pull view of the supply chain is useful when considering strategic decisions relating to supply chain design, becausea. it categorizes processes based on whether they are initiated in response to or in anticipation of customer orders.b. it specifies the roles and responsibilities of each member of the supply chain.c. it clearly defines the processes involved and the owners of each process.d. it focuses on processes that are external to the firm.e. it focuses on processes that are internal to the firm.Answer: aDifficulty: Hard33. Which of the following statements about pull processes is accurate?a. May also be referred to as speculative processes.b. Execution is initiated in anticipation of customer orders.c. At the time of execution, demand must be forecast.d. May also be referred to as reactive processes.e. None of the above are accurate.Answer: dDifficulty: Easy34. Which of the following is not an accurate statement about pull processes?a. May also be referred to as speculative processes.b. Execution is initiated in response to a customer order.c. At the time of execution, demand is known with certainty.d. May also be referred to as reactive processes.e. All of the above are accurate.Answer: aDifficulty: Easy35. Which of the following statements about push processes is accurate?a. May also be referred to as speculative processes.b. Execution is initiated in response to customer orders.c. At the time of execution, demand is known with certainty.d. May also be referred to as reactive processes.e. None of the above are accurate.Answer: aDifficulty: Easy36. Which of the following is not an accurate statement about push processes?a. May also be referred to as speculative processes.b. Execution is initiated in anticipation of customer orders.c. At the time of execution, demand must be forecast.d. May also be referred to as reactive processes.e. All of the above are accurate.Answer: dDifficulty: Easy37. Supply chain macro processes include which of the following?a. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)b. Internal Supply Chain Management (ISCM)c. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)d. all of the abovee. none of the aboveAnswer: dDifficulty: Easy38. Supply chain macro processes include which of the following?a. Internal Relationship Management (IRM)b. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)c. External Relationship Management (ERM)d. Supply Chain Relationship Management (SCRM)e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Moderate39. Supply chain macro processes include which of the following?a. Internal Relationship Management (IRM)b. External Relationship Management (ERM)c. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)d. Supply Chain Relationship Management (SCRM)e. none of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: Moderate40. Activities involved in the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) macro process includea. planning of internal production and storage.b. order fulfillment.c. marketing.d. supply planning.e. demand planning.Answer: cDifficulty: Hard41. Activities involved in the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) macro process include all of the following excepta. demand planning.b. marketing.c. sales.d. order management.e. call center management.Answer: aDifficulty: Hard42. Activities involved in the Internal Supply Chain Management (ISCM) macro process includea. marketing.b. order fulfillment.c. sales.d. order management.e. call center management.Answer: bDifficulty: Hard43. Activities involved in the Internal Supply Chain Management (ISCM) macro process include all of the following excepta. planning of internal production and storage.b. order fulfillment.c. supply planning.d. demand planning.e. order management.Answer: eDifficulty: Hard44. Activities involved in the Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) macro process includea. planning of internal production and storage.b. order fulfillment.c. supply planning.d. supplier evaluation and selection.e. order management.Answer: dDifficulty: Moderate45. Activities involved in the Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) macro process include all of the following excepta. negotiation of supply terms.b. design collaboration.c. supply planning.d. supplier evaluation and selection.e. supply collaboration.Answer: cDifficulty: Hard46. The phenomenal success of 7-Eleven Japan is attributed toa. being in the right place at the right time.b. its supply chain design and management ability.c. having 9000 locations.d. serving fresh food.e. none of the aboveAnswer: bDifficulty: Moderate47. A key issue facing Toyota isa. developing an internet marketing system.b. whether to specialize in a particular market.c. design of its global production and distribution network.d. how to implement model changes.e. all of the aboveAnswer: cDifficulty: HardEssay/Problems1. Explain the 3 decision phases (categories) that must be made in asuccessful supply chain.Answer: The 3 decision phases that occur within a supply chain aresupply chain strategy (or design), supply chain planning and supplychain operation. Decisions relate to the flow of information, productand funds. The difference between categories depends upon the frequency of each decision and the time frame over which it has an impact. During the supply chain strategy phase, a company determines what the chain’s configurations will be, how resources will be allocated, and whatprocesses each stage will perform. This will establish the structure of the supply chain for several years. Supply chain planning deals withdecisions with a time frame from 3 months up to a year. The planning。
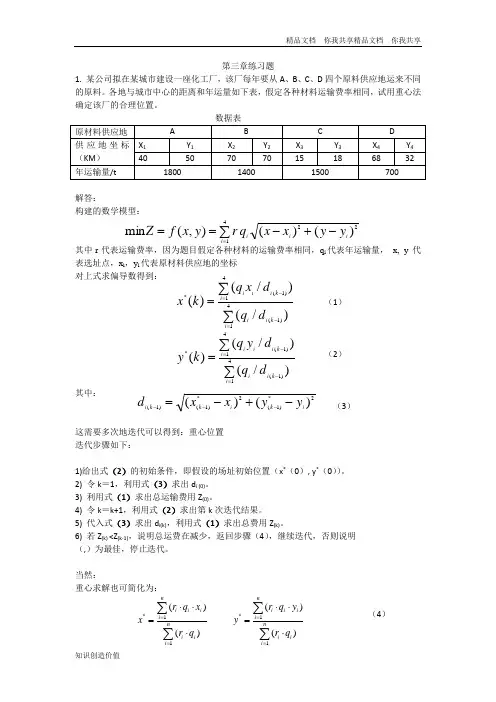
第三章练习题1. 某公司拟在某城市建设一座化工厂,该厂每年要从A 、B 、C 、D 四个原料供应地运来不同的原料。
各地与城市中心的距离和年运量如下表,假定各种材料运输费率相同,试用重心法确定该厂的合理位置。
解答:构建的数学模型:其中r 代表运输费率,因为题目假定各种材料的运输费率相同,q i 代表年运输量, x, y 代表选址点,x i ,y i 代表原材料供应地的坐标 对上式求偏导数得到:(1)(2)其中: (3)这需要多次地迭代可以得到:重心位置 迭代步骤如下:1)给出式(2)的初始条件,即假设的场址初始位置(x *(0), y *(0))。
2) 令k =1,利用式(3)求出d i (0)。
3) 利用式(1)求出总运输费用Z (0)。
4) 令k =k+1,利用式(2)求出第k 次迭代结果。
5) 代入式(3)求出d i(k),利用式(1)求出总费用Z (k)。
6) 若Z (k) <Z (k-1),说明总运费在减少,返回步骤(4),继续迭代,否则说明 (,)为最佳,停止迭代。
当然:重心求解也可简化为:(4)2241)()(),(min i i i i y y x x q r y x f Z -+-==∑=∑∑=-=-=41)1(41)1(*)/()/()(i k i i i k i i i d q d x q k x ∑∑=-=-=41)1(41)1(*)/()/()(i k i i i k i i i d q d y q k y 2*)1(2*)1()1()()(i k i k k i y y x x d -+-=---*11()()ni i i i n iii r q x x r q ==⋅⋅=⋅∑∑ *11()()n i i i i n iii r q y y r q ==⋅⋅=⋅∑∑因为假定各种材料的运输费率相同,因此根据(4),可得出:选址点的坐标为(44.5公里,44公里)2. DryIce 公司是一家空调设备制造商,它看到期市场需求量增长迅速。

Chapter 3: Customer Relationship Management Study Questions1.Explain the differences between transactional and relationship marketing. How do these differenceslead to increasing emphasis on logistical performance in supply chain management?Transactional marketing is generally focused towards short-term interaction with customers. Traditional marketing strategies followed this approach wherein exchanges/transactions are carried out with customers in order to increase their revenues and profits.Relationship marketing focuses on the long-term relations with the key supply chain partners such as the consumers, intermediate customers and suppliers. This strategy aims to develop and retain long term preference and loyalty because it has been realized in many industries that it is more important to obtain greater share of the purchases made by the existing customers than to attract new customers. This approach tries to identify the individual customers in order to satisfy their unique needs in the most cost-efficient and effective way. This requires a greater emphasis on logistical performance of the entire supply chain.2.Why are the four primary service outputs of spatial convenience, lot size, waiting time, and productvariety important to logistics management? Provide examples of competing firms that differ in the level of each service output provided to customers.Since every customer has different requirements regarding service outputs, spatial convenience, lot size, waiting or delivery time, and product variety represent the four generic outputs to accommodate customer requirements.Spatial convenience measures the amount of shopping time and effort that needs to be out by the customer.Higher convenience is offered by making the product available in more number of places. As an example some household furniture manufacturers offer their products through department store, mass merchandisers and other independent department stores whereas Ethan Allen offers its products only at its own retail stores.Lot size refers to the number of units that can be purchased in each transaction. A customer who wishes to buy larger quantity of items for example 12 or 24 rolls of paper towels to get a lower unit price can get it from Sam’s Club and Costco. However they can buy single rolls from grocery or convenient stores. The basic tradeoff in such purchases is between the unit price and the storage or maintenance cost of such volumes.Waiting time is the amount if time a customer has to wait between ordering and receiving products. The lower the waiting time, the higher is the level of service. Buying products from retail or grocery stores has no waiting time however if someone wants to order from a catalog or via the Internet, he has to wait for the product.Although higher waiting time is associated with inconvenience, customers are rewarded in the form of lower prices.Product variety refers to the different assortments or variety offered to the consumers and end-users.Supermarkets offer a large variety of items, whereas the warehouse stores offer a much less variety. And convenience stores offer even lesser variety.ing the ten categories of customer expectations in Table 3-2, develop your own examples of howcustomers might evaluate performance of a supplier.Reliability refers to performance of all activities by the supplier. If FedEx promises overnight delivery and fails to do that, then it will be considered unreliable, even if it is done faster than any other provider. Customers can judge reliability in terms of all aspects of basic service platform.Responsiveness refers to the customer’s expectation of the ability and willingness to provide timely service. If WalM art experiences a stockout of certain product, its supplier’s responsiveness will be measured by the tim e it takes for replenishment.Access measures the ease of contact and approachability of the supplier. For example the ease of obtaining information about the status of a pending order will measure accessibility.Communication means to proactively keeping the customer informed. If the supplier expects a shortage of raw material that can affect delivery in the future, an advance notice to the customer will not only help to explore alternative but also builds a stronger partnership.Credibility refers to the customer’s expectation that the communication from the suppliers will be believable and honest. The real essence of this measure is the completeness of the information.Security refers to the customer’s feeling of risk in doing business with a supplier. For example a customer bases its production schedule in anticipation of delivery. If the supply is delayed the customer faces the risk of changing its plans. Another aspect of security concerns the confidentiality of business dealings. For example, Solectron undertakes the manufacturing for competitors like Nortel and Cisco, so confidentiality is a major issue.Courtesy involves politeness, friendliness and respect of contact person. Since the customer may have to deal with different individuals in the supp lier’s organization, failure by one person can destroy the best efforts of all the others.Competency is judged by customers in every interaction with the suppliers. Therefore a truck driver’s competency is measured when deliveries are made, customer service personnel when phone calls are made, etc. Failure by any individual can affect the customer’s perception of the supplier.Tangibles refer to the customer’s expectation of the physical appearance of facilities, equipment and personnel. For example an old and dilapidated warehouse can be an indicator of the firm’s overall performance to the customers.Knowing the customer refers to the customer’s expectation regarding supplier’s understanding of their unique requirements and supplier willingness to adapt to those needs. For example WalMart would expect its suppliers to understand its unique need and respond to that accordingly.pare and contrast the customer service, customer satisfaction, and customer success philosophiesof supply chain management.Customer service, customer satisfaction, and customer represent three levels of customer accommodation.Customer service represents logistics role in fulfilling the marketing concept. It aims to provide the right amount of the right product at the right time at the right place in the right condition at the right price with right information. The fundamental attributes of customer service are availability, operational performance, and service reliability. Customer satisfaction measures the degree to which a customer is satisfied with the supplier’s performance. However, customer satisfactions depends on the customer’s expectations. Models have been developed to identify some of the gaps that arise due the failure of many firms to satisfy their customers.Customer success philosophy requires the firms to work very closely with the customers to understand their requirements, internal processes, competitive environment and try to make their customer successful. In contrast to the typical focus of basic service and satisfaction programs to meet standards and expectations of the customers, a customer success program tries to understand the entire supply chain, different levels of customers and tries to ensure that customer at each level is able to meet their customers.5.What is meant by value-added services? Why are these services considered essential in a customersuccess program?Value added services refer to the unique and specific activities that firms can jointly perform to enhance their efficiency and effectiveness. Such services foster customer success. These services are typically customer specific and therefore cannot be generalized. These services enable the customers to achieve their specific objectives. These are considered essential in customer service programs because by providing unique product packages, creating customized unit loads, offering unique information services, providing VMI, etc, firms enhance their customers’ success. Some of the value-added services like warehousing, transportation, proper sequencing and sorting of products involve specialists due to their flexibility and capability to concentrate on providing the required services.6. Explain the customer satisfaction “gaps” shown in Figure 3.1.The knowledge gap reflects management’s lack of knowledge or understanding of customers’ real expectations.The standards gap exists when internal performance standards do not accurately reflect those expectations.The performance gap arises when actual performance does not meet the standards for performance.Communications gaps exist when the firm does not meet its promises or commitments to customers. The perception gap exists when customers inaccurately perceive the actual performance of the firm. The satisfaction/quality gap arises when the custo mer’s perception of that performance is different from the performance that they expected.。
供应链管理形成性考核册答案供应链管理形成性考核册答案回目录供应链管理作业一答案:(第一---三章)一、名词解释:1、管理模式答:是一种系统化的指导与控制方法,它把企业中的人、财、物和信息等资源,高质量、低成本、快速及时地转换为市场所需要的产品和服务。
2、供应链设计答:供应链设计是企业规模的设计,是从企业整体的角度勾画企业蓝图,是扩展的企业模型3、供应链合作伙伴关系答:一般是指在供应链内部两个或以上独立的成员之间形成的一种协调关系,以保证实现某个特定的目标或效益,也就是供应商-制造商关系,或者称为卖主/供应商-买主关系、供应商关系。
二、单项选择题1、供应链的概念是在( C )提出来的。
A. 20世纪60年代B.20世纪70年代C.20世纪80年代D.20世纪90年代2、供应链管理是一种( A )的管理思想和方法。
A.集成B.松散C.积极D.消极3、供应链的管理目标呈现出( C )特征。
A(一体化B(集成化C(多元化D(一元化4、供应链管理是通过企业之间共享库存信息和通过(D)传递信息。
A(条形码 B(全球定位系统C. 地理信息系统D(电子数据交换5、一个企业应尽可能考虑(D)供应商或分销商,这样有利于从整体上了解供应链的运行状态。
A(一级B(二级C(三级D(多级6、 (A)的产品能满足基本需要,不会有太大的变化,因而需求稳定且可以预测,并且生命周期长。
A(功能型B(革新型C(复合型D(单一型7、从核心企业战略发展的角度设计供应链,有助于建立稳定的(B )。
A(供应链规划B(供应链体系模型C(供应链D(供应链原则8、对于长期需求而言,合作伙伴要求能保持较高的竞争力和增值率,因此最好选择( A )A(战略性合作伙伴关系B(普通合作伙伴C. 竞争性合作伙伴 D(技术性合作伙伴9、(A)伙伴选择主要是面向上、下游企业关系的伙伴选择。
A(纵向 B. 横向C(侧向 D. 外向10、供应链是围绕(C)建立起来的。
Chapter 3 Supply Chain Drivers and Obstacles
True/False 1. The major drivers of supply chain performance are facilities, inventory, transportation, and information. Answer: True Difficulty: Moderate
2. The major drivers of supply chain performance are customers, facilities, inventory, transportation, and information. Answer: False Difficulty: Moderate
3. The two major types of facilities are production sites and storage sites. Answer: True Difficulty: Moderate
4. The two major types of facilities are distribution sites and storage sites. Answer: False Difficulty: Moderate
5. Inventory is an important supply chain driver because changing inventory policies can dramatically alter the supply chain’s efficiency and responsiveness. Answer: True Difficulty: Moderate
6. Information is potentially the biggest driver of performance in the supply chain as it directly affects each of the other drivers. Answer: True Difficulty: Easy
7. Information is potentially the biggest driver of performance in the supply chain even though it has little impact on each of the other drivers. Answer: False Difficulty: Easy
8. A facility with little excess capacity will likely be more efficient per unit of product it produces than one with a lot of unused capacity. Answer: True Difficulty: Easy
9. A facility with little excess capacity will likely be no more or less efficient per unit of product it produces than one with a lot of unused capacity. Answer: False Difficulty: Easy 10. The high utilization facility will have difficulty responding to demand fluctuations. Answer: True Difficulty: Easy
11. The high utilization facility will have no more difficulty responding to demand fluctuations than one with a lot of unused capacity. Answer: False Difficulty: Easy
12. Stock keeping unit (SKU) storage is the warehousing methodology that uses a traditional warehouse to store all of one type of product together. Answer: True Difficulty: Moderate
13. Warehouse unit storage is the warehousing methodology that uses a traditional warehouse to store all of one type of product together. Answer: False Difficulty: Moderate
14. The components of inventory decisions include cycle inventory, safety inventory, seasonal inventory, and sourcing. Answer: True Difficulty: Easy
15. The components of inventory decisions include capacity, cycle inventory, safety inventory, seasonal inventory, and sourcing. Answer: False Difficulty: Easy
16. Cycle inventory is inventory that is built up to counter predictable variability in demand. Answer: False Difficulty: Easy
17. Seasonal inventory is inventory that is built up to counter predictable variability in demand. Answer: True Difficulty: Moderate
18. Companies using seasonal inventory will build up inventory in periods of low demand and store it for periods of high demand when they will not have the capacity to produce all that is demanded. Answer: True Difficulty: Moderate
19. Companies using seasonal inventory will maintain a level inventory increase rate of production for periods of high demand. Answer: False Difficulty: Easy 20. A company’s ability to find a balance between responsiveness and efficiency that best matches the needs of the customer it is targeting is the key to achieving strategic fit. Answer: True Difficulty: Moderate
21. Many obstacles, such as growing product variety and shorter life cycles, have made it increasingly difficult for supply chains to achieve strategic fit. Answer: True Difficulty: Moderate
Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is not a major driver of supply chain performance? a. Facilities b. Inventory c. Transportation d. Information e. All of the above are major drivers of supply chain performance. Answer: e Difficulty: Easy
2. Which of the following is not a major driver of supply chain performance? a. Customers b. Facilities c. Inventory d. Transportation e. Information Answer: a Difficulty: Moderate
3. The places in the supply chain network where product is stored, assembled, or fabricated are known as a. facilities. b. inventory. c. transportation. d. information. e. customers. Answer: a Difficulty: Easy
4. All raw materials, work in process, and finished goods within a supply chain are known as a. facilities. b. inventory. c. transportation.