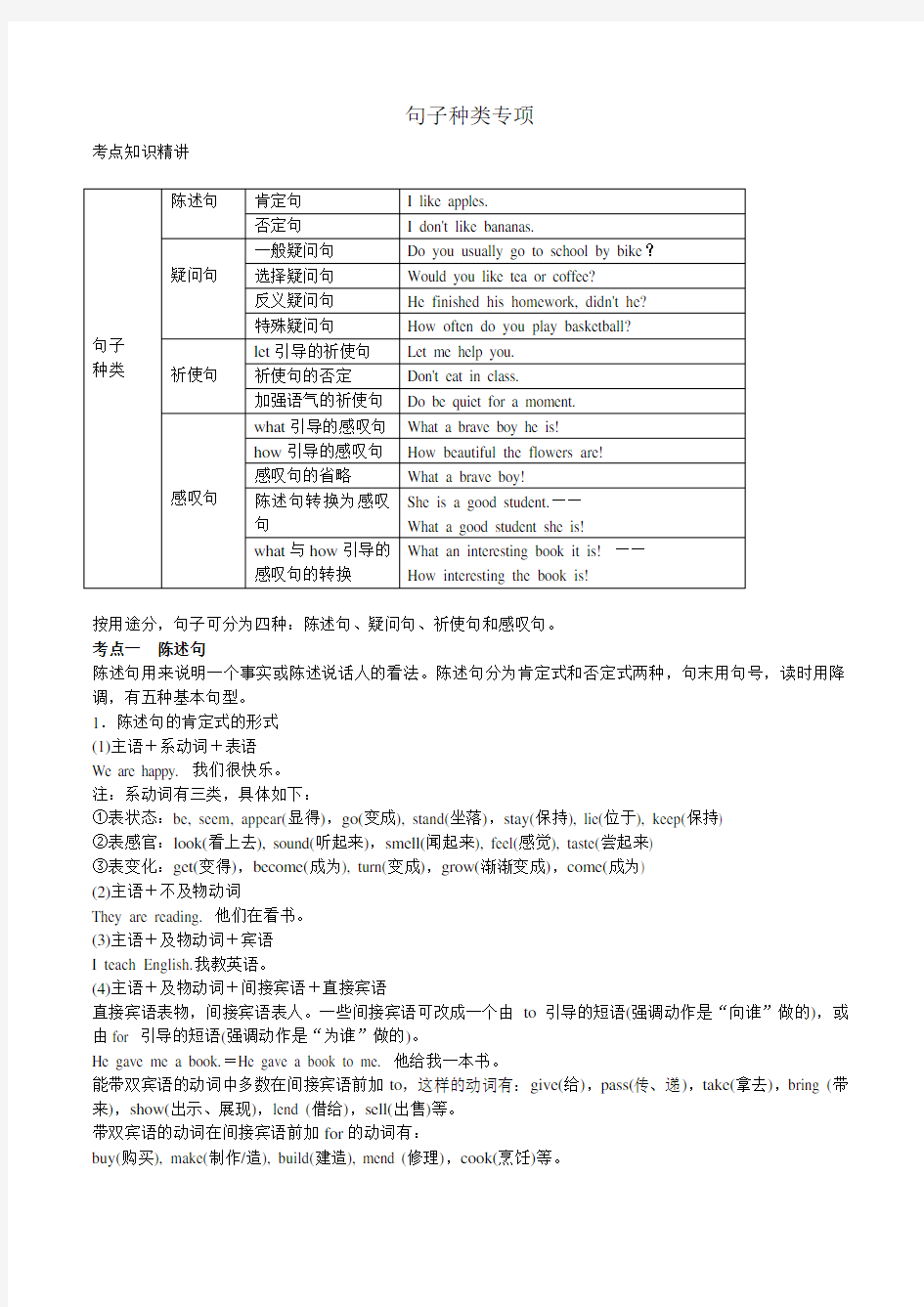

句子种类专项
考点知识精讲
按用途分,句子可分为四种:陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
考点一陈述句
陈述句用来说明一个事实或陈述说话人的看法。陈述句分为肯定式和否定式两种,句末用句号,读时用降调,有五种基本句型。
1.陈述句的肯定式的形式
(1)主语+系动词+表语
We are happy. 我们很快乐。
注:系动词有三类,具体如下:
①表状态:be, seem, appear(显得),go(变成), stand(坐落),stay(保持), lie(位于), keep(保持)
②表感官:look(看上去), sound(听起来),smell(闻起来), feel(感觉), taste(尝起来)
③表变化:get(变得),become(成为), turn(变成),grow(渐渐变成),come(成为)
(2)主语+不及物动词
They are reading. 他们在看书。
(3)主语+及物动词+宾语
I teach English.我教英语。
(4)主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语
直接宾语表物,间接宾语表人。一些间接宾语可改成一个由to引导的短语(强调动作是“向谁”做的),或由for 引导的短语(强调动作是“为谁”做的)。
He gave me a book.=He gave a book to me. 他给我一本书。
能带双宾语的动词中多数在间接宾语前加to,这样的动词有:give(给),pass(传、递),take(拿去),bring (带来),show(出示、展现),lend (借给),sell(出售)等。
带双宾语的动词在间接宾语前加for的动词有:
buy(购买), make(制作/造), build(建造), mend (修理),cook(烹饪)等。
My mother bought me a present.
=My mother bought a present for me.
我妈妈给我买了件礼物。
(5)主语+及物动词+宾语+宾补
You'd better tell the students not to make so much noise.
你最好告诉学生们不要这么大声吵闹。
①带to的不定式作宾补的动词有:tell,ask,order,want等。
②省略to的不定式作宾补的动词有:feel,hear,see,notice,have/make/let等。
2.否定句
(1)含be动词、助动词、情态动词的否定。
如果句子的谓语动词是be, have、助动词或情态动词,在它们之后加not 构成否定句。
Tom can't swim.汤姆不会游泳。
(2)行为动词的否定。
如果句子的动词是行为动词而又没有助动词或情态动词,在谓语前加do的相应形式后再加not。
They didn't want to take pictures.
他们不想拍照片。
(3)还可用nothing等否定代词,no等否定形容词和little, few, hardly等半否定词与肯定形式的谓语动词连用来表示否定。
I can hardly understand what you said.
我几乎听不明白你说的。
(4)在“I think/believe+that 从句”的句型中,若想否定从句动词的含义,必须采用否定主句动词think的形式,这叫否定的转移。
We/I don't think it's true. 我们/我认为那不是真的。
考点二疑问句
疑问句用于提出问题。句末用问号(?),可分为四种:一般疑问句、选择疑问句、反意疑问句和特殊疑问句。1.一般疑问句是可用Yes 或No 来回答的问句。它总是以be(is,am,are,was,were),have(has,had),情态动词或助动词开头。有时也可用“Not at all”,“Certainly”等回答。
—Would you like some more? 你想再来一些吗?
—No,thanks. I'm full. 不,谢谢。我饱了。
2.选择疑问句的结构有两种:(1)以一般疑问句为基础,用or 来连接不同的选择对象;(2)以特殊疑问句为基础,在其后用or来连接不同的选择对象。
Shall we go to see you or will you come to see us?
是我们去看你们,还是你们来看我们?
Which would you like better, tea or milk?
你喜欢喝哪个,茶还是牛奶?
3.反意疑问句是提出情况或看法,问对方是否同意的句子。一般由两部分组成:“陈述句+简略问句?”这两部分的肯定与否定形式正好相反,即:①“肯定的陈述句+否定的简略问句?”②“否定的陈述句+肯定的简略问句?”
(1)反意疑问句主语及谓语的确定。
反意疑问句主语与谓语的确定应以陈述部分的主语和谓语为依据,尤其是要注意一些特殊的情况,同时,简略问句部分的主语一般应用人称代词,而动词若为否定形式则一般应用缩略形式。
①陈述部分含有never,few,little,nothing,nobody,no,hardly,none,too...to...等表示否定意义的词时,其附加问句应用肯定形式。但否定意义的词是careless,dislike等含否定词缀的派生词时,仍按肯定句对待,
后边的简略问句用否定形式。
There are few people in the room, are there?
房间里几乎没有人,是吗?
②陈述句部分是“there be”结构时,疑问部分用“be there”。
There is a tree in front of the building, isn't there?
楼前面有一棵树,是吗?
③当陈述部分的主语为指事(物)的不定代词something,anything,everything等时,附加问句的主语应用it。Something is wrong with your computer,isn't it?
你的电脑出毛病了,是吗?
④当陈述部分的主语为指人的不定代词somebody,anybody,everybody等时,附加问句的主语可用he强调个体或they强调全部,但不可用it 来代替。
Somebody wants to see you, doesn't he?
有人要见你,是吗?
⑤当陈述部分的主语为this, that 等时,附加部分的主语应用it。类似地,当陈述部分的主语为these,those 等时,附加部分的主语应用they。
This is a beautiful picture, isn't it?
这是一幅美丽的图画,是吗?
Those aren't apple trees, are they?
那些不是苹果树,是吗?
⑥当陈述部分动词为have(has)时有下列几种情况:
Ⅰ. have在一般现在时中表示“有”之意,附加问句的谓语可用have,也可用助动词do。
Tom has a new watch, doesn't he (hasn't he)? 汤姆有块新表,是吗?
Ⅱ.have to 表示“不得不”“必须”之意时,附加问句的谓语应用助动词do。
Kate has to help her mother at home, doesn't she? 凯特不得不在家帮她妈妈,是吗?
Ⅲ.have表示“吃、喝、玩、度过”等意思时,其附加问句的谓语应用助动词do。
They have a good time in Beijing, don't they ? 他们在北京玩得很愉快,是吗?
Ⅳ.had better表示“最好”之意,当其用在陈述部分时,附加问句的谓语动词应用had。
We'd better stop talking, hadn't we? 我们最好停止说话,好吗?
Ⅴ.have 用在完成时中,其附加问句的谓语动词应用have。
Lucy has ever been to Japan, hasn't she? 露西曾经去过日本,是吗?
⑦当陈述部分含有need时,如果need用作行为动词,则附加问句的动词应用do;如果need用作情态动词,则附加问句的动词应用need。
We need to arrive in Shanghai at 7:00, don't we? 我们需要在七点到达上海,是吗?
We needn't leave at once, need we? 我们不必马上离开,是吗?
⑧当陈述部分含有情态动词must时,有下列几种情况:
Ⅰ.must 表示“必须”之意,附加问句的谓语用needn't。
They must come on time, needn't they?
他们必须准时到,是吗?
Ⅱ.must表示推测,意为“一定,想必”,附加问句的谓语动词的确定应根据must后面的动词。如:
That man must be Mr Wang, isn't he? 那个人想必是王先生,是吗?
⑨当陈述部分为I (am)形式时,附加问句部分应该用aren't I。如:
I'm right, aren't I?我是对的,是吗?
⑩陈述句部分若为主从复合句,疑问部分的主语通常与主句的主语一致。如:
She said he would come tomorrow,didn't she?
她说他明天会来,是吗?
注:若主句的主语是第一人称I/we,其谓语动词又是think,suppose,expect,believe,imagine等,疑问部分的主语一般与从句的主语一致。(应特别注意否定的转移)
I think he is a good student,isn't he? 我认为他是一个好学生,是吗?
We don't think you are right, are you? 我们认为你不对,是吗?
(2)反意疑问句的答语。
反意疑问句作回答时,如果答案肯定则用yes,后跟肯定形式的简略回答方式;若答案否定则用no,后跟否定形式的简略回答方式。即其回答与一般疑问句的回答方式完全一致。
特别注意有时要根据具体的语境来确定回答应为肯定形式还是否定形式。
—Lucy skates very well, doesn't she? 露西滑冰非常好,是吗?
—Yes, she does. 是的,她是。
②—You don't like the man, do you? 你不喜欢这个人,是吗?
—No,I don't. 是的,我不喜欢。
4.特殊疑问句是以疑问词引出的问句。一般为疑问语序:“疑问词+一般疑问句?”回答时要具体作答,不能用yes或no来回答。
语序:(1)当疑问词或由其所修饰的词不作主语时,用一般疑问句语序;(2)当疑问词或由其所修饰的词作主语时用陈述句语序。
①疑问词作主语或主语的定语时,要用陈述语序:“疑问词(+主语)+谓语+动词(+...)?”
Who broke the door? 谁弄坏了门?
Which boy runs the fastest? 哪个男孩跑得最快?
②问姓名、职业、外貌长相、性格、体重等用what 提问;问身体状况、年龄、身高、工作、生活情况等用how来提问。
问外貌“What's...like?”或“What do(does)...look like?”;问性格“What do(does)...think of...?”;问年龄“What age...(What's...age)?”或“How old...?”;问体重“What's...weight?”(“What weight...?”);问身体状况“How...?”;问身高“How tall...?”;问工作生活情况“How are(is)...getting on?”
③询问钟点用what time,问何时用when,问星期用what day(of the week)...,问日期用what's the date...。
④询问一段延续的时间有多长(久)用how long,答语用“for+一段时间”或“since+过去时间点”;问某事过多久将会发生用how soon,答语用“in+一段时间”;问某个动作重复发生的频率间隔用how often,答语用“次数+时间”,如“three times a day”等;问总共的次数用how many times,答案用“基数+times”等。—How long will it take us to get there by bus? 我们坐公共汽车到那要多长时间?
—About two hours. 大约两小时。
⑤询问数量时,对可数事物用how many,对不可数事物用how much, 问人口用“What's the population of +地区?”此外how much 还可以用来询问“多少钱”。
—How much is a ticket for the film Hacker Ⅱ?《黑客Ⅱ》的票价是多少?
—About forty yuan. 大约四十元。
What's the population of Liaocheng? 聊城有多少人口?
⑥询问距离用how far (away)。
⑦询问颜色用what colour。
⑧询问号码用what number 或what's...number;
What number is your car? 你的车号是多少?
What's your telephone number? 你的电话号码是多少?
考点三祈使句
1.祈使句是表示命令、请求或劝告等的句子。听话者you习惯上常省略,而由动词原形引出。否定祈使句
是在动词原形前加缩写的don't;还可在动词原形前加Do或Never来加强语气。
Do help me. 一定要帮我。
2.祈使句后,还可以加一个简略问句。祈使句为否定结构时,后加“will you?”。祈使句为肯定结构时,表邀请则加“won't you?”,表请求可用“will you?/would you?/can you?/can't you?”等。
Lucy,you clean the blackboard today,will you?
露西,你今天擦黑板,好吗?
3.以Let's 开头的句子,us的缩写“'s”包括说话人和听话人“双方”,后半部分的简略问句用“shall we?”;以Let us 开头的句子,us 仅指说话人“一方”,其后的简略问句用“will you?”。
Let's go and see him after school, shall we? 让我们放学后去看他,好吗?
Let us look at your photo,will you? 让我们看看你的照片,好吗?
考点四感叹句
1.感叹句表示喜、怒、哀、乐等强烈的感情。这种句子一般用how 或what开头,都用陈述语序,后加感叹号“!”,读降调。
2.感叹句中,how(多么)作状语,修饰形容词或副词;what(多么)作定语,修饰名词,名词前可有不定冠词a(an)和形容词。
(1)How +形容词/副词(+主语+谓语)!
How fast he runs! 他跑得多快啊!
(2)How+主语+谓语!
(3)How +形容词+a或an+单数可数名词(+主语+谓语)!
(4)What a 或an(+形容词)+单数可数名词(+主语+谓语)!
What an interesting book the girl has!
那女孩有一本多有趣的书啊!
(5)What +(形容词)+复数可数名词/不可数名词(+主语+谓语)!
What natural things they are!它们是多么自然的东西呀!
陈述句、疑问句、祈使句、感叹句考点训练
1.—________do you have an Art Festival in your school?
—Once a year.
A.How long B.How often C.How far D.How soon
【解析】本题考查由how构成的特殊疑问短语辨析。how long提问时间长度,“多久”;how often提问时间频率,“多久一次”;how far提问距离,“多远”;how soon提问将来的一段时间,“多久以后”。根据答语“Once a year.”可知问句是询问频率,故选B。
【答案】B
2.—Alice had nothing for breakfast this morning,________?
—No. She got up too late.
A.had she B.hadn't she C.did she D.didn't she
【解析】本题考查反意疑问句。本题陈述部分中含有表否定意义的不定代词nothing,根据反意疑问句“前否后肯”的原则,故要用肯定形式来反问;又因整个句子是行为动词的一般过去时态,需用助动词did。故选C。
3.You've just finished your listening exam. Please get yourself ready for the next part,________?
A.shall we B.will you C.do you D.are you
【解析】本题考查祈使句的反意疑问句。根据句子Please get yourself ready for the next part...“请……”,判断该句为祈使句。肯定祈使句的反意疑问句常用will you或won't you来表达,故选B。
【答案】B
4.—Have you ever been to Nanning? —Yes,________.
A.I was B.I do C.I am D.I have
【解析】本题考查一般疑问句的答语。因问句“你曾经去过南宁吗?”是现在完成时的一般疑问句,肯定回答要用“Yes,I have.”。故选D。
【答案】D
5.________great scientist Qian Xuesen is!
A.How B.How a C.What D.What a
【解析】本题考查感叹句。句子的中心词是名词,应用what引导感叹句;scientist是可数名词单数,故前面加不定冠词a。
【答案】D
6.—________did you sleep last night?
—Only five hours.I stayed up late to do my homework.
A.How soon B.How often C.How long D.How much
【解析】本题考查how引导的短语辨析。how soon“多久以后”,提问“in+一段时间”;how often“多久一次”,提问频率;how long“多长”,提问一段时间或距离;how much“多少”,提问不可数名词的数量或价格。由答语中的“只有5个小时”知选C。
【答案】C
7._______buy your ticket from a ticket machine. There are lots of people there.
A.Not B.Not to C.Don't D.Don't to
【解析】句意为“不要从自动售票机买票了。那儿的人太多了。”本题考查祈使句的用法。buy为实义动词,否定的祈使句应在其前加don't。
【答案】C
8.I hear the tall girl wearing glasses is your new classmate. She's from America,________?
A.has she B.isn't she C.hasn't she D.does she
【解析】本题考查反意疑问句。反意疑问句的基本结构是“前肯后否,前否后肯”,本题前面部分为肯定句,she's是she is的缩写,故选B。
【答案】B
9.—________will your mother come back?
—In two days.
A.How often B.How soon C.How long D.How far
【解析】本题考查易混疑问副词短语。how often“多久一次”,提问频率;how soon“多久以后”,提问“in +一段时间”;how long“多久,多长”,提问长度或者一段时间;how far“多远”,提问距离。由答语“两天之后”可知用how soon提问。
【答案】B
10.—Li Mei usually helps others,________?
—Yes,she is kindhearted.
A.does she B.is she C.doesn't she
【解析】本题考查反意疑问句。陈述部分用了肯定形式,根据“前肯后否”的原则,疑问部分要用否定形
【答案】C
11.Look at the photo of the Smiths.________happy they are!
A.How B.What C.How a D.What a
【解析】本题考查感叹句。句子的中心词是形容词,故用how引导感叹句。
【答案】A
12.—The CCTV reported that Premier Wen Jiabao played basketball with some students on Children's Day.
—________!And Premier Wen always encourages us to study hard and do more sports.
A.What amazing news B.How amazing news C.What an amazing news
【解析】本题考查感叹句。句子的中心词是名词,要用what引导感叹句,故排除B项;news是不可数名词,不能用a或an修饰,因此C项也被排除。故选A项。
【答案】A
13.You can hardly understand me,________you?
A.can't B.can C.are D.don't
【解析】本题考查反意疑问句。hardly意为“几乎不”,具有否定意义。根据反意疑问句“前否后肯”的原则,疑问部分要用肯定形式;陈述部分用了情态动词can,疑问部分应与其一致。故选B。
【答案】B
14._______smoke here,dad. Smoking has been banned in public places.
A.Don't be B.Don't C.Not to be D.Be not
【解析】本题考查祈使句的否定形式。祈使句除了以let开头的外,其他的否定形式是在句首加Don't。故选B。
【答案】B
15.Franklin told them all ________to be in Britain again.
A.he was now happy B.how happy he was C.how was he happy D.he was happy now
【解析】句意为“Franklin告诉他们所有人他再次来到英国是多么高兴。”本题考查宾语从句的用法。本题中的宾语从句是感叹句,且要用陈述语序,故选B。
【答案】B
16.Your English teacher has never lost his temper,________he?
A.has B.hasn't C.did D.didn't
【解析】本题考查反意疑问句。反意疑问句前后两部分必须遵循“三同一反”的原则:人称相同,助动词相同,时态相同,前肯后否,前否后肯。由never(从不)知用“前否后肯”原则,附加问句部分的时态同陈述句,故用has。
【答案】A
17.—Mr. Wang's never been to Canada,has he?
—________.He went there on business last week.
A.No,he hasn't B.Yes,he has C.No,he has D.Yes,he hasn't
【解析】本题考查反意疑问句的答语。反意疑问句要根据具体语境确定是肯定回答还是否定回答,回答方式与一般疑问句回答方式一致。句意为“王先生从来没有去过加拿大,是吗?”“不,他去过。上周他去那儿出差了。”
【答案】B
18.________bad weather it is!
A.How B.How a C.What D.What a
【解析】本题考查感叹句。句子的中心词是名词,要用what引导感叹句;weather是不可数名词,不能用a/an修饰。故选C。
【答案】C
19.________fine day it is! Let's go and fly a kite.
A.What B.What a C.How D.How a
【解析】本题考查感叹句的用法。感叹句结构:①What a/an+形容词+可数名词单数+主语+谓语!②What +形容词+复数名词/不可数名词+主语+谓语!③How+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数+主语+谓语!④How+形容词/副词+主语+谓语!故本题选B。
【答案】B
20.—________does your sister look like? —She is tall with long hair.
A.Who B.What C.Which D.How
【解析】本题考查特殊疑问句。由答语“她高个儿留着长发”可知,此处询问外貌特征,用句型“What+do/does+主语+look like?”,意为“某人看起来什么样子?”。
【答案】B
21.—You didn't go to school yesterday, did you?
—________,though there was a heavy rain.
A.Yes, I did B.No, I didn't C.Yes, I didn't D.No, I did
【解析】本题考查反意疑问句的答语。反意疑问句的回答和一般疑问句一样。本题中肯定式:Yes, I did.否定式:No, I didn't. 又由答语后面的“尽管有一场大雨”,可见是仍然上学了,用肯定式。所以选择答案A。【答案】A
22._______ good job she does! She is really a clever girl.
A.What B.How C.What a D.How a
【解析】本题考查感叹句。感叹句由How+adj./adv.或What+noun phrase构成。题中job是可数名词单数,故选择C。
【答案】C
23.—He didn't go to the lecture this morning, did he?
—________.Though he was not feeling very well.
A.No, he didn't B.Yes, he did C.No, he did D.Yes, he didn't
【解析】本题考查反意疑问句的答语。对于反意疑问句的回答,我们要根据客观事实来判断。如果事实是肯定的用yes,否定的用no。本题的意思是“他尽管身体不舒服,可是还是去听讲座了。”事实成立。故选B。
【答案】B
24.—Let's go fishing after the exam,________?—Sounds great!
A.will you B.shall we C.won't you
【解析】本题考查基本句式用法。以Let's开头的句子,后面的附加问句用“shall we?”;以Let us开头的句子,其后的附加问句用“will you”。所以选择答案B。
【答案】B
25.—There are always many volunteers in great events, ________?
—Yes.Many hands make light work!
A.aren't there B.are there C.aren't they
【解析】本题考查反意疑问句。前半句是there are的肯定形式,故反问部分应用there are疑问句式的否定形式,即aren't there。
【答案】A
26.They were all so tired that they could ________.
A.do nothing but sleep B.do anything but sleep
C.do nothing but to sleep D.do anything but to sleep
【解析】本题考查句意的理解。nothing but“除……之外(没有)”。本题题意是“他们是如此的累以至于他们除了睡觉什么都没有做。”选A。
【答案】A
27.________ more, and you'll improve your spoken English.
A.Speak B.Speaks C.Speaking D.To speak
【解析】本题考查祈使句。横线部分在句子中作谓语;祈使句谓语通常用动词原形。
【答案】A
28.—Kate has won the first prize in the singing competition.
—________ pleasant surprise this gave her classmates!
A.What B.How C.What a D.How a
【解析】本题考查感叹句的用法。题意为“在歌唱比赛中凯特赢得了第一名。”“这给了她的同学们一个惊喜!”,句子的中心词是名词,首先排除B和D,surprise是可数名词单数,因此答案为C。
【答案】C
29.—________Tshirt do you like better,the red one or the blue one?
—I prefer the red one.
A.How much B.How many C.Whose D.Which
【解析】本题考查疑问词。由答语“我更喜欢那件红色的。”知问句应是“你更喜欢哪件T恤,红色的还是蓝色的?”,故选D。
【答案】D
30.—________ will the supper be ready? I'm very hungry. —In a minute.
A.How soon B.How long C.How much D.How often
【解析】由答语In a minute可知,问句应是在将来时态中对时间段提问,故选A。
【答案】A
31.—Jimmy lost his key yesterday.
—________?It's his third time in just one month.
A.Has he B.Did he C.Was he D.Does he
【解析】上文用的是一般过去时,上下文的时态应一致,故选B。
【答案】B
32.I used to love this film when I was young, but I ________ it that way any more.
A.don't feel B.didn't feel C.haven't felt D.hadn't felt
【解析】句意为“我年轻的时候喜欢看这部电影,但现在我不那么觉得了。”由not any more知feel应发生在现在,故选A。
【答案】A
33.—All of you have passed the test!
—________ pleasant news you have told us!
A.How B.How a C.What D.What a
【解析】news是不可数名词,感叹句应用what引导,且不用冠词。
【答案】C
34.—Millions of people know about Susan Boyle now, ________?
—________,she becomes wellknown because of her success on Britain's Got Talent.
A.do they; No B.do they; Yes C.don't they; No D.don't they; Yes
【解析】反意疑问句的陈述部分为肯定形式,其疑问部分应用否定形式;反意疑问句的回答要依据事实而定,事实是肯定的,用Yes回答;事实是否定的,用No回答,故选D。【答案】D
35.)Email is very popular today.People seldom write letters now, ________?
A.did they B.do they C.didn't they D.don't they
【解析】反意疑问句的前半部分有否定词seldom,故附加问句应用肯定形式,故选B。
【答案】B
36.Boys and girls, ________ up your hands if you want to take part in the summer camp(夏令营).A.putting B.to put C.put
【解析】考查祈使句的有关用法。祈使句应用动词原形开头,故选C。【答案】C
37.—________ you ________ your drawing?
—Not yet! It will be done in a few minutes.
A.Did; finish B.Will; finish C.Do; finish D.Have; finished
【解析】由上下文可知,问句应用现在完成时态,故选D。
【答案】D
38.—What's the use of this kind of fuel?
—It can make the train ________ fast.
A.to go B.going C.went D.go
【解析】考查省略to的不定式的用法。make sb./sth. do“使某人/物……”。句意为“这种燃料有什么用?”“它能使火车运行得更快。”
【答案】D
39.—What did Jack ask you just now?
—He wanted to know how long _______ when I reached the cinema.
A.had the film been on B.the film had started
C.the film had lasted D.had the film ended
【解析】考查宾语从句及延续性动词。宾语从句用陈述语序。how long对一段时间提问,谓语动词用延续性动词,start是短暂性动词,last意为“持续”时是延续性动词。故选C。
【答案】C
40.—Dad, do you like my picture?
—________!It's the nicest one I've ever seen!
A.What beautiful B.How careful C.How wonderful D.What wonderful picture
【解析】wonderful是形容词,用how来引导感叹句,how wonderful表赞赏。
【答案】C
41.—What do you think of what she did?
—What she did still ________ us feel very sad now.
A.makes B.make C.is making D.is made
【解析】句中what she did作主语,谓语动词用单数形式,故选A。
【答案】A
42.The old man had to do all the farm work himself, ________?
A.did he B.had he C.didn't he D.hadn't he
【解析】考查反意疑问句。前肯后否,因此排除A、B,前面是动词had,后面用助动词didn't来辅助疑问。【答案】C
43.—Arthur is responsible ________ the newspaper, isn't he?
—________,but Joyce is.She's the chief editor.
A.of; Yes, he isn't B.for; Yes he is C.of; No, he is D.for; No, he isn't
【解析】上文中的空白处意思是“为了”,用介词for,be responsible for“(对某人、某物)负责的”。下文是对上文反意疑问句的回答,根据上下文句意,知要用否定形式。
【答案】D
44.—I'm leaving now.
—________ you turn off the lights.
A.To make sure B.Make sure C.Made sure D.Making sure
【解析】考查祈使句。祈使句句首应用动词原形,故选B。【答案】B
45.—They haven't paid for their tickets,have they?
—________.They didn't pay any money.
A.Yes,they have B.No,they haven't C.Yes,they haven't D.No,they have
【解析】若不看They didn't pay any money,A和B都正确。但根据句意“他们还没有付买票的钱是吗?”“是的。他们一分钱都没付。”知选B。
【答案】B
46.—Listen!Lucy is playing the piano.
—Wow!________beautiful music!I like it very much.
A.What B.How C.What a
【解析】本题考查感叹句。what修饰名词,how修饰形容词或副词。music是不可数名词,用what引导感叹句。【答案】A
句子的成分 组成句子的各个部分叫作句子的成分。句子的成分有主语、谓语、宾语(直接宾语和间接宾语)、表语、宾语补足语、定语和状语。其中主语和谓语是句子的主体,表语、宾语和宾语补足语是谓语的组成部分,其他成分如定语和状语是句子的次要部分。 1)主语表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”,通常用名词、代词、数词,不定式,动名词或从句担任。主语要放在句首,还可用“It”作形式主语(如主语从句) 2)谓语起着说明主语的动作、特征或状态的作用,必须用动词表示。谓语和主语在人称和数两方面要一致,通常在主语之后。 谓语可分为两大类:简单谓语和复合谓语。凡是由一个动词或短语动词构成的谓语,不管什么时态,语态,语气,都是简单谓语。复合谓语一般由两部分构成:一是带不定式的复合结构;一是带表语的复合结构。 3)表语用于说明主语的性质、特征、身份或状态,可以由名词、代词,数词,形容词、副词、介词,介词短语,不定式,动词的—ed形式或动词的—ing形式或从句来担任,表语要放在连系动词之后。4)宾语是及物动词所示动作的对象或介词的对象,由名词、代词、数词,名词化的形容词,名词化的分词,不定式,动名词,从句都可以担任作宾语。宾语要放在谓语动词(及物动词)或介词之后。 ①某些及物动词之后要求有双宾语(即直接宾语和间接宾语),直接宾语指物,间接宾语指人。这一类动词有:bring, give, pass,tell, hand, show, s end, read, leave, teach, find, buy, make, do, get, order, play, sing, pay 等。宾语要放在谓语动词(及物动词)或介词之后。 ②在需要的情况下,间接宾语也可以位于直接宾语之后,但此时间接宾语之前需要加介词“ to”或“for”。 ③有些及物动词的后面,其宾语还需要有一个补足语,才能表达完整的意思。这样的宾语和宾语补足语称为复合宾语。名词、形容词、不定式或介词短语都可以作宾语补足语。 5)状语用于修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。通常表示行为发生的时间、地点、目的、方式、程度等。状语一般由副词、介词短语、分词和分词短语、不定式,形容词短语。名词短语来担当。其位置一般放在句末,但也可放在句首或句中。 6)定语用于修饰名词或代词。可以担任定语的有形容词、代词、名词、数词、名词所有格、副词、不定式、分词和分词短语、介词短语及从句等等。定语的位置很灵活,凡有名词和代词的地方都可以有定语。 7)同位语是对句子的某一成分作进一步解释,说明,与前面名词在语法上处于同等地位。同位语常常置于被说明的词的后面。可以作同位语的有名词,代词,数词和从句等。 8)句子成分巧划分:主在前,谓在中,宾状后面冲。短语定语主宾后,形、代定语主宾前。间宾直宾紧相依,直、间之间to、for连,宾补位于宾语后,地状常在时状前。 第一讲主语 【语法讲解】 主语的位置通常在句首,一般不省略。它是句子所要说明的人或事物,是谓语动词所表示动作的发出者。例如: 1) The question is difficult. 2) She is difficult to understand. 3) is difficult to remember. 4) To understand his words is difficult. 5) Thinking in such a noise is difficult. 6) That they will leave ahead of time is difficult. 上述的六个例句分别说明了主语的位置、特点及能够担当主语的成分。可以担当主语的有名词(例如1)、代词(例如2)、数词(例如3)、动词不定式(例如4)、动名词(例如5)和主语从句(例如6)。 注:当动词不定式做主语时,往往放在谓语动词的后面,而用it做形式主语放在谓语动词的前面。例如上述例句4还可以改写为:It is difficult to understand his words.其中,it是形式主语,真正的主语是动词不定式to understand his words.
一.感受中考: 1. ________ nice weather it is! Let’s play football. A. What B. How C. What a 2. ---________the little girl looks!----That’s true. She can’t find her Teddy Bear. A. How sad B. What sad C. What sadly D. How sadly 3. —Excuse me. Is there a bank near here? — No, _______. But you can find one in Zhongshan Road A. There isn't B It isn't C. they aren't 4. ________ buy your ticket from a ticket machine. There are lots of people there. A. Not B. not too C. Don’t D. Don’t to 5. — There is something wrong with your hike, _______? — Yes. I'll have it ________ tomorrow. A. isn’t it; mend B. isn’t there: mended C. isn't it; mended D. isn't there; mend 6. — _______ good time we had at the party last night! — Yes. It was _____ exciting party that I would never forget it. A. What; so B. How; such C. What a; such an D. How a; so an 7. They hardly watch TV on school nights, _____? A. will they B. aren’t they C. do they D. didn't they 8. — I often chat with my friends on the Internet. — You are so smart! Will you please tell me____? A. how to do B. how to do it C. how to use D. when can I use it 9. ________ is dangerous for us to swim in the river alone. A. It B. That C. This 10. The drink is _________ delicious ________ everyone in the room enjoys it. A. such...that B. too...to C. so...that 二.句子种类考点小结: (一) 按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。 1) 陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。 Light travels faster than sound.光比声速度快。(说明事实) The film is rather boring.这部电影很乏味。(说明看法) 2) 疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。有以下四种: a. 一般疑问句(General Questions):Can you finish the work in time?你能按时完成工作吗? b. 特殊疑问句(W Questions; H Questions):Where do you live?你住那儿? c. 选择疑问句(Alternative Questions):Do you want tea or coffee?你是要茶还是要咖啡? d. 反意疑问句(Tag-Questions):He doesn't know her, does he?他不认识她,对不对?
初中英语分类练习 ——句子种类与简单句的基本句型 一、句子种类: Ⅰ. 句型转换(按要求完成句子) 1. Those children are students.(否定句, 一般疑问句) 2. We can see a lot of girls in the picture. (否定句, 一般疑问句) 3. They will go to England for a visit. (否定句, 一般疑问句) 4. The young men aren’t having a party. (肯定句, 一般疑问句) 5. She has been to Shanghai already. (否定句, 一般疑问句) 6. Don’t be noisy, please. (用quiet改为肯定句,) 7. Stand in front of the class. (否定句, 反意疑问句) 8. Both Mary and Tony are good students. (否定句, 一般疑问句) 9. All the students in our class are going to visit the Science Museum. (否定句, 一般疑问句) 10. There is an English test on Friday. (反意疑问句) 11. There will be a report on Chinese history tomorrow. (否定句, 一般疑问句) 12. Tom has his lunch in the school. (否定句, 一般疑问句, 反意疑问句) 13. John does his homework at home. (否定句, 一般疑问句, 反意疑问句) 14. He saw the TV news yesterday evening. (否定句, 一般疑问句, 反意疑问句) 15. I think you are right. (否定句, 一般疑问句) 16. This kind of car is made in Japan. (否定句, 一般疑问句) 17. Arthur runs fastest in his class.(就划线部分提问) ________ runs fastest in his class? 18. Bob”s painting was put up on the wall of our school.(同上) ________ painting was put up on the wall of our school? 19. Chapter One is very difficult to learn. (同上) ________ chapter is very difficult to learn? 20. Mary does her homework after supper in the evening. (同上) ________ ______ Mary ______ after supper in the evening? 21. He has borrowed four books from the school library. (同上) _______ _______ he borrowed from the school library? 22. It took him 30 minutes to get there. (同上) ______ ______ ______ it take him to get there? 23. My father is a teacher in the school. (同上) _______ ________ your father ______ in the school? 24. It will be Wednesday the day after tomorrow. (同上) ________ ______ will it be the day after tomorrow? 25. There are Three thousand people in the factory. (同上) _______ _______ people _______ _______ in the factory? 26. Linda’s mother works in a big hotel. (同上) _______ _______ Linda’s mother work? 27. They usually go to school by bus. (同上) _______ _______ they usually go to school?
初中英语语法——三大从句汇总 在英语中,主要有三大从句,即名词性从句(包括主语从句,宾语从句,表语从句,同位语从句)、形容词性从句(即定语从句)、副词性从句(即 状语从句,包括时间、条件、结果、目的、原因、让步、地点、方式等)。以 下是一些基本的从句的语法知识点 A、定语从句专项讲解与训练 一、定语从句概念 定语从句(attributive clause),顾名思义,就是一个句子作定语从属 于主句。定语一般是由形容词充当,所以定语从句又称作形容词从句。另外, 定语从句是由关系代词或关系副词引导的,故又称作关系从句。 定语从句一般放在它所修饰的名词或代词之后,这种名词或代词被称作先 行词。请看示例: The woman who lives next door is a teacher. 先行词定语从句 在所有的从句中,算定语从句最难掌握,因为汉语里没有定语从句,汉语 里只有定语,而且总是放在名词之前来修饰名词。 二、关系代词引导的定语从句 关系代词代替前面的先行词,并且在定语从句中充当句子成分,可以作主语、宾语、定语等。常见的关系代词有:who, that, which。它们的主格、宾格和所有格如下表所示: 先行词主格宾格所有格 人 who whom whose 物 which which whose of which 人、物 that that — (一)关系代词who, whom和 whose的用法 who代替人,是主格,在定语从句中作主语。例如: An architect is a person who designs buildings. 建筑师是设计房屋的人。 I will never forget the teacher who taught us chemistry in the first
英语中的句子可以按其作用或者按其语法结构(即句子的形式)两种标准分类。下面是具体的分类依据和结果。 (1)按其作用或使用目的,句子可分为: 陈述句:This is a truck. 这是一辆卡车。 疑问句:Is this a truck? 这是卡车吗? 祈使句:Drive the truck away. 把卡车开走。 感叹句:What a big truck it is! 多么大的卡车! 按语法结构,句子可分为:(2)简单句:I am busy. 我很忙。 并列句:I am busy washing, but he is playing Majiang with them. 我在忙着洗衣服,但他却在跟他们打麻将牌。 复合句:Although I am busy washing, he is playing Majiang with them. 尽管我在忙着洗衣服,他却在与他们一块打麻将牌。 一、陈述句:用于说明一件事,表示一种看法或表达某种心情的句子,都是陈述句。陈述句分为肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。 1肯定句 He is a middle school teacher. 他是一位中学老师。(一般现在时) She is cleaning the room. 她正在收拾屋子。(现在进行时) They have visited the museum. 他们已经参观过这所博物馆了。(现在完成时) He did a lot of washing yesterday. 他昨天洗了好多衣服。(一般过去时) They had already finished quarrelling when I came. 我来时他们已经争吵完了。(过去完成时) The meeting will begin at once. 会议马上就要开始了。(一般将来时) 2否定句 (1)使用not否定: He isn't a worker. 他不是个工人。(一般现在时) She doesn't do the cleaning every day. 她不是每天都做卫生。(一般现在时) I haven't had my breakfast yet. 我还没有吃早点。(现在完成时) You didn't do your homework seriously. 你没有认真地做你的作业。(一般过去时) You mustn't take her to your parents. 你千万不要把她带到你的父母那里去。(情态动词) She needn't quarrel with him. 她没必要跟他吵。(情态动词) The house won't be painted. 这所房子将不粉刷了。(被动语态将来时) She might not notice you.
初中英语语法大全 一、词类、句子成分和构词法: 1、词类:英语词类分十种:名词、形容词、代词、数词、冠词 动词、副词、介词、连词、感叹词。 1、名词(n.):表人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange. 2、代词(pron.):主要用来代替名词。如:who, she, you, it . 3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good, right, white, orange . 4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth. 5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am, is,are,have,see . 6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly. 7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。如:a, an, the. 8、介词(prep.):表示它后面名词或代词与其他句子成分关系。如in, on, from, above, behind. 9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。如and, but, before . 10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。如:oh, well, hi, hello. 2、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主、谓、宾、定、状、表、宾补。 1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。如:I‘m Miss Green.(我是格林小姐) 2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间) 3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名词、代词 或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。如:He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词) 有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间接宾语。 间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他给我写了一封信) 有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接宾语。如:He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信) 5、定语修饰名词或代词,通常由形容词、代词、数词等担任。如: Shanghai is a big city .(上海是个大城市) 6、状语用来修饰动词、形容词、副词,通常由副词担任。如:He works hard .(他工作努力) 7、宾语补足语用来说明宾语怎么样或干什么,通常由形容词或动词充当。如:They usually keep their classroom clean.(他们通常让教室保持清洁) / He often helps me do my lessons.(他常常帮我做功课) / The teacher wanted me to learn French all by myself.(老师要我自学法语) ☆同位语通常紧跟在名词、代词后面,进一步说明它的情况。如:Where is your classmate Tom ?(你
初中英语语法大全之句子的种类 2011-09-24 15:37:42 来源:本站原创进入论坛 句子的种类 (一)按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。 1)陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。Light travels faster than sound。光比声速度快。(说明事实) The film is rather boring。这部电影很乏味。(说明看法) 2)疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。有以下四种: a.一般疑问句(General Questions): Can you finish the work in time? 你能按时完成工作吗? b.特殊疑问句(W Questions;H Questions): Where do you live?你住那儿? How do you know that?你怎么知道那件事? c.选择疑问句(Alternative Questions): Do you want tea or coffee? 你是要茶还是要咖啡?
d.反意疑问句(Tag-Questions): He doesn‘t know her,does he? 他不认识她,对不对? 3)祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如: Sit down,please。请坐。 Don’t be nervous!别紧张! 4)感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如: What good news it is!多好的消息啊! (二)句子按其结构可以分为以下三类: 1)简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如: She is fond of collecting stamps。她喜欢集邮。 (主)(谓) 2)并列句(Compound Sentences):包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接,例如: The food was good,but he had little appetite。 (主)(谓)(主)(谓) 食物很精美,但他却没什么胃口。 3)复合句(Complex Sentences):包含一个主句从句和一个或几个从句的句子叫复合句,从句由从属连词引导,例如:
初中英语句子成分讲解 一概述:句子成分 概念:组成句子的各个部分,即主语、谓语、宾语、表语、宾语补足语、定语和状语,主语和谓语是句子的主体部分。 主语:表示句子所说的是什么人或神秘物,一般由名词、代词或不定式,V-ing和从句充当。谓语:说明主语是什么,做什么或怎么样。由动词充当,主语和谓语在人称和数上必须保持一致。谓语动词存在多种时态,它是句子的核心。 表语:说明主语是说明或怎么样,由名词、形容词、数词、副词、不定式、介词短语、句子等充当。 宾语:表示动作、行为的对象,由名词、代词、不定式、V-ing、从句充当,和及物动词一起说明主语做什么。 定语:用来修饰名词或代词。由形容词、代词、数词、介词短语、不定式、从句充当。单词作定语一般放在被修饰词之前,短语或句子作定语放在被修饰才之后。 状语:用来修饰动词、形容词或副词。一般表示行为发生的时间、地点、条件、目的、方式、程度等等。通常由副词、介词短语、不定式或句子充当。(若在同一句子中出现多个不同状语,常见的4个的顺序为:方式状语、目的状语、地点状语、时间状语。) Eg.I met my best friend Tom at the station yesterday 二详解 1.主语 主语表示句子主要说明的人或事物。 1).名词 例如:A moon cake is a delicious, round cake. The first truck is carrying a few baskets. The temperature will stay above zero. The doctor looked over Mrs. Brown very carefully. China does not want to copy the USA’s example. 2).代词 例如:It’s a young forest. I don’t know if it will grow. That’s a bit expensive. You’d better buy a new pair. I’m afraid we haven’t got any black shoes. 3).数词 例如:One and two is three. One is not enough for me. I want one more. One of them is English. Suddenly one of the bags fell off the truck. Two will be enough. 4).不定式(常以It’s adj. to do sth. 形式出现) 例如:To give is better than to receive =Its better to give. I found it difficult to get to sleep.
初中英语语法过关一一句子类型:复合句专项练习精选50题(宾语从句、定语从句、状语从句) ()1.— Do you know if our team the match tonight? ——It is hard to say.I will tell you the result if our team. A. wins;wins B.will win;will win C.wins;will win D.will win;wins ()2.— I believe Chinese astronauts will be able to land on the moon one day. —I agree with you.But I ' m not sure we can live on it. A.that;if B.that;that C.if;that D.if;if ()3.— Are you sure Li Ming has flown to London? —Yes.I saw him off at the airport just now. A.that B.if C.whether D.when ()4.— I ' m worried about I can pass the English exam. —Don' t worry.I ' m sure you will pass it. A.if; that B.whether; that C.that; if D.that; whether ()5.— Doctor,could you tell me? —Oh,nothing serious. He just has a cold. He will be fine soon. A. that there was anything wrong with my son B. if there was anything wrong with my son C. that there is anything with my son D. if there is anything wrong with my son
初中英语语法------句子的种类A英语中的句子按其使用目的,句子可分为:陈述句、疑问句、祈使句、和感叹句。 Eg: 陈述句:This is a dog. 疑问句:Is this a dog? 祈使句:Open your eyes! 感叹句:What a beautiful building it is! 简单句:I am studying. 并列句:I was born in a small village and I lived there for nearly ten years. 复合句:As soon as I get there, I'll call you. 1 陈述句凡是说明一件事情,提出一个看法,或者是表达一种心情的句子都是陈述句。大多数的句子都是陈述句,陈述句可以用肯定式和否定式。陈述句句末用句号“.”,通常用降调。 Eg:We live in Beijing. We don't live in Beijing. (1) be 动词、一般动词(实义动词)、情态动词的否定句 I am not a student. I don't know him. He can't speak English.
be 动词的否定句句型:主语+ be动词+ not + … I wasn't good at English. They weren't at home yesterday. He isn't my cousin. 进行时和被动语态都有be 动词,它们的否定句与be动词的否定句同形。 Eg:They aren't cleaning the room. The child was not looked after by anybody. 将来时(will,shall)、完成时及情态动词的被动语态不能用be动词否定句型。 They will not be sent to the front. They will be not sent to the front.× 情态动词的否定句 句型:主语+情态动词+ not + 动词原形 Eg:I can't do it myself. You mustn't take the books out. You must not go there alone. 一般动词的否定句. 句型:主语+ do/does/did + not + 动词原形 Eg: They didn't live in Shanghai. He doesn't do his homework every day.
句子成分精讲 句子成分:主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、补语等。 主要成分:主语和谓语 1、主语 一个句子中需要加以说明或描述的对象。主语的位置: 一般位于句首,由名词、代词、数词或相当于名词的词、短语等充当。The school is far from here. 名词做主语 She goes to school by bike.代词做主语 Eight is a lucky number.数词做主语 The blind need more help.名词化的形容词做主语 There is a pen on the desk. 名词做主语 Predicting the future is interesting.动名词做主语 To be a doctor is my dream.不定式短语做主语 2、谓语 表示人或事物(主语)的动作和存在的状态. 英语中由动词be、动词have和行为动词来充当谓语动词 句子的时态和语态是通过谓语表现出来。 谓语动词往往由一个或一个以上的助动词或情态动词加上主要动词构成。分析句子的主语和谓语 Mr. Li teaches English. He can play the piano. My parents and I are having dinner. 3、表语 用来说明主语的身份、特征、性质、状态。 表语的位置 用在动词be和系动词的后面。 名词、代词、数词、介词短语、副词等都可以和连系动词一起构成复合谓语。Your pen is on the desk. He got very angry. My dream is to have a robot.
初中英语语法大全-句子的种类 按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类: 陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。 陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。 疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。 图解语法 1. 陈述句 说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句 特别提示:
肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody 等。 另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。 2. 疑问句
3. 常用的特殊疑问句
4. 特殊的反意疑问句 ①主句是祈使句时,“will you?”意为“请求”,“won’t you?”表示提醒对方注意。 例句: Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you? Don’t be late again, will you? ②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式 例句: What fine weather, isn’t it? How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she? ③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?”而不用“am not I?” 例句: I'm working now, aren’t I?
句子的种类 (1)一般疑问句 用来询问一件事或情况是否属实。用yes 或 no 来回答。 (2)特殊疑问句 特殊疑问句由特殊疑问词加一般疑问句构成,不能用yes来no回答。一般用完整的回答或是直接回答疑问词的提问。Where are you from? I am from Beijing. 或Beijing. (3)选择疑问句 提供两种或两种以上的选项供对方选择,前面的选项之间用逗号分隔开来,后两项之间用or连接,回答时选择一种。 Would you like a pear, an apple or a banana ? I’d like a b anana。 (4)反意疑问句 由陈述句加一个简短问句构成,简短问句对陈述句提出相反的疑问。如果陈述句部分是肯定,后面问句就用否定形式;陈述句部分是否定,简短问句则用肯定形式。 He likes music, doesn’t he? Yes,he does. 是的,他喜欢。No,he doesn’t. 不,他不喜欢。 He doesn’t like music, does he ? Yes,he does. 不,他喜欢。No,he doesn’t. 是的,他喜欢。 即回答应该按实际情况来回答,实际情况是肯定的,就用yes。否定的就用no.
小学英语一般疑问句,否定句以及对划线部分提问的解题指导 改为一般疑问句: 先找am, is, are, was, were或can, would,放在最前面, 如没有则判断是否为过去式,是则动词改为原形,句前加Did,其余照抄; 不是则判断是否为第三人称单数,是则动词改为原形,句前加Does,其余照抄 以上都不是,则句前加Do,其余照抄。 改为否定句: 方法和上面一样, 先找am, is, are, was, were或can, would,再后加not,其余照抄 如没有则判断是否为过去式,是则动词改为原形,人后加didn’t,其余照抄; 不是则判断是否为第三人称单数,是则动词改为原形,人后加doesn’t,其余照抄 以上都不是,则人后加don’t,其余照抄 对划线部分提问: ①用适当的疑问词代替划线部分,②将剩余部分改为一般疑问句 (注:如划线部分为主语,则用who代替,其余照抄;如划线部分为动词或动词短语,则用do代替,句前加what,再改为一般疑问句)例如: He is running now.----- He isn’t ru nning now. ---Is he running now? ---Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t. They are making a puppet.---- They aren’t making a puppet.---Are they making a puppet? ---Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t. I often watch TV in the evening.------ I don’t often watch TV in the evening.---- Do you often watch TV in the evening?-----Yes, I do. No, I don’t. He plays football after school. ---- He doesn’t play football after school. Does he play football after school?----Yes, he does. No,he doesn’t. We began class at 8 o’clock yesterday.------ We didn’t begin class at 8 o’clock yesterday. Did you begin class at 8 o’clock yesterday? ---Yes,we do. No, we don’t. 练一练: 1、填入适当的疑问词。 1) _____wallet is it? It’s mine.2) ____is the Christmas Day? It’s on t he 25th of Decem ber. 3)________is the diary? It’s under the chair. 4) ______is the boy in blue? He’s Mik e.
初中英语句子成分 一.句子的成分:句子的成分是指组成句子的各个部分,即:主语、谓语、表语、 宾语(直接宾语和间接宾语)、补足语、定语、状语等。 主要成分:主语和谓语 句子的成分 次要成分:表语、宾语、补足语、定语、状语等 (一)主语:主语是一个句子的主要成分,也是句子所叙述的主体,一般位于句首,Subject 表示句子所说的是“什么人”或“什么事物”。一般由名词、代词、数词、不定式、动名词、名词化的形容词和主语从句等充当。 注意:在there be结构、疑问(当主语不是疑问词时)和倒装句中,主语位于谓 例如:Tom is a good boy. (名词) We often speak English in class. (代词) One-third of the students in this class are girls. (数词) To swim in the river is a great pleasure. (不定式) Smoking does harm to the health. (动名词) The rich should help the poor. (名词化形容词) When we are going to have an English test has not been decided. (主语从句) It is necessary to master a foreign language.(it为形式主语,真正的主语是不 定式) (二)谓语:谓语说明主语所做的动作或具有的特征和状态。说明主语“做什么”、Predicate “是什么”或“怎么样”,一般由动词或动词短语来充当,一般放在主语之后。谓语和主语在人称和数两方面必须一致。谓语的构成如下: 1.简单谓语:由一个动词或动词短语构成。例如: I like apples. ( 动词) He practices running every morning. (动词短语) 2.复合谓语:(1)由(情态动词或其他助动词+动词原形)构成; 例如:You may keep the book for two weeks. He has caught a bad cold.
初中英语句子种类一 LELE was finally revised on the morning of December 16, 2020
英语中的句子可以按其作用或者按其语法结构(即句子的形式)两种标准分类。下面是具体的分类依据和结果。 (1)按其作用或使用目的,句子可分为: 陈述句:This is a truck. 这是一辆卡车。 疑问句:Is this a truck 这是卡车吗 祈使句:Drive the truck away. 把卡车开走。 感叹句:What a big truck it is! 多么大的卡车! 按语法结构,句子可分为:(2)简单句:I am busy. 我很忙。 并列句:I am busy washing, but he is playing Majiang with them. 我在忙着洗衣服,但他却在跟他们打麻将牌。 复合句:Although I am busy washing, he is playing Majiang with them. 尽管我在忙着洗衣服,他却在与他们一块打麻将牌。 一、陈述句:用于说明一件事,表示一种看法或表达某种心情的句子,都是陈述句。陈述句分为肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。 1肯定句 He is a middle school teacher. 他是一位中学老师。(一般现在时) She is cleaning the room. 她正在收拾屋子。(现在进行时) They have visited the museum. 他们已经参观过这所博物馆了。(现在完成时) He did a lot of washing yesterday. 他昨天洗了好多衣服。(一般过去时) They had already finished quarrelling when I came. 我来时他们已经争吵完了。(过去完成时) The meeting will begin at once. 会议马上就要开始了。(一般将来时) 2否定句 (1)使用not否定: He isn't a worker. 他不是个工人。(一般现在时) She doesn't do the cleaning every day. 她不是每天都做卫生。(一般现在时) I haven't had my breakfast yet. 我还没有吃早点。(现在完成时) You didn't do your homework seriously. 你没有认真地做你的作业。(一般过去时) You mustn't take her to your parents. 你千万不要把她带到你的父母那里去。(情态动词) She needn't quarrel with him. 她没必要跟他吵。(情态动词) The house won't be painted. 这所房子将不粉刷了。(被动语态将来时) She might not notice you.