英语教学法一 2
- 格式:doc
- 大小:74.50 KB
- 文档页数:17

《英语教学法》教学大纲第四节教学环境教学要求:1. 了解:中小学英语教学要素。
2. 熟悉:教学内容。
3. 掌握:中小学英语教学要素之间的关系。
第四章中小学英语教学原则教学内容:第一节学生中心原则第二节合理目标原则第三节有效原则第四节真实原则教学要求:1. 了解:中小学英语教学原则。
2. 熟悉:中小学英语教学原则。
3. 掌握:中小学英语教学原则之间的辩证关系。
第五章中小学英语教学策略教学内容:第一节管理策略第二节提问策略第三节传授策略第四节评价策略第五节整合策略教学要求:1. 了解:课堂管理的定义及重要性。
2. 熟悉:中小学英语教学策略。
3. 掌握:中小学英语管理策略、提问策略、传授策略、评价策略、整合策略。
第六章中小学英语教学设计教学内容:第一节教学设计要素第二节教学设计方法教学要求:1. 了解:教学设计的内涵、教学设计的过程。
2. 熟悉:教学设计方法。
3. 掌握:教学设计的内涵、教学设计的过程和教学设计方法。
第七章中小学英语课堂教学过程教学内容:第一节任务教学过程第二节 PWP教学过程教学要求:1. 了解:任务教学过程。
2. 熟悉:PWP教学过程。
3. 掌握:任务教学过程、PWP教学过程的联系和区别。
第八章中小学英语教学活动教学内容:第一节课堂教学活动第二节课外教学活动教学要求:1. 了解:课堂教学活动过程。
2. 熟悉:课外教学活动的方法。
3. 掌握:课堂教学活动过程、课外教学活动的方法。
第九章中小学英语知识教学方法教学内容:第一节语音教学方法第二节词汇教学方法第三节语法教学方法教学要求:1. 了解:语音教学方法。
2. 熟悉:词汇教学方法、语法教学方法。
3. 掌握:语音教学方法、词汇教学方法、语法教学方法。
第十章中小学英语听说教学方法教学内容:第一节听力教学方法第二节口语教学方法教学要求:1. 了解:听力教学方法。
2. 熟悉:口语教学方法。
3. 掌握:听力教学方法、口语教学方法。
第十一章中小学英语读写教学方法教学内容:第一节阅读教学方法第二节写作教学方法教学要求:1. 了解:阅读教学方法。

英语教学的方法有哪些
英语教学的方法有许多种,以下是常见的几种方法:
1. 交际法(Communicative Approach):强调学生在真实的语境中进行交际,注重口语和听力技能的培养,通过实际的交际活动来学习语言。
2. 阅读法(Reading Approach):通过阅读来学习语言,注重扩大词汇量和提高阅读理解能力,培养语感和文化意识。
3. 写作法(Writing Approach):培养学生的写作能力,通过写作来学习语言结构和表达技巧,提高语言的准确性和流畅性。
4. 任务型教学法(Task-Based Approach):设置真实的任务和情境,要求学生在完成任务的过程中使用英语来表达,通过实际操作来学习语言。
5. 游戏教学法(Game-Based Approach):利用各种游戏和活动来激发学生的学习兴趣,提高他们的参与度和积极性,通过游戏的形式学习语言。
6. 任务型语法教学法(Grammar-Translation Approach):通过讲解语法规则和翻译练习来帮助学生掌握语言结构和阅读能力。
7. 多媒体教学法(Multimedia Approach):利用多媒体技术,如音频、视频、
互联网等,来增加学习材料的丰富性和趣味性,激发学生的学习兴趣。
8. 情景教学法(Situation Approach):根据不同情景设置教学活动,让学生在现实生活场景中运用所学的语言知识。
9. 外教授课法(Native Speaker Approach):请母语为英语的外教来进行授课,提供纯正的语音和语言环境,帮助学生接触和掌握地道的英语表达方式。
不同的方法适用于不同的教学目标和学生群体,教师可以根据实际情况选择合适的教学方法。
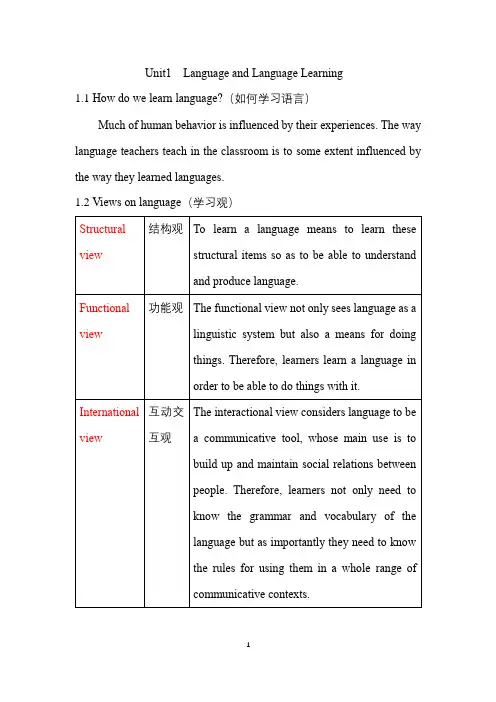
Unit1 Language and Language Learning1.1How do we learn language?(如何学习语言)Much of human behavior is influenced by their experiences. The way language teachers teach in the classroom is to some extent influenced by the way they learned languages.1.2Views on language(学习观)1.3Views on language learning and learning in generalNow, the research about language learning theories can be broadly divided into two parts. They are Process-oriented theories and Condition-oriented theories. Some researchers attempt to formulate teaching approaches directly from these theories. For example, the Natural Approach, Total physical Response, and the Silent Way are based on one or more dimensions of processes and conditions. Here are What is done in these processes.1.4What makes a good language teacher?(好教师的素质要素)①Ethic devotion ②Professional qualities ③Personal styles1.5How can we become a good language teacher?(如何成为一名好的语言老师)The most important and difficult part of the making of a good language teacher is the development of professional competence, which is the state or quality of being adequately qualified for the profession, and armed with a specific range of skills, strategies, knowledge, and ability.Teacher’s professional development1.6An overview of the bookUnit2 Communication Principles and Task-based Language Teaching 2.1 Language use in real life vs. traditional pedagogy2.2 What is communicative competence?communicative competence includes both the knowledge about the language and the knowledge about how to use the language appropriately in communicative situation.2.3 Implications for teaching and learning (略)2.4 Principles of Communicative Language Teaching(CLT)1)Communication principle: Activities that involves real communication promote learning.2) Task principle: Activities in which language is used for carry out meaningful tasks promote learning.3) Meaningfulness principle: Language that is meaningful to the learner supports the learning process.2.5 CLT and the teaching of language skills2.6 Main features of Communicative activities2.7 Task-based Language Teaching(TBLT)Task-based Language Teaching is, in fact, a further development of Communicative Language Teaching.2.7.1 Definitions of a task√√2.7.2 Four components of a task.1) A purpose: making sure the students have a reason for undertaking the task.2) A context: this can be real, simulated, or imaginary, and involves sociolinguistic issues such as the location, the participants and their relationship, the time, and other important factors.3) A process: getting the students to use learning strategies such as problemsolving, reasoning, inquiring, conceptualizing and communicating.4) A product: there well be some form of outcome, either visible(written plan, a play, a letter, etc.) or invisible (enjoying a story, learning about another country, etc.)2.7.3 Exercises, exercise-tasks and taskexercise exercise-task task2.8 PPP and Task-based Language TeachingMany teachers may be familiar with the Presentation, Practice and Production(PPP). A typical PPP lesson would start by the teacher introducing a new language item in a context followed by some controlled practice, such as drilling, repetition, dialogue reading, etc. Students then move on to produce the language in a more meaningful way, such as a role play, a drama, an interview, etc. Some teachers may also be familiar with the five-step teaching method, which is quite similar to the PPP model but adding revision at the beginning and consolidation at the end.2.8.1 Differences between PPP and TBL1) The way students use and experience language in TBL is rapidly different from PPP.2) TBL can provide a context for grammar teaching and form-focused activities. PPP is different in this aspect.2.9 How to design tasks?√√2.10 Appropriateness of CLT and TBLT in the Chinese context1)The problems of CLT: ①If CLT is culturally appropriate.(Both its advantages and constraints are recognized by teachers and students.)②It is very difficult to design a syllabus with a one to one correspondence between a function and a form.2)The problems of TBLT: ①It may not be effective for presenting new language items.(Swan,2005) ②Time. Teachers have to prepare task-based activities very carefully. ③The culture of learning. Some students may find it difficult to adapt to TBLT. ④The level of difficulty. Students mayfind task-based learning quite difficult if they do not have sufficient linguistic resources to handle holistic communication.2.11 ConclusionIt is important to remember that a method is effective only when it is appropriate to the teaching context. Therefore, when a new method or approach emerges, it is unwise to simply cast away the traditional and follow the new trend. The best thing to do is to develop one’s own teaching methods based on the context where one teaches and integrates the merits of different methodologies to serve the purpose of one’s teaching objectives and the needs of one’s students.Unit3 The National English Curriculum3.1 A brief history of foreign language teaching in ChinaUnit4 Lesson Planning4.1 Why is lesson planning important?Definition: A lesson plan is a framework of a lesson in which teachers make advance decisions about what they hope to achieve and how they would like to achieve it.Reasons: ①A clear lesson plan makes the teacher aware of the aims and language contents of the lesson.②It helps teachers distinguish thevarious stages of a lesson and see the relationship between them so that the activities of different difficulty levels can be arranged properly and the lesson can move smoothly from one stage to another.③Proper lesson planning gives teachers the opportunity to anticipate potential problems that may arise in class so that they can be prepared with some possible solutions or other options for the lesson. ④Good planning gives teachers, especially novice teachers confidence in class. ⑤When planning the lesson, the teacher also becomes aware of the teaching aids that are needed for the lesson.⑥Planning is a good practice and a sign of professionalism.4.2 Principles for good lesson planning4.3 Macro planning vs. micro planning.(宏观计划vs.微观计划)The components of macro planning:(宏观计划包含的内容)1)Knowing about the profession.2)Knowing about the institution.3)Knowing about the learners.4)Knowing about the curriculum/syllabus.5)Knowing about the textbook.6)Knowing about the objectives.4.4 Components of a lesson planDifferent teachers have different teaching styles and may use different teaching procedures, so ‘every lesson is unique’(Robertson and Acklam,2000:6), and so is every lesson plan. A lesson plan include many parts.Unit5 Classroom ManagementDefinition:Classroom management is the way teachers organize what goes on in the classroom.Goal:To create an atmosphere conductive to interacting in English in meaningful ways.(Gebhard,1996)Conditions for achieving classroom management:1)The teacher plays appropriate roles.2)The teacher provides clear instructions.3)Students are grouped in a way suitable for the learning activities.4)The teacher asks appropriate questions.5)There is discipline as well as harmony in the class.6)The students errors are treated properly.5.1 The role of the teacherWhat are the teacher’s roles defined by Harmer?①controller ②assessor ③organiser ④prompter ⑤participant⑥resource-providerWhat are teacher’s new roles?①facilitators ②guides ③researchers5.2 Classroom instructionsDefinition: Classroom instructions refer to the type of language teachers use to organize or guide learning. They include giving directions to tasks or activities; providing explanations to a concept or language structure; setting requirements; checking comprehension; drawing attention; motivating learners; giving feedback and assigning homework, etc. Generally they include all classroom language that teachers may use for teaching purposes as well as for managing teaching.What are rules to follow for making instructions effective?①To use simple instructions and make them suit the comprehensionlevel of the students.②To use the mother-tongue only when it is necessary.③To be careful not to do all the talking in class.。

一、翻译法(Translation Method)翻译法也叫语法翻译法(Grammar-Translation Method)、阅读法(Reading Method)、古典法(Classical Method)。
翻译法最早是在欧洲用来教授古典语言希腊语和拉丁语的外语教学方法,到18世纪末和19世纪中期开始被用来教授现代语言。
翻译法的教学目的是培养学生阅读外国文学作品的能力和模仿范文进行写作的能力。
其突出的特点是:教师用母语授课,授课重点是讲解与分析句子成分和语音、词汇变化与语法规则。
翻译法历史悠久,其优点是:1. 学生语法概念清晰;2. 阅读能力较强,尤其是遇到长而难的句子时通过分析句子结构便能理解意思;3. 有助于培养翻译能力和写作能力。
翻译法的缺点是:1. 忽视口语教学,学生的语音语调差,不利于培养学生用外语进行交际的能力;2. 教学方式单一,学生容易失去兴趣。
二、直接法(Direct Method)直接法也叫自然法(Natural Method)、心理法(Psychological Method)、口语法(Oral Method)、改良法(Reformed Method)。
针对翻译法不能培养学生听说能力的缺点,直接法于19世纪末在欧洲产生。
它包含三个方面的意思:直接学习、直接理解和直接应用。
其主要特点是:不允许使用母语,用动作和图画等直观手段解释词义和句子。
直接法流行甚广,其优点是:1. 采用各种直观教具,广泛运用接近实际生活的教学方式,有助于培养用外语思维的能力;2. 强调直接学习和直接应用,注重语言实践练习,学生学习积极性高,学习兴趣浓厚;3. 重视口语和语音教学,能有效地培养学生的语言运用能力。
其缺点是:1. 排斥母语,使学生对一些抽象和复杂的概念难以理解;2. 没有明晰的语法解释,导致学生说出的话语法错误较多。
三、听说法(Audiolingualism, Audiolingual Method)听说法于20世纪40至60年代盛行于美国。


外语教学法-2(总分:100.00,做题时间:90分钟)一、{{B}}Ⅰ.Multipe Choice{{/B}}(总题数:15,分数:15.00)解析:[解析] 自然法是克拉申(Krashen)和特雷尔(Terrell)提出的一种教学法,其教学原则是:强调自然的语言交际而不是规范的语法学习,并对学习者的错误持宽容态度。
1977年加利福尼亚大学的一名西班牙语教师特雷西·特雷尔提出了自然法,1983年与克拉申合著了《自然法:课堂中的语言习得》一书,从此自然法受到人们更加广泛的好评。
B威尔金斯提出了以交际为标准(communicative criteria)而设计的功能意念(functional-notional)大纲的基本要点,其著作《意念大纲》(Notional Syllabuses)对交际教学法发展有深刻影响。
D海姆斯提出的交际能力(communicative competence)为交际法奠定了基础。
2.Which of the following statements is true in the Grammar-Translation Method?(分数:1.00)A.L1 was maintained as the reference system in the acquisition of L2. √B.L2 was maintained as the reference system in the acquisition of L1.tin was maintained as the reference system in the acquisition of L2.tin was maintained as the reference system in the acquisition of L1.解析:[解析] 语法翻译法所依托的语言理论是由历史比较语言学派生出来的,通过将目标语拉丁语和希腊语和第一语言作对比,将第一语言看作是习得目标语过程中的参照系统。

英语专业英语教学法(2) 试题及答案分析Section ⅠBasic Theories and PrinciplesQuestions 1—15 are based on this part.Direction:Choose the best answer from A. B or C for each question. Write your answer on the Answer Sheet.1. What can "scrambled sentences" help to train in terms of writing?A. Unity.B. Coherence.C. Indention2. What can the following activity help to train in terms of writing?The teacher asked the students to -write two letters, one to their parents, and the other to their friends, informing them the news of his success in a competition.A. Sense of audience.B. Sense of unity.C. Sense of coherence.3. Which of the following writing activities belongs to the communicative approach of writing?A. The teacher asks the students to write on "The difference between college life and middle school life."B. The teacher asks the students to form a text from scrambled sentences.C. The teacher asks the students to write an e-mail to their parents to tell them to come to theclass meeting.4. What stage can the following grammar activity be used at?The teacher asks the students to discuss the differences between two paragraphs in terms oftense.A. Presentation.B. Practice.C. Production.5. Which of the following grammar activities is most communicative?A. Grammar dictation.B. Sentence completion.C. Guessing objects.6. If we are to present the meaning of abstract notion, which of the following techniques is the best?A. Translation.B. Pictures.C. Graphing.7. What vocabulary learning strategies does the following activity help to train? Arrange thefollowing words into three different columns;Fruity apple, pear, orange, pickpocket, mugger, bank robber, profession, gardening, teaching, managingA. Collocation.B. Classification.C. Imagery.S. Which of the following is among the human factors that influence lesson planning?A. Environment conditions of the classroom.B. Students" attitude towards the kind of instruction the teacher applies.C. The type of evaluation the teacher conducts.9. What role does the teacher play in the deductive presentation of grammar?A. Instructor.B. Prompter.C. Participant.10. What is the teacher doing in terms of instruction in the following?"Now, I"d like you to answer the comprehension questions following the text to make sure that all of us understand what precisely the text is about."A. Checking understanding.B. Assigning the task.C. Monitoring the activity.11. What is the teacher doing in terms of error correction?S: My-watch was stealing.T: What happened to Jack’s watch, Jane?A. Ignoring the student"s mistake.B. Encouraging peer correction.C. Helping the student to correct his own mistake.12. What activity is following seating arrangement most suitable for?A. Group discussion.B. Acting of a play.C. Individual reading of the text.13. Which of the following activities can be used at the practice stage of vocabulary instruction?A. Completion exercises.B. Reading to discover the meaning of words.C. Cross-word puzzles.14. Which of the following activities is most suitable for whole-class work?A. Role-play of a dialogue involving the use of the passive voice.B. Writing about the changes of one"s hometown.C. Presenting the passive voice.15. Which of the following best explains what a lesson plan involves?A. It is a reminder for the teacher, who needs to refer to the reference materials in classroom instruction.B. It is a schedule of the classroom procedure to fulfill the teaching and learning objectives.C. It is a list of activities to be conducted in a lesson.Section ⅡProblem SolvingQuestions 16—20 are based on this part.Directions: Below are five situations in classroom instruction. Each has at least one problem. First,identify the problem(s). Second, provide your solution(s) according to what you have learned in Book2. You should elaborate on the problem(s) and solution(s) properly. Write your answer on the Answer Sheet.16. Mr. Li will assign a writing task for each unit. Every time, he will give a topic similar to thetexts they learn, like "My hometown", "Sports" and so on for students to finish after class.17. Mr. Wang always conducts grammar instruction with discovery activities. He thinks students need to get familiar with the structures through reading and writing before learning the rules of grammar.18. Mr. Deng is very pleased with his new textbook. But when he asked his students to do all the exercises in the textbook, he found he could not find enough time, and some students were not veryactive in the classroom activities.19. In class, Ms Zhang assigned the students to work in groups to work on an information transfertable. When time was up, only two groups finished ahead of time, and others were still discussing.20. Jack is reporting their group task about an investigation of students" pastimes. But because he is a little nervous and not so good at speaking, he pauses here and there and always makes mistakes.To help him, the teacher inserts some correction during his report.Section ⅢMini-lesson planQuestions 21 and 22 are based on this part.Directions: Read the two texts below and complete the teaching plans. Write your answer on theAnswer Sheet.21. Design an activity to present the vocabulary in the following passage. It should involve thestudents in group discussion.My name is Adam Rous,. I"m 19 years old and I used to be a drug addict. I first started using drugswhen I -was 15. 1 bought cannabis from a man in the street. I continued to buy cannabis from the sameman for about six months. One day, he offered me some crack cocaine.Cocaine is a powerfully addictive drug. Some drug users inject cocaine, others smoke it. Both waysare dangerous. Users who inject the drug are also in more danger if they share needles with other users.Type of the activity (e. g. information-gap, role-play,problem-solving)Objective(s) of the activityClassroom organization of the activityTeacher"s role(s)Students" role(s)Teacher working timeStudent working timeTeaching aid(s)Predicted problem(s)Solution(s)Procedure 1)2)3)4)22. Design a writing activity with the following material.Lao She wrote Teahouse in 1957. The play shows the audience life in China between 1900 and 1950. It lakes place in a teahouse in old Beijing and it tells us the story of Wang Lifa and his customers. It takes us to see the teahouse as the centre of the neighborhood. Finally, it says goodbye to old Beijing and its people.The story starts in 1898 during the Qing dynasty. It continues in 1910, and finally it brings the audience to the end of Anti-Japanese War in 1945. Then the government takes the teahouse from Wang, and he dies.Lao She was barn in 1899. He wrote many plays , novels and short stories. He was born in Beijing. His parents sent the young man to the Teacher"s School in Beijing and he learned to teach. From 1924 to 1929 he taught Chinese to the English in London. He was named a "People"s Artist" and a "Great Master of Language". He was one of the greatest Chinese -writers in the twentieth century.At Lao She "s Teahouse today, waiters bring tea to the customers and sell them delicious Chinese food. If you like Beijing Opera, folk music, acrobatics or magic shows , you can enjoy them at the teahouse. Lao She"s Teahouse gives a warm welcome to everyone from China and from all over the world.Type of the activity (e.g. parallel writing, role-play,problem-solving)Objective(s) of the activityClassroom organization of the activityTeacher"s role(s)Students" role(s)Teacher working timeStudent working timeTeaching aid(s)Predicted problem(s)Solution(s)Procedure 1)2)3)4)英语教学法(2) 试题答案及评分标准Section ⅠBasic Theories and Principles (共30分,每题2分)1. B2. A3. C4. A5. C6. A7. B8. B9. A 10. B11. B 12. A 13. A 14. C 15. BSection ⅡProblem Solving (共30分,每题6分)找出问题得2分,根据交际法原则提出合理的解决方案得2分,问题和解决方案应有适当的阐述,行文逻辑1分,语法1分.16. Problems:1) Students need writing practice in class. They need to be trained in specific writing mechanism.They need to work together with others. After-class writing assignment itself is powerless to train students" writing ability.2) The topics are too general and there is not a sense of purpose in writing.3)The topics cannot give students a sense of audience in writing,4) There should be some writing requirement in terms of the process and writing skills. Solutions:1) The teacher had better incorporate writing into the classroom instruction, integrating it withreading, listening or speaking.2) If he assigns writing as after-class homework it is better to make clear the purpose of writing. For example, are they introducing their homework to attract foreign investment or something else?3) The teacher should narrow down the topic, making it easy to handle for the middle schoolstudents.4) The teacher should make it clear who, he prospective readers might be. For example, are they introducing their hometown to foreigners or someone else?(以上两部分,各回答出两点即可得4分)17. Problems:1) It fails to consider the diverse objectives of grammar instruction. We shouldn"t always use the same kind of approach in grammar instruction. The inductive approach can"t suit all grammar instruction objectives.2) It fails to consider the diverse types of grammar items and the supporting materials. It is wrong to adopt the same approach to all grammar instruction.3) It fails to consider the learning styles of the students. Some students prefer inductive learning,while others may prefer deductive learning.Solutions:1) The teacher should first do some needs analysis. He should be clear whether the students already have relevant grammar basis. Can he make use of it?2) It is better to choose an approach correspondent to students, learning styles. With analytical learners, deductive instruction may work better.3) The teacher should vary the approach according to the materials. Inductive approach may workbetter with some grammar items, but worse for others.4) We should vary our approaches to grammar instruction. Sometimes, it is better to adopt the deductive approach if the students have already had the relevant grammar knowledge.(问题部分要求写出两点,解决方式可以只写一点。

英语中常用的教学方法有哪些英语教学方法有千千万万种,但要根据自己的实际情况,灵活运用不同的方法。
下面是小编整理的英语中常用的教学方法有哪些,欢迎大家阅读分享借鉴,希望对大家有所帮助。
英语中常用的教学方法一、翻译法(Translation Method)翻译法也叫语法翻译法(Grammar-Translation Method)、阅读法(Reading Method)、古典法(Classical Method)。
翻译法最早是在欧洲用来教授古典语言希腊语和拉丁语的外语教学方法,到18世纪末和19世纪中期开始被用来教授现代语言。
翻译法的教学目的是培养学生阅读外国文学作品的能力和模仿范文进行写作的能力。
其突出的特点是:教师用母语授课,授课重点是讲解与分析句子成分和语音、词汇变化与语法规则。
翻译法历史悠久,其优点是:1. 学生语法概念清晰;2. 阅读能力较强,尤其是遇到长而难的句子时通过分析句子结构便能理解意思;3. 有助于培养翻译能力和写作能力。
翻译法的缺点是:1. 忽视口语教学,学生的语音语调差,不利于培养学生用外语进行交际的能力;2. 教学方式单一,学生容易失去兴趣。
二、直接法(Direct Method)直接法也叫自然法(Natural Method)、心理法(Psychological Method)、口语法(Oral Method)、改良法(Reformed Method)。
针对翻译法不能培养学生听说能力的缺点,直接法于19世纪末在欧洲产生。
它包含三个方面的意思:直接学习、直接理解和直接应用。
其主要特点是:不允许使用母语,用动作和图画等直观手段解释词义和句子。
直接法流行甚广,其优点是:1. 采用各种直观教具,广泛运用接近实际生活的教学方式,有助于培养用外语思维的能力;2. 强调直接学习和直接应用,注重语言实践练习,学生学习积极性高,学习兴趣浓厚;3. 重视口语和语音教学,能有效地培养学生的语言运用能力。

英语教学方法有哪些
1. 交际法:注重培养学生的交际能力,通过情境对话、角色扮演等方式进行教学。
2. 听说法:注重培养学生的听力和口语能力,通过听力训练、口语练习以及情景对话等方式进行教学。
3. 阅读法:注重培养学生的阅读能力,通过课文阅读、文章分析、阅读理解等方式进行教学。
4. 写作法:注重培养学生的写作能力,通过模仿写作、写作技巧训练以及写作指导等方式进行教学。
5. 文化法:注重培养学生对英语国家文化的了解,通过文化背景解读、文化差异比较等方式进行教学。
6. 游戏法:通过游戏、竞赛等方式激发学生的学习兴趣,提高学习的积极性和参与度。
7. 多媒体法:使用多媒体教具和技术,如音频、视频、互联网等,辅助教学,提高学生的学习效果。
8. 任务型教学法:以任务为主导,通过学生自主学习和任务完成来达到语言能力的提升。
9. 分层教学法:根据学生的不同水平和需求,制定不同的教学内容和任务,实施个性化的教学。
10. 情境教学法:通过创设真实或模拟的情境,让学生在真实的语言环境中进行学习和交流。

英语教学法王蔷笔记摘要:一、王蔷《英语教学法教程》概述二、英语学习的基本方法1.语言与学习的的关系2.学习语言的个体差异三、英语教学方法及步骤1.制定明确的教学目标2.情景教学法的应用3.常见英语教学方法的介绍四、总结与展望正文:一、英语学习的基本方法1.语言与学习的的关系语言是人类交流的基本工具,学习语言是一个持续的过程。
个体通过与他人的互动、参与各种语言活动,逐渐掌握语言技能。
2.学习语言的个体差异不同的人在学习语言过程中,由于认知能力、学习动机、语言环境等因素的不同,呈现出个体差异。
教师应关注学生的个性化需求,制定因材施教的教学策略。
二、英语教学方法及步骤1.制定明确的教学目标教学目标是课堂教学的出发点和回归点。
教师应根据学生的实际情况,制定具体、明确的教学目标,确保教学过程的有效性。
2.情景教学法的应用情景教学法是一种以生活场景为依托的教学方法。
教师应创设真实、生动、实用的情景,帮助学生将所学语言材料进行综合、创造性地表达交流。
3.常见英语教学方法的介绍(1)Task-Based Language Teaching(TBLT):以任务为导向的教学方法,强调学生在完成任务的过程中自然地学习语言。
(2)五步教学法:包括引入、练习、输出、反馈和巩固五个步骤,逐步引导学生掌握语言技能。
(3)五指教学法:一种针对听、说、读、写、译五个语言技能的教学方法,注重均衡发展学生的语言能力。
(4)3P教学法:包括呈现、实践、产出的教学过程,强调在实践中学习语言。
(5)交际型教学:以培养学生的交际能力为核心,注重语言运用的实际场景。
三、总结与展望王蔷的《英语教学法教程》为英语教师提供了丰富的教学理论和实践方法。
通过关注学生的个体差异、制定明确的教学目标,以及运用多样的教学方法,教师可以提高英语教学质量,培养学生的语言交际能力。

英语课常用的16种教学方法1. 直接教授法:老师直接向学生传授知识和技能,例如解释规则、定义和示范。
2. 互动式教学法:鼓励学生积极参与课堂讨论和活动,例如问题解答、小组讨论和角色扮演。
3. 合作学习法:鼓励学生合作完成任务和项目,例如合作写作、小组项目和角色扮演。
4. 游戏教学法:通过游戏和竞赛激发学生对学习的兴趣和积极性,例如单词拼图游戏、口语对话游戏。
5. 情景教学法:通过模拟真实情境的学习活动,让学生在实际应用中学习语言技能,例如模拟订餐、旅行等情境。
6. 任务型教学法:通过给学生提供具体任务,激发学生自主学习和解决问题的能力,例如写信、制作海报等任务。
7. 探究式学习法:鼓励学生通过探究和发现知识,培养学生的探索精神和批判性思维能力,例如实验、调查和讨论。
8. 阅读教学法:通过阅读有趣和适合学生水平的材料,提高学生的阅读理解和词汇能力,例如课堂阅读和课外阅读。
9. 写作教学法:通过指导学生写作,提高学生的写作技能和表达能力,例如写日记、作文和短文。
10. 听力教学法:通过听取真实语言材料和练习,提高学生的听力理解能力和口语表达能力,例如听力训练、对话练习。
11. 口语教学法:通过练习日常口语对话和情景,提高学生的口语表达能力和交流能力,例如角色扮演、对话练习。
12. 多媒体教学法:利用多媒体技术,如幻灯片、视频和音频,增加学习的趣味性和吸引力,例如展示图片、播放视频。
13. 演讲和展示教学法:鼓励学生进行演讲和展示,培养学生的自信和表达能力,例如个人演讲、小组展示。
14. 观察和讨论教学法:通过观察和讨论现象、问题和材料,培养学生的观察力、分析能力和批判思维,例如观察实验、小组讨论。
15. 自主学习法:鼓励学生自主探索和学习,培养学生的学习兴趣和学习能力,例如自主阅读、自主研究和学习项目。
16. 反馈和评估教学法:定期给学生提供反馈和评估,帮助学生了解自己的学习进展和需要改进的地方,例如个人反思、小组评估和作业批改。
5109英语教学法(1)试题复习提要教材《英语教学法》(1)(开卷)I: Basic Theories and Principles:Unit 1 Introduction1.The Grammar-Translation Method2.syllabus be organizition ?3.Functional-Notional Approach4.characteristic of acquisition5.Behaviorism6.The Humanist Approach?7.Audio-lingual Method8.Direct method9.What does TPR stand for?10.L inguistic competence ,Communicative competence,Discoursecompetence11.t he description of a function12.d ifferent types of syllabus13.W hat is “Needs Analysis”?14.S tage of course designUnit 2 the Communicative Approach重点单元15.T he basic characteristics of Communicative Approach16.d ifference between oral and written communication17.c ommunicative language teaching18.r oles of teachers19.c ommunicative activitiesUnit 3 Focus on Reading20.m ajor reading strategies: skimming, scanning, inferring21.t hree stages of teaching reading: pre-reading, while-reading,post-reading22.t he top-down approach of reading , The bottom-up approach ofreading, The interactive approach of readingUnit 4 Focus on Listening23.T he major listening skillsListening for gist, listening for specific information, listening for detailed information, inferring, note-taking24.T ree stages of teaching listening: pre-listening, while-listening,post-listeningUnit 5 Focus on Speaking25.Speaking syllabus26.The PPP model27.conversational technique28.features of spoken English29.designing a speaking activityAppendix: Focus on Pronunciation30. liaison in pronunciation, articulation, stress ,rhythm30.e rror tolerationII: Lesson Plan重点复习《英语教学法》(2)Unit 9 Lesson Planning,也请参考相应章节的具体教学法,如设计阅读课程参考阅读的教学法。
《英语教学法教程(第二版)》讲义第1章语言和语言学习1.1复习笔记第一章重点讨论语言观和语言学习观、优秀英语教师的基本素质以及如何成为一名优秀的英语教师。
本章要点:1.How do we learn languages?我们如何习得语言?2.\^ews on language 语言观点3.The structural view of language 结构主义语言理论4.The functional view of language 功能主义语言理论5.The interactional view of language 交互语言理论6.What are the common views on language learning?关于语言学习的普遍观点7.process-oriented theories and condition-oriented theories 强调过程的语言学习理论和强调条件的语言学习理论8.The behaviorist theory 行为主义学习理论9.Cognitive theory 认知学习理论10.Constructivist theory 建构主义理论11.Socio-constructivist theory 社会建构主义理论12.What makes a good language teacher?如何才能成为一个好的语言老师13.Teacher’s professional development教师专业技能发展本章考点:我们如何习得语言;我们如何习得语言;结构主义语言理论;功能主义语言理论;交互语言理论;关于语言学习的普遍观点;强调过程的语言学习理论和强调条件的语言学习理论;行为主义学习理论;认知学习理论;建构主义理论;社会建构主义理论;成为一个好的语言老师所要具备的基本素质;教师专业技能发展图本章内容索引:I . How do we learn languages?II.Views on language1.The structural view of language2.The functional view of language3.The interactional view of languageIII.Views on language learning and learning in general1.The behaviorist theory2.Cognitive theory3.Constructivist theory4.Socio-constructivist theoryIV.What makes a good language teacher?V.How can one become a good language teacher?VI. An overview of the book《英语教学法教程(第二版)》讲义《英语教学法教程(第二版)》讲义allowed us the opportunity to expand the original 14 units into 18 in order to include topics reflecting the recent development in English language teaching both at home and abroad, to revisit a number ofareas, to expand and clarify points that we felt were not sufficiently clear in thefirst edition, and to improve the pedagogical usefulness of the text.1.2课后习题详解TASK1Below is a list of interview questions on how people learn a foreign language. In the first column, write down your own responses. Then interview three other students in your class and enter their responses in the other columns. Discuss yourYou ST1 ST2 ST31. How many foreign languages can you speak SO far?2. When did you start learning the foreign language(s)?3. How do you feel about learning a foreign language?4. What difficulties have you experienced in learning?5 • Which skills do you find more difficult to learn?6. Have you focused on knowledge or skills? Why?7. Why do you learn the foreign language(s)?8. Do you consider yourself a successful learner? Why?9• What are your most common learning activities?10. Do you like the way you learned the foreign language(s)?TASK 2Work in groups of 4, brainstorm possible answers to the question: What is language? When you are ready, join another group and share your ideas.Key: Here are sample definitions of “language” found in dictionaries and linguistics books.•Language is a system of arbitrary, vocal symbols which permit all people in a given culture, or other people who have learned the system of that culture, to communicate or to interact. (Finocchiaro, 1964:8)•Language is any set or system of linguistic symbols as used in a more or less uniform fashion by a number of people who are thus enabled to communicate intelligibly with one another. (Random House Dictionary of the English Language 1966:806)•Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication. (Wardhaugh, 1972:3)•Language is a systematic means of communicating ideas or feelings by the use of conventionalized signs, sounds, gestures, or marks having understood meanings. (Webster’s 3rd New International Dictionary of the English Language 1993:1270)•Language is a system of communication consisting of a set of small parts and a set of rules which decide the ways in which these parts can be combined to produce messages that have meaning. (Cambridge International Dictionary of English 1995:795)TASK 3Work in groups of 4. Brainstorm the answers to the two questions stated above.When you are ready, join another group and share your ideas.Key: Generally speaking, psycholinguistic and cognitive process involved in language learning are concerned with how the mind organizes new information such as habit formation, induction, making inference, hypothesis Resting and generalization. To activate these learning process, atmosphere is very important.《英语教学法教程(第二版)》讲义TASK 4Work in groups. Reflect on your own learning experiences from early school years to the university. Have you had an excellent English teacher? Try to identify as many qualities as possible of your best English teacher(s). Note down all the qualities that you think are important for a good English teacher.Key: ethic devotion(responsible, warm-hearted, etc), professional qualities(an excellent command of English) and personal styles(enthusiastic, humourous,etc) jointly contribute to making a good teacher.TASK 5Ethic devotion, professional qualities and personal styles jointly contribute to the making of a good English teacher. All the adjectives in the box below could be used to characterize these three aspects.1.Work in groups of 4 and decide which adjectives describe ethic devotion, which describe personal styles and which describe professional qualities. Please write your answers on a separate piece of paper.2.Add any adjectives to the list which describe farther qualities that you feel are missing.3.These adjectives are intended to describe positive qualities or styles. Do you feel that any of them could have a negative side as well? If yes, in what way? For example, an authoritative teacher may make the students feel assured, but may also make the student less free to disagree with him / her.kind; dynamic; authoritative; hardworking; creative; patient well-informed; fair resourceful; attentive; warm-hearted; reflective; well-prepared; flexible; intuitive accurate; enthusiastic; humourous; caring; disciplined; professionally-trainedKey: Students’TASK 6Work in pairs and discuss how one can become a professionally competent teacher of English. For example, we have to develop our English proficiency first and also we may need to learn from experienced teachers through observations. What else can you think of? Make a list and then pool all your ideas together to find out about your common beliefs.Key: to learn teaching theory;to practice teaching skills;to reflect teaching experience;to learn from one’s own experiences as a learner.TASK 7Work in groups. Discuss possible answers to the following questions in relation to the model presented in Figure IA, _1.Why are stage 1 and stage 2 interrelated by a double arrow line?2.Why are practice and reflection connected by a circle?3.Why is professional competence *a moving target or horizon, towards which professionals travel all their professional lifebut which is never finally attained?54.Where should a TEFL methodology course fill in the model?Figure 1.1Key: 1. Stages 1 and 2 are interrelated by a double arrow line because neither of the two stages is really ever terminated. Teachers should always make a point of updating their command of English because language is always changing. This can be done while they are teaching, but very often teachers take off to have farther training in English. This is especiallyimportant for teachers who do not have enough exposure to English.2.Practice and reflection are connected by a circle because they are neither independent or separate sub-stages. Teachers do not teach one week and then reflect one week. Rather, they teach and reflect on a day to day basis.3.This is because it is believed no one can ever become a perfectly competent language teacher. There is always room for improvement. There is always something better, but never something best.4.TEFL methodology is probably the deceived knowledge” located in the second stage.第2章交际教学原则与任雜语言教学2.1复习笔记本章着重讨论交际教学原则和任务型教学思想并介绍相关的教学基本概念以及交际教学和任务型教学活动。
《英语教学法》(1)期末考试试题之二(开卷考试)Part I. Fill in the blanks with correct information: 30%1.The Grammar-Translation Method came about as a result of __________________.2.People learned Ancient Greek and Latin as________________.3.In a functional-notional syllabus, the language taught would not be described in only grammatical forms,but also___________, _________, __________ and ____________.4.The term “communicative competence” was first used by _____________ in applied linguistics.5.Krashen’s Natural Order of Langua ge Learning was based on _____________.6.Various language learning methods arose in the 70s in particular in North America and in Europe, whichconcerned the learner as a whole person, also referred to as _________.7.Imagine a situation in which students learn a language in the following way. They sit around a table withcomfortable chairs and with a tape recorder in the middle. When one wants to say something, he whispers it in his mother tongue to the teacher who is standing behind him, who then translates it into the target language and the student repeats that. This approach is called ___________.8.ESP is the abbreviation of ________________.9.In Taba’s model of curriculum processes, the last two stages are___________ and ______________.10.Knowing how to make correct sentences has very little value on its own and has to be supplementedby________________________ and _________________________ when it is used as a normal means of communication.11.A student with very limited language would be forgiven for errors of _____________.nguage processing is ______________________ and what is understood involves far more than___________________________________.13.Turn-taking is a characteristic of ___________________.14.A CLT syllabus will cover situations, topics, functions, _________________, and ________________.15.List some examples of authentic materials: _______________, ______________, _____________.Part II Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for true and F for false. 20%1.People learned Ancient Greek and Latin in order to communicate in real life situations.2.The Threshold Level was an example of the Grammar –Translation Method.3.Making errors will lead to bad habit formation, so we should correct them whenever they occur.4.Suggestopedia is believed to be the most of the humanistic methods.5. A textbook with such course design as Unit 1 Personal pronouns, Unit 2 Attributive clauses, Unit 3 Thepassive voice, etc. is based on a skills syllabus.6.It is true that inappropriately used expressions can produce more harm than structurally poor sentences.7.Back-channel responses are used by one speaker to interrupt the other speaker.8.In CLT students do not learn in the classroom; instead they learn the language in real life.9.Good learners learn different styles of speech and writing and learn to vary their language according to theformality of the situation.10.While the students are engaged in the communicative activity the teacher should not intervene, such astelling them that they are making mistakes, insisting on accuracy or asking for repetition.Part III 50%Design a reading lesson with three stages as required.Imagine that you would teach this text to a senior middle school class; think about the pre-reading activities you might design for it.The States ExplainedLike all Dads, my father sometimes seemed to be practicing for a world’s most boring competition. He used to have the habit, when I was a boy, of identifying and reporting the state of origin of all the other cars on any highway we happened to be traveling along.In America, as I expect you know, each state issues its own number plates, so you can tell at a glance where another car is from, which enabled my father to make observations like, ‘Hey, another car from Wyoming. That’s three this morning.’ Or: ‘Mississippi. Wonder what he’s doing up here?’ Then he would look around hopefully to see if anyone wanted to add a comment, but no one ever did. He could go on like that all day, and often did.I once wrote a book making good-natured fun of the old man for his many interesting and unusual talents when behind the wheel—the ability to get lost in any city, to drive the wrong way down a one-way street so many times that people would eventually come and watch from their doorways, or spend an entire afternoon driving around within sight of an amusement park or other eagerly sought attraction without actually finding the entrance. One of my teenaged children recently read that book for the first time and came with it into the kitchen where my wife was cooking and said in a tone of amazed discovery, “But this is Dad,” meaning me.I have to admit it. I have become my father. I even read number plates, though my particular interest is the slogan. Many states, you see, include a friendly message or piece of information on their plates, like “Land of Lincoln” for Illinois, “Vacationland” for Marina, “Sunshine State” for Florida, and the crazy “Shore Thing”for New Jersey.I like to make jokes and comments on these so when, for instance, we see Pennsylvania’s “You’ve got a friend in Pennsylvania”, I turn to the passengers and say in an injured tone, “Then why doesn’t he call?”However, I am the only one who finds this an amusing way to spend a long journey.All this is by way of introducing our important lesson for the day, namely that the United States isn’t so much a country as a collection of fifty small independent nations, and you forget this at your peril. It all goes back to the setting up of a federal government after the War of Independence when the former colonies didn’t trust each other. In order to keep them happy, the states were given an extraordinary range of powers. Even now each state controls all kinds of matters to do with your personal life—where, when and at what age you can legally drink, whether you can carry a concealed weapon, own fireworks, or legally gamble; how old you have to be to drive; whether you will be killed in an electric chair, by lethal injection, or not at all, and how you have to be to get yourself in such a fix; and so on.If I leave our town of Hanover, and drive over the Connecticut River to Vermont, I will find myself suddenly subject to perhaps 500 completely different laws. I must, among much else, buckle my seat belt, acquire a licence if I wish to practise dentistry and give up all hope of erecting roadside hoardings, since Vermont is one of just two states to outlaw highway advertising. On the other hand, I may carry a gun on my person without any problem, and if I am arrested for drunken driving I may legally decline to give a blood sample.Since I always buckle anyway, don’t own a gun, and haven’t the faintest desire to stick my fingers in people’s mouths, even for very good money, these matters don’t affect me. Elsewhere, however, differences between our state laws can be dramatic, even alarming.States decide what may or may not be taught in their schools, and in many places, particularly in the Deep South, textbooks must accord with very narrow religious views. In Alabama, for instance, it is illegal to teach evolution as anything other than “an unproven belief”. All biology textbooks must carry a statement saying “This textbook discusses evolution, a controversial theory some scientists present as a scientificexplanation for the origin of living things. “By laws, teachers must give equal weight to the notion that the earth was created in seven days and everything on it—fossils, coal deposits, dinosaur bones—is no more than 7,500 years old. I don’t know what slogan Alabama has on its number plates, but “Proud to be Backward: sounds suitable to me.Pre-reading activitiesActivity 1Specific steps:Reasons for your design:Activity 2Specific steps:Reasons for your design:While-reading ActivitiesActivity 1Specific steps:Reasons for your design:Activity 2Specific steps:Reasons for your design:Activity 3Specific steps:Reasons for your design:Post-reading activitiesActivity 1Specific steps:Reasons for your design:Activity 2Specific steps:Reasons for your design:《英语教学法》(1)期末考试试题之二答案和评分标准Part I. Fill in the blanks with correct information: 30%, two points each1.the teaching of Ancient Greek and Latin in the west2.an intellectual activity3.topics, situations, functions, notions4.Dell Hymes5.first language acquisition6.Th e ‘holistic’ approachmunity Language Learning8.English for Special Purposesanization of learning experiences, determination of what to evaluate and how to evaluate10.a knowledge of the appropriateness, the functional value of the language11.inappropriateness12.a constructive process, what is presented on the page or in the sound system13.oral communication14.the vocabulary and grammar structures, the skills required in typical situations15.English novels, poems, advertisements, instruction manuals, songs, films, lectures, speeches, radioannouncements, new reports, plays, etc.Part II Decide whether the following statements are true or false. Write T for true and F for false. 20%, two points each1. F2. F3. F4. T5. F6. T7. F8. F9. T 10. TPart III 50%Design a reading lesson with three stages as required.Imagine that you would teach this text to a senior middle school class; think about the pre-reading activities you might design for it. [The original text is provided for the reference of markers]The States ExplainedLike all Dads, my father sometimes seemed to be practicing for a world’s most boring competition. He used to have the habit, when I was a boy, of identifying and reporting the state of origin of all the other cars on any highway we happened to be traveling along.In America, as I expect you know, each state issues its own number plates, so you can tell at a glance where another car is from, which enabled my father to make observations like, ‘Hey, another car from Wyoming. That’s three this morning.’ Or: ‘Mississippi. Wonder what he’s doing up here?’ Then he would look around hopefully to see if anyone wanted to add a comment, but no one ever did. He could go on like that all day, and often did.I once wrote a book making good-natured fun of the old man for his many interesting and unusual talents when behind the wheel—the ability to get lost in any city, to drive the wrong way down a one-way street so many times that people would eventually come and watch from their doorways, or spend an entire afternoon driving around within sight of an amusement park or other eagerly sought attraction without actually finding the entrance. One of my teenaged children recently read that book for the first time and came with it into the kitchen where my wife was cooking and said in a tone of amazed discovery, “But this is Dad,” meaning me.I have to admit it. I have become my father. I even read number plates, though my particular interest is the slogan. Many states, you see, include a friendly message or piece of information on their plates, like “Land of Lincoln” for Illinois, “Vacationland” for Marina, “Sunshine State” for Florida, and the crazy “Shore Thing”for New Jersey.I like to make jokes and comments on these so when, for instance, we see Pennsylvania’s “You’ve got a friend in Pennsylvania”, I turn to the passengers and say in an injured tone, “Then why doesn’t he call?”However, I am the only one who finds this an amusing way to spend a long journey.All this is by way of introducing our important lesson for the day, namely that the United States isn’t so much a country as a collection of fifty small independent nations, and you forget this at your peril. It all goes back to the setting up of a federal government after the War of Independence when the former colonies didn’t trust each other. In order to keep them happy, the states were given an extraordinary range of powers. Even now each state controls all kinds of matters to do with your personal life—where, when and at what age you can legally drink, whether you can carry a concealed weapon, own fireworks, or legally gamble; how old you have to be to drive; whether you will be killed in an electric chair, by lethal injection, or not at all, and how you have to be to get yourself in such a fix; and so on.If I leave our town of Hanover, and drive over the Connecticut River to Vermont, I will find myself suddenly subject to perhaps 500 completely different laws. I must, among much else, buckle my seat belt, acquire a licence if I wish to practise dentistry and give up all hope of erecting roadside hoardings, since Vermont is one of just two states to outlaw highway advertising. On the other hand, I may carry a gun on my person without any problem, and if I am arrested for drunken driving I may legally decline to give a blood sample.Since I always buckle anyway, don’t own a gun, and haven’t the faintest desire to stick my fingers in people’s mouths, even for very good money, these matters don’t affect me. Elsewhere, however, differences between our state laws can be dramatic, even alarming.States decide what may or may not be taught in their schools, and in many places, particularly in the Deep South, textbooks must accord with very narrow religious views. In Alabama, for instance, it is illegal to teach evolution as anything other than “an unproven belief”. All biology textbooks must carry a statement saying “This textbook discusses evolution, a controversial theory some scientists present as a scientific explanation for the origin of living things. “By laws, teachers must give equal weight to the notion that the earth was created in seven days and everything on it—fossils, coal deposits, dinosaur bones—is no more than7,500 years old. I don’t know what slogan Alabama has on its number plates, but “Proud to be Backward: sounds suitable to me.Pre-reading activities (10%)five points for each activity, which are further divided between “specific steps” and “reasons for your design”, 2.5 points for each partThe following are possible pre-reading activities for the reference of markers. Students need to elaborate the activity as well as give reasonable explanation for their choices. These two parts should be done in good English.●Examine the accompanying visual information (diagrams, maps, photographs)●Reflect on the title or the topic●State what they already know about the topic●State what they would like to know about the topic●Write their own questions that they want the text to answer●Answer the teacher’s general questions about the tex t type or topic (oral or written)●Brainstorm the topic in groups or whole class●Guess the topic by looking at key words from the textWhile-reading Activities (30%)ten points for each activity, which are further divided between “specific steps” and “reaso ns for your design”, five points for each partThe following are possible while-reading activities for the reference of markers. Students need to elaborate the activity as well as give reasonable explanation for their choices. These two parts should be done in good English.●Skim reading to get the gist (main idea of the text●Locating specific information●Transferring information from the text to a diagram, table, form, map, graph or picture●Taking notes on the main points, or on specific points of the text●Drawing a diagram to show the text structure●Answering factual questions on the text●Answering inferring questions on the text (reading between the line)●Putting the events in correct order●Stating if statements given about the text are true or false●Working out the meaning of words or phrases in the text from the context●Examining referents in the text and stating what they refer to●Putting the paragraphs of a jumbled text back in the correct order●Giving sections of a text appropriate headings●Giving the text an appropriate titlePost-reading activities(10%)five points each activity, which are further divided between “specific steps” and “reasons for your design”, 2.5 points for each partThe following are possible post-reading activities for the reference of markers. Students need to elaborate the activity as well as give reasonable explanation for their choices. These two parts should be done in good English.●Oral discussion of the topic of the text●Role-play a different situation from the text but using the same characters, or role-play the same situationas in the text but using the different characters●Writing a summary of the main content of the text●Comment on the content of the text●Retelling the story of the text●Finishing the story (orally or ion writing), that means either predicting an ending or changing the endingto one of your own choice●Listening to or reading some supplementary materials.。
Unit 1 Language and Learning2. Three views of languageStructural view: language as a linguistic systemThe functional view: a linguistic system but also as a means for doing things.The interactional view:a communicative tool3. Four Language Learning Theories1)Behaviorist theory2)Cognitive theory3)Constructivist theory4)Socio-constructivist theory4. What makes a good language teacherprofessional competence1)Ethic devotion: warm-hearted, caring, enthusiastic, hardworking, well-prepared2)Professional qualities: resourceful, well-informed, professionally-trained, authoritative, disciplined, accurate, creative3)Personal styles: patient, attentive, flexible, humorous, dynamic, intuitive5. How can one become a good language teacherWallace’s (1991) ‘reflective modelStage 1: language developmentStage 2: learning, practice, reflectionGoal: professional competenceUnit 2 Communicative Principles and Activities1 Language use in real life vs. traditional pedagogyLanguage used in real lifeTo perform certain communicative functionsBoth receptive skills and productive skillsContext-relatedLanguage taught in the classroomTo focus on forms (structures or patternsTo focus on one or two language skills and ignore the otherTo isolate language from its context2. The goal of CLTThe goal of CLT is to develop students' communicative competence,2 What is communicative competenceboth the knowledge about the language and the knowledge about how to use the language appropriately in communicative situations3.Five components of communicative competence1)Linguistic competence,2)Pragmatic competence,3)Discourse competence,4)Strategic competence5)Fluency3.Implications for teaching and learning:(同上)4.Principles in communicative language teaching1)Communication principle:Activities that involve real communication promotelearning.2)Task principle: Activities in which language is used for carrying out meaningful tasks promote learning.3)Meaningfulness principle:Language that is meaningful to the learning supports the learning process.-_-||4.Main features of communicative activitiesA classification of communicative activities1)Functional communicative activitiesIdentifying picturesDiscovering identical pairsDiscovering sequences or locationsDiscovering missing informationFollowing directionsReconstructing story-sequences…2)Social interaction activitiesRole-playing through cued dialoguesRole-playing through debate or discussionLarge-scale simulation activities….Six criteria for evaluating communicative activities1)Communicative purpose2)Communicative desire3)Content, not form4)Variety of language5)No teacher intervention6)No materials controlTBLT:a further development of communicative language teaching. it share the same beliefs, as language should be learned as close as possible to how it is used in real life. however, it stressed the importance to combine form-focused teaching with communication-focused teachingA task is believed to have four components:1)a purpose,2)a context,3)a process, 4)a product.6.Differences between PPP and TBLT1.The way students use and experience language2.TBL can provide a context for grammar teaching and form-focused activities7.Problems with CLT1.Is it practical in the Chinese context?2.How to design the syllabus for classroom teaching?3.Is it suitable for all age level of learners or all competence level of learners?7.Constraints of TBLT1.It may not be effective for presenting new language items2.Time: teachers have to prepare task-based activities very carefully.3.Culture of learning4.Level of difficultyUnit 3National English Curriculum3.1 A brief history of foreign language teaching in China1)A phase of restoration (1978-1985)2)A phase of rapid development (1986-1992)3)A phase of reform (1993-2000)4)A phase of innovation from 20002,Designing principles for the National English Curriculum1) Aim for educating all students, and emphasize quality-oriented education.2) Promote learner-centeredness, and respect individual differences.3)Develop competence-based objectives, and allow flexibility and adaptability4)Pay close attention to the learning process, and advocate experiential learning and participation5) Attach particular importance to formative assessment, and give special attention to the development of competence.6)Optimize learning resources, and maximize opportunities for learning and using the language.3.3Goals and objectives of English language teachingThe new curriculum is designed to promote students’ overall language ability3.4 Design of the National English CurriculumNine competence-based levelsLevel 2,For 6th graders-_-zLevel 5,For 9th gradersLevel 7,For senior high school leaversUnit 4 Lesson Planning1.what is a Lesson plana Lesson plan is a framework of a lesson in which teachers make advance decisions about what they hope to achieve and how they would like to achieve it1.Why is lesson planning important?1)Makes teachers aware of the aims and language contents of the lesson,2)Helps teachers distinguish the various stages of a lesson and see the relationship between them3)Gives teachers the opportunity to anticipate potential problems so that they can be prepared;4)Gives teachers, esp. novice ones, confidence in class;5)Raises teachers’ awar eness of the teaching aids needed;6)Planning is a good practice and a sign of professionalism2.Principles for good lesson planning1)Aim,2)Variety,3)F lexibility, 4)Learnability ,5)Linkage3.Macro planning vs. micro planningMacro planning; is planning over timemicro planning: is planning for a specific lesson3Macro planning involves:1) Knowing about the course:2) Knowing about the institution:3) Knowing about the learners:4) Knowing about the curriculum/syllabus5)Knowing about the textbook6)Knowing about the objectivesponents of a lesson plan1)Background information2)Teaching aims3)Language contents and skills4)Stages and procedures5)Teaching aids6)end of lesson summary7)optional activities and Assignments8)after-lesson reflection5.Sample lesson plansUnit 5 Classroom Management1.What roles does the teacher playBefore the class---PlannerDuring the class---1 Controller, 2 Assessor, 3 Organizer ,4 Prompter , 5 Participant, 6 Resource-providerAfter the class---Evaluatornew roles: facilitators, guides, researchers2.Rules to follow for making instructions effectiveTo use simple instructions and make them suit the comprehension level of the students. To use the mother-tongue only when it is necessary.3. What are the most common types of Ss grouping?Whole class workPair work,Group work,Individual study:4.How to maintain discipline?P.79When students are engaged in learning, they will be disciplined.Q: How to engage students in learning?1)Ss are clear about learning purpose;2)Ss are able to do the work but find it challenging;3)Ss are emotionally, physically and intellectually involved by the tasks;4)The presentation, variety and structure of the work and activities generate curiosity and interest;5)Ss have opportunities to ask questions and try out ideas;6)Ss can see what they have achieved and how they had made progress;7)Ss get a feeling of satisfaction and enjoyment from the work.4 Harmer’s suggestions on measures for undisciplined acts and badly behaving Ss1). Act immediately2). Stop the class3).Rearrange the seats4).Change the activity5).Talk to Ss after class6).creat a code of behavior4. In order not to hurt the Ss,Ur’s advice on problems in class:1).Deal with it quietly2).Don’t take thin gs personally3).Do not use threats5How to ask effective question1)Questions should be closely linked to the learning objectives in the lesson;2)Questions should be staged so that the level of challenge increases as the lesson proceeds;3)There should be a balance between closed and open, lower-order and higher-order questions;4)Wait time is important to allow students to think through their answers;5)Ss should be provided opportunities to ask their own questions and seek their own answers;6)A secure and relaxed atmosphere of trust is needed and ss’ opinions and ideas are valued.6. correct dealing with errors and mistakeswe need to be clear whether the task or activity is focusing on accuracy or fluency.How to correct error:1)Direct teacher correction2)Indirect teacher correction3)Self correction4)Peer correction5)Whole class correctionUnit 6Teaching Pronunciation1.The role of pronunciationOn the value of teaching pronunciation, there are different opinions:1.Students do not need to learn pronunciation because pronunciation will take care of itself as the students develop overall language ability.2.Failure in pronunciation is a great hindrance to language learn.2. The goals of teaching pronunciation:目的1)Consistency 连贯性: To be smooth natural2)Intelligibility可理解性:To be understandable to the listeners3)Communicative efficiency: To help convey the speakers’ meaning3. Three aspects of pronunciation to teach?Stress, intonation, rhythm5. Ways of practicing soundsPerception practice :Using minimal pairs,Which order,Same or different,Odd one out, CompletionProduction practice: Listen and repeat,Fill in the blanks,Make up sentences,Use meaningful context,Use pictures,Use tongue twisters6. Practicing stress:Use gestures, use the voice, use the blackboard7. Practicing intonation:Use hand or arm movement to indicate change of intonatonrising/falling arrows;draw linesUnit 7. Teaching Grammar1.The role of grammar in language learningGenerally speaking, Chinese EFL learners need a certain degree of mastery of English grammar (grammatical competence is essential for communication). However, it should be noted that learning grammar itself is not the ultimate goal of learning English.2.ways of presenting/ teaching grammar1the deductive method2the inductive method3the guided discovery method3. grammar practice activitiesMechanical practicemeaningful practiceTwo types of practice can be combined.Using prompts (pictures, mimesor gestures, information sheet, key phrases or key words, chaind phrases, created situations) has proved to be an effective way of grammar practice.Unit 8 Teaching Vocabulary1. What does knowing a word involve?its pronunciation and stress;its spelling and grammatical properties;its meaning;how and when to use it to express the intended meaning.Vocabulary learning “involves at least two aspects of meaningThe first aspect involves the understanding of its denotative and connotative meaning. The second aspect involves understanding the sense relations among words.”Collocation , Synonyms,antonyms,hyponyms, Receptive and productive vocabulary2. List some ways of presenting new words1) Try to provide a visual or physical demonstration whenever possible,2) Provide a verbal context to demonstrate meaning.3) Use synonyms or antonyms to explain the meanings.4) Use lexical sets or hyponyms to show relations of words and their meanings.5) Translate and exemplify,6) Use word formation rules and common affixes7) Teach vocabulary in chunks.8) Think about the context in real life where the word might be used.9) Think about providing different context for introducing new words.10) Prepare for possible misunderstanding or confusion that student may have.3. Some vocabulary consolidation activities that can be done in class. (12)1) Labeling2) Spot the differences:3) Describe and draw4) Play a game:6) Use word series7) Word bingo:9) word association10) Synonyms and antonyms:11) categories12) Use word net-work13)use the internet resources for more ideas4. Developing vocabulary building strategies.1). Review regularly:2). Guess meaning from context:3). Organize vocabulary effectively:4). Use a dictionary:5)keep a vocabulary notebook6).Discovery strategiesUnit 9Teaching Listening1.The reason why such difficulties arise can be quire complicated. however, one major reason for students’ poor listening is often neglected in language due to1) Lack of teaching materials (audio and video tapes);2) Lack of equipment (tape players, VCRs, VCDs, computers);3) Lack of real-life situations where language learners need to understand spoken English 2 What do we listen to in everyday life? (Ur, 1996)Loudspeaker announcements1.Radio news2.Lesson, lecture3.Conversation, gossip4.Instructions5.Watching television6.Watching movies7.Telephone conversations8.Interview9.Shopping10.Story-telling11.Meetings12.Negotiations13.Theater show3.The characteristics of listening in real life1) Spontaneity2) Context3) Visual clues4) Listener’s response5) Speaker’s adjustment4 Principles of teaching listening:1). Focus on process:2). Combine listening with other skills:3). Focus on comprehending meaning:4). Grade difficulty level appropriately:4. model of teaching listening:bottom-up model up- bottom model5.the teaching of listening generally follows three stages:pre-listening stagewhile-listening stage,post-listening stage.Unit 10Teaching Speaking1.what are the differences between spoken and written language?SpokenspontaneousSentences are often incomplete, ungrammatical, and full of hesitations, false starts, and redundancies.If it is not recorded, spoken language can’t be listened to again. It is expected to be understood immediately.WrittenWell-plannedSentences are often carefully constructed and well organized.Written language is comparatively speaking permanent. It can be read as often as necessary.2.Principles for teaching speaking1) balancing between accuracy-based practice and fluency-based practices :2) Contextualizing practice3) Personalizing practice4) Building up confidence5) Maximizing meaningful interactions6) Helping students develop speaking strategies7)making the best use of classroom learning environment to provide sufficient language input and practice for the students.3.how can we design speaking activities:1). Maximum foreign talk:2). Even participation3). High motivation4). Right language level4.Types of speaking activitiesLittlewood’s (1981) framework for defining s peaking activities:Pre-communicative activitiesStructural activitiesQuasi-communicative activitiesCommunicative activitiesFunctional communication activitiesSocial interaction activities5,How to organise speaking activities.Using group work in speaking tasksUnit 11 Teaching Reading1. Effective readers do the following:1) have a clear purpose in reading;2) read silently;3) read phrase by phrase, rather than word by word;4) concentrate on the important bits, skim the rest, and skip the insignificant parts;5) use different speeds and strategies for different reading tasks;6) perceive the information in the target language rather than mentally translate;7) guess the meaning of new words from the context, or ignore them;8) have and use background information to help understand the text.3. Skills readers need:1.Specifying a purpose for reading2.Planning what to do/what steps to take3.Previewing the text4.Predicting the contents of the text5.Checking predictions6.Skimming the text for the main idea7.Scanning the text for specific information8.Distinguishing main ideas from supporting details9.Posing questions about the text10.Finding answers to posed questio…4.The role of vocabulary in reading:Day & Bamford (1998): efficient reading begins with a lightening-like automatic recognition of words, which frees one’s mind to use other resources to construct meaning. Helping ss to develop the ability of automatic word recognition is the basis for developing their reading skills.The way to develop sight vocabulary is to read extensively (‘Familiarity breeds automaticity’)5. Some principles for teaching reading(:1)The selected texts and attached tasks should be accessible to the students.2)Tasks should be clearly given in advance.3) Tasks should be designed to encourage selective and intelligent reading for the main meaning4) Tasks should help develop students' reading skills5) Teachers should help the students not merely to cope with one particular text in front of them but with their reading strategies and reading ability in general.6)Teachers should help the students to read on their own.6.three models of teaching reading1). Bottom-up modelletters---words---phrases---clauses---sentences---paragraphs---whole discours2). Top-down modelbackground knowledge--- guess meaning from the printed page3)Interactive model7.Three stages of reading:Pre-reading activities; *Predicting* Setting the scene* Skimming* ScanningWhile-reading activities;1)Focusing on the results of readingMultiple-choice questions;T/F questions;open questions,paraphrasing, translation2)Focusing on the process of understandingInformation transfer activities, ( with a transition device)comprehension questionsUnderstanding referencesMaking inference s …Post-reading ActivitiesTraditional: questions; paraphrasing; translationSuggestion:*Discussion*Role -play* Gap-filling* Retelling* WritingReading comprehension questions1).Questions for literal comprehension.2).Questions involving reorganization or reinterpretation.3).Question for inferences.4).Questions for evaluation or appreciation..5)question for personal responseUnit12 Teaching Writing1.What do we write?Writing is a real-life reality. We write letters, journals, notes, instructions, posters, essays, reports, menus, etc.2.Why do we write?We write for various reasons1)to convey messages,2)to keep a record of what is in our mind,3)to communicate with their teacher4)to raise awareness of how language works,5) to become more familiar with the linguistic and social conventions of writing in English, etc.3.How do we write?Writing can be both collaborative and solitarywe all have our own ways of writing.4.A communicative approach to writingSs are motivated by authentic writing tasks that have some communicative elements. Writing for a specific recipient (e.g. a friend, parent)Writing for an intended audience: creative writing intended to be read by other people 5.Problems in writing tasks1)They are mainly accuracy-based.2)They are designed to practice a certain target structures.3)There is insufficient preparation before the writing stage.4)There is no sense of audience.5)There is no sense of authenticity.6)Ss are given ideas to express rather than being invited to invent their own.7)There is no opportunity for creative writing, for expressing unusual for original ideas.8)Many of them are test-oriented.6.How to make a writing task more creative and communicative?Questions that the writer considers:Why should I write about the sports I like? (for communication)For what purpose?Who is going to read my writing? (a sense of audience)7.A process approach to writingFeatures of process writing1)Focus on the process of writing that leads to the final written product;2)Help ss understand their own composing process;3)Help ss build repertoires of strategies for prewriting, drafting, and rewriting;4)Give ss time to write and rewrite;5)Place central importance on the process of revision;6)Let ss discover what they want to say as they write;7)Give ss feedback throughout the composing process to consider as they attempt to bring their expression closer and closer to intention;8)Encourage feedback both from the instructor and peers;9)Include individual conferences between T and S during the process of composition Procedures of process writing1)Creating a motivation to write;2)Brainstorming;3)Mapping;4)Free writing;5)Outlining;6)Drafting;7)Editing;8)Revising;9)Proofreading;10)Conferencing.8.Motivating students to write1)Make the topic of writing as close as possible to ss’ life.2)Leave ss enough room for creativity and imagination.3)Prepare ss well before writing.4)Encourage collaborative group writing as well as individual writing.5)Provide opportunities for ss to share their writings.6)Provide constructive and positive feedback.7)Treat ss’ errors strategically.8)Give ss a sense a achievement from time to time.9.Designing writing tasksWriting tasks should be motivating and communicative.Self-study sample tasks on pagesing the Internet to promote process writing。
《英语教学法教程(第二版)》讲义一、课程概述1. 英语教学理论基础2. 教学方法与策略3. 课堂活动设计与组织4. 教学评价与反馈5. 教师专业发展二、英语教学的基本原则在深入探讨教学方法之前,我们需要了解英语教学的基本原则。
这些原则是指导我们教学实践的灯塔,帮助我们更好地服务于学生。
1. 学生中心原则:始终将学生放在教学的中心,关注他们的需求、兴趣和成长。
教学活动要贴近学生实际,激发他们的学习热情。
2. 交际性原则:英语学习的最终目的是运用语言进行有效沟通。
因此,教学过程中要注重培养学生的交际能力,让他们在实际语境中练习英语。
3. 循序渐进原则:教学应遵循由浅入深、由易到难的原则,确保学生能够在逐步学习中掌握英语知识。
4. 知识与实践相结合原则:理论学习与实践应用相结合,让学生在掌握知识的同时,提高实际运用能力。
三、课堂教学策略1. 情境教学法:通过创设真实的语言环境,让学生在模拟情境中学习英语,提高他们的语言运用能力。
2. 任务型教学法:以完成任务为目标,引导学生积极参与、合作探究,培养他们的团队协作能力和解决问题的能力。
3. 激励性评价:采用正面、鼓励性的评价方式,关注学生的进步和努力,激发他们的学习积极性。
4. 多元化教学手段:结合现代教育技术,运用多媒体、网络等资源,丰富教学手段,提高教学效果。
四、课堂活动实践2. 互动环节:设计小组讨论、角色扮演等活动,让学生在互动中提高英语听说能力。
3. 语言技能训练:针对听、说、读、写四个方面,设计专项训练活动,帮助学生全面提升英语能力。
通过本讲义的学习,希望您能在英语教学的道路上越走越远,为我国英语教育事业贡献自己的力量。
五、课程资源与材料的选择1. 教材选择:选用符合教学大纲、贴近学生实际、具有时代特色的教材。
同时,注意教材的难易程度,确保学生能够接受。
2. 辅助材料:充分利用网络资源、报刊杂志、影视作品等辅助材料,丰富教学内容,提高学生的学习兴趣。
英语有哪些教学方法英语有哪些教学方法11、导入法:包括直接导入,游戏导入,情境导入,多媒体教学,故事导入,歌曲导入,悬念导入,对比导入2、交际法:是根据意念项目和交际功能发展学生交际能力的系统教法。
其目的是为了让学生能运用言语进行交流,重要的是使学生能够考虑到进行相互交流的人们的作用和地位,考虑到所涉及的题目和情景,从而能恰如其分地运用语言。
3、游戏教学法:用游戏形式复习单词、句型,练习新语言点,使学生寓学于乐,在活泼、轻忪、愉快的气氛中自然而然地获得英语知识与技能。
游戏要求简短易行,有趣味,而且要与本课教学内容紧密相关。
4、情景教学法:情景是教师创设或模拟的生活场景,应具有真实、生动、实用的特点,便于学生将所学语言材料进行综合、创造性地进行表达交流。
这种练习方法,有接近生活的交际功能,而且能变单调、机械的句型操练为活泼、生动的交际性练习。
5、动作教学法:在低年级英语教学中,用具体形象的手势、动作来辅助英语学习,激发学生学习兴趣,提高学习效果。
6、活动教学法:就是按照学生身心发展过程中的不同阶段来设计、布置情境,提供材料,让学生积极参与自由操作、观察思考。
通过活动让学生自己认识事物、发现问题,得出答案,发掘学生潜能。
7、三位一体教学法:是根据字母、音素、音标三者的内在联系业务和交叉关系将三者融为一体进行教学的方法。
8、自然法:这种方法允许学生根据自己对已学知识的熟练程度来参加活动。
9、全身反应法:调动学生的感觉器官,让学生通过全身各个部位的不同动作达到记忆的目的。
10、合作学习法:让学生通过参加Pairwork和groupwork 活动,给学生练习语言并互相学习的条件和机会。
11、功能意念法:这种方法是教师集中提供给学生在某次会话时或某种情境中可能运用的有关语言,让他们感知其功能,在交际中运用。
英语有哪些教学方法2一、交际性原则1、开展丰富多彩的语言交际活动长期以来,在英语教学课堂里,有效地开展语言交际活动是我们所期望的结果。
英语教学法(1)试题
中央广播电视大学2003—2004学年度第一学期“开放本科”期末考试 英语(教)专业英语教学法(1)试题 2004年1月 Information for the examinees: This examination consists of THREE sections. They are: Section I: Basic Theories and Principles (30 points, 20 minutes) Section Ⅱ: Problem Solving (30 points, 50 minutes) Section Ⅲ: Mini-lesson Plan (40 points, 50 minutes) The total marks for this examination are 100 points. Time allowed for completing this examination is 2 hours.
Section I: Basic Theories and Principles 30 points
Questions 1 -- 15 are based on this part. Directions: Choose the best answer from A, B or C for each question. Write your answer on the
Answer Sheet. 1. Which of the following activities is typical of the Grammar-translation Method?
A. The students listen to and act on commands in the target language. B. The students whisper their words in the mother tongue to the teacher who then trans- late them into the target language. C. The students translate some sentences in the text into their mother tongue.
2. Which of the following is true according to Krashen? A. Babies learn their mother tongue. B. Language acquisition can be achieved even without conscious effort.
C. A foreign language learner should develop his language skills in the order of listening,
reading, speaking and writing. 3. Which of the following statements about course design is NOT true? A. The general goals of a course should be specified based on the learners" needs.
B. The contents of a course should be selected to fit in with the learning experiences.
C. The assessment activities should reflect those taught in a course. 4. Which of the following generally does NOT describe a CLT syllabus? A. The vocabulary and grammar structures needed for communicative obieetives (e. g.
telling directions, requesting information, expressing agreement, etc. ).
B. The skills required in typical situations (e. g. listening, speaking or writing skills).
C. The grammar rule appropriate for social occasions (e. g. at a conference, at a party, in
a grocery store, etc. ) 5. Which of the following is the teacher expected to do in a communicative activity?
A. To offer the students as little help as possible. B. To check if the students have understood the instructions before the activity starts.
c. To correct the students" errors immediately after they occur. 6. Which of the following activities is communicative.* A. The students are required to answer the questions about a text, B. The students are required to make sentences using the given words or sentence struc-
tures. C. The students are required to present their ideas on a topic. 7. When a reader tries to guess the meaning of a new word based on the contextual clue,
which one of the following approaches is he using? A. Bottom-up Approach. B. Top-down Approach. C. Interactive Approach. 8. When a researcher reads an academic paper to see if it is relevant to his field of interest,
which one of the reading skills is he using? A. Skimming. B. Scanning. C. Inferring. 9. When a teacher instructs the students to match the topic sentences with proper para-
graphs, which one of the skills is he intending to develop of his students?
A. Skimming. B. Scanning. C. Inferring. 10" Which of the following activities is designed to practise the skill of Listening for Gist?
A. After listening, the students are required to fill in the blanks with the words in the
text. B. After listening, the students arerequired to write a summary of the text.
C. After listening, the students are required to make a dialogue based on the text.
11. What shouId the teacher try to avoid when selecting listening materials?
A. Te texts scripted and recorded in the studio. B. The texts with implicated concepts beyond the comprehension of students.
C. The texts delivered through the accents other than RP or Standard American Pronun-
elation. 12. What purpose does NOT post-listening activities serve? A. Helping students relate the text with their personal experience.