改进蚁群算法在迷宫路径寻优中的应用研究
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:320.46 KB
- 文档页数:4

蚁群算法的应用与改进作者:宗泽宏来源:《电子技术与软件工程》2017年第01期蚁群算法(ACA)作为一种仿生进化算法,现多应用于优化领域。
它是通过对自然界蚂蚁的寻径方式进行仿真分析之后而获得一种随机搜索方法,该方法可用于处理组合优化问题。
在本文,在对该算法的基本原理进行介绍之后,对数学模型的构建以及算法的进一步优化进行阐释,最后对其应用前景予以预测。
【关键词】蚁群算法仿生进化随机搜索1 引言在信息量不断扩大的今天,数据挖掘技术所具有的优良性能开始凸现。
数据挖掘技术的改进与优化有利于帮助我们从大规模数据中筛选出有用的信息与应用模式。
对于数据挖掘技术而言,探寻一种更高效的算法是改进与优化此技术的核心。
1991年,意大利著名研究学者M.Dorigo率先提出了一种新型仿生算法ACA,也就是本文所研究的蚁群算法。
在对蚂蚁的一系列行为进行深入研究之后提出了其基本原理并构建了相应的数学模型——蚁群算法,之后将其用于获得旅行商问题(TSP)的解释。
2 蚁群算法的原理ACA是通过深入研究蚂蚁行为而形成的一种自然算法。
该算法最突出的特征是蚂蚁会通过“信息素” (pheromone)和其他蚂蚁保持间接异步联系。
蚂蚁在行动的过程中,会在其走过的路上残留下一些信息素,这些信息素能够被同群的蚂蚁伙伴所感知,并且会对蚂蚁行为产生影响。
即在相同时间内,离食物愈近的路径会被更多的蚂蚁选择,所留下的信息素也会愈来愈浓,后期蚂蚁选择此路径的概率便会更大。
该过程会持续迭代,一直持续到所有蚂蚁都选择了较短路线。
阿根廷蚂蚁在开始觅食时就会自动分泌并残留费洛蒙(pheromone)痕迹。
实验者准备了两个大槽,其中一个放入阿根廷蚁群,另外一个放入食物。
之后,在两个槽之间搭建了一个小桥。
实验者们在这座桥上进行了特别设计,即在桥的跨距1/4的地方,划分为两条路,尽管两条路都能够达到食物槽,不过其路径距离不同,其中一条路大约是另一条路的2倍。
对此,蚂蚁们会做出什么样的选择呢?就像预期的那样,蚂蚁在非常短的时间内就明确了最佳路径。

《改进的蚁群算法在TSP问题上的应用》一、引言旅行商问题(Traveling Salesman Problem,TSP)是运筹学中著名的组合优化问题,它涉及到如何确定访问一系列城市的最优顺序,使得访问每个城市一次并返回初始城市后路径最短。
长期以来,该问题吸引了众多学者和科研人员的关注,他们致力于开发出各种高效的算法以求解该问题。
其中,蚁群算法作为一种自然启发式算法,以其优秀的寻优能力和良好的全局搜索性能而受到广泛关注。
近年来,对传统蚁群算法的改进也成为研究热点,本文旨在探讨改进的蚁群算法在TSP问题上的应用。
二、蚁群算法的基本原理蚁群算法是一种模拟自然界蚂蚁觅食行为的优化算法。
它通过模拟蚂蚁之间的信息交流和协作过程,在搜索过程中不断更新信息素浓度,从而找到最优解。
在TSP问题中,蚁群算法将城市看作是蚂蚁的觅食点,通过信息素的传递和更新来寻找最优路径。
三、传统蚁群算法的不足尽管蚁群算法在TSP问题上取得了显著的成果,但仍然存在一些不足。
例如,算法在搜索过程中容易陷入局部最优解,导致寻优效率降低;同时,信息素的更新策略和挥发机制也可能影响算法的性能。
针对这些问题,学者们提出了各种改进措施。
四、改进的蚁群算法针对传统蚁群算法的不足,本文提出了一种改进的蚁群算法。
首先,在信息素更新方面,我们引入了动态调整因子,根据搜索过程中的实际情况动态调整信息素的挥发速度和增加量,以提高算法的寻优能力。
其次,为了防止算法陷入局部最优解,我们引入了多种不同的路径选择策略和随机扰动机制,以增强算法的全局搜索能力。
此外,我们还对蚂蚁的移动规则和信息素的传播机制进行了优化,以提高算法的收敛速度和准确性。
五、实验与分析为了验证改进的蚁群算法在TSP问题上的有效性,我们进行了大量的实验。
实验结果表明,改进后的蚁群算法在求解TSP问题时具有更高的寻优效率和准确性。
与传统的蚁群算法相比,改进后的算法在求解不同规模和复杂度的TSP问题时均表现出更好的性能。



蚁群算法求解迷宫最优路径
张公敬;徐熙君
【期刊名称】《青岛大学学报(自然科学版)》
【年(卷),期】2008(021)001
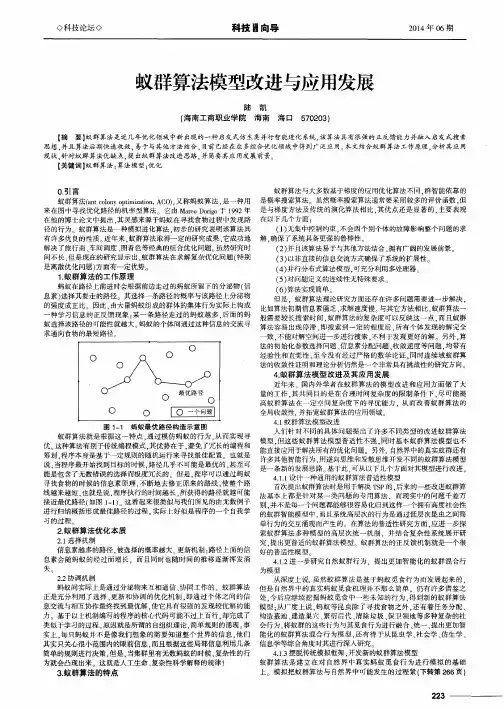
【摘要】提出了基于蚁群算法求解迷宫最优路径的算法.设定两组蚂蚁分别分布在迷宫中距离入口、出口路径长度为k的前沿位置,根据移动规则,相向爬行.迷宫中各位置记忆蚂蚁信息素量和至迷宫入口、出口的路径长度.蚂蚁爬行至一新位置后,根据当前位置的信息而修改周边位置至入口或出口的路径长度,从而形成一条宽度为3的路径信息带.蚁群在迷宫中爬行使得迷宫中记忆了大量的路径信息,从而容易实现两段路径的拼接,提高了蚂蚁寻找到达目的地最优路径的效率.不同规模迷宫的试验结果显示,该算法是一种求解迷宫最优路径问题的有效解法.
【总页数】5页(P61-65)
【作者】张公敬;徐熙君
【作者单位】青岛大学信息工程学院,山东,青岛,266071;青岛大学师范学院,山东,青岛,266071
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】TP301.6
【相关文献】
1.基于改进的蚁群算法求解最优路径方法 [J], 李云
2.基于改进蚁群算法求解迷宫最优路径 [J], 何海燕
3.改进蚁群算法求解两地间时间最优路径 [J], 崔丽群;许堃
4.注水法求解迷宫最优路径 [J], 张公敬;杨厚俊;刘征
5.蚁群算法在迷宫最优路径问题中的应用 [J], 胡小兵;黄席樾
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。

改进蚁群算法在路径规划中的应用
杨北辰;余粟
【期刊名称】《计算机应用研究》
【年(卷),期】2022(39)11
【摘要】针对传统蚁群算法在机器人路径规划时存在收敛速度慢、易陷入局部最优等问题,提出了一种基于自适应归档更新的蚁群算法。
根据路径性能指标建立多目标性能评估模型,对最优路径进行多指标优化;采用路径方案归档更新策略进行路径方案的更新和筛选,提高算法的收敛速度;当搜索路径进入不可行区域时,采用自适应路径补偿策略转移不可行路径节点,构造可行路径,减少死锁蚂蚁数量;若算法无法避开障碍或者进入停滞状态,则进行种群重新初始化,增加物种多样性,避免算法陷入局部最优。
仿真实验表明,改进后的算法收敛速度更快、收敛精度更高、稳定性更好。
【总页数】7页(P3292-3297)
【作者】杨北辰;余粟
【作者单位】上海工程技术大学电子电气工程学院
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】TP242.6
【相关文献】
1.改进蚁群算法在机器人路径规划中的应用
2.改进蚁群算法在移动机器人路径规划中的应用研究
3.改进蚁群算法在机器人路径规划中的应用
4.改进的蚁群算法在定制公交路径规划中的应用
5.分组教学蚁群算法改进及其在机器人路径规划中应用
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。


基于改进蚁群算法的优化方法及其应用IntroductionMetaheuristic algorithms are popular techniques used for solving complex optimization problems such as the traveling salesman problem, portfolio optimization, and many others. One of the famous metaheuristic algorithms is the Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) algorithm, which simulates the behavior of ants in finding the shortest path between their colony and a food source. However, the traditional ACO algorithm has some limitations that affect its performance in solving complex optimization problems. In this article, we will introduce an improved version of the ACO algorithm and its applications in various optimization problems.Chapter 1: Basic Ant Colony Optimization AlgorithmThe ACO algorithm is a population-based search algorithm that imitates the behavior of ants in finding the shortest path between their nest and food source. The algorithm consists of a set of ants that move through a graph and deposit pheromone trail on the edges they traverse. The pheromone trail acts as a form of communication among ants, and those edges with the highest pheromone concentration are more likely to be chosen by other ants.The basic steps of the traditional ACO algorithm are as follows:1. Set the number of ants, the initial pheromone concentration, and the heuristic value for each edge.2. Each ant selects a starting node and iteratively selects the next node based on a probabilistic rule that combines the pheromone trail and the heuristic value of each edge.3. After an ant completes a tour, the pheromone trail on each edge is updated based on the length of the tour. Edges with shorter tour length receive more pheromone.4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 until a stopping criterion is met.Chapter 2: Limitations of Basic ACO AlgorithmAlthough the traditional ACO algorithm is effective in solving many combinatorial optimization problems, it has some limitations that may affect its performance in solving more complex problems. Some of the limitations are:1. Premature Convergence: The ACO algorithm tends to converge prematurely to a local optimum, which means that it fails to explore the search space adequately, leading to suboptimal solutions.2. Stagnation: The algorithm can get stuck in a local optimum due to the lack of exploration.3. Inefficient Parameter Tuning: The performance of the ACO algorithm highly depends on parameter values such as the pheromone evaporation rate, the initial pheromone value, and the visibility of theedges. The selection of appropriate parameter values can be challenging and time-consuming.Chapter 3: Improved Ant Colony Optimization AlgorithmTo address the limitations of the basic ACO algorithm, several improved versions have been proposed. One of the popular improved ACO algorithms is the Max-Min Ant System (MMAS) algorithm that ensures better exploration and avoids premature convergence.The MMAS algorithm introduces several enhancements that improve the performance of the basic ACO algorithm. These enhancements include:1. Pheromone Updating Rule: The MMAS algorithm uses a max-min strategy to update the pheromone trail. Each edge's pheromone concentration is bounded by a maximum and minimum value to ensure proper pheromone evaporation and allow better exploration of the search space.2. Pheromone Initialization: The initial value of the pheromone concentration is set to a higher value than the traditional ACO algorithm to encourage global exploration.3. Dynamic Parameter Tuning: The algorithm uses a dynamic parameter tuning mechanism that adjusts the parameter values based on the current state of the search. This tuning mechanism helps to find a balance between exploration and exploitation.The MMAS algorithm has been successfully applied in many optimization problems such as the Traveling Salesman Problem, Quadratic Assignment Problem, and many others.Chapter 4: Applications of Improved ACO AlgorithmThe improved ACO algorithm has been applied in many real-world optimization problems such as:1. Wireless Sensor Network Optimization: The optimization of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) is a challenging task due to the complex nature of the network topology. The ACO algorithm has been used to optimize the WSN topology for better energy efficiency, coverage, and connectivity.2. Vehicle Routing Problem: The Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) is a combinatorial optimization problem where a set of vehicles has to visit a set of customers while minimizing the total distance traveled. The ACO algorithm has been used to optimize the route taken by the vehicles to minimize the total distance traveled.3. Image Segmentation: Image segmentation is a critical task in computer vision that involves dividing an image into separate regions. The ACO algorithm has been used to segment medical images for better diagnosis and treatment.ConclusionThe Ant Colony Optimization algorithm has been successfully applied in many optimization problems, but its performance can be further improved by introducing several enhancements. The Max-Min Ant System algorithm is an improved version of the ACO algorithm that ensures better exploration and avoids premature convergence. The improved ACO algorithm has been applied in many real-world optimization problems such as Wireless Sensor Network Optimization, Vehicle Routing Problem, and Image Segmentation.。


基于改进蚁群算法的复杂问题优化研究随着科技的不断发展,越来越多的问题需要计算机进行优化,而蚁群算法是优化问题的一种有效的方式。
但是传统的蚁群算法存在一些不足,如收敛速度慢、易陷入局部最优解等问题,因此对蚁群算法进行改进,提高其适用范围和效率,就成为了当前研究的重点。
本文将探讨基于改进蚁群算法的复杂问题优化研究的现状、发展趋势及应用前景。
一、蚁群算法的概述蚁群算法,英文名为Ant colony optimization (ACO),是一种基于自然现象仿生的优化算法。
蚁群算法最初是模拟蚂蚁寻找食物的过程,蚂蚁在寻找食物的过程中会释放一种称为信息素的物质,这种信息素具有一定的吸引力和挥发性,其他蚂蚁通过嗅觉感知这种信息素,从而找到食物。
而蚁群算法则是将这种现象转化为优化问题的求解过程。
蚂蚁释放信息素等价于在图中进行路径搜索,而蚁群算法则是利用信息素的强度来调整蚂蚁选择路径的概率,通过多次迭代产生更优的路径。
二、蚁群算法存在的问题虽然蚁群算法在优化问题上取得了可喜的成果,但是仍然存在一些问题:1. 收敛速度慢:由于信息素的强度需要迭代更新,且更新速度较慢,因此收敛速度相对较慢。
2. 易陷入局部最优解:尤其是在搜索空间较大且存在多个局部最优解的情况下,蚁群算法容易陷入局部最优解,从而得不到全局最优解。
3. 参数设置困难:蚁群算法存在多个参数,如信息素浓度、信息素挥发速度等,不同参数的设置对算法优化结果的影响较大,因此参数设置困难。
三、蚁群算法的改进针对蚁群算法存在的问题,学者们进行了不断的研究和改进,主要包括以下方面:1. 基于启发式的信息素更新策略:通过引入启发式信息来更新信息素,来加快蚁群算法的收敛速度和优化效果。
例如,利用目标函数值、距离等启发式信息来规定信息素的更新策略。
2. 多目标蚁群算法:针对多目标优化问题,基于单目标蚁群算法的多目标拓展算法。
例如,非支配排序蚁群算法 (NSGA) 可以同时优化多个目标函数。
基于改进蚁群算法的AGV路径规划研究目录一、内容概述 (2)1.1 研究背景与意义 (2)1.2 国内外研究现状综述 (3)1.3 主要研究内容与方法 (4)二、蚁群算法理论基础 (6)2.1 蚂蚁系统 (7)2.2 最大最小蚂蚁系统 (8)2.3 蚁群算法改进方向 (9)三、改进蚁群算法在AGV路径规划中的应用 (9)3.1 初始解的生成策略 (10)3.2 蚂蚁的转移规则 (12)3.3 动态信息素更新策略 (13)3.4 算法实现步骤 (14)四、仿真实验与结果分析 (15)4.1 实验环境与参数设置 (16)4.2 实验结果与对比分析 (17)4.3 结果讨论与优化建议 (18)五、结论与展望 (19)5.1 研究成果总结 (20)5.2 存在问题与不足 (22)5.3 后续研究方向与应用前景展望 (23)一、内容概述在当前制造业和物流领域,AGV路径规划对于提高生产效率、优化资源分配和降低成本等方面具有至关重要的作用。
由于复杂的生产环境和动态的任务需求,AGV路径规划面临诸多挑战,如路径选择、任务调度和避障等。
为了应对这些挑战,本文提出了一种基于改进蚁群算法的AGV路径规划方法。
本文将介绍研究背景和意义,阐述AGV路径规划的重要性和现有挑战。
概述研究的主要内容和目标,包括改进蚁群算法的设计和实现过程,以及该算法在AGV路径规划中的应用。
在此基础上,本文将详细阐述算法的具体实现过程,包括算法的关键步骤、参数设置和优化策略等。
还将讨论如何通过仿真实验验证算法的有效性和性能,总结研究成果,分析改进蚁群算法在AGV路径规划中的优势和潜在应用前景。
本文的研究对于提高AGV系统的智能化水平和实际应用的推广具有重要的理论意义和实践价值。
1.1 研究背景与意义传统方法在处理复杂环境下的路径规划时存在局限性,当环境发生变化时(如障碍物的增加或位置移动),传统方法往往难以快速适应并找到最优路径。
传统方法在计算效率方面有待提高,对于大规模的AGV网络,传统的路径规划算法需要耗费大量的计算资源和时间,这在实际应用中是不可接受的。
毕业论文蚁群算法的研究应用目录一、内容描述 (2)1.1 研究背景 (2)1.2 研究意义 (3)1.3 研究目标与内容 (5)二、蚁群算法概述 (6)2.1 蚂蚁算法的基本原理 (7)2.2 蚂蚁算法的发展历程 (8)2.3 蚂蚁算法的应用领域 (10)三、蚁群算法在毕业论文选题中的应用研究 (11)3.1 选题的重要性 (13)3.2 基于蚁群算法的选题方法 (15)3.3 实证分析与结果 (16)3.4 讨论与分析 (17)四、蚁群算法在毕业论文结构优化中的应用研究 (18)4.1 毕业论文结构优化的必要性 (20)4.2 基于蚁群算法的结构优化方法 (21)4.3 实证分析与结果 (22)4.4 讨论与分析 (23)五、蚁群算法在毕业论文关键词提取中的应用研究 (25)5.1 关键词提取的重要性 (26)5.2 基于蚁群算法的关键词提取方法 (26)5.3 实证分析与结果 (28)5.4 讨论与分析 (29)六、蚁群算法在毕业论文摘要撰写中的应用研究 (30)6.1 摘要撰写的重要性 (31)6.2 基于蚁群算法的摘要撰写方法 (32)6.3 实证分析与结果 (32)6.4 讨论与分析 (34)七、结论与展望 (35)7.1 研究成果总结 (36)7.2 研究的不足之处及局限性 (37)7.3 对未来研究的展望 (38)一、内容描述本文深入研究了蚁群算法在毕业论文选题过程中的应用,旨在通过优化算法提高选题效率和准确性。
概述了蚁群算法的基本原理和特点,分析了其在毕业论文选题中的潜在价值。
详细介绍了蚁群算法在毕业论文选题中的应用方法,包括算法设计、实验设置和性能评估等方面。
在算法设计方面,本文对蚁群算法进行了改进,引入了动态权重和精英蚂蚁策略,以提高算法的全局搜索能力和收敛速度。
为了适应毕业论文选题的特殊性,还对算法进行了任务分解和约束处理。
在实验设置方面,本文选取了多所高校的毕业论文作为数据集,构建了相应的实验环境。