C语言编写的计算器源代码
- 格式:docx
- 大小:37.62 KB
- 文档页数:8

简易计算器程序源代码下面是一个简易计算器程序的源代码,它可以执行基本的四则运算:```python#定义加法函数def add(x, y):return x + y#定义减法函数def subtract(x, y):return x - y#定义乘法函数def multiply(x, y):return x * y#定义除法函数def divide(x, y):if y == 0:return "除数不能为0"else:return x / y#显示菜单print("选择操作:")print("1. 相加")print("2. 相减")print("3. 相乘")print("4. 相除")#获取用户输入choice = input("输入你的选择(1/2/3/4): ")#获取用户输入的两个数字num1 = float(input("输入第一个数字: "))num2 = float(input("输入第二个数字: "))#根据用户选择执行相应操作if choice == '1':print(num1, "+", num2, "=", add(num1, num2))elif choice == '2':print(num1, "-", num2, "=", subtract(num1, num2)) elif choice == '3':print(num1, "*", num2, "=", multiply(num1, num2)) elif choice == '4':print(num1, "/", num2, "=", divide(num1, num2))else:print("请输入有效的选择")```运行这个程序,你将看到一个简易的计算器菜单。
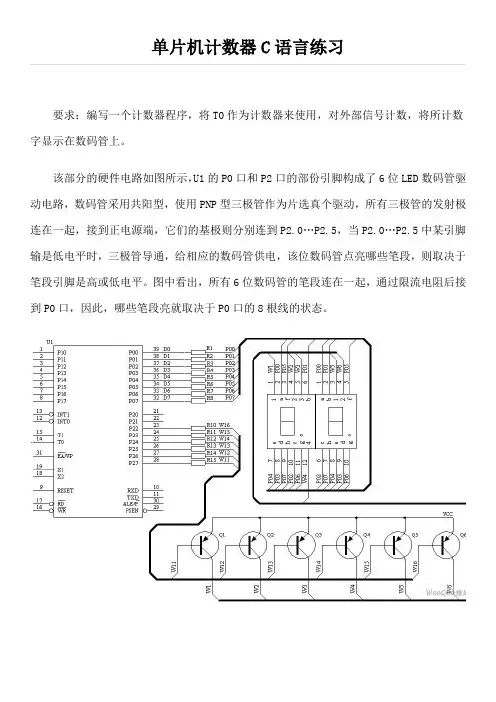
单片机计数器C语言练习要求:编写一个计数器程序,将T0作为计数器来使用,对外部信号计数,将所计数字显示在数码管上。
该部分的硬件电路如图所示,U1的P0口和P2口的部份引脚构成了6位LED数码管驱动电路,数码管采用共阳型,使用PNP型三极管作为片选真个驱动,所有三极管的发射极连在一起,接到正电源端,它们的基极则分别连到P2.0…P2.5,当P2.0…P2.5中某引脚输是低电平时,三极管导通,给相应的数码管供电,该位数码管点亮哪些笔段,则取决于笔段引脚是高或低电平。
图中看出,所有6位数码管的笔段连在一起,通过限流电阻后接到P0口,因此,哪些笔段亮就取决于P0口的8根线的状态。
编写程序时,首先根据硬件连线写出LED数码管的字形码、位驱动码,然后编写程序如下:#include "reg51.h"#define uCHAR unsigned CHAR#define uint unsigned intuCHAR code BitTab[]={0x7F,0xBF,0xDF,0xEF,0xF7,0xFB}; //位驱动码uCHAR codeDispTab[]={0xC0,0xF9,0xA4,0xB0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xF8,0x80,0x90,0x88,0x83,0xC6,0 xA1,0x86,0x8E,0xFF}; //字形码uCHAR DispBuf[6]; //显示缓冲区void Timer1() interrupt 3{ uCHAR tmp;uCHAR Count; //计数器,显示程序通过它得知现正显示哪个数码管TH1=(65536-3000)/256;TL1=(65536-3000)%256; //重置初值tmp=BitTab[Count]; //取位值P2=P2|0xfc; //P2与11111100B相或P2=P2&tmp; //P2与取出的位值相与tmp=DispBuf[Count];//取出待显示的数tmp=DispTab[tmp]; //取字形码P0=tmp;Count++;if(Count==6)Count=0;}void main(){ uint tmp;P1=0xff;P0=0xff;TMOD=0x15; //定时器0工作于计数方式1,定时器1工作于定时方式1 TH1=(65536-3000)/256;TL1=(65536-3000)%256; //定时时间为3000个周期TR0=1; //计数器0开始运行TR1=1;EA=1;ET1=1;for(;;){ tmp=TL0|(TH0<<8); //取T0中的数值DispBuf[5]=tmp%10;tmp/=10;DispBuf[4]=tmp%10;tmp/=10;DispBuf[3]=tmp%10;tmp/=10;DispBuf[2]=tmp%10;DispBuf[1]=tmp/10;DispBuf[0]=0;}}这个程序中用到了一个新的知识点,即数组,首先作一个先容。


四则运算器代码简单的四则运算器可以执行加、减、乘、除四种基本运算。
使用python和C++编写实例:(一)使用python编写:# 定义函数实现加法def add(x, y):return x + y# 定义函数实现减法def subtract(x, y):return x - y# 定义函数实现乘法def multiply(x, y):return x * y# 定义函数实现除法def divide(x, y):if y == 0:raise ValueError('除数不能为0')return x / y# 主程序,输入两个数和运算符,输出运算结果或错误信息while True:try:num1 = float(input('请输入第一个数:'))num2 = float(input('请输入第二个数:'))op = input('请输入运算符(+、-、*、/):')if op == '+':result = add(num1, num2)elif op == '-':result = subtract(num1, num2)elif op == '*':result = multiply(num1, num2)elif op == '/':result = divide(num1, num2)else:print('无效的运算符')continueprint('运算结果:', result)except ValueError as e:print('输入错误:', e)except Exception as e:print('程序错误:', e)在上面的代码中,我们定义了四个函数分别实现加、减、乘、除四种基本运算。

设计题目:计算器系统实现1.分别用API与MFC编程来实现计算器的以下功能。
2.实现计算器的基本功能:连续数据的无优先级混合运算(加减乘除)3.可以实现其他附加功能:优先级运算,加入括号,加入其他函数运算功能等。
(不在要求范围之内)4.要求界面良好,功能完整。
一.基于MFC的简单计算器1.设计思路打开MFC应用操作界面,布局计算器界面,利用组框将计算器界面分为三个部分,一个是编辑输入,一个是数字界面,一个是功能键部分。
利用布局参考线对齐按钮,使界面美观。
然后就是对各个按钮进行属性设置,关联类设置,接着对各个按钮进行源代码编程。
最后,调试找出问题,解决问题,运行MFC成品计算器。
2.简单操作以及功能说明由于本人技术有限,所以本程序只能按照正确的计算运算顺序进行,该简单计算器能进行四则混合运算,除了加减乘除外,添加了一个括号,对于有些未知的错误,由于时间有限,并未来得及全面测试使用。
该简单计算器能实现四则运算,退格运算,清零运算,并且支持输出的结果保留给直接的下一个运算。
3.系统实现的各个模块1)编辑框模块由于编辑框模块需要连续输入字符串,所以在给编辑框建立类向导时,给编辑框定义的成员变量应该是字符串(String)变量。
编辑框模块用于运算算式的输入,以及结果的输出。
2)数字键模块数字键模块比较简单,该简单计算器数字键模块设置有0~9数字,还设置有小数点,以及正负数转换实现按钮。
数字键模块按钮在建立类向导时无需定义成员变量,但是需要定义按钮响应链接,用于实现点击按钮,在编辑框上显示点击按钮信息。
3)功能键模块功能键模块包括加减乘除基本按钮,以及一个输入错误是后能用于退格功能的退格键按钮,还有一个用于区别优先级运算的括号功能,当然有最重要的计算结果输入按钮,等于号按钮。
在编辑框附近还有一个功能键,就是清除功能键,用于清除编辑框,以便实现下一轮输入。
4.设计过程1)设计总流程图2)界面的设计3)建立的变量,控件的命名,对应的消息处理函数对应表ID CAPTION MessageHandler IDD_JISUANQI_DIALOG 简易计算器N/AIDC_NUM0 0 OnNum0IDC_NUM1 1 OnNum1IDC_NUM2 2 OnNum2IDC_NUM3 3 OnNum3IDC_NUM4 4 OnNum4IDC_NUM5 5 OnNum5IDC_NUM6 6 OnNum6IDC_NUM7 7 OnNum7IDC_NUM8 8 OnNum8IDC_NUM9 9 OnNum9IDC_OPER_ADD + OnOperAdd IDC_OPER_SUB - OnOperSub IDC_OPER_MULTI * OnOperMulti IDC_OPER_DIV / OnOperDiv IDC_ADD_SUB +/- OnAddSubIDC_POINT . OnPointIDC_EQUAL = OnEqualIDC_LBRACKET ( OnLbracket1)数字键模块void CJiSuanQiDlg::OnNum0(){if(calculated == TRUE) //已经按了等号,不让其再接受字符return;UpdateData(TRUE);//刷新编辑框界面calcutateString += "0";//存储输入的数字m_data += "0";//显示输入的数字UpdateData(FALSE);}2)功能键模块①加法功能键源程序void CJiSuanQiDlg::OnOperAdd(){if(calculated == TRUE)///其前一步按了= 号{calculated = FALSE;m_data = oldResult;double temp = atof(oldResult);//定义临时变量存储上一步结果if(temp < 0){calcutateString = "0" + oldResult;}else{calcutateString = oldResult;}calcutateString += "+";//存储做完该功能后的结果m_data += "+";//显示该步骤完成的结果UpdateData(FALSE);}else ///前一步不是={UpdateData(TRUE);calcutateString += "+";//直接存储此步操作m_data += "+";//直接显示此步操作UpdateData(FALSE);}}②退格功能键源程序void CJiSuanQiDlg::OnBackspeace(){if(calculated == FALSE){UpdateData(TRUE);int count = m_data.GetLength();if(count >= 1)//判断是否能执行退格操作{m_data = m_data.Left(count -1);count = calcutateString.GetLength();calcutateString = calcutateString.Left(count -1);UpdateData(FALSE);}}}③清除功能键源程序void CJiSuanQiDlg::OnClear(){// TODO: Add your control notification handler code herem_data = "";oldResult = "";calcutateString = "";calculated = FALSE;UpdateData(FALSE);}④括号功能键源程序void CJiSuanQiDlg::OnLbracket(){// TODO: Add your control notification handler code hereif(calculated == TRUE) ///已经按了等号,不让其再接受字符return;UpdateData(TRUE);calcutateString += "(";m_data += "(";UpdateData(FALSE);}⑤正负转换功能键源程序void CJiSuanQiDlg::OnAddSub(){// TODO: Add your control notification handler code hereif(calculated == FALSE){UpdateData(TRUE);calcutateString = calcutateString + "0" + "-";m_data += "-";UpdateData(FALSE);}}6.运行结果界面截图7.制作过程中所遇问题以及解决方法过程1)源代码编写错误通过查阅资料,请教同学,逐步一一解决。

- - . 《程序设计基础(C)》课程设计报告简易计算器设计学生姓名:学号:班级:指导老师:日期:309工作室设计目录一、设计目标2二、总体设计4三、详细设计6四、调试与测试12五、分析及结论13六、参考文献14【附录】16一、设计目标设计一个C语言程序(简单计算器设计)具体要求:在功能上功能尽量模拟windows操作系统中的计算器,系统界面不做强制要求。
主要功能:进行+、-、*、/、三角函数、对数、幂等各项数学运算,能够进行进制间的相互转换与计算。
二、总体设计1、程序设计组成框图2、设计思路简单计算器的设计的程序中主要调用的函数有:数学函数的定义和I/O函数;设计思路和理念在于一切追求简便易操作原理,通过个人的构思和设计以及调试运行设计出这一款简单的计算器。
3、程序设计流程图三、详细设计1、功能函数①函数的功能:两数的+、-、*、/计算、求平均函数的入口:从main()的if(flag==1)开关结构中进入,即flag的值为1时进入该函数,从而进行该功能函数的计算。
函数调用关系:被主函数调用,由if()开关结构中进入。
函数的出口:函数的出口为printf("是否继续运算?(Y/N) :"),此时输入“Y”,继续前面的结构。
2、功能函数②函数的功能: x的y次方的计算、两数的求余、以x为底y的对数函数的入口:从main()的if(flag==2)开关结构中进入,即flag的值为2时进入该函数,从而进行该功能函数的计算。
函数调用关系:被主函数调用,由if()开关结构中进入。
函数的出口:函数的出口为printf("是否继续运算?(Y/N) :"),此时输入“Y”,继续前面的结构。
3、功能函数③函数的功能: 单个数值sin、cos、tan的计算,以e为底的指数、求绝对值函数的入口:从main()的if(flag==3)开关结构中进入,即flag的值为3时进入该函数,从而进行该功能函数的计算。



c语言计算器原理随着计算机技术的发展,计算器作为基本的数学运算工具,已经广泛地应用于各个领域。
在计算机编程中,C语言是一种通用的、面相过程的编程语言,它可以用来开发各种类型的应用程序,包括计算器。
本文将介绍使用C语言编写计算器的原理和方法。
一、计算器的基本原理计算器的基本原理是利用数学运算的原理,通过编程实现加、减、乘、除等基本运算功能。
在C语言中,可以使用各种运算符和函数来实现这些运算,例如“+”、“-”、“*”、“/”等运算符,以及“abs”、“sqrt”等函数。
这些运算符和函数可以被嵌入到程序中,以实现各种复杂的数学运算。
二、计算器的设计思路设计一个计算器需要考虑到以下几个问题:1.用户界面:计算器需要有一个直观、易于使用的用户界面,以便用户能够输入要计算的表达式并得到结果。
2.表达式解析:计算器需要能够解析用户输入的表达式,并将其转换为计算机能够处理的数学运算。
3.运算执行:计算器需要能够执行解析后的表达式,并输出结果。
4.错误处理:计算器需要能够处理各种可能的错误情况,例如无效的输入、除以零等。
基于以上思路,我们可以设计一个简单的计算器程序,它使用命令行界面,支持基本的加、减、乘、除运算,并能够处理一些常见的错误情况。
三、计算器的实现方法实现一个计算器需要使用C语言的输入输出函数、字符串处理函数和数学函数等。
下面是一个简单的计算器程序示例:```c#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<string.h>#include<math.h>intmain(){charexpression[100];printf("请输入表达式(如:2+3*4):");fgets(expression,sizeof(expression),stdin);expression[strcspn(expression,"\n")]='\0';//去掉换行符doubleresult=0;intsign='+';//默认运算符为加号inti=0;while(expression[i]!='\0'){if(expression[i]==sign){//如果是运算符,则执行相应的运算if(i+2>strlen(expression)){//确保后面还有数字printf("无效的表达式\n");return1;//返回错误码}doublenum1=atof(expression+i+1);//获取第一个数字result+=num1;//进行运算i+=2;//跳过运算符和数字}elseif(isdigit(expression[i])){//如果是数字,则添加到结果中result+=expression[i]-'0';//进行加法运算}else{//遇到非数字和非运算符字符时,结束表达式解析并输出结果break;}i++;//移动到下一个字符}printf("结果为:%f\n",result);//输出结果return0;//返回正常结束代码}```以上代码实现了一个简单的命令行计算器程序,它使用fgets函数从标准输入读取用户输入的表达式,并使用字符串处理函数和数学函数进行表达式解析和运算。

C语言经典源程序100例1. Hello, World!这是C语言中最基本的程序,用于显示"Hello, World!"。
```c#include <stdio.h>int main() {printf("Hello, World!\n");return 0;}```2. 计算两数之和这个程序用于计算两个整数的和,并将结果输出。
```c#include <stdio.h>int main() {int num1, num2, sum;printf("请输入两个整数:");scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);sum = num1 + num2;printf("两数之和为:%d\n", sum);return 0;}```3. 判断奇偶数这个程序用于判断一个整数是奇数还是偶数。
```c#include <stdio.h>int main() {int num;printf("请输入一个整数:");scanf("%d", &num);if (num % 2 == 0) {printf("该数是偶数。
\n");} else {printf("该数是奇数。
\n");}}```4. 求输入数字的平均值这个程序用于求输入数字的平均值。
```c#include <stdio.h>int main() {int count, i;double num, sum = 0.0, average;printf("请输入数字的个数:");scanf("%d", &count);printf("请输入这 %d 个数字:\n", count); for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {scanf("%lf", &num);sum += num;}average = sum / count;printf("平均值为:%lf\n", average);}```5. 判断闰年这个程序用于判断一个年份是否为闰年。

初遇C#:⼀个简单的⼩程序(圆形周长,⾯积计算器)
作为⼀个⾯向对象的语⾔,与⽤户的交互很关键!
在此,我们可以先分析⼀下我们这个⼩程序要与⽤户交互的内容:
1.命名很重要,让⽤户看见这个程序就知道这个程序的作⽤。
2.当⽤户打开这个程序时,提⽰⽤户输⼊的内容。
下⾯开始编码:
Console.Write("请输⼊圆形的半径:");
double r=double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());//接收⽤户的输⼊并将⽤户的输⼊转换成双精度型并赋值给r
double area,circle;//定义两个变量area和circle作为圆形的⾯积和周长
area= 3.14 * r * r, circle = 3.14 * 2 * r;//圆形⾯积和周长的计算公式
Console.WriteLine("圆的周长为:" + circle+ "⽶");//输⼊圆形的周长
Console.WriteLine("圆的⾯积为:" + area + "平⽅⽶");//输出圆形的⾯积
Console.WriteLine("请按回车键关闭此窗⼝");//提⽰⽤户按回车键来关闭程序
Console.ReadLine();
⼀个简单的圆形周长和⾯积的计算器就做好了,这只是⼀个很简单的程序,⽤户只能输⼊数字,⽤户如果输⼊的不是数字,程序则会崩溃,需要⽤户重新运⾏程序。
当然,我们也可以加⼊⼀个运循环语句来提⽰⽤户,如果⽤户输⼊的不是数字,则程序⼀直提⽰⽤户请输⼊数字,这⾥我们先不深究!。
c语言计时器程序代码计时器程序通常用于测量时间间隔和定时操作。
C语言提供了一些函数和库,可以方便地编写计时器程序。
本文将介绍如何编写一个简单的计时器程序,该程序可以实现计数器和定时器两个功能。
首先,我们需要声明和初始化一个计数器变量,用于记录经过的时间。
其次,我们需要定义一个定时器函数,该函数可以在一定时间后触发某个动作。
最后,我们需要编写一个主函数,该函数将调用计数器和定时器函数,并在控制台输出结果。
```#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h>#include <unistd.h>int counter = 0; // 声明计数器变量,用于记录经过的时间void timer(int seconds) // 定义定时器函数,seconds为秒数{sleep(seconds); // 程序休眠seconds秒printf("%d秒已经过去\n", seconds); // 输出已过去的秒数}if (counter == 5) // 如果已经过去5秒{timer(2); // 调用定时器函数,让程序休眠2秒}sleep(1); // 程序休眠1秒钟}clock_t t2 = clock(); // 记录程序结束执行的时间float diff = (float)t2 - (float)t1; // 计算程序执行时间printf("程序执行了%f秒\n", diff/CLOCKS_PER_SEC); // 输出程序执行时间return 0;}```解析:- 第1行到第4行:引入需要的库文件。
- 第6行:声明计数器变量`counter`,用于记录经过的时间,初始值为0。
- 第8行到第12行:定义定时器函数`timer`,`seconds`为秒数。
在函数内部,调用`sleep`函数使程序休眠`seconds`秒,然后输出已经过去的秒数。
C语言编写的计算器源代码
```c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#define MAX_EXPRESSION_SIZE 100
//栈结构定义
typedef struct
int top;
double data[MAX_EXPRESSION_SIZE];
} Stack;
//初始化栈
void initStack(Stack *s)
s->top = -1;
//入栈
void push(Stack *s, double value)
if (s->top == MAX_EXPRESSION_SIZE - 1)
printf("Stack is full. Cannot push element.\n");
} else
s->data[++(s->top)] = value;
}
//出栈
double pop(Stack *s)
if (s->top == -1)
printf("Stack is empty. Cannot pop element.\n"); return -1;
} else
return s->data[(s->top)--];
}
//获取栈顶元素
double peek(Stack *s)
if (s->top == -1)
return -1;
} else
return s->data[s->top];
}
//判断运算符的优先级
int getPriority(char operator)
switch (operator)
case '+':
case '-':
return 1;
case '*':
case '/':
return 2;
case '^':
return 3;
default:
return -1;
}
//执行四则运算
double performOperation(double operand1, double operand2, char operator)
switch (operator)
case '+':
return operand1 + operand2;
case '-':
return operand1 - operand2;
case '*':
return operand1 * operand2;
case '/':
if (operand2 != 0)
return operand1 / operand2;
} else
printf("Error: Division by zero.\n");
exit(1);
}
case '^':
return pow(operand1, operand2);
default:
return 0;
}
//计算表达式结果
double evaluateExpression(char *expression) Stack operandStack;
Stack operatorStack;
initStack(&operandStack);
initStack(&operatorStack);
int length = strlen(expression);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
//忽略空格
if (expression[i] == ' ')
continue;
}
//数字直接入栈
if (isdigit(expression[i]))
double num = 0;
while (i < length && (isdigit(expression[i]) , expression[i] == '.'))
num = num * 10 + (expression[i] - '0');
i++;
}
i--;
push(&operandStack, num);
}
//左括号入栈
else if (expression[i] == '(')
push(&operatorStack, expression[i]);
}
//右括号出栈并执行运算,直到遇到左括号
else if (expression[i] == ')')
while (peek(&operatorStack) != '(')
double operand2 = pop(&operandStack);
double operand1 = pop(&operandStack);
char operator = pop(&operatorStack);
double result = performOperation(operand1, operand2, operator);
push(&operandStack, result);
}
pop(&operatorStack);
}
//运算符出栈并执行运算,直到栈空或者遇到优先级较低的运算符else
while (peek(&operatorStack) != -1 &&
getPriority(expression[i]) <= getPriority(peek(&operatorStack))) double operand2 = pop(&operandStack);
double operand1 = pop(&operandStack);
char operator = pop(&operatorStack);
double result = performOperation(operand1, operand2, operator);
push(&operandStack, result);
}
push(&operatorStack, expression[i]);
}
}
//处理剩下的运算符
while (peek(&operatorStack) != -1)
double operand2 = pop(&operandStack);
double operand1 = pop(&operandStack);
char operator = pop(&operatorStack);
double result = performOperation(operand1, operand2, operator);
push(&operandStack, result);
}
return pop(&operandStack); // 返回最终结果
int mai
char expression[MAX_EXPRESSION_SIZE];
printf("Enter an arithmetic expression: ");
fgets(expression, MAX_EXPRESSION_SIZE, stdin);
double result = evaluateExpression(expression);
printf("Result = %.2f\n", result);
return 0;
```
这个计算器可以实现基本的四则运算,支持括号和浮点数。
运行时,用户需要输入一个算术表达式,然后计算器会输出结果。
计算器使用两个栈来实现表达式的求值,一个栈用于存储操作数,另一个栈用于存储运算符。
通过比较运算符的优先级,可以确保表达式求值的正确顺序。