毕业论文外文翻译-混凝土重力坝基础流体力学行为分析
- 格式:docx
- 大小:119.92 KB
- 文档页数:13

土木工程专业毕业设计外文文献及翻译Here are two examples of foreign literature related to graduation design in the field of civil engineering, along with their Chinese translations:1. Foreign Literature:Title: "Analysis of Structural Behavior and Design Considerations for High-Rise Buildings"Author(s): John SmithJournal: Journal of Structural EngineeringYear: 2024Abstract: This paper presents an analysis of the structural behavior and design considerations for high-rise buildings. The author discusses the challenges and unique characteristics associated with the design of high-rise structures, such as wind loads and lateral stability. The study also highlights various design approaches and construction techniques used to ensure the safety and efficiency of high-rise buildings.Chinese Translation:标题:《高层建筑的结构行为分析与设计考虑因素》期刊:结构工程学报年份:2024年2. Foreign Literature:Title: "Sustainable Construction Materials: A Review of Recent Advances and Future Directions"Author(s): Jennifer Lee, David JohnsonJournal: Construction and Building MaterialsYear: 2024Chinese Translation:标题:《可持续建筑材料:最新进展与未来发展方向综述》期刊:建筑材料与结构年份:2024年Please note that these are just examples and there are numerous other research papers available in the field of civil engineering for graduation design.。

Membrane actions of RC slabs in mitigating progressive collapseof building structures在缓解连续倒塌的钢筋混凝土板建筑结构中的膜的应用关键词:连续倒塌钢筋混凝土建筑结构倒数第二列损失膜扩张钢筋混凝土板大变形有限元分析摘要可以研究钢筋混凝土柱结构在潜在的连续倒塌的突然损失的情况下,是其中的任一内部(PI)的倒数第二个列或外部(PE)的倒数第二个列损失。
因为最关键的情况,它留下了相关的横向梁和板的子结构扩张。
受影响的板坯的膜在大的变形的情况下,组成外周压缩的膜结构。
环混凝土拉伸膜在中部地区的行动,是一个重要的道防线来组织逐步崩溃。
在本文中,已验证可用的测试数据,用于研究膜在横向变形的行为的先进的有限元模型(FEM),使得砖与PI列损失室内双跨梁的存在,沿周边旋转边缘的限制,和板坯的顶部加固。
它已被证明,在中央地区拉伸膜,更大的力量都动员起来,由于参与梁的配筋板顶部加固。
混凝土的压缩环,在外部区域中,也加强楼板负弯矩。
因此,整体的承载能力的受影响的结构,可以是增强显着,以维持重力施加的由两个双跨越效果和动态效果的载荷。
2011年爱思唯尔有限公司保留所有权利1. 简介当地面的柱在突然爆炸中被毁坏的时候,列向的轴向压缩力在消失的几毫秒内迅速将重新分配。
其结果是,以上所有楼层一楼偏转相同,并在动态均匀重力荷载下寻求新的平衡路径。
(该过程中)可能会增加内部部队在受影响的地板结构存在两个同步变化:双跨的效果:大跨度桥梁消失的列向的荷载将增加一倍。
被放大的动态效果:现有的重力荷载动态系数达到2.0。
束柱正上方的除去列向荷载的连接,以前是为开始设计占用的时刻,现在已经有进行巨大的下垂时刻. 在离柱子较远地方的连接处,作为一个二次函数的双跨度长度,可能会增加至少4倍的初始值。
如果受影响梁板结构无法抵制不断增加的弯矩,防止连续倒塌的一个替代的负载路径是必需的。

混凝土重力坝分析
水力学分析是对坝体所受水力作用进行分析,其中包括坝体测流、坝
体流力作用和渗流三个主要的方面。
坝体测流是为了确定坝体顶部的流量,主要通过建立三角点法、数值模拟法或实测法进行。
坝体流力作用是指水
流对坝体施加的压力力和摩擦力,通过水动力学公式计算。
渗流分析是为
了确定渗流量和压力,通过实测渗流量或采用渗流公式进行计算。
岩土力学分析是对坝基岩土的力学性质和稳定性进行分析。
主要包括
地质勘探,岩土试验和稳定性分析。
地质勘探是为了了解坝基的地质构造
和岩土层次情况,通过取样分析、采用地球物理勘探方法进行。
岩土试验
是为了确定土体的力学参数,通过常规试验和专用试验方法进行。
稳定性
分析是确定岩土体在外力作用下的稳定性,主要通过几何稳定性分析和强
度稳定性分析进行。
结构力学分析是对混凝土重力坝结构的承载能力和变形特性进行分析。
主要有强度分析和稳定分析两个方面。
强度分析是为了确定混凝土重力坝
的抗浮承载力和抗滑承载力,主要通过利用强度理论和材料力学建立计算
模型进行。
稳定分析是为了确定混凝土重力坝的整体稳定性,主要包括静
力稳定性分析和动力稳定性分析。
总的来说,混凝土重力坝的分析主要包括水力学分析、岩土力学分析
和结构力学分析三个方面。
这些分析有助于确定坝体的水力性能、岩土体
的力学特性和结构的承载能力,为混凝土重力坝的设计提供科学的依据,
确保其安全可靠地发挥防洪和蓄水的作用。
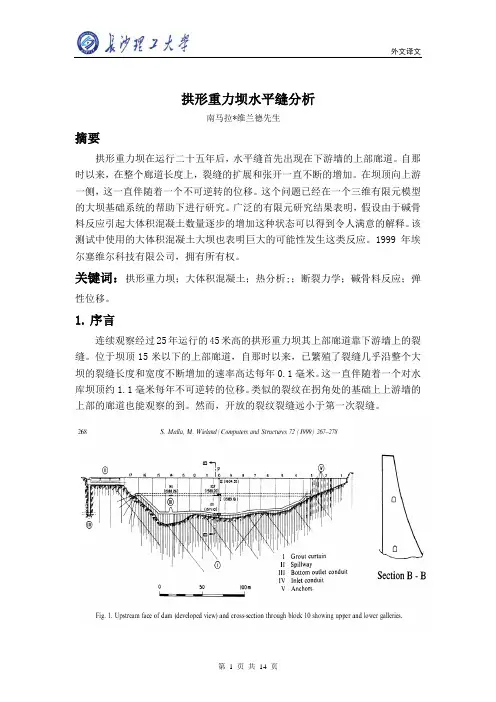
拱形重力坝水平缝分析南马拉*维兰德先生摘要拱形重力坝在运行二十五年后,水平缝首先出现在下游墙的上部廊道。
自那时以来,在整个廊道长度上,裂缝的扩展和张开一直不断的增加。
在坝顶向上游一侧,这一直伴随着一个不可逆转的位移。
这个问题已经在一个三维有限元模型的大坝基础系统的帮助下进行研究。
广泛的有限元研究结果表明,假设由于碱骨料反应引起大体积混凝土数量逐步的增加这种状态可以得到令人满意的解释。
该测试中使用的大体积混凝土大坝也表明巨大的可能性发生这类反应。
1999年埃尔塞维尔科技有限公司,拥有所有权。
关键词:拱形重力坝;大体积混凝土;热分析;;断裂力学;碱骨料反应;弹性位移。
1.序言连续观察经过25年运行的45米高的拱形重力坝其上部廊道靠下游墙上的裂缝。
位于坝顶15米以下的上部廊道,自那时以来,已繁殖了裂缝几乎沿整个大坝的裂缝长度和宽度不断增加的速率高达每年0.1毫米。
这一直伴随着一个对水库坝顶约1.1毫米每年不可逆转的位移。
类似的裂纹在拐角处的基础上上游墙的上部的廊道也能观察的到。
然而,开放的裂纹裂缝远小于第一次裂缝。
为调查这一问题,一份进行了利用三维有限元模型的大坝基础系统的研究报告。
在热弹性性能的线性弹性模型确定的帮助下,一个钟摆位于中部的部分水坝是现有的具体记录和空气温度和大坝位移测量手段。
应力分析的结果,组合的重心,温度和水的负荷表明,在夏季有相对较高的地区的拉伸应力的墙壁上部廊道的位置观察裂纹。
然而,这些拉应力是不够高,不能令人满意的解释形成的裂缝。
基于这项研究,发生碱骨料反应被确定为最可能形成在大坝上部廊道裂缝的原因。
大体积混凝土的测试也显示了碱骨料反应的大坝有相对较高的可能性。
2. 大坝的主要特点拱形重力坝,图中1显示:坝最大高度45米,坝顶长290米。
坝顶宽5米,最大的基础宽度22米。
大体积混凝土总量是7.1万立方米。
使用的混凝土大坝的属性列于表1 。
粗骨料主要包括麻岩片,或多或少丰富的云母,其最大晶粒尺寸为80毫米。
![[混凝土重力坝毕业设计计算书]混凝土重力坝毕业设计](https://uimg.taocdn.com/fd06bc688762caaedc33d478.webp)
[混凝土重力坝毕业设计计算书]混凝土重力坝毕业设计混凝土重力坝毕业设计计算书目录目录1第1章非溢流坝设计21.1坝基而高程de确定21. 2坝顶高程计算21. 2. 1基木组合情况下:21.2.2特殊组合情况下:31. 3坝宽计算41. 4坝而坡度41. 5坝基de防渗与排水设施拟定5第二章非溢流坝段荷载计算52.1计算情况de选择52. 2荷载计算52. 2. 1自重62. 2. 2静水压力及其推力62. 2. 3扬压力de计算72. 2. 4淤沙压力及其推力102. 2. 5波浪压力112. 2. 6 土压力12第3章坝体抗滑稳定性分析133. 2抗滑稳定计算153. 3抗剪断强度计算16第4章应力分析174. 1总则174. 1. 1大坝垂直应力分析174. 1. 2大坝垂直应力满足要求184. 2计算截而为建基面de情况194. 2.1荷载计算194. 2. 2运用期(计入扬压力de情况)204. 2. 3运用期(不计入扬压力de情况)214. 2. 4施工期21第5章溢流坝段设计225. 1泄流方式选择225. 2洪水标准de确定235. 3流量de确定235. 4单宽流量de选择235. 5孔口净宽de拟定235. 6溢流坝段总长度de确定245. 7堰顶高程de确定245. 8闸门高度de确定255. 9定型水头de确定255. 10泄流能力de校核265.11.1溢流坝段剖面图265.11. 2溢流坝段稳定性分析27 (1)正常蓄水情况27 (2)设计洪水情况27 (3)校核洪水情况28第6章消能防冲设计286.1洪水标准和相关参数de 选定296. 2反弧半径de确定296. 3坎顶水深de确定306. 4水舌抛距计算316. 5最大冲坑水垫厚度及最大冲坑厚度32第7章泄水孔DE设计337.1有压泄水孔de设计347. 11孔径Dde拟定347. 12进水口体形设计347. 13 闸门与门槽357. 14渐宽段357. 15出水口357. 15通气孔和平压管35参考文献36毕业设计(论文)任务书题目车家坝河水利枢纽(碾压重力坝设计)(任务起止日期20XX年3月29 ET20XX年6月18 H)院水利水电专业班学生姓名学号指导教师教研室主任院领导第一章非溢流坝设计1. 1坝基而高程de确定由《混凝土重力坝设计规范》可知,坝高100~50米时,重力坝可建在微风化至弱风化中部基岩上,本工程坝高为50~100m,由于本坝址岩层分布主要为石英砂岩,故可确定坝基面高程为832.0m。

重力坝设计毕业论文目录1基本资料 (1)仁1.流域概况 (1)1.2水文气象特征 (1)1.3地质条件 (2)1.41程枢纽任务 (3)2枢纽布置 (4)2.1工程等级及建筑物级别确建 (4)2.2坝址、坝型选择 (5)2.2.1坝址地形地质条件 (5)2.2.2选址、选型原则 (5)2.2.3亭子口坝址概况 (6)2.2.4李家嘴坝址概况 (7)2.2.5坝址比较 (8)2.3枢纽布置 (9)2.3.1布置原则: (9)2.3.2枢纽的总体布置 (9)3洪水调节 (11)3.1基本资料 (11)3.1.1洪水过程线的确泄 (11)3.1.2相关曲线图 (13)3.1.3确定天然设计洪峰流量和天然校核洪峰流量 (13)3.1.4确定下泄设计洪峰流量标准(p=0.2%)和下泄校核洪峰流量标(p=0.1%) (14)3.2洪水调苗基本原则 (14)3.2.1确定工程等别和级别 (14)3.2.2水库防洪要求 (14)3.2.3水库的运用方式 (14)3.3调洪演算 (15)3.3.1堰顶高程 (15)3.3.2设计水头Hd (15)3.3.3流呈:系数加的确定 (15)3.3.4方案拟订 (16)3.3.5计算下泄流量 (16)3.3.6半图解法调洪演算 (17)4非溢流坝剖而设计 (22)4.1设计原则 (22)4.2剖面拟订要素 (22)4.2.1坝顶高程的拟订 (22)4.2.2坝顶宽度的拟订 (25)4.2.3坝坡的拟订 (26)4.2.4上、下游起坡点位宜的确定 (26) 4.2.5剖而设计 (26)4.3抗滑稳定分析与计算 (28)4.3.1分析的目的 (28)4.3.2滑动而的选择 (28)4.3.3对坝基面进行抗滑稳定计算 (29) 4.4应力计算 (30)4.4.1分析的目的 (30)4.4.2分析方法 (30)4.4.3材料力学法的基本假设 (30) 4.4.4荷载组合 (30)4.4.5应力计算 (30)5溢流坝段设计 (32)5.1泄水建筑物方案比较 (32)5.1.1布置原则 (32)5.1.2泄洪方案选择 (32)5.2溢流表孔布置 (32)5.3溢流坝剖而设计 (33)5.3.1顶部曲线 (33)5.3.2中间直线段的确定 (34) 5.3.3反弧段 (35)5.4消能设计与计算 (35)5.4.1闸墩的设计 (36)5.4.2消能形式选择 (37)5.4.3消力池的水力计算 (38) 5.4.4辅助消能工设计 (41) 5..4.5消力池护坦的设计 (42)6细部构造设计 (42)6.1坝顶构造 (42)6.2廊道系统 (43)6.2.1基础灌浆廊道 (43)6.2.2检査排水廊道 (44)6.2.3排水管 (44)6.3坝体分缝 (45)6.3.1横缝 (45)6.3.2纵缝 (45)6.3.3水平施工缝 (45)6.4坝体止水与排水 (45)6.4.1I 上水 (45)6.4.2坝体排水 (46)6.5基础处理 (46)6.5.1坝基开挖 (46)6.5.2固结灌浆 (47)6.5.3帷幕灌浆 (47)6.5.4坝基断层及破碎带处理 (48) 6.6混凝土重力坝的分区 (48)参考文献 (50)1基本资料流域概况嘉陵江是长江上游左岸的主要支流,发源于陕西凤县东北的秦岭山脉,流经陕西、、、重庆四省(直辖市),干流全长1120km,落差有2300m,平均比降2?05%。

混凝土重力坝
混凝土重力坝是一种利用大块混凝土凭借自身重力来抵抗水压和冲击力的建筑物。
它是水利工程和水电站建设中常用的一种建筑形式。
本文将对混凝土重力坝的基本原理、设计和施工进行介绍。
首先,混凝土重力坝的原理是利用混凝土的自重,通过重力来抵抗水压和冲击力。
混凝土重力坝的主要作用是防洪和蓄水。
它的体积大,重量大,结构紧密,可以有效地阻挡洪水,保护下游地区免遭洪灾。
同时,混凝土重力坝还可以蓄水,为下游提供水源和水利发电。
其次,在混凝土重力坝的设计方面,需要考虑多个因素。
首先是坝体的强度和稳定性,也就是要保证坝体能够承受水压和冲击力,同时不发生滑移或开裂。
其次是坝体的防渗功能,保证不会发生渗漏。
此外还需要考虑坝体的变形和温度变化,保持坝体的结构完整性。
混凝土重力坝的施工需要采取一系列措施。
首先是要进行地质勘探和现场勘测,确保施工地点符合要求。
其次是要进行基础施工,确保坝体有一个稳定的基础。
接着是混凝土浇筑,需要注意混凝土的配比和施工质量。
最后是调试和验收工作,确保建成的重力坝的质量和安全。
需要指出的是,混凝土重力坝在设计和施工过程中还需要考虑环境保护问题,避免对环境造成不利影响。
为此,需要采取措施来减少噪音和振动、防止土方失控和水土流失等。
总的来说,混凝土重力坝是水利工程和水电站建设中非常重要的一种建筑形式。
它的设计和施工需要充分考虑各种因素,以保证坝体的强度和稳定性、防渗功能和环境保护。
混凝土重力坝的建设将对保护人民的生命财产、发展经济和改善环境起到重要作用。

卡拉杰大坝使用仪表数据的行为评估Edris Merufinia,土木工程,伊斯兰自由大学,德黑兰,伊朗;Mohammad H Aminfar,副教授,岩土工程,大不里士大学,大不里士,伊朗;Gholam Moradi,副教授,岩土工程,大不里士大学,大不里士,伊朗;Aref Azizian,硕士学位,岩土工程,大不里士的大学,大不里士,伊朗;摘要:其在应用仪表和监测大坝混凝土坝方面有许多用途特别是用在为了论证他们的成果方面,以扩大我们对大坝实际行为的认识。
这也就是说,每个水坝也算是一个重大的实验模型,可以正确地回答很多关于大坝和反对修建大坝的人真正关心的性能问题,无论是固定的或是可变的力量。
在大坝运行中,行为虽然基础,然而随着时间的推移,会出现变化,基牙由于固定和可变的原因出现紧张的关系;唯一的办法是对这些变化需要通知并记录水坝在建设和运营的各个阶段的行为。
根据使用仪器仪表和监测现有的实际情况,记录和评估可能关于岩体和结构的响应的真实情况。
在许多情况下对于使用变化的监测和研究的结果,检测数据是发现可能造成大坝破坏的侵蚀现象,从而避免它们或减少它们的影响以最小化最终的潜在损害避免造成下游居民出现重大损失,通过设备的观测实现时间上的更早行动。
关键词:直摆;土石坝;仪器仪表;气动压力计介绍水坝建设项目是最重要和最昂贵的重大建设项目。
应有经济学,水资源,农业,能源生产和创造就业机会的原因,水坝是最外层,重要性不言而喻。
然而,岩土工程、水文、气象和其他未知参数不断威胁大坝的稳定性和安全性。
因此,监控将实现进一步确定水坝所面临的问题并采取合理且正确的措施来维持稳定性和安全性(SERAJ,2010)。
卡拉杰大坝不像其他混凝土重力坝,只是具有悬臂织性能,混凝土拱坝具有弓悬臂式拱所以可以转移负荷,并最终用悬臂功能将负荷移向侧面。
因此混凝土拱坝可以用更少的厚度来承受比混凝土重力坝远多的负载。
但由于设计和操作的复杂性,对于混凝土拱坝,监测它们具有重大的重要性。

摘要本次设计为混凝土重力坝设计,设计的准备工作主要包括基本资料的分析、坝型选择及枢纽布置。
设计的主要内容首先是进行坝体的设计,进行坝型选择,设计采用混凝土重力坝方案,设计内容包括挡水坝段的设计,溢流坝段的设计,底孔坝段的设计等。
然后是细部构造与坝基处理,有坝基清理、坝基加固、坝基防渗及坝基排水设计、断层处理等。
设计中认真总结,运用几年来所学的理论知识及专业知识,结合毕业设计的任务进行思考、分析应用,提高了独立思考与独立工作的能力,同时也加强了计算、绘图、编写设计文件、使用规范、手册能力的培养,使我们成为合格的水利人才。
关键词水利工程、混凝土重力坝、剖面设计、荷载计算、稳定分析、应力分析Abstract:The design for the concrete gravity dam design, the design of the preparation work includes basic material analysis, dam type selection and the general layout. The main contents of the design is the first of the dam, the design of type selection, design scheme, design of concrete gravity dam block dam section includes the design, the design of the computation of the dam base, etc. Then detail structure and foundation treatment, clean, dam foundation seepage and dam foundation reinforcement, drainage design, processing, etc.In the design, use summarization years theories knowledge and professional knowledge, combined with the task of graduation design thinking and analysis of independent thinking and the ability to work independently, but also strengthen thecalculation, drawing, write design documents, use, manual competence, enable us to become qualified talents of water.Keywords:water conservancy project, concrete gravity dam, section, the load calculation, stability analysis and stress analysis目录前言 (1)第一部分设计说明书 (2)1 . 工程概况 (2)1.1 概述 (2)1.2 水库特性 (2)1.3 主要建筑物及其尺寸 (2)2. 设计基本资料 (3)2.1 地址区自然条件简况 (3)2.2 水文特性 (4)2.3 地质概况 (4)2.4 建筑材料及水源 (5)2.5 坝基岩石及砂砾石的物理力学性质 (5)2.6 水库特性表 (5)3. 坝型选择与枢纽布置 (6)3.1 坝型选择 (6)3.2 工程等别与建筑物级别 (7)3.3 坝顶高程的确定 (7)3.4 枢纽布置 (8)4. 挡水坝段设计 (12)4.1 基本剖面设计 (12)4.2 坝体稳定分析及应力分析 (13)4.3 荷载及荷载组合 (15)4.4 强度、稳定指标分析总结: (17)5. 溢流坝段设计 (19)5.1 溢流坝剖面设计 (19)5.2 堰面水深计算 (23)5.3 消能设计 (24)5.4 导水墙设计 (24)5.5 闸墩、胸墙和启闭机 (25)5.6 荷载计算 (26)6. 底孔坝段设计 (32)6.1 底孔的剖面轮廓尺寸 (32)6.2 泄洪能力校核 (34)6.3 消能设计 (34)7. 细部构造与地基处理 (35)7.1 坝体细部构造设计 (35)7.2 地基处理 (38)第二部分设计计算书 (39)1.挡水坝段设计 (39)1.1 坝顶高程的确定 (39)1.2 基本剖面尺寸确定 (40)1.3 荷载计算 (41)1.4 稳定分析 (51)1.5 应力分析 (52)2. 溢流坝段 (58)2.1 泄流能力校核 (58)2.2 空蚀验算 (60)2.3 溢流坝曲面设计 (61)2.4 堰面水深计算 (63)2.5 消能设计 (65)2.6 稳定分析及应力分析 (68)3. 底孔坝段设计 (82)3.1 孔口尺寸的确定 (82)3.2 泄流能力验算 (84)3.3 检修门槽空蚀检验 (85)3.4 消能设计 (86)参考文献 (91)谢辞 (92)附录 (93)。

陈驰(重庆腾云工程咨询有限公司,重庆400074)[摘要]文中基于渗流基本理论、渗流基本数学模型,以混凝土重力坝为实例,通过有限元软件ANSYS 建立起基本算例的有限元模型。
在有限元模型上划分网格,建立边界条件,进行计算分析,获得水头等值线分布图、渗流梯度及渗流速度矢量图,以及指定路径的渗流速度变化曲线。
并根据计算成果分析出坝基渗流规律。
[关键词]有限元;坝基;渗流分析;混凝土重力坝[中图分类号]TV64[文献标识码]B[文章编号]1002—0624(2022)02—0038—04基于ANSYS 的混凝土重力坝坝基稳态渗流研究0引言近年来,随着对水资源的不断开发利用,我国在长期的水利工程建设中积累了丰富的经验,水利事业也得到了蓬勃发展。
特别是在建国以来,数以万计的水库大坝得以修建,对人民生活水平和工农业生产等都带来了巨大的收益。
由于这些水利工程都是在不同时期建立的,基于修建时经济基础、技术水平、规划设计水平等限制,或多或少会出现一些质量缺陷,渗流问题就是其中之一[1]。
渗流是指流体通过多孔介质的流动,在水利工程大坝运行中的渗流问题有坝体和坝基渗流作用所造成的渗透变形、滑坡及冲蚀等破坏,严重的甚至会影响大坝的安全稳定,对人民生命财产安全和国家安定带来难以预计的损害。
因此,渗流分析是水工设计中不可或缺的一部分,工程实践表明,水利工程能否安全、可靠运行,很大程度上取决于能否正确进行渗流分析和选择合理的防渗措施[2]。
1渗流基本理论渗流现象普遍存在于自然界中,渗流理论也已经成为人类开发地下水、地热石油、天然气、煤炭与煤层气等诸多地下资源的重要理论基础。
早在1856年,法国工程师Darcy 通过渗透试验得到了渗流量Q 与横截面A 及水头差(H 1-H 2)成正比,与渗透路径L 成反比的规律,即:Q =kAH 1-H 2L 或v =Q A =k H 1-H 2L=kJ (1)式中:Q ——渗流量,m 3/s ;k ——渗透系数,m/s ;A ——横截面积,m 2;H 1,H 2——上、下游水深,m ;v ——流速,m/s ;J ——水力梯度。

混凝土重力坝研究混凝土重力坝是一种常见的大型水利工程结构,其主要由混凝土建筑物形成,利用重力作用来抵抗水压力和其他荷载的结构。
混凝土重力坝的研究对于水利工程的设计和建造具有重要意义。
本文将重点介绍混凝土重力坝的研究内容和相关案例。
首先,混凝土重力坝的研究内容包括坝体结构稳定性、抗震性能、渗流分析和开发坝基的研究。
坝体结构稳定性是混凝土重力坝设计的基础,包括对坝体内力、应力和变形的分析,以及对不同荷载条件下的破坏机制研究。
抗震性能是指在地震作用下,坝体能够保持稳定和安全。
渗流分析是指对坝体内部渗流和渗漏情况的分析和控制,以确保坝体的稳定性和坝后的安全。
开发坝基的研究是指对坝基地质条件的调查和分析,以确定合适的坝基处理措施。
其次,混凝土重力坝的研究还包括坝体材料的研究和结构施工技术的研究。
坝体材料的研究包括混凝土的强度、抗裂性能和耐久性等方面的研究,以确定合适的材料配合比和混凝土浇筑工艺。
结构施工技术的研究包括坝体的施工方法、浇筑工艺和施工过程的控制等方面的研究,以确保坝体的质量和施工进度。
最后,混凝土重力坝的研究还可以借助数值模拟和实验模型来进行。
数值模拟可以采用有限元方法或其他数学模型,模拟坝体的结构行为和荷载响应,以评估坝体的安全性和稳定性。
实验模型可以建立小比例的物理模型,通过加载实际荷载和观测变形来研究坝体的行为和响应。
下面以中国的七曲重力坝为例介绍混凝土重力坝的研究和实践。
七曲重力坝位于云南省澜沧江上游,是中国最大的重力坝之一、该坝的研究充分考虑了坝体的稳定性、抗震性能和渗流分析等方面。
通过数值模拟和实验模型的研究,确定了坝体的设计参数和施工方法,确保了坝体的稳定和安全。
总之,混凝土重力坝的研究是水利工程设计和建造的重要内容。
通过对坝体结构稳定性、抗震性能、渗流分析和开发坝基的研究,可以确保混凝土重力坝的稳定和安全。
数值模拟和实验模型可以为混凝土重力坝的设计和施工提供重要的技术支持。
长江工程职业技术学院大专学生毕业设计(论文)题目混凝土重力坝设计姓名学号系部水利工程系专业水利水电建筑工程指导教师年12 月25 日毕业设计任务书设计题目:混凝土重力坝设计(二)适用专业:水利水电工程指导老师:学生姓名:长江工程职业技术学院目录第一部分总则一、设计目的及要求 (2)二、设计方法 (2)第二部分设计资料和任务一、设计内容 (3)二、基本资料 (3)三、设计指导 (4)四、设计内容和时间安排 (6)五、设计成果要求 (6)六、参考文献 (7)第一部分总则一、设计目的及要求1、巩固、充实、加深、扩大学生的基本理论和专业知识通过实际工程的设计,使学生掌握混凝土重力坝的结构选型、尺寸拟定、工作条件、作用荷载及设计依据、内容、方法、步骤等。
从而达到较全面、系统地巩固、充实、提高所学的基础理论和专业知识,使之系统化。
2、培养学生独立工作、解决实际问题的能力学生在全面了解设计任务和熟悉给定资料的基础上,学会查找规范、手册、技术文献等参考资料及前人经验。
结合工程实际,在教师的指导下,独立进行工程设计。
3、训练学生的基本技能培养学生初步掌握工程设计工作的流程和方法,在设计、计算、绘图、编写设计文件等方面得到较全面的锻炼和提高。
4、培养学生形成正确的设计思想,树立严肃认真、实事求是和刻苦钻研的工作作风。
二、设计方法1、由于设计时间短、任务紧,应尽量避免重作或返工。
但必须认识到,设计工作是逐步深入的,因此某些重作是正常的,甚至是必要的。
2、每个阶段设计中,趁进入角色之机,应及时收集资料,草写阶段设计说明并备全草图,这样既可及时校对,发现错误,又为最后的文字成果整理提供素材。
3、在学生与教师研讨问题时,学生应在充分钻研的基础上,先提出自己的看法和意见,不能请老师代作和决断。
老师只向学生提出启发性的意见、解决问题的途径和工作方向、建议等。
在采纳教师建议时,也必须自我消化、理解,但不强求一定纳用。
在设计过程中,提倡开拓精神,鼓励提出新的方案或见解,同时也要遵循严肃认真的科学态度。
水利水电工程专业外文翻译、英汉互译、中英对照毕业设计,论文,外文翻译题目姚家河水电站溢流坝及消能工优化设计专业水利水电工程使用CFD模型分析规模和粗糙度对反弧泄洪洞的影响12 作者 Dae Geun Kimand Jae Hyun Park摘要在这项研究中,利用CFD模型、FLOW-3D模型详细调查流量特性如流量、水面、反弧溢洪道上的峰值压力,并考虑到模型规模和表面粗糙度对速度和压力的垂直分布特征的影响,因此,在领域中被广泛验证和使用。
由于表面粗糙度数值的误差是微不足道的,对于流量,水面平稳,波峰压力影响较小。
但是我们只是使用长度比例小于100或200在可接受的误差范围的建筑材料一般粗糙度高度和规模效应的模型,最大速度在垂直的坐标堰发生更严重的粗糙度和规模效应。
原型的速度比缩尺比模型的更大,但现却相反1的。
在任何一节的最大速度略有降低或者表面粗糙度和长度的比例增加。
最大速度出现在上游水头的增加几乎呈线性增加溢洪道前的距离和位置较低的垂直位置位上。
关键词:FLOW-3D,反弧溢洪道,粗糙度效应,规模效应1.简介工程师在大多数情况下都选着设计建造具有过流高效、安全地反弧溢洪道,并且它在使用过程中具有良好的测量能力。
反弧溢洪道的形状是从较高顶堰的直线段流到半径R的网弧形段,在反弧附近的大气压力超过设计水头。
在低于设计水头时波峰阻力减少。
在高水头的时候,顶堰的大气压较高产生负压使水流变得更缓。
虽然这是关于一般反弧从上游流量条件下的变化、修改的波峰形状或改变航的形状和其流动特性的理解,但是道由于局部几何性质等的标准设计参数的偏差都会改变的水流的流动性,影响的分析结果。
物理模型被广泛的用来确定溢洪道非常重要的大坝安全。
物理模型的缺点是成本高,它可能需要相当长的时间得到的结果。
此外,由于规模效应的误差的严重程度增加原型模型的大小比例。
因此在指导以正确的模型细节时,计算成本相对较低物理建模、数值模拟,即使它不能被用于为最终确定的设计也是非常宝贵的资料。
大坝原型反分析的新理论和方法作者:吴中如,顾冲时、郑东健期刊:2000年工程和技术科学国际会议论文集翻译人:XXX摘要:简要介绍大坝反分析的研究及其应用的过程。
指出了在反分析中急需解决的问题。
基于观测数据,研究了反分析中的热点问题而且讨论了一些新的分析理论和方法。
列举了一些工程实例。
1.引言截至目前为止,中国已经建造了87000多座坝。
在国民经济中,这些工程有着巨大的社会和经济效益。
然而,由于各种原因,例如水文地质条件、施工质量以及大坝的部分不安全因素,工程效益会受到影响且住在下游的人的财产会受到威胁。
而且,随着国家经济的快速增长,水资源保护和水能工程规模越来越大,质量要求越来越高,例如龙羊峡大坝、三峡大坝、二滩大坝、小浪底大坝等等。
这些工程的的安全非常重要,同时大坝工程的专家们对这些问题也很关注。
由于大坝和岩石基础的复杂状况、荷载、计算参数、边界条件,用计算方法是很难准确模仿的,以至于水能工程的设计与真实的大坝运行很难紧密吻合,有时错误会很大。
因此,大坝和岩石基础的反应通过用模型观测数据来反馈,这些数据可用来评估大坝和岩石基础的安全因素。
另一方面,根据在建大坝的观测数据。
分析和反分析,对设计和施工给与指导和优化。
因此,可以看出反分析的研究不仅具有非比寻常的经济价值,而且具有巨大的科学意义。
2.研究的现状大坝及其基础有非常多的不确定的及未知的因素,,这促进了原型监测和反分析研究的发展。
国内外已经深入开展了关于大坝的反分析研究,特别是混凝土坝的反分析。
吴中如已经提出了一种评估坝体弹性模量及线性热膨胀系数,这些可以用来确定性模型和统计模型以及有限元结果。
由Bonaldi, Fanali 和Giusepptti提出有清楚的概念的确定性模型被用来估计坝体的相反的弹性模量和线性热膨胀系数。
考虑到软弱层的影响,吴中如和Liu meixian提出了一种方法:混凝土的温度扩散是确定的,这基于距离坝体下游面不同深度的温度计观测值。
土木毕业设计外文文献土木毕业设计外文文献在土木工程领域,外文文献是不可或缺的资源。
它们提供了最新的研究成果、技术发展和实践经验,为土木工程师们提供了宝贵的指导和参考。
本文将介绍几篇与土木毕业设计相关的外文文献,并对其内容进行简要概述。
1. "Structural Health Monitoring of Bridges: A Review" by Fu-Kuo Chang and Hoon Sohn这篇文献综述了桥梁结构健康监测的最新研究进展。
它介绍了不同类型的监测技术,包括传感器、无损检测和数据分析方法。
文献还讨论了桥梁结构健康监测的挑战和未来发展方向。
对于土木工程学生来说,这篇文献提供了一个全面的桥梁结构监测的概述,可以帮助他们在毕业设计中选择适当的监测方法。
2. "Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Buildings" by Jack Moehle这本书是一本关于钢筋混凝土建筑抗震设计的经典著作。
它详细介绍了抗震设计的原理、方法和实践经验。
文献还包括了大量的案例研究和结构分析的示例。
对于进行毕业设计的土木工程学生来说,这本书是一个宝贵的参考资料,可以帮助他们理解抗震设计的基本原理,并应用于实际项目中。
3. "Sustainable Construction: Green Building Design and Delivery" by Charles J. Kibert可持续建筑是当今土木工程领域的一个重要话题。
这本书介绍了绿色建筑设计和施工的原则和实践。
文献探讨了可持续建筑的概念、设计方法和材料选择。
它还包括了绿色建筑认证体系和案例研究。
对于有意进行可持续建筑设计的毕业生来说,这本书提供了宝贵的指导,帮助他们在毕业设计中实现环境友好和可持续发展的目标。
4. "Geotechnical Engineering: Principles and Practices" by Donald P. Coduto,Man-chu Ronald Yeung, and William A. Kitch岩土工程是土木工程的重要分支。
毕业设计(论文)外文文献翻译文献、资料中文题目:建筑施工混凝土裂缝的预防与处理文献、资料英文题目:文献、资料来源:文献、资料发表(出版)日期:院(部):专业:工程项目管理班级:姓名:学号:指导教师:翻译日期: 2017.02.14建筑施工混凝土裂缝的预防与处理Building construction concrete crack ofprevention and processingBuilding construction concrete crack ofprevention and processingAbstractThe crack problem of concrete is a widespread existence but again difficult in solve of engineering actual problem, this text carried on a study analysis to a little bit familiar crack problem in the concrete engineering, and aim at concrete the circumstance put forward some prevention, processing measure.Keyword:Concrete crack prevention processingForewordConcrete's ising 1 kind is anticipate by the freestone bone, cement, water and other mixture but formation of the in addition material of quality brittleness not and all material.Because the concrete construction transform with oneself, control etc. a series problem, harden model of in the concrete existence numerous tiny hole, spirit cave and tiny crack, is exactly because these beginning start blemish of existence just make the concrete present one some not and all the characteristic of quality.The tiny crack is a kind of harmless crack and accept concrete heavy, defend Shen and a little bit other use function not a creation to endanger.But after the concrete be subjected to lotus carry, difference in temperature etc. function, tiny crack wouldcontinuously of expand with connect, end formation we can see without the aid of instruments of macro view the crack be also the crack that the concrete often say in the engineering. Concrete building and Gou piece usually all take sewer to make of, because of crack of existence and development usually make inner part of reinforcing bar etc. material creation decay, lower reinforced concrete material of loading ability, durable and anti- Shen ability, influence building of external appearance, service life, severity will threat arrive people's life and property safety.A lot of all of crash of engineerings is because of the unsteady development of the crack with the result that.Modern age science research with a great deal of of the concrete engineering practice certificate, in the concrete engineering crack problem is ineluctable, also acceptable in certainly of the scope just need to adopt valid of measure will it endanger degree control at certain of scope inside.The reinforced concrete norm is also explicit provision:Some structure at place of dissimilarity under the condition allow existence certain the crack of width.But at under construction should as far as possible adopt a valid measure control crack creation, make the structure don't appear crack possibly or as far as possible decrease crack of amount and width, particularly want to as far as possible avoid harmful crack of emergence, insure engineering quality thus.Concrete crack creation of the reason be a lot of and have already transformed to cause of crack:Such as temperature variety, constringency, inflation, the asymmetry sink to sink etc. reason cause of crack;Have outside carry the crack that the function cause;Protected environment not appropriate the crack etc. caused with chemical effect.Want differentiation to treat in the actual engineering, work°out a problem according to the actual circumstance.In the concrete engineering the familiar crack and the prevention1.Stem Suo crack and preventionStem the Suo crack much appear after the concrete protect be over of a period of time or concrete sprinkle to build to complete behind of around a week.In the cement syrup humidity of evaporate would creation stem Suo, and this kind of constringency is can't negative.Stem Suo crack of the creation be main is because of concrete inside outside humidity evaporate degree dissimilarity but cause to transform dissimilarity of result:The concrete is subjected to exterior condition of influence, surface humidity loss lead quick, transform bigger, inner part degree of humidity variety smaller transform smaller, bigger surface stem the Suo transform to be subjected to concrete inner part control, creation more big pull should dint but creation crack.The relative humidity is more low, cement syrup body stem Suo more big, stem the Suocrack be more easy creation.Stem the Suo crack is much surface parallel lines form or the net shallow thin crack, width many between 0.05-0.2 mm, the flat surface part much see in the big physical volume concrete and follow it more in thinner beam plank short to distribute.Stem Suo crack usually the anti- Shen of influence concrete, cause the durable of the rust eclipse influence concrete of reinforcing bar, under the function of the water pressure dint would creation the water power split crack influence concrete of loading dint etc..Concrete stem the Suo be main with water ash of the concrete ratio, the dosage of the composition, cement of cement, gather to anticipate of the dosage of the property and dosage, in addition etc. relevant.Main prevention measure:While being to choose to use the constringency quantity smaller cement, general low hot water mire and powder ash from stove cement in the adoption, lower the dosage of cement.Two is a concrete of stem the Suo be subjected to water ash ratio of influence more big, water ash ratio more big, stem Suo more big, so in the concrete match the ratio the design should as far as possible control good water ash ratio of choose to use, the Chan add in the meantime accommodation of reduce water.Three is strict control concrete mix blend with under construction of match ratio, use of concrete water quantity absolute can't big in match ratio design give settle of use water quantity.Four is the earlier period which strengthen concrete to protect, and appropriate extension protect of concrete time.Winter construction want to be appropriate extension concrete heat preservation to overlay time, and Tu2 Shua protect to protect.Five is a constitution the accommodation is in the concrete structure of the constringency sew.2.The Su constringency crack and preventionSu constringency is the concrete is before condense, surface because of lose water quicker but creation of constringency.The Su constringency crack is general at dry heat or strong wind the weather appear, crack's much presenting in the center breadth, both ends be in the centerthin and the length be different, with each other not coherent appearance.Shorter crack general long 20-30 cm, the longer crack can reach to a 2-3 m, breadth 1-5 mm.It creation of main reason is:The concrete is eventually almost having no strength or strength before the Ning very small, perhaps concrete just eventually Ning but strength very hour, be subjected to heat or compare strong wind dint of influence, the concrete surface lose water to lead quick, result in in the capillary creation bigger negative press but make a concrete physical volume sharply constringency, but at this time the strength of concrete again can't resist itsconstringency, therefore creation cracked.The influence concrete Su constringency open the main factor of crack to have water ash ratio, concrete of condense time, environment temperature, wind velocity, relative humidity...etc..Main prevention measure:One is choose to use stem the Suo value smaller higher Huo sour salt of the earlier period strength or common the Huo sour brine mire.Two is strict the control water ash ratio, the Chan add to efficiently reduce water to increment the collapse of concrete fall a degree and with easy, decrease cement and water of dosage.Three is to sprinkle before building concrete, water basic level and template even to soak through.Four is in time to overlay the perhaps damp grass mat of the plastics thin film, hemp slice etc., keep concrete eventually before the Ning surface is moist, perhaps spray to protect etc. to carry on protect in the concrete surface.Five is in the heat and strong wind the weather to want to establish to hide sun and block breeze facilities, protect in time.3.Sink to sink crack and preventionThe creation which sink to sink crack is because of the structure foundation soil quality not and evenly, loose soft or return to fill soil dishonest or soak in water but result in the asymmetry sink to decline with the result that;Perhaps because of template just degree shortage, the template propped up to once be apart from big or prop up bottom loose move etc. to cause, especially at winter, the template prop up at jelly soil up, jelly the soil turn jelly empress creation asymmetry to sink to decline and cause concrete structure creation crack.This kind crack many is deep enter or pierce through sex crack, it alignment have something to do with sinking to sink a circumstance, general follow with ground perpendicular or present 30 °s-45 °Cape direction development, bigger sink to sink crack, usually have certain of wrong, crack width usually with sink to decline quantity direct proportion relation.Crack width under the influence of temperature variety smaller.The foundation after transform stability sink to sink crack also basic tend in stability.Main prevention measure:One is rightness loose soft soil, return to fill soil foundation a construction at the upper part structure front should carry on necessity of Hang solid with reinforce.Two is the strength that assurance template is enough and just degree, and prop up firm, and make the foundation be subjected to dint even.Three is keep concrete from sprinkle infusing the foundation in the process is soak by water.Four is time that template tore down to can't be too early, and want to notice to dismantle a mold order of sequence.Five is at jelly soil top take to establish template to notice to adopt certain of prevention measure.4.Temperature crack and preventionTemperature crack much the occurrence is in big surface or difference in temperature variety of the physical volume concrete compare the earth area of the concrete structure.Concrete after sprinkling to build, in the hardening the process, cement water turn a creation a great deal of of water turn hot, .(be the cement dosage is in the 350-550 kg/m 3, each sign square the rice concrete will release a calories of 17500-27500 kJ and make concrete internal thus the temperature rise to reach to 70 ℃or so even higher)Because the physical volume of concrete be more big, a great deal of of water turn hot accumulate at the concrete inner part but not easy send forth, cause inner part the temperature hoick, but the concrete surface spread hot more quick, so formation inside outside of bigger difference in temperature, the bigger difference in temperature result in inner part and exterior hot the degree of the bulge cold Suo dissimilarity, make concrete surface creation certain of pull should dint.When pull should dint exceed the anti- of concrete pull strength extreme limit, concrete surface meeting creation crack, this kind of crack much occurrence after the concrete under construction period.In the concrete of under construction be difference in temperature variety more big, perhaps is a concrete to be subjected to assault of cold wave etc., will cause concrete surface the temperature sharply descend, but creation constringency, surface constringency of the concrete be subjected to inner part concrete of control, creation very big of pull should dint but creation crack, this kind of crack usually just in more shallow scope of the concrete surface creation.The alignment of the temperature crack usually none settle regulation, big area structure the crack often maneuver interleave;The size bigger structure of the beam plank length, the crack run parallel with short side more;Thorough with pierce through sex of temperature crack general and short side direction parallelism or close parallelism, crack along long side cent the segment appear, in the center more airtight.Crack width the size be different, be subjected to temperature variety influence more obvious, winter compare breadth, summer more narrow.The concrete temperature crack that the heat inflation cause is usually in the center the thick both ends be thin, but cold Suo crack of thick thin variety not too obvious.The emergence of the this kind crack will cause the rust eclipse of reinforcing bar, the carbonization of concrete, the anti- jelly which lower concrete melt, anti- tired and anti- Shen ability etc..Main prevention measure:One is as far as possible choose to use low hot or medium hot water mire, like mineral residue cement, powder ash from stove cement...etc..Two is a decrease cement dosage, cement dosage as far as possible the control is in the 450 kg/m 3 following.Three is to lower water ash ratio, water ash of the general concrete ratio control below 0.6.Four is improvement the bone anticipate class to go together with, the Chan add powder ash from stove or efficiently reduce water etc. to come to reduce cement dosage and lower water to turn hot.Five is an improvement concrete of mix blend to process a craft, lower sprinkle of concrete to build temperature.Six is the in addition that the Chan add a have of fixed amount to reduce water and increase Su, slow Ning etc. function in the concrete, improvement the concrete mix to match a thing of mobility, protect water, lower water to turn hot, postpone hot Feng of emergence time.Seven is the heat season sprinkle to build can the adoption take to establish to hide sun plank etc. assistance measure control concrete of Wen Sheng, lower to sprinkle temperature of build the concrete.Eight is the temperature of big physical volume concrete should the dint relate to structure size, concrete structure size more big, temperature should dint more big, so want reasonable arrangement construction work preface, layering, cent the piece sprinkle to build, for the convenience of in spread hot, let up control.Nine is at great inner part constitution of the physical volume concrete cool off piping, cold water perhaps cold air cool off, let up concrete of inside outside difference in temperature.Ten is the supervision which strengthen concrete temperature, adopt to cool off in time, protection measure.11 is to reserve temperature constringency to sew.12 is to let up to control, sprinkle proper before building concrete in the Ji rock and old concrete top build a 5 mm or so sand mat a layer or usage asphalt etc. material Tu2 Shua.13 is to strengthen concrete to protect, the concrete after sprinkle build use moist grass Lian in time, hemp slice's etc. overlay, and attention sprinkle water to protect, appropriate extension protect time, assurance the concrete surface be slow-moving cool off.At the cold season, concrete surface should constitution heat preservation measure, in order to prevent cold wave assault.14 is the allocation be a little amount in the concrete of reinforcing bar perhaps add fiber material concrete of temperature crack control at certain of scope inside.5.Crack and prevention that the chemical reaction causeAlkali bone's anticipating the crack that reaction crack and reinforcing bar rust eclipse cause is the most familiar in the reinforced concrete structure of because of chemical reaction but cause of crack.The concrete blend a future reunion creation some alkalescence ion, these ion with some activity the bone anticipate creation chemical reaction and absorb surroundings environment in of water but the physical volume enlarge, make concrete crisp loose, inflation open crack.In this kind of crack general emergence concrete structure usage period, once appear very difficult remediable, so should at under construction adopt valid the measure carry on prevention.Main of prevention measure:While being to choose to anticipate with the alkali activity small freestone bone.Two is the in addition which choose to use low lye mire with low alkali or have no alkali.Three is the Chan which choose to use accommodation with anticipate to repress an alkali bone to anticipate reaction.Because the concrete sprinkle to build, flap Dao bad perhaps is a reinforcing bar protection layer thinner, the harmful material get into concrete to make reinforcing bar creation rust eclipse, the reinforcing bar physical volume of the rust eclipse inflation, cause concrete bulge crack, the crack of this kind type much is a crack lengthways, follow the position of reinforcing bar ually of prevent measure from have:One is assurance reinforcing bar protection the thickness of the layer.Two is a concrete class to go together with to want good.Three is a concrete to sprinkle to note and flap Dao airtight solid.Four is a reinforcing bar surface layer Tu2 Shua antisepsis coating.Crack processingThe emergence of the crack not only would influence structure of whole with just degree, return will cause the rust eclipse of reinforcing bar, acceleration concrete of carbonization, lower durable and anti- of concrete tired, anti- Shen ability.Therefore according to the property of crack and concrete circumstance we want differentiation to treat, in time processing, with assurance building of safety usage.The repair measure of the concrete crack is main to have the following some method:Surface repair method, infuse syrup, the Qian sew method, the structure reinforce a method, concrete displacement method, electricity chemistry protection method and imitate to living from heal method.Surface repair the method be a kind of simple, familiar of repair method, it main be applicable to stability and to structure loading the ability don't have the surface crack of influence and deep enter crack of processing.The processing measure that is usually is a surface in crack daubery cement syrup, the wreath oxygen gum mire or at concrete surface Tu2 Shua paint, asphalt etc. antisepsis material, at protection of in the meantime for keepingconcrete from continue under the influence of various function to open crack, usually can adoption the surface in crack glue to stick glass fiber cloth etc. measure.1, infuse syrup, the Qian sew methodInfuse a syrup method main the concrete crack been applicable to have influence or have already defend Shen request to the structure whole of repair, it is make use of pressure equipments gum knot the material press into the crack of concrete, gum knot the material harden behind and concrete formation one be whole, thus reinforce of purpose.The in common use gum knot material has the cement the syrup, epoxy, A Ji C Xi sour ester and gather ammonia ester to equalize to learn material.The Qian sew a method is that the crack be a kind of most in common use method in, it usually is follow the crack dig slot, the Qian fill Su in the slot or rigid water material with attain closing crack of purpose.The in common use Su material has PVC gum mire, plastics ointment, the D Ji rubber etc.;In common use rigid water material is the polymer cement sand syrup.2, the structure reinforce a methodWhen the crack influence arrive concrete structure of function, will consideration adopt to reinforce a method to carry on processing to the concrete structure.The structure reinforce medium in common use main have the following a few method:The piece of enlargement concrete structure in every aspect accumulate, outside the Cape department of the Gou piece pack type steel, adoption prepare should the dint method reinforce, glue to stick steel plate to reinforce, increase to establish fulcrum to reinforce and jet the concrete compensation reinforce.3, concrete displacement methodConcrete displacement method is processing severity damage concrete of a kind of valid method, this method be first will damage of the concrete pick and get rid of, then again displacement go into new of concrete or other material.The in common use displacement material have:Common concrete or the cement sand syrup, polymer or change sex polymer concrete or sand syrup.4, the electricity chemistry protection methodThe electricity chemistry antisepsis is to make use of infliction electric field in lie the quality of electricity chemical effect, change concrete or reinforced concrete the environment appearance of the place, the bluntness turn reinforcing bar to attain the purpose of。
中文2300字,1350单词,7400英文字符出处:Bretas E M, Lemos J V, Lourenço P B. A DEM based tool for the safety analysis of masonry gravity dams[J]. Engineering Structures, 2014, 59(2):248–260.A DEM Based Tool for the Safety Analysis ofMasonry Gravity DamsABSTRCTA numerical model for analysis of masonry gravity dams based on the Discrete Element Method is presented. The dam and the rock foundation are represented as block assemblies, using elementary 3- and 4-node blocks. Complex block shapes are obtained by assembling the elementary blocks into macro-blocks, allowing the model to be applied in various situations ranging from equivalent continuum to fully discontinuum analysis. A contact formulation was developed, which represents the interaction between macro-blocks in terms of contacts established between elementary blocks, based on an accurate edge–edge approach. The main numerical aspects of the model are described, addressing in particular the contact creation and update procedures, and the numerical devices that support an efficient explicit solution algorithm. An application to the safety evaluation of an existing masonry dam is discussed, including stress analysis in the structure, and the assessment of sliding failure mechanisms, involving different paths in the vicinity of the dam–rock interface.1 IntroductionStructural analysis must use appropriate methods to achieve its final purposes. These methods should be capable of (i) modeling the geometrical and physical characteristics of the structure, in particular the discontinuities and joints, (ii) modelling the loads in an integrated manner, taking into account the interaction between the relevant phenomena involved, and (iii) evaluating the non-linear behaviour, particularly allowing the definition of failure mechanisms. Masonry gravity dams should be understood as a system composed of the dam itself, the reservoir, and the rock mass foundation. The dam and the rock mass are heterogeneous and discontinuous media. The dam–rock interface is also a discontinuity which requires particular attention. The discontinuity surfaces control the behaviour of masonry dams, because they are weakness planes that determine the main mechanisms of failure. In addition, dams are subject to a wide variety of loads requiring an integrated approach since they are often correlated. Theseparticular features make the majority of the available numerical tools, both commercial and scientific, not entirely suitable for modeling masonry gravity dams. In this context, the development of new analysis tools is required. Here, a tailored numerical implementation of the Discrete Element Method (DEM) for static, dynamic and hydromechanical analysis of masonry gravity dams is described.The Discrete Element Method was initially proposed as an alternative to the Finite Element Method (FEM) to address Rock Mechanics problems [1]. DEM was based on the representation of the discontinuous media as an assembly of blocks in mechanical interaction, thus differing from the standard FEM approach based on joint elements [2,3]. These numerical approaches have also been widely applied to masonry structures [e.g. 4]. The 2D code UDEC [5], which evolved from Cundall’s pioneering work, has been used in several studies involving concrete dam foundations, mostly intending to assess failure mechanisms through the rock mass [e.g.6–8]. Tatone et al. [9] performed a DEM analysis of sliding on the dam–rock interface, considering a detailed representation of the irregular geometry of this surface and the ensuing stress concentrations.Discrete Element Method codes usually represent deformable blocks by discretizing them into an internal mesh of triangular uniform strain elements (e.g., [5]). The designation ‘‘discrete finite element method’’ [10,17] is often appli ed to codes that allow the breakage of the block elements to simulate progressive failure processes. The model presented in this paper is based on DEM and was devised with three main requirements, implemented in a novel software tool fully developed by the authors. Firstly, it is intended to model in an integrated manner both the masonry dam and the rock foundation as components of a blocky system. Secondly, the software tool should provide a practical means to address both equivalent continuum and blocky models, using the same mesh. Finally, the tool needs to include all the features required in dam engineering analysis, such as water flow and pressures in the joints, reinforcement elements, such as passive or active anchors, and the means to apply the loads involved in static and seismic analysis. All these components interact through a compatible data structure. Therefore, the present model combines the standard DEM capabilities in a more general framework, which allows combining rigid and deformable blocks, continuum meshes and discrete components, as required by the application. Moreover, a non-traditional contact formulation is adopted, based on edge–edge interaction, which provides a more accurate stress representation in the interface. The new code shares with DEM the capability to simulate fracturing of a continuum into blocks through predefined paths, but adopts a representation of contact based on the joint stiffnesses and constitutive laws appropriate for masonry1and rock, not following, for example, Munjiza’s formulation of contact force potentials [17]. The aspects related to the mechanical calculation will be discussed in detail in the following sections, and an example of application to the safety assessment of a masonry dam in operation will be presented. The hydraulic analysis of the dam and rock foundation, also incorporated in the newly developed analysis tool, was described in a different paper [11].2 Model discretization and contactsThe numerical tool is intended to model systems composed of a masonry dam and its rock foundation, as shown schematically in Fig. 1. Two-dimensional analysis is conservatively assumed for these structures, following common design practices and dam safety codes [e.g. 12–14], for practical reasons: historically, masonry dams were designed as gravity dams; arching effects cannot be guaranteed; and, the computational model is simpler to understand. The fundamental element of discretization of the structure is the block with three or four edges, which may be rigid or deformable, and can be used simultaneously in the same model. The structure, characteristics and objectives of the analysis should dictate the choice of blocks. In terms of performance, the calculation is faster for the rigid blocks because the equation of motion is established only in the centroid of the element, thus reducing the degrees of freedom of the model. The computational advantage of rigid blocks is only relevant in explicit dynamic analysis, since static solutionsare usually very fast to obtain. In dam engineering, stress analysis in the structureand foundation is usually required, so deformable blocks are preferred. In case of2deformable blocks, each block is assumed here as an isoparametric linear finite element with full Gauss integration.Blocks of general shapes may be created by assembling the 3 and 4 node blocks into macroblocks. This is an important feature to model discontinuous media, such as masonry dams and rock mass foundations. In this way, it is possible to adopt an equivalent continuum representation of the whole system, or part of the system, in which each block is just an element of the FEM mesh.A macroblock is a combination of blocks, forming a continuous mesh, in which the vertices are coincident. Between the blocks of the same macroblock, relative movement is not permitted, so there are no contact forces. The macroblock is similar to a finite element (FE) mesh but with an explicit solution because the assemblage of a global stiffness matrix does not take place. Fig. 2a shows a discontinuous model composed by two individual blocks. A similar model, but continuous, composed by one macroblock, is presented in Fig. 2b. Another continuum model, similar to a FE mesh is showed in Fig. 2c. A hybrid model, composed by two macroblocks, is presented in Fig. 2d, with an explicit joint considered between the two macroblocks.The macroblock has a data structure containing a list of blocks and a list of macronodes, with a master node and several slave nodes. The macronode has the same degrees of freedom of any individual node, and all numerical operations can focus only on the master node. During the calculation cycle, all forces from the slave nodes must be concentrated in the master node, and after calculation of new coordinates, slave nodes are updated from the respective master node. Despite these procedures, the use of macroblocks has the advantage of reducing the number of contacts and the number of degrees of freedom. The same model may have several macroblocks and each macroblock can have blocks with different materials.3References[1] Cundall PA. A computer model for simulating progressive large scale movements in blocky rock systems. In: Rock fracture (ISRM), Nancy; 1971.[2] Goodman RE, Taylor RL, Brekke TL. A model for the mechanics of jointed rock. J Soil Mech Found Div ASCE 1968;94(3):637–59.[3] Wittke W. Rock mechanics. Theory and applications with case histories. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1990.[4] Louren PB. Computations of historical masonry constructions. Prog Struct Eng Mater 2002;4:301–19.[5] Itasca, Universal Distinct Element Code (UDEC) – version 5.0, Minneapolis; 2011.[6] Lemos JV. Discrete element analysis of dam foundations. In: Sharma VM, Saxena KR, Woods RD, editors. Distinct element modelling in geomechanics, Balkema, Rotterdam; 1999. p. 89–115.[7] Barla G, Bonini M, Cammarata G. Stress and seepage analyses for a gravity dam on a jointed granitic rock mass. In: 1st International UDEC/3DEC symposium, Bochum; 2004. p. 263–8.[8] Gimenes E, Fernández G. Hydromechanical analysis of flow behavior in concrete gravity dam foundations. Can Geotech J 2006;43(3):244–59.[9] Tatone BSA, Lisjak A, Mahabadi OK, Grasselli G, Donnelly CR. A preliminary evaluation of the combined finite element-discrete element method as a tool to assess gravity dam stability. In: CDA annual conference, Niagara Falls; 2010. [10]Petrinic N. Aspects of discrete element modelling involving facet-to-face contact detection and interaction, PhD thesis. University of Wales, Cardiff; 1996. [11]Bretas EM, Lemos JV, Lourenco PB. Hydromechanical analysis of masonry gravity dams and their foundations. Rock Mech Rock Eng 2012.[12]FERC (Federal Energy Regulatory Commission). Engineering guidelines for evaluation of hydropower projects –gravity dams. Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, Office of Hydropower Licensing. Report no. FERC 0119-2, Washington, DC, USA; 1991 [Chapter III].[13]USACE (US Army Corps of Engineers). Engineering and design: gravity dam design. Report EM 1110-2-2000, Washington, DC; 1995.[14]USBR (United States Bureau of Reclamation). Design of small dams, Denver, Colorado; 1987.[15]Cundall PA. Formulation of a three-dimensional distinct element model – partI. A scheme to detect and represent contacts in a system composed of many polyhedral blocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 1988;25(3):107–16.4[16]Williams JR, O’Connor R. Discrete element simulation and the contact problem. Arch Comput Methods Eng 1999;6(4):279–304.[17]Munjiza A. The combined finite-discrete element method. West Sussex: Wiley; 2004.5基于离散单元法的砌石重力坝安全分析工具摘要介绍一种基于离散单元法的砌石重力坝分析数值模型。
混凝土重力坝基础流体力学行为分析 摘要:一个在新的和现有的混凝土重力坝的滑动稳定性评价的关键要求是对孔隙压力和基础关节和剪切强度不连续分布的预测。本文列出评价建立在岩石节理上的混凝土重力坝流体力学行为的方法。该方法包括通过水库典型周期建立一个观察大坝行为的数据库,并用离散元法(DEM)数值模式模拟该行为。一旦模型进行验证,包括岩性主要参数的变化,地应力,和联合几何共同的特点都要纳入分析。斯威土地,Albigna大坝坐落在花岗岩上,进行了一个典型的水库周期的特定地点的模拟,来评估岩基上的水流体系的性质和评价滑动面相对于其他大坝岩界面的发展的潜力。目前大坝基础内的各种不同几何的岩石的滑动因素,是用德国马克也评价模型与常规的分析方法的。裂纹扩展模式和相应扬压力和抗滑安全系数的估计沿坝岩接口与数字高程模型进行了比较得出,由目前在工程实践中使用的简化程序。结果发现,在岩石节理,估计裂缝发展后的基础隆起从目前所得到的设计准则过于保守以及导致的安全性过低,不符合观察到的行为因素。 关键词:流体力学,岩石节理,流量,水库设计。 简介:评估抗滑混凝土重力坝的安全要求的理解是,岩基和他们上面的结构是一个互动的系统,其行为是通过具体的材料和岩石基础的力学性能和液压控制。大约一个世纪前,Boozy大坝的失败提示工程师开始考虑由内部产生渗漏大坝坝基系统的扬压力的影响,并探讨如何尽量减少其影响。今天,随着现代计算资源和更多的先例,确定沿断面孔隙压力分布,以及评估相关的压力和评估安全系数仍然是最具挑战性的。我们认为,观察和监测以及映射对大型水坝的行为和充分的仪表可以是我们更好地理解在混凝土重力坝基础上的缝张开度,裂纹扩展,和孔隙压力的发展。 图.1流体力学行为:(一)机械;(二)液压。 本文介绍了在过去20个来自Albigna大坝,瑞士,多年收集的水库运行周期行为的代表的监测数据,描述了一系列的数值分析结果及评估了其基础流体力学行为。比较了数值模拟和实际行为在实地的监测结果。在此基础上比较了一系列的结论得出了基本孔隙压力在节理岩体的影响可以考虑在其他工程项目,认为那里的岩石节理流体力学行为应予以考虑。这些项目包括压力管道,危险废物处置,以及对流动行为的控制断面沿岩石地质遏制依赖的其他情形。 流体力学的行为自然 对先进设备,机械和个别岩石节理的水力特性的概要。一个对岩石联合流体力学行为的更详细的描述中可以在阿尔瓦雷斯(1997年)和阿尔瓦雷斯(1995年)和在实验室调查和数值模拟模型进行了乌鸦和Gale(1985),Gentier(1987年),江崎等人(1992),和其他人中发现。
该水力行为的联合可以表示为非线性应用之间的有效正应力双曲线关系,'n
,并
联合,n
V
在装卸,重大的联合封发生在低有效正应力的地方。该单位的压力关闭规模迅速下降,但是,随着应力水平增加。双曲线的定义是由初始切线刚度定义,niK,并联 合最大的渐近结束,mcV。这种关系也是非线性,迟滞的卸载条件,直到成为有效正应力为零(图1a)。
niK和mcV的价值观通过对实验数据的回归分析来估计的。对于自然和花岗岩裂
隙,这些参数都是相互关联的下列限制范围之间的阿尔瓦雷斯等。 (1995年):
这里niK的单位是M pa/m, mcV的单位是m
粗糙关节展览最大规模的联合最高和最低的封闭初始关节僵硬,关节光滑而有最
低mcV和最大的niK 岩石的共同特点是液压行为之间的线性关系液压孔径,ha,它控制流动规模,关闭和机械联合,nV,用于水平应力。液压孔绘制相应的联合与关闭(图1b),以获取拦截线,hoa,起始水力孔径,边坡系数和耦合,f,而“刻画了联合流体力学行为,i. e,两者在液压机械孔径由于孔径的变化变化的关系,鉴于
其中hra是剩余的水力孔径 对于给定的岩石节理,两者之间是有粗糙度及耦合系数的关系,因为f的分布和沿关节面流道曲折而定。对于理想的平行板,以在整个关节面单流道,f= 1.0.对于集中流道蜿蜒穿过关节面,f<1.0。 因此,用经典的立方定律表示通过岩石节理流率:
其中Q是流量; w是水的单位重量; h是沿岩石节理头部下降;μ是水(11.005×310p•s)的动力粘度; ha是联合液压孔径而G是形状因子,由水流几何而定。直 流地下G=W/L(其中W和L是宽度和长度,分别联合),为不同径向流,G =2π/ln(re/ir),其中ir和re分别为内外圆柱面半径。
裂隙岩体渗透性随深度变化 另外,岩体等效渗透,公里,可以以同样的形式作为修改后的定律,或在液压口径计算,同样的形式占关节间距,S:
在裂隙岩体渗透性的变化,由于覆盖层和围应力,计算。 [1] - [3]。岩体的渗透性,K,理论的深度关系的结果高达1000米,采用当量。 [5]载于图2。孔的液压随
覆盖减少强调在岩体渗透性,随深度的增加,从310 cm/s到附近810的水面在600厘米深度/秒 - 1000米的结果
估计岩体渗透性得到假设f= 1.0,mcV=hoa和nik= 1033.1mcv,这是在实验室测试中取得的值与(阿尔瓦雷斯等al.1995)相似,巴西在这一测试中描述位置的花岗岩编队部分。覆盖层讲估计使用的是26.0 kN/m3单位重量。在这种情况下,它的假设是横向和纵向应力大致相同(土压力系数Ko = 1.0),这也被认为将在巴西的测试位置的火成岩地层的代表,但其他价值在原位强调可以预计,如对高e.g., for Ko<1.0,垂直节理将有较大的渗透率。 在深露天矿在巴西花岗岩开采项目获得的场渗透率测量在图2中绘制与理论的关系比较。联合间距从钻孔岩心观察值都在数米范围内,从而产生了一个5米间距是常数的计算假设。阿霍的价值在300 -1000μm范围被用来确定公里= f的理论关系(z)的,其中Z是深度,以实地测量和比较 这两个钻孔测量值相对渗透率在100至200米深处的高,可能表明的一个区或剪切节理岩带更多的存在。所测岩石渗透率稳步下降,在深度的增加,然而,它们的值与对应的岩体渗透性的理论与模型估计趋势良好。
典型液压孔径400 -500μm的和后关节僵硬=NI
K 10V的双曲线关系,与三菱商
事和mcV= hoa似乎同意这些结晶岩体观测场行为良好。 图.2.裂隙岩体渗透性随深度的关系。 虽然真正的流体力学节理岩体的行为是需要考虑具体的地点和地质因素,该方法提供了一个框架,但在设计阶段,其中岩石资料尚未提供大规模渗透。
Hydromechanical analysis of flow behavior in concrete gravity dam foundations Abstract: A key requirement in the evaluation of sliding stability of new and existing concrete gravity dams is the prediction of the distribution of pore pressure and shear strength in foundation joints and discontinuities. This paper presents a methodology for evaluating the hydromechanical behavior of concrete gravity dams founded on jointed rock. The methodology consisted of creating a database of observed dam behavior throughout typical cycles of reservoir filling and simulating this behavior with a distinct element method (DEM) numerical model. Once the model is validated, variations of key parameters including litho logy, in situ stress, joint geometry, and joint characteristics can be incorporated in the analysis. A site-specific simulation of a typical reservoir cycle was carried out for Albigna Dam, Switzer land, founded on granitic rock, to assess the nature of the flow regime in the rock foundations and to evaluate the potential for sliding surfaces other than the dam–rock interface to develop. The factor of safety against sliding of various rock wedges of differing geometry present within the dam foundations was also evaluated using the DEM model and conventional analytical procedures. Estimates of crack propagation patterns and corresponding uplift pressures and factors of safety against sliding along the dam–rock interface obtained with the DEM were also compared with those from simplified procedures currently used in engineering practice. It was found that in a jointed rock, foundation uplift estimates after crack development obtained from present design guidelines can be too conservative and result in factors of safety that are too low and do not correspond to the observed behavior. Key words: Hydromechanical, jointed rock, flow, dam design. Introduction: Evaluating the safety of concrete gravity dams against sliding requires an understanding that rock foundations and the structure above them are an interactive system whose behavior is controlled by the mechanical and hydraulic properties of concrete materials and rock foundations. About a century ago, the failure of Boozy Dam prompted dam engineers to start considering the effect of uplift pressures generated by seepage within the dam–foundation system and to explore ways to minimize its effect.. Today, with modern computational resources and much more precedent, it is still most challenging to determine the pore-pressure distribution along foundation discontinuities to assess pertinent stresses and evaluate factors of safety. It is our opinion that observing and monitoring the behavior of large dams on well mapped and adequately instrumented foundations can bring important insights for a better understanding of factors controlling joint opening, crack propagation, and pore-pressure development in foundations of concrete gravity dams. Fig.1.Hydromechanical behavior of natural joints :(a) mechanical;(b)hydraulic.