流固耦合油藏数值模拟
- 格式:doc
- 大小:25.00 KB
- 文档页数:1

裂缝性低渗透油藏流-固耦合理论与数值模拟
刘建军;张盛宗;刘先贵;胡雅档
【期刊名称】《力学学报》
【年(卷),期】2002(034)005
【摘要】根据裂缝性低渗油藏的储层特征,建立适合裂缝性砂岩油藏渗流的等效连续介质模型.将渗流力学与弹塑性力学相结合,建立裂缝性低渗透油藏的流-固耦合渗流数学模型,并给出其数值解.通过数值模拟对一实际井网开发过程中孔隙度、渗透率的变化以及开发指标进行计算,并和刚性模型以及双重介质模型的计算结果进行了分析比较.
【总页数】6页(P779-784)
【作者】刘建军;张盛宗;刘先贵;胡雅档
【作者单位】武汉工业学院土木工程系,武汉,430023;中国科学院武汉岩土力学研究所,武汉,430071;中国科学院渗流流体力学研究所,廊坊,065007;中国科学院渗流流体力学研究所,廊坊,065007;中国科学院渗流流体力学研究所,廊坊,065007【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】TE3
【相关文献】
1.流管法天然裂缝性低渗透油藏数值模拟研究 [J], 付莹;尹洪军;王美楠
2.裂缝性低渗透砂岩油藏数值模拟历史拟合方法 [J], 孙业恒
3.裂缝性低渗透油藏流-固耦合数值模拟 [J], 刘建军;冯夏庭
4.低渗透裂缝性油藏渗吸数值模拟研究 [J], 王希刚;宋学峰;姜宝益;蔡喜东;刘刚
5.生产测井资料在低渗透裂缝性油藏精细数值模拟中的应用 [J], 秦民君;李宁;郑小敏;赵慧;吴迪;张宏
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。


一、什么是油藏数值模拟油藏研究的主要目的是预测油藏未来的动态特征,并找出提高最终采收率的方法和手段。
油藏数值模拟是油藏研究的重要方法之一,它是以数值模拟软件为主要研究工具。
油藏数值模拟软件都是基于描述油藏地质和流体特征的数学物理方程,即所谓的“数学模型”。
把复杂的数学模型处理成适合计算机用数值方法求解的软件就是数值模拟软件。
使用这些软件,利用地震、测井等地质数据建立数值化的地质模型,结合油田油水井的生产动态资料,求解基本流动方程,模拟地下油、气、水运动,研究解决油藏开发的实际问题,这样的工作就叫作油藏数值模拟。
二、软件发展简介八十年代引进的黑油模型软件,研究了大量的机理问题和实际应用。
一体化黑油模型数值模拟软件,实现了从地质建模到油藏模拟结果的三维显示的一体化过程,大大地提高了数值模拟研究工作的效率和模拟结果精度。
另外,陆续开发了自动历史拟合、基于数值模拟的试井分析、微机机群并行计算数值模拟等一系列适合油田实际需要的软件。
九十年代末,引进的并行软件。
它不仅具有以往数值模拟软件的一体化处理功能,其并行化的程序设计可进行几十万,甚至上百万节点的模拟,模拟的井数可多达数百口,大大提高了计算速度和实际油田的模拟规模。
另外,软件还具有水驱、聚驱、气驱及稠油热采等功能,可以描述断层、裂缝等复杂的地质条件,是当今世界最流行的数值模拟软件之一。
三、数值模拟所需要的数据在进行数值模拟之前,必须要对研究的地区有全面的认识,需要尽可能多的地质资料才能刻画出较真实的地质状况。
建立数值模拟模型时首先要在被研究的油藏上选取一块相对独立的区块(最好以断层或天然边界作为其边界),建立地质模型。
将地质模型分割成若干网格块,按软件要求给出有关数据。
(1)数据结构油藏流体(油、气、水)性质数据初始化数据油藏描述数据油藏数值模拟数据流裂缝和聚合物参数时变运行数据(2)初始化数据1)描述油藏和流体性质的数据,包括油层水、油及岩石压缩系数等平衡区数据。
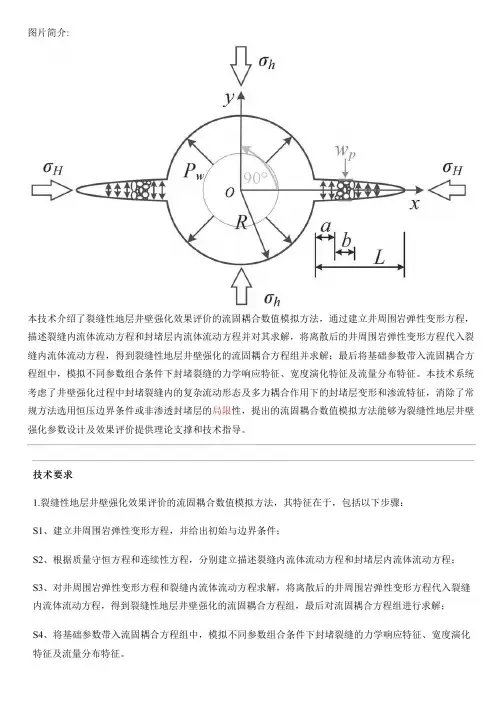
图片简介:本技术介绍了裂缝性地层井壁强化效果评价的流固耦合数值模拟方法,通过建立井周围岩弹性变形方程,描述裂缝内流体流动方程和封堵层内流体流动方程并对其求解,将离散后的井周围岩弹性变形方程代入裂缝内流体流动方程,得到裂缝性地层井壁强化的流固耦合方程组并求解;最后将基础参数带入流固耦合方程组中,模拟不同参数组合条件下封堵裂缝的力学响应特征、宽度演化特征及流量分布特征。
本技术系统考虑了井壁强化过程中封堵裂缝内的复杂流动形态及多力耦合作用下的封堵层变形和渗流特征,消除了常规方法选用恒压边界条件或非渗透封堵层的局限性,提出的流固耦合数值模拟方法能够为裂缝性地层井壁强化参数设计及效果评价提供理论支撑和技术指导。
技术要求1.裂缝性地层井壁强化效果评价的流固耦合数值模拟方法,其特征在于,包括以下步骤:S1、建立井周围岩弹性变形方程,并给出初始与边界条件;S2、根据质量守恒方程和连续性方程,分别建立描述裂缝内流体流动方程和封堵层内流体流动方程;S3、对井周围岩弹性变形方程和裂缝内流体流动方程求解,将离散后的井周围岩弹性变形方程代入裂缝内流体流动方程,得到裂缝性地层井壁强化的流固耦合方程组,最后对流固耦合方程组进行求解;S4、将基础参数带入流固耦合方程组中,模拟不同参数组合条件下封堵裂缝的力学响应特征、宽度演化特征及流量分布特征。
2.根据权利要求1所述的裂缝性地层井壁强化效果评价的流固耦合数值模拟方法,其特征在于,步骤S1中,所述井周围岩弹性变形方程为:其中公式(2)中,式中,Hij(i,j=n,s)为任意坐标位置应力分量的超奇异格林函数,MPa/m;fxy,fyy为函数f偏导数有关的应力分量,m-1;fxyy,fyyy为函数f偏导数有关的应力分量,m-2;σH为最大水平地应力,MPa;σh为最小水平地应力,MPa;σn表示裂缝面上的法向应力分布,MPa;Pf为裂缝内流体压力,MPa;为第j个单元的法向位移不连续,m;为第j个单元的剪切位移不连续,m;L为裂缝长度,m;R表示井眼半径,mm;E表示弹性模量,GPa;v为泊松比,无量纲;s为沿裂缝长度方向任意位置处裂缝单元的横坐标,m;β为裂缝单元局部坐标系与全局坐标系x方向的夹角,°。


流-固耦合的数学模型
流固耦合是指流体和固体之间相互作用的现象,它涉及了流体
动力学和固体力学两个领域。
建立流固耦合的数学模型可以帮助我
们更好地理解和预测这种复杂的相互作用。
在数学上,建立流固耦合的模型可以采用多种方法。
首先,我
们可以使用偏微分方程描述流体的运动,如Navier-Stokes方程,
同时使用弹性力学方程描述固体的变形。
然后,通过适当的边界条
件和相互作用条件,将这两个方程耦合在一起。
这种耦合可以通过
将流体和固体的速度、压力、位移等物理量在流固界面上进行匹配
来实现。
另一种建立流固耦合模型的方法是使用有限元法或有限体积法。
这些方法可以将流体和固体的运动方程离散化,然后通过相互作用
界面将它们耦合在一起。
这种方法在工程实践中得到了广泛的应用,因为它可以处理复杂的流固耦合问题,并且可以考虑到材料的非线性、大变形和接触等现象。
除了数值模拟方法,还有一些解析方法可以用于建立流固耦合
的数学模型,如边界元法和格林函数法。
这些方法在特定情况下可
以给出精确的解,但通常适用于简单的流固耦合问题。
总之,建立流固耦合的数学模型涉及到流体力学和固体力学的基本方程,以及适当的边界条件和相互作用条件。
通过合理地耦合这些方程和条件,我们可以得到描述流固耦合行为的数学模型,从而更好地理解和预测流体和固体之间复杂的相互作用。

A fluid-structure interaction algorithm applied to the piston of movementGUO Pan a WU Wen-hua a*Liu Jun b(aState Key Laboratory of Structural Analysis for Industrial Equipment,Department of Engineering Mechanics,Dalian university of technology,Dalian116024,China)(b State Key Laboratory of Structural Analysis for Industrial Equipment,School of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Dalian university of technology,Dalian116024,China)Abstract:The algorithm of transmission in information on the fluid-solid interface should be addressed of the loosely coupled algorithm which is simple and computationally efficient numerical method on simulation of fluid-structure interaction problems.It is impossible to ensure, theoretically,the equivalence of the velocity and displacement conditions at the same time.Piston problems,have the analytical solution,is solved by the loosely coupled algorithm of new GCLin this paper which based on the equivalence of displacement.The examples show that good performance of the new algorithm on the precision.And the combination of the Newmark method and the CFD has a good prospect in the numerical simulation of fluid-structure interaction.运动活塞的流固耦合数值模拟郭攀a,武文华a*,刘君b(a大连理工大学运载工程与力学学部,工程力学系,工业装备结构分析国家重点实验室,辽宁大连116024)(b大连理工大学运载工程与力学学部,航空航天学院,工业装备结构分析国家重点实验室,辽宁大连116024)摘要松耦合算法在数值模拟流固耦合问题时具有应用简单和计算高效的优势,但是需要解决流固界面上的信息传递算法。

基于流固耦合的立式拱顶储罐油气爆炸数值模拟欧益宏;李润;袁广强;李国庆;王世茂【摘要】针对1000m3立式拱顶储罐内部油气爆炸进行了数值模拟,并对625 L模拟储罐进行了模型实验验证,对耦合条件以及非耦合条件下储罐内部爆炸流场发展,不同测点超压变化进行了对比分析,同时对耦合条件下储罐结构响应进行了研究.结果表明:①非耦合条件与耦合条件下流场发展以及超压变化趋势基本相同,但耦合条件下储罐内部完全燃烧时间比非耦合条件下慢60 ms,超压荷载峰值比非耦合条件下小10%左右.②爆炸时,储罐顶部变形最大,最大应力区域出现在顶-壁,底-壁连接处,考虑到实际工程情况,设计时应遵循“弱顶盖连接设计”原则.【期刊名称】《振动与冲击》【年(卷),期】2018(037)022【总页数】8页(P231-237,268)【关键词】拱顶储罐;油气;爆炸;流固耦合;数值模拟;湍流【作者】欧益宏;李润;袁广强;李国庆;王世茂【作者单位】陆军勤务学院油料系,重庆401311;陆军勤务学院油料系,重庆401311;陆军72489部队,山东烟台265301;陆军勤务学院油料系,重庆401311;陆军勤务学院油料系,重庆401311【正文语种】中文【中图分类】X932随着石油化工事业的发展,储油罐安全问题日益增多[1-3]。
油罐区爆炸火灾事故时有发生,容易造成重大的伤亡。
因此,为确保库区安全,需要对储罐爆炸发生发展过程以及罐体结构响应进行分析研究。
国内外许多学者针对储罐内部可燃气体爆炸发生发展规律进行了研究,在不同容积模拟储罐内部进行了实验[4-5],对密闭空间内部着火模式[6-7]、超压荷载变化规律[8]进行了研究,同时采用不同燃烧模型[9-10]对不同容积[11]、罐顶结构[12-13]的大型储罐结构内部可燃气体爆炸进行了CFD数值模拟,得到了不同因素对储罐内部火焰形态,爆炸冲击载荷的影响。
由于储罐爆炸过程及其复杂,主要包括内部油气爆炸,爆炸冲击压力波的形成与传播,冲击波与储罐结构的相互作用,目前的研究大多将壁面视为刚体,不考虑结构变形对流场发展情况的影响,事实上,储罐爆炸过程是一个典型的流固耦合过程,针对耦合条件冲击响应问题,胡可等[14-15]利用采用TNT当量模型对立式柱形容器内部蒸气云爆炸进行了数值模拟进行了研究,发现耦合效应对爆炸载荷的影响很小,在计算时可将结构视为刚体,Aune 等[16-17]对薄金属板进行了冲击试验以及数值模拟研究,发现耦合条件下的结构变形更小,且更符合工程实际,在计算时不能忽略耦合效应。

流固耦合理论在特高含水期油藏开发中的研究现状与发展趋势特高含水期油藏是指水含量高达70%以上的油藏,由于含水率高,这类油藏在开发过程中会面临诸多挑战。
流固耦合理论是研究流体和固体之间相互作用的理论,近年来在特高含水期油藏开发中得到了广泛的应用。
本文将对流固耦合理论在特高含水期油藏开发中的研究现状和发展趋势进行探讨。
一、特高含水期油藏的挑战及对流固耦合理论的需求特高含水期油藏的开发面临着诸多挑战,主要包括以下几个方面:1. 残余油的开发难度大。
由于含水率高,残余油往往被水包围,油水界面模糊,难以准确确定残余油的位置和分布情况。
2. 油水混产严重。
在开采过程中,由于油水界面的不明显,会导致油水混产现象严重,降低了开采效率,增加了开采成本。
3. 地质构造复杂。
特高含水期油藏地质构造复杂,地层中存在大量裂缝、孔隙和岩石间隙,影响了油藏的渗流性能。
针对这些挑战,流固耦合理论的应用成为了特高含水期油藏开发的重要手段。
流固耦合理论可以帮助我们更加准确地了解油藏的流体运移特性和固体结构特征,从而指导油藏的开发工作。
1. 流固耦合数值模拟方法的研究。
通过数值模拟方法,可以模拟油藏中流体和固体的相互作用过程,从而预测油水流动规律、确定油水分布情况等。
2. 流固耦合实验研究。
通过在实验室中建立流固耦合实验模型,可以直接观察油藏中流体和固体的相互作用过程,从而深入了解油藏的开采规律。
3. 流固耦合理论在油藏地质调查与评价中的应用。
流固耦合理论可以帮助我们更准确地评价油藏地质构造、确定油藏渗流性能等,为后续的开发工作提供重要依据。
1. 流固耦合理论与人工智能的结合。
将流固耦合理论与人工智能技术相结合,可以更加准确地预测油藏的开发规律,为油藏开采过程提供更精确的指导。
2. 流固耦合理论在油藏监测与控制中的应用。
通过流固耦合理论,可以实现对油藏开采过程的实时监测与控制,提高开采效率,降低开采成本。
3. 流固耦合理论与新材料技术的结合。


油藏数值模拟与优化设计油藏数值模拟与优化设计是石油工程领域中一项重要的技术,它通过建立数学模型和使用计算方法来模拟油藏的流体运移过程,进而实现油藏的最优开发与生产设计。
本文将介绍油藏数值模拟与优化设计的基本原理和方法,并探讨其在油田开发中的应用。
一、油藏数值模拟的原理油藏数值模拟是基于油藏动态性质的数学方程和物性参数建立数学模型,然后通过数值计算方法求解模型,从而获得油藏内流体的分布、流动速度、压力等信息。
其基本原理为质量守恒、动量守恒和能量守恒定律,通过对油田的地质构造和流体性质进行分析,建立描述油藏特性的数学方程组。
常用的数值解法有有限差分法、有限元法和有限体积法。
二、油藏数值模拟的关键参数1. 渗透率:描述了油藏储层岩石对流体运移的阻碍程度。
通过实验室测定或重力推断方法获得,是数值模拟的基础参数之一。
2. 孔隙度:用于计算储层的有效储油空间以及油藏各组分的相对饱和度。
是描述储层孔隙结构的参数。
3. 收缩因子:油藏产量与储油体积之间的关系,可以通过实验测定得到。
在模拟时,收缩因子的选择对模拟结果的准确性具有重要影响。
4. 井底流压:地下井底静态压力,对模拟油藏开采效果具有重要意义。
井底流压的准确预测是进行数值模拟的前提条件。
5. 油藏温度:影响油藏内流体的物理性质,对油藏开采具有重要影响。
在数值模拟中,温度场的准确预测可以加强模拟对油藏动态变化的描述。
三、油藏数值模拟的应用1. 优化油藏开发方案:通过模拟不同开采方案下的油藏动态变化,评估其效果,寻找最优开发方案。
包括确定注水井和生产井的位置、井网布局、开采周期等。
2. 预测油藏产能:通过对储层物性参数进行测定和模型求解,预测油藏的产能和生产寿命。
为油田的开发规划和油藏管理提供科学依据。
3. 评估油藏油水分离效果:模拟油藏内流体的相分离,预测各组分的相对饱和度等参数,用于评估油藏中的水驱效果与气驱效果,以及采油剂的加入对驱油效果的影响。
4. 优化注采配水:基于数学模型和模拟结果,优化注水方案和注采井间的配水方案,从而提高采收率和经济效益。
凹坑表面活塞与缸套挤压润滑油的流固耦合数值模拟AbstractThe objective of this study is to investigate the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil in the interface between the piston and cylinder liner in a reciprocating internal combustion engine. A numerical model was developed to simulate the fluid dynamics and solid mechanics of the system. The oil film formation process was captured through Reynolds equation with the consideration of surface roughness and deformation under the contact pressure. The deformation and stress distribution of the surface were calculated using the finite element method. The mesh model was established based on the actual geometry of the piston and cylinder liner with the identified roughness parameters. The boundary and initial conditions of the numerical model were determined according to the real working condition of the engine. The simulation results revealed that the oil film thickness and pressure distribution were heavily influenced by the roughness parameters, and the deformation and stress distribution of the surface showed a strong correlation with the lubrication state. The study provides insights into the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil in the engine and has a significant implication for engine design and optimization.IntroductionThe interface between the piston and cylinder liner is a critical area in reciprocating internal combustion engines, where the frictional and wear losses are concentrated. Lubricating oil plays a crucial role in reducing the friction and wear between the two surfaces.The formation of an oil film on the surface of the cylinder liner is essential for the effective lubrication of the engine. The oil film thickness and pressure distribution depend on the surface roughness of the piston and cylinder liner. The deformation and stress distribution of the surface also play a crucial role in determining the lubrication state. In recent years, several studies have been conducted on the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil in the engine. However, most of them focused on the macroscopic performance of the lubrication system, neglecting the micro- and nano-scale effects of the surface roughness and deformation. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil is still lacking.In this study, a numerical model was developed to investigate the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil in the interface between the piston and cylinder liner in a reciprocating internal combustion engine. The numerical model combined the fluid dynamics and solid mechanics of the system. The oil film formation process was captured through Reynolds equation with the consideration of surface roughness and deformation under the contact pressure. The deformation and stress distribution of the surface were calculated using the finite element method. The mesh model was established based on the actual geometry of the piston and cylinder liner with the identified roughness parameters. The boundary and initial conditions of the numerical model were determined according to the real working condition of the engine. The simulation results revealed that the oil film thickness and pressure distribution were heavily influenced by the roughness parameters, and the deformation and stress distribution of the surface showed a strong correlation with the lubrication state.MethodologyNumerical modelThe numerical model was established based on the fluid-solid coupling approach. The flow equation for the lubricating oil was based on the Reynolds equation. The solid mechanics of the system was calculated using the finite element method. The oil film thickness and pressure distribution were obtained through the coupled solution of the flow and solid mechanics equations. The deformation and stress distribution of the surface were also calculated using the finite element method. The numerical model was established using ANSYS Workbench.Mesh modelThe mesh model was established based on the actual geometry of the piston and cylinder liner. The roughness parameters of the surface were identified through surface measurement techniques such as atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The mesh model was established with the identified roughness parameters to ensure the accuracy of the simulation.Boundary and initial conditionsThe boundary and initial conditions of the numerical model were determined according to the real working condition of the engine. The inlet and outlet flow rates of the lubricating oil were setaccording to the engine speed and load. The initial oil film thickness was set to zero, and the initial pressure distribution was calculated based on the roughness parameters.Results and discussionThe simulation results revealed that the oil film thickness and pressure distribution were heavily influenced by the roughness parameters. The surface deformation and stress distribution also showed a significant correlation with the lubrication state. The roughness parameters, such as the root-mean-square (RMS) roughness and the skewness, had a substantial impact on the oil film thickness and pressure distribution. The surface deformation and stress distribution occurred mainly in the contact area between the piston and cylinder liner. The deformation and stress distribution showed a strong correlation with the oil film thickness and pressure distribution. When the oil film thickness was less than the surface roughness, the deformation and stress concentration of the surface were intensified, leading to the rapid wear and damage of the surface.ConclusionThe flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil in the interface between the piston and cylinder liner in a reciprocating internal combustion engine was investigated in this study. A numerical model was developed to simulate the fluid dynamics and solid mechanics of the system. The simulation results revealed that the oil film thickness and pressure distribution were heavily influenced by the roughness parameters, and the deformation and stressdistribution of the surface showed a strong correlation with the lubrication state. The study provides insights into the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil in the engine and has a significant implication for engine design and optimization.The findings of this study highlight the importance of considering the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil in the piston-cylinder interface during engine design and optimization. The surface roughness and deformation play a critical role in determining the lubrication state and wear of the system. The results showed that the deformation and stress concentration were most severe when the oil film thickness was less than the surface roughness. Hence, minimizing the surface roughness and ensuring adequate oil film thickness are crucial in reducing wear and prolonging the lifespan of the engine.The numerical model developed in this study provides a valuable tool for predicting the performance of the lubrication system in internal combustion engines. It can be used to evaluate the effect of surface finish and oil properties on the oil film thickness and pressure distribution, thus leading to better engine designs in the future. Furthermore, the simulation results can also be used to optimize oil formulations and surface treatments to improve the engine's durability and efficiency.In conclusion, this study provides insight into the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil in the interface between the piston and cylinder liner in a reciprocating internal combustion engine. The study highlights the importance of considering the surface roughness and deformation in determining the lubrication state and wear of the system. The numerical model developed inthis study provides a valuable tool for predicting the performance of the lubrication system and optimizing engine design and efficiency.Apart from contributing to engine design and optimization, the findings of this study can also help in improving engine maintenance and reducing breakdowns. By understanding the behavior of lubricating oil in the piston-cylinder interface, maintenance teams can better diagnose tribological problems and take appropriate actions to prevent engine failures. For instance, by identifying areas of high stress concentration, maintenance teams can prioritize the inspection of those regions and implement surface treatments or coating to prevent damage.Moreover, the insights gained from this study could also help in developing new lubricants and lubrication technologies. The results showed that the properties of the lubricant, such as viscosity and shear stress, greatly influenced the oil film thickness and pressure distributions. This means that selecting the appropriate lubricant can greatly affect the engine's wear and lifespan. By understanding the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricants, researchers can develop new formulations that are tailored to specific engine designs and operating conditions, leading to better engine performance, greater fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. Finally, the findings of this study also have implications for industry standards and regulations. The insights gained from this study can help in revising existing standards and guidelines for engine design and testing. Additionally, by improving the understanding of lubrication behavior and wear mechanisms in engines, regulators and industry professionals can better evaluate the environmental impact of internal combustion engines anddevelop regulations to reduce their carbon footprint.In conclusion, this study highlights the importance of understanding the flow-solid coupling behavior of lubricating oil in the piston-cylinder interface for engine design, maintenance and lubrication technology development, and industry regulations. By improving our understanding of the underlying mechanisms, we can develop better approaches to enhance the performance and efficiency of internal combustion engines while minimizing their environmental impact.One potential application of the findings in this study is in the development of more precise and accurate simulation models for engine performance and wear prediction. The observed tribological behaviors can be integrated into simulations that can accurately predict oil film formation and pressure distribution under different working conditions. This can help engine manufacturers optimize the performance and lifespan of internal combustion engines, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and extending the service life of engines. Additionally, these models can be used to reduce the time and costs associated with physical testing and accelerate the engine design and development process.Another area where these findings could be beneficial is in the development of predictive maintenance systems for engines. By monitoring the oil flow and pressure distribution in the piston-cylinder interface, sensors could detect abnormal wear and lubrication behavior, alerting the maintenance teams to take appropriate actions. This would enable proactive maintenance, which can reduce the downtime and costs associated with reactive maintenance, where components are replaced or repaired only afterthey fail.Finally, the findings from this study have wider implications for the automotive industry, where electric vehicles are on the rise, and there is a growing demand for more sustainable and greener alternatives to internal combustion engines. By improving the efficiency and reducing the wear of internal combustion engines, we can help bridge the gap between traditional and modern powertrains, which can be essential in the transition towards more sustainable transportation models. Additionally, by improving the understanding of the lubrication behavior and wear mechanisms in engines, researchers and policy-makers can make informed decisions to reduce the emissions and carbon footprint of internal combustion engines, ultimately leading to a more sustainable future.Yes, that is correct. The findings from this study can be applied in many different areas, including engine design and development, predictive maintenance, and the transition towards more sustainable transportation solutions. By understanding the tribological behavior and lubrication mechanisms in engines, we can improve their efficiency and reduce wear, which can have a positive impact on the environment and contribute to the development of more sustainable transportation options.。
油藏数值模拟基础【实用版】目录一、油藏数值模拟基础概述二、油藏数值模拟的重要性三、油藏数值模拟的基本原理四、油藏数值模拟的方法与技术五、油藏数值模拟的发展趋势与应用前景正文【一、油藏数值模拟基础概述】油藏数值模拟是一种应用计算机技术和数学模型对油藏的动态特性和开发过程进行研究的方法。
它通过构建油藏模型,对油藏的储层、流体性质和动态变化等进行详细描述,从而为油藏开发和管理提供科学依据。
油藏数值模拟基础主要包括油藏模型构建、数学模型建立和计算方法研究等内容。
【二、油藏数值模拟的重要性】油藏数值模拟在油气田开发中具有重要意义。
首先,通过油藏数值模拟可以预测油藏的动态特性,为油藏开发提供科学依据。
其次,油藏数值模拟有助于优化油藏开发方案,提高油藏的开发效益。
此外,油藏数值模拟还可以为油藏管理提供实时监测和预警,有利于实现油藏的精细化管理。
【三、油藏数值模拟的基本原理】油藏数值模拟的基本原理是通过对油藏的静态和动态特征进行数学建模,利用计算机技术对油藏开发过程进行模拟和预测。
具体来说,油藏数值模拟包括以下几个步骤:首先是建立油藏模型,包括地质模型、流体模型和物理模型等;其次是选择合适的数学模型和计算方法,对油藏的动态特性进行模拟;最后是分析模拟结果,为油藏开发和管理提供依据。
【四、油藏数值模拟的方法与技术】油藏数值模拟的方法与技术主要包括以下几个方面:首先是油藏模型构建技术,包括地质建模、流体建模和物理建模等;其次是数学模型建立和选择技术,要根据油藏的特性选择合适的数学模型和计算方法;再次是计算方法研究,包括稳态模拟、非稳态模拟和耦合模拟等;最后是模拟结果分析和评价技术,要根据模拟结果对油藏的开发和管理提供科学依据。
【五、油藏数值模拟的发展趋势与应用前景】随着计算机技术的不断发展和油藏开发理论的深入研究,油藏数值模拟在油气田开发中的应用前景越来越广阔。
未来油藏数值模拟的发展趋势包括:模型更加精细化、计算方法更加高效化、模拟结果更加精确化和应用领域更加广泛化等。
流固耦合分析基础流固耦合分析是指通过数值模拟方法来研究流体与固体之间的相互作用和耦合效应的分析技术。
它综合考虑了流体和固体两种介质之间的物理、化学、力学以及耦合效应等因素,可以更准确地预测工程结构在复杂载荷下的响应和性能。
本文将介绍流固耦合分析的基本概念、数值模拟方法以及应用领域等方面。
流固耦合分析的基本概念主要包括两个方面,即流体力学和固体力学。
流体力学研究的是液体和气体等流体在力的作用下的行为,主要涉及流体的运动、压力、速度等参数;而固体力学研究的是固体材料在力的作用下的行为,主要包括应力、应变、变形等参数。
流固耦合分析则是将这两个方面结合起来,研究流体与固体之间的相互作用和耦合效应。
在流固耦合分析中,数值模拟方法是非常重要的工具。
常用的数值模拟方法包括有限元法、有限体积法和边界元法等。
有限元法是一种广泛应用的方法,主要适用于固体力学问题,它将结构离散成有限个小单元,并利用单元之间的接缝来模拟固体的力学行为。
有限体积法则更适用于流体力学问题,它将连续介质离散成有限个小控制体,并利用控制体之间的通量来模拟流体的运动行为。
边界元法则是将结构以及其周边的无穷域分为界面和域两个部分,只在界面上求解,要求边界积分方程的解与物理意义相关。
流固耦合分析的应用领域非常广泛。
在航空航天工程中,流固耦合分析可以用于研究飞行器的空气动力学特性,如气动载荷和机翼变形等。
在能源领域,流固耦合分析可以用于优化核电厂的冷却系统设计,以及研究水力机械的流体力学特性。
在交通运输领域,流固耦合分析可以用于优化汽车的外形设计,以及研究火车列车的气动性能。
在海洋工程领域,流固耦合分析可以用于研究海洋平台的动力特性,如浮筏的运动响应和海底管道的受力分析等。
综上所述,流固耦合分析是一项重要的工程分析技术,可以帮助工程师更准确地预测和优化结构在复杂载荷下的响应和性能。
它涉及了流体力学和固体力学等多学科的知识,以及数值模拟方法等研究工具。
流固耦合油藏数值模拟
随着石油工业的发展以及解决复杂石油工程问题的需要,流固耦合渗流的研究越来越
受到高度重视。在油藏开采过程中,油藏流体渗流与岩土变形是相互影响、相互制约的,
即油、气、水的渗流与开采要引起油藏应力的重新分布,并导致多孔介质的变形;而多孔
介质的变形则导致油藏孔隙体积的改变,引起油藏物性参数(特别是孔隙度、孔隙压缩系
数和渗透率)的变化,反过来影响油藏流体的渗流与开采。由此可见,油藏是一个流体渗
流与多孔介质变形的动态耦合统一体。因此,本质意义上的油藏数值模拟应该是对油藏流
体渗流与岩土变形的动态耦合作用过程进行仿真模拟,既要对流体的渗流过程进行模拟,
又要对岩土的变形过程进行模拟,并要体现出它们之间的动态耦合作用关系。
常规油藏数值模拟基于纯渗流力学理论,在模拟流体渗流时,不能同时对岩土变形过
程进行模拟,无法考虑流固耦合作用下油藏物性参数的变化对油气渗流的影响。用它作为
预测手段,预测流固耦合作用下的油藏开采动态是困难的,并且经常造成较大的误差。
一、 基本原理
流固耦合油藏数值模拟的数学模型由两部分组成,即流固耦合作用下的渗流数学模型
和流固耦合作用下的岩土变形数学模型
1、 流固耦合作用下的渗流数学模型
2、 流固耦合作用下的岩土变形数学模型