测井相分析和实例分析
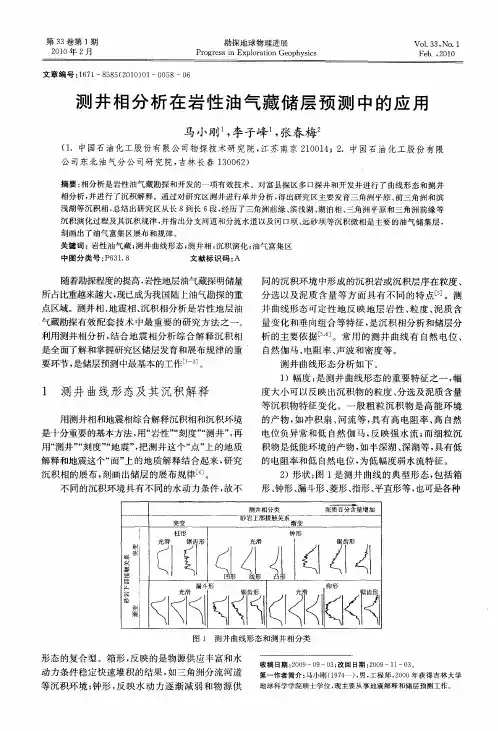
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:3.42 MB
- 文档页数:30



[转载]体系域的识别标志对于结构比较完整的层序,一般发育低水位体系域、湖侵体系域和高水位体系域和湖泊收缩体系域。
体系域是层序内同期沉积体系的组合。
在层序内部,首次湖泛面和最大湖泛面是划分体系域的根据。
一、低水位体系域低水位体系域一般沉积范围比水进及高位域分布范围小,多为加积或进积式准层序组,其下边界为层序底界,上边界为初次湖泛面。
二、初次湖泛面初次湖泛面为湖侵体系域与低水位体系域的分界面。
地震剖面上,对应着最低的湖岸上超点。
初次湖泛面之上,地震相为平行、亚平行反射,连续性中等偏好;初次湖泛面之下,地震相多为杂乱或空白反射。
界面上下沉积物类型及沉积环境均存在明显的差异性,特别是在湖盆边缘地区,界面以下多为河流与三角洲平原相沉积,局部为洪积扇沉积;界面以上变为滨浅水或较深水的细粒沉积,沉积物的颜色可能由红色变为浅灰色或深灰色。
界面以下多为进积-加积式淮层序组,界面以上变为典型的退积式准层序组。
古生物组合在界面以下为浅水、狭盐性生物化石为特征,甚至局部无生物化石;而界面以上变为较深水-深水、广盐性的生物化石组合。
三、湖侵体系域湖侵体系域位于初次湖泛面之上和最大湖泛面之下,湖盆边缘区上超反射明显,湖盆内部地震相特点为平行、亚平行反射,连续性反射,在垂向上表现为典型的退积式准层序组。
四、最大湖泛面最大湖泛面将湖侵体系域和高水位体系域分开。
在湖相地层中,最大湖泛面附近发育密集段,密集段在地震剖面上表现为强振幅、高连续反射同相轴,与最远的湖岸上超点对应,密集段在电阻率、感应、自然电位、自然伽马测井曲线上均有十分特征性的反映,地震上的标志为下超现象,这是出于高位期沉积速率大于可容空间增加速率所导致的沉积物向盆内进积所造成的。
五、高水位体系域上边界为层序顶界高水位体系域一般为加积或进积式准层序组,上边界为层序顶界,下边界为最大湖泛面。
高水位体系域经常因为剥蚀而不存在。
[转载]Petrel建模常用术语Petrel建模常用术语3D Grid –是一个用来描述三维地质模型的由水平线和垂直线组成的网格。







石油地质与工程2022年1月PETROLEUM GEOLOGY AND ENGINEERING 第36卷第1期文章编号:1673–8217(2022)01–0031–08基于MRGC聚类方法的测井相分析和岩性识别——以Z油田潜山地层为例余秋均(中国石油辽河油田分公司勘探开发研究院,辽宁盘锦124010)摘要:为了解决常规岩性识别方法对于较为精细岩性识别和复杂岩性识别困难的问题,通过论述MRGC聚类方法和KNN算法传播器的基本原理,提出基于MRGC聚类方法的测井相分析和岩性识别方法及其流程。
即优选能反映岩性特征的测井曲线,利用MRGC聚类方法进行测井相自动划分,并用录井及岩心等地质资料建立的岩相数据库对所划分的测井相进行标定,建立岩性识别模型;通过KNN算法传播器将模型推广应用于未取心井,实现岩性识别。
该方法在Z油田潜山地层应用,有效地识别出潜山地层中的风化壳角砾岩、硅质砂岩、硅质粉砂岩、硅质泥岩、灰岩、泥质灰岩、灰质泥岩、生物灰岩共8种主要岩性,其结果与录井、取心资料符合率达80%以上,表明其在潜山等地层岩性识别中具有很好的适用性。
关键词:MRGC聚类;测井相分析;岩性识别;风化壳;基岩;潜山中图分类号:P631.8 文献标识码:ALogging facies analysis and lithology identification based on MRGCclustering methodAll Rights Reserved.--by taking buried hill formation of Z oilfield as an exampleYU Qiujun(Exploration & Development Research Institute of Liaohe Oilfield Company, PetroChina, Panjin, Liaoning 124010, China) Abstract: In order to solve the difficulty of conventional lithology identification methods in fine lithologyidentification and complex lithology identification, by discussing the basic principle of MRGC clusteringmethod and KNN algorithm propagator, a logging facies analysis and lithology identification method and itsprocess based on MRGC clustering method are proposed. The logging curves that can reflect the speciallithology are optimized, the logging facies are automatically divided by MRGC clustering method, and thedivided logging facies are calibrated by the lithofacies database established by logging and core geologicaldata, to establish the lithology identification model. The model is extended to non-coring wells through KNNalgorithm propagator to realize lithology identification. The application of this method in buried hill formationof Z oilfield effectively identifies 8 main lithology in buried hill formation, including weathered crust breccia,siliceous sandstone, siliceous siltstone, siliceous mudstone, limestone, argillaceous limestone, calcareousmudstone and biological limestone. The coincidence rate between the results and logging and coring data ismore than 80%, indicating that it has good applicability in lithology identification of buried hill and otherstrata.Key words: MRGC clustering; logging facies analysis; lithology identification; weathering crust; bedrock;buried hill岩性识别是地质研究的重要内容,对于沉积相刻画、储层特征研究、储层预测和地质建模等均具收稿日期:2021–06–15;修订日期:2021–09–20。