《分子生物学》双语班作业-2
- 格式:doc
- 大小:29.00 KB
- 文档页数:2
第二章1.想想核酸的A260为什么会下降?肯定是形成双螺旋结构引起的。
那为什么相同序列的核酸,RNA 的A260下降,DNA的A260不变?这说明RNA能形成双链,DNA不能。
那么,为什么RNA能形成双链呢?原因肯定就在RNA和DNA序列上不同的碱基U和T上面。
U和T的含义完全一样,差别在于RNA分子上的U可以和G配对,而DNA分子上的T不能和G配对。
如果这时候能想到这一点,题目的答案也就有了。
本题正确的答案是:1个核酸的A260主要是4个碱基的π电子。
当一个核酸是单链的时候,π电子能吸收较大的光;但核酸为双链的时候,碱基对的堆积效应使π电子吸收较少的光。
于是,题目中的数据告诉我们,第一种序列的DNA和RNA在二级结构上没有什么大的差别。
而对于第二种序列的RNA光吸收大幅度减少,意味着RNA形成了某种双链二级结构,RNA二级结构的一个常见的特征是G和U能够配对。
从第二种序列不难看出,它能够自我配对,形成发夹结构,而降低光吸收。
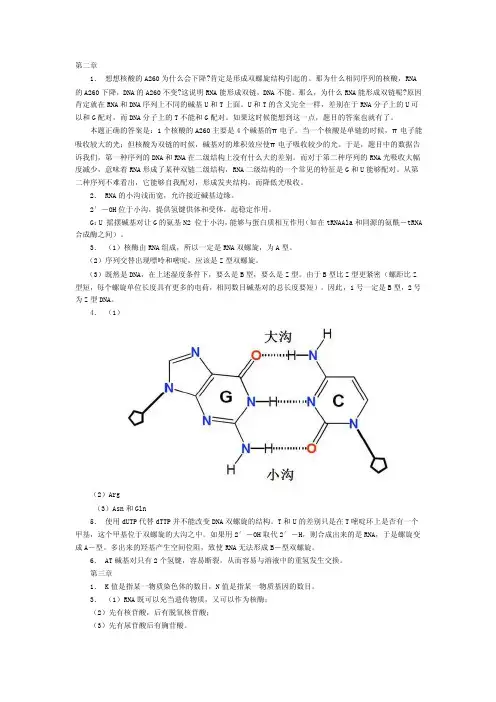
2. RNA的小沟浅而宽,允许接近碱基边缘。
2′-OH位于小沟,提供氢键供体和受体,起稳定作用。
G:U 摇摆碱基对让G的氨基N2 位于小沟,能够与蛋白质相互作用(如在tRNAAla和同源的氨酰-tRNA 合成酶之间)。
3.(1)核酶由RNA组成,所以一定是RNA双螺旋,为A型。
(2)序列交替出现嘌呤和嘧啶,应该是Z型双螺旋。
(3)既然是DNA,在上述湿度条件下,要么是B型,要么是Z型。
由于B型比Z型更紧密(螺距比Z 型短,每个螺旋单位长度具有更多的电荷,相同数目碱基对的总长度要短)。
因此,1号一定是B型,2号为Z型DNA。
4.(1)(2)Arg(3)Asn和Gln5.使用dUTP代替dTTP并不能改变DNA双螺旋的结构。
T和U的差别只是在T嘧啶环上是否有一个甲基,这个甲基位于双螺旋的大沟之中。
如果用2′-OH取代2′-H,则合成出来的是RNA,于是螺旋变成A-型。
多出来的羟基产生空间位阻,致使RNA无法形成B-型双螺旋。
Section C - properties of nucleic acids1.The sequence 5'-AGTCTGACT-3' in DNA is equivalent to which sequence in RNA?A 5'-AGUCUGUGACU -3'B 5' -UGTCTGUTC -3'C 5' -UCAGUCUGA-3'D 5'- AGUCAGACU-3'2. Which of the following correctly describes A-DNA?A a right-handed antiparallel doublehelix with 10 bp/turn and bases lyingperpendicular to the helixaxis.B a left-handed antiparalleldouble-helix with 12 bp/turn formedfrom alternating pyrimidine-purinesequences.C a right-handed antiparallel doublehelix with 11 bp/turn and bases tiltedwith respect to the helix axis.D a globular structure formed by shortintramolecular helices formed in asingle-strand nucleic acid.3. Denaturation of double stranded DNA involves.A breakage into short double-stranded fragments.B separation into single strands.C hydrolysis of the DNA backbone.D cleavage of the bases from the sugar-phosphate backbone.4. Which has the highest absorption per unit mass at a wavelength of 260 nm?A double-stranded DNA.B mononucleotides.C RNA.D protein.5. Type I DNA topoisomeraes ...A change linking number by士2B require ATP.C break one strand of a DNA double helix.D are the target of antibacterial drugs. Section D - Prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromatin structure1.Which of the following is common to both E. coli and eukaryotic chromosomes?A the DNA is circular.B the DNA is packaged into nucleosomes.C the DNA is contained in the nucleus.D the DNA is negatively supercoiled.2.A complex of 166 bp of DNA with the histone octamer plus histone HI is known as a . . .A nucleosome core.B solenoid.C 30 nm fiber.D chromatosome.3.In what region of the interphase chromosome does transcription take place?A the telomere.B the centromere.C euchromatin.D heterochromatin.4.Which statement about CpG islands and methylation is not true?A CpG islands are particularly resistant to DNase I.B CpG methylation is responsible for the mutation of CpG to TpG in eukaryotes.C CpG islands occur around the promoters of active genes.D CpG methylation is associated with inactive chromatin.5.Which of the following is an example of highly-repetitive DNA?A Alu element.B histone gene cluster.C DNA minisatellites.D dispersed repetitive DNA.Section E - DNA replication1.The number of replicons in a typical mammalian cell is . . .A 40-200.B 400.C 1000-2000.D 50000-100000.2. In prokaryotes,the lagging strand primers are removed by . . .A 3' to 5' exonuclease.B DNA ligase.C DNA polymerase I.D DNA polymerase III.3. The essential initiator protein at theE. coli origin of replication is . . .A DnaA.B DnaB.C DnaC.D DnaE.4. Prokaryotic plasmids can replicate in yeast cells if they contain a cloned yeast. . .A ORC.B CDK.C ARS.D RNA.Section F - DNA damage, repair and recombination(此章不考)1. Per nucleotide incorporated, the spontaneous mutation frequency in E. coli is . . .A 1 in 106.B 1 in 108.C 1 in 109.D 1 in 1010.2. The action of hydroxyl radicals on DNA generates a significant amount of . . .A pyrimidine dimmers.B 8-oxoguanine.C O6- methylguanine.D 7-hydroxymethylguanine.3. In methyl-directed mismatchrepair in E. coli, the daughterstrand containing the mismatchedbase is nicked by . . .A M utH endonuclease.B U vrABC endonuclease.C A P endonuclease.D3' to 5' exonuclease.4. The excision repair of UV-inducedDNA damage is defective inindividuals suffering from ...A hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer.B Crohn's disease.C classical xeroderma pigmentosum.D xeroderma pigmentosum variant. Section K - Transcription in prokaryotes1. Which two of the following statements about transcription are correct?A RNA synthesis occurs in the 3' to 5' direction.B the RNA polymerase enzyme moves along the sense strand of the DNA in a 5' to 3' direction.C the RNA polymerase enzyme movesalong the template strand of the DNA in a 5' to 3' direction.D the transcribed RNA is complementary to the template strand.E the RNA polymerase adds ribonucleotides to the 5' end of the growing RNA chain.F the RNA polymerase adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3' end of the growing RNA chain.2. Which one of the followingstatements about E. coli RNA polymerase is false?A the holoenzyme includes the sigma factor.B the core enzyme includes the sigma factor.C it requires Mg2+ for its activity.D it requires Zn2+ for its activity.3. Which one of the following statements is incorrect?A there are two αsubunits in the E. coli RNA polymerase.B there is one β subunit in the E. coli RNA polymerase.C E. coli has one sigma factor.D the β subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase is inhibited by rifampicin.E the streptolydigins inhibit transcription elongation.F heparin is a polyanion, which binds to the β’ subunit.4. Which one of the following statements about transcription in E. coli is true?A the -10 sequence is always exactly10 bp upstream from the transcription start site.B the initiating nucleotide is always a G.C the intervening sequence between the -35 and -10 sequences is conserved.D the sequence of the DNA after thesite of transcription initiation is notimportant for transcriptionefficiency.E the distance between the -35 and -10 sequences is critical for transcription efficiency.5. Which one of the following statements about transcription in E. coli is true?A loose binding of the RNA polymerase core enzyme to DNA is non-specific and unstable.B sigma factor dramatically increasesthe relative affinity of the enzymefor correct promoter sites.C almost all RNA start sites consist of a purine residue, with A being more common than G.D all promoters are inhibited by negative supercoiling.E terminators are often A-U hairpin structures.Section L - Regulation of transcription in prokaryotes1. Which two of the following statements are correct?A the double stranded DNA sequencethat has the upper strand sequence5'-GGATCGATCC-3' is apalindrome.B the double stranded DNA sequencethat has the upper strand sequence5'-GGATCCTAGG-3' isapalindrome.C the Lac repressor inhibits binding of the polymerase to the lac promoter.D the lac operon is directly induced by lactose.E binding of Lac repressor to allolactose reduces its affinity for the lac operator.F IPTG is a natural inducer of the lac promoter.2. Which one of the following statements about catabolite-regulated operons is false?A cAMP receptor protein (CRP) andcatabolite activator protein (CAP)are different names for the sameprotein.B when glucose is present in the cell cAMP levels fall.C CRP binds to cAMP and as a result activates transcription.D CRP binds to DNA in the absence of cAMP.E CRP can bend DNA, resulting in activation of transcription.3. Which one of the following statements about the trp operon is true?A the RNA product of the trp operon is very stable.B the Trp repressor is a product of the trp operon.C the Trp repressor,like the Lac repressor, is a tetramer of identical subunits.D the Trp repressor binds totryptophan.E tryptophan activates expression from the trp operon.F the trp operon is only regulated by the Trp represso4. Which two of the following statements about attenuation at the trp operon are true?A attenuation is rho-dependent.B deletion of the attenuator sequenceresults in an increase in both basaland activated levels of tran- scriptionfrom th~ trp promoter.C the attenuator lies upstream of the trp operator sequence.D attenuation does not require tight coupling between transcription and translation.E pausing of a ribosome at twotryptophan codons in the leaderpeptide when tryptophan is in shortsupply causes attenuation.F a hairpin structure called thepnti-terminator stops formation ofthe terminator hairpin, resulting intranscriptional read-through into thetrpE gene, when tryptophan isscarce.Section M - Transcription in eukaryotes1. Which one of the followingstatements about eukaryotic RNApolymerases I, II and III is false?A RNA Pol II is very sensitive to α-amanitin.B RNA Pol II is located in th~ nucleoplasm.C RNA Pol III transcribes th~ genes for tRNA.D eukaryotic cells contain other RNApolymerases in addition to RNA PolI, RNA Pol II and RNA Pol III.E each RNA polymerase containssubunits with homology to subunitsof the E. coli RNA polymerase aswell as additional subunits,whichare unique to each polymerase.F the carboxyl end of RNA Pol IIcontains a short sequence of onlyseven amino acids which is calledthe carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD)and which may be phosphorylated.2. Which two of the following statements about RNA Pol I genes are true?A RNA Pol I transcribes the genes for ribosomal RNAs.B human cells contain 40 clusters of five copies of the rRNA gene.C the 185, 5.85 and 285 rRNAs aresynthesized as separate transcripts.D RNA Pol I transcription occurs in the nucleoplasm.E RNA Pol I transcription occurs in the cytoplasm.F rRNA gene clusters are known as nucleolar organizer regions.3. Which one of the following statements about RNA Pol I transcription is false?A in RNA Pol I promoters the coreelement is 1000 bases downstreamfrom the upstream control element(UCE).B upstream binding factor (UBF)binds to both the UCE and theupstream part of the core element ofthe RNA Pol I promoter.C selectivity factor SLl stabilizes the UBF-DNA complex.D SL1 contains several subunitsincluding the TATA-binding protein TBP.E in Acanthamoeba there is a single control element in rRNA gene promoters.4. Which two of the following statements about RNA Pol III genes are true?A the transcriptional control regions of tRNA genes lie upstream of the start of transcription.B highly conserved sequences in tRNA gene coding regions are also promoter sequences.C TFIIIC contains TBP as one of its subunits.D TFIIIB is a sequence specific transcription factor on its own.E in humans 5S rRNA genes are arranged in a single cluster of 2000 copies.Section 0 - RNA processing and RNPs 1. Which ribonucleases are involved in producing mature tRNA in E. coli?A RNases A, D, E and F.B RNases D, E, F and H.C RNases D, E, F and P.D RNases A, D, H and P.2. Most eukaryotic pre-mRNAs arematured by which of the followingmodifications to their ends?A capping at the 3’-end cleavage and polyadenylation at the 5'-end.B addition of a GMP to the 5'-end,cleavage and polyadenylation to create the 3'-end.C addition of a guanine residue to the5'-end cleavage and polyadenylationto create the 3'-end.D addition of a GMP to the 5'-end,polyadenylation,then cleavage to create the 3'-end.3. Which one of the followingstatements correctly describes thesplicing process undergone bymost eukaryotic pre-mRNAs?A in a two-step reaction, thespliceosome removes the exon as alariat and joins the two intronstogether.B splicing requires conservedsequences which are the 5ιsplicesite,the 3' -splice site thebranch-point and the polypurinetract.C the U1 snRNP initially binds to the5'-splice site,U2 to the branchpointsequence and then the tri-snRNP, U4,US and U6 can bind.D in the first step of splicing the G atthe 3'-end of the intron is joined tothe 2’-hydroxyl group of the Aresidue of the branchpoint sequenceto create a lariat.Section P - The genetic code and tRNA 1. Which of the following list of features correctly apply to the genetic code?A triplet degenerate nearly universal, comma-less, nonoverlapping.B triplet universal, comma-less, degenerate, nonoverlapping.C overlapping, triplet, comma-less, degenerate nearly universal.D overlapping, comma-less nondegenerate nearly universal triplet. 2. Which of the following statementsabout tRNAs is false?A most tRNAs are about 76 residues long and have CCA as residues 74, 75 and 76.B many tRNAs contain the modifiednucleosides pseudouridinedihydrouridine ribothymidine andmosme.C tRNAs have a common L-shapedtertiary structure with threenucleotides at one end able to basepair with an anticodon on amessenger RNA molecule.D tRNAs have a common cloverleafsecondary structure containing threesingle stranded loops called the D-,T- and anticodon loops.3.Which three statements are true? The aminoacyl tRNA synthetase reaction...A joins AMP to the 3’-end of the tRNA.B is a two step reaction.C joins any amino acid to the 2'- or 3' -hydroxyl of the ribose of residue A76.D is highly specific because thesynthetases use identity elements inthe tRNAs to distinguish betweenthem.E joins AMP to the amino acid to produce an intermediate.F releases PPi in the second step. Section Q - Protein synthesis1. Which statement about the codon-anticodon interaction is false?A it is antiparallel and can include nonstandard base pairs.B inosine in the 5' -anticodon position can pair with A,C or U in the 3'-codonpositionC inosine in the 3’-anticodon position can pair with A, C or U in the 5’-codon position.D A is never found in the 5'-anticodon position as it is modified by anticodon deaminase.2.Which one of the following statements correctly describes initiation of protein synthesis in E.coli?A the initiator tRNA binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence.B three initiation factors are involved and IF2 binds to GTP.C the intermediate containing IF1, IF2,IF3, initiator tRNA and mRNA is called the 30S initiation complex.D binding of the 50S subunit releases IF1, IF2, GMP and PPi.E the initiation process is completewhen the 70S initiation complex is formed which contains the initiator tRNA in the A site of the ribosome and an empty P site.3.Which statement about elongation of protein synthesis in prokaryotes is false?A elongation can be divided into threesteps: peptidyl-tRNA deliverypeptide bond formation andtranslocation.B the peptidyl transferase center of thelarge ribosomal subunit isresponsible for peptide bond for-mation.C in the EF-Tu-Ts exchange cycleEF-Tu-GTP is regenerated by EF-Tsdisplacing GDP.D EF-G is also known as translocaseand uses GTP in its reaction.4.Which two of the following statements about initiation ofeukaryotic protein synthesis aretrue?A eukaryotes use a mRNA scanning method to locate the correct start codon.B there are at least nine eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs).C eukaryotic initiation uses N-formylmethionine.D the 80S initiation complexcompletes the initiation process andcontains the initiator tRNA base-paired to the start codon in the Asite.E ATP is hydrolysed to AMP and PPi during the scanning process.F the initiator tRNA binds after the mRNA has bound to the small subunit.。

华北理工大学《分子生物学》2020-2021学年第二学期期末试卷《分子生物学》考试内容:《分子生物学》;考试时间:120分钟;满分:100分;姓名:——;班级:——;学号:——一、选择题(每题3分,共30分)1. DNA分子的基本结构单位是:A. 核苷酸B. 碱基对C. 脱氧核糖D. 磷酸基团2. 在DNA双螺旋结构中,腺嘌呤(A)与哪种碱基形成互补配对?A. 胸腺嘧啶(T)B. 鸟嘌呤(G)C. 胞嘧啶(C)D. 尿嘧啶(U)3. PCR(聚合酶链式反应)扩增DNA片段的主要目的是:A. 确定DNA序列B. 在体外大量复制特定DNA片段C. 修饰DNA结构D. 切割DNA片段4. 真核生物基因转录的起始需要哪种酶的参与?A. DNA聚合酶B. RNA聚合酶C. 解旋酶D. 逆转录酶5. 下列哪项不是基因表达调控的主要层次?A. 转录水平调控B. 翻译水平调控C. 翻译后修饰调控D. DNA复制水平调控6. 表观遗传学主要通过什么机制来调控基因表达,而不改变DNA序列?A. 基因突变B. 染色质重塑C. 遗传密码的重新排列D. 染色体数目的变化7. 在原核生物中,基因转录和翻译的时空关系通常是:A. 相互独立,发生在细胞的不同部位B. 相互偶联,在同一空间内几乎同时进行C. 发生在细胞分裂期D. 受严格的时间顺序控制8. siRNA(小干扰RNA)在RNA干扰机制中的主要作用是:A. 催化mRNA的切割B. 作为模板合成cDNAC. 促进蛋白质翻译D. 抑制特定mRNA的翻译9. 下列哪种技术是用于检测特定DNA或RNA序列在生物体内存在与否的常用方法?A. PCR(聚合酶链式反应)B. 凝胶电泳C. Northern blotD. Southern blot10. 逆转录过程是指:A. DNA复制为DNAB. RNA复制为RNAC. DNA转录为RNAD. RNA逆转录为DNA二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. DNA的双螺旋结构由两条反向平行的_____链组成,它们通过_____键连接。

分子生物学(双语)2012A安徽大学2012 —20 13 学年第 1 学期《分子生物学(双语)》考试试卷(A 卷)(闭卷时间120分钟)考场登记表序号一、名词解释题(每小题3分,共36分)1. semiconservative replication2. Base Excision Repair3. rho dependent terminator4. polycistronic mRNA5. DNase Ⅰhypersensitivity6. C value paradox7. IS element8. primase9. elongation factor10. topoisomerase11. RNA interference12. enhancer题号一二三四五六七总分得分阅卷人得分院/系年级专业姓名学号答题勿超装订线 ------------------------------装---------------------------------------------订----------------------------------------线----------------------------------------二、填空题(每空1.5分,共21分)1. During DNA replication, unwinds double-stranded DNA,and removes RNA primers in the Okazaki fragments with its 5' to 3' exonuclease activity.2. A typical prokaryotic promoter has two consensus sequences, which are termed ________ and _______. The ideal spacing between the two consensus sequences is________ .3. Transposition occurs via two types of mechanisms. One is called ; the other is called .4. In negative control ,the regulator protein acts as a to block transcription of the operon.5. In SOS repair system, the two key regulatory proteins are and Lex A. Lex A is a (positive/ negative) regulator .6. , which locates upstream of the start codon of the mRNA, binds 3' end of the 16S rRNA in the ribosome to initiate protein synthesis7. In eukaryotes the tRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase .8. When a double-strand DNA is denatured, the absorbance at A260 will (decrease/increase). 9. The generation of antibody diversity is mainly due to .三、单项选择题(每小题1.5分,共21分.请填入下表相应题号栏中)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 141. DNA polymerase can add nucleotides toA. a free 3′end of a grow ing DNA chainB. a free 5′end of a growing DNA chainC. either a 3′or 5′end of a DN A chainD. a 5′end of RNA primerE. all of the above2. What is the first protein to bind to a eukaryotic promoter, and at which site does it bind? A. TFIID binds to a TATA box. B.RNA polymerase II binds to a TATA box. C. A regulator protein binds to a regulator region. D. An activator protein binds to an enhancer.3. Splicing is the process that does which of the following?A. Add multiple adenosine bases to the end of a primary RNA transcriptB. Remove exons and join intronsC. Remove introns and join exonsD. Remove mutated regions of primary transcript RNA4. Which subunit of the E. coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme catalyzes the synthesis of RNA ?A. α-subunitB. β-subunit得分得分得分C. rho factorD. sigma factor5. The DNA in transcriptionally active chromatin tends to beA. highly methylatedB. fully-methylatedC. Under-methylated or non--methylatedD. Semi-methylated6. The most efficient control of eukaryotic gene expression is achieved at the level ofA. Replication.B. translation initiationC. post-transcriptionD. post-translation.E. .transcription initiation.7. Translation is terminated when a stop codon is presented at the ________.A. E siteB. A siteC. P siteD. either A or BE. either A or C8. In ara operon, C protein can serve asA. an activatorB. a repressorC. either a repressor or an activator depending on presence/absence of arabinoseD. both a repressor and an activator irrespective of presence/absence of arabinose9. In a standard recombinant DNA procedure, the step which follows the construction of recombinantDNA molecule should beA re-ligation of the vectorsB. ligating the vector with the gene of interestC. digesting the vector with a restriction endonucleaseD. transformation of the molecule into host cells10. Which of the following is NOT a step in a PCR reaction:A. AnnealingB. ExtensionC. DenaturationD. dehydration11. One important difference between DNA replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes is thatA. prokaryotes do not use enzymes in the replication processB. there is only one replication origin in prokaryotesC. there are no Okazaki fragments in prokaryotesD. replication is conservative, not semiconservative, in prokaryotes12. A frameshift mutation could result fromA. a base insertion only.B. a base deletion only.C. a base substitution only.D. either an insertion or a deletion of a base.E. deletion of three consecutive bases.13. Which of the enzymes below is involved in repair of both thymine dimer and deaminate cytosine in E.coliA. DNA polymerase IB. PhotolyaseC. Uracil N-glycosylaseD. AP endonuclease14.An IRE (iron response element) regulates the expression of iron metabolism related genes byA. by binding to IRE-BPB. by forming a hair-pin structureC. at post-transcriptional or translational levelD. all of the above四、简答题(第1小题12分,第2小题10分,共22分)1. Describe how tryptophan concentration regulates the expression of the structural genes in the trp operon.2. How are eukaryotic RNA precursors processed ?。

分子生物学习题及答案第1章序言1.简述孟德尔、摩尔根和Waston等人对分子生物学发展的首要奉献。
孟德尔是遗传学的奠基人,被誉为现代遗传学之父。
他经过豌豆试验,发现了遗传学三大根本规律中的两个,别离为别离规律及自在组合规律。
摩尔根发现了染色体的遗传机制,创建染色体遗传理论,是现代试验生物学奠基人。
于1933年因为发现染色体在遗传中的效果,赢得了诺贝尔生理学或医学奖。
Watson于1953年和克里克发现DNA双螺旋结构一(包含中心法则),取得诺贝尔生理学或医学奖,被誉为''DNA之父”。
2.写出DNA、RNA、mRNA和siRNA的英文全名。
DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid 脱氧核糖核酸RNA: ribonucleic acid 核糖核酸mRNA: messenger RNA 信使RNAtRNA: transfer RNA 转运RNArRNA: ribosomal RNA 核糖体RNAsiRNA: small interfering RNA 搅扰小RNA3.试述''有其父必有其子”的生物学实质。
其生物学实质是基因遗传。
子代的性状由基因决议,而基因因为遗传的效果,其基因的一半来自于父方,一般来自于母方。
4.早期首要有哪些试验证明DNA是遗传物质?写出这些试验的首要进程。
1)肺炎链球菌转化试验:表面光滑的S型肺炎链球菌(有荚膜多糖一致病性);表面粗糙R型肺炎链球菌(无荚膜多糖)。
%1活的S型一打针一试验小鼠一小鼠死亡%1死的S型(经烧煮灭火)一打针一试验小鼠一小鼠存活%1活的R型一打针一试验小鼠一小鼠存活%1死的S型+活的R型一试验打针一小鼠死亡%1别离被杀死的S型菌体的各种组分+活的R型菌体一打针一试验小鼠一小鼠死亡(内只要死的S型菌体的DNA转化R型菌体导致致病菌)*DNA是遗传物质的载体2)噬菌体侵染细菌试验%1细菌培育基35S符号的氨基酸+无符号噬菌体一培育1-2代一子代噬菌体简直不含带有35S符号的蛋白质%1细菌培育基32N符号的核昔酸+无符号噬菌体一培育1-2代一子代噬菌体含有30% 以上32N符号的核昔酸*噬菌体传代进程中发挥效果的或许是DNA而不是蛋白质。

;14.Through their experiments with DNA from the bacterium Escherichia coli ,Meselson and Stahl showed that DNA replication is(A) conservative.;(B)dispersive ;(C) duplicative.;(D)semi-conservative15.A mutation changes a CG base pair to an AT base pair. This is a ___ mutation.(A )transversion ;(B )transition ;(C )transpositional ;(D )translocation16、Which of the following is an example of a nonsense mutation?(A )ACG to ACC ;(B )AUG to UUG ;(C )UAC to UAG ;(D )AAA to UUU17.A mutation occurs in which an AUU codon is changed to an AUC codon. Both of these codons signify the amino acid leucine. This is a ___ mutation.(A)Nonsense ;(B )missense ;(C )silent ;(D )neutral18.In a eukaryotic cell, when a positive regulatory protein interacts with a promoter element(A )transcription is activated ;(B )transcription is inhibited ;(C )translation is inhibited ;(D )replication is activated19.In eukaryotes, a protein is synthesized in the ___ and modified in the ___ .(A )nucleus; endoplasmic reticulum ;(B )endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi plex(C )Golgi plex; nucleus ; (D )nucleus; Golgi plexframeshift ;20.Utraviolet light usually causes mutations by a mechanism involving(A )one-strand breakage in DNA ;(B )light-induced change of thymine to alkylated guanine ;(C )inversion of DNA segments ;(D )induction of thymine dimmers ; (E )deletion of DNA segments21.氨酰tRNA 的作用由______决定(A )氨基酸;(B )反密码子;(C )固定的碱基区;(D )氨酰tRNA 合成酶的活性22.一个复制子是______(A )细胞分裂期间复制产物被分离之后的 DNA 片段;(B )复制的 DNA 片段和在此过程中所需的酶和蛋白;(C )任何自发复制的 DNA 序列(它与复制起始点相连);;(D )复制起点和复制叉之间的 DNA 片段23.下列哪些转录因子是装配因子(A )SP1;(B )TF ⅡB ;(C )TF ⅡH ;(D )都不是24.在原核生物复制子中以下哪种酶除去RNA 引发体并加入脱氧核糖核苷酸?(A )DNA 聚合酶Ⅲ;(B )DNA 聚合酶Ⅱ;(C )DNA 聚合酶Ⅰ;(D )DNA 连接酶25.DNA 依赖的RNA 聚合酶的通读可以靠_____(A )ρ因子蛋白与核心酶的结合;(B )抗终止蛋白与一个内在的ρ因子终止位点结合,因而封闭了终止信号;;(C )抗终止蛋白以它的作用位点与核心酶结合,因而改变其构象,使终止信号不能被核心酶识别;(D )NusA 蛋白与核心酶的结合只有在乳糖存在的条件下才能表达;在乳糖存在的条件下不能表达在乳糖不存在的条件下表达;不管乳糖存不存在都能表达三、 填空题(本大题共10小题,每空0.5分,共计10分) 1.转录因子可分为两类,即( )和( )。


老阚班双语分子生物学题型:填空、名解、选择、判断改错、简答、论述一、绪论1.molecular biology(分子生物学):分子生物学是研究核酸、蛋白质等所有生物大分子的形态、结构特征及其重要性、规律性和相互关系的科学。
2.DNA发现者:James Watson and Francis CrickDNA发现的实验:图1-1(P7)、图1-2(P8)3.DNA全称——Deoxyribonucleic AcidRNA全称——Ribonucleic Acid4.分子生物学主要研究内容:◆DNA重组技术◆基因表达调控研究◆生物大分子的结构功能研究—结构分子生物学◆基因组、功能基因组与生物信息学研究5.DNA recombinant technique(DNA重组技术):是20世纪70年代初兴起的技术科学,目的是将不同DNA片段按照人们的设计定向连接起来,在特定的受体细胞中与载体同时复制并得到表达,产生影响受体细胞的新的遗传性状二、染色体与DNA1.Nucleosome(核小体):核小体是染色体结构的基本单位、由H2A、H2B、H3、H4各两个分子生成的八聚体和由大约200bp的DNA组成的。
八聚体在中间,DNA分子盘绕在外,而H1则在核小体的外面。
每个核小体只有一个H1。
2.C值反常现象(C-value paradox):C值往往与种系进化的复杂程度不一致,某些低等生物却具有较大的C值。
3.关于DNA结构的词汇:double–helix(双螺旋)、base(碱基)sugar-phosphate backbonts(糖-磷酸骨架)、base pairs(碱基对)right/left-handed double-helix(右/左手双螺旋)4.DNA类型:右手螺旋:A-DNA,B-DNA左手螺旋:Z-DNA5.组蛋白:Octameric core (H2A、H2B、H3、H4)+外围(H1)6.真核生物重复序列类型:单拷贝、轻度(或低度)重复、中度重复、高度重复(四个空)不重复序列、中度重复序列、高度重复序列(三个空)7.真核生物基因组的特征:1)真核基因组庞大2)存在大量的重复序列3)大部分为非编码序列4)转录产物为单顺反子5)断裂基因,有内含子结构6)存在大量的顺式作用原件7)具有端粒结构8)细胞器基因, 转录和翻译在时间和空间上是不偶联的;9)有假基因化现象8.Z-DNA的特点:1)left-handed double helix with a zig-zag conformation of thebackbone (less smooth than B-DNA)2)Narrower, more elongated helix than A or B.3)Only one groove is observed, resembling the minor groove4) A high G-C content favours Z conformation.5)Z-DNA formation occurs during transcription of genes, attranscription start sites near promoters of actively transcribed.6)Base pairs nearly perpendicular to helix axis9.DNA复制所需要的元素(Requirements for DNA replication):1.原料(Precursor):四种脱氧核苷三磷酸(dATP、dGTP、dCTP、dTTP)2.模板(Template):以DNA的两条链为模板链,合成子代DNA3.引物(Primer):DNA的合成需要一段RNA链作为引物4.酶:a)引物合成酶(引发酶)(Primases)、b)DNA聚合酶(DNA polymerase)c)DNA连接酶(Ligases)d)DNA 拓扑异构酶(DNA Topisomerase)e)DNA 解螺旋酶/解链酶(DNA helicase)10.复制的几种方式(Modes of DNA replication):a)线性DNA双链的复制b)环状DNA双链的复制:1)Theta replication2)Rolling Circle Replication3) D loop11.The steps of BERa)Damaged baseb)DNA glycosylase recognize the damaged basec)Remove the base by hydrolysis of the N-glycosidic bondd)The AP endonuclease removes the AP site and neighboringnucleotidese)The gap is filled by DNA polymerase I and DNA ligase12.转座子(transposon, Tn):是存在于染色体DNA上可自主复制和位移的基因单位13.转坐(transposition):DNA转座是由可移位因子介导的遗传物质重排现象, 又称移位。

西南大学1166《分子生物学》第二次作业及参考答案以下是为大家整理的西南大学1166《分子生物学》第二次作业及参考答案的相关范文,本文关键词为西南,大学,1166,分子生物学,第二次,作业,参考,答案,,您可以从右上方搜索框检索更多相关文章,如果您觉得有用,请继续关注我们并推荐给您的好友,您可以在综合文库中查看更多范文。
西南大学1166《分子生物学》第二次作业及参考答案论述题:1.分子生物学的发展趋势是什么?2.现代分子生物学研究的主要内容有哪几方面?3.研究DnA的一级结构有什么重要的生物学意义?4.RnA的功能主要是参与蛋白质的生物合成,起着遗传信息由DnA到蛋白质的中间传递体核心功能,此外它的功能多样性还表现在哪些方面?5.实施基因工程(DnA重组技术)的重要理论基础之一是什么?参考答案1.分子生物学的发展趋势是什么?当前,人类基因组研究的重点正在由结构向功能转移,一个以基因组功能研究为主要研究内容的\后基因组”(post-genome)时代已经到来。
它的主要任务是研究细胞全部基因的表达图式和全部蛋白图式,或者说是\从基因组到蛋白质组”。
由此,分子生物学研究的重点又回到了蛋白质上来,生物信息学也应运而生。
(1)功能基因组学(2)蛋白质组学(3)生物信息学2.现代分子生物学研究的主要内容有哪几方面?按照狭义分子生物学的定义,可以将现代分子的研究内容概括为五大方面:(1)基因与基因组的结构与功能;(2)DnA的复制、转录和翻译;(3)基因表达调控的研究;(4)DnA重组技术;(5)结构分子生物学。
3.研究DnA的一级结构有什么重要的生物学意义?所谓DnA的一级结构就是指DnA分子中的核苷酸排列顺序。
生物的遗传信息通过核苷酸不同的排列顺序储存在DnA分子中,DnA 分子4种核苷酸千变万化的序列排列即反映了生物界物种的多样性。
为了阐明生物的遗传信息,首先要测定生物基因组的序列。
迄今已经测定基因组序列的生物数以百计。

分子生物学习题第二章第二章1在核酸双螺旋(如DNA)中形成发夹结构的频率比单链分子低。
发夹结构的产生需要回文序列使双链形成对称的发夹,呈十字结构。
对2病毒的遗传因子可包括1到300个基因。
与生命有机体不同,病毒的遗传因子可能是DNA或RNA(但不可能同时兼有!),因此DNA不是完全通用的遗传物质。
错3B型双螺旋是DNA的普遍构型,而Z型则被确定为仅存在与某些低等真核细胞中。
错4在高盐和低温条件下由DNA单链杂交形成的双螺旋表现出几乎完全的互补性,这一过程可看作一个复性(退火)反应。
错5在高盐和低温条件下由DNA单链杂交形成的双螺旋表现出几乎完全的互补性,这一过程可看作一个复性(退火)反应。
1DNA变性是指:A:分子中磷酸二酯键断裂B:多核苷酸链解聚选择项:C:互补碱基之间氢键断裂D:DNA分子中碱基丢失C2PCR实验的特异性主要取决于:A:DNA聚合酶的种类B:反应体系中模板DNA的量选择项:C:引物序列的结构和长度D:四种dNTP的浓度E:循环周期的次数C3限制性核酸内切酶切割DNA后产生:A:3`磷酸基末端和5`羟基末端选择项:B:5`磷酸基末端和3`羟基末端C:3`磷酸基末端和5`磷酸基末端D:5`羟基末端和3`羟基末端E:3`羟基末端和5`羟基末端和磷酸B4核酸分子中贮存、传递遗传信息的关键部分是:A:核苷酸B:碱基序列选择项:C:磷酸戊糖D:戊糖磷酸骨架B5DNA分子中的超螺旋:A:仅发生于环状DNA中B:在线性和环状DNA中均有发生。
缠绕数的增加可被碱基配对的改变和氢键的增加所控制选择项:C:可在一个闭合环状DNA分子中形成一个左手螺旋。
负超螺旋是DNA修饰的前提,为酶接触DNA提供了条件D:是双螺旋中一条链绕另一条链的旋转数和双螺旋的回转数的总和B6在基因工程中通常所使用的质粒存在于:A:细菌染色体B:酵母染色体选择项:C:细菌染色体外D:酵母染色体外E:以上都不是C7有关DNA的变性哪条正确:A:变性是分子中磷酸二酯键的断裂B:变性后紫外吸收增加选择项:C:变性后粘度增加D:DNA分子开始变性的温度叫TmB8可识别DNA的特异序列,并在识别位点或其周围切割双链DNA的一类酶称为:A:限制性外切核酸酶B:限制性内切核酸酶选择项:C:非限制性外切核酸酶D:非限制性内切核酸酶E:DNA内切酶B9组蛋白的净电荷是:A:正B:中性选择项:C:负D:不一定A10DNA和RNA完全水解后,其产物的特点是:A:核糖相同,部分碱基不同B:核糖不同,碱基相同选择项:C:核糖相同,碱基不同D:核糖不同,部分碱基不同D11自然界游离核苷酸中,磷酸最常见是位于:A:戊糖的C-5’上B:戊糖的C-2’上选择项:C:戊糖的C-3’上D:戊糖的C-2’和C-5’上A12重组DNA技术中实现目的基因与载体DNA拼接的酶是:A:DNA聚合酶B:RNA聚合酶C:DNA 连接酶D:RNA连接酶E:限制性核酸内切酶C13选择项:题干:核小体的净电荷是:选择项:A:正B:中性C:负D:不一定B14题干:限制性核酸内切酶切割DNA后产生:A:3`磷酸基末端和5`羟基末端B:5`磷酸基末端和3`羟基末端选择项:C:3`磷酸基末端和5`磷酸基末端D:5`羟基末端和3`羟基末端E:3`羟基末端和5`羟基末端和磷酸B15题干:用于重组DNA的限制性核酸内切酶识别核苷酸序列的:A:正超螺旋结构B:负超螺旋结构选择项:C:α螺旋结构D:回文结构E:锌指结构D16题干:B型DNA的双螺旋每旋转一周,沿轴上升的高度是:A:5.4nmB:3.6nm选择项:C:6.8nmD:0.34nmB17题干:α互补筛选法属于:A:抗药性标志筛选B:酶联免疫筛选选择项:C:标志补救筛选D:原位杂交筛选E:免疫化学筛选C18题干:某DNA分子中腺嘌呤的含量为15%,则胞嘧啶的含量为:A:35%B:15%选择项:C:30%D:40%A19题干:就分于结构而论,质粒是:A:环状双链DNA分子B:环状单链DNA分于选择项:C:环状单链RNA分子D:线状双链DNA分子E:线状单链DNA分子A20题干:DNA的变性:选择项:A:包括双螺旋的解链B:可以由低温产生C:是可逆的D:是磷酸二酯键的断裂A21题干:在基因工程中通常所使用的质粒存在于:A:细菌染色体B:酵母染色体选择项:C:细菌染色体外D:酵母染色体外E:以上都不是C22题干:核酸中核苷酸之间的连接方式是:A:2’-3’磷酸二酯键B:糖苷键选择项:C:2’-5’磷酸二酯键D:3’-5’磷酸二酯键D23题干:1953年Waston和Crick提出:A:多核苷酸DNA链通过氢键连接成一个双螺旋B:DNA的复制是半保留的,常常形成亲本-子代双螺旋杂合链选择项:C:三个连续的核苷酸代表一个遗传密码D:遗传物质通过通常是DNA而非RNAA 24题干:用于重组DNA的限制性核酸内切酶识别核苷酸序列的:A:正超螺旋结构B:负超螺旋结构选择项:C:α螺旋结构D:回文结构E:锌指结构D25题干:重组DNA的基本构建过程是将:A:任意两段DNA连在一起B:外源DNA接入人体DNA选择项:C:目的基因接人适当载体D:目的基因接入哺乳类DNAE:外源基因接人宿主基因C26题干:组成核酸的基本结构单位是:A:核糖和脱氧核糖B:磷酸和核糖选择项:C:含氮碱基D:单核苷酸D27题干:双链DNA中的碱基对有:A:A-U选择项:B:G-TC:C-GD:C-AC28题干:限制性核酸内切酶切割DNA后产生:A:3`磷酸基末端和5`羟基末端B:5`磷酸基末端和3`羟基末端选择项:C:3`磷酸基末端和5`磷酸基末端D:5`羟基末端和3`羟基末端E:3`羟基末端和5`羟基末端和磷酸B29题干:在分子生物学领域,分子克隆主要是指:A:DNA的大量复制B:DNA的大量转录选择项:C:DNA的大量剪切D:RNA的大量反转录E:RNA的大量剪切A30题干:在分子生物学领域,分子克隆专指:A:细胞克隆B:RNA克隆选择项:C:DNA克隆D:抗体克隆E:mRNA克隆C。
临床医学学术型硕士研究生《医学分子生物学》双语课下载提示:该文档是本店铺精心编制而成的,希望大家下载后,能够帮助大家解决实际问题。
文档下载后可定制修改,请根据实际需要进行调整和使用,谢谢!本店铺为大家提供各种类型的实用资料,如教育随笔、日记赏析、句子摘抄、古诗大全、经典美文、话题作文、工作总结、词语解析、文案摘录、其他资料等等,想了解不同资料格式和写法,敬请关注!Download tips: This document is carefully compiled by this editor. I hope that after you download it, it can help you solve practical problems. The document can be customized and modified after downloading, please adjust and use it according to actual needs, thank you! In addition, this shop provides you with various types of practical materials, such as educational essays, diary appreciation, sentence excerpts, ancient poems, classic articles, topic composition, work summary, word parsing, copy excerpts, other materials and so on, want to know different data formats and writing methods, please pay attention!《医学分子生物学双语课程介绍》1. 研究生课程概述。
大学分子生物学考试(习题卷2)说明:答案和解析在试卷最后第1部分:单项选择题,共200题,每题只有一个正确答案,多选或少选均不得分。
1.[单选题]用作DNA合成的模板不包括 ()A)tRNAB)细菌染色体DNAC)病毒RNAD)线粒体DNA2.[单选题]Berg被称为“重 组DNA技术之父”是因为他( ),A)将两个不同来源的DNA连接在一起并发挥其应有的生物学功能。
B)将一条DNA分 子切割开并保留其生物学功能。
C)将两条DNA单链分子合成在一起形成双螺旋。
D)将DNA与RNA分子 杂交在-起。
3.[单选题]DNA复制的方式是________。
A)全保留B)弥散性C)从头合成D)半保留4.[单选题]下列生物分子中能够充当遗传物质的是_______。
A)核糖B)脂肪酸C)朊病毒蛋白D)次黄嘌吟5.[单选题]通常,DNA的复制起始区富含______碱基。
A)GCB)AGC)CTD)AT6.[单选题]基因工程中常用的限制性核酸内切酶是A)Ⅰ型酶B)Ⅱ型酶C)Ⅲ型酶D)I、II型酶B)反密码子第三个碱基与密码子第一个碱基C)反密码子和密码子第一个碱基D)反密码子和密码子第三个碱基8.[单选题]表观遗传性状是指( )。
A)DNA序列没有变化但染色体变化产生的稳定可遗传的表型B)由DNA序列变化产生的稳定可遗传的表型C)染色体数量 变化产生的稳定可遗传的表型D)染色体倍数 变化产生的稳定可遗传的表型9.[单选题]在研究蛋白质合成中,可利用嘌呤霉素,因为它A)使核糖体大小亚基解聚B)使肽链提前释放C)抑制氨基酰-tRNA合成酶活性D)防止多核糖体形成10.[单选题]中心法则遗传信息的传递方式不包括()A)DNA→rRNAB)DNA→DNAC)RNA→蛋白质D)mRNA→DNA11.[单选题]下列不属于复制起始区的特征的是( )A)由多个短的重复序列组成B)常富含AT序列C)能够被特定的复制起始区结合蛋白识别并结合D)原核生物中-10区影响DNA复制的频率12.[单选题]连接相邻冈崎片段的酶是_____。
第二章一、名词解释1、DNA的一级结构:四种脱氧核苷酸按照一定的排列顺序以3’,5'磷酸二酯键相连形成的直线或环状多聚体,即四种脱氧核苷酸的连接及排列顺序.2、DNA的二级结构:DNA两条多核苷酸链反向平行盘绕而成的双螺旋结构.3、DNA的三级结构:DNA双螺旋进一步扭曲盘绕所形成的特定空间结构.4、DNA超螺旋:DNA双螺旋进一步扭曲盘绕所形成的特定空间结构,是DNA结构的主要形式,可分为正超螺旋与负超螺旋两大类。
按DNA双螺旋的相反方向缠绕而成的超螺旋成为负超螺旋,反之,则称为正超螺旋。
所有天然的超螺旋DNA均为负超螺旋.5、DNA拓扑异构体:核苷酸数目相同,但连接数不同的核酸,称拓扑异构体6、DNA的变性与复性:变性(双链→单链)在某些理化因素作用下,氢键断裂,DNA双链解开成两条单链的过程.复性(单链→双链)变性DNA在适当条件下,分开的两条单链分子按照碱基互补配对原则重新恢复天然的双螺旋构想的现象。
7、DNA的熔链温度(Tm值):DNA加热变性时,紫外吸收达到最大值的一半时的温度,即DNA分子内50%的双链结构被解开成单链。
Tm值计算公式:Tm=69.3+0.41(G+C)%;<18bp的寡核苷酸的Tm计算:Tm=4(G+C)+2(A+T)。
8、DNA退火:热变性的DNA经缓慢冷却后即可复性,称为退火9、基因:编码一种功能蛋白或RNA分子所必需的全部DNA序列.10、基因组:生物的单倍体细胞中的所有DNA,包括核DNA和线粒体、叶绿体等细胞器DNA11、C值:生物单倍体基因组中的全部DNA量称为C值12、C值矛盾:C值的大小与生物的复杂度和进化的地位并不一致,称为C值矛盾或C值悖论13、基因家族:一组功能相似、且核苷酸序列具有同源性的基因。
可能由某一共同祖先基因经重复和突变产生。
14、假基因:假基因是原始的、有活性的基因经突变而形成的、稳定的无活性的拷贝。
表示方法:Ψα1表示与α1相似的假基因15、转座:遗传可移动因子介导的物质的重排现象.16、转座子:染色体、质粒或噬菌体上可以转移位置的遗传成分.17、逆转座子:基因组内存在着通过DNA转录为RNA后,再转录为cDNA并插入到基因组的新位点上的因子。
Chapter 3
1.简列原核生物和真核生物启动子结构中的核心元件
2.何谓增强子(enhancer)?简述其作用特点
3.何谓σ因子?简述其功能
4.何谓ρ因子?简述原核生物基因转录终止的机制
5.简述真核生物主要RNA pol的种类及功能
6.简述真核生物RNA pol II 转录起始过程及其主要转录因子的功能
7.简述原核生物和真核生物mRNA的特点及其异同点
8.分别简述5’-帽子结构和3’-poly(A)尾的功能
9.RNA加工有哪些方式?简述RNA剪接的主要模式及特点
10.何谓RNA编辑?简述其基本机制及生物学意义
11.何谓核酶(ribozyme)?简述其基本机制及生物学意义Chapter 4
1.tRNA的三叶草结构特点及其与蛋白质翻译的关联
2.核糖体的结构特点及其与蛋白质翻译的关联
3.原核和真核生物的核糖体组成有哪些异同点
4.原核和真核生物的翻译起始过程有哪些区别
5.简述eIF-4F的基本结构组份及其功能
6.何谓分子伴侣?有哪些重要功能
Chapter 2
1.何谓基因(gene)?简述其基本组份
2.何谓核小体(nucleosome)?简述其基本组份
3.比较原核生物和真核生物基因组的结构特点
4.简列4种模式生物,并说明其被选择为模式生物的原因
5.基因组的大小和物种的进化程度呈正相关吗?为什么?
6.E. coli DNA复制叉上有哪些蛋白质?简述它们的功能
7.何谓PCR?简述PCR基本原理,以及体外PCR反应与体内DNA复制的异同点
8.DNA修复包括哪些机制?简述错配修复和重组修复的基本原理
9.何谓SOS修复?简述其基本机制及生物学意义
10.何谓转座(transposition)?简述其基本机制及生物学意义。