遗传算法解决10城市TSP问题程序源代码
- 格式:doc
- 大小:50.50 KB
- 文档页数:6

实验六:遗传算法求解TSP问题实验3篇以下是关于遗传算法求解TSP问题的实验报告,分为三个部分,总计超过3000字。
一、实验背景与原理1.1 实验背景旅行商问题(Traveling Salesman Problem,TSP)是组合优化中的经典问题。
给定一组城市和每两个城市之间的距离,求解访问每个城市一次并返回出发城市的最短路径。
TSP 问题具有很高的研究价值,广泛应用于物流、交通运输、路径规划等领域。
1.2 遗传算法原理遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm,GA)是一种模拟自然选择和遗传机制的搜索算法。
它通过选择、交叉和变异操作生成新一代解,逐步优化问题的解。
遗传算法具有全局搜索能力强、适用于多种优化问题等优点。
二、实验设计与实现2.1 实验设计本实验使用遗传算法求解TSP问题,主要包括以下步骤:(1)初始化种群:随机生成一定数量的个体(路径),每个个体代表一条访问城市的路径。
(2)计算适应度:根据路径长度计算每个个体的适应度,适应度越高,路径越短。
(3)选择操作:根据适应度选择优秀的个体进入下一代。
(4)交叉操作:随机选择两个个体进行交叉,生成新的个体。
(5)变异操作:对交叉后的个体进行变异,增加解的多样性。
(6)更新种群:将新生成的个体替换掉上一代适应度较低的个体。
(7)迭代:重复步骤(2)至(6),直至满足终止条件。
2.2 实验实现本实验使用Python语言实现遗传算法求解TSP问题。
以下为实现过程中的关键代码:(1)初始化种群```pythondef initialize_population(city_num, population_size): population = []for _ in range(population_size):individual = list(range(city_num))random.shuffle(individual)population.append(individual)return population```(2)计算适应度```pythondef calculate_fitness(population, distance_matrix): fitness = []for individual in population:path_length =sum([distance_matrix[individual[i]][individual[i+1]] for i in range(len(individual) 1)])fitness.append(1 / path_length)return fitness```(3)选择操作```pythondef selection(population, fitness, population_size): selected_population = []fitness_sum = sum(fitness)fitness_probability = [f / fitness_sum for f in fitness]for _ in range(population_size):individual = random.choices(population, fitness_probability)[0]selected_population.append(individual)return selected_population```(4)交叉操作```pythondef crossover(parent1, parent2):index1 = random.randint(0, len(parent1) 2)index2 = random.randint(index1 + 1, len(parent1) 1)child1 = parent1[:index1] +parent2[index1:index2] + parent1[index2:]child2 = parent2[:index1] +parent1[index1:index2] + parent2[index2:]return child1, child2```(5)变异操作```pythondef mutation(individual, mutation_rate):for i in range(len(individual)):if random.random() < mutation_rate:j = random.randint(0, len(individual) 1) individual[i], individual[j] = individual[j], individual[i]return individual```(6)更新种群```pythondef update_population(parent_population, child_population, fitness):fitness_sum = sum(fitness)fitness_probability = [f / fitness_sum for f in fitness]new_population =random.choices(parent_population + child_population, fitness_probability, k=len(parent_population)) return new_population```(7)迭代```pythondef genetic_algorithm(city_num, population_size, crossover_rate, mutation_rate, max_iterations): distance_matrix =create_distance_matrix(city_num)population = initialize_population(city_num, population_size)for _ in range(max_iterations):fitness = calculate_fitness(population, distance_matrix)selected_population = selection(population, fitness, population_size)parent_population = []child_population = []for i in range(0, population_size, 2):parent1, parent2 = selected_population[i], selected_population[i+1]child1, child2 = crossover(parent1, parent2)child1 = mutation(child1, mutation_rate)child2 = mutation(child2, mutation_rate)parent_population.extend([parent1, parent2]) child_population.extend([child1, child2])population =update_population(parent_population, child_population, fitness)best_individual =population[fitness.index(max(fitness))]best_path_length =sum([distance_matrix[best_individual[i]][best_individual[i +1]] for i in range(len(best_individual) 1)])return best_individual, best_path_length```三、实验结果与分析3.1 实验结果本实验选取了10个城市进行测试,遗传算法参数设置如下:种群大小:50交叉率:0.8变异率:0.1最大迭代次数:100实验得到的最佳路径长度为:1953.53.2 实验分析(1)参数设置对算法性能的影响种群大小:种群大小会影响算法的搜索能力和收敛速度。


解TSP问题的遗传算法C语言程序#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<math.h>#include<alloc.h>#include<conio.h>#include<float.h>#include<time.h>#include<graphics.h>#include<bios.h>#define maxpop 100#define maxstring 100struct pp{unsigned char chrom[maxstring];float x,fitness;unsigned int parent1,parent2,xsite;};struct pp *oldpop,*newpop,*p1;unsigned int popsize,lchrom,gem,maxgen,co_min,jrand;unsigned int nmutation,ncross,jcross,maxpp,minpp,maxxy;floatpcross,pmutation,sumfitness,avg,max,min,seed,maxold,oldrand[maxstring];unsigned char x[maxstring],y[maxstring]; float*dd,ff,maxdd,refpd,fm[201]; FILE *fp,*fp1;float objfunc(float);void statistics();int select();int flip(float);int crossover();void generation();void initialize();void report();float decode();void crtinit();void inversion();float random1();void randomize1();main(){unsigned int gen,k,j,tt;char fname[10];float ttt;clrscr();co_min=0;if((oldpop=(struct pp *)farmalloc(maxpop*sizeof(struct pp)))==NULL) {printf("memory requst fail!\n");exit(0);} if((dd=(float*)farmalloc(maxstring*maxstring*sizeof(float)))==NULL){printf("memory requst fail!\n");exit(0);} if((newpop=(struct pp *)farmalloc(maxpop*sizeof(struct pp)))==NULL){printf("memory requst fail!\n");exit(0);} if((p1=(struct pp*)farmalloc(sizeof(struct pp)))==NULL){printf("memory requst fail!\n");exit(0);} for(k=0;k<maxpop;k++) oldpop[k].chrom[0]='\0'; for(k=0;k<maxpop;k++) newpop[k].chrom[0]='\0'; printf("Enter Result Data Filename:"); gets(fname);if((fp=fopen(fname,"w+"))==NULL){printf("cannot open file\n");exit(0);}gen=0;randomize();initialize();fputs("this is result of the TSP problem:",fp);fprintf(fp,"city: %2d psize: %3d Ref.TSP_path:%f\n",lchrom,popsize,refpd);fprintf(fp,"Pc: %f Pm: %f Seed: %f\n",pcross,pmutation,seed);fprintf(fp,"X site:\n");for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++){if((k%16)==0) fprintf(fp,"\n"); fprintf(fp,"%5d",x[k]);}fprintf(fp,"\n Y site:\n"); for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++){if((k%16)==0) fprintf(fp,"\n"); fprintf(fp,"%5d",y[k]);}fprintf(fp,"\n");crtinit();statistics(oldpop);report(gen,oldpop);getch();maxold=min;fm[0]=100.0*oldpop[maxpp].x/ff; do {gen=gen+1;generation();statistics(oldpop);if(max>maxold){maxold=max;co_min=0;}fm[gen%200]=100.0*oldpop[maxpp].x/ff; report(gen,oldpop);gotoxy(30,25);ttt=clock()/18.2;tt=ttt/60;printf("Run Clock: %2d: %2d: %4.2f",tt/60,tt%60,ttt-tt*60.0);printf("Min=%6.4fNm:%d\n",min,co_min); }while((gen<100)&&!bioskey(1)); printf("\n gen= %d",gen);do{gen=gen+1;generation();statistics(oldpop);if(max>maxold){maxold=max;co_min=0;}fm[gen%200]=100.0*oldpop[maxpp].x/ff; report(gen,oldpop);if((gen%100)==0)report(gen,oldpop); gotoxy(30,25);ttt=clock()/18.2;tt=ttt/60;printf("Run Clock: %2d: %2d: %4.2f",tt/60,tt%60,ttt-tt*60.0);printf("Min=%6.4fNm:%d\n",min,co_min); }while((gen<maxgen)&&!bioskey(1));getch();for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++) {if((k%16)==0)fprintf(fp,"\n");fprintf(fp,"%5d",oldpop[maxpp].chrom[k]);}fprintf(fp,"\n");fclose(fp);farfree(dd);farfree(p1);farfree(oldpop);farfree(newpop);restorecrtmode();exit(0);}/*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%*/float objfunc(float x1) {float y;y=100.0*ff/x1;return y;}/*&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&*/void statistics(pop) struct pp *pop;{int j;sumfitness=pop[0].fitness; min=pop[0].fitness; max=pop[0].fitness; maxpp=0;minpp=0;for(j=1;j<popsize;j++) {sumfitness=sumfitness+pop[j].fitness;if(pop[j].fitness>max){max=pop[j].fitness;maxpp=j;}if(pop[j].fitness<min){min=pop[j].fitness;minpp=j;}}avg=sumfitness/(float)popsize;}/*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%*/void generation(){unsigned int k,j,j1,j2,i1,i2,mate1,mate2;float f1,f2;j=0;do{mate1=select();pp:mate2=select();if(mate1==mate2)goto pp;crossover(oldpop[mate1].chrom,oldpop[mate2].chrom,j);newpop[j].x=(float)decode(newpop[j].chrom);newpop[j].fitness=objfunc(newpop[j].x); newpop[j].parent1=mate1;newpop[j].parent2=mate2;newpop[j].xsite=jcross;newpop[j+1].x=(float)decode(newpop[j+1].chrom);newpop[j+1].fitness=objfunc(newpop[j+1].x); newpop[j+1].parent1=mate1;newpop[j+1].parent2=mate2;newpop[j+1].xsite=jcross;if(newpop[j].fitness>min){for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++)oldpop[minpp].chrom[k]=newpop[j].chrom[k];oldpop[minpp].x=newpop[j].x;oldpop[minpp].fitness=newpop[j].fitness;co_min++;return;}if(newpop[j+1].fitness>min){for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++)oldpop[minpp].chrom[k]=newpop[j+1].chrom[k];oldpop[minpp].x=newpop[j+1].x;oldpop[minpp].fitness=newpop[j+1].fitness;co_min++;return;}j=j+2;}while(j<popsize);}/*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%*/void initdata(){unsigned int ch,j;clrscr();printf("-----------------------\n");printf("A SGA\n");printf("------------------------\n");/*pause();*/clrscr();printf("*******SGA DATA ENTRY AND INITILIZATION *******\n");printf("\n");printf("input pop size");scanf("%d",&popsize); printf("input chrom length");scanf("%d",&lchrom); printf("input maxgenerations");scanf("%d",&maxgen); printf("input crossoverprobability");scanf("%f",&pcross); printf("input mutationprob");scanf("%f",&pmutation); randomize1();clrscr();nmutation=0;ncross=0;}/*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%*/void initreport(){int j,k;printf("pop size=%d\n",popsize);printf("chromosome length=%d\n",lchrom);printf("maxgen=%d\n",maxgen);printf("pmutation=%f\n",pmutation); printf("pcross=%f\n",pcross);printf("initial generation statistics\n"); printf("ini pop maxfitness=%f\n",max); printf("ini pop avr fitness=%f\n",avg); printf("ini pop min fitness=%f\n",min); printf("ini pop sum fit=%f\n",sumfitness); } void initpop(){unsigned char j1;unsigned int k5,i1,i2,j,i,k,j2,j3,j4,p5[maxstring];float f1,f2;j=0;for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++)oldpop[j].chrom[k]=k;for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++)p5[k]=oldpop[j].chrom[k];randomize();for(;j<popsize;j++){j2=random(lchrom);for(k=0;k<j2+20;k++){j3=random(lchrom);j4=random(lchrom);j1=p5[j3];p5[j3]=p5[j4];p5[j4]=j1;}for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++)oldpop[j].chrom[k]=p5[k]; }for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++)for(j=0;j<lchrom;j++)dd[k*lchrom+j]=hypot(x[k]-x[j],y[k]-y[j]);for(j=0;j<popsize;j++) {oldpop[j].x=(float)decode(oldpop[j].chrom); oldpop[j].fitness=objfunc(oldpop[j].x);oldpop[j].parent1=0;oldpop[j].parent2=0;oldpop[j].xsite=0;}}/*&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&*/void initialize(){int k,j,minx,miny,maxx,maxy; initdata();minx=0;miny=0;maxx=0;maxy=0;for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++){x[k]=rand();if(x[k]>maxx)maxx=x[k]; if(x[k]<minx)minx=x[k]; y[k]=rand();if(y[k]>maxy)maxy=y[k]; if(y[k]<miny)miny=y[k]; }if((maxx-minx)>(maxy-miny)){maxxy=maxx-minx;}else {maxxy=maxy-miny;}maxdd=0.0;for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++)for(j=0;j<lchrom;j++){dd[k*lchrom+j]=hypot(x[k]-x[j],y[k]-y[j]);if(maxdd<dd[k*lchrom+j])maxdd=dd[k*lchrom+j];}refpd=dd[lchrom-1];for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++)refpd=refpd+dd[k*lchrom+k+2]; for(j=0;j<lchrom;j++)dd[j*lchrom+j]=4.0*maxdd; ff=(0.765*maxxy*pow(lchrom,0.5)); minpp=0; min=dd[lchrom-1];for(j=0;j<lchrom-1;j++){if(dd[lchrom*j+lchrom-1]<min){min=dd[lchrom*j+lchrom-1];minpp=j;}}initpop();statistics(oldpop);initreport();}/*&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&*/void report(int l,struct pp *pop){int k,ix,iy,jx,jy;unsigned int tt;float ttt;cleardevice();gotoxy(1,1);printf("city:%4d para_size:%4d maxgen:%4d ref_tour:%f\n",lchrom,popsize,maxgen,refpd);printf("ncross:%4d Nmutation:%4d Rungen:%4d AVG=%8.4f MIN=%8.4f\n\n",ncross,nmutation,l,avg,min);printf("inpath:%6.4f Minpath length:%10.4f Ref_co_tour:%f\n",pop[maxpp].x/maxxy,pop[maxpp].x,ff); printf("Co_minpath:%6.4f Maxfit:%10.8f",100.0*pop[maxpp].x/ff,pop[maxpp].fitness); ttt=clock()/18.2;tt=ttt/60;printf("Run clock:%2d:%2d:%4d.2f\n",tt/60,tt%60,ttt-tt*60.0); setcolor(1%15+1);for(k=0;k<lchrom-1;k++){ix=x[pop[maxpp].chrom[k]];iy=y[pop[maxpp].chrom[k]]+110;jx=x[pop[maxpp].chrom[k+1]];jy=y[pop[maxpp].chrom[k+1]]+110;line(ix,iy,jx,jy);putpixel(ix,iy,RED);}ix=x[pop[maxpp].chrom[0]];iy=y[pop[maxpp].chrom[0]]+110;jx=x[pop[maxpp].chrom[lchrom-1]];jy=y[pop[maxpp].chrom[lchrom-1]]+110; line(ix,iy,jx,jy); putpixel(jx,jy,RED);setcolor(11);outtextxy(ix,iy,"*");setcolor(12);for(k=0;k<1%200;k++){ix=k+280;iy=366-fm[k]/3;jx=ix+1;jy=366-fm[k+1]/3;line(ix,iy,jx,jy);putpixel(ix,iy,RED);}printf("GEN:%3d",l);printf("Minpath:%f Maxfit:%f",pop[maxpp].x,pop[maxpp].fitness); printf("Clock:%2d:%2d:%4.2f\n",tt/60,tt%60,ttt-tt*60.0);}/*###############*/float decode(unsigned char *pp) {int j,k,l;float tt;tt=dd[pp[0]*lchrom+pp[lchrom-1]]; for(j=0;j<lchrom-1;j++){tt=tt+dd[pp[j]*lchrom+pp[j+1]];} l=0;for(k=0;k<lchrom-1;k++)for(j=k+1;j<lchrom;j++){if(pp[j]==pp[k])l++;}return tt+4*l*maxdd;}/*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%*/ void crtinit(){int driver,mode;struct palettetype p;driver=DETECT;mode=0;initgraph(&driver,&mode,""); cleardevice();}/*$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$*/ int select(){double rand1,partsum; float r1;int j;partsum=0.0;j=0;rand1=random1()*sumfitness; do{partsum=partsum+oldpop[j].fitness;j=j+1;}while((partsum<rand1)&&(j<popsize));return j-1;}/*$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$*/int crossover(unsigned char *parent1,unsigned char *parent2,int k5) {int k,j,mutate,i1,i2,j5;int j1,j2,j3,s0,s1,s2; unsigned charjj,ts1[maxstring],ts2[maxstring];float f1,f2;s0=0;s1=0;s2=0;if(flip(pcross)){jcross=random(lchrom-1); j5=random(lchrom-1); ncross=ncross+1;if(jcross>j5){k=jcross;jcross=j5;j5=k;}}else jcross=lchrom; if(jcross!=lchrom) {s0=1;k=0;for(j=jcross;j<j5;j++) {ts1[k]=parent1[j]; ts2[k]=parent2[j]; k++; }j3=k;for(j=0;j<lchrom;j++) {j2=0;while((parent2[j]!=ts1[j2])&&(j2<k)){j2++;}if(j2==k){ts1[j3]=parent2[j];j3++;}}j3=k;for(j=0;j<lchrom;j++){j2=0;while((parent1[j]!=ts2[j2])&&(j2<k)){j2++;}if(j2==k){ts2[j3]=parent1[j];j3++;}}for(j=0;j<lchrom;j++){newpop[k5].chrom[j]=ts1[j];newpop[k5+1].chrom[j]=ts2[j]; }}else{for(j=0;j<lchrom;j++){newpop[k5].chrom[j]=parent1[j]; newpop[k5+1].chrom[j]=parent2[j]; } mutate=flip(pmutation);if(mutate){s1=1;nmutation=nmutation+1;for(j3=0;j3<200;j3++){j1=random(lchrom);j=random(lchrom);jj=newpop[k5].chrom[j];newpop[k5].chrom[j]=newpop[k5].chrom[j1];newpop[k5].chrom[j1]=jj;}}mutate=flip(pmutation);if(mutate){s2=1;nmutation=nmutation+1;for(j3=0;j3<100;j3++){j1=random(lchrom);j=random(lchrom);jj=newpop[k5+1].chrom[j];newpop[k5+1].chrom[j]=newpop[k5+1].chrom[j1];newpop[k5+1].chrom[j1]=jj;}}}j2=random(2*lchrom/3);for(j=j2;j<j2+lchrom/3-1;j++)for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++){if(k==j)continue;if(k>j){i2=k;i1=j;}else{i1=k;i2=j;}f1=dd[lchrom*newpop[k5].chrom[i1]+newpop[k5].chrom[i2]]; f1=f1+dd[lchrom*newpop[k5].chrom[(i1+1)%lchrom]+newpop[k5].chrom[(i2+1)%lchrom]];f2=dd[lchrom*newpop[k5].chrom[i1]+newpop[k5].chrom[(i1+1)%lchrom]];f2=f2+dd[lchrom*newpop[k5].chrom[i2]+newpop[k5].chrom[(i2+1)%lchrom]];if(f1<f2){inversion(i1,i2,newpop[k5].chrom);}}j2=random(2*lchrom/3);for(j=j2;j<j2+lchrom/3-1;j++)for(k=0;k<lchrom;k++){if(k==j)continue;if(k>j){i2=k;i1=j;}else{i1=k;i2=j;}f1=dd[lchrom*newpop[k5+1].chrom[i1]+newpop[k5+1].chrom[i2]];f1=f1+dd[lchrom*newpop[k5+1].chrom[(i1+1)%lchrom]+newpop[k5+1].chrom[(i2+1)%lchrom]];f2=dd[lchrom*newpop[k5+1].chrom[i1]+newpop[k5+1].chrom[(i1+1)%lchrom]];f2=f2+dd[lchrom*newpop[k5+1].chrom[i2]+newpop[k5+1].chrom[(i2+1)%lchrom]];if(f1<f2){inversion(i1,i2,newpop[k5+1].chrom);} }return 1;}/*$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$*/void inversion(unsigned int k,unsigned int j,unsigned char *ss) {unsigned int l1,i;unsigned char tt;l1=(j-k)/2;for(i=0;i<l1;i++){tt=ss[k+i+1];ss[k+i+1]=ss[j-i];ss[j-i]=tt;}}/*%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%*/void randomize1(){int i;randomize();for(i=0;i<lchrom;i++) oldrand[i]=random(30001)/30000.0;jrand=0;}/*%%%%%%%%%%%*/float random1(){jrand=jrand+1;if(jrand>=lchrom){jrand=0;randomize1();}return oldrand[jrand]; }/*%%%%%%%%%%*/int flip(float probability) {float ppp;ppp=random(20001)/20000.0; if(ppp<=probability)return 1; return 0;}%TSP问题(又名:旅行商问题,货郎担问题)遗传算法通用matlab程序 %D是距离矩阵,n为种群个数,建议取为城市个数的1~2倍, %C为停止代数,遗传到第 C 代时程序停止,C的具体取值视问题的规模和耗费的时间而定%m为适应值归一化淘汰加速指数 ,最好取为1,2,3,4 ,不宜太大 %alpha为淘汰保护指数,可取为0~1之间任意小数,取1时关闭保护功能,最好取为0.8~1.0 %R为最短路径,Rlength为路径长度function [R,Rlength]=geneticTSP(D,n,C,m,alpha)[N,NN]=size(D);farm=zeros(n,N);%用于存储种群for i=1:nfarm(i,:)=randperm(N);%随机生成初始种群endR=farm(1,:);%存储最优种群len=zeros(n,1);%存储路径长度fitness=zeros(n,1);%存储归一化适应值counter=0;while counter<Cfor i=1:nlen(i,1)=myLength(D,farm(i,:));%计算路径长度endmaxlen=max(len);minlen=min(len);fitness=fit(len,m,maxlen,minlen);%计算归一化适应值rr=find(len==minlen);R=farm(rr(1,1),:);%更新最短路径FARM=farm;%优胜劣汰,nn记录了复制的个数nn=0;for i=1:nif fitness(i,1)>=alpha*rand nn=nn+1;FARM(nn,:)=farm(i,:);endendFARM=FARM(1:nn,:);[aa,bb]=size(FARM);%交叉和变异while aa<nif nn<=2nnper=randperm(2);elsennper=randperm(nn);endA=FARM(nnper(1),:);B=FARM(nnper(2),:);[A,B]=intercross(A,B); FARM=[FARM;A;B]; [aa,bb]=size(FARM);endif aa>nFARM=FARM(1:n,:);%保持种群规模为nendfarm=FARM;clear FARMcounter=counter+1endRlength=myLength(D,R);function [a,b]=intercross(a,b) L=length(a); if L<=10%确定交叉宽度W=1;elseif ((L/10)-floor(L/10))>=rand&&L>10W=ceil(L/10);elseW=floor(L/10);endp=unidrnd(L-W+1);%随机选择交叉范围,从p到p+W for i=1:W%交叉x=find(a==b(1,p+i-1)); y=find(b==a(1,p+i-1)); [a(1,p+i-1),b(1,p+i-1)]=exchange(a(1,p+i-1),b(1,p+i-1));[a(1,x),b(1,y)]=exchange(a(1,x),b(1,y));endfunction [x,y]=exchange(x,y) temp=x;x=y;y=temp;% 计算路径的子程序function len=myLength(D,p) [N,NN]=size(D);len=D(p(1,N),p(1,1)); for i=1:(N-1)len=len+D(p(1,i),p(1,i+1));end%计算归一化适应值子程序function fitness=fit(len,m,maxlen,minlen) fitness=len;for i=1:length(len)fitness(i,1)=(1-((len(i,1)-minlen)/(maxlen-minlen+0.000001))).^m;end。

package GA;import java.util.*;public class Tsp {private String cityName[]={"北京","上海","天津","重庆","哈尔滨","长春","沈阳","呼和浩特","石家庄","太原","济南","郑州","西安","兰州","银川","西宁","乌鲁木齐","合肥","南京","杭州","长沙","南昌","武汉","成都","贵州","福建","台北","广州","海口","南宁","昆明","拉萨","香港","澳门"};//private String cityEnd[]=new String[34];private int cityNum=cityName.length; //城市个数private int popSize = 50; //种群数量private int maxgens = 20000; //迭代次数private double pxover = 0.8; //交叉概率private double pmultation = 0.05; //变异概率private long[][] distance = new long[cityNum][cityNum];private int range = 2000; //用于判断何时停止的数组区间private class genotype {int city[] = new int[cityNum]; //单个基因的城市序列long fitness; //该基因的适应度double selectP; //选择概率double exceptp; //期望概率int isSelected; //是否被选择}private genotype[] citys = new genotype[popSize];/*** 构造函数,初始化种群*/public Tsp() {for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++) {citys[i] = new genotype();int[] num = new int[cityNum];for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++)num[j] = j;int temp = cityNum;for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {int r = (int) (Math.random() * temp);citys[i].city[j] = num[r];num[r] = num[temp - 1];temp--;}citys[i].fitness = 0;citys[i].selectP = 0;citys[i].exceptp = 0;citys[i].isSelected = 0;}initDistance();}/*** 计算每个种群每个基因个体的适应度,选择概率,期望概率,和是否被选择。

//遗传算法解决简单TSP问题,(VC6.0)//一、定义头文件(defines.h)#ifndef DEFINES_H#define DEFINES_H///////////////////////////////// DEFINES /////////////////////////////////////// //窗口定义大小#define WINDOW_WIDTH 500#define WINDOW_HEIGHT 500//城市数量及城市在窗口显示的大小#define NUM_CITIES 20#define CITY_SIZE 5//变异概率,交叉概率及种群数量#define MUTATION_RATE 0.2#define CROSSOVER_RATE 0.75#define POP_SIZE 40//倍数#define NUM_BEST_TO_ADD 2//最小容许误差#define EPSILON 0.000001#endif//二、一些用得到的小函数(utils.h)// utils.h: interface for the Cutils class.//头文件名//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////#ifndef UTILS_H#define UTILS_H#include <stdlib.h>#include <math.h>#include <sstream>#include <string>#include <iostream>using namespace std;//--------定义一些随机函数--------//----定义随机整数,随机[x,y]之间的整数---inline int RandInt(int x, int y){return rand()%(y-x+1)+x;}//--------------随机产生0到1之间的小数----------inline float RandFloat(){return rand()/(RAND_MAX + 1.0);}//-----------------随机产生0和1-------------inline bool RandBool(){if (RandInt(0,1))return true;elsereturn false;}//-----定义一些方便的小功能包括:整形转字符型,浮点型转字符型--- string itos(int arg);//converts an float to a std::stringstring ftos (float arg);//限制大小void Clamp(double &arg, double min, double max);void Clamp(int &arg, int min, int max);#endif//三、地图头文件(CmapTSP)#ifndef CMAPTSP_H#define CMAPTSP_H//如果没有定义那么就定义////////////////////////////////////////////////////类名:CmapTSP.h////描述:封装地图数据、城市坐标以及适应度计算。

TSP问题的遗传算法实验报告一、实验题目TSP问题的遗传算法实现二、实验目的1 熟悉和掌握遗传算法的基本概念和基本思想;2 加深对遗传算法的理解,理解和掌握遗传算法的各个操作算子;3 理解和掌握利用遗传算法进行问题求解的基本技能。
三、实验要求1 以10/个城市结点的TSP问题为例,用遗传算法加以求解;2 掌握遗传算法的基本原理、各个遗传操作和算法步骤;3能求出问题最优解,若得不出最优解,请分析原因;4要求界面显示每次迭代求出的局部最优解和最终求出的全局最优解。
四、实验代码Main函数%% 连续Hopfield神经网络的优化—旅行商问题优化计算% function main%% 清空环境变量、定义全局变量clear allclcglobal A D%% 导入城市位置load city_location%% 计算相互城市间距离distance=dist(citys,citys');%% 初始化网络N=size(citys,1);A=200;D=100;U0=0.1;step=0.0001;delta=2*rand(N,N)-1;U=U0*log(N-1)+delta;V=(1+tansig(U/U0))/2;iter_num=10000;E=zeros(1,iter_num);%% 寻优迭代for k=1:iter_num% 动态方程计算dU=diff_u(V,distance);% 输入神经元状态更新U=U+dU*step;% 输出神经元状态更新V=(1+tansig(U/U0))/2;% 能量函数计算e=energy(V,distance);E(k)=e;end%% 判断路径有效性[rows,cols]=size(V);V1=zeros(rows,cols);[V_max,V_ind]=max(V);for j=1:colsV1(V_ind(j),j)=1;endC=sum(V1,1);R=sum(V1,2);flag=isequal(C,ones(1,N)) & isequal(R',ones(1,N));%% 结果显示if flag==1% 计算初始路径长度sort_rand=randperm(N);citys_rand=citys(sort_rand,:);Length_init=dist(citys_rand(1,:),citys_rand(end,:)');for i=2:size(citys_rand,1)Length_init=Length_init+dist(citys_rand(i-1,:),citys_rand(i,:)');end% 绘制初始路径figure(1)plot([citys_rand(:,1);citys_rand(1,1)],[citys_rand(:,2);citys_rand(1,2)],'o-') for i=1:length(citys)text(citys(i,1),citys(i,2),[' ' num2str(i)])endtext(citys_rand(1,1),citys_rand(1,2),[' 起点' ])text(citys_rand(end,1),citys_rand(end,2),[' 终点' ])title(['优化前路径(长度:' num2str(Length_init) ')'])axis([0 1 0 1])grid onxlabel('城市位置横坐标')ylabel('城市位置纵坐标')% 计算最优路径长度[V1_max,V1_ind]=max(V1);citys_end=citys(V1_ind,:);Length_end=dist(citys_end(1,:),citys_end(end,:)');for i=2:size(citys_end,1)Length_end=Length_end+dist(citys_end(i-1,:),citys_end(i,:)');enddisp('最优路径矩阵');V1% 绘制最优路径figure(2)plot([citys_end(:,1);citys_end(1,1)],...[citys_end(:,2);citys_end(1,2)],'o-')for i=1:length(citys)text(citys(i,1),citys(i,2),[' ' num2str(i)])endtext(citys_end(1,1),citys_end(1,2),[' 起点' ])text(citys_end(end,1),citys_end(end,2),[' 终点' ])title(['优化后路径(长度:' num2str(Length_end) ')'])axis([0 1 0 1])grid onxlabel('城市位置横坐标')ylabel('城市位置纵坐标')% 绘制能量函数变化曲线figure(3)plot(1:iter_num,E);ylim([0 2000])title(['能量函数变化曲线(最优能量:' num2str(E(end)) ')']);xlabel('迭代次数');ylabel('能量函数');elsedisp('寻优路径无效');end% %=========================================== % function du=diff_u(V,d)% global A D% n=size(V,1);% sum_x=repmat(sum(V,2)-1,1,n);% sum_i=repmat(sum(V,1)-1,n,1);% V_temp=V(:,2:n);% V_temp=[V_temp V(:,1)];% sum_d=d*V_temp;% du=-A*sum_x-A*sum_i-D*sum_d;% %========================================== % function E=energy(V,d)% global A D% n=size(V,1);% sum_x=sumsqr(sum(V,2)-1);% sum_i=sumsqr(sum(V,1)-1);% V_temp=V(:,2:n);% V_temp=[V_temp V(:,1)];% sum_d=d*V_temp;% sum_d=sum(sum(V.*sum_d));% E=0.5*(A*sum_x+A*sum_i+D*sum_d);diff_u函数% % % % 计算dufunction du=diff_u(V,d)global A Dn=size(V,1);sum_x=repmat(sum(V,2)-1,1,n);sum_i=repmat(sum(V,1)-1,n,1);V_temp=V(:,2:n);V_temp=[V_temp V(:,1)];sum_d=d*V_temp;du=-A*sum_x-A*sum_i-D*sum_d;Energy函数% % % % % 计算能量函数function E=energy(V,d)global A Dn=size(V,1);sum_x=sumsqr(sum(V,2)-1);sum_i=sumsqr(sum(V,1)-1);V_temp=V(:,2:n);V_temp=[V_temp V(:,1)];sum_d=d*V_temp;sum_d=sum(sum(V.*sum_d));E=0.5*(A*sum_x+A*sum_i+D*sum_d);五、实验结果(图一、最优路径矩阵)(图二、优化前路线)(图三、优化后路线)(图三、能量函数)。

用遗传算法求解中国34个省会TSP问题一、TSP问题的描述旅行商问题(TSP)可以具体描述为:已知n个城市之间的相互距离,现有一个推销员从某一个城市出发,必须遍访这n个城市,并且每个城市只能访问一次,最后又必须返回到出发城市,如何安排他对这些城市的访问次序,可使其旅行路线的总长度最短。
现给出中国34个省会数据,要求基于此数据使用遗传算法解决该TSP问题。
中国34省会位置city =1.西藏2.云南3.四川4.青海5.宁夏6.甘肃7.内蒙古8.黑龙江9.吉林10.辽宁 11.北京 12天津 13.河北 14.山东 15.河南 16.山西 17.陕西18.安徽 19.江苏20.上海 21.浙江 22.江西 23.湖北 24.湖南 25.贵州 26.广西27.广东28.福建 29.海南 30.澳门 31.香港 32.台湾 33.重庆 34.新疆像素坐标如下:Columns 1 through 11100 187 201 187 221 202 258 352 346 336 290 211 265 214 158 142 165 121 66 85 106 127 Columns 12 through 22297 278 296 274 265 239 302 316 334 325 293 135 147 158 177 148 182 203 199 206 215 233 Columns 23 through 33280 271 221 233 275 322 250 277 286 342 220 216 238 253 287 285 254 315 293 290 263 226 Column 34 104 77二、遗传算法的介绍2.1 遗传算法遗传算法的基本原理是通过作用于染色体上的基因寻找好的染色体来求解问题,它需要对算法所产生的每个染色体进行评价,并基于适应度值来选择染色体,使适应性好的染色体有更多的繁殖机会,在遗传算法中,通过随机方式产生若干个所求解问题的数字编码,即染色体,形成初始种群;通过适应度函数给每个个体一个数值评价,淘汰低适应度的个体,选择高适应度的个体参加遗传操作,经过遗产操作后的个体集合形成下一代新的种群,对这个新的种群进行下一轮的进化。

课程实验报告1.实验目的利用遗传算法获得TSP问题的近似解。
2.实验要求要求学生了解遗传算法解决问题的基本流程。
对TSP问题有所了解,知道TSP 问题的难点在什么地方,如何使用遗传算法来获得一个较好的近似解。
3.实验内容已知n个城市之间的相互距离,现有一个推销员必须遍访这n个城市,并且每个城市只能访问一次,最后又必须返回出发城市。
如何安排他对这些城市的访问次序,可使其旅行路线的总长度最短?用图论的术语来说,假设有一个图g=(v,e),其中v是顶点集,e是边集,设d=(dij)是由顶点i和顶点j之间的距离所组成的距离矩阵,旅行商问题就是求出一条通过所有顶点且每个顶点只通过一次的具有最短距离的回路。
4.实验软硬件环境基本Windows系统基本运行环境,VS20125.实验方案(1)遗传算法是模拟达尔文生物进化论的自然选择和遗传学机理的生物进化过程的计算模型,是一种通过模拟自然进化过程搜索最优解的方法遗传算法的基本运算过程如下:a)初始化:设置进化代数计数器t=0,设置最大进化代数T,随机生成M个个体作为初始群体P(0)。
b)个体评价:计算群体P(t)中各个个体的适应度。
c)选择运算:将选择算子作用于群体。
选择的目的是把优化的个体直接遗传到下一代或通过配对交叉产生新的个体再遗传到下一代。
选择操作是建立在群体中个体的适应度评估基础上的。
d)交叉运算:将交叉算子作用于群体。
所谓交叉是指把两个父代个体的部分结构加以替换重组而生成新个体的操作。
遗传算法中起核心作用的就是交叉算子。
e)变异运算:将变异算子作用于群体。
即是对群体中的个体串的某些基因座上的基因值作变动。
群体P(t)经过选择、交叉、变异运算之后得到下一代群体P(t 1)。
f)终止条件判断:若t=T,则以进化过程中所得到的具有最大适应度个体作为最优解输出,终止计算。
(2)用遗传算法模拟TSP问题TSP问题及旅行商问题,假设有一个旅行商人要拜访n个城市,他必须选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。
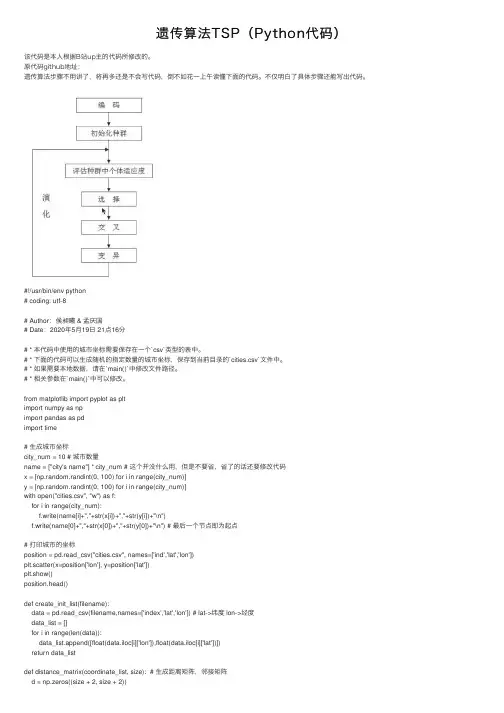
遗传算法TSP(Python代码)该代码是本⼈根据B站up主的代码所修改的。
原代码github地址:遗传算法步骤不⽤讲了,将再多还是不会写代码,倒不如花⼀上午读懂下⾯的代码。
不仅明⽩了具体步骤还能写出代码。
#!/usr/bin/env python# coding: utf-8# Author:侯昶曦 & 孟庆国# Date:2020年5⽉19⽇ 21点16分# * 本代码中使⽤的城市坐标需要保存在⼀个`csv`类型的表中。
# * 下⾯的代码可以⽣成随机的指定数量的城市坐标,保存到当前⽬录的`cities.csv`⽂件中。
# * 如果需要本地数据,请在`main()`中修改⽂件路径。
# * 相关参数在`main()`中可以修改。
from matplotlib import pyplot as pltimport numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport time# ⽣成城市坐标city_num = 10 # 城市数量name = ["city's name"] * city_num # 这个并没什么⽤,但是不要省,省了的话还要修改代码x = [np.random.randint(0, 100) for i in range(city_num)]y = [np.random.randint(0, 100) for i in range(city_num)]with open("cities.csv", "w") as f:for i in range(city_num):f.write(name[i]+","+str(x[i])+","+str(y[i])+"\n")f.write(name[0]+","+str(x[0])+","+str(y[0])+"\n") # 最后⼀个节点即为起点# 打印城市的坐标position = pd.read_csv("cities.csv", names=['ind','lat','lon'])plt.scatter(x=position['lon'], y=position['lat'])plt.show()position.head()def create_init_list(filename):data = pd.read_csv(filename,names=['index','lat','lon']) # lat->纬度 lon->经度data_list = []for i in range(len(data)):data_list.append([float(data.iloc[i]['lon']),float(data.iloc[i]['lat'])])return data_listdef distance_matrix(coordinate_list, size): # ⽣成距离矩阵,邻接矩阵d = np.zeros((size + 2, size + 2))for i in range(size + 1):x1 = coordinate_list[i][0]y1 = coordinate_list[i][1]for j in range(size + 1):if (i == j) or (d[i][j] != 0):continuex2 = coordinate_list[j][0]y2 = coordinate_list[j][1]distance = np.sqrt((x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2)if (i == 0): # 起点与终点是同⼀城市d[i][j] = d[j][i] = d[size + 1][j] = d[j][size + 1] = distanceelse:d[i][j] = d[j][i] = distancereturn ddef path_length(d_matrix, path_list, size): # 计算路径长度length = 0for i in range(size + 1):length += d_matrix[path_list[i]][path_list[i + 1]]return lengthdef shuffle(my_list):#起点和终点不能打乱temp_list=my_list[1:-1]np.random.shuffle(temp_list)shuffle_list=my_list[:1]+temp_list+my_list[-1:]return shuffle_listdef product_len_probability(my_list,d_matrix,size,p_num): # population, d, size,p_numlen_list=[] # 种群中每个个体(路径)的路径长度pro_list=[]path_len_pro=[]for path in my_list:len_list.append(path_length(d_matrix,path,size))max_len=max(len_list)+1e-10gen_best_length=min(len_list) # 种群中最优路径的长度gen_best_length_index=len_list.index(gen_best_length) # 最优个体在种群中的索引# 使⽤最长路径减去每个路径的长度,得到每条路径与最长路径的差值,该值越⼤说明路径越⼩ mask_list=np.ones(p_num)*max_len-np.array(len_list)sum_len=np.sum(mask_list) # mask_list列表元素的和for i in range(p_num):if(i==0):pro_list.append(mask_list[i]/sum_len)elif(i==p_num-1):pro_list.append(1)else:pro_list.append(pro_list[i-1]+mask_list[i]/sum_len)for i in range(p_num):# 路径列表路径长度概率path_len_pro.append([my_list[i],len_list[i],pro_list[i]])# 返回最优路径最优路径的长度每条路径的概率return my_list[gen_best_length_index],gen_best_length,path_len_prodef choose_cross(population,p_num): # 随机产⽣交配者的索引,越优的染⾊体被选择⼏率越⼤ jump=np.random.random() # 随机⽣成0-1之间的⼩数if jump<population[0][2]:return 0low=1high=p_nummid=int((low+high)/2)# ⼆分搜索# 如果jump在population[mid][2]和population[mid-1][2]之间,那么返回midwhile(low<high):if jump>population[mid][2]:low=midmid=(low+high) // 2elif jump<population[mid-1][2]: # 注意这⾥⼀定是mid-1high=midmid=(low+high) // 2else:return middef product_offspring(size, parent_1, parent_2, pm): # 产⽣后代son = parent_1.copy()product_set = np.random.randint(1, size+1)parent_cross_set=set(parent_2[1:product_set]) # 交叉序列集合cross_complete=1for j in range(1,size+1):if son[j] in parent_cross_set:son[j]=parent_2[cross_complete]cross_complete+=1if cross_complete>product_set:breakif np.random.random() < pm: #变异son=veriation(son,size,pm)return sondef veriation(my_list,size,pm):#变异,随机调换两城市位置ver_1=np.random.randint(1,size+1)ver_2=np.random.randint(1,size+1)while ver_2==ver_1:#直到ver_2与ver_1不同ver_2 = np.random.randint(1, size+1)my_list[ver_1],my_list[ver_2]=my_list[ver_2],my_list[ver_1]return my_listdef main(filepath, p_num, gen, pm):start = time.time()coordinate_list=create_init_list(filepath)size=len(coordinate_list)-2 # 除去了起点和终点d=distance_matrix(coordinate_list,size) # 各城市之间的邻接矩阵path_list=list(range(size+2)) # 初始路径# 随机打乱初始路径以建⽴初始种群路径population = [shuffle(path_list) for i in range(p_num)]# 初始种群population以及它的最优路径和最短长度gen_best,gen_best_length,population=product_len_probability(population,d,size,p_num)# 现在的population中每⼀元素有三项,第⼀项是路径,第⼆项是长度,第三项是使⽤时转盘的概率 son_list = [0] * p_num # 后代列表best_path=gen_best # 最好路径初始化best_path_length=gen_best_length # 最好路径长度初始化every_gen_best=[gen_best_length] # 每⼀代的最优值for i in range(gen): #迭代gen代son_num=0while son_num < p_num: # 循环产⽣后代,⼀组⽗母亲产⽣两个后代father_index = choose_cross(population, p_num) # 获得⽗母索引mother_index = choose_cross(population, p_num)father = population[father_index][0] # 获得⽗母的染⾊体mother = population[mother_index][0]son_list[son_num] = product_offspring(size, father, mother, pm) # 产⽣后代加⼊到后代列表中 son_num += 1if son_num == p_num:breakson_list[son_num] = product_offspring(size, mother, father, pm) # 产⽣后代加⼊到后代列表中 son_num += 1# 在新⼀代个体中找到最优路径和最优值gen_best, gen_best_length,population = product_len_probability(son_list,d,size,p_num)if(gen_best_length < best_path_length): # 这⼀代的最优值⽐有史以来的最优值更优best_path=gen_bestbest_path_length=gen_best_lengthevery_gen_best.append(gen_best_length)end = time.time()print(f"迭代⽤时:{(end-start)}s")print("史上最优路径:", best_path, sep=" ")#史上最优路径print("史上最短路径长度:", best_path_length, sep=" ")#史上最优路径长度# 打印各代最优值和最优路径x = [coordinate_list[point][0] for point in best_path] # 最优路径各节点经度y = [coordinate_list[point][1] for point in best_path] # 最优路径各节点纬度plt.figure(figsize=(8, 10))plt.subplot(211)plt.plot(every_gen_best) # 画每⼀代中最优路径的路径长度 plt.subplot(212)plt.scatter(x,y) # 画点plt.plot(x,y) # 画点之间的连线plt.grid() # 给画布添加⽹格plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__':filepath = r'cities.csv' # 城市坐标数据⽂件p_num = 200 #种群个体数量gen = 1000 #进化代数pm = 0.1 #变异率main(filepath, p_num, gen, pm)运⾏结果:迭代⽤时:3.543527126312256s史上最优路径: [0, 8, 1, 9, 7, 5, 4, 3, 2, 6, 10]史上最短路径长度: 303.83238696200436。

TSP问题的遗传算法求解方案算法的软件实现4.1 开发环境介绍本文中的所有算法是在Visual C++ 6.0 的操作平台上进行开发的,并结合STL进行编程。
1、Visual C++ 6.0简介Visual C++ 6.0 是微软公司最新出品的功能最为强大的可视化开放工具,是计算机界公认的最优秀的应用开发工具之一。
Microsoft的基本类库使得开发Windows应用程序比以往任何时候都要容易。
Visual C++作为一种程序设计语言,它同时也是一个集成开发工具,提供了软件代码自动生成和可视化的资源编辑功能。
2、Visual C++ 6.0的优势(1).拥有强大的编辑环境。
(2).拥有强大的类库的支持。
(3).拥有强大的调试环境。
(4).拥有较强的低层控制能力。
(5).拥有强大的帮助系统MSDN的支持。
(6).拥有一个高效的编译器,产生的可执行文件体积小巧、运行速度快。
3、STL简介STL(Standard Template Library),即标准模板库,是一个具有工业强度的,高效的C++程序库。
它被容纳于C++标准程序库(C++ Standard Library)中,是ANSI /ISO C++标准中最新的也是极具革命性的一部分。
该库包含了诸多在计算机科学领域里所常用的基本数据结构和基本算法。
为广大C++程序员们提供了一个可扩展的应用框架,高度体现了软件的可复用性。
这种现象有些类似于Microsoft Visual C++中的MFC(Microsoft Foundation Class Library),或者是Borland C++ Builder中的VCL (Visual Component Library),但是它比二者具有更强的优势。
更加值得一提的是,它具备以下几个区别于其它软件库的优点:(1).经过类属编程方法精心组织的,可互换的编程模块能够提供比传统组件设图4.1 遗传算法解TSP的具体流程图计方法丰富得多的组合方式。

用模拟退火算法或者遗传算法解决TSP问题程序用模拟退火算法、遗传算法(或蚁群算法)求解10城市的TSP (旅行商)问题,计算旅行封闭的最短旅行距离。
解:用遗传算法解决TSP 问题,首先需要确定城市个数及城市间的距离,随机产生城市序列作为一个个体,确定目标函数,通过遗传算法的复制、交叉、变异求出最优解。
目标函数f x = d i ,i +1 +d (n ,0)n i =0适应度函数F x = ?f x +C max f x <="" p="">遗传算法的步骤为复制+交叉+变异=新一代遗传算法主程序:DG=0.9;MAXDD=100;ZQDX=150;Pc=0.7;Pm=0.01;ZQ=[0 118 1272 2567 1653 2097 1425 1177 3947 1574118 0 1253 2511 1633 2077 1369 1157 3961 15181272 1253 0 1462 380 1490 821 856 3660 3852567 2511 1462 0 922 2335 1562 2165 3995 9331653 1633 380 922 0 1700 1041 1135 3870 4562097 2077 1490 2335 1700 0 2311 920 2170 19201425 1369 821 1562 1041 2311 0 1420 4290 6261177 1157 856 2165 1135 920 1420 0 2870 12903947 3961 3660 3995 3870 2170 4290 2870 0 40901574 1518 385 993 456 1920 626 1290 4090 0];D=size(ZQ,1);EE=CSHZQ(ZQDX,D);disp('初始种群中的一个随机值:')SCXL(EE(1,:));RTH=XLCD(ZQ,EE(1,:));disp('总距离:');disp(num2str(RTH));Q=0;OV=XLCD(ZQ,EE);POV=min(OV);while (Q<maxdd)< p=""> OV=XLCD(ZQ,EE);POV=min(OV);SYD=SHYD(OV);XZ=XUANZE(EE,SYD,DG);XZ=JIAOC(XZ,Pc);XZ=BY(XZ,Pm);XZ=NZ(XZ,ZQ);EE=CCZ(EE,XZ,OV);Q=Q+1;endOV=XLCD(ZQ,EE); [minOV,minInd]=min(OV); disp('最优解:')p=SCXL(EE(minInd(1),:)); disp('总距离:');disp(num2str(OV(minInd(1)))); 初始化全局变量:function EE=CSHZQ(ZQDX,D) EE=zeros(ZQDX,D);for (i=1: ZQDX)EE(i,:)=randperm(D);end适应度函数:function SYD=SHYD(len)SYD=1./len;选择程序:function XZ=XUANZE(EE,SYD,DG)ZQDX =size(EE,1);NSel=max(floor(ZQDX *DG+.5),2);ChrIx=sus(SYD,NSel);XZ=EE(ChrIx,:);function NewChrIx=sus(SYD,Nsel)[Nind,ans]=size(SYD);cumfit=cumsum(SYD);trials=cumfit(Nind)/Nsel*(rand+(0:Nsel-1)');Mf=cumfit(:,ones(1,Nsel));Mt=trials(:,ones(1,Nind))';[NewChrIx,ans]=find(Mt<="Mt);" [ans,shuf]="sort(rand(Nsel,1));</p">NewChrIx=NewChrIx(shuf);交叉:function XZ=JIAOC(XZ,Pc)NSel=size(XZ,1);for (i=1:2:NSel-mod(NSel,2))if (Pc>=rand)[XZ(i,:),XZ(i+1,:)]=ICS(XZ(i,:),XZ(i+1,:));endendICS函数function [a,b]=ICS(a,b)L=length(a);r1=randsrc(1,1,[1:L]);r2=randsrc(1,1,[1:L]);if r1~=r2a0=a;b0=b;s=min([r1,r2]);e=max([r1,r2]);for i=s:ea1=a;b1=b;a(i)=b0(i);b(i)=a0(i);x=find(a==a(i));y=find(b==b(i));i1=x(x~=i);i2=y(y~=i);if ~isempty(i1)a(i1)=a1(i);endif ~isempty(i2)b(i2)=b1(i);endendend变异:function XZ=BY(XZ,Pm) [NSel,L]=size(XZ);for (i=1:NSel)if (Pm>=rand)R=randperm(L);XZ(i,R(1:2))=XZ(i,R(2:-1:1)); endend进化逆转:function XZ=NZ(XZ,ZQ)[row,col]=size(XZ);OV=XLCD(ZQ,XZ);XZ1=XZ;for i=1:rowr1=randsrc(1,1,[1:col]);r2=randsrc(1,1,[1:col]);mininverse=min([r1,r2]);maxinverse=max([r1,r2]);XZ1(1,mininverse:maxinverse)=XZ1(i,maxinverse:-1:mininverse); endOV1=XLCD(ZQ,XZ1);index=OV1<ov;< p="">XZ(index,:)=XZ(index,:);得到新一代:function EE=CCZ(EE,XZ,OV)ZQDX =size(EE,1);NSel=size(XZ,1);[TobjV,index]=sort(OV);EE=[EE(index(1: ZQDX -NSel),:);XZ]; 计算线路长度:function len=XLCD(ZQ,EE)[row,col]=size(ZQ);ZQDX =size(EE,1);len=zeros(ZQDX,1);for (i=1: ZQDX)p=[EE(i,:) EE(i,1)];i1=p(1:end-1);i2=p(2:end);len(i,1)=sum(ZQ ((i1-1)*col+i2)); end输出线路长度:function p=SCXL(R)R=[R,R(1)];N=length(R);p=num2str(R(1));for (i=2:N)p=[p,'->',num2str(R(i))]; enddisp(p)</ov;<></maxdd)<>。
应用遗传算法解决10城市TSP问题的方案设计姓名:学号:2010-12-27一、问题描述××计划近期在北京、天津、武汉、深圳、长沙、成都、杭州、西安、拉萨、南昌10个城市间进行一次自驾周游旅行,为了尽量节省旅行开支,××希望能通过某种方法,找到一条使自驾选择路线里程数最少或相对较少的旅行路线。
对于以上问题,若给定已知10个城市之间的公路里程如表1所示,并要求应用遗传算法编程实现求解,该如何处理?二、算法设计根据任务要求,本文采用遗传算法实现编程求解。
在具体求解之前,还需确定以下几点:编码方法,种群规模,选择算子,交叉概率和变异概率。
①编码方法常用的遗传算法编码方法有:二进制编码、Gray编码、实数编码、有序串编码等。
采用二进制编码在求解中容易导致Hamming悬崖,并且要求给出求解精度以确定位串长度;Gray编码虽然能较好地克服Hamming悬崖,但在进行交叉变异时,交叉和变异位的选择也会使得问题复杂。
综合分析,本文中选择实数编码方法,分别用数字0—9表示北京、天津、武汉、深圳、长沙、成都、杭州、西安、拉萨、南昌10个城市。
图1 代价数组这样,城市间的距离信息就可以用如图1所示二维数组表示:即对于编号分别为a 、b 的两个城市,它们之间的距离在代价数组中表示为元素Cost_table[a][b]的值。
②种群规模遗传算法中,初始种群的生成、选择、交叉以及变异都是随机进行的,因此,对于同一个问题,种群规模的大小将直接影响到算法的进化速度。
这是因为,当种群规模较大时,在每一代中通过交叉、变异产生以往没有出现过的个体的概率会大大增加,这样也会使得在下一代中出现靠近最优解个体的概率增加,再通过合适的选择算法,就能达到加快进化的目的。
本文中选择种群规模为100。
③选择算子最常用的选择算子是“轮盘赌”法,其次还有“确定性”法和最佳个体保存方法。
若采用“轮盘赌”法,则需要计算每个个体被选中的概率1()()()i i N ii F x p x F x ==∑,考虑到本文中种群规模取为100,因此平均每个个体被选中的概率相对较小,实际进行“轮盘赌”效果不一定会很好,本文中不选该方法。
用遗传算法解决TSP问题设计思路:1.初始化城市距离采用以城市编号(i,j=1代表北京,=2代表上海,=3代表天津,=4代表重庆,=5代表乌鲁木齐)为矩阵行列标的方法,输入任意两个城市之间的距离,用矩阵city表示,矩阵中的元素city(i,j)代表第i个城市与第j个城市间的距离。
2.初始化种群通过randperm函数,生成一个一维随机向量(是整数1,2,3,4,5的任意排列),然后将其赋给二维数组group的第一列,作为一个个体。
如此循环N次(本例生成了50个个体),生成了第一代种群,种群的每个个体代表一条路径。
3.计算适应度采用的适应度函数为个体巡回路径的总长度的函数。
具体为adapt(1,i)=(5*maxdis-dis) (1) 在式(1)中,adapt(1,i)表示第i个个体的适应度函数,maxdis为城市间的最大距离,为4077km,dis为个体巡回路径的总长度,这样定义的适应度,当路经越短时适应度值越大。
在适应度值的基础上,给出的计算个体期望复制数的表达式为adaptnum(1,i)=(N* adapt(1,i)/ sumadapt) (2) 其中,sumadapt为种群适应度之和。
4.复制采用优秀个体的大比例保护基础上的随机数复制法。
具体做法为在生成下一代个体时,先将最大适应度对应的路径个体以较大的比例复制到下一代,然后再用随机数复制法生成下一代的其他个体。
其中,有一个问题必须考虑,即若某一次生成的随机数过大,结果能复制一个或极少个样本。
为了避免这一情况,采用了限制措施,即压低了随机数的上限。
5.交叉采用的方法为按步长的单点交叉,为随机选择一对样本,再随机选择一个交叉点位置,按一定的步长进行交叉点的选择。
选择一个步长而不是将其设为1,是因为若某一位置处的城市代码因为进行了交叉而发生了改变,则其经过该处的两个距离都会改变。
这种交叉兼有遗传和变异两方面的作用,因为若交叉点处的城市编号都相同,则对两个个体而言交叉后样本无变化,否则样本有变化。
遗传算法解决TSP问题(C++版)遗传算法流程:交叉,编译,计算适应度,保存最优个体。
其中交叉过程是选择最优的两个染色体进行交叉操作,本文采用的是轮盘赌算法。
#include<iostream>#include<cstdlib>#include<ctime>using namespace std;#define population 200//种群数量#define pc 0.9//交叉的概率#define pm 0.1//变异的概率#define count 200//迭代的次数#define num 10//城市的数量int** city;//存放每个个体的访问顺序int path[10][10] = {//0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9{ 0, 23, 93, 18, 40, 34, 13, 75, 50, 35 },//0{ 23, 0, 75, 4, 72, 74, 36, 57, 36, 22 },//1{ 93, 75, 0, 64, 21, 73, 51, 25, 74, 89 },//2{ 18, 4, 64, 0, 55, 52, 8, 10, 67, 1 }, //3{ 40, 72, 21, 55, 0, 43, 64, 6, 99, 74 }, //4{ 34, 74, 73, 52, 43, 0, 43, 66, 52, 39 },//5{ 13, 36, 51, 8, 64, 43, 0, 16, 57, 94 },//6{ 75, 57, 25, 10, 6, 66, 16, 0, 23, 11 }, //7{ 50, 36, 74, 67, 99, 52, 57, 23, 0, 42 },//8{ 35, 22, 89, 1, 74, 39, 94, 11, 42, 0 }//9};int* dis;//存放每个个体的访问顺序下的路径长度double* fitness;//存放灭个个体的适应度int min_dis = 1000000;int min_index = -1;int* min_path;//初始化种群void init(){int *a = new int[num];for (int i = 0; i<num; i++){a[i] = i;}city = new int*[population];for (int i = 0; i<population; i++){city[i] = new int[num];}for (int i = 0; i<population; i++){for (int j = num - 1; j >= 0; j--){int n = rand() % (j + 1);//产出的数是0-j,保证交换的后面的数不会再被交换swap(a[j], a[n]);//保证a里面全是0-(num-1)的数,无重复的数,只是顺序颠倒city[i][j] = a[j];}}delete[]a;dis = new int[population];fitness = new double[population];min_path = new int[num];}//计算适应度void compute(){//cout << "do compute now. " << endl;double total = 0;for (int i = 0; i<population; i++){//计算每种情况下,路径的长度dis[i] = 0;int a = city[i][0], b;for (int j = 1; j<num; j++){b = city[i][j];dis[i] += path[a][b];a = b;}dis[i] += path[b][city[i][0]];fitness[i] = 1.0 / dis[i];//以距离的倒数作为适应度函数值total += fitness[i];}}//选择适应度高的物种,采用轮盘赌算法int select(){double total = 0;for (int i = 0; i<population; i++){total += fitness[i];}double size = rand() / (double)RAND_MAX * total;//保证//cout << "size " << size << endl;double sum = 0;int i = 0;while (sum <= size&&i<population){sum += fitness[++i];}return --i;//返回被选中的个体}int getMinDis(){int result = dis[0];int index = 0;for (int i = 1; i<population; i++) {if (result > dis[i]){result = dis[i];index = i;}}return index;}int getMaxDis(){int result = dis[0];int index = 0;for (int i = 1; i<population; i++) {if (result < dis[i])result = dis[i];index = i;}}return index;}void save(){int current_min_index = getMinDis();int current_max_index = getMaxDis();if (dis[current_min_index] < min_dis){min_dis = dis[current_min_index];for (int i = 0; i < num; i++){min_path[i] =city[current_min_index][i];}//cout << "current min dis is: " << min_dis << endl;}else{for (int i = 0; i<num; i++){city[current_max_index][i] = min_path[i];}dis[current_max_index] = min_dis;fitness[current_max_index] = 1.0 / min_dis;}}//最优保存算法bool isExist(int value, int* array, int len) {for (int i = 0; i<len; i++){if (value == array[i])return true;}return false;}void convert(int p1, int p2, int* src, int* dst) {int len = p2 - p1 + 1;int* temp = new int[len];for (int i = p1; i <= p2; i++){temp[i - p1] = src[i];}int j = (p2 + 1) % num;for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++){int index = (i + p2) % num;if (!isExist(dst[index], temp, len)){dst[j] = dst[index];j = (j + 1) % num;}}for (int i = p1; i <= p2; i++){dst[i] = src[i];}delete[]temp;}//交叉,采用次序交叉算法void cross(){//cout << "do cross now. " << endl;for (int k = 0; k<population; k += 2){int a = select();int b = select();while (a == b){b = select();//保证被选中的个体不是一样的//cout << "same " << b << endl;}//cout << "choose popuilation " << a << " " << b << endl;double p = rand() / double(RAND_MAX);//cout << "cross rate is " << p << endl;int* a1 = new int[num];int* a2 = new int[num];int* b1 = new int[num];int* b2 = new int[num];for (int i = 0; i<num; i++){a1[i] = city[a][i];a2[i] = city[b][i];b1[i] = a2[i];b2[i] = a1[i];}if (p<pc)//满足交叉条件{//选择交叉的两点,并保证p1<p2int p1 = -1;int p2 = -1;while (p1 == p2){p1 = rand() % num;p2 = rand() % num;if (p1>p2){swap(p1, p2);}}//cout << "choose pos " << p1 << " " << p2 << endl;//开始交叉convert(p1, p2, a1, b1);convert(p1, p2, a2, b2);for (int i = 0; i<num; i++){city[k][i] = b1[i];city[k + 1][i] = b2[i];}}else{for (int i = 0; i<num; i++){city[k][i] = a1[i];city[k + 1][i] = a2[i];}}delete[]a1;delete[]a2;delete[]b1;delete[]b2;}}//变异,采用对换操作进行变异void morphis(){//cout << "do morphis now. " << endl;for (int i = 0; i<population; i++){double p = rand() / double(RAND_MAX);//cout << "morphis rate is " << p << endl;if (p<pm)//执行变异{int a = -1, b = -1;while (a == b){a = rand() % num;b = rand() % num;}swap(city[i][a], city[i][b]);}}}int getdis(){//compute();int result = dis[0];int index = 0;for (int i = 1; i<population; i++){if (result > dis[i]){result = dis[i];index = i;}}return result;}//释放申请的数组的空间void dispose(){for (int i = 0; i<population; i++){delete[]city[i];}delete[]city;delete[]dis;delete[]fitness;}int main(){init();//初始化种群int i = 0;srand(time(0));compute();while (i<count){cross();//交叉morphis();//变异compute();//计算适应度save();//保存当前最优的个体//cout << "count " << i++ << endl;实用文档cout << getdis() << " ";//输出结果//cout << min_index << " ";if (++i % 10 == 0)cout << endl;}compute();cout << "min distance is: " << min_dis << endl;for (int i = 0; i<num; i++)cout << min_path[i] << " ";cout << endl;dispose();//释放空间return 0;}。
遗传算法解决旅行商(TSP)问题旅行商问题(traveling saleman problem,简称tsp):已知N个城市之间的相互距离,现有一个推销员必须遍访这n个城市,并且每个城市只能访问一次,最后又必须返回出发城市。
如何安排他对这些城市的访问次序,可使其旅行路线的总长度最短?本程序使用MATLAB软件,利用遗传算法解决TSP问题。
程序使用如下:gatsp 为主程序,cityNum为城市个数,在此程序中可以设置为30、50和70。
Inn是种群个数,gnmax是最大迭代次数,pc是交叉概率,pm是变异概率。
算法程序运行结果如下:算法程序如下(不同的function需放在不同的.m文件中):注:红色部分不属于算法内容,仅作间隔标致。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------%主程序:%遗传算法求解tspfunction gaTSPCityNum=30;[dislist,Clist]=tsp(CityNum);inn=100; %初始种群大小gnmax=1000; %最大代数pc=0.9; %交叉概率pm=0.08; %变异概率%产生初始种群for i=1:inns(i,:)=randperm(CityNum);end[f,p]=objf(s,dislist);gn=1;while gn<gnmax+1for j=1:2:innseln=sel(s,p); %选择操作scro=cro(s,seln,pc); %交叉操作scnew(j,:)=scro(1,:);scnew(j+1,:)=scro(2,:);smnew(j,:)=mut(scnew(j,:),pm); %变异操作smnew(j+1,:)=mut(scnew(j+1,:),pm);ends=smnew; %产生了新的种群[f,p]=objf(s,dislist); %计算新种群的适应度%记录当前代最好和平均的适应度[fmax,nmax]=max(f);ymean(gn)=1000/mean(f);ymax(gn)=1000/fmax;%记录当前代的最佳个体x=s(nmax,:);drawTSP(Clist,x,ymax(gn),gn,0);gn=gn+1;%pause;endgn=gn-1;figure(2);plot(ymax,'r'); hold on;plot(ymean,'b');grid;title('搜索过程');legend('最优解','平均解');string1=['最终度',num2str(ymax(gn))];gtext(string1);End----------------------------------------------------------------- %交叉程序:function scro=cro(s,seln,pc);bn=size(s,2);pcc=pro(pc); %根据交叉概率决定是否进行交叉操作,1则是,0则否scro(1,:)=s(seln(1),:);scro(2,:)=s(seln(2),:);if pcc==1c1=round(rand*(bn-2))+1; %在[1,bn-1]范围内随机产生一个交叉位c2=round(rand*(bn-2))+1;chb1=min(c1,c2);chb2=max(c1,c2);middle=scro(1,chb1+1:chb2);scro(1,chb1+1:chb2)=scro(2,chb1+1:chb2);scro(2,chb1+1:chb2)=middle;for i=1:chb1while find(scro(1,chb1+1:chb2)==scro(1,i))zhi=find(scro(1,chb1+1:chb2)==scro(1,i));y=scro(2,chb1+zhi);scro(1,i)=y;endwhile find(scro(2,chb1+1:chb2)==scro(2,i))zhi=find(scro(2,chb1+1:chb2)==scro(2,i));y=scro(1,chb1+zhi);scro(2,i)=y;endendfor i=chb2+1:bnwhile find(scro(1,1:chb2)==scro(1,i))zhi=find(scro(1,1:chb2)==scro(1,i));y=scro(2,zhi);scro(1,i)=y;endwhile find(scro(2,1:chb2)==scro(2,i))zhi=find(scro(2,1:chb2)==scro(2,i));y=scro(1,zhi);scro(2,i)=y;endendendEnd----------------------------------------------------------------- %变异程序:function snnew=mut(snew,pm);bn=size(snew,2);snnew=snew;pmm=pro(pm); %根据变异概率决定是否进行变异操作,1则是,0则否if pmm==1c1=round(rand*(bn-2))+1; %在[1,bn-1]范围内随机产生一个变异位c2=round(rand*(bn-2))+1;chb1=min(c1,c2);chb2=max(c1,c2);x=snew(chb1+1:chb2);snnew(chb1+1:chb2)=fliplr(x);endend----------------------------------------------------------------- %适应度计算:function [f,p]=objf(s,dislist);inn=size(s,1); %读取种群大小for i=1:innf(i)=caldist(dislist,s(i,:)); %计算函数值,即适应度endf=1000./f';%计算选择概率fsum=0;for i=1:innfsum=fsum+f(i)^15;endfor i=1:innps(i)=f(i)^15/fsum;end%计算累积概率p(1)=ps(1);for i=2:innp(i)=p(i-1)+ps(i);endp=p';end----------------------------------------------------------------- %选着个体程序:function seln=sel(s,p);inn=size(p,1);%从种群中选择两个个体for i=1:2r=rand; %产生一个随机数prand=p-r;j=1;while prand(j)<0j=j+1;endseln(i)=j; %选中个体的序号endend-----------------------------------------------------------------%城市坐标:function [DLn,cityn]=tsp(n)if n==10city10=[0.4 0.4439;0.2439 0.1463;0.1707 0.2293;0.2293 0.761;0.5171 0.9414;0.8732 0.6536;0.6878 0.5219;0.8488 0.3609;0.6683 0.2536;0.6195 0.2634];%10 cities d'=2.691for i=1:10for j=1:10DL10(i,j)=((city10(i,1)-city10(j,1))^2+(city10(i,2)-city10(j,2))^ 2)^0.5;endendDLn=DL10;cityn=city10;endif n==30city30=[41 94;37 84;54 67;25 62;7 64;2 99;68 58;71 44;54 62;83 69;64 60;18 54;22 60;83 46;91 38;25 38;24 42;58 69;71 71;74 78;87 76;18 40;13 40;82 7;62 32;58 35;45 21;41 26;44 35;4 50];%30 cities d'=423.741 by D B Fogelfor i=1:30for j=1:30DL30(i,j)=((city30(i,1)-city30(j,1))^2+(city30(i,2)-city30(j,2))^ 2)^0.5;endendDLn=DL30;cityn=city30;endif n==50city50=[31 32;32 39;40 30;37 69;27 68;37 52;38 46;31 62;30 48;21 47;25 55;16 57;17 63;42 41;17 33;25 32;5 64;8 52;12 42;7 38;5 25; 10 77;45 35;42 57;32 22;27 23;56 37;52 41;49 49;58 48;57 58;39 10;46 10;59 15;51 21;48 28;52 33;58 27;61 33;62 63;20 26;5 6;13 13;21 10;30 15;36 16;62 42;6369;52 64;43 67];%50 cities d'=427.855 by D B Fogelfor i=1:50for j=1:50DL50(i,j)=((city50(i,1)-city50(j,1))^2+(city50(i,2)-city50(j,2))^ 2)^0.5;endendDLn=DL50;cityn=city50;endif n==75city75=[48 21;52 26;55 50;50 50;41 46;51 42;55 45;38 33;33 34;45 35;40 37;50 30;55 34;54 38;26 13;15 5;21 48;29 39;33 44;15 19;16 19;12 17;50 40;22 53;21 36;20 30;26 29;40 20;36 26;62 48;67 41;62 35;65 27;62 24;55 20;35 51;30 50;45 42;21 45;36 6;6 25;11 28;26 59;30 60;22 22;27 24;30 20;35 16;54 10;50 15;44 13;35 60;40 60;40 66;31 76;47 66;50 70;57 72;55 65;2 38;7 43;9 56;15 56;10 70;17 64;55 57;62 57;70 64;64 4;59 5;50 4;60 15;66 14;66 8;43 26];%75 cities d'=549.18 by D B Fogelfor i=1:75for j=1:75DL75(i,j)=((city75(i,1)-city75(j,1))^2+(city75(i,2)-city75(j,2))^ 2)^0.5;endendDLn=DL75;cityn=city75;endend----------------------------------------------------------------- %根据交叉概率决定是否进行交叉操作:function pcc=pro(pc);test(1:100)=0;l=round(100*pc);test(1:l)=1;n=round(rand*99)+1;pcc=test(n);end----------------------------------------------------------------- %计算城市距离矩阵:function F=caldist(dislist,s)distan=0;n=size(s,2);for i=1:n-1distan=distan+dislist(s(i),s(i+1));enddistan=distan+dislist(s(n),s(1));F=distan;----------------------------------------------------------------- %作图:function m=drawTSP(Clist,BSF,bsf,p,f)CityNum=size(Clist,1);for i=1:CityNum-1plot([Clist(BSF(i),1),Clist(BSF(i+1),1)],[Clist(BSF(i),2),Clist(B SF(i+1),2)],'ms-','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','MarkerFace Color','g');hold on;endplot([Clist(BSF(CityNum),1),Clist(BSF(1),1)],[Clist(BSF(CityNum), 2),Clist(BSF(1),2)],'ms-','LineWidth',2,'MarkerEdgeColor','k','Ma rkerFaceColor','g');title([num2str(CityNum),'城市TSP']);if f==0text(1.5,1.5,['第',int2str(p),' 步',' 最短距离为',num2str(bsf)]);elsetext(1,1,['最终搜索结果:最短距离 ',num2str(bsf)]);endhold off;pause(0.05)-----------------------------------------------------------------。
遗传算法解决10个城市TSP问题姓名:方震学号:S2******* 一﹑问题描述10个城市的坐标如下:该问题的理论解为2.6907.二﹑方案设计1.编码及初始化种群以城市号编码,随机产生得到初始种群,利用randperm(城市数)函数产生,例如:6 7 4 9 5 3 2 8 10 12.计算适应度直接计算每条染色体(路径)的长度,取倒数为适应度。
3.轮盘赌选择4.交叉——常规交配法(CM)设有父代1和父代2,随机选择一个交配位,子代1交配位之前的基因为父代1交配位之前的基因,交配位之后的基因,从父代2中按顺序选择那些没有出现过的基因,子代2也做类似的处理,例如(|为交配位):父代1: 1 2 3 4|5 6 7 8父代2: 5 2 1 7|3 8 4 6子代1: 1 2 3 4|5 7 8 6子代2: 5 2 1 7|3 4 6 85.变异随机选择一条染色体中两个基因进行交换,例如,随机选择两个位置如3和7则:6 7 4 9 5 3 2 8 10 1→6 7 2 9 5 3 4 8 10 16.更新种群将本代中初始种群s和变异后得到的种群s3合并为A,更新的种群s’中一半来自A中最优秀的,其余一半来自A中除了被选走的最优秀的,其他基因的随机。
三﹑结果输出与统计程序输出结果如下:》myGA近似最近路径为: 5 4 2 1 10 9 8 7 6 3近似最小路程为: 2.6907运行几次后输出表格:附录:源代码●distance.mfunction [distan] = distance(coord)m=length(coord);distan=zeros(m);for i=1:mfor j=i:mdistan(i,j)=(sum((coord(:,i)-coord(:,j)).^2))^0.5; distan(j,i)=distan(i,j);endend●fit.mfunction [ f,g,p ] = fit(s,distan)[inn,m]=size(s);f=zeros(1,inn);g=zeros(1,inn);p=zeros(1,inn);fsum=0;for i=1:inn;for j=2:m;g(i)=g(i)+distan(s(i,j-1),s(i,j));endg(i)=g(i)+distan(s(i,m),s(i,1));f(i)=1/g(i);endfsum=sum(f);for i=1:inn;p(i)=f(i)/fsum;endend●select.mfunction[s1]=select(s,p)pl=length(p);sel=zeros(1,pl);pr=rand(1,pl);for i=1:plsump=0;j=ceil(pl*rand);while sump<pr(i);sump=sump+p(mod(j-1,pl)+1);j=j+1;endsel(i)=mod(j-2,pl)+1;s1(i,:)=s(sel(i),:);end●cross.mfunction [s2] = cross(s1,pcross)[inn,m]=size(s1);s11=zeros(inn,m);s12=zeros(inn,m);l=zeros(1,m);for i=1:inn;if rand<=pcrosss11(i,:)=s1(i,:);l(i)=1;elses12(i,:)=s1(i,:);l(i)=0;endendif mod(sum(l),2)==1i=0;while i==0j=ceil(m*rand);i=l(j);endl(j)=0;s12(j,:)=s11(j,:);s11(j,:)=zeros(1,m);ends11(all(s11==0,2),:)=[];s12(all(s12==0,2),:)=[];[u,v]=size(s11);if u==0s2=s1;elsefor i=1:(u/2)[s11(2*i-1,:),s11(2*i,:)]=crosschrom(s11(2*i-1,:),s11(2*i,:));ends2=[s11;s12];end●dif.mfunction [ C ] = dif( A,B )la=length(A);lb=length(B);n=1;for i=1:laisequal=0;for j=1:lbif A(i)==B(j)isequal=1;break;endendif isequal==0C(n)=A(i);n=n+1;endendend●crosschrom.mfunction [ ss1,ss2 ] = crosschrom( s1,s2 ) ls1=length(s1);ls2=length(s2);r=ceil((ls1-1)*rand);a1=s1(1:r);a2=s2(1:r);ss1=[a1 dif(s2,a1)];ss2=[a2 dif(s1,a2)];end●vari.mfunction [s3] = vari( s2,pvari )[u,v]=size(s2);for i=1:uif rand<pvarip=1;q=1;while p-q==0p=ceil(10*rand);q=ceil(10*rand);endj=s2(i,p);s2(i,p)=s2(i,q);s2(i,q)=j;endends3=s2;myGA.mclear;coord=[0.6683 0.6195 0.4000 0.2439 0.1707 0.2293 0.5171 0.8732 0.6878 0.8488;...0.2536 0.2634 0.4439 0.1463 0.2293 0.7610 0.9414 0.6536 0.5219 0.3609]; m=length(coord);inn=20;pcross=0.88;pvari=0.1;gnmax=1000;distan=distance(coord);s=zeros(inn,m);for i=1:inns(i,:)=randperm(m);endfor i=1:gnmax[f,g,p]=fit(s,distan);A=s;A(:,end+1)=g;s1=select(s,p);s2=cross(s1,pcross);s3=vari(s2,pvari);[f3,g3,p3]=fit(s3,distan);A3=s3;A3(:,end+1)=g3;B=[A;A3];B0=sortrows(B,(m+1));best(i,:)=B0(1,:);s(1:(inn/2),1:m)=B0(1:(inn/2),1:m);B00=B0((inn/2)+1:end,1:m);for j=1:(inn/2)k=ceil(1.5*inn*rand);s((inn/2)+j,:)=B00(k,:);endend。
1.遗传算法解决TSP 问题(附matlab源程序)2.知n个城市之间的相互距离,现有一个推销员必须遍访这n个城市,并且每个城市3.只能访问一次,最后又必须返回出发城市。
如何安排他对这些城市的访问次序,可使其4.旅行路线的总长度最短?5.用图论的术语来说,假设有一个图g=(v,e),其中v是顶点集,e是边集,设d=(dij)6.是由顶点i和顶点j之间的距离所组成的距离矩阵,旅行商问题就是求出一条通过所有顶7.点且每个顶点只通过一次的具有最短距离的回路。
8.这个问题可分为对称旅行商问题(dij=dji,,任意i,j=1,2,3,…,n)和非对称旅行商9.问题(dij≠dji,,任意i,j=1,2,3,…,n)。
10.若对于城市v={v1,v2,v3,…,vn}的一个访问顺序为t=(t1,t2,t3,…,ti,…,tn),其中11.ti∈v(i=1,2,3,…,n),且记tn+1= t1,则旅行商问题的数学模型为:12.min l=σd(t(i),t(i+1)) (i=1,…,n)13.旅行商问题是一个典型的组合优化问题,并且是一个np难问题,其可能的路径数目14.与城市数目n是成指数型增长的,所以一般很难精确地求出其最优解,本文采用遗传算法15.求其近似解。
16.遗传算法:17.初始化过程:用v1,v2,v3,…,vn代表所选n个城市。
定义整数pop-size作为染色体的个数18.,并且随机产生pop-size个初始染色体,每个染色体为1到18的整数组成的随机序列。
19.适应度f的计算:对种群中的每个染色体vi,计算其适应度,f=σd(t(i),t(i+1)).20.评价函数eval(vi):用来对种群中的每个染色体vi设定一个概率,以使该染色体被选中21.的可能性与其种群中其它染色体的适应性成比例,既通过轮盘赌,适应性强的染色体被22.选择产生后台的机会要大,设alpha∈(0,1),本文定义基于序的评价函数为eval(vi)=al23.pha*(1-alpha).^(i-1) 。
#include "stdio.h"#include "stdlib.h"#include "conio.h"#include "math.h"#include "time.h"#define num_C 10 //城市个数#define N 100 //群体规模为100#define pc 0.9 //交叉概率为0.9#define pm 0.1 //变异概率为10%#define ps 0.6 //进行选择时保留的比例#define genmax 200 //最大代数200int RandomInteger(int low,int high);void Initial_gen(struct unit group[N]);void Sort(struct unit group[N]);void Copy_unit(struct unit *p1,struct unit *p2);int search_son(int son[num_C],int k);void Cross(struct unit *p1,struct unit *p2);void Varation(struct unit group[N],int i);void Evolution(struct unit group[N]);void Calculate_cost(struct unit *p);void Print_optimum(struct unit group[N]);/* 定义个体信息*/typedef struct unit{int path[num_C]; //个体的路径信息int cost; //个体代价值};struct unit group[N]; //种群变量groupint num_gen=0; //记录当前达到第几代/***************************************************************************/ /* 城市间的距离信息:*/ /* 北京天津武汉深圳长沙成都杭州西安拉萨南昌*/ /* (0) (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) *//* 北京(0) 0 118 1272 2567 1653 2097 1425 1177 3947 1574 */ /* 天津(1) 118 0 1253 2511 1633 2077 1369 1157 3961 1518 */ /* 武汉(2) 1272 1253 0 1462 380 1490 821 856 3660 385 */ /* 深圳(3) 2567 2511 1462 0 922 2335 1562 2165 3995 933 */ /* 长沙(4) 1653 1633 380 922 0 1700 1041 1135 3870 456 */ /* 成都(5) 2097 2077 1490 2335 1700 0 2311 920 2170 1920 */ /* 杭州(6) 1425 1369 821 1562 1041 2311 0 1420 4290 626 */ /* 西安(7) 1177 1157 856 2165 1135 920 1420 0 2870 1290 */ /* 拉萨(8) 3947 3961 3660 3995 3870 2170 4290 2870 0 4090 */ /* 南昌(9) 1574 1518 385 993 456 1920 626 1290 4090 0 */ /***************************************************************************/int Cost_table[10][10]={{0,118,1272,2567,1653,2097,1425,1177,3947,1574},{118,0,1253,2511,1633,2077,1369,1157,3961,1518},{1272,1253,0,1462,380,1490,821,856,3660,385},{2567,2511,1462,0,922,2335,1562,2165,3995,933},{1653,1633,380,922,0,1700,1041,1135,3870,456},{2097,2077,1490,2335,1700,0,2311,920,2170,1920},{1425,1369,821,1562,1041,2311,0,1420,4290,626},{1177,1157,856,2165,1135,920,1420,0,2870,1290},{3947,3961,3660,3995,3870,2170,4290,2870,0,4090},{1574,1518,385,993,456,1920,626,1290,4090,0}};int main(){srand((int)time(NULL)); //初始化随机数发生器Initial_gen(group); //初始化种群Evolution(group); //进化:选择、交叉、变异getch();return 0;}/* 初始化种群*/void Initial_gen(struct unit group[N]){int i,j,k;struct unit *p;for(i=0;i<=N-1;i++) //初始化种群里的100个个体{p=&group[i]; //p指向种群的第i个个体for(j=0;j<=num_C-1;j++) //生成10个城市间的一个随机路径{k=0;if(j==0) p->path[j]=RandomInteger(0,num_C-1);else{p->path[j]=RandomInteger(0,num_C-1);while(k<j){//与之前城市重复,重新生成一个城市if(p->path[j]==p->path[k]){p->path[j]=RandomInteger(0,num_C-1); k=0; }else k++;}//end while}}//end 生成路径Calculate_cost(p); //计算该路径的代价值}//end 初始化种群}/* 种群进化,进化代数由genmax决定*/void Evolution(struct unit group[N]){int i,j;int temp1,temp2,temp3,temp4,temp5;temp1=N*pc/2;temp2=N*(1-pc);temp3=N*(1-pc/2);temp4=N*(1-ps);temp5=N*ps;for(i=1;i<=genmax;i++){//选择Sort(group);Print_optimum(group,i-1); //输出当代(第i-1代)种群for(j=0;j<=temp4-1;j++){ Copy_unit(&group[j],&group[j+temp5]); }//交叉for(j=0;j<=temp1-1;){Cross(&group[temp2+j],&group[temp3+j]);j+=2;}//变异Varation(group,i);}Sort(group);Print_optimum(group,i-1); //输出当代(第i-1代)种群}/* 交叉*/void Cross(struct unit *p1,struct unit *p2){int i,j,cross_point;int son1[num_C],son2[num_C];for(i=0;i<=num_C-1;i++) //初始化son1、son2{son1[i]=-1;son2[i]=-1;}cross_point=RandomInteger(1,num_C-1); //交叉位随机生成//交叉,生成子代//子代1//子代1前半部分直接从父代复制for(i=0;i<=cross_point-1;i++) son1[i]=p1->path[i];for(i=cross_point;i<=num_C-1;i++){for(j=0;j<=num_C-1;j++) //补全p1{if(search_son(son1,p2->path[j])==1){ son1[i]=p2->path[j]; break; }else ;}}//end 子代1//子代2//子代1后半部分直接从父代复制for(i=cross_point;i<=num_C-1;i++) son2[i]=p2->path[i]; for(i=0;i<=cross_point-1;i++){for(j=0;j<=num_C-1;j++) //补全p2{if(search_son(son2,p1->path[j])==1){ son2[i]=p1->path[j]; break; }else ;}}//end 子代2//end 交叉for(i=0;i<=num_C-1;i++){p1->path[i]=son1[i];p2->path[i]=son2[i];}Calculate_cost(p1); //计算子代p1的代价Calculate_cost(p2); //计算子代p2的代价}/* 变异*/void Varation(struct unit group[N],int flag_v){int flag,i,j,k,temp;struct unit *p;flag=RandomInteger(1,100);//在进化后期,增大变异概率if(flag<=(flag_v>100)?(5*100*pm):(100*pm)){i=RandomInteger(0,N-1); //确定发生变异的个体j=RandomInteger(0,num_C-1); //确定发生变异的位k=RandomInteger(0,num_C-1);p=&group[i]; //变异temp=p->path[j];p->path[j]=p->path[k];p->path[k]=temp;Calculate_cost(p); //重新计算变异后路径的代价}}/* 检查k是否在son[num_C]中已出现过*/int search_son(int son[num_C],int k){int i;for(i=0;i<=num_C-1;i++){if(son[i]==k) return -1;else ;}return 1;}/* 将种群中个体按代价从小到大排序*/void Sort(struct unit group[N]){int i,j;struct unit temp,*p1,*p2;for(j=1;j<=N-1;j++) //排序总共需进行N-1轮{for(i=1;i<=N-1;i++){p1=&group[i-1];p2=&group[i];if(p1->cost>p2->cost) //代价值大的往后排{Copy_unit(p1,&temp);Copy_unit(p2,p1);Copy_unit(&temp,p2);}//end if}//end 一轮排序}//end 排序}/* 计算某个路径的代价值*/void Calculate_cost(struct unit *p){int j;p->cost=0;for(j=1;j<=num_C-1;j++){ p->cost+=Cost_table[p->path[j-1]][p->path[j]]; }p->cost+=Cost_table[p->path[num_C-1]][p->path[0]];}/* 复制种群中的p1到p2中*/void Copy_unit(struct unit *p1,struct unit *p2){int i;for(i=0;i<=num_C-1;i++) p2->path[i]=p1->path[i];p2->cost=p1->cost;}/* 生成一个介于两整型数之间的随机整数*/int RandomInteger(int low,int high){int k;double d;k=rand();k=(k!=RAND_MAX)?k:(k-1); //RAND_MAX是VC中可表示的最大整型数d=(double)k/((double)(RAND_MAX));k=(int)(d*(high-low+1));return (low+k);}/* 输出当代种群中的每个个体*/void Print_optimum(struct unit group[N],int k){int i,j;struct unit *p;printf("当前第%d 代:\n",k);for(i=0;i<=N-1;i++){printf("第%d 代,个体%d :",k,i);p=&group[i];for(j=0;j<=num_C-1;j++) printf("%d ",p->path[j]);printf(" 代价值为:%d \n",p->cost);}}。