材料概论材料科学概论课件双语
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:5.46 MB
- 文档页数:72





Material: Solids used by man kind to produce items which constitute the support for his living environmentCharacteristics of materials◆Have certain compositions;◆Can be processed;◆With certain shape and color;◆Can be used and reused or recycled.◆特点:☐具有一定的成分和配比;☐可成型加工;☐保持一定形状和外观;☐具有使用价值并可回收再利用。
材料性能的决定因素◆组成材料的各元素的原子结构,◆原子间的相互作用、相互结合,◆原子或分子在空间的排列分布和运动规律,◆原子集合体的形貌特征。
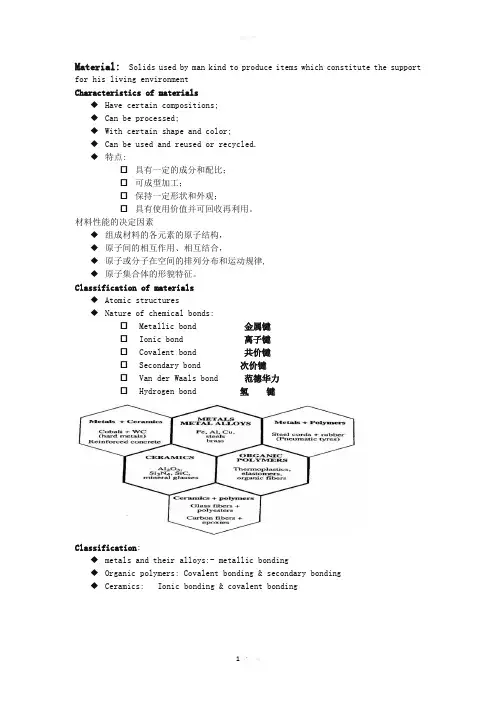
Classification of materials◆Atomic structures◆Nature of chemical bonds:☐ Metallic bond 金属键☐ Ionic bond 离子键☐ Covalent bond 共价键☐ Secondary bond 次价键☐ Van der Waals bond 范德华力☐ Hydrogen bond 氢键Classification:◆metals and their alloys:- metallic bonding◆Organic polymers: Covalent bonding & secondary bonding◆Ceramics:Ionic bonding & covalent bondingMetals and their alloys:◆ are good conductors of heat and electricity;◆ are opaque to visible light;◆ are hard, rigid;◆ can undergo plastic deformation◆ have a high melting temperature (Tm).Organic polymers:◆made up of long-chain molecules;◆ are electrical and thermal insulators;◆ are light and easily formable;◆ the best-known organic polymers are:☐ poly (vinyl chloride) (聚氯乙烯,PVC);☐ polyethylene (聚乙烯,PE);☐ polystyrene (聚苯乙烯,PS)。



•材料概论•材料简介•课程安排章Ⅰ简介2小时第Ⅱ章材质属性6小时章Ⅲ高分子材料12小时章Ⅳ复合材料6小时第Ⅴ陶瓷材料2小时章Ⅶ金属材料2小时评论2小时总32hrs第一章材料概述•第一章简介材料•简介1.1材料简介1.2材料周期1.3材料家庭•1.1材料简介1.1.1定义材料1.1.2材料科学与工程1.1.3材料的发展•1.1.1材料定义•材料已使他们有用的机器(机器)结构(建筑物),宇宙(宇宙)的物质,设备(设备),产品(产品),系统(系统)。
•例如,PDF 1:4-21;简史材料,PDF 1:22-361.1.2材料科学与工程材料科学与工程(MSE)已成为一个主要的研究领域,一个关键的涉及到许多其他领域。
•MSE的定义由美国科学院研究所的研究,涉及到有关的知识的组成,结构和材料处理其性能和用途的发现和应用。
•“科学”专注于发现的材料,这反过来又导致理论解释结构如何组成,性质和行为的性质。
“工程”,另一方面,涉及使用的科学,以开发(开发),准备,修改和申请材料,以满足特定的需求。
材料科学与工程是跨学科或跨学科(交叉学科),拥抱(包含)领域,如冶金(冶金学),陶瓷,固态物理,高分子物理与化学,等等。
科学家和工程师是专家谁是完全参与调查和材料设计。
•为什么要研究材料科学与工程•要了解材料•要选择材料•设计材料•1.1.3材料的发展•材料飞机第一架飞机纯铝于1930的Al合金的开始1970 CC复合材料•材料成熟度曲线•1.2材料循环的制造商(制造业者)开始的原料如原油,天然气,树木,和棉花,以化学化合物,如乙烷,三氯甲烷,氟化氢,包括氯化乙烯。
从这些原料的单体(单分子)的生产和乙烯,甲基丙烯酸甲酯和氯乙烯。
•如果我们使总的材料循环效率,从而保护环境和自然资源,为子孙后代,我们必须制定正确的态度和习惯,在我们的公民(养成)。
•1.3材料家庭•聚合物1。
电气绝缘2。
保温3。
耐化学性4。
极轻的重量5。
透明度6。


材料科学与工程导论(双语)Chater_8INTRODUCTION TO MATERIALSSCIENCE AND ENGINEERING国家级双语教学示范课程ISSUES TO ADDRESSCHAPTER 9BIOMATERIALS/NANOMATERIALS/SMART MATERIALS What are biomaterials What is nano What are smart materials Applications of smart materialsAn Interdisciplinary FieldBioengineersMaterial ScientistsImmunologistsChemistsBiologistsSurgeons.9.1 BiomaterialsA Little History on BiomaterialsRomans, Chinese, and Aztecs used gold indentistry over 2000 years ago, Cu not good Ivory & wood teethAsepticsurgery 1860 ListerBone plates 1900, joints 1930Turn of the century, synthetic plastics came intouseWWII, shards of PMMA unintentionally gotlodged into eyes of aviatorsParachute cloth used for vascular prosthesis1960- Polyethylene and stainless steel beingused for hip implantsWhat’s a biomaterial?1980 - Passive and inert point of viewAny substance or drugs, of synthetic or naturalorigin, which can be used for any period aloneor as part of a system and that increases orreplaces any tissue, organ or function of thebody.1990 ? Active point of viewNon-living material used in a medical deviceand designed to interact with biologicalsystems.Classification of BiomaterialsFirst generation: INERT Do not trigger any reaction in the host: neitherrejected nor recognition “ do not bring anygood result”Second generation: BIOACTIVE Ensure a more stable performance in a longtime or for the period you wantThird generation: BIODEGRADABLE It can be chemically degraded or decomposedby natural effectors weather, soil bacteria,plants, animalsMean Features for Medical ApplicationsBIOFUNCTIONALITY Playing a specific function in physical andmechanical termsBIOCOMPATIBILITY Concept that refers to a set of properties that amaterial must have to be used safely in abiological organism The ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response in a specificapplication Host response: the reaction of a living system to the presence of a material.What is a biocompatible material?1 Synthetic or natural material used in intimatecontact with living tissue it can be implanted,partially implanted or totally external.2 Biocompatible materials are intended tointerface with biological system to EVALUATE,TREAT, AUGMENT or REPLACE any tissue,organ or function of the body A biocompatible device must be fabricated frommaterials that will not elicit an adverse biologicalresponse.Biocompatible material features1 Absence of carcinogenicity 致癌性 the abilityor tendency to produce cancer2 Absence of immunogenicity 致免疫性absence of a recognition of an external factorwhich could create rejection3 Absence of teratogenicity 致畸性 ability tocause birth defects4 Absence of toxicityWhat’s a bi odegradable implant Once implanted, should maintain its mechanical properties until it is no longerneeded and then be absorbed and excretedby the body, leaving no trace Biodegradable implants are designed to overcome the disadvantages of permanentmetal-based devices.BiomaterialsPolymeric biomaterialsBioceramicsMetallic biomaterialsBiocompositeBiologically based derived biomaterials Polymeric Biomaterials: Adv. & Disadv.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯,俗称“有机玻璃”。