分布式系统领域经典论文翻译集
- 格式:docx
- 大小:26.04 KB
- 文档页数:7

分布式系统概念--第⼀篇⼀致性协议、⼀致性模型、拜占庭问题、租约、副本协议1,⼀致性协议两阶段提交协议与Raft协议、Paxos协议①两阶段提交协议在分布式系统中,每个节点虽然可以知晓⾃⼰的操作时成功或者失败,却⽆法知道其他节点的操作的成功或失败。
当⼀个事务跨越多个节点时,为了保持事务的特性,需要引⼊⼀个作为协调者的组件来统⼀掌控所有节点(称作参与者)的操作结果并最终指⽰这些节点是否要把操作结果进⾏真正的提交(⽐如将更新后的数据写⼊磁盘等等)。
因此,⼆阶段提交的算法思路可以概括为:参与者将操作成败通知协调者,再由协调者根据所有参与者的反馈情报决定各参与者是否要提交操作还是中⽌操作。
因此,系统包含两类节点,⼀类是协调者,⼀类是参与者,协议的执⾏由两个阶段组成:具体参考:两阶段协议是阻塞的,节点在等待对⽅的应答消息时,它不能做其他事情且持有的资源也不释放。
它主要是⽤来保证跨多个节点的操作的原⼦性--要么都操作,要么都不操作,⽽像Raft协议则诸如⽤来保证操作的⼀致性,即各个节点都执⾏相同的操作。
两阶段协议的举例参考:②Raft协议和Paxos协议Raft与Paxos 在分布式应⽤中的基本功能相似,但是Paxos难于理解,相对⽽⾔Raft算法要简单⼀些。
关于Raft协议有⼀篇经典的论⽂:其中⽂翻译地址参考:还有⼀篇⽂章详细解释了Raft算法的相关实现:Raft论⽂的第 31 号参考⽂献。
下⾯仅记录⼀下看论⽂过程中出现的⼀个问题:为什么 “⼤多数规则” 能够保证对于⼀个给定的任期,只会有⼀个候选⼈最终赢得选举成为Leader?在Raft中,对于⼀个给定的任期号,每⼀台Server按照先来先服务原则对该任期号最多只投⼀张票,若某Candidate发送的请求投票RPC带有的任期号获得超过半数的Server的同意,则该Candidate成为Leader。
正是由于每个Server对某个任期只最多投⼀次票,且获得的投票要超过半数才能成为Leader,故在⼀个给定的任期投票中,最终只会有⼀个Candidate成为Leader。


Sensing Human Activity:GPS Tracking感应人类活动:GPS跟踪Stefan van der Spek1,*,Jeroen van Schaick1,Peter de Bois1,2and Remco de Haan1Abstract:The enhancement of GPS technology enables the use of GPS devices not only as navigation and orientation tools,but also as instruments used to capture travelled routes:assensors that measure activity on a city scale or the regional scale.TU Delft developed aprocess and database architecture for collecting data on pedestrian movement in threeEuropean city centres,Norwich,Rouen and Koblenz,and in another experiment forcollecting activity data of13families in Almere(The Netherlands)for one week.Thequestion posed in this paper is:what is the value of GPS as‘sensor technology’measuringactivities of people?The conclusion is that GPS offers a widely useable instrument tocollect invaluable spatial-temporal data on different scales and in different settings addingnew layers of knowledge to urban studies,but the use of GPS-technology and deploymentof GPS-devices still offers significant challenges for future research.摘要:增强GPS技术支持使用GPS设备不仅作为导航和定位工具,但也为仪器用来捕捉旅行路线:作为传感器,测量活动在一个城市或区域范围内规模。
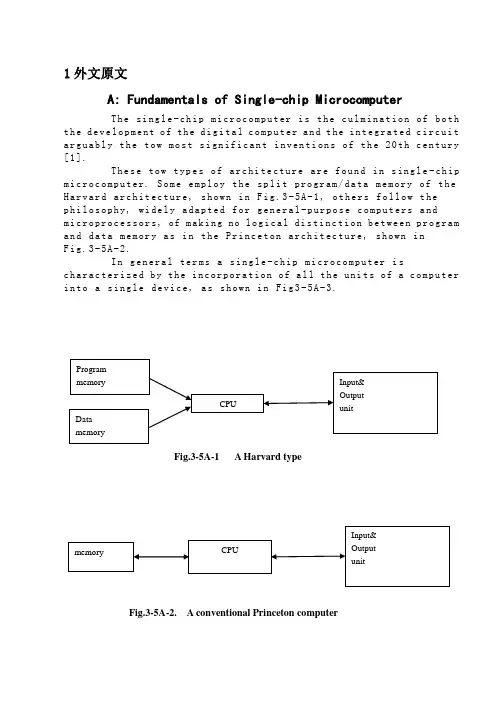
1外文原文A: Fundamentals of Single-chip MicrocomputerTh e si ng le-ch i p mi cr oc om pu ter is t he c ul mi nat i on o f bo th t h e d ev el op me nt o f th e d ig it al com p ut er an d t he int e gr at ed ci rc ui ta r gu ab ly th e t ow m os t s i gn if ic ant i nv en ti on s o f t h e 20t h c en tu ry[1].Th es e to w typ e s of a rc hi te ctu r e ar e fo un d i n s in gl e-ch ip m i cr oc om pu te r. So m e em pl oy t he sp l it p ro gr am/d ata me mo ry o f th e H a rv ar d ar ch it ect u re, sh ow n in Fi g.3-5A-1, o th ers fo ll ow t hep h il os op hy, wi del y a da pt ed f or ge n er al-p ur po se co m pu te rs a ndm i cr op ro ce ss o r s, of ma ki ng no lo gi c al di st in ct io n be tw ee n p ro gr am a n d da ta m em or y a s i n th e Pr in cet o n ar ch it ec tu re,sh ow n inF i g.3-5A-2.In g en er al te r ms a s in gl e-chi p m ic ro co mp ut er i sc h ar ac te ri zed b y the i nc or po ra tio n of al l t he uni t s o f a co mp ut er i n to a s in gl e d ev i ce, as s ho wn in Fi g3-5A-3.Fig.3-5A-1 A Harvard typeFig.3-5A-2. A conventional Princeton computerFig3-5A-3. Principal features of a microcomputerRead only memory (ROM).R OM i s u su al ly f or th e p er ma ne nt,n o n-vo la ti le s tor a ge o f an a pp lic a ti on s pr og ra m .M an ym i cr oc om pu te rs an d mi cr oc on tr ol le r s a re in t en de d fo r h ig h-v ol ume a p pl ic at i o ns a nd h en ce t he e co nom i ca l ma nu fa ct ure of t he d ev ic es r e qu ir es t ha t the co nt en ts o f the pr og ra m me mo ry b e co mm it te dp e rm an en tl y d ur in g th e m an uf ac tu re o f c hi ps . Cl ear l y, th is im pl ie sa ri g or ou s a pp roa c h t o R OM co de d e ve lo pm en t s in ce c ha ng es ca nn otb e m a d e af te r man u fa ct ur e .T hi s d e ve lo pm en t pr oce s s ma y in vo lv e e m ul at io n us in g a s op hi st ic at ed deve lo pm en t sy st em w i th a ha rd wa re e m ul at io n ca pa bil i ty a s we ll a s th e u se of po we rf ul so ft wa re t oo ls.So me m an uf act u re rs p ro vi de ad d it io na l RO M opt i on s byi n cl ud in g i n th ei r ra ng e de vi ce s wi th (or i nt en de d fo r us e wi th) u s er pr og ra mm ab le m em or y. Th e s im p le st of th es e i s us ua ll y d ev ice w h ic h ca n op er ate in a m ic ro pr oce s so r mo de b y usi n g so me o f th e i n pu t/ou tp ut li ne s as a n ad dr es s an d da ta b us f or acc e ss in g e xt er na l m e mo ry. T hi s t ype o f d ev ic e c an b e ha ve fu nc ti on al l y a s t he si ng le c h ip mi cr oc om pu te r fr om wh ic h i t i s de ri ve d a lb eit w it h r es tr ic ted I/O an d a mo di fie d e xt er na l ci rcu i t. T he u se o f t h es e RO Ml es sd e vi ce s is c om mo n e ve n in p ro du ct io n c ir cu it s wh er e t he v ol um e do es n o t ju st if y th e d e ve lo pm en t co sts of c us to m on-ch i p RO M[2];t he rec a n st il l b e a si g ni fi ca nt s a vi ng in I/O a nd ot he r c hi ps co mp ar ed t o a c on ve nt io nal mi cr op ro ce ss or b as ed c ir cu it. M o re e xa ctr e pl ac em en t fo r RO M d ev ic es c an b e o bt ai ne d in t he f o rm o f va ri an ts w i th 'pi gg y-ba ck'EP RO M(Er as ab le p ro gr am ma bl e ROM)s oc ke ts o rd e vi ce s w it h EP ROM i ns te ad o f R OM 。

Google Spanner (中文版)翻译者:厦门大学计算机系教师林子雨翻译时间:2012年9月E-mail: ziyulin@ 个人主页:/linziyu【摘要】:Spanner是谷歌公司研发的、可扩展的、多版本、全球分布式、同步复制数据库。
它是第一个把数据分布在全球范围内的系统,并且支持外部一致性的分布式事务。
本文描述了Spanner的架构、特性、不同设计决策的背后机理和一个新的时间API,这个API可以暴露时钟的不确定性。
这个API及其实现,对于支持外部一致性和许多强大特性而言,是非常重要的,这些强大特性包括:非阻塞的读、不采用锁机制的只读事务、原子模式变更。
【关键词】Google Spanner, Bigtable, distributed database【全文目录结构】1. 介绍2. 实现2.1 Spanserver软件栈2.2 目录和放置2.3 数据模型3. TrueTime4. 并发控制4.1 时间戳管理4.2 细节5. 实验分析5.1 微测试基准5.2 可用性5.3 TrueTime5.4 F16. 相关工作7. 未来的工作8. 总结致谢参考文献1 介绍Spanner是一个可扩展的、全球分布式的数据库,是在谷歌公司设计、开发和部署的。
在最高抽象层面,Spanner就是一个数据库,把数据分片存储在许多Paxos[21]状态机上,这些机器位于遍布全球的数据中心内。
复制技术可以用来服务于全球可用性和地理局部性。
客户端会自动在副本之间进行失败恢复。
随着数据的变化和服务器的变化,Spanner会自动把数据进行重新分片,从而有效应对负载变化和处理失败。
Spanner被设计成可以扩展到几百万个机器节点,跨越成百上千个数据中心,具备几万亿数据库行的规模。
应用可以借助于Spanner来实现高可用性,通过在一个洲的内部和跨越不同的洲之间复制数据,保证即使面对大范围的自然灾害时数据依然可用。
我们最初的客户是F1[35],一个谷歌广告后台的重新编程实现。

毕业论文:基于HDFS的云灾备存储系统——可靠存储及负载均衡方法研究毕业论文:基于HDFS的云灾备存储系统——可靠存储及负载均衡方法研究毕业论文:基于HDFS的云灾备存储系统——可靠存储及负载均衡方法研究:2013-8-15 17:54:55毕业设计论文题目:基于HDFS的云灾备存储系统——可靠存储及负载均衡方法研究院(系)计算机科学与技术专业网络工程届别 2012 摘要随着计算机技术及因特网技术的发展,数据信息已成为现代企业以及每个人的重要资源,数据的丢失或被窃取将带来重大的损失,数据的安全存储及备份显得尤为重要。
本文设计一个基于Hadoop的云灾备存储系统来存储数据。
论文采用在Linux虚拟机上创建hadoop分布式文件系统,由分布式系统管理并备份用户的数据。
分布式系统由一个名字节点和多个数据节点构成,名字节点对数据的存储进行管理,而数据节点则负责数据的物理存储。
为了防止名字节点的故障导致系统的崩溃,必须配置一个第二名字节点来作为冗余并定时处理保存名字节点的系统日志。
为了数据的安全备份,必须把数据复制为多个副本存储在多个数据节点上。
系统不仅要实现海量数据的存储,同时也要实现海量用户的的管理。
为了防止某个数据节点的负载过重,导致用户的操作延迟太大,还必须处理好系统数据节点的负载均衡,使海量用户能够同时流畅的访问hdfs系统。
本文,通过配置多台数据节点,并在名字节点上设置一个文件要保存的副本数,来实现数据的安全备份,用户数据分为多份存储在不同的服务器上。
名字节点则通过一张排序表来控制用户访问数据时是由哪个数据节点负责响应,排序表实现了负载低的数据节点首先响应用户的访问,从而达到各数据节点的负载均衡。
关键词:Hadoop;云灾备;可靠存储;负载均衡ABSTRACTWith the development of computer technology and Internet technology, information has become a modern enterprise as well as important resources for everyone.So data’s lost or stolen will bring a significantloss. Secure storage and backup of data is particularly important. This paper designed a cloud disaster recovery storage system witch based on Hadoop to store data.Paper using the Linux virtual machine to create a hadoop distributed file system, distributed systems ma nagement and backup the user’s data. The distributed system consists of a namenode and multiple datanodes, the namenode manage the data’s storage.And the datanode is responsible for the physical storage of data. In order to prevent the namenode’failured le d to the collapse of the system, we should configure a secondary namenode as the namenode’s redundancy and regularly deal with save system log. For the security of data backup, data replication for the storage of multiple copies of multiple datanodes. The system must not only mass data storage, but also mass user’s management. In order to prevent the overloading of a datanode, which lead to the delay become too large for users operation, we must deal with the datanodes’ load balancing, so that the mass us ers’ access will be simultaneously smooth.The article, by configuring multiple datanodes and set the number of copiesf to save for each file on the namenode to achieve the security of data backup, user data is divided into pay would be stored on different servers. The namenode control witch datanode for user’s access through a sorting table .This sorting table is used to achieve the low-loaded datanode first to respond to user access, so as to achieve load balancing of all datanodes .Key words: hadoop clould disaster recoveryreliable storageload balancing 目录1 绪论11.1研究背景 11.2 研究现状21.3 论文主要工作 31.4 论文组织与结构 42 HADOOP的相关知识52.1 数据的存储和分析52.2 HADOOP的发展和现状52.3 HADOOP在数据容灾的优越性72.4 HADOOP分布式文件系统82.4.1 HDFS的设计82.4.2 数据块92.4.3 名称节点和数据节点 92.5命令行接口92.6 HADOOP文件系统103 构建HADOOP集群123.1 集群说明 123.2 LINUX上集群的建立和安装123.2.1 Linux系统的安装123.2.2 开启SSH服务并实现无密码登录133.2.3 Java环境的配置153.2.4 安装Hadoop 153.3 配置文件的设置153.3.1 配置管理163.3.2 Hadoop配置文件163.4 HADOOP集群的运行184 实现HDFS的可靠存储194.1 二级名字节点194.2 数据节点的冗余备份204.3网络割裂215 实现HDFS的负载均衡225.1 概述225.2 负载均衡的重要性225.3 实现HDFS的负载均衡226 HADOOP集群的测试256.1 HADOOP运行的测试256.2 本地文件的上传测试266.3文件的下载297 总结317.1 工作总结 317.2 心得体会 317.3 进一步的改进32参考文献33后记34附录1 外文翻译(译文)35附录2 外文翻译(英文原文)42 1 绪论1.1 研究背景互联网的高速发展,使计算机成为了个人或企业的必不可少的工具,在日常生活,工作,学习中等等计算机都给人们带来了方便和高效的应用,然而每每都离不开数据,人们不再是仅仅利用文本记录数据,那太缺乏效率,而需要用计算机来存储。


第6章数据库第一部分阅读和翻译A部分分布式数据库介绍分布式数据库是受一个中央数据库管理系统控制的数据库,其中的控制存贮设备不全部受控于共同的CPU。
(1)它可以是位于同一个实际位置的多台计算机,也可以是被存放或者被分散在互联的计算机网络上。
数据的收集(在数据库中)可以横跨多个实际位置进行分布。
一个分布式数据库被分布入分开的不同部分。
一个分布式数据库的每个分开的片段可以被复制(即重复故障转移,像独立冗余磁盘阵列一样)。
除了分布式数据库复制和分散,还有许多其他分配数据库的设计技术。
例如自主式的,同步和异步分布式数据库技术。
这些技术的实施取决于事务和敏感性的数据的需要或者机密性要求,花费则是在数据保密、一贯性和正常花费上。
[1]基本的框架数据库用户访问分布式数据库:●本地应用—不要求其他站点的数据的应用。
●全球性应用—要求从其他站点的数据的应用。
要点采取分布式数据库的要求如下:●发布是透明的——用户一定能与系统互动,就像它是一个逻辑系统。
这适用于其他事之中通入系统性能和方法。
●交易是透明的——每种交易必须维护横跨多个数据库的正确性。
每个交易也划分成不同部分,各个部分保证整个数据库系统的运行。
分布式数据库的优点●反射式组织结构——数据库片段位于与他们相关的部分。
●本地独立性——可能控制与之相关的数据(因为他们较熟悉它)。
●被改进的好处——在一个数据库系统的一个错误只影响一个片段,而不是整个数据库。
●被改进的表现——数据极大的要求其附近的站点,并且数据库系统被并行化,数据库的装载可以在服务器之中平衡。
(2) (数据库中的一个模块装载在一个分布式数据库中不会影响数据库的其他模块)。
●经济——花费较少,用一台大规模计算机的力量创建小型计算机网络。
●模块化——系统可以从分布式数据库修改,增加和删除,不影响其他模块(系统)。
分布式数据库的缺点●复杂性——必须由DBAs完成额外劳动来保证系统分布的本质透明。
必须也完成额外劳动维护多个不同的系统,而不是一个大的。

Spark经典论⽂笔记---ResilientDistributedDatasets:AF。
Spark 经典论⽂笔记Resilient Distributed Datasets : A Fault-Tolerant Abstraction for In-Memory Cluster Computing为什么要设计spark现在的计算框架如Map/Reduce在⼤数据分析中被⼴泛采⽤,为什么还要设计新的spark?Map/Reduce提供了⾼级接⼝可以⽅便快捷的调取计算资源,但是缺少对分布式内存有影响的抽象。
这就造成了计算过程中需要在机器间使⽤中间数据,那么只能依靠中间存储来保存中间结果,然后再读取中间结果,造成了时延与IO性能的降低。
虽然有些框架针对数据重⽤提出了相应的解决办法,⽐如Pregel针对迭代图运算设计出将中间结果保存在内存中,HaLoop提供了迭代Map/Reduce的接⼝,但是这些都是针对特定的功能设计的不具备通⽤性。
针对以上问题,Spark提出了⼀种新的数据抽象模式称为RDD(弹性分布式数据集),RDD是容错的并⾏的数据结构,并且可以让⽤户显式的将数据保存在内存中,并且可以控制他们的分区来优化数据替代以及提供了⼀系列⾼级的操作接⼝。
RDD数据结构的容错机制设计RDD的主要挑战在与如何设计⾼效的容错机制。
现有的集群的内存的抽象都在可变状态(啥是可变状态)提供了⼀种细粒度(fine-grained)更新。
在这种接⼝条件下,容错的唯⼀⽅法就是在不同的机器间复制内存,或者使⽤log⽇志记录更新,但是这两种⽅法对于数据密集(data-intensive⼤数据)来说都太昂贵了,因为数据的复制及时传输需要⼤量的带宽,同时还带来了存储的⼤量开销。
与上⾯的系统不同,RDD提供了⼀种粗粒度(coarse-grained)的变换(⽐如说map,filter,join),这些变换对数据项应⽤相同的操作。

分布式系统的应用的论文摘要:随着计算机网络的出现,分布式计算成为可能。
当用户需要完成任何任务时,分布式计算提供对尽可能多的计算机能力和数据的透明访问,同时实现高性能与高可靠性的目标。
文章针对分布式系统的定义、应用、标准以及在如何构建基于志愿者计算的分布式系统上,给出了观点,并进行了分析。
关键词:分布式系统;网络:志愿者计算一、前言在20世纪50年代,计算机是串行处理机,一次运行一个作业直至完成。
这些处理机通过一个操作员从控制台操纵,而对于普通用户则是不可访问的。
在60年代,需求相似的作业作为一个组以批处理的方式通过计算机运行以减少计算机的空闲时间。
同一时期还提出了其他一些技术,如利用缓冲、假脱机和多道程序等的脱机处理。
70年代产生了分时系统,不仅作为提高计算机利用率的手段,也使用户离计算机更近了。
分时是迈向分布式系统的第一步:用户可以在不同的地点共享并访问资源。
80年代是个人计算的10年;人们有了他们自己专用的机器。
随着基于微处理器的系统所提供的出色的性能/价格比和网络技术的稳步提高,一个新的梦想成为可能一分布式计算。
当用户需要完成任何任务时,分布式计算提供对尽可能多的计算机能力和数据的透明访问,同时实现高性能与高可靠性的目标。
在过去的10年里,人们对分布式计算系统的兴趣迅猛发展。
有关分布式计算的主题是多种多样的,许多研究人员正在研究关于分布式硬件结构和分布式软件设计的各方面问题以开发利用其潜在的并行性和容错性。
二、分布式系统定义当讨论分布式系统时,我们面临许多以下这些形容词所描述的不同类型:分布式的、网络的、并行的、并发的和分散的。
分布式处理是一个相对较新的领域,所以还没有一致的定义。
与顺序计算相比、并行的、并发的和分布式的计算包括多个pe间的集体协同动作。
这些术语在范围上相互覆盖,有时也交换使用。
●“并行的”意味着从一个单一控制线程对数据集的锁步(10ckstep)动作。
在并行计算机级别上,单指令流多数据流(slmd)计算机就是一个使用多个数据处理单元在许多数据项上同时进行相同或相似操作的例子。

华北水利水电大学资环学院论文专 业: webGIS班 级: 2013011 学 号: 201301125姓 名: 彭程________ _ 指导教师: 李名勇分布式计算和网格计算摘要:随着社会的发展,人们的应用需求不断提高,同时原有问题的求解领域的不断扩展和复杂化,并层出不穷的涌现出新问题需求,但是现有的计算机和设备无论从自身的性能还是从局部的合作上都无法满足人们日益增加的要求,然而由于网络等相关技术的发展,使得世界各地的计算机可以联网协同工作,利用空闲的以前无法使用和共享的设备等空闲资源。
关键词:分布式计算,网格计算,分别,特点一、分布式计算和网格计算的定义1)分布式计算的定义所谓分布式计算是一门计算机科学,它研究如何把一个需要非常巨大的计算能力才能解决的问题分成许多小的部分,然后把这些部分分配给许多计算机进行处理,最后把这些计算结果综合起来得到最终的结果。
最近的分布式计算项目已经被用于使用世界各地成千上万位志愿者的计算机的闲置计算能力,通过因特网,您可以分析来自外太空的电讯号,寻找隐蔽的黑洞,并探索可能存在的外星智慧生命;您可以寻找超过1000万位数字的梅森质数;您也可以寻找并发现对抗艾滋病病毒的更为有效的药物。
这些项目都很庞大,需要惊人的计算量,仅仅由单个的电脑或是个人在一个能让人接受的时间内计算完成是决不可能的。
分布式计算是一种新的计算方式。
所谓分布式计算就是在两个或多个软件互相共享信息,这些软件既可以在同一台计算机上运行,也可以在通过网络连接起来的多台计算机上运行。
分布式计算比起其它算法具有以下几个优点:1、稀有资源可以共享。
2、通过分布式计算可以在多台计算机上平衡计算负载。
3、可以把程序放在最适合运行它的计算机上。
其中,共享稀有资源和平衡负载是计算机分布式计算的核心思想之一。
2)网格计算的定义实际上,网格计算就是分布式计算的一种。
网格计算即分布式计算,是一门计算机科学。
它研究如何把一个需要非常巨大的计算能力才能解决的问题分成许多小的部分,然后把这些部分分配给许多计算机进行处理,最后把这些计算结果综合起来得到最终结果。
1, Electromechanical integration and the development of technology trends 一、机电一体化技术发展历程及其趋势Since an electronic technology birth of electronic technology and mechanical technology integration began, only a semiconductor integrated circuit, particularly in a microprocessor representative of thelarge-scale integrated circuits for the future, "mechatronics," a technical after significant progress, and has attracted widespread attention.自电子技术一问世,电子技术与机械技术的结合就开始了,只是出现了半导体集成电路,尤其是出现了以微处理器为代表的大规模集成电路以后,"机电一体化"技术之后有了明显进展,引起了人们的广泛注意.(1) mechanical-electrical integration, "the course of development(一)机电一体化"的发展历程1. CNC machine tools come out, wrote "mechatronics," the first page of history;1.数控机床的问世,写下了"机电一体化"历史的第一页;2. Microelectronic technology, "mechatronics''bring a great vitality;2.微电子技术为"机电一体化''带来勃勃生机;3. PLC, "Power Electronics" for the development of "mechatronics" providea firm foundation;3.可编程序控制器、"电力电子"等的发展为"机电一体化"提供了坚强基础;4. Laser technology, fuzzy technology, information technology and other new technologies to "mechanical and electrical integration," a new and higher level.4.激光技术、模糊技术、信息技术等新技术使"机电一体化"跃上新台阶.(2) mechanical-electrical integration, "the development trend(二)机电一体化"发展趋势1. Integration of optical and electrical machinery. General mechanical and electrical integration system by sensing systems, energy systems, information processing systems, machinery, and other components of the structure. Therefore, the introduction of optical technology, the realization of the inherent advantages of optical technology is effective Improved mechanical-electrical integration system sensing system, energy (power) systems and information processing system. optical and electrical machinery integration is the development of mechanical and electrical products trend.1.光机电一体化.一般的机电一体化系统是由传感系统、能源系统、信息处理系统、机械结构等部件组成的.因此,引进光学技术,实现光学技术的先天优点是能有效地改进机电一体化系统的传感系统、能源(动力)系统和信息处理系统.光机电一体化是机电产品发展的重要趋势.2. Systematic self-distribution - Flexible Future electromechanical integration products, and implementation of control systems are adequate "redundancy" and more "flexible" and can better deal with an emergency, is designed "self-distribution system." Self-discipline in thedistribution system, the various subsystems are independent of each other's work, the subsystem for system services, and has its own "self-discipline", according to different environmental conditions react differently. Its characteristics are subsystem can generate its own information and additional information given in the overall premise, specific "action" can be changed. In this way, significantly increase the system's ability to adapt (flexible), not because of the failure of a subsystem of the whole system.2.自律分配系统化——柔性化.未来的机电一体化产品,控制和执行系统有足够的“冗余度”,有较强的“柔性”,能较好地应付突发事件,被设计成“自律分配系统”。
分布式机床的设计FIP现场总线的用途Daping SONG, Thierry DIVOUX,费朗西斯勒帕热自动化中心研究所的Nancy摘要:本文中我们基于FIP现场总线上提出了一种分布式控制系统。
它将取代传统的CNC(计算机数字控制装置)用于机床上。
该系统是由一套以微处理机为基础的模块(PC机、运动控制器、I/O接口) 利用FLP实时网络相互联接的。
这主要是使每个模块智能化以提高整个系统的灵活性和容错能力。
每个模块都是一个分控系统,用于实现自己的分控任务,其中有些模块用于运动控制,另一些模块用于传感器评价和执行器调节。
FIP决定了这些模块之间的通讯(信息交流和同步),同时执行任务分配以及设备布局分布。
我们讨论一些分布标准并描述实验的执行。
1.引言近几年,一直对分布式体系结构进行了许多研究。
分布式体系结构在系统集成上发挥主要作用。
在机床控制域,目前CNC技术有它内在的缺点。
将几根固定数量的轴容入CIM环境中是非常费时,灵活和不易的。
超大规模集成电路微处理器技术和通信网络的迅速发展使分布式控制成为可能。
虽然逐步扩展没有完全替代硬件更换但分布式控制系统的性能,模块化,完整性和可靠性正在提高。
它为替代控制系统架构提供了一个很好的前景。
本文致力于对分布式机床结构的研究。
它建立在智能设备与通信相联系的基础上。
分布式机床的特点是分布式任务和分布式数据,且具有独特的控制方法。
它是结合标准设备和FIP系统总线设计而成,通过实验证明该系统具有可执行性,在实验中该系统控制了复合轴系,成功执行坐标之间的关系同时也反应了对传感器值的变化。
该论文结构如下:第2部分描述了机床控制系统构架。
第3部分简要介绍了FIP 现场总线。
第4部分概述了我们实验的实施。
最后,我们在第5部分总结了一些一般性意见和今后的研究前景。
2.机床控制系统架构该机床控制系统是一个实时多任务系统。
其功能结构如图1所示。
它包括三种单元:用户接口/ 监控单元/规划单元,伺服单元,传感器/制动器单位。
DCS分布式控制系统中英文资料对照外文翻译文献综述中文:DCSDCS是分布式控制系统的英文缩写(Distributed Control System),在国内自控行业又称之为集散控制系统。
即所谓的分布式控制系统,或在有些资料中称之为集散系统,是相对于集中式控制系统而言的一种新型计算机控制系统,它是在集中式控制系统的基础上发展、演变而来的。
它是一个由过程控制级和过程监控级组成的以通信网络为纽带的多级计算机系统,综合了计算机,通信、显示和控制等4C技术,其基本思想是分散控制、集中操作、分级管理、配置灵活以及组态方便。
在系统功能方面,DCS和集中式控制系统的区别不大,但在系统功能的实现方法上却完全不同。
首先,DCS的骨架—系统网络,它是DCS的基础和核心。
由于网络对于DCS 整个系统的实时性、可靠性和扩充性,起着决定性的作用,因此各厂家都在这方面进行了精心的设计。
对于DCS的系统网络来说,它必须满足实时性的要求,即在确定的时间限度内完成信息的传送。
这里所说的“确定”的时间限度,是指在无论何种情况下,信息传送都能在这个时间限度内完成,而这个时间限度则是根据被控制过程的实时性要求确定的。
因此,衡量系统网络性能的指标并不是网络的速率,即通常所说的每秒比特数(bps),而是系统网络的实时性,即能在多长的时间内确保所需信息的传输完成。
系统网络还必须非常可靠,无论在任何情况下,网络通信都不能中断,因此多数厂家的DCS均采用双总线、环形或双重星形的网络拓扑结构。
为了满足系统扩充性的要求,系统网络上可接入的最大节点数量应比实际使用的节点数量大若干倍。
这样,一方面可以随时增加新的节点,另一方面也可以使系统网络运行于较轻的通信负荷状态,以确保系统的实时性和可靠性。
在系统实际运行过程中,各个节点的上网和下网是随时可能发生的,特别是操作员站,这样,网络重构会经常进行,而这种操作绝对不能影响系统的正常运行,因此,系统网络应该具有很强在线网络重构功能。
《西里尔蒙古文—汉文机器翻译系统的实现》篇一一、引言随着科技的发展,人工智能领域中机器翻译技术得到了广泛的应用。
西里尔蒙古文与汉文之间的交流日益频繁,因此,开发一款高效、准确的西里尔蒙古文—汉文机器翻译系统变得尤为重要。
本文旨在探讨该系统的实现方法,分析其关键技术,以期为相关研究和应用提供参考。
二、系统需求分析1. 功能需求:该系统应具备西里尔蒙古文到汉文的翻译功能,支持文本和语音输入输出,并保证翻译的准确性和实时性。
2. 性能需求:系统应具备良好的性能,包括高吞吐量、低延迟和良好的用户体验。
3. 安全与可靠性需求:系统应保证数据的安全性,防止数据泄露和未经授权的访问,同时应具备故障恢复和容错能力。
三、关键技术分析1. 自然语言处理技术:自然语言处理是机器翻译的核心技术,包括分词、词性标注、句法分析、语义理解等。
在西里尔蒙古文到汉文的翻译过程中,需要利用这些技术对源语言进行解析,生成中间表示形式,再将其转换为目标语言。
2. 深度学习技术:深度学习在机器翻译领域取得了显著的成果。
通过训练大量的双语语料库,可以学习到语言之间的映射关系,提高翻译的准确性和流畅度。
在本系统中,我们采用基于深度学习的神经网络模型进行翻译。
3. 文本编码与解码技术:为了实现文本的输入输出,需要采用合适的文本编码与解码技术。
在西里尔蒙古文到汉文的翻译过程中,应确保编码与解码的兼容性和准确性。
四、系统设计1. 系统架构:本系统采用分层架构设计,包括数据层、业务逻辑层和用户界面层。
数据层负责存储和管理语料库、模型等数据;业务逻辑层负责实现翻译算法和业务逻辑;用户界面层提供用户与系统的交互界面。
2. 算法流程:系统首先对输入的西里尔蒙古文进行解析,提取关键信息,然后通过神经网络模型进行翻译,最后将生成的汉文文本或语音输出给用户。
3. 技术选型:采用Python作为开发语言,利用TensorFlow 等深度学习框架实现神经网络模型。
End-to-endargumentsinsystemdesign翻译设计系统中的端到端原则这篇论文提出了分布式系统中各模块间功能定位的设计原理,称为端到端原则,与底层内置的功能相比,那些系统低层提供的功能也许是冗余的或是无价值的。
例如在这篇论文中讨论过的位错误恢复、安全加密、复制消息抑制、系统崩溃恢复、交付确认等。
底层机制支持一些想性能增强这样合理的功能。
1.介绍确定功能间的边界对于计算机系统设计者来说可能是基本的行为。
对于系统设计者来说,最重要的工具是能够为功能定位决策提供指导的设计原则。
这篇论文讨论了多年使用却并没有明确定义的一类功能定位观点。
然而,随着数据通信网作为计算机系统组成成分的出现,通过其更清晰的应用环境和得以应用的原因形成了行功能布局。
该论文明确表述了这一论点,以便观察其本质并理解它实际上是怎样的。
这一观点吸引着应用需求,并为分层系统中的功能上移来靠近应用提供了基本原理,我们从通信网络版本开始思考。
在一个能够通信的系统中,通常会定义一个通信子系统的模块化边界和边界与系统之间的接口。
当这样做时,很显然存在一个通过多种方式可能实现的功能列表:通过通信子系统或是通过他们的客户,作为一种冒险,或者是冗余的,每次运行它们各自的版本。
之所以这样做,是因为应用需求为以下各类的观点提供的一个基础:考虑中的功能能够完全并正确的由常识在通信系统的端程序的帮助下实现,所以,将提供不确定的功能作为通信系统的特点是不可能的。
(有时一个不完整版本的通信系统提供的功能对于性能能够增强是有用的)这一系列的原因反对低层功能实现的端到端论点,以下部分来详细考察端到端论点,首先通过一个使用端到端的例子来研究——可靠的数据传输是考虑中的功能——并且通过展示功能的范围使得相同的论点可以得以应用。
在数据通信系统中,这个范围包括加密、重传信息检测、消息序列、有保证的消息传输、主机错误检测和交付回单。
在广阔的环境下,这一论点被应用于很多其他功能的计算机操作系统,包括自身的文件系统。
18. PowerDrill:Processing a Trillion Cells per Mouse Click
19. Google-Wide Profiling:A Continuous Profiling Infrastructure for Data Centers
20. Spanner: Google’s Globally-Distributed Database
21. Dapper, a Large-Scale Distributed Systems Tracing Infrastructure
22. The Datacenter as a Computer
google系列论文翻译集(合集)
二.分布式理论系列
00. Appraising Two Decades of Distributed Computing Theory Research
0. 分布式理论系列译序
1. A brief history of Consensus_ 2PC and Transaction Commit (译)
2. 拜占庭将军问题(译) --Leslie Lamport
3. Impossibility of distributed consensus with one faulty process (译)
4. Leases:租约机制(译)
5. Time Clocks and the Ordering of Events in a Distributed System(译) --Leslie Lamport
6. The Part Time Parliament (译zz) --Leslie Lamport
7. How to Build a Highly Available System Using Consensus
8. Paxos Made Simple (译) --Leslie Lamport
9. Fast Paxos --Leslie Lamport
10. Paxos Made Live - An Engineering Perspective(译)
11. Paxos made code - Implementing a high throughput Atomic Broadcast
12. Distributed Snapshots: Determining Global States of a Distributed System
--Leslie Lamport
13. Virtual Time and Global States of Distributed Systems
14. Timestamps in Message-Passing Systems That Preserve the Partial Ordering
15. Fundamentals of Distributed Computing:A Practical Tour of Vector Clock Systems
16. Unreliable Failure Detectors for Reliable Distributed Systems
17. Wait-Free Synchronization
18. Knowledge and Common Knowledge in a Distributed Environment
19. Uniform consensus is harder than consensus
三.数据库理论系列
0. A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks --E.F.Codd 1970
1. SEQUEL:A Structured English Query Language 1974
2. Implentation of a Structured English Query Language 1975
3. A System R: Relational Approach to Database Management 1976
4. Granularity of Locks and Degrees of Consistency in a Shared DataBase --Jim Gray 1976
5. Access Path Selection in a RDBMS 1979
6. The Transaction Concept:Virtues and Limitations --Jim Gray
7. 2pc-2阶段提交:Notes on Data Base Operating Systems --Jim Gray
8. 3pc-3阶段提交:NONBLOCKING COMMIT PROTOCOLS
9. Life beyond Distributed Transactions:an Apostate’s Opinion
10. A Comparison of the Byzantine Agreement Problem and the Transaction Commit Problem --Jim Gray
11. Consensus on Transaction Commit --Jim Gray & Leslie Lamport
12. What Goes Around Comes Around - Michael Stonebraker, Joseph M. Hellerstein
13. A Formal Model of Crash Recovery in a Distributed System - Skeen, D. Stonebraker
14. ARIES: A Transaction Recovery Method Supporting Fine-Granularit y Locking and Partial Rollbacks Using Write-Ahead Logging-1992
四.大规模存储与计算(NoSql理论系列)
0. Towards Robust Distributed Systems:Brewer's 2000 PODC key notes
1. CAP理论
2. Harvest, Yield, and Scalable Tolerant Systems
九.其他
On Computable Numbers with an Application to the
Entscheidungsproblem-1936.5.28-A.M.Turing
The First Draft Report on the EDVAC-1945.6.30-John von Neumann
Reflections on Trusting Trust --Ken Thompson
Who Needs an Architect?
Go To statements considered harmfull --Edsger W.Dijkstra
No Silver Bullet Essence and Accidents of Software Engineering --Frederick P. Brooks
转载请注明作者:phylips@bmy 2011-4-30
出处:/blog/static/709717672011330101333271/再推荐一个相关文章:/html/1647.html
列举的大部分论文都是相同的,不过也有一些是各自独有的。