AOAC 15.1.04 AOAC Official Method 998.10 Efficacy of Preservation-国外标准规范
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:38.41 KB
- 文档页数:3

39.1.08AOAC Official Method 991.36 Fat (Crude) in Meat and Meat ProductsSolvent Extraction (Submersion) MethodFirst Action 1991Final Action 1996[Applicable to meat and meat food products that can be analyzed using 960.39 (see 39.1.05), 976.21 (see 39.1.06), and 985.15 (see39.1.07).]Results of the interlaboratory study supporting acceptance of the method:x—, 4.34% fat: s r= 0.106; s R = 0.112; RSD r= 2.44%; RSD R = 2.59%x—, 27.29% fat: s r= 0.534; s R = 0.637; RSD r= 1.95%; RSD R = 2.33%x—, 27.95% fat: s r= 0.648; s R = 0.739; RSD r= 2.32%; RSD R = 2.84%x—, 34.51% fat: s r= 0.764; s R = 0.799; RSD r= 2.21%; RSD R = 2.31%x—, 33.57% fat: s r= 0.340; s R = 0.516; RSD r= 1.01%; RSD R = 1.53%x—, 26.20% fat: s r= 0.406; s R = 0.631; RSD r= 1.55%; RSD R = 2.34%A. Apparatus装置(a) Extraction system.—Capable of simultaneous extraction of 6 test portions. Extraction unit for solvent addition to cups, 2-stage extraction process, and solvent recovery cycle. Service unit to supply hot oil through insulated tubing to extraction unit and to pump air for evaporation of last traces of solvent from cups (Soxtec System meets these specifications).(b) Thimbles and stand.—26 *60 mm, cellulose thimbles, and stand to hold 6 thimbles.(c) Extraction cups.—Al, 44 id, 60 mm height.(d) Glass beads.—3–4 mm diameter.(e) Mechanical convection oven. — Maintaining 125° ± 1°C.Items (a)–(c) are available as Soxtec sys tem from Perstorp Analytical/Tecator, Inc. (2875 C Towerview Rd, Herndon, V A 22071, USA).B. Reagents(a) Petroleum ether. — To meet specifications in 945.16A (see 27.4.04).(b) Sand.—<0.004 g extractables/5 g.(c) Cotton.—Defatted.C. DeterminationAccurately weigh ca 3 g test portion into thimble. Add sand to test portion and mix with glass rod. Place thimble in thimble stand and dry 1 h in 125°C oven. Remove from oven and let cool. Loosen test portion/sand mixture using glass rod. Wipe glass rod with small amount of cotton and place cotton in top of thimble. Transfer thimble to extraction unit. Accurately weigh extraction cup containing a few glass beads.Extract thimble with dried mixture with 40 mL petroleum ether in boiling position for 25 min and in rinsing position for 30 min. Adjust temperature of extraction unit to ensure condensation rate≥5 drops/s. At completion of extraction, close condenser valves and recover ether.Dry cup and contents 30 min in 125°C oven. Cool and weigh.D. CalculationsCalculate percent fat in test sample as follows:Fat content, % = (B -C) *100Awhere A = g test portion weight, B = g weight of extraction cup afterdrying, and C = g weight of extraction cup prior to extraction.Reference: J. AOAC Int. 75, 289(1992).39.1.07AOAC Official Method 985.15Fat (Crude) in Meat and Poultry 家禽Products Rapid Microwave-Solvent Extraction Method First Action 1985Final Action 1991A. Reagents and Apparatus(a) Automated solvent extractor.—Enclosed, self-contained, thermostatically controlled 恒温控制fat extraction and solvent recovery system with 0.5 mg fat sensitivity and 0–100% fat measurement range (CEM Corp., PO Box 200, Matthews, NC 28106, USA), or equivalent.(b) Methylene chloride.二氯甲烷—Reagent grade (Fisher Scientific Co., No. D-37) , or equivalent.(c) Glass fiber pads.玻璃纤维垫子—9.8 *10.2 cm rectangular 矩形and 11 cm round (CEM Corp.), or equivalent.(d) Microwave moisture analyzer.—0.2 mg H2O sensitivity, moisture/solids range of 0.1–99.9%,0.01% resolution分辨率. Includes automatic tare electronic balance, microwave drying system,and microprocessor digital computer control. Electronic balance pan is located inside drying chamber. (Balance sensitivity: 0.2 mg at 15 g capacity or 1.0 mg at 40 g capacity [CEM Corp., or equivalent].)B. DeterminationPrepare test samples as in 983.18 (see 39.1.01). Place 2 rectangular and one round glass fiber pad on balance pan inside microwave moisture analyzer, and tare. Remove rectangular pads and evenly spread ca 4 g well-mixed test portion onto rough side of one pad, cover with second pad, and place together with round pad on balance pan. Dry 3–5 min at 80–100% power, depending on product type. At end of drying cycle, remove from balance pan. Fold rectangular pads, with dried test portion, in half and place in automated solvent extractor chamber. Place round pad in recessed area at top of extractor chamber, close and latch lid. Start extraction cycle (test portion and rectangular pads are blended at this time with sufficient CH2Cl2to extract fat). After completion of extraction cycle, remove round pad with residue, and place on balance pan in microwave moisture analyzer. Redry pad and residue to constant weight (ca 30 s at 80–100% power) to re move residual solvent or moisture. Weight loss due to solvent extraction is converted to % fat by microprocessor and displayed on digital read out panel.Certain product classes require addition of adjustment factors to read out for accurate results, as follows: fresh meats, pre-blends, emulsions, cured/cooked meats, factor = 0.40; cooked sausages, factor = 0.80.Reference: JAOAC 68, 876(1985).39.1.06AOAC Official Method 976.21Fat (Crude) in Meat Rapid Specific Gravity MethodFirst Action 1976Final Action 1979A. Apparatus and Reagents(a) Foss-let fat analyzer.—Includes orbital shaker, specific gravity readout unit, solvent dispenser, reference standard oil (specific gravity at 23°C = 0.915; for periodic check of potentiometer calibration), stainless steel cup with cover and 8 mm bore brass hammer, pressure filtration device, and conversion chart (Foss Food Technology Corp.).(b) Drying agent.—Plaster of Paris (available locally through paint, hardware, or building supply dealers), 8 mesh Drierite, or an hydrous CaSO4.(c) Tetrachloroethylene.—Technical grade C2Cl4 (distributed locally through dry cleaning sup pliers or Fisher Scientific Co.,No. C-182).B. Deter mi na tionPrepare test sam ples as in 983.18 (see 39.1.01). Check calibration of Foss-let potentiometer daily by us ing C2Cl4 alone to set zero point.Use mixture of 22.5 g reference standard oil and 120 mL C2Cl4(specific gravity of mixture at 37° = 1.4763) to set 50% fat point at 850.0.Using either top-load or triple-beam balance with 0.1 g sensitivity, tare Foss-let cup after setting brass ham mer on itsspin dle. To an a lyze prod ucts con tain ing £60% fat, weigh 45.0 gtest sam ple into cup; for prod ucts con tain ing >60% fat, weigh22.5 g. Add ca 80 g Plas ter of Paris (or ca 60 g an hy drous CaSO4).Dis pense 120 mL C2Cl4 into cup. Press cover onto cup and in stall inor bital shaker. Set shaker timer for 2 min and turn unit on. Whileex trac tion pro ceeds, as sem ble pres sure fil tra tion de vice by plac inginto per fo rated base 7 cm fil ter pa per. To pro duce clear fil trate freeof mois ture drop lets (for very wet test sam ples), first place highre ten tion pa per, Whatman No. 50, or equiv a lent, and then phasesep a rat ing pa per, Whatman No. 1PS, or equiv a lent. Af ter 2 minex trac tion, re move cup from shaker, lift cover, and re move brassham mer from cup. Im merse cup in ice-water bath ca 0.4 min whilestir ring con tents with ther mom e ter to cool con tents from 47°–52°Cto ca 40°C. Wipe H2O from outer sur face of cup and pour con tentsinto as sem bled fil ter. Place pis ton at top of fil tra tion de vice andslowly press ex tract through mea sur ing sys tem. De press drain valvebut ton when ex tract ap pears in over flow tube and let cham ber drain;then re lease valve but ton. Re peat fill ing and drain ing 2 more timesun til 40–50 mL ex tract has flowed through, re tain ing fi nal 10 mLex tract in mea sur ing cham ber. Re move fil tra tion de vice, slideview ing lens into po si tion, ro tate con trol of read out po ten ti om e terclock wise un til hy drom e ter rises, and re cord read ing. Es tab lish thatex tract is at cham ber tem per a ture by re peat ing read ing 3–4 times.Av er age read ings and con vert into % fat by means of con ver sion chart. (Mul ti ply chart % fat by 2 if a 22.5 g por tion of high-fat product was used.)Ref er ences: JAOAC 58, 1182(1975); 60, 853(1977);68, 240(1985).。


AOAC 官方方法999.03 食品中总果糖的测定酶/分光光度法1999年第一次执行(适用于食品中果糖的测定。
不适用于高度解聚的果糖,无论是酸的还是酶的。
)支持方法验收的实验室间研究结果见表999.03。
A.原理用热水提取产物以溶解果聚糖。
将等份的提取物用特定的蔗糖酶处理以将蔗糖水解成葡萄糖和果糖,并用纯淀粉降解酶的混合物将淀粉水解成葡萄糖。
所有还原糖用碱性硼氢化物还原成糖醇。
果聚糖用纯化的果聚糖酶(外切-菊粉酶加内切-菊粉酶)水解成果糖和葡萄糖,并且这些糖通过β-羟基苯甲酸酰肼(PAHBAH)方法测量用于还原糖。
B.装置设备(a)研磨机。
(b)热板。
带磁力搅拌器。
(c)水浴.保持40±0.1℃。
(d)沸水浴。
(e)涡旋混合器。
(f)pH计。
(g)停止计时器。
(h)滤纸。
(i)真空烘箱。
用于干燥果糖标准品。
(j)分光光度计。
在410nm下操作。
(k)移液管。
用一次性吸头输送100和200μL。
或者,可以使用机动手持式分液器。
(l)正位移移液器。
(m)玻璃试管。
(n)容量瓶。
(0)聚丙烯容器。
C.试剂所有试剂应具有分析纯度等级。
(a)马来酸钠缓冲液。
100mM。
pH 6.5。
将11.6g马来酸溶于900mL蒸馏水中,用2M NaOH(8.0g NaOH / 100mL)将pH调节至6.5,并用水稀释至体积1L容量瓶中。
储存在4℃。
(b)乙酸钠缓冲液。
100mM。
pH 4.5。
将5.8 mL冰醋酸(1.05 g / mL)吸取到900 mL蒸馏水中。
使用1M NaOH调节至pH 4.5并用水稀释至1L。
储存在4°C。
(c)对羟基苯甲酸酰肼(PAHBAH)还原糖分析试剂.(1)溶液A.-在磁力搅拌器上,在250mL烧杯中加入10g PAHBAH至60mL水中。
搅拌浆液并加入10mL浓HCl。
用蒸馏水调节至200 mL并在室温(约22°C)下储存。
溶液稳定至少2年。
(2)溶液B.-将24.9g柠檬酸三钠二水合物加入500mL蒸馏水中并搅拌溶解。


Page 1 of 2 ColiComplete ®AOAC Official Method 992.30General DescriptionColiComplete ® contains 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-ß-Dgalactopyranoside (X-Gal) and 4-methyl umbelliferyl-ß-D-glucuronide (MUG). Discs are added to LST inoculated with selected dilutions of samples. Samples are incubated at 35–37 °C and examined after 24 and 48 ±2 h for confirmed total coliforms and after 30 ±2 h for confirmed E. coli results. ß-Galactosidase, from coliforms present in samples, cleaves X-Gal into 5-bromo-4-chloro-indoxyl intermediate which undergoes oxidation to yield water-insoluble blue dimer, visually detectable on disc or in surrounding medium as confirmed positive result for total coliform activity. ß-Glucuronidase, from E. coli present in samples, cleaves MUG into glucuronide and methyl umbelliferone which fluoresces under long wave UV light (366 nm) as confirmed positive result for E. coli presence.NOTE : As E. coli O157:H7 does not produce ß-glucuronidase, ColiComplete ® is not suitable for the detection of E. coli O157:H7.A. Sample PreparationPrepare appropriate serial dilutions as indicated in FDA Bacteriological Analytical Manual (BAM), or AOAC Official Methods of Analysis according to sample type.B. InoculationInoculate LST tubes with appropriate sample dilution series selected to determine MPN levels or presence/absence of total coliforms and E. coli in sample. Aseptically add a single ColiComplete ® disc to each tube. Incubate at 35–37 °C.C. Reading ColiComplete ®a. For total coliforms — After at least 24 h incubation, examine each tube for visually detectable blue color on disc or in surrounding medium. Presence of blue color indicates confirmed positive result for total coliforms.NOTE: A wide range of blue color intensity may be expected, depending on sample composition and microflora. All blue reactions are positive regardless of intensity of color.Reincubate at 35–37 °C. After additional 24 ±2 h re-examine. Continued absence of blue indicates negative result; presence of blue indicates confirmed positive result for total coliforms. Read and record the MPN code or presence/absence of total coliforms in the sample.b. For E.coli — After 30 ±2 h from start of initial incubation, examine tubes under long-wave UV light (366 nm). Fluorescent tubes indicate confirmed positive result for E. coli. Read and record the MPN code or presence/absence of E. coli in the sample.D. CONTROLSPositive and negative controls should be used to facilitate interpretation of MUG fluorescent reaction. Use one known positive E. coli tube and two negative controls - one non -E. coli /coliform tube (e.g., Klebsiella spp.) and one uninoculated media tube.NOTE: Use borosilicate glass tubes, flint glass gives fluorescence that may be misinterpreted for a positive result.Lit. No. MK_UG4655EN Merck KGaAFrankfurter Strasse 25064293 DarmstadtGermanyPage 2 of 2 E. Method Modification for Certain JuicesApplicable to juice products/processors which rely on treatments that do not come into direct contact with all parts of the juice, as contained in 21 CFR Part 120: Rules and Regulations. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HAACP); Procedures for the Safe and Sanitary Processing and Importing of Juice; Final Rule. Vol 66 No. 13. 6137-6202. Use the modified method “Analysis for Escherichia coli in Citrus Juices - Modifi cation of AOAC Official Method 992.30” as stated in Section 120.25 (a).F. StorageStore unused discs at 2–8 °C (36–46 °F) in a sealed container, with desiccant.G. DisposalAfter use, all tubes must be steam-sterilized at 121 °C for at least 30 min before discarding. For in-vitro diagnostic use only.Manufacturing EntityBioControl Systems, Inc, 12822 SE 32nd St, Bellevue, WA 98005, USA.BioControl Systems, Inc is an affiliate of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany.。

AOAC Official Method 995.03Capsaicinoids in Capsicums and Their ExtractivesLiquid Chromatographic MethodFirst Action 1995[Applicable for determination of 750-650000 Scoville Heat Units (SHU) of capsaicinoids in ground and crushed red pepper, chili pepper, ground cayenne pepper, ground jalapeno pepper, and red pepper oleoresins. Not applicable to chili powders or products containing oregano or thyme.](Caution: See Appendix B, safety notes for the safe handling of organic solvents and special chemical hazards-acetone, acetonitrile, and ethanol. See Material Safety Data Sheets, or equivalent, for each reagent. N-Vanillyi-nnonanamide is an extreme irritant; do not inhale. Dispose of waste solvents in an appropriate manner compatible with applicable environmental rules and regulations.)Method Performance:See Table 995.03 for method performance data.A. PrincipleTest sample is extracted in warm ethanol using reflux condenser. Extract is filtered and injected into liquid chromatograph equipped with UV or fluorescence detector.B. Apparatus (a) Liquid chromatograph (LC).--Equipped with I V integrator, 20 gL sample injector, and with UV detector set at 280 run. wavelength or fluorometer with excitation 280 nm and emission 325 nm. Operating conditions: temperature, ambient (20-25'C); flow rate, 1.5 mL/min., isocratic; relative retention times: N-vanillyl-n-nonanamide, 1.00; nordihydrocapsaicin, 0.90; capsaicin, 1.00; dihydrocapsaicin, 1.58. See Figure 995.03 for baseline separation of major capsaicinoids.(b) LC column.--Stainless, C18, 150 x 4.6 mm id, packed with 5 micrometer particle size. Use guard column, if desired.(c) Reflux condenser.(d) Syringe filter.- 0.45 micrometer.(e) C18 solid-phase extraction cartridge.C. Reagents(a) Ethanol-95% or denatured, suitable for chromatography(b) Acetone.-ACS grade.(c) LC mobile phase@Acetonitrile-water. Use LC grade solvents, or equivalent. Mix400 mL acetonitrile with 600 mL H20 containing 1% acetic acid (v/v). De-gas with helium or by other suitable technique.(d) N-Vanillyl-n-nonanamide standard solutions. -N-Vanillyln-nonanamide standard, 99%, is available as synthetic capsaicin from Penta International Corp., 50 Okner Pkwy, Livingston, NJ 07039. Keep solutions out of direct sunlight. (1) Standard solution A.-0. 15 mg/mL. Accurately weigh 75 mg N-vanillyl-n-nonanamide and transfer it into 500 mL volumetric flask. Dilute to volume with ethanol, and mix. Use standard solution A for analyzing all peppers except chili pepper.(2) Standard solution B.-0.015 mglmL. Transfer 10 mL standard solution A into I 00 mL volumetric flask, dilute to volume with ethanol, and mix. Use standard solution B when analyzing chili peppers.D. Extraction(a) Ground or crushed peppers.-Accurately weigh ca 25 g pepper into 500 ITIL boiling flask. Place 200 mL ethanol into same flask, add several glass beads, and attach flask to reflux condenser. Gently reflux test sample 5 h and then allow to cool. Filter 1-4 mL sample through 0.45 gm syringe filter into small glass vial. Use for LC analysis.(b) Red pepper oleoresins.-Accurately weigh 1-2 g oleoresin into 50 mL volumetric flask. Increase weight of sample, if total capsaicinoid concentration is < 1 %. Note: Do not allow any oleoresin to coat sides of flask.Add 5 mL acetone, C(b), to flask and swirl contents of flask until test sample is completely dispersed (no oleoresin can coat bottom of flask when turning flask neck at 45' angle). Add five 3-5 mL portions ethanol, swirling flask during each addition. Dilute contents of flask to volume with ethanol and mix well.Figure 995.03-Red pepper extract analyzed by (a) fluorescence detection, and (b) UV detection.Peak 1 = nordihydrocapsaicin; peak 2 = capsaicin; peak 3 = dihydrocapsaicinHold C18 solid-phase extraction cartridge over 25 mL volumetric flask or place cartridge on 10 mL glass syringe and hold over 25 mL volumetric flask. Transfer 5 mL solution from flask to cartridge or syringe. (Note: When using syringe, deliver solution to bottom of syringe so that sides of syringe are not coated with sample.) Pass aliquot through cartridge and collect in 25 mL flask. Wash cartridge 3 times with 5 mL ethanol, collecting washings in same flask. Dilute contents of flask to volume with ethanol and mix. Filter 1-4 mL solution through 0.45 micrometer syringe filter into small glass vial. Use for LC analysis.E. LC DeterminationInject 20 microliters standard solution B, C(d)(2), onto LC column, when analyzing chili peppers. When analyzing other matrices inject 20 microliters standard solution A, C(d)(1). Re-inject standard solution at intervals of 6 sample injections, or less.Inject in duplicate 20 microliter test sample from D onto LC column.After <30 sample injections, purge LC column 30 min with 100% acetonitrile at 1.5 mL/min flow rate. Use LC mobile phase, C(c), for further analysis.F. CalculationCapsaicinoids contain 3 major compounds: nordihydrocapsaicin (N), capsaicin (C), and dihydrocapsaicin (D). Calculate capsaicinoids as sum of these compounds [N + C + D; in Scoville Heat Units (SHU); 1 microgram total capsaicinoids/g = ca 15 SHU], as follows: (a) UV detection(1) Ground peppers and chili pepper.-N = (Pn/Ps) x (Cs/Wt) x (200/0.98) x 9300C = (Pc/Ps) x (Cs/Wt x (200/0.89) x 16100D = (Pd/Ps) x (Cs/Wt) x (200/0.93) x 16100where Pn, Pc, and Pd = average peak areas for nordihydrocapsaicin, capsaicin, and dihydrocapsaicin, respectively, from duplicate injections; Ps = average peak area of appropriate standard solution; Cs = concentration of standard solution, mg/mL; Wt = weight of test sample, g(2) Red pepper oleoresins:N= (Pn/Ps) x (Cs/Wt) x (250/0.98) x 9300C = (Pc/Ps) x (CS/Wt) x (250/0.89) x 16100D = (Pd/Ps) x (CS/Wt) x (250/0.93) x 16100(b) Fluorescence detection (1) Ground peppers and chili pepper.N= (Pn/Ps) x (Cs/Wt) x (200/0.92) x 9300C = (Pc/Ps) x (CS/Wt) x (200/0.88) x 16100D = (Pd/Ps) x (CS/Wt) x (200/0.93) x 16100(2) Red pepper oleoresins:N= (Pn/Ps) x (Cs/Wt) x (250/0.92) x 9300C = (Pc/Ps) x (CS/Wt) x (250/0.88) x 16100D = (Pd/Ps) x (CS/Wt) x (250/0.93) x 16100Reference: J. AOAC Int. (future issue).(c) 1996 AOAC INTERNATIONAL。

31.5.04AOAC Official Method980.13Fructose,Glucose,Lactose,Maltose,and Sucrose in Milk ChocolateLiquid Chromatographic MethodFirst Action1980Final ActionA.Apparatus(a)Liquid chromatograph.—With Waters Associates,Inc. M6000A pump,R401refractive index detector,or equivalent,and 10mV recorder.(b)Column packing.—Waters Associates,Inc.µ-Bondapak car-bohydrate column,300×4(id)mm.Column must meet following criteria:Capacity factor for fructose=K′=(t R−t0)/t0≥5where t R=retention time for fructose=time from injection to maxi-mum peak height of fructose;t0=retention time for solvent=time from injection to maximum peak height of first baseline distortion or solvent peak.Resolution factor(distance between2band centers divided by av-erage band width)=R s=(t2-t1)/0.5(t w1+t w2)where t2and t1=times from injection to maximum peak heights of second peak(glucose)and first peak(fructose),respectively;and t w1 and t w2=baseline widths(in time units)of first and second peaks,re-spectively.For fructose:glucose ratios of2.0–0.5,R s≥1.0;for ratios ≥2,R s≥1.25.Replace column when either or both criteria are not met.(c)Injection valve.—Waters Associates,Inc.7120LC injector with50µL loop,or equivalent.(d)Ancillary equipment.—Bransonic12ultrasonic bath (Branson Ultrasonics Corp.,Eagle Rd,Danbury CT06810-1961, USA,No.B1210MT),or equivalent,to degas solvents;Corning PC353stirrer(replaced by PC510);and filtration apparatus for solvent purification.B.Reagents(a)Sugar standard solution.—10µg/mL.Dry individual sugar standards(fructose,glucose,sucrose,lactose,and maltose;available from Sigma Chemical Co.)12h at60°C under vacuum.Dissolve in H2O and serially dilute to concentration of10µg/mL.Prepare daily.(b)Mobile phase.—CH3CN(No.2442,Mallinckrodt Nanograde,or equivalent)+H2O(charcoal filtered)(80+20).Filter through Whatman GF/F0.7µm glass fiber filter,and degas in ultra-sonic bath before use.C.Preparation of Test SampleWeigh10.0g finely divided milk chocolate into≥100mL centri-fuge bottle and add50mL petroleum ether.Centrifuge ca15min at ca1800rpm.Decant and discard supernate.Repeat extraction. Pulverize residue with glass rod,add100g H2O,and weigh. Place in85–90°C H2O bath25min.Cool to room temperature and add H2O to original weight.Centrifuge10min at2000rpm,with-draw portion of clear supernate,and filter through0.45µm Swinney syringe filter.D.DeterminationFill50µL injection loop with test sample solution and inject into col-umn with mobile solvent flowing at1.5–2.0mL/min.Calculate concen-trations of each sugar by comparing peak heights or areas of each sugar peak from test sample with corresponding height or area of standard. Use same method of measurement(area or height)throughout. Reference:JAOAC63,595(1980).CAS-57-48-7(fructose)CAS-50-99-7(glucose)CAS-63-42-3(lactose)CAS-69-79-4(maltose)CAS-57-50-1(sucrose)©2000AOAC INTERNATIONAL。

膳食纤维标准方法
膳食纤维是指人体无法消化吸收的碳水化合物类物质。
膳食纤维对人体健康具有重要的作用,包括促进消化系统健康、调节血糖和胆固醇水平、预防便秘以及控制体重等。
为了准确测量食物中的膳食纤维含量,需要进行标准方法的测定。
目前,国际通用的膳食纤维含量测定方法有两种:AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists)方法和ISO (International Organization for Standardization)方法。
1. AOAC方法:AOAC方法是美国官方方法,也是国际上最常用的方法。
根据AOAC 991.43或AOAC 985.29方法,首先将食物样品经过一系列处理,如酶解、水解等,获得可溶性和不可溶性纤维。
然后,借助酶解、滴定、重量等技术手段,可以得到总纤维、不可溶性纤维和可溶性纤维的含量。
2. ISO方法:ISO方法是由国际标准化组织制定的方法,与AOAC方法相似。
ISO 13904和ISO 15954方法是常用的ISO 方法。
这些方法主要利用酶解、水解、甲弹法等技术,将膳食纤维分为不可溶性纤维和可溶性纤维,并使用滴定、重量等手段进行测定。
无论使用AOAC方法还是ISO方法,都需要进行样品的预处理、酶解、滴定等步骤,以获得准确的膳食纤维含量。
这些方法在实验室条件下进行,需要仪器设备和专业操作人员进行操作。
需要注意的是,虽然AOAC和ISO方法都是国际通用的标准方法,但在具体的实验操作过程中,可能会存在一些差异,因此在测定过程中应当依据相应的方法详细操作,并遵循实验室的操作规程。
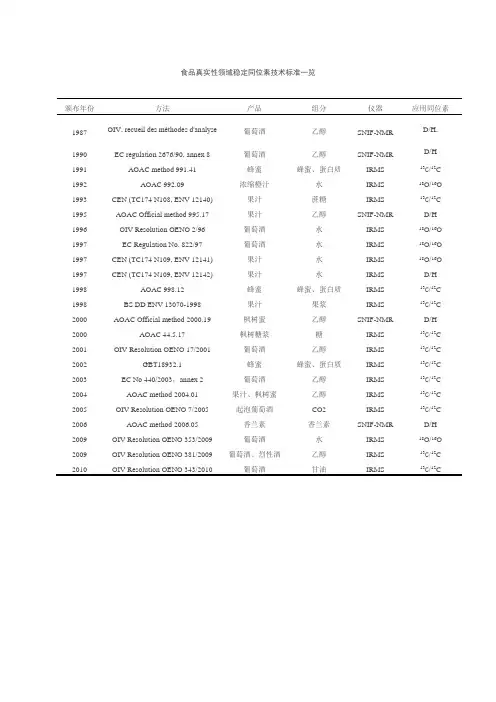
食品真实性领域稳定同位素技术标准一览颁布年份方法产品组分仪器应用同位素1987OIV, recueil des méthodes d'analyse葡萄酒乙醇SNIF-NMR D/H,1990EC regulation 2676/90, annex 8葡萄酒乙醇SNIF-NMR D/H 1991AOAC method 991.41蜂蜜蜂蜜、蛋白质IRMS13C/12C 1992AOAC 992.09浓缩橙汁水IRMS18O/16O 1993CEN (TC174 N108, ENV 12140)果汁蔗糖IRMS13C/12C 1995AOAC Official method 995.17果汁乙醇SNIF-NMR D/H 1996OIV Resolution OENO 2/96葡萄酒水IRMS18O/16O 1997EC Regulation No. 822/97葡萄酒水IRMS18O/16O 1997CEN (TC174 N109, ENV 12141)果汁水IRMS18O/16O 1997CEN (TC174 N109, ENV 12142)果汁水IRMS D/H 1998AOAC 998.12蜂蜜蜂蜜、蛋白质IRMS13C/12C 1998BS DD ENV 13070-1998果汁果浆IRMS13C/12C 2000AOAC Official method 2000.19枫树蜜乙醇SNIF-NMR D/H 2000AOAC 44.5.17枫树糖浆糖IRMS13C/12C 2001OIV Resolution OENO 17/2001葡萄酒乙醇IRMS13C/12C 2002GBT18932.1蜂蜜蜂蜜、蛋白质IRMS13C/12C 2003EC No 440/2003,annex 2葡萄酒乙醇IRMS13C/12C 2004AOAC method 2004.01果汁、枫树蜜乙醇IRMS13C/12C 2005OIV Resolution OENO 7/2005起泡葡萄酒CO2IRMS13C/12C 2006AOAC method 2006.05香兰素香兰素SNIF-NMR D/H 2009OIV Resolution OENO 353/2009葡萄酒水IRMS18O/16O 2009OIV Resolution OENO 381/2009葡萄酒、烈性酒乙醇IRMS13C/12C 2010OIV Resolution OENO 343/2010葡萄酒甘油IRMS13C/12C。

凯氏方法测牛奶中蛋白质含量牛奶的蛋白质含量大约为3.2g/100ml(512mg氮),人奶的蛋白质含量较少,约为1g/100ml,而其他动物的奶的蛋白质含量比牛奶还高(如羊奶5.6g/100ml)。
检测流程:1、样品:5ml(新鲜牛奶中大约有25 ~ 26mg氮)放在消化管内2、消化用的催化剂:加在每一个放有试样的消化管内:7gK2SO45mg硒粉(Se)7ml浓硫酸H2SO4(98%)5ml双氧水H2O2 35%(130 voll)2~3片沸石3、消化:420℃下加热30分钟4、冷却:将消化管冷却到50~60℃5、蒸馏:将消化管放在蒸馏装置的位置上,选择标准方法1按开始键进行蒸馏,实验中的参数如下:系数:6.38稀释水=50mlH3BO3=30mlNaOH=50ml滴定液:HCl 0.1mol/L6、参考:AOAC,“Official methods of analysis”, method 991.20凯氏方法测定杏仁,坚果,榛子中蛋白质的含量过程:1、样品:将样品粉碎,精确称量0.5-0.8g样品,精度为0.1mg,放在消化管内2、消化用的催化剂:加在每一个放有试样的消化管内:7g硫酸钾K2SO40.8g五水硫酸铜CuSO412ml浓硫酸H2SO4(98%)2-3滴辛醇或消泡剂轻轻摇晃消化管,将其混匀3、消化:420℃下加热60分钟4、冷却:将消化管冷却到50~60℃5、蒸馏:将消化管放在蒸馏装置的位置上,选择标准方法2按开始键进行蒸馏,实验中的参数如下:系数:5.18稀释水=50mlH3BO3=30mlNaOH=50ml滴定液:HCl 0.2mol/L6、参考:AOAC,“Official methods of analysis”, method 950.48凯氏方法测定椰子中蛋白质的含量过程:1、样品:将样品粉碎,精确称量0.5-0.8g样品,精度为0.1mg,放在消化管内2、消化用的催化剂:加在每一个放有试样的消化管内:7g硫酸钾K2SO40.8g五水硫酸铜CuSO412ml浓硫酸H2SO4(98%)2-3滴辛醇或消泡剂轻轻摇晃消化管,将其混匀3、消化:420℃下加热60分钟4、冷却:将消化管冷却到50~60℃5、蒸馏:将消化管放在蒸馏装置的位置上,选择标准方法3按开始键进行蒸馏,实验中的参数如下:系数:5.30稀释水=50mlH3BO3=30mlNaOH=50ml滴定液:HCl 0.2mol/L6、参考:AOAC,“Official methods of analysis”, method 950.48凯氏方法测定花生及巴西果中蛋白质的含量过程:1、样品:将样品粉碎,精确称量0.5-0.8g样品,精度为0.1mg,放在消化管内2、消化用的催化剂:加在每一个放有试样的消化管内:7g硫酸钾K2SO40.8g五水硫酸铜CuSO412ml浓硫酸H2SO4(98%)2-3滴辛醇或消泡剂轻轻摇晃消化管,将其混匀3、消化:420℃下加热60分钟4、冷却:将消化管冷却到50~60℃5、蒸馏:将消化管放在蒸馏装置的位置上,选择标准方法4按开始键进行蒸馏,实验中的参数如下:系数:5.46稀释水=50mlH3BO3=30mlNaOH=50ml滴定液:HCl 0.2mol/L6、参考:AOAC,“Official methods of analysis”, method 950.48啤酒中的可溶性提取物有蛋白质和一些氨类物质,可占到啤酒重量的3%-12%。
中国合格评定国家认可委员会实验室认可证书附件(AS L2215)名称:东莞出入境检验检疫局检验检疫综合技术中心地址:广东省东莞市建设路3号签发日期:2009年08月21日有效期至:2010年09月05日附件1-1 认可的检测能力范围CHINA NATIONAL ACCREDITATION SERVICE FOR CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT APPENDIX OF LABORATORY ACCREDITATION CERTIFICATE(AS L2215)NAME: Integrated Technology Center of Dongguan Entry-exit Inspection and Quarantine BureauADDRESS:No.3, Jianshe Road, Dongguan, Guangdong, China Date of issue: 2009-08-21 Date of expiry: 2010-09-05 APPENDIX1-1 LIST OF ACCREDITED TESTING SCOPE中国合格评定国家认可委员会实验室认可证书附件(AS L2215)名称:东莞出入境检验检疫局检验检疫综合技术中心地址:广东省东莞市建设路3号签发日期:2009年08月21日有效期至:2010年09月05日附件2 认可的授权签字人及其授权签字领域CHINA NATIONAL ACCREDITATION SERVICE FOR CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT APPENDIX OF LABORATORY ACCREDITATION CERTIFICATE(AS L2215)NAME: Integrated Technology Center of Dongguan Entry-exit Inspection and Quarantine BureauADDRESS:No.3, Jianshe Road, Dongguan, Guangdong, China Date of issue: 2009-08-21 Date of expiry: 2010-09-05 APPENDIX2 LIST OF ACCREDITED SIGNATORY AND SCOPE中国合格评定国家认可委员会实验室认可证书附件(AS L2215)名称:东莞出入境检验检疫局检验检疫综合技术中心地址:广东省东莞市体育路28号A座签发日期:2009年08月21日有效期至:2010年09月05日附件1-1 认可的检测能力范围CHINA NATIONAL ACCREDITATION SERVICE FOR CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT APPENDIX OF LABORATORY ACCREDITATION CERTIFICATE(AS L2215)NAME: Integrated Technology Center of Dongguan Entry-exit Inspection and Quarantine BureauADDRESS:No.28A Tiyu Road, Dongguan, Guangdong, ChinaDate of issue: 2009-08-21 Date of expiry: 2010-09-05 APPENDIX1-1 LIST OF ACCREDITED TESTING SCOPE。
膳食纤维的测定方法作者:赵升鹏周超进来源:《都市家教·上半月》2013年第05期【摘要】膳食纤维被称为人体的第七营养素,对维持人体健康具有重要作用。
膳食纤维通过发酵产物短链脂肪酸和对肠道菌群的调节作用从而影响肠道健康,本文对膳食纤维的测定方法进行了综述。
【关键词】膳食纤维;定义;测定膳食纤维已被确认为与传统的六大营养素并列的“第七营养素”,对维持人体健康具有重要的生理作用。
膳食纤维的理化特性概括起来是膨胀作用、持水能力、胶体形成、离子交换、改善胃肠微生物菌落和产生低热量等。
这些特性产生的生理作用如下:使人产生饱腹感并抑制进食,从而预防肥胖;润肠通便,防治肠道疾病和便秘;调控血清胆固醇,降血压,防治冠状动脉硬化,胆石症和预防心脑血管疾病;降血糖,防治糖尿病等。
目前,结肠癌、炎症性肠炎和其他结肠紊乱疾病已经严重影响身体健康。
膳食纤维为肠道微生物生长提供均衡的能量和营养,这是维持结肠生态系统平衡所必需的,另外,膳食纤维的发酵,特别是丁酸发酵,有利于结肠健康。
目前国内外业已研究开发的膳食纤维共有6大类约30余种,其中实际生产和应用的不超过10种。
一、膳食纤维膳食纤维(Dietary Fiber,DF)被认为是食物中不被人体胃肠道消化酶水解,但能被肠道微生物消化的物质,特别是植物成分。
膳食纤维包括非淀粉多糖,如纤维素、半纤维素、树胶、果胶,以及木质素、抗性糊精和抗性淀粉。
二、膳食纤维的测定世界卫生组织建议的总膳食纤维摄入量下限为每人每天27.0克,上限为每人每天40.0克。
由此可见:膳食纤维检测结果的表示及产品标签标示等方面的问题应该作为膳食纤维研究中的又一个重要方面,而检测结果是由膳食纤维的检测方法和检测标准决定的,因此有必要建立统一的检测方法和标准。
DF的不同测定方法因其测定原理不同结果差异较大。
自20世纪60年代初以来,分析化学家们建立起大量的检测方法,具有代表性的几种方法为非酶重量法、酶-重量和酶-化学法。
30.1.23AAOAC Official Method995.13Carbohydrates in Soluble(Instant)CoffeeAnion-Exchange Chromatographic Methodwith Pulsed Amperometric DetectionFirst Action1995(Applicable for determination of free and total carbohydrates[ex-cept total fructose,which is degraded]in soluble[instant]coffee.) See Tables995.13A–J for the results of the interlaboratory study supporting the acceptance of the method.A.PrincipleFree carbohydrates.—Coffee is dissolved in H2O.Solution is fil-tered through C18disposable cartridge,and then through0.2µm membrane filter.Filtered solution is injected onto LC system.Car-bohydrates are separated on pellicular anion-exchange column and measured by pulsed amperometric detector.Total carbohydrates.—Coffee is hydrolyzed with1M HCl.Solu-tion is filtered and then passed through cation-exchange disposable cartridge in the Ag form to neutralize solution and to eliminate the Cl anion prior to injection onto LC system.B.Apparatus(a)Balance.—Analytical,weighing to0.1mg.(b)Flasks.—250mL round-bottom.(c)Volumetric flasks.—100and1000mL.(d)Pipets.—Delivering200–1000µL and5µL;with disposable tips.(e)Cylinders.—50and1000mL,tall-form,graduated.(f)Funnels.—Analytical,60°C.(g)Vacuum filtering system.—Aspirator with regulating device. System should include:heavy-walled filtering flask with ground cone neck,1L;funnel with ground glass joint,300mL;aluminum assembly clip;connection with vacuum outlet;filter holder,47mm id;and low-water extractable membrane filters,0.2µm porosity, 47mm diameter.(h)Filter papers.—Qualitative,folded,medium fast.(i)C18cartridges.—Octadecylated silica(ca10%C);6mL car-tridge volume;capable of holding500mg test portion;disposable.Con-dition and use cartridges according to manufacturer’s instructions. (j)Cation-exchange cartridges.—Styrene-based resin,Ag form, 1.8–2.0milliequivalent capacity/cartridge;disposable.Condition and use cartridges according to manufacturer’s instructions. (k)Membrane filters.—0.2µm porosity,25mm diameter;dis-posable;polypropylene.(l)Water bath.—Maintaining98±2°C.(m)Liquid chromatograph(LC).—Metal-free,compatible with 300mM NaOH.Operating conditions:mobile phase,isocratic(see Table995.13for mobile phase conditions);column temperature, ambient;flow rate,1.0mL/min;post-column solvent,300mM NaOH at0.6mL/min;detector settings,optimum parameters as pro-vided by e with computing integrator.(n)LC column.—250×4mm id;packed with polystyrene divinylbenzene substrate(10µm diameter)agglomerated with microbead quaternary amine functionalized latex(350nm diame-ter);5%cross-linked.(o)Pulsed amperometric detector.—With gold electrode.Fill reference cell with300mM NaOH.Select the detector range to avoid saturation of the major peak in chromatogram.(p)Guard column.—50×4mm id,packed with the same mate-rial as analytical column,(n).(q)Post-column solvent delivery system.—Compatible with 300mM NaOH.C.ReagentsUse18MΩ⋅cm demineralized H2O throughout.(a)Sodium hydroxide.—50%(w/w)aqueous solution,contain-ing minimum amount of Na2CO3and Hg.Do not shake or stir solu-tion before use.(b)Hydrochloric acid solution.—1.00M standard volumetric so-lution(83.3mL HCl/L).(c)Eluent A.—18MΩ⋅cm demineralized water.Filter through0.2µm membrane filter.Degas by sparging with He20–30min.Pre-pare fresh eluent A daily.(d)Eluent B.—300mM NaOH.Pipet15.6mL50%NaOH into 985mL eluent A.Degas by sparging with He20–30min.Eluent B is stable2days if stored at room temperature under He.(Note:It is crit-ical to remove dissolved CO2from eluents.Carbonate acts as strong “pusher”on LC column,resulting in drastic reduction in resolution.)(e)Carbohydrates standard solutions.—(1)Standard stock solu-tions.—1mg/mL aqueous stock solutions of arabinose,fructose, fucose,galactose,glucose,mannose,rhamnose monohydrate, ribose,xylose,sucrose,and mannitol.Weigh100mg each carbohy-drate to the nearest0.1mg into separate100mL volumetric flasks, dissolve in H2O,and dilute to volume with H2O.(2)Mixed carbohy-drates standard solution.—Further dilute and mix carbohydrates stock solutions to reach carbohydrate concentrations similar to those found in nonhydrolyzed or hydrolyzed soluble coffee test solutions. Pass diluted carbohydrates standard solution through0.2µm mem-brane filter prior to injection onto LC column.(Note:If resolution of rhamnose from arabinose is difficult to achieve,do not add rhamnose to mixed standard solution.)D.Isolation of CarbohydratesUse soluble coffee as is without grinding or homogenization.(a)Free carbohydrates.—Weigh300mg coffee to the nearest0.1mg into100mL volumetric flask.Add70mL H2O and shake until dissolution is complete.Dilute solution to volume with H2O.Filter 5–10mL solution through C18cartridge.Discard the first1mL.Pass fil-trate through0.2µm membrane filter prior to LC injection.(b)Total carbohydrates.—Weigh300mg coffee to the nearest0.1mg into100mL volumetric flask.Add50mL1.00M HCl and swirl.Place flask in boiling water bath for2.5h.(Note:Always keep the level of solution in flask below that of H2O in bath.)Swirl flaskTable995.13Conditions of mobile phase for determinationof free and total carbohydrates in solublecoffee by anion-exchange chromatographicmethod with pulsed amperometric detection Time,min Eluent A,%Eluent B,%01000(start acquisition) 50.01000(stop acquisition) 50.10100(start cleanup) 65.00100(stop cleanup) 65.11000(start re-equilibrium) 80.01000(stop re-equilibrium)Test sample N a Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 17(2)0.024 1.6590.0010.041 1′11(0)0.1797.0500.0350.021 211(1)0.0600.91580.0020.10 2′11(0)0.1517.6460.0320.20 311(0) 1.5 2.89.90.120.44 3′11(1) 1.85 2.2180.120.94 411(0)0.619 3.6240.0630.42 4′11(0)0.782 4.6210.100.45 59(1)0.1928.2340.0450.18 5′11(0)0.30011370.0910.32 68(1)0.0597.1490.0120.083 6′10(0)0.1799.8500.050.25 a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).Table995.13B Interlaboratory study results of the determination of free arabinose in soluble coffeeTest sample N a Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 111(0)0.891 3.7140.0920.035 1′11(0) 3.54 6.6210.66 2.1 29(2) 1.320 1.6 5.10.0600.19 2′11(0) 4.83 3.3170.45 2.4 311(0)0.464 3.8110.0490.14 3′11(0) 4.76 3.1130.42 1.7 411(0)0.7477.3120.150.25 4′11(0) 4.54 4.618.40.59 2.4 510(1)0.505 4.47.70.0630.11 5′9(2) 4.08 3.0 4.90.340.56 611(0)0.629 4.18.90.0730.16 6′11(0) 3.79 5.7200.61 2.2a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).Table995.13C Interlaboratory study results of the determination of free galactose in soluble coffeeTest sample N Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 111(0)0.562 3.0 5.30.0470.084 1′10(1)17.88.18.9 4.1 4.8 211(0)0.339 4.18.00.0390.077 2′10(1)18.5 2.312 1.2 6.2 311(0)0.1919.8130.0530.070 3′11(0)8.08 2.78.00.6208.0 411(0)0.438 5.98.30.0740.10 4′11(0)13.3 3.913 1.8 5.9 59(2)0.475 3.1 4.10.0410.055 5′9(2)18.40 1.77.50.87 3.9 611(0)0.362 5.0120.0510.13 6′10(1)17.7 4.38.5 2.2 4.3a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).Test sample N a Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 111(0)0.1059.9210.0290.062 1′11(0)0.6848.7170.170.32 29(1)0.0421020.00.0120.024 2′10(1)0.8267.4220.170.50 310(1) 2.04 2.5 6.20.140.360 3′11(0)16.6 5.924.0 2.811.0 410(1) 1.66 4.1 6.10.190.29 4′11(0) 4.38 3.8240.47 2.9 510(1)0.18610210.0530.11 5′11(0) 1.95 5.7130.310.69 611(0)0.18610240.0520.12 6′11(0) 1.027.9140.230.40 a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).Table995.13E Interlaboratory study results of the determination of free mannose in soluble coffeeTest sample N a Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 111(0)0.583 4.9240.0800.40 1′10(1)17.9 5.811 2.9 5.7 210(0)0.1558.2360.0130.16 2′11(0)14.4 2.615 1.1 6.2 311(0)0.470 4.2180.0560.23 3′11(0) 2.60 2.0140.15 1.0 411(0)0.3297.0190.06517 4′11(0) 5.60 3.0150.48 2.4 510(1)0.277 4.2400.0330.31 5′11(0)7.65 2.8110.60 2.3 611(0)0.991 3.8170.110.48 6′10(0)19.1 2.222 1.212.00 a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).Table995.13F Interlaboratory study results of the determination of free fructose in soluble coffeeTest sample N a Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 19(0)0.17117310.0820.15 1′6(0)0.18924680.130.37 28(1)0.05421340.0320.052 39(2) 3.62 2.9180.30 1.9 3′9(0) 2.01 5.7720.32 4.1 410(1) 3.12 2.9180.26 1.6 4′7(1) 1.37 5.5700.21 2.7 510(0)0.2829.0450.0720.36 5′7(0)0.24420590.140.41 68(2)0.460 5.6160.0670.2 6′9(1)0.3637.3680.0750.70 a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).Test sample N a Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 17(2)0.07315740.0310.15 27(l)0.04528600.0350.077 58(0)0.10215980.0430.28 55(1)0.08016180.0360.041 67(l)0.1209.1810.0310.28 a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).Table995.13H Interlaboratory study results of the determination of free xylose in soluble coffeeTest sample N a Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 18(2)0.09723380.0630.10 29(0)0.1469.8200.0400.084 311(0) 1.86 4.6230.240.42 411(0)0.736 3.7280.0770.56 57(0)0.02925230.0200.023 511(0) 1.837.4220.38 1.2 69(0)0.13314240.0530.090 a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).Table995.13I Interlaboratory study results of the determination of free sucrose in soluble coffeeTest sample N a Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 210(0)0.149 4.8380.0200.16 310(1) 1.32 1.8100.0660.370 410(1)0.746 6.8120.140.25 511(0)0.18115420.0770.21 69(1)0.158 3.4330.0150.15 a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).Table995.13J Interlaboratory study results of the determination of free fucose in soluble coffeeTest sample N a Mean,%RSD r RSD R r R 27(1)0.01620.0460.0090.021 38(0)0.0547.0670.0110.10 47(1)0.03623770.0230.074 57(1)0.011 5.4450.0020.014 66(1)0.02510360.0070.025 a N=No.of laboratories after removal of outliers(in parentheses).by hand every30min.Cool to room temperature under tap water. Dilute solution to100mL with H2O and filter through folded filter paper.Pass3mL filtrate through cation-exchange cartridge.Discard the first1mL.Filter neutralized solution through0.2µm membrane filter prior to LC injection.E.LC DeterminationInject equal volumes(10–20µL)of standard,C(e),and test solu-tions from D(a)or(b)onto LC column.[Note:Retention times and resolution tend to vary from column to column.Start clean-up and re-equilibration sequence only when the last monosaccharide (ribose)has been eluted.It may be necessary to perform2–3injec-tions of carbohydrates standard solution or to increase the re-equilibrium time in order to achieve a good separation of glucose, sucrose,and xylose.]Under normal conditions,approximate retention times of carbo-hydrates are:mannitol,4min;fucose,7min;rhamnose,15min;arabinose,16min;galactose,22min;glucose,25min;sucrose, 27min;xylose,30min;mannose,32min;fructose,40min;and ribose,43min.See Figure995.13for chromatogram of mixed carbo-hydrates standard solution.F.CalculationsCalculate concentration of carbohydrate in sample solution as follows:Carbohydrate,%=(R1/R2)×(W0/V0)×(V/W)×100 where R1=peak response of carbohydrate in test solution;R2=peak response of carbohydrate in carbohydrate standard solution;W0= mass of carbohydrate in the standard solution,mg;V0=total volume of the standard solution,mL;V=volume of standard solution,mL; and W=weight of test portion,mg.Express results as percent free or percent total carbohydrates (as is).References:J.AOAC Int.78,768(1995);79,1400(1996). Revised:June2000Figure995.13—HPAE-PAD chromatogram of mixed carbohydrates standard solution:mannitol,15m g;fucose,15m g/mL;rhamnose,35m g/mL;arabinose,40m g/mL;galactose,50m g/mL;glucose,55m g/mL;sucrose,45m g/mL; xylose,55m g/mL;mannose,45m g/mL;fructose,90m g/mL;and ribose,90m g/mL.。
47.3.43AOAC Of f i c ial Method 990.28Sul f ites in FoodsOp t i m ized Monier–Wil l iams MethodFirst Ac t ion 1990Fi n al Ac t ion1994(Ap p li c a b le of de t er m i n a t ion of ³10 ppm (m g/g) sul f ites in foods. Ap p li c a b le in pres e nce of other vol a t ile sul f ur com p ounds; not ap p li c a b le to dried on i ons, leeks, and cab b age.)See Table 990.28 for the results of the interlaboratory study supporting acceptance of the method.A.Prin c i p leMethod mea s ures free sul f ite plus re p ro d uc i ble por t ion of bound sul f ites, such as car b onyl ad d i t ion prod u cts, in foods. Test por t ion is heated with refluxing HCl (ca 1M) to con v ert sul f ite to SO2. Stream of N2 in t ro d uced be l ow sur f ace of refluxing so l u t ion sweeps SO2 through wa t er-cooled con d enser and, via bubbler at t ached to con d enser, with 3% H2O2 so l u t ion, where SO2 is ox i d ized to H2SO4. Sul f ite con t ent is di r ectly re l ated to gen e r a ted H2SO4, which is de t er m ined by ti t ra t ion with stan d ard i zed NaOH so l u t ion.For ver i f i c a t ion,sul f ate can be de t er m ined gravimetrically as BaSO4.B. Ap p a r a t us(a)Dis t il l a t ion ap p a r a t us.—(Note: In this method, back pres s ure in s ide ap p a r a t us is lim i ted to un a void a ble pres s ure due to height of 3% H2O2 so l u t ion above tip of bubbler (F). Keep back pres s ure as low as pos s i b le to avoid loss of SO2 through leaks. Use thin film of stop c ock grease on seal i ng sur f aces of all joints ex c ept joint be t ween sepa r a t ory fun n el and flask. Clamp to g ether each joint to en s ure com p lete seal through o ut anal y s is.) As s em b le ap p a r a t us (Fig u re 990.28A), which in c ludes (1) in l et adapter (A) with hose con n ec t or (Kontes 183000). Adapter pro v ides means of ap p ly i ng head pres s ure above so l u t ion. Use of pres s ure-equalizing drop p ing fun n el is not rec o m m ended be c ause con d en s ate, per h aps con t ain i ng SO2, is de p os i ted in fun n el and side arm. (2) Sepa r a t ory fun n el (B),³100 mL ca p ac i ty. (3) Round-bottom flask (C), 1 L, with three 24/40 ta p ered joints. (4) Gas in l et tube (D) (Kontes 179000) of suf f i c ient length to per m it in t ro d uc t ion of N2 within 2.5 cm of bot t om of flask.(5) Allihn con d enser (E) (Kontes 431000-2430), jacket length 300 mm. (6) Bubbler (F), fab r i c ated from glass ac c ord i ng to di m en s ions in Fig u re 990.28B. (7) Ves s el (G), ca 2.5 cm id and18 cm deep.(b) Buret.—10 mL (Kimble Glass, Inc., No. 17124-F) with over f low tube and hose con n ec t ions for Ascarite tube or equiv a l ent air-scrubbing ap p a r a t us to per m it main t e n ance of CO2-free at m o s phere over stan d ard i zed 0.010M NaOH.(c)Chilled wa t er circulator.—Chill con d enser with cool a nt, such as meth a n ol–water (20 + 40, v/v), main t ained at £15°C. Cir c u l ating pump, Neslab Coolflow 33 (Neslab In s tru m ents, Inc.,PO Box 1178, Portsmouth, NH 03801, USA), or equiv a l ent, is suit a ble.C. Re a gents(a) Aque o us hy d ro c hlo r ic acid.—4M. For each anal y s is, pre p are90 mL so l u t ion by add i ng 30 mL HCl to 60 mL deionized(18 meg o hm) wa t er.(b) Methy l red in d i c a t or.—Dis s olve 250 mg methy l red in 100 mL eth a n ol.(c) Stan d ard i zed titrant.—0.010M NaOH. Cer t ified re a gent may be used (Fisher SO-5-284). Stan d ard i ze so l u t ion with ref e r e nce stan d ard po t as s ium acid phthalate.(d) Hy d ro g en per o x i de so l u t ion.—3%. For each anal y s is, di l ute3 mL ACS re a gent grade 30% H2O2 to 30 mL with deionized (18 megohm) wa t er. Just prior to use, add 3 drops methy l red in d i c a t or and ti t rate with 0.010M NaOH to yel l ow end point. If end point is ex c eeded, dis c ard so l u t ion.(e) Ni t ro g en.—High pu r ity, used with reg u l a t or to main t ain flow of 200 mL/min. To guard against ox y g en in N2 gas, use GC-type trap (Oxy-Purge N [Alltech-Applied Sci e nce Lab o r a t ories, Inc.; ], or equiv a l ent).Al t er n a t ively,ox y g en-scrubbing so l u t ion,such as al k a l ine pyrogallol, in gas-washing bot t le (Kimble Glass, Inc.) may be used.ã 2005 AOAC IN T ER N A T IONALTable 990.28. Interlaboratory study results for sulfites in foodsMatrix Mean,m g/g s r RSD r, %s R RSD R, %HorRatHominy9.17 1.3314.5 1.4215.5 1.36 Fruit juice8.05 1.3616.9 1.6220.1 1.73 Protein (seafood)10.41 1.4714.1 2.7726.62.38Fig u r e990.28A.Ap p a r a t us for op t i m izedMonier-Williams method: A, in l et adapter; B, sepa r a t ory fun n el; C, round-bottom flask; D, gas in l et tube; E, Allihn con d enser; F, bubbler; G, ves s el.Pre p are trap as fol l ows: (1) Add 4.5 g pyrogallol to trap. (2) Purge trap with N 2 for 2–3 min. (3) Pre p are KOH so l u t ion by add i ng 65 g KOH to 85 mL H 2O. (Cau t ion: Heat is gen e r a ted.) (4) Add KOH so l u t ion to trap while at m o s phere of N 2 is main t ained in trap.D. Prep a r a t ion of Test Suspension(a )Solids .—Trans f er 50 g food, or quan t ity that con t ains 500–1500 m g SO 2, to food pro c es s or or blender. Add 100 mL eth a n ol–water (5 + 95, v/v) and briefly grind mix t ure. Con t inue grind i ng or blend i ng only un t il food is chopped into pieces small enough to pass through stan d ard taper 24/40 joint of flask (C).(b ) Liq u ids .—Mix 50 g test portion, or quan t ity that con t ains 500–1500 m g SO 2 with 100 mL eth a n ol–water (5 + 95, v/v).(Note: Carry out test suspension prep a r a t ion and anal y s is as quickly as pos s i b le to avoid loss of la b ile forms of sul f ite.)E.Sys t em Prep a r a t ionUsing ap p a r a t us as s em b led as shown in Fig u re 990.28A ,po s i t ionflask (C) in heat i ng man t le con t rolled by power-regulating de v ice (rheo s tat), and add 400 mL H 2O to flask. Close stop c ock of sepa r a t ory fun n el (B) and add 90 mL 4M HCl to sepa r a t ory fun n el.Be g in N 2 flow at 200 ± 10 mL/min. Ini t i a te con d enser cool a nt flow at this time. To ves s el (G) add 30 mL 3% H 2O 2, which has been ti t rated to y el l ow end point with 0.010M NaOH. Af t er 15 min,ap p a r a t us and wa t er will be thor o ughly deoxygenated and pre p ared test suspension may be in t ro d uced into sys t em.F. Suspension In t ro d uc t ion and Dis t il l a t ionRe m ove sepa r a t ory fun n el (B) and quan t i t a t ively trans f er test suspension in aque o us eth a n ol to flask (C). Wipe ta p ered joint clean with lab o r a t ory tis s ue, quickly ap p ly stop c ock grease to outer joint of sepa r a t ory fun n el, and re t urn sepa r a t ory fun n el to flask. Ni t ro g en flow through 3% H 2O 2 so l u t ion re s umes as soon as sepa r a t ory fun n el is re i n s erted into ap p ro p ri a te joint in flask. Ex a m i ne each joint to be sure that it is sealed.Use rub b er bulb equipped with valve to ap p ly head pres s ure above HCl in sepa r a t ory fun n el. Open stop c ock in sepa r a t ory fun n el and let HCl flow into flask. Con t inue to main t ain suf f i c ient pres s ure above acid so l u t ion to force so l u t ion into flask. Stop c ock may be closed, if nec e s s ary , to pump up pres s ure above acid, and then opened again. Close stop c ock be f ore last 2–3 mL drain out of sepa r a t ory fun n el to guard against es c ape of SO 2 into sepa r a t ory fun n el.Ap p ly power to heat i ng man t le. Use power set t ing that causes 80–90 drops/min of con d en s ate to re t urn to flask from con d enser.Let con t ents of flask boil 1.7 h, and then re m ove ves s el (G).G.De t er m i n a t ion(a ) Ti t ra t ion .—Im m e d i a tely ti t rate con t ents of ves s el (G)with 0.010M NaOH to yel l ow end point that per s ists ³20 s. Com p ute sul f ite con t ent, ex p ressed in m g SO 2/g food (ppm), as fol l ows:SO 2, m g/g (ppm ) =32031000.´´´V M weightB where 32.03 = milliequivalent weight of SO 2; V B = vol u me (mL) ofNaOH of molarity M re q uired to reach end point; 1000 = fac t or to con v ert milliequivalents to microequivalents; weight = weight, g, of test por t ion in t ro d uced into 1 L flask.(b ) Gravimetric de t er m i n a t ion .—Op t ional.Fol l ow i ng ti t ra t ion,rinse con t ents of ves s el (G) into 400 mL beaker. Add 4 drops 1M HCl and ex c ess of fil t ered 10% BaCl 2 so l u t ion, and let mix t ure stand over n ight. Wash pre c ip i t ate by decantation 3 times with hot wa t er through weighed Gooch cru c i b le. Wash with 20 mL al c o h ol and 20 mL ether, and dry at 105°–110°C.SO 2, m g/g (ppm) =mg BaSO g test portion4´27446.(c ) Blank de t er m i n a t ion .—De t er m ine blank on re a gents both by ti t ra t ion and gravimetrically, and cor r ect re s ults ac c ord i ngly.H .Re c ov e ry As s aysTo be c ome fa m il i ar and pro f i c ient with method be f ore rou t ine use, an a l yze foods con t ain i ng known amounts of sul f ite. Per f orm anal y s is in man n er that pre c ludes any loss of sul f ite by ox i d a t ion or re a c t ion with com p o n ents in food. Since sul f ites are re a c t ive with air and food ma t rixes and lack sta b il i ty, for t ify por t ions with sta b le source of sul f ite, not so d ium sul f ite or sim i l ar salts. So d ium hydroxymethylsulfonate (HMS), which is bisulfite ad d i t ion prod u ct of form a l d e h yde and is struc t ur a lly sim i l ar to some com b ined forms of sul f ite in foods, is use f ul for pre p ar i ng sta b le for t i f ied test ma t e r i a ls.For anal y s is, trans f er 50 g pre p ared test portion of sul f ite-free food to Monier-Williams flask. Add aliquot of aque o us so l u t ion of HMS so d ium salt.An a l y ze so l u t ion im m e d i a tely .HMS re c ov e r i es of ³80% from food ma t rixes for t i f ied at 10 m g/g are rec o m m ended to en s ure ac c u r ate an a l y t i c al data.Ref e r e nce:JAOAC 72, 470(1989).CAS-7446-09-5 (sul f ur di o x i de)ã 2005 AOAC IN T ER N A TIONALFig u r e 990.28B.En l ar ged di a g r am of bubbler for Monier-Williams ap p a r a t us (lengths in mm).。
9.2.22AOAC Official Method 971.21Mercury in FoodFlameless Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometric MethodFirst Action 1971Final Action 1976(Rinse all glassware before use with HNO 3 [1 + 9]. Caution: See Appendix B , safety notes on wet oxidation, nitric acid, perchloric acid, sulfuric acid, and mercury salts.)A. Apparatus(a ) Atomic absorption spectrophotometer .—(Instrumentation Laboratory, Inc., 113 Hartwell Ave, Lexington, MA 02173, Model 153 [or successors], or equivalent.) Equipped with Hg hollow cath-ode lamp and gas flow-through cell (Figure 971.21), 25 (id) × 115mm with quartz windows cemented in place. Operating conditions:Wavelength 253.7 nm, slit width 160 µm, lamp current 3 ma, and sensitivity scale 2.5.(b ) Diaphragm pump .—(Neptune Dyna-Pump, or equivalent.)Coat diaphragm and internal parts of pump with acrylic-type plastic spray. Use 16 gage Teflon tubing for all connections.(c ) Water condenser .—12–18 (id) × 400 mm borosilicate, 24/40standard taper joint, modified to hold 6 mm Raschig rings. Fill condenser with Raschig rings to height of 100 mm; then place 20mm layer of 4 mm diameter glass beads on top of rings.(d ) Gas inlet adapter .—24/40 standard taper, e.g., Kontes Glass Co. No. 181000.(e ) Digestion flask .—250 mL flat-bottom boiling flask with 24/40 standard taper joint.B. Reagents(a ) Reducing solution .—Mix 50 mL H 2SO 4 with ca 300 mL H 2O.Cool to room temperature and dissolve 15 g NaCl, 15 g hydroxyl-amine sulfate, and 25 g SnCl 2 in solution. Dilute to 500 mL.(b ) Diluting solution .—To 1 L volumetric flask containing 300–500 mL H 2O, add 58 mL HNO 3 and 67 mL H 2SO 4. Dilute to volume with H 2O.(c ) Magnesium perchlorate .—Drying agent placed in filter flask (Figure 971.21). Replace as needed. [Caution: Mg(ClO 4)2 is explo-sive when in contact with organic substances.](d ) Mercury standard solutions .—(1) Stock solution .—1000µg/mL. Dissolve 0.1354 g HgCl 2 in 100.0 mL H 2O. (2) Working solution .—1 µg/mL. Dilute 1 mL stock solution to 1 L with 1N H 2SO 4. Prepare fresh daily.C. DeterminationWeigh 5.0 g sample into digestion flask; add 25 mL 18N H 2SO 4,20 mL 7N HNO 3, 1 mL 2% sodium molybdate solution , and 5–6boiling chips. Connect condenser (with H 2O circulating through it)and apply gentle heat ca 1 h. Remove heat and let stand 15 min.Add 20 mL HNO 3-HClO 4 (1 +1) through condenser. Turn off H 2O circulating through condenser and boil vigorously until white fumes appear in flask. Continue heating 10 min.Cool. Cautiously add 10 mL H 2O through condenser while swirl-ing liquid in flask. Again boil solution 10 min. Remove heat and wash condenser with three 15 mL portions H 2O.Cool solution to room temperature. Completely transfer digested sample with H 2O to 100 mL volumetric flask and dilute to volume with H 2O. Transfer 25.0 mL aliquot from each sample to another digestion flask. Adjust volume to ca 100 mL with diluting solution,(b ).Adjust output of pump to ca 2 L air/min by regulating speed of pump with variable transformer. Connect apparatus as in Figure 971.21, except for gas inlet adapter. With pump working and spec-trophotometer zeroed, add 20 mL reducing solution to diluted ali-quot. Immediately connect gas inlet adapter and aerate ca 3 min.(Adjust aeration time to obtain maximum A .) Record A , disconnect pressure on ‘‘out’’ side of pump, and open vent on filter flask to flush system.Prepare reagent blank and standard curve by adding 0, 0.2, 0.4,0.6, 0.8, and 1.0 µg Hg to series of digestion flasks. To each flask add 100 mL diluting solution. Finally, add reducing solution and aerate standards as for sample.Plot standard curve from least squares linear regression of A against µg Hg. (See‘‘Definitions of Terms and ExplanatoryFigure 971.21—Apparatus for flameless atomic absorption analysisNotes,’’ item [25], or use calculator which performs linear regres-sion.) D etermine µg Hg in aliquot from curve. If µg Hg determined falls o utside r ange o f c alibration, r epeat d etermination w ith s maller aliquot of sample solution to bring µg Hg into region of standard curve. From size of aliquot used, determine total µg Hg in original sample.ppm Hg = µg Hg/g sampleReference:JAOAC 54, 202(1971).CAS-7439-97-6 (mercury)。
15.1.04AOAC Official Method998.10Efficacy of Preservationof Non-Eye Area Water-Miscible Cosmeticand Toiletry FormulationsFirst Action1998Caution:A knowledge of microbiological techniques is required for these procedures.Follow general aseptic and safetyprocedures(1).See Table998.10for the results of the interlaboratory study sup-porting the acceptance of the method.A.PrincipleBacteria,yeast,and mold are grown on laboratory media,har-vested,calibrated,and inoculated into test ing serial di-lutions and plate counts,the numbers of organisms surviving in the test products are determined over time.Products meeting the speci-fied criteria are considered adequately preserved for manufacture and consumer use.Products not meeting criteria are considered in-adequately preserved.B.Apparatus(a)Jars.—2–4oz.wide-mouth,straight-side flint glass ointment jars with linerless metal,polypropylene or Teflon®lined screw caps.(b)Disposable borosilicate glass culture tubes.—16×125mm, with caps.(c)Disposable borosilicate glass culture tubes.—20×150mm, with screw caps.(d)Petri plates.—100×15mm.(e)Sterile2.2mL pipets.(f)Sterile swabs.(g)Glass beads.(h)Sterile gauze.(i)10–20µL inoculating loops.(j)Vortex mixer.C.ReagentsFor convenience,dehydrated media of any brand equivalent in function may be used.Test each lot of medium for sterility and growth-promotion using suitable organisms.(a)Letheen agar.—Contains5.0g pancreatic digest of casein,1.0g dextrose,3.0g beef extract,1.0g lecithin,7.0g polysorbate80, and15.0g agar per L.Prepare according to manufacturer’s directions. Dispense into suitable containers and sterilize by autoclaving at 121E C for15min.Final pH should be7.0±0.2at25E C.Place in45E C water bath until agar is45±2E e for pour plates.(b)D/E neutralizing broth(Dey/Engley).—Contains5.0g pan-creatic digest of casein,2.5g yeast extract,10g dextrose,1.0g so-dium thioglycollate,6.0g Na2S2O3⋅5H2O,2.5g NaHSO3,7.0g lecithin,5.0g polysorbate80,and0.02g bromcresol purple per L. Prepare according to manufacturer’s directions.Dispense9or 9.9mL aliquot into tubes and sterilize by autoclaving at121E C for 15min.Final pH should be7.6±0.2at25E e for aerobic plate count,L,dilutions.(c)Nutrient agar.—Contains5.0g pancreatic digest of gelatin,3.0g beef extract,and15.0g agar per L.Prepare according to manu-facturer’s directions.Dispense into tubes and sterilize by autoclaving at121E C for15min.Final pH should be6.8±0.2at 25E C.Cool in inclined position to form a e for bacterial cul-ture maintenance and inoculum preparation.(d)Y/M agar(yeast/malt extract).—Contains3.0g yeast extract,3.0g malt extract,5.0g peptone,10.0g dextrose,and20.0g agar per L.Prepare according to manufacturer’s directions.Dispense into tubes and sterilize by autoclaving at121E C for15min.Final pH should be6.2±0.2at25E C.Cool in slanted e for yeast culture maintenance and inoculum preparation.(e)Potato dextrose agar(PDA).—Contains200g potato infu-sion,20.0g dextrose,and15.0g agar per L.Prepare according to manufacturer’s directions.Dispense into tubes and sterilize by autoclaving at121E C for15min.Final pH should be5.6±0.2at 25E C.Cool in slanted e for mold culture maintenance and inoculum preparation.(f)0.85%Saline.—Dissolve8.50g NaCl in water and dilute to 1L.Dispense into flasks or bottles and sterilize by autoclaving at 121E C for15min.(g)0.85%Saline with0.05%polysorbate80.—Dissolve8.5g NaCl in water,mix in0.50g polysorbate80,and dilute to1L.Dis-pense into suitable containers and sterilize by autoclaving at121E C for15min.(h)Barium sulfate standard No.2.—(1)Prepare a1.0% BaCl2solution by dissolving1.0g BaCl2⋅2H2O in100mL water.(2)Prepare a1.0%H2SO4solution by mixing1.0mL H2SO4in 100mL water.(3)Mix0.2mL solution,(1),with9.8mL solu-tion,(2),in a screw-capped test tube.Cap tightly and store in dark at room temperature.(i)Barium sulfate standard No.7.—Use solutions from C(h).Mix0.7mL solution,(h)(1),with9.3mL solution,(h)(2),in a screw-capped test tube.Cap tightly and store in dark at room temperature.D.Microorganisms(a)Staphylococcus aureus.—ATCC6538.(b)Staphylococcus epidermidis.—ATCC12228.(c)Klebsiella pneumoniae.—ATCC10031.(d)Escherichia coli.—ATCC8739.(e)Enterobacter gergoviae.—ATCC33028.(f)Pseudomonas aeruginosa.—ATCC9027.(g)Burkholderia cepacia.—ATCC25416.(h)Acinetobacter baumannii.—ATCC19606.(i)Candida albicans.—ATCC10231.(j)Aspergillus niger.—ATCC16404.(Note:Environmental microorganism(s)likely to be contami-nants of concern during product manufacture or use are included as a separate inoculum.Predominant environmental microbes isolated during manufacturing,equipment cleaning,and sanitizing,or from related deionized water systems are used as supplemental test inocula.)For culture revival and maintenance,consult references1and2.E.Product Quality Check(a)Weigh1.0g product into a screw-capped culture tube con-taining9.0mL sterile neutralizing broth to make a1:10dilution.If necessary to disperse product,add10to twenty3mm diameter glass beads to tube.Mix on Vortex mixer until homogeneous.(b)Pipet1.0mL of the1:10dilution into each of4sterile Petri plates.Pour15–20mL sterile molten Letheen agar(45±2E C)into each plate.Mix by rotating plates to disperse the dilution thoroughly. Let solidify.(c)Invert and incubate2plates at35±2E C for48h and2plates at 25±2E C for5days.(d)Count the number of colonies on all plates,add,and multiply by2.5to determine the number of colony forming units per gram (cfu/g)in the product.(e)Save plates to be used for the neutralization validation in M by refrigerating.F.Product Preparation(a)Measure20mL sterile saline into4sterile jars,B(a).Cap tightly and store at room temperature.(b)Weigh20g product into each of4sterile jars,B(a).Cap tightly and store at room temperature.G.Bacterial Inocula Preparation(a)Streak each bacterial culture,D(a)–(h),onto a nutrient agar, C(c),slant.Incubate48h at35±2E C.Wash each slant with5.0mL sterile saline,loosening the culture from the agar surface.Transfer the suspension into a sterile tube.Repeat the wash with second 5.0mL aliquot of bine washes and mix on Vortex mixer to disperse evenly.(b)Adjust each wash with sterile saline to yield a suspension of ca108cfu/mL using a McFarland BaSO4standard No.2,C(h),direct microscopic count,turbidimetry,absorbance,or other method cor-related to an aerobic plate count(APC),L.Perform an APC,L,on each suspension to confirm standardization.H.Fungal Inoculum Preparation(a)Streak C.albicans,D(i),on3slants of Y/M agar,C(d).Incu-bate at25±2E C for48h.Wash each slant sequentially with5.0mL aliquot of sterile saline.Repeat with a second5.0mL aliquot of ster-ile bine washes to produce10mL suspension.Mix on Vortex mixer to disperse evenly.(b)Adjust the wash with sterile saline to yield a suspension of ca 107cfu/mL using a McFarland BaSO4standard No.7,C(i),direct microscopic count,turbidimetry,absorbance,or other method that has been correlated to an APC,L.Perform an APC,L,on the suspen-sion to confirm standardization.(c)Streak A.Niger,D(j),on5slants of potato dextrose agar, C(e).Incubate at25±2E C for10days.Dislodge mold spores by add-ing5.0mL sterile saline containing0.05%polysorbate80to each tube and vigorously rubbing the surface of the agar slant with a ster-ile swab.Repeat with a second5.0mL aliquot in each bine the10washes to produce50mL suspension.Filter into a sterile con-tainer through3–5layers of sterile gauze supported in a funnel.Per-form an APC,L,using appropriate dilutions.Adjust mold suspen-sion to ca107per mL using sterile e immediately or refrigerate at2–5E C for up to1month.Verify mold viability by an APC,L,before each use.I.Inoculum Pools(a)Pool equal parts of the S.aureus and S.epidermidis suspen-sions,G(b),in a sterile container to make Inoculum Pool1: Gram-positive cocci.(b)Pool equal parts of the K.pneumoniae,E.coli,and E. gergoviae suspensions,G(b),in a sterile container to make Inoculum Pool2:Gram-negative fermentors.(c)Pool equal parts of the P.aeruginosa,B.cepacia,and A. baumanii suspensions,G(b),in a sterile container to make Inoculum Pool3:Gram-negative nonfermentors.(d)Pool equal parts of C.albicans,H(b),and A.niger,H(c),sus-pensions in a sterile container to make Inoculum Pool4:Fungi. (e)Use organism pools immediately or refrigerate them at2–5E C for no more than72h.J.Inoculation(a)Inoculate each of the four20.0mL aliquots of sterile saline,F(a), with0.2mL of its respective Inoculum Pool,I(a)–(d).Mix thoroughly. Use these suspensions to determine inoculum counts[see K(a)]. (b)Inoculate each of the four20g product suspensions,F(b), with0.2mL of its respective Inoculum Pool,I(a)–(d).Mix thor-oughly by shaking,Vortex mixing,or stirring,so that each suspen-sion contains106bacteria or105fungi per gram,evenly distributed throughout the product.Tightly close inoculated containers and store at ambient temperature(20–25E C).K.Sampling Intervals(a)Sample each inoculated saline suspension,J(a),for APC,L, within1h after inoculation to obtain inoculum count.(b)Test each inoculated product,J(b),for APC,L,at7,14,and 28days after inoculation to obtain product interval count.L.Aerobic Plate Count(APC)(a)Mix suspension thoroughly.Weigh1.0g product into a screw-capped culture tube containing9.0mL sterile neutralizing broth for a1:10dilution.If necessary to disperse product,add 10–20sterile3mm diameter glass beads to the tube.Mix on Vortex mixer until homogeneous.Table998.10Interlaboratory study results for determination of the efficacy of preservation of non-eye area water-miscible cosmetic and toiletry formulationsProduct name Incidence of false-negatives amongtotal positive samples aSensitivity rateIncidence of false-positives amongtotal negative samples bSpecificity rate Number Percentage Number PercentageShampoo2/494960/530100 Conditioner3/486940/540100 Water in oil emulsion0/5201001/50298 Oil in water emulsion0/5101000/510100 All combined5/2002981/2080.599.5a False-negative analysis indicates a sample is adequately preserved.b False-positive analysis indicates a sample is not adequately preserved.(b)Aseptically pipet0.1mL of the1:10dilution into a9.9mL tube of neutralizing broth to obtain a1:1000dilution.Vortex mix. Pipet0.1mL of the1:1000dilution into9.9mL neutralizing broth to obtain a1:100000dilution.The number of dilutions may be de-creased if previous counts of microbial populations show reduction.(c)Using a2.2mL pipet,aseptically pipet1.0and0.1mL aliquots from the1:10dilution into duplicate Petri dishes for the1:10 and1:100plates.If necessary,transfer duplicate1.0and0.1mL aliquots from the1:1000dilution for plates1:1000and1:10000,and from the1:100000dilution for plates1:100000and1:1000000. Pour15–20mL sterile Letheen agar,C(a),(45±2E C)into each plate.Mix by rotating the plates to disperse the suspension thor-oughly,and let solidify.(d)Invert bacterial plates and incubate at35±2°C.Examine bacterial plates after48–72h.Count plates in a suitable range (30–300colonies).If no countable plates fall in that range,count the plate(s)nearest that range showing distinct colonies.Average dupli-cate plate counts and express results as cfu/g of product.(e)Invert and incubate fungal plates at25±2°C.Read fungal plates at2–3days and record results.Count plates in a suitable range (30–300colonies).If no countable plates fall in that range,count the plate(s)nearest that range showing distinct colonies.Reincubate plates for another2–3days.Read and record additional colonies. Add to previous results to obtain total counts.Average duplicate plate counts and record as cfu/g of product.For information on aver-aging,refer to reference3.M.Neutralization CheckMake a1:10000dilution in sterile saline of Pools1,2,and3, I(a)–(c),and a1:1000dilution of Pool4,I(d).Streak each dilution for isolation with a10µL loop on the plates saved from E(e).If plates are not usable due to either desiccation or surface growth,re-peat section E,and streak freshly prepared plates.Incubate as in L(d)–(e).N.Data Analysis(a)Product quality check,E(d),must be found to contain <100cfu/g to proceed with the challenge test.(b)Inoculum counts,K(a),should be between1to9.9×106cfu/g product for bacteria and1to9.9×105cfu/g product for fungi,or the test should be repeated with different dilutions.(c)Neutralization check,M,must show significant growth of all pools to confirm adequate neutralization.A neutralizing broth other than D/E broth can be used.If neutralization does not occur,the test is invalid.Refer to references4–6for assistance.(d)Calculate the percent reduction:Reduction,%=inoculum count–product interval countinoculum count100(e)The test product is considered adequately preserved if(1)bac-teria show at least99.9%(3log)reduction within1week following challenge and remain at or below that level thereafter,and(2)fungi show at least a90%(1log)reduction within1week following chal-lenge,a99%(2log)reduction within2weeks following challenge, and remain at or below that level thereafter.These criteria apply to freshly prepared formulations.References:J.AOAC Int.84,101(2001).(1)Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology(1993)P.Gerhardt(Ed.),American Society for Mi-crobiology,1752N St NW,Washington,DC20036-2804,USA.(2)Gherna,R.,Pienta,P.,&Cote,R.(1996)Catalogue of Bacteria and Phages,19th Ed.,ATCCBooks,PO Box753,Waldorf,MD20604-0753,USA.(3)U.S.Food and Drug Administration(1995)Bacteriological Analytical Manual,8th Ed.,AOACINTERNATIONAL,Gaithersburg,MD20877,USA.(4)“Standard Test Methods for EvaluatingInactivators of Antimicrobial Agents Used in Disin-fectant,Sanitizer,and Antiseptic Products(Designa-tion E1054-91)”(1998)in ASTM1998Annual Bookof Standards on Water and Environmental Technol-ogy,ASTM,100Barr Harbor Dr,WestConshohocken,PA19428-2959,USA.(5)Russell,A.D.(1999)in Principles and Practiceof Disinfection,Preservation,and Sterilization,3rdEd.,A.D.Russell,W.B.Hugo,&G.A.J.Ayliffe(Eds),Blackwell Scientific Publications,Oxford,UK,pp89–113.ISBN0632041943(6)Singer,S.(1987)Cosmetics&Toiletries,102,55–59.。