H3C交换机操作手册
- 格式:doc
- 大小:1.31 MB
- 文档页数:28

目录第1章 802.1x配置..................................................................................................................1-11.1 802.1x简介.........................................................................................................................1-11.1.1 802.1x标准简介.......................................................................................................1-11.1.2 802.1x体系结构.......................................................................................................1-11.1.3 802.1x的认证过程....................................................................................................1-21.1.4 802.1x在以太网交换机中的实现..............................................................................1-31.2 802.1x配置.........................................................................................................................1-31.2.1 开启/关闭802.1x特性..............................................................................................1-41.2.2 设置端口接入控制的模式.........................................................................................1-41.2.3 设置端口接入控制方式............................................................................................1-41.2.4 检测通过代理登录交换机的用户..............................................................................1-51.2.5 设置端口接入用户数量的最大值..............................................................................1-51.2.6 设置允许DHCP触发认证.........................................................................................1-61.2.7 设置802.1x用户的认证方法....................................................................................1-61.2.8 开启/关闭Guest VLAN功能......................................................................................1-71.2.9 设置802.1x重认证功能...........................................................................................1-71.2.10 设置对802.1x客户端的版本验证功能....................................................................1-91.2.11 设置认证请求帧的最大可重复发送次数...............................................................1-101.2.12 配置定时器参数...................................................................................................1-101.2.13 打开/关闭quiet-period定时器...............................................................................1-121.3 802.1x的显示和调试........................................................................................................1-121.4 802.1x典型配置举例........................................................................................................1-12第2章 Portal配置...................................................................................................................2-12.1 Portal简介..........................................................................................................................2-12.1.1 Portal概述................................................................................................................2-12.1.2 Portal的系统组成.....................................................................................................2-12.1.3 Portal认证的过程.....................................................................................................2-22.1.4 Portal的运行方式.....................................................................................................2-22.1.5 Portal免认证用户与免费IP.......................................................................................2-32.1.6 交换机与用户PC的ARP报文握手............................................................................2-32.1.7 Portal限速功能.........................................................................................................2-32.2 Portal基本配置...................................................................................................................2-42.2.1 配置准备..................................................................................................................2-42.2.2 Portal基本配置过程.................................................................................................2-42.2.3 Portal直接认证方式配置举例...................................................................................2-52.2.4 Portal二次地址分配方式配置举例............................................................................2-72.2.5 三层Portal认证方式配置举例...................................................................................2-92.3 Portal免认证用户及免费IP配置........................................................................................2-102.3.1 配置准备................................................................................................................2-102.3.2 Portal免认证用户及免费IP配置过程......................................................................2-102.3.3 免认证用户及免费IP配置举例................................................................................2-112.4 Portal限速功能配置..........................................................................................................2-122.4.1 Portal限速功能配置过程........................................................................................2-122.4.2 Portal限速功能配置举例........................................................................................2-122.5 删除Portal用户.................................................................................................................2-132.5.1 删除Portal用户配置过程........................................................................................2-132.5.2 删除Portal用户配置举例........................................................................................2-13第3章 AAA和RADIUS协议配置.............................................................................................3-13.1 AAA和RADIUS协议简介....................................................................................................3-13.1.1 AAA概述..................................................................................................................3-13.1.2 RADIUS协议概述....................................................................................................3-13.1.3 AAA/RADIUS在交换机中的实现..............................................................................3-23.2 AAA配置.............................................................................................................................3-33.2.1 创建/删除ISP域........................................................................................................3-33.2.2 配置ISP域的相关属性..............................................................................................3-43.2.3 开启/关闭信使提醒功能...........................................................................................3-53.2.4 开启/关闭自助服务器定位功能................................................................................3-53.2.5 创建本地用户...........................................................................................................3-63.2.6 设置本地用户的属性................................................................................................3-63.2.7 强制切断用户连接....................................................................................................3-73.2.8 配置动态VLAN下发.................................................................................................3-83.3 RADIUS协议配置...............................................................................................................3-93.3.1 创建/删除RADIUS方案..........................................................................................3-103.3.2 设置RADIUS服务器的IP地址和端口号..................................................................3-103.3.3 设置RADIUS报文的加密密钥................................................................................3-113.3.4 设置RADIUS服务器响应超时定时器.....................................................................3-123.3.5 设置RADIUS请求报文的最大传送次数..................................................................3-123.3.6 打开RADIUS计费可选开关....................................................................................3-123.3.7 设置实时计费间隔..................................................................................................3-133.3.8 设置允许实时计费请求无响应的最大次数.............................................................3-133.3.9 使能停止计费报文缓存功能...................................................................................3-143.3.10 设置停止计费请求报文的最大发送次数...............................................................3-143.3.11 配置设备重启用户再认证功能.............................................................................3-153.3.12 设置支持何种类型的RADIUS服务器...................................................................3-163.3.13 设置RADIUS服务器的状态..................................................................................3-173.3.14 设置主、备份RADIUS服务器切换的时间间隔.....................................................3-173.3.15 设置发送给RADIUS服务器的用户名格式............................................................3-183.3.16 设置发送给RADIUS服务器的数据流的单位........................................................3-183.3.17 配置本地RADIUS认证服务器..............................................................................3-193.4 AAA和RADIUS协议的显示和调试....................................................................................3-193.5 AAA和RADIUS协议典型配置举例....................................................................................3-203.5.1 FTP/Telnet用户远端RADIUS服务器认证配置.......................................................3-203.5.2 FTP/Telnet用户本地RADIUS服务器认证配置.......................................................3-223.5.3 动态VLAN下发配置...............................................................................................3-223.6 AAA和RADIUS协议故障的诊断与排除............................................................................3-23第4章 EAD配置.....................................................................................................................4-14.1 EAD简介............................................................................................................................4-14.2 EAD配置的典型组网应用...................................................................................................4-14.3 EAD配置............................................................................................................................4-24.4 EAD典型配置过程举例.......................................................................................................4-3第5章 HABP特性配置............................................................................................................5-15.1 HABP特性简介...................................................................................................................5-15.2 HABP特性配置...................................................................................................................5-15.2.1 配置HABP Server....................................................................................................5-15.2.2 配置HABP Client.....................................................................................................5-25.3 HABP的显示和调试............................................................................................................5-2第1章 802.1x配置1.1 802.1x简介1.1.1 802.1x标准简介IEEE 802.1x标准(以下简称802.1x)的主要内容是一种基于端口的网络接入控制(Port Based Network Access Control)协议。

H3C S6850 Series Data Center Switches Release Date: Nov, 2022New H3C Technologies Co., LimitedH3C S6850 Series Data Center SwitchesProduct overviewH3C S6850 high-density intelligent switch series is developed for data centers and cloud computing networks. It provides powerful hardware forwarding capacity and abundant data center features. It provides up to 48*25G ports and 8*100G ports. The switch supports modular power modules and fan trays. By using different fan trays, the switch can provide field-changeable airflows.The switch is an ideal product for high-density 25GE switching and aggregation at data centers and cloud computing networks. It can also operate as a TOR access switch on an overlay or integrated network.Product AppearanceThe S6850 series come in the following models.∙S6850-56HF: The switch provides 48 × 25G SFP28 ports, 8 × 100G QSFP28 ports, and 2 × 1G SFP portsS6850-56HF front panel S6850-56HF rear panel∙S6850-2C: The switch provides 2 service slots, 2 × 100G QSFP28 portsS6850-2C front panel S6850-2C rear panelFeatures and BenefitsHigh-Density 25GE Access∙The switch offers high-density 100G/40G/25G/10G ports and a wire-speed forwarding capacity as high as 4 Tbps. With standard 25G ports, it can provide high-density server access in high-end data centers.IRF2 (Second Generation Intelligent Resilience Architecture)∙Facing the application requirements of the unified switching architecture of the data center, the series switches support the IRF2 technology, which virtualizes multiple devices into one logical.∙The equipment has strong advantages in scalability, reliability, distributed and availability.∙ IRF2 not only can achieve a long-distance intelligent elastic architecture within a rack, across racks, and even across regions.Abundant Data Center FeaturesThe switch supports abundant data center features, including:∙H3C S6850 switch series supports VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN), which provides two major benefits, higher scalability of Layer 2 segmentation and better utilization of available network paths.∙H3C S6850 switch series supports MP-BGP EVPN (Multiprotocol Border Gateway Protocol Ethernet Virtual Private Network) which can run as VXLAN control plane to simplify VXLAN configuration,eliminate traffic flooding and reduce full mesh requirements between VTEPs via the introduction of BGP RR.∙H3C S6850 switch series support Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), which permits storage, data, and computing services to be transmitted on one network, reducing the costs of networkconstruction and maintenance.∙H3C S6850 switch series support Priority-based Flow Control (PFC), Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS) and Data Center Bridging eXchange (DCBX). These features ensure low latency and zero packet loss for FC storage, RDMA applications and high-speed computing services.H3C Distributed Resilient Network Interconnection (DRNI)∙H3C S6850 switch series support DRNI(M-LAG), which enables links of multiple switches to aggregate into one to implement device-level link backup. DRNI is applicable to servers dual-homed to a pair of access devices for node redundancy.∙ Streamlined topology: DRNI simplifies the network topology and spanning tree configuration by virtualizing two physical devices into one logical device.∙Independent upgrading: The DR member devices can be upgraded independently one by one to minimize the impact on traffic forwarding.∙High availability: The DR system uses a keepalive link to detect multi-active collision to ensure that only one member device forwards traffic after a DR system splits.Powerful VisibilityWith the rapid development of data center, the scale of the data center expands rapidly; reliability, operation and maintenance become the bottleneck of data center for further expansion. H3C S6850 switch series conform to the trend of automated data operation and maintenance, and support visualization of data center.∙INT (Inband-Telemetry) is a network monitoring technology used to collect data from the device.Compared with the traditional network monitoring technology featuring one query, one reporting, INT requires only one-time configuration for continuous data reporting, thereby reducing therequest processing load of the device. INT can collect timestamp information, device ID, portinformation, and buffer information in real time. INT can be implemented in IP, EVPN, and VXLANnetworks.∙Provides a variety of traffic monitoring and analytic tools, including sFlow, NetStream, SPAN/RSPAN/ERSPAN mirroring, and port mirroring to help customers perform precise trafficanalysis and gain visibility into network application traffic. With these tools, customers can collectnetwork traffic data to evaluate network health status, create traffic analysis reports, perform traffic engineering, and optimize resource allocation.∙Supports realtime monitoring of buffer and port queues, allowing for visible and dynamic network optimization.∙Supports PTP (Precision Time Protocol) to achieve highly precise clock synchronization.RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet)∙Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) directly transmits the user application data to the storage space of the servers, and uses the network to fast transmit the data from the local system to thestorage of the remote system. RDMA eliminates multiple data copying and context switchingoperations during the transmission process, and reduces the CPU load.∙RoCE supports RDMA on standard Ethernet infrastructures. H3C S6850 switch support RoCE and can be used to build a lossless Ethernet network to ensure zero packet loss.∙RoCE include the following key features,include PFC(Priority based Flow Control), ECN(Explicit Congestion Notification), DCBX(Data Center Bridging Capability Exchange Protocol), ETS(Enhanced Transmission Selection).Flexible programmability∙The switch uses industry-leading programmable switching chips that allow users to define the forwarding logic as needed.∙Users can develop new features that meet the evolving trend of their networks through simple software updates.Powerful SDN capacity∙ H3C S6850 switch series adopt the next-generation chip with more flexible Openflow FlowTable, more resources and accurate ACL matching, which greatly improves the software-defined network (SDN) capabilities and meet the demand of data center SDN network.∙ H3C S6850 switch series can interconnect with H3C SeerEngine-DC Controller through standard protocols such as OVSDB, Netconf and SNMP to implement network automatic deployment andconfiguration.Comprehensive security control policies∙H3C S6850 series switch supports AAA, RADIUS and user account based authentication, IP, MAC, VLAN, port-based user identification, dynamic and static binding; when working with the H3C iMC platform, it can conduct real time management, instant diagnosis and crackdown on illicit network behavior.∙H3C S6850 series switch supports enhanced ACL control logic, which enables an enormous amount of in-port and out-port ACL, and delegate VLAN based ACL. This simplifies user deployment process and avoids ACL resource wastage. S6850 series switch can also take advantage of Unicast ReversePath Forwarding (Unicast RFP). When the device receives a packet, it will perform the reverse check to verify the source address from which the packets are supposedly originated, and will drop thepacket if such path doesn’t exist. This can effectively prevent the source address spoofing in thenetwork.Multiple reliability protection∙The S6850 series switch provides multiple reliability protection at both switch and link levels. With over current, overvoltage, and overheat protection, all models have a redundant pluggable powermodule, which enables flexible configuration of AC or DC power modules based on actual needs.The entire switch supports fault detection and alarm for power supply and fan, allowing fan speed to change to suit different ambient temperatures.∙The switch supports diverse link redundancy technologies such as H3C proprietary RRPP, VRRPE, and Smart Link. These technologies ensure quick network convergence even when large amount of traffic of multiple services runs on the network.∙Flexible choice of airflow∙To cope with data center cooling aisle design, the H3C S6850 series switch comes with flexible airflow design, which features bi-cooling aisles in the front and back. Users may also choose thedirection of airflow (from front to back or vice versa) by selecting a different fan tray.Excellent manageabilityThe switch improves system management through the following ways:∙Provides multiple management interfaces, including the serial console port, mini USB console port, USB port, two out-of-band management ports, and two SFP ports. The SFP ports can be used as in-band management port through which encapsulated sampling packets are sent to the controller or other management devices for deep analysis.∙Supports multiple access methods, including SNMPv1/v2c/v3, Telnet, SSH 2.0, SSL, and FTP.∙Supports standard NETCONF APIs that allow users to configure and manage the switch, enhancing the compatibility with third-party applications.Hardware SpecificationItem S6850-56HF S6850-2CDimensions (H × W × D) 43.6 × 440 × 460 mm (1.72 × 17.32 × 18.11 in) 44.2 × 440 × 660 mm (1.74 × 17.32 × 18.11 in) Weight ≤ 15 kg (33.07 lb) ≤ 16 kg (35.27 lb)Serial console port 1 1Out-of-band management port One GE copper port and one GE fiber port One GE copper port and one GE fiber port Mini USB console port 1 1USB port 1 1QSFP28 port 8 2SFP28 port 48 -SFP port 2 -Expansion slot - 2CPU 2.2GHz@4Core 2.2GHz@4CoreFlash/SDRAM 4GB/8GB 4GB/8GBLatency <1μs <1μsSwitching capacity 4 Tbps 3.6TbpsForwarding capacity 2024 Mpps 2024 MppsBuffer(byte) 32M 32MAC-input voltage 90v AC to 264v AC 90v AC to 264v ACDC-input voltage –40v DC to –72v DC –40v DC to –72v DCPower module slot 2 2Fan tray slot 5 Hot-swappable fan, fan speed adjustable and wind invertibleAir flow direction From front to rear or from rear to front From front to rear or from rear to frontStatic power consumption Single AC: 167 WDual AC: 179 WSingle DC: 154 WDual DC: 174 WSingle AC: 136 WDual AC: 148 WSingle DC: 132 WDual DC: 146 WTypical power consumption Single AC: 201 WDual AC: 224 WSingle DC: 198 WDual DC: 210 WSingle AC: 273 W ( with LSWM18CQ)Dual AC: 282 W( with LSWM18CQ)Single DC: 268 W( with LSWM18CQ)Dual DC: 275 W( with LSWM18CQ)Maximum heat consumption (BTU/hour) Single AC: 686Dual AC: 765Single DC: 676Dual DC: 717Single AC:932 ( with LSWM18CQ)Dual AC:963( with LSWM18CQ)Single DC:915( with LSWM18CQ)Dual DC: 939( with LSWM18CQ)Operating temperature 0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) Operating humidity 5% to 95%, noncondensingSoftware SpecificationItem Feature descriptionDevice Virtualization IRF2.0M-LAG(DRNI) S-MLAGNetwork Virtualization BGP-EVPN VxLAN EVPN ESVxLAN L2 VxLAN gatewayL3 VxLAN gateway Distributed VxLAN gateway Centralized VxLAN gateway EVPN VxLANmanual configured VxLAN IPv4 VxLAN tunnelIPv6 VxLAN tunnelQinQ VxLAN accessSDN H3C SeerEngine-DCLossless network PFC and ECNDCBXRDMA and ROCEPFC deadlock watchdog ECN overlayROCE stream analysisProgrammability Openflow1.3NetconfAnsiblePython//TCL/Restful API to realize DevOps automated operation and maintenanceTraffic analysis SflowNetstream, only S6850-2CVLAN Port-based VLANsMac-based VLAN ,Subnet-based VLAN and Protocol VLAN VLAN mappingQinQMVRP(Multiple VLAN Registration Protocol)Super VLANPVLANMAC address Dynamic learning and aging of mac address entries Dynamic,static and blackhole entriesMac address limiting on portsIPv4 routing RIP(Routing Information Protocol) v1/2OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) v1/v2ISIS(Intermediate System to Intermediate system) BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)Routing policyVRRPPBRItem SpecificationIPv6 routing RIPng OSPFv3IPv6 ISIS BGP4+ Routing policy VRRPPBRMPLS/VPLS Support L3 MPLS VPNSupport L2 VPN: VLL (Martini, Kompella) Support VPLS, VLLSupport hierarchical VPLS and QinQ+VPLS access Support P/PE functionSupport LDP protocolSupport MCESupport MPLS OAMMulticast IGMP snoopingMLD snoopingIPv4 and IPv6 multicast VLAN IPv4 and IPv6 PIM snooping IGMP and MLDPIM and IPv6 PIMMSDPMulticast VPNReliability LACPSTP/RSTP/MSTP protocol, PVST compatibleSTP Root Guard and BPDU GuardRRPP and ERPSEthernet OAMSmartlinkDLDPBFD for OSPF/OSPFv3, BGP/BGP4, IS-IS/IS-ISv6, PIM/IPM for IPv6 and Static route VRRP and VRRPEQOS Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) and tail dropFlexible queue scheduling algorithms based on port and queue, including strict priority (SP), Weighted Deficit Round Robin (WDRR), Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ), SP + WDRR, and SP + WFQ. Traffic shapingPacket filtering at L2 (Layer 2) through L4 (Layer 4); flow classification based on source MAC address, destination MAC address, source IP (IPv4/IPv6) address, destination IP (IPv4/IPv6) address, port, protocol, and VLAN to apply qos policy,including mirroring,redirection,priority remark etc. Committed access rate (CAR)Account by packet and byteCOPPFC/FOCE FC, FC subcard is supported on S6850-2C FCOETelemetry gRPC ERSPAN Mirror on dropItem SpecificationTelemetry Telemetry StreamINTiNQAPacket trace, Packet captureConfiguration and maintenance Console telnet and SSH terminalsSNMPv1/v2/v3ZTPSystem logFile upload and download via FTP/TFTP, BootRom update and remote update NQAping,tracertVxLAN ping and VxLAN tracertNTPPTP(1588v2)GIR Graceful Insertion and RemovalSecurity and management Macsec, Macsec subcard is supported on S6850-2C and only 100G macsec subcard can support 256-bit AES encryptionMicro-SegmentationHierarchical management and password protection of usersAuthentication methods,including AAA,RADIUS and HWTACACSSupport DDos, ARP attack and ICMP attack functionIP-MAC-port binding and IP Source GuardSSH 2.0HTTPSSSLPKIBoot ROM access control (password recovery)RMONEMC FCC Part 15 Subpart B CLASS A ICES-003 CLASS AVCCI CLASS ACISPR 32 CLASS AEN 55032 CLASS AAS/NZS CISPR32 CLASS A CISPR 24EN 55024EN 61000-3-2EN 61000-3-3ETSI EN 300 386GB/T 9254YD/T 993IEEE Standard 802.3x/802.3ad/802.3AH/802.1P/802.1Q/802.1X/802.1D/802.1w/802.1s/802.1AG 802.1x/802.1Qbb/802.1az/802.1QazSafety UL 60950-1CAN/CSA C22.2 No 60950-1 IEC 60950-1EN 60950-1AS/NZS 60950-1FDA 21 CFR Subchapter JPerformance and scalabilityPerformance and scalabilityDescriptionPerformance RIB 1MMSTP instance 64PVST instance 510PVST logical port number 2000VRRP VRID 255VRRP group 256NQA group 32Static table static mac-address 4000static multicast mac-address 1Kstatic ARP 1Kstatic ND 4Kstatic IPv4 routing table 2Kstatic IPv6 routing table 4000Data Center ApplicationThe typical data center application is an EVPN-VxLAN design,S12500G-AF or S12500X-AF switches work as spine or spine/border, S68XX series work as leaf and border or ED. From this design, the usres can get a non-blocking large L2 system.Order informationNew H3C Technologies Co., LimitedBeijing HeadquartersTower 1, LSH Center, 8 Guangshun South Street, Chaoyang District, Beijing, ChinaZip: 100102Hangzhou HeadquartersNo.466 Changhe Road, Binjiang District, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, ChinaZip: 310052Tel: +86-571-86760000 Copyright ©2022 New H3C Technologies Co., Limited Reserves all rightsDisclaimer: Though H3C strives to provide accurate information in this document, we cannot guarantee that details do not contain any technical error or printing error. Therefore, H3C cannot accept responsibility for any inaccuracy in this document. H3C reserves the right for the modification of the contents herein without prior notification。


H3C S3100-52P以太网交换机操作手册-Release 1702-6W10001-CLI操作目录1 CLI(命令行接口)1.1 认识命令行接口1.2 进入命令行接口1.2.1 通过Console口进行命令行接口1.2.2 通过Telnet方式进入命令行接口1.3 H3C产品命令行接口的说明1.3.1 手册中命令行格式约定1.3.2 命令行视图说明1.4 命令行接口使用技巧1.4.1 使用命令行在线帮助1.4.2 解读输入错误提示信息1.4.3 快速输入命令行1.4.4 查看及重复执行历史命令1.4.5 命令的undo格式1.4.6 命令行显示信息控制1.5 命令行相关配置1.5.1 配置命令行的别名1.5.2 配置命令行输入防打断功能1.5.3 配置命令行级别1.5.4 配置保存1 CLI(命令行接口)1.1 认识命令行接口命令行接口是用户与设备之间的文本类指令交互界面,用户键入文本类命令,通过输入回车键提交设备执行相关命令。
通过命令行接口,用户可以输入命令对设备进行配置,并可以通过查看输出的信息确认配置结果,方便用户配置和管理设备。
H3C系列交换机的命令行接口界面如图1-1所示:图1-1 命令行接口界面示意图1.2 进入命令行接口H3C S3100-52P以太网交换机支持多种方式进入命令行接口:●通过Console口进入命令行接口界面,具体请参见1.2.1 通过Console口进行命令行接口。
●通过Telnet方式进入命令行接口界面,具体请参见1.2.2 通过Telnet方式进入命令行接口。
●通过SSH方式以加密方式进入命令行接口界面,具体请参见“SSH”章节的介绍。
1.2.1 通过Console口进行命令行接口H3C系列交换机在初次使用命令行接口时,只能通过Console口进行登录并进入命令行接口界面。
具体请按以下步骤进行操作:(1)请使用产品随机附带的配置口电缆连接PC机和交换机。




02-登录交换机配置目录1 登录以太网交换机1.1 登录以太网交换机方法简介1.2 用户界面简介1.2.1 交换机支持的用户界面1.2.2 用户与用户界面的关系1.2.3 交换机用户界面编号1.2.4 用户界面公共配置2 通过Console口进行本地登录2.1 通过Console口进行本地登录简介2.2 通过Console口登录交换机的配置环境搭建2.3 配置Console口登录方式的公共属性2.4 Console口登录配置任务简介2.5 认证方式为None时Console口登录方式的配置2.5.1 配置过程2.5.2 配置举例2.6 认证方式为Password时Console口登录方式的配置2.6.1 配置过程2.6.2 配置举例2.7 认证方式为Scheme时Console口登录方式的配置2.7.1 配置过程2.7.2 配置举例3 通过Telnet/SSH进行远程登录3.1 通过Telnet进行远程登录3.1.1 通过Telnet登录简介3.1.2 Telnet配置环境搭建3.1.3 配置Telnet登录方式的公共属性3.1.4 Telnet登录配置任务简介3.1.5 认证方式为None时Telnet登录方式的配置3.1.6 认证方式为Password时Telnet登录方式的配置3.1.7 认证方式为Scheme时Telnet登录方式的配置3.2 通过SSH进行登录3.2.1 通过SSH进行登录简介3.2.2 通过SSH进行登录配置4 通过Web网管登录4.1 通过Web网管登录简介4.2 通过Web网管登录配置4.3 Web用户显示4.4 通过Web网管登录举例5 通过NMS登录5.1 通过NMS登录简介5.2 通过NMS方式登录组网结构6 Telnet业务报文指定源IP6.1 Telnet业务报文指定源IP简介6.2 配置Telnet业务报文指定源IP6.3 配置Telnet业务报文指定源IP显示7 对登录用户的控制7.1 对登录用户的控制简介7.2 配置对Telnet的控制7.2.1 配置准备7.2.2 通过源IP对Telnet进行控制7.2.3 通过源IP、目的IP对Telnet进行控制7.2.4 通过源MAC地址对Telnet进行控制7.2.5 配置举例7.3 通过源IP对网管用户进行控制7.3.1 配置准备7.3.2 通过源IP对网管用户进行控制7.3.3 配置举例7.4 通过源IP对Web用户进行控制7.4.1 配置准备7.4.2 通过源IP对Web用户进行控制7.4.3 强制在线Web用户下线7.4.4 配置举例1 登录以太网交换机1.1 登录以太网交换机方法简介用户可以通过以下几种方式登录以太网交换机:●通过Console口进行本地登录●通过Telnet或SSH进行远程登录●通过Web网管登录●通过NMS登录1.2 用户界面简介1.2.1 交换机支持的用户界面在S5120-SI系列以太网交换机中,AUX口(Auxiliary port,辅助端口)和Console口是同一个端口,以下称为Console口,与其对应的用户界面类型只有AUX用户界面类型。
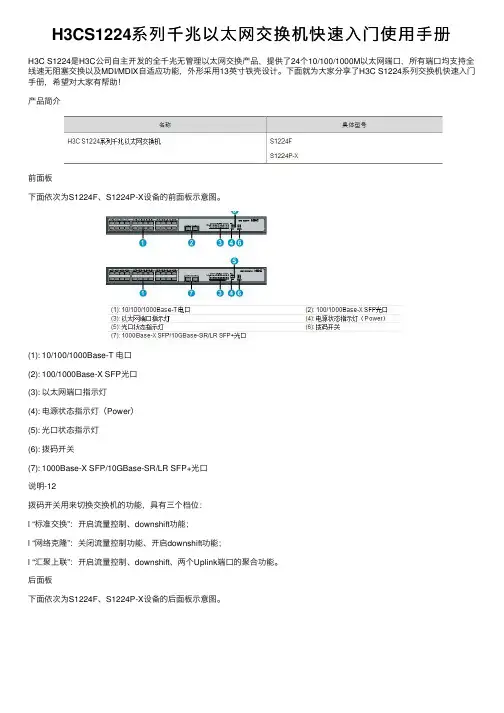
H3CS1224系列千兆以太⽹交换机快速⼊门使⽤⼿册H3C S1224是H3C公司⾃主开发的全千兆⽆管理以太⽹交换产品,提供了24个10/100/1000M以太⽹端⼝,所有端⼝均⽀持全线速⽆阻塞交换以及MDI/MDIX⾃适应功能,外形采⽤13英⼨铁壳设计。
下⾯就为⼤家分享了H3C S1224系列交换机快速⼊门⼿册,希望对⼤家有帮助!产品简介前⾯板下⾯依次为S1224F、S1224P-X设备的前⾯板⽰意图。
(1): 10/100/1000Base-T 电⼝(2): 100/1000Base-X SFP光⼝(3): 以太⽹端⼝指⽰灯(4): 电源状态指⽰灯(Power)(5): 光⼝状态指⽰灯(6): 拨码开关(7): 1000Base-X SFP/10GBase-SR/LR SFP+光⼝说明-12拨码开关⽤来切换交换机的功能,具有三个档位:l “标准交换”:开启流量控制、downshift功能;l “⽹络克隆”:关闭流量控制功能、开启downshift功能;l “汇聚上联”:开启流量控制、downshift、两个Uplink端⼝的聚合功能。
后⾯板下⾯依次为S1224F、S1224P-X设备的后⾯板⽰意图。
(1): 接地螺钉(2): 交流电源接⼝指⽰灯说明安装设备交换机既可以安装在19英⼨标准机柜上,也可以直接放置在⼯作台上。
为避免使⽤不当造成设备损坏或对⼈⾝的伤害,请遵从以下的注意事项:l 请不要将交换机放在⽔边或潮湿的地⽅,并防⽌⽔或湿⽓进⼊交换机机壳;l 请保证交换机⼯作环境的清洁,过多的灰尘会造成静电吸附,不但会影响设备寿命,⽽且容易造成通信故障;l 请保持交换机通⽓孔畅通,请勿堆砌放置;l 请确保交换机在⼀个正确、稳定的电压下⼯作;l 在使⽤交换机前,请务必通过交换机后⾯板的接地端⼦可靠接地;l 在清洁交换机前,应先将交换机电源插头拔出。
请不要⽤湿润的布料擦拭交换机,也不要使⽤液体清洗交换机;l 在交换机⼯作时请不要打开机壳。


总述目录目录第1章资料获取方式..............................................................................................................1-11.1 随机光盘.............................................................................................................................1-11.2 H3C网站.............................................................................................................................1-11.3 软件版本发布配套资料.......................................................................................................1-1第2章资料与版本的配套关系................................................................................................2-12.1 配套资料清单.....................................................................................................................2-12.2 手册对应的软件版本..........................................................................................................2-1第3章产品简介.....................................................................................................................3-13.1 引言....................................................................................................................................3-13.2 系统特性.............................................................................................................................3-13.3 业务特性.............................................................................................................................3-3第4章组网应用.....................................................................................................................4-14.1 城域接入组网方案..............................................................................................................4-14.2 教育网组网方案..................................................................................................................4-14.3 多业务承载VLAN规划方案.................................................................................................4-2总述第1章资料获取方式第1章资料获取方式杭州华三通信技术有限公司(下文简称H3C公司)提供多种获取资料的途径,方便用户及时获得产品相关的资料和新增特性文档。
H3C S5000PV3-EI-PWR系列千兆管理型交换机产品概述H3C S5000PV3-EI-PWR系列以太网交换机是H3C基于业内领先的comware V7平台,面向中小商业市场(SMB市场)推出的新一代高性能全千兆管理型交换机产品,支持IRF2堆叠,并提供完备的安全接入策略和更强的网络管理维护易用性;可广泛应用于政府、中小型企业、学校、酒店等行业的网络建设场景。
S5024PV3-EI-PWRS5024PV3-EI-HPWRS5048PV3-EI-PWRS5000PV3-EI-PWR系列千兆交换机产品特点丰富的端口类型全系列支持“以太网口+光口”组合,适应各种场景组网需求,方便用户灵活组网;提供24/48多规格端口产品,所有端口均具备千兆线速转发能力,满足不同用户所需。
1产品彩页IRF2(第二代智能弹性架构)H3C S5000PV3系列交换机支持IRF2(第二代智能弹性架构)技术,就是把多台物理设备互相连接起来,使其虚拟为一台逻辑设备,也就是说,用户可以将这多台设备看成一台单一设备进行管理和使用。
IRF可以为用户带来以下好处:简化管理IRF架构形成之后,可以连接到任何一台设备的任何一个端口就以登录统一的逻辑设备,通过对单台设备的配置达到管理整个智能弹性系统以及系统内所有成员设备的效果,而不用物理连接到每台成员设备上分别对它们进行配置和管理。
简化业务IRF形成的逻辑设备中运行的各种控制协议也是作为单一设备统一运行的,例如路由协议会作为单一设备统一计算,而随着跨设备链路聚合技术的应用,可以替代原有的生成树协议,这样就可以省去了设备间大量协议报文的交互,简化了网络运行,缩短了网络动荡时的收敛时间。
弹性扩展可以按照用户需求实现弹性扩展,保证用户投资。
并且新增的设备加入或离开IRF架构时可以实现“热插拔”,不影响其他设备的正常运行。
高可靠IRF的高可靠性体现在链路,设备和协议三个方面。
成员设备之间物理端口支持聚合功能,IRF系统和上、下层设备之间的物理连接也支持聚合功能,这样通过多链路备份提高了链路的可靠性;IRF系统由多台成员设备组成,一旦Master设备故障,系统会迅速自动选举新的Master,以保证通过系统的业务不中断,从而实现了设备级的1:N备份;IRF系统会有实时的协议热备份功能负责将协议的配置信息备份到其他所有成员设备,从而实现1:N的协议可靠性。
华三交换机登陆管理:通过Console口进行本地登录通过Web网管登录管理地址:192.168.20.24Vlan 10 192.168.20.0 网关192.168.20.24Vlan 20 192.168.10.0 网关192.168.10.254Vlan 30 192.168.30.0 网关192.168.30.254通过Console口登录交换机第一步:如图2-1所示,建立本地配置环境,只需将PC机(或终端)的串口通过配置电缆与以太网交换机的Console口连接。
图1-1通过Console口搭建本地配置环境PC第二步:在PC机上运行终端仿真程序(如Windows 3.X的Terminal或Windows 9X/Windows 2000/Windows XP的超级终端等,以下配置以Windows XP为例),选择与交换机相连的串口,设置终端通信参数:传输速率为9600bit/s、8位数据位、1位停止位、无校验和无流控,如图2-2至图2-4所示。
图1-2新建连接图1-3连接端口设置图1-4端口通信参数设置第三步:以太网交换机上电,终端上显示设备自检信息,自检结束后提示用户键入回车,之后将出现命令行提示符(如<H3C>),如图2-5所示。
图1-5以太网交换机配置界面通过Web网管登录1.2 通过Web网管登录简介S5500-EI系列以太网交换机提供一个内置的Web服务器,用户可以通过Web网管终端(PC)登录到交换机上,利用内置的Web服务器以Web方式直观地管理和维护以太网交换机。
交换机和Web网管终端(PC)都要进行相应的配置,才能保证通过Web网管正常登录交换机。
表1-1通过Web网管登录交换机需要具备的条件1.3 通过Web网管登录配置表1-2通过Web网管登录配置需要注意的是,用户采用Scheme认证方式登录以太网交换机时,其所能访问的命令级别取决于AAA方案中定义的用户级别。
(H3C)system-view[H3C] interface Vlan-interface 1(进入管理VLAN)[H3C-Vlan-interface1] undo ip address(取消管理VLAN原有的IP地址)[H3C-Vlan-interface1] ip address 10.153.17.82 255.255.255.0(配置以太网交换机管理VLAN 的IP地址为10.153.17.82)第二步:用户通过Console口,在以太网交换机上配置欲登录的WEB网管用户名和认证口令。
通过Console口,添加以太网交换机的WEB用户,用户级别设为3(管理级用户)[H3C] local-user admin(设置用户名为admin)[H3C-luser-admin] service-type telnet level 3(设置级别3)[H3C-luser-admin] password simple admin(设置密码admin)配置交换机到网关的静态路由[H3C] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 192.168.0.50 (网关的IP地址为192.168.0.50)<H3C>%Apr 2 00:18:38:359 2000 H3C SHELL/5/LOGIN:- 1 - Console(aux0) in unit1 login <H3C>?User view commands:boot Set boot optioncd Change current directoryclock Specify the system clockcluster Run cluster commandcopy Copy from one file to anotherdebugging Enable system debugging functionsdelete Delete a filedir List files on a file systemdisplay Display current system informationfixdisk Recover lost chains in storage deviceformat Format the devicefree Clear user terminal interfaceftp Open FTP connectionlock Lock current user terminal interfacemkdir Create a new directorymore Display the contents of a filemove Move a filenslookup Query Internet name serversntdp Run NTDP commandsping Ping functionpwd Display current working directoryquit Exit from current command viewreboot Reset switchrename Rename a file or directoryreset Reset operationrmdir Remove an existing directorysave Save current configurationschedule Schedule system tasksend Send information to other user terminal interfacesstacking Run command on stack switchstartup Specify system startup parameterssuper Set the current user priority levelsystem-view Enter the System Viewtelnet Establish one TELNET connectionterminal Set the terminal line characteristicstftp Open TFTP connectiontracemac Trace MAC functiontracert Trace route functionundelete Recover a deleted fileundo Cancel current settingxmodem Establish an xmodem connection 用户视图命令:启动系统启动选项cd切换当前目录时钟指定系统时钟群集运行群集命令从一个文件拷贝复制到另一个调试启用系统调试功能delete删除一个文件一个文件系统目录列表文件显示屏显示当前系统信息fixdisk存储设备中恢复丢失的链条格式格式化设备免费清晰的用户终端接口打开FTP连接的FTP锁锁的当前用户终端界面mkdir创建一个新的目录更显示文件的内容移动移动文件Nslookup的互联网域名服务器查询NTDP的运行NTDP的命令平平功能pwd显示当前工作目录退出当前命令查看退出重启复位开关重命名一个文件或目录重命名复位复位操作rmdir删除现有目录保存当前配置保存附表系统任务发送信息发送到其他用户终端接口堆叠堆叠开关运行命令指定系统的启动参数启动超级设置当前用户的优先级系统视图进入系统视图建立一个TELNET连接的telnet终端设置终端线路特点TFTP的打开连接的TFTPtracemac跟踪MAC功能tracert命令跟踪路由功能恢复已删除的文件反删除撤消取消当前设置XModem协议建立一个连接图所示<H3C>sysSystem View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.[H3C]?System view commands:acl Specify acl configuration informationam Access managementapply Apply qos-profilearp Add static ARP entrybroadcast-suppression Specify the broadcast storm controlburst-mode Specify burst-modecluster Specify cluster configuration informationcommand-alias Specify command aliascommand-privilege Specify the command levelcopy Copy source port configuration to destination port copyright-info Displaying copyright informationcut Cut connectiondelete Delete route informationdhcp DHCP configuration subcommandsdhcp-snooping DHCP snoopingdisplay Display current system informationdldp Specify configuration information of DLDPdns Specify domain name systemdomain Add domain or modify domain attributesdot1x Specify 802.1X configuration informationend-station Configure ip address of end stationexecute Batch Commandfile Specify file system configuration informationftp Specify FTP server configuration informationgarp Generic Attribute Registration Protocolgratuitous-arp-learning Gratuitous Arp learning functiongvrp GARP VLAN Registration Protocolhabp Specify HABP configuration informationheader Specify the login bannerhwping Specify HWPing test classhwping-agent Specify HWPing agent task functionhwping-server Specify HWPing server task functionhwtacacs Specify HWTACACS servericmp Specify ICMP(the Internet Control Message Protocol)configuration informationigmp-snooping IGMP snoopinginfo-center Specify information center configuration information interface Specify the interface configuration viewip Specify IP(Internet Protocol) configurationinformation系统视图命令:指定的ACL ACL配置信息上午访问管理适用于应用QoS台ARP表添加静态ARP表项广播抑制指定广播风暴控制突发模式指定突发模式群集指定群集配置信息命令别名指定命令别名命令指定的命令级别特权复印件源端口目标端口配置版权信息显示版权信息切割切割连接delete删除路由信息DHCP的DHCP配置子DHCP的监听DHCP Snooping功能显示屏显示当前系统信息DLDP协议指定的DLDP的配置信息指定的DNS域名系统域添加域或修改域属性命令dot1x指定802.1X的配置信息终端站配置终端站的IP地址执行批处理命令文件指定文件系统的配置信息指定FTP服务器的FTP配置信息GARP的通用属性注册协议无偿-琶音学习免费ARP的学习功能GVRP的GARP VLAN注册协议HABP特性指定HABP特性的配置信息头指定登录旗帜维护与调试指定HWPing测试类维护与调试代理指定维护与调试代理任务功能维护与调试服务器指定HWPing服务器任务函数 HWTACACS的指定HWTACACS服务器ICMP的指定的ICMP(互联网控制消息协议)配置信息IGMP的侦听IGMP侦听信息中心指定信息中心配置信息接口指定接口配置视图知识产权指定IP(因特网协议)的配置信息ipv6 Specify IPv6(Internet Protocol Version 6)configuration informationjob Schedule a system tasklacp Configure LACP Protocollink-aggregation Configure a link aggregation grouplldp Link Layer Discovery Protocol(802.1ab)local-server Specify local RADIUS server configurationinformationlocal-user Specify local user configuration informationloopback-detection Detect if loopback existsmac-address Configure MAC addressmac-authentication Specify MAC authentication configuration information management-vlan Specify management-vlanmirrored-to Mirror the packetsmirroring-group Specify mirroring-groupmonitor-link Configure Monitor Linkmulticast-source-deny Multicast source port denyndp Neighbor discovery protocolnslookup Query Internet name serversntdp Specify NTDP configuration informationntp-service Specify NTP(Network Time Protocol) configurationinformationpacket-filter Filter packets based on aclping Ping functionpki Specify PKI module configuration informationport-mac Config port MAC start addressport-security Specify port-security configuration informationpriority Specify prioritypriority-trust Specify priority trust modepublic-key Specify public-key module configuration information qos QoS configuration informationqos-profile Specify qos-profile configuration informationqueue-scheduler Specify queue scheduling mode and parametersquit Exit from current command viewradius Specify RADIUS configuration informationreset Reset operationreturn Exit to User Viewrmon Specify RMONrsa Specify RSA module configuration informationsave Save current configurationschedule Schedule system tasksftp Set SFTP service attributesmart-link Configure Smart Linksnmp-agent Specify SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol)configuration informationssh Specify SSH (secure shell) configuration information IPv6的指定IPv6(互联网协议第6版)配置信息作业调度系统任务LACP协议配置LACP协议链路聚合链路聚合配置一组LLDP的链路层发现协议(802.1ab)本地服务器的指定本地RADIUS服务器配置信息本地用户指定本地用户配置信息环回检测检测是否存在环回MAC地址配置MAC地址MAC的认证指定MAC地址认证的配置信息管理VLAN的指定管理VLAN的镜像到镜像包镜像组指定镜像组监控链路配置监视器链接组播源的组播源端口否认否认新民主党邻居发现协议Nslookup的互联网域名服务器查询NTDP的指定NTDP的配置信息NTP的服务指定NTP(网络时间协议)的配置信息包过滤基于ACL包过滤器上平平功能公钥基础设施PKI的模块指定配置信息端口- MAC的配置端口MAC地址开始港口安全指定端口安全配置信息优先指定优先级优先级信托指定优先信任模式公钥指定公钥模块的配置信息服务质量QoS的配置信息QoS的配置文件指定的QoS配置文件的配置信息队列调度队列调度模式,并指定参数退出当前命令查看退出半径指定RADIUS配置信息复位复位操作返回退出到用户视图指定远程监控远程监控指定的RSA RSA模块的配置信息保存当前配置保存附表系统任务SFTP发布服务属性设置SFTP发布智能连接配置智能链接SNMP的代理指定SNMP(简单网络管理协议)配置信息SSH的指定SSH(安全壳)配置信息ssh2 Open a secure shell client connectionssl Specify SSL (Secure Socket Layer) configurationinformationstacking Specify stack configuration informationstorm-constrain Port storm-constrainstp Spanning tree protocolsuper Modify super password parameterssysname Specify system name and the command line prompt system-guard System-guard module optionssystem-monitor Specify system-monitor configuration information tcp Specify TCP(Transmission Control Protocol)configuration informationtftp Open TFTP connectiontftp-server TFTP Servertime-range Specify time-range configuration information tracemac Trace MAC functiontracert Trace route functiontraffic-limit Limit the rate of the packetstraffic-priority Specify new priority of the packetstraffic-redirect Redirect the packetstraffic-statistic Count the packetsundo Cancel current settingunknown-multicast Unknown multicastuser-interface Configure the user terminal interfacevlan Configure VLANvlan-vpn Specify vlan-vpnvoice Specify voice vlanSSH2的安全壳打开一个客户端连接指定的SSL SSL(安全套接字层)的配置信息指定堆栈堆叠配置信息风暴制约港口风暴约束生成树协议STP协议超级超级密码参数修改数据类型为sysname指定系统名称和命令行提示符系统防范系统后卫模块选项系统监测指定系统监视器配置信息指定的TCP TCP(传输控制协议)配置信息TFTP的打开连接的TFTP的TFTP服务器TFTP服务器时间范围指定时间段的配置信息tracemac跟踪MAC功能tracert命令跟踪路由功能交通限制限制了数据包速率交通优先指定新的数据包优先级交通重定向报文重定向流量统计的数据包数撤消取消当前设置未知组播未知组播用户界面配置用户终端接口VLAN的配置VLAN的VLAN - VPN指定的VLAN - VPN语音指定语音VLAN[H3C]vlan 2[H3C-vlan2]?Vlan view commands:arp ARP packetdescription Description of VLANdisplay Display current system informationigmp-snooping IGMP snoopingmulticast Specify multicast configuration information name Name of VLANnslookup Query Internet name serversping Ping functionport Add ports to or delete ports from VLAN quit Exit from current command viewremote-probe Specify remote-probe vlanreturn Exit to User Viewsave Save current configurationservice-type Specify Service-VLAN characteristic tracemac Trace MAC functiontracert Trace route functionundo Cancel current setting VLAN视图命令: ARP包的ARP描述VLAN的说明显示屏显示当前系统信息IGMP的侦听IGMP侦听多播组播指定配置信息对VLAN的名称Nslookup的互联网域名服务器查询平平功能港口新增的港口或删除VLAN端口退出当前命令查看退出远程探测指定远程探测VLAN返回退出到用户视图保存当前配置保存服务类型指定服务的VLAN特性 tracemac跟踪MAC功能tracert命令跟踪路由功能撤消取消当前设置。
H3C交换机操作手册
H3C交换机操作手册
一、设备连接
1、将设备连接在路由器上,确保网络畅通。
2、打开电脑的浏览器,输入设备的 IP 地址:192.168.1.254。
3、在登录界面输入用户名和密码,默认用户名是 admin,密码是admin。
4、选择“网络”选项卡,然后单击“连接配置”按钮。
二、配置交换机
1、在“连接”选项卡中,选择要配置的交换机。
2、在“交换机管理”选项卡中,选择“配置”。
3、在“配置”选项卡中,选择要配置的交换机的端口数量。
4、在“端口配置”选项卡中,选择要配置的端口的类型。
5、在“VLAN配置”选项卡中,可以配置 VLAN(虚拟局域网)。
6、单击“应用”按钮,然后单击“确定”按钮。
三、管理交换机
1、在“管理”选项卡中,可以查看交换机的状态、端口状态、流量统计等信息。
2、如果需要对交换机进行软件升级,可以在“维护”选项卡中选择“软件升级”。
3、如果需要备份交换机的配置文件,可以在“维护”选项卡中选择“备份配置”。
4、如果交换机出现故障,可以在“维护”选项卡中选择“重启”。
四、常见问题及解决方法
1、无法登录设备:请确认设备的连接是否正确,IP 地址是否正确,路由器的设置是否正确。
2、配置失败:请确认配置的参数是否正确,是否符合网络规划。
3、交换机无法上网:请确认交换机的端口设置是否正确,是否配置了正确的 IP 地址和子网掩码。
本操作手册仅提供了基本的配置和操作方法,实际操作中可能需要根据具体情况进行调整。
如有其他问题,请咨询 H3C 技术支持人员。
目录实验一H3C以太网交换机的基本操作 (4)1.1 知识准备 (4)1.2 操作目的 (4)1.3 网络拓扑 (5)1.4 配置步骤 (5)1.4.1 串口操作配置 (5)1.4.2 查看配置及日志操作 (8)1.4.3 设置密码操作 (9)1.5 验证方法 (10)实验二H3C以太网交换机VLAN配置 (10)2.1 知识准备 (10)2.2 操作目的 (10)2.3 操作内容 (10)2.4 设备准备 (11)2.5 拓扑 (11)2.6 配置步骤 (11)实验三H3C以太网交换机链路聚合配置 (12)3.1 知识准备 (12)3.2 操作目的 (12)3.3 操作内容 (12)3.4 设备准备 (12)3.5 网络拓扑 (13)3.6 配置步骤 (13)3.7 验证方法 (15)实验四H3C以太网交换机STP配置 (15)4.1 知识准备 (15)4.2 操作目的 (15)4.3 操作内容 (15)4.4 设备准备 (15)4.5 网络拓扑 (16)4.6 配置步骤 (16)4.7 验证方法 (17)实验五H3C以太网交换机VRRP配置 (18)5.2 操作目的 (18)5.3 操作内容 (18)5.4 设备准备 (18)5.5 网络拓扑 (19)5.6 配置步骤 (19)5.7 验证方法 (21)实验六H3C以太网交换机镜像配置 (22)6.1 知识准备 (22)6.2 操作目的 (22)6.3 操作内容 (22)6.4 设备准备 (22)6.5 网络拓扑 (22)6.6 配置步骤 (23)6.7 验证方法 (24)实验七H3C以太网交换机路由配置 (24)7.1 知识准备 (24)7.2 操作目的 (24)7.4 设备准备 (24)7.5 网络拓扑 (25)7.6 配置步骤 (25)7.7 验证方法 (26)实验八H3C以太网交换机ACL配置 (26)8.1 知识准备 (26)8.2 操作目的 (27)8.3 操作内容 (27)8.4 网路拓扑 (27)8.5 配置步骤 (27)8.6 验证方法 (28)实验一H3C以太网交换机的基本操作备注:H3C以太网交换机采用统一软件平台VRP,交换机命令完全相同。
1.1知识准备了解交换机的基本知识,了解交换机的基本原理。
阅读H3C S7500系列以太网交换机操作手册。
1.2操作目的通过以下举例学会通过串口操作交换机,并对交换机的端口进行基本配置;能够查看所配置的内容;学会如何重新设置密码,实验内容通过串口线连接到7506交换机,对7506交换机进行配置,配置7506交换机端口以及察看配置信息,设置7506交换机密码,包实验设备7506 一台PC 一台串口线一条平行网线一条1.3网络拓扑1.4配置步骤1.4.1串口操作配置H3C 7506的调试配置一般是通过Console口连接的方式进行,Console口连接配置采用VT100终端方式,下面以Windows操作系统提供的超级终端工具配置为例进行说明。
1. .............. 将PC机与H3C 7506进行正确连线之后,点击系统的[开始→程序→附件→通讯→超级终端],进行超级终端连接,如错误!未找到引用源。
所示。
图1.4-1 超级终端连接2. .............. 在出现错误!未找到引用源。
时,按要求输入有关的位置信息:国家/地区代码、地区电话号码编号和用来拨外线的电话号码。
图1.4-2 位置信息3. .............. 弹出[连接说明]对话框时,为新建的连接输入名称并为该连接选择图标。
如错误!未找到引用源。
所示。
图1.4-3 新建连接4. .............. 根据配置线所连接的串行口,选择连接串行口为COM1(依实际情况选择PC机所使用的串口)。
如错误!未找到引用源。
所示。
图1.4-4 连接配置资料5. .............. 设置所选串行口的端口属性端口属性的设置主要包括以下内容:波特率“9600”,数据位“8”,奇偶校验“无”,停止位“1”,数据流控制“无”,如错误!未找到引用源。
所示。
图1.4-5 端口属性配置设置检查前面设定的各项参数正确无误后,H3C 7506就可以加电启动,进行系统的初始化,进入配置模式进行操作。
以太网交换机上电,终端上显示设备自检信息,自检结束后提示用户键入回车,之后将出现命令行提示符(如<H3C>)。
第四步:键入命令,配置以太网交换机或查看以太网交换机运行状态。
需要帮助可以随时键入“?”,具体的配置命令请参考本书中以后各章节的内容。
1.4.2查看配置及日志操作在所有模式下均可以查看交换机的配置。
执行display current-configuration 命令将会看到系统的全部配置在全局配置模式下,使用saveconfig命令来保存配置信息。
要查看终端的监控和交换机日志信息,可执行如下操作:[H3C] # display interface //所有可以使用display命令的模式下都可以使用此命令,用于查看接口状态[H3C] # display mac-address //所有可以使用display命令的模式下都可以使用此命令,用于查看mac-address 信息[H3C] # display log //所有可以使用display命令的模式下都可以使用此命令,用于查看日志信息1.4.3设置密码操作由于全局配置模式下可以对设备进行全部功能的操作,所以进入全局配置模式的密码非常重要,设备在实际应用中都要求修改进入全局配置模式的密码,具体示例如下:<H3C> system-view //进入全局配置模式password:***** //输入进入全局配置模式的密码,缺省没有密码[H3C] # //已经进入全局配置模式为了便于对设备的维护,有时需要修改登录用户名或密码,配置如下:[H3C] #user-interface aux //进入进入AUX用户界面视图[H3C-ui-aux0] authentication-mode password //设置通过Console口登录交换机的用户进行Password认证[H3C-ui-aux0] set authentication password simple 123456 //设置用户的认证口令为明文方式,口令为123456端口基本配置和端口信息查看下面在H3C 7506上,对端口基本参数进行配置,如自动协商、双工模式、速率、流量控制等,端口参数的配置在全局配置模式下进行。
[H3C] interface ethernet2/0/1 //进入端口Ethernet2/0/1[H3C-Ethernet2/0/1] undo shutdown //使能端口1[H3C-Ethernet2/0/1] undo duplex auto //关闭端口1的自适应功能[H3C-Ethernet2/0/1] duplex full //设置端口1的工作方式为全双工[H3C-Ethernet2/0/1] speed 10 //设置端口1的速率为10M[H3C-Ethernet2/0/1]jumboframe enable //允许长帧通过当前端口使用display 命令可以查看端口的相关信息。
[H3C] display interface2/0/1 //显示端口1的配置和工作状态1.5验证方法退出重新登陆,验证密码配置是否正确。
其它的可通过display命令查看。
实验二H3C以太网交换机VLAN配置2.1知识准备了解交换机的基本知识,了解交换机的基本原理,了解VLAN的原理。
2.2操作目的掌握H3C系列交换机产品VLAN的配置和使用2.3操作内容VLAN业务的配置2.4设备准备7506 一台PC机2台直连网线3条串口线一条2.5拓扑创建VLAN2、VLAN3,指定VLAN2的描述字符串为home;通过配置将端口Ethernet2/0/1和Ethernet2/0/2加入到VLAN2中,将端口Ethernet2/0/3和Ethernet2/0/4加入到VLAN3中。
2.6配置步骤交换机A的具体配置如下:[H3C]vlan 2 //创建VLAN2并进入其视图[H3C-vlan2] description home //指定VLAN2的描述字符串为home[H3C-vlan2] port Ethernet 2/0/1 Ethernet 2/0/2 //向VLAN2中加入端口Ethernet2/0/1和Ethernet2/0/2[H3C-vlan2] vlan 3 //创建VLAN3并进入其视图[H3C-vlan3] port Ethernet 2/0/3 Ethernet 2/0/4 //向VLAN3中加入端口Ethernet2/0/3和Ethernet2/0/42.7验证方法1、PC-1和PC-2能互通(同一个VLAN 内)2、PC-1和PC-2不能互通(不同一个VLAN 内)实验三H3C以太网交换机链路聚合配置3.1知识准备了解链路聚合原理,了解LACP协议。
3.2操作目的掌握H3C交换机链路聚合的配置和使用。
3.3操作内容学会聚合配置3.4设备准备7506 两台直连网线四条PC机二台串口线一条3.5网络拓扑3.6配置步骤以下只列出了Switch A的配置,Switch B上应作相应的配置,汇聚才能实际有效:l采用手工汇聚方式:# 创建手工汇聚组1。
<H3C> system-viewSystem View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z[H3C] link-aggregation group 1 mode manual# 将以太网端口Ethernet2/0/1至Ethernet2/0/3加入汇聚组1。
[H3C] interface ethernet2/0/1[H3C-Ethernet2/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1[H3C-Ethernet2/0/1] interface ethernet2/0/2[H3C-Ethernet2/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1[H3C-Ethernet2/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1l采用静态LACP汇聚方式:# 创建静态汇聚组1。
[H3C] link-aggregation group 1 mode static# 将以太网端口Ethernet2/0/1至Ethernet2/0/3加入汇聚组1。
[H3C] interface ethernet2/0/1[H3C-Ethernet2/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1[H3C-Ethernet2/0/1] interface ethernet0/2[H3C-Ethernet2/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1[H3C-Ethernet2/0/2] interface ethernet0/3[H3C-Ethernet2/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1l采用动态LACP汇聚方式:# 开启以太网端口Ethernet2/0/1至Ethernet2/0/3的LACP协议。