罗斯公司理财Chap004全英文题库及答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:1.04 MB
- 文档页数:86
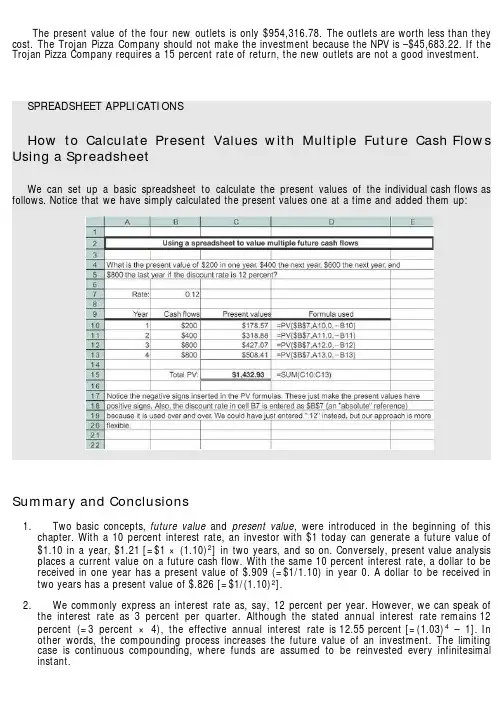
The present value of the four new outlets is only $954,316.78. The outlets are worth less than they cost. The Trojan Pizza Company should not make the investment because the NPV is –$45,683.22. If the Trojan Pizza Company requires a 15 percent rate of return, the new outlets are not a good investment.SPREADSHEET APPLICATIONSHow to Calculate Present Values with Multiple Future Cash Flows Using a SpreadsheetWe can set up a basic spreadsheet to calculate the present values of the individual cash flows as follows. Notice that we have simply calculated the present values one at a time and added them up:Summary and Conclusions1. Two basic concepts, future value and present value, were introduced in the beginning of thischapter. With a 10 percent interest rate, an investor with $1 today can generate a future value of $1.10 in a year, $1.21 [=$1 × (1.10)2] in two years, and so on. Conversely, present value analysis places a current value on a future cash flow. With the same 10 percent interest rate, a dollar to be received in one year has a present value of $.909 (=$1/1.10) in year 0. A dollar to be received in two years has a present value of $.826 [=$1/(1.10)2].2. We commonly express an interest rate as, say, 12 percent per year. However, we can speak ofthe interest rate as 3 percent per quarter. Although the stated annual interest rate remains 12 percent (=3 percent × 4), the effective annual interest rate is 12.55 percent [=(1.03)4 – 1]. In other words, the compounding process increases the future value of an investment. The limiting case is continuous compounding, where funds are assumed to be reinvested every infinitesimal instant.3. A basic quantitative technique for financial decision making is net present value analysis. Thenet present value formula for an investment that generates cash flows (C i) in future periods is:The formula assumes that the cash flow at date 0 is the initial investment (a cash outflow).4. Frequently, the actual calculation of present value is long and tedious. The computation of thepresent value of a long-term mortgage with monthly payments is a good example of this. We presented four simplifying formulas:5. We stressed a few practical considerations in the application of these formulas:1. The numerator in each of the formulas, C, is the cash flow to be received one full periodhence.2. Cash flows are generally irregular in practice. To avoid unwieldy problems, assumptions tocreate more regular cash flows are made both in this textbook and in the real world.3. A number of present value problems involve annuities (or perpetuities) beginning a fewperiods hence. Students should practice combining the annuity (or perpetuity) formula withthe discounting formula to solve these problems.4. Annuities and perpetuities may have periods of every two or every n years, rather thanonce a year. The annuity and perpetuity formulas can easily handle such circumstances.5. We frequently encounter problems where the present value of one annuity must beequated with the present value of another annuity.Concept Questions1. Compounding and Period As you increase the length of time involved, what happens tofuture values? What happens to present values?2. Interest Rates What happens to the future value of an annuity if you increase the rate r?What happens to the present value?3. Present Value Suppose two athletes sign 10-year contracts for $80 million. In one case, we’retold that the $80 million will be paid in 10 equal installments. In the other case, we’re told that the $80 million will be paid in 10 installments, but the installments will increase by 5 percent per year.Who got the better deal?4. APR and EAR Should lending laws be changed to require lenders to report EARs instead ofAPRs? Why or why not?5. Time Value On subsidized Stafford loans, a common source of financial aid for collegestudents, interest does not begin to accrue until repayment begins. Who receives a bigger subsidy,a freshman or a senior? Explain.Use the following information to answer the next five questions:Toyota Motor Credit Corporation (TMCC), a subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation, offered some securities for sale to the public on March 28, 2008. Under the terms of the deal, TMCC promised to repay the owner of one of these securities $100,000 on March 28, 2038, but investors would receive nothing until then. Investors paid TMCC $24,099 for each of these securities; so they gave up $24,099 on March 28, 2008, for the promise of a $100,000 payment 30 years later.6. Time Value of Money Why would TMCC be willing to accept such a small amount today($24,099) in exchange for a promise to repay about four times that amount ($100,000) in the future?7. Call Provisions TMCC has the right to buy back the securities on the anniversary date at aprice established when the securities were issued (this feature is a term of this particular deal).What impact does this feature have on the desirability of this security as an investment?8. Time Value of Money Would you be willing to pay $24,099 today in exchange for $100,000 in30 years? What would be the key considerations in answering yes or no? Would your answerdepend on who is making the promise to repay?9. Investment Comparison Suppose that when TMCC offered the security for $24,099 the U.S.Treasury had offered an essentially identical security. Do you think it would have had a higher or lower price? Why?10. Length of Investment The TMCC security is bought and sold on the New York StockExchange. If you looked at the price today, do you think the price would exceed the $24,099 original price? Why? If you looked in the year 2019, do you think the price would be higher or lower than today’s price? Why?Questions and Problems: connect™BASIC (Questions 1–20)1. Simple Interest versus Compound Interest First City Bank pays 9 percent simple intereston its savings account balances, whereas Second City Bank pays 9 percent interest compounded annually. If you made a $5,000 deposit in each bank, how much more money would you earn from your Second City Bank account at the end of 10 years?2. Calculating Future Values Compute the future value of $1,000 compounded annually for1. 10 years at 6 percent.2. 10 years at 9 percent.3. 20 years at 6 percent.4. Why is the interest earned in part (c) not twice the amount earned in part (a)?3. Calculating Present Values For each of the following, compute the present value:4. Calculating Interest Rates Solve for the unknown interest rate in each of the following:5. Calculating the Number of Periods Solve for the unknown number of years in each of thefollowing:6. Calculating the Number of Periods At 9 percent interest, how long does it take to doubleyour money? To quadruple it?7. Calculating Present Values Imprudential, Inc., has an unfunded pension liability of $750million that must be paid in 20 years. To assess the value of the firm’s stock, financial analysts want to discount this liability back to the present. If the relevant discount rate is 8.2 percent, what is the present value of this liability?8. Calculating Rates of Return Although appealing to more refined tastes, art as a collectiblehas not always performed so profitably. During 2003, Sotheby’s sold the Edgar Degas bronze sculpture Petite Danseuse de Quartorze Ans at auction for a price of $10,311,500. Unfortunately for the previous owner, he had purchased it in 1999 at a price of $12,377,500. What was his annual rate of return on this sculpture?9. Perpetuities An investor purchasing a British consol is entitled to receive annual paymentsfrom the British government forever. What is the price of a consol that pays $120 annually if the next payment occurs one year from today? The market interest rate is 5.7 percent.10. Continuous Compounding Compute the future value of $1,900 continuously compounded for1. 5 years at a stated annual interest rate of 12 percent.2. 3 years at a stated annual interest rate of 10 percent.3. 10 years at a stated annual interest rate of 5 percent.4. 8 years at a stated annual interest rate of 7 percent.11. Present Value and Multiple Cash Flows Conoly Co. has identified an investment projectwith the following cash flows. If the discount rate is 10 percent, what is the present value of these cash flows? What is the present value at 18 percent? At 24 percent?12. Present Value and Multiple Cash Flows Investment X offers to pay you $5,500 per year fornine years, whereas Investment Y offers to pay you $8,000 per year for five years. Which of these cash flow streams has the higher present value if the discount rate is 5 percent? If the discount rate is 22 percent?13. Calculating Annuity Present Value An investment offers $4,300 per year for 15 years, withthe first payment occurring one year from now. If the required return is 9 percent, what is the value of the investment? What would the value be if the payments occurred for 40 years? For 75 years? Forever?14. Calculating Perpetuity Values The Perpetual Life Insurance Co. is trying to sell you aninvestment policy that will pay you and your heirs $20,000 per year forever. If the required return on this investment is 6.5 percent, how much will you pay for the policy? Suppose the Perpetual Life Insurance Co. told you the policy costs $340,000. At what interest rate would this be a fair deal? 15. Calculating EAR Find the EAR in each of the following cases:16. Calculating APR Find the APR, or stated rate, in each of the following cases:17. Calculating EAR First National Bank charges 10.1 percent compounded monthly on itsbusiness loans. First United Bank charges 10.4 percent compounded semiannually. As a potential borrower, to which bank would you go for a new loan?18. Interest Rates Well-known financial writer Andrew Tobias argues that he can earn 177percent per year buying wine by the case. Specifically, he assumes that he will consume one $10 bottle of fine Bordeaux per week for the next 12 weeks. He can either pay $10 per week or buy a case of 12 bottles today. If he buys the case, he receives a 10 percent discount and, by doing so, earns the 177 percent. Assume he buys the wine and consumes the first bottle today. Do you agree with his analysis? Do you see a problem with his numbers?19. Calculating Number of Periods One of your customers is delinquent on his accounts payablebalance. You’ve mutually agreed to a repayment schedule of $600 per month. You will charge .9 percent per month interest on the overdue balance. If the current balance is $18,400, how long will it take for the account to be paid off?20. Calculating EAR Friendly’s Quick Loans, Inc., offers you “three for four or I knock on yourdoor.” This means you get $3 today and repay $4 when you get your paycheck in one week (orelse). What’s the effective annual return Friendly’s earns on this lending business? If you were brave enough to ask, what APR would Friendly’s say you were paying?INTERMEDIATE (Questions 21–50)21. Future Value What is the future value in seven years of $1,000 invested in an account with astated annual interest rate of 8 percent,1. Compounded annually?2. Compounded semiannually?3. Compounded monthly?4. Compounded continuously?5. Why does the future value increase as the compounding period shortens?22. Simple Interest versus Compound Interest First Simple Bank pays 6 percent simpleinterest on its investment accounts. If First Complex Bank pays interest on its accounts compounded annually, what rate should the bank set if it wants to match First Simple Bank over an investment horizon of 10 years?23. Calculating Annuities You are planning to save for retirement over the next 30 years. To dothis, you will invest $700 a month in a stock account and $300 a month in a bond account. The return of the stock account is expected to be 10 percent, and the bond account will pay 6 percent.When you retire, you will combine your money into an account with an 8 percent return. How much can you withdraw each month from your account assuming a 25-year withdrawal period?24. Calculating Rates of Return Suppose an investment offers to quadruple your money in 12months (don’t believe it). What rate of return per quarter are you being offered?25. Calculating Rates of Return You’re trying to choose between two different investments, bothof which have up-front costs of $75,000. Investment G returns $135,000 in six years. Investment H returns $195,000 in 10 years. Which of these investments has the higher return?26. Growing Perpetuities Mark Weinstein has been working on an advanced technology in lasereye surgery. His technology will be available in the near term. He anticipates his first annual cash flow from the technology to be $215,000, received two years from today. Subsequent annual cash flows will grow at 4 percent in perpetuity. What is the present value of the technology if the discount rate is 10 percent?27. Perpetuities A prestigious investment bank designed a new security that pays a quarterlydividend of $5 in perpetuity. The first dividend occurs one quarter from today. What is the price of the security if the stated annual interest rate is 7 percent, compounded quarterly?28. Annuity Present Values What is the present value of an annuity of $5,000 per year, with thefirst cash flow received three years from today and the last one received 25 years from today? Usea discount rate of 8 percent.29. Annuity Present Values What is the value today of a 15-year annuity that pays $750 a year?The annuity’s first payment occurs six years from today. The annual interest rate is 12 percent for years 1 through 5, and 15 percent thereafter.30. Balloon Payments Audrey Sanborn has just arranged to purchase a $450,000 vacation homein the Bahamas with a 20 percent down payment. The mortgage has a 7.5 percent stated annualinterest rate, compounded monthly, and calls for equal monthly payments over the next 30 years.Her first payment will be due one month from now. However, the mortgage has an eight-year balloon payment, meaning that the balance of the loan must be paid off at the end of year 8. There were no other transaction costs or finance charges. How much will Audrey’s balloon payment be in eight years?31. Calculating Interest Expense You receive a credit card application from Shady BanksSavings and Loan offering an introductory rate of 2.40 percent per year, compounded monthly for the first six months, increasing thereafter to 18 percent compounded monthly. Assuming you transfer the $6,000 balance from your existing credit card and make no subsequent payments, how much interest will you owe at the end of the first year?32. Perpetuities Barrett Pharmaceuticals is considering a drug project that costs $150,000 todayand is expected to generate end-of-year annual cash flows of $13,000, forever. At what discount rate would Barrett be indifferent between accepting or rejecting the project?33. Growing Annuity Southern California Publishing Company is trying to decide whether to reviseits popular textbook, Financial Psychoanalysis Made Simple. The company has estimated that the revision will cost $65,000. Cash flows from increased sales will be $18,000 the first year. These cash flows will increase by 4 percent per year. The book will go out of print five years from now.Assume that the initial cost is paid now and revenues are received at the end of each year. If the company requires an 11 percent return for such an investment, should it undertake the revision? 34. Growing Annuity Your job pays you only once a year for all the work you did over theprevious 12 months. Today, December 31, you just received your salary of $60,000, and you plan to spend all of it. However, you want to start saving for retirement beginning next year. You have decided that one year from today you will begin depositing 5 percent of your annual salary in an account that will earn 9 percent per year. Your salary will increase at 4 percent per year throughout your career. How much money will you have on the date of your retirement 40 years from today?35. Present Value and Interest Rates What is the relationship between the value of an annuityand the level of interest rates? Suppose you just bought a 12-year annuity of $7,500 per year at the current interest rate of 10 percent per year. What happens to the value of your investment if interest rates suddenly drop to 5 percent? What if interest rates suddenly rise to 15 percent?36. Calculating the Number of Payments You’re prepared to make monthly payments of $250,beginning at the end of this month, into an account that pays 10 percent interest compounded monthly. How many payments will you have made when your account balance reaches $30,000? 37. Calculating Annuity Present Values You want to borrow $80,000 from your local bank tobuy a new sailboat. You can afford to make monthly payments of $1,650, but no more. Assuming monthly compounding, what is the highest APR you can afford on a 60-month loan?38. Calculating Loan Payments You need a 30-year, fixed-rate mortgage to buy a new home for$250,000. Your mortgage bank will lend you the money at a 6.8 percent APR for this 360-month loan. However, you can only afford monthly payments of $1,200, so you offer to pay off any remaining loan balance at the end of the loan in the form of a single balloon payment. How large will this balloon payment have to be for you to keep your monthly payments at $1,200?39. Present and Future Values The present value of the following cash flow stream is $6,453when discounted at 10 percent annually. What is the value of the missing cash flow?40. Calculating Present Values You just won the TVM Lottery. You will receive $1 million todayplus another 10 annual payments that increase by $350,000 per year. Thus, in one year you receive $1.35 million. In two years, you get $1.7 million, and so on. If the appropriate interest rate is 9 percent, what is the present value of your winnings?41. EAR versus APR You have just purchased a new warehouse. To finance the purchase, you’vearranged for a 30-year mortgage for 80 percent of the $2,600,000 purchase price. The monthly payment on this loan will be $14,000. What is the APR on this loan? The EAR?42. Present Value and Break-Even Interest Consider a firm with a contract to sell an asset for$135,000 three years from now. The asset costs $96,000 to produce today. Given a relevant discount rate on this asset of 13 percent per year, will the firm make a profit on this asset? At what rate does the firm just break even?43. Present Value and Multiple Cash Flows What is the present value of $4,000 per year, at adiscount rate of 7 percent, if the first payment is received 9 years from now and the last payment is received 25 years from now?44. Variable Interest Rates A 15-year annuity pays $1,500 per month, and payments are madeat the end of each month. If the interest rate is 13 percent compounded monthly for the first seven years, and 9 percent compounded monthly thereafter, what is the present value of the annuity? 45. Comparing Cash Flow Streams You have your choice of two investment accounts.Investment A is a 15-year annuity that features end-of-month $1,200 payments and has an interest rate of 9.8 percent compounded monthly. Investment B is a 9 percent continuously compounded lump-sum investment, also good for 15 years. How much money would you need to invest in B today for it to be worth as much as Investment A 15 years from now?46. Calculating Present Value of a Perpetuity Given an interest rate of 7.3 percent per year,what is the value at date t = 7 of a perpetual stream of $2,100 annual payments that begins at date t = 15?47. Calculating EAR A local finance company quotes a 15 percent interest rate on one-year loans.So, if you borrow $26,000, the interest for the year will be $3,900. Because you must repay a total of $29,900 in one year, the finance company requires you to pay $29,900/12, or $2,491.67, per month over the next 12 months. Is this a 15 percent loan? What rate would legally have to be quoted? What is the effective annual rate?48. Calculating Present Values A 5-year annuity of ten $4,500 semiannual payments will begin 9years from now, with the first payment coming 9.5 years from now. If the discount rate is 12 percent compounded monthly, what is the value of this annuity five years from now? What is the value three years from now? What is the current value of the annuity?49. Calculating Annuities Due Suppose you are going to receive $10,000 per year for five years.The appropriate interest rate is 11 percent.1. What is the present value of the payments if they are in the form of an ordinary annuity?What is the present value if the payments are an annuity due?2. Suppose you plan to invest the payments for five years. What is the future value if thepayments are an ordinary annuity? What if the payments are an annuity due?3. Which has the highest present value, the ordinary annuity or annuity due? Which has thehighest future value? Will this always be true?50. Calculating Annuities Due You want to buy a new sports car from Muscle Motors for$65,000. The contract is in the form of a 48-month annuity due at a 6.45 percent APR. What will your monthly payment be?CHALLENGE (Questions 51–76)51. Calculating Annuities Due You want to lease a set of golf clubs from Pings Ltd. The leasecontract is in the form of 24 equal monthly payments at a 10.4 percent stated annual interest rate, compounded monthly. Because the clubs cost $3,500 retail, Pings wants the PV of the lease payments to equal $3,500. Suppose that your first payment is due immediately. What will your monthly lease payments be?52. Annuities You are saving for the college education of your two children. They are two yearsapart in age; one will begin college 15 years from today and the other will begin 17 years from today. You estimate your children’s college expenses to be $35,000 per year per child, payable at the beginning of each school year. The annual interest rate is 8.5 percent. How much money must you deposit in an account each year to fund your children’s education? Your deposits begin one year from today. You will make your last deposit when your oldest child enters college. Assume four years of college.53. Growing Annuities Tom Adams has received a job offer from a large investment bank as aclerk to an associate banker. His base salary will be $45,000. He will receive his first annual salary payment one year from the day he begins to work. In addition, he will get an immediate $10,000 bonus for joining the company. His salary will grow at 3.5 percent each year. Each year he will receive a bonus equal to 10 percent of his salary. Mr. Adams is expected to work for 25 years.What is the present value of the offer if the discount rate is 12 percent?54. Calculating Annuities You have recently won the super jackpot in the Washington StateLottery. On reading the fine print, you discover that you have the following two options:1. You will receive 31 annual payments of $175,000, with the first payment being deliveredtoday. The income will be taxed at a rate of 28 percent. Taxes will be withheld when the checks are issued.2. You will receive $530,000 now, and you will not have to pay taxes on this amount. Inaddition, beginning one year from today, you will receive $125,000 each year for 30 years.The cash flows from this annuity will be taxed at 28 percent.Using a discount rate of 10 percent, which option should you select?55. Calculating Growing Annuities You have 30 years left until retirement and want to retirewith $1.5 million. Your salary is paid annually, and you will receive $70,000 at the end of the current year. Your salary will increase at 3 percent per year, and you can earn a 10 percent return on the money you invest. If you save a constant percentage of your salary, what percentage of your salary must you save each year?56. Balloon Payments On September 1, 2007, Susan Chao bought a motorcycle for $25,000. Shepaid $1,000 down and financed the balance with a five-year loan at a stated annual interest rate of8.4 percent, compounded monthly. She started the monthly payments exactly one month after thepurchase (i.e., October 1, 2007). Two years later, at the end of October 2009, Susan got a new job and decided to pay off the loan. If the bank charges her a 1 percent prepayment penalty based on the loan balance, how much must she pay the bank on November 1, 2009?57. Calculating Annuity Values Bilbo Baggins wants to save money to meet three objectives.First, he would like to be able to retire 30 years from now with a retirement income of $20,000 per month for 20 years, with the first payment received 30 years and 1 month from now. Second, he would like to purchase a cabin in Rivendell in 10 years at an estimated cost of $320,000. Third, after he passes on at the end of the 20 years of withdrawals, he would like to leave an inheritance of $1,000,000 to his nephew Frodo. He can afford to save $1,900 per month for the next 10 years.If he can earn an 11 percent EAR before he retires and an 8 percent EAR after he retires, how much will he have to save each month in years 11 through 30?58. Calculating Annuity Values After deciding to buy a new car, you can either lease the car orpurchase it with a three-year loan. The car you wish to buy costs $38,000. The dealer has a special leasing arrangement where you pay $1 today and $520 per month for the next three years. If you purchase the car, you will pay it off in monthly payments over the next three years at an 8 percent APR. You believe that you will be able to sell the car for $26,000 in three years. Should you buy or lease the car? What break-even resale price in three years would make you indifferent between buying and leasing?59. Calculating Annuity Values An All-Pro defensive lineman is in contract negotiations. Theteam has offered the following salary structure:All salaries are to be paid in a lump sum. The player has asked you as his agent to renegotiate the terms. He wants a $9 million signing bonus payable today and a contract value increase of $750,000. He also wants an equal salary paid every three months, with the first paycheck three months from now. If the interest rate is 5 percent compounded daily, what is the amount of his quarterly check? Assume 365 days in a year.60. Discount Interest Loans This question illustrates what is known as discount interest. Imagineyou are discussing a loan with a somewhat unscrupulous lender. You want to borrow $20,000 for one year. The interest rate is 14 percent. You and the lender agree that the interest on the loan will be .14 × $20,000 = $2,800. So, the lender deducts this interest amount from the loan up front and gives you $17,200. In this case, we say that the discount is $2,800. What’s wrong here?61. Calculating Annuity Values You are serving on a jury. A plaintiff is suing the city for injuriessustained after a freak street sweeper accident. In the trial, doctors testified that it will be five years before the plaintiff is able to return to work. The jury has already decided in favor of the plaintiff. You are the foreperson of the jury and propose that the jury give the plaintiff an award to cover the following: (1) The present value of two years’ back pay. The plaintiff’s annual salary for the last two years would have been $42,000 and $45,000, respectively. (2) The present value of five years’ future salary. You assume the salary will be $49,000 per year. (3) $150,000 for pain and suffering. (4) $25,000 for court costs. Assume that the salary payments are equal amounts paid at the end of each month. If the interest rate you choose is a 9 percent EAR, what is the size of the settlement? If you were the plaintiff, would you like to see a higher or lower interest rate?62. Calculating EAR with Points You are looking at a one-year loan of $10,000. The interest rateis quoted as 9 percent plus three points. A point on a loan is simply 1 percent (one percentage point) of the loan amount. Quotes similar to this one are very common with home mortgages. The interest rate quotation in this example requires the borrower to pay three points to the lender up front and repay the loan later with 9 percent interest. What rate would you actually be paying here? What is the EAR for a one-year loan with a quoted interest rate of 12 percent plus two points? Is your answer affected by the loan amount?63. EAR versus APR Two banks in the area offer 30-year, $200,000 mortgages at 6.8 percent andcharge a $2,100 loan application fee. However, the application fee charged by Insecurity Bank and Trust is refundable if the loan application is denied, whereas that charged by I. M. Greedy and Sons Mortgage Bank is not. The current disclosure law requires that any fees that will be refunded if the applicant is rejected be included in calculating the APR, but this is not required with nonrefundable。

罗斯公司理财第四章全英文题库及答案Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow ValuationChapter 04 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Answer KeyMultiple Choice Questions1. An annuity stream of cash flow payments is a set of:A. level cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.B. level cash flows occurring each time period forever.C. increasing cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.D. increasing cash flows occurring each time period forever.E. arbitrary cash flows occurring each time period for no more than10 years.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ANNUITY Type: DEFINITIONS2. Annuities where the payments occur at the end of each time period are called _____, whereas_____ refer to annuity streams with payments occurring at the beginning of each time period.A. ordinary annuities; early annuitiesB. late annuities; straight annuitiesC. straight annuities; late annuitiesD. annuities due; ordinary annuitiesE. ordinary annuities; annuities dueDifficulty level: Easy Topic: ANNUITIES DUE Type: DEFINITIONS4-1Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation 3. An annuity stream where the payments occur forever is called a(n):A. annuity due.B. indemnity.C. perpetuity.D. amortized cash flow stream.E. amortization table.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: PERPETUITY Type: DEFINITIONS4. The interest rate expressed in terms of the interest payment made each period is called the_____ rate.A. stated annual interestB. compound annual interestC. effective annual interestD. periodic interestE. daily interestDifficulty level: Easy Topic: STATED INTEREST RATES Type: DEFINITIONS5. The interest rate expressed as if it were compounded once per year is called the _____ rate.A. stated interestB. compound interestC. effective annualD. periodic interestE. daily interestDifficulty level: Easy Topic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATE Type: DEFINITIONS4-2Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation6. The interest rate charged per period multiplied by the number of periods per year is called the_____ rate.A. effective annualB. annual percentageC. periodic interestD. compound interestE. daily interestDifficulty level: Easy Topic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATE Type: DEFINITIONS7. Paying off long-term debt by making installment payments is called: A. foreclosing on the debt.B. amortizing the debt.C. funding the debt.D. calling the debt.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: AMORTIZATION Type: DEFINITIONS8. You are comparing two annuities which offer monthly payments for ten years. Both annuitiesare identical with the exception of the payment dates. Annuity A pays on the first of each monthwhile annuity B pays on the last day of each month. Which one of the following statements iscorrect concerning these two annuities?A. Both annuities are of equal value today.B. Annuity B is an annuity due.C. Annuity A has a higher future value than annuity B.D. Annuity B has a higher present value than annuity A.E. Both annuities have the same future value as of ten years from today.Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUE Type: CONCEPTS4-3Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation9. You are comparing two investment options. The cost to invest in either option is the same today. Both options will provide you with $20,000 of income. Option A pays five annual payments starting with $8,000 the first year followed by four annual payments of $3,000 each. Option B pays five annual payments of $4,000 each. Which one of the following statements is correct given these two investment options?A. Both options are of equal value given that they both provide $20,000 of income.B. Option A is the better choice of the two given any positive rate of return.C. Option B has a higher present value thanoption A given a positive rate of return. D. Option B has a lower future value at year 5 than option A given a zero rate of return. E. Option A is preferable because it is an annuity due.Difficulty level: Medium Topic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: CONCEPTS10. You are considering two projects with the following cash flows:Which of the following statements are true concerning these two projects?I. Both projects have the same future value at the end of year 4, given a positive rate of return. II. Both projects have the same future value given a zero rate of return. III. Both projects have the same future value at any point in time, given a positive rate of return. IV. Project A has a higher future value than project B, given a positive rate of return. A. II onlyB. IV onlyC. I and III onlyD. II and IV onlyE. I, II, and III onlyDifficulty level: Medium Topic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND FUTURE VALUE Type: CONCEPTS4-4Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation11. A perpetuity differs from an annuity because:A. perpetuity payments vary with the rate of inflation.B. perpetuity payments vary with the market rate of interest.C. perpetuity payments are variable while annuity payments are constant.D. perpetuity payments never cease.E. annuity payments never cease.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: PERPETUITY VERSUS ANNUITY Type: CONCEPTS12. Which one of the following statements concerning the annual percentage rate is correct? A. The annual percentage rate considers interest on interest.B. The rate of interest you actually pay on a loan is called the annual percentage rate.C. The effective annual rate is lower than the annual percentage rate when an interest rate is compounded quarterly.D. When firms advertise the annual percentage rate they areviolating U.S. truth-in-lending laws.E. The annual percentage rate equals the effective annual rate when the rate on an account is designated as simple interest.Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATE Type: CONCEPTS13. Which one of the following statements concerning interest ratesis correct? A. The stated rate is the same as the effective annual rate.B. An effective annual rate is the rate that applies if interest were charged annually.C. The annual percentage rate increases as the number of compounding periods per year increases.D. Banks prefer more frequent compounding on their savings accounts.E. For any positive rate of interest, the effective annual rate will always exceed the annual percentage rate.Difficulty level: Medium Topic: INTEREST RATES Type: CONCEPTS4-5Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation14. Which of the following statements concerning the effectiveannual rate are correct? I. When making financial decisions, you should compare effective annual rates rather than annual percentage rates.II. The more frequently interest is compounded, the higher the effective annual rate. III. A quoted rate of 6% compounded continuously has a higher effective annual rate than if the rate were compounded daily.IV. When borrowing and choosing which loan to accept, you should select the offer with the highest effective annual rate.A. I and II onlyB. I and IV onlyC. I, II, and III onlyD. II, III, and IV onlyE. I, II, III, and IVDifficulty level: Medium Topic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATE Type: CONCEPTS15. The highest effective annual rate that can be derived from an annual percentage rate of 9% is computed as:A. .09e - 1.B. e.09 , q.C. e , (1 + .09).D. e.09 - 1.E. (1 + .09)q.Difficulty level: Medium Topic: CONTINUOUS COMPOUNDING Type: CONCEPTS16. The time value of money concept can be defined as:A. the relationship between the supply and demand of money.B. the relationship between money spent versus money received.C. the relationship between a dollar to be received in the future and a dollar today.D. the relationship between interest rate stated and amount paid.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: TIME VALUE Type: CONCEPTS4-6Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation17. Discounting cash flows involves:A. discounting only those cash flows that occur at least 10 years in the future.B. estimating only the cash flows that occur in the first 4 years of a project.C. multiplying expected future cash flows by the cost of capital.D. discounting all expected future cash flows toreflect the time value of money. E. taking the cash discount offered on trade merchandise.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: CASH FLOWS Type: CONCEPTS18. Compound interest:A. allows for the reinvestment of interest payments.B. does not allow for the reinvestment of interest payments.C. is the same as simple interest.D. provides a value that is less than simple interest.E. Both A and D.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: INTEREST Type: CONCEPTS19. An annuity:A. is a debt instrument that pays no interest.B. is a stream of payments that varies with current market interest rates.C. is a level stream of equal payments through time.D. has no value.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ANNUITY Type: CONCEPTS4-7Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation20. The stated rate of interest is 10%. Which form of compounding will give the highesteffective rate of interest?A. annual compoundingB. monthly compoundingC. daily compoundingD. continuous compoundingE. It is impossible to tell without knowing the term of the loan.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: COMPOUNDING Type: CONCEPTS21. The present value of future cash flows minus initial cost is called:A. the future value of the project.B. the net present value of the project.C. the equivalent sum of the investment.D. the initial investment risk equivalent value.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: PRESENT VALUE Type: CONCEPTS22. Find the present value of $5,325 to be received in one period if the rate is 6.5%.A. $5,000.00B. $5,023.58C. $5,644.50D. $5,671.13E. None of the above.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: PRESENT VALUE - SINGLE SUM Type: PROBLEMS4-8Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation23. If you have a choice to earn simple interest on $10,000 forthree years at 8% or annually compounded interest at 7.5% for threeyears which one will pay more and by how much? A. Simple interest by $50.00B. Compound interest by $22.97C. Compound interest by $150.75D. Compound interest by $150.00E. None of the above.Simple Interest = $10,000 (.08)(3) = $2,400; 3Compound Interest = $10,000((1.075) - 1) = $2,422.97;Difference = $2,422.97 - $2,400 = $22.97Difficulty level: Easy Topic: SIMPLE & COMPOUND INTEREST Type: PROBLEMS24. Bradley Snapp has deposited $7,000 in a guaranteed investment account with a promised rate of 6% compounded annually. He plans toleave it there for 4 full years when he will make a down payment on acar after graduation. How much of a down payment will he be able to make?A. $1,960.00B. $2,175.57C. $8,960.00D. $8,837.34E. $9,175.574$7,000 (1.06) = $8,837.34Difficulty level: Easy Topic: FUTURE VALUE - SINGLE SUM Type: PROBLEMS4-9Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation25. Your parents are giving you $100 a month for four years whileyou are in college. At a 6% discount rate, what are these payments worth to you when you first start college? A. $3,797.40B. $4,167.09C. $4,198.79D. $4,258.03E. $4,279.32Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-10Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation26. You just won the lottery! As your prize you will receive $1,200a month for 100 months. Ifyou can earn 8% on your money, what is this prize worth to you today?A. $87,003.69B. $87,380.23C. $87,962.77D. $88,104.26E. $90,723.76Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-11Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation27. Todd is able to pay $160 a month for five years for a car. If the interest rate is 4.9%, howmuch can Todd afford to borrow to buy a car? A. $6,961.36B. $8,499.13C. $8,533.84D. $8,686.82E. $9,588.05Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-12Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation28. You are the beneficiary of a life insurance policy. Theinsurance company informs you that you have two options for receiving the insurance proceeds. You can receive a lump sum of $50,000 today or receive payments of $641 a month for ten years. You can earn 6.5% on your money. Which option should you take and why?A. You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,451.91 today.B. You should accept the payments because they are worth$56,523.74 today. C. You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,737.08 today. D. You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47,757.69 today. E. You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47,808.17 today.Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-13Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation29. Your employer contributes $25 a week to your retirement plan. Assume that you work for your employer for another twenty years and that the applicable discount rate is 5%. Given theseassumptions, what is this employee benefit worth to you today? A. $13,144.43B. $15,920.55C. $16,430.54D. $16,446.34E. $16,519.02Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-14Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation30. You have a sub-contracting job with a local manufacturing firm. Your agreement calls forannual payments of $50,000 for the next five years. At a discount rate of 12%, what is this jobworth to you today?A. $180,238.81B. $201,867.47C. $210,618.19D. $223,162.58E. $224,267.10Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-15Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation31. The Ajax Co. just decided to save $1,500 a month for the next five years as a safety net for recessionary periods. The money will be set aside in a separate savings account which pays 3.25% interest compounded monthly. It deposits the first $1,500 today. If the company had wanted to deposit an equivalent lump sum today, how much would it have had to deposit? A. $82,964.59B. $83,189.29C. $83,428.87D. $83,687.23E. $84,998.01Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-16Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation32. You need some money today and the only friend you have that has any is your ‘miserly' friend. He agrees to loan you the money you need, if you make payments of $20 a month for the next six months. In keeping with his reputation, he requires that the first payment be paid today. He also charges you 1.5% interest per month. How much money are you borrowing? A. $113.94B. $115.65C. $119.34D. $119.63E. $119.96Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-17Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation33. You buy an annuity which will pay you $12,000 a year for ten years. The payments are paid on the first day of each year. What is the value of this annuity today at a 7% discount rate? A. $84,282.98B. $87,138.04C. $90,182.79D. $96,191.91E. $116,916.21Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-18Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation34. You are scheduled to receive annual payments of $10,000 for each of the next 25 years. Your discount rate is 8.5%. What is the difference in the present value if you receive these payments at the beginning of each year rather than at the end of each year? A. $8,699B. $9,217C. $9,706D. $10,000E. $10,850Difference = $111,040.97 - $102,341.91 = $8,699.06 = $8,699 (rounded) Note: The difference = .085 , $102,341.91 = $8,699.06Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUE Type: PROBLEMS4-19Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation35. You are comparing two annuities with equal present values. The applicable discount rate is 7.5%. One annuity pays $5,000 on the first day of each year for twenty years. How much does the second annuity pay each year for twenty years if it pays at the end of each year? A. $4,651B. $5,075C. $5,000D. $5,375E. $5,405Because each payment is received one year later, then the cash flow has to equal: $5,000 , (1+ .075) = $5,375Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUE Type: PROBLEMS4-20Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation36. Martha receives $100 on the first of each month. Stewartreceives $100 on the last day of each month. Both Martha and Stewartwill receive payments for five years. At an 8% discount rate, what is the difference in the present value of these two sets of payments? A. $32.88B. $40.00C. $99.01D. $108.00E. $112.50Difference = $4,964.72 - $4,931.84 = $32.88Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUE Type: PROBLEMS4-21Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation 37. What is the future value of $1,000 a year for five years at a 6% rate of interest?A. $4,212.36B. $5,075.69C. $5,637.09D. $6,001.38E. $6,801.91Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUE Type: PROBLEMS38. What is the future value of $2,400 a year for three years at an 8% rate of interest?A. $6,185.03B. $6,847.26C. $7,134.16D. $7,791.36E. $8,414.67Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-22Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation39. Janet plans on saving $3,000 a year and expects to earn 8.5%.How much will Janet have atthe end of twenty-five years if she earns what she expects? A. $219,317.82B. $230,702.57C. $236,003.38D. $244,868.92E. $256,063.66Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-23Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation40. Toni adds $3,000 to her savings on the first day of each year. Tim adds $3,000 to his savingson the last day of each year. They both earn a 9% rate of return. What is the difference in theirsavings account balances at the end of thirty years?A. $35,822.73B. $36,803.03C. $38,911.21D. $39,803.04E. $40,115.31Difference = $445,725.65 - $408,922.62 = $36,803.03Note: Difference = $408,922.62 , .09 = $36,803.03Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ANNUITY DUE VERSUS ORDINARY ANNUITY Type: PROBLEMS4-24Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation41. You borrow $5,600 to buy a car. The terms of the loan call for monthly payments for fouryears at a 5.9% rate of interest. What is the amount of each payment?A. $103.22B. $103.73C. $130.62D. $131.26E. $133.04Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS Type: PROBLEMS4-25Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation42. You borrow $149,000 to buy a house. The mortgage rate is 7.5% and the loan period is 30 years. Payments are made monthly. If you pay for the house according to the loan agreement, how much total interest will you pay?A. $138,086B. $218,161C. $226,059D. $287,086E. $375,059Total interest = ($1,041.83 , 30 , 12) - $149,000 = $226,058.80 = $226,059 (rounded)Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND COST OF INTEREST Type: PROBLEMS4-26Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation43. The Great Giant Corp. has a management contract with its newly hired president. The contract requires a lump sum payment of $25 millionbe paid to the president upon the completion of her first ten years of service. The company wants to set aside an equal amount of funds each year to cover this anticipated cash outflow. The company can earn 6.5% on these funds. How much must the company set aside each year for this purpose? A. $1,775,042.93B. $1,798,346.17C. $1,801,033.67D. $1,852,617.25E. $1,938,018.22Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-27Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation44. You retire at age 60 and expect to live another 27 years. On the day you retire, you have $464,900 in your retirement savings account. You are conservative and expect to earn 4.5% on your money during your retirement. How much can you withdraw from your retirement savings each month if you plan to die on the day you spend your last penny?A. $2,001.96B. $2,092.05C. $2,398.17D. $2,472.00E. $2,481.27Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-28Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation45. The McDonald Group purchased a piece of property for $1.2 million. It paid a down payment of 20% in cash and financed the balance. The loan terms require monthly payments for 15 years at an annual percentage rate of 7.75% compounded monthly. What is the amount of each mortgage payment?A. $7,440.01B. $8,978.26C. $9,036.25D. $9,399.18E. $9,413.67Amount financed = $1,200,000 , (1 - .2) = $960,000Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-29Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation46. You estimate that you will have $24,500 in student loans by the time you graduate. Theinterest rate is 6.5%. If you want to have this debt paid in full within five years, how much mustyou pay each month?A. $471.30B. $473.65C. $476.79D. $479.37E. $480.40Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-30Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation47. You are buying a previously owned car today at a price of $6,890. You are paying $500down in cash and financing the balance for 36 months at 7.9%. What is the amount of each loanpayment?A. $198.64B. $199.94C. $202.02D. $214.78E. $215.09Amount financed = $6,890 - $500 = $6,390Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-31Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation48. The Good Life Insurance Co. wants to sell you an annuity which will pay you $500 per quarter for 25 years. You want to earn a minimum rate of return of 5.5%. What is the most youare willing to pay as a lump sum today to buy this annuity? A. $26,988.16B. $27,082.94C. $27,455.33D. $28,450.67E. $28,806.30Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-32Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation49. Your car dealer is willing to lease you a new car for $299 a month for 60 months. Payments are due on the first day of each month starting with the day you sign the lease contract. If your cost of money is 4.9%, what is the current value of the lease? A. $15,882.75B. $15,906.14C. $15,947.61D. $16,235.42E. $16,289.54Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-33Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation50. Your great-aunt left you an inheritance in the form of a trust. The trust agreement states that you are to receive $2,500 on the firstday of each year, starting immediately and continuing for fifty years. What is the value of this inheritance today if the applicable discount rate is 6.35%? A. $36,811.30B. $37,557.52C. $39,204.04D. $39,942.42E. $40,006.09Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS51. Beatrice invests $1,000 in an account that pays 4% simple interest. How much more could she have earned over a five-year period if the interest had compounded annually? A. $15.45B. $15.97C. $16.65D. $17.09E. $21.67Ending value at 4% simple interest = $1,000 + ($1,000 , .04 , 5) = $1,200.00; Ending value at 54% compounded annually = $1,000 , (1 +.04) = $1,216.65;Difference = $1,216.65 - $1,200.00 = $16.65Difficulty level: Easy Topic: SIMPLE VERSUS COMPOUND INTEREST Type: PROBLEMS4-34Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation52. Your firm wants to save $250,000 to buy some new equipment three years from now. The plan is to set aside an equal amount of money on the first day of each year starting today. The firm can earn a 4.7% rate of return. How much does the firm have to save each year to achieve its goal?A. $75,966.14B. $76,896.16C. $78,004.67D. $81.414.14E. $83,333.33Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-35Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation53. Today is January 1. Starting today, Sam is going to contribute $140 on the first of each month to his retirement account. His employer contributes an additional 50% of the amount contributed by Sam. If both Sam and his employer continue to do this and Sam can earn a monthly rateof ? of 1 percent, how much will he have in his retirement account 35 years from now?A. $199,45.944B. $200,456.74C. $249,981.21D. $299,189.16E. $300,685.11Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUE Type: PROBLEMS54. You are considering an annuity which costs $100,000 today. The annuity pays $6,000 a year. The rate of return is 4.5%. What is the length of the annuity time period? A. 24.96 yearsB. 29.48 yearsC. 31.49 yearsD. 33.08 yearsE. 38.00 yearsDifficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-36Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation55. Today, you signed loan papers agreeing to borrow $4,954.85 at 9% compounded monthly.The loan payment is $143.84 a month. How many loan payments must you make before theloan is paid in full?A. 29.89B. 36.00C. 38.88D. 40.00E. 41.03Difficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-37Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation56. Winston Enterprises would like to buy some additional land and build a new factory. The anticipated total cost is $136 million. The owner of the firm is quite conservative and will only do this when the company has sufficient funds to pay cash for the entire expansion project. Management has decided to save $450,000 a month for thispurpose. The firm earns 6% compounded monthly on the funds it saves. How long does the company have to wait before expanding its operations?A. 184.61 monthsB. 199.97 monthsC. 234.34 monthsD. 284.61 monthsE. 299.97 monthsDifficulty level: Medium Topic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND FUTURE VALUE Type: PROBLEMS4-38Chapter 04 - Discounted Cash Flow Valuation57. Today, you are retiring. You have a total of $413,926 in your retirement savings and have the funds invested such that you expect to earn an average of 3%, compounded monthly, on this money throughout your retirement years. You want to withdraw $2,500 at the beginning of every month, starting today. How long will it be until you run out of money? A. 185.00 monthsB. 213.29 monthsC. 227.08 monthsD. 236.84 months。

Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate FinanceChapter 01 Introduction to Corporate Finance Answer KeyMultiple Choice Questions1. The person generally directly responsible for overseeing the tax management, cost accounting, financial accounting, and information system functions is the:A. treasurer.B. director.C. controller.D. chairman of the board.E. chief executive officer.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: CONTROLLERType: DEFINITIONS2. The person generally directly responsible for overseeing the cash and credit functions,financial planning, and capital expenditures is the:A. treasurer.B. director.C. controller.D. chairman of the board.E. chief operations officer.1-1Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance3. The process of planning and managing a firm's long-term investments is called:A. working capital management.B. financial depreciation.C. agency cost analysis.D. capital budgeting.E. capital structure.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: CAPITAL BUDGETINGType: DEFINITIONS4. The mixture of debt and equity used by a firm to finance its operations is called:A. working capital management.B. financial depreciation.C. cost analysis.D. capital budgeting.E. capital structure.5. The management of a firm's short-term assets and liabilities is called:A. working capital management.B. debt management.C. equity management.D. capital budgeting.E. capital structure.1-2Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance6. A business owned by a single individual is called a:A. corporation.B. sole proprietorship.C. general partnership.D. limited partnership.E. limited liability company.7. A business formed by two or more individuals who each have unlimited liability for businessdebts is called a:A. corporation.B. sole proprietorship.C. general partnership.D. limited partnership.E. limited liability company.8. The division of profits and losses among the members of a partnership is formalized in the:A. indemnity clause.B. indenture contract.C. statement of purpose.D. partnership agreement.E. group charter.9. A business created as a distinct legal entity composed of one or more individuals or entities iscalled a:A. corporation.B. sole proprietorship.C. general partnership.D. limited partnership.E. unlimited liability company.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: CORPORATIONType: DEFINITIONS1-3Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance10. The corporate document that sets forth the business purpose of a firm is the:A. indenture contract.B. state tax agreement.C. corporate bylaws.D. debt charter.E. articles of incorporation.11. The rules by which corporations govern themselves are called:A. indenture provisions.B. indemnity provisions.C. charter agreements.D. bylaws.E. articles of incorporation.12. A business entity operated and taxed like a partnership, but with limited liability for theowners, is called a:A. limited liability company.B. general partnership.C. limited proprietorship.D. sole proprietorship.E. corporation.13. The primary goal of financial management is to:A. maximize current dividends per share of the existing stock.B. maximize the current value per share of the existing stock.C. avoid financial distress.D. minimize operational costs and maximize firm efficiency.E. maintain steady growth in both sales and net earnings.14. A conflict of interest between the stockholders and management of a firm is called:A. stockholders' liability.B. corporate breakdown.C. the agency problem.D. corporate activism.E. legal liability.1-4Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance15. Agency costs refer to:A. the total dividends paid to stockholders over the lifetime of a firm.B. the costs that result from default and bankruptcy of a firm.C. corporate income subject to double taxation.D. the costs of any conflicts of interest between stockholders and management.E. the total interest paid to creditors over the lifetime of the firm.16. A stakeholder is:A. any person or entity that owns shares of stock of a corporation.B. any person or entity that has voting rights based on stock ownership of a corporation.C. a person who initially started a firm and currently has management control over the cashflows of the firm due to his/her current ownership of company stock.D. a creditor to whom the firm currently owes money and who consequently has a claim on thecash flows of the firm.E. any person or entity other than a stockholder or creditor who potentially has a claim on thecash flows of the firm.17. The Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002 is intended to:A. protect financial managers from investors.B. not have any effect on foreign companies.C. reduce corporate revenues.D. protect investors from corporate abuses.E. decrease audit costs for U.S. firms.18. The treasurer and the controller of a corporation generally report to the:A. board of directors.B. chairman of the board.C. chief executive officer.D. president.E. chief financial officer.19. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning the organizational structure ofa corporation?A. The vice president of finance reports to the chairman of the board.B. The chief executive officer reports to the board of directors.C. The controller reports to the president.D. The treasurer reports to the chief executive officer.E. The chief operations officer reports to the vice president of production.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTUREType: CONCEPTS1-5Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance20. Which one of the following is a capital budgeting decision?A. determining how much debt should be borrowed from a particular lenderB. deciding whether or not to open a new storeC. deciding when to repay a long-term debtD. determining how much inventory to keep on handE. determining how much money should be kept in the checking account21. The Sarbanes Oxley Act was enacted in:A. 1952.B. 1967.C. 1998.D. 2002.E. 2006.22. Since the implementation of Sarbanes-Oxley, the cost of going public in the United Stateshas:A. increased.B. decreased.C. remained about the same.D. been erratic, but over time has decreased.E. It is impossible to tell since Sarbanes-Oxley compliance does not involve direct cost to thefirm.23. Working capital management includes decisions concerning which of the following?I. accounts payableII. long-term debtIII. accounts receivableIV. inventoryA. I and II onlyB. I and III onlyC. II and IV onlyD. I, II, and III onlyE. I, III, and IV onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENTType: CONCEPTS1-6Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance24. Working capital management:A. ensures that sufficient equipment is available to produce the amount of product desired on adaily basis.B. ensures that long-term debt is acquired at the lowest possible cost.C. ensures that dividends are paid to all stockholders on an annual basis.D. balances the amount of company debt to the amount of available equity.E. is concerned with the upper portion of the balance sheet.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENTType: CONCEPTS25. Which one of the following statements concerning a sole proprietorship is correct?A. A sole proprietorship is the least common form of business ownership.B. The profits of a sole proprietorship are taxed twice.C. The owners of a sole proprietorship share profits as established by the partnership agreement.D. The owner of a sole proprietorship may be forced to sell his/her personal assets to paycompany debts.E. A sole proprietorship is often structured as a limited liability company.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SOLE PROPRIETORSHIPType: CONCEPTS26. Which one of the following statements concerning a sole proprietorship is correct?A. The life of the firm is limited to the life span of the owner.B. The owner can generally raise large sums of capital quite easily.C. The ownership of the firm is easy to transfer to another individual.D. The company must pay separate taxes from those paid by the owner.E. The legal costs to form a sole proprietorship are quite substantial.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SOLE PROPRIETORSHIPType: CONCEPTS1-7Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance27. Which one of the following best describes the primary advantage of being a limited partnerrather than a general partner?A. entitlement to a larger portion of the partnership's incomeB. ability to manage the day-to-day affairs of the businessC. no potential financial lossD. greater management responsibilityE. liability for firm debts limited to the capital investedDifficulty level: EasyTopic: PARTNERSHIPType: CONCEPTS28. A general partner:A. has less legal liability than a limited partner.B. has more management responsibility than a limited partner.C. faces double taxation whereas a limited partner does not.D. cannot lose more than the amount of his/her equity investment.E. is the term applied only to corporations which invest in partnerships.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PARTNERSHIPType: CONCEPTS29. A partnership:A. is taxed the same as a corporation.B. agreement defines whether the business income will be taxed like a partnership or acorporation.C. terminates at the death of any general partner.D. has less of an ability to raise capital than a proprietorship.E. allows for easy transfer of interest from one general partner to another.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PARTNERSHIPType: CONCEPTS1-8Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance30. Which of the following are disadvantages of a partnership?I. limited life of the firmII. personal liability for firm debtIII. greater ability to raise capital than a sole proprietorshipIV. lack of ability to transfer partnership interestA. I and II onlyB. III and IV onlyC. II and III onlyD. I, II, and IV onlyE. I, III, and IV onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: PARTNERSHIPType: CONCEPTS31. Which of the following are advantages of the corporate form of business ownership?I. limited liability for firm debtII. double taxationIII. ability to raise capitalIV. unlimited firm lifeA. I and II onlyB. III and IV onlyC. I, II, and III onlyD. II, III, and IV onlyE. I, III, and IV onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: CORPORATIONType: CONCEPTS32. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning corporations?A. The largest firms are usually corporations.B. The majority of firms are corporations.C. The stockholders are usually the managers of a corporation.D. The ability of a corporation to raise capital is quite limited.E. The income of a corporation is taxed as personal income of the stockholders.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: CORPORATIONType: CONCEPTS1-9Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance33. Which one of the following statements is correct?A. Both partnerships and corporations incur double taxation.B. Both sole proprietorships and partnerships are taxed in a similar fashion.C. Partnerships are the most complicated type of business to form.D. Both partnerships and corporations have limited liability for general partners and shareholders.E. All types of business formations have limited lives.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: BUSINESS TYPESType: CONCEPTS34. The articles of incorporation:A. can be used to remove company management.B. are amended annually by the company stockholders.C. set forth the number of shares of stock that can be issued.D. set forth the rules by which the corporation regulates its existence.E. can set forth the conditions under which the firm can avoid double taxation.35. The bylaws:A. establish the name of the corporation.B. are rules which apply only to limited liability companies.C. set forth the purpose of the firm.D. mandate the procedure for electing corporate directors.E. set forth the procedure by which the stockholders elect the senior managers of the firm.36. The owners of a limited liability company prefer:A. being taxed like a corporation.B. having liability exposure similar to that of a sole proprietor.C. being taxed personally on all business income.D. having liability exposure similar to that of a general partner.E. being taxed like a corporation with liability like a partnership.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANYType: CONCEPTS1-10Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance37. Which one of the following business types is best suited to raising large amounts ofcapital?A. sole proprietorshipB. limited liability companyC. corporationD. general partnershipE. limited partnershipDifficulty level: EasyTopic: CORPORATIONType: CONCEPTS38. Which type of business organization has all the respective rights and privileges ofa legalperson?A. sole proprietorshipB. general partnershipC. limited partnershipD. corporationE. limited liability companyDifficulty level: EasyTopic: CORPORATIONType: CONCEPTS39. Financial managers should strive to maximize the current value per share of the existingstock because:A. doing so guarantees the company will grow in size at the maximum possible rate.B. doing so increases the salaries of all the employees.C. the current stockholders are the owners of the corporation.D. doing so means the firm is growing in size faster than its competitors.E. the managers often receive shares of stock as part of their compensation.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: GOAL OF FINANC IAL MANAGEMENTType: CONCEPTS1-11Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance40. The decisions made by financial managers should all be ones which increase the:A. size of the firm.B. growth rate of the firm.C. marketability of the managers.D. market value of the existing owners' equity.E. financial distress of the firm.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: GOAL OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTType: CONCEPTS41. Which one of the following actions by a financial manager creates an agency problem?A. refusing to borrow money when doing so will create losses for the firmB. refusing to lower selling prices if doing so will reduce the net profitsC. agreeing to expand the company at the expense of stockholders' valueD. agreeing to pay bonuses based on the book value of the company stockE. increasing current costs in order to increase the market value of the stockholders' equity42. Which of the following help convince managers to work in the best interest of the stockholders?I. compensation based on the value of the stockII. stock option plansIII. threat of a proxy fightIV. threat of conversion to a partnershipA. I and II onlyB. II and III onlyC. I, II and III onlyD. I and III onlyE. I, II, III, and IVDifficulty level: MediumTopic: AGENCY PROBLEMType: CONCEPTS1-12Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance43. Which form of business structure faces the greatest agency problems?A. sole proprietorshipB. general partnershipC. limited partnershipD. corporationE. limited liability company44. A proxy fight occurs when:A. the board solicits renewal of current members.B. a group solicits proxies to replace the board of directors.C. a competitor offers to sell their ownership in the firm.D. the firm files for bankruptcy.E. the firm is declared insolvent.45. Which one of the following parties is considered a stakeholder of a firm?A. employeeB. short-term creditorC. long-term creditorD. preferred stockholderE. common stockholderDifficulty level: EasyTopic: STAKEHOLDERSType: CONCEPTS46. Which of the following are key requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act?I. Officers of the corporation must review and sign annual reports.II. Officers of the corporation must now own more than 5% of the firm's stock. III. Annual reports must list deficiencies in internal controlsIV. Annual reports must be filed with the SEC within 30 days of year end.A. I onlyB. II onlyC. I and III onlyD. II and III onlyE. II and IV onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: SARBANES-OXLEYType: CONCEPTS1-13Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance47. Insider trading is:A. legal.B. illegal.C. impossible to have in our efficient market.D. discouraged, but legal.E. list only the securities of the largest firms.48. Sole proprietorships are predominantly started because:A. they are easily and cheaply setup.B. the proprietorship life is limited to the business owner's life.C. all business taxes are paid as individual tax.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SOLE PROPRIETORSHIPSType: CONCEPTS49. Managers are encouraged to act in shareholders' interests by:A. shareholder election of a board of directors who select management.B. the threat of a takeover by another firm.C. compensation contracts that tie compensation to corporate success.D. Both A and B.E. All of the above.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: GOVERNANCEType: CONCEPTS50. The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 focuses on:A. all stock transactions.B. sales of existing securities.C. issuance of new securities.D. insider trading.E. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) insurance.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: REGULATIONType: CONCEPTS1-14Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance51. The basic regulatory framework in the United States was provided by:A. the Securities Act of 1933.B. the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.C. the monetary system.D. A and B.E. All of the above.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: REGULATIONType: CONCEPTS52. The Securities Act of 1933 focuses on:A. all stock transactions.B. sales of existing securities.C. issuance of new securities.D. insider trading.E. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) insurance.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: REGULATIONType: CONCEPTS53. In a limited partnership:A. each limited partner's liability is limited to his net worth.B. each limited partner's liability is limited to the amount he put into the partnership.C. each limited partner's liability is limited to his annual salary.D. there is no limitation on liability; only a limitation on what the partner can earn.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: LIMITED PARTNERSHIPType: CONCEPTS1-15Chapter 01 - Introduction to Corporate Finance54. Accounting profits and cash flows are:A. generally the same since they reflect current laws and accounting standards.B. generally the same since accounting profits reflect when the cash flows are received.C. generally not the same since GAAP allows for revenue recognition separate from the receiptof cash flows.D. generally not the same because cash inflows occur before revenue recognition.E. Both c and d.1-16。

公司理财习题答案第四章Chapter 4: Net Present Value4.1 a. $1,000 ⨯ 1.0510 = $1,628.89b. $1,000 ⨯ 1.0710 = $1,967.15c. $1,000 ⨯ 1.0520 = $2,653.30d. Interest compounds on the I nterest already earned. Therefore, the interest earnedin part c, $1,653.30, is more than double the amount earned in part a, $628.89.4.2 a. $1,000 / 1.17 = $513.16b. $2,000 / 1.1 = $1,818.18c. $500 / 1.18 = $233.254.3 You can make your decision by computing either the present value of the $2,000 that youcan receive in ten years, or the future value of the $1,000 that you can receive now.Present value: $2,000 / 1.0810 = $926.39Future value: $1,000 ⨯ 1.0810 = $2,158.93Either calculation indicates you should take the $1,000 now.4.4 Since this bond has no interim coupon payments, its present value is simply the presentvalue of the $1,000 that will be received in 25 years. Note: As will be discussed in the next chapter, the present value of the payments associated with a bond is the price of that bond.PV = $1,000 /1.125 = $92.304.5 PV = $1,500,000 / 1.0827 = $187,780.234.6 a. At a discount rate of zero, the future value and present value are always the same.Remember, FV = PV (1 + r) t. If r = 0, then the formula reduces to FV = PV.Therefore, the values of the options are $10,000 and $20,000, respectively. Youshould choose the second option.b. Option one: $10,000 / 1.1 = $9,090.91Option two: $20,000 / 1.15 = $12,418.43Choose the second option.c. Option one: $10,000 / 1.2 = $8,333.33Option two: $20,000 / 1.25 = $8,037.55Choose the first option.d. You are indifferent at the rate that equates the PVs of the two alternatives. Youknow that rate must fall between 10% and 20% because the option you wouldchoose differs at these rates. Let r be the discount rate that makes you indifferentbetween the options.$10,000 / (1 + r) = $20,000 / (1 + r)5(1 + r)4 = $20,000 / $10,000 = 21 + r = 1.18921r = 0.18921 = 18.921%4.7 PV of Joneses’ offer = $150,000 / (1.1)3 = $112,697.22Since the PV of Joneses’ offer is less than Smiths’ offer, $115,000, you should chooseSmiths’ offer.4.8 a. P0 = $1,000 / 1.0820 = $214.55b. P10 = P0 (1.08)10 = $463.20c. P15 = P0 (1.08)15 = $680.594.9 The $1,000 that you place in the account at the end of the first year will earn interest for sixyears. The $1,000 that you place in the account at the end of the second year will earninterest for five years, etc. Thus, the account will have a balance of$1,000 (1.12)6 + $1,000 (1.12)5 + $1,000 (1.12)4 + $1,000 (1.12)3= $6,714.614.10 PV = $5,000,000 / 1.1210 = $1,609,866.184.11 a. The cost of investment is $900,000.PV of cash inflows = $120,000 / 1.12 + $250,000 / 1.122 + $800,000 / 1.123= $875,865.52Since the PV of cash inflows is less than the cost of investment, you should notmake the investment.b. NPV = -$900,000 + $875,865.52= -$24,134.48c. NPV = -$900,000 + $120,000 / 1.11 + $250,000 / 1.112 + $800,000 / 1.113= $-4,033.18Since the NPV is still negative, you should not make the investment.4.12 NPV = -($340,000 + $10,000) + ($100,000 - $10,000) / 1.1+ $90,000 / 1.12 + $90,000 / 1.13 + $90,000 / 1.14 + $100,000 / 1.15= -$2,619.98Since the NPV is negative, you should not buy it.If the relevant cost of capital is 9 percent,NPV = -$350,000 + $90,000 / 1.09 + $90,000 / 1.092 + $90,000 / 1.093+ $90,000 / 1.094 + $100,000 / 1.095= $6,567.93Since the NPV is positive, you should buy it.4.13 a. Profit = PV of revenue - Cost = NPVNPV = $90,000 / 1.15 - $60,000 = -$4,117.08No, the firm will not make a profit.b. Find r that makes zero NPV.$90,000 / (1+r)5 - $60,000 = $0(1+r)5 = 1.5r = 0.08447 = 8.447%4.14 The future value of the decision to own your car for one year is the sum of the trade-invalue and the benefit from owning the car. Therefore, the PV of the decision to own thecar for one year is$3,000 / 1.12 + $1,000 / 1.12 = $3,571.43Since the PV of the roommate’s offer, $3,500, is lower than the aunt’s offer, you shouldaccept aunt’s offer.4.15 a. $1.000 (1.08)3 = $1,259.71b. $1,000 [1 + (0.08 / 2)]2 ⨯ 3 = $1,000 (1.04)6 = $1,265.32c. $1,000 [1 + (0.08 / 12)]12 ⨯ 3 = $1,000 (1.00667)36 = $1,270.24d. $1,000 e0.08 ⨯ 3 = $1,271.25公司理财习题答案第四章e. The future value increases because of the compounding. The account is earninginterest on interest. Essentially, the interest is added to the account balance at theend of every compounding period. During the next period, the account earnsinterest on the new balance. When the compounding period shortens, the balancethat earns interest is rising faster.4.16 a. $1,000 e0.12 ⨯ 5 = $1,822.12b. $1,000 e0.1 ⨯ 3 = $1,349.86c. $1,000 e0.05 ⨯ 10 = $1,648.72d. $1,000 e0.07 ⨯ 8 = $1,750.674.17 PV = $5,000 / [1+ (0.1 / 4)]4 ⨯ 12 = $1,528.364.18 Effective annual interest rate of Bank America= [1 + (0.041 / 4)]4 - 1 = 0.0416 = 4.16%Effective annual interest rate of Bank USA= [1 + (0.0405 / 12)]12 - 1 = 0.0413 = 4.13%You should deposit your money in Bank America.4.19 The price of the consol bond is the present value of the coupon payments. Apply theperpetuity formula to find the present value. PV = $120 / 0.15 = $8004.20 Quarterly interest rate = 12% / 4 = 3% = 0.03Therefore, the price of the security = $10 / 0.03 = $333.334.21 The price at the end of 19 quarters (or 4.75 years) from today = $1 / (0.15 ÷ 4) = $26.67The current price = $26.67 / [1+ (.15 / 4)]19 = $13.254.22 a. $1,000 / 0.1 = $10,000b. $500 / 0.1 = $5,000 is the value one year from now of the perpetual stream. Thus,the value of the perpetuity is $5,000 / 1.1 = $4,545.45.c. $2,420 / 0.1 = $24,200 is the value two years from now of the perpetual stream.Thus, the value of the perpetuity is $24,200 / 1.12 = $20,000.4.23 The value at t = 8 is $120 / 0.1 = $1,200.Thus, the value at t = 5 is $1,200 / 1.13 = $901.58.4.24 P = $3 (1.05) / (0.12 - 0.05) = $45.004.25 P = $1 / (0.1 - 0.04) = $16.674.26 The first cash flow will be generated 2 years from today.The value at the end of 1 year from today = $200,000 / (0.1 - 0.05) = $4,000,000.Thus, PV = $4,000,000 / 1.1 = $3,636,363.64.4.27 A zero NPV-$100,000 + $50,000 / r = 0-r = 0.54.28 Apply the NPV technique. Since the inflows are an annuity you can use the present valueof an annuity factor.NPV = -$6,200 + $1,200 8A1.0= -$6,200 + $1,200 (5.3349)= $201.88Yes, you should buy the asset.4.29 Use an annuity factor to compute the value two years from today of the twenty payments.Remember, the annuity formula gives you the value of the stream one year before the first payment. Hence, the annuity factor will give you the value at the end of year two of the stream of payments. Value at the end of year two = $2,000 20A08.0= $2,000 (9.8181)= $19,636.20The present value is simply that amount discounted back two years.PV = $19,636.20 / 1.082 = $16,834.884.30 The value of annuity at the end of year five= $500 15A = $500 (5.84737) = $2,923.6915.0The present value = $2,923.69 / 1.125 = $1,658.984.31 The easiest way to do this problem is to use the annuity factor. The annuity factor must beequal to $12,800 / $2,000 = 6.4; remember PV =C A t r. The annuity factors are in theappendix to the text. To use the factor table to solve this problem, scan across the rowlabeled 10 years until you find 6.4. It is close to the factor for 9%, 6.4177. Thus, the rate you will receive on this note is slightly more than 9%.You can find a more precise answer by interpolating between nine and ten percent.10% ⎤ 6.1446 ⎤a ⎡ r ⎥bc ⎡ 6.4 ⎪ d⎣ 9% ⎦⎣ 6.4177 ⎦By interpolating, you are presuming that the ratio of a to b is equal to the ratio of c to d.(9 - r ) / (9 - 10) = (6.4177 - 6.4 ) / (6.4177 - 6.1446)r = 9.0648%The exact value could be obtained by solving the annuity formula for the interest rate.Sophisticated calculators can compute the rate directly as 9.0626%.公司理财习题答案第四章4.32 a. The annuity amount can be computed by first calculating the PV of the $25,000which you need in five years. That amount is $17,824.65 [= $25,000 / 1.075].Next compute the annuity which has the same present value.$17,824.65 = C 5A.007$17,824.65 = C (4.1002)C = $4,347.26Thus, putting $4,347.26 into the 7% account each year will provide $25,000 fiveyears from today.b. The lump sum payment must be the present value of the $25,000, i.e., $25,000 /1.075 = $17,824.65The formula for future value of any annuity can be used to solve the problem (seefootnote 14 of the text).4.33The amount of loan is $120,000 ⨯ 0.85 = $102,000.20C A= $102,000.010The amount of equal installments isC = $102,000 / 20A = $102,000 / 8.513564 = $11,980.8810.04.34 The present value of salary is $5,000 36A = $150,537.53.001The present value of bonus is $10,000 3A = $23,740.42 (EAR = 12.68% is used since.01268bonuses are paid annually.)The present value of the contract = $150,537.53 + $23,740.42 = $174,277.944.35 The amount of loan is $15,000 ⨯ 0.8 = $12,000.C 48A = $12,0000067.0The amount of monthly installments isC = $12,000 / 48A = $12,000 / 40.96191 = $292.960067.04.36 Option one: This cash flow is an annuity due. To value it, you must use the after-taxamounts. The after-tax payment is $160,000 (1 - 0.28) = $115,200. Value all except the first payment using the standard annuity formula, then add back the first payment of$115,200 to obtain the value of this option.Value = $115,200 + $115,200 30A10.0= $115,200 + $115,200 (9.4269)= $1,201,178.88Option two: This option is valued similarly. You are able to have $446,000 now; this is already on an after-tax basis. You will receive an annuity of $101,055 for each of the next thirty years. Those payments are taxable when you receive them, so your after-taxpayment is $72,759.60 [= $101,055 (1 - 0.28)].Value = $446,000 + $72,759.60 30A.010= $446,000 + $72,759.60 (9.4269)= $1,131,897.47Since option one has a higher PV, you should choose it.4.37 The amount of loan is $9,000. The monthly payment C is given by solving the equation: C 60008.0A = $9,000 C = $9,000 / 47.5042 = $189.46In October 2000, Susan Chao has 35 (= 12 ⨯ 5 - 25) monthly payments left, including the one due in October 2000.Therefore, the balance of the loan on November 1, 2000 = $189.46 + $189.46 34008.0A = $189.46 + $189.46 (29.6651) = $5,809.81Thus, the total amount of payoff = 1.01 ($5,809.81) = $5,867.91 4.38 Let r be the rate of interest you must earn. $10,000(1 + r)12 = $80,000 (1 + r)12 = 8 r = 0.18921 = 18.921%4.39 First compute the present value of all the payments you must make for your children’s education. The value as of one year before matriculation of one child’s education is$21,000 415.0A= $21,000 (2.8550) = $59,955. This is the value of the elder child’s education fourteen years from now. It is the value of the younger child’s education sixteen years from today. The present value of these is PV = $59,955 / 1.1514 + $59,955 / 1.1516 = $14,880.44You want to make fifteen equal payments into an account that yields 15% so that the present value of the equal payments is $14,880.44. Payment = $14,880.44 / 1515.0A = $14,880.44 / 5.8474 = $2,544.804.40 The NPV of the policy isNPV = -$750 306.0A - $800306.0A / 1.063 + $250,000 / [(1.066) (1.0759)] = -$2,004.76 - $1,795.45 + $3,254.33= -$545.88 Therefore, you should not buy the policy.4.41 The NPV of the lease offer isNPV = $120,000 - $15,000 - $15,000 908.0A - $25,000 / 1.0810= $105,000 - $93,703.32 - $11,579.84 = -$283.16 Therefore, you should not accept the offer.4.42 This problem applies the growing annuity formula. The first payment is $50,000(1.04)2(0.02) = $1,081.60. PV = $1,081.60 [1 / (0.08 - 0.04) - {1 / (0.08 - 0.04)}{1.04 / 1.08}40]= $21,064.28 This is the present value of the payments, so the value forty years from today is $21,064.28 (1.0840) = $457,611.46公司理财习题答案第四章4.43 Use the discount factors to discount the individual cash flows. Then compute the NPV ofthe project. Notice that the four $1,000 cash flows form an annuity. You can still use the factor tables to compute their PV. Essentially, they form cash flows that are a six year annuity less a two year annuity. Thus, the appropriate annuity factor to use with them is 2.6198 (= 4.3553 - 1.7355).Year Cash Flow Factor PV 1 $700 0.9091 $636.37 2 900 0.8264 743.76 3 1,000 ⎤ 4 1,000 ⎥ 2.6198 2,619.80 5 1,000 ⎥ 6 1,000 ⎦ 7 1,250 0.5132 641.50 8 1,375 0.4665 641.44 Total $5,282.87NPV = -$5,000 + $5,282.87 = $282.87 Purchase the machine.4.44 Weekly inflation rate = 0.039 / 52 = 0.00075 Weekly interest rate = 0.104 / 52 = 0.002 PV = $5 [1 / (0.002 - 0.00075)] {1 – [(1 + 0.00075) / (1 + 0.002)]52 ⨯ 30} = $3,429.384.45 Engineer:NPV = -$12,000 405.0A + $20,000 / 1.055 + $25,000 / 1.056 - $15,000 / 1.057- $15,000 / 1.058 + $40,000 2505.0A / 1.058= $352,533.35 Accountant:NPV = -$13,000 405.0A + $31,000 3005.0A / 1.054= $345,958.81 Become an engineer.After your brother announces that the appropriate discount rate is 6%, you can recalculate the NPVs. Calculate them the same way as above except using the 6% discount rate. Engineer NPV = $292,419.47 Accountant NPV = $292,947.04Your brother made a poor decision. At a 6% rate, he should study accounting.4.46 Since Goose receives his first payment on July 1 and all payments in one year intervalsfrom July 1, the easiest approach to this problem is to discount the cash flows to July 1 then use the six month discount rate (0.044) to discount them the additional six months. PV = $875,000 / (1.044) + $650,000 / (1.044)(1.09) + $800,000 / (1.044)(1.092) + $1,000,000 / (1.044)(1.093) + $1,000,000/(1.044)(1.094) + $300,000 / (1.044)(1.095)+ $240,000 1709.0A / (1.044)(1.095) + $125,000 1009.0A / (1.044)(1.0922) = $5,051,150Remember that the use of annuity factors to discount the deferred payments yields the value of the annuity stream one period prior to the first payment. Thus, the annuity factor applied to the first set of deferred payments gives the value of those payments on July 1 of 1989. Discounting by 9% for five years brings the value to July 1, 1984. The use of the six month discount rate (4.4%) brings the value of the payments to January 1, 1984. Similarly, the annuity factor applied to the second set of deferred payments yields the value of those payments in 2006. Discounting for 22 years at 9% and for six months at 4.4% provides the value at January 1, 1984.The equivalent five-year, annual salary is the annuity that solves: $5,051,150 = C 509.0A C = $5,051,150/3.8897C = $1,298,596The student must be aware of possible rounding errors in this problem. The differencebetween 4.4% semiannual and 9.0% and for six months at 4.4% provides the value at January 1, 1984. 4.47 PV = $10,000 + ($35,000 + $3,500) [1 / (0.12 - 0.04)] [1 - (1.04 / 1.12) 25 ]= $415,783.604.48 NPV = -$40,000 + $10,000 [1 / (0.10 - 0.07)] [1 - (1.07 / 1.10)5 ] = $3,041.91 Revise the textbook.4.49The amount of the loan is $400,000 (0.8) = $320,000 The monthly payment is C = $320,000 / 3600067.0.0A = $ 2,348.10 Thirty years of payments $ 2,348.10 (360) = $ 845,316.00 Eight years of payments $2,348.10 (96) = $225,417.60 The difference is the balloon payment of $619,898.404.50 The lease payment is an annuity in advanceC + C 2301.0A = $4,000 C (1 + 20.4558) = $4,000 C = $186.424.51 The effective annual interest rate is[ 1 + (0.08 / 4) ] 4 – 1 = 0.0824The present value of the ten-year annuity is PV = 900 100824.0A = $5,974.24 Four remaining discount periodsPV = $5,974.24 / (1.0824) 4 = $4,352.43公司理财习题答案第四章4.52The present value of Ernie’s retirement incomePV = $300,000 20A / (1.07) 30 = $417,511.5407.0The present value of the cabinPV = $350,000 / (1.07) 10 = $177,922.25The present value of his savingsPV = $40,000 10A = $280,943.26.007In present value terms he must save an additional $313,490.53 In future value termsFV = $313,490.53 (1.07) 10 = $616,683.32He must saveC = $616.683.32 / 20A = $58,210.5407.0。

CHAPTER 8MAKING CAPITAL INVESTMENT DECISIONSAnswers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions1.In this context, an opportunity cost refers to the value of an asset or other input that will be used in aproject. The relevant cost is what the asset or input is actually worth today, not, for example, what it cost to acquire.2. a.Yes, the reduction in the sales of the company’s other products, referred to as erosion, andshould be treated as an incremental cash flow. These lost sales are included because they are a cost (a revenue reduction) that the firm must bear if it chooses to produce the new product.b. Yes, expenditures on plant and equipment should be treated as incremental cash flows. Theseare costs of the new product line. However, if these expenditures have already occurred, they are sunk costs and are not included as incremental cash flows.c. No, the research and development costs should not be treated as incremental cash flows. Thecosts of research and development undertaken on the product during the past 3 years are sunk costs and should not be included in the evaluation of the project. Decisions made and costs incurred in the past cannot be changed. They should not affect the decision to accept or reject the project.d. Yes, the annual depreciation expense should be treated as an incremental cash flow.Depreciation expense must be taken into account when calculating the cash flows related to a given project. While depreciation is not a cash expense that directly affects cash flow, it decreases a firm’s net income and hence, lowers its tax bill for the year. Because of this depreciation tax shield, the firm has more cash on hand at the end of the year than it would have had without expensing depreciation.e.No, dividend payments should not be treated as incremental cash flows. A firm’s decision topay or not pay dividends is independent of the decision to accept or reject any given investment project. For this reason, it is not an incremental cash flow to a given project. Dividend policy is discussed in more detail in later chapters.f.Yes, the resale value of plant and equipment at the end of a project’s life should be treated as anincremental cash flow. The price at which the firm sells the equipment is a cash inflow, and any difference between the book value of the equipment and its sale price will create gains or lossesthat result in either a tax credit or liability.g.Yes, salary and medical costs for production employees hired for a project should be treated asincremental cash flows. The salaries of all personnel connected to the project must be included as costs of that project.3.Item I is a relevant cost because the opportunity to sell the land is lost if the new golf club is produced. Item II is also relevant because the firm must take into account the erosion of sales of existing products when a new product is introduced. If the firm produces the new club, the earnings from the existing clubs will decrease, effectively creating a cost that must be included in the decision.Item III is not relevant because the costs of Research and Development are sunk costs. Decisions made in the past cannot be changed. They are not relevant to the production of the new clubs.4.For tax purposes, a firm would choose MACRS because it provides for larger depreciationdeductions earlier. These larger deductions reduce taxes, but have no other cash consequences.Notice that the choice between MACRS and straight-line is purely a time value issue; the total depreciation is the same; only the timing differs.5.It’s probably only a mild over-simplification. Current liabilities will all be paid, presumably. Thecash portion of current assets will be retrieved. Some receivables won’t be collected, and some inventory will not be sold, of course. Counterbalancing these losses is the fact that inventory sold above cost (and not replaced at the end of the project’s life) acts to increase working capital. These effects tend to offset one another.6.Management’s discretion to set the firm’s capital structure is applicable at the firm level. Since anyone particular project could be financed entirely with equity, another project could be financed with debt, and the firm’s overall capital structure remains unchanged, financing cost s are not relevant in the analysis of a project’s incremental cash flows according to the stand-alone principle.7.The EAC approach is appropriate when comparing mutually exclusive projects with different livesthat will be replaced when they wear out. This type of analysis is necessary so that the projects havea common life span over which they can be compared; in effect, each project is assumed to existover an infinite horizon of N-year repeating projects. Assuming that this type of analysis is valid implies that the project cash flows remain the same forever, thus ignoring the possible effects of, among other things: (1) inflation, (2) changing economic conditions, (3) the increasing unreliability of cash flow estimates that occur far into the future, and (4) the possible effects of future technology improvement that could alter the project cash flows.8.Depreciation is a non-cash expense, but it is tax-deductible on the income statement. Thusdepreciation causes taxes paid, an actual cash outflow, to be reduced by an amount equal to the depreciation tax shield, t c D. A reduction in taxes that would otherwise be paid is the same thing as a cash inflow, so the effects of the depreciation tax shield must be added in to get the total incremental aftertax cash flows.9.There are two particularly important considerations. The first is erosion. Will the “essentialized”book simply displace copies of the existing book that would have otherwise been sold? This is of special concern given the lower price. The second consideration is competition. Will other publishers step in and produce such a product? If so, then any erosion is much less relevant. A particular concern to book publishers (and producers of a variety of other product types) is that the publisher only makes money from the sale of new books. Thus, it is important to examine whether the new book would displace sales of used books (good from the publisher’s perspective) or new books (not good). The concern arises any time there is an active market for used product.10.Definitely. The damage to Porsche’s reputation is definitely a factor the company needed to consider.If the reputation was damaged, the company would have lost sales of its existing car lines.11.One company may be able to produce at lower incremental cost or market better. Also, of course,one of the two may have made a mistake!12.Porsche would recognize that the outsized profits would dwindle as more products come to marketand competition becomes more intense.Solutions to Questions and ProblemsNOTE: All end-of-chapter problems were solved using a spreadsheet. Many problems require multiple steps. Due to space and readability constraints, when these intermediate steps are included in this solutions manual, rounding may appear to have occurred. However, the final answer for each problem is found without rounding during any step in the problem.Basicing the tax shield approach to calculating OCF, we get:OCF = (Sales – Costs)(1 – t C) + t C DepreciationOCF = [($5 × 2,000 – ($2 × 2,000)](1 – 0.35) + 0.35($10,000/5)OCF = $4,600So, the NPV of the project is:NPV = –$10,000 + $4,600(PVIFA17%,5)NPV = $4,7172.We will use the bottom-up approach to calculate the operating cash flow for each year. We also mustbe sure to include the net working capital cash flows each year. So, the total cash flow each year will be:Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Sales Rs.7,000 Rs.7,000 Rs.7,000 Rs.7,000Costs 2,000 2,000 2,000 2,000Depreciation 2,500 2,500 2,500 2,500EBT Rs.2,500 Rs.2,500 Rs.2,500 Rs.2,500Tax 850 850 850 850Net income Rs.1,650 Rs.1,650 Rs.1,650 Rs.1,650OCF 0 Rs.4,150 Rs.4,150 Rs.4,150 Rs.4,150Capital spending –Rs.10,000 0 0 0 0NWC –200 –250 –300 –200 950Incremental cashflow –Rs.10,200 Rs.3,900 Rs.3,850 Rs.3,950 Rs.5,100The NPV for the project is:NPV = –Rs.10,200 + Rs.3,900 / 1.10 + Rs.3,850 / 1.102 + Rs.3,950 / 1.103 + Rs.5,100 / 1.104NPV = Rs.2,978.333. Using the tax shield approach to calculating OCF, we get:OCF = (Sales – Costs)(1 – t C) + t C DepreciationOCF = (R2,400,000 – 960,000)(1 – 0.30) + 0.30(R2,700,000/3)OCF = R1,278,000So, the NPV of the project is:NPV = –R2,700,000 + R1,278,000(PVIFA15%,3)NPV = R217,961.704.The cash outflow at the beginning of the project will increase because of the spending on NWC. Atthe end of the project, the company will recover the NWC, so it will be a cash inflow. The sale of the equipment will result in a cash inflow, but we also must account for the taxes which will be paid on this sale. So, the cash flows for each year of the project will be:Year Cash Flow0 – R3,000,000 = –R2.7M – 300K1 1,278,0002 1,278,0003 1,725,000 = R1,278,000 + 300,000 + 210,000 + (0 – 210,000)(.30)And the NPV of the project is:NPV = –R3,000,000 + R1,278,000(PVIFA15%,2) + (R1,725,000 / 1.153)NPV = R211,871.465. First we will calculate the annual depreciation for the equipment necessary for the project. Thedepreciation amount each year will be:Year 1 depreciation = R2.7M(0.3330) = R899,100Year 2 depreciation = R2.7M(0.4440) = R1,198,800Year 3 depreciation = R2.7M(0.1480) = R399,600So, the book value of the equipment at the end of three years, which will be the initial investment minus the accumulated depreciation, is:Book value in 3 years = R2.7M – (R899,100 + 1,198,800 + 399,600)Book value in 3 years = R202,500The asset is sold at a gain to book value, so this gain is taxable.Aftertax salvage value = R202,500 + (R202,500 – 210,000)(0.30)Aftertax salvage value = R207,750To calculate the OCF, we will use the tax shield approach, so the cash flow each year is:OCF = (Sales – Costs)(1 – t C) + t C DepreciationYear Cash Flow0 – R3,000,000 = –R2.7M – 300K1 1,277,730.00 = (R1,440,000)(.70) + 0.30(R899,100)2 1,367,640.00 = (R1,440,000)(.70) + 0.30(R1,198,800)3 1,635,630.00 = (R1,440,000)(.70) + 0.30(R399,600) + R207,750 + 300,000Remember to include the NWC cost in Year 0, and the recovery of the NWC at the end of the project.The NPV of the project with these assumptions is:NPV = – R3.0M + (R1,277,730/1.15) + (R1,367,640/1.152) + (R1,635,630/1.153)NPV = R220,655.206. First, we will calculate the annual depreciation of the new equipment. It will be:Annual depreciation charge = €925,000/5Annual depreciation charge = €185,000The aftertax salvage value of the equipment is:Aftertax salvage value = €90,000(1 – 0.35)Aftertax salvage value = €58,500Using the tax shield approach, the OCF is:OCF = €360,000(1 – 0.35) + 0.35(€185,000)OCF = €298,750Now we can find the project IRR. There is an unusual feature that is a part of this project. Accepting this project means that we will reduce NWC. This reduction in NWC is a cash inflow at Year 0. This reduction in NWC implies that when the project ends, we will have to increase NWC. So, at the end of the project, we will have a cash outflow to restore the NWC to its level before the project. We also must include the aftertax salvage value at the end of the project. The IRR of the project is:NPV = 0 = –€925,000 + 125,000 + €298,750(PVIFA IRR%,5) + [(€58,500 – 125,000) / (1+IRR)5]IRR = 23.85%7.First, we will calculate the annual depreciation of the new equipment. It will be:Annual depreciation = £390,000/5Annual depreciation = £78,000Now, we calculate the aftertax salvage value. The aftertax salvage value is the market price minus (or plus) the taxes on the sale of the equipment, so:Aftertax salvage value = MV + (BV – MV)t cVery often, the book value of the equipment is zero as it is in this case. If the book value is zero, the equation for the aftertax salvage value becomes:Aftertax salvage value = MV + (0 – MV)t cAftertax salvage value = MV(1 – t c)We will use this equation to find the aftertax salvage value since we know the book value is zero. So, the aftertax salvage value is:Aftertax salvage value = £60,000(1 – 0.34)Aftertax salvage value = £39,600Using the tax shield approach, we find the OCF for the project is:OCF = £120,000(1 – 0.34) + 0.34(£78,000)OCF = £105,720Now we can find the project NPV. Notice that we include the NWC in the initial cash outlay. The recovery of the NWC occurs in Year 5, along with the aftertax salvage value.NPV = –£390,000 – 28,000 + £105,720(PVIFA10%,5) + [(£39,600 + 28,000) / 1.15]NPV = £24,736.268.To find the BV at the end of four years, we need to find the accumulated depreciation for the firstfour years. We could calculate a table with the depreciation each year, but an easier way is to add the MACRS depreciation amounts for each of the first four years and multiply this percentage times the cost of the asset. We can then subtract this from the asset cost. Doing so, we get:BV4 = $9,300,000 – 9,300,000(0.2000 + 0.3200 + 0.1920 + 0.1150)BV4 = $1,608,900The asset is sold at a gain to book value, so this gain is taxable.Aftertax salvage value = $2,100,000 + ($1,608,900 – 2,100,000)(.40)Aftertax salvage value = $1,903,5609. We will begin by calculating the initial cash outlay, that is, the cash flow at Time 0. To undertake theproject, we will have to purchase the equipment and increase net working capital. So, the cash outlay today for the project will be:Equipment –€2,000,000NWC –100,000Total –€2,100,000Using the bottom-up approach to calculating the operating cash flow, we find the operating cash flow each year will be:Sales €1,200,000Costs 300,000Depreciation 500,000EBT €400,000Tax 140,000Net income €260,000The operating cash flow is:OCF = Net income + DepreciationOCF = €260,000 + 500,000OCF = €760,000To find the NPV of the project, we add the present value of the project cash flows. We must be sure to add back the net working capital at the end of the project life, since we are assuming the net working capital will be recovered. So, the project NPV is:NPV = –€2,100,000 + €760,000(PVIFA14%,4) + €100,000 / 1.144NPV = €173,629.3810.We will need the aftertax salvage value of the equipment to compute the EAC. Even though theequipment for each product has a different initial cost, both have the same salvage value. The aftertax salvage value for both is:Both cases: aftertax salvage value = $20,000(1 – 0.35) = $13,000To calculate the EAC, we first need the OCF and NPV of each option. The OCF and NPV for Techron I is:OCF = – $34,000(1 – 0.35) + 0.35($210,000/3) = $2,400NPV = –$210,000 + $2,400(PVIFA14%,3) + ($13,000/1.143) = –$195,653.45EAC = –$195,653.45 / (PVIFA14%,3) = –$84,274.10And the OCF and NPV for Techron II is:OCF = – $23,000(1 – 0.35) + 0.35($320,000/5) = $7,450NPV = –$320,000 + $7,450(PVIFA14%,5) + ($13,000/1.145) = –$287,671.75EAC = –$287,671.75 / (PVIFA14%,5) = –$83,794.05The two milling machines have unequal lives, so they can only be compared by expressing both on an equivalent annual basis, which is what the EAC method does. Thus, you prefer the Techron II because it has the lower (less negative) annual cost.。

公司理财第九版罗斯课后案例答案 Case Solutions CorporateFinance1. 案例一:公司资金需求分析问题:一家公司需要资金支持其新项目。
通过分析现金流量,推断该公司是否需要向外部借款或筹集其他资金。
解答:为了确定公司是否需要外部资金,我们需要分析公司的现金流量状况。
首先,我们需要计算公司的净现金流量(净收入加上非现金项目)。
然后,我们需要将净现金流量与项目的投资现金流量进行对比。
假设公司预计在项目开始时投资100万美元,并在项目运营期为5年。
预计该项目每年将产生50万美元的净现金流量。
现在,我们需要进行以下计算:净现金流量 = 年度现金流量 - 年度投资现金流量年度投资现金流量 = 100万美元年度现金流量 = 50万美元净现金流量 = 50万美元 - 100万美元 = -50万美元根据计算结果,公司的净现金流量为负数(即净现金流出),意味着公司每年都会亏损50万美元。
因此,公司需要从外部筹集资金以支持项目的运营。
2. 案例二:公司股权融资问题:一家公司正在考虑通过股权融资来筹集资金。
根据公司的财务数据和资本结构分析,我们需要确定公司最佳的股权融资方案。
解答:为了确定最佳的股权融资方案,我们需要参考公司的财务数据和资本结构分析。
首先,我们需要计算公司的资本结构比例,即股本占总资本的比例。
然后,我们将不同的股权融资方案与资本结构比例进行对比,选择最佳的方案。
假设公司当前的资本结构比例为60%的股本和40%的债务,在当前的资本结构下,公司的加权平均资本成本(WACC)为10%。
现在,我们需要进行以下计算:•方案一:以新股发行筹集1000万美元,并将其用于项目投资。
在这种方案下,公司的资本结构比例将发生变化。
假设公司的股本增加至80%,债务比例减少至20%。
根据资本结构比例的变化,WACC也将发生变化。
新的WACC可以通过以下公式计算得出:新的WACC = (股本比例 * 股本成本) + (债务比例 * 债务成本)假设公司的股本成本为12%,债务成本为8%:新的WACC = (0.8 * 12%) + (0.2 * 8%) = 9.6%•方案二:以新股发行筹集5000万美元,并将其用于项目投资。

Chapter 04 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Answer KeyMultiple Choice Questions1. An annuity stream of cash flow payments is a set of:A.level cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.B.level cash flows occurring each time period forever.C.increasing cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.D.increasing cash flows occurring each time period forever.E.arbitrary cash flows occurring each time period for no more than 10 years. Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITYType: DEFINITIONS2. Annuities where the payments occur at the end of each time period are called _____, whereas _____ refer to annuity streams with payments occurring at the beginning of each time period.A.ordinary annuities; early annuitieste annuities; straight annuitiesC.straight annuities; late annuitiesD.annuities due; ordinary annuitiesE.ordinary annuities; annuities dueDifficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITIES DUEType: DEFINITIONS3. An annuity stream where the payments occur forever is called a(n):A.annuity due.B.indemnity.C.perpetuity.D.amortized cash flow stream.E.amortization table.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PERPETUITYType: DEFINITIONS4. The interest rate expressed in terms of the interest payment made each period is called the _____ rate.A.stated annual interestpound annual interestC.effective annual interestD.periodic interestE.daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: STATED INTEREST RATESType: DEFINITIONS5. The interest rate expressed as if it were compounded once per year is called the _____ rate.A.stated interestpound interestC.effective annualD.periodic interestE.daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATEType: DEFINITIONS6. The interest rate charged per period multiplied by the number of periods per year is called the _____ rate.A.effective annualB.annual percentageC.periodic interestpound interestE.daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATEType: DEFINITIONS7. Paying off long-term debt by making installment payments is called:A.foreclosing on the debt.B.amortizing the debt.C.funding the debt.D.calling the debt.E.None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: AMORTIZATIONType: DEFINITIONS8. You are comparing two annuities which offer monthly payments for ten years. Both annuities are identical with the exception of the payment dates. Annuity A pays on the first of each month while annuity B pays on the last day of each month. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning these two annuities?A.Both annuities are of equal value today.B.Annuity B is an annuity due.C.Annuity A has a higher future value than annuity B.D.Annuity B has a higher present value than annuity A.E.Both annuities have the same future value as of ten years from today. Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: CONCEPTS9. You are comparing two investment options. The cost to invest in either option is the same today. Both options will provide you with $20,000 of income. Option A pays five annual payments starting with $8,000 the first year followed by four annual payments of $3,000 each. Option B pays five annual payments of $4,000 each. Which one of the following statements is correct given these two investment options?A.Both options are of equal value given that they both provide $20,000 of income.B.Option A is the better choice of the two given any positive rate of return.C.Option B has a higher present value than option A given a positive rate of return.D.Option B has a lower future value at year 5 than option A given a zero rate of return.E.Option A is preferable because it is an annuity due.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND PRESENT VALUEType: CONCEPTS10. You are considering two projects with the following cash flows:Which of the following statements are true concerning these two projects? I. Both projects have the same future value at the end of year 4, given a positive rate of return.II. Both projects have the same future value given a zero rate of return. III. Both projects have the same future value at any point in time, given a positive rate of return.IV. Project A has a higher future value than project B, given a positive rate of return.A.II onlyB.IV onlyC.I and III onlyD.II and IV onlyE.I, II, and III onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND FUTURE VALUEType: CONCEPTS11. A perpetuity differs from an annuity because:A.perpetuity payments vary with the rate of inflation.B.perpetuity payments vary with the market rate of interest.C.perpetuity payments are variable while annuity payments are constant.D.perpetuity payments never cease.E.annuity payments never cease.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PERPETUITY VERSUS ANNUITYType: CONCEPTS12. Which one of the following statements concerning the annual percentage rate is correct?A.The annual percentage rate considers interest on interest.B.The rate of interest you actually pay on a loan is called the annual percentage rate.C.The effective annual rate is lower than the annual percentage rate when an interest rate is compounded quarterly.D.When firms advertise the annual percentage rate they are violating U.S. truth-in-lending laws.E.The annual percentage rate equals the effective annual rate when the rate on an account is designated as simple interest.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATEType: CONCEPTS13. Which one of the following statements concerning interest rates is correct?A.The stated rate is the same as the effective annual rate.B.An effective annual rate is the rate that applies if interest were charged annually.C.The annual percentage rate increases as the number of compounding periods per year increases.D.Banks prefer more frequent compounding on their savings accounts.E.For any positive rate of interest, the effective annual rate will always exceed the annual percentage rate.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: INTEREST RATESType: CONCEPTS14. Which of the following statements concerning the effective annual rate are correct?I. When making financial decisions, you should compare effective annual rates rather than annual percentage rates.II. The more frequently interest is compounded, the higher the effective annual rate.III. A quoted rate of 6% compounded continuously has a higher effective annual rate than if the rate were compounded daily.IV. When borrowing and choosing which loan to accept, you should select the offer with the highest effective annual rate.A.I and II onlyB.I and IV onlyC.I, II, and III onlyD.II, III, and IV onlyE.I, II, III, and IVDifficulty level: MediumTopic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATEType: CONCEPTS15. The highest effective annual rate that can be derived from an annual percentage rate of 9% is computed as:A..09e - 1.B. e.09 ⨯ q.C. e ⨯ (1 + .09).D. e.09 - 1.E.(1 + .09)q.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: CONTINUOUS COMPOUNDINGType: CONCEPTS16. The time value of money concept can be defined as:A.the relationship between the supply and demand of money.B.the relationship between money spent versus money received.C.the relationship between a dollar to be received in the future and a dollar today.D.the relationship between interest rate stated and amount paid.E.None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: TIME VALUEType: CONCEPTS17. Discounting cash flows involves:A.discounting only those cash flows that occur at least 10 years in the future.B.estimating only the cash flows that occur in the first 4 years of a project.C.multiplying expected future cash flows by the cost of capital.D.discounting all expected future cash flows to reflect the time value of money.E.taking the cash discount offered on trade merchandise.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: CASH FLOWSType: CONCEPTS18. Compound interest:A.allows for the reinvestment of interest payments.B.does not allow for the reinvestment of interest payments.C.is the same as simple interest.D.provides a value that is less than simple interest.E.Both A and D.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: INTERESTType: CONCEPTS19. An annuity:A.is a debt instrument that pays no interest.B.is a stream of payments that varies with current market interest rates.C.is a level stream of equal payments through time.D.has no value.E.None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITYType: CONCEPTS20. The stated rate of interest is 10%. Which form of compounding will give the highest effective rate of interest?A.annual compoundingB.monthly compoundingC.daily compoundingD.continuous compoundingE.It is impossible to tell without knowing the term of the loan.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: COMPOUNDINGType: CONCEPTS21. The present value of future cash flows minus initial cost is called:A.the future value of the project.B.the net present value of the project.C.the equivalent sum of the investment.D.the initial investment risk equivalent value.E.None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRESENT VALUEType: CONCEPTS22. Find the present value of $5,325 to be received in one period if the rate is 6.5%.A.$5,000.00B.$5,023.58C.$5,644.50D.$5,671.13E.None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRESENT VALUE - SINGLE SUMType: PROBLEMS23. If you have a choice to earn simple interest on $10,000 for three years at 8% or annually compounded interest at 7.5% for three years which one will pay more and by how much?A.Simple interest by $50.00pound interest by $22.97pound interest by $150.75pound interest by $150.00E.None of the above.Simple Interest = $10,000 (.08)(3) = $2,400;Compound Interest = $10,000((1.075)3 - 1) = $2,422.97;Difference = $2,422.97 - $2,400 = $22.97Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SIMPLE & COMPOUND INTERESTType: PROBLEMS24. Bradley Snapp has deposited $7,000 in a guaranteed investment account witha promised rate of 6% compounded annually. He plans to leave it there for 4 full years when he will make a down payment on a car after graduation. How much of a down payment will he be able to make?A.$1,960.00B.$2,175.57C.$8,960.00D.$8,837.34E.$9,175.57$7,000 (1.06)4 = $8,837.34Difficulty level: EasyTopic: FUTURE VALUE - SINGLE SUMType: PROBLEMS25. Your parents are giving you $100 a month for four years while you are in college. At a 6% discount rate, what are these payments worth to you when you first start college?A.$3,797.40B.$4,167.09C.$4,198.79D.$4,258.03E.$4,279.32Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS26. You just won the lottery! As your prize you will receive $1,200 a month for 100 months. If you can earn 8% on your money, what is this prize worth to you today?A.$87,003.69B.$87,380.23C.$87,962.77D.$88,104.26E.$90,723.76Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS27. Todd is able to pay $160 a month for five years for a car. If the interest rate is 4.9%, how much can Todd afford to borrow to buy a car?A.$6,961.36B.$8,499.13C.$8,533.84D.$8,686.82E.$9,588.05Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS28. You are the beneficiary of a life insurance policy. The insurance company informs you that you have two options for receiving the insurance proceeds. You can receive a lump sum of $50,000 today or receive payments of $641 a month for ten years. You can earn 6.5% on your money. Which option should you take and why?A.You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,451.91 today.B.You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,523.74 today.C.You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,737.08 today.D.You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47,757.69 today.E.You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47,808.17 today.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS29. Your employer contributes $25 a week to your retirement plan. Assume that you work for your employer for another twenty years and that the applicable discount rate is 5%. Given these assumptions, what is this employee benefit worth to you today?A.$13,144.43B.$15,920.55C.$16,430.54D.$16,446.34E.$16,519.02Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS30. You have a sub-contracting job with a local manufacturing firm. Your agreement calls for annual payments of $50,000 for the next five years. At a discount rate of 12%, what is this job worth to you today?A.$180,238.81B.$201,867.47C.$210,618.19D.$223,162.58E.$224,267.10Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS31. The Ajax Co. just decided to save $1,500 a month for the next five years as a safety net for recessionary periods. The money will be set aside in a separate savings account which pays 3.25% interest compounded monthly. It deposits the first $1,500 today. If the company had wanted to deposit an equivalent lump sum today, how much would it have had to deposit?A.$82,964.59B.$83,189.29C.$83,428.87D.$83,687.23E.$84,998.01Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS32. You need some money today and the only friend you have that has any is your ‘miserly' friend. He agrees to loan you the money you need, if you make payments of $20 a month for the next six months. In keeping with his reputation, he requires that the first payment be paid today. He also charges you 1.5% interest per month. How much money are you borrowing?A.$113.94B.$115.65C.$119.34D.$119.63E.$119.96Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS33. You buy an annuity which will pay you $12,000 a year for ten years. The payments are paid on the first day of each year. What is the value of this annuity today at a 7% discount rate?A.$84,282.98B.$87,138.04C.$90,182.79D.$96,191.91E.$116,916.21Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS34. You are scheduled to receive annual payments of $10,000 for each of the next 25 years. Your discount rate is 8.5%. What is the difference in the present value if you receive these payments at the beginning of each year rather than at the end of each year?A.$8,699B.$9,217C.$9,706D.$10,000E.$10,850Difference = $111,040.97 - $102,341.91 = $8,699.06 = $8,699 (rounded) Note: The difference = .085 $102,341.91 = $8,699.06Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS35. You are comparing two annuities with equal present values. The applicable discount rate is 7.5%. One annuity pays $5,000 on the first day of each year for twenty years. How much does the second annuity pay each year for twenty years if it pays at the end of each year?A.$4,651B.$5,075C.$5,000D.$5,375E.$5,405Because each payment is received one year later, then the cash flow has to equal: $5,000 (1 + .075) = $5,375Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS36. Martha receives $100 on the first of each month. Stewart receives $100 on the last day of each month. Both Martha and Stewart will receive payments for five years. At an 8% discount rate, what is the difference in the present value of these two sets of payments?A.$32.88B.$40.00C.$99.01D.$108.00E.$112.50Difference = $4,964.72 - $4,931.84 = $32.88Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS37. What is the future value of $1,000 a year for five years at a 6% rate of interest?A.$4,212.36B.$5,075.69C.$5,637.09D.$6,001.38E.$6,801.91Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS38. What is the future value of $2,400 a year for three years at an 8% rate of interest?A.$6,185.03B.$6,847.26C.$7,134.16D.$7,791.36E.$8,414.67Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS39. Janet plans on saving $3,000 a year and expects to earn 8.5%. How much will Janet have at the end of twenty-five years if she earns what she expects?A.$219,317.82B.$230,702.57C.$236,003.38D.$244,868.92E.$256,063.66Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS40. Toni adds $3,000 to her savings on the first day of each year. Tim adds $3,000 to his savings on the last day of each year. They both earn a 9% rate of return. What is the difference in their savings account balances at the end of thirty years?A.$35,822.73B.$36,803.03C.$38,911.21D.$39,803.04E.$40,115.31Difference = $445,725.65 - $408,922.62 = $36,803.03Note: Difference = $408,922.62 .09 = $36,803.03Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE VERSUS ORDINARY ANNUITYType: PROBLEMS41. You borrow $5,600 to buy a car. The terms of the loan call for monthly payments for four years at a 5.9% rate of interest. What is the amount of each payment?A.$103.22B.$103.73C.$130.62D.$131.26E.$133.04Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTSType: PROBLEMS42. You borrow $149,000 to buy a house. The mortgage rate is 7.5% and the loan period is 30 years. Payments are made monthly. If you pay for the house according to the loan agreement, how much total interest will you pay?A.$138,086B.$218,161C.$226,059D.$287,086E.$375,059Total interest = ($1,041.83 ⨯ 30 ⨯ 12) - $149,000 = $226,058.80 = $226,059 (rounded)Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND COST OF INTERESTType: PROBLEMS43. The Great Giant Corp. has a management contract with its newly hired president. The contract requires a lump sum payment of $25 million be paid to the president upon the completion of her first ten years of service. The company wants to set aside an equal amount of funds each year to cover this anticipated cash outflow. The company can earn 6.5% on these funds. How much must the company set aside each year for this purpose?A.$1,775,042.93B.$1,798,346.17C.$1,801,033.67D.$1,852,617.25E.$1,938,018.22Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS44. You retire at age 60 and expect to live another 27 years. On the day you retire, you have $464,900 in your retirement savings account. You are conservative and expect to earn 4.5% on your money during your retirement. How much can you withdraw from your retirement savings each month if you plan to die on the day you spend your last penny?A.$2,001.96B.$2,092.05C.$2,398.17D.$2,472.00E.$2,481.27Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS45. The McDonald Group purchased a piece of property for $1.2 million. It paida down payment of 20% in cash and financed the balance. The loan terms require monthly payments for 15 years at an annual percentage rate of 7.75% compounded monthly. What is the amount of each mortgage payment?A.$7,440.01B.$8,978.26C.$9,036.25D.$9,399.18E.$9,413.67Amount financed = $1,200,000 (1 - .2) = $960,000Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS46. You estimate that you will have $24,500 in student loans by the time you graduate. The interest rate is 6.5%. If you want to have this debt paid in full within five years, how much must you pay each month?A.$471.30B.$473.65C.$476.79D.$479.37E.$480.40Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS47. You are buying a previously owned car today at a price of $6,890. You are paying $500 down in cash and financing the balance for 36 months at 7.9%. What is the amount of each loan payment?A.$198.64B.$199.94C.$202.02D.$214.78E.$215.09Amount financed = $6,890 - $500 = $6,390Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS48. The Good Life Insurance Co. wants to sell you an annuity which will pay you $500 per quarter for 25 years. You want to earn a minimum rate of return of 5.5%. What is the most you are willing to pay as a lump sum today to buy this annuity?A.$26,988.16B.$27,082.94C.$27,455.33D.$28,450.67E.$28,806.30Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS49. Your car dealer is willing to lease you a new car for $299 a month for 60 months. Payments are due on the first day of each month starting with the day you sign the lease contract. If your cost of money is 4.9%, what is the current value of the lease?A.$15,882.75B.$15,906.14C.$15,947.61D.$16,235.42E.$16,289.54Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS50. Your great-aunt left you an inheritance in the form of a trust. The trust agreement states that you are to receive $2,500 on the first day of each year, starting immediately and continuing for fifty years. What is the value of this inheritance today if the applicable discount rate is 6.35%?A.$36,811.30B.$37,557.52C.$39,204.04D.$39,942.42E.$40,006.09Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS51. Beatrice invests $1,000 in an account that pays 4% simple interest. How much more could she have earned over a five-year period if the interest had compounded annually?A.$15.45B.$15.97C.$16.65D.$17.09E.$21.67Ending value at 4% simple interest = $1,000 + ($1,000 ⨯ .04 ⨯ 5) = $1,200.00; Ending value at 4% compounded annually = $1,000 ⨯ (1 +.04)5 = $1,216.65; Difference = $1,216.65 - $1,200.00 = $16.65Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SIMPLE VERSUS COMPOUND INTERESTType: PROBLEMS52. Your firm wants to save $250,000 to buy some new equipment three years from now. The plan is to set aside an equal amount of money on the first day of each year starting today. The firm can earn a 4.7% rate of return. How much does the firm have to save each year to achieve its goal?A.$75,966.14B.$76,896.16C.$78,004.67D.$81.414.14E.$83,333.33Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS53. Today is January 1. Starting today, Sam is going to contribute $140 on the first of each month to his retirement account. His employer contributes an additional 50% of the amount contributed by Sam. If both Sam and his employer continue to do this and Sam can earn a monthly rate of ½of 1 percent, how much will he have in his retirement account 35 years from now?A.$199,45.944B.$200,456.74C.$249,981.21D.$299,189.16E.$300,685.11Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS54. You are considering an annuity which costs $100,000 today. The annuity pays $6,000 a year. The rate of return is 4.5%. What is the length of the annuity time period?A.24.96 yearsB.29.48 yearsC.31.49 yearsD.33.08 yearsE.38.00 yearsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS55. Today, you signed loan papers agreeing to borrow $4,954.85 at 9% compounded monthly. The loan payment is $143.84 a month. How many loan payments must you make before the loan is paid in full?A.29.89B.36.00C.38.88D.40.00E.41.03Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS56. Winston Enterprises would like to buy some additional land and build a new factory. The anticipated total cost is $136 million. The owner of the firm is quite conservative and will only do this when the company has sufficient funds to pay cash for the entire expansion project. Management has decided to save $450,000 a month for this purpose. The firm earns 6% compounded monthly on the funds it saves. How long does the company have to wait before expanding its operations?A.184.61 monthsB.199.97 monthsC.234.34 monthsD.284.61 monthsE.299.97 monthsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS57. Today, you are retiring. You have a total of $413,926 in your retirement savings and have the funds invested such that you expect to earn an average of 3%, compounded monthly, on this money throughout your retirement years. You want to withdraw $2,500 at the beginning of every month, starting today. How long will it be until you run out of money?A.185.00 monthsB.213.29 monthsC.227.08 monthsD.236.84 monthsE.249.69 monthsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS58. The Bad Guys Co. is notoriously known as a slow-payer. It currently needs to borrow $25,000 and only one company will even deal with Bad Guys. The terms of the loan call for daily payments of $30.76. The first payment is due today. The interest rate is 21% compounded daily. What is the time period of this loan?A. 2.88 yearsB. 2.94 yearsC. 3.00 yearsD. 3.13 yearsE. 3.25 yearsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE TIME PERIODSType: PROBLEMS59. The Robertson Firm is considering a project which costs $123,900 to undertake. The project will yield cash flows of $4,894.35 monthly for 30 months. What is the rate of return on this project?A.12.53%B.13.44%C.13.59%D.14.02%E.14.59%This can not be solved directly, so it's easiest to just use the calculator method to get an answer. You can then use the calculator answer as the rate in the formula just to verify that your answer is correct.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY INTEREST RATEType: PROBLEMS60. Your insurance agent is trying to sell you an annuity that costs $100,000 today. By buying this annuity, your agent promises that you will receive payments of $384.40 a month for the next 40 years. What is the rate of return on this investment?A. 3.45%B. 3.47%C. 3.50%D. 3.52%E. 3.55%This can not be solved directly, so it's easiest to just use the calculator method to get an answer. You can then use the calculator answer as the rate in the formula just to verify that you answer is correct.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY INTEREST RATEType: PROBLEMS61. You have been investing $120 a month for the last 15 years. Today, your investment account is worth $47,341.19. What is your average rate of return on your investments?A.9.34%B.9.37%C.9.40%D.9.42%E.9.46%This can not be solved directly, so it's easiest to just use the calculator method to get an answer. You can then use the calculator answer as the rate in the formula just to verify that you answer is correct.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY INTEREST RATEType: PROBLEMS。

Chapter 04 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Answer KeyMultiple Choice Questions1. An annuity stream of cash flow payments is a set of:A.level cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.B.level cash flows occurring each time period forever.C.increasing cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.D.increasing cash flows occurring each time period forever.E.arbitrary cash flows occurring each time period for no more than 10 years.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITYType: DEFINITIONS2. Annuities where the payments occur at the end of each time period are called _____, whereas _____ refer to annuity streams with payments occurring at the beginning of each time period.A.ordinary annuities; early annuitieste annuities; straight annuitiesC.straight annuities; late annuitiesD.annuities due; ordinary annuitiesE.ordinary annuities; annuities dueDifficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITIES DUEType: DEFINITIONS3. An annuity stream where the payments occur forever is called a(n):A.annuity due.B.indemnity.C.perpetuity.D.amortized cash flow stream.E.amortization table.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PERPETUITYType: DEFINITIONS4. The interest rate expressed in terms of the interest payment made each period is called the _____ rate.A.stated annual interestpound annual interestC.effective annual interestD.periodic interestE.daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: STATED INTEREST RATESType: DEFINITIONS5. The interest rate expressed as if it were compounded once per year is called the _____ rate.A.stated interestpound interestC.effective annualD.periodic interestE.daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATEType: DEFINITIONS6. The interest rate charged per period multiplied by the number of periods per year is called the _____ rate.A.effective annualB.annual percentageC.periodic interestpound interestE.daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATEType: DEFINITIONS7. Paying off long-term debt by making installment payments is called:A.foreclosing on the debt.B.amortizing the debt.C.funding the debt.D.calling the debt.E.None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: AMORTIZATIONType: DEFINITIONS8. You are comparing two annuities which offer monthly payments for ten years. Both annuities are identical with the exception of the payment dates. Annuity A pays on the first of each month while annuity B pays on the last day of each month. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning these two annuitiesA.Both annuities are of equal value today.B.Annuity B is an annuity due.C.Annuity A has a higher future value than annuity B.D.Annuity B has a higher present value than annuity A.E.Both annuities have the same future value as of ten years from today.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: CONCEPTS9. You are comparing two investment options. The cost to invest in either option is the same today. Both options will provide you with $20,000 of income. Option A pays five annual payments starting with $8,000 the first year followed by four annual payments of $3,000 each. Option B pays five annual payments of $4,000 each. Which one of the following statements is correct given these two investment optionsA.Both options are of equal value given that they both provide $20,000 of income.B.Option A is the better choice of the two given any positive rate of return.C.Option B has a higher present value than option A given a positive rate of return.D.Option B has a lower future value at year 5 than option A given a zero rate of return.E.Option A is preferable because it is an annuity due.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND PRESENT VALUEType: CONCEPTS10. You are considering two projects with the following cash flows:Which of the following statements are true concerning these two projects?I. Both projects have the same future value at the end of year 4, given a positive rate of return.II. Both projects have the same future value given a zero rate of return.III. Both projects have the same future value at any point in time, given a positive rate of return.IV. Project A has a higher future value than project B, given a positive rate of return.A.II onlyB.IV onlyC.I and III onlyD.II and IV onlyE.I, II, and III onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND FUTURE VALUE Type: CONCEPTS11. A perpetuity differs from an annuity because:A.perpetuity payments vary with the rate of inflation.B.perpetuity payments vary with the market rate of interest.C.perpetuity payments are variable while annuity payments are constant.D.perpetuity payments never cease.E.annuity payments never cease.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PERPETUITY VERSUS ANNUITYType: CONCEPTS12. Which one of the following statements concerning the annual percentage rate is correctA.The annual percentage rate considers interest on interest.B.The rate of interest you actually pay on a loan is called the annual percentage rate.C.The effective annual rate is lower than the annual percentage rate when an interest rate is compounded quarterly.D.When firms advertise the annual percentage rate they are violating . truth-in-lending laws.E.The annual percentage rate equals the effective annual rate when the rate on an account is designated as simple interest.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATEType: CONCEPTS13. Which one of the following statements concerning interest rates is correctA.The stated rate is the same as the effective annual rate.B.An effective annual rate is the rate that applies if interest were charged annually.C.The annual percentage rate increases as the number of compounding periods per year increases.D.Banks prefer more frequent compounding on their savings accounts.E.For any positive rate of interest, the effective annual rate will always exceed the annual percentage rate.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: INTEREST RATESType: CONCEPTS14. Which of the following statements concerning the effective annual rate are correct?I. When making financial decisions, you should compare effective annual rates rather than annual percentage rates.II. The more frequently interest is compounded, the higher the effective annual rate.III. A quoted rate of 6% compounded continuously has a higher effective annual rate than if the rate were compounded daily.IV. When borrowing and choosing which loan to accept, you should select the offer with the highest effective annual rate.A.I and II onlyB.I and IV onlyC.I, II, and III onlyD.II, III, and IV onlyE.I, II, III, and IVDifficulty level: MediumTopic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATEType: CONCEPTS15. The highest effective annual rate that can be derived from an annual percentage rate of 9% is computed as:A..09e - 1.B. q.C. e (1 + .09).D. - 1.E.(1 + .09)q.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: CONTINUOUS COMPOUNDINGType: CONCEPTS16. The time value of money concept can be defined as:A.the relationship between the supply and demand of money.B.the relationship between money spent versus money received.C.the relationship between a dollar to be received in the future and a dollar today.D.the relationship between interest rate stated and amount paid.E.None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: TIME VALUEType: CONCEPTS17. Discounting cash flows involves:A.discounting only those cash flows that occur at least 10 years in the future.B.estimating only the cash flows that occur in the first 4 years of a project.C.multiplying expected future cash flows by the cost of capital.D.discounting all expected future cash flows to reflect the time value of money.E.taking the cash discount offered on trade merchandise.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: CASH FLOWSType: CONCEPTS18. Compound interest:A.allows for the reinvestment of interest payments.B.does not allow for the reinvestment of interest payments.C.is the same as simple interest.D.provides a value that is less than simple interest.E.Both A and D.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: INTERESTType: CONCEPTS19. An annuity:A.is a debt instrument that pays no interest.B.is a stream of payments that varies with current market interest rates.C.is a level stream of equal payments through time.D.has no value.E.None of the above.Difficulty level: Easy Topic: ANNUITYType: CONCEPTS20. The stated rate of interest is 10%. Which form of compounding will give the highest effective rate of interestA.annual compoundingB.monthly compoundingC.daily compoundingD.continuous compoundingE.It is impossible to tell without knowing the term of the loan.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: COMPOUNDINGType: CONCEPTS21. The present value of future cash flows minus initial cost is called:A.the future value of the project.B.the net present value of the project.C.the equivalent sum of the investment.D.the initial investment risk equivalent value.E.None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRESENT VALUEType: CONCEPTS22. Find the present value of $5,325 to be received in one period if the rate is %.A.$5,B.$5,C.$5,D.$5,E.None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRESENT VALUE - SINGLE SUMType: PROBLEMS23. If you have a choice to earn simple interest on $10,000 for three years at 8% or annually compounded interest at % for three years which one will pay more and by how muchA.Simple interest by $pound interest by $pound interest by $pound interest by $E.None of the above.Simple Interest = $10,000 (.08)(3) = $2,400;Compound Interest = $10,000(3 - 1) = $2,;Difference = $2, - $2,400 = $Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SIMPLE & COMPOUND INTERESTType: PROBLEMS24. Bradley Snapp has deposited $7,000 in a guaranteed investment account witha promised rate of 6% compounded annually. He plans to leave it there for 4 full years when he will make a down payment on a car after graduation. How much of a down payment will he be able to makeA.$1,B.$2,C.$8,D.$8,E.$9,$7,000 4 = $8,Difficulty level: EasyTopic: FUTURE VALUE - SINGLE SUMType: PROBLEMS25. Your parents are giving you $100 a month for four years while you are in college. At a 6% discount rate, what are these payments worth to you when you first start collegeA.$3,B.$4,C.$4,D.$4,E.$4,Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS26. You just won the lottery! As your prize you will receive $1,200 a month for 100 months. If you can earn 8% on your money, what is this prize worth to you todayA.$87,B.$87,C.$87,D.$88,E.$90,Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS27. Todd is able to pay $160 a month for five years for a car. If the interest rate is %, how much can Todd afford to borrow to buy a carA.$6,B.$8,C.$8,D.$8,E.$9,Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS28. You are the beneficiary of a life insurance policy. The insurance company informs you that you have two options for receiving the insurance proceeds. You can receive a lump sum of $50,000 today or receive payments of $641 a month for ten years. You can earn % on your money. Which option should you take and whyA.You should accept the payments because they are worth $56, today.B.You should accept the payments because they are worth $56, today.C.You should accept the payments because they are worth $56, today.D.You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47, today.E.You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47, today.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS29. Your employer contributes $25 a week to your retirement plan. Assume that you work for your employer for another twenty years and that the applicable discount rate is 5%. Given these assumptions, what is this employee benefit worth to you todayA.$13,B.$15,C.$16,D.$16,E.$16,Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS30. You have a sub-contracting job with a local manufacturing firm. Your agreement calls for annual payments of $50,000 for the next five years. At a discount rate of 12%, what is this job worth to you todayA.$180,B.$201,C.$210,D.$223,E.$224,Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS31. The Ajax Co. just decided to save $1,500 a month for the next five years as a safety net for recessionary periods. The money will be set aside in a separate savings account which pays % interest compounded monthly. It deposits the first $1,500 today. If the company had wanted to deposit an equivalent lump sum today, how much would it have had to depositA.$82,B.$83,C.$83,D.$83,E.$84,Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS32. You need some money today and the only friend you have that has any is your ‘miserly' friend. He agrees to loan you the money you need, if you make payments of $20 a month for the next six months. In keeping with his reputation, he requires that the first payment be paid today. He also charges you % interest per month. How much money are you borrowingA.$B.$C.$D.$E.$Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS33. You buy an annuity which will pay you $12,000 a year for ten years. The payments are paid on the first day of each year. What is the value of this annuity today at a 7% discount rateA.$84,B.$87,C.$90,D.$96,E.$116,Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS34. You are scheduled to receive annual payments of $10,000 for each of the next 25 years. Your discount rate is %. What is the difference in the present value if you receive these payments at the beginning of each year rather than at the end of each yearA.$8,699B.$9,217C.$9,706D.$10,000E.$10,850Difference = $111, - $102, = $8, = $8,699 (rounded) Note: The difference = .085 $102, = $8,Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS35. You are comparing two annuities with equal present values. The applicable discount rate is %. One annuity pays $5,000 on the first day of each year for twenty years. How much does the second annuity pay each year for twenty years if it pays at the end of each yearA.$4,651B.$5,075C.$5,000D.$5,375E.$5,405Because each payment is received one year later, then the cash flow has to equal: $5,000 (1 + .075) = $5,375Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUE Type: PROBLEMS36. Martha receives $100 on the first of each month. Stewart receives $100 on the last day of each month. Both Martha and Stewart will receive payments for five years. At an 8% discount rate, what is the difference in the present value of these two sets of paymentsA.$B.$C.$D.$E.$Difference = $4, - $4, = $Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUE Type: PROBLEMS37. What is the future value of $1,000 a year for five years at a 6% rate of interestA.$4,B.$5,C.$5,D.$6,E.$6,Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS38. What is the future value of $2,400 a year for three years at an 8% rate of interestA.$6,B.$6,C.$7,D.$7,E.$8,Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS39. Janet plans on saving $3,000 a year and expects to earn %. How much will Janet have at the end of twenty-five years if she earns what she expectsA.$219,B.$230,C.$236,D.$244,E.$256,Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS40. Toni adds $3,000 to her savings on the first day of each year. Tim adds $3,000 to his savings on the last day of each year. They both earn a 9% rate of return. What is the difference in their savings account balances at the end of thirty yearsA.$35,B.$36,C.$38,D.$39,E.$40,Difference = $445, - $408, = $36,Note: Difference = $408, .09 = $36,Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE VERSUS ORDINARY ANNUITY Type: PROBLEMS41. You borrow $5,600 to buy a car. The terms of the loan call for monthly payments for four years at a % rate of interest. What is the amount of each paymentA.$B.$C.$D.$E.$Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTSType: PROBLEMS42. You borrow $149,000 to buy a house. The mortgage rate is % and the loan period is 30 years. Payments are made monthly. If you pay for the house according to the loan agreement, how much total interest will you payA.$138,086B.$218,161C.$226,059D.$287,086E.$375,059Total interest = ($1, 30 12) - $149,000 = $226, = $226,059 (rounded)Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND COST OF INTERESTType: PROBLEMS43. The Great Giant Corp. has a management contract with its newly hired president. The contract requires a lump sum payment of $25 million be paid to the president upon the completion of her first ten years of service. The company wants to set aside an equal amount of funds each year to cover this anticipated cash outflow. The company can earn % on these funds. How much must the company set aside each year for this purposeA.$1,775,B.$1,798,C.$1,801,D.$1,852,E.$1,938,Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS44. You retire at age 60 and expect to live another 27 years. On the day you retire, you have $464,900 in your retirement savings account. You are conservative and expect to earn % on your money during your retirement. How much can you withdraw from your retirement savings each month if you plan to die on the day you spend your last pennyA.$2,B.$2,C.$2,D.$2,E.$2,Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS45. The McDonald Group purchased a piece of property for $ million. It paida down payment of 20% in cash and financed the balance. The loan terms require monthly payments for 15 years at an annual percentage rate of % compounded monthly. What is the amount of each mortgage paymentA.$7,B.$8,C.$9,D.$9,E.$9,Amount financed = $1,200,000 (1 - .2) = $960,000Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS。
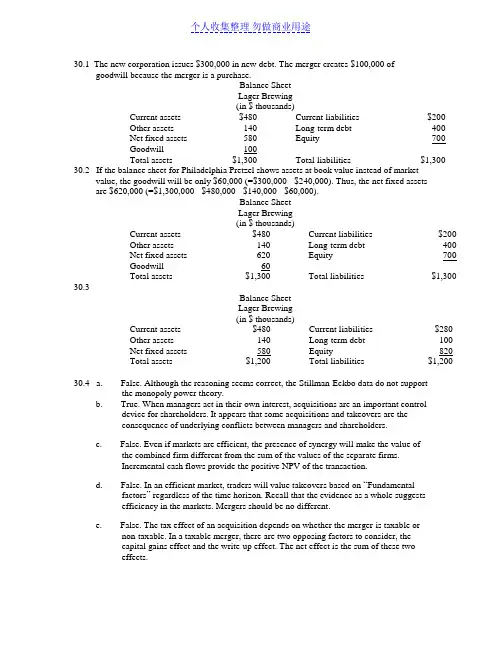
30.1 The new corporation issues $300,000 in new debt. The merger creates $100,000 ofgoodwill because the merger is a purchase.Balance SheetLager Brewing(in $ thousands)Current assets $480 Current liabilities $200Other assets 140 Long-term debt 400Net fixed assets 580 Equity 700Goodwill 100Total assets $1,300 Total liabilities $1,300 30.2 If the balance sheet for Philadelphia Pretzel shows assets at book value instead of marketvalue, the goodwill will be only $60,000 (=$300,000 - $240,000). Thus, the net fixed assetsare $620,000 (=$1,300,000 - $480,000 - $140,000 - $60,000).Balance SheetLager Brewing(in $ thousands)Current assets $480 Current liabilities $200Other assets 140 Long-term debt 400Net fixed assets 620 Equity 700Goodwill 60Total assets $1,300 Total liabilities $1,300 30.3Balance SheetLager Brewing(in $ thousands)Current assets $480 Current liabilities $280Other assets 140 Long-term debt 100Net fixed assets 580 Equity 820Total assets $1,200 Total liabilities $1,200 30.4 a. False. Although the reasoning seems correct, the Stillman-Eckbo data do not supportthe monopoly power theory.b. True. When managers act in their own interest, acquisitions are an important controldevice for shareholders. It appears that some acquisitions and takeovers are theconsequence of underlying conflicts between managers and shareholders.c. False. Even if markets are efficient, the presence of synergy will make the value ofthe combined firm different from the sum of the values of the separate firms.Incremental cash flows provide the positive NPV of the transaction.d. False. In an efficient market, traders will value takeovers based on “Fundamentalfactors” regardless of the time horizon. Recall that the evidence as a whole suggestsefficiency in the markets. Mergers should be no different.e. False. The tax effect of an acquisition depends on whether the merger is taxable ornon-taxable. In a taxable merger, there are two opposing factors to consider, thecapital gains effect and the write-up effect. The net effect is the sum of these twoeffects.f. True. Because of the coinsurance effect, wealth might be transferred from thestockholders to the bondholders. Acquisition analysis usually disregards this effectand considers only the total value.30.530.6 a. The weather conditions are independent. Thus, the joint probabilities are theproducts of the individual probabilities.Possible states Joint probabilityRain Rain 0.1 x 0.1=0.01Rain Warm 0.1 x 0.4=0.04Rain Hot 0.1 x 0.5=0.05Warm Rain 0.4 x 0.1=0.04Warm Warm 0.4 x 0.4=0.16Warm Hot 0.4 x 0.5=0.20Hot Rain 0.5 x 0.1=0.05Hot Warm 0.5 x 0.4=0.20Hot Hot 0.5 x 0.5=0.25Since the state Rain Warm has the same outcome (revenue) as Warm Rain, theirprobabilities can be added. The same is true of Rain Hot, Hot Rain and Warm Hot,Hot Warm. Thus the joint probabilities arePossibleJoint probabilitystatesRain Rain 0.01Rain Warm 0.08Rain Hot 0.10Warm Warm 0.16Warm Hot 0.40Hot Hot 0.25The joint values are the sums of the values of the two companies for the particularstate.Possible states Joint valueRain Rain $200,000Rain Warm 300,000Warm Warm 400,000Rain Hot 500,000Warm Hot 600,000Hot Hot 800,000b. Recall, if a firm cannot service its debt, the bondholders receive the value of the assets.Thus, the value of the debt is the value of the company if the face value of the debt isgreater than the value of the company. If the value of the company is greater than the value of the debt, the value of the debt is its face value. Here the value of the common stock is always the residual value of the firm over the value of the debt.Joint Prob. Joint Value Debt Value Stock Value0.01 $200,000 $200,000 $00.08 300,000 300,000 00.16 400,000 400,000 00.10 500,000 400,000 100,0000.40 600,000 400,000 200,0000.25 800,000 400,000 400,000c. To show that the value of the combined firm is the sum of the individual values, youmust show that the expected joint value is equal to the sum of the separate expected values.Expected joint value= 0.01($200,000) + 0.08($300,000) + 0.16($400,000) + 0.10($500,000) +0.40($600,000) + 0.25($800,000)= $580,000Since the firms are identical, the sum of the expected values is twice the expectedvalue of either.Expected individual value = 0.1($100,000) + 0.4($200,000) + 0.5($400,000) = $290,000 Expected combined value = 2($290,000) = $580,000d. The bondholders are better off if the value of the debt after the merger is greater thanthe value of the debt before the merger.Value of the debt before the merger:The value of debt for either company= 0.1($100,000) + 0.4($200,000) + 0.5($200,000) = $190,000Total value of debt before the merger = 2($190,000) = $380,000Value of debt after the merger= 0.01($200,000) + 0.08($300,000) + 0.16($400,000) + 0.10($400,000) +0.40($400,000) +0.25($400,000)= $390,000The bondholders are $10,000 better off after the merger.30.7 The decision hinges upon the risk of surviving. The final decision should hinge on thewealth transfer from bondholders to stockholders when risky projects are undertaken.High-risk projects will reduce the expected value of the bondholders’ claims on the firm.The telecommunications business is riskier than the utilities business. If the total value of the firm does not change, the increase in risk should favor the stockholder. Hence,management should approve this transaction. Note, if the total value of the firm dropsbecause of the transaction and the wealth effect is lower than the reduction in total value, management should reject the project.30.8 If the market is “smart,” the P/E ratio will not be constant.a. Value = $2,500 + $1,000 = $3,500b. EPS = Post-merger earnings / Total number of shares=($100 + $100)/200 =$1c. Price per share = Value/Total number of shares=$3,500/200 =$17.50d. If the market is “fooled,” the P/E ratio will be constant at $25.Value = P/E * Total number of shares= 25 * 200 = $5,000EPS = Post-merger earnings / Total number of shares=$5,000/200 = $25.0030.9 a. After the merger, Arcadia Financial will have 130,000 [=10,000 + (50,000)(6/10)]shares outstanding. The earnings of the combined firm will be $325,000. The earningsper share of the combined firm will be $2.50 (=$325,000/130,000). The acquisition will increase the EPS for the stockholders from $2.25 to $2.50.b. There will be no effect on the original Arcadia stockholders. No synergies exist in thismerger since Arcadia is buying Coldran at its market price. Examining the relativevalues of the two firms sees the latter point.Share price of Arcadia = (16 * $225,000) / 100,000=$36Share price of Coldran = (10.8 * $100,000) / 50,000=$21.60The relative value of these prices is $21.6/$36 = 0.6. Since Coldran’s shareholdersreceive 0.6 shares of Arcadia for every share of Coldran, no synergies exist.30.10 a. The synergy will be the discounted incremental cash flows. Since the cash flows areperpetual, this amount isb. The value of Flash-in-the-Pan to Fly-by-Night is the synergy plus the current marketvalue of Flash-in-the-Pan.V = $7,500,000 + $20,000,000= $27,500,000c. Cash alternative = $15,000,000Stock alternative = 0.25($27,500,000 + $35,000,000)= $15,625,000d. NPV of cash alternative = V - Cost=$27,500,000 - $15,000,000=$12,500,000NPV of stock alternative = V - Cost=$27,500,000 - $15,625,000=$11,875,000e. Use the cash alternative, its NPV is greater.30.11 a. The value of Portland Industries before the merger is $9,000,000 (=750,000x12). Thisvalue is also the discounted value of the expected future dividends.$9,000,000 =r = 0.1025 = 10.25%r is the risk-adjusted discount rate for Portland’s expected future dividends.the value of Portland Industries after the merger isThis is the value of Portland Industries to Freeport.b. NPV = Gain - Cost= $14,815,385 - ($40x250, 000)= $4,815,385c. If Freeport offers stock, the value of Portland Industries to Freeport is the same, but thecost differs.Cost = (Fraction of combined firm owned by Portland’s stockholders)x(Value of the combined firm)Value of the combined firm = (Value of Freeport before merger)+ (Value of Portland to Freeport)= $15x1,000,000 + $14,815,385= $29,815,385Cost = 0.375x$29,815,385= $11,180,769NPV= $14,815,385 - $11,180,769=$3,634,616d. The acquisition should be attempted with a cash offer since it provides a higher NPV.e. The value of Portland Industries after the merger isThis is the value of Portland Industries to Freeport.NPV = Gain-Cost=$11,223,529 - ($40x250,000)=$1,223,529If Freeport offers stock, the value of Portland Industries to Freeport is the same, but the cost differs.Cost = (Fraction of combined firm owned by Portland’s stockholders)x(Value of the combined firm)Value of the combined firm = (Value of Freeport before merger)+ (Value of Portland to Freeport)= $15x1,000,000 + $11,223,529= $26,223,529Cost = 0.375 * $26,223,529=$9,833,823NPV = $11,223,529 - $9,833,823=$1,389,706The acquisition should be attempted with a stock offer since it provides a higher NPV.30.12 a. Number of shares after acquisition=30 + 15 = 45 milStock price of Harrods after acquisition = 1,000/45=22.22 poundsb. Value of Selfridge stockholders after merger:α * 1,000 = 300α = 30%New shares issued = 12.86 mil12.86:20 = 0.643:1The proper exchange ratio should be 0.643 to make the stock offer’s value to Selfridgeequivalent to the cash offer.30.13 To evaluate this proposal, look at the present value of the incremental cash flows.Cash Flows to Company A(in $ million)Year 0 1 2 3 4 5Acquisition of B -550Dividends from B 150 32 5 20 30 45Tax-loss carryforwards 25 25Terminal value 600Total -400 32 30 45 30 645 The additional cash flows from the tax-loss carry forwards and the proposed level of debt should be discounted at the cost of debt because they are determined with very littleuncertainty.The after-tax cash flows are subject to normal business risk and must be discounted at anormal rate.Beta coefficient for the bond = 0.25 = [(8%-6%)/8%].Beta coefficient for the company = 1 = [(0.25)2 + (1.25)(0.75)]Discount rate for normal operations:r = 6% + 8% (1) = 14%Discount rate for dividends:The new beta coefficient for the company, 1, must be the weighted average of the debtbeta and the stock beta.1 = 0.5(0.25) + 0.5(βs)βs = 1.75r = 6% + 8%(1.75) = 20%Because the NPV of the acquisition is negative, Company A should not acquireCompany B.30.14 The commonly used defensive tactics by target-firm managers include:i. corporate charter amendments like super-majority amendment or staggering theelection of board members.ii. repurchase standstill agreements.iii. exclusionary self-tenders.iv. going private and leveraged buyouts.v. other devices like golden parachutes, scorched earth strategy, poison pill, ..., etc.Mini Case: U.S.Steel’s case.You have 3 choices: tender, or do not tender or sell in the market. If you do sell your shares in the market, at some point, somebody else would need to make a decision in “tender” or “not tender” as well.It is important to recognize that the firm has about 60 million shares outstanding (since 30 million shares will give US Steel 50.1% of Marathon shares). Let’s consider the possible sellingthe market price.If you choose not to tender, and 30 million shares were tendered US Steel succeeds to gain50.1% control, you will only receive $85 a share. If you do tender, the price you will receive will be no worse than $85 a share and can be as high as $125 a share. Depending on the number of shares tendered, you will receive one of the following prices.If only 50.1% tendered, you will get $125 per share.If the shares tendered exceed 50.1% but less than 100%, you will get more than $105 ashare.If all 60 million shares were tendered, you will get $105 per share. (which is )It is clear that, in the above 3 cases, when you are not sure about whether US Steel will succeed or not, you will be better off to tender your shares than not tender. This is because at best, you will only receive $85 per share if you choose not to tender.版权申明本文部分内容,包括文字、图片、以及设计等在网上搜集整理。

CHAPTER 7NET PRESENT VALUE AND OTHER INVESTMENT CRITERIAAnswers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions1. A payback period less than the project’s life means that the NPV is positive for a zero discount rate,but nothing more definitive can be said. For discount rates greater than zero, the payback period will still be less than the project’s life, but the NPV may be positive, zero, or negative, depending on whether the discount rate is less than, equal to, or greater than the IRR. The discounted payback includes the effect of the relevant discount rate. If a project’s discounted payback period is less than the project’s life, it must be the case that NPV is positive.2.If a project has a positive NPV for a certain discount rate, then it will also have a positive NPV for azero discount rate; thus, the payback period must be less than the project life. Since discounted payback is calculated at the same discount rate as is NPV, if NPV is positive, the discounted payback period must be less than the project’s life. If NPV is positive, then the present value of future cash inflows is greater than the initial investment cost; thus PI must be greater than 1. If NPV is positive for a certain discount rate R, then it will be zero for some larger discount rate R*; thus, the IRR must be greater than the required return.3. a.Payback period is simply the accounting break-even point of a series of cash flows. To actuallycompute the payback period, it is assumed that any cash flow occurring during a given period isrealized continuously throughout the period, and not at a single point in time. The payback isthen the point in time for the series of cash flows when the initial cash outlays are fullyrecovered. Given some predetermined cutoff for the payback period, the decision rule is toaccept projects that payback before this cutoff, and reject projects that take longer to payback.The worst problem associated with payback period is that it ignores the time value of money. Inaddition, the selection of a hurdle point for payback period is an arbitrary exercise that lacksany steadfast rule or method. The payback period is biased towards short-term projects; it fullyignores any cash flows that occur after the cutoff point.b.The average accounting return is interpreted as an average measure of the accountingperformance of a project over time, computed as some average profit measure attributable tothe project divided by some average balance sheet value for the project. This text computesAAR as average net income with respect to average (total) book value. Given somepredetermined cutoff for AAR, the decision rule is to accept projects with an AAR in excess ofthe target measure, and reject all other projects. AAR is not a measure of cash flows and marketvalue, but a measure of financial statement accounts that often bear little resemblance to therelevant value of a project. In addition, the selection of a cutoff is arbitrary, and the time valueof money is ignored. For a financial manager, both the reliance on accounting numbers ratherthan relevant market data and the exclusion of time value of money considerations are troubling.Despite these problems, AAR continues to be used in practice because (1) the accountinginformation is usually available, (2) analysts often use accounting ratios to analyze firmperformance, and (3) managerial compensation is often tied to the attainment of targetaccounting ratio goals.c.The IRR is the discount rate that causes the NPV of a series of cash flows to be identically zero.IRR can thus be interpreted as a financial break-even rate of return; at the IRR discount rate,the net value of the project is zero. The acceptance and rejection criteria are:If C0 < 0 and all future cash flows are positive, accept the project if the internal rate ofreturn is greater than or equal to the discount rate.If C0 < 0 and all future cash flows are positive, reject the project if the internal rate ofreturn is less than the discount rate.If C0 > 0 and all future cash flows are negative, accept the project if the internal rate ofreturn is less than or equal to the discount rate.If C0 > 0 and all future cash flows are negative, reject the project if the internal rate ofreturn is greater than the discount rate.IRR is the interest rate that causes NPV for a series of cash flows to be zero. NPV is preferred in all situations to IRR; IRR can lead to ambiguous results if there are non-conventional cash flows, and it also ambiguously ranks some mutually exclusive projects. However, for stand-alone projects with conventional cash flows, IRR and NPV are interchangeable techniques. The IRR decision rule for projectsd.The profitability index is the present value of cash inflows relative to the project cost. As such,it is a benefit/cost ratio, providing a measure of the relative profitability of a project. The profitability index decision rule is to accept projects with a PI greater than one, and to reject projects with a PI less than one. The profitability index can be expressed as: PI = (NPV + cost)/cost = 1 + (NPV/cost). If a firm has a basket of positive NPV projects and is subject to capital rationing, PI may provide a good ranking measure of the projects, indicating the “bang for the buck” of each particu lar project.e.NPV is simply the present value of a project’s cash flows. NPV specifically measures, afterconsidering the time value of money, the net increase or decrease in firm wealth due to the project. The decision rule is to accept projects that have a positive NPV, and reject projects with a negative NPV. NPV is superior to the other methods of analysis presented in the text because it has no serious flaws. The method unambiguously ranks mutually exclusive projects, and can differentiate between projects of different scale and time horizon. The only drawback to NPV is that it relies on cash flow and discount rate values that are often estimates and not certain, but this is a problem shared by the other performance criteria as well. A project with NPV = $2,500 implies that the total shareholder wealth of the firm will increase by $2,500 if the project is accepted.4.For a project with future cash flows that are an annuity:Payback = I / CAnd the IRR is:0 = – I + C / IRRSolving the IRR equation for IRR, we get:IRR = C / INotice this is just the reciprocal of the payback. So:IRR = 1 / PBFor long-lived projects with relatively constant cash flows, the sooner the project pays back, the greater is the IRR.5.There are a number of reasons. Two of the most important have to do with transportation costs andexchange rates. Manufacturing in the U.S. places the finished product much closer to the point of sale, resulting in significant savings in transportation costs. It also reduces inventories because goods spend less time in transit. Higher labor costs tend to offset these savings to some degree, at least compared to other possible manufacturing locations. Of great importance is the fact that manufacturing in the U.S. means that a much higher proportion of the costs are paid in dollars. Since sales are in dollars, the net effect is to immunize profits to a large extent against fluctuations in exchange rates. This issue is discussed in greater detail in the chapter on international finance.6.The single biggest difficulty, by far, is coming up with reliable cash flow estimates. Determining anappropriate discount rate is also not a simple task. These issues are discussed in greater depth in the next several chapters. The payback approach is probably the simplest, followed by the AAR, but even these require revenue and cost projections. The discounted cash flow measures (discounted payback, NPV, IRR, and profitability index) are really only slightly more difficult in practice.7.Yes, they are. Such entities generally need to allocate available capital efficiently, just as for-profitsdo. However, it is frequently the case that the “revenues” from not-for-profit ventures are not tangible. For example, charitable giving has real opportunity costs, but the benefits are generally hard to measure. To the extent that benefits are measurable, the question of an appropriate required return remains. Payback rules are commonly used in such cases. Finally, realistic cost/benefit analysis along the lines indicated should definitely be used by the U.S. government and would go a long way toward balancing the budget!8.The statement is false. If the cash flows of Project B occur early and the cash flows of Project Aoccur late, then for a low discount rate the NPV of A can exceed the NPV of B. Observe the following example.C0C1C2IRR NPV @ 0% Project A –$1,000,000 $0 $1,440,000 20% $440,000 Project B –$2,000,000 $2,400,000 $0 20% 400,000However, in one particular case, the statement is true for equally risky Projects. If the lives of the two Projects are equal and the cash flows of Project B are twice the cash flows of Project A in every time period, the NPV of Project B will be twice the NPV of Project A.9. Although the profitability index (PI) is higher for Project B than for Project A, Project A should bechosen because it has the greater NPV. Confusion arises because Project B requires a smaller investment than Project A requires. Since the denominator of the PI ratio is lower for Project B than for Project A, B can have a higher PI yet have a lower NPV. Only in the case of capital rationing could the company’s decision have been incorrect.10. a.Project A would have a higher IRR since initial investment for Project A is less than that ofProject B, if the cash flows for the two projects are identical.b.Yes, since both the cash flows as well as the initial investment are twice that of Project B.11.Project B would have a more sensitive NPV to changes in the discount rate. The reason is the timevalue of money. Cash flows that occur further out in the future are always more sensitive to changes in the interest rate. This is similar to the interest rate risk of a bond.12.The MIRR is calculated by finding the present value of all cash outflows, the future value of all cashinflows to the end of the project, and then calculating the IRR of the two cash flows. As a result, the cash flows have been discounted or compounded by one interest rate (the required return), and then the interest rate between the two remaining cash flows is calculated. As such, the MIRR is not a true interest rate. In contrast, consider the IRR. If you take the initial investment, and calculate the future value at the IRR, you can replicate the future cash flows of the project exactly.13.The criticism is incorrect. It is true that if you calculate the future value of all intermediate cashflows to the end of the project at the required return, then calculate the NPV of this future value and the initial investment, you will get the same NPV. However, NPV says nothing about reinvestment of intermediate cash flows. The NPV is the present value of the project cash flows. The fact that the reinvestment works is an artifact of the time value of money.14.The criticism is incorrect for several reasons. It is true that if you calculate the future value of allintermediate cash flows to the end of the project at the IRR, then calculate the IRR of this future value and the initial investment, you will get the same IRR. This only occurs if the intermediate cash flows are reinvested at the IRR. However, similar to the previous question, IRR deals with the present value of the cash flows, not the future value. There is also another important point. This criticism deals with the reinvestment of the intermediate cash flows. As we will see in the next chapter, any reinvestment assumption concerning the intermediate cash flows is incorrect. The reason is that when we are calculating the cash flows for a project, we are concerned with the incremental cash flows from the project, that is, the cash flows the project creates. Reinvestment violates this principal. Consider the following example:C0C1C2IRR Project A –$100 $10 $110 10% Suppose this is a deposit into a bank account. The IRR of the cash flows is 10 percent. Does it the IRR change if the Year 1 cash flow is reinvested in the account, or if it is withdrawn and spent on pizza? No. Finally, think back to the yield to maturity calculation on a bond. The YTM is the IRR of the bond investment, but no mention of a reinvestment assumption of the bond coupons is inferred.The reason is that the reinvestment assumption is irrelevant to calculating the YTM on a bond; in the same way, the reinvestment assumption is irrelevant in the IRR calculation.Solutions to Questions and ProblemsNOTE: All end-of-chapter problems were solved using a spreadsheet. Many problems require multiple steps. Due to space and readability constraints, when these intermediate steps are included in this solutions manual, rounding may appear to have occurred. However, the final answer for each problem is found without rounding during any step in the problem.Basic1. a.The payback period is the time that it takes for the cumulative undiscounted cash inflows toequal the initial investment.Project A:Cumulative cash flows Year 1 = €4,000 = €4,000Cumulative cash flows Year 2 = €4,000 +3,500 = €7,500 Payback period = 2 yearsProject B:Cumulative cash flows Year 1 = €2,500 = €2,500Cumulative cash flows Year 2 = €2,500 + 1,200 = €3,700Cumulative cash flows Year 3 = €2,500 + 1,200 + 3,000 = €6,700 Companies can calculate a more precise value using fractional years. To calculate the fractionalpayba ck period, find the fraction of year 3’s cash flows that is needed for the company to have cumulative undiscounted cash flows of €5,000. Divide the difference between the initial investment and the cumulative undiscounted cash flows as of year 2 by the undiscounted cashflow of year 3.Payback period = 2 + (€5,000 –€3,700) / €3,000Payback period = 2.43Since project A has a shorter payback period than project B has, the company should chooseproject A.b.Discount each project’s cash flows at 15 percent. Choose the project with the highest NPV.Project A:NPV = –€7,500 + €4,000 / 1.15 + €3,500 / 1.152 + €1,500 / 1.153NPV = –€388.96Project B:NPV = –€5,000 + €2,500 / 1.15 + €1,200 / 1.152 + €3,000 / 1.153NPV = €53.83The firm should choose Project B since it has a higher NPV than Project A has.2.To calculate the payback period, we need to find the time that the project has recovered its initialinvestment. The cash flows in this problem are an annuity, so the calculation is simpler. If the initial cost is £3,000, the payback period is:Payback = 3 + (£300 / £900) = 3.33 yearsThere is a shortcut to calculate the payback period if the future cash flows are an annuity. Just divide the initial cost by the annual cash flow. For the £3,000 cost, the payback period is:Payback = £3,000 / £900 = 3.33 yearsFor an initial cost of £5,000, the payback period is:Payback = 5 + (£500 / £900) = 5.55 yearsThe payback period for an initial cost of £10,000 is a little trickier. Notice that the total cash inflows after nine years will be:Total cash inflows = 8(£900) = £7,200If the initial cost is £10,000, the project never pays back. Notice that if you use the shortcut forannuity cash flows, you get:Payback = £10,000 / £900 = 11.11 years.This answer does not make sense since the cash flows stop after nine years, so the payback period is never.3.When we use discounted payback, we need to find the value of all cash flows today. The value todayof the project cash flows for the first four years is:Value today of Year 1 cash flow = $7,000/1.14 = $6,140.35Value today of Year 2 cash flow = $7,500/1.142 = $5,771.01Value today of Year 3 cash flow = $8,000/1.143 = $5,399.77Value today of Year 4 cash flow = $8,500/1.144 = $5,032.68To find the discounted payback, we use these values to find the payback period. The discounted first year cash flow is $6,140.35, so the discounted payback for an $8,000 initial cost is:Discounted payback = 1 + ($8,000 – 6,140.35)/$5,771.01 = 1.32 yearsFor an initial cost of $13,000, the discounted payback is:Discounted payback = 2 + ($13,000 – 6,140.35 – 5,771.01)/$5,399.77 = 2.20 yearsNotice the calculation of discounted payback. We know the payback period is between two and three years, so we subtract the discounted values of the Year 1 and Year 2 cash flows from the initial cost.This is the numerator, which is the discounted amount we still need to make to recover our initial investment. We divide this amount by the discounted amount we will earn in Year 3 to get the fractional portion of the discounted payback.If the initial cost is $18,000, the discounted payback is:Discounted payback = 3 + ($18,000 – 6,140.35 – 5,771.01 – 5,399.77) / $5,032.68 = 3.14 years4.To calculate the discounted payback, discount all future cash flows back to the present, and use thesediscounted cash flows to calculate the payback period. Doing so, we find:R = 0%: 4 + (£1,100 / £2,100) = 4.52 yearsDiscounted payback = Regular payback = 4.52 yearsR = 5%: £2,100/1.05 + £2,100/1.052 + £2,100/1.053 + £2,100/1.054 + £2,100/1.055 = £9,091.90 £2,100/1.056 = £1,567.05Discounted payback = 5 + (£9,500 – 9,091.90) / £1,567.05 = 5.26 years R = 15%: £2,100/1.15 + £2,100/1.152 + £2,100/1.153 + £2,100/1.154 + £2,100/1.155 + £2,100/1.156 = £7,947.41; The project never pays back.5. a.The average accounting return is the average project earnings after taxes, divided by theaverage book value, or average net investment, of the machine during its life. The book value of the machine is the gross investment minus the accumulated depreciation.Average book value = (Book Value0 + Book Value1 + Book Value2 + Book Value3 +Book Value4 + Book Value5) / (Economic Life)Average book value = ($16,000 + 12,000 + 8,000 + 4,000 + 0) / (5 years)Average book value = $8,000Average Project Earnings = $4,500To find the average accounting return, we divide the average project earnings by the average book value of the machine to calculate the average accounting return. Doing so, we find:Average Accounting Return = Average Project Earnings / Average Book ValueAverage Accounting Return = $4,500 / $8,000Average Accounting Return = 0.5625 or 56.25%6.First, we need to determine the average book value of the project. The book value is the grossinvestment minus accumulated depreciation.Purchase Date Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Gross Investment €8,000 €8,000 €8,000 €8,000Less: Accumulated Depreciation 0 4,000 6,500 8,000Net Investment €8,000 €4,000 €1,500 €0 Now, we can calculate the average book value as:Average book value = (€8,000 + 4,000 + 1,500 + 0) / (4 years)Average book value = €3,375To calculate the average accounting return, we must remember to use the aftertax average netincome when calculating the average accounting return. So, the average aftertax net income is:Average aftertax net income = (1 – t c) Annual pretax net incomeAverage aftertax net income = (1 – 0.25) €2,000Average aftertax net income = €1,500The average accounting return is the average after-tax net income divided by the average book value, which is:Average accounting return = €1,500 / €3,375Average accounting return = 0.4444 or 44.44%7.The IRR is the interest rate that makes the NPV of the project equal to zero. So, the equation that definesthe IRR for this project is:0 = C0 + C1 / (1 + IRR) + C2 / (1 + IRR)2 + C3 / (1 + IRR)30 = –¥8,000,000 + ¥4,000,000/(1 + IRR) + ¥3,000,000/(1 + IRR)2 + ¥2,000,000/(1 + IRR)3Using a spreadsheet, financial calculator, or trial and error to find the root of the equation, we find that: IRR = 6.93%Since the IRR is less than the required return we would reject the project.8.The IRR is the interest rate that makes the NPV of the project equal to zero. So, the equation that definesthe IRR for this Project A is:0 = C0 + C1 / (1 + IRR) + C2 / (1 + IRR)2 + C3 / (1 + IRR)30 = – £2,000 + £1,000/(1 + IRR) + £1,500/(1 + IRR)2 + £2,000/(1 + IRR)3Using a spreadsheet, financial calculator, or trial and error to find the root of the equation, we find that: IRR = 47.15%And the IRR for Project B is:0 = C0 + C1 / (1 + IRR) + C2 / (1 + IRR)2 + C3 / (1 + IRR)30 = – £1,500 + £500/(1 + IRR) + £1,000/(1 + IRR)2 + £1,500/(1 + IRR)3Using a spreadsheet, financial calculator, or trial and error to find the root of the equation, we find that: IRR = 36.19%9.The profitability index is defined as the PV of the cash inflows divided by the PV of the cashoutflows. The cash flows from this project are an annuity, so the equation for the profitability index is:PI = C(PVIFA R,t) / C0PI = €41,000(PVIFA15%,7) / €160,000PI = 1.066110. a.The profitability index is the present value of the future cash flows divided by the initial cost.So, for Project Alpha, the profitability index is:PI Alpha = [$300 / 1.10 + $700 / 1.102 + $600 / 1.103] / $500 = 2.604And for Project Beta the profitability index is:PI Beta = [$300 / 1.10 + $1,800 / 1.102 + $1,700 / 1.103] / $2,000 = 1.519b.According to the profitability index, you would accept Project Alpha. However, remember theprofitability index rule can lead to incorrect decision when ranking mutually exclusive projects.Intermediate11. a.To have a payback equal to the project’s life, given C is a constant cash flow for N years:C = I/Nb.To have a positive NPV, I < C (PVIFA R%, N). Thus, C > I / (PVIFA R%, N).c.Benefits = C (PVIFA R%, N) = 2 × costs = 2IC = 2I / (PVIFA R%, N)12. a.The IRR is the interest rate that makes the NPV of the project equal to zero. So, the equationthat defines the IRR for this project is:0 = C0 + C1 / (1 + IRR) + C2 / (1 + IRR)2 + C3 / (1 + IRR)3 + C4 / (1 + IRR)40 = ₩5,000 –₩2,500 / (1 + IRR) –₩2,000 / (1 + IRR)2–₩1,000 / (1 + IRR)3–₩1,000 / (1 +IRR)4Using a spreadsheet, financial calculator, or trial and error to find the root of the equation, we find that:IRR = 13.99%b.This problem differs from previous ones because the initial cash flow is positive and all futurecash flows are negative. In other words, this is a financing-type project, while previous projects were investing-type projects. For financing situations, accept the project when the IRR is less than the discount rate. Reject the project when the IRR is greater than the discount rate.IRR = 13.99%Discount Rate = 12%IRR > Discount RateReject the offer when the discount rate is less than the IRR.ing the same reason as part b., we would accept the project if the discount rate is 20 percent.IRR = 13.99%Discount Rate = 19%IRR < Discount RateAccept the offer when the discount rate is greater than the IRR.d.The NPV is the sum of the present value of all cash flows, so the NPV of the project if thediscount rate is 10 percent will be:NPV = ₩5,000 –₩2,500 / 1.12 –₩2,000 / 1.122–₩1,000 / 1.123–₩1,000 / 1.124NPV = –₩173.83When the discount rate is 12 percent, the NPV of the offer is –₩359.95. Reject the offer.And the NPV of the project is the discount rate is 19 percent will be:NPV = ₩5,000 –₩2,500 / 1.19 –₩2,000 / 1.192–₩1,000 / 1.193–₩1,000 / 1.194NPV = ₩394.75When the discount rate is 19 percent, the NPV of the offer is ₩466.82. Accept the offer.e.Yes, the decisions under the NPV rule are consistent with the choices made under the IRR rulesince the signs of the cash flows change only once.13. a.The IRR is the interest rate that makes the NPV of the project equal to zero. So, the IRR foreach project is:Deepwater Fishing IRR:0 = C0 + C1 / (1 + IRR) + C2 / (1 + IRR)2 + C3 / (1 + IRR)30 = –$600,000 + $270,000 / (1 + IRR) + $350,000 / (1 + IRR)2 + $300,000 / (1 + IRR)3Using a spreadsheet, financial calculator, or trial and error to find the root of the equation, we find that:IRR = 24.30%Submarine Ride IRR:0 = C0 + C1 / (1 + IRR) + C2 / (1 + IRR)2 + C3 / (1 + IRR)30 = –$1,800,000 + $1,000,000 / (1 + IRR) + $700,000 / (1 + IRR)2 + $900,000 / (1 + IRR)3Using a spreadsheet, financial calculator, or trial and error to find the root of the equation, we find that:IRR = 21.46%Based on the IRR rule, the deepwater fishing project should be chosen because it has the higher IRR.b.To calculate the incremental IRR, we s ubtract the smaller project’s cash flows from the largerproject’s cash flows. In this case, we subtract the deepwater fishing cash flows from the submarine ride cash flows. The incremental IRR is the IRR of these incremental cash flows. So, the incremental cash flows of the submarine ride are:Year 0Year 1Year 2 Year 3 Submarine Ride –$1,800,000 $1,000,000 $700,000 $900,000Deepwater Fishing –600,000 270,000 350,000 300,000Submarine – Fishing –$1,200,000 $730,000 $350,000 $600,000 Setting the present value of these incremental cash flows equal to zero, we find the incremental IRR is:0 = C0 + C1 / (1 + IRR) + C2 / (1 + IRR)2 + C3 / (1 + IRR)30 = –$1,200,000 + $730,000 / (1 + IRR) + $350,000 / (1 + IRR)2 + $600,000 / (1 + IRR)3Using a spreadsheet, financial calculator, or trial and error to find the root of the equation, we find that:Incremental IRR = 19.92%For investing-type projects, accept the larger project when the incremental IRR is greater than the discount rate. Since the incremental IRR, 19.92%, is greater than the required rate of return of 15 percent, choose the submarine ride project. Note that this is the choice when evaluating only the IRR of each project. The IRR decision rule is flawed because there is a scale problem.That is, the submarine ride has a greater initial investment than does the deepwater fishing project. This problem is corrected by calculating the IRR of the incremental cash flows, or by evaluating the NPV of each project.c.The NPV is the sum of the present value of the cash flows from the project, so the NPV of eachproject will be:Deepwater fishing:NPV = –$600,000 + $270,000 / 1.15 + $350,000 / 1.152 + $300,000 / 1.153NPV = $96,687.76Submarine ride:NPV = –$1,800,000 + $1,000,000 / 1.15 + $700,000 / 1.152 + $900,000 / 1.153NPV = $190,630.39Since the NPV of the submarine ride project is greater than the NPV of the deepwater fishingproject, choose the submarine ride project. The incremental IRR rule is always consistent withthe NPV rule.14. a.The profitability index is the PV of the future cash flows divided by the initial investment. Thecash flows for both projects are an annuity, so:PI I = 元15,000(PVIFA10%,3 ) / 元30,000 = 1.243PI II = 元2,800(PVIFA10%,3) / 元5,000 = 1.393The profitability index decision rule implies that we accept project II, since PI II is greater thanthe PI I.b.The NPV of each project is:NPV I = –元30,000 + 元15,000(PVIFA10%,3) = 元7,302.78NPV II = –元5,000 + 元2,800(PVIFA10%,3) = 元1,963.19The NPV decision rule implies accepting Project I, since the NPV I is greater than the NPV II.ing the profitability index to compare mutually exclusive projects can be ambiguous whenthe magnitudes of the cash flows for the two projects are of different scale. In this problem,project I is roughly 3 times as large as project II and produces a larger NPV, yet the profit-ability index criterion implies that project II is more acceptable.15. a.The equation for the NPV of the project is:NPV = –₦28,000,000 + ₦53,000,000/1.11 –₦8,000,000/1.112 = ₦13,254,768.28The NPV is greater than 0, so we would accept the project.b.The equation for the IRR of the project is:0 = –₦28,000,000 + ₦53,000,000/(1+IRR) –₦8,000,000/(1+IRR)2From Descartes rule of signs, we know there are two IRRs since the cash flows change signstwice. From trial and error, the two IRRs are:IRR = 72.75%, –83.46%。

Chapter 03 Financial Statements Analysis and Long-Term Planning Answer KeyMultiple Choice Questions1. One key reason a long-term financial plan is developed is because:A. the plan determines your financial policy.B. the plan determines your investment policy.C. there are direct connections between achievable corporate growth and the financial policy.D. there is unlimited growth possible in a well-developed financial plan.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: LONG-TERM PLANNINGType: DEFINITIONS2. Projected future financial statements are called:A. plug statements.B. pro forma statements.C. reconciled statements.D. aggregated statements.E. none of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRO FORMA STATEMENTSType: DEFINITIONS3. The percentage of sales method:A. requires that all accounts grow at the same rate.B. separates accounts that vary with sales and those that do not vary with sales.C. allows the analyst to calculate how much financing the firm will need to support the predicted sales level.D. Both A and B.E. Both B and C.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: PERCENTAGE OF SALESType: DEFINITIONS4. A _____ standardizes items on the income statement and balance sheet as a percentage of total sales and total assets, respectively.A. tax reconciliation statementB. statement of standardizationC. statement of cash flowsD. common-base year statementE. common-size statementDifficulty level: EasyTopic: COMMON-SIZE STATEMENTSType: DEFINITIONS5. Relationships determined from a firm's financial information and used for comparison purposes are known as:A. financial ratios.B. comparison statements.C. dimensional analysis.D. scenario analysis.E. solvency analysis.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: FINANCIAL RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS6. Financial ratios that measure a firm's ability to pay its bills over the short run without undue stress are known as _____ ratios.A. asset managementB. long-term solvencyC. short-term solvencyD. profitabilityE. market valueDifficulty level: EasyTopic: SHORT-TERM SOLVENCY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS7. The current ratio is measured as:A. current assets minus current liabilities.B. current assets divided by current liabilities.C. current liabilities minus inventory, divided by current assets.D. cash on hand divided by current liabilities.E. current liabilities divided by current assets.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: CURRENT RATIOType: DEFINITIONS8. The quick ratio is measured as:A. current assets divided by current liabilities.B. cash on hand plus current liabilities, divided by current assets.C. current liabilities divided by current assets, plus inventory.D. current assets minus inventory, divided by current liabilities.E. current assets minus inventory minus current liabilities.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: QUICK RATIOType: DEFINITIONS9. The cash ratio is measured as:A. current assets divided by current liabilities.B. current assets minus cash on hand, divided by current liabilities.C. current liabilities plus current assets, divided by cash on hand.D. cash on hand plus inventory, divided by current liabilities.E. cash on hand divided by current liabilities.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: CASH RATIOType: DEFINITIONS10. Ratios that measure a firm's financial leverage are known as _____ ratios.A. asset managementB. long-term solvencyC. short-term solvencyD. profitabilityE. market valueDifficulty level: EasyTopic: LONG-TERM SOLVENCY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS11. The financial ratio measured as total assets minus total equity, divided by total assets, is the:A. total debt ratio.B. equity multiplier.C. debt-equity ratio.D. current ratio.E. times interest earned ratio.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: TOTAL DEBT RATIOType: DEFINITIONS12. The debt-equity ratio is measured as total:A. equity minus total debt.B. equity divided by total debt.C. debt divided by total equity.D. debt plus total equity.E. debt minus total assets, divided by total equity.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: DEBT-EQUITY RATIOType: DEFINITIONS13. The equity multiplier ratio is measured as total:A. equity divided by total assets.B. equity plus total debt.C. assets minus total equity, divided by total assets.D. assets plus total equity, divided by total debt.E. assets divided by total equity.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: EQUITY MULTIPLIERType: DEFINITIONS14. The financial ratio measured as earnings before interest and taxes, divided by interest expense is the:A. cash coverage ratio.B. debt-equity ratio.C. times interest earned ratio.D. gross margin.E. total debt ratio.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: TIMES INTEREST EARNED RATIOType: DEFINITIONS15. The financial ratio measured as earnings before interest and taxes, plus depreciation, divided by interest expense, is the:A. cash coverage ratio.B. debt-equity ratio.C. times interest earned ratio.D. gross margin.E. total debt ratio.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: CASH COVERAGE RATIOType: DEFINITIONS16. Ratios that measure how efficiently a firm uses its assets to generate sales are known as _____ ratios.A. asset managementB. long-term solvencyC. short-term solvencyD. profitabilityE. market valueDifficulty level: EasyTopic: ASSET MANAGEMENT RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS17. The inventory turnover ratio is measured as:A. total sales minus inventory.B. inventory times total sales.C. cost of goods sold divided by inventory.D. inventory times cost of goods sold.E. inventory plus cost of goods sold.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: INVENTORY TURNOVERType: DEFINITIONS18. The financial ratio days' sales in inventory is measured as:A. inventory turnover plus 365 days.B. inventory times 365 days.C. inventory plus cost of goods sold, divided by 365 days.D. 365 days divided by the inventory.E. 365 days divided by the inventory turnover.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: DAYS' SALES IN INVENTORYType: DEFINITIONS19. The receivables turnover ratio is measured as:A. sales plus accounts receivable.B. sales divided by accounts receivable.C. sales minus accounts receivable, divided by sales.D. accounts receivable times sales.E. accounts receivable divided by sales.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: RECEIVABLES TURNOVERType: DEFINITIONS20. The financial ratio days' sales in receivables is measured as:A. receivables turnover plus 365 days.B. accounts receivable times 365 days.C. accounts receivable plus sales, divided by 365 days.D. 365 days divided by the receivables turnover.E. 365 days divided by the accounts receivable.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: DAYS' SALES IN RECEIVABLESType: DEFINITIONS21. The total asset turnover ratio is measured as:A. sales minus total assets.B. sales divided by total assets.C. sales times total assets.D. total assets divided by sales.E. total assets plus sales.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: TOTAL ASSET TURNOVERType: DEFINITIONS22. Ratios that measure how efficiently a firm's management uses its assets and equity to generate bottom line net income are known as _____ ratios.A. asset managementB. long-term solvencyC. short-term solvencyD. profitabilityE. market valueDifficulty level: EasyTopic: PROFITABILITY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS23. The financial ratio measured as net income divided by sales is known as the firm's:A. profit margin.B. return on assets.C. return on equity.D. asset turnover.E. earnings before interest and taxes.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PROFIT MARGINType: DEFINITIONS24. The financial ratio measured as net income divided by total assets is known as the firm's:A. profit margin.B. return on assets.C. return on equity.D. asset turnover.E. earnings before interest and taxes.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: RETURN ON ASSETSType: DEFINITIONS25. The financial ratio measured as net income divided by total equity is known as the firm's:A. profit margin.B. return on assets.C. return on equity.D. asset turnover.E. earnings before interest and taxes.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: RETURN ON EQUITYType: DEFINITIONS26. The financial ratio measured as the price per share of stock divided by earnings per share is known as the:A. return on assets.B. return on equity.C. debt-equity ratio.D. price-earnings ratio.E. Du Pont identity.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRICE-EARNINGS RATIOType: DEFINITIONS27. The market-to-book ratio is measured as:A. total equity divided by total assets.B. net income times market price per share of stock.C. net income divided by market price per share of stock.D. market price per share of stock divided by earnings per share.E. market value of equity per share divided by book value of equity per share. Difficulty level: MediumTopic: MARKET-TO-BOOK RATIOType: DEFINITIONS28. The _____ breaks down return on equity into three component parts.A. Du Pont identityB. return on assetsC. statement of cash flowsD. asset turnover ratioE. equity multiplierDifficulty level: MediumTopic: DU PONT IDENTITYType: DEFINITIONS29. The External Funds Needed (EFN) equation does not measure the:A. additional asset requirements given a change in sales.B. additional total liabilities raised given the change in sales.C. rate of return to shareholders given the change in sales.D. net income expected to be earned given the change in sales.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: EXTERNAL FUNDS NEEDEDType: DEFINITIONS30. To calculate sustainable growth rate without using return on equity, the analyst needs the:A. profit margin.B. payout ratio.C. debt-to-equity ratio.D. total asset turnover.E. All of the above.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: SUSTAINABLE GROWTH RATEType: DEFINITIONS31. Growth can be reconciled with the goal of maximizing firm value:A. because greater growth always adds to value.B. because growth must be an outcome of decisions that maximize NPV.C. because growth and wealth maximization are the same.D. because growth of any type cannot decrease value.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: GROWTHType: DEFINITIONS32. Sustainable growth can be determined by the:A. profit margin, total asset turnover and the price to earnings ratio.B. profit margin, the payout ratio, the debt-to-equity ratio, and the asset requirement or asset turnover ratio.C. Total growth less capital gains growth.D. Either A or B.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: SUSTAINABLE GROWTHType: DEFINITIONS33. Which of the following will increase sustainable growth?A. Buy back existing stockB. Decrease debtC. Increase profit marginD. Increase asset requirement or asset turnover ratioE. Increase dividend payout ratioDifficulty level: MediumTopic: SUSTAINABLE GROWTHType: DEFINITIONS34. The main objective of long-term financial planning models is to:A. determine the asset requirements given the investment activities of the firm.B. plan for contingencies or uncertain events.C. determine the external financing needs.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: LONG TERM PLANNINGType: DEFINITIONS35. On a common-size balance sheet, all _____ accounts are shown as a percentage of _____.A. income; total assetsB. liability; net incomeC. asset; salesD. liability; total assetsE. equity; salesDifficulty level: MediumTopic: COMMON-SIZE BALANCE SHEETType: DEFINITIONS36. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning ratio analysis?A. A single ratio is often computed differently by different individuals.B. Ratios do not address the problem of size differences among firms.C. Only a very limited number of ratios can be used for analytical purposes.D. Each ratio has a specific formula that is used consistently by all analysts.E. Ratios can not be used for comparison purposes over periods of time.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: RATIO ANALYSISType: DEFINITIONS37. Which of the following are liquidity ratios?I. cash coverage ratioII. current ratioIII. quick ratioIV. inventory turnoverA. II and III onlyB. I and II onlyC. II, III, and IV onlyD. I, III, and IV onlyE. I, II, III, and IVDifficulty level: MediumTopic: LIQUIDITY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS38. An increase in which one of the following accounts increases a firm's current ratio without affecting its quick ratio?A. accounts payableB. cashC. inventoryD. accounts receivableE. fixed assetsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: LIQUIDITY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS39. A supplier, who requires payment within ten days, is most concerned with which one of the following ratios when granting credit?A. currentB. cashC. debt-equityD. quickE. total debtDifficulty level: MediumTopic: LIQUIDITY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS40. A firm has a total debt ratio of .47. This means that that firm has 47 cents in debt for every:A. $1 in equity.B. $1 in total sales.C. $1 in current assets.D. $.53 in equity.E. $.53 in total assets.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: LONG-TERM SOLVENCY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS41. The long-term debt ratio is probably of most interest to a firm's:A. credit customers.B. employees.C. suppliers.D. mortgage holder.E. shareholders.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: LONG-TERM SOLVENCY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS42. A banker considering loaning a firm money for ten years would most likely prefer the firm have a debt ratio of _____ and a times interest earned ratio of _____.A. .75; .75B. .50; 1.00C. .45; 1.75D. .40; 2.50E. .35; 3.00Difficulty level: MediumTopic: LONG-TERM SOLVENCY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS43. From a cash flow position, which one of the following ratios best measures a firm's ability to pay the interest on its debts?A. times interest earned ratioB. cash coverage ratioC. cash ratioD. quick ratioE. Interval measureDifficulty level: MediumTopic: LONG-TERM SOLVENCY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS44. The higher the inventory turnover measure, the:A. faster a firm sells its inventory.B. faster a firm collects payment on its sales.C. longer it takes a firm to sell its inventory.D. greater the amount of inventory held by a firm.E. lesser the amount of inventory held by a firm.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ASSET MANAGEMENT RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS45. Which one of the following statements is correct if a firm has a receivables turnover measure of 10?A. It takes a firm 10 days to collect payment from its customers.B. It takes a firm 36.5 days to sell its inventory and collect the payment from the sale.C. It takes a firm 36.5 days to pay its creditors.D. The firm has an average collection period of 36.5 days.E. The firm has ten times more in accounts receivable than it does in cash.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ASSET MANAGEMENT RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS46. A total asset turnover measure of 1.03 means that a firm has $1.03 in:A. total assets for every $1 in cash.B. total assets for every $1 in total debt.C. total assets for every $1 in equity.D. sales for every $1 in total assets.E. long-term assets for every $1 in short-term assets.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ASSET MANAGEMENT RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS47. Puffy's Pastries generates five cents of net income for every $1 in sales. Thus, Puffy's has a _____ of 5%.A. return on assetsB. return on equityC. profit marginD. Du Pont measureE. total asset turnoverDifficulty level: MediumTopic: PROFITABILITY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS48. If a firm produces a 10% return on assets and also a 10% return on equity, then the firm:A. has no debt of any kind.B. is using its assets as efficiently as possible.C. has no net working capital.D. also has a current ratio of 10.E. has an equity multiplier of 2.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: PROFITABILITY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS49. If shareholders want to know how much profit a firm is making on their entire investment in the firm, the shareholders should look at the:A. profit margin.B. return on assets.C. return on equity.D. equity multiplier.E. earnings per share.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: PROFITABILITY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS50. BGL Enterprises increases its operating efficiency such that costs decrease while sales remain constant. As a result, given all else constant, the:A. return on equity will increase.B. return on assets will decrease.C. profit margin will decline.D. equity multiplier will decrease.E. price-earnings ratio will increase.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: PROFITABILITY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS51. The only difference between Joe's and Moe's is that Joe's has old, fully depreciated equipment. Moe's just purchased all new equipment which will be depreciated over eight years. Assuming all else equal:A. Joe's will have a lower profit margin.B. Joe's will have a lower return on equity.C. Moe's will have a higher net income.D. Moe's will have a lower profit margin.E. Moe's will have a higher return on assets.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: PROFITABILITY RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS52. Last year, Alfred's Automotive had a price-earnings ratio of 15. This year, the price earnings ratio is 18. Based on this information, it can be stated with certainty that:A. the price per share increased.B. the earnings per share decreased.C. investors are paying a higher price for each share of stock purchased.D. investors are receiving a higher rate of return this year.E. either the price per share, the earnings per share, or both changed.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: MARKET VALUE RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS53. Turner's Inc. has a price-earnings ratio of 16. Alfred's Co. has a price-earnings ratio of 19. Thus, you can state with certainty that one share of stock in Alfred's:A. has a higher market price than one share of stock in Turner's.B. has a higher market price per dollar of earnings than does one share of Turner's.C. sells at a lower price per share than one share of Turner's.D. represents a larger percentage of firm ownership than does one share of Turner's stock.E. earns a greater profit per share than does one share of Turner's stock.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: MARKET VALUE RATIOType: DEFINITIONS54. Which two of the following are most apt to cause a firm to have a higher price-earnings ratio?I. slow industry outlookII. high prospect of firm growthIII. very low current earningsIV. investors with a low opinion of the firmA. I and II onlyB. II and III onlyC. II and IV onlyD. I and III onlyE. III and IV onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: MARKET VALUE RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS55. Vinnie's Motors has a market-to-book ratio of 3. The book value per share is $4.00. Holding market-to-book constant, a $1 increase in the book value per share will:A. cause the accountants to increase the equity of the firm by an additional $2.B. increase the market price per share by $1.C. increase the market price per share by $12.D. tend to cause the market price per share to rise.E. only affect book values but not market values.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: MARKET VALUE RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS56. Which one of the following sets of ratios applies most directly to shareholders?A. return on assets and profit marginB. quick ratio and times interest earnedC. price-earnings ratio and debt-equity ratioD. market-to-book ratio and price-earnings ratioE. cash coverage ratio and times equity multiplierDifficulty level: MediumTopic: MARKET VALUE RATIOSType: DEFINITIONS57. The three parts of the Du Pont identity can be generally described as:I. operating efficiency, asset use efficiency and firm profitability.II. financial leverage, operating efficiency and asset use efficiency.III. the equity multiplier, the profit margin and the total asset turnover.IV. the debt-equity ratio, the capital intensity ratio and the profit margin.A. I and II onlyB. II and III onlyC. I and IV onlyD. I and III onlyE. III and IV onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: DU PONT IDENTITYType: DEFINITIONS58. If a firm decreases its operating costs, all else constant, then:A. the profit margin increases while the equity multiplier decreases.B. the return on assets increases while the return on equity decreases.C. the total asset turnover rate decreases while the profit margin increases.D. both the profit margin and the equity multiplier increase.E. both the return on assets and the return on equity increase.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: DU PONT IDENTITYType: DEFINITIONS59. Which one of the following statements is correct?A. Book values should always be given precedence over market values.B. Financial statements are frequently the basis used for performance evaluations.C. Historical information has no value when predicting the future.D. Potential lenders place little value on financial statement information.E. Reviewing financial information over time has very limited value.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: EVALUATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTSType: DEFINITIONS60. It is easier to evaluate a firm using its financial statements when the firm:A. is a conglomerate.B. is global in nature.C. uses the same accounting procedures as other firms in its industry.D. has a different fiscal year than other firms in its industry.E. tends to have one-time events such as asset sales and property acquisitions.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: EVALUATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTSType: DEFINITIONS61. Which two of the following represent the most effective methods of directly evaluating the financial performance of a firm?I. comparing the current financial ratios to those of the same firm from prior time periodsII. comparing a firm's financial ratios to those of other firms in the firm's peer group who have similar operationsIII. comparing the financial statements of the firm to the financial statements of similar firms operating in other countriesIV. comparing the financial ratios of the firm to the average ratios of all firms located in the same geographic areaA. I and II onlyB. II and III onlyC. III and IV onlyD. I and IV onlyE. I and III onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: EVALUATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTSType: DEFINITIONS62. In the financial planning model, external funds needed (EFN) is equal to changes inA. assets - (liabilities - equity).B. assets - (liabilities + equity).C. (assets + liabilities - equity).D. (assets + equity - liabilities).E. assets - equity.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: EXTERNAL FUNDS NEEDEDType: DEFINITIONS63. Which of the following represent problems encountered when comparing the financial statements of one firm with those of another firm?I. Either one, or both, of the firms may be conglomerates and thus have unrelated lines of business.II. The operations of the two firms may vary geographically.III. The firms may use differing accounting methods for inventory purposes.IV. The two firms may be seasonal in nature and have different fiscal year ends.A. I and II onlyB. II and III onlyC. I, III, and IV onlyD. I, II, and III onlyE. I, II, III, and IVDifficulty level: MediumTopic: EVALUATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTSType: DEFINITIONS64. A firm's sustainable growth rate in sales directly depends on its:A. debt to equity ratio.B. profit margin.C. dividend policy.D. asset efficiency.E. All of the above.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: SUSTAINABLE GROWTH RATEType: DEFINITIONS65. The sustainable growth rate will be equivalent to the internal growth rate when:A. a firm has no debt.B. the growth rate is positive.C. the plowback ratio is positive but less than 1.D. a firm has a debt-equity ratio exactly equal to 1.E. net income is greater than zero.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: SUSTAINABLE GROWTH RATEType: DEFINITIONS66. The sustainable growth rate:A. assumes there is no external financing of any kind.B. is normally higher than the internal growth rate.C. assumes the debt-equity ratio is variable.D. is based on receiving additional external debt and equity financing.E. assumes that 100% of all income is retained by the firm.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: SUSTAINABLE GROWTH RATEType: DEFINITIONS67. If a firm bases its growth projection on the rate of sustainable growth, and shows positive net income, then the:A. fixed assets will have to increase at the same rate, regardless of the current capacity level.B. number of common shares outstanding will increase at the same rate of growth.C. debt-equity ratio will have to increase.D. debt-equity ratio will remain constant while retained earnings increase.E. fixed assets, debt-equity ratio, and number of common shares outstanding will all increase. Difficulty level: MediumTopic: SUSTAINABLE GROWTH RATEType: DEFINITIONS68. Marcie's Mercantile wants to maintain its current dividend policy, which is a payout ratio of 40%. The firm does not want to increase its equity financing but is willing to maintain its current debt-equity ratio. Given these requirements, the maximum rate at which Marcie's can grow is equal to:A. 40% of the internal rate of growth.B. 60% of the internal rate of growth.C. the internal rate of growth.D. the sustainable rate of growth.E. 60% of the sustainable rate of growth.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: SUSTAINABLE GROWTH RATEType: DEFINITIONS69. One of the primary weaknesses of many financial planning models is that they:A. rely too much on financial relationships and too little on accounting relationships.B. are iterative in nature.C. ignore the goals and objectives of senior management.D. are based solely on best case assumptions.E. ignore the size, risk, and timing of cash flows.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: FINANCIAL PLANNING MODELSType: DEFINITIONS70. Financial planning, when properly executed:A. ignores the normal restraints encountered by a firm.B. ensures that the primary goals of senior management are fully achieved.C. reduces the necessity of daily management oversight of the business operations.D. helps ensure that proper financing is in place to support the desired level of growth.E. eliminates the need to plan more than one year in advance.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: FINANCIAL PLANNINGType: DEFINITIONS71. When examining the EBITDA ratio, lower numbers are:A. considered good.B. considered mediocre.C. considered poor.D. indifferent to higher numbers.E. it is impossible to garner information from this ratio.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: EBITDA RATIOType: DEFINITIONS。
Chapter 04 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Answer KeyMultiple Choice Questions1. An annuity stream of cash flow payments is a set of:A. level cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.B. level cash flows occurring each time period forever.C. increasing cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.D. increasing cash flows occurring each time period forever.E. arbitrary cash flows occurring each time period for no more than 10 years.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITYType: DEFINITIONS2. Annuities where the payments occur at the end of each time period are called _____, whereas _____ refer to annuity streams with payments occurring at the beginning of each time period.A. ordinary annuities; early annuitiesB. late annuities; straight annuitiesC. straight annuities; late annuitiesD. annuities due; ordinary annuitiesE. ordinary annuities; annuities dueDifficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITIES DUEType: DEFINITIONS3. An annuity stream where the payments occur forever is called a(n):A. annuity due.B. indemnity.C. perpetuity.D. amortized cash flow stream.E. amortization table.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PERPETUITYType: DEFINITIONS4. The interest rate expressed in terms of the interest payment made each period is called the _____ rate.A. stated annual interestB. compound annual interestC. effective annual interestD. periodic interestE. daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: STATED INTEREST RATESType: DEFINITIONS5. The interest rate expressed as if it were compounded once per year is called the _____ rate.A. stated interestB. compound interestC. effective annualD. periodic interestE. daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATEType: DEFINITIONS6. The interest rate charged per period multiplied by the number of periods per year is called the _____ rate.A. effective annualB. annual percentageC. periodic interestD. compound interestE. daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATEType: DEFINITIONS7. Paying off long-term debt by making installment payments is called:A. foreclosing on the debt.B. amortizing the debt.C. funding the debt.D. calling the debt.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: AMORTIZATIONType: DEFINITIONS8. You are comparing two annuities which offer monthly payments for ten years. Both annuities are identical with the exception of the payment dates. Annuity A pays on the first of each month while annuity B pays on the last day of each month. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning these two annuities?A. Both annuities are of equal value today.B. Annuity B is an annuity due.C. Annuity A has a higher future value than annuity B.D. Annuity B has a higher present value than annuity A.E. Both annuities have the same future value as of ten years from today.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: CONCEPTS9. You are comparing two investment options. The cost to invest in either option is the same today. Both options will provide you with $20,000 of income. Option A pays five annual payments starting with $8,000 the first year followed by four annual payments of $3,000 each. Option B pays five annual payments of $4,000 each. Which one of the following statements is correct given these two investment options?A. Both options are of equal value given that they both provide $20,000 of income.B. Option A is the better choice of the two given any positive rate of return.C. Option B has a higher present value than option A given a positive rate of return.D. Option B has a lower future value at year 5 than option A given a zero rate of return.E. Option A is preferable because it is an annuity due.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND PRESENT VALUEType: CONCEPTS10. You are considering two projects with the following cash flows:Which of the following statements are true concerning these two projects?I. Both projects have the same future value at the end of year 4, given a positive rate of return. II. Both projects have the same future value given a zero rate of return.III. Both projects have the same future value at any point in time, given a positive rate of return. IV. Project A has a higher future value than project B, given a positive rate of return.A. II onlyB. IV onlyC. I and III onlyD. II and IV onlyE. I, II, and III onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND FUTURE VALUEType: CONCEPTS11. A perpetuity differs from an annuity because:A. perpetuity payments vary with the rate of inflation.B. perpetuity payments vary with the market rate of interest.C. perpetuity payments are variable while annuity payments are constant.D. perpetuity payments never cease.E. annuity payments never cease.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PERPETUITY VERSUS ANNUITYType: CONCEPTS12. Which one of the following statements concerning the annual percentage rate is correct?A. The annual percentage rate considers interest on interest.B. The rate of interest you actually pay on a loan is called the annual percentage rate.C. The effective annual rate is lower than the annual percentage rate when an interest rate is compounded quarterly.D. When firms advertise the annual percentage rate they are violating U.S. truth-in-lending laws.E. The annual percentage rate equals the effective annual rate when the rate on an account is designated as simple interest.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATEType: CONCEPTS13. Which one of the following statements concerning interest rates is correct?A. The stated rate is the same as the effective annual rate.B. An effective annual rate is the rate that applies if interest were charged annually.C. The annual percentage rate increases as the number of compounding periods per year increases.D. Banks prefer more frequent compounding on their savings accounts.E. For any positive rate of interest, the effective annual rate will always exceed the annual percentage rate.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: INTEREST RATESType: CONCEPTS14. Which of the following statements concerning the effective annual rate are correct?I. When making financial decisions, you should compare effective annual rates rather than annual percentage rates.II. The more frequently interest is compounded, the higher the effective annual rate.III. A quoted rate of 6% compounded continuously has a higher effective annual rate than if the rate were compounded daily.IV. When borrowing and choosing which loan to accept, you should select the offer with the highest effective annual rate.A. I and II onlyB. I and IV onlyC. I, II, and III onlyD. II, III, and IV onlyE. I, II, III, and IVDifficulty level: MediumTopic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATEType: CONCEPTS15. The highest effective annual rate that can be derived from an annual percentage rate of 9% is computed as:A. .09e - 1.B. e.09 ⨯ q.C. e ⨯ (1 + .09).D. e.09 - 1.E. (1 + .09)q.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: CONTINUOUS COMPOUNDINGType: CONCEPTS16. The time value of money concept can be defined as:A. the relationship between the supply and demand of money.B. the relationship between money spent versus money received.C. the relationship between a dollar to be received in the future and a dollar today.D. the relationship between interest rate stated and amount paid.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: TIME VALUEType: CONCEPTS17. Discounting cash flows involves:A. discounting only those cash flows that occur at least 10 years in the future.B. estimating only the cash flows that occur in the first 4 years of a project.C. multiplying expected future cash flows by the cost of capital.D. discounting all expected future cash flows to reflect the time value of money.E. taking the cash discount offered on trade merchandise.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: CASH FLOWSType: CONCEPTS18. Compound interest:A. allows for the reinvestment of interest payments.B. does not allow for the reinvestment of interest payments.C. is the same as simple interest.D. provides a value that is less than simple interest.E. Both A and D.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: INTERESTType: CONCEPTS19. An annuity:A. is a debt instrument that pays no interest.B. is a stream of payments that varies with current market interest rates.C. is a level stream of equal payments through time.D. has no value.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITYType: CONCEPTS20. The stated rate of interest is 10%. Which form of compounding will give the highest effective rate of interest?A. annual compoundingB. monthly compoundingC. daily compoundingD. continuous compoundingE. It is impossible to tell without knowing the term of the loan.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: COMPOUNDINGType: CONCEPTS21. The present value of future cash flows minus initial cost is called:A. the future value of the project.B. the net present value of the project.C. the equivalent sum of the investment.D. the initial investment risk equivalent value.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRESENT VALUEType: CONCEPTS22. Find the present value of $5,325 to be received in one period if the rate is 6.5%.A. $5,000.00B. $5,023.58C. $5,644.50D. $5,671.13E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRESENT VALUE - SINGLE SUMType: PROBLEMS23. If you have a choice to earn simple interest on $10,000 for three years at 8% or annually compounded interest at 7.5% for three years which one will pay more and by how much?A. Simple interest by $50.00B. Compound interest by $22.97C. Compound interest by $150.75D. Compound interest by $150.00E. None of the above.Simple Interest = $10,000 (.08)(3) = $2,400;Compound Interest = $10,000((1.075)3 - 1) = $2,422.97;Difference = $2,422.97 - $2,400 = $22.97Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SIMPLE & COMPOUND INTERESTType: PROBLEMS24. Bradley Snapp has deposited $7,000 in a guaranteed investment account with a promised rate of 6% compounded annually. He plans to leave it there for 4 full years when he will make a down payment on a car after graduation. How much of a down payment will he be able to make?A. $1,960.00B. $2,175.57C. $8,960.00D. $8,837.34E. $9,175.57$7,000 (1.06)4 = $8,837.34Difficulty level: EasyTopic: FUTURE VALUE - SINGLE SUMType: PROBLEMS25. Your parents are giving you $100 a month for four years while you are in college. At a 6% discount rate, what are these payments worth to you when you first start college?A. $3,797.40B. $4,167.09C. $4,198.79D. $4,258.03E. $4,279.32Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS26. You just won the lottery! As your prize you will receive $1,200 a month for 100 months. If you can earn 8% on your money, what is this prize worth to you today?A. $87,003.69B. $87,380.23C. $87,962.77D. $88,104.26E. $90,723.76Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS27. Todd is able to pay $160 a month for five years for a car. If the interest rate is 4.9%, how much can Todd afford to borrow to buy a car?A. $6,961.36B. $8,499.13C. $8,533.84D. $8,686.82E. $9,588.05Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS28. You are the beneficiary of a life insurance policy. The insurance company informs you that you have two options for receiving the insurance proceeds. You can receive a lump sum of $50,000 today or receive payments of $641 a month for ten years. You can earn 6.5% on your money. Which option should you take and why?A. You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,451.91 today.B. You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,523.74 today.C. You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,737.08 today.D. You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47,757.69 today.E. You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47,808.17 today.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS29. Your employer contributes $25 a week to your retirement plan. Assume that you work for your employer for another twenty years and that the applicable discount rate is 5%. Given these assumptions, what is this employee benefit worth to you today?A. $13,144.43B. $15,920.55C. $16,430.54D. $16,446.34E. $16,519.02Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS30. You have a sub-contracting job with a local manufacturing firm. Your agreement calls for annual payments of $50,000 for the next five years. At a discount rate of 12%, what is this job worth to you today?A. $180,238.81B. $201,867.47C. $210,618.19D. $223,162.58E. $224,267.10Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS31. The Ajax Co. just decided to save $1,500 a month for the next five years as a safety net for recessionary periods. The money will be set aside in a separate savings account which pays 3.25% interest compounded monthly. It deposits the first $1,500 today. If the company had wanted to deposit an equivalent lump sum today, how much would it have had to deposit?A. $82,964.59B. $83,189.29C. $83,428.87D. $83,687.23E. $84,998.01Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS32. You need some money today and the only friend you have that has any is your ‘miserly' friend. He agrees to loan you the money you need, if you make payments of $20 a month for the next six months. In keeping with his reputation, he requires that the first payment be paid today. He also charges you 1.5% interest per month. How much money are you borrowing?A. $113.94B. $115.65C. $119.34D. $119.63E. $119.96Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS33. You buy an annuity which will pay you $12,000 a year for ten years. The payments are paid on the first day of each year. What is the value of this annuity today at a 7% discount rate?A. $84,282.98B. $87,138.04C. $90,182.79D. $96,191.91E. $116,916.21Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS34. You are scheduled to receive annual payments of $10,000 for each of the next 25 years. Your discount rate is 8.5%. What is the difference in the present value if you receive these payments at the beginning of each year rather than at the end of each year?A. $8,699B. $9,217C. $9,706D. $10,000E. $10,850Difference = $111,040.97 - $102,341.91 = $8,699.06 = $8,699 (rounded)Note: The difference = .085 $102,341.91 = $8,699.06Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS35. You are comparing two annuities with equal present values. The applicable discount rate is 7.5%. One annuity pays $5,000 on the first day of each year for twenty years. How much does the second annuity pay each year for twenty years if it pays at the end of each year?A. $4,651B. $5,075C. $5,000D. $5,375E. $5,405Because each payment is received one year later, then the cash flow has to equal: $5,000 (1 + .075) = $5,375Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS36. Martha receives $100 on the first of each month. Stewart receives $100 on the last day of each month. Both Martha and Stewart will receive payments for five years. At an 8% discount rate, what is the difference in the present value of these two sets of payments?A. $32.88B. $40.00C. $99.01D. $108.00E. $112.50Difference = $4,964.72 - $4,931.84 = $32.88Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS37. What is the future value of $1,000 a year for five years at a 6% rate of interest?A. $4,212.36B. $5,075.69C. $5,637.09D. $6,001.38E. $6,801.91Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS38. What is the future value of $2,400 a year for three years at an 8% rate of interest?A. $6,185.03B. $6,847.26C. $7,134.16D. $7,791.36E. $8,414.67Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS39. Janet plans on saving $3,000 a year and expects to earn 8.5%. How much will Janet have at the end of twenty-five years if she earns what she expects?A. $219,317.82B. $230,702.57C. $236,003.38D. $244,868.92E. $256,063.66Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS40. Toni adds $3,000 to her savings on the first day of each year. Tim adds $3,000 to his savings on the last day of each year. They both earn a 9% rate of return. What is the difference in their savings account balances at the end of thirty years?A. $35,822.73B. $36,803.03C. $38,911.21D. $39,803.04E. $40,115.31Difference = $445,725.65 - $408,922.62 = $36,803.03Note: Difference = $408,922.62 .09 = $36,803.03Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE VERSUS ORDINARY ANNUITYType: PROBLEMS41. You borrow $5,600 to buy a car. The terms of the loan call for monthly payments for four years at a 5.9% rate of interest. What is the amount of each payment?A. $103.22B. $103.73C. $130.62D. $131.26E. $133.04Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTSType: PROBLEMS42. You borrow $149,000 to buy a house. The mortgage rate is 7.5% and the loan period is 30 years. Payments are made monthly. If you pay for the house according to the loan agreement, how much total interest will you pay?A. $138,086B. $218,161C. $226,059D. $287,086E. $375,059Total interest = ($1,041.83 ⨯ 30 ⨯ 12) - $149,000 = $226,058.80 = $226,059 (rounded) Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND COST OF INTERESTType: PROBLEMS43. The Great Giant Corp. has a management contract with its newly hired president. The contract requires a lump sum payment of $25 million be paid to the president upon the completion of her first ten years of service. The company wants to set aside an equal amount of funds each year to cover this anticipated cash outflow. The company can earn 6.5% on these funds. How much must the company set aside each year for this purpose?A. $1,775,042.93B. $1,798,346.17C. $1,801,033.67D. $1,852,617.25E. $1,938,018.22Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS44. You retire at age 60 and expect to live another 27 years. On the day you retire, you have $464,900 in your retirement savings account. You are conservative and expect to earn 4.5% on your money during your retirement. How much can you withdraw from your retirement savings each month if you plan to die on the day you spend your last penny?A. $2,001.96B. $2,092.05C. $2,398.17D. $2,472.00E. $2,481.27Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS45. The McDonald Group purchased a piece of property for $1.2 million. It paid a down payment of 20% in cash and financed the balance. The loan terms require monthly payments for 15 years at an annual percentage rate of 7.75% compounded monthly. What is the amount of each mortgage payment?A. $7,440.01B. $8,978.26C. $9,036.25D. $9,399.18E. $9,413.67Amount financed = $1,200,000 (1 - .2) = $960,000Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS46. You estimate that you will have $24,500 in student loans by the time you graduate. The interest rate is 6.5%. If you want to have this debt paid in full within five years, how much must you pay each month?A. $471.30B. $473.65C. $476.79D. $479.37E. $480.40Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS47. You are buying a previously owned car today at a price of $6,890. You are paying $500 down in cash and financing the balance for 36 months at 7.9%. What is the amount of each loan payment?A. $198.64B. $199.94C. $202.02D. $214.78E. $215.09Amount financed = $6,890 - $500 = $6,390Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS48. The Good Life Insurance Co. wants to sell you an annuity which will pay you $500 per quarter for 25 years. You want to earn a minimum rate of return of 5.5%. What is the most you are willing to pay as a lump sum today to buy this annuity?A. $26,988.16B. $27,082.94C. $27,455.33D. $28,450.67E. $28,806.30Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS49. Your car dealer is willing to lease you a new car for $299 a month for 60 months. Payments are due on the first day of each month starting with the day you sign the lease contract. If your cost of money is 4.9%, what is the current value of the lease?A. $15,882.75B. $15,906.14C. $15,947.61D. $16,235.42E. $16,289.54Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS50. Your great-aunt left you an inheritance in the form of a trust. The trust agreement states that you are to receive $2,500 on the first day of each year, starting immediately and continuing for fifty years. What is the value of this inheritance today if the applicable discount rate is 6.35%?A. $36,811.30B. $37,557.52C. $39,204.04D. $39,942.42E. $40,006.09Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS51. Beatrice invests $1,000 in an account that pays 4% simple interest. How much more could she have earned over a five-year period if the interest had compounded annually?A. $15.45B. $15.97C. $16.65D. $17.09E. $21.67Ending value at 4% simple interest = $1,000 + ($1,000 ⨯ .04 ⨯ 5) = $1,200.00; Ending value at 4% compounded annually = $1,000 ⨯ (1 +.04)5 = $1,216.65;Difference = $1,216.65 - $1,200.00 = $16.65Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SIMPLE VERSUS COMPOUND INTERESTType: PROBLEMS52. Your firm wants to save $250,000 to buy some new equipment three years from now. The plan is to set aside an equal amount of money on the first day of each year starting today. The firm can earn a 4.7% rate of return. How much does the firm have to save each year to achieve its goal?A. $75,966.14B. $76,896.16C. $78,004.67D. $81.414.14E. $83,333.33Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS53. Today is January 1. Starting today, Sam is going to contribute $140 on the first of each month to his retirement account. His employer contributes an additional 50% of the amount contributed by Sam. If both Sam and his employer continue to do this and Sam can earn a monthly rate of ½ of 1 percent, how much will he have in his retirement account 35 years from now?A. $199,45.944B. $200,456.74C. $249,981.21D. $299,189.16E. $300,685.11Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS54. You are considering an annuity which costs $100,000 today. The annuity pays $6,000 a year. The rate of return is 4.5%. What is the length of the annuity time period?A. 24.96 yearsB. 29.48 yearsC. 31.49 yearsD. 33.08 yearsE. 38.00 yearsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS55. Today, you signed loan papers agreeing to borrow $4,954.85 at 9% compounded monthly. The loan payment is $143.84 a month. How many loan payments must you make before the loan is paid in full?A. 29.89B. 36.00C. 38.88D. 40.00E. 41.03Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS56. Winston Enterprises would like to buy some additional land and build a new factory. The anticipated total cost is $136 million. The owner of the firm is quite conservative and will only do this when the company has sufficient funds to pay cash for the entire expansion project. Management has decided to save $450,000 a month for this purpose. The firm earns 6% compounded monthly on the funds it saves. How long does the company have to wait before expanding its operations?A. 184.61 monthsB. 199.97 monthsC. 234.34 monthsD. 284.61 monthsE. 299.97 monthsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS57. Today, you are retiring. You have a total of $413,926 in your retirement savings and have the funds invested such that you expect to earn an average of 3%, compounded monthly, on this money throughout your retirement years. You want to withdraw $2,500 at the beginning of every month, starting today. How long will it be until you run out of money?A. 185.00 monthsB. 213.29 monthsC. 227.08 monthsD. 236.84 monthsE. 249.69 monthsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS58. The Bad Guys Co. is notoriously known as a slow-payer. It currently needs to borrow $25,000 and only one company will even deal with Bad Guys. The terms of the loan call for daily payments of $30.76. The first payment is due today. The interest rate is 21% compounded daily. What is the time period of this loan?A. 2.88 yearsB. 2.94 yearsC. 3.00 yearsD. 3.13 yearsE. 3.25 yearsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE TIME PERIODSType: PROBLEMS59. The Robertson Firm is considering a project which costs $123,900 to undertake. The project will yield cash flows of $4,894.35 monthly for 30 months. What is the rate of return on this project?A. 12.53%B. 13.44%C. 13.59%D. 14.02%E. 14.59%This can not be solved directly, so it's easiest to just use the calculator method to get an answer. You can then use the calculator answer as the rate in the formula just to verify that your answer is correct.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY INTEREST RATEType: PROBLEMS60. Your insurance agent is trying to sell you an annuity that costs $100,000 today. By buying this annuity, your agent promises that you will receive payments of $384.40 a month for the next 40 years. What is the rate of return on this investment?A. 3.45%B. 3.47%C. 3.50%D. 3.52%E. 3.55%This can not be solved directly, so it's easiest to just use the calculator method to get an answer. You can then use the calculator answer as the rate in the formula just to verify that you answer is correct.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY INTEREST RATEType: PROBLEMS61. You have been investing $120 a month for the last 15 years. Today, your investment account is worth $47,341.19. What is your average rate of return on your investments?A. 9.34%B. 9.37%C. 9.40%D. 9.42%E. 9.46%This can not be solved directly, so it's easiest to just use the calculator method to get an answer. You can then use the calculator answer as the rate in the formula just to verify that you answer is correct.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY INTEREST RATEType: PROBLEMS。
(完整版)公司理财-罗斯课后习题答案-CAL-FENGHAI-(2020YEAR-YICAI)_JINGBIAN第一章1.在所有权形式的公司中,股东是公司的所有者。
股东选举公司的董事会,董事会任命该公司的管理层。
企业的所有权和控制权分离的组织形式是导致的代理关系存在的主要原因。
管理者可能追求自身或别人的利益最大化,而不是股东的利益最大化。
在这种环境下,他们可能因为目标不一致而存在代理问题。
2.非营利公司经常追求社会或政治任务等各种目标。
非营利公司财务管理的目标是获取并有效使用资金以最大限度地实现组织的社会使命。
3.这句话是不正确的。
管理者实施财务管理的目标就是最大化现有股票的每股价值,当前的股票价值反映了短期和长期的风险、时间以及未来现金流量。
4.有两种结论。
一种极端,在市场经济中所有的东西都被定价。
因此所有目标都有一个最优水平,包括避免不道德或非法的行为,股票价值最大化。
另一种极端,我们可以认为这是非经济现象,最好的处理方式是通过政治手段。
一个经典的思考问题给出了这种争论的答案:公司估计提高某种产品安全性的成本是30美元万。
然而,该公司认为提高产品的安全性只会节省20美元万。
请问公司应该怎么做呢?”5.财务管理的目标都是相同的,但实现目标的最好方式可能是不同的,因为不同的国家有不同的社会、政治环境和经济制度。
6.管理层的目标是最大化股东现有股票的每股价值。
如果管理层认为能提高公司利润,使股价超过35美元,那么他们应该展开对恶意收购的斗争。
如果管理层认为该投标人或其它未知的投标人将支付超过每股35美元的价格收购公司,那么他们也应该展开斗争。
然而,如果管理层不能增加企业的价值,并且没有其他更高的投标价格,那么管理层不是在为股东的最大化权益行事。
现在的管理层经常在公司面临这些恶意收购的情况时迷失自己的方向。
7.其他国家的代理问题并不严重,主要取决于其他国家的私人投资者占比重较小。
较少的私人投资者能减少不同的企业目标。
【公司理财】罗斯公司理财名词解释习题答案xxxx年xx月xx日xxxxxxxx集团企业有限公司Please enter your company's name and contentvCONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 11.1•What are the three basic questions of corporate finance?a. Investment decision (capital budgeting): What long-terminvestment strategy should a firm adopt?b. Financing decision (capital structure): How much cash must be raised for therequired investments?c.Short-term finance decision (working capital): How much short-term cash flow does company need to pay its bills.•Describe capital structure.Capital structure is the mix of different securities used to finance afirm's investments.•List three reasons why value creation is difficult.Value creation is difficult because it is not easy to observe cash flows directly. The reasons are:a. Cash flows are sometimes difficult to identify.b. The timing of cash flows is difficult to determine.c. Cash flows are uncertain and therefore risky.1.2•What is a contingent claim?A contingent claim is a claim whose payoffs are dependent on thevalue of the firm at the end of the year. In more general terms,contingent claims depend on the value of an underlying asset.•Describe equity and debt as contingent claims.Both debt and equity depend on the value of the firm. If the valueof the firm is greater than the amount owed to debt holders, theywill get what the firm owes them, while stockholders will get the2A- Answers to Concept Questionsdifference. But if the value of the firm is less than equity,bondholders will get the value of the firm and equity holdersnothing.1.3•Define a proprietorship, a partnership and a corporation.A proprietorship is a business owned by a single individual withunlimited liability. A partnership is a business owned by two ormore individuals with unlimited liability. A corporation is a business which is a "legal person" with many limited liability owners.•What are the advantages of the corporate form of business organization?Limited liability, east of ownership transfer and perpetual succession.1.4•What are the two types of agency costs?Monitoring costs of the shareholders and the incentive fees paid to the managers.•How are managers bonded to shareholders?a.Shareholders determine the membership to the board ofdirectors, which selects management.b.Management contracts and incentives are build intocompensation arrangements.c.If a firm is taken over because the firm's price dropped, managerscould lose their jobs.petition in the managerial labor market makes managersperform in the best interest of stockholders.•Can you recall some managerial goals?Maximization of corporate wealth, growth and company size.•What is the set-of-contracts perspective?The view of the corporation as a set of contracting relationshipsamong individuals who have conflicting objectives.1.5•Distinguish between money markets and capital markets.Money markets are markets for debt securities that pay off in lessthan one year, while capital markets are markets for long-term debt and equity shares.•What is listing?Listing refers to the procedures by which a company applies andqualifies so that its stock can be traded on the New York StockExchange.•What is the difference between a primary market and a secondary market?The primary market is the market where issuers of securities sellthem for the first time to investors, while a secondary market is amarket for securities previously issued.CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 22.1•What is the balance-sheet equation?Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' equity•What three things should be kept in mind when looking at a balance sheet?Accounting liquidity, debt vs. equity, and value vs. cost.2.2•What is the income statement equation?4A- Answers to Concept QuestionsRevenue - expenses = Income•What are the three things to keep in mind when looking at anincome statement?Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), noncash items,and time and costs.•What are noncash expenses?Noncash expenses are items included as expenses but which do not directly affect cash flow. The most important one is depreciation.2.3•What is net working capital?It is the difference between current assets and current liabilities.•What is the change in net working capital?To determine changes in net working capital you subtract uses ofnet working capital from sources of net working capital.2.4 •How is cash flow different from changes in net working capital?The difference between cash flow and changes in new workingcapital is that some transactions affect cash flow and not networking capital. The acquisition of inventories with cash is a goodexample of a change in working capital requirements.•What is the difference between operating cash flow and totalcash flow of the firm?The main difference between the two is capital spending andadditions to working capital, that is, investment in fixed assets and"investment" in working capital.CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 33.1 •What is an interest rate?It is the payment required by the lender of money for the use of itduring a determined period of time. It is expressed in percentage.• What are institutions that match borrowers and lenders called?They are called financial institutions.•What do we mean when we say a market clears? What is anequilibrium rate of interest?A market clears if the amount of money borrowers want to borrow isequal to the amount lenders wish to lend. An equilibrium rate ofinterest is the interest rate at which markets clear.3.2 •How does an individual change his consumption across periods throughborrowing and lending.By borrowing and lending different amounts the person can achieve any of all consumption possibilities available.•How do interest rate changes affect one's degree of impatience?A person's level of patience depends upon the interest rate he orshe faces in the market. A person eager to borrow money at a lowinterest rate will become less eager if that interest rate is raised and may prefer to lend money to take advantage of higher interest rates.3.3 •What is the most important feature of a competitive financial market?6A- Answers to Concept QuestionsNo investor, individual or corporation can have a significant effecton total lending or on interest rates. Therefore, investors are pricetakers.•What conditions are likely to lead to this?a.Trading is costless.rmation about borrowing and lending opportunities isavailablec.There are many traders.3.4 •Describe the basic financial principle of investment decision-making?An investment project is worth undertaking only if it is moresdesirable than what is available in the financial markets.3.5 •Describe how the financial markets can be used to evaluate investmentalternatives?The financial markets can be used as a benchmark. If the proposedinvestment provides a better alternative than the financial markets, it should be undertaken.•What is the separation theorem? Why is it important?The separation theorem says that the decision as to whether toundertake a project (compared to the financial markets) isindependent of the consumption preferences of the individual. It isimportant because we can make investment decisions based onobjective data, disregarding personal preferences.3.6 •Give the definitions of net present value, future value and present value?New present value is the difference in present value terms betweencash inflows and cash outflows. Given the financial market, thefuture value is an amount equivalent to the amount currently held,and present value is the amount equivalent now to an amount to be received or given in the future.•What information does a person need to compute an investment's net presentvalue?Cash inflows, cash outflows and an interest or discount rate.3.7 •In terms of the net-present-value rule, what is the essential differencebetween the individual and the corporation.The main difference is that firms have no consumption endowment. CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 44.1 •Define future value and present value.Future value is the value of a sum after investing over one or moreperiods. Present value is the value today of cash flows to bereceived in the future.•How does one use net present value when making an investment decision?One determines the present value of future cash flows and thensubtracts the cost of the investment. If this value is positive, theinvestment should be undertaken. If the NPV is negative, then theinvestment should be rejected.8A- Answers to Concept Questions4.2 • What is the difference between simple interest and compound interest?With simple interest, the interest on the original investment is notreinvested. With compound interest, each interest payment isreinvested and one earns interest on interest.•What is the formula for the net present value of a project?TNPV = -C0 + ∑ C t /(1+I)tt=14.3 •What is a stated annual interest rate?The stated annual interest rate is the annual interest rate withoutconsideration of compounding.•What is an effective annual interest rate?An effective annual interest rate is a rate that takes compoundinginto account.• What is the relationship between the stated annual interest rate and the effective annual interest rate?Effective annual interest rate = (1 + (r/m) )m - 1.•Define continuous compounding.Continuous compounding compounds investments every instant.4.4 •What are the formulas for perpetuity, growing-perpetuity, annuity, andgrowing annuity?Perpetuity: PV = C/rGrowing Perpetuity: PV = C/(r-g)Annuity: PV = (C/r) [1-1/(1+r)T]Growing Annuity: PV = [C/(r-g)] [1-((1+g) / (1+r))T ]•What are three important points concerning the growing perpetuity formula?1.The numerator.2.The interest rate and the growth rate.3.The timing assumption.•What are four tricks concerning annuities?1. A delayed annuity.2.An annuity in advance3.An infrequent annuity4.The equating of present values of two annuities.CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 55.2 •Define pure discount bonds, level-coupon bonds, and consols.A pure discount bond is one that makes no intervening interestpayments. One receives a single lump sum payment at maturity. Alevel-coupon bond is a combination of an annuity and a lump sumat maturity. A consol is a bond that makes interest paymentsforever.•Contrast the state interest rate and the effective annual interest rate for bonds paying semi-annual interest.Effective annual interest rate on a bond takes into account twoperiods of compounding per year received on the coupon payments.The state rate does not take this into account.10A- Answers to Concept Questions5.3 •What is the relationship between interest rates and bond prices?There is an inverse relationship. When one goes up, the other goes down.•How does one calculate the yield to maturity on a bond?One finds the discount rate that equates the promised future cashflows with the price of the bond.5.8 •What are the three factors determining a firm's P/E ratio?1.Today's expectations of future growth opportunities.2.The discount rte.3.The accounting method.5.9 •What is the closing price of General Data?The closing price of General Data is 6 3/16.•What is the PE of General House?The PE of General House is 29.•What is the annual dividend of General Host?The annual dividend of General Host is zero.CONCEPT QUESTIONS - Appendix to Chapter 5•What is the difference between a spot interest rate and the yield to maturity?The yield to maturity is the geometric average of the spot ratesduring the life of the bond.•Define the forward rate.Given a one-year bond and a two-year bond, one knows the spotrates for both. The forward rate is the rate of return implicit on aone-year bond purchased in the second year that would equate the terminal wealth of purchasing the one-year bond today and another in one year with that of the two-year bond.•What is the relationship between the one-year spot rate, the two-year spot rate and the forward rate over the second year?The forward rate f2 = [(1+r2)2 /(1+r1 )] - 1•What is the expectation hypothesis?Investors set interest rates such that the forward rate over a givenperiod equals the spot rate for that period.•What is the liquidity-preference hypothesis?This hypothesis maintains that investors require a risk premium forholding longer-term bonds (i.e. they prefer to be liquid or short-term investors). This implies that the market sets the forward ratefor a given period above the expected spot rate for that period. CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 66.2 •List the problems of the payback period rule.1.It does not take into account the time value of money.2.It ignores payments after the payback period.3.The cutoff period is arbitrary.•What are some advantages?1.It is simple to implement.12A- Answers to Concept Questions2.It may help in controlling and evaluating managers.6.4 •What are the three steps in calculating AAR?1.Determine average net income.2.Determine average investment3.Divide average net income by average investment.•What are some flaws with the AAR approach?1.It uses accounting figures.2.It takes no account of timing.3.The cutoff period is arbitrary.6.5 •How does one calculate the IRR of a project?Using either trial-and-error or a financial calculator, one finds thediscount rate that produces an NPV of zero.6.6 •What is the difference between independent projects and mutually exclusiveprojects?An independent project is one whose acceptance does not affect the acceptance of another. A mutually exclusive project, on the otherhand is one whose acceptance precludes the acceptance of another.•What are two problems with the IRR approach that apply to both independent and mutually exclusive projects?1.The decision rule depends on whether one is investing offinancing.2.Multiple rates of return are possible.•What are two additional problems applying only to mutually exclusive projects?1.The IRR approach ignores issues of scale.2.The IRR approach does not accommodate the timing of the cashflows properly.6.7 •How does one calculate a project's profitability index?Divide the present value of the cash flows subsequent to the initialinvestment by the initial investment.•How is the profitability index applied to independent projects, mutually exclusive projects, and situations of capital rationing?1.With independent projects, accept the project if the PI is greaterthan 1.0 and reject if less than 1.0.2.With mutually exclusive projects, use incremental analysis,subtracting the cash flows of project 2 from project 1. Find the PI.If the PI is greater than 1.0, accept project 1. If less than 1.0,accept project 2.3.In capital rationing, the firm should simply rank the projectsaccording to their respective PIs and accept the projects with thehighest PIs, subject to the budget constrain.CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 77.1 •What are the three difficulties in determining incremental cash flows?1.Sunk costs.2.Opportunity costs3.Side effects.•Define sunk costs, opportunity costs, and side effects.14A- Answers to Concept Questions1.Sunk costs are costs that have already been incurred and that willnot be affected by the decision whether to undertake theinvestment.2.Opportunity costs are costs incurred by the firm because, if itdecides to undertake a project, it will forego other opportunitiesfor using the assets.3.Side effects appear when a project negatively affects cash flowsfrom other parts of the firm.7.2 •What are the items leading to cash flow in any year?Cash flow from operations (revenue-operating costs-taxes) plus cash flow of investment (cost of new machines + changes in net working capital + opportunity costs).•Why did we determine income when NPV Analysis discounts cash flows, not income?Because we need to determine how much is paid out in taxes.•Why is working capital viewed as a cash outflow?Because increases in working capital must be funded by cashgenerated elsewhere in the firm.7.3 •What is the difference between the nominal and the real interest rate?The nominal interest rate is the real interest rate with a premium for inflation.•What is the difference between nominal and real cash flows?Real cash flows are nominal cash flows adjusted for inflation.7.4 •What is the equivalent annual cost method of capital budgeting?The decision as to which of various mutually exclusive machines tobuy is based on the equivalent annual cost. The EAC is determinedby dividing the net present value of costs by an annuity factor thathas the same life as the machines. The machine with the lowest EAC should be acquired.•Can you list the assumptions that we must to use EAC?1.All machines do the same job.2.They have different operating costs and lives3.The machine will be indefinitely replaced.CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 88.1 •What are the ways a firm can create positive NPV.1.Be first to introduce a new product.2.Further develop a core competency to product goods or servicesat lower costs than competitors.3.Create a barrier that makes it difficult for the other firms tocompete effectively.4.Introduce variation on existing products to take advantage ofunsatisfied demand5.Create product differentiation by aggressive advertising andmarketing networks.e innovation in organizational processes to do all of the above.•How can managers use the market to help them screen out negative NPV projects?8.2 •What is a decision tree?16A- Answers to Concept QuestionsIt is a method to help capital budgeting decision-makers evaluating projects involving sequential decisions. At every point in the tree,there are different alternatives that should be analyzed.•What are potential problems in using a decision tree?Potential problems 1) that a different discount rate should be usedfor different branches in the tree and 2) it is difficult for decisiontrees to capture managerial options.8.3 •What is a sensitivity analysis?It is a technique used to determine how the result of a decisionchanges when some of the parameters or assumptions change.•Why is it important to perform a sensitivity analysis?Because it provides an analysis of the consequences of possibleprediction or assumption errors.•What is a break-even analysis?It is a technique used to determine the volume of productionnecessary to break even, that is, to cover not only variable costs but fixed costs as well.•Describe how sensitivity analysis interacts with break-even analysis.Sensitivity analysis can determine how the financial break-even point changes when some factors (such as fixed costs, variable costs, orrevenue) change.CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 99.1 •What are the two parts of total return?Dividend income and capital gain (or loss)•Why are unrealized capital gains or losses included in the calculation of returns?Because it is as much a part of returns as dividends, even if theinvestor decides to hold onto the stock and not to realize the capital gain.•What is the difference between a dollar return and a percentage return?A dollar return is the amount of money the original investmentprovided, while percentage return is the percentage of the originalinvestment represented by the total return.9.2 •What is the largest one-period return in the 63-year history of commonstocks we have displayed, and when did it occur? What is thesmallest return, and when did it occur?Largest common stock return: 53.99% in 1933. Smallest commonstock return: -43.34% in 1931.•In how many years did the common stock return exceed 30 percent, and inhow many years was it below 20 percent?It exceeded 30% in 16 years. It was below 20% in 39 years.•For common stocks, what is the longest period of time without a single losingyear? What is the longest streak of losing years?18A- Answers to Concept QuestionsThere are 6 consecutive years of positive returns. The longest losing streak was 4 years.•What is the longest period of time such that if you have invested at thebeginning of the period, you would still not have had a positivereturn on your common-stock investment by the end?The longest period of time was 14 years (from 1929 to 1942).9.4 •What is the major observation about capital markets that we will seek toexplain?That the return on risky assets has been higher on average than thereturn on risk-free assets.•What does the observation tell us about investors for the period from 1926through 1994.An investor in this period was rewarded for investment in the stockmarket with an extra or excess return over what would haveachieved by simply investing in T-bills.9.5 •What is the definition of sample estimates of variance and standarddeviation?Variance is given by Var (R) = (1 / (T-1) ) ∑t (R t - R)2 where T is thenumber of periods, R t is the period return and R is the sample mean.Standard deviation is given by SD = Var 1/2. For large T, (T-1) may be approximated by T.•How does the normal distribution help us interpret standard deviation?For a normal distribution, the probability of having a return that isabove or below the men by a certain amount only depends on thestandard deviation.9.6 •How can financial managers use the history of capital markets to estimatethe required rate of return on nonfinancial investments with the same risk as the average common stock?They can determine the historical risk premium and add this amount to the current risk-free rate to determine the required return oninvestments of that risk.CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 1010.3 •What are the formulas for the expected return, variance, and standarddeviation of a portfolio of two assets?E{R p } = X i R i + X j R jVar p = (X i2 (R i - R i )2 + X j2 (R j - R j )2 + 2X i X j (R i - R i ) (R j - R j )SD p = Var p 1/2•What is the diversification effect?As long as the correlation coefficient between two securities is lessthan one, the standard deviation of a portfolio of two securities is20A- Answers to Concept Questions。
Chapter 6: Some Alternative Investment Rules6.1 a. Payback period of Project A = 1 + ($7,500 - $4,000) / $3,500 = 2 yearsPayback period of Project B = 2 + ($5,000 - $2,500 -$1,200) / $3,000 = 2.43 yearsProject A should be chosen.b. NPVA = -$7,500 + $4,000 / 1.15 + $3,500 / 1.152 + $1,500 / 1.153 = -$388.96NPVB = -$5,000 + $2,500 / 1.15 + $1,200 / 1.152 + $3,000 / 1.153 = $53.83Project B should be chosen.6.2 a. Payback period = 6 + {$1,000,000 - ($150,000 ( 6)} / $150,000 = 6.67 yearsYes, the project should be adopted.b. $150,000 = $974,259The discounted payback period = 11 + ($1,000,000 - $974,259) / ($150,000 / 1.112)= 11.54 yearsc. NPV = -$1,000,000 + $150,000 / 0.10 = $500,0006.3 a. Average Investment:($16,000 + $12,000 + $8,000 + $4,000 + 0) / 5 = $8,000Average accounting return:$4,500 / $8,000 = 0.5625 = 56.25%b. 1. AAR does not consider the timing of the cash flows, hence it does notconsider the time value of money.2. AAR uses an arbitrary firm standard as the decision rule.3. AAR uses accounting data rather than net cash flows.6.4 Average Investment = ($2,000,000 + 0) / 2 = $1,000,000Average net income = [$100,000 {(1 + g)5 - 1} / g] / 5= {$100,000A (1.075 - 1} / 0.07} / 5= $115,014.78AAR = $115,014.78 / $1,000,000 = 11.50%No, since the machine’s AAR is less than the firm’s cutoff AAR.6.5 aPI = $40,000 / $160,000 = 1.04Since the PI exceeds one accept the project.6.7 The IRR is the discount rate at which the NPV = 0.-$3,000 + $2,500 / (1 + IRRA) + $1,000 / (1 + IRRA)2 = 0By trial and error, IRRA = 12.87%Since project B’s cash flows are two times of those of project A, the IRRB = IRRA = 12.87% 6.8 a. Solve x by trial and error:-$4,000 + $2,000 / (1 + x) + $1,500 / (1 + x)2 + $1,000 / (1 + x)3 = 0x = 6.93%b. No, since the IRR (6.93%) is less than the discount rate of 8%.6.9 Find the IRRs of project A analytically. Since the IRR is the discount rate that makes the NPV equal to zero, the following equation must hold.-$200 + $200 / (1 + r) + $800 / (1 + r)2 - $800 / (1 + r)3 = 0$200 [-1 + 1 / (1 + r)] - {$800 / (1 + r)2}[-1 + 1 / (1 + r)] = 0[-1 + 1 / (1 + r)] [$200 - $800 / (1 + r)2] = 0For this equation to hold, either [-1 + 1 / (1 + r)] = 0 or [$200 - $800 / (1 + r)2] = 0.Solve each of these factors for the r that would cause the factor to equal zero. The resulting rates are the two IRRs for project A. They are either r = 0% or r = 100%.Note: By inspection you should have known that one of the IRRs of project A is zero. Notice that the sum of the un-discounted cash flows for project A is zero. Thus, not discounting the cash flows would yield a zero NPV. The discount rate which is tantamount to not discounting is zero.Here are some of the interactions used to find the IRR by trial and error.Sophisticated calculators can compute this rate without all of the tedium involved in the trial-and-error method.NPV = -$150 + $50 / 1.3 + $100 / 1.32 + $150 / 1.33 = $15.91NPV = -$150 + $50 / 1.4 + $100 / 1.42 + $150 / 1.43 = -$8.60NPV = -$150 + $50 / 1.37 + $100 / 1.372 + $150 / 1.373 = -$1.89NPV = -$150 + $50 / 1.36 + $100 / 1.36 2 + $150 / 1.363 = $0.46NPV = -$150 + $50 / 1.36194 + $100 / 1.361942 + $150 / 1.361943= $0.0010NPV = -$150 + $50 / 1.36195 + $100 / 1.361952 + $150 / 1.361953= -$0.0013NPV = -$150 + $50 / 1.361944 + $100 / 1.3619442 + $150 / 1.3619443= $0.0000906Thus, the IRR is approximately 36.1944%.6.10 a. Solve r in the equation:$5,000 - $2,500 / (1 + r) - $2,000 / (1 + r)2 - $1,000 / (1 + r)3- $1,000 / (1 + r)4 = 0By trial and error,IRR = r = 13.99%b. Since this problem is the case of financing, accept the project if the IRR is less than the required rate of return.IRR = 13.99% > 10%Reject the offer.c. IRR = 13.99% < 20%Accept the offer.d. When r = 10%:NPV = $5,000 - $2,500 / 1.1 - $2,000 / 1.12 - $1,000 / 1.13 - $1,000 / 1.14= -$359.95When r = 20%:NPV = $5,000 - $2,500 / 1.2 - $2,000 / 1.22 - $1,000 / 1.23 - $1,000 / 1.24= $466.82Yes, they are consistent with the choices of the IRR rule since the signs of the cash flows change only once.6.11 a. Project A:NPV = -$5,000 + $3,500 / (1 + r) + $3,500 / (1 + r)2 = 0IRR = r = 25.69%Project B:NPV = -$100,000 + $65,000 / (1 + r) + $65,000 / (1 + r)2 = 0IRR = r = 19.43%b. Choose project A because it has a higher IRR.c. The difference in scale is ignored.d. Apply the incremental IRR method.e.C0C1C2B - A-$95,000$61,500$61,500NPV = -$95,000 + $61,500 / (1 + r) + $61,500 / (1 + r)2 = 0Incremental IRR = r = 19.09%f. If the discount rate is less than 19.09%, choose project B.Otherwise, choose project A.g. NPVA = -$5,000 + $3,500 / 1.15 + $3,500 / 1.152 = $689.98NPVB = -$100,000 + $65,000 / 1.15 + $65,000 / 1.152 = $5,671.08Choose project B.6.12 a. PVA = {$5,000 / (0.12 - 0.04)} / 1.122 = $49,824.61PVB = (-$6,000 / 0.12) / 1.12 = -$44,642.86b. The IRR for project C must solve{$5,000 / (x - 0.04)} / (1 + x)2 + (-$6,000 / x) / (1 + x) = 0$5,000 / (x - 0.04) - $6,000 (1 + x) / x = 025 x2 + 3.17 x - 1 =0x = {-3.17 - (110.0489)0.5} / 50 or {-3.17 + (110.0489)0.5} / 50The relevant positive root is IRR = x = 0.1464 = 14.64%c. To arrive at the appropriate decision rule, we must graph the NPV as a function of the discount rate. At a discount rate of 14.64% the NPV is zero. To determine if the graph is upward or downward sloping, check the NPV at another discount rate. At a discount rate of 10% the NPV is $14,325.07 [= $68,870.52 - $54,545.54]. Thus, the graph of the NPV is downward sloping. From the discussion in the text, if an NPV graph is downward sloping, the projectis an investing project. The correct decision rule for an investing project is to accept the project if the discount rate is below 14.64%.6.13 Generally, the statement is false. If the cash flows of project B occur early and the cash flows of project A occur late, then for a low discount rate the NPV of A can exceed the NPV of B. Examples are easy to construct.C0C1C2IRRNPV @ 0%A:-$1,000,000$0$1,440,0000.20$440,000B:-2,000,0002,400,0000.20400,000In one particular case, the statement is true for equally risky projects. If the lives of thetwo projects are equal and in every time period the cash flows of the project B are twice the cash flows of project A, then the NPV of project B will be twice as great as the NPV of project A for any discount rate between 0% and 20%.6.14 a. NPV( = $756.57 - $500 = $256.57NPV( = $2,492.11 - $2,000 = $492.11b. Choose project beta.6.15 Although the profitability index is higher for project B than for project A, the NPV is the increase in the value of the company that will occur if a particular project is undertaken. Thus, the project with the higher NPV should be chosen because it increases the value of the firm the most. Only in the case of capital rationing could the pension fund manager be correct.6.16 a. PIA = ($70,000 / 1.12 + $70,000 / 1.122) / $100,000 = 1.183PIB = ($130,000 / 1.12 + $130,000 / 1.122) / $200,000 = 1.099PIC = ($75,000 / 1.12 + $60,000 / 1.122) / $100,000 = 1.148b. NPVA = -$100,000 + $118,303.57 = $18,303.57NPVB = -$200,000 + $219,706.63 = $19,706.63NPVC = -$100,000 + $114,795.92 = $14,795.92c. Accept all three projects because PIs of all the three projects are greater than one.d. Based on the PI rule, project C can be eliminated because its PI is less than the oneof project A, while both have the same amount of the investment. We can compute the PI of the incremental cash flows between the two projects,ProjectC0C1C2PIB - A-$100,000$60,000$60,0001.014We should take project B since the PI of the incremental cash flows is greater than one.e. Project B has the highest NPV, while A has the next highest NPV.Take both projects A and B.6.17 a. The payback period is the time it takes to recoup the initial investment of a project.Accept any project that has a payback period that is equal to or shorter than the company’s standard payback period. Reject all other projects.b. The average accounting return (AAR) is defined asAverage project earnings ( Average book value of the investment.Accept projects for which the AAR is equal to or greater than the firm’s standard.Reject all other projects.c. The internal rate of return (IRR) is the discount rate which makes the net presentvalue (NPV) of the project zero. The accept / reject criteria is:If C0 < 0 and all future cash flows are positive, accept the project if IRR ( discount rate.If C0 < 0 and all future cash flows are positive, reject the project if IRR < discount rate.If C0 > 0 and all future cash flows are negative, accept the project if IRR ( discount rate.If C0 > 0 and all future cash flows are negative, reject the project if IRR > discount rate.If the project has cash flows that alternate in sign, there is likely to be more thanone positive IRR. In that situation, there is no valid IRR accept / reject rule.d. The profitability index (PI) is defined as:(The present value of the cash flows subsequent to the initial investment (The initial investment)Accept any project for which the profitability index is equal to or greater than one. Reject project for which that is not true.e. The net present value (NPV) is the sum of the present values of all project cashflows. Accept those projects with NPVs which are equal to or greater than zero.Rejects proposals with negative NPVs.6.18 Let project A represent New Sunday Early Edition; and let project B represent New Saturday Late Edition.a. Payback period of project A = 2 + ($1,200 - $1,150) / $450 = 2.11 yearsPayback period of project B = 2 + ($2,100 - $1,900) / $800 = 2.25 yearsBased on the payback period rule, you should choose project A.b. Project A:Average investment = ($1,200 + $0) / 2 = $600Depreciation = $400 / yearAverage income = [($600 - $400) + ($550 - $400) + ($450 - $400)] / 3= $133.33AAR = $133.33 / $600 = 22.22%Project B:Average investment = ($2,100 + $0) / 2 = $1,050Depreciation = $700 / yearAverage income = [($1,000 - $700) + ($900 - $700) + ($800 - $700)] / 3= $200AAR = $200 / $1,050 = 19.05%c. IRR of project A:-$1,200 + $600 / (1 + r) + $550 / (1 + r)2 + $450 / (1 + r)3 = 0IRR = r = 16.76%IRR of project B:-$2,100 + $1,000 / (1 + r) + $900 / (1 + r)2 + $800 / (1 + r)3 = 0IRR = r = 14.29%Project A has a greater IRR.d. IRR of project B-A:Incremental cash flowsYear123B - A-$900$400$350$350-$900 + $400 / (1 + r) + $350 / (1 + r)2 + $350 / (1 + r)3 = 0Incremental IRR = r = 11.02%If the required rate of return is greater than 11.02%, then choose project A.If the required rate of return is less than 11.02%, then choose project B.6.19 Let project A be Deepwater Fishing; let project B be New Submarine Ride.a. Project A:YearDiscounted CFCumulative CF-$600,000-$600,0001234,783-365,2172264,650-100,5673197,255Discounted payback period of project A = 2 + $100,567 / $197,255= 2.51 yearsProject B:YearDiscounted CFCumulative CF-$1,800,000-$1,800,0001869,565-930,4352529,301-401,1343591,765Discounted payback period of project B = 2 + $401,134 / $591,765= 2.68 yearsProject A should be chosen.b. IRR of project A:-$600,000 + $270,000 / (1 + r) + $350,000 / (1 + r)2 + $300,000 / (1 + r)3 = 0IRR = r = 24.30%IRR of project B:-$1,800,000 + $1,000,000 /(1 + r) + $700,000 / (1 + r)2 + $900,000 / (1 + r)3 = 0IRR = r = 21.46%Based on the IRR rule, project A should be chosen since it has a greater IRR.c. Incremental IRR:Year23B - A-$1,200,000$730,000$350,000$600,000-$1,200,000 + $730,000 / (1 + r) + $350,000 / (1 + r)2 + $600,000 / (1 + r)3 = 0Incremental IRR = r = 19.92%Since the incremental IRR is greater than the required rate of return, 15%, choose project B.d. NPVA = -$600,000 + $270,000 / 1.15 + $350,000 / 1.152 + $300,000 / 1.153= $96,687.76NPVB = -$1,800,000 + $1,000,000 / 1.15 + $700,000 / 1.152 + $900,000 / 1.153= $190,630.39Since NPVB > NPVA, choose project B.Yes, the NPV rule is consistent with the incremental IRR rule.6.20 a. The IRR is the discount rate at which the NPV = 0-$600,000 +IRR (18.56%b. Yes, the mine should be opened since its IRR exceeds its required return of 10%.。
罗斯《公司理财》第9版精要版英文原书课后部分章节答案详细»1 / 17 CH5 11,13,18,19,20 11. To find the PV of a lump sum, we use: PV = FV / (1 + r) t PV = $1,000,000 / (1.10) 80 = $488.19 13. To answer this question, we can use either the FV or the PV formula. Both will give the same answer since they are the inverse of each other. We will use the FV formula, that is: FV = PV(1 + r) t Solving for r, we get: r = (FV / PV) 1 / t –1 r = ($1,260,000 / $150) 1/112 – 1 = .0840 or 8.40% To find the FV of the first prize, we use: FV = PV(1 + r) t FV = $1,260,000(1.0840) 33 = $18,056,409.94 18. To find the FV of a lump sum, we use: FV = PV(1 + r) t FV = $4,000(1.11) 45 = $438,120.97 FV = $4,000(1.11) 35 = $154,299.40 Better start early! 19. We need to find the FV of a lump sum. However, the money will only be invested for six years, so the number of periods is six. FV = PV(1 + r) t FV = $20,000(1.084)6 = $32,449.33 20. To answer this question, we can use either the FV or the PV formula. Both will give the same answer since they are the inverse of each other. We will use the FV formula, that is: FV = PV(1 + r) t Solving for t, we get: t = ln(FV / PV) / ln(1 + r) t = ln($75,000 / $10,000) / ln(1.11) = 19.31 So, the money must be invested for 19.31 years. However, you will not receive the money for another two years. From now, you’ll wait: 2 years + 19.31 years = 21.31 years CH6 16,24,27,42,58 16. For this problem, we simply need to find the FV of a lump sum using the equation: FV = PV(1 + r) t 2 / 17 It is important to note that compounding occurs semiannually. To account for this, we will divide the interest rate by two (the number of compounding periods in a year), and multiply the number of periods by two. Doing so, we get: FV = $2,100[1 + (.084/2)] 34 = $8,505.93 24. This problem requires us to find the FVA. The equation to find the FVA is: FV A = C{[(1 + r) t – 1] / r} FV A = $300[{[1 + (.10/12) ] 360 – 1} / (.10/12)] = $678,146.38 27. The cash flows are annual and the compounding period is quarterly, so we need to calculate the EAR to make the interest rate comparable with the timing of the cash flows. Using the equation for the EAR, we get: EAR = [1 + (APR / m)] m – 1 EAR = [1 + (.11/4)] 4 – 1 = .1146 or 11.46% And now we use the EAR to find the PV of each cash flow as a lump sum and add them together: PV = $725 / 1.1146 + $980 / 1.1146 2 + $1,360 / 1.1146 4 = $2,320.36 42. The amount of principal paid on the loan is the PV of the monthly payments you make. So, the present value of the $1,150 monthly payments is: PVA = $1,150[(1 – {1 / [1 + (.0635/12)]} 360 ) / (.0635/12)] = $184,817.42 The monthly payments of $1,150 will amount to a principal payment of $184,817.42. The amount of principal you will still owe is: $240,000 – 184,817.42 = $55,182.58 This remaining principal amount will increase at the interest rate on the loan until the end of the loan period. So the balloon payment in 30 years, which is the FV of the remaining principal will be: Balloon payment = $55,182.58[1 + (.0635/12)] 360 = $368,936.54 58. To answer this question, we should find the PV of both options, and compare them. Since we are purchasing the car, the lowest PV is the best option. The PV of the leasing is simply the PV of the lease payments, plus the $99. The interest rate we would use for the leasing option is the same as the interest rate of the loan. The PV of leasing is: PV = $99 + $450{1 –[1 / (1 + .07/12) 12(3) ]} / (.07/12) = $14,672.91 The PV of purchasing the car is the current price of the car minus the PV of the resale price. The PV of the resale price is: PV = $23,000 / [1 + (.07/12)] 12(3) = $18,654.82 The PV of the decision to purchase is: $32,000 – 18,654.82 = $13,345.18 3 / 17 In this case, it is cheaper to buy the car than leasing it since the PV of the purchase cash flows is lower. To find the breakeven resale price, we need to find the resale price that makes the PV of the two options the same. In other words, the PV of the decision to buy should be: $32,000 – PV of resale price = $14,672.91 PV of resale price = $17,327.09 The resale price that would make the PV of the lease versus buy decision is the FV ofthis value, so: Breakeven resale price = $17,327.09[1 + (.07/12)] 12(3) = $21,363.01 CH7 3,18,21,22,31 3. The price of any bond is the PV of the interest payment, plus the PV of the par value. Notice this problem assumes an annual coupon. The price of the bond will be: P = $75({1 – [1/(1 + .0875)] 10 } / .0875) + $1,000[1 / (1 + .0875) 10 ] = $918.89 We would like to introduce shorthand notation here. Rather than write (or type, as the case may be) the entire equation for the PV of a lump sum, or the PV A equation, it is common to abbreviate the equations as: PVIF R,t = 1 / (1 + r) t which stands for Present Value Interest Factor PVIFA R,t = ({1 – [1/(1 + r)] t } / r ) which stands for Present Value Interest Factor of an Annuity These abbreviations are short hand notation for the equations in which the interest rate and the number of periods are substituted into the equation and solved. We will use this shorthand notation in remainder of the solutions key. 18. The bond price equation for this bond is: P 0 = $1,068 = $46(PVIFA R%,18 ) + $1,000(PVIF R%,18 ) Using a spreadsheet, financial calculator, or trial and error we find: R = 4.06% This is the semiannual interest rate, so the YTM is: YTM = 2 4.06% = 8.12% The current yield is: Current yield = Annual coupon payment / Price = $92 / $1,068 = .0861 or 8.61% The effective annual yield is the same as the EAR, so using the EAR equation from the previous chapter: Effective annual yield = (1 + 0.0406) 2 – 1 = .0829 or 8.29% 20. Accrued interest is the coupon payment for the period times the fraction of the period that has passed since the last coupon payment. Since we have a semiannual coupon bond, the coupon payment per six months is one-half of the annual coupon payment. There are four months until the next coupon payment, so two months have passed since the last coupon payment. The accrued interest for the bond is: Accrued interest = $74/2 × 2/6 = $12.33 And we calculate the clean price as: 4 / 17 Clean price = Dirty price –Accrued interest = $968 –12.33 = $955.67 21. Accrued interest is the coupon payment for the period times the fraction of the period that has passed since the last coupon payment. Since we have a semiannual coupon bond, the coupon payment per six months is one-half of the annual coupon payment. There are two months until the next coupon payment, so four months have passed since the last coupon payment. The accrued interest for the bond is: Accrued interest = $68/2 × 4/6 = $22.67 And we calculate the dirty price as: Dirty price = Clean price + Accrued interest = $1,073 + 22.67 = $1,095.67 22. To find the number of years to maturity for the bond, we need to find the price of the bond. Since we already have the coupon rate, we can use the bond price equation, and solve for the number of years to maturity. We are given the current yield of the bond, so we can calculate the price as: Current yield = .0755 = $80/P 0 P 0 = $80/.0755 = $1,059.60 Now that we have the price of the bond, the bond price equation is: P = $1,059.60 = $80[(1 – (1/1.072) t ) / .072 ] + $1,000/1.072 t We can solve this equation for t as follows: $1,059.60(1.072) t = $1,111.11(1.072) t –1,111.11 + 1,000 111.11 = 51.51(1.072) t 2.1570 = 1.072 t t = log 2.1570 / log 1.072 = 11.06 11 years The bond has 11 years to maturity.31. The price of any bond (or financial instrument) is the PV of the future cash flows. Even though Bond M makes different coupons payments, to find the price of the bond, we just find the PV of the cash flows. The PV of the cash flows for Bond M is: P M = $1,100(PVIFA 3.5%,16 )(PVIF 3.5%,12 ) + $1,400(PVIFA 3.5%,12 )(PVIF 3.5%,28 ) + $20,000(PVIF 3.5%,40 ) P M = $19,018.78 Notice that for the coupon payments of $1,400, we found the PV A for the coupon payments, and then discounted the lump sum back to today. Bond N is a zero coupon bond with a $20,000 par value, therefore, the price of the bond is the PV of the par, or: P N = $20,000(PVIF 3.5%,40 ) = $5,051.45 CH8 4,18,20,22,24 4. Using the constant growth model, we find the price of the stock today is: P 0 = D 1 / (R – g) = $3.04 / (.11 – .038) = $42.22 5 / 17 18. The priceof a share of preferred stock is the dividend payment divided by the required return. We know the dividend payment in Year 20, so we can find the price of the stock in Year 19, one year before the first dividend payment. Doing so, we get: P 19 = $20.00 / .064 P 19 = $312.50 The price of the stock today is the PV of the stock price in the future, so the price today will be: P 0 = $312.50 / (1.064) 19 P 0 = $96.15 20. We can use the two-stage dividend growth model for this problem, which is: P 0 = [D 0 (1 + g 1 )/(R – g 1 )]{1 – [(1 + g 1 )/(1 + R)] T }+ [(1 + g 1 )/(1 + R)] T [D 0 (1 + g 2 )/(R –g 2 )] P 0 = [$1.25(1.28)/(.13 – .28)][1 –(1.28/1.13) 8 ] + [(1.28)/(1.13)] 8 [$1.25(1.06)/(.13 – .06)] P 0 = $69.55 22. We are asked to find the dividend yield and capital gains yield for each of the stocks. All of the stocks have a 15 percent required return, which is the sum of the dividend yield and the capital gains yield. To find the components of the total return, we need to find the stock price for each stock. Using this stock price and the dividend, we can calculate the dividend yield. The capital gains yield for the stock will be the total return (required return) minus the dividend yield. W: P 0 = D 0 (1 + g) / (R – g) = $4.50(1.10)/(.19 – .10) = $55.00 Dividend yield = D 1 /P 0 = $4.50(1.10)/$55.00 = .09 or 9% Capital gains yield = .19 – .09 = .10 or 10% X: P 0 = D 0 (1 + g) / (R – g) = $4.50/(.19 – 0) = $23.68 Dividend yield = D 1 /P 0 = $4.50/$23.68 = .19 or 19% Capital gains yield = .19 – .19 = 0% Y: P 0 = D 0 (1 + g) / (R – g) = $4.50(1 – .05)/(.19 + .05) = $17.81 Dividend yield = D 1 /P 0 = $4.50(0.95)/$17.81 = .24 or 24% Capital gains yield = .19 – .24 = –.05 or –5% Z: P 2 = D 2 (1 + g) / (R – g) = D 0 (1 + g 1 ) 2 (1 +g 2 )/(R – g 2 ) = $4.50(1.20) 2 (1.12)/(.19 – .12) = $103.68 P 0 = $4.50 (1.20) / (1.19) + $4.50(1.20) 2 / (1.19) 2 + $103.68 / (1.19) 2 = $82.33 Dividend yield = D 1 /P 0 = $4.50(1.20)/$82.33 = .066 or 6.6% Capital gains yield = .19 – .066 = .124 or 12.4% In all cases, the required return is 19%, but the return is distributed differently between current income and capital gains. High growth stocks have an appreciable capital gains component but a relatively small current income yield; conversely, mature, negative-growth stocks provide a high current income but also price depreciation over time. 24. Here we have a stock with supernormal growth, but the dividend growth changes every year for the first four years. We can find the price of the stock in Year 3 since the dividend growth rate is constant after the third dividend. The price of the stock in Year 3 will be the dividend in Year 4, divided by the required return minus the constant dividend growth rate. So, the price in Year 3 will be: 6 / 17 P 3 = $2.45(1.20)(1.15)(1.10)(1.05) / (.11 – .05) = $65.08 The price of the stock today will be the PV of the first three dividends, plus the PV of the stock price in Year 3, so: P 0 = $2.45(1.20)/(1.11) + $2.45(1.20)(1.15)/1.11 2 + $2.45(1.20)(1.15)(1.10)/1.11 3 + $65.08/1.11 3 P 0 = $55.70 CH9 3,4,6,9,15 3. Project A has cash flows of $19,000 in Year 1, so the cash flows are short by $21,000 of recapturing the initial investment, so the payback for Project A is: Payback = 1 + ($21,000 / $25,000) = 1.84 years Project B has cash flows of: Cash flows = $14,000 + 17,000 + 24,000 = $55,000 during this first three years. The cash flows are still short by $5,000 of recapturing the initial investment, so the payback for Project B is: B: Payback = 3 + ($5,000 / $270,000) = 3.019 years Using the payback criterion and a cutoff of 3 years, accept project A and reject project B. 4. When we use discounted payback, we need to find the value of all cash flows today. The value today of the project cash flows for the first four years is: Value today of Year 1 cash flow = $4,200/1.14 = $3,684.21 Value today of Year 2 cash flow = $5,300/1.14 2 = $4,078.18 Value today of Year 3 cash flow = $6,100/1.14 3 = $4,117.33 V alue today of Year 4 cash flow = $7,400/1.14 4 = $4,381.39 To find the discounted payback, we use these values to find the payback period. The discounted first year cash flow is $3,684.21, so the discounted payback for a $7,000 initial cost is: Discounted payback= 1 + ($7,000 – 3,684.21)/$4,078.18 = 1.81 years For an initial cost of $10,000, the discounted payback is: Discounted payback = 2 + ($10,000 –3,684.21 – 4,078.18)/$4,117.33 = 2.54 years Notice the calculation of discounted payback. We know the payback period is between two and three years, so we subtract the discounted values of the Year 1 and Year 2 cash flows from the initial cost. This is the numerator, which is the discounted amount we still need to make to recover our initial investment. We divide this amount by the discounted amount we will earn in Year 3 to get the fractional portion of the discounted payback. If the initial cost is $13,000, the discounted payback is: Discounted payback = 3 + ($13,000 – 3,684.21 – 4,078.18 – 4,117.33) / $4,381.39 = 3.26 years 7 / 17 6. Our definition of AAR is the average net income divided by the average book value. The average net income for this project is: Average net income = ($1,938,200 + 2,201,600 + 1,876,000 + 1,329,500) / 4 = $1,836,325 And the average book value is: Average book value = ($15,000,000 + 0) / 2 = $7,500,000 So, the AAR for this project is: AAR = Average net income / Average book value = $1,836,325 / $7,500,000 = .2448 or 24.48% 9. The NPV of a project is the PV of the outflows minus the PV of the inflows. Since the cash inflows are an annuity, the equation for the NPV of this project at an 8 percent required return is: NPV = –$138,000 + $28,500(PVIFA 8%, 9 ) = $40,036.31 At an 8 percent required return, the NPV is positive, so we would accept the project. The equation for the NPV of the project at a 20 percent required return is: NPV = –$138,000 + $28,500(PVIFA 20%, 9 ) = –$23,117.45 At a 20 percent required return, the NPV is negative, so we would reject the project. We would be indifferent to the project if the required return was equal to the IRR of the project, since at that required return the NPV is zero. The IRR of the project is: 0 = –$138,000 + $28,500(PVIFA IRR, 9 ) IRR = 14.59% 15. The profitability index is defined as the PV of the cash inflows divided by the PV of the cash outflows. The equation for the profitability index at a required return of 10 percent is: PI = [$7,300/1.1 + $6,900/1.1 2 + $5,700/1.1 3 ] / $14,000 = 1.187 The equation for the profitability index at a required return of 15 percent is: PI = [$7,300/1.15 + $6,900/1.15 2 + $5,700/1.15 3 ] / $14,000 = 1.094 The equation for the profitability index at a required return of 22 percent is: PI = [$7,300/1.22 + $6,900/1.22 2 + $5,700/1.22 3 ] / $14,000 = 0.983 8 / 17 We would accept the project if the required return were 10 percent or 15 percent since the PI is greater than one. We would reject the project if the required return were 22 percent since the PI。
Chapter 04 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Answer KeyMultiple Choice Questions1. An annuity stream of cash flow payments is a set of:A. level cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.B. level cash flows occurring each time period forever.C. increasing cash flows occurring each time period for a fixed length of time.D. increasing cash flows occurring each time period forever.E. arbitrary cash flows occurring each time period for no more than 10 years.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITYType: DEFINITIONS2. Annuities where the payments occur at the end of each time period are called _____, whereas _____ refer to annuity streams with payments occurring at the beginning of each time period.A. ordinary annuities; early annuitiesB. late annuities; straight annuitiesC. straight annuities; late annuitiesD. annuities due; ordinary annuitiesE. ordinary annuities; annuities dueDifficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITIES DUEType: DEFINITIONS3. An annuity stream where the payments occur forever is called a(n):A. annuity due.B. indemnity.C. perpetuity.D. amortized cash flow stream.E. amortization table.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PERPETUITYType: DEFINITIONS4. The interest rate expressed in terms of the interest payment made each period is called the _____ rate.A. stated annual interestB. compound annual interestC. effective annual interestD. periodic interestE. daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: STATED INTEREST RATESType: DEFINITIONS5. The interest rate expressed as if it were compounded once per year is called the _____ rate.A. stated interestB. compound interestC. effective annualD. periodic interestE. daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATEType: DEFINITIONS6. The interest rate charged per period multiplied by the number of periods per year is called the _____ rate.A. effective annualB. annual percentageC. periodic interestD. compound interestE. daily interestDifficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATEType: DEFINITIONS7. Paying off long-term debt by making installment payments is called:A. foreclosing on the debt.B. amortizing the debt.C. funding the debt.D. calling the debt.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: AMORTIZATIONType: DEFINITIONS8. You are comparing two annuities which offer monthly payments for ten years. Both annuities are identical with the exception of the payment dates. Annuity A pays on the first of each month while annuity B pays on the last day of each month. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning these two annuities?A. Both annuities are of equal value today.B. Annuity B is an annuity due.C. Annuity A has a higher future value than annuity B.D. Annuity B has a higher present value than annuity A.E. Both annuities have the same future value as of ten years from today.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: CONCEPTS9. You are comparing two investment options. The cost to invest in either option is the same today. Both options will provide you with $20,000 of income. Option A pays five annual payments starting with $8,000 the first year followed by four annual payments of $3,000 each. Option B pays five annual payments of $4,000 each. Which one of the following statements is correct given these two investment options?A. Both options are of equal value given that they both provide $20,000 of income.B. Option A is the better choice of the two given any positive rate of return.C. Option B has a higher present value than option A given a positive rate of return.D. Option B has a lower future value at year 5 than option A given a zero rate of return.E. Option A is preferable because it is an annuity due.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND PRESENT VALUEType: CONCEPTS10. You are considering two projects with the following cash flows:Which of the following statements are true concerning these two projects?I. Both projects have the same future value at the end of year 4, given a positive rate of return. II. Both projects have the same future value given a zero rate of return.III. Both projects have the same future value at any point in time, given a positive rate of return. IV. Project A has a higher future value than project B, given a positive rate of return.A. II onlyB. IV onlyC. I and III onlyD. II and IV onlyE. I, II, and III onlyDifficulty level: MediumTopic: UNEVEN CASH FLOWS AND FUTURE VALUEType: CONCEPTS11. A perpetuity differs from an annuity because:A. perpetuity payments vary with the rate of inflation.B. perpetuity payments vary with the market rate of interest.C. perpetuity payments are variable while annuity payments are constant.D. perpetuity payments never cease.E. annuity payments never cease.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PERPETUITY VERSUS ANNUITYType: CONCEPTS12. Which one of the following statements concerning the annual percentage rate is correct?A. The annual percentage rate considers interest on interest.B. The rate of interest you actually pay on a loan is called the annual percentage rate.C. The effective annual rate is lower than the annual percentage rate when an interest rate is compounded quarterly.D. When firms advertise the annual percentage rate they are violating U.S. truth-in-lending laws.E. The annual percentage rate equals the effective annual rate when the rate on an account is designated as simple interest.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATEType: CONCEPTS13. Which one of the following statements concerning interest rates is correct?A. The stated rate is the same as the effective annual rate.B. An effective annual rate is the rate that applies if interest were charged annually.C. The annual percentage rate increases as the number of compounding periods per year increases.D. Banks prefer more frequent compounding on their savings accounts.E. For any positive rate of interest, the effective annual rate will always exceed the annual percentage rate.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: INTEREST RATESType: CONCEPTS14. Which of the following statements concerning the effective annual rate are correct?I. When making financial decisions, you should compare effective annual rates rather than annual percentage rates.II. The more frequently interest is compounded, the higher the effective annual rate.III. A quoted rate of 6% compounded continuously has a higher effective annual rate than if the rate were compounded daily.IV. When borrowing and choosing which loan to accept, you should select the offer with the highest effective annual rate.A. I and II onlyB. I and IV onlyC. I, II, and III onlyD. II, III, and IV onlyE. I, II, III, and IVDifficulty level: MediumTopic: EFFECTIVE ANNUAL RATEType: CONCEPTS15. The highest effective annual rate that can be derived from an annual percentage rate of 9% is computed as:A. .09e - 1.B. e.09 ⨯ q.C. e ⨯ (1 + .09).D. e.09 - 1.E. (1 + .09)q.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: CONTINUOUS COMPOUNDINGType: CONCEPTS16. The time value of money concept can be defined as:A. the relationship between the supply and demand of money.B. the relationship between money spent versus money received.C. the relationship between a dollar to be received in the future and a dollar today.D. the relationship between interest rate stated and amount paid.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: TIME VALUEType: CONCEPTS17. Discounting cash flows involves:A. discounting only those cash flows that occur at least 10 years in the future.B. estimating only the cash flows that occur in the first 4 years of a project.C. multiplying expected future cash flows by the cost of capital.D. discounting all expected future cash flows to reflect the time value of money.E. taking the cash discount offered on trade merchandise.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: CASH FLOWSType: CONCEPTS18. Compound interest:A. allows for the reinvestment of interest payments.B. does not allow for the reinvestment of interest payments.C. is the same as simple interest.D. provides a value that is less than simple interest.E. Both A and D.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: INTERESTType: CONCEPTS19. An annuity:A. is a debt instrument that pays no interest.B. is a stream of payments that varies with current market interest rates.C. is a level stream of equal payments through time.D. has no value.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ANNUITYType: CONCEPTS20. The stated rate of interest is 10%. Which form of compounding will give the highest effective rate of interest?A. annual compoundingB. monthly compoundingC. daily compoundingD. continuous compoundingE. It is impossible to tell without knowing the term of the loan.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: COMPOUNDINGType: CONCEPTS21. The present value of future cash flows minus initial cost is called:A. the future value of the project.B. the net present value of the project.C. the equivalent sum of the investment.D. the initial investment risk equivalent value.E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRESENT VALUEType: CONCEPTS22. Find the present value of $5,325 to be received in one period if the rate is 6.5%.A. $5,000.00B. $5,023.58C. $5,644.50D. $5,671.13E. None of the above.Difficulty level: EasyTopic: PRESENT VALUE - SINGLE SUMType: PROBLEMS23. If you have a choice to earn simple interest on $10,000 for three years at 8% or annually compounded interest at 7.5% for three years which one will pay more and by how much?A. Simple interest by $50.00B. Compound interest by $22.97C. Compound interest by $150.75D. Compound interest by $150.00E. None of the above.Simple Interest = $10,000 (.08)(3) = $2,400;Compound Interest = $10,000((1.075)3 - 1) = $2,422.97;Difference = $2,422.97 - $2,400 = $22.97Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SIMPLE & COMPOUND INTERESTType: PROBLEMS24. Bradley Snapp has deposited $7,000 in a guaranteed investment account with a promised rate of 6% compounded annually. He plans to leave it there for 4 full years when he will make a down payment on a car after graduation. How much of a down payment will he be able to make?A. $1,960.00B. $2,175.57C. $8,960.00D. $8,837.34E. $9,175.57$7,000 (1.06)4 = $8,837.34Difficulty level: EasyTopic: FUTURE VALUE - SINGLE SUMType: PROBLEMS25. Your parents are giving you $100 a month for four years while you are in college. At a 6% discount rate, what are these payments worth to you when you first start college?A. $3,797.40B. $4,167.09C. $4,198.79D. $4,258.03E. $4,279.32Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS26. You just won the lottery! As your prize you will receive $1,200 a month for 100 months. If you can earn 8% on your money, what is this prize worth to you today?A. $87,003.69B. $87,380.23C. $87,962.77D. $88,104.26E. $90,723.76Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS27. Todd is able to pay $160 a month for five years for a car. If the interest rate is 4.9%, how much can Todd afford to borrow to buy a car?A. $6,961.36B. $8,499.13C. $8,533.84D. $8,686.82E. $9,588.05Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS28. You are the beneficiary of a life insurance policy. The insurance company informs you that you have two options for receiving the insurance proceeds. You can receive a lump sum of $50,000 today or receive payments of $641 a month for ten years. You can earn 6.5% on your money. Which option should you take and why?A. You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,451.91 today.B. You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,523.74 today.C. You should accept the payments because they are worth $56,737.08 today.D. You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47,757.69 today.E. You should accept the $50,000 because the payments are only worth $47,808.17 today.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS29. Your employer contributes $25 a week to your retirement plan. Assume that you work for your employer for another twenty years and that the applicable discount rate is 5%. Given these assumptions, what is this employee benefit worth to you today?A. $13,144.43B. $15,920.55C. $16,430.54D. $16,446.34E. $16,519.02Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS30. You have a sub-contracting job with a local manufacturing firm. Your agreement calls for annual payments of $50,000 for the next five years. At a discount rate of 12%, what is this job worth to you today?A. $180,238.81B. $201,867.47C. $210,618.19D. $223,162.58E. $224,267.10Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS31. The Ajax Co. just decided to save $1,500 a month for the next five years as a safety net for recessionary periods. The money will be set aside in a separate savings account which pays 3.25% interest compounded monthly. It deposits the first $1,500 today. If the company had wanted to deposit an equivalent lump sum today, how much would it have had to deposit?A. $82,964.59B. $83,189.29C. $83,428.87D. $83,687.23E. $84,998.01Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS32. You need some money today and the only friend you have that has any is your ‘miserly' friend. He agrees to loan you the money you need, if you make payments of $20 a month for the next six months. In keeping with his reputation, he requires that the first payment be paid today. He also charges you 1.5% interest per month. How much money are you borrowing?A. $113.94B. $115.65C. $119.34D. $119.63E. $119.96Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS33. You buy an annuity which will pay you $12,000 a year for ten years. The payments are paid on the first day of each year. What is the value of this annuity today at a 7% discount rate?A. $84,282.98B. $87,138.04C. $90,182.79D. $96,191.91E. $116,916.21Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS34. You are scheduled to receive annual payments of $10,000 for each of the next 25 years. Your discount rate is 8.5%. What is the difference in the present value if you receive these payments at the beginning of each year rather than at the end of each year?A. $8,699B. $9,217C. $9,706D. $10,000E. $10,850Difference = $111,040.97 - $102,341.91 = $8,699.06 = $8,699 (rounded)Note: The difference = .085 $102,341.91 = $8,699.06Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS35. You are comparing two annuities with equal present values. The applicable discount rate is 7.5%. One annuity pays $5,000 on the first day of each year for twenty years. How much does the second annuity pay each year for twenty years if it pays at the end of each year?A. $4,651B. $5,075C. $5,000D. $5,375E. $5,405Because each payment is received one year later, then the cash flow has to equal: $5,000 (1 + .075) = $5,375Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS36. Martha receives $100 on the first of each month. Stewart receives $100 on the last day of each month. Both Martha and Stewart will receive payments for five years. At an 8% discount rate, what is the difference in the present value of these two sets of payments?A. $32.88B. $40.00C. $99.01D. $108.00E. $112.50Difference = $4,964.72 - $4,931.84 = $32.88Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY VERSUS ANNUITY DUEType: PROBLEMS37. What is the future value of $1,000 a year for five years at a 6% rate of interest?A. $4,212.36B. $5,075.69C. $5,637.09D. $6,001.38E. $6,801.91Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS38. What is the future value of $2,400 a year for three years at an 8% rate of interest?A. $6,185.03B. $6,847.26C. $7,134.16D. $7,791.36E. $8,414.67Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS39. Janet plans on saving $3,000 a year and expects to earn 8.5%. How much will Janet have at the end of twenty-five years if she earns what she expects?A. $219,317.82B. $230,702.57C. $236,003.38D. $244,868.92E. $256,063.66Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS40. Toni adds $3,000 to her savings on the first day of each year. Tim adds $3,000 to his savings on the last day of each year. They both earn a 9% rate of return. What is the difference in their savings account balances at the end of thirty years?A. $35,822.73B. $36,803.03C. $38,911.21D. $39,803.04E. $40,115.31Difference = $445,725.65 - $408,922.62 = $36,803.03Note: Difference = $408,922.62 .09 = $36,803.03Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE VERSUS ORDINARY ANNUITYType: PROBLEMS41. You borrow $5,600 to buy a car. The terms of the loan call for monthly payments for four years at a 5.9% rate of interest. What is the amount of each payment?A. $103.22B. $103.73C. $130.62D. $131.26E. $133.04Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTSType: PROBLEMS42. You borrow $149,000 to buy a house. The mortgage rate is 7.5% and the loan period is 30 years. Payments are made monthly. If you pay for the house according to the loan agreement, how much total interest will you pay?A. $138,086B. $218,161C. $226,059D. $287,086E. $375,059Total interest = ($1,041.83 ⨯ 30 ⨯ 12) - $149,000 = $226,058.80 = $226,059 (rounded) Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND COST OF INTERESTType: PROBLEMS43. The Great Giant Corp. has a management contract with its newly hired president. The contract requires a lump sum payment of $25 million be paid to the president upon the completion of her first ten years of service. The company wants to set aside an equal amount of funds each year to cover this anticipated cash outflow. The company can earn 6.5% on these funds. How much must the company set aside each year for this purpose?A. $1,775,042.93B. $1,798,346.17C. $1,801,033.67D. $1,852,617.25E. $1,938,018.22Difficulty level: EasyTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS44. You retire at age 60 and expect to live another 27 years. On the day you retire, you have $464,900 in your retirement savings account. You are conservative and expect to earn 4.5% on your money during your retirement. How much can you withdraw from your retirement savings each month if you plan to die on the day you spend your last penny?A. $2,001.96B. $2,092.05C. $2,398.17D. $2,472.00E. $2,481.27Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS45. The McDonald Group purchased a piece of property for $1.2 million. It paid a down payment of 20% in cash and financed the balance. The loan terms require monthly payments for 15 years at an annual percentage rate of 7.75% compounded monthly. What is the amount of each mortgage payment?A. $7,440.01B. $8,978.26C. $9,036.25D. $9,399.18E. $9,413.67Amount financed = $1,200,000 (1 - .2) = $960,000Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS46. You estimate that you will have $24,500 in student loans by the time you graduate. The interest rate is 6.5%. If you want to have this debt paid in full within five years, how much must you pay each month?A. $471.30B. $473.65C. $476.79D. $479.37E. $480.40Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS47. You are buying a previously owned car today at a price of $6,890. You are paying $500 down in cash and financing the balance for 36 months at 7.9%. What is the amount of each loan payment?A. $198.64B. $199.94C. $202.02D. $214.78E. $215.09Amount financed = $6,890 - $500 = $6,390Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS48. The Good Life Insurance Co. wants to sell you an annuity which will pay you $500 per quarter for 25 years. You want to earn a minimum rate of return of 5.5%. What is the most you are willing to pay as a lump sum today to buy this annuity?A. $26,988.16B. $27,082.94C. $27,455.33D. $28,450.67E. $28,806.30Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS49. Your car dealer is willing to lease you a new car for $299 a month for 60 months. Payments are due on the first day of each month starting with the day you sign the lease contract. If your cost of money is 4.9%, what is the current value of the lease?A. $15,882.75B. $15,906.14C. $15,947.61D. $16,235.42E. $16,289.54Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS50. Your great-aunt left you an inheritance in the form of a trust. The trust agreement states that you are to receive $2,500 on the first day of each year, starting immediately and continuing for fifty years. What is the value of this inheritance today if the applicable discount rate is 6.35%?A. $36,811.30B. $37,557.52C. $39,204.04D. $39,942.42E. $40,006.09Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS51. Beatrice invests $1,000 in an account that pays 4% simple interest. How much more could she have earned over a five-year period if the interest had compounded annually?A. $15.45B. $15.97C. $16.65D. $17.09E. $21.67Ending value at 4% simple interest = $1,000 + ($1,000 ⨯ .04 ⨯ 5) = $1,200.00; Ending value at 4% compounded annually = $1,000 ⨯ (1 +.04)5 = $1,216.65;Difference = $1,216.65 - $1,200.00 = $16.65Difficulty level: EasyTopic: SIMPLE VERSUS COMPOUND INTERESTType: PROBLEMS52. Your firm wants to save $250,000 to buy some new equipment three years from now. The plan is to set aside an equal amount of money on the first day of each year starting today. The firm can earn a 4.7% rate of return. How much does the firm have to save each year to achieve its goal?A. $75,966.14B. $76,896.16C. $78,004.67D. $81.414.14E. $83,333.33Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS53. Today is January 1. Starting today, Sam is going to contribute $140 on the first of each month to his retirement account. His employer contributes an additional 50% of the amount contributed by Sam. If both Sam and his employer continue to do this and Sam can earn a monthly rate of ½ of 1 percent, how much will he have in his retirement account 35 years from now?A. $199,45.944B. $200,456.74C. $249,981.21D. $299,189.16E. $300,685.11Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS54. You are considering an annuity which costs $100,000 today. The annuity pays $6,000 a year. The rate of return is 4.5%. What is the length of the annuity time period?A. 24.96 yearsB. 29.48 yearsC. 31.49 yearsD. 33.08 yearsE. 38.00 yearsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS55. Today, you signed loan papers agreeing to borrow $4,954.85 at 9% compounded monthly. The loan payment is $143.84 a month. How many loan payments must you make before the loan is paid in full?A. 29.89B. 36.00C. 38.88D. 40.00E. 41.03Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS56. Winston Enterprises would like to buy some additional land and build a new factory. The anticipated total cost is $136 million. The owner of the firm is quite conservative and will only do this when the company has sufficient funds to pay cash for the entire expansion project. Management has decided to save $450,000 a month for this purpose. The firm earns 6% compounded monthly on the funds it saves. How long does the company have to wait before expanding its operations?A. 184.61 monthsB. 199.97 monthsC. 234.34 monthsD. 284.61 monthsE. 299.97 monthsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY TIME PERIODS AND FUTURE VALUEType: PROBLEMS57. Today, you are retiring. You have a total of $413,926 in your retirement savings and have the funds invested such that you expect to earn an average of 3%, compounded monthly, on this money throughout your retirement years. You want to withdraw $2,500 at the beginning of every month, starting today. How long will it be until you run out of money?A. 185.00 monthsB. 213.29 monthsC. 227.08 monthsD. 236.84 monthsE. 249.69 monthsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE TIME PERIODS AND PRESENT VALUEType: PROBLEMS58. The Bad Guys Co. is notoriously known as a slow-payer. It currently needs to borrow $25,000 and only one company will even deal with Bad Guys. The terms of the loan call for daily payments of $30.76. The first payment is due today. The interest rate is 21% compounded daily. What is the time period of this loan?A. 2.88 yearsB. 2.94 yearsC. 3.00 yearsD. 3.13 yearsE. 3.25 yearsDifficulty level: MediumTopic: ANNUITY DUE TIME PERIODSType: PROBLEMS59. The Robertson Firm is considering a project which costs $123,900 to undertake. The project will yield cash flows of $4,894.35 monthly for 30 months. What is the rate of return on this project?A. 12.53%B. 13.44%C. 13.59%D. 14.02%E. 14.59%This can not be solved directly, so it's easiest to just use the calculator method to get an answer. You can then use the calculator answer as the rate in the formula just to verify that your answer is correct.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY INTEREST RATEType: PROBLEMS60. Your insurance agent is trying to sell you an annuity that costs $100,000 today. By buying this annuity, your agent promises that you will receive payments of $384.40 a month for the next 40 years. What is the rate of return on this investment?A. 3.45%B. 3.47%C. 3.50%D. 3.52%E. 3.55%This can not be solved directly, so it's easiest to just use the calculator method to get an answer. You can then use the calculator answer as the rate in the formula just to verify that you answer is correct.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY INTEREST RATEType: PROBLEMS61. You have been investing $120 a month for the last 15 years. Today, your investment account is worth $47,341.19. What is your average rate of return on your investments?A. 9.34%B. 9.37%C. 9.40%D. 9.42%E. 9.46%This can not be solved directly, so it's easiest to just use the calculator method to get an answer. You can then use the calculator answer as the rate in the formula just to verify that you answer is correct.Difficulty level: MediumTopic: ORDINARY ANNUITY INTEREST RATEType: PROBLEMS。