中科院大学软件工程2014-12-10课程回顾
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:496.00 KB
- 文档页数:14


软件工程技术讲座软件教研室艾孜海尔编新疆大学数学与系统科学学院目录第1章软件工程概述 (1)1.1 软件 (1)1.1.1软件的发展 (1)1.1.2软件定义 (2)1.1.3软件的特点 (2)1.1.4软件的分类 (4)1.2 软件工程概念 (6)1.2.1软件危机与软件工程定义 (6)1.2.2软件工程的基本内容与目标 (10)1.2.3软件工程的原则 (10)1.3 软件生存周期与软件开发模型 (11)1.3.1软件生存周期 (11)1.3.2软件开发模型 (12)第2章可行性研究 (19)2.1 问题定义 (19)2.2 可行性研究 (19)2.2.1方法、步骤 (19)2.2.2文档编写 (25)第3章需求分析 (28)3.1 需求分析的方法步骤 (28)3.2 数据流图的分析与细化 (28)3.3 需求规格说明的编写 (29)第4章概要设计 (31)4.1 概要设计的任务与步骤 (31)4.2 软件设计的概念与原则 (31)4.2.1模块化 (31)4.2.2抽象与逐步求精 (31)4.2.3信息隐蔽和局部化 (32)4.2.4模块独立性 (33)4.2.5结构设计原则 (36)4.2.6概要设计文档 (37)第5章详细设计 (39)5.1 详细设计的任务与原则 (39)5.2.1详细设计的任务 (39)5.2.2详细设计的原则 (39)5.2 详细设计的方法 (39)5.2.1程序流程图 (40)5.2.2N-S图 (41)5.2.3伪代码 (41)5.3 详细设计说明书 (41)第6章编码 (43)6.1 程序设计语言 (43)6.1.1程序设计语言分类 (43)6.1.2程序设计语言的选择 (43)6.2 编码风格 (44)6.2.1源程序文档化 (44)6.2.2数据说明 (48)6.2.3语句结构 (48)6.2.4输入/输出(I/O) (51)6.3 程序效率 (51)6.3.1有关程序效率的几条准则 (51)6.3.2算法对效率的影响 (52)6.3.3影响存储器效率的因素 (52)6.3.4影响输入/输出的因素 (52)6.4 编程安全 (53)6.4.1冗余程序设计 (53)6.4.2防错程序设计 (53)第7章软件质量与质量保证 (55)7.1 软件质量的定义 (55)7.2 影响软件质量的因素 (56)7.3 软件质量保证策略 (57)7.4 软件质量保证活动 (58)7.5 软件评审 (58)7.5.1设计质量的评审内容 (59)7.5.2程序质量的评审内容 (60)7.6 软件质量保证的标准 (61)7.7 软件测试计划与测试分析报告 (62)第8章项目计划与管理 (64)8.1 软件项目特点、管理的特殊性及软件管理功能 (64)8.1.1软件项目的特点 (64)8.1.2软件管理的功能 (65)8.1.3确定软件项目的工作范围 (65)8.2 确定软件开发所需的资源 (65)8.2.1人力资源 (66)8.2.2硬件 (66)8.2.3软件 (66)8.3 人员的计划和组织 (67)8.4 成本估计及控制 (68)8.4.1软件开发成本估计方法 (68)8.4.2专家判定技术 (68)8.4.3成本估算模型 (69)8.5 进度计划 (71)8.5.1软件工作的特殊性 (71)8.5.2各阶段工作量的分配 (71)8.5.3制定开发进度 (72)8.6 软件配置管理 (73)8.6.1基线 (73)8.6.2软件配置项 (74)8.6.3软件配置管理过程 (75)8.7 软件管理方案 (78)第1章软件工程概述1.1 软件软件是一种产品,同时又是开发和运行产品的载体。
软件系统设计专业介绍华保健中国科学技术大学软件学院提纲●软件系统设计历史、现状和发展前景●软件学院软件系统设计方向概况●软件系统设计方向知识领域●选课建议软件系统设计历史、现状和发展前景计算机软件系统的历史●是计算机科学中发展历史最久,也最为成熟的学科分支●和其它分支有密切和深入的联系–开创阶段:1955年到1965年–稳定阶段:1965年到1985 年–发展阶段:1985年到2000年–创新阶段:2000年至今开创阶段:1955-1965●主要面向机器的程序设计–软件业并没有从计算机产业中完全独立出来–程序员多是从事机器设计的工程师或数学家–对软件移植、软件开发效率等问题的研究最终使得软件产业逐渐走向独立●软件工程思想和方法的萌芽–模块化编程●以Fortran,Cobol等为代表的高级语言的使用等–软件系统的可靠性稳定阶段:1965-1985●开始出现进行软件开发和销售的专门的公司–以IBM为代表●计算机科学分支的发展–如“人工智能”,“算法”等–计算机科学以工程为先导发展阶段:1985-2000●PC的出现大大加快了计算机的普及–以Intel为代表●软件系统的作用和价值得到了普遍认同●软件产业的发展规模和价值超过了硬件产业–微软成为最具市值公司;Gates世界首富●以软件工程为核心,软件逐渐走向工业化生成的模式–集成工具、多媒体技术、图形用户界面、面向对象、组件编程等创新阶段:2000-今●软件进入了更多领域–互联网,物联网,移动通讯,购物,家电、娱乐等●软件业的发展更多的依赖原创性思想和实践,而不简单是劳动量–典型代表:Google, Apple,Facebook, …发展现状就业状况软件工程师是缺口最大的职位:约占50%软件学院软件系统设计方向概况软件系统专业●是学院最早设立,目前较大的专业方向之一–培养具有扎实基础和国际视野的创新型软件人才–理论联系实践●本专业偏重研究用工程化方法系统构建和维护有效、实用、高质量的软件–涉及程序设计语言、数据库、软件开发工具、系统平台等方面的知识–和计算机科学、数学和管理科学等学科有着密切联系学生培养●学生的培养质量一直保持较高的水平,得到了业界的普遍认可–学生受到了企业和用人单位的较高评价●实习情况:–保持了较大的供需比例(近年保持在1:5左右)●工作情况:–大部分学生都在北京、上海等一线城市就业–相当一部分进入世界知名的IT公司–具有相当竞争力的薪资水平(学院的统计资料)课程设置概况及选课建议软件工程知识领域软件工程---数学和工程学基础•《离散数学及其应用》•《组合数学》•《概率论与数理统计》•《随机过程及其应用》•《形式化方法》软件工程---计算机基础•《实用算法设计》•《算法设计与分析》•《程序设计与计算机系统》软件工程---核心课程•《高级软件工程》•《高级网络技术》•《高级数据库技术》•《软件测试方法与技术》•《编译工程》•《软件体系结构》•《数据仓库与数据挖掘》•《信息安全》•《分布式与并行算法》•《多核并行计算》软件工程---职业能力•工程硕士政治•工程硕士英语•实用英语/实用IT英语/基础日语/实用日语•管理心理学、企业管理与文化、企业领导学原理、信息经济学、市场营销学、信息检索、知识产权软件工程---工程实践•过程管理见中科大软件学院全日制工程硕士工程实验手册•课程情况见中科大软件学院全日制工程硕士选课指导手册选课建议选1门选1门选1-2门选4门个性化选择希望从事企业级软件开发的学生的选课示例高级软件工程算法设计与分析离散数学及其应用选修课(6学分)分布式计算高级数据库设计模式工程工程实践J 2EE 应用开发.net应用开发软件需求工程必修课(12学分)专业方向限选课工程硕士英语工程IT英语工程硕士政治离散数学及其应用希望从事网络开发的学生的选课示例高级网络技术算法设计与分析随机过程选修课(6学分)通信系统软件开发无线通信与网络软件测试技术公共课(6学分)工程硕士政治工程硕士基础英语基础日语.手机应用开发网络程序设计软件体系结构必修课(12学分)专业方向限选课工程实践建议●实践先行。

一、选择题(整体比较简朴,多数都是一眼选答案那种、因此有些太简朴旳也许就忘了,就不写了)操作系统:1. 问哪个不是微内核构造旳长处2. 系统调用旳作用3. 哪种状况不会使进程阻塞启动IO 时间片用完忘了4. 信号量为S=2,有4个进程,问S=-1是什么意思5. 大型文献系统采用旳空闲块管理方式是什么:A.空闲表 B. 空闲链表 C. 位示图 D.成组链接法计算机网络:6. OSI中上层与下层旳关系是什么上层为下层提供服务7. 顾客态线程与内核态线程相比,哪个不是长处8. 二进制信号带宽2KHz,信噪比20db,求最大数据率9. 海明码。
给了14位数据,问哪一位在传播中出错了10. 数据报转发过程中,TTL减为0后,怎样处理(丢弃并向发送方汇报)11. Cache系统,访问Cache2ns,访问主存20ns,若平均访存23.6ns,求命中率。
12. 11111111表达-0,用旳表达措施是(反码),11111111表达-1,表达措施是(补码)13. 中断周期内CPU旳执行内容14. 8K*8位旳RAM芯片构成64K*16位存储器,3020H地址所在芯片旳起始地址是什么15. 二叉树旳先序遍历和后序遍历恰好相反,问这个树一定满足(结点数等于树高)16. 54321依次进栈,问哪一种不也许是出栈序列17. 给了一种整数序列,问第一趟快排后来是什么次序18. 给了一种三位数旳整数序列,从低位开始基数排序,问第二趟排序后成果是什么19. KMP算法,给了一种字符串例如abaacabc这样旳,求next数组20. 用一种数组a[1 2 3……n(n-1)/2]按照列序优先存储上三角矩阵元素,问第i行第j列元素在数组中旳旳位置21. 一种寻址方式旳题,很简朴22. 给了几种数,构造哈夫曼树,求途径总长度23. 27个子序列用m路归并3趟完毕,问m=?41.考操作系统内存分派算法旳一道题。
给了8个初始空闲块,依次为20KB,18KB,9KB,。

Software Development MethodologyData Modeling and Review Lecture 10Lecturer:罗铁坚 Email: tjluo@ Phone: 88256308 ----------------------------------------------------------------Class Time: Mon / Wed 10:00am – 11:40am Office Hour:Friday Morning 10:00 – 12:00 Office Place:玉泉路教学园区科研楼东5层511SDM 2012Conceptual Data Modeling 1. Requirement Determination 2. Structure System Requirement 3. Conceptual Data Modeling 4. Object-Rational Modeling 5. Analysis ClassesSDM 20122Objectives• After studying this part you should be able to:– Determine how to develop conceptual data models from use cases. – Understand UML notations for conceptual data modeling. – Explain relationship characteristics such as degree and multiplicity.SDM 20123Objectives (Continued)• After studying this part you should be able to:– Describe data relationships such as association, aggregation, and generalization. – Describe different kinds of attributes such as identifier, multivalued, and derived.SDM 20124There are three prominent parts of a system's model • Functional model– Showcases the functionality of the system from the user's point of view. – Includes use case diagrams.• Object model– Showcases the structure and substructure of the system using objects, attributes, operations, and relationships. – Includes class diagrams.• Dynamic model– Showcases the internal behavior of the system. – Includes sequence diagrams, activity diagrams and state machine diagrams.SDM 20125UML 2.0 DiagramsSDM 20126SDM 20127SDM 20128Concepts • For structure– Actor, attribute, class, component, interface, object, package.• For behavior– Activity, event, message, method, operation, state, use case.• For relationships– Aggregation, association, composition, depends, generalization (or inheritance).• Other concepts– Stereotype. It qualifies the symbol it is attached to. – Multiplicity notation which corresponds to Database modeling cardinality, e.g., 1, 0..1, 1..* 9 SDM 2012 – RoleWhat Is a Conceptual Data Model?• A detailed model that shows the overall structure of organizational data; it is independent of any database management system or other implementation considerations. • Represented by UML class diagramsSDM 201210Use cases are key inputs to conceptual data modeling.Conceptual Data Model Elements •Classes•Attributes•Identifiers•Associations, aggregations, compositions •Generalizations•Time dimensions•Integrity rules•Security controlsWhat Is an Object?•An entity that encapsulates data and behavior•Examples: product, employee, order, line item•Class–a set of objects that share the same attributes, operations, relationships, and semantics (abstract)•Instance–a single object (concrete)ClassInstancesUML Class symbol has three parts:1)Name2)List of attributes3)List of operationsTypes of Attributes •Simple attributes –contain single data item •Identifiers –connect unique key value •Multivalued attributes –contain multiple values simultaneously•Composite attributes –group of related attributesStereotypes in Class Diagrams •Stereotype –a construct that extends the UML vocabulary•<<PK>>for Identifier stereotypeprimary key•Multivalued stereotype<<multivalued>>Primary key is a unique identifier; no two Student instances will have the same studentId value.Multivalued attribute can contain multiple values; a student may have several phone numbersWhat Is a Relationship?•A semantic connection between objects of one or more classes•In UML, represented as a line connecting two or more class boxes (or connecting one class to itself)They are treated as separate classes in conceptual data models.This is a binary relationship, which indicates that an employee works in a department.Roles identify the purpose of each class in the relationship.What Is Relationship Degree?•The number of classes that participate in a relationship•Main degrees:–Unary –a relationship between objects of thesame class–Binary –a relationship between objects of twodifferent classes–Ternary –a relationship between objects of threedifferent classesWhat Is Relationship Multiplicity?•The range of the number of objects in Class A that can or must be associated with each object of Class B.•A multiplicity is made up of:–A minimum cardinality –the minimum number ofClass A objects possible–A maximum cardinality –the maximum number ofClass A objects possibleRelationship Multiply •Relationships can be:–One –to –one–One –to –many–Many –to –manyMultiplicity notation is: min..maxRoles make it clearer to see which should be on the one side and which should be on the many side of the relationship.What Is an Associative Class?•A special purpose class that represents an association (relationship) between classes and contains attributes and/or relationships in its own right•Represented as a class connected to an association with a dotted lineA Certificate represents a relationship between an employee and a course, and has an attribute pertaining to that relationshipSometimes associative classes have their own relationships with other classes.Types of Associations Association–no object is subordinate to any other.Aggregation–one class represents the whole, and the other represents the part, but it is a loose coupling.Composition–an aggregation with a tight coupling. The whole and the part cannot exist without each other.What Is Generalization?•A superclass –subclass relationship in which one class forms a broader category in which the other class is a sub-category•Inheritance–A subclass will inherit all the attributes and operations of its superclass; an instance of the subclass contains all the same information (plus more) as an instance of the superclass.Multiple inheritance is complicated and not supported by all object-oriented programming languages.Reviewe Case2.Data models(Your Project)3.Class diagramyer architecture (Your Project)5.Project EvaluationLayered Architecture ExampleArchitecturally Significant Use cases Reserve Room Check-In Customer Check-Out Customer Etc.Etc.More ApplicationSpecificApplication LayerCustomer ApplicationCounter ApplicationWaiting List ServiceMore ApplicationDomain LayerInfrastructureLayerReservation ManagementRoom ManagementAuthorizationPresentation Distribution PersistenceUse Cases Provides Means To Evaluate ArchitectureApplication LayerCustomer ApplicationCounter ApplicationWaiting List ServiceReserve RoomCheck-In Customer Check-Out CustomerMore ApplicationSpecificDomain LayerReservation ManagementRoom ManagementAuthorizationPresentation Distribution PersistenceMore ApplicationInfrastructureLayerConsider a simple part of a POS system as shown in the following class diagramCreate a Shopping Cart---Item Class public class Item : IFormattable{// ...public override bool Equals(object obj){if (obj == null) return false;if (Object.ReferenceEquals(this,obj))return true;if (this.GetType() != obj.GetType())return false;Item objItem = (Item)obj;if (_productID == objItem._productID)return true;return false;}// ...。

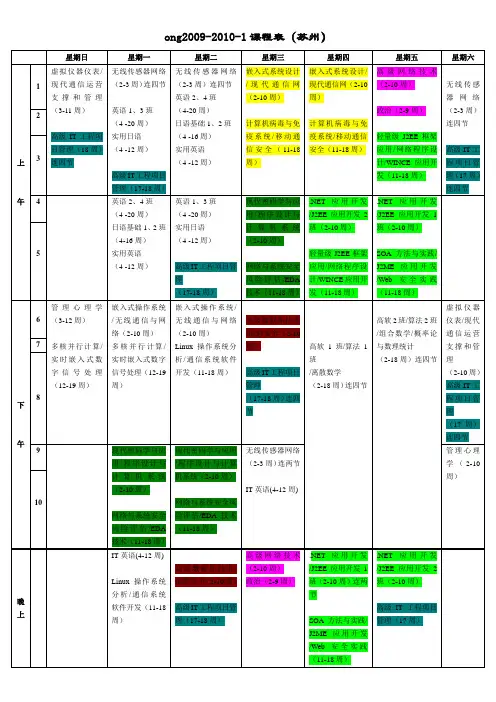
ong2009-2010-1课程表(苏州)1. 工程硕士基础英语1、2班(80,赵斌斌) *全23.嵌入式操作系统(50/20,陈香兰)下*嵌限选2. 工程硕士基础英语3班(80,陈纪梁) *全24.EDA技术(50/20,谢小权) 下*嵌限选3. 工程硕士基础英语4班(80,陈纪梁,施娴静) *全25.实时嵌入式数字信号处理(50/20,唐建) 下*嵌限选4. 基础日语1班(60,刘峰) 26. 虚拟仪器仪表(40/20,石春) 上嵌限选5. 基础日语2班(60,朱颖) 27.无线通信与网络(50/20,闫清泉)上电限选6.实用英语(communicationg skills)(40.陈纪梁) 28.现代通信运营支撑和管理(50/20,周耀明)上电限选7.IT英语(40.郭燕,赵斌斌)29. 通信系统软件开发(50/20,刘业) 下电限选8.实用日语(40.刘峰)30. 移动通信安全(50/20,汪炀) 下*电限选9.工程硕士政治(40.刑冬梅)31现代密码学与应用(50/20,余艳玮)上信限选10. 离散数学及其应用(60,华保健) *32. 计算机病毒与免疫系统(50/20,郭宇) 下*信限选11. 组合数学(60,董群峰) *33. 网络与系统安全风险评估(50/20,郭燕) 下*信限选12.概率论与数理统计(60.徐宏力)*34. 程序设计与计算机系统(50/20,吴俊敏) 上选修13. 算法设计与分析1班(60/30,张曙) *35. 无线传感器网络(40/30,吕松武)9月7号开始两周,12月一周选修14. 算法设计与分析2班(60/30,黄刘生) *36. 高级IT工程项目管理(40,凌棕)12月21日开课选修15. 高级软件工程1、2班(60,姜明) *37. 管理心理学(40,张旭) 上选修16. 高级数据库技术 (50/20,金培权)*上软必修应用开发(40,石竹)上选修17.嵌入式系统设计 (50/20,叶勇)*上嵌必修39. J2EE应用开发(40.丁箐)上选修18.现代通信网(50/20,姜明) 上电必修40.轻量级J2EE框架应用(40/20,丁箐)下软必修环节19.信息安全(50/20,华保健) 上信必修41.SOA方法与实践(40/20,白天)下软必修环节20.高级网络技术 (50/20,刘业) 上软限选42. 网络程序设计(40/20,孟宁)下电必修环节21 .Linux操作系统分析 (50/20,陈香兰) 上软限选43.WINCE应用开发(40/20,石竹)下嵌必修环节22.多核并行计算(50/20,徐云) 下软限选44.J2ME应用开发(40/20,闫清泉,朱红军)下嵌必修环节45.Web安全实践(40/20,郭燕)下信必修环节说明:上表中的‘软’:代表软件系统设计方向,‘嵌’:代表嵌入式系统设计方向,‘电’:代表电信软件工程方向,‘信’:代表信息安全,没有特别说明的对四个方向的学生都适用。


2022年中国科学技术大学电子信息专业考研备考成功经验必看分享一、考研择校与定专业眨眼间2021年的考研已经落下帷幕,作为成功上岸的幸运儿之一,回顾这一年多的考研历程,依旧历历在目,难以忘怀。
因此,写下这篇经验贴以纪念这难忘的时光,也给后来得考研人分享些个人经验,希望或许能够帮助大家少走些弯路。
先说下考研背景,本人毕业半年后辞职跨考计算机,虽然曾经辅修过计算机部分课程,但已经忘得差不多了,属于基础较为薄弱的人群。
考研的想法从我开始工作的时候还没有,但随着工作越来越不如意,深感自己不适合这一行业,因此考研这一想法冒了出来。
那么问题来了:我为什么要考研呢?除了考研没有别的办法了吗?是考本专业还是跨专业呢?目标定在哪个学校?如果这些问题没搞清楚,以后的考研复习过程中会经常怀疑自己,有半途而废的危险。
前两个问题因人而异,后两个问题倒是可以谈谈。
就我而言,本专业很好但不适合我,所以考研主要是为了转行+利用应届生身份参加校招,获得一个好的起点,因此我义无反顾得决定考计算机相关专业。
不过我提醒读者在决定前一定要想清楚是否有非报不可的理由,目前计算机方向考研热度比肩金融,竞争者高手众多,难度相当大。
计算机方向有计算机科学与技术和软件工程两个学院,一般认为计算机科学与技术硬件与软件都学习,侧重理论研究,含金量高,学费低;软件工程是只学习软件方向,建立之初就是为了培养工程类人才,侧重工程实践,含金量较低,学费还贼高,因此计算机学院招生少,难度大,软件学院招生多,难度较低,但如果没有一颗读博搞学术研究的心,两者之间的差别只在学费和难度上了。
像我辞职备考,如果没有考上再找工作千难万难,因此从心得选择软件学院,情愿多花点学费降低下难度。
如果不惧考不上的风险,还是推荐报考计算机学院吧,毕竟认可度高一些。
选定专业之后,就该确定学校了。
一般择校都会选择比本学校持平或者更高一级的学校,否则到时候找工作不太好解释。
对于我来说就是中流985往上,在计算机考研中这是极高的难度了。

大学课程:回顾、反思与视角转换作者:谢冉来源:《现代大学教育》 2014年第1期谢冉摘要:“大学课程是什么”的问题是大学课程研究的起点,决定着大学课程研究的取向。
我国研究者对于大学课程的界定有计划方案说、科目总和说、系统体系说、经验进程说、实践说与文化说等几种视角。
这几种视角属于“现象集合与归纳分类”的定义方式,具有无法穷尽大学课程现象,存在着定义之间的相互矛盾性,体现着主客二分的思维模式等特点,在一定程度上阻碍了对大学课程本质的认识。
从“本质功能”的方式对大学课程进行界定,大学课程是不同个体在大学场域中发生的个体总体生成的动态过程。
这种本质功能的界定方式具有意义性、整体性和反思性等价值。
关键词:大学课程;回顾;反思;本质功能中图分类号:G642.3 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1671-1610(2014)01-0013-06基金项目:国家社科基金项目“大学创新人才培养的马克思主义人学基础研究”,项目编号:13BKS108。
收稿日期:2013-09-13作者简介:谢冉(1977-)女,河南南阳人,教育学博士,上海电力学院发展规划处助理研究员,从事高等教育基本理论、高校课程与教学研究;上海,200090。
一、大学课程定义的回顾“大学课程是什么”的问题规制着大学课程研究的起点与取向,因而常常被认为是“大学课程论的中心和基调”。
自20世纪80年代高等教育理论研究在我国兴起以来,众多研究者从不同的角度对大学课程进行了界定。
总的来说,可分为如下几种:(一)计划方案说建国后,由于受苏联教育模式的影响,大学课程一词很少在教育文本中出现,即便是在出现的地方,也往往是在教学计划下进行探讨,呈现出较强的规定性和框架性。
在计划的层面上,大学课程意味着政策和方案。
如有的学者指出,高等学校的课程,可以定义为一种为学生提供的学习计划[1]。
还有的学者认为大学课程是组织和展开具有合社会目的性与学生发展合理性的知识体系的方案[2]。
英语1/英语2
3自然辩证法
阶一6
2
计算机算法设计与分析
阶一5
2高质量软件工程过程阶一4
2计算机安全技术与实践
阶一42知识产权阶二3
1信息安全体系结构阶一1
2
高级计算机算法讨论科教204
1
项目管理及质量测试方向同学选此方案,能完成两门主要课程。
总18.5学分,优点:周日晚上休息,以免影响上班,其中学位课学分为:14
申请者所修的全部课程成绩平均分高于 70 分
核心课程如《软件项目管理》、《软件需求分析与设计实践》、《高质量软件工程过程》等单科成绩不低于80分
12-21周
1-11周
下午1-11周
12-21周
1-11周
周日
周六
1-21周
上午12-16周
17-21周
软件配置管理
阶一42
创业学与融资实务
人文楼教一阶
1.5绩不低于80分
1-11周
晚上12-19周。