6案例分析-自来水工程职业病危害评价
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:394.00 KB
- 文档页数:13

某饮用水厂职业病危害因素日常检测与评价本文以某饮用水厂锅炉房、空压机房、注塑车间、吹瓶车间、灌装车间的主要岗位劳动定员及人员接触职业病危害因素的检测与评价,提出改进措施和建议有效地控制工作场所职业病危害因素,保障劳动者的健康。
噪声职业接触限值;测试条件和样品采集;检测结果与评价1、前言职业病危害因素是指职业活动中影响劳动者健康的、存在于生产工艺过程以及劳动过程和生产环境中的各种危害因素的统称,本文的检测与评价范围为饮用水单体生产车间,其中包括锅炉房、空压机房、注塑车间、吹瓶车间、灌装车间的噪声。
2、噪声职业接触限值3、现场情况该饮用水厂创办于1999年,是一家集科研、生产、销售、服务于一体的现代化高科技企业。
该公司占地面积11.3万平方米,建筑面积5万平方米,是亚洲最大的饮用水单体生产车间,其中包括注塑车间、吹瓶车间、灌装车间等。
3.1平面布局及检测点布置图3.2简单工艺流程3.3工艺流程简介根据现场职业卫生调查、工艺分析^p ,该企业生产工艺过程中存在的主要职业病危害因素为空压机、吹瓶机、瓶胚机、瓶盖机、灌装机、冷水机运行中产生的噪声。
锅炉房使用管道加湿式煤浆,操作密闭化,管道化,本次不对煤尘做检测。
本次检测与评价职业病危害因素有:噪声。
3.4主要生产设备1台全自动燃油(气)锅炉、1台水煤浆蒸汽锅炉、6台K 白力仕40BAR空压机、6台吹瓶机、4台瓶胚机、2台瓶盖机。
(采样当天1#、2#、3#吹瓶机未开,7#瓶胚机未开,3#瓶盖机未开,其余生产设备均正常开启)3.5主要防护设施无3.6主要个人防护用品 3M1110防噪耳塞。
(采样当天部分工人未佩戴)3.7生产制度和劳动定员本次所有岗位工人每周工作5天,锅炉房岗位和空压机岗位每天工作12小时,其他岗位每天工作10小时。
4、测试条件和样品采集本次检测样本按日常监测要求采样,于某年某月某日在企业正常生产(未满负荷)的情况下进行。
采样日的生产情况与近期生产规模基本一致,采样、检测结果具有代表性。

水利工程建设职业病危害分析及预防一、粉尘(一)粉尘的危害能够较长时间浮游于空气中的固体微粒叫做粉尘。
从胶体化学观念来看,粉尘是固态分散性气溶胶。
其分散质是空气,分散相是固体微粒。
在生产过程中形成,并能长时间悬浮在空气中的固体微粒叫做生产性粉尘。
生产性粉尘对人体有多方面的不良影响,尤其是含有游离二氧化硅的粉尘、能引起严重的职业病――矽肺。
水利水电工程建设接触的粉尘主要是岩尘、电焊尘、水泥尘等。
吸入人体的粉尘有97%~98%可通过人体呼吸道的清除功能排出体外,余下的沉积于肺内。
粉尘对人体健康最普遍且严重的危害是引起各种尘肺病,其次是粉尘沉着症、粉尘性支气管炎、肺炎、支气管哮喘以及中毒等病症。
由于粉尘的性质、成分不同,对肺所造成的损害,引起纤维化程度也有所不同,依据《职业病分类和目录》(国卫疾控发〔2013〕48号),法定尘肺包括:矽肺、煤工尘肺、石墨尘肺、炭黑尘肺、石棉肺、滑石尘肺、水泥尘肺、云母尘肺、陶工尘肺、铝尘肺、电焊工尘肺、铸工尘肺及根据《尘肺病诊断标准》(GBZ 70)和《尘肺病理诊断标准》(GBZ 25)可以诊断的其他尘肺。
(二)防尘措施采用工程技术措施消除和降低粉尘危害,是防止尘肺发生的根本措施。
防治粉尘的工程技术措施主要有:(1)改革工艺过程,使生产过程机械化、密闭化、自动化。
(2)湿式作业,特点是防尘效果可靠,易于管理,投资较低。
(3)采取密闭、通风、除尘系统。
(4)个体防护和个人卫生。
综合以上方法,在水利水电工程建设中,可具体采用下列防尘措施:(1)混凝土搅拌站,木加工、金属切削加工等产生粉尘的场所,装置除尘器或吸尘罩,将尘粒捕捉后送到储仓内或经过净化后排放,以减少对大气的污染。
(2)施工和作业现场经常洒水、控制和减少灰尘飞扬。
(3)钻孔采取湿式作业或采取干式捕尘措施,不打干钻。
(4)水泥储存、运送、混凝土拌和等作业采取隔离、密封措施。
(5)密闭容器、构件及狭窄部位进行电焊作业时加强通风,并佩戴防护电焊烟尘的防护用品。

自来水厂危险源辨识与评估报告范文英文回答:Water treatment plants are essential for providing clean and safe drinking water to communities. However, they also pose potential risks and hazards that need to be identified and assessed to ensure the safety of the workers and the public. In this report, I will discuss the process of hazard identification and assessment in a water treatment plant.Firstly, it is important to identify the potential hazards in the water treatment plant. These hazards can include chemical, biological, and physical hazards. For example, the presence of hazardous chemicals such as chlorine or fluoride can pose risks to the workers if not handled properly. Biological hazards, such as bacteria or viruses, can also be present in the water and need to be effectively treated to prevent contamination. Physical hazards, such as slippery floors or faulty equipment, canalso lead to accidents and injuries.Once the hazards are identified, the next step is to assess the risks associated with these hazards. This involves evaluating the likelihood and severity ofpotential accidents or incidents. For example, the risk of a chemical spill can be assessed by considering the probability of a spill occurring and the potential harm it can cause to the workers or the environment. By assessing the risks, appropriate control measures can be implemented to minimize or eliminate the risks.Control measures can include engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment (PPE). Engineering controls involve modifying the equipment or processes to reduce or eliminate the hazards. For example, installing safety guards on machinery or implementing automated systems can help prevent accidents. Administrative controls involve implementing policies and procedures to ensure safe work practices. This can include training programs, regular inspections, and emergency response plans. PPE, such as gloves, goggles, orrespirators, can also be provided to workers to protect them from specific hazards.Regular monitoring and review of the control measures are also important to ensure their effectiveness. This can include conducting inspections, audits, and risk assessments on a regular basis. Any changes in the plant's operations or new hazards should be promptly identified and assessed to determine if additional control measures are required.In conclusion, identifying and assessing the hazards in a water treatment plant is crucial for ensuring the safety of the workers and the public. By implementing appropriate control measures and regularly reviewing their effectiveness, the risks can be minimized or eliminated. This will help to create a safe working environment and provide clean and safe drinking water to the community.中文回答:自来水厂是为社区提供清洁安全饮用水的重要设施。



自来水厂危险源辨识与评估报告范文英文回答:As a professional in the field of water supply and management, I have conducted a comprehensive identification and assessment of potential hazards in the water treatment plant. The purpose of this report is to outline the potential risks and provide recommendations for mitigating these hazards to ensure the safety of workers and the community.First and foremost, one of the major hazards identified in the water treatment plant is the presence of hazardous chemicals. These chemicals are used in the treatment process to disinfect the water and remove impurities. However, improper handling and storage of these chemicals can pose serious risks to the workers and the surrounding environment. For example, the accidental release ofchlorine gas can result in respiratory problems and even fatalities. Therefore, it is crucial to implement strictprotocols for handling, storing, and disposing of these chemicals to minimize the risk of exposure.Another significant hazard in the water treatment plant is the potential for electrical accidents. The plant relies heavily on electrical equipment to power pumps, motors, and control systems. Any malfunction or electrical failure can lead to fires, electric shocks, and other serious accidents. For instance, a faulty electrical connection in a pump can cause a fire, putting the entire plant at risk. To address this hazard, regular maintenance and inspection ofelectrical systems are essential to identify and rectifyany potential issues before they escalate into major safety concerns.Furthermore, the risk of slips, trips, and falls is a common concern in the water treatment plant. The presenceof water, chemicals, and uneven surfaces can create a hazardous environment for workers. For example, a spill of chemicals on the floor can lead to slips and falls,resulting in injuries. To mitigate this risk, it is important to maintain good housekeeping practices, providenon-slip flooring, and ensure that workers are equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment such as non-slip shoes.In addition to the physical hazards, the water treatment plant also faces the risk of biological contamination. The presence of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens in the water supply can pose a serious healthrisk to the workers and the community. For instance, a breach in the filtration system can result in the contamination of the water with harmful microorganisms. To address this risk, it is essential to implement stringent monitoring and testing procedures to ensure the quality and safety of the water supply.In conclusion, the identification and assessment of potential hazards in the water treatment plant have revealed several critical risks that need to be addressed to ensure the safety of workers and the community. By implementing strict protocols for handling hazardous chemicals, conducting regular maintenance of electrical systems, maintaining good housekeeping practices, andimplementing stringent monitoring of water quality, these hazards can be effectively mitigated. It is imperative for the management to prioritize the safety of the plant and take proactive measures to prevent accidents and protect the well-being of all stakeholders.中文回答:作为水务供应和管理领域的专业人士,我对水处理厂潜在危险进行了全面的辨识和评估。

自来水厂危险源辨识与评估报告范文英文回答:Identification and Assessment of Hazards in Water Treatment Plants Report.1. Introduction.Water treatment plants (WTPs) are essential infrastructure for providing clean and safe drinking water to communities. However, these facilities also present a variety of potential hazards that can have serious consequences if not properly managed. This report provides a comprehensive identification and assessment of hazards present in WTPs, with the aim of developing effective strategies for mitigating risks and ensuring the safety of water supplies.2. Hazard Identification.A thorough hazard identification process was conducted using a combination of methods, including:Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP): A systematic approach to identifying hazards and determining critical control points for controlling them.Job Hazard Analysis (JHA): A review of specific tasks and activities performed within the WTP to identify potential hazards.Historical Data: A review of past incidents and near-misses to identify patterns and trends.The following categories of hazards were identified:Physical Hazards: Hazards that can cause physical injury or damage, such as falls, slips, chemical spills, and machinery accidents.Chemical Hazards: Hazards posed by chemicals used in the treatment process, such as chlorine, ammonia, andcoagulants.Biological Hazards: Hazards posed by microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.Environmental Hazards: Hazards related to the natural environment, such as flooding, earthquakes, and extreme weather events.Operational Hazards: Hazards related to the operation of the WTP, such as power outages, equipment failures, and human errors.3. Hazard Assessment.Once hazards were identified, they were assessed based on their severity and probability of occurrence using a risk assessment matrix. The following factors were considered:Severity: The potential consequences of the hazard, including injuries, fatalities, property damage, andenvironmental impact.Probability: The likelihood of the hazard occurring, based on historical data, expert judgment, and industry best practices.The results of the hazard assessment were used to prioritize hazards and develop appropriate mitigation strategies.4. Mitigation Strategies.Based on the hazard assessment, a comprehensive set of mitigation strategies was developed to reduce the risks associated with the identified hazards. These strategies include:Engineering Controls: Physical barriers, equipment modifications, and process changes to eliminate or reduce hazards.Administrative Controls: Policies, procedures,training, and inspections to minimize the likelihood of hazards occurring.Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Protective clothing and equipment worn by workers to protect against hazards.Emergency Response Plans: Detailed plans to respond to emergencies and minimize their impact.5. Conclusion.This hazard identification and assessment report provides a valuable tool for WTPs to proactively identify and manage potential hazards. By implementing themitigation strategies outlined in this report, WTPs can significantly reduce risks and ensure the safety of water supplies for their communities.中文回答:自来水厂危险源辨识与评估报告。

典型行业职业病危害案例分析讲义典型行业职业病案例分析讲义一、案例背景介绍目前,随着工业化和城市化的快速发展,各行各业的发展壮大,同时也带来了各种职业病的高发问题。
其中,建筑行业作为典型的人力密集型产业,存在较高的职业病危害风险。
本文将以某建筑公司的职业病危害案例为例,进行分析和讲解。
二、案例分析某建筑公司是一家中型企业,主要从事高层建筑的施工工作。
该公司施工范围广泛,施工工人众多,工作量大,施工现场环境恶劣,存在一定的职业病危害风险。
经过对该公司职业病问题的调查和分析,以下为案例分析的主要内容。
1.粉尘污染由于建筑施工需要使用水泥、石灰等材料,在施工过程中产生大量的粉尘。
长期吸入粉尘会导致呼吸系统疾病,如慢性支气管炎、肺结核等。
调查发现,大部分工人没有佩戴个人防护设备,导致粉尘污染问题日益严重。
2.噪音危害在建筑施工现场,机械设备的噪音较大,严重超过了国家标准。
长期暴露在噪音环境中,会导致听力损伤、神经系统疾病等后果。
调查发现,虽然公司购买了一些隔音设备,但工人的佩戴率较低,没有得到充分的保护。
3.高温作业某建筑公司多数项目位于南方城市,施工期间常有高温天气。
工人在高温环境下长时间作业,易患中暑、日益严重的脱水等健康问题。
调查发现,公司对室外作业人员的高温保护做得不到位,没有及时提供足够的饮水和休息时间。
4.劳动强度过大建筑施工工作需要长时间站立、搬运重物等,劳动强度较大。
工人经常超时工作,休息时间不够充分,没有得到充分的身体调节,容易导致肌肉酸痛、劳损等问题。
调查发现,公司未能合理安排工作时间和休息时间,过度追求工期,给工人身体健康带来了危害。
三、案例分析结果1.职业病危害问题的存在从以上分析可见,某建筑公司存在粉尘污染、噪音危害、高温作业和劳动强度过大等职业病危害问题。
这些问题严重危害了工人的身体健康,不利于公司的可持续发展。
2.职业病防护措施不到位调查发现,公司在职业病防护方面的措施和管理不到位。

某包装饮用水生产过程中的职业病危害因素及关键控制点分析和控制顾文勍(青岛啤酒优家健康饮品(上海)有限公司,上海 200137)摘 要:目的:识别和分析上海市某包装饮用水厂的瓶/桶装饮用水生产过程中的职业病危害因素,确定其职业病危害的关键控制点,为包装饮用水行业职业病预防提供参考依据。
方法:2021年7—9月通过职业卫生调查定性识别职业病危害因素,通过现场职业病危害因素监测,定量分析职业病危害程度。
结果:该厂注塑、吹瓶和内洗有较大噪声危害。
结论:包装饮用水生产厂在设计布局时,应将注塑机、吹瓶机和内洗机单独分隔,降低噪声对工作人员的伤害。
关键词:包装饮用水生产;职业病危害因素;关键控制点Analysis and Control of Occupational Hazard Factors and Key Control Points in the Production of Packaged Drinking WaterGU Wenqing(Tsingtao Beverage Pure Family Health Drinks (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200137, China)Abstract: Objective: To identify and analyze the occupational hazard factors in the production of bottled / barreled drinking water in a packaged drinking water plant in Shanghai, and determine the key control points of occupational hazards, so as to provide a reference basis for the prevention of occupational diseases in the packaged drinking water industry. Method: From July to September 2021, the occupational hazard factors were identified qualitatively through occupational health survey, and the degree of occupational hazard was analyzed quantitatively through on-site monitoring of occupational hazard factors. Result: The injection molding, bottle blowing and internal washing of the factory had great noise hazards. Conclusion: When designing the layout of packaging drinking water production plant, injection molding machine, bottle blowing machine and internal washing machine should be separated separately to reduce the harm of noise to workers.Keywords: packaged drinking water production; occupational hazards; critical control points自从20世纪90年代某外国著名食品公司将包装饮用水引入中国市场后,人们为了自身健康逐步接受包装饮用水作为一种健康饮品的存在和价值。
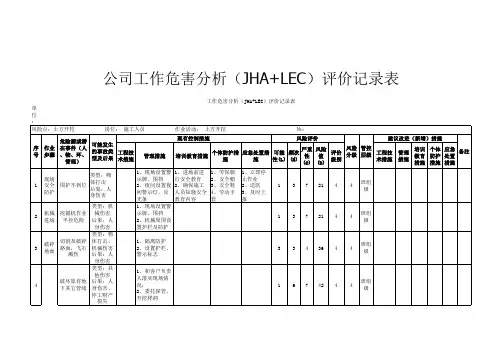

报告编号:KX(评)2017063 XXXX水力发电有限公司职业病危害现状评价报告XXXX有限公司二〇一七年十二月声明XXXX有限公司遵守国家有关法律法规和标准规范,在为XXXX水力发电有限公司提供职业病危害因素评价检测服务过程中,坚持客观、真实、公正的原则,并对出具的《XXXX水力发电有限公司职业病危害现状评价报告》承担法律责任。
此报告未经我公司书面批准,再次复印无效.法人代表:XXXX有限公司2017年12月15日目录1 总论 01.1 评价目的 01.2 评价依据 (1)1。
2。
1 法律、法规 (1)1。
2。
2 评价依据的技术规范和标准 (3)1.2.3 评价依据的基础技术资料 (4)1。
3 评价目的 (4)1.4 评价范围 (4)1。
5 评价内容 (4)1.6 评价方法 (5)1。
7 评价单元 (5)1.8 评价程序 (6)1。
9 质量控制 (8)2 用人单位概况 (10)2。
1 用人单位基本情况 (10)2.2 地理位置 (10)2.3 自然环境概况 (10)2.4 水文 (11)2。
5 生产制度及劳动定员调查 (11)3 总体布局和设备布局调查与评价 (12)3。
1 总体布局调查与评价 (12)3.1.1 总平面布置 (12)3.1.2 竖向布置 (13)3。
2 设备布局调查与评价 (14)3。
2.1 设备布局调查 (14)3。
2。
2 设备布局评价 (15)4 职业病危害因素调查、检测与评价 (17)4。
1 职业病危害因素概述 (17)4.1.1生产工艺过程中的职业病危害因素及分布 (17)4.1.2 原辅料年使用情况 (17)4。
1。
3 生产过程中的职业病危害因素及分布 (17)4。
1。
4生产环境及劳动过程中的职业病危害因素 (18)4。
1.5 作业人员接触职业病危害因素情况 (19)4。
1.6 职业病危害因素对人体健康的影响 (19)4。
2 职业病危害因素检测 (19)4。
2。
1 职业病危害因素检测方法及使用仪器 (20)4.2.2 检测点设置及检测频率 (20)4.3 职业病危害因素检测结果 (21)4.4 职业病危害因素评价 (22)5 职业病危害防护设施调查与评价 (23)5.1 防护设施设置及运行情况 (23)5.1.1 噪声防护设施 (23)5.1。
水电建设项目职业病危害控制效果评价摘要目的:对中航动力科技工程有限责任公司承接的水电建设项目进行职业病危害控制效果评价,确定该项目建成投产后的职业病危害因素,分析其危害程度,评价相应防护措施的运行效果。
方法:采用现场调查法、检测检验法和调查表法相结合的原则进行综合评价。
结果:该建设项目存在的职业病危害因素为化学性职业病危害因素锰、一氧化碳、臭氧、苯、甲苯、二甲苯、汽油、丙酮、乙酸乙酯、氯氧化物、甲醛等;粉尘有电焊尘、金属尘、玻璃棉尘、其他类粉尘等;物理性职业病危害因素有噪声、紫外线等。
结论:项目对《职业病危害预评价报告书》和在设计阶段卫生行政部门提出应采取的职业病危害控制措施要求,在建设中逐条与建设项目进行同步配套建设,基本落实了各职业病防护措施,但所有作业区同处联合厂房的设计存在缺陷,职业卫生管理措施还需完善。
关键词:水电建设项目;职业病危害控制;方法为预防、控制和消除职业病危害,识别、分析、评价水电建设项目可能产生的职业病危害因素,确定水电建设项目在职业病防治方面的可行性,并为公司水电建设项目提供必要的职业病危害防护对策和建议,为水电建设项目进行职业病危害控制效果评价,现将评价结果报告如下:一、对象和方法(一)对象公司水电建设项目(二)评价的范围和内容针对该水电建设项目内定子磁极作业、线圈作业、总装配作业、金加工作业、焊接作业、辅助生产作业进行职业病危害控制效果评价。
依据《建设项目职业病危害评价规范》(1)要求,评价内容是选址、总体布局、生产工艺和设备布局、建筑卫生学要求、职业病危害因素和危害程度及对劳动者健康的影响、职业病危害防护设施及效果、辅助用室基本卫生要求、应急救援、个人使用的职业病防护用品、职业卫生管理等。
(三)评价的方法和程序采用现场调查法、检测检验法和检查表法相结合的原则进行综合评价。
评价程序按《建设项目职业病危害控制效果评价技术导则》进行。
二、结果(一)职业病危害因素该水电建设项目在生产过程中可能产生和存在的职业病危害因素有锰、一氧化碳、臭氧、苯、甲苯、二甲苯、汽油、丙酮、乙酸乙酯、氯氧化物、甲醛等、电焊尘、金属尘、玻璃棉尘、其他类粉尘、噪声、紫外线等。
兰州自来水苯超标事件工程伦理分析目录一、内容描述 (2)1.1 研究背景与意义 (3)1.2 研究目的与方法 (4)1.3 论文结构安排 (5)二、兰州自来水苯超标事件概述 (5)三、工程伦理学理论框架 (6)3.1 工程伦理学的定义与特点 (7)3.2 工程伦理学的基本原则 (8)3.3 工程伦理学的研究对象与方法 (8)四、兰州自来水苯超标事件的伦理问题分析 (10)4.1 监管失责与责任归属 (11)4.2 技术不端与创新挑战 (13)4.3 利益冲突与决策困境 (14)4.4 信息不对称与透明度缺失 (15)五、案例中的伦理责任探讨 (16)5.1 政府部门伦理责任分析 (18)5.2 企业伦理责任探讨 (19)5.3 社会团体与媒体伦理责任 (21)5.4 公众知情权与参与权保障 (22)六、解决兰州自来水苯超标事件的伦理建议 (23)6.1 完善监管体系与机制建设 (24)6.2 加强技术研发与创新 (25)6.3 构建多元利益协调机制 (26)6.4 提升信息公开与透明度 (27)6.5 培育公民道德意识与社会监督 (29)七、结论 (29)7.1 研究总结 (30)7.2 研究不足与展望 (32)一、内容描述本篇文档将针对兰州自来水苯超标事件,从工程伦理的角度进行深入分析。
事件回顾将先简述事件的发生过程,包括 Benzene 的超标情况、影响范围及由此引发的高度关注。
工程设计的伦理责任:探究水处理厂设计方案、安全风险评估和环保措施等方面是否存在伦理瑕疵,以及相关工程人员是否履行了职业道德和社会责任。
项目实施过程中的伦理问题:分析施工过程、材料采购、监管把控等环节是否存在违规操作或伦理失守,导致 Benzene 超标问题的发生。
信息公开透明与公众信任:探讨事件中信息公开的及时性和完整性,以及相关部门对公众的沟通和解释是否充分透明,并分析此事对公众对工程建设信息及水资源安全信任的影响。