流体力学与传热学基础(次英)思维导图
- 格式:xmin
- 大小:6.65 KB
- 文档页数:1

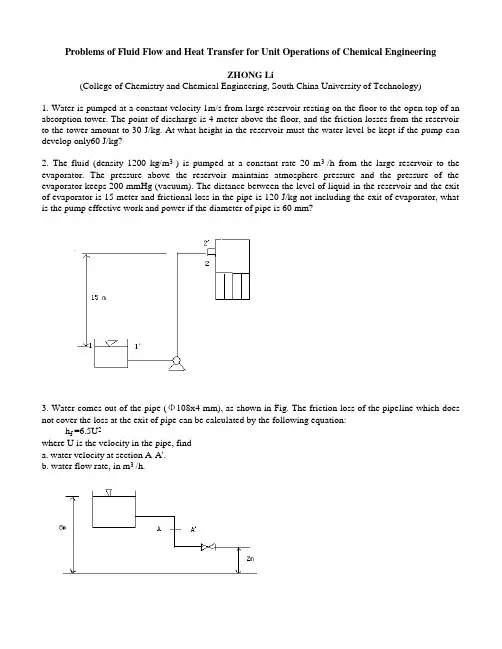
Problems of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer for Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringZHONG Li(College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology)1. Water is pumped at a constant velocity 1m/s from large reservoir resting on the floor to the open top of an absorption tower. The point of discharge is 4 meter above the floor, and the friction losses from the reservoir to the tower amount to 30 J/kg. At what height in the reservoir must the water level be kept if the pump can develop only60 J/kg?2. The fluid (density 1200 kg/m3 ) is pumped at a constant rate 20 m3 /h from the large reservoir to the evaporator. The pressure above the reservoir maintains atmosphere pressure and the pressure of the evaporator keeps 200 mmHg (vacuum). The distance between the level of liquid in the reservoir and the exit of evaporator is 15 meter and frictional loss in the pipe is 120 J/kg not including the exit of evaporator, what is the pump effective work and power if the diameter of pipe is 60 mm?3. Water comes out of the pipe (Φ108x4 mm), as shown in Fig. The friction loss of the pipeline which does not cover the loss at the exit of pipe can be calculated by the following equation:h f =6.5U2where U is the velocity in the pipe, finda. water velocity at section A-A'.b. water flow rate, in m3 /h.4. Water passes through the variable pipe. The velocity in the small pipe is 2.5 m/s. The vertical glass tubes are inserted respectively at the section A and B to measure the pressure (see fig.) If the friction loss between two section is 15 J/kg, what is the water column difference between two glass tubes? By the way, draw the relative liquid column height of two tubes in the Fig.5. A centrifugal pump takes brine (density 1180 kg/m3 , viscosity 1.2 cp) from the bottom of a supply tank and delivers it into another tank. The line between the tanks is 300 m of 25 mm diameter pipe (inner diameter). The flow rate is 2 m3 /h. In this line, there are two gate valves, four elbows (90o ) and one return bend, what is the friction loss if the roughness of pipe is 0.025 mm?6. The orifice meter (diameter of orifice 0.0001 m) is installed for measuring the flow rate. The indicating liquid of orifice is mercury if U shape pressure gauge reading is 0.6 meter and orifice coefficient can be taken as 0.61, what is the flow rate of water?7. Water flows through a pipe with a diameter di 100 mm as shown in figure.a. when the valve is closed, R is 600 mm and h equals 1500 mm. While the valve opens partially, R=400 mm and h=1400 mm, f=0.00625 (Finning factor) and k c =0.5 (contraction coefficient), what is the flow rate of water, in m3 /h?b. If the valve opens fully, what is the pressure of section 2-2', in N/m2 ? The equivalent length of the valve is1.5 m and the Fanning factor f keeps the same?(ρH2O=1000kg/m3, ρHg=13600kg/m3)8. The rotameter is installed to measure the water flow rate, as shown in figure. If the total length includingequivalent length of pipeline A is 10 m and the reading of rotameter is 2.72 m3 /h, what is the flow rate for pipeline B? (f A =0.0075, f B =0.0045)9. Water is transported by a pump (efficiency of pump 65%) from reactor to higher tank, as shown in Figure. The total equivalent length of pipe is 200 m including all local frictional loss. The pipeline is φ89⨯4.5 mm , theorifice coefficient C o and orifice diameter d o are 0.61 and 20 mm, respectively. Frictional coefficient λis 0.025 and the readings of vacuum gauge in reactor and pressure gauge in tank are 200 mm Hg and 49000N/m2 , respectively.Find:(1) Water mass flow rate, in kg/s when the reading R of U pressure gauge in orifice meter is 600 mm Hg? (ρH2O =1000 kg/m3, ρHg =13600 kg/m3)(2)Effective work of pump, in J/kg?C (density of air 1.205 kg/m3 , viscosity 1x10-5 Pa.s). Calculate the maximum diameter of particle if the settle obeys the Stoke s’ Law?11. A filter press(A=0.1 m2 ) is used for filtering slurry. The vacuum inside the filter is 500 mm Hg. One liter filtrate can be got after filtering of 5 min and 0.6 more liter filtrate is obtained after 5 more min. How much filtrate will be got after filtering of 5 more min?12. The following data are obtained for a filter press (A=0.0093 m2) in a lab.------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------pressure difference (kg f /cm2 ) filtering time (s) filtrate volume (m3 )1.05 502.27⨯10-3660 9.10⨯10-33.50 17.1 2.27⨯10-3233 9.10⨯10-3Find1) filtering constant K, q e , t e at pressure difference 1.05 kg f /cm2 ?2) if the frame of filter is filled with the cake at 660 s, what is the end filtering rate (dV/dt)E at P 1.05 kg f /cm2 ?3) compressible constant of cake s?13. A slurry is filtered by a 0.1 m2 filter press at constant pressure if the cake is incompressible. The filter basic equation is as follows:(q+10)2 = 250(t+ 0.4)where q---l/m2 t----minfind (1) how much filtrate is got after 249.6 min?(2) if the pressure difference is double and the resistance of cake is constant, how much filtrate can be obtained after 249.6 min? (cake is incompressible)14. A flat furnace wall is constructed of 120 mm layer of sil-o-cel brick, with a thermal conductivity 0.08 w/(m o C), backed by a 150 mm of common brick, of conductivity 0.8 w/(m o C), the temperature of inner face of the wall is 1400 o , and that of the outer face is 200o C.a. What is the heat loss through the wall in w per square meter.b. To reduce the heat loss to 600 w/m2 by adding a layer of cork with k 0.2 w/(m o C) on the outside of common brick, how many meters of cork are required?15. The vapor pipe (d o=426 mm) is covered by a 426 mm insulating layer (k=0.615 w/m o C). If the temperature of outer surface of pipe is 177 o C and the temperature outside the insulating layer is 38 o C, what are the heat loss per meter pipe and the temperature profile within the insulating layer?16. A steel spherical shell has inside radius r i and outside radius r o. The temperatures inside and outside walls are t i and t o, respectively and the conductivity is k. Derive the equation for heat transfer by conduction.17. Air at the normal pressure passes through the pipe (d i 20 mm) and is heated from 20o C to 100o C. What is the film heat transfer coefficient between the air and pipe wall if the average velocity of air is 10 m/s? The properties of air at 60 o C are as follows:density 1.06 kg/m3 , viscosity 0.02 cp, conductivity 0.0289 w/(m o C), and heat capacity 1 kJ/kg-K18. A hot fluid with a mass flow rate 2250 kg/h passes through a ∅25⨯2.5(outer diameter of pipe⨯ thickness of pipe wall) mm tube. The physical properties of fluid are as follows:k=0.5 w/(m o C), C p =4 kJ/kg-K, viscosity 10-3 N-s/m2 , density 1000 kg/m3 Find:a. Heat transfer film coefficient h i , in w/(m2 -K).b. If the flow rate decreases to 1125 kg/h and other conditions are the same, what is the h i ?c. If the diameter of tube (inside diameter) is decreased to 10 mm, and the velocity u keeps the same as that ofcase a, calculate h i .d. When the average temperature of fluid and quantity of heat flow per meter of tube are 40o C and 400 w/m, respectively, what is the average temperature of pipe wall for case a?e. From this problem, in order to increase the heat transfer film coefficient and enhance heat transfer, what kinds of methods can you use and which is better, explain why?Hint: for laminar flow, Nu=1.86[Re Pr]1/3for turbulent flow Nu=0.023Re0.8 Pr1/319. In a double pipe exchange (Φ23⨯2 mm), the cold fluid (Cp=1 kJ/kg, flow rate 500 kg/h) passes through the pipe and the hot fluid goes through the outside. The inlet and outlet temperatures of cold fluid are 20 and 80 o , and the inlet and outlet temperatures of hot fluid are 150 and 90o , respectively. The h i (film coefficient inside pipe) is 700 w/(m2 o C)and overall heat transfer coefficient U o (based on the outside surface of pipe) is 300w/(m2 o C), respectively. If the heat loss is ignored and the conductivity of pipe wall (steel) is taken as 45 w/(m o C), find:(1) heat transfer film coefficient outside the pipe h o?(2) the pipe length required for counter flow, in m?(3) what is the pipe length required if the heating medium changes to saturated vapor(140 o C) and it condenses to saturated liquid and other conditions keep unchanged?(4) When the exchanger is used for a year, it is found that it cannot meet the need of production (the outlet temperature of cold fluid cannot reach 80o C), explain why?20. Water flows turbulently in the pipe of Φ25⨯2.5 mm shell tube exchanger. When the velocity of water u is 1 m/s, overall heat transfer coefficient Uo (based on the outer surface area of pipe) is 2115 w/(m2 o C). If the u becomes 1.5 m/s and other conditions keep unchanged, Uo is 2660 w/( m2 o C ). What is the film coefficient ho outside the pipe? (Heat resistances of pipe wall and scale are ignored)21. Water and oil pass parallelly through a exchanger which is 1 m long. The inlet and outlet temperatures of water are 15 and 40 o C, and those of oil are 150 and 100 o C, respectively. If the outlet temperature of oil decreases to 80 o C, and the flow rates and physical properties and inlet temperatures of water and oil maintain the same, what is the pipe length of new exchanger? (Heat loss and pipe wall resistance are neglected)22. Air which passes through the pipe in turbulent flow is heated from 20 to 80 o C. The saturated vapor at 116.3 o C condenses to saturated water outside the pipe. If air flow rate increases to 120% of the origin and inlet and outlet temperatures of air stay constant, what kind of method can you employ in order to do that? (Heat resistance of pipe wall and scale can be ignored)23. Water flows through the pipe of a Φ25⨯2.5 mm shell-tube exchanger from 20 to 50 o C. The hot fluid (C p 1.9 kJ/kg o C, flow rate 1.25 kg/s) goes along the shell and the temperatures change from 80 to 30 o C. Film coefficients of water and hot fluid are 0.85kw/(m2 o C) and 1.7 kw/(m2 o C). What is the overall heat transfer coefficient Uo and heat transfer area if the scale resistance can be ignored? (the conductivity of steel is 45w/(m o C).思考问答题1. If the inlet and outlet temperatures of fluids are given, the LMTD of countercurrent flow is always larger than that of parallel-current flow?2. For countercurrent flow, the outlet temperature of cold fluid can be higher than that of hot one.3. The value of overall heat transfer coeff. U is closed to that of larger heat transfer film coeff.4. Dirty overall heat transfer coef. is smaller than clean overall heat transfer coef.5. If h i and h o are 10 and 1000 w/(m2o C), respectively, we should try to increase h o in order to elevate overall heat transfer coefficient U.6. For no phase change, ΔT of 1-2 pass shell-tube exchanger is smaller than LMTD of countercurrent flow.7. Explain simply the advantages of countercurrent flow over parallel-current flow and in what situations, parallel flow should be used.8.Dimensional analysis can directly produce the numerical results without experimental data.9. Decrease of thermal boundary layer thickness can increase h and enhance heat transfer.10. Newton's cooling law says that heat transfer film coefficient is a constant.11. The tube length changes only affect the heat transfer area during the convection heat transfer.12. Increase of Reynolds Number can elevate the heat transfer film coeff. of free convection.13. Increase of Reynolds Number can raise the heat transfer film coeff. of forced convection.14. Heat transfer film coeff. of the return bend pipe is larger than that of the same diameter straight pipe.15. The smaller the heat transfer film coef. h, the less the convective heat transfer resistance.16. What happens to the viscosity of liquid or gas when the temperature increases?17. At steady-state heat transfer by conduction, the temperature at all points in a solid is equal.18. Direction of heat flow is opposite to that of the temperature gradient.19. The thicker the insulating layer, the smaller the heat loss.20. For heat transfer through a series of layers at steady-state, the smaller the temperature drop at a certain layer, the larger the heat resistance at the same layer.21. At steady-state heat transfer conduction through a pipe wall, q/A is a constant.22. For heat transfer through two layers of insulating materials having the same thickness but different conductivities at a flat wall. Temperatures of both sides of insulating materials keep constant. If two layers of insulating materials change their places how does heat loss change? Explain why?23. For the same conditions as the above question, but heat transfer through a cylinder, how does heat loss change? Explain why?24. Which can develop more total head H, one pump or two same pump which work in series?25. The dimension for viscosity in SI system is______, and what about the unit for it?26. What is the relationship between the gauge and absolute pressure, the vacuum and absolute pressure? If the reading at entrance of pump is 0.029 MPa(vacuum), what are vacuum in mmHg and gauge pressure in mmHg? If reading at the exit of pump is 0.67 Mpa (gauge), what is absolute pressure (atmosphere pressure 0.1MPa)?27. The total (developed) head of centrifugal pump H means______ and maximum suction lift implies________ and net positive suction head (NPSH) is_______.28. What is cavitation? At what situations, the cavitation will occur?29. If the temperature of fluids increases, what happen to viscosities of liquid and gas?30. The pressure or pressure difference of liquid can be measured by U-shape pressure gauge. If the reading of R becomes smaller, what kind of gauge can be used in order to keep the accurate measurement?31. What are going on flow rate, total head and brakepower of centrifugal pump if the fluid of density 1200 kg/m3 is transported in the same pipe line compared to? (Other properties of fluid are the same as those of water).32. Somebody says that the total mechanical energy entering section 1-1 equals that leaving section 2-2, what do you think about that? If you consider that it is wrong, what is the correct statement?33. When the pipe changes from horizontal to vertical position and velocity keeps the same, what happens to energy loss?34. The solid dust is removed from gases in a gravity-settling chamber. If settling is within the laminar region, compare the productivity at 20 and 200 o C and which is larger?35. For shell-tube exchangers, what is one-pass? When the flow rate is given, velocity of fluid will _________ and Reynolds Number will______and convective film coefficient will ______ if one-pass change to two-pass.36. For the same velocity entering cyclone, separation factor (efficiency) will _____ with the increase of diameter of cyclone.37. The filter basic equation is derived based on __________.38. What is equivalent diameter for 0.5m square?39. How do you adjust the flow rate of centrifugal and reciprocating pumps?。

物理差的学生赶紧收藏了,初中物理全部知识都在以下思维导
图中了
这是为大家整理的初中物理全部章节的思维导图。
物理差的同学收藏起来,关注我。
试着搭建物理知识体系架构,总的来说,初中的物理就研究声光电力热,(力和电是重点,分值占的也比较多)以下的思维导图也是从声光电力热顺序
大家可以配合之前分享给大家的课堂笔记一起学习,先复习笔记,再看着思维导图,独立复述,导图的意义在于把知识链接成网,导图是对应章节的提纲。
试着掌握好每个知识模块,吃透每个知识点用导图复习,考试做题的时候能游刃有余,更快。
1 声现象
生现象
2 光现象
3 透镜及其应用
4 物态变化
5 电流和电路
6 电压和电阻
7 欧姆定律
8 电功率(一)——电能与电功率
9、电功率(二)——电热与安全用电
10、电与磁
11 力与运动
12 力和机械(一)——常见的力
13、力和机械(一)——简单机械
14 压强和浮力(一)——压强
15 、压强和浮力(二)——浮力
16 功和机械能
17 热和能
18 信息的传递
19能源与可持续发展
初中的学习思维导图正在制作中,需要一定的时间。
弄好再上传。







