上海大学822基础英语2018年考研专业课大纲
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:172.23 KB
- 文档页数:1
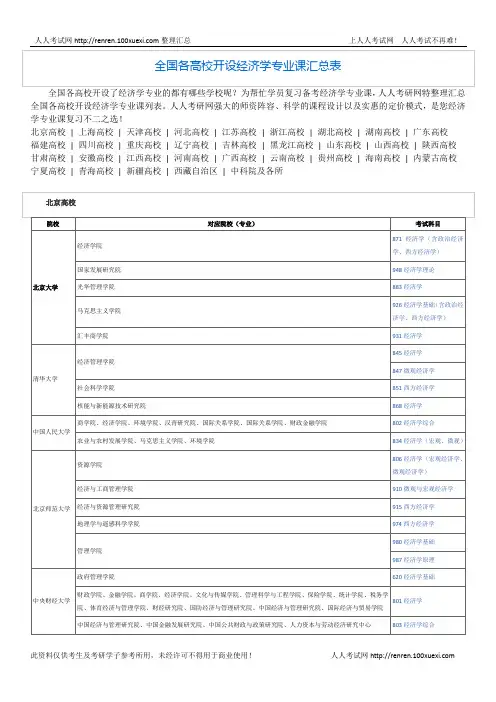
全国各高校开设了经济学专业的都有哪些学校呢?为帮忙学员复习备考经济学专业课,人人考研网特整理汇总全国各高校开设经济学专业课列表。
人人考研网强大的师资阵容、科学的课程设计以及实惠的定价模式,是您经济学专业课复习不二之选!
北京高校| 上海高校| 天津高校| 河北高校| 江苏高校| 浙江高校| 湖北高校| 湖南高校| 广东高校
福建高校| 四川高校| 重庆高校| 辽宁高校| 吉林高校| 黑龙江高校| 山东高校| 山西高校| 陕西高校甘肃高校| 安徽高校| 江西高校| 河南高校| 广西高校| 云南高校| 贵州高校| 海南高校| 内蒙古高校宁夏高校| 青海高校| 新疆高校| 西藏自治区| 中科院及各所
此资料仅供考生及考研学子参考所用,未经许可不得用于商业使用!人人考试网。

2018年在职研究生考试英语二考试大纲与题型和分值(非英语专业)(2017 年版)I.考试性质英语(二)考试主要是为高等院校和科研院所招收专业学位硕士研究生而设置的具有选拔性质的全国统一入学考试科目。
其目的是科学、公平、有效地测试考生对英语语言的运用能力,评价的标准是高等学校非英语专业本科毕业生所能达到的及格或及格以上水平,以保证被录取者具有一定的英语水平,并有利于各高等学校和科研院所在专业上择优选拔。
II.考查内容考生应掌握下列语言知识和技能:(一)语言知识1. 语法知识考生应能熟练地运用基本的语法知识,其中包括:(1)名词、代词的数和格的构成及其用法;(2)动词时态、语态的构成及其用法;(3)形容词与副词的比较级和最高级的构成及其用法;(4)常用连接词的词义及其用法;(5)非谓语动词(不定式、动名词、分词)的构成及其用法;(6)虚拟语气的构成及其用法;(7)各类从句(定语从句、主语从句、表语从句等)及强调句型的结构及其用法;(8)倒装句、插入语的结构及其用法。
2. 词汇考生应能较熟练地掌握5 500 个左右常用英语词汇以及相关常用词组(详见附录相关部分)。
考生应能根据具体语境、句子结构或上下文理解一些非常用词的词义。
(二)语言技能阅读考生应能读懂不同题材和体裁的文字材料。
题材包括经济、管理、社会、文化、科普等,体裁包括说明文、议论文和记叙文等。
根据阅读材料,考生应能:(1)理解主旨要义;(2)理解文中的具体信息;(3)理解语篇的结构和上下文的逻辑关系;(4)根据上下文推断重要生词或词组的含义;(5)进行一定的判断和推理;(6)理解作者的意图、观点或态度。
2. 写作考生应能根据所给的提纲、情景或要求完成相应的短文写作。
短文应中心思想明确、切中题意、结构清晰、条理清楚、用词恰当、无明显语言错误。
III.考试形式、考试内容与试卷结构(一)考试形式考试形式为笔试。
考试时间为180 分钟。
满分为100 分。

2018年新闻与传播考研学校排名随着技术手段的不断更新,网络媒体处在“盛行期”,具有巨大的发展潜力。
正因如此,网络媒体行业急需大批通晓媒体和网络知识、富有创造力的人才来开拓市场,在远未饱和的市场上抢滩登陆,打造未来数字时代的“传媒航母”。
这也带起了新闻与传播、新闻传播学研究生的报考热潮。
本文勤思考研网为大家整理出了开设新闻与传播、新闻传播学的各院校的排名、分数线、报录比、考试科目等内容。
如果你还没有决定报考哪所学校,希望在对比院校的以上各项因素后,能够确定报考的范围。
加入新闻与传播考研群,了解各大院校研究生考试初试复试的小秘密1464-37967【学科门类:05 文学;一级学科:0503 新闻传播学;专业名称:050300新闻传播学】【学科门类:05 文学;一级学科:0552新闻与传播;专业名称:055200新闻与传播】一、2018年新闻与传播院校排名以下是新闻传播学和新闻与传播硕士的院校排名,考生在择校时可以作为参考1、学硕排序学校名称得分星级学校数5★981 中国传媒大学100.0002 中国人民大学79.412 5★983 武汉大学59.973 5★984 复旦大学54.749 5★985 四川大学49.150 5★986 浙江大学47.730 4★987 暨南大学47.678 4★988 南京师范大学44.821 4★989 华中科技大学40.750 4★9810 北京大学39.510 4★9811 厦门大学38.118 4★9812 清华大学36.903 4★9813 上海大学36.741 4★9814 安徽大学34.961 4★9815 山东大学34.686 4★9816 河北大学32.611 4★9817 湖南大学32.172 4★9818 南京大学31.177 4★9819 华东师范大学31.131 4★9820 西南政法大学30.820 4★98 2、专硕排序学校名称得分星级学校数1 中国人民大学5★50100.0002 武汉大学96.273 5★503 中国传媒大学94.143 4★504 南京师范大学74.187 4★505 暨南大学73.857 4★506 四川大学68.546 4★507 浙江大学56.113 4★508 复旦大学54.778 4★509 北京大学53.024 4★5010 清华大学49.552 4★50注:以上数据来自中国科教评价网二、新闻与传播分数线【勤思考研网整理】分数线很大程度上反应了备考难度,是择校时必须考虑的因素。


研究生基础综合英语(邱东林版)课文中英对照加课后习题答案Unit One:EducationText:In Praise of the F Word对F的赞美Tens of thousands of 18-year-olds will graduate this year and be handed meaningless diplomas. These diplomas won’t look any different from those awarded their luckier classmates.Their validity will be questioned only when their employers discover that these graduates are semiliterate.今年,将有成千上万的18岁学生毕业并被授于毫无意义的文凭。
这些文凭对每个人都是一样的,没有一点差别,而不管学生的成绩如何.但当雇主发现他们没有实际能力时,文凭的有效性就会被质疑。
Eventually a fortunate few will find their way into educational repair shops-adult-literacy programs, such as the one where I teach basic grammar and writing. There, high school graduates and high school dropouts pursuing graduate-equivalency certificates will learn the skills they should have learned in school . They will also discover they have been cheated by our educational system.即使少数幸运的人找到了成人进修的地方,像我教语法和写作的地方。

中南财经政法大学2010年招收攻读硕士学位研究生参考书目(含初试与复试)2009-10-25 18:15:02 中南财经政法大学考研共济网点击浏览:2039次·[考研一站式]中南财经政法大学硕士招生相关文章索引·[考研一站式]中南财经政法大学硕士专业课试题、[订购]考研参考书、专业目录241 二外法语112室1、《大学法语简明教程》,薛建成主编,外语教学与研究出版社,1995年版。
课242 二外日语2000921、中日交流《标准日本语》初级(上、下册),人民教育出版社,2006年版。
济243 二外德语正门对面1、《大学德语》(修订本)1、2册,张书良总主编,高等教育出版社,2001年版。
正门601 政治学原理同济1、《政治学基础》,王浦劬著,北京大学出版社,2006年版。
共602 马克思主义基本原理专1、《马克思主义基本原理概论》,高等教育出版社,2008年版。
同济大学四平路2、《毛泽东思想和中国特色社会主义理论体系概论》,高等教育出版社,2009年修订版。
课603 马克思主义哲学原理kaoyangj1、《马克思主义哲学原理》,肖前、黄楠森、陈晏清主编,中国人民大学出版社第二版。
336 260382、《辩证唯物主义与历史唯物主义》第五版,李秀林主编,中国人民大学出版社,2004年版。
共604 社会学原理336 260381、《普通社会学理论新编》,庞树奇等主编,上海大学出版社,2005年版。
共济网2、《西方社会思想史》,于海著,复旦大学出版社,2007年版。
共605 法学基础共济1、《法学通论》(法学理论、宪法学部分),吴汉东主编,北京大学出版社,2007年修订版(或以后各版本)。
336260 37606 基础英语共济网1、新世纪高等院校英语专业本科生系列教材《综合教程》(1、2、3、4),何兆熊主编,上海外语音像出版社,2005年版。
网络督察2、《高级英语》(修订本1、2),张汉熙主编,外语教学与研究出版社,1995年版。


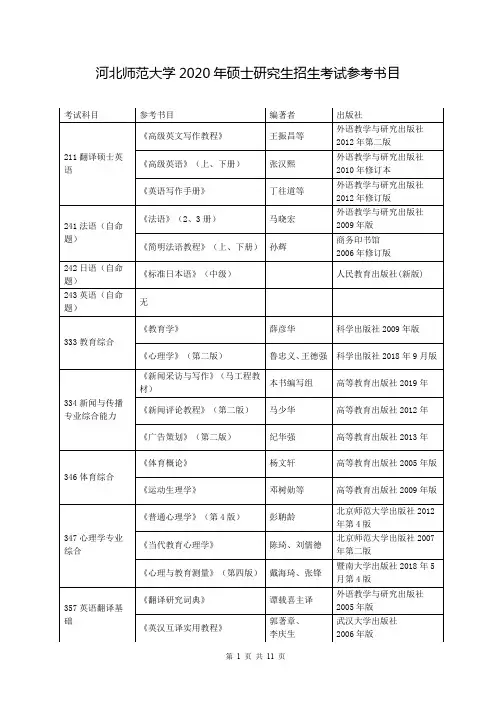
江西师范大学 2018 年全日制硕士研究生入学考试试题( A 卷)专业:学科教学(英语)科目:英语综合注:考生答题时,请写在考点下发的答题纸上,写在本试题纸或其他答题纸上的一律无效。
(本试题共11 页)I Grammar and Vocabulary (20×1’)There are 20 incomplete sentences in this section. For each blank there are four choices marked A, B, C, and D. Choose the one that best completes the sentence on ANSWER SHEET.1.It is very hard to him to give up smoking and drinking alcohol.A.endeavor B. refresh C. assert D. induce2.The man that his car was the fastest in the world and nobody could compete with him in the race.A.reproachedB. braggedC. inferredD. converted3.The space capsule is with all the materials necessary for a ten-day flight.A.preservedB. probedC. furnishedD. profiled4.The modern child finds it difficult to of a time when there was no radio or TV.A. concealB. conceiveC. consoleD. fancy5.The woman standing in the doorway the sleeping baby in her arms.A. claspingB. soothingC. rollingD. quenching6.Ninety percent of the inhabitants are in productive work of some kind.A. engagedB. involvedC. concernedD. related7.To get my travelers’ cheques I had to a special cheque to the bank for the total amount.A. make forB. make offC. make outD. make over8.The information is not given in Chapter one or Chapter five; it must be one of thechapter.A. interveningB. interferingC. integralD. interacting9.All foreign merchants were made to put heavy on the goods they sold and bought.A.feesB. pricesC. revenuesD. duties10.The broad aim of the meeting was that experts working in the same technical area should meet to exchange .A. experimentB. expositionC. expertiseD. emotion11.The landscape will have a(n) change after a rainstorm in the desert.A. mysteriousB. incisiveC. ambiguousD. abrupt12.Mary has bought a carpet, which she will send to her mother as a birthday present.A. Chinese beautiful greenB. beautiful green ChineseC. green beautiful ChineseD. Chinese green beautiful13.A person’s calorie requirements vary his life.A. acrossB. throughoutC. overD. within14.It seems oil from his pipe for some time. We’ll have to take the machine apart to put it right.A. had leakedB. is leakingC. leakedD. has been leaking15., but it also filters out harmful sun rays.A.The atmosphere gives us air to breatheB.Not only the atmosphere gives us air to breatheC.Not only does the atmosphere give us air to breatheD.The atmosphere which gives us air to breathe16.If you are a , determined person you stand a better chance of surviving in difficult circumstances.A. respectfulB. reflectiveC. resoluteD. resourceful17.She nurtured dreams of opening ceremony night, being onstage in a mink coat to share a bow of her successful husband.A. purgedB. strodeC. ponderedD. coaxed18.The club members voted to the ban on smoking.A. repealB. repelC. refrainD. reside19.With price so much, it’s hard to plan a budget.A. fluctuatingB. tiltingC. tumblingD. flapping20.I don’t know if the story is true, but I’ll try to it.A. reinforceB. verifyC. identifyD. conformII Cloze text (20×1’)Directions: Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C or D on ANSWER SHEETResearchers have found more evidence that hostility can 21 to heart disease, according to a report in the current issue of the journal Psychosomatic Medicine. They found that hostility may be linked to the metabolic 22 , a set of risk factors23 with heart disease, including obesity, blood pressure, and insulin resistance. Isulin resistance occurs when the body become less 24 to the hormone insulin, and may be a precursor of diabetes. “It has not really been clear how hostility plays itself out in terms of physiological risk,” said Dr Raymond Niaura. “We’re seeing how all these things 25 for the first time.”The researchers studied over 1,000 men aged 44 to 92 who 26 in the Normative Aging Study between 1987 and 1991. When 27 on the Cook-Hedley Hostility Scale, the participants 28 higher hostility scores were also more likely to be overweight, have abdominal and upper body obesity, and have insulin resistance all risk factors for heart d isease.“I’m not sure you could say that if you scored a certain number on the hostility 29 , you’d be two or three times more likely to 30 heart disease,” said Niaura.“Finally,we’ll look at how it all plays out in 31 of disease.” Since 98%of the initial 32 were older white men, the researchers suggest that it is not known 33 its findings are applicable to women, young men or men of different races. “If people have the metabolic risk factors, they really need to see their doctor,”34 Niaura.Their study also found more evidence that men 35 fewer years of education were more 36 to be hostile. The finding suggests “that hostility may be part of the cognitive/ emotional / behavioral response to the 37 stress of low socioeconomic 38 ”, said Niaura in a statement. More research is needed to take socioeconomic factors into 39 , and to look for the biological connection40 hostility, obesity and heart risk, he said.21.A. contribute B. lead C. attribute D. link22.A. disorder B. condition C. epidemic D. syndrome23.A. coincided B. connected C. related D. associated24.A. reactionary B. responsive C. conducive D. acute25.A. behave B. function C. interconnect D. involved26.A. participated B. entered C. displayed D. enforeced27.A. measuring B. measured C. counting D. counted28.A. had B. possessed C. with D. on29.A. balance B. scale C. hierarchy D. rank30.A form B. infect C. contact D. develop31.A. relations B. terms C. place D. behalf32.A. sample B. subject C. group D. team33.A. that B. how C. why D. if34.A. advised B. argued C. declared D. proclaimed35.A. had B. for C. with D. who36.A. likely B. likeable C. lovable D. liable37.A. pervasive B. chronic C. persuasive D. prevalent38.A. state B. class C. status D. classification39.A. considerations B. concern C. thoughts D. account40.A. with B. to C. between D. amongIII Reading (20×2’)TEXT AScientists say they may have solved a far-out mystery: how Uranus and Neptune came to exist at the very edges of the solar system. A new study says the two icy planets may have been born much closer to the sun than previously thought, and ended up in their current orbits after gravitational forces from Jupiter violently hurled them away. That would explain how the two planetary giants--- each more than 10 times the mass of the Earth--- could exist at the far edge of the solar system, where there was not enough gas and dust to make a planet eons ago.The study is based on computer simulations conducted by Martin Duncan ofQueen’s University in Kingston, Ontario, and colleagues. It was published in Thursday’s issue of the journal Nature. All of the planets in the solar system are believed to have evolved through the accumulation of a large number of small bodies that circulated in a huge disk around the sun. The researchers theorize that Uranus and Neptune formed their cores near the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn, within a ring of about 5 to 10 astronomical units from the sun. One astronomical unit equals the distance from the sun to the Earth. (Earth, however, is thought to have formed much later than the big planets.Previous estimates of 10 to 20 AU have been given for the birthplaces of Uranus and Neptune, which now orbit at 19 and 30 AU, respectively. Duncan said Jupiter grew fastest because it was closest to the sun, where the planet-forming disk was the most dense, and then exerted gravitational forces on its smaller planetary siblings. Saturn may have helped eject Uranus and Neptune.Renu Malhotra, a scientist at the Lunar and Planetary Institute in Houston, said the study does not explain why Uranus and Neptune did not accumulate gas like Jupiter and Saturn, since the four planets formed at roughly the same time and in roughly the same place.Malhotra said the evidence shows that Uranus and Neptune were formed perhaps 30% closer to the sun than their present locations--- but not as close as Duncan proposes. The planets then may have gently migrated out to their current locations, she said. He also said that gravity and friction from gas that surrounded Uranus and Neptune could have prevented them from being hurled out. Alan Boss, an astrophysicist at the Caregie Institution in Washington, said more research is needed on Duncan’s theory. “It’s a radical idea.” He said, “but since we’re in a stalemate on Neptune and Uranus, maybe we need a radical idea.”41.Which of the following is NOT true?A.Uranus and Neptune may have been born close to the sun.B.Uranus and Neptune may have been hurled away by Jupiter.C.Both Uranus and Neptune are larger than the earth.D.There was not enough gas and dust to make a giant planet at the far end of the solar system.42.Duncan’s study indicates .A.that all the planets evolve from many small bodies around the sunB.that Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar systemC.that Uranus and Neptune may have been born closer to the sun.D.why Uranus and Jeptune did not accumulate gas43.Malhotra’s view differs from that of Duncan’s in that .A.she argues Uranus and Neptune have greatly migrated to their present locationsB.she thinks Uranus and Neptune were 70% further away from the sunC.She believes Uranus and Jeptune were 10 to 20 AU around the sunD.She proposes Uranus and Neptune were 30% closer to the sun44.According to the passage, the reason why Uranus and Neptune were not hurled far out as a result of .A. gravityB. frictionC. gasD. sun45.The author’s attitude toward the proposed solutions to the mystery is .A. radicalB. impartialC. uncertainD. funnyTEXT BPublic relations is management function that creates, develops, and carries out policies and programs to influence public opinion or reaction about an idea, a product or an organization. The field of public relations has become an important part of the economic, social and political pattern of life in many nations. That field includes advertising, promotional activities, and press contact. Public relations also exists at the same time in business with marketing and merchandising to create the climate in which all selling functions occur.Public relations activities in the modern world help institutions to cope successfully with many problems, to build prestige for an individual or a group, to promote products, and to win elections. The majority of public relations workers are staff employers working within a corporate or institutional framework. Other operate in public relations counseling firms.In industry, public relations personnel keep management informed of changes in the opinions of various publics (that is, the groups of people whose support is needed): employee, stockholders, customers and so on. These professionals counsel management as to the impact of any action---- or lack of action on the behavior of the target audiences. Once an organizational decision has been made, the public relations person has the task of communicating this information to the public using methods that promote understanding, consent, and desired behavior. For example, a hospital merger, an industrial plant closing, or the introduction of a new product all require public relations planning and skill.Public relations activities are a major part of the political process in many nations. Politicians seeking office, government agencies seeking acceptance and cooperation, officials seeking support of their policies, and foreign governments seeking aid and allies abroad all make extensive use of counseling services provided by public relations specialists.Public relations also plays an important role in the entertainment industry. The theater, motion pictures, sports, restaurants, and individuals all use public relations services to increase their business or add to their image. Other public relations clients are educational, social service, and charitable institutions, trade unions, religious groups, and professional societies.The successful public relations practitioner is a specialist in communication arts and persuasion. Specialized skills are required to handle opinion research, media relations, direct mail activities, institutional advertising, publications, film and video production, and special events. Public relations services are so far virtually unused in many developing nations, but they are likely to be a future government concern.46.The first paragraph focuses on .A. the definitions of public relationsB. the procedures of public relationsC. the classification of public relationsD. the increasing role of public relations47.Which of the following is true about public relations personnel in industry?A.They spend considerable time conducting opinion rolls.B.They offer advice to management in decision making.C.They are employed to serve the interests of management.D.They seem primarily concerned with building prestige for companies.48.Which of the following might have little to do with public relations?A. ClimateB. ChurchC. CorporationD. sports49.Which of the following is not correct about public relations operations?A.Quite a number of them are operated by self-employed individuals.B.The work involved is often complicated and challenging.C.They are developing rapidly in nearly every country.D.The practitioners are often artists and good at persuasion.50.Which can NOT be inferred from the passage?A.Movie stars may use public relations activities to build up their image.B.Eager politicians often resort to public relations for personal advancement.C.Public relations sometimes extend beyond the boundaries of a nation.D.Public relations is a promising subject to study in developing nationsTEXT CYears of watching and comparing bright children and those not bright, or less bright, have shown that they are very different kinds of people. The bright child is curious about life and reality, eager to get in touch with it, embrace it, unite himself with it. There is no wall, no barrier between him and life. The dull child is far less curious, far less interested in what goes on and what is real, more inclined to live in worlds of fantasy. The bright child likes to experiment, to try things out. He lives by the maxim that there is more than one way to skin a cat. If he can’t do something one way, he’ll try another. The dull child is usually afraid to try at all. It takes a good deal of urging to get him to try even once; if that try fails he is through.The bright child is patient. He can tolerate uncertainty and failure, and will keep trying until he gets an answer. When all his experiments fail, he can even admit to himself and others that for the time being he is not going to get an answer. This may annoy him, but he can wait. Very often, he does not want to be told how to do the problem or solve the puzzle he has struggled with, because he does not want to be cheated out of the chance to figure it out for himself in the future. Not so the dull child. He cannot stand uncertainty or failure. To him, an unanswered question is not a challenge or an opportunity, but a threat. If he can’t find the answer quickly, it must be given to him, and quickly; and he must have answers for everything. Such are the children of whom a second grade teacher once said, “but my children like to have questions for which there is only one answer.” They did; and by a mysterious coincidence, so did she.The bright child is willing to go ahead on the basis of incomplete understanding and information. He will take risks, sail uncharted seas, explore when the landscape is dim, the land marks few, the light poor. To give only one example, he will often readbooks he does not understand in the hope that after a while enough understanding will emerge to make it worthwhile to go on. In this spirit some of my fifth graders tried to read Moby Dick. But the dull child will go ahead only when he thinks he knows exactly where he stands and exactly what is ahead of him. If he does not feel he knows exactly what an experience will be like, and if it will not be exactly like other experience he already knows, he wants no part of it. For while the bright child feels that the universe is on the whole a sensible, reasonable, and trustworthy place, the dull child feels that it is senseless, unpredictable, and treacherous. He feels that he can never tell what may happen, particularly in a new situation, except that it will probably be bad.51.If the dull child fails in the first attempt, he will .A try again B. be encouraged to go onC. get advice from othersD. lose confidence52.What does the rod “maxim” in the first paragraph most probably mean?A. ExampleB. PrincipleC. ToleranceD. Understanding53.Why does the bright child refuse to get help from others even when he fails?A.Because he is confident of his own ability.B.Because he looks down upon other people.C.Because he wants to have another chance to try by himself.D.Because he is willing to have difficulties all his life.54.According to the author, the reason why some fifth grade students want to read “Moby Dick” is probably that .A.they enjoy reading a difficult book and understanding it bit by bitB.they think the book is well-written and worth readingC.they want to show off their ability to their teachersD.they are fond of taking risks and trying everything by themselves55.It is implied but not stated in the text that .A.when the dull child doesn’t know what will happen, he is sure that the situation will be a bad one.B.some teachers like to provide answers to their students, thus the students will always depend on their teachers for help.C.the dull child is afraid of difficulties and does not want to try anything unpredictable or challenging.D.the bright child is always confident of himself and enjoys finding answers to difficult questions.TEXD DFor parents who send their kids off to college saying, “These will be the best years of your life,” it would be very appropriate to add, “If you can handle the stress of college life.” Freshmen are showing up already stressed out, according to the latest research study that reported students’ emotional health levels at their lowest since the survey started in 1985. While in school, more students are working part-time and near-full-time jobs. At graduation, only 29 percent of seniors have jobs lined up.Pressure to excel often creates stress, and many students are not learning how to effectively handle this stress. Let me show five facts that I believe every college student should know about stress.First, stress can make smart people do stupid things. Stress causes what brain researchers call “cortical inhibition.” In simple terms, stress inhibits a part of the brain responsible for decision-making and reaction time and can adversely affect other mental abilities as well.Second, the human body doesn’t discriminate between a big stressful event and a little one. Any stressful experience will create about 1,400 biochemical events in your body. If any amount of stress is left unchecked, many things can occur within the body, including premature aging, impaired cognitive function and energy drain.Third, stress can become your new pattern. When you regularly experience negative feelings and high amounts of stress, your brain recognizes this as your normal state. This then becomes the new norm, or baseline for your emotional state.Fourth, stress can be controlled. Countless studies demonstrate that people can restructure their emotional state using emotion-refocusing techniques. These techniques help you recognize how you are feeling and shift to a more positive emotional, mental and physical state.One technique involves slowing your thoughts and focusing on your heartbeat, breathing slowly and deeply, and focusing on the positive feeling that you receive.Finally, stress can be lessened by loving what you study. Barbara Frederickson, a leading international authority on the importance of positive emotions, says humans are genetically programmed to seek positive emotions such as love and joy. It's suggested to choose a major or career path you love and enjoy. Otherwise, you could end up fighting against your own biology.56.The author cites the latest research study in order to show that .A.students are studying harder in collegeB.most students have part-time job nowC.stress continues to the time of graduationD.students only feel stressed while in school57.According to the passage, stress might cause all the following negative effects EXCEPT .A. socialB. mentalC. emotionalD. physical58.In the author’s opinion, stress can be controlled by_ .A. doing what you preferB. identifying your present emotional state firstC. finding a more positive feeling firstD. focusing on your emotional state59.According to the context, what does "your own biology” mean in the last paragraph?A. Your current major.B. Your future job.C. Your future research.D. Your preference.60.Which of the following is the best as the title of the passage?A. Causes of Stress.B. Type of Stress.C. Life and Stress.D. Stress and Control Methods.IV Translation (2×20’)Section A Chinese to EnglishTranslate the following text into English。

2018年会计硕士考研辅导课件管理类联考强化班讲义英语二阅读阅读1.考点分析2.题型方法3.真题讲解第一章考点分析考试要求1.理解主旨要义2.理解文中的具体信息3.理解语篇的结构和上下文的逻辑关系4.根据上下文推断重要生词或词组的含义5.进行一定的判断和推理6.理解作者的意图、观点或态度能力考察1.词汇量与词汇处理能力一词多义熟词僻义(convention)2.阅读能力长难句3.背景知识4.解题招数篇幅特征共四篇文章,总长度为1500词左右,每篇文章的长度多在375词左右,多由4~6段组成。
话题特征多选取西方国家尤其是美、英等国广泛关注的话题,文章主题可分为管理、商业经济、社会生活、文化教育、科普知识等。
体裁与结构模式现象分析型主张反主张观点/结论——论证概括——具体第二章题型方法阅读题型1.具体信息题2.语义理解题3.观点态度题4.推断题5.主旨要义题6.篇章结构题具体信息题1.题干特征According to the author/thetext/Paragraph X, ...whWhich of the following is true of...?Which of the following is true according to the text/the first two paragraphs?We learn from the lastparagraph/Paragraph X/the text that......feature/were characterized by.2.正确项特征是原文的同义重述(替换)——对原文进行重新加工,用不同的词语或句型表达相同的意思。
1)同义词、近义词 2)替换3.干扰项特征偷换概念: A B答非所问:以偏概全:范围无中生有:正反混淆: not过于绝对: most all the only逻辑颠倒: A导出B4.解法单一信息题:一般只涉及某一个或多个句子综合信息题:针对文章的某一段或数段甚至全文进行提问,内容覆盖面较广选项代入语义理解题1.题干特征(1)词义题The word/phrase “...”(Line X,The word “...”(Line X, Paragraph X)Which of the following best defines the word “...”(Line X, Paragraph X)?(2)句意题The sentence “...”(Line X, ParagraphBy (saying)“...”(Line X, ParagraphWhat does the author mean by “...”(Line X, Paragraph X)?2.正确项特征原文中存在其同义词、近义词、反义词、原词、概括词或其他解释说明。
WeLearn·2018考研英语大纲新增词汇解析讲义accustom vt.使习惯于•【助记】accustom=ac(加强)+ custom(风俗,习惯)•【用法】~ oneself to doing/do sth.使习惯于做某事•【同义词】adjust, acquaint, familiarize•【例句】I live near an airport and passing planes can be heard night and day. So I have to accustom myself to the noise of the planes.我往在飞机场附近,日夜能听到过往的飞机声,所以我不得不使自己习惯这飞机的声音。
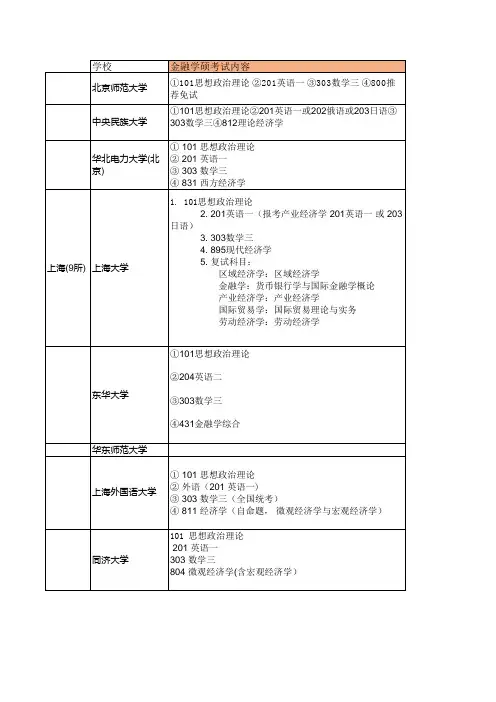
amateur a.&n.业余(水平)的(运动员、艺术家等)【助记】amateur adj.(an amateur athlete)•amateurish. adj. 业余的,非专门的,不熟练的•amateurishly. adv 外行地,生手地•amateurishness. n. 业余;外行;不熟练(贬)•amateurism. n. 业余性,非职业的作为eg. 1. She played soccer as an amateur before turning professional2. These photos were taken by both amateurs and professionals.Origin: French, from Latin amator Lover, from amare to love扫码购买18新增词汇串讲课程ambassador n.大使;特使,(派驻国际组织的)代表•ambassadorial adj. 大使的,使节的•ambassadorship n. 大使的职位eg. 1. Embassy officials met with the ambassador.2. A beloved entertainer who has often been sent abroad by the president as his country's goodwill ambassador.Origin:Middle English ambassadour,from Anglo-Franch ambassateur,ultimately of Germanic origin;akin to Old High German ambaht service.ambiguous a.引起歧义的,模棱两可的,含糊不清的•ambiguously adv.含糊不清地•ambiguousness n.含糊,歧义性eg: 1.we were confused by the ambiguous wording of the message.2.He looked at her with an ambiguous smile.3.Due to the ambiguous nature of the question, it was difficult to choose the right answer.Origin:Latin ambiguus,from ambigere to be undecided,from ambi-+agree to drive--more at agent扫码购买18新增词汇串讲课程ambition n.对(成功、权力等)的强烈欲望,野心;雄心•ambitionless adj.无野心的;无名利心的;谦虚的eg. 1.My first ambition as child was to be in the circus .2. He lacked ambition and couldn't compete with the others.Origin: Middle English, from Middle French of Latin; Middle French, from Latin ambition-,ambitio, literally, act of soliciting for votes, from ambire to go around, solicit.ambulance n.救护车,救护船,救护飞机Full Definition:a vehicle used for taking hurt or sick people to the hospital especially in emergencies.amend vt.修改,修订,改进•amendable adj. 可修正余地的•amender n. 改正者,修真者eg. 1. The country's constitution was amended to allow women to vote.2. They voted to amend the law in 1920.3. He tried to amend the situation by apologizing to me .amiable a.和蔼可亲的,友善的,亲切的•amiability n. 和蔼可亲,友善,亲切•amiableness n. 和蔼可亲;敦厚•amiably adv. 和蔼可亲地,亲切地扫码购买18新增词汇串讲课程eg. 1. Everyone knew him as an amiable fellow.2.She had an amiable conversation with her friend.Origin: Middle English, from Anglo-French ,from Late Latin amicabilis friendly, from Latin amicus friend;akin to Latin amare to love.hatch v. 秘密策划,(尤指)密谋;孵化;孵出,破壳而出;使(小鸟、小鱼、小虫等)孵出;开口;(船甲板或飞机底部装货物的)舱口;(飞机或宇宙飞船的)舱门;(尤指厨房和餐厅之间供传递食物的)两室之间的小窗口;•hatchability n. 孵化能力;孵化可能;孵化率•hatchable adj. 可孵化的•hatcher n .策划者;孵卵的动物•hazard vt. 冒险;使遭受危险;危险;冒险的事;机会;双骰子游戏;Full Definition:1. a game of chance like craps played with two dice2. a source of danger( hazards on the roadway)at hazard: at stakeeg: 1. the tumbledown old barn was considered a fire hazard.2. it was only by hazard and good futune that we found our way back to the trail扫码购买18新增词汇串讲课程Heal vt. 恢复健康的状态;使恢复正常;使(某人)精神恢复健康;vi. 变得完整和健全;Full Definition:1. to become healthy or well again.2. to make (someone or something)healthy or well again.eg: 1.You've got to give the injury time to heal.2.After the divorce ,he needed some time to heal.3. The ointment will help heal the wound.Synonyms:cure, fix, mend ,rehab, rehabilitate ,set uphail vi. 下冰雹;如冰雹般地降下;vt. 致敬;打招呼;•hailer n.1.汽笛;高声信号器 2. 欢呼者;招呼者•hail from: to be or have been native to or a resident of <She hails from Chicago>hinder vt.阻碍,妨碍;成为阻碍;adj. 后面的,后方的;Other forms:hindered; hindering; hinderereg: 1.the witness refused to cooperate, hindering the investigation.2.The country's economic growth is being hindered by the sanctions.3.it's not clear whether the change will help or hinder our project.erupt v. 爆发;喷发;突然发生;出疹;•eruptible adj.喷发的,爆发的;能喷出的;•eruptive adj.喷发的;即将爆发的•eruptively adv.突发地;爆发地扫码购买18新增词汇串讲课程eg. 1. The volcano erupted with tremendous force.2. A bitter dispute has erupted among the members of the team.Synonyms: belch, disgorge, eject, eruct, expel, jet, spew, spout, spur tessence n.本质,实质;精华,精髓;eg. 1. The essence of love is unselfishness.2. The book's illustrations capture the essence of the story.Synonyms: being, essentiality, nature, quiddity, quintessence, soul, stuff, substance, name of the gameOrigin: Middle English essencia ,from Latin essential ,from esse to be --more at iseternal adj. 永生的;不朽的;永恒的,永久的;似乎不停的,没完没了的;永恒的事物;•eternalize v. 使永恒;使不变;不朽•eternally adv.永久地,永恒地•eternalness n.永恒eg: 1. the eternal flames of hell.2. in search of eternal wisdow.3. When will his eternal whining stop?Eternal 上帝,与定冠词the连用Synonyms: ageless, continuing, dateless, enduring, abiding, everlasting, immortal ,lasting, ongoing, perennial, perpetual ,timeless, undyingAntonyms: impermanent, mortal, temporary, transient.扫码购买18新增词汇串讲课程evaluate vt. 评价;求…的值(或数);对…评价;[数学、逻辑学]求…的数值;vi. 评价,估价;•evaluation n. 估算;估计价值;赋值•evaluative adj.评估的,评价的•evaluator n.评估员;求值程序;鉴别器eg: 1.We need to evaluate our options.2.evaluate a training program as effective.Synonyms: appraise, assess, estimate, guesstimate, rate, set, valuate, valueevaporate vi. 蒸发;消失;发散气体;vt. 使脱水;使蒸发;使挥发;使沉淀;•evaporation n.蒸发,消失;挥发;升华•evaporative adj.蒸发的,使蒸发的•evaporator n.蒸发器eg: 1.Let the liquid start to evaporate.2. The heat evaporated the water.3. The opportunity evaporated before he could act on it.Synonyms: dematerialize ,dissolve, evanesce, disappear, fade, flee ,melt, sink, vanish Antonyms: appear materializeexaggerate vt. 夸张;(使)扩大;(使)增加;•exaggeratedly adv.夸大地;夸张地;过度地•exaggeratedness n.夸张;做作,过度扫码购买18新增词汇串讲课程•exaggeration n.夸张;夸大;夸大之词;夸张的手法•exaggerative adj.夸大的;夸张的;言过其实的,浮夸的•exaggerator n.言过其实的人;浮夸的人•exaggeratory adj.言过其实的eg: 1. The book exaggerates the difficulties he faced in starting his career.eg: 2. it's impossible to exaggerate the improtance of his discovery.3.He tends to exaggerate when talking about his accomplishments.Synonyms: color, elaborate(on),embellish, embroider, hyperbolize, magnify, pad, stretch Antonyms: understate.alienate vt.使疏远,使不友好;转移(资产等)•【助记】alienate=ali(alter其他的,改变状态)+en(动词、名词后缀)+ate(动词后缀) •【用法】~ sth./sb. from使得某事/某人与疏远•alienate lands转让土地•【派生词】alien adj. 外国的;相异的,性质不同的;不相容的•. 外国人,外侨;外星人•【例句】His attempts to alienate the two friends failed because they had complete faith.allegiance n. 忠诚,效忠;拥戴;臣服•【用法】~ to sb./sth.对某人/某机构效忠•【同义词】loyalty, faithfulne•【例句】You have seen duty and allegiance in the determined faces of our soldiers.•你们从美军士兵坚毅的表情中看到了责任和忠诚。
2007年批准国家重点学科开设学校名单管理科学与工程管理科学与工程全国学科排名历年国家线(A区)2011 管理学[12] 350 55 832010 管理学[12] 330↑46↓69↓2009 管理学[12] 315↓47↓71↓2008 管理学[12] 330 54 812007 管理学[12] 330 54 812006 管理学[12] 340 54 812005 管理学[12] 335 53 80985名单一期(34所)清华大学北京大学厦门大学中国科学技术大学南京大学复旦大学天津大学哈尔滨工业大学浙江大学南开大学西安交通大学华中科技大学东南大学武汉大学上海交通大学中国海洋大学山东大学湖南大学中国人民大学北京理工大学吉林大学重庆大学电子科技大学大连理工大学四川大学中山大学华南理工大学北京航空航天大学兰州大学东北大学西北工业大学北京师范大学同济大学中南大学二期(5所)中国农业大学国防科技大学西北农林科技大学华东师范大学中央民族大学三期中国地质大学(武汉)中国矿业大学中国石油大学中央财经大学北京科技大学211名单:北京(26所)•北京中医药大学•北京外国语大学•中国地质大学(北京)管理科学与工程③303数学三④836管理学《管理学》徐国华清华大学出版社•中国矿业大学(北京)管理科学与工程③303数学(三)④435管理概论或 436经济学原理•工程管理③303数学(三)④435管理概论或 436经济学原理•工程管理(力学与建筑工程学院)③303数学(三)④435管理概论或 442建设项目管理础•金融工程与风险管理③303数学(三)④435管理概论或 436经济学原理•中国石油大学(北京)管理科学与工程③303数学三④852微观经济学或855管理学原理或856运筹学••中国政法大学•中央财经大学电子商务303数学三807C语言程序设计•投资学303数学三801经济学•技术经济及管理303数学三802管理学•华北电力大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④872运筹学•物流工程③302数学二④874管理原理•工业工程③302数学二④874管理原理或825电力系统分析基础二或815工程热力学•项目管理③302数学二④874管理原理••北京体育大学上海(10所)•上海外国语大学•复旦大学管理科学与工程③301数学一④863运筹学或893管理经济学•项目管理②204英语二③302数学二④952管理学基础••华东师范大学•上海大学管理科学与工程4.方向01-方向06:828运筹学或方向07829数据结构与程序设计(二)••东华大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④805运筹学与数据库技术•物流工程③302数学二④806管理学原理上海财经大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④822管理学或823管理信息系统•电子商务③303数学三④822管理学或823管理信息系统•华东理工大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④819运筹学或821管理学原理••同济大学管理科学与工程③301数学一④818管理学概论•上海交通大学管理科学与工程③301数学一④816自动控制理论或840运筹学与概率统计或845管理学•情报学③303数学三④873情报学基础•档案学③637档案管理学④872档案学概论••第二军医大学天津(3所)•南开大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④886管理信息系统或887运筹学(商学院•天津大学管理科学与工程任选一④408计算机学科专业基础综合④803机械原理与机械设计④812自动控制理论④818结构力学④832 运筹学基础④851环境分析监测及物理化学•工程管理同上•信息管理与信息系统④408计算机学科专业基础综合④832运筹学基础••天津医科大学重庆(2所)•重庆大学管理科学与工程经济与工商管理学院③303数学三④804微观经济学(含宏观经济学•管理科学与工程机械工程学院③303数学三④827系统工程导论(含运筹学及系统工程导论•管理科学与工程建设管理与房地产学院③301数学一④809工程项目管理一•西南大学辽宁(4所)•大连理工大学管理科学与工程③301数学一④875信息管理与信息系统、⑤408计算机学科专业基础综合、⑥804高等代数、⑦806量子力学、⑧816材料力学、⑨821控制工程基础、⑩852信号系统与通信原理、?854自动控制原理(含现代20%)•物流工程同上•信息管理与电子政务③301数学一④875信息管理与信息系统、⑤408计算机学科专业基础综合、⑥804高等代数、⑦821控制工程基础、⑧854自动控制原理(含现代20%)、⑨876管理学•金融管理③303数学三④876管理学、⑤804高等代数、⑥806量子力学、⑦816材料力学(选一)•项目管理③303数学三④876管理学•东北大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④848管理与运筹学••辽宁大学•大连海事大学、、管理科学与工程数学(一)(301)4、管理信息系统与数据结构(813)数学(一)(301)4、管理信息系统与数据结构(813)吉林(3所)•吉林大学管理学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④839生产管理《生产运作管理》李全喜编北京大学出版社《管理信息系统实用教程》李松编北京大学出版社•项目管理③302数学二④840工程经济学•工程项目管理③303数学三④840工程经济学•商学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④848运筹学•信用经济与管理(新增)③303数学三④847西方经济学•东北师范大学•延边大学黑龙江(4所)河北(2所)•华北电力大学(保定)120100管理科学与工程③303数学三④825微观经济学•120120★工程与项目管理③303数学三④825微观经济学•120121★信息管理工程③303数学三④825微观经济学山西(1所)•太原理工大学经济管理学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④864宏微观经济学•计算机与软件学院管理科学与工程③301数学一④864宏微观经济学内蒙古(1所)江苏(11所)•南京大学工程管理学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④922管理与运筹学基础•信息管理工程③303数学三④962管理学与计算机基础•东南大学经济管理学院管理科学与工程③301数学一或303数学三④933高等代数或945管理原理•土木工程学院管理科学与工程③301数学一④926工程经济或972运筹学••苏州大学计算机科学与技术学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④839管理信息系统与数据结构•南京师范大学计算机科学与技术学院管理科学与工程③数学三④01、02方向:管理原理03方向:数据库原理•中国矿业大学管理学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④830运筹学•金融工程与风险管理③303数学三④863金融学•工程管理③303数学三④826技术经济学•物流工程③302数学二④830运筹学•项目管理③302数学二④826技术经济学•科技与教育管理③303数学三④832管理学•建筑工程学院工程管理③303数学三④856工程经济学•矿业工程学院管理科学与工程③301数学一④822工业工程•中国药科大学•河海大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④870管理学•南京理工大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④828管理学原理•江南大学③303数学三④823管理学原理③303数学三④823管理学原理•南京农业大学•南京航空航天大学管理科学与工程824运筹学或826工程经济学或827经济学浙江(1所)•浙江大学•管理学院管理科学与工程•①101政治②201英语第一组:③303数学(三)④862管理学第二组至第五组:③301数学(一)④832机械设计基础或408计算机学科专业基础综合(含数据结构、计算机组成原理、操作系统和计算机网络)或845自动控制原理或840电路•建筑工程学院工程管理•③303数学(三)④848建筑工程经济与管理信息资源管理③303数学(三)或739情报学基础④866管理学综合安徽(3所)福建(2所)江西(1所)山东(3所)河南(1所)湖北(7所)•武汉大学经济与管理学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④818运筹学与技术经济学•信息管理学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④810数据结构与信息系统(含数据结构、管理信息系统)•信息资源管理③610信息系统(含信息系统原理、信息系统分析与设计)④813信息管理基础(含信息管理学、数据库原理)•电子商务③303数学三④811电子商务综合(含电子商务概论、数据库原理与应用)•华中科技大学管理学院③303数学三④851运筹学(二)852管理经济学(851、852选一)•土木工程与力学学院工程管理③301数学一④843工程经济及项目管理•管理科学与工程③301数学一④843工程经济及项目管理•武汉理工大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④881运筹学、883管理学原理、885应急管理导论(选一)•土木工程与建筑学院土木工程建造与管理③301数学一④863工程项目管理•物流管理③301数学一④868现代物流学•中南财经政法大学金融保险学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④807管理学•信息学院管理科学与工程①101思想政治理论②201英语一、202俄语、203日语任选其一③303数学三④807管理学•信息安全管理③303数学三④818管理学•华中师范大学信息管理系管理科学与工程③301数学(一)④846管理学原理••华中农业大学•中国地质大学(武汉)③303数学三④882管理学原理或883运筹学湖南(4所)•湖南大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④824管理学原理••中南大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④966运筹学(B)或967管理学(信息系统教程、生产运作管理)•项目管理工程③301数学一或302数学二④950工程经济学•土木工程规划与管理③301数学一④950工程经济学系信息系统工程•湖南师范大学•国防科学技术大学广东(4所)•中山大学管理学院管理科学与工程③301数学一④837运筹学与管理信息系统•岭南学院管理科学与工程数三管理经济学与管理学•暨南大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④827管理学••华南理工大学物流工程与管理③301数学一④869管理学•工业工程与管理工程③301数学一④869管理学•管理决策与系统理论③301数学一④869管理学•••华南师范大学广西(共1所)四川(共5所)•四川大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④975运筹学••西南交通大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④853运筹学或925微观经济学•工业工程③302数学二④960管理学•电子科技大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④809管理学原理••四川农业大学•西南财经大学经济技术及管理③303数学三④403管理学•物流管理③303数学三④403管理学云南(1所)贵州(1所)•贵州大学管理学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④847管理学原理•教育部现代制造重点实验室管理科学与工程③301数学一④842运筹学陕西(8所)•公共管理学院管理科学与工程③303数学三④803管理学与运筹学(管理学占100分,运筹学占50分•西安交通大学管理科学与工程③301数学一④817管理学•工业工程③301数学一④817管理学•西北工业大学管理学院管理科学与工程③303数学(三)④811管理学或814运筹学•机电学院管理科学与工程③303数学(三)④803设施规划与设计•长安大学•西北农林科技大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④812管理学原理与技术经济学或815管理学原理与运筹学•陕西师范大学•西安电子科技大学管理科学与工程③303数学三④862运筹学与管理学原理(各占50%)••第四军医大学甘肃(1所)•兰州大学海南(1所)•海南大学宁夏(1所)•宁夏大学青海(1所)•青海大学西藏(1所)•西藏大学新疆(2所)•新疆大学石河子大学•。
大学英语课程目录及课程简介1.大学英语A级(1)(4学分)课程编号:03004382任课教师:白岸杨等课程目标:在国家教委大学英语教学大纲的指导下,培养非英语专业学生具有较高英语应用水平和人文素养。
首要任务为帮助学生打下扎实的语言基础,掌握良好的语言学习方法,培养学生具有较高的听说水平,较强的阅读能力,并能够完成较为地道流畅的日常一般性写作和简单翻译工作,从而实现中英双语有效的交流。
此外,还要提高学生的人文素养以及评判性和独立性思维的能力;并且培养学生的国际视野,提升他们跨文化交际的能力,以适应社会发展和经济建设的需要。
课程内容:本课程主要通过学习国外原版听说读写教材,并结合国内优秀精读课本以及学生自主选择参加的英语第二课堂活动来培养学生英语实际应用能力和跨文化交际能力。
教材与主要参考书:1. 《Total English 大学通识英语》3 Will Moreton 著复旦大学出版社2008年9月第一版;2. 《新世纪大学英语阅读教程》(第四册),上海外语教育出版社,秦秀白总主编,2007年;3. Reader’s Choice,(第四版)[美] 桑德拉·希尔伯斯坦等编著,世界图书出版公司2007年;4. 课外原版辅助阅读材料若干。
先修课程:无2.大学英语A级(2)(4学分)课程编号:03004383任课教师:白岸杨等课程目标:在国家教委大学英语教学大纲的指导下,培养非英语专业学生具有较高英语应用水平和人文素养。
首要任务为帮助学生打下扎实的语言基础,掌握良好的语言学习方法,培养学生具有较高的听说水平,较强的阅读能力,并能够完成较为地道流畅的日常一般性写作和简单翻译工作,从而实现中英双语有效的交流。
此外,还要提高学生的人文素养以及评判性和独立性思维的能力;并且培养学生的国际视野,提升他们跨文化交际的能力,以适应社会发展和经济建设的需要。
课程内容:本课程主要通过学习国外原版听说读写教材,并结合国内优秀精读课本以及学生自主选择参加的英语第二课堂活动来培养学生英语实际应用能力和跨文化交际能力。
上海大学2018硕士研究生招生简章考研招生简章是考生了解目标院校招生相关信息的重要途径,目前各高校正陆续发布2018考研招生简章,文都考研官网会在第一时间整理汇总发布全国各院校2018考研招生简章讯息,考生们敬请关注。
下面是上海大学2018考研招生简章,有意报考上海大学2018年硕士研究生的同学可以参考阅读。
一、培养目标培养热爱祖国,拥护中国共产党的领导,拥护社会主义制度,遵纪守法,品德良好,具有服务国家服务人民的社会责任感,掌握本学科坚实的基础理论和系统的专业知识,具有创新精神、创新能力和从事科学研究、教学、管理等工作能力的高层次学术型专门人才以及具有较强解决实际问题的能力、能够承担专业技术或管理工作、具有良好职业素养的高层次应用型专门人才。
二、学习方式国家教育部规定硕士研究生按其学习方式分为全日制和非全日制硕士研究生。
我校招生简章中所列专业均招收全日制研究生,部分专业招收非全日制研究生。
全日制研究生是指符合国家研究生招生规定,通过研究生入学考试或者国家承认的其他入学方式,被具有实施研究生教育资格的高等学校或其他高等教育机构录取,在基本修业年限或者学校规定年限内,全脱产在校学习的研究生。
非全日制研究生指符合国家研究生招生规定,通过研究生入学考试或者国家承认的其他入学方式,被具有实施研究生教育资格的高等学校或其他高等教育机构录取,在基本修业年限或者学校规定的修业年限(一般应适当延长基本修业年限)内,在从事其他职业或者社会实践的同时,采取多种方式和灵活时间安排进行非脱产学习的研究生。
三、招生计划全日制和非全日制招生计划,教育部预计在2018年2-3月份正式下达当年硕士研究生招生规模。
全日制招生计划:我校2018年招生简章公布的总招生人数(包含推免生)是参考2017年实际录取人数暂定的,仅供参考。
正式录取时,各学院、专业的招生人数将根据国家正式下达的招生计划结合我校实际生源情况作相应调整。
非全日制招生计划:我校2018年共有18个专业学位领域招收非全日制研究生,具体可查看我校《2018年攻读硕士学位研究生招生目录》中标记有(非全日制)字样的研究方向均可招收非全日制研究生。
2019年上海大学考研专业课初试大纲
考试科目:822基础英语
一、复习要求:
要求考生熟悉英语语言的功能、规则、形式与结构,学会优化自己使用的语言,掌握与语言和文学等有关的基本概念和理论,能够合理、有效、且灵活自如地运用各种语体的英语,具备较为精深的英语读、写、译方面的功底。
二、主要复习内容:
2.1 From About Languages: A Reader for Writers
(1) Gender, Race, and Language Conflict: Sexism in English; rapport-talk and
report-talk; anti-male bias in English; how names define relationships; names for the race; black English.
(2) Right Words, Wrong Words, My Words: What dictionaries can do for us; four-
letter words; the E word; taboo language; English that belongs to everybody.
(3) Language and Cultural Diversity: Vanishing languages; whether English
should be the law; bilingual children; Americanization; names in the melting pot.
(4) The Language of Politics and Advertising: How language may serve as the
rhetoric of democracy; the doublespeak of weasel words; unprotected sex talk; types of propaganda.
(5) Writers and the Writing Process: Some instructions on writing and life; how
to hold the reader; writing as rewriting; concision; computers and writing.
2.2 From Reader’s Choice
(1) Unit 2: International Agency Reports and Essay (Social Essay); Mystery;
Essay and International Agency Reports.
(2) Units 3, 4 and 6: Newspaper Advertisements; News and Information; Science
Reporting; News and Advertisements.
(3) Units 7 and 10: Poetry; Science Reporting (Genetic Engineering); Short
Story.
(4) Units 8 and 9: Technical Prose and Sicence Reporting (Economics); Magazine
Article (Popular Psychology); Bus Schedule.
(5) Units 12, 13 and 14: Textbook (Psychology); Psychology; Suspense; Family
Narratives; Business text
精都考研网(专业课精编资料、一对一辅导、视频网课)。