CASIO 9860 GII 线路计算程序V2[1].0加强版使用说明
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1000.60 KB
- 文档页数:25

程序使用说明--CASIO 9860G 公路三维坐标计算程序程序说明:本程序是一款运行用CASIO 9860G 系列上的公路三维坐标计算程序,程序约8KB大小,使用9860中的表文件作为程序数据,由于受9860主存大小限制,一次约能进行200个交点(交点法)或是约600个线元(线元法)的公路平面坐标和中桩高程,如使用内部后备存储器(1.5M)在需要时手动调入进行计算,或是使用SD卡为数据载体则计算只受这两个容量的限制。
程序功能:程序能选择交点法(一般适用用主线)或是线元法(一般适用于岔道)计算,他们有相同的功能:1、全线三维坐标正算,计算全线路上任一桩号偏距点坐标(支持斜交)2、全线三维坐标反算,实测一点坐标,计算该点所在的桩号及偏距3,线路任一点放样工作,设站后输入任一点桩号偏距斜交即计算测站到该点平距及方位4、批量计算三维坐标,从指定的桩号向结束处或开始处按(以+或-的为间距间距)连续计算点的三维坐标5、路面挂线测量,支持全站仪和水准仪操作,实测一点计算该点到指定的结构层的高度,用于指导结构层抄平工作6、任意断面隧道超欠挖程序,实测断面上任一点即可得到该点的超或是欠挖值,支持单独断面,或是将断面加入到线路中去(该程序需单独起动不在统一界面选择下)5、结构物相对位置正反算,计算结构物前后左右的点在线路上的坐标或是实测一点后反算实测点到结构特轴线的前后左右(该程序需单独起动不在统一界面选择下)注意:路线上任一点三维坐标中(程序中现计算的是中心高程,如要计算断面点高程则表中要有相应的超高数据并把调用时的Prog”SQX”改成0(零)->O(欧):Prog "CHAOGAO",即可计算断面点高程),反算路线上任一坐标的里程和距中心的位置,程序界面及提示说明:主起动程序:MainProg (该程序只起一引导作用,执行时可以直接选择交点法或是线元法直接执行)起动后屏幕显示:Ji SHuan Fang Fa:‘计算方法选择JiaoDianFa: (F1)‘按F1选交点法XianYuanFa: (F2)‘按F2选线元法每个计算所显示提示都是以拼音或是显见的字符表示,对于交点法和线元法,都提两种输入数据方式:一是在EXCEL中组织好数据存成CSV文件后直接导入(当然也可以在程序指定的列表中输入);二是程序运行时输入,即在运行程序是,根据相应的提示输入数据,由程序自动存入列表中,下面以交点法来说明各阶段的各种提示的意思和处理注意事项,F1交点法按9860面板上最上面一行的功能键F1就直接选择了交点法进行计算,会弹出下面的提示:DuBiaoGeShuJu(1)ShouGongShuRu(123)1读表格中数据直接计算(表格中数据格式见后面说明)1.1)输1后执行还会弹出提示:YaoChuShiHuaBiaoGe?‘要不要初始化表格Chu Shi Huan (-1)‘要初始化输-1Zhi Jie Shi Yong‘-1外的任意值就直接使用表格中数据计算注解:要不要初始化表格,表格中倒进9860的数据在第一次使用时必须要初始化后才能计算,这主要是基于提高处理速度和可能要把表格中的数据输出作为资料使用,初始化计算的内容是每个交点的主点桩号和主点坐标,初始化是一个费时的过程,在第一次初始化后,以后只要表格中的数据没有破坏,就可按非-1的任意值计算了,建议把初始化后的表格备份到寄存器或是SD卡上。



Ck-1重要!請將您的手冊与所有材料保存于方便存取之處,以便于未來參考使用。
目錄1 按鍵与顯示屏 (3)按鍵 ..........................................................................................................................3按鍵索引 ..................................................................................................................3顯示屏 . (5)2 快速入門 (6)打開与關閉電源 ........................................................................................................6使用模式 ..................................................................................................................6基本計算 ..................................................................................................................6重放特征 ..................................................................................................................7分數計算 ..................................................................................................................7指數計算 ..................................................................................................................8圖示功能 ..................................................................................................................8雙圖形 ......................................................................................................................9動態圖形 ................................................................................................................10表列函數 (11)3 舉例 (12)例1:積分計算 .....................................................................................................12例2:矩陣計算 .....................................................................................................13例3:統計計算 ......................................................................................................14例4:電子數据表 ...................................................................................................15例5:電子數据表 ...................................................................................................16例6:圖形(二次不等式) ......................................................................................17例7:動態圖形 ......................................................................................................18例8:表格(指數函數) ..........................................................................................19例9:遞歸(遞歸圖形) ..........................................................................................20例10:橢圓圖形 ...................................................................................................21例11:聯立方程 ...................................................................................................22例12:財務計算(單利) ........................................................................................23例13:財務計算(分期償還) (24)4 附錄 (26)電源 ........................................................................................................................26輸入范圍 (28)操作注意事項 .................................................................................................30在連接計算機時的注意事項 (30)本手冊使用許多實例,闡述fx-9860GSD/fx-9860G的基本操作,從而幫助您更快捷地掌握此計算器的使用方法。


目录第一章GPS 测量概况........................................ 1-1 §1.1 GPS接受机与卫星信号1-1§1.2 测量技术1-2§1.3 GPS在测量工作中的应用 1-2CASIO采集器 .................................................. 2-1 §2.1简介2-1§2.2 CASIO掌上机的结构及各部分名称2-1§2.3 电池的安装与更换2-2§2.4 键盘及其部分功能键简介2-3§2.5 CASIO基本用法2-4§2.6 交互状态下的常用命令简介2-6第三章CASIO型控制器使用说明.................... 3-1 §3.1控制器软件安装3-1§3.2具体操作步骤3-1第四章测量前的准备 ......................................... 4-1 §4.1 坐标系统的确定4-1§4.2 选定测量的类型4-1第五章仪器的连接 ............................................. 5-1 §5.1 接收机和电台连接示意图5-1§5.2仪器的连接5-2第六章测量步骤 ................................................. 6-1 §6.1控制器软件操作指南6-1§6.1.1坐标系.................................................................................... 6-2§6.1.2设置基准站............................................................................ 6-4 §6.2开始测量6-7§6.2.1流动站的操作........................................................................ 6-7§6.2.2碎步测量................................................................................ 6-7§6.2.3 坐标库................................................................................... 6-8§6.2.4 点放样.................................................................................. 6-11§6.2.5 解模式................................................................................. 6-12 §6.3卫星状况6-12§6.3.1查看卫星信息...................................................................... 6-13§6.3.2设置卫星参数...................................................................... 6-14§6.3.3卫星删除.............................................................................. 6-14 §6.4工具6-14§6.4.1求转换参数.......................................................................... 6-15§6.4.2 BL与XY间互换 ........................................................... 6-17§6.4.3 工程文件........................................................................... 6-17§6.4.4 软件注册........................................................................... 6-17§6.5其他6-17§6.5.1基准站距离.......................................................................... 6-18§6.5.2软件信息.............................................................................. 6-18§6.5.3坐标浏览.............................................................................. 6-18§6.5.4文件输出.............................................................................. 6-19 第七章常用RTK作业方法及步骤................... 7-1 第八章常见问题解决办法 ................................. 8-1 附录GPS技术规格……………………………………………………….A-1第一章GPS 测量概况§1.1 GPS接收机与卫星信号GPS卫星发送两种信号,第一种较为简单的信号叫C/A码,第二种信号叫P码(精确)。



白色国际版9750GII 计算器升级刷机到9860GII 2.0系统详细图文操作步骤(大歪哥实战刷机图文步骤提供给不会刷机操作VIP会员使用)白色的国际版版本号应该为:一、刷机前的准备工作。
(一) 首先在升级前可以按照下述操作检查看到目前白色国际版9750的上述版本号,确认后,那么你就可以把你的9750GII用该文件进行安全滴升级了。
AC/ON开机后按MENU键,然后按“REPLAY方向键的向下键箭头”找到计算器SYSTEM模块菜单,然后EXE,按F4:Version 可以首先查看到版本,是如下显示:VersionOS2.00.0700然后EXIT,后按SHIFT+AC/ON关闭计算器,进行如下步骤操作进一步确定目前的机子版本号与上述是否吻合。
操作如下:1:用两个手指同时按下OPTN 、EXP不要松开放后,再用一个手指按AC/on这三个键,计算器屏幕将如下显示=DIAGNOSTIC MODE=Factory Use Only!Press :[EXIT]那么此时直接按F1键。
2、紧接着按数字键9 就可,目的是清除计算器的RAM。
3、再然后按数字键4就可以得到版本号,出现DataO和DataA 字样,DataA显示就是是:2009.0203.1852。
如果这些都和开头的版本号对应,那么就可以准备开始刷机了。
(二) 电脑上(最好是在WINDOWS XP系统上当然WINDOWS7 32位版本系统上也可,64位系统就是不能行的,注意)进行安装FA-124 V2.0版本这个计算器与电脑的通讯软件(随计算器的光盘或者网上百度都可搜索到下载),安装完毕这个软件,目的就是同时也自动安装了计算器与电脑连接的驱动程序CEGS502了。
那么紧接着先关闭计算器状态下,第一次将你的计算器与你的这台(安装过FA-124软件的)电脑进行连接,第一次电脑会提示自动安装驱动软件的提示界面,选择自动安装下一步就是了,待电脑显示CEGS502驱动安装完毕(注意:第一次连接会这样提示安装该驱动,以后再连接就不会提示了的),那么计算器屏幕上就会显示几个选项,计算器上按F1键,计算器屏幕就会显示如下“接收”状态Receiving。
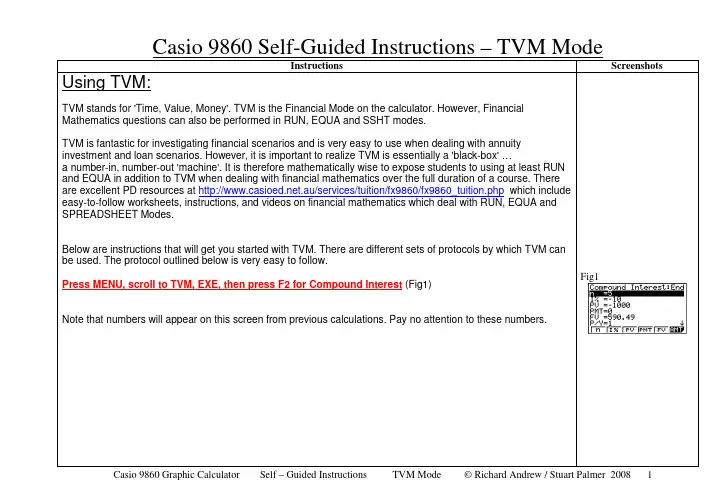
Casio 9860 Self-Guided Instructions – TVM ModeInstructions Screenshots Using TVM:TVM stands for 'Time, Value, Money'. TVM is the Financial Mode on the calculator. However, FinancialMathematics questions can also be performed in RUN, EQUA and SSHT modes.TVM is fantastic for investigating financial scenarios and is very easy to use when dealing with annuityinvestment and loan scenarios. However, it is important to realize TVM is essentially a 'black-box' …a number-in, number-out 'machine'. It is therefore mathematically wise to expose students to using at least RUNand EQUA in addition to TVM when dealing with financial mathematics over the full duration of a course. Thereare excellent PD resources at .au/services/tuition/fx9860/fx9860_tuition.php which includeeasy-to-follow worksheets, instructions, and videos on financial mathematics which deal with RUN, EQUA andSPREADSHEET Modes.Below are instructions that will get you started with TVM. There are different sets of protocols by which TVM canbe used. The protocol outlined below is very easy to follow.Press MENU, scroll to TVM, EXE, then press F2 for Compound Interest (Fig1)Note that numbers will appear on this screen from previous calculations. Pay no attention to these numbers. Fig1The TVM protocols to be used are:n = number of time intervals (could be 8 years or 32 quarters or 96 months)I% = the per annum interest rate, as a percentage eg 11.5% is entered as 11.5 (not 0.115) PV = Present ValuePMT = Payment, per time periodFV = Future ValueP/Y = It is best to consider both P/Y and C/Y as the number of compounding periods per year; ie both values will always be identical. (P/Y is meant to stand for 'payments/year' but this does not make sense for this protocol)C/Y =Same as P/YEg.If the investment (or loan) is compounding annually (once per year), then P/Y=C/Y=1.If the investment (or loan) is compounding quarterly (4 times per year), then P/Y=C/Y=4.If the investment (or loan) is compounding monthly (12 times per year), then P/Y=C/Y=12. NOTE: The dollar values (PV, PMT and FV) need to be entered either as positives or negatives, depending on the situation. This seems confusing at first, but is actually very simple. Consider each situation to be money either LEAVING your pocket OR RETURNING to your pocket.•If money is LEAVING your pocket, the number is entered as a negative.•If money is returning to you, the number is entered as a positive.Therefore:•receiving a loan of $5000: PV = 5000• a regular payment from you of $260: PMT = -260•investing $50 000: PV = -50 000•an investment that will be worth $100 000 in 10 years time: FV = 100 000Below are two examples that involve a once-only investment that receives compound interest.Example 1:A sum of $2 000 is invested at 8%pa interest, compounded monthly, for 20 years. What is the future value of this investment?Enter the values as they appear in the question, pressing EXE after each entry. Leave FV as the pre-existing value. Check your entries with Fig2NOTES:n=20x12; is the number of months. A good habit for students to enter n as (eg 20x12) so as to minimize careless error. I%=8; in TVM, the interest is always paPV is negative because $2000 'left' your pocket PMT=0; there were no regular paymentsFV CAN BE ANYTHING! It is what we want to know so it makes no difference what number is showing here. P/Y and C/Y = 12; the interest compounds 12 times every year. P/Y and C/Y are always equal.Now press F5 for FV (Future Value). See Fig3.The answer can be read in the previous screen by pressing EXIT (Fig4)Note that FV is positive, not negative, because after 20 years the investment goes 'back into your pocket'. The investment has grown from $2000 to $9853.61Example 2:What annual interest rate will be required for an investment of $12 000 to become $18 000 in 5 years , if the interest compounds annually ?Enter the values as they appear in the question, pressing EXE after each entry. Check your entries with Fig5.NOTES: n=5 (years)I%=ANYTHING; It is what we want to know so it makes no difference what number is entered here. PV is negative because $12000 'left' your pocket. PMT=0; there were no regular paymentsFV is positive because $18000 will 'return' to your pocket in the future.P/Y and C/Y = 1; the interest compounds once a year. P/Y and C/Y are always equal. Now press F2 for the interest rate (Fig6)Fig3Fig4Fig5Fig6Press EXIT to view solution in previous screen. (Fig7)Below is an example that involves repeated investments (an annuity) that receives compound interest.Example 1a):A sum of $2 000 is invested at the end of every year, at 8%pa interest, compounded yearly, for 20 years. What is the future value of this investment?Enter the values as they appear in the question, pressing EXE after each entry . Check your entries with Fig8.NOTES:n=20 (years)I%=8; in TVM, the interest is always pa. PV=0; the annuity started with nothingPMT is negative; each payment 'leaves' your pocket.FV CAN BE ANYTHING! It is what we want to know so it makes no difference what number is showing here. P/Y and C/Y = 1; the interest compounds once a year. P/Y and C/Y are always equal.Now press F5 for FV (Fig9)Press EXIT (Fig10)Note that FV is positive, not negative, because after 20 years the investment goes back into your pocket. The investment was $2000 x 20, which is $40 000(The investment has grown from $40 000 to $91 523.93) (to the nearest cent) Example 1b:What is the present value of the annuity in example 1a?ORWhat single investment (earning the same rate of compound interest for 20 years) would give the same future value as the repeated investments in example 1a?Enter the values as they appear in the question, pressing EXE after each entry. Check your entries with Fig11.Fig8Fig9Fig10Fig11NOTES:All that needs to change from the Q1a) entries is PMT to be changed to zero! The FV for 1b) is the same FV as in 1a).Now press F3 for PV (Present Value). See Fig12.Press EXIT to view in original screen (Fig13)Note that PV is negative, not positive, because the money is leaving your pocket to make the single investment.A single investment of $19 636.29 NOW will produce the same result in 20 years."Don't students get confused when being taught TVM because values have to entered differently to the formulae?" This is a question often asked by teachers learning TVM. The main difference of course, is that interest rates need to be entered as whole-pa-percentages into TVM but as per-time-period-decimals in the formulae. From experience, whenteaching TVM protocols, if the formulae protocols are referred to simultaneously students understand quickly and with little confusion. Over the long term these differences prove to be a very minor disadvantage when compared to the ease and versatility of using TVM.TVM Graded Question Series:The 'Financial_Maths_TVM_Sheets 1-3' are an excellent, graded worksheet series with solutions designed for students to gain practice in using TVM.For further and more advanced information including practice questions refer to the manual 'Mathematics with a Graphics Calculator – Casio fx-9860 AU' by Barry Kissane & Marian Kemp, available at .au/downloads/books/fx9860/orderBarryBook.pdfFig13。
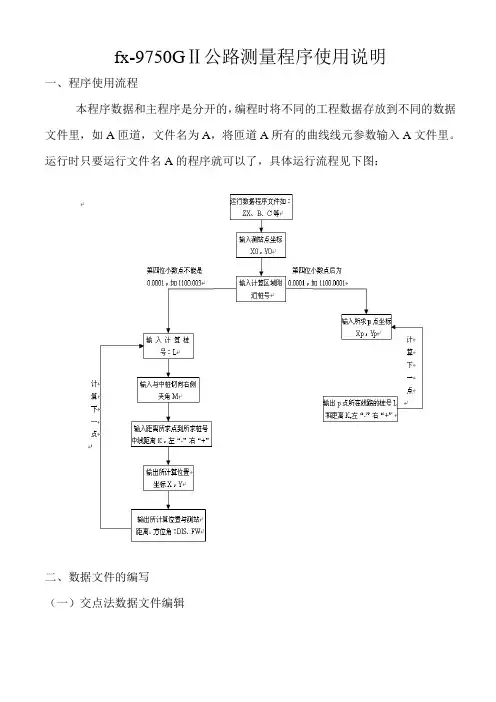
fx-9750GⅡ公路测量程序使用说明一、程序使用流程本程序数据和主程序是分开的,编程时将不同的工程数据存放到不同的数据文件里,如A匝道,文件名为A,将匝道A所有的曲线线元参数输入A文件里。
运行时只要运行文件名A的程序就可以了,具体运行流程见下图:二、数据文件的编写(一)交点法数据文件编辑交点法编写数据文件必须是对称型的,即直线段→缓和曲线段→圆曲线段→缓和曲线段→直线段,(如果任意一端没有直线段,则把直线段长度看做是0),另外圆曲线两侧缓和曲线的旋转常数必须相等,并且和直线段连接处的半径必须是无穷大。
交点法数据文件编写一般是根据设计图纸提供的平面曲线参数一览表提供的参数来编写,每个弯道包括:弯道起点方位角(C),交点X坐标(D),交点Y坐标(E),缓和曲线长度(F,当没有设缓和曲线时,F=0),交点转交(G,向左转弯,G为负值,向右转弯,G取正值),交点桩号(H),弯道圆曲线半径(R)。
下图是一段市政道路设计参数数据。
根据上图提供的数据,可以编辑成如下的数据文件:文件名:CHLNR在上图中,有两个条件转移语句即If L>0:Then 98°39°35.12°→C:4774.384→D: 2415.861→E:140→F:31°17°23°→G:410.007→H:600→R:IfEndIf L>1060:Then 129°56°58.19°→C:4206.421→D: 3093.946→E:70→F:-33°50°48°→G:1285.437→H:600→R:IfEnd……如果还有其他弯道,可以继续完后加。
在这些存放设计参数的语句前后的程序表达式是固定的。
说明:编辑曲线参数时,每个曲线参数放在一个If L>***.***(两个弯道中间直线段上的任意桩号):Then ***°**°**.**°→C(弯道起点方位角):****.***→D(交点X坐标):****.****→E(交点Y坐标):***.***→F(缓和曲线长度:**°**°**°→G(转角,向左转为负值,向右转为正值):***.***→H(交点里程桩号):***→R(圆曲线半径):IfEnd 条件式语句里,如果有多个弯道,一直按上述形式编下去,变量说明:1、L>***.***弯道参数的起点范围,可以是弯道起点,也可以是弯道前直线段里的任意点桩号2、***°**°**.**°→C 弯道起点方位角3、****.***→D、****.****→E交点X坐标、Y坐标4、***.***→F缓和曲线长度,如果没设置缓和曲线,则缓和曲线长度看做05、**°**°**°→G 转角,向左转为负值,向右转为正值6、***.***→H、交点里程桩号7、***→R 圆曲线半径注意,运行程序时,第一部是输入测站坐标X0,Y0,然后输入近似桩号,主要是为了加快收敛,输入时注意当根据桩号和距中距离计算所求点坐标时,请不要把小数点第四位输入0.0001,如K21+369.0921,请把桩号输入21369.092即可,相反,当根据坐标反算桩号和距中距离时,请在输入时把第四位小数数位0.0001,如K21+200,输入时请输入21200.0001。
9860计算器[教材]9860计算器经过几个月刻苦研究,本人开发的全能三维坐标计算程序(适用于卡西欧9860折叠式图形计算器及系列卡西欧图形计算器)终于完成。
本人开发的全能三维坐标计算程序,适应性强,地形、建筑、鉄路、公路、各种管线沟渠等都适用。
程序中的核心程序就是网上发表的线元通用积分程序,它适应各种线元,直线、折线、完整缓和曲线、非完整缓和曲线、园曲线、S型曲线、卵型曲线、复曲线等由各种线元组合的复杂曲线。
线元通用积分程序在本人开发的程序中,线元输入,坐标正算,坐标反算,隧道超欠挖都在应用。
本人开发的全能三维坐标计算程序功能最全,地形测量、建筑放线、路基分层测量、斜交、超高、加宽、边坡放线、隧道超欠挖等均可使用,你只需要在程序运行中根据程序中的提示输入相应的参数即可运行相应的功能。
建筑放线你只需要在线元输入中按直线元输入一个线元数据即可,K+即是你确定的纵向建筑放线方向距离,-C就是相对应横向距离,运行后即可显示你需要的放线数据水平角Hr及水平距离HD.你需要做的是设置仪器数据中以你定的建筑原点(N=0,E=0)输入相应坐标数据。
本人开发的全能三维坐标计算程序中,道路加宽及超高在缓和曲线全段范围内进行,加宽曲率变化按四次曲线公式计算,超高曲率变化按三次曲线公式计算,超高计算以道路中心旋转计算。
本人开发的全能三维坐标计算程序,在进行道路加宽及超高计算时,程序根据里程自动判断所在位置(直线段、前缓和曲线段、园曲线段、后缓和曲线段)及线路转向(左转、右转)并计算加宽值和超高值,加宽值自动设置为曲线内侧值,超高值按横向距离值自动计算加入设计标高中,同时显示该位置超高计算的坡度。
本人开发的全能三维坐标计算程序中,数据库功能最全(按MENU键,按2键。
进入统计模式),第一行数据是程序运行中的各种参数数据,第二行及以后数据是:第一列到第十一列为测量数据库,包括坐标正反算中所有数据(输入的和输出的数据),第十二列到第十五列为标准点数据库,第十六列到二十一列为线元数据(包括平曲线,竖曲线,边坡断面,隧道断面等)。
卡西欧9860GIISD坐标正反算程序主程序XY-LCLbi 0:“1LC-XY,2XY-LC”?→V:If V=1:Then Goto 1:Else Goto2:IfEnd:Lbi 1: “K”?→L:“Dj-Dy”?→Q: “F0”?->J:Prog “1-N”: Prog “ZSZB”: “X=”:X◢“Y=”:Y ◢“FWJ=”:O◥DMS◢Goto 0:Lbi 2:0→Q:0→J: “XO”?→M: “YO”?→R: “KL”?→L: Prog “FSZB”: LC=”?→Q◢Goto 0: 正算子程序ZSZBL-S→H:(T-I)H/(K-S) →U7→N: Lbi 0:C+90(NU/8+2I)(NH/8)/3.141592654→List 1[N]:Dsz N: Goto 0C+90(U+2I)H/3.141592654→O:O+J→P:A+Abs H(Cos C+4(Cos List 1[1]+ Cos List 1[3]+ Cos List 1[5]+ Cos List 1[7])+2(Cos List 1[2]+ Cos List 1[4]+ Cos List 1[6])+Cos O)/24+Q Cos P→X:B+Abs H(Sin C+4(Sin List 1[1]+ Sin List 1[3]+ Sin List 1[5]+ Sin List 1[7])+2(Sin List 1[2]+ Sin List 1[4]+ Sin List 1[6])+ Sin O)/24+Q Sin P→Y:反算子程序FSZBLbi 0: Prog “1-N”:Prog “ZSZB”:O-90→Z:(R-Y)Cos Z-(M-X)Sin Z→P:P+L→L:If Abs P≧0.001:Then Goto 0:Else Goto 1:IfEnd:Lbi 1 (R-Y)Cos O-(M-X)Sin O→Q:路线选择子程序1-N“1-N”→V:If V=0:Then Prog “X-0”: IfEnd:If V=1:Then Prog “X-1”: IfEnd:If V=2:Then Prog “X-2”: IfEnd:数据库X-0 X-1 X-2 X-3If L≧起点桩号And L<终点桩号:Thdn起点桩号→S:起点X坐标→A:起点Y坐标→B:起点方位角→C:终点桩号→K:起点半径曲率→I: 终点半径曲率→T: IfEnd 、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、式中:I、T为1/I、1/T(曲线中右正左负);直线段I、T经为0,第一缓和段I=0、T=1/T,圆曲线中I=1/I、T=1/T,第二缓和段I=1/I、T=0。
CASIO fx-9750GII-9860隧道超欠挖放样程序主程序名称:SDCQW说明:该程序适用于CASIO fx-9750GII/9860计算器,适用隧道类型为1圆心、2圆心、3圆心隧道超欠挖轮廓线放样程序“暂不支持偏心隧道”,计算以隧道中心为准,若线路中心与隧道中心不重合需要将数据库线路中心坐标转为隧道中心坐标。
程序演示:运行:SDCQW显示:1.DK=>ZS2.XY=>FS(输入1为坐标正算、输入2为坐标反算和超欠挖计算)J?=2DK?=10010(输入近似里程“程序属于线元法,调用数据库”)X?=3377709.896(输入隧道超欠挖实测坐标X)Y?=455860.992(输入隧道超欠挖实测坐标Y)0=>FS:1=CQWJ?=1(输入0为只显示反算结果,输入1为显示隧道超欠挖)Z?=339.004(输入隧道超欠挖实测高程Z)超欠挖显示结果如下:K=坐标反算结果,里程。
W=坐标反算结果,偏距。
CQW=超欠挖计算结果,(正为超挖、负为欠挖)。
程序源码下载地址:CASIO fx-9750GII、9860G隧道放样程序.rar程序列表:备注:凡使用该程序者请仔细核对程序内存占用字节大小,以防他人修改造成失误。
CASIO fx-9750GII/9860 HFJH后方交会程序主程序名称:HFJH说明:该程序适用于CASIO fx-9750GII/9860计算器。
HFJH:(边角后方交会)本程序适用于在一个未知点上设测站,观测两到个已知点的距离及夹角求坐标。
HFJH1:(距离后方交会)本程序适用于在一个未知点上设测站,观测两到个已知点的距离后求坐标。
1、程序提示:HFJH运行:HFJH显示:XA?=3371514.173(输入P1点坐标X)YA?=459856.1150(输入P1点坐标Y)XB?=3370811.988(输入P2点坐标X)YB?=460138.7470(输入P2点坐标Y)D1?=444.8900(输入L1水平距离)D2?=314.6723(输入L2水平距离)α?=170°18ˊ50″(输入∠B水平夹角)XP=3371090.8515(计算结果:P点坐标X)YP=459992.9592 (计算结果:P点坐标Y)2、程序提示:坐标反算运行:HFJH1显示:XA?=10066.027(输入P1点坐标X)YA?=10624.322(输入P1点坐标Y)XB?=10066.027(输入P2点坐标X)YB?=10754.224(输入P2点坐标Y)D1?=79.70797(输入L1水平距离)D2?=87.07341(输入L2水平距离)Q?=1(观测方向:1为P1到P2顺时针观测、1为P2到P1逆时针观测)XP=10013.810(计算结果:P点坐标X)YP=10684.545(计算结果:P点坐标Y)ASIO fx-9750GII/9860 ZXZFS直线正反算程序主程序名称:ZXZFS说明:该程序适用于CASIO fx-9750GII/9860计算器,本程序主要对直线正反算设计,正算可算直线中边桩坐标及其斜交、反算可推算直线距线路中心的里程偏距。
整理编绎:林牧兴编绎日期:2013年4月13日星期六QQ:9725291 Email:croptree@ FX-9860GII SD 测量程序使用说明书2013.03.13 更新一、程序文件的安装:1.解压文件“Fx9860 Celang Addin.rar”。
2.打开CASIO FA-124 程序,将CL2012.g1a 插件和要素文件上传到计算器的内存中。
关于文件安装及同步的详细步就不讲了,不清楚的请百度一下。
3.打开计算器会发现多了一个项目。
4. 注册是为了收集反馈使用情况和插件的兼容性,方便下次修改。
5.注册是完全免费的。
6.从12.09版开始取消试用的功能。
7.主界面:按F1~F6选择功能。
F1:坐标正算放样功能F2:坐标反算功能F3:隧道断面测量功能F4:边坡放样功能F5:水准测量功能F6:坐标计算工具二.功能介绍:F1坐标正算:K=待求点的桩号D=待求点与中桩的偏距(左负右正)V=待求点与线路方位角的夹角,一般都是90度(斜交除外)。
Ht=结构物的厚度(正减负加)。
Rou:选择路线。
Set:设置参数。
K+:里程加上桩间距。
K-:里程减去桩间距。
K.D:切换显示结果样式按F1进入“选择数据库”(如右图)按上、下键移动选项,按EXE键选定文件,按F1查看平曲线要素;按F2查看竖曲线要素;按F3查看横坡/超高要素;按EXIT键重新选择文件。
整理编绎:林牧兴编绎日期:2013年4月13日星期六QQ:9725291 Email:croptree@ 按EXE 确认并返回(第一行显示打开的文件路径及要素数据文件名)参数设置:Mk=正算时为与下一个桩号的间距。
Mk=反算时为辅助桩号。
Pd=平坡距;即平曲线设计线到高程设计线的距离,一般是1米吧。
Hd=最大横坡距;就是超出这个范围的偏距不算横坡超高。
(不含平坡距的距离。
)设置好按F3或Exit确定并返回。
坐标显示结果:K=待求点的桩号X=待求点的X坐标Y=待求点的Y坐标Z=待求点的(中桩)设计高程F=待求点线路方位角HP=待求点横坡坡度BH=待求点(边桩)高程。