casio计算器fx-82es使用说明.pdf[1]
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:694.07 KB
- 文档页数:52
![casio计算器fx-82es使用说明.pdf[1]](https://uimg.taocdn.com/44c1966b7e21af45b307a88f.webp)

S M 2 8 -x fO I S A CMASTERING THE CALCULATOR USING THE CASIO fx-82MSLearning and Teaching Support Unit (LTSU)The Learning CentreGuide bookWritten byLinda GalliganPublished byUniversity of Southern QueenslandToowoomba Queensland 4350Australia.au©University of Southern Queensland, 2006.1.Copyrighted materials reproduced herein are used under the provisions of the Copyright Act 1968 as amended, or as a result of application to the copyright owner.No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise without prior permission.Produced by the Distance and e-Learning Centre using FrameMaker5.5.6 on a Pentium workstation.TABLE OFCONTENTSPAGE Introduction1A word about starting out21.Addition and subtraction42.Multiplication and division83.Brackets104.Powers115.Fractions17ing the x–1 key197.Scientific notation208.Factorial x!22ing memory2310.Statistics2511.Linear regression3112.Trigonometric functions3413.Exponential and logarithmic functions3614.Degrees, minutes, seconds38 Review calculator exercises41 Calculator solutions42 Your notes44Mastering the Calculator using the Casio fx-82MS1IntroductionThis is one in a series of booklets prepared to assist students who are learning to use a calculator. They have been prepared by staff in The Learning Centre from the Learning and Teaching Support Unit (LTSU) at USQ. The series comprises:Mastering the calculator•Using the Casio fx-100s (also suitable for Casio fx-570)•Using the Casio fx-100AU•Using the Casio fx-82LB•Using the Casio fx-82TL•Using the Casio fx-82MS•Using the Sharp EL-531LH•Using the Sharp EL-556L•Using the Sharp EL-531RHThe instructions in this booklet only explain some of the keys available on your calculator necessary for basic work in data manipulation. If you require more assistance please contact The Learning Centre. If you would like information about other support services available from The Learning Centre, please contactThe Learning Centre (TLC)Learning and Teaching Support Unit (LTSU), S-BlockThe University of Southern QueenslandTelephone: 07 4631 2751Email:***********.auFax: 07 4631 1801Home page: .au/ltsuNote the booklets are also available online at the above address (follow the prompts).2Mastering the Calculator using the Casio fx -82MSA word about starting out•Make sure you are in the correct mode selection and that all previous data is cleared.•Example: To perform arithmetic operations press •To clear all values press •To clear memory pressThe screen displaysPress to clear memory•If your calculator has FIX or SCI on the display pressthree timesappears on the screenpress 3, then 2 so you are in Normal mode.•If your calculator has RAD or GRAD on the display press two timesappears on the screenpress 1 so you are in Degree mode.Mcl ModeAllMastering the Calculator using the Casio fx-82MS3•There is also a mode which gives you a preference for displaying the decimal point as a dot or comma as 34.26 or 34, 26.PressPressPress Press4Mastering the Calculator using the Casio fx -82MS1.Addition and subtraction1.1 To add numbers(it is shown on the photograph of the calculator here).ExampleTo add 7 and 3, typeThe display should read 10ExampleI want to find the total amount I earned in the past four weeks. If I earned $471, $575, $471 and $528, the key strokes would beThe display should read 2045.Mastering the Calculator using the Casio fx-82MS5and continue.ExampleExampleIf I want to add 471 and 575 but I typedThe display should read 1 046.‘Try practising cancelling with the1.3 The keys are used when you to delete other dataExampleIf you typed:471 + 546PressThe display should read 1 047.Practice using this key when replacing digits, operation keys (+ – ×÷), or more than one digit (use the DEL key).You can also use the insert key to insert anything you omitted. ExampleIf you typed 471 + 56the display should read 1047.1.4 To subtract numbersFind the key (it is shown on the photograph of the calculator following). ExampleTo subtract 35 from 257, typeThe display should read 222Example348 – 24 – 19The keystrokes areThe display should read 305.Sometimes you may have a sum like this:-7 + 4You can use theThe key strokes areThe display should read -3.You could also use the keystrokesIn this case the calculator recognises the – as a negative (not recommended to do it this way).2.Multiplication and division 2.1 To multiply numbersFind the key (it is shown on the photograph of your calculator here).ExampleTo multiply 7 and 3, typeThe display should read 21To find 753 × 492, typeThe display should read 370 4762.2 To divide numbersExampleTo divide 35 by 7, type The display should read 5To divide 7 905 by 85, typeThe display should read 93To divide 56 by 23947 typeThe display should read 0.002338497If it reads 2.3385×10-03 or something similar, then your calculator is in SCI (Scientific mode).See page 2 to change to NORM (normal mode).2.3 Combining multiplication and divisionExampleIf the question isthen it is really 27 ÷ 7 ÷ 4.Try it.The display should read 0.9642857142774×-----------3.BracketsFind the set of bracket keys on your calculator.The fx-100AU allows you to use many sets of brackets.ExampleDo the calculation 471 – (93 + 11 + 2) on the calculator. (Make sure your calculation is in ordinary comp. mode –)The keystrokes required are The display should read 365.Sometimes in calculations you will see other grouping symbols, for example, { } (called braces), [ ] (called square brackets).Try these examples:Exercise 1(a)25 + (7 + 2 – 4)(b)18 (3 + 7) [a multiplication sign is understood 18 × (3 + 7)] but you don’t need to press the× key(c)4 + 5 [2 (3 + 7)][to use two sets of brackets just press the same button](d)Answers:30; 180; 104; 14.Powers4.1 Squaring and higher powers62 means 6 × 6. You can use the square key to do this calculation. (It is shown on the photograph of your calculator here.)532+()----------------Pressthe display should read 36.Or you can use the power key on your calculator.Find the ^ key on your calculator (similar to the key on your computer keyboard).ExampleTo square 6,that is, find 62, typeThe display should read 36To find 273 the required key strokes areand the display should read 19683.If you have learnt your multiplication tables you will already know the squares of the whole numbers from 1 to 12 and thus be able to complete much of the following table.__________________________________________________________________________Exercise 2Use your calculator to find the squares of the whole numbers from 13 to 25 and any other squares you are unsure of.__________________________________________________________________________12 = 1112 =212 =22 = 4122 =222 =32 = 9132 =232 = 52942 =142 =242 = 57652 =152 =252 = 62562 =162 =72 =172 =82 =182 =92 =192 =102202Exercise 3You can use this key for other powers as well. Try these examples(a)74(b)810(c)(0.4)6 (you do not have to type the brackets in)(d)(–7)6 (you need to type the brackets in)(e)50.4(f)5–4__________________________________________________________________________Answers:(a)2401(b)1073741824(c)4.096 × 10–3 or 0.004096 (you move the decimal 3 places to the left)(d)(e)1.903653939(f)0.0016 [Just press–4 is the same as so you could press__________________________________________________________________________4.2 Square rootFinding the square root of a number ‘undoes’ or ‘neutralises’ the squaring of the number and vice versa. The symbol for square root is(This is called the radical sign)The square root of 36 is written as Now because 62 = 36, .Find the square root key on your calculator and type154-----36366=The display will read 6.What do you think is? =__________________________________________________________________________You should have said 9 because 92 = 81(Check your calculator)__________________________________________________________________________What do you think will be? You should have said ‘you can’t find the square root of a negative’ since you can’t find a number that squares to give a positive. Your calculator will say Math ERROR.Exercise 4Try these by looking at the table of squares you completed on the previous page and then check your answers on your calculator__________________________________________________________________________The answers are 4, 12, 10, 21, 7, 13, 11, 19.Let’s now check that taking the square root neutralises squaring.Try this on your calculator.Find the square root of 3 squared that is, The key strokes required are The display should read 3Because squaring and taking square roots are inverse operations , the order of the operatons can be reversed and the number is unaffected.So the square, of the square root of 3, should also equal 3Try it on your calculator. The key strokes required are__________________________________________________________________________(a) =(e)=(b) =(f) =(c) =(g) =(d) =(h) =818149–164914416910012144136132Exercise 5Complete the following without using the calculator(a)=(b)=(c)=(d)=10(e)=625(f)=144(g)=,because 82=(h)=,because =121(i)=,because =Check your answers on the calculator.__________________________________________________________________________4.3 Other rootson your calculator. To get to thiskey you must press shift first.727210222264121225Look at the examples below.Examples(a)9½and the display should read 3.orand the display should read 3.(b)and the display should read 2.(c)16¼and the display should read 2.Note:•Root key is a function at the back of the power key, so you will need to activate it with theSHIFT key•See the key . The x stands for the root you want to take so it is typed first.•From the examples above you may have seen that . is called a fractionalindex.813--x 813--83=813--5.FractionsHow do you add and ? Normally you would have to find a common denominator of252.So:Or you can use your calculator to add fractions. Find the key On the key the ‘a ’ represents the whole part of a mixednumber and the ‘’ represents the fraction part of a mixed number.When the number you are typing is a proper or improper fraction the ‘a ’ is zero and there is no need to type a value for it.112-----463-----112-----463-----+21252--------16252--------+37252--------==a b c--fraction keya bc --bc--The key storkes required for the calculation are:and the display will show 37252 which is read as ExampleFindUsing the calculator the key strokes are:and the display will show 87172 which is read asNote if you now press. So this key turns a mixed fractionIf you press thei.e. 8.9861111112-----463-----+d37252--------819--6372-----+d d87172-----64772--------ing the x –1 keyThis is a very useful key in more complex calculations. Find the key on your calculator.ExampleLook at this simple example is the same as You can input this in your calculator by pressingThe answer should be 0.571428571. This would be the same as if you just typed 4 ÷ 7Take another example Type:The answer should be 0.05194805147--417--×483+()7×-------------------------7.Scientific notationSometimes you may have numbers expressed in scientific notation, i.e., 7.24 × 103 instead of 7240. When a number is multiplied by 103right. You can do this on the calculator by using the key.PressIf you want to multiply two numbers e.g. 8.34 × 10–2 × 4.28 × 105. Pressand the display will read 35695.2If you presswhich means 3.56952 × 104. Pressing the mode three times gives youthe displayThe puts the calculator in scientific notation. The calculator then asks SCI 0~9? Thisgives the option of how many digits are displayed. The gives you 10 digits. Notice asmall sci appears in the screen.If you press ×1004whichmeans3.570 × 104. This rounds the number to 4 digits.Practise using the and keys on your calculator8.Factorial x!Look at your calculator and find the key with the symbol x! on it. You will come across this symbol when doing the Binomial Distribution. This is called the factorial key.3! means 3 × 2 × 1 and 5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 13! = 65! = 120How many ways would you guess that we could arrange ten people?That is, how large would you estimate 10! to be? Use your calculator to find 10!You should get 3 628 800.10! = 10 × 9 × 8 × ... × 3 × 2 × 1(Thank goodness this can be done on the calculator.)Factorial ruleThe number of ways of arranging n items in order is known as ‘factorial n’ which is symbolised as n! where:n! = n× (n – 1) × (n – 2) × ... × 3 × 2 × 1ing memoryTo calculate the following it may be useful to use the memory key for each term:Example:To make sure memory is clear, first pressorand make sure you are in normal calculation mode [may need to press mode 1].An M appears in the display when you put something in memory.916–()216---------------------2316–()216------------------------1716–()216------------------------++key to activate M–)To do the calculation above, press the following keys- this puts the first term (3.0625) into the memory then press- this adds the second term (3.0625) into memory then press- this adds the third term 0.0625 to memory.To find the answer press The answer should be 6.1875.Example 2calculate the following:firstpress the following keys:your answer should be 11.39917438(There are other memory keys in your calculator – the A to F keys, accessed by using SHIFTSTO and RCL – try them yourselves.)1817---------1717---------1217---------++10.Statistics10.1 Mean and standard deviation – single dataThe formula for the mean is The formulas for the sample standard deviation are(sample)(population)Your calculator will calculate the mean and standard deviation for you (the populationstandard deviation or the sample standard deviation – in data calculations you will usually use the sample standard deviation.)On the Casio fx -82MS , σ and s are found in s-V AR. The positions of keys needed are shown on the diagram below.x Σxn-----=σn σn -1input data keyTo find the mean and standard deviation,firstly you must access the statistics mode of the calculator by using the keysfollowed bySD will appear in the centre of the screen.Note that once you are in the statistics mode, the keys shown within the blue lines are active.There are 3 such keys on the Casio fx -82MS. Make sure you can locate them. Before starting any computations always clear the statistic’s memories using Scl. PressI will use the data set A (–5, 2, 3, 4, 11) to demonstrate the use of the calculator. Note that I have shown the use of thekey where necessary.Step 1: Input the e theThe display should read n = 5. (This means 5 observations have been input).Step 3: Display the mean and standard deviation.Pressthe display shows three alternativesPressx σn = 5.099019514Pressx σn –1 = 5.700877126ExampleUse your calculator to find the mean, standard deviation and variance for data set B: –18, 1, 3, 9, 20.(the variance is the square of the standard deviation)__________________________________________________________________________After you are in the statistics mode and cleared the statistics memories, the keystrokes required are:The mean is 3, the standard deviation is 13.87 and the variance is 192.5. button accesses a number of extra statistical functions.If you have made an error with inputting your data you can correct it by using the up and down key.For example, you inputreads x 3 = 60, then pressIn the example below, the progressive calculations are shown simply to give you someunderstanding of the underlying processes – you should do one or two examples in detail and then check them by calculator.=Σx 2 =815=Σx = 15=n= 510.2 Mean and standard deviation of frequency distributionGiven below is the frequency table for the weights (kg) of a random sample of 30 first year university female students. Find the standard deviation, the variance and the mean.The calculations needed to obtain the standard deviation without statistical keys for these data are:Σx 2 = 602 × 2 + 612 × 14 + 622 × 8 + 632 + 642 × 5 = 114 495Σx = 60 × 2 + 61 × 14 + 62 × 8 + 63 + 64 × 5 = 1 853s = = Thus:s= 1.2 kg and s 2 = 1.4 kg 2= Note: In calculations like the above you should carry as many decimals as possible until thefinal result. The number of decimals to be retained at the end depends on the accuracy of the data values – one rule of thumb is to have one more decimal than in the original data.Notice how the frequencies were used in the above calculation.The calculator usage now has a small modification because we have been given the frequencies for the variable values. (There is no need to input each single observation.)Graduate’s weight(kg)FrequencyCumulative frequency6022611416628246312564530Σx i 2Σx i ()2n ⁄–n 1–--------------------------------------114 495 1 853()230⁄–29-------------------------------------------------------114 495114 453.6333–29--------------------------------------------------------- 1.4264==Σx n -----185330-----------61.8 kg==The keystrokes required are:The display should read n = 30.Thus, as expecteds = 1.2 kg, s 2 = 1.4 kg 2 and = 61.8 kg Exercise 6Find the mean, standard deviation and variance of (a)The annual rainfall data for the years 1971 – 1990Year 1971197219731974197519761977197819791980Rain (mm) 1 3409901 1201 7362601 1001 3791 1251 4301 446Year 1981198219831984198519861987198819891990Rain (mm)1 4591 6781 3459781 0021 1101 5461 6721 4671 123x(b)The sample of snail foot lengthsAnswers:(a)Rainfall statisticsmean:µ = 1 265.3 mm standard deviation:= 336.4 mm variance:σ2 = 113141.7 mm2 (b)Snail statistics mean:standard deviation:s = 0.70 cm variance:s2 = 0.49 cm2Snail foot length (cm)2.2 4.13.54.5 3.2 3.7 3.0 2.63.4 1.6 3.1 3.3 3.8 3.14.7 3.72.5 4.33.4 3.6 2.9 3.3 3.9 3.13.3 3.1 3.74.4 3.2 4.1 1.9 3.44.7 3.8 3.2 2.6 3.9 3.0 4.2 3.5σn-111.Linear regressionTo access the linear regression mode you presskey once followed bythen a small REG appearsExampleSuppose we had a sample of 10 of the same type of banana. Their lengths and skin thicknesses were measured. Below is a summary of the results.STEPS1.(1 = Linear Regression; there are 5 other types)2.Think of the sample of bananas as having two variables:– let x be the variable length of banana – let y be the variable thickness of bananaBanana 12345678910Length (mm)16.215.816.514.916.916.815.615.615.715.4Thickness (mm)1.11.21.11.00.91.21.11.20.90.8accesses the keys with ⎡ ⎤ in blueFor each banana you have to put in both numbers.To put in the first set of numbers, press the following keys:is used for the 2nd variableContinue in this mannerAfter you have input all the numbers.The display should read n = 10To find the linear regression equation in the formy = a + b xPressPress∴There is not a high correlation between the thickness of bananas and the length of bananas tested.The calculator will also give you other statistics about this sample. Use to get the mean thickness (1.055mm) or the standard deviation (0.64mm).x σy σn –1:12.Trigonometric functionsThe keys involved are:Important : Make sure that your calculator is in the correct mode. For example, if your calculator has R or G on the display and you wish to work in degrees, press mode twice and then select 1 for degrees. Your screen should now display D.Example 1In the right-angled triangle below, the length of the side opposite the 20° angle needs to be calculated.To find the length of the side labelled xcm, useThe keystrokes on the calculator are:Example 2In the right-angled triangle below, the length of the hypotenuse needs to be calculated.To find the length of the side labelled x cm, use:The keystrokes on the calculator are:The display should read 20.466631, so the length of the hypotenuse is about 20.5 cm.Example 3Given the lengths of two of the sides in the right-angled triangle below, find the value of the angle θin degrees:To find the value of θ, you need to use the cos –1 key. The calculator keystrokes are:Note: You must first get the value of the division by using the brackets.Your display should read 60°. If it does not, check that you are in degree mode.13.Exponential and logarithmic functionsThere are two log keys on your calculator, with their associated exponential keys. The latter are accessed by first using the shift key:The ‘log’ key uses base 10 and the ‘ln’ key uses base e (natural logarithm).Example 1Solve equation Taking logs of both sides;To find the value of a , the keystrokes are:The display should read 4.3219281.So, . Confirm this by using theExample 2Given , find the value of y The key is above the log key. Hence the keystrokes are:The display should read 38.370725Example 3 (harder)Given , find the value of xTo find log x , the calculator keystrokes are:2a 20=4.32220≈log y 1.584=log y 1.584= y ⇒101.584=10x log x 6 1.5=The display should read 0.5187675.Since this is the value of log x , you still need to find x where Without removing the answer of 0.5187675 on your display, press:Your display should now read 3.3019272Note: You could use the ‘ln’ key instead of the ‘log’ key – the answer would still be the same. Try it!14.Degrees, minutes, secondsThe key involved isThis key can be used for problems involving degrees, minutes and seconds or hours, minutes and seconds.0.518767510x=Example 1Suppose that you have a trigonometric problem where the angle involved is given in degreesand minutes. e.g. Find x where ’The keystrokes involved are:The display should show 1.728343, so x is approximately 1.73Example 2If you wish to convert an angle in degrees to its equivalent in degrees, minutes and seconds:e.g. 34.88°, the keystrokes are:The display should read 34°52°48.Example 3To find the sum of 5 hours 52 minutes 30 seconds and 7 hours 45 minutes 49 seconds:The keystrokes are:The display should read 13.638611 (hours).x 4sin 25° 36×=Review calculator exercises1.Perform the following calculations(i)(5 + 4) × 3(ii)12.5 – 8 ÷ 0.5(iii)(iv)(v)(vi)(vii)(viii)(ix)(x)(xi)2.The following data is on growth (in $m) in an economy over a 8 year period:2.56.2-2.10.048.27.42.1-1.7Calculate (i) Σx(ii) Σx 2(iii) (Σx )2Explain in words what each of these mean.368–×4--------------------12.816.5 3.8–-----------------------70.4117+×47+()2×-------------------------------2.434--------145.617.225⁄–345.617.22–5⁄25327×1.0230--------------------+4.1333 3.000–() 2.0150.136626------------------0.200026------------------+±10090–()290---------------------------5060–()260------------------------2030–()230------------------------++Calculator solutions1.(i)(5 + 4) ×3= 27Make sure your calculation is in comp mode.(ii)12.5 – 8 ÷ 0.5= -3.5(iii)= 2.5Either (3 × 6 – 8) ÷ 4 = or 3 × 6 – 8 = ÷ 4 =(iv)= 1.007874Either 12.8 ÷ (16.5 – 3.8) = or 16.5 – 3.8 = x –1× 12.8 =(v)= 0.9Either ... ÷ ((4 + 7) × 2) = or ... ÷ (4 + 7) ÷ 2 =(vi)= 3.2Either 2.4 ÷ (3 ÷ 4) =, or 2.4 ÷ 3 a b/c 4 = (vii)= 9.296..Either 145.6 – 17.2x 2 ÷ 5 = √ =, or √ (145.6 – 17.2x 2 ÷ 5) =(viii)= 1.41..Either 345.6 – 17.2x 2 = √ ÷ 5 = or (345.6 – 17.2x 2) √ ÷ 5 =(ix)= 39.498525 + 3 × 27 ÷ 1.02 ÷ √ 30 =(x)= 1.3325 or 0.9341368–×4--------------------12.816.5 3.8–-----------------------70.417+×47+()2×----------------------------2.434--------145.617.225⁄–345.617.22–5⁄25327×1.0230--------------------+4.1333 3.000–() 2.0150.136626------------------0.200026------------------+±Calculator keys:0.1366 x 2 ÷ 6 + .2 x 2 ÷ 6 = √ = x 2.015 ==(xi)= 6.1111Calculator keys:(100 – 90) x 2 ÷ 90 + (50 – 60) x 2 ÷ 60 + (20 – 30) x 2 ÷ 30 =2.The following data is on growth (in $m) in an economy over a 8 year period:2.56.2-2.10.048.27.42.1-1.7Calculate (i) Σx(ii) Σx 2(iii) (Σx )2Explain in words what each of these mean.To do this on the calculator, you must be in SD mode. Enter the data:mode 1 2.5 M+ 6.2 M+ (–) 2.1 M+ .04 M+ 8.2 M+ 7.4 M+ 2.1 M+ (–) 1.7 M+(i)22.64Press the key that says ΣxThis gives the total growth over the last 8 years(ii)178.4016Press the key that says Σx 2of the squares of the growth in each year(iii)512.5696Press Σx and x 2. This gives the square of the sum of the growth.10090–()290---------------------------5060–()260------------------------2030–()230------------------------++Your notes。

CASIO电子计算器fx-82ES-PLUS-A说明书关键信息项:1、产品名称:CASIO 电子计算器 fx-82ESPLUSA2、功能特点:____________________________3、操作指南:____________________________4、显示屏信息:____________________________5、按键说明:____________________________6、电源与电池:____________________________7、计算模式:____________________________8、错误提示与处理:____________________________9、维护与保养:____________________________1、产品概述11 CASIO 电子计算器 fx-82ESPLUSA 是一款具有多种功能的计算工具,旨在为用户提供高效、准确的计算体验。
111 它适用于各种数学计算、科学计算以及日常的数值运算需求。
2、功能特点21 具备基本的四则运算功能,包括加法、减法、乘法和除法。
211 支持小数和分数的计算与转换。
212 拥有科学计数法功能,方便处理较大或较小的数值。
22 具备开方、平方、指数、对数等数学函数计算功能。
221 可以进行三角函数(正弦、余弦、正切等)的计算。
222 提供统计计算功能,如平均数、标准差等。
3、操作指南31 电源开启与关闭按下“ON”键开启计算器,按下“OFF”键关闭计算器。
311 在长时间不使用计算器时,建议关闭电源以节省电池电量。
32 数字与运算符输入使用数字键输入数值,运算符键输入相应的运算符号。
321 输入错误时,可使用“DEL”键删除错误的输入。
33 结果显示与查看计算结果将在显示屏上显示,可清晰查看。
331 部分复杂计算结果可能会以科学计数法或小数形式显示。
4、显示屏信息41 显示屏能够显示多行数字和字符,以提供清晰的计算过程和结果。
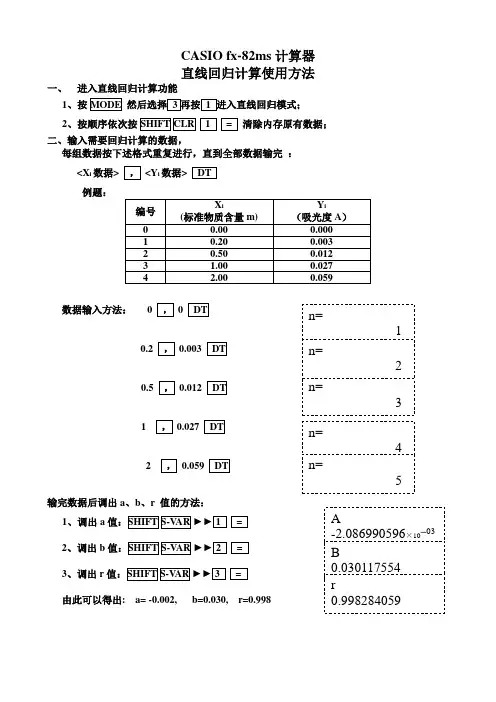
一、 进入直线回归计算功能
1、按
2、按顺序依次按
清除内存原有数据;
二、输入需要回归计算的数据,
每组数据按下述格式重复进行,直到全部数据输完 :
<X i 数据> <Y i 数据> 例题:
数据输入方法: 0 0
0.2 0.003
0.5 0.012
1 0.027
2 0.059
输完数据后调出a 、b 、r 值的方法:
1、调出
a
2、调出
b
3、调出r
由此可以得出: a= -0.002, b=0.030, r=0.998
二、 进入直线回归计算功能
1、按顺序依次按
清除内存原有数据;
2、按A+BX )进入直线回归模式,将看到以下数据输入屏幕:
二、输入需要回归计算的数据, 例题:
数据输入方法:
输入数值后,按下
键。
可用方向键选择要输入的单元格。
X 、Y 数值均输完后,按下键,切换到STAT 计算屏幕。
三、输完数据后调出A 、B
、r 值的方法:
1、调出A
2、调出B
3、调出r
由此可以得出: a= -0.002, b=0.030, r=0.998。

一、 进入直线回归计算功能
1、按
2、按顺序依次按
清除内存原有数据;
二、输入需要回归计算的数据,
每组数据按下述格式重复进行,直到全部数据输完 :
<X i 数据> <Y i 数据> 例题:
数据输入方法: 0 0
0.2 0.003
0.5 0.012
1 0.027
2 0.059
输完数据后调出a 、b 、r 值的方法:
1、调出
a
2、调出
b
3、调出r
由此可以得出: a= -0.002, b=0.030, r=0.998
二、 进入直线回归计算功能
1、按顺序依次按
清除内存原有数据;
2、按A+BX )进入直线回归模式,将看到以下数据输入屏幕:
二、输入需要回归计算的数据, 例题:
数据输入方法:
输入数值后,按下
键。
可用方向键选择要输入的单元格。
X 、Y 数值均输完后,按下键,切换到STAT 计算屏幕。
三、输完数据后调出A 、B
、r 值的方法:
1、调出A
2、调出B
3、调出r
由此可以得出: a= -0.002, b=0.030, r=0.998。

CASIO计算器(fx-82ES)所能做到的极致MODE功能中有三种一、COMP 普通二、STAT 统计三、TABLE 函数一、COMP 普通1. 7个储值功能A , B , C , D , X , Y , M使用:输入数值,STO(SHIFT + RCL),A(B , C , D , X , Y , M)用于复杂计算(多次出现同一个数值)2.极坐标&直角坐标POL(SHIFT + +): 将直角坐标转化为极坐标使用:POL(SHIFT + +),输入X坐标,,(SHIFT + ) ),输入Y坐标,=显示:R=,θ=,即此极坐标为(R,θ)REC(SHIFT + -): 将极坐标转化为直角坐标使用:REC(SHIFT + -),输入R,,(SHIFT + ) ),输入θ,=显示:X=,Y=,即此极坐标为(X,Y)二、STAT 统计进入界面,MODE , 2显示为一列表格,输入各个数值,做统计用,输入完毕后,AC接下来就是数据的平方和:STAT(SHIFT +1), 4 , 1数据的和:STAT(SHIFT +1), 4 , 2数据的平均数:STAT(SHIFT +1), 5 , 2数据的标准差:STAT(SHIFT +1), 5 , 3 (注,标准差的平方就是方差)数据的样本差:STAT(SHIFT +1), 5 , 4数据的最小值:STAT(SHIFT +1), 6 , 1数据的最大值:STAT(SHIFT +1), 6 , 2重点来了三、TABLE 函数进入界面,MODE , 3显示f(x)= 函数表达式,输入表达式,强调:表达式中必须含有X接着按=显示START?(初始值)1 (即X从1开始)输入你所希望X开始数值=显示END? (结束值)5 (即X在5结束)输入你所希望X结束数值=显示STEP? (间隔)1 (即每个相邻X相差1)输入你所希望每个相邻X之差(特别注意:(START-END)/30<STEP,计算机只能计算30个X值)=显示两行N列,n∈[1,30]第一列为X列,第二列为Y列,即每一个X在表达式中所对应的Y值此函数功能极其使用,一元二次方程,不等式,函数单调性,函数奇偶性,函数周期性,最大值最小值计算,等等等等……接下来就是本人原创的十分法原来的二分法极为复杂,需要不断相加,再除以2但是如果用计算器的TABLE 函数使用十分法那就大大的方便了精确一个无理数了原理例如根号6=2.449489743……利用十分法f(x) = x - 根号6输入START=0 , END=10 , STEP=1显示0 -2.4494897431 -1.4494897432 -0.4494897433 0.55051025724 1.55051025725 2.55051025726 3.55051025727 4.55051025728 5.55051025729 6.550510257210 7.5505102572得知0介于2于3之间,按AC,=再输入START=2 , END=3 , STEP=0.1显示……得知0介于2.4于2.5之间,按AC,=再输入START=2.4 , END=2.5 , STEP=0.01显示……得知0介于2.44于2.45之间,按AC,=再输入START=2.44 , END=2.45 , STEP=0.001显示……得知0介于a于b之间,按AC,=再输入START=a , END=b , STEP=1*10^n显示……可以无数精确,只要计算器显示得出,你连π也算得出。
![[转] 计算器(fx-82ES)玩得好是可以很变态的(必看)](https://uimg.taocdn.com/ac929cfb0242a8956bece4c7.webp)
[转] 计算器(fx-82ES)玩得好是可以很变态的(必看)我四处搜刮来的资料,我拿我的计算器试过了,都可以,不知道你们的如何?一、shift+7+on,不多说了,很多人都知道二、CMPLX(复数计算),MAT(矩阵),VCT(向量)!没想到吧,俺们的计算器还能算复数。
说到这里,先要讲怎么进入异常状态!这可是好多种变态功能使用的必须状态!进入异常状态:(依次按下列键,不能多一下或少一下,期间不管计算器怎么显示错误都无视)on, shift+加号(Pol), 1, shift+右括号(逗号), 0, =, AC, 6下分数线, =, AC, 左, 1, x^n(x 平方右边那个), =, AC, 上, AC, 3下左, DEL(此时显示r=1,fai o=0,惊讶了吧), 分数线, 在分数线上下都输入1, =异常状态进入成功!然后继续凹:8下Ans, 然后不断按sin直到显示错误, AC, shift+9, 1, =, AC, shift+9, 2, =, AC(前面几步也叫2次清空), 5下根号, 6下x^n(此时出现乱码,可以看见乘以10), 15下DEL(正好到r前面,小心点按哦,按过头就要重来了。
), 右括号, =, AC, shift+9, 2, =, AC, 2下右, DEL(正好把那个右括号删了), 1, alpha+x^3(是个双引号), 2下等于, mode看到什么了!2就是复数计算,4不明,5也不明,6就是矩阵,8就是向量,平时看不见吧~1、 CMPLX:按完2之后屏幕突然变亮,然后按on,再用shift+mode调节屏幕亮度(可以看得清楚点。
)为了保证能正常使用,shift+mode, 3, shift+mode, 8, 1, shift+mode, 下, 4, 1。
OK啦~~~现在ENG就是i!!!不过计算结果如果带i的话不会显示出来比如答案是-1+i,显示就是-11,按shift+2再按4就能显示出来了,shift+2还有其他几个功能,自己研究吧~~2、MAT:按完6之后按一下AC,然后同样调节亮度。

CASIO fx82ES PLUSA计算器
默认分数结果转为默认小数以及去除科学计数法
新买了个casio计算器用来提高学习效率和考试用。
到手后发现,计算所有的不能除尽的算式结果都是分数,看说明书说要按S﹣D键才能转成小数,这还不算,按了那个键出来的数字不仅是小数,而且还是科学计数法,现将默认分数结果转为默认小数以及去除科学计数法的步骤分享如下:
首先要让默认分数显示的计算结果转为默认小数显示计算结果,按左上角shift,再按右上角mode,按数字键1,再按数字键2即可。
这样就可以默认显示小数了。
还得解决科学计数法问题,不然你就慢慢数10的负几次方吧。
按shift,再按mode,按8,按2即可。
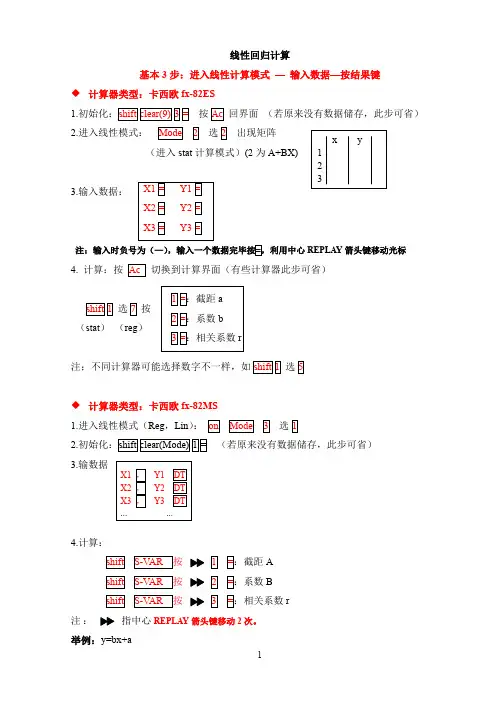
线性回归计算
基本3步:进入线性计算模式—输入数据—按结果键
◆计算器类型:卡西欧fx-82ES
1.
按
回界面(若原来没有数据储存,此步可省)
2.进入线性模式:选出现矩阵
(进入stat计算模式)(2为A+BX)
3.输入数据:
注:输入时负号为(—)
REPLAY箭头键移动光标
4. 计算:按切换到计算界面(有些计算器此步可省)
选按
(stat)(reg)
注;不同计算器可能选择数字不一样,如选
◆计算器类型:卡西欧
fx-82MS
1.进入线性模式(Reg,Lin):选
2.(若原来没有数据储存,此步可省)
3.输数据
4.计算:
A
B
r
注:指中心REPLAY箭头键移动2次。
举例:y=bx+a
x:-1 -2 -3 -4
y:2 4 6 8.05
计算结果:
比例系数b= -2.015,截距a= -0.025,线性相关系数r= -0.9998。
![[转] 计算器(fx-82ES)玩得好是可以很变态的(必看)](https://uimg.taocdn.com/ac929cfb0242a8956bece4c7.webp)
[转] 计算器(fx-82ES)玩得好是可以很变态的(必看)我四处搜刮来的资料,我拿我的计算器试过了,都可以,不知道你们的如何?一、shift+7+on,不多说了,很多人都知道二、CMPLX(复数计算),MAT(矩阵),VCT(向量)!没想到吧,俺们的计算器还能算复数。
说到这里,先要讲怎么进入异常状态!这可是好多种变态功能使用的必须状态!进入异常状态:(依次按下列键,不能多一下或少一下,期间不管计算器怎么显示错误都无视)on, shift+加号(Pol), 1, shift+右括号(逗号), 0, =, AC, 6下分数线, =, AC, 左, 1, x^n(x 平方右边那个), =, AC, 上, AC, 3下左, DEL(此时显示r=1,fai o=0,惊讶了吧), 分数线, 在分数线上下都输入1, =异常状态进入成功!然后继续凹:8下Ans, 然后不断按sin直到显示错误, AC, shift+9, 1, =, AC, shift+9, 2, =, AC(前面几步也叫2次清空), 5下根号, 6下x^n(此时出现乱码,可以看见乘以10), 15下DEL(正好到r前面,小心点按哦,按过头就要重来了。
), 右括号, =, AC, shift+9, 2, =, AC, 2下右, DEL(正好把那个右括号删了), 1, alpha+x^3(是个双引号), 2下等于, mode看到什么了!2就是复数计算,4不明,5也不明,6就是矩阵,8就是向量,平时看不见吧~1、 CMPLX:按完2之后屏幕突然变亮,然后按on,再用shift+mode调节屏幕亮度(可以看得清楚点。
)为了保证能正常使用,shift+mode, 3, shift+mode, 8, 1, shift+mode, 下, 4, 1。
OK啦~~~现在ENG就是i!!!不过计算结果如果带i的话不会显示出来比如答案是-1+i,显示就是-11,按shift+2再按4就能显示出来了,shift+2还有其他几个功能,自己研究吧~~2、MAT:按完6之后按一下AC,然后同样调节亮度。

/edu/RCA502139-001V01Chfx-82ES fx-83ES fx-85ES fx-300ES fx-350ES User's Guide用戶說明書REPLAY按鍵功能第二功能有關本說明書•圖樣MATH 顯示出使用數學格式的範例,而圖樣LINE 表示的是線性的格式。
有關輸入輸出格式的詳細內容,請見「指定輸入 / 輸出的格式」章節。
•按鍵上的圖樣表示該鍵輸入值或是它所執行的功能。
範例:1,2,+,-,!,A 等。
•按下1或是S 鍵,接著按下第二鍵,將會執行第二鍵的第二功能。
該鍵的第二功能標示在該鍵上方。
•以下顯示出第二功能鍵的不同顏色的文字標記。
假如按鍵圖樣它代表的意義是的文字是黃色按下1鍵和本鍵就可以使用本應用鍵的功能。
紅色按下S 鍵和本鍵就可以輸入可用的變數、常數和符號。
•以下顯示出本說明書中如何表示第二功能操作的範例。
範例:1s (sin –1)1=括弧內顯示加上(1s )鍵之後真正執行的功能。
請注意本說明並非您實際鍵盤操作的一部分。
•以下顯示出本說明書如何示範按鍵操作以便選定螢幕上選單項目的範例。
範例:1(Setup )顯示出由之前的數字鍵操作(1)所選定的選單項目。
請注意本說明並非您實際鍵盤操作的一部分。
•游標鍵是由四個箭頭鍵來標示,表示其方向,如以下圖示。
本說明書中,游標鍵操作是由f 、c 、d 、e來表示。
•本說明書和另外的附錄中的顯示和說明(例如:按鍵圖樣),僅供說明使用,和它們實際所代表的項目可能會有些許的不同。
•本說明書的內容可能會有所更動,不再另行通知。
•在任何情況下,卡西歐計算機株式會社不因任何人在購買本產品及所屬項目,所引起的特殊、附帶的,或結果性的損害,而有連帶責任或任何牽連。
除此之外,卡西歐計算機株式會社對於因任何一方由於使用本產品及其所屬項目而引起的任何求償不負有任何賠償責任。
■ 使用另外的附錄每當您在本說明書中看到附錄符號時,它代表您應該參閱另外的附錄。