WFMC-TC-1003-工作流参考模型(ch)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:587.98 KB
- 文档页数:47


工作流平台需求架构分析作者:刘磊来源:《电脑知识与技术》2013年第30期摘要:工作流平台的需求问题一直困扰着广大架构师及咨询师、对于需求两字实在感觉难以入手、目前由于各行各业的需求五花八门、种类各不相同,故想做到以点概面的需求是不大可能的。
所以定制则被重点突出、用以解决这些不同的需求、可视化的定制既满足了广大需求调研者及开发者,大大降低了其工作的强度。
再加上移动事业的日新月异,移动化办公也可以加入工作流平台的需求里面。
关键词:需求;工作流;可视化;定制;移动办公中图分类号:TP311 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1009-3044(2013)30-6789-09工作流技术作为解决业务流问题的主要方法越来越受到人们的重视,它应用逻辑与业务逻辑分离,可以不修改具体的功能实现而只修改业务过程模型改变系统功能,从而能够快四应对市场需求。
本文章为工作流平台的业务需求架构剖析及提出解决方案,阅读对象主要针对设计、及研发、测试、及相关业务人员。
主要内容包括:工作流平台所涉及的业务需求。
1 术语及缩写词业务流:是针对业务需求,按照一定的业务规则对企业业务流程进行可视化建模。
定义业务流主要包括:活动、关系、转移信息、组织结构、角色模型、异常、配置以及周期。
通过提供界面定义工具支持用户进行业务流定义。
2 工作流概述及规范2.1 工作流概述工作流现在主要解决的问题是:为了实现某些业务目标,在单个或者多个参与者之间,利用计算机,按某种预先订下的规则自动传递文档、数据、信息或者任务。
简单一点的说,工作流就是一条相互衔接、自动流转的任务圈。
我们可以将整个过程看做是一个流水作业线,其中作业线上的任务就是需要审核的表单。
与工作流相关的概念特别多,下面几个是比较常见的:2.1.1 Workflow就是指“业务流程的部分或整体在计算机应用环境下的自动化”,WorkFlow就是工作流程的计算模型,即将工作流中的工作如何前后组织在一起的逻辑和规则再加算计中以恰当的模型进行标示对其实施计算。

Workflow Management Coalition Workflow Reference Model________________________________________________________________________________ ____________Copyright ã 1995 The Workflow Management Coalition - 1 -翻译人:张敬波(网名:踏冰) OICQ:42508298Email:say4ever2u@ MSN:tabingfly@翻译人:韩伟(网名:浆糊) OICQ:3413384Email:java_cn@ MSN:Java_cn@欢迎访问我们的网站: 工作流管理联盟规范WFMC ——工作流参考模型文档编号 TC00-100395年1月19 日版权ã2002WFMCPDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version Workflow Management Coalition Workflow Reference Model________________________________________________________________________________ ____________Copyright ã 1995 The Workflow Management Coalition - 2 -目录目录.................................................................................................................................. - 2 -1.简介.............................................................................................................................................. - 4 -1.1. 背景.................................................................................................................................... - 4 -1.2. 目的.................................................................................................................................... - 4 -1.3. 范围.................................................................................................................................... - 4 -1.4. 对象.................................................................................................................................... - 5 -1.5. 如何阅读............................................................................................................................. - 5 -1.6. 参考.................................................................................................................................... - 5 -1.7. 修订历史............................................................................................................................. - 5 -2.工作流系统简介........................................................................................................................... - 6 -2.1. 什么是工作流(workflow).............................................................................................. - 6 -2.1.1. 建立时期功能.......................................................................................................... - 7 -2.1.2. 运行时期过程控制功能........................................................................................... - 8 -2.1.3. 运行时期活动交互.................................................................................................. - 8 -2.1.4. 分配与系统接口...................................................................................................... - 8 -2.2. 工作流的发展..................................................................................................................... - 9 -2.3. 产品实现模型..................................................................................................................... - 9 -2.4. 可选择的实现方式(Alternative Implementation Scenarios)....................................... - 14 - 2.5. 对标准化的需要(The Need for Standardization)........................................................ - 17 - 3.工作流参考模型(Workflow Reference Model)..................................................................... - 18 -3.1. 简介.................................................................................................................................. - 18 -3.2. 工作流模型(The Workflow Model)............................................................................ - 18 -3.3. 工作流执行服务器(Workflow Enactment Services)................................................... - 19 - 3.3.1. 什么是工作流执行服务器?................................................................................. - 19 -3.3.2. 工作流机(The Workflow Engine)..................................................................... - 20 -3.3.3. 同种和异种的工作流执行服务器(Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Workflow Enactment Services)........................................................................................................ - 21 -3.3.4. 工作流应用编程接口与数据交换(Workflow Application programming Interface & Interchange)................................................................................................................... - 23 -PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version Workflow Management Coalition Workflow Reference Model____________________________________________________________________________________________Copyright ã 1995 The Workflow Management Coalition - 3 -3.3.5. 工作流控制,工作流相关数据和工作流应用数据............................................. - 23 -3.3.6. 数据交换(Data Interchange)............................................................................. - 24 -3.4. 过程定义(Process Definition)...................................................................................... - 25 -3.4.1. 过程定义工具(Process Definition Tools)......................................................... - 25 -3.4.2. 工作流定义转换(接口1).................................................................................. - 26 -3.5. 工作流客户端功能(Workflow Client Functions)........................................................ - 29 - 3.5.1. 工作流客户端应用程序(Workflow Client Applications)................................ - 29 -3.5.2. 工作流客户端应用程序接口(接口2).............................................................. - 30 -3.6. 应用程序调用功能(Invoked Application Functions).................................................. - 32 - 3.6.1. 应用程序调用(Invoked Applications).............................................................. - 32 -3.6.2. 应用程序调用接口(接口3).............................................................................. - 33 -3.7. 工作流协同工作流能力(Workflow Interoperability)................................................. - 35 - 3.7.1. 异种工作流执行服务器......................................................................................... - 35 -3.7.2 模型1 ——链锁式(Chained)......................................................................... - 35 -3.7.3. 模型2 ——子过程嵌套(Nested Subprocesses)............................................ - 36 -3.7.4. 模型3 ——P2P (Peer-to-Peer)....................................................................... - 37 -3.7.5. 模型 4 ——相似同步(Parallel Synchronised)............................................... - 38 -3.7.6. WAPI 协调工作功能(接口4)........................................................................... - 38 -3.8. 系统管理(Systems Administration)............................................................................. - 41 -3.8.1 管理和监视工具(Administration & Monitoring Tools).................................... - 41 -3.8.2. 管理和监视接口(接口5).................................................................................. - 41 -4. WAPI 结构、协议和一致性....................................................................................................... - 44 -4.1. WAPI——API功能简介................................................................................................... - 44 -4.2. WAPI协议......................................................................................................................... - 45 -4.3. 一直性原则....................................................................................................................... - 45 -4.3.1. 一致性的意义........................................................................................................ - 46 -4.4. 协同工作能力分类和一致性级别.................................................................................... - 46 -4.4.1 定义工具、工作流执行软件.................................................................................. - 46 -4.4.2 可户端应用程与工作流执行服务器序协同工作.................................................. - 46 -4.4.3. 应用程序和工具集成............................................................................................ - 47 -4.4.4. 工作流执行服务器协同工作................................................................................. - 47 -4.4.5. 公共工作流管理.................................................................................................... - 47 -PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version Workflow Management Coalition Workflow Reference Model________________________________________________________________________________ ____________Copyright ã 1995 The Workflow Management Coalition - 4 -1.简介1.1. 背景工作流管理系统一项快速发展的技术,各种行业渐渐的采用工作流技术。

1介绍工作流(Workflow)[1],就是“业务过程的部分或整体在计算机应用环境下的自动化”,它主要解决的是“使在多个参与者之间按照某种预定义的规则传递文档、信息或任务的过程自动进行,从而实现某个预期的业务目标,或者促使此目标的实现”。
工作流引擎流程审批功能包括:数据表定义、表单定义、流程定义(B/S 架构图形化流程定义工具)及工作流审批引擎,天生创想OA系统采用WFMC 的流程标淮实现各种复杂流程的电子化流转, 并且采用插件式的设计方法让工作流模块还可以被其它功能模块调用,完成相关的业务流程,复杂的流转还支持人员设定、顺序流、分支流、并发流;支持会签、撤销、分发等;[2]2概述2.1计算模型工作流(Foundare WorkFlow)就是工作流程的计算模型,即将工作流程中的工作如何前后组织在一起的逻辑和规则在计算机中以恰当的模型进行表示并对其实施计算。
工作流要解决的主要问题是:为实现某个业务目标,在多个参与者之间,利用计算机,按某种预定规则自动传递文档、信息或者任务。
简单地说,工作流就是一系列相互衔接、自动进行的任务。
我们可以将整个业务过程看作是一条河,其中流过的河水就是待审核的表单。
工作流属于计算机支持的协同工作(Computer Supported Cooperative Work,CSCW)的一部分。
后者是普遍地研究一个群体如何在计算机的帮助下实现协同工作的。
许多公司采用纸张表单,手工传递的方式,一级一级审批签字,工作效率非常低下,对于统计报表功能则不能实现。
而采用方蝶工作流软件,使用者只需在电脑上填写有关表单,会按照定义好的流程自动往下跑,下一级审批者将会收到相关资料,并可以根据需要修改、跟踪、管理、查询、统计、打印等,大大提高了效率,实现了知识管理,提升了公司的核心竞争力。
2.2ECP的工作流ECP工作流的定义是:实现工作过程管理的自动化、智能化和整合化。
工作流最主要的特征就是可以灵便的实现数据整合和数据统计,消除信息孤岛,既能实现OA办公系统内部工作流之间的数据整合,如借款与报销、预算与决算等,又能实现OA办公系统工作流与其他业务系统之间的数据整合,如HR、ERP、CRM等。
![[工作规范]工作流联盟WfMC规范](https://uimg.taocdn.com/5eb7745702d276a201292e5f.webp)
(工作规范)工作流联盟WfMC规范工作流管理联盟规范工作流管理联盟工作流标准工作流过程定义接口――XML过程定义语言文档号:WFMC-TC-1025文档状态:草案1.0(β)2002.07.31Version1.0(β)版权©2002工作流管理联盟Allrightsreserved.Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproduced,storedinaretrievalsystem,o rtransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans,electronic,mechanical,photocopying,recordingor otherwise,withoutthepriorwrittenpermissionoftheWorkflowManagementCoalitionexce ptthatreproduction,storageortransmissionwithoutpermissionispermittedifallcopiesofth epublication(orportionsthereof)producedtherebycontainanoticethattheWorkflowMana gementCoalitionanditsmembersaretheownersofthecopyrighttherein.WorkflowManagementCoalition2436N.FederalHighway#374LighthousePoint,Fl33064USATel:+19547823376Fax:+19547826365Email:wfmc@WWW:http://)、Contributors:SethOsher(IntuitiveProductsInternationalCorp.)及RobertShapiro(CapeVisions).●从模式中去除InlineBlock和BlockName元素。

过程视图是工作流模型的核心视图。
它描述企业的业务流程,定义业务过程中包含的活动以及这些活动之间的逻辑关系。
活动和活动间以连接弧表示控制关系。
通过描述活动的基本属性,如活动由谁执行,有哪些人员、组织或盟员企业负责执行,活动执行需要的软件(如应用程序)和硬件(如机床设备)资源,以及活动的触发条件、执行状态等,可以建立过程视图、资源视图和组织视图的关系。
过程视图是本文研究的主要内容,本文通过ECA规则来表达过程视图。
基于ECA规则和元操作的工作流建模原理3.1 工作流模型的结构图:工作流模型的结构1.1.1过程视图过程视图是工作流模型的核心视图。
它描述企业的业务流程,定义业务过程中包含的活动以及这些活动之间的逻辑关系。
活动和活动间以连接弧表示控制关系。
通过描述活动的基本属性,如活动由谁执行,有哪些人员、组织或盟员企业负责执行,活动执行需要的软件(如应用程序)和硬件(如机床设备)资源,以及活动的触发条件、执行状态等,可以建立过程视图、资源视图和组织视图的关系。
过程视图是本文研究的主要内容,本文通过ECA规则来表达过程视图。
1.1.2组织视图组织视图描述企业中的组织单元和组织单元间的关系。
组织单元是具有一定功能和责任的组织实体,一般会承担过程模型产生的各种任务。
组织单元之间往往存在从属或协作关系,形成一定的对应关系。
本文对组织视图描述中,采用一种面向对象的关系模型,不同于传统的层次结构。
是在组织模型中引入类的概念(如角色类、组织类、人员类、职位类等),建立类之间的关系模型,支持层次化的查找和匹配规则,便于工作流的任务分配和执行者绑定。
1.1.3资源视图资源视图描述企业中资源的类型以及资源实体的属性。
资源是工作流模型中非常重要的一个概念,是活动可以执行的必备条件。
资源类型可以是执行活动所需的软件和硬件设施等,或者是活动执行后产生的新的物理实体。
组织视图和资源视图之间存在着映射关系,即每一个资源实体都有与其对应的责任组织单元,该组织单元负责对此资源实体的使用和维护。

工作流参考模型英文Workflow Reference ModelIntroductionIn today's highly competitive business environment, organizations strive to optimize their operations and processes to improve efficiency and productivity. One of the key ways to achieve this is by implementing effective workflow management systems. A workflow refers to the series of tasks, activities, and steps that are necessary to complete a specific process or project. A workflow management system enables organizations to streamline their processes, automate tasks, and monitor progress, leading to improved productivity and better quality output. This article will provide a comprehensive reference model for designing and implementing a workflow management system.1. Workflow DefinitionThe first step in implementing a workflow management system is to define the workflows. This involves identifying the key processes and tasks within an organization and mapping out the sequence of activities required to complete these processes. It is important to involve all relevant stakeholders, including employees, managers, and subject matter experts, in this process to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the workflows.2. Workflow AnalysisAfter defining the workflows, the next step is to analyze them.This involves identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where automation can be implemented. A thorough analysis of the workflows allows organizations to identify areas for improvement and design more efficient processes. Workflow analysis can be done through process mapping, data analysis, and collaboration with the employees involved in the workflows.3. Workflow DesignOnce the workflows have been defined and analyzed, the next step is to design the workflows. This involves determining the sequence of tasks, setting up standards and guidelines, and designing the workflow structure. Workflow design also includes creating decision points, defining inputs and outputs, and identifying the roles and responsibilities of individuals involved in the workflows. It is important to consider the organization's goals, resources, and constraints during the workflow design phase.4. Workflow AutomationAutomation is a key aspect of workflow management systems as it eliminates manual, repetitive tasks and allows employees to focus on more value-added activities. Workflow automation involves implementing software tools and technologies that automate tasks, facilitate communication and collaboration, and monitor progress. Automation can be achieved through the use of workflow management software, integration with other systems, and the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies.5. Workflow ImplementationAfter designing the workflows and automating tasks, the next step is to implement the workflows. This involves training employees on the new processes, communicating the changes, and integrating the workflows into the organization's existing systems and processes. Workflow implementation also involves monitoring and evaluating the workflows to ensure they are delivering the desired outcomes. Feedback from employees and stakeholders should be collected and used to make any necessary adjustments or improvements to the workflows.6. Workflow Monitoring and ControlOnce the workflows have been implemented, it is important to monitor and control them to ensure they are functioning effectively. Workflow monitoring involves tracking the progress of tasks, identifying bottlenecks, and monitoring key performance indicators to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of the workflows. Workflow control involves taking corrective actions when necessary, such as reassigning tasks, reallocating resources, or making process improvements based on the monitoring data.7. Continuous ImprovementWorkflow management is an iterative process that requires continuous improvement. Organizations should regularly review and evaluate their workflows, gather feedback from employees and stakeholders, and identify areas for further optimization. Continuous improvement involves making ongoing adjustments and enhancements to the workflows to ensure they remain alignedwith the organization's goals and objectives.ConclusionImplementing an effective workflow management system is essential for organizations to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve better outcomes. This reference model provides a comprehensive framework for designing and implementing a workflow management system. By following this model, organizations can streamline their processes, automate tasks, and monitor progress to achieve higher productivity, better quality output, and a competitive edge in the market.8. Workflow IntegrationAnother important aspect of workflow management is integrating workflows with other systems and processes within the organization. This ensures smooth flow of information and tasks, eliminating silos and improving efficiency. Workflow integration involves connecting the workflow management system with other software applications, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and project management tools. Integration allows data and tasks to be seamlessly transferred between systems, reducing manual effort and data duplication.Integration also enables real-time data sharing, providing stakeholders with a comprehensive view of the workflows and facilitating better decision-making. For example, integrating the workflow management system with a CRM system allows sales teams to access customer data and update it in real-time, improvingcustomer service and sales effectiveness. Similarly, integrating the workflow management system with a project management tool enables project managers to track project progress and allocate resources efficiently.9. Workflow CollaborationCollaboration is a crucial aspect of workflow management as it promotes communication, knowledge sharing, and teamwork. A workflow management system should include features that facilitate collaboration among team members working on a workflow. This includes features such as task assignment, notification system, and document sharing.Task assignment allows workflow managers to assign tasks to specific individuals or teams, ensuring clear accountability and ownership of tasks. A notification system notifies team members about new tasks, task updates, or deadlines, ensuring everyone is aware of their responsibilities and can take appropriate action. Document sharing enables team members to collaborate on documents, share feedback, and make updates in real-time, improving productivity and reducing version control issues.10. Workflow OptimizationContinuous optimization is a key aspect of workflow management. Once the workflows have been implemented, organizations should regularly review and evaluate their effectiveness. This involves analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and gathering feedback from employees and stakeholders.KPIs can include metrics such as cycle time, throughput, and error rates, which provide insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of the workflows. Gathering feedback from employees and stakeholders allows organizations to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to the workflows.Workflow optimization may involve making process improvements, reallocating resources, or reassigning tasks to improve efficiency and reduce bottlenecks. It may also involve exploring new technologies or tools that can further optimize the workflows, such as artificial intelligence or machine learning algorithms that can automate decision-making or predict behavior patterns in the workflows.11. Workflow ScalabilityAs businesses grow and evolve, their workflows may need to be scaled up or down to accommodate changing demands. Therefore, a workflow management system should be designed to be scalable, allowing organizations to easily adjust their workflows as needed. Scalability can be achieved through flexible workflow design, modular architecture, and the ability to easily add or remove tasks and processes. It also involves having a robust infrastructure that can handle increased workflow volume without sacrificing performance or causing system downtime.Additionally, a scalable workflow management system should be able to integrate with other systems and technologies seamlessly,allowing for future expansion or integration with new systems. 12. Workflow Security and ComplianceAnother important aspect of workflow management is ensuring the security and compliance of the workflows. Organizations need to protect sensitive data and ensure that workflows adhere to applicable regulations and industry standards.Workflow management systems should have built-in security features, such as access control, authentication, and encryption, to protect data from unauthorized access or breaches. They should also support auditing and logging capabilities to track and monitor workflow activities, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.Moreover, organizations should regularly assess their workflows for risks and vulnerabilities and implement appropriate controls to mitigate them. This may involve conducting risk assessments, implementing cybersecurity measures, and training employees on data protection and compliance standards.ConclusionA well-designed and implemented workflow management system can significantly improve productivity, efficiency, and quality of output for organizations. This reference model provides a comprehensive framework for organizations to follow when designing, implementing, and managing their workflows.By defining and analyzing workflows, designing efficient processes, automating tasks, and integrating systems, organizations can streamline their operations and achieve better outcomes. Collaboration, optimization, scalability, and security are all essential considerations to ensure the ongoing success of the workflows.Continuous improvement is crucial in maintaining the effectiveness of workflows, as organizations need to adapt to changing business demands and leverage emerging technologies. By following this model and continuously optimizing their workflows, organizations can stay competitive and achieve their goals in today's fast-paced business environment.。
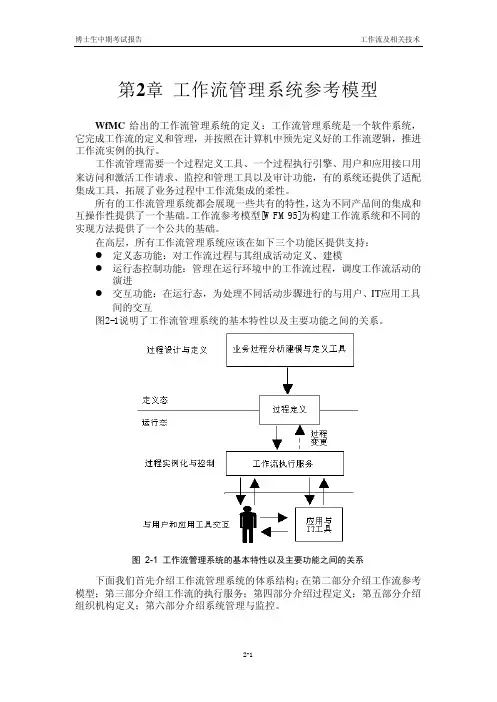
第2章工作流管理系统参考模型WfMC给出的工作流管理系统的定义:工作流管理系统是一个软件系统,它完成工作流的定义和管理,并按照在计算机中预先定义好的工作流逻辑,推进工作流实例的执行。
工作流管理需要一个过程定义工具、一个过程执行引擎、用户和应用接口用来访问和激活工作请求、监控和管理工具以及审计功能,有的系统还提供了适配集成工具,拓展了业务过程中工作流集成的柔性。
所有的工作流管理系统都会展现一些共有的特性,这为不同产品间的集成和互操作性提供了一个基础。
工作流参考模型[WFM95]为构建工作流系统和不同的实现方法提供了一个公共的基础。
在高层,所有工作流管理系统应该在如下三个功能区提供支持:l 定义态功能:对工作流过程与其组成活动定义、建模l 运行态控制功能:管理在运行环境中的工作流过程,调度工作流活动的演进l 交互功能:在运行态,为处理不同活动步骤进行的与用户、IT应用工具间的交互图2-1说明了工作流管理系统的基本特性以及主要功能之间的关系。
图2-1 工作流管理系统的基本特性以及主要功能之间的关系下面我们首先介绍工作流管理系统的体系结构;在第二部分介绍工作流参考模型;第三部分介绍工作流的执行服务;第四部分介绍过程定义;第五部分介绍组织机构定义;第六部分介绍系统管理与监控。
2.1 工作流管理系统的体系结构为了能够更好地支持企业业务过程建模、分析和实施,适应世界市场的多元化趋势,需要建立工作流管理系统的相关标准,从系统结构、术语使用、接口实施方面提供标准化与规范化的定义,并以此为基础实现不同工作流产品之间的互操作,便于与其他应用系统的集成。
在建立工作流的相关规范和标准方面,国际上成立了一个称为“工作流管理联盟”(简称WfMC)的国际组织。
它提出了有关工作流管理系统的一些规范,定义了工作流管理系统的结构及其与应用、管理工具和其他工作流管理系统之间的应用编程接口,其主要目的是为了实现工作流技术的标准化和开放性,从而支持异构工作流管理系统与产品之间的互操作,并且使得其他的应用可以使用该结构和定义好的通用API(应用编程接口)访问不同的工作流管理系统提供的服务,实现与其他应用的快速有效集成。

什么是工作流管理系统(WFMC)什么是工作流管理系统(WFMC)工作流标准组织(WFMC )是在1993年成立,这是由多家公司联合成立的国际标准组织。
(这个标准组织的链接地址是中科永联,估计文章出自他们。
真正的地址可以搜索到。
)有许多软件厂商提供各自的工作流软件产品,而且新的产品也不断涌现,用户有很大的选择余地,但是如果没有可遵循的行业标准,就会使这些产品之间存在巨大差异,导致这些产品之间不能协同工作,成为一个个信息的"孤岛"。
在这种背景下,工作流管理联盟(WfMC)于1993年成立了,这是由多家公司联合成立的国际标准组织,其目的是通过制定工作流技术及其标准,提高不同工作流产品之间的连通性和协同工作能力。
通过使用标准可以使不同的产品之间协同工作,也可以改善工作流产品与其他IT服务(电子邮件、文档管理)之间的集成。
该组织由三个委员会组成,分别是技术委员会、对外关系委员会和筹划指导委员会,WfMC目前有270多个成员组织,遍布世界各地。
经过该组织的不懈努力,工作流标准的制定和推广工作进展得非常迅速,目前,多数工作流产品的生产厂商已经在产品中遵循了全部和部分标准。
一概述企业在进行业务处理时,政府在进行公文审批时,都是以流程形式而进行的,在信息化的过程中,企业、政府也将这些业务处理、公文审批的过程信息化了,早期通常是通过程序硬编码的方式来处理这些业务、公文的流转,随着业务、公文的复杂的处理情况不断出现以及需求的不断变更,这种硬编码的方式显然已无法应对,这个时候工作流管理系统应运而生,掀起了一股工作流管理系统的热潮。
那么到底工作流管理系统能够带来什么好处?工作流管理系统通过对业务、公文流转进行分析以及抽象,将不变和变化的部分进行划分,用户可轻松的通过可视化的工具对事项的流程、流程环节涉及的人员(角色)、流程环节的表单、流程环节的操作进行修改,从而到达了应对不断变化的需求的目的,而工作流管理系统通常提供的流程监控、查询统计模块更是极大程度的为用户优化流程提供支持,以提高企业、政府的工作效率。

基于Web的分布式工作流模型在南宁市发改委办公自动化系统中的应用南宁市经济信息中心摘要:科学化的管理需要依靠现代化的办公工具、智能化决策、无纸化办公已经成为企事业单位现代化管理的趋势,而办公自动化系统将在现代化管理中发挥越来越重要的作用。
本文首先介绍了工作流管理系统的概念及其体系结构模型。
基于Web 平台,针对模型中工作流引擎模块的设计提出了一个行之有效解决方案。
1、引言工作流(Workflow)就是工作流程的计算模型,即将工作流程中的工作如何前后组织在一起的逻辑和规则在计算机中以恰当的模型进行表示并对其实施计算。
工作流要解决的主要问题是:为实现某个业务目标,在多个参与者之间,利用计算机,按某种预定规则自动传递文档、信息或者任务。
然而,随着Internet技术的飞速发展和全球经济一体化的趋势,人们对工作流管理技术有了新的要求。
在这种环境下,传统工作流系统那种缺乏柔性,不能及时响应变化和相互之间缺乏互操作的缺点显然不能满足现代业务流程管理的要求。
正是在这样的背景之下,Web 服务技术应运而生。
Web 服务是一种基于标准的应用集成方式,它可以将运行在通过Intrant、或Internet 连接的分布式服务器上的应用集成在一起。
Web 服务具有动态特性,它把一切都看作服务,这种服务可以通过在网络上使用消息传递动态地被发现和组织。
把Web服务加入到工作流系统中,必然会极大提高工作流系统的性能。
本文对如何利用Web 等先进技术实现工作流管理进行了探讨。
本文在此基础上,提出了办公自动化系统中分布式工作流模型的设计和实现。
2、工作流管理系统2.1 工作流的概念根据WfMC 的定义,工作流(Work Flow)就是自动运作的业务过程部分或整体,表现为参与者对文件、信息或任务按照规程采取行动,并令其在参与者之间传递。
它包括一组活动(activity)及其相互顺序关系,包括过程及活动的启动和终止条件,以及对每个活动的描述,如活动的执行者、相关应用程序、需要或产生的数据等。

翻译人:张敬波(网名:踏冰)OICQ:42508298Email:say4ever2u@ MSN:tabingfly@翻译人:韩伟(网名:浆糊)OICQ:3413384Email:java_cn@ MSN:Java_cn@欢迎访问我们的网站:工作流管理联盟规范WFMC ——工作流参考模型文档编号TC00-100395年1月19日版权©2002WFMC目录目录...................................................................................................................................- 2 -1.简介...............................................................................................................................................- 4 -1.1. 背景.....................................................................................................................................- 4 -1.2. 目的.....................................................................................................................................- 4 -1.3. 范围.....................................................................................................................................- 4 -1.4. 对象.....................................................................................................................................- 5 -1.5. 如何阅读.............................................................................................................................- 5 -1.6. 参考.....................................................................................................................................- 5 -1.7. 修订历史.............................................................................................................................- 5 -2.工作流系统简介...........................................................................................................................- 6 -2.1. 什么是工作流(workflow)..............................................................................................- 6 -2.1.1. 建立时期功能..........................................................................................................- 7 -2.1.2. 运行时期过程控制功能...........................................................................................- 8 -2.1.3. 运行时期活动交互..................................................................................................- 8 -2.1.4. 分配与系统接口......................................................................................................- 8 -2.2. 工作流的发展.....................................................................................................................- 9 -2.3. 产品实现模型.....................................................................................................................- 9 -2.4. 可选择的实现方式(Alternative Implementation Scenarios).......................................- 14 -2.5. 对标准化的需要(The Need for Standardization)........................................................- 17 -3.工作流参考模型(Workflow Reference Model).....................................................................- 18 -3.1. 简介...................................................................................................................................- 18 -3.2. 工作流模型(The Workflow Model)............................................................................- 18 -3.3. 工作流执行服务器(Workflow Enactment Services)...................................................- 19 -3.3.1. 什么是工作流执行服务器?.................................................................................- 19 -3.3.2. 工作流机(The Workflow Engine).....................................................................- 20 -3.3.3. 同种和异种的工作流执行服务器(Homogeneous & Heterogeneous WorkflowEnactment Services)........................................................................................................- 21 -3.3.4. 工作流应用编程接口与数据交换(Workflow Application programming Interface &Interchange)....................................................................................................................- 23 -3.3.5. 工作流控制,工作流相关数据和工作流应用数据.............................................- 23 -3.3.6. 数据交换(Data Interchange).............................................................................- 24 -3.4. 过程定义(Process Definition)......................................................................................- 25 -3.4.1. 过程定义工具(Process Definition Tools).........................................................- 25 -3.4.2. 工作流定义转换(接口1)..................................................................................- 26 -3.5. 工作流客户端功能(Workflow Client Functions)........................................................- 29 -3.5.1. 工作流客户端应用程序(Workflow Client Applications)................................- 29 -3.5.2. 工作流客户端应用程序接口(接口2)..............................................................- 30 -3.6. 应用程序调用功能(Invoked Application Functions)..................................................- 32 -3.6.1. 应用程序调用(Invoked Applications)..............................................................- 32 -3.6.2. 应用程序调用接口(接口3)..............................................................................- 33 -3.7. 工作流协同工作流能力(Workflow Interoperability).................................................- 35 -3.7.1. 异种工作流执行服务器.........................................................................................- 35 -3.7.2 模型1 ——链锁式(Chained).........................................................................- 35 -3.7.3. 模型2 ——子过程嵌套(Nested Subprocesses)............................................- 36 -3.7.4. 模型3 —— P2P (Peer-to-Peer).......................................................................- 37 -3.7.5. 模型4 ——相似同步(Parallel Synchronised)...............................................- 38 -3.7.6. WAPI协调工作功能(接口4)...........................................................................- 38 -3.8. 系统管理(Systems Administration).............................................................................- 41 -3.8.1 管理和监视工具(Administration & Monitoring Tools)....................................- 41 -3.8.2. 管理和监视接口(接口5)..................................................................................- 41 -4. WAPI 结构、协议和一致性.......................................................................................................- 44 -4.1. WAPI——API功能简介...................................................................................................- 44 -4.2. WAPI协议.........................................................................................................................- 45 -4.3. 一直性原则.......................................................................................................................- 45 -4.3.1. 一致性的意义........................................................................................................- 46 -4.4. 协同工作能力分类和一致性级别....................................................................................- 46 -4.4.1 定义工具、工作流执行软件..................................................................................- 46 -4.4.2 可户端应用程与工作流执行服务器序协同工作..................................................- 46 -4.4.3. 应用程序和工具集成............................................................................................- 47 -4.4.4. 工作流执行服务器协同工作.................................................................................- 47 -4.4.5. 公共工作流管理....................................................................................................- 47 -1.简介1.1. 背景工作流管理系统一项快速发展的技术,各种行业渐渐的采用工作流技术。
OSWorkflow在企业办公自动化系统中的应用研究摘要:阐述了办公自动化概念和工作流技术、工作流管理系统;并对常用开源工作流引擎OSWorkflow进行了介绍;对工作流管理系统开发过程中经常碰到任务时间调度问题进行了深入分析,并针对这些问题提供了相应的解决方案,实践证明提出的解决方案起到了良好的效果。
关键词:OSWorkflow;Quartz;工作流;任务调度1 办公自动化办公自动化系统就是利用先进的科学技术,使部分办公业务活动物化于人以外的各种现代化办公设备中,由人与技术设备构成服务于某种办公业务目的的人——机信息处理系统。
为了实现办公自动化,处理文档审批的流转、通知的发布、文档的分发等一系列用户权限相关的自动流转程序,工作流技术在系统中起到了重要作用。
1.1 工作流技术工作流就是工作流程的计算模型,即将工作流程中的工作如何前后组织在一起的逻辑和规则在计算机中以恰当的模型进行表示并对其实施计算。
工作流要解决的主要问题是:为实现某个业务目标,在多个参与者之间,利用计算机按照某种预定规则自动传递文档、信息或者任务。
1.2 工作流管理系统工作流管理系统主要功能是通过计算机技术的支持去定义、执行和管理工作流,协调工作流执行过程中工作之间以及群体成员之间的信息交互。
工作流管理联盟(WfMC)给出的工作流参考模型中,定义了工作流管理系统的各部分组件以及它们之间的接口。
主要包括流程定义工具、工作流执行服务、其他工作流执行服务、可调用外部程序、工作流客服端应用程序、监视管理工具等部分。
2 OSWorkflow框架OSWorkflow是一个纯Java编写的开源工作流引擎,以其独有的灵活性和面向开发者的特点著称。
基于有限状态机(finite state machine)原理,每一种状态(state)被描述成为step ID和status。
从一种状态(state)转移到另一种状态由动作(action)触发。
使用XML文件来描述业务工作流程。
金蝶E A S系统部署方案(新)集成管理随需应变-----金蝶EAS系统部署方案金蝶软件(中国)有限公司EAS产品事业部金蝶EAS通过国际厂商和国际组织的权威测试和认证!目录1.前言 (3)2.技术架构 (4)3.系统部署方式 (5)3.1.标准方案 (5)3.2.双机热备方案 (6)3.3.应用级集群部署方案 (6)3.3.1.集群模型特点 (7)3.3.2.集群部署建议 (7)3.4.系统级集群方案 (8)3.4.1.IBM P系列服务器群集技术(HACMP) (8)3.4.2.HP MC/ServiceGuard 集群方案 (9)3.5.分区技术 (9)4.网络安全 (10)4.1.EAS客户端与服务器连接 (10)4.2.VPN技术 (11)5.网络环境 (13)5.1.局域网 (13)5.2.广域网 (13)5.3.带宽要求 (14)6.服务器选型与配置 (14)6.1.EAS运行支持环境 (14)6.2.服务器硬件选型 (15)6.3.磁盘存储系统 (16)6.4.数据备份 (17)6.5.数据库选型 (19)6.6.应用服务器选型 (19)6.7.客户端硬件配置 (20)7.典型配置 (20)7.1.20个并发用户以内 (21)7.2.20-50个并发用户数 (22)7.3.50-100个并发用户数 (24)7.4.100-200个并发用户数 (25)7.5.200-500个并发用户数 (26)7.6.500个并发用户数以上 (28)7.7.IBM I系列集成服务器部署 (31)8.附件:性能测试报告 (33)8.1.EAS IBM IIC(上海)性能测试报告 (33)8.2.EAS HP方案解决中心性能测试报告 (36)8.3.EAS S UN F IRE服务器兼容性暨性能测试报告 (40)8.4.IBM O PEN P OWER 解决方案测试证书 (44)1.前言金蝶EAS(Enterprise Application Suite),是金蝶国际软件集团推出的新一代企业应用套件。
一种分布式工作流引擎负载均衡的调度算法摘要:提出了一种在异构环境下负载均衡调度策略,来解决各节点执行引擎负载不平衡的问题。
新的调度策略与轮询算法相比,更加能够保证各执行引擎之间负载保持平衡。
此外,当多引擎之间任务调度出现不平衡的状态时,该调度算法能动态地调整各节点引擎之间的负载,使之达到平衡状态。
关键词:工作流引擎;负载均衡;轮询算法0 引言伴随着Internet技术的飞速发展,企业经营过程全球化的推进,许多现代企业的信息资源出现了新的特点:广泛异类集合。
工作流技术作为现代化企业实现过程管理与过程控制的一项关键技术,为企业经营过程提供了一个从模型分析、建立、管理、仿真到运行的完整框架。
经过十几年的发展,工作流技术已经逐渐走向成熟,至今已被应用于生产制造、电信、银行等诸多领域。
但是,也必须看到,工作流技术无论在理论上还是在技术本身上还有诸多的不足,导致其应用还不够广泛。
提高工作流管理系统整体性能的一个重要策略是工作流引擎的分布,各分布工作流引擎的协作将使系统结构变得更加合理,它是提高工作流管理系统可靠性和性能的关键之一,合理的负载均衡调度策略是提高分布式工作流引擎性能所要考虑重点,然而要设计一个好的负载均衡调度策略,需要关注以下几点:①采用何种方式来描述或者衡量一个工作流引擎的负载等级;②采用何种方式完成各工作流引擎之间的通信和数据交换;③选择何种调度策略来给各个节点工作流引擎分配任务。
1 工作流概述工作流技术是一项快速发展的技术,得到各种行业逐渐的采用。
WFMC是由一些公司联合到一起成立的一个组织,从事上述问题的研究。
按照WFMC提出的工作流参考模型如图1所示,一个工作流管理系统包括过程定义工具、工作流引擎、工作流管理工具、工作流客户应用和工作流引擎直接调用的应用等功能模块。
对于分布式工作流管理,一般将其分为3个层次:工作流系统体系结构的分布;工作流引擎的分布;工作流模型的分布。
其中,工作流引擎的分布是其核心。
什么是工作流管理系统(WFMS)2007-01-25 1311定义工作流系统是以规格化的流程描述作为输入的软件组件,它维护流程的运行状态,并在人和应用之间分派活动。
为了后面的描述,我们先定义一些基本的术语:流程定义(process definition)和流程实例(process instance). 一个流程定义是一个业务流程或过程的规格化描述。
一个流程实例是流程定义的一个运行实体。
都目前为止,概念还比较清晰是不是?但当再深入一步时,我们就要小心使用文字了。
如何阐述流程中的步骤,现在还没有一个统一的方式。
这是各种工作流规范和工具之间主要的分歧。
为什么应当禁止使用术语“活动(activity)”...流程定义通常用一些活动表述。
我认为这是导致工作流领域所有混乱的主要原因。
我告诉你为什么:因为术语“活动”混淆了状态(state)和动作(action)之间的差异。
在流程中,状态(或者说等待状态)代表了一种对外部参与者(actor)的依赖。
在流程运行时,这意味着流程引擎必须等待,直到外部参与者通知工作流管理系统指定的状态完成了。
比如,等待可进一步运行的认可。
动作是在流程运行过程中,工作流系统为响应指定事件(event)运行的一段程序逻辑(program ming logic)。
当流程运行过程中指定的事件发生时,工作流系统启动并执行这些动作。
比如,当状态分配给一个参与者时,发一封Em ail。
你也能看出,状态和动作是如此不同,因此使用同样的术语去描述这些概念是一个坏习惯。
我的建议是避免使用术语“活动”,使用“状态”或者“动作”代替它。
工作流系统另一个重要的职责是维护每一个流程运行的上下文信息。
流程上下文变量(process contex t variable),或简称变量,是与流程实例相关的变量。
如,休假申请的开始日期、数据库中一条记录的键值、文档管理系统中一篇文档的索引等。
通常在流程定义中声明这些变量,然后在流程实例生成时,这些流程变量被实例化。
翻译人:张敬波(网名:踏冰)OICQ:42508298Email:say4ever2u@ MSN:tabingfly@翻译人:韩伟(网名:浆糊)OICQ:3413384Email:java_cn@ MSN:Java_cn@欢迎访问我们的网站:工作流管理联盟规范WFMC ——工作流参考模型文档编号TC00-100395年1月19日版权©2002WFMC目录目录...................................................................................................................................- 2 -1.简介...............................................................................................................................................- 4 -1.1. 背景.....................................................................................................................................- 4 -1.2. 目的.....................................................................................................................................- 4 -1.3. 范围.....................................................................................................................................- 4 -1.4. 对象.....................................................................................................................................- 5 -1.5. 如何阅读.............................................................................................................................- 5 -1.6. 参考.....................................................................................................................................- 5 -1.7. 修订历史.............................................................................................................................- 5 -2.工作流系统简介...........................................................................................................................- 6 -2.1. 什么是工作流(workflow)..............................................................................................- 6 -2.1.1. 建立时期功能..........................................................................................................- 7 -2.1.2. 运行时期过程控制功能...........................................................................................- 8 -2.1.3. 运行时期活动交互..................................................................................................- 8 -2.1.4. 分配与系统接口......................................................................................................- 8 -2.2. 工作流的发展.....................................................................................................................- 9 -2.3. 产品实现模型.....................................................................................................................- 9 -2.4. 可选择的实现方式(Alternative Implementation Scenarios).......................................- 14 -2.5. 对标准化的需要(The Need for Standardization)........................................................- 17 -3.工作流参考模型(Workflow Reference Model).....................................................................- 18 -3.1. 简介...................................................................................................................................- 18 -3.2. 工作流模型(The Workflow Model)............................................................................- 18 -3.3. 工作流执行服务器(Workflow Enactment Services)...................................................- 19 -3.3.1. 什么是工作流执行服务器?.................................................................................- 19 -3.3.2. 工作流机(The Workflow Engine).....................................................................- 20 -3.3.3. 同种和异种的工作流执行服务器(Homogeneous & Heterogeneous WorkflowEnactment Services)........................................................................................................- 21 -3.3.4. 工作流应用编程接口与数据交换(Workflow Application programming Interface &Interchange)....................................................................................................................- 23 -3.3.5. 工作流控制,工作流相关数据和工作流应用数据.............................................- 23 -3.3.6. 数据交换(Data Interchange).............................................................................- 24 -3.4. 过程定义(Process Definition)......................................................................................- 25 -3.4.1. 过程定义工具(Process Definition Tools).........................................................- 25 -3.4.2. 工作流定义转换(接口1)..................................................................................- 26 -3.5. 工作流客户端功能(Workflow Client Functions)........................................................- 29 -3.5.1. 工作流客户端应用程序(Workflow Client Applications)................................- 29 -3.5.2. 工作流客户端应用程序接口(接口2)..............................................................- 30 -3.6. 应用程序调用功能(Invoked Application Functions)..................................................- 32 -3.6.1. 应用程序调用(Invoked Applications)..............................................................- 32 -3.6.2. 应用程序调用接口(接口3)..............................................................................- 33 -3.7. 工作流协同工作流能力(Workflow Interoperability).................................................- 35 -3.7.1. 异种工作流执行服务器.........................................................................................- 35 -3.7.2 模型1 ——链锁式(Chained).........................................................................- 35 -3.7.3. 模型2 ——子过程嵌套(Nested Subprocesses)............................................- 36 -3.7.4. 模型3 —— P2P (Peer-to-Peer).......................................................................- 37 -3.7.5. 模型4 ——相似同步(Parallel Synchronised)...............................................- 38 -3.7.6. WAPI协调工作功能(接口4)...........................................................................- 38 -3.8. 系统管理(Systems Administration).............................................................................- 41 -3.8.1 管理和监视工具(Administration & Monitoring Tools)....................................- 41 -3.8.2. 管理和监视接口(接口5)..................................................................................- 41 -4. WAPI 结构、协议和一致性.......................................................................................................- 44 -4.1. WAPI——API功能简介...................................................................................................- 44 -4.2. WAPI协议.........................................................................................................................- 45 -4.3. 一直性原则.......................................................................................................................- 45 -4.3.1. 一致性的意义........................................................................................................- 46 -4.4. 协同工作能力分类和一致性级别....................................................................................- 46 -4.4.1 定义工具、工作流执行软件..................................................................................- 46 -4.4.2 可户端应用程与工作流执行服务器序协同工作..................................................- 46 -4.4.3. 应用程序和工具集成............................................................................................- 47 -4.4.4. 工作流执行服务器协同工作.................................................................................- 47 -4.4.5. 公共工作流管理....................................................................................................- 47 -1.简介1.1. 背景工作流管理系统一项快速发展的技术,各种行业渐渐的采用工作流技术。