期权期货与其他衍生产品第九版课后习题与答案Chapter(.
- 格式:doc
- 大小:773.50 KB
- 文档页数:7

CHAPTER 31Interest Rate Derivatives: Models of the Short Rate Practice QuestionsProblem 31.1.What is the difference between an equilibrium model and a no-arbitrage model?Equilibrium models usually start with assumptions about economic variables and derive the behavior of interest rates. The initial term structure is an output from the model. In ano-arbitrage model the initial term structure is an input. The behavior of interest rates in ano-arbitrage model is designed to be consistent with the initial term structure.Problem 31.2.Suppose that the short rate is currently 4% and its standard deviation is 1% per annum. What happens to the standard deviation when the short rate increases to 8% in (a) Vasicek’s model;(b) Rendleman and Bartter’s mod el; and (c) the Cox, Ingersoll, and Ross model?In Vasicek’s model the standard deviation stays at 1%. In the Rendleman and Bartter model the standard deviation is proportional to the level of the short rate. When the short rate increases from 4% to 8% the standard deviation increases from 1% to 2%. In the Cox, Ingersoll, and Ross model the standard deviation of the short rate is proportional to the square root of the short rate. When the short rate increases from 4% to 8% the standard deviation increases from 1% to 1.414%.Problem 31.3.If a stock price were mean reverting or followed a path-dependent process there would be market inefficiency. Why is there not market inefficiency when the short-term interest rate does so?If the price of a traded security followed a mean-reverting or path-dependent process there would be market inefficiency. The short-term interest rate is not the price of a traded security. In other words we cannot trade something whose price is always the short-term interest rate. There is therefore no market inefficiency when the short-term interest rate follows amean-reverting or path-dependent process. We can trade bonds and other instruments whose prices do depend on the short rate. The prices of these instruments do not followmean-reverting or path-dependent processes.Problem 31.4.Explain the difference between a one-factor and a two-factor interest rate model.In a one-factor model there is one source of uncertainty driving all rates. This usually means that in any short period of time all rates move in the same direction (but not necessarily by the same amount). In a two-factor model, there are two sources of uncertainty driving all rates. The first source of uncertainty usually gives rise to a roughly parallel shift in rates. The second gives rise to a twist where long and short rates moves in opposite directions.Problem 31.5.Can the approach described in Section 31.4 for decomposing an option on a coupon-bearing bond into a portfolio of options on zero-coupon bonds be used in conjunction with a two-factor model? Explain your answer.No. The approach in Section 31.4 relies on the argument that, at any given time, all bond prices are moving in the same direction. This is not true when there is more than one factor.Problem 31.6.Suppose that 01a =. and 01b =. in both the Vasicek and the Cox, Ingersoll, Ross model. In both models, the initial short rate is 10% and the initial standard deviation of the short rate change in a short time t ∆is 0.zero-coupon bond that matures in year 10.In Vasicek’s model, 01a =., 01b =., and 002σ=. so that01101(10)(1)63212101B t t e -.⨯,+=-=..22(63212110)(010100002)00004632121(10)exp 00104A t t ⎡⎤.-.⨯.-..⨯.,+=-⎢⎥..⎣⎦071587=. The bond price is therefore 63212101071587038046e -.⨯..=.In the Cox, Ingersoll, and Ross model, 01a =., 01b =.and 00200632σ=.=.. Also013416γ==. Define10()(1)2092992a e γβγγ=+-+=.102(1)(10)607650e B t t γβ-,+==.225()2(10)069746ab a e A t t σγγβ/+⎛⎫,+==. ⎪⎝⎭The bond price is therefore 60765001069746037986e -.⨯..=.Problem 31.7.Suppose that 01a =., 008b =., and 0015σ=. in Vasicek’s model with the initial value of the short rate being 5%. Calculate the price of a one-year European call option on azero-coupon bond with a principal of $100 that matures in three years when the strike price is $87.Using the notation in the text, 3s =, 1T =, 100L =, 87K =, and2010015(1002588601P e σ-⨯..=-=.. From equation (31.6), (01)094988P ,=., (03)085092P ,=., and 114277h =. so thatequation (31.20) gives the call price as call price is 100085092(114277)87094988(111688)259N N ⨯.⨯.-⨯.⨯.=. or $2.59.Problem 31.8.Repeat Problem 31.7 valuing a European put option with a strike of $87. What is the put –call parity relationship between the prices of European call and put options? Show that the put and call option prices satisfy put –call parity in this case.As mentioned in the text, equation (31.20) for a call option is essentially the same as Bl ack’s model. By analogy with Black’s formulas corresponding expression for a put option is (0)()(0)()P KP T N h LP s N h σ,-+-,- In this case the put price is 87094988(111688)100085092(114277)014N N ⨯.⨯-.-⨯.⨯-.=.Since the underlying bond pays no coupon, put –call parity states that the put price plus the bond price should equal the call price plus the present value of the strike price. The bond price is 85.09 and the present value of the strike price is 870949888264⨯.=.. Put –call parity is therefore satisfied:82642598509014.+.=.+.Problem 31.9.Suppose that 005a =., 008b =., and 0015σ=. in Vasicek’s model with the initialshort-term interest rate being 6%. Calculate the price of a 2.1-year European call option on a bond that will mature in three years. Suppose that the bond pays a coupon of 5% semiannually. The principal of the bond is 100 and the strike price of the option is 99. The strike price is the cash price (not the quoted price) that will be paid for the bond.As explained in Section 31.4, the first stage is to calculate the value of r at time 2.1 years which is such that the value of the bond at that time is 99. Denoting this value of r by r *, we must solve(2125)(2130)25(2125)1025(2130)99B r B r A e A e **-.,.-.,...,.+..,.=where the A and B functions are given by equations (31.7) and (31.8). In this case A (2.1, 2.5)=0.999685, A (2.1,3.0)=0.998432, B(2.1,2.5)=0.396027, and B (2.1, 3.0)= 0.88005. and Solver shows that 065989.0*=r . Since434745.2)5.2,1.2(5.2*)5.2,1.2(=⨯-r B e Aand56535.96)0.3,1.2(5.102*)0.3,1.2(=⨯-r B e Athe call option on the coupon-bearing bond can be decomposed into a call option with a strike price of 2.434745 on a bond that pays off 2.5 at time 2.5 years and a call option with a strike price of 96.56535 on a bond that pays off 102.5 at time 3.0 years. The options are valued using equation (31.20).For the first option L =2.5, K = 2.434745, T = 2.1, and s =2.5. Also, A (0,T )=0.991836, B (0,T ) = 1.99351, P (0,T )=0.880022 while A (0,s )=0.988604, B (0,s )=2.350062, andP (0,s )=0.858589. Furthermore σP = 0.008176 and h = 0.223351. so that the option price is 0.009084.For the second option L =102.5, K = 96.56535, T = 2.1, and s =3.0. Also, A (0,T )=0.991836, B (0,T ) = 1.99351, P (0,T )=0.880022 while A (0,s )=0.983904, B (0,s )=2.78584, andP (0,s )=0.832454. Furthermore σP = 0.018168 and h = 0.233343. so that the option price is0.806105.The total value of the option is therefore 0.0090084+0.806105=0.815189.Problem 31.10.Use the answer to Problem 31.9 and put –call parity arguments to calculate the price of a put option that has the same terms as the call option in Problem 31.9.Put-call parity shows that: 0()c I PV K p B ++=+ or 0()()p c PV K B I =+--where c is the call price, K is the strike price, I is the present value of the coupons, and 0B is the bond price. In this case 08152c =., ()99(021)871222PV K P =⨯,.=., 025(025)1025(03)874730B I P P -=.⨯,.+.⨯,=. so that the put price is0815287122287473004644.+.-.=.Problem 31.11.In the Hull –White model, 008a =. and 001σ=.. Calculate the price of a one-year European call option on a zero-coupon bond that will mature in five years when the term structure is flat at 10%, the principal of the bond is $100, and the strike price is $68.Using the notation in the text 011(0)09048P T e -.⨯,==. and 015(0)06065P s e -.⨯,==.. Also4008001(100329008P e σ-⨯..=-=.. and 04192h =-. so that the call price is10006065()6809048()0439P N h N h σ⨯.-⨯.-=.Problem 31.12.Suppose that 005a =. and 0015σ=. in the Hull –White model with the initial term structure being flat at 6% with semiannual compounding. Calculate the price of a 2.1-year European call option on a bond that will mature in three years. Suppose that the bond pays a coupon of 5% per annum semiannually. The principal of the bond is 100 and the strike price of the option is 99. The strike price is the cash price (not the quoted price) that will be paid for the bond.This problem is similar to Problem 31.9. The difference is that the Hull –White model, which fits an initial term structure, is used instead of Vasicek’s model where the initial term structure is determined by the model.The yield curve is flat with a continuously compounded rate of 5.9118%.As explained in Section 31.4, the first stage is to calculate the value of r at time 2.1 years which is such that the value of the bond at that time is 99. Denoting this value of r by r *, we must solve(2125)(2130)25(2125)1025(2130)99B r B r A e A e **-.,.-.,...,.+..,.=where the A and B functions are given by equations (31.16) and (31.17). In this case A (2.1, 2.5)=0.999732, A (2.1,3.0)=0.998656, B(2.1,2.5)=0.396027, and B (2.1, 3.0)= 0.88005. and Solver shows that 066244.0*=r . Since434614.2)5.2,1.2(5.2*)5.2,1.2(=⨯-r B e Aand56539.96)0.3,1.2(5.102*)0.3,1.2(=⨯-r B e Athe call option on the coupon-bearing bond can be decomposed into a call option with a strike price of 2.434614 on a bond that pays off 2.5 at time 2.5 years and a call option with a strike price of 96.56539 on a bond that pays off 102.5 at time 3.0 years. The options are valued using equation (31.20).For the first option L =2.5, K = 2.434614, T = 2.1, and s =2.5. Also, P (0,T )=exp(-0.059118×2.1)=0.88325 and P (0,s )= exp(-0.059118×2.5)=0.862609. Furthermore σP = 0.008176 and h = 0.353374. so that the option price is 0.010523. For the second option L =102.5, K = 96.56539, T = 2.1, and s =3.0. Also, P (0,T )=exp(-0.059118×2.1)=0.88325 and P (0,s )= exp(-0.059118×3.0)=0.837484. Furthermore σP = 0.018168 and h = 0.363366. so that the option price is 0.934074.The total value of the option is therefore 0.010523+0.934074=0.944596.Problem 31.13.Observations spaced at intervals ∆t are taken on the short rate. The ith observation is r i (1 ≤ i ≤ m). Show that the maximum likelihood estimates of a, b, and σ in Vasicek’s model are given by maximizing[]∑=--⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛∆σ∆----∆σ-m i i i i t t r b a r r t 122112)()ln(What is the corresponding result for the CIR model?The change r i –r i -1 is normally distributed with mean a (b − r i -1) and variance σ2∆t. The probability density of the observation is⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛∆σ---∆πσ--t r b a r r ti i i 21122)(exp 21We wish to maximize∏=--⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛∆σ---∆πσmi i i i t r b a r r t121122)(exp 21Taking logarithms, this is the same as maximizing[]∑=--⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛∆σ∆----∆σ-m i i i i t t r b a r r t 122112)()ln(In the case of the CIR model, the change r i –r i -1 is normally distributed with mean a (b − r i -1) and variance t r i ∆σ-12and the maximum likelihood function becomes[]∑=----⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛∆σ∆----∆σ-mi i i i i i t r t r b a r r t r 11221112)()ln(Problem 31.14.Suppose 005a =., 0015σ=., and the term structure is flat at 10%. Construct a trinomial tree for the Hull –White model where there are two time steps, each one year in length.The time step, t ∆, is 1 so that 0002598r ∆=.=.. Also max 4j = showing that the branching method should change four steps from the center of the tree. With only three steps we never reach the point where the branching changes. The tree is shown in Figure S31.1.Figure S31.1: Tree for Problem 31.14Problem 31.15.Calculate the price of a two-year zero-coupon bond from the tree in Figure 31.6.A two-year zero-coupon bond pays off $100 at the ends of the final branches. At nodeB it is worth 01211008869e -.⨯=.. At nodeC it is worth 010********e -.⨯=.. At nodeD it is worth 00811009231e -.⨯=.. It follows that at node A the bond is worth 011(88690259048059231025)8188e -.⨯.⨯.+.⨯.+.⨯.=. or $81.88Problem 31.16.Calculate the price of a two-year zero-coupon bond from the tree in Figure 31.9 and verify that it agrees with the initial term structure.A two-year zero-coupon bond pays off $100 at time two years. At nodeB it is worth 0069311009330e -.⨯=.. At nodeC it is worth 0052011009493e -.⨯=.. At nodeD it is worth 0034711009659e -.⨯=.. It follows that at node A the bond is worth 003821(933001679493066696590167)9137e -.⨯.⨯.+.⨯.+.⨯.=.or $91.37. Because 00451229137100e -.⨯.=, the price of the two-year bond agrees with the initial term structure.Problem 31.17.Calculate the price of an 18-month zero-coupon bond from the tree in Figure 31.10 and verify that it agrees with the initial term structure.An 18-month zero-coupon bond pays off $100 at the final nodes of the tree. At node E it is worth 0088051009570e -.⨯.=.. At node F it is worth 00648051009681e -.⨯.=.. At node G it is worth 00477051009764e -.⨯.=.. At node H it is worth 00351051009826e -.⨯.=.. At node I it is worth 00259051009871e .⨯.=.. At node B it is worth 0056405(011895700654968102289764)9417e -.⨯..⨯.+.⨯.+.⨯.=.Similarly at nodes C and D it is worth 95.60 and 96.68. The value at node A is therefore 0034305(016794170666956001679668)9392e -.⨯..⨯.+.⨯.+.⨯.=.The 18-month zero rate is 0181500800500418e -.⨯..-.=.. This gives the price of the 18-month zero-coupon bond as 00418151009392e -.⨯.=. showing that the tree agrees with the initial term structure.Problem 31.18.What does the calibration of a one-factor term structure model involve?The calibration of a one-factor interest rate model involves determining its volatility parameters so that it matches the market prices of actively traded interest rate options as closely as possible.Problem 31.19.Use the DerivaGem software to value 14⨯, 23⨯, 32⨯, and 41⨯ European swap options to receive fixed and pay floating. Assume that the one, two, three, four, and five year interest rates are 6%, 5.5%, 6%, 6.5%, and 7%, respectively. The payment frequency on the swap is semiannual and the fixed rate is 6% per annum with semiannual compounding. Use the Hull –White model with 3a %= and 1%σ=. Calcula te the volatility implied by Black’s model for each option.The option prices are 0.1302, 0.0814, 0.0580, and 0.0274. The implied Black volatilities are 14.28%, 13.64%, 13.24%, and 12.81%Problem 31.20.Prove equations (31.25), (31.26), and (31.27).From equation (31.15) ()()()()r t B t t t P t t t A t t t e -,+∆,+∆=,+∆ Also ()()R t t P t t t e -∆,+∆= so that()()()()R t t r t B t t t e A t t t e -∆-,+∆=,+∆or()()()()()()()()R t B t T t B t t t r t B t T B t T B t t t e eA t t t -,∆/,+∆-,,/,+∆=,+∆ Hence equation (31.25) is true with()ˆ()(B t T t Bt T B t t t ,∆,=,+∆ and()()()ˆ()()B t T B t t t A t T At T A t t t ,/,+∆,,=,+∆ or()ˆln ()ln ()ln ()()B t T At T A t T A t t t B t t t ,,=,-,+∆,+∆Problem 31.21.(a) What is the second partial derivative of P(t,T) with respect to r in the Vasicek and CIR models?(b) In Section 31.2, ˆDis presented as an alternative to the standard duration measure D. What is a similar alternative ˆCto the convexity measure in Section 4.9? (c) What is ˆCfor P(t,T)? How would you calculate ˆC for a coupon-bearing bond? (d) Give a Taylor Series expansion for ∆P(t,T) in terms of ∆r and (∆r)2 for Vasicek and CIR.(a) ),(),(),(),(),(2),(222T t P T t B e T t A T t B rT t P r T t B ==∂∂- (b) A corresponding definition for Cˆis 221r QQ ∂∂(c) When Q =P (t ,T ), 2),(ˆT t B C=For a coupon-bearing bond C ˆis a weighted average of the Cˆ’s for the constituent zero -coupon bonds where weights are proportional to bond prices. (d)+∆+∆-=+∆∂∂+∆∂∂=∆22222),(),(21),(),(),(21),(),(r T t P T t B r T t P T t B r rT t P r r T t P T t PProblem 31.22.Suppose that the short rate r is 4% and its real-world process is0.1[0.05]0.01dr r dt dz =-+while the risk-neutral process is0.1[0.11]0.01dr r dt dz =-+(a) What is the market price of interest rate risk?(b) What is the expected return and volatility for a 5-year zero-coupon bond in the risk-neutral world?(c) What is the expected return and volatility for a 5-year zero-coupon bond in the real world?(a) The risk neutral process for r has a drift rate which is 0.006/r higher than the real world process. The volatility is 0.01/r . This means that the market price of interest rate risk is −0.006/0.01 or −0.6.(b) The expected return on the bond in the risk-neutral world is the risk free rate of 4%. The volatility is 0.01×B (0,5) where935.31.01)5,0(51.0=-=⨯-e Bi.e., the volatility is 3.935%.(c) The process followed by the bond price in a risk-neutral world isPdz Pdt dP 03935.004.0-=Note that the coefficient of dz is negative because bond prices are negatively correlated with interest rates. When we move to the real world the return increases by the product of the market price of dz risk and −0.03935. The bond price process becomes:Pdz Pdt dP 03935.0)]03935.06.0(04.0[--⨯-+=orPdz Pdt dP 03935.006361.0-=The expected return on the bond increases from 4% to 6.361% as we move from the risk-neutral world to the real world.Further QuestionsProblem 31.23.Construct a trinomial tree for the Ho and Lee model where 002σ=.. Suppose that the initial zero-coupon interest rate for a maturities of 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 years are 7.5%, 8%, and 8.5%. Use two time steps, each six months long. Calculate the value of a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $100 and a remaining life of six months at the ends of the final nodes of the tree. Use the tree to value a one-year European put option with a strike price of 95 on the bond. Compare the price given by your tree with the analytic price given by DerivaGem.The tree is shown in Figure S31.2. The probability on each upper branch is 1/6; the probability on each middle branch is 2/3; the probability on each lower branch is 1/6. The six month bond prices nodes E, F, G, H, I are 0144205100e -.⨯., 0119705100e -.⨯., 0095205100e -.⨯., 0070705100e -.⨯., and 0046205100e -.⨯., respectively. These are 93.04, 94.19, 95.35, 96.53, and 97.72. The payoffs from the option at nodes E, F, G, H, and I are therefore 1.96, 0.81, 0, 0, and 0. The value at node B is 0109505(0166719606667081)08192e -.⨯..⨯.+.⨯.=.. The value at node C is00851050166708101292e -.⨯..⨯.⨯=.. The value at node D is zero. The value at node A is 0075005(01667081920666701292)0215e -.⨯..⨯.+.⨯.=. The answer given by DerivaGem using the analytic approach is 0.209.Figure S31.2: Tree for Problem 31.23Problem 31.24.A trader wishes to compute the price of a one-year American call option on a five-year bond with a face value of 100. The bond pays a coupon of 6% semiannually and the (quoted) strike price of the option is $100. The continuously compounded zero rates for maturities of sixmonths, one year, two years, three years, four years, and five years are 4.5%, 5%, 5.5%, 5.8%, 6.1%, and 6.3%. The best fit reversion rate for either the normal or the lognormal model has been estimated as 5%.A one year European call option with a (quoted) strike price of 100 on the bond is actively traded. Its market price is $0.50. The trader decides to use this option for calibration. Use the DerivaGem software with ten time steps to answer the following questions.(a) Assuming a normal model, imply the σ parameter from the price of the European option.(b) Use the σ parameter to calculate the price of the option when it is American. (c) Repeat (a) and (b) for the lognormal model. Show that the model used does notsignificantly affect the price obtained providing it is calibrated to the known European price.(d) Display the tree for the normal model and calculate the probability of a negative interest rate occurring.(e) Display the tree for the lognormal model and verify that the option price is correctly calculated at the node where, with the notation of Section 31.7, 9i = and 1j =-.Using 10 time steps:(a) The implied value of σ is 1.12%.(b) The value of the American option is 0.595(c) The implied value of σ is 18.45% and the value of the American option is 0.595. Thetwo models give the same answer providing they are both calibrated to the same European price.(d) We get a negative interest rate if there are 10 down moves. The probability of this is0.16667×0.16418×0.16172×0.15928×0.15687×0.15448×0.15212×0.14978×0.14747 ×0.14518=8.3×10-9 (e) The calculation is0052880101641791707502789e -.⨯..⨯.⨯=.Problem 31.25.Use the DerivaGem software to value 14⨯, 23⨯, 32⨯, and 41⨯ European swap options to receive floating and pay fixed. Assume that the one, two, three, four, and five year interest rates are 3%, 3.5%, 3.8%, 4.0%, and 4.1%, respectively. The payment frequency on the swap is semiannual and the fixed rate is 4% per annum with semiannual compounding. Use thelognormal model with 5a %=, 15%σ=, and 50 time steps. Calculate the volatility implied by Black’s model for each option.The values of the four European swap options are 1.72, 1.73, 1.30, and 0.65, respectively. The implied Black volatilities are 13.37%, 13.41%, 13.43%, and 13.42%, respectively.Problem 31.26.Verify that the DerivaGem software gives Figure 31.11 for the example considered. Use the software to calculate the price of the American bond option for the lognormal and normalmodels when the strike price is 95, 100, and 105. In the case of the normal model, assume that a = 5% and σ = 1%. Discuss the results in the context of the heavy-tails arguments of Chapter 20.With 100 time steps the lognormal model gives prices of 5.585, 2.443, and 0.703 for strike prices of 95, 100, and 105. With 100 time steps the normal model gives prices of 5.508, 2.522, and 0.895 for the three strike prices respectively. The normal model gives a heavier left tail and a less heavy right tail than the lognormal model for interest rates. This translates into a less heavy left tail and a heavier right tail for bond prices. The arguments in Chapter 20 show that we expect the normal model to give higher option prices for high strike prices and lower option prices for low strike. This is indeed what we find.Problem 31.27.Modify Sample Application G in the DerivaGem Application Builder software to test theconvergence of the price of the trinomial tree when it is used to price a two-year call option on a five-year bond with a face value of 100. Suppose that the strike price (quoted) is 100, the coupon rate is 7% with coupons being paid twice a year. Assume that the zero curve is as in Table 31.2. Compare results for the following cases:(a) Option is European; normal model with 001σ=. and 005a =..(b) Option is European; lognormal model with 015σ=. and 005a =..(c) Option is American; normal model with 001σ=. and 005a =..(d) Option is American; lognormal model with 015σ=. and 005a =..The results are shown in Figure S31.3.Figure S31.3: Tree for Problem 31.27Problem 31.28.Suppose that the (CIR) process for short-rate movements in the (traditional) risk-neutral world is()dr a b r dt =-+and the market price of interest rate risk is λ(a) What is the real world process for r?(b) What is the expected return and volatility for a 10-year bond in the risk-neutral world? (c) What is the expected return and volatility for a 10-year bond in the real world?(a) The volatility of r (i.e., the coefficient of rdz in the process for r ) is real world process for r is therefore increased by r r λσ⨯ so that the process isdz r dt r r b a dr σ+λσ+-=])([(b) The expected return is r and the volatility is (,B t T σin the risk-neutral world.(c) The expected return is r T t B r ),(λσ+ and the volatility is as in (b) in the real world.。

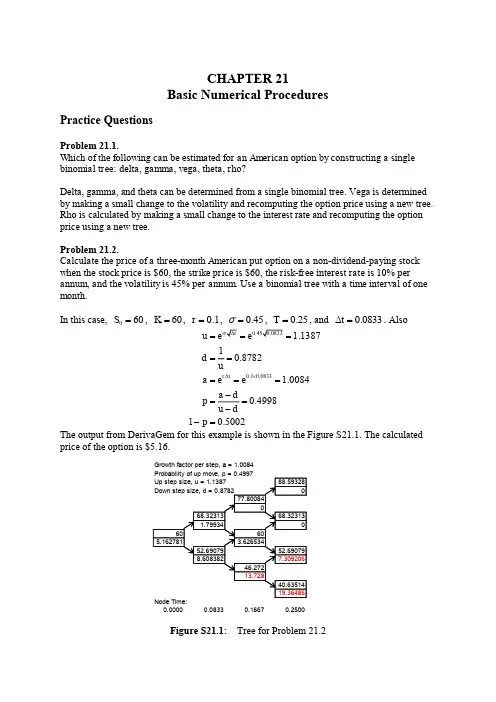
cHAPTra KI betUrM M«4duxn«x<^ ar ••••• f«g ・t plM OM<a to MB ll ・—TL —▼rMdV — ■ M 9•&・ Mtw«aH 叩■厂 1—、M»A-l S*2*0«M ■■ ^7521 1*4SeM 0|«tc4WB* ap*w ^«K « <* o az «•«!io •e ・fOMHVu ・w« Aft. xW*・9«v MBMk t» W*»|w «WM !•«•••— %-V> K ・9. ■・•( •*©> T-»» ■.空竺J 马A 空兰.…计•A SK<•4 «>A7・・1・•・R ・08*・5ZE 11*.F<<O<MI4WV ■❷•waw JttM <«•<«■■ J ・I9H74・ MrtMyiiPH—W ・(VAlw«・・,•■■■>•・" M «M 4 MI « E f R —W •字•字)vfViurutMjnr^vMtai 111 A —i"・^«hW —WI4»••一 y wt 卯 v >•*♦ *» <wr* 戸 x« tv•I Mt «wM ■*■<> «W ■・vfl !• mtvwvF k» VKM »> t»l • p< c» IW Mk vtt»•••• MM• tl»>■斗・4r.•丄防| n*kw !•*J M **vWatAM)' H MB*・朴・卜:卞”・ 4tJJ• Mm K -W ・ r ・Q.・ 9-QS.M > T-«» ・4CMP»c»to« A ■a0>■!«<•(■・•《 Mkwtaa 血”•>« «WE>y«»«vP • IF —・••—■—■科M4_ <tl ・oaMalWMi .11创n 11MM ■— 一A""・v«r■n«^»a w'«•!•<.•..»■ •> i- a-k>―初|・(« _F0R »*i!<■<■« i ・9” ■*!•«••«・》MM E ・》*k>e« —«E.r ■MIC ■一* »» ■•• ”・$«s» •• ts. no ¥ wr ■5— wK ・・«■•*・•••■•••・•••• *♦"■・••••・”•・•・~•l*« f*ASK"*""b QU ,,•・"♦(■* rI・・t ・K •WR XVIM •一刪・0|«・・・<||"• 8K kfk •■>•••<• ■…m»«*w<WH ” IK* lMW«IM iewr mu ■・—A« 巧 ki j«"U >• >^*10* t••<!•.»<»• ••••(■a * 、・r R if 。


CHAPTER 1IntroductionPractice QuestionsProblem 1.1.What is the difference between a long forward position and a short forward position?When a trader enters into a long forward contract, she is agreeing to buy the underlying asset for a certain price at a certain time in the future. When a trader enters into a short forward contract, she is agreeing to sell the underlying asset for a certain price at a certain time in the future.Problem 1.2.Explain carefully the difference between hedging, speculation, and arbitrage.A trader is hedging when she has an exposure to the price of an asset and takes a position in a derivative to offset the exposure. In a speculation the trader has no exposure to offset. She is betting on the future movements in the price of the asset. Arbitrage involves taking a position in two or more different markets to lock in a profit.Problem 1.3.What is the difference between entering into a long forward contract when the forward price is $50 and taking a long position in a call option with a strike price of $50?In the first case the trader is obligated to buy the asset for $50. (The trader does not have a choice.) In the second case the trader has an option to buy the asset for $50. (The trader does not have to exercise the option.)Problem 1.4.Explain carefully the difference between selling a call option and buying a put option.Selling a call option involves giving someone else the right to buy an asset from you. It gives you a payoff ofmax(0)min(0)T T S K K S --,=-, Buying a put option involves buying an option from someone else. It gives a payoff of max(0)T K S -,In both cases the potential payoff is T K S -. When you write a call option, the payoff is negative or zero. (This is because the counterparty chooses whether to exercise.) When you buy a put option, the payoff is zero or positive. (This is because you choose whether to exercise.)Problem 1.5.An investor enters into a short forward contract to sell 100,000 British pounds for US dollars at an exchange rate of 1.5000 US dollars per pound. How much does the investor gain or lose if the exchange rate at the end of the contract is (a) 1.4900 and (b) 1.5200?(a)The investor is obligated to sell pounds for 1.5000 when they are worth 1.4900. Thegain is (1.5000−1.4900) ×100,000 = $1,000.(b)The investor is obligated to sell pounds for 1.5000 when they are worth 1.5200. Theloss is (1.5200−1.5000)×100,000 = $2,000Problem 1.6.A trader enters into a short cotton futures contract when the futures price is 50 cents per pound. The contract is for the delivery of 50,000 pounds. How much does the trader gain or lose if the cotton price at the end of the contract is (a) 48.20 cents per pound; (b) 51.30 cents per pound?(a)The trader sells for 50 cents per pound something that is worth 48.20 cents per pound.Gain ($05000$04820)50000$900=.-.⨯,=.(b)The trader sells for 50 cents per pound something that is worth 51.30 cents per pound.Loss ($05130$05000)50000$650=.-.⨯,=.Problem 1.7.Suppose that you write a put contract with a strike price of $40 and an expiration date in three months. The current stock price is $41 and the contract is on 100 shares. What have you committed yourself to? How much could you gain or lose?You have sold a put option. You have agreed to buy 100 shares for $40 per share if the party on the other side of the contract chooses to exercise the right to sell for this price. The option will be exercised only when the price of stock is below $40. Suppose, for example, that the option is exercised when the price is $30. You have to buy at $40 shares that are worth $30; you lose $10 per share, or $1,000 in total. If the option is exercised when the price is $20, you lose $20 per share, or $2,000 in total. The worst that can happen is that the price of the stock declines to almost zero during the three-month period. This highly unlikely event would cost you $4,000. In return for the possible future losses, you receive the price of the option from the purchaser.Problem 1.8.What is the difference between the over-the-counter market and the exchange-traded market? What are the bid and offer quotes of a market maker in the over-the-counter market?The over-the-counter market is a telephone- and computer-linked network of financial institutions, fund managers, and corporate treasurers where two participants can enter into any mutually acceptable contract. An exchange-traded market is a market organized by an exchange where the contracts that can be traded have been defined by the exchange. When a market maker quotes a bid and an offer, the bid is the price at which the market maker is prepared to buy and the offer is the price at which the market maker is prepared to sell.Problem 1.9.You would like to speculate on a rise in the price of a certain stock. The current stock price is $29, and a three-month call with a strike of $30 costs $2.90. You have $5,800 to invest.Identify two alternative strategies, one involving an investment in the stock and the other involving investment in the option. What are the potential gains and losses from each?One strategy would be to buy 200 shares. Another would be to buy 2,000 options. If the share price does well the second strategy will give rise to greater gains. For example, if the share price goes up to $40 you gain [2000($40$30)]$5800$14200,⨯--,=,from the second strategy and only 200($40$29)$2200⨯-=,from the first strategy. However, if the share price does badly, the second strategy gives greater losses. For example, if the share price goes down to $25, the first strategy leads to a loss of 200($29$25)$800⨯-=,whereas the second strategy leads to a loss of the whole $5,800 investment. This example shows that options contain built in leverage.Problem 1.10.Suppose you own 5,000 shares that are worth $25 each. How can put options be used to provide you with insurance against a decline in the value of your holding over the next four months?You could buy 50 put option contracts (each on 100 shares) with a strike price of $25 and an expiration date in four months. If at the end of four months the stock price proves to be less than $25, you can exercise the options and sell the shares for $25 each.Problem 1.11.When first issued, a stock provides funds for a company. Is the same true of anexchange-traded stock option? Discuss.An exchange-traded stock option provides no funds for the company. It is a security sold by one investor to another. The company is not involved. By contrast, a stock when it is first issued is sold by the company to investors and does provide funds for the company.Problem 1.12.Explain why a futures contract can be used for either speculation or hedging.If an investor has an exposure to the price of an asset, he or she can hedge with futures contracts. If the investor will gain when the price decreases and lose when the price increases, a long futures position will hedge the risk. If the investor will lose when the price decreases and gain when the price increases, a short futures position will hedge the risk. Thus either a long or a short futures position can be entered into for hedging purposes.If the investor has no exposure to the price of the underlying asset, entering into a futures contract is speculation. If the investor takes a long position, he or she gains when the asset’s price increases and loses when it decreases. If the investor takes a short position, he or she loses when the asset’s price increases and gains when it decreases.Problem 1.13.Suppose that a March call option to buy a share for $50 costs $2.50 and is held until March. Under what circumstances will the holder of the option make a profit? Under what circumstances will the option be exercised? Draw a diagram showing how the profit on a long position in the option depends on the stock price at the maturity of the option.The holder of the option will gain if the price of the stock is above $52.50 in March. (This ignores the time value of money.) The option will be exercised if the price of the stock isabove $50.00 in March. The profit as a function of the stock price is shown in Figure S1.1.Figure S1.1:Profit from long position in Problem 1.13Problem 1.14.Suppose that a June put option to sell a share for $60 costs $4 and is held until June. Under what circumstances will the seller of the option (i.e., the party with a short position) make a profit? Under what circumstances will the option be exercised? Draw a diagram showing how the profit from a short position in the option depends on the stock price at the maturity of the option.The seller of the option will lose money if the price of the stock is below $56.00 in June. (This ignores the time value of money.) The option will be exercised if the price of the stock is below $60.00 in June. The profit as a function of the stock price is shown in Figure S1.2.Figure S1.2:Profit from short position in Problem 1.14Problem 1.15.It is May and a trader writes a September call option with a strike price of $20. The stock price is $18, and the option price is $2. Describe the investor’s cash flo ws if the option is held until September and the stock price is $25 at this time.The trader has an inflow of $2 in May and an outflow of $5 in September. The $2 is the cash received from the sale of the option. The $5 is the result of the option being exercised. The investor has to buy the stock for $25 in September and sell it to the purchaser of the optionfor $20.Problem 1.16.A trader writes a December put option with a strike price of $30. The price of the option is $4. Under what circumstances does the trader make a gain?The trader makes a gain if the price of the stock is above $26 at the time of exercise. (This ignores the time value of money.)Problem 1.17.A company knows that it is due to receive a certain amount of a foreign currency in four months. What type of option contract is appropriate for hedging?A long position in a four-month put option can provide insurance against the exchange rate falling below the strike price. It ensures that the foreign currency can be sold for at least the strike price.Problem 1.18.A US company expects to have to pay 1 million Canadian dollars in six months. Explain how the exchange rate risk can be hedged using (a) a forward contract and (b) an option.The company could enter into a long forward contract to buy 1 million Canadian dollars in six months. This would have the effect of locking in an exchange rate equal to the current forward exchange rate. Alternatively the company could buy a call option giving it the right (but not the obligation) to purchase 1 million Canadian dollars at a certain exchange rate in six months. This would provide insurance against a strong Canadian dollar in six months while still allowing the company to benefit from a weak Canadian dollar at that time. Problem 1.19.A trader enters into a short forward contract on 100 million yen. The forward exchange rate is $0.0090 per yen. How much does the trader gain or lose if the exchange rate at the end of the contract is (a) $0.0084 per yen; (b) $0.0101 per yen?a)The trader sells 100 million yen for $0.0090 per yen when the exchange rate is $0.0084⨯.millions of dollars or $60,000.per yen. The gain is 10000006b)The trader sells 100 million yen for $0.0090 per yen when the exchange rate is $0.0101⨯.millions of dollars or $110,000.per yen. The loss is 10000011Problem 1.20.The CME Group offers a futures contract on long-term Treasury bonds. Characterize the investors likely to use this contract.Most investors will use the contract because they want to do one of the following: a) Hedge an exposure to long-term interest rates.b) Speculate on the future direction of long-term interest rates.c) Arbitrage between the spot and futures markets for Treasury bonds.This contract is discussed in Chapter 6.Problem 1.21.“Options and futures are zero -sum games.” What do you think is meant by this statement?The statement means that the gain (loss) to the party with the short position is equal to the loss (gain) to the party with the long position. In aggregate, the net gain to all parties is zero.Problem 1.22.Describe the profit from the following portfolio: a long forward contract on an asset and a long European put option on the asset with the same maturity as the forward contract and a strike price that is equal to the forward price of the asset at the time the portfolio is set up.The terminal value of the long forward contract is:0T S F -where T S is the price of the asset at maturity and 0F is the delivery price, which is the same as the forward price of the asset at the time the portfolio is set up). The terminal value of the put option is:0max (0)T F S -,The terminal value of the portfolio is therefore00max (0)T T S F F S -+-,0max (0]T S F =,-This is the same as the terminal value of a European call option with the same maturity as the forward contract and a strike price equal to 0F . This result is illustrated in the Figure S1.3. The profit equals the terminal value of the call option less the amount paid for the put option. (It does not cost anything to enter into the forward contract.Figure S1.3: Profit from portfolio in Problem 1.22Problem 1.23.In the 1980s, Bankers Trust developed index currency option notes (ICONs). These are bonds in which the amount received by the holder at maturity varies with a foreign exchange rate. One example was its trade with the Long Term Credit Bank of Japan. The ICON specified that if the yen –U.S. dollar exchange rate,T S , is greater than 169 yen per dollar at maturity(in 1995), the holder of the bond receives $1,000. If it is less than 169 yen per dollar, the amount received by the holder of the bond is 1691000max 010001T S ⎡⎤⎛⎫,-,,-⎢⎥ ⎪⎝⎭⎣⎦ When the exchange rate is below 84.5, nothing is received by the holder at maturity. Show that this ICON is a combination of a regular bond and two options.Suppose that the yen exchange rate (yen per dollar) at maturity of the ICON is T S . The payofffrom the ICON is1000if 169169100010001if 8451690if 845T T T T S S S S ,>⎛⎫,-,-.≤≤ ⎪⎝⎭<.When 845169T S .≤≤ the payoff can be written 1690002000TS ,,-The payoff from an ICON is the payoff from:(a) A regular bond(b) A short position in call options to buy 169,000 yen with an exercise price of 1/169 (c) A long position in call options to buy 169,000 yen with an exercise price of 1/84.5 This is demonstrated by the following table, which shows the terminal value of the various components of the positionProblem 1.24.On July 1, 2011, a company enters into a forward contract to buy 10 million Japanese yen on January 1, 2012. On September 1, 2011, it enters into a forward contract to sell 10 million Japanese yen on January 1, 2012. Describe the payoff from this strategy.Suppose that the forward price for the contract entered into on July 1, 2011 is 1F and thatthe forward price for the contract entered into on September 1, 2011 is 2F with both 1F and 2F being measured as dollars per yen. If the value of one Japanese yen (measured in USdollars) is T S on January 1, 2012, then the value of the first contract (in millions of dollars)at that time is110()T S F -while the value of the second contract at that time is:210()T F S -The total payoff from the two contracts is therefore122110()10()10()T T S F F S F F -+-=-Thus if the forward price for delivery on January 1, 2012 increased between July 1, 2011 and September 1, 2011 the company will make a profit. (Note that the yen/USD exchange rate is usually expressed as the number of yen per USD not as the number of USD per yen)Problem 1.25.Suppose that USD-sterling spot and forward exchange rates are as follows :What opportunities are open to an arbitrageur in the following situations?(a) A 180-day European call option to buy £1 for $1.52 costs 2 cents.(b) A 90-day European put option to sell £1 for $1.59 costs 2 cents.Note that there is a typo in the problem in the book. 1.42 and 1.49 should be 1.52 and 1.59 in the last two lines of the problem s(a) The arbitrageur buys a 180-day call option and takes a short position in a 180-day forward contract. If T S is the terminal spot rate, the profit from the call option is 02.0)0,52.1max(--T SThe profit from the short forward contract isT S -5518.1The profit from the strategy is thereforeT T S S -+--5518.102.0)0,52.1max(orT T S S -+-5318.1)0,52.1max(This is1.5318−S T when S T <1.520.0118 when S T >1.52This shows that the profit is always positive. The time value of money has been ignored in these calculations. However, when it is taken into account the strategy is still likely to be profitable in all circumstances. (We would require an extremely high interest rate for $0.0118 interest to be required on an outlay of $0.02 over a 180-day period.)(b) The trader buys 90-day put options and takes a long position in a 90 day forwardcontract. If T S is the terminal spot rate, the profit from the put option is02.0)0,59.1max(--T SThe profit from the long forward contract isS T −1.5556The profit from this strategy is therefore5556.102.0)0,59.1max(-+--T T S Sor5756.1)0,59.1max(-+-T T S SThis isS T −1.5756 when S T >1.590.0144 when S T <1.59The profit is therefore always positive. Again, the time value of money has been ignored but is unlikely to affect the overall profitability of the strategy. (We would require interest rates to be extremely high for $0.0144 interest to be required on an outlay of $0.02 over a 90-day period.)Problem 1.26.A trader buys a call option with a strike price of $30 for $3. Does the trader ever exercise the option and lose money on the trade. Explain.If the stock price is between $30 and $33 at option maturity the trader will exercise the option, but lose money on the trade. Consider the situation where the stock price is $31. If the trader exercises, she loses $2 on the trade. If she does not exercise she loses $3 on the trade. It is clearly better to exercise than not exercise.Problem 1.27.A trader sells a put option with a strike price of $40 for $5. What is the trader's maximum gain and maximum loss? How does your answer change if it is a call option?The trader’s maximum gain from the put option is $5. The maximum loss is $35,corresponding to the situation where the option is exercised and the price of the underlying asset is zero. If the option were a call, the trader’s maxim um gain would still be $5, but there would be no bound to the loss as there is in theory no limit to how high the asset price could rise.Problem 1.28.``Buying a put option on a stock when the stock is owned is a form of insurance.'' Explain this statement.If the stock price declines below the strike price of the put option, the stock can be sold for the strike price.Further QuestionsProblem 1.29.On May 8, 2013, as indicated in Table 1.2, the spot offer price of Google stock is $871.37 and the offer price of a call option with a strike price of $880 and a maturity date ofSeptember is $41.60. A trader is considering two alternatives: buy 100 shares of the stock and buy 100 September call options. For each alternative, what is (a) the upfront cost, (b)the total gain if the stock price in September is $950, and (c) the total loss if the stockprice in September is $800. Assume that the option is not exercised before September andif stock is purchased it is sold in September.a)The upfront cost for the stock alternative is $87,137. The upfront cost for the optionalternative is $4,160.b)The gain from the stock alternative is $95,000−$87,137=$7,863. The total gain fromthe option alternative is ($950-$880)×100−$4,160=$2,840.c)The loss from the stock alternative is $87,137−$80,000=$7,137. The loss from theoption alternative is $4,160.Problem 1.30.What is arbitrage? Explain the arbitrage opportunity when the price of a dually listed mining company stock is $50 (USD) on the New York Stock Exchange and $52 (CAD) on the Toronto Stock Exchange. Assume that the exchange rate is such that 1 USD equals 1.01 CAD. Explain what is likely to happen to prices as traders take advantage of this opportunity. Arbitrage involves carrying out two or more different trades to lock in a profit. In this case, traders can buy shares on the NYSE and sell them on the TSX to lock in a USD profit of52/1.01−50=1.485 per share. As they do this the NYSE price will rise and the TSX price will fall so that the arbitrage opportunity disappearsProblem 1.31 (Excel file)Trader A enters into a forward contract to buy an asset for $1000 in one year. Trader B buys a call option to buy the asset for $1000 in one year. The cost of the option is $100. What is the difference between the positions of the traders? Show the profit as a function of the price of the asset in one year for the two traders.Trader A makes a profit of S T 1000 and Trader B makes a profit of max (S T 1000, 0) –100 where S T is the price of the asset in one year. Trader A does better if S T is above $900 as indicated in Figure S1.4.Figure S1.4: Profit to Trader A and Trader B in Problem 1.31Problem 1.32.In March, a US investor instructs a broker to sell one July put option contract on a stock. The stock price is $42 and the strike price is $40. The option price is $3. Explain what the investor has agreed to. Under what circumstances will the trade prove to be profitable? What are the risks?The investor has agreed to buy 100 shares of the stock for $40 in July (or earlier) if the party on the other side of the transaction chooses to sell. The trade will prove profitable if the option is not exercised or if the stock price is above $37 at the time of exercise. The risk to the investor is that the stock price plunges to a low level. For example, if the stock price drops to $1 by July , the investor loses $3,600. This is because the put options are exercised and $40 is paid for 100 shares when the value per share is $1. This leads to a loss of $3,900 which is only a little offset by the premium of $300 received for the options.Problem 1.33.A US company knows it will have to pay 3 million euros in three months. The current exchange rate is 1.3500 dollars per euro. Discuss how forward and options contracts can be used by the company to hedge its exposure.The company could enter into a forward contract obligating it to buy 3 million euros in three months for a fixed price (the forward price). The forward price will be close to but not exactly the same as the current spot price of 1.3500. An alternative would be to buy a call option giving the company the right but not the obligation to buy 3 million euros for a particular exchange rate (the strike price) in three months. The use of a forward contract locks in, at no cost, the exchange rate that will apply in three months. The use of a call option provides, at a cost, insurance against the exchange rate being higher than the strike price. Problem 1.34. (Excel file)A stock price is $29. An investor buys one call option contract on the stock with a strike price of $30 and sells a call option contract on the stock with a strike price of $32.50. The market prices of the options are $2.75 and $1.50, respectively. The options have the same maturity date. Describe the investor's position.This is known as a bull spread (see Chapter 12). The profit is shown in Figure S1.5.Figure S1.5: Profit in Problem 1.34Problem 1.35.The price of gold is currently $1,400 per ounce. The forward price for delivery in one year is $1,500. An arbitrageur can borrow money at 4% per annum. What should the arbitrageur do? Assume that the cost of storing gold is zero and that gold provides no income.The arbitrageur should borrow money to buy a certain number of ounces of gold today and short forward contracts on the same number of ounces of gold for delivery in one year. This means that gold is purchased for $1,400 per ounce and sold for $1,500 per ounce. Interest on the borrowed funds will be 0.04×$1400 or $56 per ounce. A profit of $44 per ounce will therefore be made.Problem 1.36.The current price of a stock is $94, and three-month call options with a strike price of $95 currently sell for $4.70. An investor who feels that the price of the stock will increase istrying to decide between buying 100 shares and buying 2,000 call options (20 contracts). Both strategies involve an investment of $9,400. What advice would you give? How high does the stock price have to rise for the option strategy to be more profitable?The investment in call options entails higher risks but can lead to higher returns. If the stock price stays at $94, an investor who buys call options loses $9,400 whereas an investor who buys shares neither gains nor loses anything. If the stock price rises to $120, the investor who buys call options gains⨯--=,$2000(12095)940040600An investor who buys shares gains$⨯-=,100(12094)2600The strategies are equally profitable if the stock price rises to a level, S, where⨯-=--100(94)2000(95)9400S SorS=100The option strategy is therefore more profitable if the stock price rises above $100.Problem 1.37.On May 8, 2013, an investor owns 100 Google shares. As indicated in Table 1.3, the share price is about $871 and a December put option with a strike price $820 costs $37.50. The investor is comparing two alternatives to limit downside risk. The first involves buying one December put option contract with a strike price of $820. The second involves instructing a broker to sell the 100 shares as so on as Google’s price reaches $820. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the two strategies.The second alternative involves what is known as a stop or stop-loss order. It costs nothing and ensures that $82,000, or close to $82,000, is realized for the holding in the event the stock price ever falls to $820. The put option costs $3,750 and guarantees that the holding can be sold for $8,200 any time up to December. If the stock price falls marginally below $820 and then rises the option will not be exercised, but the stop-loss order will lead to the holding being liquidated. There are some circumstances where the put option alternative leads to a better outcome and some circumstances where the stop-loss order leads to a better outcome.If the stock price ends up below $820, the stop-loss order alternative leads to a better outcome because the cost of the option is avoided. If the stock price falls to $800 in November and then rises to $850 by December, the put option alternative leads to a betteroutcome. The investor is paying $3,750 for the chance to benefit from this second type of outcome.Problem 1.38.A bond issued by Standard Oil some time ago worked as follows. The holder received no interest. At the bond’s maturity the company promised to pay $1,000 plus an additionalamount based on the price of oil at that time. The additional amount was equal to the product of 170 and the excess (if any) of the price of a barrel of oil at maturity over $25. The maximum additional amount paid was $2,550 (which corresponds to a price of $40 per barrel). Show that the bond is a combination of a regular bond, a long position in call options on oil with a strike price of $25, and a short position in call options on oil with a strike price of $40.Suppose T S is the price of oil at the bond’s maturity. In addition to $1000 the Standard Oilbond pays:$250$40$25170(25)$402550T T T T S S S S <:>>:->:,This is the payoff from 170 call options on oil with a strike price of 25 less the payoff from 170 call options on oil with a strike price of 40. The bond is therefore equivalent to a regular bond plus a long position in 170 call options on oil with a strike price of $25 plus a short position in 170 call options on oil with a strike price of $40. The investor has what is termed a bull spread on oil. This is discussed in Chapter 12.Problem 1.39.Suppose that in the situation of Table 1.1 a cor porate treasurer said: “I will have £1 million to sell in six months. If the exchange rate is less than 1.52, I want you to give me 1.52. If it is greater than 1.58 I will accept 1.58. If the exchange rate is between 1.52 and 1.58, I will sell the sterling for the exchange rate.” How could you use options to satisfy the treasurer?You sell the treasurer a put option on GBP with a strike price of 1.52 and buy from the treasurer a call option on GBP with a strike price of 1.58. Both options are on one million pounds and have a maturity of six months. This is known as a range forward contract and is discussed in Chapter 17.Problem 1.40.Describe how foreign currency options can be used for hedging in the situation considered in Section 1.7 so that (a) ImportCo is guaranteed that its exchange rate will be less than 1.5700, and (b) ExportCo is guaranteed that its exchange rate will be at least 1.5300. Use DerivaGem to calculate the cost of setting up the hedge in each case assuming that the exchange rate volatility is 12%, interest rates in the United States are 5% and interest rates in Britain are 5.7%. Assume that the current exchange rate is the average of the bid and offer in Table 1.1.ImportCo should buy three-month call options on $10 million with a strike price of 1.5700. ExportCo should buy three-month put options on $10 million with a strike price of 1.5300. In this case the spot foreign exchange rate is 1.5543 (the average of the bid and offer quotes in。


CHAPTER 3Hedging Strategies Using FuturesPractice QuestionsProblem 3.1.Under what circumstances are (a) a short hedge and (b) a long hedge appropriate?A short hedge is appropriate when a company owns an asset and expects to sell that asset in the future. It can also be used when the company does not currently own the asset but expects to do so at some time in the future. A long hedge is appropriate when a company knows it will have to purchase an asset in the future. It can also be used to offset the risk from an existing short position.Problem 3.2.Explain what is meant by basis risk when futures contracts are used for hedging.Basis risk arises from the hedger’s uncertainty as to the difference between the spot price and futures price at the expiration of the hedge.Problem 3.3.Explain what is meant by a perfect hedge. Does a perfect hedge always lead to a better outcome than an imperfect hedge? Explain your answer.A perfect hedge is one that completely eliminates the hedger’s risk. A p erfect hedge does not always lead to a better outcome than an imperfect hedge. It just leads to a more certain outcome. Consider a company that hedges its exposure to the price of an asset. Suppose the asset’s price movements prove to be favorable to the company. A perfect hedge totally neutralizes the company’s gain from these favorable price movements. An imperfect hedge, which only partially neutralizes the gains, might well give a better outcome.Problem 3.4.Under what circumstances does a minimum-variance hedge portfolio lead to no hedging at all?A minimum variance hedge leads to no hedging when the coefficient of correlation between the futures price changes and changes in the price of the asset being hedged is zero.Problem 3.5.Give three reasons why the treasurer of a company might not hedge the company’s exposure to a particular risk.(a) If the company’s competitors are not hedging, the treasurer might feel that the company will experience less risk if it does not hedge. (See Table 3.1.) (b) The shareholders might not want the company to hedge because the risks are hedged within their portfolios. (c) If there is a loss on the hedge and a gain from the company’s exposure to the underlying asset, the treasurer might feel that he or she will have difficulty justifying the hedging to other executives within the organization.Problem 3.6.Suppose that the standard deviation of quarterly changes in the prices of a commodity is $0.65, the standard deviation of quarterly changes in a futures price on the commodity is $0.81, and the coefficient of correlation between the two changes is 0.8. What is the optimal hedge ratio for a three-month contract? What does it mean?The optimal hedge ratio is 065080642081..⨯=.. This means that the s ize of the futures position should be 64.2% of the size of the company’s exposure in a three-month hedge.Problem 3.7.A company has a $20 million portfolio with a beta of 1.2. It would like to use futures contracts on a stock index to hedge its risk. The index futures is currently standing at 1080, and each contract is for delivery of $250 times the index. What is the hedge that minimizes risk? What should the company do if it wants to reduce the beta of the portfolio to 0.6?The formula for the number of contracts that should be shorted gives 20000000128891080250,,.⨯=.⨯ Rounding to the nearest whole number, 89 contracts should be shorted. To reduce the beta to 0.6, half of this position, or a short position in 44 contracts, is required.Problem 3.8.In the corn futures contract, the following delivery months are available: March, May, July, September, and December. State the contract that should be used for hedging when the expiration of the hedge is in a) June, b) July, and c) JanuaryA good rule of thumb is to choose a futures contract that has a delivery month as close aspossible to, but later than, the month containing the expiration of the hedge. The contracts that should be used are therefore(a) July(b)September(c)MarchProblem 3.9.Does a perfect hedge always succeed in locking in the current spot price of an asset for a future transaction? Explain your answer.No. Consider, for example, the use of a forward contract to hedge a known cash inflow in a foreign currency. The forward contract locks in the forward exchange rate — which is in general different from the spot exchange rate.Problem 3.10.Explain why a short hedger’s position improves when the basis strengthens unexpectedly and worsens when the basis weakens unexpectedly.The basis is the amount by which the spot price exceeds the futures price. A short hedger is long the asset and short futures contracts. The value of his or her position therefore improves as the basis increases. Similarly, it worsens as the basis decreases.Problem 3.11.Imagine you are the treasurer of a Japanese company exporting electronic equipment to the United States. Discuss how you would design a foreign exchange hedging strategy and the arguments you would use to sell the strategy to your fellow executives.The simple answer to this question is that the treasurer should1.Estimate the company’s future cash flows in Japanese yen and U.S. dollars2.Enter into forward and futures contracts to lock in the exchange rate for the U.S. dollarcash flows.However, this is not the whole story. As the gold jewelry example in Table 3.1 shows, the company should examine whether the magnitudes of the foreign cash flows depend on the exchange rate. For example, will the company be able to raise the price of its product in U.S. dollars if the yen appreciates? If the company can do so, its foreign exchange exposure may be quite low. The key estimates required are those showing the overall effect on the company’s profitability of changes in the exchange rate at various times in the future. Once these estimates have been produced the company can choose between using futures and options to hedge its risk. The results of the analysis should be presented carefully to other executives. It should be explained that a hedge does not ensure that profits will be higher. It means that profit will be more certain. When futures/forwards are used both the downside and upside are eliminated. With options a premium is paid to eliminate only the downside.Problem 3.12.Suppose that in Example 3.2 of Section 3.3 the company decides to use a hedge ratio of 0.8. How does the decision affect the way in which the hedge is implemented and the result?If the hedge ratio is 0.8, the company takes a long position in 16 December oil futures contracts on June 8 when the futures price is $88.00. It closes out its position on November 10. The spot price and futures price at this time are $90.00 and $89.10. The gain on the futures position is(89.10 − 88.00) × 16,000 = 17,600The effective cost of the oil is therefore20,000 × 90 – 17,600 = 1,782, 400or $89.12 per barrel. (This compares with $88.90 per barrel when the company is fully hedged.)Problem 3.13.“If the minimum -variance hedge ratio is calculated as 1.0, the hedge must be perfect." Is this statement true? Explain your answer.The statement is not true. The minimum variance hedge ratio is S Fσρσ It is 1.0 when 05=.ρ and 2S F =σσ. Since 10<.ρ the hedge is clearly not perfect.Problem 3.14.“If there is no basis risk, the minimum variance hedge ratio is always 1.0." Is this statement true? Explain your answer.The statement is true. Using the notation in the text, if the hedge ratio is 1.0, the hedger locks in a price of 12F b +. Since both 1F and 2b are known this has a variance of zero and must be the best hedge.Problem 3.15“For an asset where futures prices for contracts on the asset are usually less than spot prices, long hedges are likely to be particularly attractive." Explain this statement.A company that knows it will purchase a commodity in the future is able to lock in a price close to the futures price. This is likely to be particularly attractive when the futures price is less than the spot price.Problem 3.16.The standard deviation of monthly changes in the spot price of live cattle is (in cents per pound)1.2. The standard deviation of monthly changes in the futures price of live cattle for the closestcontract is 1.4. The correlation between the futures price changes and the spot price changes is 0.7. It is now October 15. A beef producer is committed to purchasing 200,000 pounds of live cattle on November 15. The producer wants to use the December live-cattle futures contracts to hedge its risk. Each contract is for the delivery of 40,000 pounds of cattle. What strategy should the beef producer follow?The optimal hedge ratio is 12070614..⨯=.. The beef producer requires a long position in 20000006120000⨯.=, lbs of cattle. The beef producer should therefore take a long position in 3 December contracts closing out the position on November 15.Problem 3.17.A corn farmer argues “I do not use futures co ntracts for hedging. My real risk is not the price of corn. It is that my whole crop gets wiped out by the weather.”Discuss this viewpoint. Should the farmer estimate his or her expected production of corn and hedge to try to lock in a price for expected production?If weather creates a significant uncertainty about the volume of corn that will be harvested, the farmer should not enter into short forward contracts to hedge the price risk on his or her expected production. The reason is as follows. Suppose that the weather is bad and the farmer’sproduction is lower than expected. Other farmers are likely to have been affected similarly. Corn production overall will be low and as a consequence the price of corn will be relatively high. The farmer’s problems arising from the bad harvest will be made worse by losses on the short futures position. This problem emphasizes the importance of looking at the big picture when hedging. The farmer is correct to question whether hedging price risk while ignoring other risks is a good strategy.Problem 3.18.On July 1, an investor holds 50,000 shares of a certain stock. The market price is $30 per share. The investor is interested in hedging against movements in the market over the next month and decides to use the September Mini S&P 500 futures contract. The index is currently 1,500 and one contract is for delivery of $50 times the index. The beta of the stock is 1.3. What strategy should the investor follow? Under what circumstances will it be profitable?A short position in 50000301326501500,⨯.⨯=⨯,contracts is required. It will be profitable if the stock outperforms the market in the sense that its return is greater than that predicted by the capital asset pricing model.Problem 3.19.Suppose that in Table 3.5 the company decides to use a hedge ratio of 1.5. How does the decision affect the way the hedge is implemented and the result?If the company uses a hedge ratio of 1.5 in Table 3.5 it would at each stage short 150 contracts. The gain from the futures contracts would be.1=⨯50.2$5570.1per barrel and the company would be $0.85 per barrel better off than with a hedge ratio of 1.Problem 3.20.A futures contract is used for hedging. Explain why the daily settlement of the contract can give rise to cash flow problems.Suppose that you enter into a short futures contract to hedge the sale of an asset in six months. If the price of the asset rises sharply during the six months, the futures price will also rise and you may get margin calls. The margin calls will lead to cash outflows. Eventually the cash outflows will be offset by the extra amount you get when you sell the asset, but there is a mismatch in the timing of the cash outflows and inflows. Your cash outflows occur earlier than your cash inflows.A similar situation could arise if you used a long position in a futures contract to hedge the purchase of an asset at a future time and the asset’s price fe ll sharply. An extreme example of what we are talking about here is provided by Metallgesellschaft (see Business Snapshot 3.2).Problem 3.21.An airline executive has argued: “There is no point in our using oil futures. There is just as much chance that the price of oil in the future will be less than the futures price as there is that it will be greater than this price.” Discuss the executive’s viewpoint.It may well be true that there is just as much chance that the price of oil in the future will be above the futures price as that it will be below the futures price. This means that the use of a futures contract for speculation would be like betting on whether a coin comes up heads or tails. But it might make sense for the airline to use futures for hedging rather than speculation. The futures contract then has the effect of reducing risks. It can be argued that an airline should not expose its shareholders to risks associated with the future price of oil when there are contracts available to hedge the risks.Problem 3.22.Suppose the one-year gold lease rate is 1.5% and the one-year risk-free rate is 5.0%. Both rates are compounded annually. Use the discussion in Business Snapshot 3.1 to calculate the maximum one-year forward price Goldman Sachs should quote for gold when the spot price is $1,200.Goldman Sachs can borrow 1 ounce of gold and sell it for $1200. It invests the $1,200 at 5% so that it becomes $1,260 at the end of the year. It must pay the lease rate of 1.5% on $1,200. This is $18 and leaves it with $1,242. It follows that if it agrees to buy the gold for less than $1,242 in one year it will make a profit.Problem 3.23.The expected return on the S&P 500 is 12% and the risk-free rate is 5%. What is the expected return on the investment with a beta of (a) 0.2, (b) 0.5, and (c) 1.4?a)00502(012005)0064.+.⨯.-.=. or 6.4%b)00505(012005)0085.+.⨯.-.=. or 8.5%c)00514(012005)0148.+.⨯.-.=. or 14.8%Further QuestionsProblem 3.24.It is now June. A company knows that it will sell 5,000 barrels of crude oil in September.It uses the October CME Group futures contract to hedge the price it will receive. Each contract is on 1,000 barrels of ‘‘light sweet crude.’’ What position should it take? What price risks is it still exposed to after taking the position?It should short five contracts. It has basis risk. It is exposed to the difference between the October futures price and the spot price of light sweet crude at the time it closes out its position in September. It is also possibly exposed to the difference between the spot price of light sweet crude and the spot price of the type of oil it is selling.Problem 3.25.Sixty futures contracts are used to hedge an exposure to the price of silver. Each futures contract is on 5,000 ounces of silver. At the time the hedge is closed out, the basis is $0.20per ounce. What is the effect of the bas is on the hedger’s financial position if (a) the traderis hedging the purchase of silver and (b) the trader is hedging the sale of silver?The excess of the spot over the futures at the time the hedge is closed out is $0.20 per ounce. If the trader is hedging the purchase of silver, the price paid is the futures price plus the basis. Thetrader therefore loses 60×5,000×$0.20=$60,000. If the trader is hedging the sales of silver, the price received is the futures price plus the basis. The trader therefore gains $60,000.Problem 3.26.A trader owns 55,000 units of a particular asset and decides to hedge the value of her position with futures contracts on another related asset. Each futures contract is on 5,000 units. The spot price of the asset that is owned is $28 and the standard deviation of the change in this price over the life of the hedge is estimated to be $0.43. The futures price of the related asset is $27 and the standard deviation of the change in this over the life of the hedge is $0.40. The coefficient of correlation between the spot price change and futures price change is 0.95.(a) What is the minimum variance hedge ratio?(b) Should the hedger take a long or short futures position?(c) What is the optimal number of futures contracts with no tailing of the hedge?(d) What is the optimal number of futures contracts with tailing of the hedge?(a) The minimum variance hedge ratio is 0.95×0.43/0.40=1.02125.(b) The hedger should take a short position.(c) The optimal number of contracts with no tailing is 1.02125×55,000/5,000=11.23 (or 11 when rounded to the nearest whole number)(d) The optimal number of contracts with tailing is 1.012125×(55,000×28)/(5,000×27)=11.65 (or 12 when rounded to the nearest whole number).Problem 3.27.A company wishes to hedge its exposure to a new fuel whose price changes have a 0.6correlation with gasoline futures price changes. The company will lose $1 million for each 1 cent increase in the price per gallon of the new fuel over the next three months. The new fuel's price change has a standard deviation that is 50% greater than price changes in gasoline futures prices. If gasoline futures are used to hedge the exposure what should the hedge ratio be? What is the company's exposure measured in gallons of the new fuel? What position measured in gallons should the company take in gasoline futures? How many gasoline futures contracts should be traded? Each contract is on 42,000 gallons.Equation (3.1) shows that the hedge ratio should be 0.6 × 1.5 = 0.9. The company has anexposure to the price of 100 million gallons of the new fuel. It should therefore take a position of 90 million gallons in gasoline futures. Each futures contract is on 42,000 gallons. The number of contracts required is therefore9.2142000,42000,000,90 or, rounding to the nearest whole number, 2143.Problem 3.28.A portfolio manager has maintained an actively managed portfolio with a beta of 0.2. During the last year the risk-free rate was 5% and equities performed very badly providing a return of−30%. The portfolio manage produced a return of −10% and claims that in the circumstances it was good. Discuss this claim.When the expected return on the market is −30% the expected return on a portfolio with a beta of 0.2 is0.05 + 0.2 × (−0.30 − 0.05) = −0.02or –2%. The actual return of –10% is worse than the expected return. The portfolio manager done 8% worse than a simple strategy of forming a portfolio that is 20% invested in an equity index and 80% invested in risk-free investments. (The manager has achieved an alpha of –8%!)Problem 3.29. (Excel file)The following table gives data on monthly changes in the spot price and the futures price for a certain commodity. Use the data to calculate a minimum variance hedge ratio.Denote i x and i y by the i -th observation on the change in the futures price and the change in the spot price respectively.096130i i x y =.=.∑∑222447423594i i x y =.=.∑∑2352i i x y =.∑ An estimate of F σ is05116=. An estimate of S σ is04933=.An estimate of ρ is0981=.The minimum variance hedge ratio is049330981094605116SF.=.⨯=..σρσProblem 3.30.It is July 16. A company has a portfolio of stocks worth $100 million. The beta of the portfolio is 1.2. The company would like to use the December futures contract on a stock index to change beta of the portfolio to 0.5 during the period July 16 to November 16. The index is currently1,000, and each contract is on $250 times the index.a)What position should the company take?b)Suppose that the company changes its mind and decides to increase the beta of theportfolio from 1.2 to 1.5. What position in futures contracts should it take?a)The company should short(1205)1000000001000250.-.⨯,,⨯or 280 contracts.b)The company should take a long position in(1512)1000000001000250.-.⨯,,⨯or 120 contracts.Problem 3.31. (Excel file)A fund manager has a portfolio worth $50 million with a beta of 0.87. The manager is concerned about the performance of the market over the next two months and plans to use three-month futures contracts on the S&P 500 to hedge the risk. The current level of the index is 1250, one contract is on 250 times the index, the risk-free rate is 6% per annum, and the dividend yield on the index is 3% per annum. The current 3 month futures price is 1259.a)What position should the fund manager take to eliminate all exposure to the market overthe next two months?b)Calculate the effect of your strategy on the fund manager’s returns if the level of themarket in two months is 1,000, 1,100, 1,200, 1,300, and 1,400. Assume that the one-month futures price is 0.25% higher than the index level at this time.a) The number of contracts the fund manager should short is 50000000087138201259250,,.⨯=.⨯ Rounding to the nearest whole number, 138 contracts should be shorted.b) The following table shows that the impact of the strategy. To illustrate the calculations in the table consider the first column. If the index in two months is 1,000, the futures price is 1000×1.0025. The gain on the short futures position is therefore(1259100250)2501388849250$-.⨯⨯=,,The return on the index is 3212⨯/=0.5% in the form of dividend and250125020%-/=- in the form of capital gains. The total return on the index istherefore 195%-.. The risk-free rate is 1% per two months. The return is therefore205%-. in excess of the risk-free rate. From the capital asset pricing model we expect the return on the portfolio to be 0872*******%%.⨯-.=-. in excess of the risk-free rate. The portfolio return is therefore 16835%-.. The loss on the portfolio is01683550000000.⨯,, or $8,417,500. When this is combined with the gain on the futures the total gain is $431,750.Problem 3.32.It is now October 2014. A company anticipates that it will purchase 1 million pounds of copper in each of February 2015, August 2015, February 2016, and August 2016. The company has decided to use the futures contracts traded in the COMEX division of the CME Group to hedge its risk. One contract is for the delivery of 25,000 pounds of copper. The initial margin is $2,000per contract a nd the maintenance margin is $1,500 per contract. The company’s policy is to hedge 80% of its exposure. Contracts with maturities up to 13 months into the future are considered to have sufficient liquidity to meet the company’s needs. Devise a hedging stra tegy for the company. (Do not make the “tailing” adjustment described in Section 3.4.)Assume the market prices (in cents per pound) today and at future dates are as follows. What is the impact of the strategy you propose on the price the company pays for copper? What is the initial margin requirement in October 2014? Is the company subject to any margin calls?To hedge the February 2015 purchase the company should take a long position in March 2015 contracts for the delivery of 800,000 pounds of copper. The total number of contracts required is 8000002500032,/,=. Similarly a long position in 32 September 2015 contracts is required to hedge the August 2015 purchase. For the February 2016 purchase the company could take a long position in 32 September 2015 contracts and roll them into March 2016 contracts during August 2015. (As an alternative, the company could hedge the February 2016 purchase by taking a long position in 32 March 2015 contracts and rolling them into March 2016 contracts.) For the August 2016 purchase the company could take a long position in 32 September 2015 and roll them into September 2016 contracts during August 2015.The strategy is therefore as followsOct. 2014: Enter into long position in 96 Sept. 2015 contractsEnter into a long position in 32 Mar. 2015 contractsFeb 2015: Close out 32 Mar. 2015 contractsAug 2015: Close out 96 Sept. 2015 contractsEnter into long position in 32 Mar. 2016 contractsEnter into long position in 32 Sept. 2016 contractsFeb 2016: Close out 32 Mar. 2016 contractsAug 2016: Close out 32 Sept. 2016 contractsWith the market prices shown the company pays.+.⨯.-.=.3690008(3723036910)37156for copper in February, 2015. It pays.+.⨯.-.=.3650008(3728036480)37140for copper in August 2015. As far as the February 2016 purchase is concerned, it loses 3728036480800.-.=. on the .-.=. on the September 2015 futures and gains 37670364301240 February 2016 futures. The net price paid is therefore.+.⨯.-.⨯.=.377000880008124037348.-.=. on theAs far as the August 2016 purchase is concerned, it loses 3728036480800.-.=. on the September 2016 futures. The September 2015 futures and gains 38820364202400net price paid is therefore388000880008240037520.+.⨯.-.⨯.=.The hedging strategy succeeds in keeping the price paid in the range 371.40 to 375.20.In October 2014 the initial margin requirement on the 128 contracts is 1282000$⨯, or $256,000. There is a margin call when the futures price drops by more than 2 cents. This happens to the March 2015 contract between October 2014 and February 2015, to the September 2015 contract between October 2014 and February 2015, and to the September 2015 contract between February 2015 and August 2015. (Under the plan above the March 2016 contract is not held between February 2015 and August 2015, but if it were there would be a margin call during this period.)。

CHAPTER 15The Black-Scholes-Merton ModelPractice QuestionsProblem 15.1.What does the Black –Scholes –Merton stock option pricing model assume about the probability distribution of the stock price in one year? What does it assume about theprobability distribution of the continuously compounded rate of return on the stock during the year?The Black –Scholes –Merton option pricing model assumes that the probability distribution of the stock price in 1 year (or at any other future time) is lognormal. It assumes that thecontinuously compounded rate of return on the stock during the year is normally distributed.Problem 15.2.The volatility of a stock price is 30% per annum. What is the standard deviation of the percentage price change in one trading day?The standard deviation of the percentage price change in time t ∆is where σ is the volatility. In this problem 03=.and, assuming 252 trading days in one year, 12520004t ∆=/=. so that 00019=.=. or 1.9%.Problem 15.3.Explain the principle of risk-neutral valuation.The price of an option or other derivative when expressed in terms of the price of theunderlying stock is independent of risk preferences. Options therefore have the same value in a risk-neutral world as they do in the real world. We may therefore assume that the world is risk neutral for the purposes of valuing options. This simplifies the analysis. In a risk-neutral world all securities have an expected return equal to risk-free interest rate. Also, in arisk-neutral world, the appropriate discount rate to use for expected future cash flows is the risk-free interest rate.Problem 15.4.Calculate the price of a three-month European put option on a non-dividend-paying stock with a strike price of $50 when the current stock price is $50, the risk-free interest rate is 10% per annum, and the volatility is 30% per annum.In this case 050S =, 50K =, 01r=., 03σ=., 025T =., and12102417000917d d d ==.=-.=.The European put price is 0102550(00917)50(02417)N e N -.⨯.-.--.0102550046345004045237e -.⨯.=⨯.-⨯.=.or $2.37.Problem 15.5.What difference does it make to your calculations in Problem 15.4 if a dividend of $1.50 is expected in two months?In this case we must subtract the present value of the dividend from the stock price before using Black –Scholes-Merton. Hence the appropriate value of 0S is01667010501504852S e -.⨯.=-.=.As before 50K =, 01r =., 03σ=., and 025T =.. In this case12100414001086d d d ==.=-.=-.The European put price is 0102550(01086)4852(00414)N e N -.⨯..-.-. 010255005432485204835303e -.⨯.=⨯.-.⨯.=. or $3.03.Problem 15.6.What is implied volatility? How can it be calculated?The implied volatility is the volatility that makes the Black –Scholes-Merton price of an option equal to its market price. The implied volatility is calculated using an iterativeprocedure. A simple approach is the following. Suppose we have two volatilities one too high (i.e., giving an option price greater than the market price) and the other too low (i.e., giving an option price lower than the market price). By testing the volatility that is half way between the two, we get a new too-high volatility or a new too-low volatility. If we search initially for two volatilities, one too high and the other too low we can use this procedure repeatedly to bisect the range and converge on the correct implied volatility. Other more sophisticated approaches (e.g., involving the Newton-Raphson procedure) are used in practice.Problem 15.7.A stock price is currently $40. Assume that the expected return from the stock is 15% and its volatility is 25%. What is the probability distribution for the rate of return (with continuous compounding) earned over a two-year period?In this case 015=.μ and 025=.σ. From equation (15.7) the probability distribution for the rate of return over a two-year period with continuous compounding is:⎪⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛-ϕ225.0,225.015.022i.e.,)03125.0,11875.0(ϕThe expected value of the return is 11.875% per annum and the standard deviation is 17.7%per annum.Problem 15.8.A stock price follows geometric Brownian motion with an expected return of 16% and a volatility of 35%. The current price is $38.a) What is the probability that a European call option on the stock with an exercise price of $40 and a maturity date in six months will be exercised?b) What is the probability that a European put option on the stock with the same exercise price and maturity will be exercised?a) The required probability is the probability of the stock price being above $40 in six months time. Suppose that the stock price in six months is T S⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡⨯⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-+5.035.0,5.0235.016.038ln ~ln 22ϕT Si.e.,()2247.0,687.3~ln ϕT SSince ln 403689=., we require the probability of ln(S T )>3.689. This is3689368711(0008)0247N N .-.⎛⎫-=-. ⎪.⎝⎭Since N(0.008) = 0.5032, the required probability is 0.4968.b) In this case the required probability is the probability of the stock price being less than $40 in six months time. It is10496805032-.=.Problem 15.9.Using the notation in the chapter, prove that a 95% confidence interval for T S is between22(2)196(2)19600andT T S e S e -/-.-/+.μσμσFrom equation (15.3):⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-+T T S S T 220,2ln ~ln σσμϕ95% confidence intervals for ln T S are therefore20ln ()1962S T +--.σμand20ln ()1962S T +-+.σμσ95% confidence intervals for T S are therefore2200ln (2)196ln (2)196and S T S T e e +-/-.+-/+.μσμσi.e.22(2)196(2)19600andT T S e S e -/-.-/+.μσμσProblem 15.10.A portfolio manager announces that the average of the returns realized in each of the last 10 years is 20% per annum. In what respect is this statement misleading?This problem relates to the material in Section 15.3. The statement is misleading in that a certain sum of money, say $1000, when invested for 10 years in the fund would have realized a return (with annual compounding) of less than 20% per annum.The average of the returns realized in each year is always greater than the return per annum (with annual compounding) realized over 10 years. The first is an arithmetic average of the returns in each year; the second is a geometric average of these returns.Problem 15.11.Assume that a non-dividend-paying stock has an expected return of μ and a volatility of σ. An innovative financial institution has just announced that it will trade a derivative that pays off a dollar amount equal to ln S T at time T where T S denotes the values of the stock price at time T .a) Use risk-neutral valuation to calculate the price of the derivative at time t in term of the stock price, S, at time tb) Confirm that your price satisfies the differential equation (15.16)a) At time t , the expected value of ln S T is from equation (15.3) 2ln (/2)()S T t μσ+--In a risk-neutral world the expected value of ln S T is therefore2ln (/2)()S r T t σ+--Using risk-neutral valuation the value of the derivative at time t is()2[ln (/2)()]r T t e S r T t σ--+--b) If()2[ln (/2)()]r T t f e S r T t σ--=+--then()()2()2()2()22[ln (/2)()]/2r T t r T t r T t r T t fre S r T t e r tf e S S f e S S σσ--------∂=+----∂∂=∂∂=-∂The left-hand side of the Black-Scholes-Merton differential equation is()222()2ln (/2)()(/2)/2ln (/2)()r T t r T t e r S r r T t r r e r S r r T t rfσσσσ----⎡⎤+----+-⎣⎦⎡⎤=+--⎣⎦=Hence the differential equation is satisfied.Problem 15.12.Consider a derivative that pays off n T S at time T where T S is the stock price at that time. When the stock pays no dividends and its price follows geometric Brownian motion, it can be shown that its price at time t ()t T ≤ has the form()n h t T S ,where S is the stock price at time t and h is a function only of t and T .(a) By substituting into the Black –Scholes –Merton partial differential equation derive an ordinary differential equation satisfied by ()h t T ,.(b) What is the boundary condition for the differential equation for ()h t T ,? (c) Show that2[05(1)(1)]()()n n r n T t h t T eσ.-+--,= where r is the risk-free interest rate and σ is the stock price volatility.If ()()n G S t h t T S ,=, then n t G t h S ∂/∂=, 1n G S hnS -∂/∂=, and 222(1)n G S hn n S -∂/∂=- where t h h t =∂/∂. Substituting into the Black –Scholes –Merton differential equation we obtain21(1)2t h rhn hn n rh σ++-=The derivative is worth n S when t T =. The boundary condition for this differential equation is therefore ()1h T T ,= The equation2[05(1)(1)]()()n n r n T t h t T e σ.-+--,=satisfies the boundary condition since it collapses to 1h = when t T =. It can also be shown that it satisfies the differential equation in (a). Alternatively we can solve the differential equation in (a) directly. The differential equation can be written21(1)(1)2t h r n n n h σ=----The solution to this is21ln [(1)(1)]()2h r n n n T t σ=-+--or2[05(1)(1)]()()n n r n T t h t T e σ.-+--,=Problem 15.13.What is the price of a European call option on a non-dividend-paying stock when the stock price is $52, the strike price is $50, the risk-free interest rate is 12% per annum, the volatility is 30% per annum, and the time to maturity is three months?In this case 052S =, 50K =, 012r =., 030=.σ and 025T =..212105365003865d d d ==.=-.=. The price of the European call is 01202552(05365)50(03865)N e N -.⨯..-. 00352070425006504e -.=⨯.-⨯. 506=. or $5.06.Problem 15.14.What is the price of a European put option on a non-dividend-paying stock when the stock price is $69, the strike price is $70, the risk-free interest rate is 5% per annum, the volatility is 35% per annum, and the time to maturity is six months?In this case 069S =, 70K =, 005r =., 035=.σ and 05T =..212101666000809d d d ==.=-.=-. The price of the European put is 0050570(00809)69(01666)e N N -.⨯..--. 002570053236904338e -.=⨯.-⨯.640=. or $6.40.Problem 15.15.Consider an American call option on a stock. The stock price is $70, the time to maturity is eight months, the risk-free rate of interest is 10% per annum, the exercise price is $65, and the volatility is 32%. A dividend of $1 is expected after three months and again after sixmonths. Show that it can never be optimal to exercise the option on either of the two dividend dates. Use DerivaGem to calculate the price of the option.Using the notation of Section 15.12, 121D D ==, 2()0101667(1)65(1)107r T t K e e ---.⨯.-=-=., and 21()01025(1)65(1)160r t t K e e ---.⨯.-=-=.. Since 2()1(1)r T t D K e --<- and 21()2(1)r t t D K e --<-It is never optimal to exercise the call option early. DerivaGem shows that the value of the option is 1094..Problem 15.16.A call option on a non-dividend-paying stock has a market price of $2.50. The stock price is $15, the exercise price is $13, the time to maturity is three months, and the risk-free interest rate is 5% per annum. What is the implied volatility?In the case 25c =., 015S =, 13K =, 025T =., 005r =.. The implied volatility must becalculated using an iterative procedure.A volatility of 0.2 (or 20% per annum) gives 220c =.. A volatility of 0.3 gives 232c =.. A volatility of 0.4 gives 2507c =.. A volatility of 0.39 gives 2487c =.. By interpolation the implied volatility is about 0.396 or 39.6% per annum.The implied volatility can also be calculated using DerivaGem. Select equity as theUnderlying Type in the first worksheet. Select Black-Scholes European as the Option Type. Input stock price as 15, the risk-free rate as 5%, time to exercise as 0.25, and exercise price as 13. Leave the dividend table blank because we are assuming no dividends. Select the button corresponding to call. Select the implied volatility button. Input the Price as 2.5 in the second half of the option data table. Hit the Enter key and click on calculate. DerivaGem will show the volatility of the option as 39.64%.Problem 15.17.With the notation used in this chapter (a) What is ()N x '?(b) Show that ()12()()r T t SN d Ke N d --''=, where S is the stock price at time t21d =22d =(c) Calculate 1d S ∂/∂ and 2d S ∂/∂. (d) Show that when()12()()r T t c SN d Ke N d --=-()21()(r T t c rKe N d SN d t --∂'=--∂ where c is the price of a call option on a non-dividend-paying stock. (e) Show that 1()c S N d ∂/∂=.(f) Show that the c satisfies the Black –Scholes –Merton differential equation.(g) Show that c satisfies the boundary condition for a European call option, i.e., thatmax(0)c S K =-, as t tends to T.(a) Since ()N x is the cumulative probability that a variable with a standardized normal distribution will be less than x , ()N x ' is the probability density function for a standardized normal distribution, that is,22()x N x -'=(b)12()(N d N d ''=+2221()22d d T t σσ⎡⎤=---⎢⎥⎣⎦221()exp ()2N d d T t σσ⎡⎤'=--⎢⎥⎣⎦Because22d =it follows that()21exp ()2r T t Ked T t S σσ--⎡⎤--=⎢⎥⎣⎦As a result()12()()r T t SN d Ke N d --''=which is the required result.(c)22212S K d σσ==Hence1d S ∂=∂ Similarly222d σ=and2d S ∂=∂ Therefore:12d d S S∂∂=∂∂(d)()12()()12122()()()()()r T t r T t r T t c SN d Ke N d d d c SN d rKe N d Ke N d t t t------=-∂∂∂''=--∂∂∂ From (b):()12()()r T t SN d Ke N d --''=Hence()1221()()r T t d d c rKe N d SN d t tt --∂∂∂⎛⎫'=-+- ⎪∂∂∂⎝⎭ Since12d d -=12(d d t t t∂∂∂-=∂∂∂=Hence()21()(r T t c rKe N d SN d t --∂'=--∂(e) From differentiating the Black –Scholes –Merton formula for a call price weobtain()12112()()()r T t d d cN d SN d Ke N d S S dS--∂∂∂''=+-∂∂ From the results in (b) and (c) it follows that1()cN d S ∂=∂(f) Differentiating the result in (e) and using the result in (c), we obtain21121()(d cN d S SN d ∂∂'=∂∂'= From the results in d) and e)222()2122211()121()(21()(2[()()]r T t r T t c c c rS S rKe N d SN d t S S rSN d S N d r SN d Ke N d rcσσ----∂∂∂'++=--∂∂∂'++=-=This shows that the Black –Scholes –Merton formula for a call option does indeed satisfy the Black –Scholes –Merton differential equation(g) Consider what happens in the formula for c in part (d) as t approaches T . IfS K >, 1d and 2d tend to infinity and 1()N d and 2()N d tend to 1. If S K <, 1d and 2d tend to zero. It follows that the formula for c tends to max(0)S K -,.Problem 15.18.Show that the Black –Scholes –Merton formulas for call and put options satisfy put –call parity.The Black –Scholes –Merton formula for a European call option is 012()()rT c S N d Ke N d -=- so that 012()()rT rT rT c Ke S N d Ke N d Ke ---+=-+ or 012()[1()]rT rT c Ke S N d Ke N d --+=+- or 012()()rT rT c Ke S N d Ke N d --+=+-The Black –Scholes –Merton formula for a European put option is 201()()rT p Ke N d S N d -=--- so that 02010()()rT p S Ke N d S N d S -+=---+ or 0201()[1()]rT p S Ke N d S N d -+=-+-- or 0201()()rT p S Ke N d S N d -+=-+ This shows that the put –call parity result 0rT c Ke p S -+=+ holds.Problem 15.19.A stock price is currently $50 and the risk-free interest rate is 5%. Use the DerivaGemsoftware to translate the following table of European call options on the stock into a table of implied volatilities, assuming no dividends. Are the option prices consistent with the assumptions underlying Black –Scholes –Merton?Using DerivaGem we obtain the following table of implied volatilitiesBlack-Scholes European as the Option Type. Input stock price as 50, the risk-free rate as 5%, time to exercise as 0.25, and exercise price as 45. Leave the dividend table blank because we are assuming no dividends. Select the button corresponding to call. Select the implied volatility button. Input the Price as 7.0 in the second half of the option data table. Hit theEnter key and click on calculate. DerivaGem will show the volatility of the option as 37.78%. Change the strike price and time to exercise and recompute to calculate the rest of the numbers in the table.The option prices are not exactly consistent with Black –Scholes –Merton. If they were, the implied volatilities would be all the same. We usually find in practice that low strike price options on a stock have significantly higher implied volatilities than high strike price options on the same stock. This phenomenon is discussed in Chapter 20.Problem 15.20.Explain carefully why Black’s approach to evaluating an American call option on a dividend-paying stock may give an approximate answer even when only one dividend is anticipated. Does the answer given by Black’s approach understate or overstate the true option value? Explain your answer.Black’s approach in effect assumes that the holder of option must decide at time zero whether it is a European option maturing at time n t (the final ex-dividend date) or a European optionmaturing at time T . In fact the holder of the option has more flexibility than this. The holder can choose to exercise at time n t if the stock price at that time is above some level but nototherwise. Furthermore, if the option is not exercised at time n t , it can still be exercised attime T .It appears that Black ’s approach should understate the true option value. This is because the holder of the option has more alternative strategies for deciding when to exercise the option than the two strategies implicitly assumed by the approach. These alternative strategies add value to the option.However, this is not the whole story! The standard approach to valuing either an American or a European option on a stock paying a single dividend applies the volatility to the stock price less the present value of the dividend. (The procedure for valuing an American option is explained in Chapter 21.) Black’s approach when considering exercise just prior to the dividend date applies the volatility to the stock price itself. Black’s approach thereforeassumes more stock price variability than the standard approach in some of its calculations. In some circumstances it can give a higher price than the standard approach.Problem 15.21.Consider an American call option on a stock. The stock price is $50, the time to maturity is 15 months, the risk-free rate of interest is 8% per annum, the exercise price is $55, and the volatility is 25%. Dividends of $1.50 are expected in 4 months and 10 months. Show that it can never be optimal to exercise the option on either of the two dividend dates. Calculate the price of the option.With the notation in the text12121500333308333125008and 55D D t t T r K ==.,=.,=.,=.,=.=2()00804167155(1)180r T t K e e ---.⨯.⎡⎤⎢⎥⎣⎦-=-=. Hence2()21r T t D K e --⎡⎤⎢⎥⎣⎦<- Also:21()00805155(1)216r t t K e e ---.⨯.⎡⎤⎢⎥⎣⎦-=-=. Hence:21()11r t t D K e --⎡⎤⎢⎥⎣⎦<- It follows from the conditions established in Section 15.12 that the option should never be exercised early.The present value of the dividends is033330080833300815152864e e -.⨯.-.⨯..+.=.The option can be valued using the European pricing formula with:05028644713655025008125S K r T σ=-.=.,=,=.,=.,=.212100545003340d d d ==-.=-.=-.12()04783()03692N d N d =.,=.and the call price is00812547136047835503692417e -.⨯..⨯.-⨯.=. or $4.17.Problem 15.22.Show that the probability that a European call option will be exercised in a risk-neutral world is, with the notation introduced in this chapter, 2()N d . What is an expression for the value of a derivative that pays off $100 if the price of a stock at time T is greater than K ?The probability that the call option will be exercised is the probability that T S K > where T S is the stock price at time T . In a risk neutral world[]T T r S S T 220,)2/(ln ~ln σσϕ-+The probability that T S K > is the same as the probability that ln ln T S K >. This is21N ⎡⎤-2N =2()N d =The expected value at time T in a risk neutral world of a derivative security which pays off $100 when T S K > is therefore2100()N dFrom risk neutral valuation the value of the security at time zero is2100()rT e N d -Problem 15.23.Use the result in equation (15.17) to determine the value of a perpetual American put option on a non-dividend-paying stock with strike price K if it is exercised when the stock price equals H where H<K. Assume that the current stock price S is greater than H. What is the value of H that maximizes the option value? Deduce the value of a perpetual American put option with strike price K.If the perpetual American put is exercised when S=H , it provides a payoff of (K −H ). We obtain its value, by setting Q=K−H in equation (15.17), as 22/2/2)()(σσ-⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-=⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-=r r S H H K H S H K VNow1/222/222222/21/22/2222222)(212)(212-σσσ-σσ⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛σ⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛σ-+-+⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛σ-=⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛σ-+-⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛=⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛σ-+⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-=r r r r r S H S r H H K r S H H rK dH V d H H K r S H S H r S H K S H dH dVdV/dH is zero when222σ+=r rK H and, for this value of H , d 2V /dH 2 is negative indicating that it gives the maximum value of V .The value of the perpetual American put is maximized if it is exercised when S equals this value of H . Hence the value of the perpetual American put is 2/2)(σ-⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-r H S H Kwhen H =2rK /(2r +σ2). The value is 2/22222)2(2σ-⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛σ+σ+σr rK r S r K This is consistent with the more general result produced in Chapter 26 for the case where the stock provides a dividend yield.Problem 15.24.A company has an issue of executive stock options outstanding. Should dilution be taken into account when the options are valued? Explain you answer.The answer is no. If markets are efficient they have already taken potential dilution intoaccount in determining the stock price. This argument is explained in Business Snapshot 15.3.Problem 15.25.A company’s stock price is $50 and 10 million shares are outstanding. The company is considering giving its employees three million at-the-money five-year call options. Option exercises will be handled by issuing more shares. The stock price volatility is 25%, the five-year risk-free rate is 5% and the company does not pay dividends. Estimate the cost to the company of the employee stock option issue.The Black-Scholes-Merton price of the option is given by setting 050S =, 50K =, 005r =., 025σ=., and 5T =. It is 16.252. From an analysis similar to that in Section 15.10 the cost to the company of the options is 1016252125103⨯.=.+ or about $12.5 per option. The total cost is therefore 3 million times this or $37.5 million. Ifthe market perceives no benefits from the options the stock price will fall by $3.75.Further QuestionsProblem 15.26.If the volatility of a stock is 18% per annum, estimate the standard deviation of the percentage price change in (a) one day, (b) one week, and (c) one month.(a) %13.125218=(b) %50.25218=(c) %20.51218=Problem 15.27.A stock price is currently $50. Assume that the expected return from the stock is 18% per annum and its volatility is 30% per annum. What is the probability distribution for the stock price in two years? Calculate the mean and standard deviation of the distribution. Determine the 95% confidence interval.In this case 050S =, 018=.μ and 030=.σ. The probability distribution of the stock price in two years, T S , is lognormal and is, from equation (15.3), given by:⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡⨯⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-+23.0,2209.018.050ln ~ln 2ϕT Si.e.,)42.0,18.4(~ln 2ϕT SThe mean stock price is from equation (15.4)018203650507167e e .⨯.==.and the standard deviation is from equation (15.5)018503183e .⨯=.95% confidence intervals for ln T S are418196042and 418196042.-.⨯..+.⨯.i.e.,335and 501..These correspond to 95% confidence limits for T S of 335501and e e ..i.e.,2852and 15044..Problem 15.28. (Excel file)Suppose that observations on a stock price (in dollars) at the end of each of 15 consecutive weeks are as follows:30.2, 32.0, 31.1, 30.1, 30.2, 30.3, 30.6, 33.0,32.9, 33.0, 33.5, 33.5, 33.7, 33.5, 33.2Estimate the stock price volatility. What is the standard error of your estimate?The calculations are shown in the table below2009471001145i i uu =.=.∑∑and an estimate of standard deviation of weekly returns is:002884=.The volatility per annum is therefore 002079.=. or 20.79%. The standard error of this estimate is 00393=. or 3.9% per annum.Problem 15.29.A financial institution plans to offer a security that pays off a dollar amount equal to 2T S at time T .(a) Use risk-neutral valuation to calculate the price of the security at time t in terms of the stock price, S , at time t . (Hint: The expected value of 2T S can be calculatedfrom the mean and variance of T S given in section 15.1.)(b) Confirm that your price satisfies the differential equation (15.16).(a) The expected value of the security is 2[()]T E S From equations (15.4) and (15.5), at time t :2()2()()2()var()[1]T t T T t T t T E S Se S S e e μμσ---==-Since 22var()[()][()]T T T S E S E S =-, it follows that 22[()]var()[()]T T T E S S E S =+ so that 22222()()22()(2)()2[()][1]T t T t T t T T t E S S e e S e S e μσμμσ---+-=-+=In a risk-neutral world r μ= so that222(2)()ˆ[()]r T t T E S S e σ+-= Using risk-neutral valuation, the value of the derivative security at time t is()2ˆ[()]r T t Te E S --22(2)()()r T t r T t S e e σ+---=22()()r T t S e σ+-=(b) If: 22222()()()()22()()2()()2()22r T t r T t r T t r T t f S e f S r e tf Se Sf e S σσσσσ+-+-+-+-=∂=-+∂∂=∂∂=∂ The left-hand side of the Black-Scholes –Merton differential equation is:222222()()2()()22()()()()2()2r T t r T t r T t r T t S r e rS e S e rS e rfσσσσσσ+-+-+-+--+++==Hence the Black-Scholes equation is satisfied.Problem 15.30.Consider an option on a non-dividend-paying stock when the stock price is $30, the exercise price is $29, the risk-free interest rate is 5% per annum, the volatility is 25% per annum, and the time to maturity is four months.a. What is the price of the option if it is a European call?b. What is the price of the option if it is an American call?c. What is the price of the option if it is a European put?d. Verify that put –call parity holds.In this case 030S =, 29K =, 005r =., 025=.σ and 412T =/2104225d ==.2202782d ==.(04225)06637(02782)06096N N .=.,.=.(04225)03363(02782)03904N N -.=.,-.=.a. The European call price is00541230066372906096252e -.⨯/⨯.-⨯.=.or $2.52.b. The American call price is the same as the European call price. It is $2.52.c. The European put price is00541229039043003363105e -.⨯/⨯.-⨯.=.or $1.05.d. Put-call parity states that:rT p S c Ke -+=+In this case 252c =., 030S =, 29K =, 105p =. and 09835rT e -=. and it is easy to verify that the relationship is satisfied,Problem 15.31.Assume that the stock in Problem 15.30 is due to go ex-dividend in 1.5 months. The expected dividend is 50 cents.a. What is the price of the option if it is a European call?b. What is the price of the option if it is a European put?c. If the option is an American call, are there any circumstances when it will beexercised early?a. The present value of the dividend must be subtracted from the stock price. This givesa new stock price of:01250053005295031e -.⨯.-.=.and 2103068d ==. 2201625d ==.12()06205()05645N d N d =.;=. The price of the option is therefore005412295031062052905645221e -.⨯/.⨯.-⨯.=.or $2.21.b. Because12()03795()04355N d N d -=.,-=. the value of the option when it is a European put is005412290435529503103795122e -.⨯/⨯.-.⨯.=.。

期权期货与其他衍生产品第九版课后习题与答案ChapterCHAPTER 29Interest Rate Derivatives: The Standard Market Models Practice QuestionsProblem 29.1.A company caps three-month LIBOR at 10% per annum. The principal amount is $20 million. On a reset date, three-month LIBOR is 12% per annum. What payment would this lead to under the cap? When would the payment be made?An amount20000000002025100000$$,,?.?.=,would be paid out 3 months later.Problem 29.2.Explain why a swap option can be regarded as a type of bond option.A swap option (or swaption) is an option to enter into an interest rate swap at a certain time in the future with a certain fixed rate being used. An interest rate swap can be regarded as the exchange of a fixed-rate bond for a floating-rate bond. A swaption is therefore theoption to exchange a fixed-rate bond for a floating-rate bond. The floating-rate bond will be worth its face value at the beginning of the life of the swap. The swaption is therefore an option on a fixed-rate bond with the strike price equal to the face value of the bond.Problem 29.3.Use the Black’s model to value a one -year European put option on a 10-year bond. Assume that the current value of the bond is $125, the strike price is $110, the one-year risk-free interest rate is 10% per annum, the bond’s forward price volatility is 8% per annum, and the present value of the coupons to be paid during the life of the option is $10.In this case, 0110(12510)12709F e .?=-=., 110K =, 011(0)P T e -.?,=, 008B σ=., and 10T =.. 2121ln(12709110)(0082)1845600800817656d d d ./+./==..=-.=. From equation (29.2) the value of the put option is011011110(17656)12709(18456)012e N e N -.?-.?-.-.-.=.or $0.12.Problem 29.4.Explain carefully how you would use (a) spot volatilities and (b) flat volatilities to value a five-year cap.When spot volatilities are used to value a cap, a different volatility is used to value eachcaplet. When flat volatilities are used, the same volatility is used to value each caplet within a given cap. Spot volatilities are a function of the maturity of the caplet. Flat volatilities are afunction of the maturity of the cap.Problem 29.5.Calculate the price of an option that caps the three-m onth rate, starting in 15 months’time, at 13% (quoted with quarterly compounding) on a principal amount of $1,000. The forward interest rate for the period in question is 12% per annum (quoted with quarterly compounding), the 18-month risk-free interest rate (continuously compounded) is 11.5% per annum, and the volatility of the forward rate is 12% per annum.In this case 1000L =, 025k δ=., 012k F =., 013K R =., 0115r =., 012k σ=., 125k t =., 1(0)08416k P t +,=..250k L δ=2120529505295006637d d ==-.=-.-.=-. The value of the option is25008416[012(05295)013(06637)]N N ?.?.-.-.-.059=. or $0.59.Problem 29.6.A bank uses Black’s model to price European bond options. Suppose that an implied price volatility for a 5-year option on a bond maturing in 10 years is used to price a 9-year option on the bond. Would you expect the resultant price to be too high or too low? Explain. The implied volatility measures the standard deviation of the logarithm of the bond price at the maturity of the option divided by the square root of the time to maturity. In the case of a five year option on a ten year bond, the bond has five years left at option maturity. In the case of a nine year option on a ten year bond it has one year left. The standard deviation of a one yearbond price observed in nine years can be normally be expected to be considerably less than that of a five year bond price observed in five years. (See Figure 29.1.) We would therefore expect the price to be too high. Problem 29.7.Calculate the value of a four-year European call option on bond that will mature five years from today using Black’s model. The five -year cash bond price is $105, the cash price of a four-year bond with the same coupon is $102, the strike price is $100, the four-year risk-free interest rate is 10% per annum with continuous compounding, and the volatility for the bond price in four years is 2% per annum.The present value of the principal in the four year bond is 40110067032e -?.=.. The present value of the coupons is, therefore, 1026703234968-.=.. This means that the forward price of the five-year bond is401(10534968)104475e ?.-.=. The parameters in Black’s model are therefore 104475B F =., 100K =, 01r =., 4T =,and 002B =.σ.212111144010744d d d ==.=-.=. The price of the European call is014[104475(11144)100(10744)]319e N N -.?..-.=.or $3.19.Problem 29.8.If the yield volatility for a five-year put option on a bond maturing in 10 years time isspecified as 22%, how should the option be valued? Assume that, based on today’s interest rates the modified duration of the bond at the maturity of the option will be 4.2 years and the forward yield on the bond is 7%.The option should be valued using Black’s model in equation (29.2) with the bond price volatility being 4200702200647.?.?.=. or 6.47%.Problem 29.9.What other instrument is the same as a five-year zero-cost collar where the strike price of the cap equals the strike price of the floor? What does the commonstrike price equal?A 5-year zero-cost collar where the strike price of the cap equals the strike price of the floor is the same as an interest rate swap agreement to receive floating and pay a fixed rate equal to the strike price. The common strike price is the swap rate. Note that the swap is actually a forward swap that excludes the first exchange. (See Business Snapshot 29.1)Problem 29.10.Derive a put –call parity relationship for European bond options.There are two way of expressing the put –call parity relationship for bond options. The first is in terms of bond prices:0RT c I Ke p B -++=+where c is the price of a European call option, p is the price of the corresponding European put option, I is the present value of the bond coupon payments during the life of the option, K is the strike price, T is the time to maturity, 0B is the bond price, and Ris the risk-free interest rate for a maturity equal to the life of the options. To prove this we can consider twoportfolios. The first consists of a European put option plus the bond; the second consists of the European call option, and an amount of cash equal to the present value of the coupons plus the present value of the strike price. Both can be seen to be worth the same at the maturity of the options.The second way of expressing the put –call parity relationship isRT RT B c Ke p F e --+=+where B F is the forward bond price. This can also be proved by considering two portfolios. The first consists of a European put option plus a forward contract on the bond plus the present value of the forward price; the second consists of a European call option plus the present value of the strike price. Both can be seen to be worth the same at the maturity of the options. Problem 29.11.Derive a put–call parity relationship for European swap options.The put–call parity relationship for European swap options is+=c V pwhere c is the value of a call option to pay a fixed rate ofs and receive floating, p isKthe value of a put option to receive a fixed rate ofs and pay floating, and V is the valueKof the forward swap underlying the swap option where s is received and floating is paid.KThis can be proved by considering two portfolios. The first consists of the put option; the second consists of the call option and the swap. Suppose that the actual swap rate at thes. The call will be exercised and the put will not be maturity of the options is greater thanKexercised. Both portfolios are then worth zero. Suppose next that the actual swap rate at thes. The put option is exercised and the call option is not maturity of the options is less thanKs is received and floating is paid. exercised. Both portfolios are equivalent to a swap whereKIn all states of the world the two portfolios are worth the same at time T. They must therefore be worth the same today. This proves the result.Problem 29.12.Explain why there is an arbitrage opportunity if the implied Black (flat) volatility of a cap is different from that of a floor. Do the broker quotes in Table 29.1 present an arbitrage opportunity?Suppose that the cap and floor have the same strike price and the same time to maturity. The following put–call parity relationship must hold:+=cap swap floorwhere the swap is an agreement to receive the cap rate and pay floating over the whole life of the cap/floor. If the implied Black volatilities for the cap equal those for the floor, the Black formulas show that this relationship holds. In other circumstances it does not hold andthere is an arbitrage opportunity. The broker quotes in Table 29.1 do not present an arbitrage opportunity because the cap offer is always higher than the floor bid and the floor offer is always higher than the cap bid.Problem 29.13.When a bond’s price is lognormal can the bond’s yield be negative? Explain your answer.Yes. If a zero-coupon bond price at some future time is lognormal, there is some chance that the price will be above par. This in turn implies that the yield to maturity on the bond is negative.Problem 29.14.What is the value of a European swap option that gives the holder the right to enter into a3-year annual-pay swap in four years where a fixed rate of 5% is paid and LIBOR is received? The swap principal is $10 million. Assume that the LIBOR/swap yield curve is used for discounting and is flat at 5% per annum with annual compounding and the volatility of the swap rate is 20%. Compare your answer to that given by DerivaGem.Now suppose that allswap rates are 5% and all OIS rates are 4.7%. Use DerivaGem to calculate the LIBOR zero curve and the swap option value?In equation (29.10), 10000000L =,,, 005K s =., 0005s =., 10202d =.=., 2.02-=d , and 56711122404105105105A =++=.... The value of the swap option (in millions of dollars) is1022404[005(02)005(02)]0178N N ?...-.-.=.This is the same as the answer given by DerivaGem. (For the purposes of using theDerivaGem software, note that the interest rate is 4.879% with continuous compounding for all maturities.)When OIS discounting is used the LIBOR zero curve is unaffected because LIBOR swap rates are the same for all maturities. (This can be verified with the Zero Curve worksheet in DerivaGem). The only difference is that 2790.2047.11047.11047.11765=++=Aso that the value is changed to 0.181. This is also the value given by DerivaGem. (Note that the OIS rate is4.593% with annual compounding.)Problem 29.15.Suppose that the yield, R , on a zero-coupon bond follows the processdR dt dz μσ=+where μand σare functions of R and t , and dz is a Wiener process. Use Ito’s lemma to show that the volatility of the zero-coupon bond price declines to zero as it approaches maturity.The price of the bond at time t is ()R T t e -- where T is the time when the bond matures. Using It?’s lemma the volatility of the bond price is ()()()R T t R T t e T t e R σσ----?=--? This tends to zero as t approaches T . Problem 29.16.Carry out a manual calculation to verify the option prices in Example 29.2.The cash price of the bond is 005050005100005100051044410012282e e 卐 e -.?.-.?.-.?-.?++++=.As there is no accrued interest this is also the quoted price of the bond. The interest paid during the life of the option has a present value of00505005100515005244441504e e e e -.?.-.?-.?.-.?+++=.The forward price of the bond is therefore005225(122821504)12061e .?..-.=. The yield with semiannual compounding is 5.0630%.The duration of the bond at option maturity is 005025005775005775 005025005075005775005775 02547754775100444100e 卐 e e e 卐 e -.?.-.?.-.?.-.?.-.?.-.?.-.?..?++.?+.?++++ or 5.994. The modified duration is 5.994/1.025315=5.846. The bond price volatility is therefore 584600506300200592.?.?.=.. We can therefore value the bond option using Black’s model with 12061B F =., 005225(0225)08936P e -.?.,.==., 592B %=.σ, and 225T =.. When the strike price is the cash price 115K = and the value of the option is 1.74. When the strike price is the quoted price 117K = and the value of the option is 2.36. This is in agreement with DerivaGem.Problem 29.17.Suppose that the 1-year, 2-year, 3-year, 4-year and 5-year LIBOR-for-fixed swap rates for swaps withsemiannual payments are 6%, 6.4%, 6.7%, 6.9%, and 7%. The price of a 5-year semiannual cap with a principal of $100 at a cap rate of 8% is $3. Use DerivaGem (the zero rate and Cap_and_swap_opt worksheets) to determine(a) The 5-year flat volatility for caps and floors with LIBOR discounting(b) The floor rate in a zero-cost 5-year collar when the cap rate is 8% and LIBOR discounting is used(c) Answer (a) and (b) if OIS discounting is used and OIS swap rates are 100 basis points below LIBOR swap rates.(a) First we calculate the LIBOR zero curve using the zero curve worksheet of DerivaGem.The 1-, 2-, 3-, 4-, and 5_year zero rates with continuous compounding are 5.9118%,6.3140%, 6.6213%, 6.8297%, and 6.9328%, respectively. We then transfer these to the choose the Caps and Swap Options worksheet and choose Cap/Floor as the Underlying Type. We enter Semiannual for the Settlement Frequency, 100 for the Principal, 0 for the Start (Years), 5 for the End (Years), 8% for the Cap/FloorRate, and $3 for the Price. We select Black-European as the Pricing Model and choose the Cap button. We check the Imply Volatility box and Calculate. The implied volatility is 25.4%.(b) We then uncheck Implied Volatility, select Floor, check Imply Breakeven Rate. Thefloor rate that is calculated is 6.71%. This is the floor rate for which the floor is worth $3.A collar when the floor rate is 6.61% and the cap rate is 8% has zero cost.(c) The zero curve worksheet now shows that LIBOR zero rates for 1-, 2-, 3-, 4-, 5-yearmaturities are 5.9118%, 6.3117%, 6.6166%, 6.8227%, and 6.9249%. The OIS zero rates are 4.9385%, 5.3404%, 5.6468%, 5.8539%, and 5.9566%, respectively. When these are transferred to the cap and swaption worksheet and the Use OIS Discounting box is checked, the answer to a) becomes 24.81%% and the answer to b) becomes 6.60%.Problem 29.18.Show that 12V f V += where 1V is the value of a swaption to pay a fixed rate of K s and receive LIBOR between times 1T and 2T , f is the value of a forwardswap to receive a fixed rate of K s and pay LIBOR between times 1T and 2T , and 2V is the value of a swap option to receive a fixed rate of K s between times 1T and 2T . Deduce that 12V V = when K s equals the current forward swap rate.We prove this result by considering two portfolios. The first consists of the swap option toreceive K s ; the second consists of the swap option to pay K s and the forward swap.Suppose that the actual swap rate at the maturity of the options is greater than K s . The swapoption to pay K s will be exercised and the swap option to receive K s will not be exercised.Both portfolios are then worth zero since the swap option to pay K s is neutralized by theforward swap. Suppose next that the actual swap rate at the maturity of the options is less than K s . The swap option to receive K s is exercised and the swap option to pay K s is not exercised. Both portfolios are then equivalent to a swap where K s is received and floating ispaid. In all states of the world the two portfolios areworth the same at time 1T . They musttherefore be worth the same today. This proves the result. When K s equals the currentforward swap rate 0f = and 12V V =. A swap option to pay fixed is therefore worth thesame as a similar swap option to receive fixed when the fixed rate in the swap option is the forward swap rate. Problem 29.19.Suppose that LIBOR zero rates are as in Problem 29.17. Use DerivaGem to determine the value of an option to pay a fixed rate of 6% and receive LIBOR on a five-year swap starting in one year. Assume that the principal is $100 million, payments are exchanged semiannually, and the swap rate volatility is 21%. Use LIBOR discounting.We choose the Caps and Swap Options worksheet of DerivaGem and choose Swap Option as the Underlying Type. We enter 100 as the Principal, 1 as the Start (Years), 6 as the End (Years), 6% as the Swap Rate, and Semiannual as the Settlement Frequency. We choose Black-European as the pricing model, enter 21% as the Volatility and check the Pay Fixed button. We do notcheck the Imply Breakeven Rate and Imply Volatility boxes. The value of the swap option is 5.63.Problem 29.20.Describe how you would (a) calculate cap flat volatilities from cap spot volatilities and (b) calculate cap spot volatilities from cap flat volatilities.(a) To calculate flat volatilities from spot volatilities we choose a strike rate and use the spot volatilities to calculate caplet prices. We then sum the caplet prices to obtain cap prices and imply flat volatilities from Black’s model. The answe r is slightlydependent on the strike price chosen. This procedure ignores any volatility smile in cap pricing.(b) To calculate spot volatilities from flat volatilities the first step is usually to interpolate between the flat volatilities so that we have a flat volatility for each caplet payment date. We choose a strike price and use the flat volatilities to calculate cap prices. By subtracting successive cap prices we obtain caplet prices from which we can imply spot volatilities. The answer is slightly dependent on the strike price chosen. Thisprocedure also ignores any volatility smile in caplet pricing.Further QuestionsProblem 29.21.Consider an eight-month European put option on a Treasury bond that currently has 14.25 years to maturity. The current cash bond price is $910, the exercise price is $900, and the volatility for the bond price is 10% per annum. A coupon of $35 will be paid by the bond in three months. The risk-free interest rate is 8% for all maturities up to one year. Use Black’s model to determine the price of the option. Consider both the case where the strike price corresponds to the cash price of the bond and the case where it corresponds to the quoted price.The present value of the coupon payment is 008025353431e -.?.=.Equation (29.2) can therefore be used with 008812(9103431)92366B F e .?/=-.=., 008r =., 010B σ=. and 06667T =.. When the strike price is a cash price, 900K = and12103587002770d d d ==.=-.=.The option price is therefore00806667900(02770)87569(03587)1834e N N -.?.-.-.-.=.or $18.34.When the strike price is a quoted price 5 months of accrued interest must be added to 900 to get the cash strike price. The cash strike price is 900350833392917+?.=.. In this case12100319001136d d d ==-.=-.=-.and the option price is0080666792917(01136)87569(00319)3122e N N -.?...-..=.or $31.22.Problem 29.22.Calculate the price of a cap on the 90-day LIBOR rate in nine months’time when the principal amount is$1,000. Use Black’s model with LIBOR discounting and the following information:(a) The quoted nine-month Eurodollar futures price =92. (Ignore differences betweenfutures and forward rates.)(b) The interest-rate volatility implied by a nine-month Eurodollar option = 15% perannum.(c) The current 12-month risk-free interest rate with continuous compounding = 7.5%per annum.(d) The cap rate = 8% per annum. (Assume an actual/360 day count.)The quoted futures price corresponds to a forward rate of 8% per annum with quarterly compounding and actual/360. The parameters for Black’s model are therefore: 008k F =., 008K =., 0075R =., 015k σ=., 075k t =., and 007511(0)09277k P t e -.?+,==.21220065000650d d ==.==-. and the call price, c , is given by[]025100009277008(00650)008(00650)096c N N =.?,?...-.-..=.Problem 29.23.Suppose that the LIBOR yield curve is flat at 8% with annual compounding. A swaption gives the holder the right to receive 7.6% in a five-year swap starting in four years. Payments are made annually. The volatility of the forward swap rate is 25% per annum and the principal is $1 million. Use Black’s model to price the swaption with LIBOR discounting. Compare your answer to that given by DerivaGem.The payoff from the swaption is a series of five cash flows equal to max[00760]T s .-, in millions of dollars where T s is the five-year swap rate in four years. The value of an annuity that provides $1 per year at the end of years 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 is 95129348108i i ==..∑The value of the swaption in millions of dollars is therefore2129348[0076()008()]N d N d ..--.-where2103526d ==. and2201474d ==-. The value of the swaption is29348[0076(01474)008(03526)]003955N N ...-.-.=.or $39,550. This is the same answer as that given by DerivaGem. Note that for the purposes of using DerivaGem the zero rate is 7.696% continuously compounded for all maturities.Problem 29.24.Use the DerivaGem software to value a five-year collar that guarantees that the maximum and minimum interest rates on a LIBOR-based loan (with quarterly resets) are 7% and 5% respectively. The LIBOR and OIS zero curves are currently flat at 6% and 5.8% respectively (with continuous compounding). Use a flat volatility of 20%. Assume that the principal is $100. Use OIS discountingWe use the Caps and Swap Options worksheet of DerivaGem. Set the LIBOR zero curve as 6% with continuous compounding. ( It is only necessary to enter 6% for one maturity.) . Set the OIS zero curve as 5.8% with continuous compounding. ( It is only necessary to enter5.8% for one maturity.) To value the cap we select Cap/Floor as the Underlying Type, enter Quarterly for the Settlement Frequency, 100 for the Principal, 0 for the Start (Years), 5 for the End (Years), 7% for the Cap/Floor Rate, and 20% for the Volatility. We select Black-European as the Pricing Model and choose the Cap button. We do not check the ImplyBreakeven Rate and Imply Volatility boxes. We do check the Use OIS Discounting button. The value of the cap is 1.576. To value the floor we change the Cap/Floor Rate to 5% and select the Floor button rather than the Cap button. The value is 1.080. The collar is a long position in the cap and a short position in the floor. The value of the collar is therefore1.576 ─1.080 = 0.496Problem 29.25.Use the DerivaGem software to value a European swap option that gives you the right in two years to enter into a 5-year swap in which you pay a fixed rate of 6% and receive floating. Cash flows are exchanged semiannually on the swap. The 1-year, 2-year, 5-year, and 10-year LIBOR-for-fixed swap rate wherepayments are exchanged semiannually are 5%, 6%, 6.5%, and 7%, respectively. Assume a principal of $100 and a volatility of 15% per annum. (a) Use LIBOR discounting (b) Use OIS discounting assuming that OIS swap rates are 80 basis points below LIBOR swap rates (c) Use the incorrect approach where OIS discounting is applied to swap rates calculate from LIBOR discounting. What is the error from using the incorrect approach? We first use the zero rates worksheet to calculate the LIBOR zero curve with LIBOR discounting. We then calculate the LIBOR and OIS zero curve with OIS discounting.(a)The LIBOR zero rates are transferred to the cap and swap option worksheet. Thevalue of the swaption is 4.602(b)The LIBOR and OIS zero rates are transferred to the cap and swap option worksheet.The value of the swaption is 4.736(c)The LIBOR zero curve from (a) and the OIS zero curve from (b) are transferred tothe cap and swap option worksheet. The value of the swaption is 4.783. The errorfrom using the incorrect approach is 4.783?4.736 = 0.047 or 4.7 basis points.。

期权期货和其他衍生品约翰赫尔第九版答案简介《期权期货和其他衍生品》是由约翰·赫尔(John C. Hull)编写的一本经典教材,是金融衍生品领域的权威参考书籍之一。
该书第九版是在第八版的基础上进行了更新和修订,以适应当前金融市场的动态变化。
本文档旨在提供《期权期货和其他衍生品第九版》的答案,帮助读者更好地理解和应用书中的知识点。
以下将按照书籍的章节顺序,逐一给出答案。
第一章期权市场的基本特征1.什么是期权?答:期权是一种金融衍生品,它赋予买方在特定时间以特定价格买入或卖出标的资产的权力,而不是义务。
可以将期权分为看涨期权和看跌期权。
2.期权的四个基本特征是什么?答:期权的四个基本特征是价格、到期日、标的资产和行权方式。
价格即期权的成交价,到期日是期权到期的日期,标的资产是期权合约要买入或卖出的资产,而行权方式则决定了期权何时可以行使。
3.什么是期权合约?答:期权合约是买卖双方约定的具体规定和条件,包括标的资产、行权价格、到期日等。
它规定了买方在合约到期前是否可以行使期权。
第二章期权定价:基础观念1.定价模型的基本原理是什么?答:期权定价模型的基本原理是假设市场是有效的,即不存在无风险套利机会。
通过建立基于风险中性概率的模型,可以计算期权的理论价值。
2.什么是风险中性概率?答:风险中性概率是指在假设市场是有效的情况下,使得在无套利条件下资产价格在期望值与当前价格之间折现的概率。
风险中性概率的使用可以将市场中的现金流折算为无风险利率下的现值。
3.什么是期权的内在价值和时间价值?答:期权的内在价值是指期权当前即时的价值,即行权价格与标的资产价格之间的差额。
时间价值是期权除去内在价值后剩余的价值,它受到时间、波动率和利率等因素的影响。
第三章期权定价模型:基础知识1.什么是布莱克斯科尔斯期权定价模型?答:布莱克斯科尔斯期权定价模型是一种用于计算欧式期权价格的数学模型。
它基于连续性投资组合原理,使用了假设市场是完全有效的和无交易成本的条件,可以通过著名的布拉克斯科尔斯公式来计算期权的价格。

赫尔《期权、期货及其他衍生产品》(第9版)笔记和课后习题详解完整版>精研学习䋞>无偿试用20%资料全国547所院校视频及题库全收集考研全套>视频资料>课后答案>往年真题>职称考试第1章引言1.1复习笔记1.2课后习题详解第2章期货市场的运作机制2.1复习笔记2.2课后习题详解第3章利用期货的对冲策略3.1复习笔记3.2课后习题详解第4章利率4.1复习笔记4.2课后习题详解第5章如何确定远期和期货价格5.1复习笔记5.2课后习题详解第6章利率期货6.1复习笔记6.2课后习题详解第7章互换7.1复习笔记7.2课后习题详解第8章证券化与2007年信用危机8.1复习笔记8.2课后习题详解第9章OIS贴现、信用以及资金费用9.1复习笔记9.2课后习题详解第10章期权市场机制10.1复习笔记10.2课后习题详解第11章股票期权的性质11.1复习笔记11.2课后习题详解第12章期权交易策略12.1复习笔记12.2课后习题详解第13章二叉树13.1复习笔记13.2课后习题详解第14章维纳过程和伊藤引理14.1复习笔记14.2课后习题详解第15章布莱克-斯科尔斯-默顿模型15.1复习笔记15.2课后习题详解第16章雇员股票期权16.1复习笔记16.2课后习题详解第17章股指期权与货币期权17.1复习笔记17.2课后习题详解第18章期货期权18.1复习笔记18.2课后习题详解第19章希腊值19.1复习笔记19.2课后习题详解第20章波动率微笑20.1复习笔记20.2课后习题详解第21章基本数值方法21.1复习笔记21.2课后习题详解第22章风险价值度22.1复习笔记22.2课后习题详解第23章估计波动率和相关系数23.1复习笔记23.2课后习题详解第24章信用风险24.1复习笔记24.2课后习题详解第25章信用衍生产品25.1复习笔记25.2课后习题详解第26章特种期权26.1复习笔记26.2课后习题详解第27章再谈模型和数值算法27.1复习笔记27.2课后习题详解第28章鞅与测度28.1复习笔记28.2课后习题详解第29章利率衍生产品:标准市场模型29.1复习笔记29.2课后习题详解第30章曲率、时间与Quanto调整30.1复习笔记30.2课后习题详解第31章利率衍生产品:短期利率模型31.1复习笔记31.2课后习题详解第32章HJM,LMM模型以及多种零息曲线32.1复习笔记32.2课后习题详解第33章再谈互换33.1复习笔记33.2课后习题详解第34章能源与商品衍生产品34.1复习笔记34.2课后习题详解第35章章实物期权35.1复习笔记35.2课后习题详解第36章重大金融损失与借鉴36.1复习笔记36.2课后习题详解。
CHAPTER 24 Credit RiskPractice QuestionsProblem 24.1.The spread between the yield on a three-year corporate bond and the yield on a similarrisk-free bond is 50 basis points. The recovery rate is 30%. Estimate the average hazard rate per year over the three-year period.From equation (24.2) the average hazard rate over the three years is 00050(103)00071./-.=. or 0.71% per year.Problem 24.2.Suppose that in Problem 24.1 the spread between the yield on a five-year bond issued by the same company and the yield on a similar risk-free bond is 60 basis points. Assume the same recovery rate of 30%. Estimate the average hazard rate per year over the five-year period. What do your results indicate about the average hazard rate in years 4 and 5?From equation (24.2) the average hazard rate over the five years is 00060(103)00086./-.=. or 0.86% per year. Using the results in the previous question, the hazard rate is 0.71% per year for the first three years and000865000713001072.⨯-.⨯=.or 1.07% per year in years 4 and 5.Problem 24.3.Should researchers use real-world or risk-neutral default probabilities for a) calculating credit value at risk and b) adjusting the price of a derivative for defaults?Real-world probabilities of default should be used for calculating credit value at risk.Risk-neutral probabilities of default should be used for adjusting the price of a derivative for default.Problem 24.4.How are recovery rates usually defined?he recovery rate for a bond is the value of the bond immediately after the issuer defaults as a percent of its face value.Problem 24.5.Explain the difference between an unconditional default probability density and a hazard rate.The hazard rate, ()h t at time t is defined so that ()h t t ∆ is the probability of default between times t and t t +∆ conditional on no default prior to time t . The unconditional default probability density ()q t is defined so that ()q t t ∆ is the probability of default between times t and t t +∆ as seen at time zero.Problem 24.6.Verify a) that the numbers in the second column of Table 24.3 are consistent with the numbers in Table 24.1 and b) that the numbers in the fourth column of Table 24.4 are consistent with the numbers in Table 24.3 and a recovery rate of 40%.The first number in the second column of Table 24.3 is calculated as1--.=.ln(1000245)000035047or 0.04% per year when rounded. Other numbers in the column are calculated similarly. The numbers in the fourth column of Table 24.4 are the numbers in the second column of Table 24.3 multiplied by one minus the expected recovery rate. In this case the expected recovery rate is 0.4.Problem 24.7.Describe how netting works. A bank already has one transaction with a counterparty on its books. Explain why a new transaction by a bank with a counterparty can have the effect of increasing or reducing the bank’s credit exposure to the counterparty.Suppose company A goes bankrupt when it has a number of outstanding contracts with company B. Netting means that the contracts with a positive value to A are netted against those with a negative value in order to determine how much, if anything, company A owes company B. Company A is not allowed to “cherry pick” by keeping the positive-value contracts and defaulting on the negative-value contracts.The new transaction will increase the bank’s exposure to the counterparty if the contract tends to have a positive value whenever the existing contract has a positive value and a negative value whenever the existing contract has a negative value. However, if the new transaction tends to offset the existing transaction, it is likely to have the incremental effect of reducing credit risk.Problem 24.8.“DVA can improve the bottom line when a bank is experiencing financial difficulty.” Explain why this statement is true.When a bank is experiencing financial difficulties, its credit spread is likely to increase. This increases q i* and DVA increases. This is a benefit to the bank: the fact that it is more likely to default means that its derivatives are worth less.Problem 24.9.Explain the difference between the Gaussian copula model for the time to default and CreditMetrics as far as the following are concerned: a) the definition of a credit loss and b) the way in which default correlation is modeled.(a) In the Gaussian copula model for time to default a credit loss is recognized only whena default occurs. In CreditMetrics it is recognized when there is a credit downgrade aswell as when there is a default.(b) In the Gaussian copula model of time to default, the default correlation arises becausethe value of the factor M. This defines the default environment or average defaultrate in the economy. In CreditMetrics a copula model is applied to credit ratings migration and this determines the joint probability of particular changes in the credit ratings of two companies.Problem 24.10.Suppose that the LIBOR/swap curve is flat at 6% with continuous compounding and afive-year bond with a coupon of 5% (paid semiannually) sells for 90.00. How would an asset swap on the bond be structured? What is the asset swap spread that would be calculated in this situation?Suppose that the principal is $100. The asset swap is structured so that the $10 is paidinitially. After that $2.50 is paid every six months. In return LIBOR plus a spread is received on the principal of $100. The present value of the fixed payments is00605006100650065102525251001053579e e 卐e -.⨯.-.⨯-.⨯-.⨯+.+.++.+=.The spread over LIBOR must therefore have a present value of 5.3579. The present value of $1 received every six months for five years is 8.5105. The spread received every six months must therefore be 535798*********$./.=.. The asset swap spread is therefore 20629612592%⨯.=. per annum.Problem 24.11.Show that the value of a coupon-bearing corporate bond is the sum of the values of its constituent zero-coupon bonds when the amount claimed in the event of default is theno-default value of the bond, but that this is not so when the claim amount is the face value of the bond plus accrued interest.When the claim amount is the no-default value, the loss for a corporate bond arising from a default at time t isˆ()(1)v t R B *-where ()v t is the discount factor for time t and B * is the no-default value of the bond at time t . Suppose that the zero-coupon bonds comprising the corporate bond have no-default values at time t of 1Z , 2Z , …, n Z , respectively. The loss from the i th zero-coupon bond arising from a default at time t isˆ()(1)i v t R Z -The total loss from all the zero-coupon bonds is垐()(1)()(1)ni iv t R Z v t R B *-=-∑This shows that the loss arising from a default at time t is the same for the corporate bond as for the portfolio of its constituent zero-coupon bonds. It follows that the value of the corporate bond is the same as the value of its constituent zero-coupon bonds.When the claim amount is the face value plus accrued interest, the loss for a corporate bond arising from a default at time t isˆ()()[()]v t B v t R L a t *-+where L is the face value and ()a t is the accrued interest at time t . In general this is not the same as the loss from the sum of the losses on the constituent zero-coupon bonds.Problem 24.12.A four-year corporate bond provides a coupon of 4% per year payable semiannually and has a yield of 5% expressed with continuous compounding. The risk-free yield curve is flat at 3% with continuous compounding. Assume that defaults can take place at the end of each year (immediately before a coupon or principal payment and the recovery rate is 30%. Estimate the risk-neutral default probability on the assumption that it is the same each year.Define Q as the risk-free rate. The calculations are as followsThe bond pays a coupon of 2 every six months and has a continuously compounded yield of 5% per year. Its market price is 96.19. The risk-free value of the bond is obtained bydiscounting the promised cash flows at 3%. It is 103.66. The total loss from defaults should therefore be equated to 103669619746.-.=.. The value of Q implied by the bond price is therefore given by 27269746Q .=.. or 00274Q =.. The implied probability of default is 2.74% per year.Problem 24.13.A company has issued 3- and 5-year bonds with a coupon of 4% per annum payable annually. The yields on the bonds (expressed with continuous compounding) are 4.5% and 4.75%, respectively. Risk-free rates are 3.5% with continuous compounding for all maturities. The recovery rate is 40%. Defaults can take place half way through each year. The risk-neutral default rates per year are 1Q for years 1 to 3 and 2Q for years 4 and 5. Estimate 1Q and 2Q .The table for the first bond isThe market price of the bond is 98.35 and the risk-free value is 101.23. It follows that 1Q is given by 117831101239835Q .=.-.so that 100161Q =..The table for the second bond isThe market price of the bond is 96.24 is and the risk-free value is 101.97. It follows that121805610853101979624Q Q .+.=.-.From which we get 200260Q =. The bond prices therefore imply a probability of default of 1.61% per year for the first three years and 2.60% for the next two years.Problem 24.14.Suppose that a financial institution has entered into a swap dependent on the sterling interest rate with counterparty X and an exactly offsetting swap with counterparty Y. Which of the following statements are true and which are false.(a) The total present value of the cost of defaults is the sum of the present value of the cost of defaults on the contract with X plus the present value of the cost of defaults on the contract with Y.(b) The expected exposure in one year on both contracts is the sum of the expected exposure on the contract with X and the expected exposure on the contract with Y. (c) The 95% upper confidence limit for the exposure in one year on both contracts is the sum of the 95% upper confidence limit for the exposure in one year on the contract with X and the 95% upper confidence limit for the exposure in one year on the contract with Y. Explain your answers.The statements in (a) and (b) are true. The statement in (c) is not. Suppose that X v and Y v are the exposures to X and Y. The expected value of X Y v v + is the expected value of X v plus the expected value of Y v . The same is not true of 95% confidence limits.Problem 24.15.“A long forward contract subject to credit risk is a combination of a short position in a no-default put and a long position in a call subject to credit risk.” Explain this statement.Assume that defaults happen only at the end of the life of the forward contract. In adefault-free world the forward contract is the combination of a long European call and a short European put where the strike price of the options equals the delivery price and the maturity of the options equals the maturity of the forward contract. If the no-default value of the contract is positive at maturity, the call has a positive value and the put is worth zero. The impact of defaults on the forward contract is the same as that on the call. If the no-default value of the contract is negative at maturity, the call has a zero value and the put has a positive value. In this case defaults have no effect. Again the impact of defaults on theforward contract is the same as that on the call. It follows that the contract has a value equal to a long position in a call that is subject to default risk and short position in a default-free put.Problem 24.16.Explain why the credit exposure on a matched pair of forward contracts resembles a straddle.Suppose that the forward contract provides a payoff at time T . With our usual notation, the value of a long forward contract is rT T S Ke --. The credit exposure on a long forward contract is therefore max(0)rT T S Ke --,; that is, it is a call on the asset price with strike pricerT Ke -. Similarly the credit exposure on a short forward contract is max(0)rT T Ke S --,; thatis, it is a put on the asset price with strike price rT Ke -. The total credit exposure is, therefore, a straddle with strike price rT Ke -.Problem 24.17.Explain why the impact of credit risk on a matched pair of interest rate swaps tends to be lessthan that on a matched pair of currency swaps.The credit risk on a matched pair of interest rate swaps is fixed floating |B B |-. As maturity is approached all bond prices tend to par and this tends to zero. The credit risk on a matched pair of currency swaps is foreign fixed |SB B |- where S is the exchange rate. The expected value of this tends to increase as the swap maturity is approached because of the uncertainty in S .Problem 24.18.“When a bank is negotiating currency swaps, it should try to ensure that it is receiving th e lower interest rate currency from a company with a low credit risk.” Explain.As time passes there is a tendency for the currency which has the lower interest rate tostrengthen. This means that a swap where we are receiving this currency will tend to move in the money (i.e., have a positive value). Similarly a swap where we are paying the currency will tend to move out of the money (i.e., have a negative value). From this it follows that our expected exposure on the swap where we are receiving the low-interest currency is much greater than our expected exposure on the swap where we are receiving the high-interestcurrency. We should therefore look for counterparties with a low credit risk on the side of the swap where we are receiving the low-interest currency. On the other side of the swap we are far less concerned about the creditworthiness of the counterparty.Problem 24.19.Does put –call parity hold when there is default risk? Explain your answer.No, put –call parity does not hold when there is default risk. Suppose c * and p * are the no-default prices of a European call and put with strike price K and maturity T on a non-dividend-paying stock whose price is S , and that c and p are the corresponding values when there is default risk. The text shows that when we make the independence assumption (that is, we assume that the variables determining the no-default value of the option are independent of the variables determining default probabilities and recovery rates),[()()]y T yT Tc c e **--= and [()()]y T yT Tp p e **--=. The relationship()y T T c Ke p S **-*+=+which holds in a no-default world therefore becomes()[()()]y T T y T y T T c Ke p Se *---+=+when there is default risk. This is not the same as regular put –call parity. What is more, the relationship depends on the independence assumption and cannot be deduced from the same sort of simple no-arbitrage arguments that we used in Chapter 11 for the put –call parity relationship in a no-default world.Problem 24.20.Suppose that in an asset swap B is the market price of the bond per dollar of principal, B * is the default-free value of the bond per dollar of principal, and V is the present value ofthe asset swap spread per dollar of principal. Show that V B B *=-.We can assume that the principal is paid and received at the end of the life of the swap without changing the swap’s value. If the spread were zero the present value of the floating payments per dollar of principal would be 1. The payment of LIBOR plus the spread therefore has a present value of 1V +. The payment of the bond cash flows has a present value per dollar of principal of B *. The initial payment required from the payer of the bond cash flows per dollar of principal is 1B -. (This may be negative; an initial amount of 1B - is then paid by the payer of the floating rate). Because the asset swap is initially worth zero we have11V B B *+=+- so that V B B *=-Problem 24.21.Show that un der Merton’s model in Section 24.6 the credit spread on a T -year zero-coupon bond is 21ln[()()]N d N d L T -+-// where 0rT L De V -=/.The value of the debt in Merton’s model is 00V E - or2010201()()()()rT rT De N d V N d V De N d V N d ---+=+-If the credit spread is s this should equal ()r s T De -+ so that ()201()()r s T rT De De N d V N d -+-=+-Substituting 0rT De LV -=00201()()sT LV e LV N d V N d -=+-or21()()sT Le LN d N d -=+-so that21ln[()()]s N d N d L T =-+-//Problem 24.22.Suppose that the spread between the yield on a 3-year zero-coupon riskless bond and a 3-year zero-coupon bond issued by a corporation is 1%. By how much doesBlack-Scholes-Merton overstate the value of a 3-year European option sold by the corporation.When the default risk of the seller of the option is taken into account the option value is the Black –Scholes price multiplied by 001309704e -.⨯=.. Black –Scholes overprices the option by about 3%.Problem 24.23.Give an example of a) right-way risk and b) wrong-way risk.Right way risk describes the situation when a default by the counterparty is most likely to occur when the contract has a positive value to the counterparty. An example of right way risk would be when a counterparty’s future depends on the price of a commodity and it enters into a contract to partially hedging that exposure.Wrong way risk describes the situation when a default by the counterparty is most likely to occur when the contract has a negative value to the counterparty. An example of right way risk would be when a counterparty is a speculator and the contract has the same exposure as the rest of the counterparty’s portfolio.Further QuestionsProblem 24.24. (Spreadsheet Provided)Suppose a three-year corporate bond provides a coupon of 7% per year payable semiannually and has a yield of 5% (expressed with semiannual compounding). The yields for all maturities on risk-free bonds is 4% per annum (expressed with semiannual compounding). Assume that defaults can take place every six months (immediately before a coupon payment) and the recovery rate is 45%. Estimate the hazard rate (assumed constant) for the three yearsThe market price of the bond is 105.51. The risk-free price is 108.40. The expected cost of defaults is therefore 2.89. We need to find the hazard rate λ that leads to the expected cost of defaults being 2.89. We need to make an assumption about how the probability of default at a time is calculated from the hazard rate. A natural assumption is that the probability of default at a six month point equals the probability of default given by the hazard rate for the previous six months. The following table shows then shows the calculationsSolver can be used to determine the value of λ such that(1−e−0.5λ)×64.28 + (e−1.0λ−e−0.5λ)×61.73 + (e−1.5λ−e−1.0λ)×59.20 + (e−2.0λ−e−1.5λ)×56.74+ ( e−2.5λ−e−2.0λ)×54.32 + ( e−3.0λ−e−2.5λ)×51.95 = 2.89It is 1.70%.An alternative (better) assumption is that the probability of default at times 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 and 3.0 years are1−e −0.75λ, e −1.25λ−e −0.75λ, e −1.75λ−e −1.25λ, e −2.25λ−e −1.75λ, e −2.75λ−e −2.25λ, and e −3.25λ−e −2.75λThe estimate of the hazard rate is then 1.56%.Problem 24.25.A company has one- and two-year bonds outstanding, each providing a coupon of 8% per year payable annually. The yields on the bonds (expressed with continuous compounding are 6.0% and 6.6%, respectively. Risk-free rates are 4.5% for all maturities. The recovery rate is 35%. Defaults can take place half way through each year. Estimate the risk-neutral default rate each year.Consider the first bond. Its market price is 006110810171e -.⨯=.. Its default-free price is 0045110810325e -.⨯=.. The present value of the loss from defaults is therefore 1.54. In this case losses can take place at only one time, halfway through the year. Suppose that the probability of default at this time is 1Q . The default-free value of the bond is00450510810560e -.⨯.=.. The loss in the event of a default is 10560357060.-=.. The present value of the expected loss is 0045051170606903e Q Q -.⨯..=.. It follows that16903154Q .=.so that 100223Q =..Now consider the second bond. It market price is 102.13 and its default-free value is 106.35. The present value of the loss from defaults is therefore 4.22. At time 0.5 the default free value of the bond is 108.77. The loss in the event of a default is therefore 73.77. The present value of the loss from defaults at this time is 17213Q . or 1.61. This means that the present value of the loss from defaults at the 1.5 year point is 422161.-. or 2.61. Thedefault-free value of the bond at the 1.5 year point is 105.60. The loss in the event of a default is 70.60. The present value of the expected loss is 26599Q . where 2Q is the probability of default in the second year. It follows that 26599261Q .=.so that 200396Q =..The probabilities of default in years one and two are therefore 2.23% and 3.96%.Problem 24.26.Explain carefully the distinction between real-world and risk-neutral defaultprobabilities. Which is higher? A bank enters into a credit derivative where it agrees to pay $100 at the end of one year if a certain company’s credit rating falls from A to Baa or lower during the year. The one-year risk-free rate is 5%. Using Table 24.5, estimate a value for the derivative. What assumptions are you making? Do they tend to overstate or understate the value of the derivative?Real world default probabilities are the true probabilities of defaults. They can be estimated from historical data. Risk-neutral default probabilities are the probabilities ofdefaults in a world where all market participants are risk neutral. They can be estimated from bond prices. Risk-neutral default probabilities are higher. This means that returns in the risk-neutral world are lower. From Table 24.5 the probability of a company moving from A to Baa or lower in one year is 5.73%. An estimate of the value of the derivative is therefore005100573100545e -.⨯.⨯⨯=.. The approximation in this is that we are using the real-world probability of a downgrade. To value the derivative correctly we should use the risk-neutral probability of a downgrade. Since the risk-neutral probability of a default is higher than the real-world probability, it seems likely that the same is true of a downgrade. This means that5.45 is likely to be too low as an estimate of the value of the derivative.Problem 24.27.The value of a company’s equity is $4 million and the volatility of its equity is 60%. The debt that will have to be repaid in two years is $15 million. The risk-free interest rate is 6% per annum. Use Merton’s model to estimate the expected loss from default, theprobability of default, and the recovery rate in the event of default. (Hint The Solver function in Excel can be used for this question, as indicated in footnote 10)In this case 04E =, 060E σ=., 15D =, 006r =.. Setting up the data in Excel, we can solve equations (24.3) and (24.4) by using the approach in footnote 10. The solution to the equations proves to be 017084V =. and 01576V σ=.. The probability of default is 2()N d - or 15.61%. The market value of the debt is 17084413084.-=.. The present value of the promised payment on the debt is 00621513304e -.⨯=.. The expected loss on the debt is, therefore, (1330413084)13304.-./. or 1.65% of its no-default value. The expected recovery rate in the event of default is therefore (1561165)1561.-./. or about 89%. The reason the recovery rate is so high is as follows. There is a default if the value of the assets moves from 17.08 to below 15. A value for the assets significantly below 15 is unlikely. Conditional on a default, the expected value of the assets is, therefore, not a huge amount below 15. In practice it is likely that companies manage to delay defaults until asset values are well below the face value of the debt.Problem 24.28.Suppose that a bank has a total of $10 million of exposures of a certain type. Theone-year probability of default averages 1% and the recovery rate averages 40%. The copula correlation parameter is 0.2. Estimate the 99.5% one-year credit VaR.From equation (24.10) the 99.5% worst case probability of default is00946N =.This gives the 99.5% credit VaR as 10(104)009460568⨯-.⨯.=. millions of dollars or $568,000.Problem 24.29. (Excel file)Extend Example 24.6 to calculate CVA when default can happen in the middle of each month. Assume that the default probability per month during the first year is 0.001667 and the default probability per month during the second year is 0.0025.The spreadsheet shows the answer is 5.73Problem 24.30. (Excel file)Calculate DVA in Example 24.6. Assume that default can happen in the middle of each month. The default probability of the bank is 0.001 per month for the two years.In this case we look at the exposure from the point of view of the coumnterparty. The exposure at time t is()max[,0]r T t t e K F ---The expected exposure at time t is therefore[]()201(()(()r T t e KN d t F N d t -----The spreadsheet shows that the DVA is 1.13. This assumes that the recovery rate of the counterparty when the bank defaults is 0.3, the same as the recovery rate of the bank when the counterparty defaults.。
CHAPTER 2Mechanics of Futures MarketsPractice QuestionsProblem 2.1.Distinguish between the terms open interest and trading volume.The open interest of a futures contract at a particular time is the total number of long positions outstanding. (Equivalently, it is the total number of short positions outstanding.) The trading volume during a certain period of time is the number of contracts traded during this period. Problem 2.2.What is the difference between a local and a futures commission merchant?A futures commission merchant trades on behalf of a client and charges a commission. A local trades on his or her own behalf.Problem 2.3.Suppose that you enter into a short futures contract to sell July silver for $17.20 per ounce. The size of the contract is 5,000 ounces. The initial margin is $4,000, and the maintenance margin is $3,000. What change in the futures price will lead to a margin call? What happens if you do not meet the margin call?There will be a margin call when $1,000 has been lost from the margin account. This will occur when the price of silver increases by 1,000/5,000 = $0.20. The price of silver must therefore rise to $17.40 per ounce for there to be a margin call. If the margin call is not met, your broker closes out your position.Problem 2.4.Suppose that in September 2015 a company takes a long position in a contract on May 2016 crude oil futures. It closes out its position in March 2016. The futures price (per barrel) is $88.30 when it enters into the contract, $90.50 when it closes out its position, and $89.10 at the end of December 2015. One contract is for the delivery of 1,000 barrels. What is the company’s total profit? When is it realized? How is it taxed if it is (a) a hedger and (b) a speculator? Assume that the company has a December 31 year-end.The total profit is ($90.50 - $88.30) ⨯ 1,000 = $2,200. Of this ($89.10 - $88.30) ⨯ 1,000 or $800 is realized on a day-by-day basis between September 2015 and December 31, 2015. A further ($90.50 - $89.10) ⨯ 1,000 or $1,400 is realized on a day-by-day basis between January1, 2016, and March 2016. A hedger would be taxed on the whole profit of $2,200 in 2016. A speculator would be taxed on $800 in 2015 and $1,400 in 2016.Problem 2.5.What does a stop order to sell at $2 mean? When might it be used? What does a limit order to sell at $2 mean? When might it be used?A stop order to sell at $2 is an order to sell at the best available price once a price of $2 or less is reached. It could be used to limit the losses from an existing long position. A limit order to sell at $2 is an order to sell at a price of $2 or more. It could be used to instruct a broker that a short position should be taken, providing it can be done at a price more favorable than $2.Problem 2.6.What is the difference between the operation of the margin accounts administered by a clearing house and those administered by a broker?The margin account administered by the clearing house is marked to market daily, and the clearing house member is required to bring the account back up to the prescribed level daily. The margin account administered by the broker is also marked to market daily. However, the account does not have to be brought up to the initial margin level on a daily basis. It has to be brought up to the initial margin level when the balance in the account falls below the maintenance margin level. The maintenance margin is usually about 75% of the initial margin.Problem 2.7.What differences exist in the way prices are quoted in the foreign exchange futures market, the foreign exchange spot market, and the foreign exchange forward market?In futures markets, prices are quoted as the number of US dollars per unit of foreign currency. Spot and forward rates are quoted in this way for the British pound, euro, Australian dollar, and New Zealand dollar. For other major currencies, spot and forward rates are quoted as the number of units of foreign currency per US dollar.Problem 2.8.The party with a short position in a futures contract sometimes has options as to the precise asset that will be delivered, where delivery will take place, when delivery will take place, and so on. Do these options increase or decrease the futures price? Explain your reasoning.These options make the contract less attractive to the party with the long position and more attractive to the party with the short position. They therefore tend to reduce the futures price.Problem 2.9.What are the most important aspects of the design of a new futures contract?The most important aspects of the design of a new futures contract are the specification of the underlying asset, the size of the contract, the delivery arrangements, and the delivery months. Problem 2.10.Explain how margin accounts protect investors against the possibility of default.A margin is a sum of money deposited by an investor with his or her broker. It acts as a guarantee that the investor can cover any losses on the futures contract. The balance in the margin account is adjusted daily to reflect gains and losses on the futures contract. If losses are above a certain level, the investor is required to deposit a further margin. This system makes it unlikely that the investor will default. A similar system of margin accounts makes it unlikely that the investor’s broker will default on the contract it has with the clearing house member and unlikely that the clearing house member will default with the clearing house.Problem 2.11.A trader buys two July futures contracts on frozen orange juice. Each contract is for the delivery of 15,000 pounds. The current futures price is 160 cents per pound, the initial margin is $6,000 per contract, and the maintenance margin is $4,500 per contract. What price change would lead to a margin call? Under what circumstances could $2,000 be withdrawn from the margin account?There is a margin call if more than $1,500 is lost on one contract. This happens if the futures price of frozen orange juice falls by more than 10 cents to below 150 cents per pound. $2,000 can be withdrawn from the margin account if there is a gain on one contract of $1,000. This will happen if the futures price rises by 6.67 cents to 166.67 cents per pound.Problem 2.12.Show that, if the futures price of a commodity is greater than the spot price during the delivery period, then there is an arbitrage opportunity. Does an arbitrage opportunity exist if the futures price is less than the spot price? Explain your answer.If the futures price is greater than the spot price during the delivery period, an arbitrageur buys the asset, shorts a futures contract, and makes delivery for an immediate profit. If the futures price is less than the spot price during the delivery period, there is no similar perfect arbitrage strategy. An arbitrageur can take a long futures position but cannot force immediate delivery of the asset. The decision on when delivery will be made is made by the party with the short position. Nevertheless companies interested in acquiring the asset may find it attractive to enterinto a long futures contract and wait for delivery to be made.Problem 2.13.Explain the difference between a market-if-touched order and a stop order.A market-if-touched order is executed at the best available price after a trade occurs at a specified price or at a price more favorable than the specified price. A stop order is executed at the best available price after there is a bid or offer at the specified price or at a price less favorable than the specified price.Problem 2.14.Explain what a stop-limit order to sell at 20.30 with a limit of 20.10 means.A stop-limit order to sell at 20.30 with a limit of 20.10 means that as soon as there is a bid at20.30 the contract should be sold providing this can be done at 20.10 or a higher price. Problem 2.15.At the end of one day a clearing house member is long 100 contracts, and the settlement price is $50,000 per contract. The original margin is $2,000 per contract. On the following day the member becomes responsible for clearing an additional 20 long contracts, entered into at a price of $51,000 per contract. The settlement price at the end of this day is $50,200. How much does the member have to add to its margin account with the exchange clearing house?The clearing house member is required to provide 20$2000$40000⨯,=, as initial margin for the new contracts. There is a gain of (50,200 - 50,000)⨯ 100 = $20,000 on the existing contracts. There is also a loss of (5100050200)20$16000,-,⨯=, on the new contracts. The member must therefore add,-,+,=,400002000016000$36000to the margin account.Problem 2.16.Explain why collateral requirements will increase in the OTC market as a result of new regulations introduced since the 2008 credit crisis.Regulations require most standard OTC transactions entered into between derivatives dealers to be cleared by CCPs. These have initial and variation margin requirements similar to exchanges. There is also a requirement that initial and variation margin be provided for most bilaterally cleared OTC transactions.Problem 2.17.The forward price on the Swiss franc for delivery in 45 days is quoted as 1.1000. The futures price for a contract that will be delivered in 45 days is 0.9000. Explain these two quotes. Which is more favorable for an investor wanting to sell Swiss francs?The 1.1000 forward quote is the number of Swiss francs per dollar. The 0.9000 futures quote is the number of dollars per Swiss franc. When quoted in the same way as the futures price the /.=.. The Swiss franc is therefore more valuable in the forward forward price is11100009091market than in the futures market. The forward market is therefore more attractive for an investor wanting to sell Swiss francs.Problem 2.18.Suppose you call your broker and issue instructions to sell one July hogs contract. Describe what happens.Live hog futures are traded by the CME Group. The broker will request some initial margin. The order will be relayed by telephone to your broker’s trading desk on the floor of the exchange (or to the trading desk of another broker). It will then be sent by messenger to a commission broker who will execute the trade according to your instructions. Confirmation of the trade eventually reaches you. If there are adverse movements in the futures price your broker may contact you to request additional margin.Problem 2.19.“Speculation in futures markets is pure gambling. It is not in the public interest to allow speculators to trade on a futures exchange.” Discuss this viewpoint.Speculators are important market participants because they add liquidity to the market. However, contracts must be useful for hedging as well as speculation. This is because regulators generally only approve contracts when they are likely to be of interest to hedgers as well as speculators.Problem 2.20.Explain the difference between bilateral and central clearing for OTC derivatives.In bilateral clearing the two sides enter into an agreement governing the circumstances under which transactions can be closed out by one side, how transactions will be valued if there is a close out, how the collateral posted by each side is calculated, and so on. In central clearing a CCP stands between the two sides in the same way that an exchange clearing house stands between two sides for transactions entered into on an exchangeProblem 2.21.What do you think would happen if an exchange started trading a contract in which the qualityof the underlying asset was incompletely specified?The contract would not be a success. Parties with short positions would hold their contracts until delivery and then deliver the cheapest form of the asset. This might well be viewed by the party with the long position as garbage! Once news of the quality problem became widely known no one would be prepared to buy the contract. This shows that futures contracts are feasible only when there are rigorous standards within an industry for defining the quality of the asset. Many futures contracts have in practice failed because of the problem of defining quality.Problem 2.22.“When a futures contract is traded on the floor of the exchange, it may be the case that the open interest increases by one, stays the same, or decreases by one.” Explain this statement.If both sides of the transaction are entering into a new contract, the open interest increases by one. If both sides of the transaction are closing out existing positions, the open interest decreases by one. If one party is entering into a new contract while the other party is closing out an existing position, the open interest stays the same.Problem 2.23.Suppose that on October 24, 2015, a company sells one April 2016 live-cattle futures contracts. It closes out its position on January 21, 2016. The futures price (per pound) is 121.20 cents when it enters into the contract, 118.30 cents when it closes out its position, and 118.80 cents at the end of December 2015. One contract is for the delivery of 40,000 pounds of cattle. What is the total profit? How is it taxed if the company is (a) a hedger and (b) a speculator?Assume that the company has a December 31 year end.The total profit is40,000×(1.2120−1.1830) = $1,160If the company is a hedger this is all taxed in 2016. If it is a speculator40,000×(1.2120−1.1880) = $960is taxed in 2015 and40,000×(1.1880−1.1830) = $200is taxed in 2016.Problem 2.24.A cattle farmer expects to have 120,000 pounds of live cattle to sell in three months. The live-cattle futures contract traded by the CME Group is for the delivery of 40,000 pounds of cattle. How can the farmer use the contract for hedging? From the farmer’s viewpoint, what are thepros and cons of hedging?The farmer can short 3 contracts that have 3 months to maturity. If the price of cattle falls, the gain on the futures contract will offset the loss on the sale of the cattle. If the price of cattle rises, the gain on the sale of the cattle will be offset by the loss on the futures contract. Using futures contracts to hedge has the advantage that the farmer can greatly reduce the uncertainty about the price that will be received. Its disadvantage is that the farmer no longer gains from favorable movements in cattle prices.Problem 2.25.It is July 2014. A mining company has just discovered a small deposit of gold. It will take six months to construct the mine. The gold will then be extracted on a more or less continuous basis for one year. Futures contracts on gold are available with delivery months every two months from August 2014 to December 2015. Each contract is for the delivery of 100 ounces. Discuss how the mining company might use futures markets for hedging.The mining company can estimate its production on a month by month basis. It can then short futures contracts to lock in the price received for the gold. For example, if a total of 3,000 ounces are expected to be produced in September 2015 and October 2015, the price received for this production can be hedged by shorting 30 October 2015 contracts.Problem 2.26.Explain how CCPs work. What are the advantages to the financial system of requiring all standardized derivatives transactions to be cleared through CCPs?A CCP stands between the two parties in an OTC derivative transaction in much the same way that a clearing house does for exchange-traded contracts. It absorbs the credit risk but requires initial and variation margin from each side. In addition, CCP members are required to contribute to a default fund. The advantage to the financial system is that there is a lot more collateral (i.e., margin) available and it is therefore much less likely that a default by one major participant in the derivatives market will lead to losses by other market participants. There is also more transparency in that the trades of different financial institutions are more readily known. The disadvantage is that CCPs are replacing banks as the too-big-to-fail entities in the financial system. There clearly needs to be careful oversight of the management of CCPs.Further QuestionsProblem 2.27.Trader A enters into futures contracts to buy 1 million euros for 1.3 million dollars in three months. Trader B enters in a forward contract to do the same thing. The exchange rate (dollarsper euro) declines sharply during the first two months and then increases for the third month to close at 1.3300. Ignoring daily settlement, what is the total profit of each trader? When the impact of daily settlement is taken into account, which trader does better?The total profit of each trader in dollars is 0.03×1,000,000 = 30,000. Trader B’s profit is realized at the end of the three months. Trader A’s profit is realized day-by-day during the three months. Substantial losses are made during the first two months and profits are made during the final month. It is likely that Trader B has done better because Trader A had to finance its losses during the first two months.Problem 2.28.Explain what is meant by open interest. Why does the open interest usually decline during the month preceding the delivery month? On a particular day, there were 2,000 trades in a particular futures contract. This means that there were 2000 buyers (going long) and 2000 sellers (going short). Of the 2,000 buyers, 1,400 were closing out positions and 600 were entering into new positions. Of the 2,000 sellers, 1,200 were closing out positions and 800 were entering into new positions. What is the impact of the day's trading on open interest?Open interest is the number of contract outstanding. Many traders close out their positions just before the delivery month is reached. This is why the open interest declines during the month preceding the delivery month. The open interest went down by 600. We can see this in two ways. First, 1,400 shorts closed out and there were 800 new shorts. Second, 1,200 longs closed out and there were 600 new longs.Problem 2.29.One orange juice future contract is on 15,000 pounds of frozen concentrate. Suppose that in September 2014 a company sells a March 2016 orange juice futures contract for 120 cents per pound. In December 2014 the futures price is 140 cents; in December 2015 the futures price is 110 cents; and in February 2016 it is closed out at 125 cents. The company has a December year end. What is the company's profit or loss on the contract? How is it realized? What is the accounting and tax treatment of the transaction if the company is classified as a) a hedger and b) a speculator?The price goes up during the time the company holds the contract from 120 to 125 cents per pound. Overall the company therefore takes a loss of 15,000×0.05 = $750. If the company is classified as a hedger this loss is realized in 2016, If it is classified as a speculator it realizes a loss of 15,000×0.20 = $3000 in 2014, a gain of 15,000×0.30 = $4,500 in 2015, and a loss of 15,000×0.15 = $2,250 in 2016.Problem 2.30.A company enters into a short futures contract to sell 5,000 bushels of wheat for 750 cents per bushel. The initial margin is $3,000 and the maintenance margin is $2,000. What price changewould lead to a margin call? Under what circumstances could $1,500 be withdrawn from the margin account?There is a margin call if $1000 is lost on the contract. This will happen if the price of wheat futures rises by 20 cents from 750 cents to 770 cents per bushel. $1500 can be withdrawn if the futures price falls by 30 cents to 720 cents per bushel.Problem 2.31.Suppose that there are no storage costs for crude oil and the interest rate for borrowing or lending is 5% per annum. How could you make money if the June and December futures contracts for a particular year trade at $80 and $86?You could go long one June oil contract and short one December contract. In June you take delivery of the oil borrowing $80 per barrel at 5% to meet cash outflows. The interest accumulated in six months is about 80×0.05×1/2 or $2. In December the oil is sold for $86 per barrel which is more than the $82 that has to be repaid on the loan. The strategy therefore leads to a profit. Note that this profit is independent of the actual price of oil in June and December. It will be slightly affected by the daily settlement procedures.Problem 2.32.What position is equivalent to a long forward contract to buy an asset at K on a certain date and a put option to sell it for K on that date?The long forward contract provides a payoff of S T−K where S T is the asset price on the date and K is the delivery price. The put option provides a payoff of max (K−S T, 0). If S T> K the sum of the two payoffs is S T–K. If S T< K the sum of the two payoffs is 0. The combined payoff is therefore max (S T–K, 0). This is the payoff from a call option. The equivalent position is therefore a call option.Problem 2.33.A company has derivatives transactions with Banks A, B, and C which are worth +$20 million, −$15 million, and −$25 million, respectively to t he company. How much margin or collateral does the company have to provide in each of the following two situations?a) The transactions are cleared bilaterally and are subject to one-way collateral agreements where the company posts variation margin, but no initial margin. The banks do not have to post collateral.b) The transactions are cleared centrally through the same CCP and the CCP requires a total initial margin of $10 million.If the transactions are cleared bilaterally, the company has to provide collateral to Banks A, B, and C of (in millions of dollars) 0, 15, and 25, respectively. The total collateral required is $40 million. If the transactions are cleared centrally they are netted against each other and thecompany’s total variation margin (i n millions of dollars) is –20 + 15 + 25 or $20 million in total. The total margin required (including the initial margin) is therefore $30 million.Problem 2.34.A bank’s derivatives transactions with a counterparty are worth +$10 million to the bank and are cleared bilaterally. The counterparty has posted $10 million of cash collateral. What credit exposure does the bank have?The counterparty may stop posting collateral and some time will then elapse before the bank is able to close out the transaction s. During that time the transactions may move in the bank’s favor, increasing its exposure. Note that the bank is likely to have hedged the transactions and will incur a loss on the hedge if the transactions move in the bank’s favor. For example, if the transactions change in value from $10 to $13 million after the counterparty stops postingcollateral, the bank loses $3 million on the hedge and will not necessarily realize an offsetting gain on the transactions.Problem 2.35. (Excel file)The author’s website (www.rotman.utoronto.ca/~hull/data) contains daily closing prices for the crude oil futures contract and gold futures contract. (Both contracts are traded on NYMEX.) You are required to download the data for crude oil and answer the following:(a) Assuming that daily price changes are normally distributed with zero mean, estimate the daily price movement that will not be exceeded with 99% confidence.(b) Suppose that an exchange wants to set the maintenance margin for traders so that it is 99% certain that the margin will not be wiped out by a two-day price move. (It chooses two daysbecause the margin calls are made at the end of a day and the trader has until the end of the next day to decide whether to provide more margin.) How high does the margin have to be when the normal distribution assumption is made?(c) Suppose that the maintenance margin is as calculated in (b) and is 75% of the initial margin. How frequently would the margin have been wiped out by a two-day price movement in the period covered by the data for a trader with a long position? What do your results suggest about the appropriateness of the normal distribution assumption.(a) For crude oil, the standard deviation of daily changes is $1.5777 per barrel or $1577.7 percontract. We are therefore 99% confident that daily changes will not exceed 1577.7×2.326 or 3669.73.(b) The maintenance margin should be set at 3263.227.1577⨯⨯ or 5,191 when rounded.(c)The initial margin is set at 6,921 for on crude oil. (This is the maintenance margin of5,191 divided by 0.75.) As the spreadsheet shows, for a long investor in oil there are 157 margin calls and 9 times (out of 1039 days) where the trader is tempted to walk away. As9 is approximately 1% of 1039 the normal distribution assumption appears to workreasonably well in this case.。
CHAPTER 3Hedging Strategies Using FuturesPractice QuestionsProblem 3.1.Under what circumstances are (a) a short hedge and (b) a long hedge appropriate?A short hedge is appropriate when a company owns an asset and expects to sell that asset in the future. It can also be used when the company does not currently own the asset but expects to do so at some time in the future. A long hedge is appropriate when a company knows it will have to purchase an asset in the future. It can also be used to offset the risk from an existing short position.Problem 3.2.Explain what is meant by basis risk when futures contracts are used for hedging.Basis risk arises from the hedger’s uncertainty as to the difference between the spot price and futures price at the expiration of the hedge.Problem 3.3.Explain what is meant by a perfect hedge. Does a perfect hedge always lead to a better outcome than an imperfect hedge? Explain your answer.A perfect hedge is one that completely eliminates the hedger’s risk. A p erfect hedge does not always lead to a better outcome than an imperfect hedge. It just leads to a more certain outcome. Consider a company that hedges its exposure to the price of an asset. Suppose the asset’s price movements prove to be favorable to the company. A perfect hedge totally neutralizes the company’s gain from these favorable price movements. An imperfect hedge, which only partially neutralizes the gains, might well give a better outcome.Problem 3.4.Under what circumstances does a minimum-variance hedge portfolio lead to no hedging at all?A minimum variance hedge leads to no hedging when the coefficient of correlation between the futures price changes and changes in the price of the asset being hedged is zero.Problem 3.5.Give three reasons why the treasurer of a company might not hedge the company’s exposure to a particular risk.(a) If the company’s competitors are not hedging, the treasurer might feel that the company will experience less risk if it does not hedge. (See Table 3.1.) (b) The shareholders might not want the company to hedge because the risks are hedged within their portfolios. (c) If there is a loss on the hedge and a gain from the company’s exposure to the underlying asset, the treasurer might feel that he or she will have difficulty justifying the hedging to other executives within the organization.Problem 3.6.Suppose that the standard deviation of quarterly changes in the prices of a commodity is $0.65, the standard deviation of quarterly changes in a futures price on the commodity is $0.81, and the coefficient of correlation between the two changes is 0.8. What is the optimal hedge ratio for a three-month contract? What does it mean?The optimal hedge ratio is 065080642081..⨯=.. This means that the s ize of the futures position should be 64.2% of the size of the company’s exposure in a three-month hedge.Problem 3.7.A company has a $20 million portfolio with a beta of 1.2. It would like to use futures contracts on a stock index to hedge its risk. The index futures is currently standing at 1080, and each contract is for delivery of $250 times the index. What is the hedge that minimizes risk? What should the company do if it wants to reduce the beta of the portfolio to 0.6?The formula for the number of contracts that should be shorted gives 20000000128891080250,,.⨯=.⨯ Rounding to the nearest whole number, 89 contracts should be shorted. To reduce the beta to 0.6, half of this position, or a short position in 44 contracts, is required.Problem 3.8.In the corn futures contract, the following delivery months are available: March, May, July, September, and December. State the contract that should be used for hedging when the expiration of the hedge is in a) June, b) July, and c) JanuaryA good rule of thumb is to choose a futures contract that has a delivery month as close aspossible to, but later than, the month containing the expiration of the hedge. The contracts that should be used are therefore(a) July(b)September(c)MarchProblem 3.9.Does a perfect hedge always succeed in locking in the current spot price of an asset for a future transaction? Explain your answer.No. Consider, for example, the use of a forward contract to hedge a known cash inflow in a foreign currency. The forward contract locks in the forward exchange rate — which is in general different from the spot exchange rate.Problem 3.10.Explain why a short hedger’s position improves when the basis strengthens unexpectedly and worsens when the basis weakens unexpectedly.The basis is the amount by which the spot price exceeds the futures price. A short hedger is long the asset and short futures contracts. The value of his or her position therefore improves as the basis increases. Similarly, it worsens as the basis decreases.Problem 3.11.Imagine you are the treasurer of a Japanese company exporting electronic equipment to the United States. Discuss how you would design a foreign exchange hedging strategy and the arguments you would use to sell the strategy to your fellow executives.The simple answer to this question is that the treasurer should1.Estimate the company’s future cash flows in Japanese yen and U.S. dollars2.Enter into forward and futures contracts to lock in the exchange rate for the U.S. dollarcash flows.However, this is not the whole story. As the gold jewelry example in Table 3.1 shows, the company should examine whether the magnitudes of the foreign cash flows depend on the exchange rate. For example, will the company be able to raise the price of its product in U.S. dollars if the yen appreciates? If the company can do so, its foreign exchange exposure may be quite low. The key estimates required are those showing the overall effect on the company’s profitability of changes in the exchange rate at various times in the future. Once these estimates have been produced the company can choose between using futures and options to hedge its risk. The results of the analysis should be presented carefully to other executives. It should be explained that a hedge does not ensure that profits will be higher. It means that profit will be more certain. When futures/forwards are used both the downside and upside are eliminated. With options a premium is paid to eliminate only the downside.Problem 3.12.Suppose that in Example 3.2 of Section 3.3 the company decides to use a hedge ratio of 0.8. How does the decision affect the way in which the hedge is implemented and the result?If the hedge ratio is 0.8, the company takes a long position in 16 December oil futures contracts on June 8 when the futures price is $88.00. It closes out its position on November 10. The spot price and futures price at this time are $90.00 and $89.10. The gain on the futures position is(89.10 − 88.00) × 16,000 = 17,600The effective cost of the oil is therefore20,000 × 90 – 17,600 = 1,782, 400or $89.12 per barrel. (This compares with $88.90 per barrel when the company is fully hedged.)Problem 3.13.“If the minimum -variance hedge ratio is calculated as 1.0, the hedge must be perfect." Is this statement true? Explain your answer.The statement is not true. The minimum variance hedge ratio is S Fσρσ It is 1.0 when 05=.ρ and 2S F =σσ. Since 10<.ρ the hedge is clearly not perfect.Problem 3.14.“If there is no basis risk, the minimum variance hedge ratio is always 1.0." Is this statement true? Explain your answer.The statement is true. Using the notation in the text, if the hedge ratio is 1.0, the hedger locks in a price of 12F b +. Since both 1F and 2b are known this has a variance of zero and must be the best hedge.Problem 3.15“For an asset where futures prices for contracts on the asset are usually less than spot prices, long hedges are likely to be particularly attractive." Explain this statement.A company that knows it will purchase a commodity in the future is able to lock in a price close to the futures price. This is likely to be particularly attractive when the futures price is less than the spot price.Problem 3.16.The standard deviation of monthly changes in the spot price of live cattle is (in cents per pound)1.2. The standard deviation of monthly changes in the futures price of live cattle for the closestcontract is 1.4. The correlation between the futures price changes and the spot price changes is 0.7. It is now October 15. A beef producer is committed to purchasing 200,000 pounds of live cattle on November 15. The producer wants to use the December live-cattle futures contracts to hedge its risk. Each contract is for the delivery of 40,000 pounds of cattle. What strategy should the beef producer follow?The optimal hedge ratio is 12070614..⨯=.. The beef producer requires a long position in 20000006120000⨯.=, lbs of cattle. The beef producer should therefore take a long position in 3 December contracts closing out the position on November 15.Problem 3.17.A corn farmer argues “I do not use futures co ntracts for hedging. My real risk is not the price of corn. It is that my whole crop gets wiped out by the weather.”Discuss this viewpoint. Should the farmer estimate his or her expected production of corn and hedge to try to lock in a price for expected production?If weather creates a significant uncertainty about the volume of corn that will be harvested, the farmer should not enter into short forward contracts to hedge the price risk on his or her expected production. The reason is as follows. Suppose that the weather is bad and the farmer’sproduction is lower than expected. Other farmers are likely to have been affected similarly. Corn production overall will be low and as a consequence the price of corn will be relatively high. The farmer’s problems arising from the bad harvest will be made worse by losses on the short futures position. This problem emphasizes the importance of looking at the big picture when hedging. The farmer is correct to question whether hedging price risk while ignoring other risks is a good strategy.Problem 3.18.On July 1, an investor holds 50,000 shares of a certain stock. The market price is $30 per share. The investor is interested in hedging against movements in the market over the next month and decides to use the September Mini S&P 500 futures contract. The index is currently 1,500 and one contract is for delivery of $50 times the index. The beta of the stock is 1.3. What strategy should the investor follow? Under what circumstances will it be profitable?A short position in 50000301326501500,⨯.⨯=⨯,contracts is required. It will be profitable if the stock outperforms the market in the sense that its return is greater than that predicted by the capital asset pricing model.Problem 3.19.Suppose that in Table 3.5 the company decides to use a hedge ratio of 1.5. How does the decision affect the way the hedge is implemented and the result?If the company uses a hedge ratio of 1.5 in Table 3.5 it would at each stage short 150 contracts. The gain from the futures contracts would be.1=⨯50.2$5570.1per barrel and the company would be $0.85 per barrel better off than with a hedge ratio of 1.Problem 3.20.A futures contract is used for hedging. Explain why the daily settlement of the contract can give rise to cash flow problems.Suppose that you enter into a short futures contract to hedge the sale of an asset in six months. If the price of the asset rises sharply during the six months, the futures price will also rise and you may get margin calls. The margin calls will lead to cash outflows. Eventually the cash outflows will be offset by the extra amount you get when you sell the asset, but there is a mismatch in the timing of the cash outflows and inflows. Your cash outflows occur earlier than your cash inflows.A similar situation could arise if you used a long position in a futures contract to hedge the purchase of an asset at a future time and the asset’s price fe ll sharply. An extreme example of what we are talking about here is provided by Metallgesellschaft (see Business Snapshot 3.2).Problem 3.21.An airline executive has argued: “There is no point in our using oil futures. There is just as much chance that the price of oil in the future will be less than the futures price as there is that it will be greater than this price.” Discuss the executive’s viewpoint.It may well be true that there is just as much chance that the price of oil in the future will be above the futures price as that it will be below the futures price. This means that the use of a futures contract for speculation would be like betting on whether a coin comes up heads or tails. But it might make sense for the airline to use futures for hedging rather than speculation. The futures contract then has the effect of reducing risks. It can be argued that an airline should not expose its shareholders to risks associated with the future price of oil when there are contracts available to hedge the risks.Problem 3.22.Suppose the one-year gold lease rate is 1.5% and the one-year risk-free rate is 5.0%. Both rates are compounded annually. Use the discussion in Business Snapshot 3.1 to calculate the maximum one-year forward price Goldman Sachs should quote for gold when the spot price is $1,200.Goldman Sachs can borrow 1 ounce of gold and sell it for $1200. It invests the $1,200 at 5% so that it becomes $1,260 at the end of the year. It must pay the lease rate of 1.5% on $1,200. This is $18 and leaves it with $1,242. It follows that if it agrees to buy the gold for less than $1,242 in one year it will make a profit.Problem 3.23.The expected return on the S&P 500 is 12% and the risk-free rate is 5%. What is the expected return on the investment with a beta of (a) 0.2, (b) 0.5, and (c) 1.4?a)00502(012005)0064.+.⨯.-.=. or 6.4%b)00505(012005)0085.+.⨯.-.=. or 8.5%c)00514(012005)0148.+.⨯.-.=. or 14.8%Further QuestionsProblem 3.24.It is now June. A company knows that it will sell 5,000 barrels of crude oil in September.It uses the October CME Group futures contract to hedge the price it will receive. Each contract is on 1,000 barrels of ‘‘light sweet crude.’’ What position should it take? What price risks is it still exposed to after taking the position?It should short five contracts. It has basis risk. It is exposed to the difference between the October futures price and the spot price of light sweet crude at the time it closes out its position in September. It is also possibly exposed to the difference between the spot price of light sweet crude and the spot price of the type of oil it is selling.Problem 3.25.Sixty futures contracts are used to hedge an exposure to the price of silver. Each futures contract is on 5,000 ounces of silver. At the time the hedge is closed out, the basis is $0.20per ounce. What is the effect of the bas is on the hedger’s financial position if (a) the traderis hedging the purchase of silver and (b) the trader is hedging the sale of silver?The excess of the spot over the futures at the time the hedge is closed out is $0.20 per ounce. If the trader is hedging the purchase of silver, the price paid is the futures price plus the basis. Thetrader therefore loses 60×5,000×$0.20=$60,000. If the trader is hedging the sales of silver, the price received is the futures price plus the basis. The trader therefore gains $60,000.Problem 3.26.A trader owns 55,000 units of a particular asset and decides to hedge the value of her position with futures contracts on another related asset. Each futures contract is on 5,000 units. The spot price of the asset that is owned is $28 and the standard deviation of the change in this price over the life of the hedge is estimated to be $0.43. The futures price of the related asset is $27 and the standard deviation of the change in this over the life of the hedge is $0.40. The coefficient of correlation between the spot price change and futures price change is 0.95.(a) What is the minimum variance hedge ratio?(b) Should the hedger take a long or short futures position?(c) What is the optimal number of futures contracts with no tailing of the hedge?(d) What is the optimal number of futures contracts with tailing of the hedge?(a) The minimum variance hedge ratio is 0.95×0.43/0.40=1.02125.(b) The hedger should take a short position.(c) The optimal number of contracts with no tailing is 1.02125×55,000/5,000=11.23 (or 11 when rounded to the nearest whole number)(d) The optimal number of contracts with tailing is 1.012125×(55,000×28)/(5,000×27)=11.65 (or 12 when rounded to the nearest whole number).Problem 3.27.A company wishes to hedge its exposure to a new fuel whose price changes have a 0.6correlation with gasoline futures price changes. The company will lose $1 million for each 1 cent increase in the price per gallon of the new fuel over the next three months. The new fuel's price change has a standard deviation that is 50% greater than price changes in gasoline futures prices. If gasoline futures are used to hedge the exposure what should the hedge ratio be? What is the company's exposure measured in gallons of the new fuel? What position measured in gallons should the company take in gasoline futures? How many gasoline futures contracts should be traded? Each contract is on 42,000 gallons.Equation (3.1) shows that the hedge ratio should be 0.6 × 1.5 = 0.9. The company has anexposure to the price of 100 million gallons of the new fuel. It should therefore take a position of 90 million gallons in gasoline futures. Each futures contract is on 42,000 gallons. The number of contracts required is therefore9.2142000,42000,000,90 or, rounding to the nearest whole number, 2143.Problem 3.28.A portfolio manager has maintained an actively managed portfolio with a beta of 0.2. During the last year the risk-free rate was 5% and equities performed very badly providing a return of−30%. The portfolio manage produced a return of −10% and claims that in the circumstances it was good. Discuss this claim.When the expected return on the market is −30% the expected return on a portfolio with a beta of 0.2 is0.05 + 0.2 × (−0.30 − 0.05) = −0.02or –2%. The actual return of –10% is worse than the expected return. The portfolio manager done 8% worse than a simple strategy of forming a portfolio that is 20% invested in an equity index and 80% invested in risk-free investments. (The manager has achieved an alpha of –8%!)Problem 3.29. (Excel file)The following table gives data on monthly changes in the spot price and the futures price for a certain commodity. Use the data to calculate a minimum variance hedge ratio.Denote i x and i y by the i -th observation on the change in the futures price and the change in the spot price respectively.096130i i x y =.=.∑∑222447423594i i x y =.=.∑∑2352i i x y =.∑ An estimate of F σ is05116=. An estimate of S σ is04933=.An estimate of ρ is0981=.The minimum variance hedge ratio is049330981094605116SF.=.⨯=..σρσProblem 3.30.It is July 16. A company has a portfolio of stocks worth $100 million. The beta of the portfolio is 1.2. The company would like to use the December futures contract on a stock index to change beta of the portfolio to 0.5 during the period July 16 to November 16. The index is currently1,000, and each contract is on $250 times the index.a)What position should the company take?b)Suppose that the company changes its mind and decides to increase the beta of theportfolio from 1.2 to 1.5. What position in futures contracts should it take?a)The company should short(1205)1000000001000250.-.⨯,,⨯or 280 contracts.b)The company should take a long position in(1512)1000000001000250.-.⨯,,⨯or 120 contracts.Problem 3.31. (Excel file)A fund manager has a portfolio worth $50 million with a beta of 0.87. The manager is concerned about the performance of the market over the next two months and plans to use three-month futures contracts on the S&P 500 to hedge the risk. The current level of the index is 1250, one contract is on 250 times the index, the risk-free rate is 6% per annum, and the dividend yield on the index is 3% per annum. The current 3 month futures price is 1259.a)What position should the fund manager take to eliminate all exposure to the market overthe next two months?b)Calculate the effect of your strategy on the fund manager’s returns if the level of themarket in two months is 1,000, 1,100, 1,200, 1,300, and 1,400. Assume that the one-month futures price is 0.25% higher than the index level at this time.a) The number of contracts the fund manager should short is 50000000087138201259250,,.⨯=.⨯ Rounding to the nearest whole number, 138 contracts should be shorted.b) The following table shows that the impact of the strategy. To illustrate the calculations in the table consider the first column. If the index in two months is 1,000, the futures price is 1000×1.0025. The gain on the short futures position is therefore(1259100250)2501388849250$-.⨯⨯=,,The return on the index is 3212⨯/=0.5% in the form of dividend and250125020%-/=- in the form of capital gains. The total return on the index istherefore 195%-.. The risk-free rate is 1% per two months. The return is therefore205%-. in excess of the risk-free rate. From the capital asset pricing model we expect the return on the portfolio to be 0872*******%%.⨯-.=-. in excess of the risk-free rate. The portfolio return is therefore 16835%-.. The loss on the portfolio is01683550000000.⨯,, or $8,417,500. When this is combined with the gain on the futures the total gain is $431,750.Problem 3.32.It is now October 2014. A company anticipates that it will purchase 1 million pounds of copper in each of February 2015, August 2015, February 2016, and August 2016. The company has decided to use the futures contracts traded in the COMEX division of the CME Group to hedge its risk. One contract is for the delivery of 25,000 pounds of copper. The initial margin is $2,000per contract a nd the maintenance margin is $1,500 per contract. The company’s policy is to hedge 80% of its exposure. Contracts with maturities up to 13 months into the future are considered to have sufficient liquidity to meet the company’s needs. Devise a hedging stra tegy for the company. (Do not make the “tailing” adjustment described in Section 3.4.)Assume the market prices (in cents per pound) today and at future dates are as follows. What is the impact of the strategy you propose on the price the company pays for copper? What is the initial margin requirement in October 2014? Is the company subject to any margin calls?To hedge the February 2015 purchase the company should take a long position in March 2015 contracts for the delivery of 800,000 pounds of copper. The total number of contracts required is 8000002500032,/,=. Similarly a long position in 32 September 2015 contracts is required to hedge the August 2015 purchase. For the February 2016 purchase the company could take a long position in 32 September 2015 contracts and roll them into March 2016 contracts during August 2015. (As an alternative, the company could hedge the February 2016 purchase by taking a long position in 32 March 2015 contracts and rolling them into March 2016 contracts.) For the August 2016 purchase the company could take a long position in 32 September 2015 and roll them into September 2016 contracts during August 2015.The strategy is therefore as followsOct. 2014: Enter into long position in 96 Sept. 2015 contractsEnter into a long position in 32 Mar. 2015 contractsFeb 2015: Close out 32 Mar. 2015 contractsAug 2015: Close out 96 Sept. 2015 contractsEnter into long position in 32 Mar. 2016 contractsEnter into long position in 32 Sept. 2016 contractsFeb 2016: Close out 32 Mar. 2016 contractsAug 2016: Close out 32 Sept. 2016 contractsWith the market prices shown the company pays.+.⨯.-.=.3690008(3723036910)37156for copper in February, 2015. It pays.+.⨯.-.=.3650008(3728036480)37140for copper in August 2015. As far as the February 2016 purchase is concerned, it loses 3728036480800.-.=. on the .-.=. on the September 2015 futures and gains 37670364301240 February 2016 futures. The net price paid is therefore.+.⨯.-.⨯.=.377000880008124037348.-.=. on theAs far as the August 2016 purchase is concerned, it loses 3728036480800.-.=. on the September 2016 futures. The September 2015 futures and gains 38820364202400net price paid is therefore388000880008240037520.+.⨯.-.⨯.=.The hedging strategy succeeds in keeping the price paid in the range 371.40 to 375.20.In October 2014 the initial margin requirement on the 128 contracts is 1282000$⨯, or $256,000. There is a margin call when the futures price drops by more than 2 cents. This happens to the March 2015 contract between October 2014 and February 2015, to the September 2015 contract between October 2014 and February 2015, and to the September 2015 contract between February 2015 and August 2015. (Under the plan above the March 2016 contract is not held between February 2015 and August 2015, but if it were there would be a margin call during this period.)。
E ( ST Se (T t var( ST S 2e2 (T t [e 2 2 2 (T t 1] Sincevar(ST E[(ST ] [ E(ST ] , it follows that E[(ST 2 ] var(ST [ E (ST ]2 so that E[( ST 2 ] S 2e2 (T t [e 2 2 (T t 1] S 2e2 (T t S 2e(2(T t In a risk-neutral world r so that ˆ [(S 2 ] S 2e(2 r 2 (T t E T Using risk-neutral valuation, the value of the derivative security at time t is ˆ [(S 2 ] e r (Tt E T S 2e(2 r 2 (T t r (T t e S 2e( r 2 (T t (b If: f S 2 e( r2 (T t 2 f S 2 (r 2 e( r (T t t 2 f 2 Se( r (T t S 2 2 f 2e( r (T t 2 S The left-hand side of the Black-Scholes–Merton differential equation is: 2 2 2 S 2 (r 2 e( r (T t 2rS 2e( r (T t2 S 2e( r (T t rS 2e( r 2 (T t rf Hence the Black-Scholes equation is satisfied. Problem 15.30. Consider an option on a non-dividend-paying stock when the stock price is $30, the exercise price is $29, the risk-free interest rate is 5% per annum, the volatility is 25% per annum, and the time to maturity is four months. a. What is the price of the option if it is a European call? b. What is the price of the option if it is an American call? c. What is the price of the option if it is a European put? d. Verify that put–call parity holds. In this case S0 30 , K 29 , r 005 , 025 and T4 12 d1 ln(30 29 (005 0252 2 4 12 04225 025 03333d2 ln(30 29 (005 0252 2 4 12 02782 025 03333 N (04225 06637 N (02782 06096 N (04225 03363 N (02782 03904 a. The European call price is 30 0663729e005412 06096 252 or $2.52. b. The American call price is the same as the European call price. It is $2.52. c. The European put price is29e005412 03904 30 03363 105 or $1.05. d. Put-call parity states that: p S c Ke rT In this case c 252 , S0 30 , K 29 , p105 and e rT 09835 and it is easy to verify that the relationship is satisfied, Problem 15.31. Assume that the stock in Problem 15.30 is due to go ex-dividend in 1.5 months. The expected dividend is 50 cents. a. What is the price of the option if it is aEuropean call? b. What is the price of the option if it is a European put? c. If the option is an American call, are there any circumstances when it will be exercised early? a. The present value of the dividend must be subtracted from the stock price. This gives a new stock price of: 30 05e0125005 295031 and ln(295031 29 (005 0252 2 03333 d1 03068 025 03333 ln(29503129 (005 0252 2 03333 d2 01625 025 03333 N (d1 06205 N (d2 05645 The price of the option is therefore 295031 06205 29e005412 05645 221 or $2.21. b. Because N (d103795 N (d2 04355 the value of the option when it is a European put is29e005412 04355 295031 03795 122or $1.22. c. If t1 denotes the time when the dividend is paid: K (1 e r (T t1 29(1 e00502083 03005 This is less than the dividend. Hence the option should be exercised immediately before the ex-dividend date for a sufficiently high value of the stock price. Problem 15.32. Consider an American call option when the stock price is $18, the exercise price is $20, the time to maturity is six months, the volatility is 30% per annum, and the risk-free interest rate is 10% per annum. Two equal dividends are expected during the life of the option, with ex-dividend dates at the end of two months and five months. Assume the dividends are 40 cents. Use Black’s approximation and the DerivaGem software to value the option. Suppose now that the dividend is D on each ex-dividend date. Use the results in the Appendix to determine how high D can be without the American option being exercised early. We first value the option assuming that it is not exercised early, we set the time to maturity equal to 0.5. There is a dividend of 0.4 in 2 months and 5 months. Other parameters are S0 18 , K 20 , r 10% , 30% . DerivaGem gives the price as 0.7947. We next value the option assuming that it is exercised at the five-month point just before the final dividend. DerivaGem gives the price as 0.7668. The price given by Black’s approximation is therefore 0.7947. (DerivaGem also shows that the American option price calculated using the binomial model with 100 time steps is 0.8243. It is never optimal to exercise theoption immediately before the first ex-dividend date when D1 K[1 e r (t2 t1 ] where D1 is the size of the first dividend, and t1 and t2 are the times of the first and second dividend respectively. Hence we must have: D1 20[1 e(01025 ] that is, D1 0494 It is never optimal to exercise the option immediately before the second ex-dividend date when: D2 K (1 e r (T t2 where D2 is the size of the second dividend. Hence we must have: D2 20(1 e0100833 that is, D2 0166 It follows that the dividend can be as high as 16.6 cents per share without the American option being worth more than the corresponding European option.。