兰州大学外科学2019年考博真题试卷
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:59.30 KB
- 文档页数:2

全国外科学考博试题总结名词解释:1.高钾血症;2.心脏按摩;3.中心静脉压;4.非少尿型急性肾功能衰竭;5.呼吸性酸中毒;6.肠源性感染;7.脓毒症(sepsis);8.Superinfection;9.ARDS;10.过继免疫疗法;11.CARS12.GVHR;13.SIADH;14.基因诊断;15.条件性感染;16.SIADH;17.SIRS;18. 预存式自体输血;19.休克抑制期;20. 痈;21.海绵状血管瘤;22.负氮平衡;23. 脑再灌注损伤;24.中厚皮片;25. 脓血症26.烧伤面积的中国九分法;27.systemic inflammatory response syndrome ;28.功能性细胞外液;29.心肺复苏;30.MSOF;31.ARF;32.ARDS;33.ICU;34.休克指数;35.MODS;36.条件感染;37.载体和重组质粒;38.MAC;39.导向复苏40.精准医疗论述题:1、较广泛的或剧烈的创伤性炎症对机体可引起哪些不利影响?(10 分)2、成人呼吸窘迫综合症的临床表现和分期(15 分)。
3.输血适应症4.外科抗菌药应用原则5.理想手术切口应具备的条件6.肾替代疗法应达到的指标7.DIC 的临床表现8.创伤治愈的分期、处理原则9.理想的肿瘤标志物应具备的特点10. 肾在体内酸碱平衡调节的机制11. 肠外营养的适应证和并发症12. 自体输血的方式和禁忌证13.试述肠内营养适应证14.试述自体输血的适应证与禁忌症15.分输血的种类和适应症16.肠源性感染的发病机制17.代谢性酸中毒的分型及常见原因18.创伤的检查与诊断步骤(13)19.脑复苏的现代观念及主要方法20.灭菌与消毒有何区别?21.高钾血症的原因和诊断处理?22.肠外营养有哪些常见并发症如何处理23.简述外科如何选择和使用抗菌药物?24..创伤后组织修复分几个阶段?简述其修复过程?25.创伤后组织修复过程分为哪几个阶段?各阶段的主要特点是什么?26.试述肿瘤浸润与转移过程中的相关因素?27.试述创伤的代谢变化及其临床意义?28.溶血反应的发病机理及病理变化?29.感染性休克病理生理变化过程中血流动力学改变有何特征?治疗要点是什么?30.全胃肠外营养的并发症31..肠细菌移位的发生机制32.腹部外科术后心力衰竭的紧急处理,应从哪些方面着手?33.有哪些腹部外科疾病与病毒感染有关?如何预防和治疗。

2019医学考博英语真题电子版part ⅡVocabulary (10%)Section ADirections: In this section all the sentences are incomplete. Four words or phrases, marked A B, C D, are given beneath each of them. You are to choose the word or phrase that best completes the sentences. Then, mark your answer on the ANSWER SHEET.1.appetite2.purition(水净化步骤)3.gratitude(感激烈士牺牲做贡献)4.surveyed(调查一堆人)5.futile(没有用)6.accidental7.vulnerable8.likewise9.in turn10.turn toSection BDirections: Each of the following sentences has a word or phrase underlined. There are four words or phrases beneath each sentence. Choose the word or phrase which can best keep the meaning of the original sentence if it is substituted for the underlined part. Mark youranswer on the ANSWER SHEET.1.disaster(灾难)2.malformation(畸形)3.increased4.immerse(好像是什么腿肿了浸泡在冰里)5.restrain6.Maintenance (保养维修什么东西)7.inactive8.tedious(好像是什么)monotonous(单调的乏味的)9.apparent(明显的划线的词是)distinct10.slender(说的女性什么追求苗条划线词是slim)。

去年在小木虫、百度文库、丁香园、爱爱医收集的博士入学考试外科学简答题,是好几个学校在一块的,北医、上交、协和、山大,301,华科的,受益颇大,当时下载也花了不少心血,总结费了不少时间,分享给大家,一份耕耘,一份收获,但愿好运常相随!!!考博问答题整理无菌术1.什么是无菌术?无菌术的内容包括那些?无菌术是针对微生物及感染途径所采取的一系列预防措施。
无菌术的内容包括灭菌、消毒法、操作规则及管理制度。
2.无菌术、灭菌?所谓灭菌就是杀灭一切活的微生物。
而消毒是指杀灭病原微生物和其他活动有害微生物,但不要求奢靡额和清除所有微生物3.常用的灭菌消毒法有:(1)高压蒸汽法。
(2)煮沸法。
(3)火烧法。
(4)药液浸泡法。
(5)甲醛蒸汽熏蒸法。
4.手术过程中的无菌原则(1)手术人员穿无菌手术衣和戴无菌手套之后,手不能接触背部、腰部以下和肩部以上部位,这些区域属于有菌地带;同样,也不要接触手术台边缘以下的布单。
(2)不可在手术人员的背后传递手术器械及用品。
坠落到无菌巾或手术台边以外的器械物品,不准拾回再用。
(3)手术中如手套破损或接触到有菌地方,应更换无菌手套。
如前臂或肘部触碰有菌地方,应更换无菌手术衣或加套无菌袖套。
如无菌巾、布单等物已被湿透,其无菌隔离作用不再完整,应加盖干的无菌布单。
(4)在手术过程中,同侧手术人员如需调换位置,一人应先退后一步,背对背地转身到达另一位置,以防触及对方背部不洁区。
(5)手术开始前要清点器械、敷料,手术结束时,检查胸、腹等体腔,待核对器械、敷料数无误后,才能关闭切口,以免异物遗留腔内产生严重后果。
(6)切口边缘应以无菌大纱布垫或手术巾遮盖,并用巾钳或缝线固定,仅显露手术切口。
术前手术区粘贴无菌塑料薄膜可达到相同目的。
(7)做皮肤切口以及缝合皮肤之前,需再消毒皮肤一次。
(8)切开空腔脏器前,要先用纱布垫保护周围组织,以防止或减少污染。
(9)参观手术的人员不可太靠近手术人员或站得太高,也不可经常在室内走动,以减少污染的机会。

历年考博外科题目总汇. .1、Tme及直肠系膜的概念2、胰头癌引起梗阻性黄疸的处理办法3、原位肝移植的手术方式与适应症胃癌的淋巴结清扫范围与手术根治程度分级乳腺癌的内分泌治疗的方法与药物乳癌治疗原则Sirs sepsis MODS的概念与相互关系营养不良的分类与支持的适应症直肠癌前切除术的主要并发症胰岛素瘤的定位诊断肝癌的综合治疗, 肝癌的治疗原则门脉高压上消化道出血的治疗MODS的发病机理MODS的治疗。
胆道出血的诊治慢性甲状腺炎的诊治SAP的治疗:胰腺炎的治疗Bismuth的分类;医源性胆管损伤按Bismuth分类:Ⅰ型:距肝总管起始部向远端2cm以上。
Ⅱ型:距肝总管起始部向远端2cm以内。
Ⅲ型:左右肝管汇合部。
Ⅳ型:左侧肝管或右侧肝管。
Ⅴ型:左右肝管分支处。
甲状腺癌的病理特点胃癌的治疗原则如何正确的对手术病人进行术前肝功能评估,以利手术顺利进行?Child 评分Child-1、Tme及直肠系膜的概念2、胰头癌引起梗阻性黄疸的处理办法3、原位肝移植的手术方式与适应症胃癌的淋巴结清扫范围与手术根治程度分级乳腺癌的内分泌治疗的方法与药物乳癌治疗原则Sirs sepsis MODS的概念与相互关系营养不良的分类与支持的适应症直肠癌前切除术的主要并发症胰岛素瘤的定位诊断肝癌的综合治疗, 肝癌的治疗原则门脉高压上消化道出血的治疗MODS的发病机理MODS的治疗。
胆道出血的诊治慢性甲状腺炎的诊治SAP的治疗:胰腺炎的治疗Bismuth的分类;医源性胆管损伤按Bismuth分类:Ⅰ型:距肝总管起始部向远端2cm以上。
Ⅱ型:距肝总管起始部向远端2cm以内。
Ⅲ型:左右肝管汇合部。
Ⅳ型:左侧肝管或右侧肝管。
Ⅴ型:左右肝管分支处。
甲状腺癌的病理特点胃癌的治疗原则如何正确的对手术病人进行术前肝功能评估,以利手术顺利进行?Child 评分Child:二问答1 PMC(甲状腺乳头状微小腺癌)及其目前治疗原则2 Budd-Chiari syndrome的分型及手术治疗方法布加综合征由各种原因所致肝静脉和其开口以上段下腔静脉阻塞性病变引起的常伴有下腔静脉高压为特点的一种肝后门脉高压症。


考博外科学外科学总论(共50分)⼀名词解释:1.基因诊断2.⾼温灭菌法3.NHSTR4.GHTRS5.MODS⼆简答题:1 简述外科疾病的分类2 外科⼿术进⾏中的⽆菌原则3 感染性休克的治疗三问答题低渗性缺⽔的定义病因临床表现诊断治疗普外科各论(50分)⼀名词解释mastopathy 原发性腹膜炎strangulated hernia (狂晕刚意识到答成绞窄性肠梗阻了)abdominal compartment syndrome 第五个忘了⾼选择⾏迷⾛神经切断术(英⽂)⼆问答题甲状腺功能亢进症的病因术前术中注意事项⼿术适应症⼿术禁忌症术后常见并发症及处理原则原发性肝癌的病因病理临床表现诊断和鉴别诊断治疗2007年第⼆军医⼤学考博普通外科学⼀、多选题(12题,每题1分)1、腹腔镜⼿术禁忌:2、能叩诊出移动性浊⾳的腹腔积液:A、100ml B、200ml C、300ml D、400ml E、⼤于500ml3、急性胰腺炎⾎淀粉酶的变化:4、胆囊癌最佳的诊断⽅法:B超、CT、ERCP、?、?5、⼩⼉肠扭转病例6、肝脓肿病例7、以下胃、⼗⼆指肠穿孔描述不正确的是:⼆、填空题(8分)1、影响胃癌预后的因素有:(7空)2、下消化道出⾎的诊断⽅法有:(5空)3、下肢深静脉栓塞分为四型:_____型(4空)三、名词解释(6分,每题2分)1、buerger病2、charcot 综合征3、TME四、问答题1、家族性结肠息⾁病的发病原理、诊断、⼿术⽅式、术后随访原则?(20分)2、甲亢术后并发症及处理?(24分)3、肠梗阻按梗阻原因的分类;肠梗阻的治疗原则以及⾮⼿术治疗⽅法?(30分)第三军医⼤学2013博⼠普外专业⼀、名词解释1、richer疝2、倾倒综合征(英⽂)3、布加综合征(英⽂)4、⼆、简答题1、乳腺癌根治术切除范围2、胰腺癌⼿术切除范围3、简述直肠癌超低位保肛术4、chiold分级及其临床意义三、问答题1、急性梗阻性黄疸治疗原则2、论述胃癌外科治疗的最新进展2013南京医科⼤学普外科学(总论+普外)考博真题回忆版简答4分*61、创伤组织修补基本过程?2、30秒内确定⼼搏骤停的⽅法?3、输⾎后常见并发症?4、低钾的常见病因?5、营养⽀持⽅法选择原则?6、⼿术中的⽆菌原则?问答19分*41、胰腺假性囊肿的⼿术指征、⽅式、要点?2、甲状腺⼿术并发症及治疗?3、腹膜后⼗⼆指肠破裂诊断依据及治疗?4、完善的科研设计标志有哪些?第三军医⼤学2013年外科专业基础之⼈体解剖真题名词解释:胸⾻⾓纵隔膜迷路动脉韧带肺段简答脑屏障的主要特点喉的结构,运动及功能的关系胆汁的产⽣,排出的主要特点问答⽪质核束的主要特点内脏传导通路的主要特点迷⾛神经的主要特点腰丛的主要特点2013中⼭⼤学博⼠⽣⼊学考试(普外)1糖⽪质激素外科感染性休克2糖尿病围术期准备要点3开放⽓胸处理原则4影像学在泌尿系结⽯的诊断应⽤5胃癌腹腔镜禁忌6胆管囊性扩张的分型7下肢静脉体格检查名称8外科真菌感染因素和抗真菌药物9切⼝裂开预防10⿊⾊素瘤的临床表现11CEA.AFP.CA199.CA125.PSA,中⽂名称及诊断价值12门脉⾼压⾮⼿术治疗及贲门⾎管离断理由13 低渗性缺⽔的原因14乳腺癌分⼦分型及治疗建议15胃癌根治原则,根治划分,远端胃癌根治切除范围16慢性胰腺炎⼿术指征,⼿术原则,⼿术⽅式。

Listening :无Vocabulary :Section A31. According to the Geneva ______no prisoners of war shall be subject to abuse.A. CustomsB. CongressesC. ConventionsD. Routines 32. Environmental officials insist that something be done to ______acid rain.A. curbB. sueC. detoxifyD. condemn33. It is impossible to say how it will take place, because it will happen______, and itwill not be a long process.A. spontaneouslyB. simultaneouslyC. principallyD. approximately34. Diabetes is one of the most______ and potentially dangerous disease in the world.A. crucialB. virulentC. colossalD. prevalent35. Rheumatologist advises that those with ongoing aches and pains first seek medicalhelp to ______the problem.A. affiliateB. alleviateC. aggravateD. accelerate36. How is it possible that such______ deception has come to take place right underour noses?A. obviousB. significantC. necessaryD. widespread37. Now a paper in Science argues that organic chemicals in the rock come mostly from______on earth rather than bacteria on Mars.A. configurationB. constitutionC. condemnationD. contamination38. Chronic high-dose intake of vitamin A has been shown to have ______effects onbones.A. adverseB. prevalentC. instantD. purposeful39. Generally, vaccine makers _____ the virus in fertilized chicken eggs in a processthat can take four to six months.A. penetrateB. designateC. generateD. exaggerate40. We are much quicker to respond, and we respond far too quickly by giving ______to our anger.A. ventB. impulseC. temperD. offenceSection B41. The patient's condition has worsened since last night.A. improvedB. returnedC. deterioratedD. changed42. Beijing Television-Station Transmitting Tower really looks magnificent at nightwhen it ’s lit up.A. decoratedB. illustratedC. illuminatedD. entertained43. Attempts to restrict parking in the city centre have further aggravated the problemof traffic congestion.A. amelioratedB. aggregatedC. deterioratedD. duplicated44. The applications of genetic engineering are abundant and choosing oneappropriate for this case can be rather difficult.A. sufficientB. plentifulC. adequateD. countable45. The defect occurs in the first eight weeks of pregnancy, though no one understandswhy.A. deficitB. deviationC. draw backD. discrepancy46. He has been on hormone alternate therapy for four years and looks fantastic.A. successorB. replacementC. surrogateD. choice47. It had over 2,000 apartment complexes, a great market, a large number ofindustrial workshops, an administrative center, a number of massive religious edifices,and a regular grid pattern of streets and buildings.A. ancientB. carefullyC. very largeD. carefully protected48. When patients spend extended periods in hospital, they tend to become overlydependent and lose interest in taking care of themselves.A. extremelyB. exclusivelyC. exactlyD. explicitly49. The anxious parent was vigilant over the injured child in spite of a full array ofemergency room of doctors and nurses.A. preoccupiedB. unwaryC. watchfulD. dozing50. The doctor vacillated so frequently on disease-preventiontechniques that hiscolleagues accused him of inconsistency.A. waveredB. instigatedC. experimentedD. reliedClozeWe spend a lot of time looking at the eyes of others for social 51 —it helpsus understand a person ’emotions, and make decisions about how to respond to them. We also know that adults avoid eye contact when anxious. But researchers have knownfar 52 about eye gazing patterns in children.According to new research by Kalina Michalska, assistant professor of psychologyat the University of California, Riverside, we now, know that anxious children tend toavoid making eye contact, and this has consequences for how they experience fear. The53 and less frequently they look at the eyes of others, the more likely they are to beafraid of them, even when there may be no reason to be. Her study, “Anxiety Sympand Children's Eye Gaze During Fear Leaming”w,as published in the journal TheJournal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry."Looking at someone ’s eyes helps us understand whether a person is feeling sad, angry, fearful, or surprised. As adults, we then make decisions about how to respondand what to do next. But, we know much less about eye patterns in children —so,understanding those patterns can help us learn more about the development of sociallearning, ”Michalska said.Michalska and the team of researchersshowed 82 children, 9 to 13 years old,images of two women ’s faces on a computer screen. The computer was equipped withan eye tracking device that allowed them to measure54 on the screen children werelooking, and for how long. The participants were originally shown each of the twowomen a total of four times. Next, one of the images was55 with a loud scream anda fearful expression, and the other one was not. At the end, children saw both facesagain without any sound or scream.The following three conclusions can be drawn from the study:1. All children spent more time looking at the eyes of a face that was paired withthe loud scream t han the face that was not paired with the scream, 56 they payattention to potential threats even in the absence of outward cues.2. Children who were more anxious avoided eye contact during all three phases of the experiment, for both kinds of faces. This had consequences for how afraid they wereof the faces.3. The more children avoided eye conta;cthe more afraid they were 57 the faces.The conclusions suggest that children spend more time looking at the eyes of aface when previously paired with something frightening suggesting they pay moreattention to potentially threatening information as a way to learn more about thesituation and plan what to do next.However, anxious children tend to avoid making eye contact, which leads togreater 58 experience. Even though avoiding eye contact may reduce anxiety59 , the study finds that — over time — children may be m i s s6i n0g_ o i m u p t ortantsocial information. This includes that a person may no longer be threatening or scary,and yet the child continues feeling fearful of that person.51. A. environment B. cues C. relations D. answers52. A. less B. more C. enough D. beyond53. A. longer B. more anxious C. shorter D. more54. A. where B. when C. how D. what55. A. followed B. recorded C. paired D. marked56. A. suggest B. suggesting C. suggests D. being suggested57. A. to B. of C.at D. about58. A. fear B. surprise C. sad D. angry59. A. in the long run B. for a long timeC. in the short timeD. in a long time60. A. with B. without C. of D. onReading ComprehensionPassage OneThe British psychoanalyst John Bowlby maintains that separation from the parentsduring the sensitive “attachment p”e riod from birth to three may scar a child ’s personality and predispose to emotional problems in later life.Some people have drawn the conclusion from Bowlby' s work that children shouldnot be subjected to day care before the age of three because of the parental separationit entails, and many people do believe this. It has been argued that an infant under threewho is cared for outside the home may suffer because of the separation from his parents. But there are also arguments against such a strong conclusion.But traditional societies are so different from modem societies that comparisonsbased on just one factor are hard to interpret. Firstly, anthropologists point out that theinsulated love affair between children and parents found in modem societies does notusually exist in traditional societies. For example, in some tribal societies, such as theNgoni, the father and mother of a child did not rear their infant alone —far from i Certainty, Bowlby ’s analysis raises the possibilities that early day care had delayedeffects. The possibility that such care might lead to, say, more mental illness or crime15 or 20 years later can only explored by the use of statistics. However, statisticalstudies of this kind have not yet been carried out, and even if they were, the resultswould certainly be complicated and controversial. Secondly, common sense tells us that day care would not be so widespread today if parents, care-takers found children hadproblems with it. Thirdly, in the last decade, t here have been a number of careful American studies of children in day care, and they have uniformly reported that care had a neutral or slightly positive effect on children ’s development.Whatever the long-term effects, parents sometimes find the immediate effectsdifficult to deal with. Children under three are likely to protest at leaving their parentsand show unhappiness. At the age of three or three and a half almost all children findthe transition to nursery eas,yand this is undoubtedly why more and more parents make use of child care at this time. The matter, then, is far from clear-cut, though experienceand available evidence indicate early care is reasonable for infants.61. According to the passage, the consequence of parental separation________.A. still needs more statistical studiesB. has been found negative is more seriousC. is obviousD. in modem times62. The author thinks that John Bowlby ’s concern___________.A. is relevant and justifiableB. is too strong to RelieveC. is utterly groundlessD. has something that deserve our attention63. What ’s the result of American studies of children in day care in the last decade?A. The children ’s unhappiness and protest was due to the day care the children received.B. The bad effects of parental separation were hard to deal with.C. The effect of day care was not necessarily negative on children ’s development.D. Early care was reasonable for babies since it ’p sracti c ed by so many peoplenowadays.64. According to the passage, which of the following is probably a reason forparents to send their children under three to day care?A. They don ’t know about day care ’s negative effect.B. They are too busy to care fortheir children.C. They want their children to be independent as early as possible.D. They want to facilitate their children to adapt to nursery at the age of about three.65. What ’s the author ’s attitude to people who have drawn the conclusion fromBowlby’s work that children should not be subjected to day care before the age ofthree?A. He supports most of their belief because Bowlby's proposition is well-grounded.B. He is sympathetic for them, for he thinks they have been misled by Bowlby.C. He doesn't totally agree with them, since the long-term effect of day care still needsfurther study.D. He doesn't quite understand them, as they are contradictory in themselves.Passage TwoBy the end of this century, the average world temperature is expected to increasebetween one and four degrees, with widespread effects on rainfall, sea levels and animalhabitats. But in the Arctic, where the effects of climate change are most intense, the risein temperature could be twice as much.Understanding how Arctic warming will affect the people, animals, plant andmarine life and economic activity in Canada’N sort h are important to the country's future, says Kent Moore, an atmospheric physicist at University of Toronto Mississaugawho is participating in a long-term, international study of the marine ecosystem alongthe Beaufort Sea, from Alaska to the Mackenzie delta.The study will add to our knowledge of everything from the extent of sea ice inthe region to how fish stocks will change to which areas could become targets for oiland gas exploration to the impact on the indigenous people who call this part of thecountry home.Moore, who has worked in the Arctic for more than 20 years, says his research hasalready found that thinning sea ice and changes in wind patterns are causing animportant change in the marine food chain: phytoplankton(淳游植物) is blooming two to three weeks earlier. Manyanimals time their annual migration to the Arctic forwhen food is plentiful, and have not adapted to the earlier bloom. " ' Animals' behaviorcan evolve over a long time, but these climate changes are happening in the space of adecade, r ather than hundreds of years, ”says Moore, " Animals can't change theirbehavior that quickly. ”A warmer Arctic is expected to have important effects on human activity in theregion, as the Northwest Passage becomes navigable during the summer, and resourceextraction becomes more feasible. Information gained from the study will helpgovernment, industry and communities make decisions about resource management,economic development and environmental protection.Moore says the study — which involves Canadian, American and Europeanresearchersand government agencies will also use a novel technology to gatheratmospheric data: remotely piloted drones. "The drones have the capability of a largeresearch aircraft,and they ’re easier to deploy, ” he says, showing the researchers to gather information on a more regular basis than they would be able to with pilotedaircraft.66. By the end of this century, according to the author, global warming will ______.A. start to bring about extreme weather events to humans and animalsB. increase the average world temperature by four degreesC. cause more damages to the whole world than expectedD. affect the Arctic more than any other parts of the earth67. To help understand the destructive mechanism of Arctic warming, as indicatedby the passage, the international study ______.A. is conducted with every single discipline of University of TorontoB. pioneers in pursuing the widespread effects of climate changeC. involves so many countries for different investigationsD. is intended to deal with various aspects in research68. When he ways, “Animals can ’t change their behavior that quickly, ”what doesMoore mean by that quickly?A. The migration of the animals to the Arctic.B. The widespread effects of global warming.C. The rate of the climate change in the Arctic.D. The phytoplankton within the marine ecosystem.69. According to the author, to carry out proper human activities in theArctic______.A. becomes more difficult than ever beforeB. is likely to build a novel economy in the regionC. will surely lower the average world temperatureD. needs the research-based supporting information70. With the drones deployed, as Moore predicts, the researchers will _______.A. involve more collaborating countries than they do nowB. get more data to be required for their researchC. use more novel technologies in researchD. conduct their research at a regular basisPassage ThreeHaving too much caffeine during pregnancy may impair baby ’s liver development and increase the risk of liver disease in adulthood, according to a study published in theJournal of Endocrinology. Pregnant rats given caffeine had offspring with lower birth weights, altered growth and stress hormonelevels and impaired liver development. Thestudy findings indicate that consumption of caffeine equivalent to 2-3 cups of coffee may alter stress and growth hormone levels in a manner that can impair growth and development, and increase the risk of liver disease in adulthood.Previous studies have indicated that prenatal caffeine intake of 300 mg/day ormore in women, which is approximately 2 to 3 cups coffee per day, can result in lower birth weights of their children. Animalstudies have further suggestedthat prenatalcaffeine consumption may have more detrimental long-term effects on liverdevelopment with an increased susceptibility to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, adebilitating condition normally associated w ith obesity and diabetes. However, theunderlying link between prenatal caffeine exposure and impaired liver developmentremains poorly understood. A better understanding of how caffeine mediates theseeffects could help prevent these health issues in people in the future.In this study, Prof Hui Wang and colleagues at Wuhan University in China,investigated the effects of low (equivalent to 2-3 cups of coffee) and high dose(equivalent of 6-9 cups of coffee) caffeine, given to pregnant rats, on liver function andhormone levels of their offspring. Offspring exposed to prenatal caffeine had lower levels of the liver hormone, insulin likegrowth factor (IGF-1), and higher levels of thestress hormone, corticosteroid at birth. However, liver development after birth showed a compensatory 'catch up' phase, characterised by increased levels of IGF-1, which is important for growth.Dr. Yinxian Wen, study co-author, says, “Our results indicate that prenatal caffeine causes an excess of stress hormone activity in the mother, which inhibits IGF-1 activityfor liver development before birth. However, compensatory mechanisms do occur after birth to accelerate growth and restore normalliver function, as IGF-1 activity increasesand stress hormone signalling decreases. The increased risk of fatty liver disease causedby prenatal caffeine exposure is most likely a consequence of this enhanced,compensatory postnatal IGF-1 activity. ”These findings not only confirm that prenatal caffeine exposure leads to lowerbirth weight and impaired liver development before birth but also expand our currentunderstanding of the hormonal changes underlying these changes and suggest thepotential mechanism for increased risk of liver disease in the future. However, theseanimal findings need to be confirmed in humans.Dr. Wen comments, "Our work suggeststhat prenatal caffeine is not good for babies and although these findingsstill need to be confirmed in people, I wouldrecommend that women avoid caffeine during pregnancy."71. Which of the following is NOT the problem of baby rats of pregnant rats givencaffeine?A. Lower birth weight.B. Smaller stress.C. Liver development problem.D. Growth problem.72. If a pregnant woman takes 3 cups of coffee, what will probably happen?A. Her weight will get lower and lower.B. The weight of her baby will get lower and lower.C. She will suffer from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a long run.D. Her baby will be more vulnerable to obesity and diabetes because of liver problem.73. Which of following is not correct according to the passage?A. A better understanding of the relationship between caffeine and effects has beenachieved.B. 4-5 cups of coffee could be categorized as medium-dose intake.C. Liver development problem may be remedied after birth by increased growth factor.D. The study is mainly conducted on the rats instead of human.74. What is the relationship between stress hormone and liver development whentaking in prenatal caffeine?A. Lower stress hormone, lower birth weight before birth.B. Higher stress hormone, lower growth hormone before birth.C. Higher stress hormone, more accelerated growth of weight after birth.D. Lower stress hormone, less accelerated growth of liver after birth.75. What can be the best summary of the last paragraph?A. The research hasn ’t been done on humans so pregnant women can ignore the results.B. The compensatory mechanism for liver growth makes prenatal caffeine intake safe.C. Experts suggest pregnant women should still avoid caffeine.D. We have known enough about the hormone changes underlying the healthPassage FourThe bizarre antics of sleepwalkers have puzzled police, perplexed scientists, and fascinated writers for centuries. There is an endless supply of stories about sleepwalkers.Persons have been said to climb on steep roofs, solve mathematical problems, composemusic, walk through plate-glass windows, and commit murder in their sleepHow many of these stories have a basis in fact, and how many are pure fakery?No one knows, but if some of the most sensational stories should be taken with a barrelof salt, others are a matter of record.In Revere, Massachusetts, a hundred policemen combed a waterfrontneighborhood for a lost boy who left his home in his sleep and woke up five hours lateron a strange sofa in a strange living room, with no idea how he had got there.There is an early medical record of a somnambulist who wrote a novel in his sleep.And the great French writer V oltaire knew a sleepwalker who once got out of bed,dressed himself, made a polite bow, danced a minuet, and then undressed and went backto bed.At the University of Iowa, a student was reported to have the habit of getting upin the middle of the night and walking three-quarters of a mile to the Iowa River. He would take a swim and then go back tohis room to bed.The world's champion sleepwalker was supposed to have been an Indian, PanditRamrakha, who walked sixteen miles along a dangerous road without realizing that hehad left his bed. Second in line for the title is probably either a Vienna housewife or a British farmer. The woman did all her shopping on busy streets in her sleep. The farmer,in his sleep, visited a veterinarian miles away.The leading expert on sleep in America claims that he has never seen a sleepwalker.He is Dr. Nathaniel Kleitman, a physiologist at the University of Chicago. He is said toknow more about sleep than any other living man, and during the last thirty-five yearshad lost a lot of sleep watching people sleep. Says he, "Of course, I know that there are sleepwalkers becauseI have read about them in the newspapers. B ut none of mysleepers ever walked, and if I were to advertise for sleepwalkers for an experiment, Idoubt that I'd get many takers."Sleepwalking, nevertheless, is a scientific reality. Like hypnosis, it is one of thosedramatic, eerie, awe-inspiring phenomena that sometimes border on the fantastic. Itlends itself to controversy and misconceptions, what is certain about sleepwalking isthat it is a symptom of emotional disturbance, and that the only way to cure it is to remove the worries and anxieties that cause it. Doctors say that somnambulism is muchmore common than is generally supposed.Some have estimated that there are fourmillion somnambulists in the United States. Others set the figure even higher. Manysleepwalkers do not seek help and so are never put on record, which means that anaccurate count can never be made.The simplest explanation of sleepwalking is that it is the acting out of a vividdream. The dream usually comes from guilt, worry, nervousness, o r some otheremotional conflict. The classic sleepwalker is Shakespeare ’L asdy Macbeth. Hernightly wanderings were caused by her guilty conscience at having committed murder. Shakespeare said of her, “The eyes are open but their sense is shut. ”The age-old question is: Is the sleepwalker actually awake or asleep. Scientists have decided that he is about half-and-half. Like Lady Macbeth, he has weightyproblems on his mind. Dr. Zeida Teplitz, who made a ten-year study of the subject, says, “Some people stay awake all night worrying about t heir problems. The sleepwalker thrashes them out in his sleep. He is awake in the muscular area, partially asleep in the sensory area." In other words, a person can walk in his sleep, move around, and do other things, but he does not think about what he is doing.76. The second sentence in the second paragraph means that_________.A. no one knows, but certainly all the sleep walking stories have something incredibleB. the sleepwalking stories are like salt adding flavor to people ’s lifeC. sleepwalking stories that are most fantastic should be sorted out from ordinary storiesD. the most fantastic sleepwalking stories may be just fictions, yet there are stilltruthfully recorded stories77. ________was supposed to be the world's champion sleepwalker.A. The student habitually walked to the Iowa River and swam in his sleepB. The man danced a minuet in his sleepC. The man walker sixteen miles along a dangerous roadD. The boy walked five hours in his sleep78. Sleepwalking is the result of ______ according to the passage.A. emotional disorderB. a vivid dreamC. lack of sleep and great anxietyD. insanity79. Dr. Zeida Teplitz seemed to_________.A. agree that sleepwalking sometimes leads to dangerous actsB. conclude that sleepwalkers are awake in their sensory areaC. disagree with the belief that sleep walkers are immune to injuryD. think that sleepwalking can turn into madness80. The writer makes it obvious that_________.A. sleepwalkers are often awakened by dangersB. most sleepwalkers can find ways to avoid self-injuryC. it is important to find out the underlying cause of sleepwalkingD. sleepwalking is actually a kind of hypnosisPassage FiveBeyond the basic animal instincts to seek food and avoid pain, Freud identifiedtwo sources of psychic energy, which he called "drives ”: aggression and libido. The keto his theory is that these were unconscious drives, shaping our behavior without themediation of our waking minds; they surface, heavily disguised, only in our dreams.The work of the past half-century in psychology and neuroscience has been to downplaythe role of unconscious universal drives, focusing instead on rational processesinconscious life. But researchers have found evidence that Freud s drives really do exist,and they have their roots in the limbic system, a primitive part of the brain that operatesmostly below the horizon of consciousness.Now more commonly referred to as emotions, the modem suite of drives comprises five: rage, panic, separation distress,lust and a variation on libido sometimes called seeking.The seeking drive is proving a particularly fruitful subject for researchers.Although like the others it originates in the limbic system, it also involves parts of theforebrain, the seat of higher mental functions. In the 1980s, Jaak Panksepp, aneurobiologist at Bowling Green State University in Ohio, became interested in a placenear the cortex known as the ventraltegmental area, which in humans lies just abovethe hairline. When Panksepp stimulated the corresponding region in a mouse, theanimal would sniff the air and walk around, as though it were looking for something.Was it hungry? No. The mouse would walk right by a plate of food, or for that matterany other object Panksepp could think of. This brain tissue seemed to cause a generaldesire for something new. “What I was seeing, ” he says, “was the urge to do stuff.Panksepp called this seeking.To neuropsychologist Mark Solms of University College in London, that soundsvery much like libido. “Freud needed some sort of general, appetitive desire to seekpleasure in the world of objects, ” says Solms. "Panksepp discovered as a neuroscientist what Freud discovered psychologically. ” Solms studied the same region of the brain forhis work on dreams. Since the 1970s, neurologists have known that dreaming takesplace during a particular form of sleep known as REM — rapid eye movement — whichis associated with a primitive part of the brain known as the pons. Accordingly, they regarded dreaming as a low-level phenomenon of no great psychological interest. WhenSolms looked into it, though, it turned out that the key structure involved in dreaming was actually the ventral tegmental, the same structure that Panksepp had identified as the seat of the “”s e e m k i o n t g i o n. Dreams, it seemed, originate with the libid—o which is just what Freud had believed.Freud's psychological map may have been flawed in many ways, but it alsohappensto be the most coherent and, from the standpoint of individual experience,meaningful theory of the mind. “Freud should be placed in the same category as Darwin,who lived before the discovery of genes, ” says Panksepp. “Freud gave us a vision ofmental apparatus. We need to talk about it, develop it, test it. ” Perhaps it ’sof proving Freud wrong or right, but of finishing the job.。

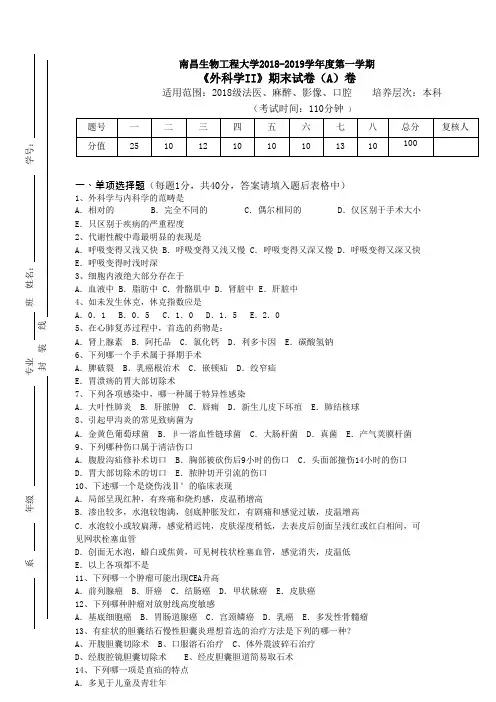
《外科学II》期末试卷(A)卷适用范围:2018级法医、麻醉、影像、口腔培养层次:本科(考试时间:110分钟)一、单项选择题(每题1分,共40分,答案请填入题后表格中)1、外科学与内科学的范畴是A.相对的B.完全不同的C.偶尔相同的D.仅区别于手术大小E.只区别于疾病的严重程度2、代谢性酸中毒最明显的表现是A.呼吸变得又浅又快 B.呼吸变得又浅又慢 C.呼吸变得又深又慢 D.呼吸变得又深又快E.呼吸变得时浅时深3、细胞内液绝大部分存在于A.血液中 B.脂肪中 C.骨骼肌中 D.肾脏中 E.肝脏中4、如未发生休克,休克指数应是A.0.1 B.0.5 C.1.0 D.1.5 E.2.05、在心肺复苏过程中,首选的药物是:A.肾上腺素B.阿托品C.氯化钙D.利多卡因E.碳酸氢钠6、下列哪一个手术属于择期手术A.脾破裂B.乳癌根治术C.嵌顿疝D.绞窄疝E.胃溃疡的胃大部切除术7、下列各项感染中,哪一种属于特异性感染A.大叶性肺炎 B. 肝脓肿C.唇痈D.新生儿皮下坏疽E.肺结核球8、引起甲沟炎的常见致病菌为A.金黄色葡萄球菌B.β—溶血性链球菌C.大肠杆菌D.真菌E.产气荚膜杆菌9、下列哪种伤口属于清洁伤口A.腹股沟疝修补术切口B.胸部被砍伤后9小时的伤口C.头面部撞伤14小时的伤口D.胃大部切除术的切口E.脓肿切开引流的伤口10、下述哪一个是烧伤浅Ⅱ°的临床表现A.局部呈现红肿,有疼痛和烧灼感,皮温稍增高B.渗出较多,水泡较饱满,创底肿胀发红,有剧痛和感觉过敏,皮温增高C.水泡较小或较扁薄,感觉稍迟钝,皮肤湿度稍低,去表皮后创面呈浅红或红白相间,可见网状栓塞血管D.创面无水泡,蜡白或焦黄,可见树枝状栓塞血管,感觉消失,皮温低E.以上各项都不是11、下列哪一个肿瘤可能出现CEA升高A.前列腺癌B.肝癌C.结肠癌D.甲状脉癌E.皮肤癌12、下列哪种肿瘤对放射线高度敏感A.基底细胞癌B.胃肠道腺癌C.宫颈鳞癌D.乳癌E.多发性骨髓瘤13、有症状的胆囊结石慢性胆囊炎理想首选的治疗方法是下列的哪一种?A、开腹胆囊切除术B、口服溶石治疗C、体外震波碎石治疗D、经腹腔镜胆囊切除术E、经皮胆囊胆道简易取石术14、下列哪一项是直疝的特点A.多见于儿童及青壮年B.经腹股沟管突出,可进阴囊C.疝块呈椭圆或梨形,上部呈蒂柄形D.疝囊颈在腹壁下动脉内侧E.较易嵌顿15、腹部最易受损的内脏是A.肝脏B.十二指肠C.横结肠D.脾E.肾脏16、微小胃癌是指A.癌灶的直径<2cmk B.癌灶的直径<1.5cm C.癌灶的直径<1cm D.癌灶的直径<8mmnE.癌灶的直径<5mm17、下述哪一种是血运性肠梗阻A.寄生虫堵塞肠腔引起的肠梗阻B.肠系膜血管栓塞引起的肠梗阻C.肿瘤压迫引起的肠梗阻D.先天性肠道闭锁引起的肠梗阻E.由于肠管痉挛引起的肠梗阻18、小儿急性阑尾炎的特点是A.大网膜发育不全,且盲肠位置较高,病情不同于成人B.病情发展快且重,早期即出现高热、呕吐等C.右下腹体征不明显、很少有局部的明显压痛和肌紧张D.穿孔率可达30%,并发症及死亡率也比较高E.以上均是19、直肠肛管周围脓肿中哪一种是临床上最常见的A.坐骨肛管间隙脓肿B.骨盆直肠间隙脓肿C.肛管括约肌间隙脓肿D.肛门周围脓肿E.直肠后间隙脓肿20、在肝、胆疾病的诊断中,被认为是首选诊断方法的是A.B型超声检查B.腹部x线平片C.内镜逆行胰胆管造影D.低张性十二指肠检查E.核素显像扫描21、前列腺增生的患者,尿流梗阻的程度与下列哪个因素关系最密切A.前列腺增生的程度B.前列腺增生持续的时间C.前列腺增生部分的位置D.睾硐、双氢睾硐及雌激素的多寡E.前列腺增生结节的种类22、下列哪一项是骨折的早期并发症A.脂肪栓塞B.坠积性肺炎C.创伤性关节炎D.关节僵直E.缺血性骨坏死23、骨折的专有体征是A.压痛与疼痛、局部肿脓和淤斑、功能障碍B.疼痛与压痛、局部肿胀与淤斑、骨擦音或骨擦感C.畸形、反常活动、骨擦音或骨擦感D.畸形、局部肿胀与淤斑、骨擦音或骨擦感E.反常活动、局部肿胀和淤斑、骨擦音或骨擦感24、Codman三角是下项哪种骨肿瘤的特点A.骨巨细胞瘤B.骨肉瘤C.骨软骨瘤D.骨纤维内瘤E.尤文肉瘤25、在各种直肠癌手术中,术后控制排便功能最为满意的是A.Hartmann手术B.拉下式直肠癌切除术C.乙状结肠造口术D.Miles手术E.Dixon手术26、在发生骨转移的肿瘤中,原发病灶以下列哪项为最多见A.前列腺癌B.甲状腺癌C.乳腺癌D.胃肠道恶性肿瘤E.肾癌27、下列哪类甲状腺肿患者不宜行甲状腺大部切除术A.妊娠期的甲状腺肿B.巨大甲状腺肿影响工作和生活者C.结节性甲状腺肿继发有功能亢进者D.肿大的甲状腺压迫气管、食管或喉迫神经而引进临床症状者E.胸骨后甲状腺肿28、早期食管癌的x线表现不包括A.食管下端呈光滑的鸟嘴状狭窄B.局限性粘膜皱襞增粗和断裂C.局限性管壁僵硬D.局限、小的充盈缺损E.小龛影29、肾损伤非手术疗法中下列哪项不恰当A.抗感染治疗B.应用止血剂C.观察血压、脉搏及腰部肿块和血尿的变化D.血尿消失后宜早期下床活动E.抗休克治疗30、下列关于闭式胸膜腔引流术的叙述中,错误的是A.如胸膜腔内为气体,选在锁中线第二肋间前胸膜腔上引流为宜B.如胸膜腔内为液体,选在腋中线和腋后线之间的第6~8肋间插管引流C.为保持管腔通畅,要经常挤压引流管D.拔管时,待病人深吸气后屏气,再迅速拔除引流管E.病人宜取平卧位31、颅内压调节主要依靠:A.颅内静脉血被排挤到颅外B.部分脑脊液被挤入脊髓蛛网膜C.脑脊液量的增减D.脑血管收缩E.脑血管舒张32、当颅内压急剧增高时病人可出现A.血压升高,脉搏减慢B.血压升高,脉搏加快C.血压下降,脉搏减慢D.血压下降,脉搏加快E.血压、脉搏无变化33、哪种头皮损伤后触诊容易误诊为颅骨凹陷性骨折()A.头皮血肿B.头皮下血肿C.帽状腱膜下血肿D.骨膜下血肿E.头皮感染34、急性硬脑膜外血肿典型的意识障碍程是()A .昏迷–清醒B.昏迷–清醒–昏迷C.昏迷–昏迷D.清醒–昏迷E.昏迷–好转35、多根多处肋骨骨折导致呼吸衰竭的主要原因是:A.剧痛不敢呼吸B.反常呼吸运动C.肺不张D.纵隔摆动E.继发肺部感染36、临床诊断进行性血胸,下列哪项意义最大?A.胸腔积血量>1000ml B.胸壁伤口流血不止C.经输血补液血压回升后又下降D.胸穿抽出不凝血E.胸部x线检查见大片阴影37、急性脓胸的最主要的治疗方法是:A.全身大量应用抗菌药物B.胸腔注入抗菌药物C.胸腔穿刺抽脓D.胸腔闭式引流E.胸腔开放式引流38、男,20岁,右胸撞伤后疼痛,呼吸20次/分,脉搏85次/分,X线胸部透视见右肺萎缩25%,下列哪项处置最恰当A胸膜腔穿刺抽气B.胸膜腔闭式引流C.镇痛,观察D.输液E.吸氧39、下列哪种胆囊息肉的征象支持良性息肉的诊断?A.单发 B.多发 C.不规则状 D.>1cm E.生长迅速40、男性,50岁,上腹不适,食欲不振三个月。

外科学考博试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 外科感染中最常见的致病菌是:A. 金黄色葡萄球菌B. 大肠杆菌C. 肺炎链球菌D. 真菌答案:A2. 以下哪项不是外科手术的基本原则?A. 无菌原则B. 无创原则C. 快速原则D. 安全原则答案:C3. 以下哪项是开放性骨折的特点?A. 骨折端不与外界相通B. 骨折端与外界相通C. 骨折线完全在皮肤下D. 骨折线完全在骨髓内答案:B4. 急性阑尾炎最典型的临床表现是:A. 腹痛B. 恶心呕吐C. 右下腹固定压痛D. 发热答案:C5. 以下哪项是乳腺癌的高危因素?A. 长期吸烟B. 长期饮酒C. 家族遗传史D. 长期素食答案:C二、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. 简述外科手术切口的分类及其特点。
答案:外科手术切口根据其感染风险分为三类:清洁切口、可能污染切口和污染切口。
清洁切口是指手术区域无炎症,无感染,且手术过程中未进入呼吸道、消化道、泌尿生殖道及口咽部。
可能污染切口是指手术区域可能存在细菌,但无明显感染,如胃肠道手术。
污染切口是指手术区域有明显感染或手术过程中进入有菌环境,如脓肿切开引流。
2. 描述急性胆囊炎的诊断要点。
答案:急性胆囊炎的诊断要点包括:右上腹疼痛,尤其是Murphy征阳性;发热和白细胞计数升高;腹部超声检查发现胆囊壁增厚、胆囊内结石或胆囊周围积液;有时可伴有黄疸。
3. 解释何为“无菌技术”及其在外科手术中的重要性。
答案:无菌技术是指在手术过程中采取的一系列措施,以防止手术区域受到微生物污染。
这包括使用无菌器械、穿戴无菌手术衣和手套、保持手术区域清洁等。
无菌技术在外科手术中至关重要,因为它可以显著降低术后感染的风险,提高手术成功率。
三、论述题(每题25分,共50分)1. 论述外科手术前的准备要点。
答案:外科手术前的准备要点包括:详细的病史采集和体格检查,以评估患者的整体健康状况和手术风险;必要的辅助检查,如血常规、凝血功能、心电图、肝肾功能等;术前禁食和禁水,以减少术中呕吐和误吸的风险;术前抗生素的使用,以预防感染;心理支持和教育,以减轻患者的焦虑和恐惧。

博士考试外科学试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 以下哪项不是外科手术的基本原则?A. 无菌原则B. 无创原则C. 快速原则D. 个体化原则2. 外科手术中,最常见的感染类型是:A. 细菌性感染B. 真菌性感染C. 病毒性感染D. 寄生虫感染3. 以下哪个不是外科手术的常见并发症?A. 出血B. 感染C. 疼痛D. 过敏4. 外科手术中,以下哪个操作不属于基本操作?A. 切开B. 缝合C. 切除D. 放射治疗5. 以下哪个是外科手术中常用的止血方法?A. 电凝B. 冷冻C. 药物D. 按摩6. 外科手术中,以下哪个不是常用的麻醉方式?A. 局部麻醉B. 椎管内麻醉C. 全身麻醉D. 表面麻醉7. 以下哪个不是外科手术的术后护理措施?A. 观察生命体征B. 伤口护理C. 预防感染D. 立即进食8. 外科手术中,以下哪种情况需要紧急处理?A. 轻微出血B. 术中发现肿瘤C. 术中出现心跳骤停D. 术后轻度疼痛9. 以下哪个不是外科手术的术前准备?A. 血常规检查B. 心电图检查C. 禁食禁水D. 术后饮食计划10. 外科手术中,以下哪个不是手术器械?A. 手术刀B. 镊子C. 止血钳D. 听诊器答案:1. C2. A3. D4. D5. A6. D7. D8. C9. D 10. D二、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. 请简述外科手术的无菌操作原则。
2. 描述一下外科手术中常见的止血方法。
3. 术后护理中,如何预防感染?三、论述题(每题25分,共50分)1. 论述外科手术中的风险评估和风险管理的重要性。
2. 论述外科手术的术前准备和术后护理的重要性。
结束语:外科手术是医学领域中非常重要的一部分,它不仅要求医生具备高超的技艺,还需要对手术的每一个环节都有深入的了解和严格的控制。
通过本试题,我们希望考生能够对外科手术的基本原则、操作技巧、风险管理以及术前术后的护理有更全面的认识,从而在未来的医学实践中能够更好地服务于患者。
外科学考博试题库及答案外科学是一门研究外科疾病的诊断、治疗和预防的医学科学。
以下是一份外科学考博试题库及答案,供参考:一、选择题1. 以下哪项不是外科手术的基本原则?A. 无菌原则B. 无创原则C. 快速原则D. 安全原则答案:C2. 外科手术中,下列哪项不是无菌操作的基本要求?A. 穿戴无菌手术衣和手套B. 保持手术区域的清洁C. 手术器械直接接触患者皮肤D. 手术室内保持空气流通答案:C3. 以下哪项是外科手术中常见的并发症?A. 术后出血B. 术后感染C. 术后肺栓塞D. 所有选项都是答案:D二、简答题1. 简述外科手术的无菌技术的重要性。
答:无菌技术是外科手术中非常重要的一环,它可以有效预防术后感染,保证手术的安全性和成功率。
无菌技术包括手术人员穿戴无菌手术衣和手套、手术器械的消毒、手术区域的清洁以及手术室内环境的控制等。
2. 描述外科手术中的麻醉方法有哪些,并简要说明其特点。
答:外科手术中的麻醉方法主要包括局部麻醉、椎管内麻醉和全身麻醉。
局部麻醉作用于身体的某一部位,使该部位失去痛觉,适用于小手术;椎管内麻醉作用于脊髓,使下半身失去痛觉,适用于下肢和下腹部手术;全身麻醉使患者在整个手术过程中处于无痛和无意识状态,适用于大型手术。
三、论述题1. 论述外科手术中止血的重要性及其常用方法。
答:止血是外科手术中至关重要的环节,它不仅可以防止患者失血过多,还能减少术中并发症的发生。
常用的止血方法包括物理止血(如压迫止血、冷敷止血)、药物止血(如使用止血药物)、电凝止血、结扎止血等。
选择合适的止血方法需要根据出血的类型、部位和量来决定。
结束语外科学作为一门实践性极强的学科,对医生的理论知识和操作技能都有很高的要求。
通过不断的学习和实践,医生可以提高自己的专业水平,更好地为患者服务。
希望这份试题库能够帮助考生们更好地复习和掌握外科学的相关知识。