SCM-6
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:411.50 KB
- 文档页数:30
钢铁导航网站,提供本对照表。
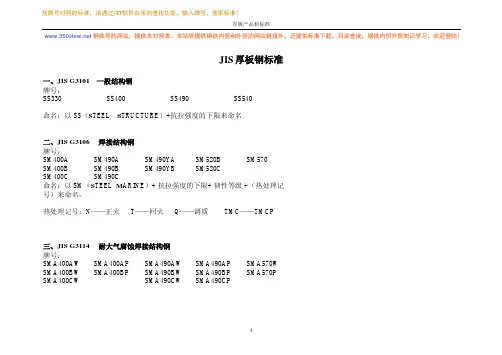
本站除提供钢铁内贸和外贸的网站链接外,还提供标准下载,目录查询,钢铁内贸外贸知识学习,欢迎登陆!找牌号对照的标准,请通过PDF软件自带的查找功能,输入牌号,搜索标准!厚板产品和标准JIS 厚板钢标准一、JIS G3101 一般结构钢 牌号: SS330 SS400 SS490SS540命名:以 SS (S TEEL S TRUCTURE )+抗拉强度的下限来命名二、JIS G3106 焊接结构钢牌号:SM400A SM400B SM400C SM490A SM490B SM490C SM490YA SM490YB SM520B SM520CSM570命名:以SM (S TEEL M ARINE )+ 抗拉强度的下限+ 韧性等级 +(热处理记号)来命名。
热处理记号:N ——正火 T ——回火 Q ——调质 TMC ——TMCP三、JIS G3114 耐大气腐蚀焊接结构钢牌号:SMA400AW SMA400BW SMA400CW SMA400AP SMA400BP SMA490AW SMA490BW SMA490CW SMA490AP SMA490BP SMA490CP SMA570WSMA570P命名:以SMA(S TEEL M ARINE A TMOSPHERIC)+ 抗拉强度的下限+ 韧性等级 +使用种类+(热处理记号)来命名。
使用种类:W:通常裸露使用(含Ni且Cr、Cu的含量更多)P:通常涂装使用热处理记号:N——正火 Q——调质 TMC——TMCP四、JIS G3128 焊接结构用高屈服强度钢牌号:SHY685 SHY685N SHY685NS SHY685NS-F命名:以SHY(S TEEL H IGH-YIELD Y(焊接))+ 屈服强度的下限命名N:N ICKEL S:S PECIAL F:F INE五、JIS G3129 铁塔用高强度钢牌号:SH590P命名:以SH(S TEEL H IGH STRENGTH )+抗拉强度下限+P(P LATE)表示六、JIS G3136 建筑结构钢牌号:SN400A SN400B SN400C SN490BSN490C命名:以SN(S TEEL N EW STRUCTURE + 抗拉强度的下限+ 韧性等级 +(热处理记号)+(UT记号)来命名热处理记号:N——正火 T——回火 TMC——TMCP 七、JIS G3103 锅炉及压力容器用碳素钢板及钼钢板牌号:SB410 SB450SB450M SB480SB480M命名:SB(S TEEL B OILER)+ 抗拉强度的下限+(热处理记号) M—M OLYBDENUM热处理记号:N——正火TN——试验片热处理记号SR——试验片去应力处理例:SB450NSB480NSR SB480TNSR SB480TN3SR八、JIS G3115 常温压力容器用钢板牌号:SPV235 SPV315 SPV355 SPV410 SPV450 SPV490 命名:SPV(S TEEL P RESSURE V ESSEL)+ 屈服强度的下限+(热处理记号)热处理记号:N——正火TN——试验片热处理记号 SR——试验片去应力处理 TMC——TMCPQ——调质TQ——试验片调质例:SPV410TMC SPV450QSPV450NSR SPV450TNSPV490TNSR SPV490TN3SR SPV490TQ2SR九、JIS G3118 中、常温压力容器用碳素钢板牌号:SGV410 SGV450 SGV480命名:SGV(S TEEL G ENERAL V ESSEL)+ 抗拉强度的下限+(热处理记号)热处理记号:N——正火TN——试验片热处理记号 SR——试验片去应力处理 TMC——TMCP 例: SGV410NSGV480NSRSGV480TNSR SGV480TMCSR十、JIS G3119 锅炉及压力容器用Mn-Mo 和Mn-Mo-Ni钢板牌号:SBV1A(Mn-Mo)SBV1B(Mn-Mo)SBV2(Mn-Mo-Ni)SBV3(Mn-Mo-Ni)命名:SBV(S TEEL B OILER V ESSEL) +成分系列号+强度等级+(热处理记号)强度等级A:315MPA B:345MPA热处理记号:N——正火P——钢板去应力热处理 SR——试验片去应力处理 TN——试验片正火处理例: SBV2NSBV2NPSBV2NSR SBV2PTNSBV2PTNSR SBV2TNSR十一、JIS G3120 压力容器用Mn-Mo 和Mn-Mo-Ni调质钢板牌号:SQV1A(Mn-Mo)SQV1B(Mn-Mo)SQV2A(Mn-Mo-Ni)SQV2B(Mn-Mo-Ni)SQV3A(Mn-Mo-Ni)SQV3B(Mn-Mo-Ni)命名:SQV(S TEEL Q UENCH V ESSEL) +成分系列号+强度等级+(热处理记号)强度等级: A:345MPA B:480MPA热处理记号:Q——调质P——钢板去应力热处理 SR——试验片去应力处理 TQ——试验片调质处理例:SQV1AQSQV1AQSR SQV1APTQSQV1APTQSR SQV1ATQSR十二、JIS G3124 中、常温压力容器用高强度钢板牌号:SEV245 SEV295 SEV345命名:SEV(S TEEL E LEVATED TEMPERATURE V ESSEL)+ 350℃下屈服强度的下限+(热处理记号)热处理记号:R——轧态N——正火NT——正火+回火P——钢板低温退火TN——试验片正火TNT——试验片正火+回火 SR——试验片去应力处理例: SEV245NSEV295NTSR SEV295PTNTSR十三、JIS G3126 低温压力容器用碳素钢板牌号:SLA235A最低温度-30℃SLA235B 最低温度-45℃SLA325A最低温度-45℃SLA325B最低温度-60℃SLA365最低温度-60℃SLA410最低温度-60℃命名:SLA(S TEEL L OW-TEMPERATURE A l-KILLED)+屈服强度的下限+韧性等级+(热处理记号)热处理记号: N——正火TMC——TMCPQ——调质SR——试验片去应力处理例: SLA235BTMC SLA325ANSLA365QSLA235BN3SR十四、JIS G3127 低温压力容器用Ni钢板牌号:SL2N255 最低温度-70℃SL3N255最低温度-101℃SL3N275最低温度-101℃SL3N440最低温度-110℃SL5N590最低温度-130℃SL9N520最低温度-196℃SL9N590最低温度-196℃命名:SL(S TEEL L OW-TEMPERATURE )+Ni含量+N+屈服强度的下限 +(热处理记号) Ni含量:2——2.25%Ni3——3.5%Ni5——5%Ni9——9%Ni热处理记号: N——正火TMC——TMCPNT——正火+回火NNT——正火+正火+回火Q——调质TN——试验片正火TNT——试验片正火+回火T2NT——试验片正火+回火2次 SR——试验片去应力处理例: SL2N255NSL3N275NTSL3N255TMC SL9N520NNTSL9N590QSL3N255NTNSR SL3N275N3SR SL3N255TNSR十五、JIS G4109 锅炉及压力容器用Cr-Mo 钢板牌号:SCMV1-1 SCMV1-2 SCMV2-1 SCMV2-2 SCMV3-1 SCMV3-2 SCMV4-1 SCMV4-2 SCMV5-1 SCMV5-2 SCMV6-1 SCMV6-2 命名:SCMV (S TEEL C r-M o V ESSEL )+Cr-Mo 成分系列号 + 强度等级 +(热处理记号)Cr-Mo 成分系列:1——0.5Cr-0.5Mo2——1.0Cr-0.5Mo 3——1.25Cr-0.5Mo 4——2.25Cr-1.0Mo5——3.0Cr-1.0Mo6——5.0Cr-0.5Mo强度等级:1——抗拉400MPa 级 2——抗拉500MPa 级热处理记号:A ——退火NT ——正火+回火 P ——去应力处理 TA ——试验片退火TNT ——试验片正火+回火SR ——试验片去应力处理例 SCMV1-1A SCMV1-1NTSR SCMV4-2PTNT2SR十六、JIS G4110 高温 压力容器用高强度Cr-Mo 钢板牌号:SCMQ4E SCMQ4V SCMQ5V Cr-Mo 成分系列: 4——2.25Cr-1.0MoV :V ANADIUM5——3.0Cr-1.0Mo命名:SCMQ(S TEEL C r-M o Q UENCH)+ 成分系列号 + (热处理记号)热处理记号:Q——调质NT——正火+回火P——钢板低温退火TNT——试验片正火+回火 TQ——试验片调质SR——试验片去应力处理例 SCMQ4VNTSRSCMQ5VPTNT2SR十七、JIS G4051 机械结构用碳素钢 S××C (S TEEL C ARBON)××为碳含量的100倍(10~58)十八、JIS G4401 碳素工具钢 SK×××(K:工具)×××为碳含量的100倍(60~140)十九、JIS G4404 合金工具钢 SKS (S TEEL+工具+S PECIAL)DIN厚板钢标准一、DIN EN 10025 热轧非合金结构钢牌号:S185 S235JRS235JRG1S235JRG2S235J0S235J2G3S235J2G4 S275JRS275J0S275J2G3S275J2G4S355JRS355J0S355J2G3S355J2G4S355K2G3S355K2G4E295E335E360命名:S:S TRUCTURAL STEELE:E NGINEERING STEEL二、DIN EN 10113 热轧可焊接细晶粒结构钢牌号:S275N S275NL S275M S275ML S355NS355NLS355MS355MLS420NS420NLS420MS420MLS460NS460NLS460MS460MLN:正火或正火轧制M:热机轧制L:低温用三、DIN EN 10137 高强度结构钢——调质或沉淀硬化交货牌号:S460QS460QL S460QL1 S500QS500QLS500QL1S550QS550QLS550QL1S620QS620QLS620QL1S690QS690QLS690QL1S890QS890QLS890QL1S960QS960QLQ:调质第1位:J=27JK=40JL=60J第2位:R=室温0=0℃2=-20℃3=-30℃4=-40℃5=-50℃6=-60℃L:低温用(到-40℃)L1:低温用(到-60℃)四、DIN EN 10155 耐大气腐蚀结构钢牌号:S235J0W S235J2W S355J0WPS355J2WPS355J0WS355J2G1WS355J2G2WS355K2G1WS355K2G2WW:WEATHER RESISTANTP:PILING——小于12mm的钢板五、DIN EN 10225 海洋平台用焊接结构钢牌号:S420G1+Q S420G2+Q S420G1+MS420G2+MS460G1+QS460G2+QS460G1+MS460G2+MS355G2+N S355G3+N S355G7+N S355G8+N S355G9+N S355G10+N S355G5+MS355G6+MS355G7+MS355G8+MS355G9+MS355G10+M+N:正火或正火轧制+M:热机轧制+Q:调质六、DIN EN 10028 压力容器钢PART 1 通用要求PART 2 具有较高温性能的非合金及合金钢牌号:P235GH P265GH P295GH P355GH 16Mo3 13CrMo4-5 10CrMo9-10 11CrMo9-10P :STEEL FOR P RESSURE PURPOSES G :其他特性 H :HIGH TEMPERATUR PART3 正火状态的可焊接细粒钢(不同系列分别适用常温,较高温度、低温)牌号:P275N P275NH P275NL1 P275NL2 P355N P355NH P355NL1 P355NL2 P460N P460NH P460NL1 P460NL2N :正火或正火轧制H :HIGH TEMPERATURE L1、L2:LOW TEMPERATURE PART4 极低温用Ni 钢牌号:11MnNi5-3 (0.5Ni)(最低使用温度-60℃) 交货状态:N(+T)13MnNi6-3 (0.5Ni)(最低使用温度-60℃) 交货状态:N(+T)15NiMn6 (1.5Ni) (最低使用温度-80℃) 交货状态:N 、N+T 、Q+T 12Ni14 (3.5Ni) (最低使用温度-100℃) 交货状态:N 、N+T 、Q+T 12Ni19 (5.0Ni) (最低使用温度-120℃) 交货状态:N 、N+T 、Q+T X8Ni9 (9.0Ni) (最低使用温度-196℃) 交货状态:N+N+T 、Q+TX7Ni9 (9.0Ni) (最低使用温度-196℃) 交货状态:Q+TPART5 可焊接细粒钢——热机轧制牌号:P355M P355ML1 P355ML2 P420M P420ML1 P420ML2 P460MP460ML1P460ML2PART6 可焊接细粒钢——调质钢牌号:P355QP355QH P355QL1 P355QL2 P460QP460QHP460QL1P460QL2P500Q500QHP500QL1P500QL2P690QP690QHP690QL1P690QL2ASTM厚板钢标准压力容器用钢系列:A20 压力容器钢通用要求A202 压力容器用Cr-Mn-Si 钢A203 压力容器用Ni 钢, 2.25 Ni 3.5 NiA204 压力容器用Mo 钢A225 压力容器用Mn-V-Ni 钢A299 C-Mn-Si压力容器钢A285 压力容器用,中低强度碳钢A302 Mn-Mo 和Mn-Mo-Ni 压力容器钢A353 9 Ni压力容器钢 N+N+TA387 Cr-Mo压力容器钢A455 碳素压力容器钢 500MPa,最大20mm,一般为非镇静钢A515 碳素压力容器钢中、高温A516 碳素压力容器钢中温、低温A517 高强度压力容器调质钢 YP≥690MPa 十三个成分系列A537 C-Mn压力容器钢热处理 CLASS1 正火 CLASS2、3调质A662 C-Mn压力容器钢室温、低温A533 Mn-Mo 和Mn-Mo-Ni 压力容器钢、调质A841 压力容器钢、TMCP工艺A542 压力容器钢、调质、Cr-Mo 和Cr-Mo-VA543 压力容器钢、调质、Ni-Cr-Mo 一般板厚50mm以上A553 压力容器钢、调质、8%Ni 、9%NiA645 容器钢、特殊热处理、5%NiA724 多层压力容器用C-Mn-Si 钢调质A736 压力容器用沉淀硬化钢低C-Ni-Cu-Cr-Mo-Nb或低C-Ni-Cu-Mn-Mo-Nb A737 压力容器用HSLA钢A738 中、低温压力容器用C-Mn-Si 钢热处理A832 压力容器钢 Cr-Mo-V N+T结构钢系列:A6 结构钢通用要求A36 碳素结构钢A283 中低强度钢板A529 高强度C-Mn 结构钢 Gr.50、Gr.55A572 HSLA 钢(Nb、V、N 微合金钢)A573 具有改善韧性的碳素结构钢(室温使用)A242 HSLA钢——Cu、PA588 HSLA 钢耐侯 YP≥345MPa Gr.A、Gr.B、Gr.C、Gr.K 四个成分系列A871 HSLA 钢耐侯 YP≥415MPa 和 YP≥450MPa ,四个成分系列A514 高屈服强度调质钢 YP≥690MPa 十四个成分系列A709 桥梁钢 G r.36=A36G r.50=A572 G r.50G r.50W=A588G r.100、G r.100W =A514G r. HPS 70WA710 沉淀硬化钢,低C-Ni-Cu-Cr-Mo-NbA633 正火HSLA钢(-45℃以上使用)A678 碳素或HSLA钢调质 600MPa 及以下级GB厚板钢标准一、GB1591 低合金高强度结构钢Q295A Q295B Q345AQ345BQ345CQ345DQ345EQ390AQ390BQ390CQ390DQ390EQ420AQ420BQ420CQ420DQ420EQ460CQ460DQ460E二、GB699 优质碳素结构钢技术条件三、GB700 碳素结构钢Q195 Q215AQ215B Q235AQ235BQ235CQ235DQ235EQ255AQ255BQ275四、GB711 优质碳素结构钢热轧厚钢板和宽钢带05F~70 20Mn~65Mn五、GB710 优质碳素结构钢热轧簿钢板和宽钢带05F~70 20Mn~65Mn六、GB912 碳素结构钢和低合金结构钢热轧簿钢板和宽钢带牌号为GB700和GB1591中的牌号七、GB3274 碳素结构钢和低合金结构钢热轧厚钢板和宽钢带牌号为GB700和GB1591中的牌号八、GB713 锅炉用钢板20g 22Mng 15CrMog 16Mng 19Mng 13MnNiCrMoNbg 12Cr1MoVg九、GB3531 低温压力容器用低合金钢钢板16MnDR 15MnNiDR 09MnNiDR十、GB6654 压力容器用钢板20R 16MnR 15MnVR 15MnVNR 18MnMoNbR 13MnNiMoNbR 15CrMoR十一GB714 桥梁用结构钢Q235Cq(16q) Q235Dq(16q)Q345Cq(16Mnq)Q345Dq(16Mnq)Q345Eq(16Mnq)Q370Cq(14MnNbq)Q370Dq(14MnNbq)Q370Eq(14MnNbq)Q420Cq(15MnVNq)Q420Dq(15MnVNq)Q420Eq(15MnVNq)厚板产品和标准24十二、GB4172 焊接结构用耐候钢16CuCr 12MnCuCr 15MnCuCr 15MnCuCr-QT十三、GB16270 高强度结构钢热处理和控轧钢板、钢带Q420C Q420D Q420E Q460C Q460D Q460E Q500D Q500E Q550D Q550E Q620DQ620EQ690D Q690E十四、GB11251 合金结构钢热轧厚钢板十五、GB3077 合金结构钢技术条件。

ERP、SCM、CRM、BPR、OMS、WMS 企业管理的6大核心系统SRM是Supplier Relationship Management的缩写,即供应商关系管理。
是企业供应链(Supply Chain)上的一个基本环节,它建立在对企业的供方(包括原料供应商,设备及其他资源供应商,服务供应商等)以及与供应相关信息完整有效的管理与运用的基础上,对供应商的现状、历史,提供的产品或服务,沟通、信息交流、合同、资金、合作关系、合作项目以及相关的业务决策等进行全面的管理与支持。
ERP是Enterprise Resource Planning的缩写,即企业资源计划(或企业资源管理)。
ERP系统是指建立在信息技术基础上,以系统化的管理思想,为企业决策层及员工提供决策运行手段的管理平台。
它是从MRP(物料需求计划)发展而来的新一代集成化管理信息系统,它扩展了MRP的功能,其核心思想是供应链管理。
它跳出了传统企业边界,从供应链范围去优化企业的资源。
ERP系统集中信息技术与先进的管理思想於一身,成为现代企业的运行模式,反映时代对企业合理调配资源,最大化地创造社会财富的要求,成为企业在信息时代生存、发展的基石。
它对于改善企业业务流程、提高企业核心竞争力的作用是显而易见的。
(business process reengineering)业务流程重组、企业流程再造,是当前管理学领域非常有争议的话题,支持者声称BPR 是恢复美国竞争力的惟一途径,并将取代工业革命,使之进入重建革命的时代,而反对者则提出了实施BPR的失败率高达70%。
1990年著名管理学家Michael Hammer"Reengineering Work:Don't Automate, But Obliterate " 一文中首次提出了BPR的概念。
1993年,Michael Hammer和James Champy在"Reengineering The Corporation" 一书中正式对BPR做了如下定义:企业流程再造工程是对企业的业务流程作根本性的思考和彻底重建,其目的是在成本、质量、服务和速度等方面取得显著的改善,使得企业能最大限度地适应以顾客(Customer)、竞争(Competition)、变化(Change)为特征的现代企业经营环境。

MIC-6精密铸铝板
MIC-6特性
1.良好的可成型性、可焊接性。
2.强度高。
3.可使用性好,接口特点优良。
4.易于加工,容易涂层。
5.抗腐蚀性、抗氧化性好。
主要用途
航空固定装置,卡车,塔式建筑,船,管道及其他需要有强度、可焊性和抗腐蚀性能的建筑上的应用的领域。
如:飞机零件、照相机镜头、耦合器、船舶配件和五金、电子配件和接头、装饰用或各种五金、铰链头、磁头、刹车活塞、水利活塞、电器配件、阀门和阀门零件。
物理性能
硬度:150HB;密度:2810
抗拉强度:524Mpa;0.2%屈服强度455Mpa
化学成分
硅Si:0.40
铁Fe: 0.50
铜Cu:1.2-2.0
锰Mn:0.30
镁Mg:2.1-2.9
铬Cr:0.18-0.28
锌Zn:5.1-6.1
钛Ti:0.20
铝Al:余量
其他:
单个:0.05 合计:0.15
此板一般用于有特殊要求的场合,价格相对较高,68元/Kg。
© 2017 NXP B.V.SCM-i.MX 6 Series Yocto Linux User'sGuide1. IntroductionThe NXP SCM Linux BSP (Board Support Package) leverages the existing i.MX 6 Linux BSP release L4.1.15-2.0.0. The i.MX Linux BSP is a collection of binary files, source code, and support files that can be used to create a U-Boot bootloader, a Linux kernel image, and a root file system. The Yocto Project is the framework of choice to build the images described in this document, although other methods can be also used.The purpose of this document is to explain how to build an image and install the Linux BSP using the Yocto Project build environment on the SCM-i.MX 6Dual/Quad Quick Start (QWKS) board and the SCM-i.MX 6SoloX Evaluation Board (EVB). This release supports these SCM-i.MX 6 Series boards:• Quick Start Board for SCM-i.MX 6Dual/6Quad (QWKS-SCMIMX6DQ)• Evaluation Board for SCM-i.MX 6SoloX (EVB-SCMIMX6SX)NXP Semiconductors Document Number: SCMIMX6LRNUGUser's GuideRev. L4.1.15-2.0.0-ga , 04/2017Contents1. Introduction........................................................................ 1 1.1. Supporting documents ............................................ 22. Enabling Linux OS for SCM-i.MX 6Dual/6Quad/SoloX .. 2 2.1. Host setup ............................................................... 2 2.2. Host packages ......................................................... 23.Building Linux OS for SCM i.MX platforms .................... 3 3.1. Setting up the Repo utility ...................................... 3 3.2. Installing Yocto Project layers ................................ 3 3.3. Building the Yocto image ....................................... 4 3.4. Choosing a graphical back end ............................... 4 4. Deploying the image .......................................................... 5 4.1. Flashing the SD card image .................................... 5 4.2. MFGTool (Manufacturing Tool) ............................ 6 5. Specifying displays ............................................................ 6 6. Reset and boot switch configuration .................................. 7 6.1. Boot switch settings for QWKS SCM-i.MX 6D/Q . 7 6.2. Boot switch settings for EVB SCM-i.MX 6SoloX . 8 7. SCM uboot and kernel repos .............................................. 8 8. References.......................................................................... 8 9.Revision history (9)Enabling Linux OS for SCM-i.MX 6Dual/6Quad/SoloX1.1. Supporting documentsThese documents provide additional information and can be found at the NXP webpage (L4.1.15-2.0.0_LINUX_DOCS):•i.MX Linux® Release Notes—Provides the release information.•i.MX Linux® User's Guide—Contains the information on installing the U-Boot and Linux OS and using the i.MX-specific features.•i.MX Yocto Project User's Guide—Contains the instructions for setting up and building the Linux OS in the Yocto Project.•i.MX Linux®Reference Manual—Contains the information about the Linux drivers for i.MX.•i.MX BSP Porting Guide—Contains the instructions to port the BSP to a new board.These quick start guides contain basic information about the board and its setup:•QWKS board for SCM-i.MX 6D/Q Quick Start Guide•Evaluation board for SCM-i.MX 6SoloX Quick Start Guide2. Enabling Linux OS for SCM-i.MX 6Dual/6Quad/SoloXThis section describes how to obtain the SCM-related build environment for Yocto. This assumes that you are familiar with the standard i.MX Yocto Linux OS BSP environment and build process. If you are not familiar with this process, see the NXP Yocto Project User’s Guide (available at L4.1.15-2.0.0_LINUX_DOCS).2.1. Host setupTo get the Yocto Project expected behavior on a Linux OS host machine, install the packages and utilities described below. The hard disk space required on the host machine is an important consideration. For example, when building on a machine running Ubuntu, the minimum hard disk space required is about 50 GB for the X11 backend. It is recommended that at least 120 GB is provided, which is enough to compile any backend.The minimum recommended Ubuntu version is 14.04, but the builds for dizzy work on 12.04 (or later). Earlier versions may cause the Yocto Project build setup to fail, because it requires python versions only available on Ubuntu 12.04 (or later). See the Yocto Project reference manual for more information.2.2. Host packagesThe Yocto Project build requires that the packages documented under the Yocto Project are installed for the build. Visit the Yocto Project Quick Start at /docs/current/yocto-project-qs/yocto-project-qs.html and check for the packages that must be installed on your build machine.The essential Yocto Project host packages are:$ sudo apt-get install gawk wget git-core diffstat unzip texinfo gcc-multilib build-essential chrpath socat libsdl1.2-devThe i.MX layers’ host packages for the Ubuntu 12.04 (or 14.04) host setup are:$ sudo apt-get install libsdl1.2-dev xterm sed cvs subversion coreutils texi2html docbook-utils python-pysqlite2 help2man make gcc g++ desktop-file-utils libgl1-mesa-dev libglu1-mesa-dev mercurial autoconf automake groff curl lzop asciidocThe i.MX layers’ host packages for the Ubuntu 12.04 host setup are:$ sudo apt-get install uboot-mkimageThe i.MX layers’ host packages for the Ubuntu 14.04 host s etup are:$ sudo apt-get install u-boot-toolsThe configuration tool uses the default version of grep that is on your build machine. If there is a different version of grep in your path, it may cause the builds to fail. One workaround is to rename the special versi on to something not containing “grep”.3. Building Linux OS for SCM i.MX platforms3.1. Setting up the Repo utilityRepo is a tool built on top of GIT, which makes it easier to manage projects that contain multiple repositories that do not have to be on the same server. Repo complements the layered nature of the Yocto Project very well, making it easier for customers to add their own layers to the BSP.To install the Repo utility, perform these steps:1.Create a bin folder in the home directory.$ mkdir ~/bin (this step may not be needed if the bin folder already exists)$ curl /git-repo-downloads/repo > ~/bin/repo$ chmod a+x ~/bin/repo2.Add this line to the .bashrc file to ensure that the ~/bin folder is in your PATH variable:$ export PATH=~/bin:$PATH3.2. Installing Yocto Project layersAll the SCM-related changes are collected in the new meta-nxp-imx-scm layer, which is obtained through the Repo sync pointing to the corresponding scm-imx branch.Make sure that GIT is set up properly with these commands:$ git config --global "Your Name"$ git config --global user.email "Your Email"$ git config --listThe NXP Yocto Project BSP Release directory contains the sources directory, which contains the recipes used to build, one (or more) build directories, and a set of scripts used to set up the environment. The recipes used to build the project come from both the community and NXP. The Yocto Project layers are downloaded to the sources directory. This sets up the recipes that are used to build the project. The following code snippets show how to set up the SCM L4.1.15-2.0.0_ga Yocto environment for the SCM-i.MX 6 QWKS board and the evaluation board. In this example, a directory called fsl-arm-yocto-bsp is created for the project. Any name can be used instead of this.Building Linux OS for SCM i.MX platforms3.2.1. SCM-i.MX 6D/Q quick start board$ mkdir fsl-arm-yocto-bsp$ cd fsl-arm-yocto-bsp$ repo init -u git:///imx/fsl-arm-yocto-bsp.git -b imx-4.1-krogoth -m scm-imx-4.1.15-2.0.0.xml$ repo sync3.2.2. SCM-i.MX 6SoloX evaluation board$ mkdir my-evb_6sxscm-yocto-bsp$ cd my-evb_6sxscm-yocto-bsp$ repo init -u git:///imx/fsl-arm-yocto-bsp.git -b imx-4.1-krogoth -m scm-imx-4.1.15-2.0.0.xml$ repo sync3.3. Building the Yocto imageNote that the quick start board for SCM-i.MX 6D/Q and the evaluation board for SCM-i.MX 6SoloX are commercially available with a 1 GB LPDDR2 PoP memory configuration.This release supports the imx6dqscm-1gb-qwks, imx6dqscm-1gb-qwks-rev3, and imx6sxscm-1gb-evb. Set the machine configuration in MACHINE= in the following section.3.3.1. Choosing a machineChoose the machine configuration that matches your reference board.•imx6dqscm-1gb-qwks (QWKS board for SCM-i.MX 6DQ with 1 GB LPDDR2 PoP)•imx6dqscm-1gb-qwks-rev3 (QWKS board Rev C for SCM-i.MX 6DQ with 1GB LPDDR2 PoP) •imx6sxscm-1gb-evb (EVB for SCM-i.MX 6SX with 1 GB LPDDR2 PoP)3.4. Choosing a graphical back endBefore the setup, choose a graphical back end. The default is X11.Choose one of these graphical back ends:•X11•Wayland: using the Weston compositor•XWayland•FrameBufferSpecify the machine configuration for each graphical back end.The following are examples of building the Yocto image for each back end using the QWKS board for SCM-i.MX 6D/Q and the evaluation board for SCM-i.MX 6SoloX. Do not forget to replace the machine configuration with what matches your reference board.3.4.1. X11 image on QWKS board Rev C for SCM-i.MX 6D/Q$ DISTRO=fsl-imx-x11 imx6dqscm-1gb-qwks-rev3 source fsl-setup-release.sh -b build-x11$ bitbake fsl-image-gui3.4.2. FrameBuffer image on evaluation board for SCM-i.MX 6SX$ DISTRO=fsl-imx-fb MACHINE=imx6sxscm-1gb-evb source fsl-setup-release.sh –b build-fb-evb_6sxscm$ bitbake fsl-image-qt53.4.3. XWayland image on QWKS board for SCM-i.MX 6D/Q$ DISTRO=fsl-imx-xwayland MACHINE=imx6dqscm-1gb-qwks source fsl-setup-release.sh –b build-xwayland$ bitbake fsl-image-gui3.4.4. Wayland image on QWKS board for SCM-i.MX 6D/Q$ DISTRO=fsl-imx-wayland MACHINE=imx6dqscm-1gb-qwks source fsl-setup-release.sh -b build-wayland$ bitbake fsl-image-qt5The fsl-setup-release script installs the meta-fsl-bsp-release layer and configures theDISTRO_FEATURES required to choose the graphical back end. The –b parameter specifies the build directory target. In this build directory, the conf directory that contains the local.conf file is created from the setup where the MACHINE and DISTRO_FEATURES are set. The meta-fslbsp-release layer is added into the bblayer.conf file in the conf directory under the build directory specified by the –e parameter.4. Deploying the imageAfter the build is complete, the created image resides in the <build directory>/tmp/deploy/images directory. The image is (for the most part) specific to the machine set in the environment setup. Each image build creates the U-Boot, kernel, and image type based on the IMAGE_FSTYPES defined in the machine configuration file. Most machine configurations provide the SD card image (.sdcard), ext4, and tar.bz2. The ext4 is the root file system only. The .sdcard image contains the U-Boot, kernel, and rootfs, completely set up for use on an SD card.4.1. Flashing the SD card imageThe SD card image provides the full system to boot with the U-Boot and kernel. To flash the SD card image, run this command:$ sudo dd if=<image name>.sdcard of=/dev/sd<partition> bs=1M && syncFor more information about flashing, see “P reparing an SD/MMC Card to Boot” in the i.MX Linux User's Guide (document IMXLUG).Specifying displays4.2. MFGTool (Manufacturing Tool)MFGTool is one of the ways to place the image on a device. To download the manufacturing tool for the SCM-i.MX 6D/Q and for details on how to use it, download the SCM-i.MX 6 Manufacturing Toolkit for Linux 4.1.15-2.0.0 under the "Downloads" tab from /qwks-scm-imx6dq. Similarly, download the manufacturing tool for the SCM-i.MX 6SoloX evaluation board under the "Downloads" tab from /evb-scm-imx6sx.5. Specifying displaysSpecify the display information on the Linux OS boot command line. It is not dependent on the source of the Linux OS image. If nothing is specified for the display, the settings in the device tree are used. Find the specific parameters in the i.MX 6 Release Notes L4.1.15-2.0.0 (available at L4.1.15-2.0.0_LINUX_DOCS). The examples are shown in the following subsections. Interrupt the auto-boot and enter the following commands.5.1.1. Display options for QWKS board for SCM-i.MX 6D/QHDMI displayU-Boot > setenv mmcargs 'setenv bootargs console=${console},${baudrate} ${smp}root=${mmcroot} video=mxcfb0:dev=hdmi,1920x1080M@60,if=RGB24'U-Boot > run bootcmd5.1.2. Display options for EVB for SCM-i.MX 6SXNote that the SCM-i.MX 6SX EVB supports HDMI with a HDMI accessory card (MCIMXHDMICARD) that plugs into the LCD connector on the EVB.Accessory boards:•The LVDS connector pairs with the NXP MCIMX-LVDS1 LCD display board.•The LCD expansion connector (parallel, 24-bit) pairs with the NXP MCIMXHDMICARD adapter board.LVDS displayU-Boot > setenv mmcargs 'setenv bootargs console=${console},${baudrate} ${smp}root=${mmcroot} ${dmfc} video=mxcfb0:dev=ldb,1024x768M@60,if=RGB666 ldb=sep0'U-Boot > run bootcmdHDMI display (dual display for the HDMI as primary and the LVDS as secondary)U-Boot > setenv mmcargs 'setenv bootargs console=${console},${baudrate} ${smp}root=${mmcroot} video=mxcfb0:dev=hdmi,1920x1080M@60,if=RGB24video=mxcfb1:dev=ldb,LDBXGA,if=RGB666'U-Boot > run bootcmdLCD displayu-boot > setenv mmcargs 'setenv bootargs ${bootargs}root=${mmcroot} rootwait rw video=mxcfb0:dev=lcd,if=RGB565'u-boot> run bootcmd6. Reset and boot switch configuration6.1. Boot switch settings for QWKS SCM-i.MX 6D/QThere are two push-button switches on the QWKS-SCMIMX6DQ board. SW1 (SW3 for QWKS board Rev B) is the system reset that resets the PMIC. SW2 is the i.MX 6Dual/6Quad on/off button that is needed for Android.There are three boot options. The board can boot either from the internal SPI-NOR flash inside the SCM-i.MX6Dual/6Quad or from either of the two SD card slots. The following table shows the switch settings for the boot options.Table 1.Boot configuration switch settingsBoot from top SD slot (SD3)Boot from bottom SD slot (SD2)Boot from internal SPI NORDefault1.References6.2. Boot switch settings for EVB SCM-i.MX 6SoloXThis table shows the jumper configuration to boot the evaluation board from the SD card slot SD3.7. SCM uboot and kernel repositoriesThe kernel and uboot patches for both SCM-i.MX 6 QWKS board and evaluation board are integrated in specific git repositories. Below are the git repos for SCM-i.MX 6 uboot and kernel:uBoot repo: /git/cgit.cgi/imx/uboot-imx.gitSCM Branch: scm-imx_v2016.03_4.1.15_2.0.0_gakernel repo: /git/cgit.cgi/imx/linux-imx.gitSCM branch: scm-imx_4.1.15_2.0.0_ga8. References1.For details about setting up the Host and Yocto Project, see the NXP Yocto Project User’s Guide(document IMXLXYOCTOUG).2.For information about downloading images using U-Boot, see “Downloading images usingU-Boot” in the i.MX Linux User's Guide (document IMXLUG).3.For information about setting up the SD/MMC card, see “P reparing an SD/MMC card to boot” inthe i.MX Linux User's Guide (document IMXLUG).9. Revision historyDocument Number: SCMIMX6LRNUGRev. L4.1.15-2.0.0-ga04/2017How to Reach Us: Home Page: Web Support: /supportInformation in this document is provided solely to enable system and softwareimplementers to use NXP products. There are no express or implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated circuits based on the information in this document. NXP reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein.NXP makes no warranty, representation, or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does NXP assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequentia l or incidental damages. “Typical”parameters that may be provided in NXP data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications, and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including “typicals,” must be valida ted for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. NXP does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. NXP sells products pursuant to standard terms and conditions of sale, which can be found at the following address: /SalesTermsandConditions .NXP, the NXP logo, NXP SECURE CONNECTIONS FOR A SMARTER WORLD, Freescale, and the Freescale logo are trademarks of NXP B.V. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.ARM, the ARM Powered logo, and Cortex are registered trademarks of ARM Limited (or its subsidiaries) in the EU and/or elsewhere. All rights reserved. © 2017 NXP B.V.。


MIC-6MIC-6铝合金是一种高性能的铝合金材料,具有优异的平坦度、可加工性和热处理性能。
下面将从执行标准、化学成分、特性、用途和性能等方面进行详细介绍。
1. 执行标准:MIC-6铝合金的执行标准为ASTM B209-14《标准规范铝及铝合金板、带、箔》。
2. 化学成分:MIC-6铝合金的化学成分主要包括铝(Al)、硅(Si)、镁(Mg)、铜(Cu)和锰(Mn)。
其中,铝是主要元素,占比为97.4-99.5%;硅的含量为0.4-1.0%;镁的含量为0.05-0.20%;铜的含量为0.03-0.15%;锰的含量为0.03-0.10%。
此外,还可能包含少量的铁(Fe)、锌(Zn)等元素。
3. 特性:-优异的平坦度:MIC-6铝合金具有出色的平坦度和表面光洁度,适用于对平整度要求较高的应用。
-良好的可加工性:该合金具有良好的可加工性,可进行切割、冷弯、焊接等加工操作。
-热处理性能:MIC-6铝合金具有良好的热处理性能,可以通过热处理进一步提高其强度和硬度。
-耐腐蚀性:该合金具有较好的耐腐蚀性能,能够抵抗常见的大气和化学介质的侵蚀。
4. 用途:MIC-6铝合金广泛应用于精密机械、半导体设备、光学仪器、模具制造等领域。
具体应用包括但不限于:-精密机械:用于制造平板、底座、夹具等精密机械零部件。
-半导体设备:用于制造半导体冷却器、封装底座等。
-光学仪器:用于制造光学平台、反射镜底座等。
-模具制造:用于制造模具基板、压铸模具等。
5. 性能:-机械性能:MIC-6铝合金的抗拉强度为≥172MPa,屈服强度为≥138MPa,伸长率为≥5%。
-热处理性能:该合金可通过热处理,如固溶处理和时效处理,进一步提高其强度和硬度。
-耐腐蚀性:MIC-6铝合金具有良好的耐腐蚀性能,能够在大气和一些化学介质中保持较好的稳定性。
综上所述,MIC-6铝合金是一种具有优异平坦度、可加工性和热处理性能的铝合金。
它广泛应用于精密机械、半导体设备、光学仪器和模具制造等领域。

铸铁牌号的表示方法:(根据GB5612-85)各种铸铁代号,由表示该铸铁特征的汉语拼音字母的第一个大写正体字母组成。
当两种铸铁名称的代号字母相同时,可在该大写正体字母后加小写正体字母来区别。
同一名称铸铁,需要细分时,取其细分特点的汉语拼音第一个大写正体字母,排列在后面。
铸铁名称,代号及牌号表示方法铸铁名称...............代号牌号..................表示方法实例灰铸铁....................HT.........................HT100蠕墨铸铁..................RuT........................RuT400球墨铸铁..................QT.........................QT400-17黑心可锻铸铁..............KHT........................KHT300-06白心可锻铸铁..............KBT........................KBT350-04珠光体可锻铸铁............KZT........................KZT450-06耐磨铸铁..................MT.........................MT Cu1PTi-150抗磨白口铸铁..............KmBT.......................KmBTMn5Mo2Cu抗磨球墨铸铁..............KmQT.......................KmQTMn6冷硬铸铁..................LT.........................LTCrMoR耐蚀铸铁..................ST.........................STSi15R耐蚀球墨铸铁..............SQT........................SQTAl15Si5耐热铸铁..................RT.........................RTCr2耐热球墨铸铁..............RQT........................RQTA16奥氏体铸铁................AT.........................----...牌号中代号后面的一组数字,表示抗拉强度值;有两组数字时,第一组表示抗拉强度值,第二组表示延伸率值。


MIC-6精密铸铝板
MIC-6特性
1.良好的可成型性、可焊接性。
2.强度高。
3.可使用性好,接口特点优良。
4.易于加工,容易涂层。
5.抗腐蚀性、抗氧化性好。
主要用途
航空固定装置,卡车,塔式建筑,船,管道及其他需要有强度、可焊性和抗腐蚀性能的建筑上的应用的领域。
如:飞机零件、照相机镜头、耦合器、船舶配件和五金、电子配件和接头、装饰用或各种五金、铰链头、磁头、刹车活塞、水利活塞、电器配件、阀门和阀门零件。
物理性能
硬度:150HB;密度:2810
抗拉强度:524Mpa;0.2%屈服强度455Mpa
化学成分
硅Si:0.40
铁Fe: 0.50
铜Cu:1.2-2.0
锰Mn:0.30
镁Mg:2.1-2.9
铬Cr:0.18-0.28
锌Zn:5.1-6.1
钛Ti:0.20
铝Al:余量
其他:
单个:0.05 合计:0.15
此板一般用于有特殊要求的场合,价格相对较高,68元/Kg。
螺纹规格对照表螺纹底孔径公制粗牙螺纹 JIS B 0209-1982(单位:mm)(注1)(注2) 2级崁合度区分:中(注1)(注2) 崁合度区分:中2级内螺纹小径螺纹尺寸钻头直径下孔径最小直径最大直径M 1 × 0.25 0.75 0.78 (80%) 0.729 0.785 1.1 × 0.25 0.85 0.88 (80%) 0.829 0.885 1.2 × 0.25 0.95 0.98 (80%) 0.929 0.985 1.4 × 0.3 1.1 1.14 (80%) 1.075 1.142 1.6 × 0.35 1.25 1.32 (75%) 1.221 1.321 1.8 × 0.351.45 1.52 (75%) 1.421 1.521 2 × 0.4 1.6 1.65 (80%) 1.567 1.6792.2 × 0.45 1.75 1.83 (75%) 1.713 1.838 2.5 × 0.45 2.1 2.13 (75%) 2.013 2.1383 × 0.5 2.5 2.59 (75%) 2.459 2.599 3.5 × 0.6 2.9 3.01 (75%) 2.8503.010 4 × 0.7 3.3 3.39 (80%) 3.242 3.4224.5 × 0.75 3.8 3.85 (80%)3.688 3.878 5 × 0.84.2 4.31 (80%) 4.134 4.334 6 × 1 55.13 (80%)4.9175.153 7 × 1 66.13 (80%) 5.917 6.153 8 × 1.25 6.8 6.85 (85%)6.647 6.912 9 × 1.257.8 7.85 (85%) 7.647 7.912 10 × 1.58.5 8.62 (85%) 8.376 8.676 11 × 1.59.5 9.62 (85%) 9.376 9.676 12 × 1.75 10.3 10.40 (85%) 10.106 10.441 14 × 2 12 12.2 (85%) 11.835 12.210 16 × 2 14 14.2 (85%) 13.835 14.210 18 × 2.5 15.5 15.7 (85%) 15.294 15.744 20 × 2.5 17.5 17.7 (85%) 17.294 17.744 22 × 2.5 19.5 19.2 (85%) 19.294 19.744 24 × 3 21 21.2 (85%) 20.752 21.252 27 × 3 24 24.2 (85%) 23.752 24.252 30 × 3.5 26.5 26.6 (90%) 26.211 26.771 33 × 3.5 29.5 29.6 (90%) 29.211 29.771 36 × 4 32 32.1 (90%) 31.670 32.270 39 × 4 35 35.1 (90%) 34.67035.270 42 × 4.5 37.5 37.6 (90%) 37.129 37.799 45 × 4.5 40.5 40.6 (90%) 40.129 40.799 48 × 5 43 43.1 (90%) 42.587 43.297注(1)M1.4以下等级:5H、M1.6以上等级:6H(2)基于JIS B 0209-1982标准螺纹下孔径表公制细牙螺纹 JIS B 0211-1982(单位:mm) (注1)(注2) 2级崁合度区分:中(注1)(注2) 崁合度区分:中2级内螺纹小径螺纹尺寸钻头直径下孔径最小直径最大直径M 2.5 × 0.35 2.2 2.22 (75%) 2.121 2.221 3 × 0.35 2.7 2.72 (75%) 2.621 2.721 3.5 × 0.35 3.23.22 (75%) 3.121 3.221 4 × 0.5 3.5 3.59 (75%) 3.459 3.5994.5 × 0.5 44.09 (75%) 3.959 4.099 5 × 0.5 4.5 4.59 (75%) 4.459 4.5995.5 × 0.5 55.09 (75%) 4.959 5.099 6 × 0.75 5.3 5.35 (80%) 5.188 5.378 7 × 0.756.3 6.35 (80%) 6.188 6.378 8 × 1 77.13 (80%) 6.917 7.153 8 × 0.75 7.37.35 (80%) 7.188 7.378 9 × 1 8 8.13 (80%) 7.917 8.153 9 × 0.75 8.38.35 (80%) 8.188 8.378 10 × 1.25 8.8 8.85 (85%) 8.647 8.912 10 × 1 99.13 (80%) 8.917 9.153 10 × 0.75 9.3 9.35 (80%) 9.188 9.378 11 × 1 1010.13 (80%) 9.917 10.153 11 × 0.75 10.3 10.35 (80%) 10.188 10.378 12 × 1.5 10.5 10.62 (85%) 10.376 10.676 12 × 1.25 10.8 10.85 (85%) 10.647 10.912 12 × 1 11 11.13 (80%) 10.917 11.153 14 × 1.5 12.5 12.62 (85%) 12.376 12.676 14 × 1 13 13.13 (80%) 12.917 13.153 15 × 1.5 13.5 13.62 (85%) 13.376 13.676 15 × 1 14 14.13 (80%) 13.917 14.153 16 × 1.5 14.514.62 (85%) 14.376 14.676 16 × 1 15 15.13 (80%) 14.917 15.153 17 × 1.515.5 15.62 (85%) 15.376 15.676 17 × 1 16 16.13 (80%) 15.917 16.153 18 × 2 16 16.2 (85%) 15.835 16.210 18 × 1.5 16.5 16.62 (85%) 16.37616.676 18 × 1 17 17.13 (80%) 16.917 17.153 20 × 2 18 18.2 (85%) 17.835 18.210 20 × 1.5 18.5 18.62 (85%) 18.376 18.676 20 × 1 19 19.13 (80%) 18.917 19.153 22 × 2 20 20.2 (85%) 19.835 20.210 22 × 1.5 20.5 20.62 (85%) 20.376 20.676 22 × 1 21 21.13 (80%) 20.917 21.153 24 × 2 22 22.2 (85%) 21.835 22.210 24 × 1.5 22.5 22.62 (85%) 22.376 22.676 24 × 1 23 23.13 (80%) 22.917 23.153 25 × 2 23 23.2 (85%) 22.835 23.21025 × 1.5 23.5 23.62 (85%) 23.376 23.676 25 × 1 24 24.13 (80%)23.917 24.153螺纹下孔径表公制细牙螺纹 JIS B 0211-1982(单位:mm)(注1)(注2) 2级崁合度区分:中(注1)(注2) 崁合度区分:中2级内螺纹小径螺纹尺寸钻头直径下孔径最小直径最大直径M 26 × 1.5 24.5 24.62 (85%) 24.376 24.676 27 × 2 25 25.2 (85%)24.835 25.210 27 × 1.5 25.5 25.62 (85%) 25.376 25.676 27 × 1 26 26.13 (80%) 25.917 26.153 28 × 2 26 26.2 (85%) 25.835 26.210 28 × 1.5 26.526.62 (85%) 26.376 26.676 28 × 1 27 27.13 (80%) 26.917 27.153 30 × 327 27.2 (85%) 26.752 27.252 30 × 2 28 28.2 (85%) 27.835 28.210 30 × 1.5 28.5 28.62 (85%) 28.376 28.676 30 × 1 29 29.13 (80%) 28.917 29.153 32 × 2 30 30.2 (85%) 29.835 30.210 32 × 1.5 30.5 30.62 (85%) 30.37630.676 33 × 3 30 30.2 (85%) 29.752 30.252 33 × 2 31 31.2 (85%) 30.83531.210 33 × 1.5 31.5 31.62 (85%) 31.376 31.676 35 × 1.5 33.5 33.62 (85%) 33.376 33.676 36 × 3 33 33.2 (85%) 32.752 33.252 36 × 2 34 34.2 (85%) 33.835 34.210 36 × 1.5 34.5 34.62 (85%) 34.376 34.676 38 × 1.536.5 36.62 (85%) 36.376 36.676 39 × 3 36 36.2 (85%) 35.752 36.252 39 × 2 37 37.2 (85%) 36.835 37.210 39 × 1.5 37.5 37.62 (85%) 37.376 37.676 40 × 3 37 37.2 (85%) 36.752 37.252 40 × 2 38 38.2 (85%) 37.835 38.210 40 × 1.5 38.5 38.62 (85%) 38.376 38.676 42 × 4 38 38.1 (90%) 37.670 38.270 42 × 3 39 39.2 (85%) 38.752 39.252 42 × 2 40 40.2 (85%) 39.835 40.210 42 × 1.5 40.5 40.62 (85%) 40.376 40.676 45 × 4 41 41.1 (90%) 40.670 41.270 45 × 3 42 42.2 (85%) 41.752 42.252 45 × 2 43 43.2 (85%) 42.835 43.210 45 × 1.5 43.5 43.62 (85%) 43.376 43.676 48 × 4 44 44.1 (90%) 43.670 44.27048 × 3 45 45.2 (85%) 44.752 45.25246.2 (85%) 48 × 2 46 45.835 46.21048 × 1.5 46.5 46.62 (85%) 46.376 46.67650 × 3 47 47.2 (85%) 46.752 47.25250 × 2 48 48.2 (85%) 47.835 48.21050 × 1.5 48.5 48.62 (85%) 48.376 48.676 注(1)等级:6H(2)基于JIS B 0211-1982标准螺纹下孔径表美制粗牙螺纹 (单位:mm)内螺纹小径 2B级螺纹螺纹尺寸钻头直径下孔径最小直径最大直径NO.1 -64UNC 1.55 1.57 (65%) 1.425 1.5822 -56 1.8 1.86 (65%) 1.695 1.8713 -48 2.1 2.14 (65%) 1.941 2.1464 -40 2.3 2.36 (70%) 2.157 2.3855 -40 2.6 2.69 (70%) 2.487 2.6976 -32 2.8 2.86 (75%) 2.642 2.8958 -32 3.4 3.52 (75%) 3.302 3.53010 -24 3.9 3.91 (80%) 3.683 3.96212 -24 4.5 4.57 (80%) 4.344 4.5971/4 -20 5.1 5.25 (80%) 4.979 5.257 5/16 -18 6.6 6.72 (80%) 6.4016.7313/8 -16 8 8.15 (80%) 7.798 8.153 7/16 -14 9.4 9.5(80%) 9.144 9.550 1/2 -13 10.8 11.0 (80%) 10.592 11.0239/16 -12 12.2 12.3 (85%) 11.989 12.4465/8 -11 13.6 13.8 (85%) 13.386 13.8683/4 -10 16.5 16.8 (80%) 16.307 16.8407/8 - 9 19.5 19.6 (85%) 19.177 19.7611 - 8 22.2 22.5 (85%) 21.971 22.6061 1/8 - 7 25 25.2 (85%) 24.638 25.3491 1/4 - 7 28.2 28.4 (85%) 27.813 28.5241 3/8 - 6 30.8 31.0 (85%) 30.353 31.1151 1/2 - 6 34 34.2 (85%) 33.528 34.2901 3/4 - 5 39.5 39.8 (85%) 38.964 39.8272 - 4 45.2 45.3 (90%) 44.679 45.593螺纹下孔径表美制细牙螺纹 (单位:mm)内螺纹小径 2B级螺纹螺纹尺寸钻头直径下孔径最小直径最大直径 NO. 0 1.25 1.30 (65%) 1.182 1.305 -80UNF1 -72 1.55 1.61 (65%) 1.474 1.6122 -64 1.85 1.90 (65%) 1.756 1.9123 -56 2.1 2.17 (70%) 2.025 2.1974 -48 2.4 2.44 (70%) 2.271 2.4585 -44 2.7 2.74 (70%) 2.551 2.7406 -40 2.9 3.02 (70%) 2.820 3.0228 -36 3.5 3.59 (75%) 3.404 3.60610 -32 4.1 4.14 (80%) 3.963 4.16512 -28 4.6 4.70 (80%) 4.496 4.7241/4 -28 5.5 5.56 (80%) 5.360 5.588 5/16 -24 6.9 7.02 (80%) 6.782 7.0353/8 -24 8.5 8.61 (80%) 8.382 8.6367/16 -20 9.9 10.01 (80%) 9.729 10.0331/2 -20 11.5 11.60 (80%) 11.329 11.6079/16 -18 12.9 13.07 (80%) 12.751 13.0815/8 -18 14.5 14.65 (80%) 14.351 14.6813/4 -16 17.5 17.59 (85%) 17.323 17.6787/8 -14 20.5 20.6 (85%) 20.270 20.6751 -12 23.2 23.5 (85%) 23.114 23.5711 1/8 -12 26.5 26.7 (80%) 26.289 26.7461 1/4 -12 29.5 29.9 (80%) 29.464 29.9211 3/8 -12 32.8 33.0 (85%) 32.639 33.0961 1/2 -12 36 36.2 (85%) 35.814 36.271螺纹下孔径表缝纫机螺纹(SM) (单位:mm)2级内螺纹小径 2B级螺纹螺纹尺寸钻头直径下孔径最小直径最大直径 SM 1/16 - 1.25 1.28 (75%) 1.211 1.281 805/64 - 64 1.55 1.57 (80%) 1.513 1.593 3/32 -100 2.10 2.15 (70%)2.081 2.156 3/32 - 56 1.85 1.91 (80%) 1.841 1.936 1/8 - 44 2.50 2.58 (80%) 2.485 2.605 1/8 - 40 2.45 2.52 (80%) 2.421 2.551 9/64 - 40 2.852.91 (80%) 2.818 2.948 11/64 - 403.65 3.71 (80%) 3.612 3.742 3/16 - 323.90 3.94 (80%) 3.820 3.980 3/16 - 28 3.70 3.82 (80%) 3.684 3.844 7/32 - 324.70 4.73 (80%) 4.614 4.774 15/64 - 28 4.905.01 (80%) 4.875 5.0551/4 - 40 5.60 5.69 (80%) 5.596 5.726 1/4 - 28 5.30 5.41 (80%) 5.2725.452 缝纫机螺纹(SM) (单位:mm)2级内螺纹小径 2B 级螺纹螺纹尺寸钻头直径下孔径最小直径最大直径 SM 1/4 - 5.10 5.25 (80%) 5.086 5.266 249/32 - 28 6.10 6.20 (80%) 6.066 6.2569/32 - 20 5.70 5.82 (80%) 5.634 5.8245/16 - 28 6.90 6.00 (80%) 6.860 7.0505/16 - 24 6.70 6.84 (80%) 6.674 6.8645/16 - 18 6.30 6.38 (85%) 6.254 6.4443/8 - 28 8.50 8.58 (80%) 8.447 8.6373/8 - 18 7.90 7.97 (85%) 7.843 8.0537/16 - 28 10.10 10.17 (80%) 10.034 10.2247/16 - 16 9.30 9.36 (85%) 9.220 9.4401/2 - 28 11.70 11.76 (80%) 11.622 11.8121/2 - 20 11.30 11.38 (80%) 11.190 11.4101/2 - 12 10.30 10.36 (85%) 10.180 10.420 螺纹下孔径表英制粗牙螺纹 (单位:mm)、切削速度与切削液切削速度(m/min) 切削液加工材料高速同步丝水溶性直槽丝攻螺旋丝攻先端丝攻钨钢丝攻无屑丝攻管用丝攻油性半干式干式攻 (乳化液)低碳素钢 C0.25,以下 8~13 8~13 15~25 , 8~13 27~32 3~6 ◎ ? ? ?C0.25,中碳素钢7~12 7~12 10~15 , 7~10 27~32 3~6 ◎ ? ? ? 0.45,高碳素钢 C0.45,以上6~9 6~9 8~13 , 5~8 22~27 2~5 ◎ ? ? ? 合金钢SCM 7~12 7~12 10~15 , 5~8 22~27 2~5 ◎ ? ? ?3~5 3~5 4~6 调质钢25,45HRC , , , 2~5 ◎ ? , , (4~8) (4~8) (6~10) 不锈钢 SUS 4~7 5~8 8~13 , 5~10 , 3~6 ◎ ? , ,SUS630 不锈钢3~5 3~5 4~6 , , , 2~5 ◎ , , , SUS631工具钢SKD 6~9 6~9 7~10 , , , 2~5 ◎ , , , 铸钢 SC 6~11 6~1110~15 , , 17~22 2~5 ◎ ? , , 铸铁FC 10~15 , , 10~20 , , 2~5 ◎ ? ? ? 球铸铁FCD 7~12 7~12 10~20 10~20 , , 4~8 ◎ ? ? ,铜 Cu 6~9 6~11 7~12 10~20 7~12 27~32 2~5 ? ? , , 黄铜‧ Bs‧BsC 10~15 10~20 15~25 15~25 7~12 27~32 5~10 ? ? ? ? 黄铜铸件青铜‧ PB‧PBC 6~11 6~11 10~20 10~20 7~12 , 6~11 ? ? , , 青铜铸件变形AL 10~20 10~20 10~25 , 10~20 100~300 5~10 ◎ ? ? , 铝合金铝合金 AC‧ADC 10~15 10~15 15~20 10~20 10~15 80~300 10~15 ◎ ? ? , 铸件镁合金MC 7~12 7~12 10~15 10~20 , , 10~15 ◎ ? ? , 锌铸件 ZDC7~12 7~12 10~15 10~20 7~12 27~100 10~15 ◎ ? ? ,Thermo Setting 热硬塑料 10~20 , , 15~25 , , 5~10 , ? ? ? Plastic 热可塑性Thermo 10~20 10~15 10~20 10~20 , 27~32 5~10 , ? ? ? 塑料Plastic。
供应链术语缩写及含义供应链管理是现代企业运营中的重要环节,涉及到众多的专业术语和缩写。
以下是一些常见的供应链术语缩写及其含义。
1. SCM - 供应链管理(Supply Chain Management)供应链管理是指通过整合和协调企业内外部资源,以最优化的方式管理从供应商到最终客户的整个流程。
SCM包括计划、采购、生产、物流及售后服务等方面。
2. ERP - 企业资源规划(Enterprise Resource Planning)企业资源规划是一种集成管理系统,用于管理企业内部的各个业务功能,包括采购、销售、生产、财务等。
ERP系统可以帮助企业更好地协调供应链中的信息流,提高运营效率。
3. KPI - 关键绩效指标(Key Performance Indicator)关键绩效指标是衡量企业或部门绩效的重要指标。
在供应链管理中,KPI可以包括各种指标,如成本效益、交货准时率、库存周转率等,以评估供应链的表现并作出进一步改进。
4. JIT - 准时制生产(Just-in-Time)准时制生产是一种以精确控制物料供应时间和数量的生产方式。
它通过减少库存和交货周期,提高生产效率,实现供需高度匹配。
5. RFID - 射频识别技术(Radio-Frequency Identification)射频识别技术使用无线电信号来识别和追踪物品。
在供应链中,RFID可以用于物流管理、库存追踪和反偷窃等方面,提高物流效率。
6. OEM - 原始设备制造商(Original Equipment Manufacturer)原始设备制造商指的是生产和销售给其他公司用于再加工、组装或重新包装的产品的企业。
在供应链中,OEM通常是重要的供应商,通过向其他公司提供关键部件或成品来支持整个供应链运营。
7. SKU - 库存单位(Stock Keeping Unit)库存单位是指企业管理库存时所定义的最小单元。
每个SKU通常与特定产品的规格、颜色、尺寸等属性相关联,方便库存管理和出入库操作。