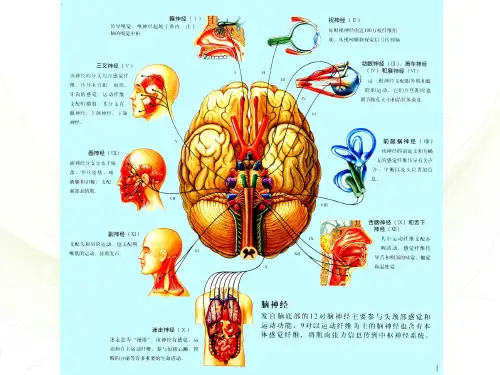
十二对颅神经中英文对照
- 格式:doc
- 大小:20.00 KB
- 文档页数:1

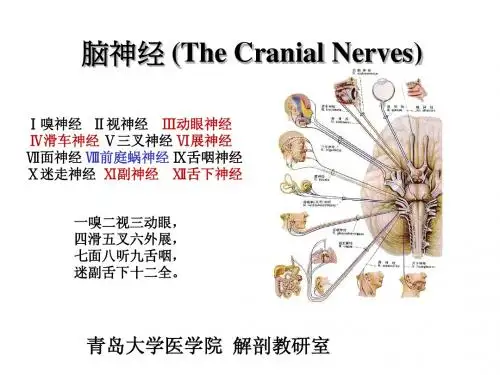
一嗅二视三动眼,四划五叉六外展,七面八听九舌咽,迷走及副舌下全。
(最后一句改为“迷副舌下神经全”,背起来更舒服,你们说呢?)股静脉(V)、股动脉(A)和股神经(N)在股三角内的排列正好构成van(行李车)这个英语单词连接椎骨的韧带主要有五种,其中长韧带有三条(棘上韧带、前纵韧带和后纵韧带),短韧带有两条(黄韧带和棘间韧带),可概括为“三长两短”眼球的结构一孔(瞳孔)、二体(晶状体、玻璃体)、三层膜(外膜、中膜、内膜)8块腕骨舟月三角豆,大小头状钩。
腹主动脉的分支肾上中肾动加睾丸[女性为卵巢动脉],肠上肠下腹腔干。
进出入肺门的主要结构(肺动脉——动,肺静脉——静和支气管——支)的排列:从前到后(左右肺根相同)是肺静脉,肺动脉、支气管,从上到下左肺根是肺动脉,支气管,肺静脉,右肺根是支气管,肺动脉、肺静脉。
由于自前向后及从上往下排列不同,记起来易颠倒出错。
假设一个姓秦的同志,叫“秦同志”(静、动、支———便是左右肺根从前往后排列顺序);英语称“ComradeQin”(同志秦———动、支、静,即自上到下左肺根的排列顺序),最后用倒念(志同秦———支、动、静,右肺根从上往下排列顺序)。
大隐静脉末端五属支腹壁旋髂阴部外,股内股外浅静脉。
防止记忆名称乱,强调四“浅”“阴部外”。
股管股鞘内份为隙腔,名叫股管漏斗状。
一二厘米计长度,股三角底内侧部。
上口称环朝腹腔,腹膜结缔盖其上;下为盲端位有常---隐静脉孔后上方。
腹股沟韧带环前盖,耻骨梳韧带环后埋,腔隙韧带绕环内,环外紧贴股静脉。
淋巴结缔充满腔,结构薄弱疝是殃。
全身骨全身骨头虽难记,抓住要点就容易;头颅躯干加四肢,二百零六分开记;脑面颅骨二十三,躯干总共五十一;四肢一百二十六,全身骨头基本齐;还有六块体积小,藏在中耳鼓室里。
各部椎骨特点椎骨外形不规范,各有特点记心间;颈椎体小棘发叉,横突有孔很明显;胸椎两侧有肋凹,棘突迭瓦下斜尖;腰椎特点体积大,棘突后伸宽双扁。

十二对脑神经口诀十二对脑神经的名称,性质和主要分布十二对脑神经口诀|十二对脑神经的名称,性质和主要分布一嗅二视三动眼,四划五叉六外展,七面八听九舌咽,迷走及副舌下全。
(1)嗅神经(2)视神经(3)动眼神经(4)滑车神经(5)三叉神经(6)外展神经(7)面神经(8)位听神经(9)舌咽神经(10)迷走神经(11)副神经(12)舌下神经、嗅神经转导嗅觉冲动,由上鼻甲及鼻中隔上部粘膜内嗅细胞的中枢突聚集成15~20条嗅丝,穿过筛板入颅前窝,连于大脑腹侧的嗅球。
BACK2、视神经传导视觉冲动,起于眼球视网膜,由眶内经视神经管入颅中窝,续于视交叉。
BACK3、动眼神经为运动神经,自中脑腹侧离脑,穿硬脑膜入海绵窦外侧壁继续前行,经眶上裂入眶动眼神经含一般体躯和一般内脏运动纤维。
前者支配大部分眼外肌,后者即动眼神经的副交感节前纤维,至眶内睫状神经节,节细胞发起之节后纤维至眼球,支配瞳孔括约肌和睫状肌。
BACK4、滑车神经为躯体运动神经于中脑背侧前髓帆处出脑,绕大脑脚向前穿入海绵窦外侧壁,在动眼神经下方继续前行,经动眼神经外上方穿眶上裂入眶,支配上斜肌。
滑车神经和动眼神经亦含本体感觉纤维。
BACK、三叉神经 5为脑神经之最大者,是头面部主要的感觉神经,也是咀嚼肌的运动神经。
躯体感觉纤维大部分起源于三叉神经节。
三叉神经节位于颞骨岩部尖端的三叉神经压迹处,由节的前外缘分出3大支:(1)眼神经:是感觉神经,最小哦,向前穿入海绵窦外侧壁,居滑车神经下方,继经眶上裂入眶。
(2)上颌神经:较大,亦为感觉神经,向前穿入海绵窦外侧壁下部,继水平向前,经圆孔出颅腔进入翼腭窝,再由眶下裂入眶,续为眶下神经。
(3)下颌神经:最大,为混合神经,经卵圆孔至颞下窝。
BACK6、展神经是躯体运动神经,于脑桥延髓之间正中线两旁离脑,在鞍背外侧方穿硬脑膜进入海绵窦内,在颈内动脉外侧行向前出海绵窦,继而经眶上裂内端入眶,至外直肌。
BACK7、面神经是混合神经,于延髓脑桥沟的外侧部附于脑,经内耳门入内耳道,穿过颞骨岩部骨质内弯曲的面神经管,最后出茎乳孔离颅。


十二对脑神经知识点英语The Twelve Cranial Nerves: A Comprehensive Overview.The cranial nerves are twelve pairs of nerves that emerge directly from the brain, innervating various structures in the head and neck. They play a crucial role in sensory perception, motor function, and autonomic regulation. Understanding the anatomy and functions of these nerves is essential for a comprehensive understanding of neurology.Classification of Cranial Nerves.The cranial nerves are classified into two main types: sensory and motor. Sensory nerves transmit sensory information from the periphery to the brain, while motor nerves carry motor commands from the brain to muscles and glands.Sensory Cranial Nerves.Olfactory Nerve (CN I): Responsible for the sense of smell.Optic Nerve (CN II): Transmits visual information from the retina to the brain.Oculomotor Nerve (CN III): Innervates muscles responsible for eye movements, pupillary constriction, and eyelid closure.Trochlear Nerve (CN IV): Innervates the superior oblique muscle of the eye, controlling downward and outward eye movements.Trigeminal Nerve (CN V): Provides sensory innervation to the face, including the skin, teeth, and mucous membranes. It also innervates the muscles of mastication.Abducens Nerve (CN VI): Innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye, controlling outward eye movements.Facial Nerve (CN VII): Innervates the muscles offacial expression, lacrimal glands, and taste buds on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII): Transmits auditory and vestibular information from the inner ear to the brain.Motor Cranial Nerves.Hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII): Innervates the muscles of the tongue, controlling its movements for speech and swallowing.Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX): Innervates the muscles of the pharynx and soft palate, plays a role in swallowing, and provides taste sensation to the posterior third of the tongue.Vagus Nerve (CN X): The longest cranial nerve, it innervates structures throughout the thorax and abdomen, including the heart, lungs, digestive system, and vocal cords.Accessory Nerve (CN XI): Innervates the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, controlling head and neck movements.Autonomic Cranial Nerves.The vagus nerve and glossopharyngeal nerve are considered autonomic cranial nerves, as they contain both sensory and motor fibers involved in regulating involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and salivation.Innervation Territories.Each cranial nerve supplies a specific region of the head and neck, known as its innervation territory. Knowledge of these territories is essential for diagnosing and treating neurological conditions.Clinical Significance.Damage to the cranial nerves can result in a wide rangeof neurological symptoms, depending on the affected nerve. Examples include:Olfactory nerve: Loss of smell (anosmia)。

神经系统词汇中英互译:parahippocampal gyrus 海马旁回pia mater 软脑膜basilar artery 基底动脉cerebral arterial circle 大脑动脉环cerebrospinal fluid 脑脊液Nervous System 神经系统peripheral nervous system 周围神经系统neuron 神经元neuroglia 神经胶质nucleus 神经核tract 神经束ganglion 神经节nerve 神经spinal nerves 脊神经cervical plexus 颈丛phrenic nerve 膈神经brachial plexus 臂丛longthoracic nerve 胸长神经thoracodorsal nerve 胸背神经axillary nerve 腋神经musculocutaneous nerve 肌皮神经ulnar nerve 尺神经radial nerve 桡神经thoracic nerves 胸神经intercostal nerve 肋间神经lumbar plexus 腰丛lumbosacral trunk 腰骶干femoral nerve 股神经obturator nerve 闭孔神经sacral plexus 骶丛sciatic nerve 坐骨神经tibial nerve 胫神经common peroneal nerve 腓总神经superficial peroneal nerve 腓浅神经 deepp eroneal nerve 腓深神经cranial nerves 脑神经olfactory nerve 神经optic nerve 视神经oculomotor nerve 动眼神经trochlear nerve 滑车神经trigeminal nerve 三叉神经abducent nerve 展神经facial nerve 面神经vestibulocochlear nerve 前庭蜗神经 glossopharyngeal nerve 舌咽神经accessory nerve 副神经hypoglossal nerve 舌下神经visceral nervous system 内脏神经系autonomic nervous system 自主神经系vegetative nervous system 植物性神经系 sympathetic nerve 交感神经parasympathetic nerve 副交感神经central nervous system 中枢神经系统spinal cord 脊髓gray matter 灰质white matter 白质substantia gelatinosa 胶状质nucleus thoracicus 胸核fasciculus gracilis 薄束fasciculus cuneatus 楔束spinothalamic tract 脊髓丘脑束corticospinal tract 皮质脊髓束brain encephalon 脑brain stem 脑干medulla oblongata 延髓pons 脑桥midbrain mesencephalon 中脑pyramid 锥体pyramidal decussation 锥体交叉inferior olive nucleus 下橄榄核gracilis tubercule 薄束结节cuneate tubercule 楔束结节inferior cerebellar peduncle 小脑下脚fourth ventricle 第四脑室rhomboid fossa 菱形窝striae medullaris 髓纹hypoglossal trigone 舌下神经三角vagal trigone 迷走神经三角area postrema 最后区obex 闩medial eminence 内侧隆起facial colliculus 面丘vestibular area前庭区acoustic tubercle 听结节middle cerebellar peduncle 小脑中脚superior cerebellar peduncle 小脑上脚inferior colliculus 下丘superior colliculus 上丘crus cerebri 大脑脚cerebral aqueduct 中脑导水管medial lemniscus 内侧丘系spinal trigeminal tract 三叉神经脊髓束 spinal trigeminal nucleus 三叉神经脊束核 solitary nucleus 孤束核nucleus ambiguus 疑核pontine nuclei 脑桥核trapezoid body 斜方体lateral lemniscus 外侧丘系locus ceruleus 蓝斑substantia nigra 黑质red nucleus 红核reticular formation 网状结构 raphe nuclei 中缝核cerebellum 小脑diencephalon 间脑thalamus 丘脑metathalamus 后丘脑epithalamus 上丘脑uncus 海马旁回钩paracentral lobule 旁中央小叶 cingulate gyrus 扣带回lateral ventricle 侧脑室basal nuclei 基底核caudate nucleus 尾状核lentiform nucleus 豆状核putamen 壳globus palidus 苍白球corpus striatum 纹状体fornix 穹窿internal capsule 内囊cerebral cortex 大脑皮质dura mater 硬脑膜arachnoid 蛛网膜subthalamus 底丘脑hypothalamus 下丘脑opticchiasma 视交叉telencephalon cerebrum 端脑大脑 temporal lobe 颞叶frontal lobe 额叶parietal lobe 顶叶occipital lobe 枕叶insula 岛叶limbic lobe 边缘叶corpus callosum 胼胝体central sulcus 中央沟lateral sulcus 外侧沟parieo-occipital sulcus 顶枕沟 calcarine sulcus 距状沟precentral gyrus 中央前回postcentral gyrus 中央后回angular gyrus 角回supramarginal gyrus 缘上回lingual gyrus 舌回cuneus gyrus 楔回dentate gyrus 齿状回感谢您的阅读,祝您生活愉快。

颅神经英文对照cranialnerve;cranialnerves;cranialneural,颅神经又称“脑神经”。
属周围神经,从脑内发出的左右成对的神经。
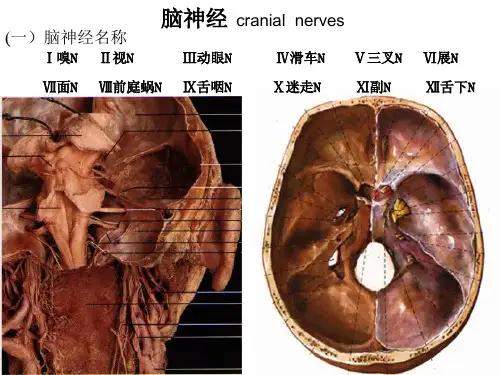
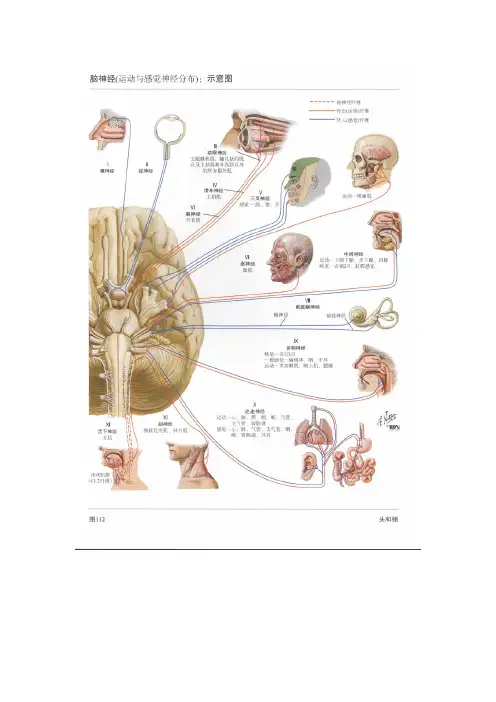
人的12对脑神经是嗅神经、视神经、动眼神经、滑车神经、三叉神经、外展神经、面神经、听神经、舌咽神经、迷走神经、脊髓副神经和舌下神经。
这些神经的分布限于头部和颈部,但迷走神经例外,其分布扩展至胸腔和腹腔的内脏器官。
编辑摘要目录[隐藏]1 组成2 三叉神经定位3 病变4 症状5 病因6 嗅神经损害7 视神经损害8 动眼神经损害9 三叉神经损害10 面神经损害颅神经- 组成十二对颅神经人体共有十二对颅神经:第一对叫做嗅神经,主要负责鼻子的嗅觉.第二对叫做视神经,主管眼睛的视物功能.第三对动眼神经,主管眼球向上、向下向内等方向的运动和上睑上提及瞳孔的缩小.第四对滑车神经,主管眼球向外下方的运动.第六对外展神经,主管眼球向外方向的运动。
第五对三叉神经,此神经分为两部分,较大的一部分负责面部的痛、温、触等感觉;较小的一部分主管吃东西时的咀嚼动作。
大的感觉神经又分为三支:第一支叫做眼支,主要负责眼裂以上之皮肤、粘膜的感觉,如额部皮肤、睑结膜、角膜等处的感觉。
第二支叫做上颌支、主管眼、口之间的皮肤、粘膜之感觉,如颊部、上颌部皮肤、鼻腔粘膜、口腔粘膜上部及上牙的感觉.。
第三支叫做下颌支,主管口以下的皮肤、粘膜之感觉,如下颌部皮肤、口腔粘膜下部及下牙的感觉。
第七对面神经,主管面部表情肌的运动,此外还主管一部分唾液腺的分泌以及舌前三分之二的味觉感觉。
第八对颅神经,由两部分组成,一部分叫做听神经,主管耳对声音的感受.另一部分叫做前庭神经,其主要作用是保持人体的平衡。
第九对舌咽神经,主管咽喉部粘膜的感觉,一部分唾液腺的分泌和舌后三分之一的味觉,益与第十对迷走神经一起主管咽喉部肌肉的运动。
第十对迷走神经,除与第九对舌咽神经一起主管咽喉部肌肉的运动外,还负责心脏、血管、胃肠道平滑肌的运动。
Ⅰ嗅神经:olfactory nerves1、性质:特殊内脏感觉纤维。
2、位置、行程、分布:由上鼻甲以上和鼻中隔上部粘膜内的嗅细胞中枢突聚集而成,包括20多条嗅丝,嗅神经穿过筛孔入颅前窝,进入嗅球传导嗅觉。
3、损伤后的表现:(1)颅前窝骨折累及筛板时,可撕脱嗅丝和脑膜,造成嗅觉障碍,同时脑脊液也可流入鼻腔。
(2)鼻炎时,炎症延至鼻上部粘膜,也可造成一时性嗅觉迟钝Ⅱ视神经:optic nerve1、性质:由特殊躯体感觉纤维组成,传导视觉冲动。
2、位置、行程、分布:由视网膜节细胞的轴突,在视神经盘处聚集后穿过巩膜筛板而构成。
在眶内行向后内,穿经视神经管入颅中窝,向后内走行于垂体前方连于视交叉,再经视束连于间脑。
3、临床联系:当ICP增高时,常出现视神经盘水肿。
由于视神经是胚胎发生时间脑向外突出形成视器过程中的一部分,故视神经外面包有由三层脑膜延续而来的三层被膜,脑蛛网膜下腔也随之延续到视神经周围。
所以颅内压增高时,常出现视神经盘水肿。
Ⅲ动眼神经:oculomotor nerve1、性质:运动性神经,含一般躯体运动和一般内脏运动纤维。
2、位置、行程:起于中脑动眼神经核和动眼神经副核,自中脑腹侧脚间窝出脑,紧贴小脑幕切迹缘和蝶鞍后床突侧方前行,穿行于海绵窦外侧壁上部继续前行,经眶上裂入眶,分为上、下两支。
3、分布:(1)动眼神经上支分布于上睑提肌、上直肌;(2)动眼神经下支分布于下直肌、内直肌、下斜肌;(3)睫状神经节短根经睫状神经节换元后,节后纤维分布于睫状肌和瞳孔括约肌。
4、损伤后的表现:(1)上睑提肌瘫痪,眼睑下垂;(2)动眼神经支配的上、下、内直肌及下斜肌瘫痪,产生外斜视;(3)瞳孔括约肌和睫状肌瘫痪,瞳孔扩大,丧失对光反射及调节能力;(4)眼外肌大多数瘫痪松弛,眼球稍向前突;(5)复视。
Ⅳ滑车神经:trochlear nerve1、性质:运动性脑神经。
2、位置、行程、分布:起于中脑下丘平面对侧的滑车神经核,自中脑背侧下丘下方出脑,是脑神经中最细者,绕过大脑脚外侧前行,也穿经海绵窦外侧壁向前,经眶上裂入眶,越过上直肌和上睑提肌向前内侧行,进入并支配上斜肌。