java读取文件目录结构并生成xml树
- 格式:doc
- 大小:47.50 KB
- 文档页数:3

java读取XML⽂件的四种⽅法总结(必看篇)JAVA操作XML⽂档主要有四种⽅式,分别是DOM、SAX、JDOM和DOM4J,DOM和SAX是官⽅提供的,⽽JDOM和DOM4J 则是引⽤第三⽅库的,其中⽤的最多的是DOM4J⽅式。
运⾏效率和内存使⽤⽅⾯最优的是SAX,但是由于SAX是基于事件的⽅式,所以SAX⽆法在编写XML的过程中对已编写内容进⾏修改,但对于不⽤进⾏频繁修改的需求,还是应该选择使⽤SAX。
下⾯基于这四种⽅式来读取XML⽂件。
第⼀,以DOM的⽅式实现。
package xmls;import org.w3c.dom.Document;import org.w3c.dom.Element;import org.w3c.dom.Node;import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;import org.xml.sax.SAXException;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;import java.io.File;import java.io.IOException;/*** Created by lenovo on 2017-6-3.*/public class DOMReadDemo {public static void main(String[] args){DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();try{DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();Document document = db.parse("src/xmls/DOM.xml");NodeList booklist = document.getElementsByTagName("book");for(int i = 0; i < booklist.getLength(); i++){System.out.println("--------第" + (i+1) + "本书----------");Element ele = (Element) booklist.item(i);NodeList childNodes= ele.getChildNodes();for(int j = 0; j < childNodes.getLength(); j++){Node n = childNodes.item(j);if(n.getNodeName() != "#text"){System.out.println(n.getNodeName() + ":" + n.getTextContent());}}System.out.println("---------------------------------");}}catch (ParserConfigurationException e){e.printStackTrace();}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}catch (SAXException e){e.printStackTrace();}}}第⼆,以SAX的⽅式实现。


java读取xml配置⽂件(⼩结)使⽤DOM解析XML⽂档时,需要读⼊整个XML⽂档,然后在内存中创建DOM树,⽣成DOM树上的每个节点对象。
只有在整个DOM树创建完毕后,我们才能做其他的操作,即使我们只需要修改根元素节点的第⼆个⼦节点,仍然需要在进⾏这个⼩⼩的修改之间分析整个⽂档,在内存中构建⽂档树。
当XML⽂档⽐较⼤时,构建DOM树将花费⼤量的时间和内存。
⼀种替代的技术就是使⽤SAX,SAX允许你在读取⽂档的时候,即对它进⾏处理,解析完毕处理也就完成了,不必等待整个⽂档被分析存储之后才进⾏操作。
三步过程为了使⽤ XML ⽂件中的信息,必须解析⽂件以创建⼀个 Document 对象。
Document 对象是⼀个接⼝(??为了统⼀吗 ),因⽽不能直接将它实例化;⼀般情况下,应⽤程序会相应使⽤⼀个⼯⼚。
准确的过程因实现⽽异,但是基本思想是相同的。
(同样,Level 3 标准化了这个任务。
)在这个例⼦ Java 环境中,解析⽂件是⼀个三步过程:1.创建 DocumentBuilderFactory。
DocumentBuilderFactory 对象创建 DocumentBuilder。
2.创建 DocumentBuilder。
DocumentBuilder 执⾏实际的解析以创建 Document 对象。
3.解析⽂件以创建 Document 对象。
现在您可以开始构建应⽤程序了。
基本的应⽤程序⾸先创建⼀个基本的应⽤程序,即⼀个名为 OrderProcessor 的类。
『『 『 『第⼀步是⽣成⼀个DocumentBuilderFactory对象,newInstance()是静态⽅法,所以可以直接类名点调⽤。
第⼆步是⽤⼯⼚⽣成⼀个DocumentBuilder对象,但是newDocumentBuilder()是抽象⽅法,还没实现,在这⾥就可以调⽤了吗?还是像你以前说的,只要能产⽣⼀个抽象类的对象,那么这个抽象类的所以抽象⽅法就都已经实现了?是这样吗newDocumentBuilder()抽象⽅法肯定会被⾮抽象⼦类实现,这就发⽣了多态,执⾏时调⽤⼦类的重写后的⽅法public class DocumentBuilderFactoryImpl extends DocumentBuilderFactory {......................}sun的newInstance()⽅法public static DocumentBuilderFactory newInstance() {try {return (DocumentBuilderFactory) FactoryFinder.find(/* The default property name according to the JAXP spec */"javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory",/* The fallback implementation class name */".apache.xerces.internal.jaxp.DocumentBuilderFactoryImpl");} catch (FactoryFinder.ConfigurationError e) {throw new FactoryConfigurationError(e.getException(),e.getMessage());}}它应该是⽤反射返回了⼀个DocumentBuilderFactoryImpl的实例,然后⽤DocumentBuilderFactory强转,也就是:DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance()返回⼀个Object类型的DocumentBuilderFactory实例,下⾯的就不⽤说了吧!』import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;import java.io.File;import org.w3c.dom.Document;public class OrderProcessor {public static void main (String args[]) {File docFile = new File("orders.xml");Document doc = null;try {DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();doc = db.parse(docFile);} catch (Exception e) {System.out.print("Problem parsing the file: "+e.getMessage());}}}⾸先,Java 代码导⼊必要的类,然后它创建 OrderProcessor 应⽤程序。


使用要导入dom4j-1.6.1.jar文件我的dom4j文件在讲解生成xml 1:先通过DocumentHelper类的.createDocument()方法生成Document文件2:接着通过DocumentHelper类的createElement("根节点字符串形式")创建根节点3:通过通过生成的Document的实例的setRootElement(根节点)设置根节点4:接着可以通过Document的实例的getRootElement()方法得到根节点5:接着通过根节点(Element类的实例)的.addElement("子节点的字符串形式")添加子节点6:通过节点类(Element类的实例)的setText("字符串“)设置节点对应的值7:通过Document类的实例的.asXML();的方式的得到xml字符串;(注意:xml 是字符串String的形式。
可以设置几个同名的根节点(<user>username1<user><<user>username2<user>)解析时通过Elment的.elementIterator("user");方法得到迭代器)解析xml 1:通过new SAXReader();得到SAXReader的一个实例2:通过StringReader(参数是字符串)将xml字符串转化为一个Reader字符输入流3:通过SAXReader的实例.read(参数是个Reader)得到得到Document4:通过Document的getRootElement()方法得到根节点(Element类的实例)5:通过根节点的element("子节点的字符串形式")方法得到子节点(若有多个同名子节点通过根节点的.elementIterator("user")得到同名节点迭代器)6:通过节点的getTxt();方法得到节点的值生成xml 例子:private static Document constructDocument()//此处会被下面调用{Document document = DocumentHelper.createDocument();Element root = DocumentHelper.createElement("message");document.setRootElement(root);return document;}document文件。

java读取xml4种方法XML 文件格式如下:测试方法:采用 JSP 端调用Bean(至于为什么采用JSP来调用,请参考:/rosen/archive/2004/10/15/138324.aspx),让每一种方案分别解析10K、100K、1000K、10000K的 XML 文件,计算其消耗时间(单位:毫秒)。
JSP 文件:测试1、首先出场的是 DOM(JAXP Crimson 解析器)DOM 是用与平台和语言无关的方式表示 XML 文档的官方 W3C 标准。
DOM 是以层次结构组织的节点或信息片断的集合。
这个层次结构允许开发人员在树中寻找特定信息。
分析该结构通常需要加载整个文档和构造层次结构,然后才能做任何工作。
由于它是基于信息层次的,因而 DOM 被认为是基于树或基于对象的。
DOM 以及广义的基于树的处理具有几个优点。
首先,由于树在内存中是持久的,因此可以修改它以便应用程序能对数据和结构作出更改。
它还可以在任何时候在树中上下导航,而不是像 SAX 那样是一次性的处理。
DOM 使用起来也要简单得多。
另一方面,对于特别大的文档,解析和加载整个文档可能很慢且很耗资源,因此使用其他手段来处理这样的数据会更好。
这些基于事件的模型,比如 SAX。
Bean文件:10k消耗时间:265 203 219 172100k消耗时间:9172 9016 8891 90001000k消耗时间:691719 675407 708375 73965610000k消耗时间:OutOfMemoryError2、接着是 SAX这种处理的优点非常类似于流媒体的优点。
分析能够立即开始,而不是等待所有的数据被处理。
而且,由于应用程序只是在读取数据时检查数据,因此不需要将数据存储在内存中。
这对于大型文档来说是个巨大的优点。
事实上,应用程序甚至不必解析整个文档;它可以在某个条件得到满足时停止解析。
一般来说,SAX 还比它的替代者 DOM 快许多。


* Inc.* Copyright (c) 2005-2008 All Rights Reserved.*/package com.alipay.client.base;import java.io.InputStream;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;import org.w3c.dom.Document;import org.w3c.dom.Element;import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;/***** @author feng.chenf* @version $Id: ClientConfig.java, v 0.1 2008-12-24 ????09:31:39 feng.chenf Exp $ */public class ClientConfig {/*** ????????????????????? ????????https://*/private String serverUrl = "http://115.124.16.16";/*** ????????????????????? ???????????????? ?????443???private String serverPort = "80";/*** ?????partnerId*/private String partnerId = "";/*** ??????????ú?*/private String secId = "";/*** ???????*/private String prikey = "";/*** ???????*/private String pubkey = "";/*** ????????????????????*/private String alipayVeriPubKey = ""; /*** ?????????????????????????private String alipayEncPubKey = "";/*** ?????? ?????????????RSA*/private String signAlgo = "RSA";/*** ??????? ?????????????RSA*/private String encryptAlgo = "RSA";public ClientConfig() {try {InputStream iss = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream( "com/alipay/client/config/config.xml");DocumentBuilderFactory domfac = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); DocumentBuilder dombuilder = domfac.newDocumentBuilder();Document doc = dombuilder.parse(iss);Element rootElement = doc.getDocumentElement();NodeList paramNode = doc.getElementsByTagName("partnerId");partnerId = paramNode.item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue().trim(); NodeList secNode = doc.getElementsByTagName("secId");secId = secNode.item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue().trim();NodeList signAlgoNode = doc.getElementsByTagName("signAlgo");this.signAlgo = signAlgoNode.item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue().trim();NodeList prikeyNode = doc.getElementsByTagName("prikey");this.prikey = prikeyNode.item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue().trim();NodeList pubkeyNode = doc.getElementsByTagName("pubkey");this.pubkey = pubkeyNode.item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue().trim();NodeList alipayVeriPubKeyNode = doc.getElementsByTagName("alipayVeriPubKey");this.alipayVeriPubKey =alipayVeriPubKeyNode.item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue().trim();NodeList alipayEncPubKeyNode = doc.getElementsByTagName("alipayEncPubKey");this.alipayEncPubKey = alipayEncPubKeyNode.item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue().trim();} catch (Exception e) {//??????//??????????? ????????????e.printStackTrace();}}/*** @return Returns the serverUrl.*/public String getServerUrl() {return serverUrl;}/*** @param serverUrl The serverUrl to set.*/this.serverUrl = serverUrl;}/*** @return Returns the serverPort.*/public String getServerPort() {return serverPort;}/*** @param serverPort The serverPort to set.*/public void setServerPort(String serverPort) { this.serverPort = serverPort;}/*** @return Returns the partnerId.*/public String getPartnerId() {return partnerId;}/*** @param partnerId The partnerId to set.*/this.partnerId = partnerId;}/*** @return Returns the secId.*/public String getSecId() {return secId;}/*** @param secId The secId to set.*/public void setSecId(String secId) { this.secId = secId;}/*** @return Returns the prikey.*/public String getPrikey() {return prikey;}/*** @param prikey The prikey to set. */public void setPrikey(String prikey) { this.prikey = prikey;}/*** @return Returns the pubkey.*/public String getPubkey() {return pubkey;}/*** @param pubkey The pubkey to set.*/public void setPubkey(String pubkey) { this.pubkey = pubkey;}/*** @return Returns the signAlgo.*/public String getSignAlgo() {return signAlgo;}/*** @param signAlgo The signAlgo to set. */public void setSignAlgo(String signAlgo) {this.signAlgo = signAlgo;}/*** @return Returns the encryptAlgo.*/public String getEncryptAlgo() {return encryptAlgo;}/*** @param encryptAlgo The encryptAlgo to set.*/public void setEncryptAlgo(String encryptAlgo) {this.encryptAlgo = encryptAlgo;}/*** @return Returns the alipayVeriPubKey.*/public String getAlipayVeriPubKey() {return alipayVeriPubKey;}/*** @param alipayVeriPubKey The alipayVeriPubKey to set. */public void setAlipayVeriPubKey(String alipayVeriPubKey) { this.alipayVeriPubKey = alipayVeriPubKey;}/*** @return Returns the alipayEncPubKey.*/public String getAlipayEncPubKey() {return alipayEncPubKey;}/*** @param alipayEncPubKey The alipayEncPubKey to set.*/public void setAlipayEncPubKey(String alipayEncPubKey) { this.alipayEncPubKey = alipayEncPubKey;}}。

Java读取XML⽂件使⽤Java读取XML⽂件有四种⽅式:1. DOM2. SAX3. JDOM4. DOM4jbook.xml⽂件内容:1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>2<书架>3<书>4<书名编号="a_1">JavaWeb程序开发⼊门</书名>5<作者分类="AA">传智播客</作者>6<售价单位="元">60</售价>7</书>8<书>9<书名编号="a_2">JavaWeb从⼊门到精通</书名>10<作者分类="BB">明⽇科技</作者>11<售价>80</售价>12</书>13<书>14<书名编号="a_3">计算机⽂化基础</书名>15<作者分类="CC">⼭东商务</作者>16<售价>40</售价>17</书>18</书架>1.DOMDOM 解析 XML 的步骤:1) 创建⼀个 DocumentBuilderFactory 的对象。
2) 创建⼀个 DocumentBuilder 对象。
3) 通过DocumentBuilder的parse(...)⽅法得到Document对象。
4) 通过 getElementsByTagName(...)⽅法获取到节点的列表。
5) 通过 for 循环遍历每⼀个节点。
6) 得到每个节点的属性和属性值。
7) 得到每个节点的节点名和节点值。

Java XML处理解析和生成XML数据Java作为一种广泛使用的编程语言,提供了丰富的API和工具来处理和操作XML数据。
本文将介绍Java中处理和解析XML数据的基本方法,并探讨如何使用Java生成XML数据。
一、XML简介XML(可扩展标记语言)是一种用于描述数据的标记语言,它的设计目标是传输数据而不仅仅是显示数据。
XML以一种结构化的方式存储数据,使得数据具有良好的可读性和可扩展性。
二、XML解析XML解析是指将XML数据转换为Java程序可以理解和处理的格式。
Java提供了几种XML解析方法,包括DOM(文档对象模型)、SAX(简单API for XML)和StAX(流API for XML)。
1. DOM解析DOM解析是最常用和最常见的XML解析方法之一。
DOM将XML文档视为一个树形结构,通过解析整个文档并将其加载到内存中,以方便对数据的操作和访问。
使用DOM解析XML的基本步骤如下:(1)创建一个DocumentBuilder对象。
(2)使用DocumentBuilder对象的parse()方法解析XML文件,返回一个Document对象。
(3)通过Document对象获取XML文件中的节点和元素。
以下是一个使用DOM解析XML的示例代码:```DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();Document document = builder.parse(new File("example.xml"));// 获取根节点Element rootElement = document.getDocumentElement();// 获取子节点NodeList nodeList = rootElement.getElementsByTagName("book");for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {Element bookElement = (Element) nodeList.item(i);String title =bookElement.getElementsByTagName("title").item(0).getTextContent( );String author =bookElement.getElementsByTagName("author").item(0).getTextContent();System.out.println("Title: " + title + ", Author: " + author);}```2. SAX解析SAX解析是一种基于事件驱动的解析方法。
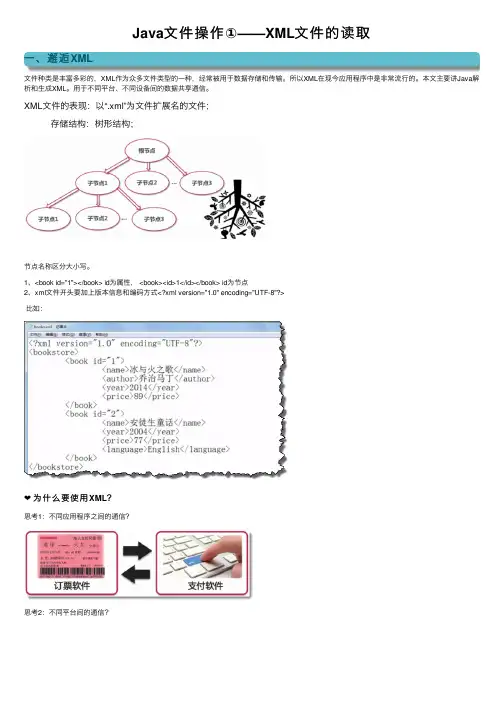
Java⽂件操作①——XML⽂件的读取⼀、邂逅XML⽂件种类是丰富多彩的,XML作为众多⽂件类型的⼀种,经常被⽤于数据存储和传输。
所以XML在现今应⽤程序中是⾮常流⾏的。
本⽂主要讲Java解析和⽣成XML。
⽤于不同平台、不同设备间的数据共享通信。
XML⽂件的表现:以“.xml”为⽂件扩展名的⽂件; 存储结构:树形结构;节点名称区分⼤⼩写。
1、<book id="1"></book> id为属性, <book><id>1</id></book> id为节点2、xml⽂件开头要加上版本信息和编码⽅式<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>⽐如:❤为什么要使⽤XML?思考1:不同应⽤程序之间的通信?思考2:不同平台间的通信?思考3:不同平台间的数据共享?答案就是我们要学习的XML⽂件。
我们可以使⽤相同的xml把不同的⽂件联系起来⼆、应⽤ DOM ⽅式解析 XML❤在Java程序中如何获取XML⽂件的内容解析的⽬的:获取节点名、节点值、属性名、属性值;四种解析⽅式:DOM、SAX、DOM4J、JDOMDOM、SAX :java 官⽅⽅式,不需要下载jar包DOM4J、JDOM :第三⽅,需要⽹上下载jar包⽰例:解析XML⽂件,⽬标是解析XML⽂件后,Java程序能够得到xml⽂件的所有数据思考:如何在Java程序中保留xml数据的结构?如何保留节点之间的层级关系?注意常⽤的节点类型:下⾯介绍DOM⽅式解析XML:功能说明:代码⽰例:1package com.study.domtest;23import java.io.IOException;45import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;6import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;7import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;89import org.w3c.dom.Document;10import dNodeMap;11import org.w3c.dom.Node;12import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;13import org.xml.sax.SAXException;1415/**16 * DOM⽅式解析xml17*/18public class DOMTest {1920public static void main(String[] args) {21//1、创建⼀个DocumentBuilderFactory的对象22 DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();23//2、创建⼀个DocumentBuilder的对象24try {25//创建DocumentBuilder对象26 DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();27//3、通过DocumentBuilder对象的parser⽅法加载books.xml⽂件到当前项⽬下28/*注意导⼊Document对象时,要导⼊org.w3c.dom.Document包下的*/29 Document document = db.parse("books.xml");//传⼊⽂件名可以是相对路径也可以是绝对路径30//获取所有book节点的集合31 NodeList bookList = document.getElementsByTagName("book");32//通过nodelist的getLength()⽅法可以获取bookList的长度33 System.out.println("⼀共有" + bookList.getLength() + "本书");34//遍历每⼀个book节点35for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getLength(); i++) {36 System.out.println("=================下⾯开始遍历第" + (i + 1) + "本书的内容================="); 37//❤未知节点属性的个数和属性名时:38//通过 item(i)⽅法获取⼀个book节点,nodelist的索引值从0开始39 Node book = bookList.item(i);40//获取book节点的所有属性集合41 NamedNodeMap attrs = book.getAttributes();42 System.out.println("第 " + (i + 1) + "本书共有" + attrs.getLength() + "个属性");43//遍历book的属性44for (int j = 0; j < attrs.getLength(); j++) {45//通过item(index)⽅法获取book节点的某⼀个属性46 Node attr = attrs.item(j);47//获取属性名48 System.out.print("属性名:" + attr.getNodeName());49//获取属性值50 System.out.println("--属性值" + attr.getNodeValue());51 }52//❤已知book节点有且只有1个id属性:53/*54 //前提:已经知道book节点有且只能有1个id属性55 //将book节点进⾏强制类型转换,转换成Element类型56 Element book1 = (Element) bookList.item(i);57 //通过getAttribute("id")⽅法获取属性值58 String attrValue = book1.getAttribute("id");59 System.out.println("id属性的属性值为" + attrValue);60*/6162//解析book节点的⼦节点63 NodeList childNodes = book.getChildNodes();64//遍历childNodes获取每个节点的节点名和节点值65 System.out.println("第" + (i+1) + "本书共有" + childNodes.getLength() + "个⼦节点");66for (int k = 0; k < childNodes.getLength(); k++) {67//区分出text类型的node以及element类型的node68if(childNodes.item(k).getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE){69//获取了element类型节点的节点名70 System.out.print("第" + (k + 1) + "个节点的节点名:" + childNodes.item(k).getNodeName());71//获取了element类型节点的节点值72 System.out.println("--节点值是:" + childNodes.item(k).getFirstChild().getNodeValue());73// System.out.println("--节点值是:" + childNodes.item(k).getTextContent());74 }75 }76 System.out.println("======================结束遍历第" + (i + 1) + "本书的内容=================");77 }7879 } catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {80 e.printStackTrace();81 } catch (SAXException e) {82 e.printStackTrace();83 } catch (IOException e) {84 e.printStackTrace();85 }86 }8788 }三、应⽤ SAX ⽅式解析 XMLSAX是SIMPLE API FOR XML的缩写,与DOM⽐较⽽⾔,SAX是⼀种轻量型的⽅法。
Java遍历输出指定⽬录、树形结构所有⽂件包括⼦⽬录下的⽂件下⾯通过⼀段代码介绍下Java输出指定⽬录、树形结构下的所有⽂件包括⼦⽬录中的⽂件的⽅法,并附有效果图。
import java.io.File;public class ReadDirectory {// ⽂件所在的层数private int fileLevel;/*** ⽣成输出格式* @param name 输出的⽂件名或⽬录名* @param level 输出的⽂件名或者⽬录名所在的层次* @return 输出的字符串*/public String createPrintStr(String name, int level) {// 输出的前缀String printStr = "";// 按层次进⾏缩进for (int i = ; i < level; i ++) {printStr = printStr + " ";}printStr = printStr + "- " + name;return printStr;}/*** 输出初始给定的⽬录* @param dirPath 给定的⽬录*/public void printDir(String dirPath){// 将给定的⽬录进⾏分割String[] dirNameList = dirPath.split("\\\\");// 设定⽂件level的basefileLevel = dirNameList.length;// 按格式输出for (int i = ; i < dirNameList.length; i ++) {System.out.println(createPrintStr(dirNameList[i], i));}}/*** 输出给定⽬录下的⽂件,包括⼦⽬录中的⽂件* @param dirPath 给定的⽬录*/public void readFile(String dirPath) {// 建⽴当前⽬录中⽂件的File对象File file = new File(dirPath);// 取得代表⽬录中所有⽂件的File对象数组File[] list = file.listFiles();// 遍历file数组for (int i = ; i < list.length; i++) {if (list.isDirectory()) {System.out.println(createPrintStr(list.getName(), fileLevel));fileLevel ++;// 递归⼦⽬录readFile(list.getPath());fileLevel --;} else {System.out.println(createPrintStr(list.getName(), fileLevel));}}}public static void main(String[] args) {ReadDirectory rd = new ReadDirectory();String dirPath = "D:\\有道词典";rd.printDir(dirPath);rd.readFile(dirPath);}}输出结果如下:以上就是本⽂的全部内容,希望⼤家喜欢。
java读取解析xml文件实例java读取解析xml文件实例如何在Java中读取解析文件呢?下面店铺为大家整理了java读取解析xml文件实例,希望能帮到大家!读取本地的xml文件,通过DOM进行解析,DOM解析的特点就是把整个xml文件装载入内存中,形成一颗DOM树形结构,树结构是方便遍历和和操纵。
DOM解析的特性就是读取xml文件转换为 dom树形结构,通过节点进行遍历。
这是W3c关于节点的概念如果xml中包含有大量的数据,由于dom一次性把xml装入内存中的特性,所以dom不适合于包含大量数据的xml解析。
当包含有大量xml的时候,用SAX进行解析比较节省内存。
下面是一个运用DOM进行解析xml文件的例子:xml文件结构如下:<"1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1">Giada De Laurentiis200530.00J K. Rowling200529.99James McGovern200349.99Erik T. Ray200339.95创建解析xml的类如下:package xml.dom;import java.io.File;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;importjavax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;importorg.w3c.dom.Document;import org.w3c.dom.Element;import org.w3c.dom.Node;import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;public class ReadXmlFile { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ File xmlFile = new File("src/resource/book.xml"); DocumentBuilderFactory builderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); DocumentBuilderbuilder = builderFactory.newDocumentBuilder(); Document doc =builder.parse(xmlFile); doc.getDocumentElement().normalize(); System.out.println("Root element: "+doc.getDocumentElement().getNodeName()); NodeList nList = doc.getElementsByTagName("book"); for(int i = 0 ; i<nList.getLength();i++){ Node node = nList.item(i); System.out.println("Node name: "+ node.getNodeName()); Element ele = (Element)node; System.out.println("----------------------------"); if(node.getNodeType() == Element.ELEMENT_NODE){ System.out.println("book category: "+ ele.getAttribute("category")); System.out.println("title name: "+ele.getElementsByTagName("title").item(0).getTextContent()); Sy stem.out.println("author name: "+ele.getElementsByTagName("author").item(0).getTextContent( )); System.out.println("year :"+ele.getElementsByTagName("year ").item(0).getTextContent()); System.out.println("price : "+ele.getElementsByTagName("price").item(0).getTextContent()); System.out.println("-------------------------"); } }解析结果:Root element: bookstoreNode name: book----------------------------book category: cookingtitle name: Everyday Italianauthor name: Giada De Laurentiisyear :2005price : 30.00-------------------------Node name: book----------------------------book category: childrentitle name: Harry Potterauthor name: J K. Rowlingyear :2005price : 29.99-------------------------Node name: book----------------------------book category: webtitle name: XQuery Kick Startauthor name: James McGovernyear :2003price :49.99-------------------------Node name: book----------------------------book category: webtitle name: Learning XMLauthor name: Erik T. Rayyear :2003price : 39.95------------------------- 以上是通过name获得对应的'值,下面利用循环节点的方式输出:循环节点输出方式的代码如下:package xml.dom;import java.io.File;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;importjavax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;importorg.w3c.dom.Document;importdNodeMap;importorg.w3c.dom.Node;import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;public class ReadXmlFile2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ File xmlFile = new File("src/resource/book.xml"); DocumentBuilderFactory builderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); DocumentBuilder builder = builderFactory.newDocumentBuilder(); Document doc =builder.parse(xmlFile); doc.getDocumentElement().normalize(); System.out.println("Root element: "+doc.getDocumentElement().getNodeName()); if(doc.hasChil dNodes()){ printNode(doc.getChildNodes()); } }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void printNode(NodeList nodeList){ System.out.println("------------------------"); // System.out.println(nodeList.getLength()); for(int i = 0; i<nodeList.getLength(); i++){ Node node = (Node)nodeList.item(i); if(node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE){ System.out.println("node name: "+node.getNodeName()); System.out.println("node value:"+node.getTextContent());if(node.hasAttributes()){ NamedNodeMap nodeMap = node.getAttributes(); for(int j = 0; j < nodeMap.getLength() ; j++){ Node nodenew = nodeMap.item(j); System.out.println("node name "+nodenew.getNodeName()); System.out.println("node value "+nodenew.getNodeValue()); } } if(node.hasChildNodes()){ printNode(node.getChildNodes()); } } } }}输出结果如下:Root element: bookstore------------------------node name: bookstorenode value: Everyday Italian Giada De Laurentiis 2005 30.00 Harry Potter J K. Rowling 2005 29.99 XQuery Kick Start James McGovern 2003 49.99 Learning XML Erik T. Ray 2003 39.95 ------------------------node name: booknode value: Everyday Italian Giada De Laurentiis 2005 30.00 node name categorynode value cooking------------------------node name: titlenode value: Everyday Italiannode name langnode value en------------------------node name: authornode value: Giada De Laurentiis------------------------node name: yearnode value: 2005------------------------node name: pricenode value: 30.00------------------------node name: booknode value: Harry Potter J K. Rowling 2005 29.99 node name categorynode value children------------------------node name: titlenode value: Harry Potternode name langnode value en------------------------node name: authornode value: J K. Rowling------------------------node name: yearnode value: 2005------------------------node name: pricenode value: 29.99------------------------node name: booknode value: XQuery Kick Start James McGovern 2003 49.99 node name categorynode value web------------------------node name: titlenode value: XQueryKick Startnode name langnode value en------------------------node name: authornode value: James McGovern------------------------node name: yearnode value: 2003------------------------node name: pricenode value: 49.99------------------------node name: booknode value: Learning XML Erik T. Ray 2003 39.95 node name categorynode value webnode name covernode value paperback------------------------node name: titlenode value: Learning XMLnode name langnode value en------------------------node name: authornode value: Erik T. Ray------------------------node name: yearnode value: 2003------------------------node name: pricenode value: 39.95------------------------关于节点的问题:Giada De Laurentiis200530.00对于 book应用:doc.getChildNodes() 得到一个NodeList其中NodeList的长度为99个节点分别如下:title节点lang节点Everyday节点author节点Giada De Laurentiis节点year节点2005节点price节点30.00节点下载全文。
java读取xml⽂件以及Jsoup解析xml基本介绍xml基本语法:1.xml⽂档的后缀名为.xml2.xml第⼀⾏必须定义为⽂档声明3.xml⽂档有且仅有⼀个根标签4.属性值必须使⽤引号(单双都可以)引起来5.标签必须正确关闭6.xml标签名区分⼤⼩写组成部分1.⽂档声明格式:<?xml 属性列表 ?>version:版本号(必须); encoding:编码格式; standalone:是否独⽴取值:yes,no2.标签:名称⾃定义,并且按照规则3.属性:id属性值唯⼀4.⽂本:CDATA区:在该区域中的数据会被原样展⽰,格式:<![CDATA[ 数据 ]]>约束:规定xml⽂档的书写规则dtd:简单的约束技术schema:复杂的约束技术DTD:内部dtd:将约束规则定义在xml⽂档中;外部dtd:将约束定义在外部dtd⽂件中外部dtd:本地:<! DOCTYPE 根标签名 SYSTEM "dtd⽂件的位置">⽹络:<! DOCTYPE 根标签名 PUBLIC "dtd⽂件名字" "dtd⽂件的位置URL">java解析xml⽂件的⼏种⽅法解析xml有两种形式,其分别为:1. DOM:将标记语⾔⽂档⼀次性加载进内存,在内存中形成⼀颗dom树优点:操作⽅便,可以对⽂档进⾏CRUD(增删改查)的所有操作缺点:占内存2. SAX:逐⾏读取,基于事件驱动优点:不占内存缺点:只能读取以下⾯这个简单的xml⽂件的解析为例,具体内容参考https:///xmldom/dom_parser.asp<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><peoples><people number="1"><name id="zs">张三</name><age>12</age></people><people><name>李四</name><age>15</age></people></peoples>第⼀种,使⽤DOM对xml进⾏解析import org.w3c.dom.Document;import org.w3c.dom.Element;import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;import java.io.File;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;public class testXml {public static void main(String[] args) {try{File xml = new File("test/test.xml");DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();Document doc = builder.parse(xml);NodeList list = doc.getElementsByTagName("people");for(int i=0;i<list.getLength();i++){Element e = (Element)list.item(i);System.out.println("姓名:"+e.getElementsByTagName("name").item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue()+"年龄:"+e.getElementsByTagName("age").item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue());}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}第⼆种形式,DOM4J进⾏解析import java.io.*;import java.util.*;import org.dom4j.*;import org.dom4j.io.*;public class testDOM4J {public static void main(String[] args) {try{File f = new File("test/test.xml");SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();Document doc = reader.read(f);Element root = doc.getRootElement();Element n;for (Iterator i=root.elementIterator("people");i.hasNext();) {n = (Element) i.next();System.out.println("姓名:"+n.elementText("name")+" 年龄:"+n.elementText("age"));}}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}第三种形式,JDOM进⾏解析import java.util.*;import org.jdom2.*;import org.jdom2.input.*;import java.io.File;public class testJDOM {public static void main(String[] args) {try{File f = new File("test/test.xml");SAXBuilder builder = new SAXBuilder();Document doc = builder.build(f);Element e = doc.getRootElement();List li = e.getChildren();Element temp;for(int i=0;i<li.size();i++){temp = (Element) li.get(i);System.out.println("姓名:"+temp.getChild("name").getText()+" 年龄:"+temp.getChild("age").getText());}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}Jsoup是⼀款Java 的HTML解析器,可直接解析某个URL地址、HTML、XML⽂本内容。
JAVA读取XML⽂件解析XML的步骤如下:1.创建DocumentBuilder⼯⼚2.创建DocumentBuilder对象3.DocumentBuilder对象的parse⽅法得到Document对象4.Document对象的getElementsByTagName得到NodeList集合5.通过getFirstChild和getNextSibling进⾏遍历⽤到的包:import javax.xml.parsers.*;import org.w3c.dom.*;import org.xml.sax.*;⽤到的对象:DocumentBuilderFactory:创建DocumentBuilder的抽象⼯⼚DocumentBuilder:可以从 XML 获取⼀个 DocumentDocument:提供供对⽂档数据的基本访问⽤到的⽅法:DocumentBuilder.parse(String)':将给定 URI 的内容解析为⼀个 XML ⽂档,并且返回⼀个新的 DOM Document对象Document.getElementsByTagName(String)':返回具有给定标记名称的所有Element的NodeListElement.getAttribute(String)':通过名称获得属性值下⾯来解析⼀个XML⽂件1import javax.xml.parsers.*;2import org.w3c.dom.*;3import org.xml.sax.*;45public class Test6 {7public static void main(String[] args)8 {9 DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();10try11 {12 DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();13 Document doc = db.parse("pet2.xml");1415 NodeList dogList = doc.getElementsByTagName("dog");16 System.out.println("共有" + dogList.getLength() + "个dog节点");17for (int i = 0; i < dogList.getLength(); i++)18 {19 Node dog = dogList.item(i);20 Element elem = (Element) dog;21 System.out.println("id:" + elem.getAttribute("id"));22for (Node node = dog.getFirstChild(); node != null; node = node.getNextSibling())23 {24if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE)25 {26 String name = node.getNodeName();27 String value = node.getFirstChild().getNodeValue();28 System.out.print(name + ":" + value + "\t");29 }30 }31 System.out.println();32 }33 }34catch (Exception e)35 {36 e.printStackTrace();37 }38 }39 }XML⽂件1 <pets>2 <dogs>3 <dog id="1">4 <name>YAYA</name>5 <health>100</health>6 <love>0</love>7 <strain>酷酷的雪娜瑞</strain>8 </dog>9 <dog id="2">10 <name>OUOU</name>11 <health>90</health>12 <love>15</love>13 <strain>聪明的拉布拉多⽝</strain>14 </dog>15 </dogs>16 <penguins>17 <penguin id="3">18 <name>QQ</name>19 <health>100</health>20 <love>20</love>21 <sex>Q仔</sex>22 </penguin>23 </penguins>24 </pets>。
Java parse XML methods(4)关键字: xml1. 介绍1>DOM(JAXP Crimson解析器)DOM是用与平台和语言无关的方式表示XML文档的官方W3C标准。
DOM是以层次结构组织的节点或信息片断的集合。
这个层次结构允许开发人员在树中寻找特定信息。
分析该结构通常需要加载整个文档和构造层次结构,然后才能做任何工作。
由于它是基于信息层次的,因而DOM被认为是基于树或基于对象的。
DOM 以及广义的基于树的处理具有几个优点。
首先,由于树在内存中是持久的,因此可以修改它以便应用程序能对数据和结构作出更改。
它还可以在任何时候在树中上下导航,而不是像SAX那样是一次性的处理。
DOM使用起来也要简单得多。
2>SAXSAX处理的优点非常类似于流媒体的优点。
分析能够立即开始,而不是等待所有的数据被处理。
而且,由于应用程序只是在读取数据时检查数据,因此不需要将数据存储在内存中。
这对于大型文档来说是个巨大的优点。
事实上,应用程序甚至不必解析整个文档;它可以在某个条件得到满足时停止解析。
一般来说,SAX还比它的替代者DOM快许多。
选择DOM还是选择SAX?对于需要自己编写代码来处理XML文档的开发人员来说,选择DOM还是SAX解析模型是一个非常重要的设计决策。
DOM采用建立树形结构的方式访问XML文档,而SAX 采用的事件模型。
DOM解析器把XML文档转化为一个包含其内容的树,并可以对树进行遍历。
用DOM解析模型的优点是编程容易,开发人员只需要调用建树的指令,然后利用 navigation APIs访问所需的树节点来完成任务。
可以很容易的添加和修改树中的元素。
然而由于使用DOM解析器的时候需要处理整个XML文档,所以对性能和内存的要求比较高,尤其是遇到很大的XML文件的时候。
由于它的遍历能力,DOM解析器常用于XML文档需要频繁的改变的服务中。
SAX解析器采用了基于事件的模型,它在解析XML文档的时候可以触发一系列的事件,当发现给定的tag的时候,它可以激活一个回调方法,告诉该方法制定的标签已经找到。
java读取文件目录结构并生成xml树,具体实现代码如下:
package org.wendong.file;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentHelper;
import org.dom4j.Element;
/**
* 多线程读取本地文件中的所有文件目录结构及文件大小
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class ThreadReader extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.err.println("当前线程名:"+name);
File file = new File(name);
Document doc = DocumentHelper.createDocument();
Element el = doc.addElement(file.getName());
el = getFile(file, el);
File docFile = new File(name+"/目录结构.xml");
if(!docFile.exists()){
docFile.createNewFile();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(docFile);
fos.write(doc.asXML().getBytes());
fos.flush();
fos.close();
}
Long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("目录建立成功! 耗时:"+(end - start)+"ms");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("异常"+e);
}
}
public static Element getFile(File file, Element el){
try {
File[] list = file.listFiles();
if(list != null && list.length > 0){
for(File f : list){
if(f.isDirectory()){//目录
Element e = el.addElement("Folder");
e.addAttribute("name",
f.getName());
e.addAttribute("lastModify", parseDate(
stModified()));
getFile(f, e);
}else{//文件
Element e = el.addElement("File");
e.addAttribute("name",
f.getName());
e.addAttribute("lastModify", parseDate(
stModified()));
e.addAttribute("size", parseSize(
f.length()));
}
System.out.println(el.asXML());
}
}
return el;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("异常"+e);
}
return null;
}
public static String parseSize(Long l){
String strSize = "0";
if(l < 1000){
strSize = l + "B";
}else if(l < 1000*1000){
strSize = l/1000+"."+l%1000+"K";
}else if(l < 1000*1000*1000){
strSize = l/(1000*1000)+"."+l%(1000*1000)+"M";
}else if(l < 1000*1000*1000*1000){
strSize = l/(1000*1000*1000)+"."+l%(1000*1000*1000)+"G";
}
return strSize;
}
public static String parseDate(Long l){
Calendar calendar = GregorianCalendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTimeInMillis(l);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
return sdf.format(calendar.getTime());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File[] file = File.listRoots();
for(File f : file){
ThreadReader tr = new ThreadReader();
tr.setName(f.getName());
tr.setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);
tr.start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("异常"+e);
}
}
}。