计算机程序设计竞赛-第1讲
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:581.04 KB
- 文档页数:87


第1讲C++语言入门学习目标1、了解计算机语言发展的3个阶段。
2、理解程序设计的一般步骤。
3、掌握什么是算法。
4、掌握对给定的问题进行算法描述。
5、学会编写简单的程序。
随着科技的发展和社会的进步,计算机已经走入寻常百姓家。
人们可以使用同一台计算机做不同的事,我们可以看到其他机器或设备做不到这点。
计算机之所以能执行不同的工作任务,是基于其硬件和软件协同工作的工作机制。
要使计算机按人们指定的步骤有效地工作,必须事先编制好一组让计算机执行的指令,这就是程序。
随着计算机软件技术的发展,人们可以使用不同的计算机语言来编写程序。
一、计算机语言发展要使计算机按照人的规定完成一系列的工作,首先要解决一个“语言”沟通问题:在人和计算机之间找到一种两者都能识别的特定的语言,使计算机具备理解并执行人们给出的各种指令的能力。
这种特定的语言称为计算机语言,也叫程序设计语言,它是人和计算机沟通的桥梁。
随着计算机技术的迅速发展,程序设计语言经历了由低级向高级发展的多个阶段,程序设计方法也得到不断的发展和提高。
计算机语言按其发展程度可以划分为:机器语言、汇编语言和高级语言。
1、机器语言计算机并不能理解和执行人们使用的自然语言。
计算机能够直接识别的指令时由一连串的0和1组合起来的二进制编码,称为机器指令。
每一条指令规定计算机要完成的某个操作。
机器语言是计算机能够直接识别的指令的集合,它是最早出现的计算机语言。
例如,下图所示的是某一种型号计算机的一组二进制编码机器指令,用来完成一个简单加法操作。
1011000000001001000001000000100011110100显然,用机器语言编写的程序“难学、难记、难写、难检查、难调试”,给使用者带来很大的不便。
机器语言编写的程序另一个缺点是完全依赖于机器硬件,不同型号的机器语言指令不相同,程序的可移植性差。
其优点是计算机能直接识别、执行效率高。
2 、汇编语言20世纪50年代初,为了克服机器语言的缺点,人们对机器语言进行了改进,用一些容易记忆和辨别的有意义的符号代替机器指令。

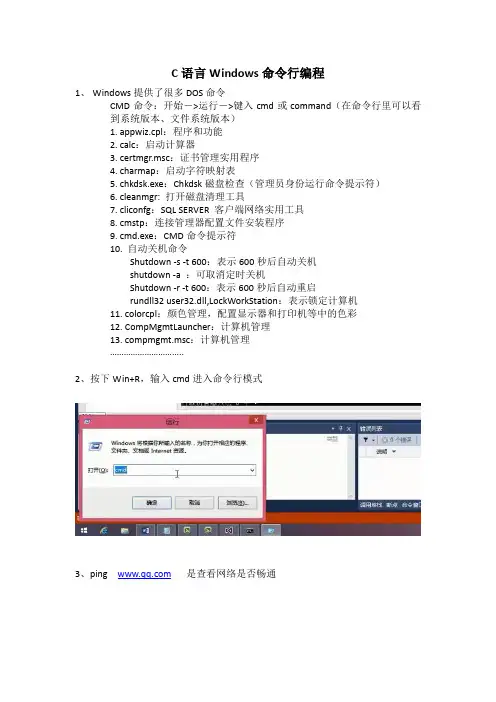
C语言Windows命令行编程
1、Windows提供了很多DOS命令
CMD命令:开始->运行->键入cmd或command(在命令行里可以看
到系统版本、文件系统版本)
1. appwiz.cpl:程序和功能
2. calc:启动计算器
3. certmgr.msc:证书管理实用程序
4. charmap:启动字符映射表
5. chkdsk.exe:Chkdsk磁盘检查(管理员身份运行命令提示符)
6. cleanmgr: 打开磁盘清理工具
7. cliconfg:SQL SERVER 客户端网络实用工具
8. cmstp:连接管理器配置文件安装程序
9. cmd.exe:CMD命令提示符
10. 自动关机命令
Shutdown -s -t 600:表示600秒后自动关机
shutdown -a :可取消定时关机
Shutdown -r -t 600:表示600秒后自动重启
rundll32 user32.dll,LockWorkStation:表示锁定计算机
11. colorcpl:颜色管理,配置显示器和打印机等中的色彩
12. CompMgmtLauncher:计算机管理
13. compmgmt.msc:计算机管理
…………………………..
2、按下Win+R,输入cmd进入命令行模式
3、ping 是查看网络是否畅通
4、运行如下的代码,打开本地用户和组管理器
运行效果如下
4、把IP路由打印出来
运行效果如下:
5、下面有很多的DOS命令通过system函数在程序中运行。

![计算机程序设计竞赛-第1讲[详版课资]](https://uimg.taocdn.com/41fe9d4d4431b90d6d85c744.webp)





INTERMEDIATE DIVISION PROGRAMMING PROBLEMWRAP AROUND CODEPROBLEM: This is yet another in a long list of ACSL code programs. You would think wewould have run out of them by now. In this program you will be given a set of letters to encode. The difference here is that different rules are used for different letters and the counting process starts where the last letter ends. Using the numerical value of each letter (A=1, B=2, … Z= 26) the rules are as follows :As an example, if the set of letters to encode consists of the letters B, G and Z, then the B with a numerical value of 2 encodes to a 4. Counting 4 letters from A produces an E. The G, with a numerical value of 7, encodes to a 5. Counting down 5 letters from the E produces the letter J. The Z with a numerical value of 26 has 13 as its largest factor. Counting 156 letters ( 12 * 13) has the effect of wrapping around the alphabet 6 complete times and ending at J. The encoded solution for the letter set B, G, I is E J J.INPUT : There will be 5 input lines. Each will consist of a series of upper case letters and will end with a $. You may enter the letters one at a time. The commas shown are for clarification and do not have to be entered. The $ is not encoded.OUTPUT: For each set of letters, print the results of the encoding.SAMPLE INPUT SAMPLE OUTPUT1. B,G,Z,$ 1. E J J2. A,R,J,$ 2. C O T3. A,C,S,L,$ 3. C I E CNote: Students have 72 hours in which to submit a solution. Students may not consult any person for assistance. The program must accept all the data and print all the solutions in one RUN of the program. We suggest that you print the solution for each input prior to entering the next input since, if the program stops, you will not be allowed to enter the remaining data.. Make sure that you put your name, your school name and your division at the top of your program file. Advisors must send to ACSL the program file of all students who score a 10 for the contest.INTERMEDIATE DIVISION PROGRAMMING PROBLEMTEST DATATEST INPUTSTEST OUTPUTS1. A,B,C,$ 1. C G M2.L,U,C,K,$ 2. Y E K A3.A,E,I,O,U,$ 3. C M M K Q4.C,O,N,T,E,S,T,$ 4. G E C W G C W5.M,O,N,T,R,E,A,L,$ 5. Y W U O A K M K。